Math Assignment 2
|
|
|
- Martina Blanche Ross
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math Assignment 2 Dylan Zwick Spring 2014 Section 1.5-1, 15, 21, 29, 38, 42 Section 1.6-1, 3, 13, 16, 22, 26, 31, 36, 56 Section 2.1-1, 8, 11, 16, 29 Section 2.2-1, 10, 21, 23, 24 1
2 Section Linear First-Order Equations Find the solution to the initial value problem y + y = 2 y(0) = 0 2
3 Find the solution to the initial value problem y + 2xy = x, y(0) = 2. 3
4 Find the solution to the initial value problem xy = 3y + x 4 cos x, y(2π) = 0. 4
5 Express the general solution of dy/dx = 1+2xy in terms of the error function erf(x) = 2 π x 0 e t2 dt. 5
6 Consider the cascade of two tanks shown below with V1 = 100 (gal) and V = 200 (gal) the volumes of brine in the two tanks. Each tank also initially contains 50 lbs of salt. The three flow rates indicated in the figure are each 5 gal/mm, with pure water flowing into tank 1. 1 (a) Find the amount x(t) of salt in tank 1 at time t. 16
7 (b) Suppose that y(t) is the amount of salt in tank 2 at time t. Show first that dy dt = 5x 100 5y 200. and then solve for y(t), using the function x(t) found in part (a). 7
8 (c) Finally, find the maximum amount of salt ever in tank 2. 8
9 Suppose that a falling hailstone with density δ = 1 starts from rest with negligible radius r = 0. Thereafter its radius is r = kt (k is a constant) as it grows by accreation during its fall. Use Newton s secon d law - according to which the net force F acting on a possibly variable mass m equals the time rate of change dp/dt of its momentum p = mv - to set up and solve the initial value problem d (mv) = mg, v(0) = 0, dt where m is the variable mass of the hailstone, v = dy/dt is its velocity, and the positive y-axis points downward. Then show that dv/dt = g/4. Thus the hailstone falls as though it were under one-fourth the influence of gravity. 9
10 Section Substitution Methods and Exact Equations Find the general solution of the differential equation (x + y)y = x y 10
11 1.6.3 Find the general solution of the differential equation xy = y + 2 xy 11
12 Find the general solution of the differential equation xy = y + x 2 + y 2 Hint - You may find the following integral useful: dv 1 + v 2 = ln(v v 2 ). 12
13 Find the general solution of the differential equation y = x + y
14 Find the general solution of the differential equation x 2 y + 2xy = 5y 4 14
15 Find the general solution of the differential equation 3y 2 y + y 3 = e x 15
16 Verify that the differential equation (2x + 3y)dx + (3x + 2y)dy = 0 is exact; then solve it. 16
17 Verify that the differential equation (1 + ye xy )dx + (2y + xe xy )dy = 0 is exact; then solve it. 17
18 Suppose that n 0 and n 1. Show that the substitutuion v = y 1 n transforms the Bernoulli equation dy + P(x)y = Q(x)yn dx into the linear equation dv + (1 n)p(x)v(x) = (1 n)q(x). dx 18
19 Section Population Models Separate variables and use partial fractions to solve the initial value problem: dx dt = x x2 x(0) = 2. 19
20 2.1.8 Separate variables and use partial fractions to solve the initial value problem: dx dt = 7x(x 13) x(0) =
21 More space, if necessary, for problem
22 Suppose that when a certain lake is stocked with fish, the birth and death rates β and δ are both inversely proportional to P. (a) Show that P(t) = ( 1 2 kt + ) 2 P 0. (b) If P 0 = 100 and after 6 months there are 169 fish in the lake, how many will there be after 1 year? 22
23 More space, if necessary, for problem
24 Consider a rabbit population P(t) satisfying the logistic equation dp/dt = ap bp 2. If the initial population is 120 rabbits and there are 8 births per month and 6 deaths per month occuring at time t = 0, how many months does it take for P(t) to reach 95% of the limiting population M? 24
25 More space, if necessary, for problem
26 During the period from 1790 to 1930 the U.S. population P(t) (t in years) grew from 3.9 million to million. Throughout this period, P(t) remained close to the solution of the initial value problem dp dt = P P 2, P(0) = 3.9. (a) What 1930 population does this logistic equation predict? (b) What limiting population does it predict? (c) Has this logistic equation continued since 1930 to accurately model the U.S. population? [This problem is based on the computation by Verhulst, who in 1845 used the U.S. population data to predict accurately the U.S. population through the year 1930 (long after his own death, of course).] 26
27 More space, if necessary, for problem
28 Section Equilibrium Solutions and Stability Find the critical points of the autonomous equation dx dt = x 4. Then analyze the sign of the equation to determine whether each critical point is stable or unstable, and construct the corresponding phase diagram for the differential equation. Next, solve the differential equation explicitly for x(t) in terms of t. Finally, use either the exact solution or a computer-generated slope field to sketch typical solution curves for the given differential equation, and verify visually the stability of each critical point. 28
29 More space, if necessary, for problem
30 Find the critical points of the autonomous equation dx dt = 7x x2 10. Then analyze the sign of the equation to determine whether each critical point is stable or unstable, and construct the corresponding phase diagram for the differential equation. Next, solve the differential equation explicitly for x(t) in terms of t. Finally, use either the exact solution or a computer-generated slope field to sketch typical solution curves for the given differential equation, and verify visually the stability of each critical point. 30
31 More space, if necessary, for problem
32 Consider the differential equation dx/dt = kx x 3. (a) If k 0, show that the only critical value c = 0 of x is stable. (b) If k > 0, show that the critical point c = 0 is now unstable, but that the critical points c = ± k are stable. Thus the qualitative nature of the solutions changes at k = 0 as the parameter k increases, and so k = 0 is a bifurcation point for the differential equation with parameter k. The plot of all points of the form (k, c) where c is a critical point of the equation x = kx x 3 is the pitchform diagram show in figure of the textbook. 32
33 More space, if necessary, for problem
34 Suppose that the logistic equation dx/dt = kx(m x) models a population x(t) of fish in a lake after t months during which no fishing occurs. Now suppose that, because of fishing, fish are removed from the lake at a rate of hx fish per month (with h a positive constant). Thus fish are harvested at a rate proportional to the existing fish population, rather than at the constant rate of Example 4 from the textbook. (a) If 0 < h < km, show that the population is still logistic. What is the new limiting population? (b) If h km, show that x(t) 0 as t, so the lake is eventually fished out. 34
35 More space, if necessary, for problem
36 Separate variables in the logistic harvesting equation dx/dt = k(n x)(x H) and then use partial fractions to derive the solution given in equation 15 of the textbook (also appearing in the lecture notes). 36
37 More space, if necessary, for problem
Differential equations
 Differential equations Math 27 Spring 2008 In-term exam February 5th. Solutions This exam contains fourteen problems numbered through 4. Problems 3 are multiple choice problems, which each count 6% of
Differential equations Math 27 Spring 2008 In-term exam February 5th. Solutions This exam contains fourteen problems numbered through 4. Problems 3 are multiple choice problems, which each count 6% of
Homework #4 Solutions
 MAT 303 Spring 03 Problems Section.: 0,, Section.:, 6,, Section.3:,, 0,, 30 Homework # Solutions..0. Suppose that the fish population P(t) in a lake is attacked by a disease at time t = 0, with the result
MAT 303 Spring 03 Problems Section.: 0,, Section.:, 6,, Section.3:,, 0,, 30 Homework # Solutions..0. Suppose that the fish population P(t) in a lake is attacked by a disease at time t = 0, with the result
Math 266, Midterm Exam 1
 Math 266, Midterm Exam 1 February 19th 2016 Name: Ground Rules: 1. Calculator is NOT allowed. 2. Show your work for every problem unless otherwise stated (partial credits are available). 3. You may use
Math 266, Midterm Exam 1 February 19th 2016 Name: Ground Rules: 1. Calculator is NOT allowed. 2. Show your work for every problem unless otherwise stated (partial credits are available). 3. You may use
Math 2214 Solution Test 1D Spring 2015
 Math 2214 Solution Test 1D Spring 2015 Problem 1: A 600 gallon open top tank initially holds 300 gallons of fresh water. At t = 0, a brine solution containing 3 lbs of salt per gallon is poured into the
Math 2214 Solution Test 1D Spring 2015 Problem 1: A 600 gallon open top tank initially holds 300 gallons of fresh water. At t = 0, a brine solution containing 3 lbs of salt per gallon is poured into the
It is convenient to think that solutions of differential equations consist of a family of functions (just like indefinite integrals ).
 Section 1.1 Direction Fields Key Terms/Ideas: Mathematical model Geometric behavior of solutions without solving the model using calculus Graphical description using direction fields Equilibrium solution
Section 1.1 Direction Fields Key Terms/Ideas: Mathematical model Geometric behavior of solutions without solving the model using calculus Graphical description using direction fields Equilibrium solution
Modeling with differential equations
 Mathematical Modeling Lia Vas Modeling with differential equations When trying to predict the future value, one follows the following basic idea. Future value = present value + change. From this idea,
Mathematical Modeling Lia Vas Modeling with differential equations When trying to predict the future value, one follows the following basic idea. Future value = present value + change. From this idea,
Solutions to the Review Questions
 Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: (a) Equilibrium solutions are only defined
Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: (a) Equilibrium solutions are only defined
Math 217 Practice Exam 1. Page Which of the following differential equations is exact?
 Page 1 1. Which of the following differential equations is exact? (a) (3x x 3 )dx + (3x 3x 2 ) d = 0 (b) sin(x) dx + cos(x) d = 0 (c) x 2 x 2 = 0 (d) (1 + e x ) + (2 + xe x ) d = 0 CORRECT dx (e) e x dx
Page 1 1. Which of the following differential equations is exact? (a) (3x x 3 )dx + (3x 3x 2 ) d = 0 (b) sin(x) dx + cos(x) d = 0 (c) x 2 x 2 = 0 (d) (1 + e x ) + (2 + xe x ) d = 0 CORRECT dx (e) e x dx
Math 308, Sections 301, 302, Summer 2008 Review before Test I 06/09/2008
 Math 308, Sections 301, 302, Summer 2008 Review before Test I 06/09/2008 Chapter 1. Introduction Section 1.1 Background Definition Equation that contains some derivatives of an unknown function is called
Math 308, Sections 301, 302, Summer 2008 Review before Test I 06/09/2008 Chapter 1. Introduction Section 1.1 Background Definition Equation that contains some derivatives of an unknown function is called
Problem Set. Assignment #1. Math 3350, Spring Feb. 6, 2004 ANSWERS
 Problem Set Assignment #1 Math 3350, Spring 2004 Feb. 6, 2004 ANSWERS i Problem 1. [Section 1.4, Problem 4] A rocket is shot straight up. During the initial stages of flight is has acceleration 7t m /s
Problem Set Assignment #1 Math 3350, Spring 2004 Feb. 6, 2004 ANSWERS i Problem 1. [Section 1.4, Problem 4] A rocket is shot straight up. During the initial stages of flight is has acceleration 7t m /s
ENGR 213: Applied Ordinary Differential Equations
 ENGR 213: Applied Ordinary Differential Equations Youmin Zhang Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Concordia University Phone: x5741 Office Location: EV 4-109 Email: ymzhang@encs.concordia.ca
ENGR 213: Applied Ordinary Differential Equations Youmin Zhang Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Concordia University Phone: x5741 Office Location: EV 4-109 Email: ymzhang@encs.concordia.ca
Chapter1. Ordinary Differential Equations
 Chapter1. Ordinary Differential Equations In the sciences and engineering, mathematical models are developed to aid in the understanding of physical phenomena. These models often yield an equation that
Chapter1. Ordinary Differential Equations In the sciences and engineering, mathematical models are developed to aid in the understanding of physical phenomena. These models often yield an equation that
Math 232, Final Test, 20 March 2007
 Math 232, Final Test, 20 March 2007 Name: Instructions. Do any five of the first six questions, and any five of the last six questions. Please do your best, and show all appropriate details in your solutions.
Math 232, Final Test, 20 March 2007 Name: Instructions. Do any five of the first six questions, and any five of the last six questions. Please do your best, and show all appropriate details in your solutions.
Solutions to the Review Questions
 Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: This is an isocline associated with a slope
Solutions to the Review Questions Short Answer/True or False. True or False, and explain: (a) If y = y + 2t, then 0 = y + 2t is an equilibrium solution. False: This is an isocline associated with a slope
First Order Differential Equations Chapter 1
 First Order Differential Equations Chapter 1 Doreen De Leon Department of Mathematics, California State University, Fresno 1 Differential Equations and Mathematical Models Section 1.1 Definitions: An equation
First Order Differential Equations Chapter 1 Doreen De Leon Department of Mathematics, California State University, Fresno 1 Differential Equations and Mathematical Models Section 1.1 Definitions: An equation
Math Applied Differential Equations
 Math 256 - Applied Differential Equations Notes Existence and Uniqueness The following theorem gives sufficient conditions for the existence and uniqueness of a solution to the IVP for first order nonlinear
Math 256 - Applied Differential Equations Notes Existence and Uniqueness The following theorem gives sufficient conditions for the existence and uniqueness of a solution to the IVP for first order nonlinear
SMA 208: Ordinary differential equations I
 SMA 208: Ordinary differential equations I Modeling with First Order differential equations Lecturer: Dr. Philip Ngare (Contacts: pngare@uonbi.ac.ke, Tue 12-2 PM) School of Mathematics, University of Nairobi
SMA 208: Ordinary differential equations I Modeling with First Order differential equations Lecturer: Dr. Philip Ngare (Contacts: pngare@uonbi.ac.ke, Tue 12-2 PM) School of Mathematics, University of Nairobi
. For each initial condition y(0) = y 0, there exists a. unique solution. In fact, given any point (x, y), there is a unique curve through this point,
 1.2. Direction Fields: Graphical Representation of the ODE and its Solution Section Objective(s): Constructing Direction Fields. Interpreting Direction Fields. Definition 1.2.1. A first order ODE of the
1.2. Direction Fields: Graphical Representation of the ODE and its Solution Section Objective(s): Constructing Direction Fields. Interpreting Direction Fields. Definition 1.2.1. A first order ODE of the
MATH 1014 N 3.0 W2015 APPLIED CALCULUS II - SECTION P. Perhaps the most important of all the applications of calculus is to differential equations.
 MATH 1014 N 3.0 W2015 APPLIED CALCULUS II - SECTION P Stewart Chapter 9 Differential Equations Perhaps the most important of all the applications of calculus is to differential equations. 9.1 Modeling
MATH 1014 N 3.0 W2015 APPLIED CALCULUS II - SECTION P Stewart Chapter 9 Differential Equations Perhaps the most important of all the applications of calculus is to differential equations. 9.1 Modeling
Math 2930 Worksheet Introduction to Differential Equations. What is a Differential Equation and what are Solutions?
 Math 2930 Worksheet Introduction to Differential Equations Week 1 January 25, 2019 What is a Differential Equation and what are Solutions? A differential equation is an equation that relates an unknown
Math 2930 Worksheet Introduction to Differential Equations Week 1 January 25, 2019 What is a Differential Equation and what are Solutions? A differential equation is an equation that relates an unknown
( ) ( ). ( ) " d#. ( ) " cos (%) " d%
 Math 22 Fall 2008 Solutions to Homework #6 Problems from Pages 404-407 (Section 76) 6 We will use the technique of Separation of Variables to solve the differential equation: dy d" = ey # sin 2 (") y #
Math 22 Fall 2008 Solutions to Homework #6 Problems from Pages 404-407 (Section 76) 6 We will use the technique of Separation of Variables to solve the differential equation: dy d" = ey # sin 2 (") y #
Math Lecture 46
 Math 2280 - Lecture 46 Dylan Zwick Fall 2013 Today we re going to use the tools we ve developed in the last two lectures to analyze some systems of nonlinear differential equations that arise in simple
Math 2280 - Lecture 46 Dylan Zwick Fall 2013 Today we re going to use the tools we ve developed in the last two lectures to analyze some systems of nonlinear differential equations that arise in simple
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems
 Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source of preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source of preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
3.2 Systems of Two First Order Linear DE s
 Agenda Section 3.2 Reminders Lab 1 write-up due 9/26 or 9/28 Lab 2 prelab due 9/26 or 9/28 WebHW due 9/29 Office hours Tues, Thurs 1-2 pm (5852 East Hall) MathLab office hour Sun 7-8 pm (MathLab) 3.2 Systems
Agenda Section 3.2 Reminders Lab 1 write-up due 9/26 or 9/28 Lab 2 prelab due 9/26 or 9/28 WebHW due 9/29 Office hours Tues, Thurs 1-2 pm (5852 East Hall) MathLab office hour Sun 7-8 pm (MathLab) 3.2 Systems
Math 2250 Lab 3 Due Date : 2/2/2017
 Math 2250 Lab Due Date : 2/2/2017 Name: UID: Unless stated otherwise, show all your work and explain your reasoning. You are allowed to use any results from lecture or the text as long as they are referenced
Math 2250 Lab Due Date : 2/2/2017 Name: UID: Unless stated otherwise, show all your work and explain your reasoning. You are allowed to use any results from lecture or the text as long as they are referenced
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems
 Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 308 Exam I Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture and all suggested homework problems..
Math 210 Differential Equations Mock Final Dec *************************************************************** 1. Initial Value Problems
 Math 210 Differential Equations Mock Final Dec. 2003 *************************************************************** 1. Initial Value Problems 1. Construct the explicit solution for the following initial
Math 210 Differential Equations Mock Final Dec. 2003 *************************************************************** 1. Initial Value Problems 1. Construct the explicit solution for the following initial
Use separation of variables to solve the following differential equations with given initial conditions. y 1 1 y ). y(y 1) = 1
 Chapter 11 Differential Equations 11.1 Use separation of variables to solve the following differential equations with given initial conditions. (a) = 2ty, y(0) = 10 (b) = y(1 y), y(0) = 0.5, (Hint: 1 y(y
Chapter 11 Differential Equations 11.1 Use separation of variables to solve the following differential equations with given initial conditions. (a) = 2ty, y(0) = 10 (b) = y(1 y), y(0) = 0.5, (Hint: 1 y(y
Calculus IV - HW 2 MA 214. Due 6/29
 Calculus IV - HW 2 MA 214 Due 6/29 Section 2.5 1. (Problems 3 and 5 from B&D) The following problems involve differential equations of the form dy = f(y). For each, sketch the graph of f(y) versus y, determine
Calculus IV - HW 2 MA 214 Due 6/29 Section 2.5 1. (Problems 3 and 5 from B&D) The following problems involve differential equations of the form dy = f(y). For each, sketch the graph of f(y) versus y, determine
Chain Rule. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 3.33pt Chain Rule MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2019 Single Variable Chain Rule Suppose y = g(x) and z = f (y) then dz dx = d (f (g(x))) dx = f (g(x))g (x)
3.33pt Chain Rule MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2019 Single Variable Chain Rule Suppose y = g(x) and z = f (y) then dz dx = d (f (g(x))) dx = f (g(x))g (x)
MATH 251 Examination I October 10, 2013 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination I October 10, 2013 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
MATH 251 Examination I October 10, 2013 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 13 questions for a total of 100 points. Show all you your work! In order to obtain full credit for partial credit
Differential Equations: Homework 2
 Differential Equations: Homework Alvin Lin January 08 - May 08 Section.3 Exercise The direction field for provided x 0. dx = 4x y is shown. Verify that the straight lines y = ±x are solution curves, y
Differential Equations: Homework Alvin Lin January 08 - May 08 Section.3 Exercise The direction field for provided x 0. dx = 4x y is shown. Verify that the straight lines y = ±x are solution curves, y
Name: October 24, 2014 ID Number: Fall Midterm I. Number Total Points Points Obtained Total 40
 Math 307O: Introduction to Differential Equations Name: October 24, 204 ID Number: Fall 204 Midterm I Number Total Points Points Obtained 0 2 0 3 0 4 0 Total 40 Instructions.. Show all your work and box
Math 307O: Introduction to Differential Equations Name: October 24, 204 ID Number: Fall 204 Midterm I Number Total Points Points Obtained 0 2 0 3 0 4 0 Total 40 Instructions.. Show all your work and box
LECTURE 4-1 INTRODUCTION TO ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 130 LECTURE 4-1 INTRODUCTION TO ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: A differential equation (DE) is an equation involving an unknown function and one or more of its derivatives. A differential
130 LECTURE 4-1 INTRODUCTION TO ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: A differential equation (DE) is an equation involving an unknown function and one or more of its derivatives. A differential
Basic Theory of Differential Equations
 page 104 104 CHAPTER 1 First-Order Differential Equations 16. The following initial-value problem arises in the analysis of a cable suspended between two fixed points y = 1 a 1 + (y ) 2, y(0) = a, y (0)
page 104 104 CHAPTER 1 First-Order Differential Equations 16. The following initial-value problem arises in the analysis of a cable suspended between two fixed points y = 1 a 1 + (y ) 2, y(0) = a, y (0)
2r 2 e rx 5re rx +3e rx = 0. That is,
 Math 4, Exam 1, Solution, Spring 013 Write everything on the blank paper provided. You should KEEP this piece of paper. If possible: turn the problems in order (use as much paper as necessary), use only
Math 4, Exam 1, Solution, Spring 013 Write everything on the blank paper provided. You should KEEP this piece of paper. If possible: turn the problems in order (use as much paper as necessary), use only
First-Order Differential Equations
 CHAPTER 1 First-Order Differential Equations 1. Diff Eqns and Math Models Know what it means for a function to be a solution to a differential equation. In order to figure out if y = y(x) is a solution
CHAPTER 1 First-Order Differential Equations 1. Diff Eqns and Math Models Know what it means for a function to be a solution to a differential equation. In order to figure out if y = y(x) is a solution
Introduction to First Order Equations Sections
 A B I L E N E C H R I S T I A N U N I V E R S I T Y Department of Mathematics Introduction to First Order Equations Sections 2.1-2.3 Dr. John Ehrke Department of Mathematics Fall 2012 Course Goals The
A B I L E N E C H R I S T I A N U N I V E R S I T Y Department of Mathematics Introduction to First Order Equations Sections 2.1-2.3 Dr. John Ehrke Department of Mathematics Fall 2012 Course Goals The
MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B Calculus Section 3A: - First order ODEs.
 MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B 2010. For use in Dr Chris Tisdell s lectures. Calculus Section 3A: - First order ODEs. Created and compiled by Chris Tisdell S1: What is an ODE? S2: Motivation S3: Types and orders
MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B 2010. For use in Dr Chris Tisdell s lectures. Calculus Section 3A: - First order ODEs. Created and compiled by Chris Tisdell S1: What is an ODE? S2: Motivation S3: Types and orders
EXAM. Exam #1. Math 3350 Summer II, July 21, 2000 ANSWERS
 EXAM Exam #1 Math 3350 Summer II, 2000 July 21, 2000 ANSWERS i 100 pts. Problem 1. 1. In each part, find the general solution of the differential equation. dx = x2 e y We use the following sequence of
EXAM Exam #1 Math 3350 Summer II, 2000 July 21, 2000 ANSWERS i 100 pts. Problem 1. 1. In each part, find the general solution of the differential equation. dx = x2 e y We use the following sequence of
UCLA: Math 3B Problem set 8 (solutions) Fall, 2016
 This week you will get practice applying the exponential and logistic models and describing their qualitative behaviour. Some of these questions take a bit of thought, they are good practice if you generally
This week you will get practice applying the exponential and logistic models and describing their qualitative behaviour. Some of these questions take a bit of thought, they are good practice if you generally
1.2. Direction Fields: Graphical Representation of the ODE and its Solution Let us consider a first order differential equation of the form dy
 .. Direction Fields: Graphical Representation of the ODE and its Solution Let us consider a first order differential equation of the form dy = f(x, y). In this section we aim to understand the solution
.. Direction Fields: Graphical Representation of the ODE and its Solution Let us consider a first order differential equation of the form dy = f(x, y). In this section we aim to understand the solution
Practice Midterm 1 Solutions Written by Victoria Kala July 10, 2017
 Practice Midterm 1 Solutions Written by Victoria Kala July 10, 2017 1. Use the slope field plotter link in Gauchospace to check your solution. 2. (a) Not linear because of the y 2 sin x term (b) Not linear
Practice Midterm 1 Solutions Written by Victoria Kala July 10, 2017 1. Use the slope field plotter link in Gauchospace to check your solution. 2. (a) Not linear because of the y 2 sin x term (b) Not linear
Sample Questions, Exam 1 Math 244 Spring 2007
 Sample Questions, Exam Math 244 Spring 2007 Remember, on the exam you may use a calculator, but NOT one that can perform symbolic manipulation (remembering derivative and integral formulas are a part of
Sample Questions, Exam Math 244 Spring 2007 Remember, on the exam you may use a calculator, but NOT one that can perform symbolic manipulation (remembering derivative and integral formulas are a part of
Math 2a Prac Lectures on Differential Equations
 Math 2a Prac Lectures on Differential Equations Prof. Dinakar Ramakrishnan 272 Sloan, 253-37 Caltech Office Hours: Fridays 4 5 PM Based on notes taken in class by Stephanie Laga, with a few added comments
Math 2a Prac Lectures on Differential Equations Prof. Dinakar Ramakrishnan 272 Sloan, 253-37 Caltech Office Hours: Fridays 4 5 PM Based on notes taken in class by Stephanie Laga, with a few added comments
dt 2 The Order of a differential equation is the order of the highest derivative that occurs in the equation. Example The differential equation
 Lecture 18 : Direction Fields and Euler s Method A Differential Equation is an equation relating an unknown function and one or more of its derivatives. Examples Population growth : dp dp = kp, or = kp
Lecture 18 : Direction Fields and Euler s Method A Differential Equation is an equation relating an unknown function and one or more of its derivatives. Examples Population growth : dp dp = kp, or = kp
Homework 2 Solutions Math 307 Summer 17
 Homework 2 Solutions Math 307 Summer 17 July 8, 2017 Section 2.3 Problem 4. A tank with capacity of 500 gallons originally contains 200 gallons of water with 100 pounds of salt in solution. Water containing
Homework 2 Solutions Math 307 Summer 17 July 8, 2017 Section 2.3 Problem 4. A tank with capacity of 500 gallons originally contains 200 gallons of water with 100 pounds of salt in solution. Water containing
DON T PANIC! If you get stuck, take a deep breath and go on to the next question. Come back to the question you left if you have time at the end.
 Math 307A, Midterm 1 Spring 2013 Name: Instructions. DON T PANIC! If you get stuck, take a deep breath and go on to the next question. Come back to the question you left if you have time at the end. There
Math 307A, Midterm 1 Spring 2013 Name: Instructions. DON T PANIC! If you get stuck, take a deep breath and go on to the next question. Come back to the question you left if you have time at the end. There
Practice Final Exam Solutions
 Important Notice: To prepare for the final exam, study past exams and practice exams, and homeworks, quizzes, and worksheets, not just this practice final. A topic not being on the practice final does
Important Notice: To prepare for the final exam, study past exams and practice exams, and homeworks, quizzes, and worksheets, not just this practice final. A topic not being on the practice final does
Math 2930 Worksheet Introduction to Differential Equations
 Math 2930 Worksheet Introduction to Differential Equations Week 1 August 24, 2017 Question 1. Is the function y = 1 + t a solution to the differential equation How about the function y = 1 + 2t? How about
Math 2930 Worksheet Introduction to Differential Equations Week 1 August 24, 2017 Question 1. Is the function y = 1 + t a solution to the differential equation How about the function y = 1 + 2t? How about
Review of Lecture 5. F = GMm r 2. = m dv dt Expressed in terms of altitude x = r R, we have. mv dv dx = GMm. (R + x) 2. Max altitude. 2GM v 2 0 R.
 Review of Lecture 5 Models could involve just one or two equations (e.g. orbit calculation), or hundreds of equations (as in climate modeling). To model a vertical cannon shot: F = GMm r 2 = m dv dt Expressed
Review of Lecture 5 Models could involve just one or two equations (e.g. orbit calculation), or hundreds of equations (as in climate modeling). To model a vertical cannon shot: F = GMm r 2 = m dv dt Expressed
Solutions of Math 53 Midterm Exam I
 Solutions of Math 53 Midterm Exam I Problem 1: (1) [8 points] Draw a direction field for the given differential equation y 0 = t + y. (2) [8 points] Based on the direction field, determine the behavior
Solutions of Math 53 Midterm Exam I Problem 1: (1) [8 points] Draw a direction field for the given differential equation y 0 = t + y. (2) [8 points] Based on the direction field, determine the behavior
Mathematics Engineering Calculus III Fall 13 Test #1
 Mathematics 2153-02 Engineering Calculus III Fall 13 Test #1 Instructor: Dr. Alexandra Shlapentokh (1) Which of the following statements is always true? (a) If x = f(t), y = g(t) and f (1) = 0, then dy/dx(1)
Mathematics 2153-02 Engineering Calculus III Fall 13 Test #1 Instructor: Dr. Alexandra Shlapentokh (1) Which of the following statements is always true? (a) If x = f(t), y = g(t) and f (1) = 0, then dy/dx(1)
ME3.6 Sheet 2 Answers
 ME36 Sheet 2 Answers (i) We have dx/dt Ý6x 2xy Ý 8 fx,y,dy/dt y 2 Ý x 2 gx,y The critical points satisfy g y x and f Ý6x 2xy Ý 8 Substitute y x to get Ý6x 2x 2 Ý 8 x Ý 4x x 4 or Ý If instead we substitute
ME36 Sheet 2 Answers (i) We have dx/dt Ý6x 2xy Ý 8 fx,y,dy/dt y 2 Ý x 2 gx,y The critical points satisfy g y x and f Ý6x 2xy Ý 8 Substitute y x to get Ý6x 2x 2 Ý 8 x Ý 4x x 4 or Ý If instead we substitute
HW2 Solutions. MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22]
![HW2 Solutions. MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22] HW2 Solutions. MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22]](/thumbs/73/68538384.jpg) HW2 Solutions MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, 2013 Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22] Section 3.1: 1, 2, 3, 9, 16, 18, 20, 23 Section 3.2: 1, 2,
HW2 Solutions MATH 20D Fall 2013 Prof: Sun Hui TA: Zezhou Zhang (David) October 14, 2013 Checklist: Section 2.6: 1, 3, 6, 8, 10, 15, [20, 22] Section 3.1: 1, 2, 3, 9, 16, 18, 20, 23 Section 3.2: 1, 2,
Find the slope of the curve at the given point P and an equation of the tangent line at P. 1) y = x2 + 11x - 15, P(1, -3)
 Final Exam Review AP Calculus AB Find the slope of the curve at the given point P and an equation of the tangent line at P. 1) y = x2 + 11x - 15, P(1, -3) Use the graph to evaluate the limit. 2) lim x
Final Exam Review AP Calculus AB Find the slope of the curve at the given point P and an equation of the tangent line at P. 1) y = x2 + 11x - 15, P(1, -3) Use the graph to evaluate the limit. 2) lim x
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous on [a, b]. 1.) If G(x) = x. f(t)dt = F (b) F (a) where F is any antiderivative
![The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous on [a, b]. 1.) If G(x) = x. f(t)dt = F (b) F (a) where F is any antiderivative The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous on [a, b]. 1.) If G(x) = x. f(t)dt = F (b) F (a) where F is any antiderivative](/thumbs/96/128959530.jpg) 1 Calulus pre-requisites you must know. Derivative = slope of tangent line = rate. Integral = area between curve and x-axis (where area can be negative). The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f
1 Calulus pre-requisites you must know. Derivative = slope of tangent line = rate. Integral = area between curve and x-axis (where area can be negative). The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f
Math 2Z03 - Tutorial # 3. Sept. 28th, 29th, 30th, 2015
 Math 2Z03 - Tutorial # 3 Sept. 28th, 29th, 30th, 2015 Tutorial Info: Tutorial Website: http://ms.mcmaster.ca/ dedieula/2z03.html Office Hours: Mondays 3pm - 5pm (in the Math Help Centre) Tutorial #3: 2.8
Math 2Z03 - Tutorial # 3 Sept. 28th, 29th, 30th, 2015 Tutorial Info: Tutorial Website: http://ms.mcmaster.ca/ dedieula/2z03.html Office Hours: Mondays 3pm - 5pm (in the Math Help Centre) Tutorial #3: 2.8
Math 2300 Calculus II University of Colorado Final exam review problems
 Math 300 Calculus II University of Colorado Final exam review problems. A slope field for the differential equation y = y e x is shown. Sketch the graphs of the solutions that satisfy the given initial
Math 300 Calculus II University of Colorado Final exam review problems. A slope field for the differential equation y = y e x is shown. Sketch the graphs of the solutions that satisfy the given initial
Math 225 Differential Equations Notes Chapter 1
 Math 225 Differential Equations Notes Chapter 1 Michael Muscedere September 9, 2004 1 Introduction 1.1 Background In science and engineering models are used to describe physical phenomena. Often these
Math 225 Differential Equations Notes Chapter 1 Michael Muscedere September 9, 2004 1 Introduction 1.1 Background In science and engineering models are used to describe physical phenomena. Often these
y0 = F (t0)+c implies C = y0 F (t0) Integral = area between curve and x-axis (where I.e., f(t)dt = F (b) F (a) wheref is any antiderivative 2.
 Calulus pre-requisites you must know. Derivative = slope of tangent line = rate. Integral = area between curve and x-axis (where area can be negative). The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous
Calulus pre-requisites you must know. Derivative = slope of tangent line = rate. Integral = area between curve and x-axis (where area can be negative). The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Suppose f continuous
First order differential equations
 First order differential equations Samy Tindel Purdue University Differential equations and linear algebra - MA 262 Taken from Differential equations and linear algebra by Goode and Annin Samy T. First
First order differential equations Samy Tindel Purdue University Differential equations and linear algebra - MA 262 Taken from Differential equations and linear algebra by Goode and Annin Samy T. First
Math 116 Second Midterm November 14, 2012
 Math 6 Second Midterm November 4, Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section:. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so.. This exam has pages including this cover. There are 8 problems. Note that
Math 6 Second Midterm November 4, Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section:. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so.. This exam has pages including this cover. There are 8 problems. Note that
Assignment # 3, Math 370, Fall 2018 SOLUTIONS:
 Assignment # 3, Math 370, Fall 2018 SOLUTIONS: Problem 1: Solve the equations: (a) y (1 + x)e x y 2 = xy, (i) y(0) = 1, (ii) y(0) = 0. On what intervals are the solution of the IVP defined? (b) 2y + y
Assignment # 3, Math 370, Fall 2018 SOLUTIONS: Problem 1: Solve the equations: (a) y (1 + x)e x y 2 = xy, (i) y(0) = 1, (ii) y(0) = 0. On what intervals are the solution of the IVP defined? (b) 2y + y
AP Physics C Summer Homework. Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB
![AP Physics C Summer Homework. Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB AP Physics C Summer Homework. Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB](/thumbs/96/128301637.jpg) 1. AP Physics C Summer Homework NAME: Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB 2. Fill in the radian conversion of each angle and the trigonometric
1. AP Physics C Summer Homework NAME: Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB 2. Fill in the radian conversion of each angle and the trigonometric
MATH 307: Problem Set #3 Solutions
 : Problem Set #3 Solutions Due on: May 3, 2015 Problem 1 Autonomous Equations Recall that an equilibrium solution of an autonomous equation is called stable if solutions lying on both sides of it tend
: Problem Set #3 Solutions Due on: May 3, 2015 Problem 1 Autonomous Equations Recall that an equilibrium solution of an autonomous equation is called stable if solutions lying on both sides of it tend
Solutions to Section 1.1
 Solutions to Section True-False Review: FALSE A derivative must involve some derivative of the function y f(x), not necessarily the first derivative TRUE The initial conditions accompanying a differential
Solutions to Section True-False Review: FALSE A derivative must involve some derivative of the function y f(x), not necessarily the first derivative TRUE The initial conditions accompanying a differential
Autonomous Equations and Stability Sections
 A B I L E N E C H R I S T I A N U N I V E R S I T Y Department of Mathematics Autonomous Equations and Stability Sections 2.4-2.5 Dr. John Ehrke Department of Mathematics Fall 2012 Autonomous Differential
A B I L E N E C H R I S T I A N U N I V E R S I T Y Department of Mathematics Autonomous Equations and Stability Sections 2.4-2.5 Dr. John Ehrke Department of Mathematics Fall 2012 Autonomous Differential
Practice Questions From Calculus II. 0. State the following calculus rules (these are many of the key rules from Test 1 topics).
 Math 132. Practice Questions From Calculus II I. Topics Covered in Test I 0. State the following calculus rules (these are many of the key rules from Test 1 topics). (Trapezoidal Rule) b a f(x) dx (Fundamental
Math 132. Practice Questions From Calculus II I. Topics Covered in Test I 0. State the following calculus rules (these are many of the key rules from Test 1 topics). (Trapezoidal Rule) b a f(x) dx (Fundamental
Problem set 7 Math 207A, Fall 2011 Solutions
 Problem set 7 Math 207A, Fall 2011 s 1. Classify the equilibrium (x, y) = (0, 0) of the system x t = x, y t = y + x 2. Is the equilibrium hyperbolic? Find an equation for the trajectories in (x, y)- phase
Problem set 7 Math 207A, Fall 2011 s 1. Classify the equilibrium (x, y) = (0, 0) of the system x t = x, y t = y + x 2. Is the equilibrium hyperbolic? Find an equation for the trajectories in (x, y)- phase
for any C, including C = 0, because y = 0 is also a solution: dy
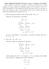 Math 3200-001 Fall 2014 Practice exam 1 solutions 2/16/2014 Each problem is worth 0 to 4 points: 4=correct, 3=small error, 2=good progress, 1=some progress 0=nothing relevant. If the result is correct,
Math 3200-001 Fall 2014 Practice exam 1 solutions 2/16/2014 Each problem is worth 0 to 4 points: 4=correct, 3=small error, 2=good progress, 1=some progress 0=nothing relevant. If the result is correct,
FLAP M6.1 Introducing differential equations COPYRIGHT 1998 THE OPEN UNIVERSITY S570 V1.1
 F1 (a) This equation is of first order and of first degree. It is a linear equation, since the dependent variable y and its derivative only appear raised to the first power, and there are no products of
F1 (a) This equation is of first order and of first degree. It is a linear equation, since the dependent variable y and its derivative only appear raised to the first power, and there are no products of
Solution. Your sketch should show both x and y axes marked from 5 to 5 and circles of radius 1, 3, and 5 centered at the origin.
 Solutions of the Sample Problems for the First In-Class Exam Math 246, Fall 208, Professor David Levermore () (a) Sketch the graph that would be produced by the following Matlab command. fplot(@(t) 2/t,
Solutions of the Sample Problems for the First In-Class Exam Math 246, Fall 208, Professor David Levermore () (a) Sketch the graph that would be produced by the following Matlab command. fplot(@(t) 2/t,
FINAL EXAM CALCULUS 2. Name PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS
 FINAL EXAM CALCULUS MATH 00 FALL 08 Name PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS Please answer all of the questions, and show your work. You must explain your answers to get credit. You will be graded on the clarity of
FINAL EXAM CALCULUS MATH 00 FALL 08 Name PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS Please answer all of the questions, and show your work. You must explain your answers to get credit. You will be graded on the clarity of
MA 137 Calculus 1 with Life Science Application A First Look at Differential Equations (Section 4.1.2)
 MA 137 Calculus 1 with Life Science Application A First Look at Differential Equations (Section 4.1.2) Alberto Corso alberto.corso@uky.edu Department of Mathematics University of Kentucky October 12, 2015
MA 137 Calculus 1 with Life Science Application A First Look at Differential Equations (Section 4.1.2) Alberto Corso alberto.corso@uky.edu Department of Mathematics University of Kentucky October 12, 2015
Lecture 19: Solving linear ODEs + separable techniques for nonlinear ODE s
 Lecture 19: Solving linear ODEs + separable techniques for nonlinear ODE s Geoffrey Cowles Department of Fisheries Oceanography School for Marine Science and Technology University of Massachusetts-Dartmouth
Lecture 19: Solving linear ODEs + separable techniques for nonlinear ODE s Geoffrey Cowles Department of Fisheries Oceanography School for Marine Science and Technology University of Massachusetts-Dartmouth
Solution. It is evaluating the definite integral r 1 + r 4 dr. where you can replace r by any other variable.
 Solutions of Sample Problems for First In-Class Exam Math 246, Fall 202, Professor David Levermore () (a) Give the integral being evaluated by the following MATLAB command. int( x/(+xˆ4), x,0,inf) Solution.
Solutions of Sample Problems for First In-Class Exam Math 246, Fall 202, Professor David Levermore () (a) Give the integral being evaluated by the following MATLAB command. int( x/(+xˆ4), x,0,inf) Solution.
Solutions of the Sample Problems for the First In-Class Exam Math 246, Fall 2017, Professor David Levermore
 Solutions of the Sample Problems for the First In-Class Exam Math 246, Fall 207, Professor David Levermore () (a) Give the integral being evaluated by the following Matlab command. int( x/(+xˆ4), x,0,inf)
Solutions of the Sample Problems for the First In-Class Exam Math 246, Fall 207, Professor David Levermore () (a) Give the integral being evaluated by the following Matlab command. int( x/(+xˆ4), x,0,inf)
Ordinary Differential Equations
 Ordinary Differential Equations Swaroop Nandan Bora swaroop@iitg.ernet.in Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati-781039 A first-order differential equation is an equation
Ordinary Differential Equations Swaroop Nandan Bora swaroop@iitg.ernet.in Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati-781039 A first-order differential equation is an equation
The final is comprehensive (8-9 pages). There will be two pages on ch 9.
 Closing Wed: HW_9A,9B (9.3/4,3.8) Final: Sat, Dec. 9 th, 1:30-4:20, KANE 130 Assigned seats, for your seat go to: catalyst.uw.edu/gradebook/aloveles/102715 The final is comprehensive (8-9 pages). There
Closing Wed: HW_9A,9B (9.3/4,3.8) Final: Sat, Dec. 9 th, 1:30-4:20, KANE 130 Assigned seats, for your seat go to: catalyst.uw.edu/gradebook/aloveles/102715 The final is comprehensive (8-9 pages). There
Differential Equations & Separation of Variables
 Differential Equations & Separation of Variables SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: As you work through the problems listed below, you should reference Chapter 8. of the recommended textbook (or the equivalent
Differential Equations & Separation of Variables SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: As you work through the problems listed below, you should reference Chapter 8. of the recommended textbook (or the equivalent
MATH 317 Fall 2016 Assignment 5
 MATH 37 Fall 26 Assignment 5 6.3, 6.4. ( 6.3) etermine whether F(x, y) e x sin y îı + e x cos y ĵj is a conservative vector field. If it is, find a function f such that F f. enote F (P, Q). We have Q x
MATH 37 Fall 26 Assignment 5 6.3, 6.4. ( 6.3) etermine whether F(x, y) e x sin y îı + e x cos y ĵj is a conservative vector field. If it is, find a function f such that F f. enote F (P, Q). We have Q x
The functions in all models depend on two variables: time t and spatial variable x, (x, y) or (x, y, z).
 Review of Multi-variable calculus: The functions in all models depend on two variables: time t and spatial variable x, (x, y) or (x, y, z). The spatial variable represents the environment where the species
Review of Multi-variable calculus: The functions in all models depend on two variables: time t and spatial variable x, (x, y) or (x, y, z). The spatial variable represents the environment where the species
Math 266: Ordinary Differential Equations
 Math 266: Ordinary Differential Equations Long Jin Purdue University, Spring 2018 Basic information Lectures: MWF 8:30-9:20(111)/9:30-10:20(121), UNIV 103 Instructor: Long Jin (long249@purdue.edu) Office
Math 266: Ordinary Differential Equations Long Jin Purdue University, Spring 2018 Basic information Lectures: MWF 8:30-9:20(111)/9:30-10:20(121), UNIV 103 Instructor: Long Jin (long249@purdue.edu) Office
MTH4100 Calculus I. Week 6 (Thomas Calculus Sections 3.5 to 4.2) Rainer Klages. School of Mathematical Sciences Queen Mary, University of London
 MTH4100 Calculus I Week 6 (Thomas Calculus Sections 3.5 to 4.2) Rainer Klages School of Mathematical Sciences Queen Mary, University of London Autumn 2008 R. Klages (QMUL) MTH4100 Calculus 1 Week 6 1 /
MTH4100 Calculus I Week 6 (Thomas Calculus Sections 3.5 to 4.2) Rainer Klages School of Mathematical Sciences Queen Mary, University of London Autumn 2008 R. Klages (QMUL) MTH4100 Calculus 1 Week 6 1 /
Math RE - Calculus II Differential Equations Page 1 of 9
 Math 201-203-RE - Calculus II Differential Equations Page 1 of 9 Introduction to Differential equation (O.D.E) A differential equation is an equation containing derivatives such as: (1) xy = y 5 (2) d2
Math 201-203-RE - Calculus II Differential Equations Page 1 of 9 Introduction to Differential equation (O.D.E) A differential equation is an equation containing derivatives such as: (1) xy = y 5 (2) d2
sections June 11, 2009
 sections 3.2-3.5 June 11, 2009 Population growth/decay When we model population growth, the simplest model is the exponential (or Malthusian) model. Basic ideas: P = P(t) = population size as a function
sections 3.2-3.5 June 11, 2009 Population growth/decay When we model population growth, the simplest model is the exponential (or Malthusian) model. Basic ideas: P = P(t) = population size as a function
Section 11.1 What is a Differential Equation?
 1 Section 11.1 What is a Differential Equation? Example 1 Suppose a ball is dropped from the top of a building of height 50 meters. Let h(t) denote the height of the ball after t seconds, then it is known
1 Section 11.1 What is a Differential Equation? Example 1 Suppose a ball is dropped from the top of a building of height 50 meters. Let h(t) denote the height of the ball after t seconds, then it is known
Math 222 Spring 2013 Exam 3 Review Problem Answers
 . (a) By the Chain ule, Math Spring 3 Exam 3 eview Problem Answers w s w x x s + w y y s (y xy)() + (xy x )( ) (( s + 4t) (s 3t)( s + 4t)) ((s 3t)( s + 4t) (s 3t) ) 8s 94st + 3t (b) By the Chain ule, w
. (a) By the Chain ule, Math Spring 3 Exam 3 eview Problem Answers w s w x x s + w y y s (y xy)() + (xy x )( ) (( s + 4t) (s 3t)( s + 4t)) ((s 3t)( s + 4t) (s 3t) ) 8s 94st + 3t (b) By the Chain ule, w
Calculus II. George Voutsadakis 1. LSSU Math 152. Lake Superior State University. 1 Mathematics and Computer Science
 Calculus II George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 152 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Calculus II February 2015 1 / 28 Outline 1 Introduction to Differential
Calculus II George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 152 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Calculus II February 2015 1 / 28 Outline 1 Introduction to Differential
Practice Final Exam Solutions
 Important Notice: To prepare for the final exam, one should study the past exams and practice midterms (and homeworks, quizzes, and worksheets), not just this practice final. A topic not being on the practice
Important Notice: To prepare for the final exam, one should study the past exams and practice midterms (and homeworks, quizzes, and worksheets), not just this practice final. A topic not being on the practice
Old Math 330 Exams. David M. McClendon. Department of Mathematics Ferris State University
 Old Math 330 Exams David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University Last updated to include exams from Fall 07 Contents Contents General information about these exams 3 Exams from Fall
Old Math 330 Exams David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University Last updated to include exams from Fall 07 Contents Contents General information about these exams 3 Exams from Fall
Boyce/DiPrima/Meade 11 th ed, Ch 1.1: Basic Mathematical Models; Direction Fields
 Boyce/DiPrima/Meade 11 th ed, Ch 1.1: Basic Mathematical Models; Direction Fields Elementary Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems, 11 th edition, by William E. Boyce, Richard C. DiPrima,
Boyce/DiPrima/Meade 11 th ed, Ch 1.1: Basic Mathematical Models; Direction Fields Elementary Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems, 11 th edition, by William E. Boyce, Richard C. DiPrima,
LAURENTIAN UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITÉ LAURENTIENNE
 Page 1 of 15 LAURENTIAN UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITÉ LAURENTIENNE Friday, December 14 th Course and No. 2007 MATH 2066 EL Date................................... Cours et no........................... Total no.
Page 1 of 15 LAURENTIAN UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITÉ LAURENTIENNE Friday, December 14 th Course and No. 2007 MATH 2066 EL Date................................... Cours et no........................... Total no.
Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Differential Equations 7. An Introduction to Differential Equations Motivating Questions In this section, we strive to understand the ideas generated by the following important questions: What
Chapter 7 Differential Equations 7. An Introduction to Differential Equations Motivating Questions In this section, we strive to understand the ideas generated by the following important questions: What
MATH 4B Differential Equations, Fall 2016 Final Exam Study Guide
 MATH 4B Differential Equations, Fall 2016 Final Exam Study Guide GENERAL INFORMATION AND FINAL EXAM RULES The exam will have a duration of 3 hours. No extra time will be given. Failing to submit your solutions
MATH 4B Differential Equations, Fall 2016 Final Exam Study Guide GENERAL INFORMATION AND FINAL EXAM RULES The exam will have a duration of 3 hours. No extra time will be given. Failing to submit your solutions
Do not write in this space. Problem Possible Score Number Points Total 48
 MTH 337. Name MTH 337. Differential Equations Exam II March 15, 2019 T. Judson Do not write in this space. Problem Possible Score Number Points 1 8 2 10 3 15 4 15 Total 48 Directions Please Read Carefully!
MTH 337. Name MTH 337. Differential Equations Exam II March 15, 2019 T. Judson Do not write in this space. Problem Possible Score Number Points 1 8 2 10 3 15 4 15 Total 48 Directions Please Read Carefully!
Chapters 8.1 & 8.2 Practice Problems
 EXPECTED SKILLS: Chapters 8.1 & 8. Practice Problems Be able to verify that a given function is a solution to a differential equation. Given a description in words of how some quantity changes in time
EXPECTED SKILLS: Chapters 8.1 & 8. Practice Problems Be able to verify that a given function is a solution to a differential equation. Given a description in words of how some quantity changes in time
8. Qualitative analysis of autonomous equations on the line/population dynamics models, phase line, and stability of equilibrium points (corresponds
 c Dr Igor Zelenko, Spring 2017 1 8. Qualitative analysis of autonomous equations on the line/population dynamics models, phase line, and stability of equilibrium points (corresponds to section 2.5) 1.
c Dr Igor Zelenko, Spring 2017 1 8. Qualitative analysis of autonomous equations on the line/population dynamics models, phase line, and stability of equilibrium points (corresponds to section 2.5) 1.
MA 102 Mathematics II Lecture Feb, 2015
 MA 102 Mathematics II Lecture 1 20 Feb, 2015 Differential Equations An equation containing derivatives is called a differential equation. The origin of differential equations Many of the laws of nature
MA 102 Mathematics II Lecture 1 20 Feb, 2015 Differential Equations An equation containing derivatives is called a differential equation. The origin of differential equations Many of the laws of nature
