Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
|
|
|
- Merilyn Pearson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 9, 21 Sep Rate and State Friction Velocity step test to measure RSF parameters SHS test to measure RSF parameters Happy Fall The equinox is tomorrow at 4:02 pm EDT
2 Rate (v) and State (θ) Friction Constitutive Laws Recall (as motivation for going beyond other friction laws) Time-dependent static friction Velocity dependent sliding friction Memory effects, state dependence Repetitive stick-slip instability Key Observations log-time strengthening log-velocity dependence Application to earthquakes One set of constitutive relations to describe entire seismic cycle
3 Rate (v) and State (θ) Friction Constitutive Laws state variable, characterizes physical state of surface or shearing region reference velocity reference value of base friction critical slip distance Dieterich, aging law Ruina, slip law
4 Rate (v) and State (θ) Friction Constitutive Laws 1) 2) Implies: Vo V 1 Direct Effect µ Evolution Effect D c Steady-state sliding: => Fading memory of past state then (1) becomes:
5 Rate (v) and State (θ) Friction Constitutive Laws 1) 2) Convention is to use a, b for friction and A, B for Stress Steady-state velocity strengthening if a-b > 0, velocity weakening if a-b < 0 velocity strengthening µ velocity weakening Log V
6 Rate (v) and State (θ) Friction Constitutive Laws 1) 2) Steady-state velocity strengthening if a-b > 0, velocity weakening if a-b < 0 µ velocity strengthening velocity weakening a & b are small, dimensionless constants determined from experiments Log V Dc has units of length Modeling experimental data 3) Elastic Coupling
7 Rate (v) and State (θ) Friction Constitutive Laws 1) 2) Modeling experimental data 3) Elastic Coupling Solve:
8 1) 2) 3) Typical Values of the RSF parameters (Marone et al., 1990)
9 1) 2) 3) Typical Values of the RSF parameters (Marone et al., 1990)
10 1) 2) Typical Values of the RSF parameters (Carpenter, Ikari & Marone 2016) 3)
11 Measuring the velocity dependence of friction Frictional Instability Requires (a-b) < 0 µ " θ,v$ = µ # % 0 + aln " v v $ + bln " v o θ & & o ' & dθ dt = 1 vθ D c θ ss = D c v Δµ ss = ( a b)ln v v & o dµ dt Constitutive Modelling Rate and State Friction Law Elastic Interaction, Testing Apparatus = * " k v lp v # " # $ % # $ ' % % # D c $ ' ' %
12 Results: Velocity stepping Measuring the velocity dependence of friction Frictional Instability Requires K < K c This example shows steady-state velocity strengthening: (a-b) > 0
13 s hold, V s/r = 10 µm/s Coefficient of Friction m080 Hold Reload Displacement (mm) Sheared layer of quartz particles ( µm), 25 MPa normal stress. Marone, m080 Hold 1044 s hold, V s/r = 10 µm/s Coefficient of Friction s Δµ Reload Time (s)
14 Load point s hold, V s/r = 10 µm/s Fault surface Coefficient of Friction m080 Hold Reload Load point Fault surface 1) Displacement (mm) 2) 3) Elastic Coupling
15 Derivation of the healing rate
16 Time Dependence of static friction Stressed Aging Monodisperse, angular quartz particles
17 Time Dependence of static friction Effect of loading velocity
18 µm/s 3 µm/s 10 µm/s 30 µm/s 100 µm/s Stressed Aging Aging rate depends on the rate of shearing Frictional Healing, Δµ Hold Time (s) (Marone, 1998, Nature)
19 0.10 Dieterich V s/r Law (µm/s) Ruina Law Friction Law µ = µ o + a ln(v/v o ) + b ln(v o θ/d c ) State Evolution dθ/dt = 1 - V θ/d c dθ/dt = - V θ/d c ln( Vθ/D c ) Elastic Coupling dµ/dt = k( V lp - V) Healing, Δµ 0.05 b = 0.009, b-a = D c = 5 µm, k= 1x10-3 µm Hold Time (s) The rate of frictional healing depends on the rate of shearing (Marone, 1998, Nature) Rate State Friction Laws predict this behavior
20 Phase Plane Plots shs test: 1 µm/s 10 µm/s
21 shs test: 1 µm/s 10 µm/s Phase Plane Plots
22 Stick-Slip Instability Requires Some Form of Weakening: Velocity Weakening, Slip Weakening, Thermal/hydraulic Weakening 1) 2 ) Vo V 1 Direct Effect µ Evolution Effect Stability Criterion K c = n (b a) D c (b > a), K < K c Unstable, stick-slip (a > b), K > K c Stable sliding D c [1 + mv 2 o ] nad c K/K c < 1 Fading memory of past state
23 Time (state) dependence of friction: Healing Velocity (rate) dependence of friction. Duality of time and displacement dependence of friction. Static and dynamic friction are just special cases of a more general behavior called rate and state friction
24 Stick-Slip Instability Requires Some Form of Weakening: Velocity Weakening, Slip Weakening, Thermal/hydraulic Weakening 1) 2 ) N L Stability Criterion K c = n (b a) D c [1 + mv 2 o ] nad c W Rupture area, A Slip contours, u (b > a), K < K c Unstable, stick-slip K/K c < 1 (a > b), K > K c Stable sliding
25 Dislocation model for fault slip and earthquake rupture r Relation between stress drop and slip: Δσ = 16 7π G Δu r K = K/K c < 1 Unstable, stick-slip Δσ Δu = 16 G 7π r r c = 24 7π D c G σ (b a) K/Kc > 1 Stable, aseismic slip
26 Stick-slip stress-drop amplitude varies with loading rate. Mair, Frye and Marone, JGR 2002 Duality of time and displacement dependence of friction. Static and dynamic friction are just special cases of a more general behavior called rate and state friction
27 Sheared layer of quartz particles. Marone, 1998 Time, displacement, and velocity dependence of static and dynamic friction Load point Fault surface
28 Time dependent yield strength: µ= τ S = σn σy Dieterich and Kilgore [1994] Time dependent growth of contact (acyrlic plastic)- true static contact
29 Other measures of changes in static friction, contact area, or strength hold test after Dieterich [1972] time dependent closure (westerly granite) - approximately static contact Modified from Beeler, 2003
30 Rate dependence of contact shear strength hold test µ = τ σ n = S σ y Rate dependent response S = S o + g( V) Modified from Beeler, 2003
31 Summary of friction observations: 0. Friction is to first order a constant 1. Time dependent increase in contact area (strengthening) 2. Slip dependent decrease in contact area (weakening); equivalently increase in dilatancy 3. Slip rate dependent increase in shear resistance (non-linear viscous) Modified classic theory of friction: µ = S = S o + g( V) σ y σ o + f age ( ) µ = S o + g ( V ) σ o + f age ( ) # σ o f ( age) & $ % σ o f ( age) '( Discard products of second order terms: µ = S o + g( V ) σ o σ o S o f ( age ) 2 σ o [e.g., Dieterich, 1978, 1979] Modified from Beeler, 2003
32 Summary of friction observations: 0. Friction is to first order a constant 1. Time dependent increase in contact area (strengthening) µ = S o + g( V ) σ o σ o S o f ( age) 2 σ o 2. Slip dependent decrease in contact area (weakening); equivalently increase in dilatancy 3. Slip rate dependent increase in shear resistance (non-linear viscous) 1st order term second order terms Rate and state equations: µ = µ 0 + aln V V 0 + b ln V 0θ D c & 2. θ is contact age Dieterich [1979] Rice [1983] Ruina [1983] dθ dt = 1 θv D c time dependence slip dependence dθ dt = # θ & % ( $ t ' d # + θ & % ( $ d ' t V # θ & % ( $ t ' d = 1 # θ & % ( $ d ' t = θ D c Modified from Beeler, 2003
Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors
 Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors Chris Marone, The Pennsylvania State University John Leeman, Marco Scuderi, Elisa Tinti, Cristiano
Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors Chris Marone, The Pennsylvania State University John Leeman, Marco Scuderi, Elisa Tinti, Cristiano
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law
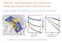 Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Friction in Rocks Assigned Reading: {Marone, 1998 #3905; Chapter 8 in \Paterson, 2005 #5865} Resource reading: {Scholz, 1990 #4288; Ruina, 1985 #1586}
 12.524, 2005 09 28 LE04: Friction and Constitutive Laws 1 Friction in Rocks Assigned Reading: {Marone, 1998 #3905; Chapter 8 in \Paterson, 2005 #5865} Resource reading: {Scholz, 1990 #4288; Ruina, 1985
12.524, 2005 09 28 LE04: Friction and Constitutive Laws 1 Friction in Rocks Assigned Reading: {Marone, 1998 #3905; Chapter 8 in \Paterson, 2005 #5865} Resource reading: {Scholz, 1990 #4288; Ruina, 1985
Friction. Why friction? Because slip on faults is resisted by frictional forces.
 Friction Why friction? Because slip on faults is resisted by frictional forces. We first describe the results of laboratory friction experiments, and then discuss the implications of the friction constitutive
Friction Why friction? Because slip on faults is resisted by frictional forces. We first describe the results of laboratory friction experiments, and then discuss the implications of the friction constitutive
LABORATORY-DERIVED FRICTION LAWS AND THEIR APPLICATION TO SEISMIC FAULTING
 Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1998. 26:643 96 Copyright c 1998 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved LABORATORY-DERIVED FRICTION LAWS AND THEIR APPLICATION TO SEISMIC FAULTING Chris Marone Department
Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1998. 26:643 96 Copyright c 1998 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved LABORATORY-DERIVED FRICTION LAWS AND THEIR APPLICATION TO SEISMIC FAULTING Chris Marone Department
A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing
 A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing Jiyang Ye, Mirko Van Der Baan (Email: jiyang1@ualberta.ca, Mirko.VanderBaan@ualberta.ca)
A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing Jiyang Ye, Mirko Van Der Baan (Email: jiyang1@ualberta.ca, Mirko.VanderBaan@ualberta.ca)
friction friction a-b slow fast increases during sliding
 µ increases during sliding faster sliding --> stronger fault --> slows sliding leads to stable slip: no earthquakes can start velocity-strengthening friction slow fast µ velocity-strengthening friction
µ increases during sliding faster sliding --> stronger fault --> slows sliding leads to stable slip: no earthquakes can start velocity-strengthening friction slow fast µ velocity-strengthening friction
Rate and State Friction and the Modeling of Aseismic Slip
 Rate and State Friction and the Modeling of Aseismic Slip Hugo Perfettini 1,2 1 : Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) 2 : Institut des Sciences de la Terre (ISTerre) Characteristics of Afterslip
Rate and State Friction and the Modeling of Aseismic Slip Hugo Perfettini 1,2 1 : Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) 2 : Institut des Sciences de la Terre (ISTerre) Characteristics of Afterslip
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ).
 Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip
 Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
Frictional rheologies have a wide range of applications in engineering
 A liquid-crystal model for friction C. H. A. Cheng, L. H. Kellogg, S. Shkoller, and D. L. Turcotte Departments of Mathematics and Geology, University of California, Davis, CA 95616 ; Contributed by D.
A liquid-crystal model for friction C. H. A. Cheng, L. H. Kellogg, S. Shkoller, and D. L. Turcotte Departments of Mathematics and Geology, University of California, Davis, CA 95616 ; Contributed by D.
Rock and fluid thermodynamics control the dynamics of induced earthquakes
 Rock and fluid thermodynamics control the dynamics of induced earthquakes M. Acosta, F. Passelègue, A. Schubnel et M. Violay (mateo.acosta@epfl.ch) Context Induced Seismicity in Enhanced Geothermal Systems
Rock and fluid thermodynamics control the dynamics of induced earthquakes M. Acosta, F. Passelègue, A. Schubnel et M. Violay (mateo.acosta@epfl.ch) Context Induced Seismicity in Enhanced Geothermal Systems
Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture Propagation: Evidence from Geological and Seismological Observations
 Euroconference of Rock Physics and Geomechanics: Natural hazards: thermo-hydro-mechanical processes in rocks Erice, Sicily, 25-30 September, 2007 Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture
Euroconference of Rock Physics and Geomechanics: Natural hazards: thermo-hydro-mechanical processes in rocks Erice, Sicily, 25-30 September, 2007 Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture
On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent faults
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15303, doi:10.1029/2007gl030337, 2007 On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15303, doi:10.1029/2007gl030337, 2007 On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent
4.05 The Mechanics of Frictional Healing and Slip Instability During the Seismic Cycle
 4.5 The Mechanics of Frictional Healing and Slip Instability During the Seismic Cycle C Marone and DM Saffer, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA ã 15 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
4.5 The Mechanics of Frictional Healing and Slip Instability During the Seismic Cycle C Marone and DM Saffer, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA ã 15 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Influence of dilatancy on the frictional constitutive behavior of a saturated fault zone under a variety of drainage conditions
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008556, 2011 Influence of dilatancy on the frictional constitutive behavior of a saturated fault zone under a variety of drainage conditions
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008556, 2011 Influence of dilatancy on the frictional constitutive behavior of a saturated fault zone under a variety of drainage conditions
Why are earthquake slip zones so narrow?
 Why are earthquake slip zones so narrow? John W. Rudnicki Northwestern University Evanston, IL (with Jim Rice, Harvard University) October 9, 9 University o Minnesota. Geomechanics Seminar F. Chester,
Why are earthquake slip zones so narrow? John W. Rudnicki Northwestern University Evanston, IL (with Jim Rice, Harvard University) October 9, 9 University o Minnesota. Geomechanics Seminar F. Chester,
Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta. California Institute of Technology
 Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta California Institute of Technology Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip
Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta California Institute of Technology Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Standard Solids and Fracture Fluids: Mechanical, Chemical Effects Effective Stress Dilatancy Hardening and Stability Mead, 1925
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Standard Solids and Fracture Fluids: Mechanical, Chemical Effects Effective Stress Dilatancy Hardening and Stability Mead, 1925
Potential for earthquake triggering from transient deformations
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005277, 2008 Potential for earthquake triggering from transient deformations Heather M. Savage 1,2 and Chris Marone
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005277, 2008 Potential for earthquake triggering from transient deformations Heather M. Savage 1,2 and Chris Marone
3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA
 3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA Li Xiaofan MEE09177 Supervisor: Bunichiro Shibazaki ABSTRACT We perform 3D modeling of earthquake generation of the Xianshuihe
3D MODELING OF EARTHQUAKE CYCLES OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT, SOUTHWESTERN CHINA Li Xiaofan MEE09177 Supervisor: Bunichiro Shibazaki ABSTRACT We perform 3D modeling of earthquake generation of the Xianshuihe
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting 5 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Work of deformation, shear and volume strain Importance of volume change and diltancy rate (rate of volume strain with
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting 5 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Work of deformation, shear and volume strain Importance of volume change and diltancy rate (rate of volume strain with
Effect of varying normal stress on stability and dynamic motion of a spring-slider system with rate- and state-dependent friction
 Earthq Sci (2014) 27(6):577 587 DOI 10.1007/s11589-014-0098-4 RESEARCH PAPER Effect of varying normal stress on stability and dynamic motion of a spring-slider system with rate- and state-dependent friction
Earthq Sci (2014) 27(6):577 587 DOI 10.1007/s11589-014-0098-4 RESEARCH PAPER Effect of varying normal stress on stability and dynamic motion of a spring-slider system with rate- and state-dependent friction
Fault Representation Methods for Spontaneous Dynamic Rupture Simulation. Luis A. Dalguer
 Fault Representation Methods for Spontaneous Dynamic Rupture Simulation Luis A. Dalguer Computational Seismology Group Swiss Seismological Service (SED) ETH-Zurich July 12-18, 2011 2 st QUEST Workshop,
Fault Representation Methods for Spontaneous Dynamic Rupture Simulation Luis A. Dalguer Computational Seismology Group Swiss Seismological Service (SED) ETH-Zurich July 12-18, 2011 2 st QUEST Workshop,
Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area. Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC
 Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC Constitutive law on the fault: Rate-and-state friction at low slip rates + Potential
Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC Constitutive law on the fault: Rate-and-state friction at low slip rates + Potential
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI: /,
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, 1 2 Self-similar slip pulses during rate-and-state earthquake nucleation Allan M. Rubin 3 4 Department of Geosciences, Princeton University,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, 1 2 Self-similar slip pulses during rate-and-state earthquake nucleation Allan M. Rubin 3 4 Department of Geosciences, Princeton University,
Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law
 Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law Naoyuki Kato (1), Kazuro Hirahara (2) and Mikio Iizuka (3) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University
Numerical simulation of seismic cycles at a subduction zone with a laboratory-derived friction law Naoyuki Kato (1), Kazuro Hirahara (2) and Mikio Iizuka (3) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University
Abstract. We have devised an original laboratory experiment where we investigate
 1 1 Long Term Friction: from Stick-Slip to Stable Sliding 2 3 4 Christophe Voisin 1, François Renard 1,2 and Jean-Robert Grasso 1 1 Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique, CNRS, Observatoire
1 1 Long Term Friction: from Stick-Slip to Stable Sliding 2 3 4 Christophe Voisin 1, François Renard 1,2 and Jean-Robert Grasso 1 1 Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique, CNRS, Observatoire
Hitoshi Hirose (1), and Kazuro Hirahara (2) Abstract. Introduction
 Three dimensional simulation for the earthquake cycle at a subduction zone based on a rate- and state-dependent friction law: Insight into a finiteness and a variety of dip-slip earthquakes Hitoshi Hirose
Three dimensional simulation for the earthquake cycle at a subduction zone based on a rate- and state-dependent friction law: Insight into a finiteness and a variety of dip-slip earthquakes Hitoshi Hirose
Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities
 Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities Strasbourg, 15 Nov. 2007 François Renard LGCA, CNRS-OSUG, University of Grenoble, France PGP, University of Oslo, Norway Collaborators:
Transition from stick-slip to stable sliding: the crucial effect of asperities Strasbourg, 15 Nov. 2007 François Renard LGCA, CNRS-OSUG, University of Grenoble, France PGP, University of Oslo, Norway Collaborators:
Earthquake nucleation. Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab
 Earthquake nucleation Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab How do earthquakes start? Do small and large earthquakes start differently? Predictive value of earthquake onset and foreshock sequences? Seismological
Earthquake nucleation Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab How do earthquakes start? Do small and large earthquakes start differently? Predictive value of earthquake onset and foreshock sequences? Seismological
On rate-state and Coulomb failure models
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 105, NO. B4, PAGES 7857 7871, APRIL 10, 2000 On rate-state and Coulomb failure models J. Gomberg U.S. Geological Survey, Center for Earthquake Research and Information,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 105, NO. B4, PAGES 7857 7871, APRIL 10, 2000 On rate-state and Coulomb failure models J. Gomberg U.S. Geological Survey, Center for Earthquake Research and Information,
The effect of inertia, viscous damping, temperature and normal stress on chaotic behaviour of the rate and state friction model
 J. Earth Syst. Sci. (018) 17:45 c Indian Academy of Sciences https://doi.org/10.1007/s1040-018-0935- The effect of inertia, viscous damping, temperature and normal stress on chaotic behaviour of the rate
J. Earth Syst. Sci. (018) 17:45 c Indian Academy of Sciences https://doi.org/10.1007/s1040-018-0935- The effect of inertia, viscous damping, temperature and normal stress on chaotic behaviour of the rate
Megathrust Earthquakes
 Megathrust Earthquakes Susan Schwartz University of California Santa Cruz CIDER 2017 UC Berkeley July 5, 2017 The largest megathrust events are not uniformally distributed at all subduction zones. M>8
Megathrust Earthquakes Susan Schwartz University of California Santa Cruz CIDER 2017 UC Berkeley July 5, 2017 The largest megathrust events are not uniformally distributed at all subduction zones. M>8
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
Frictional restrengthening in simulated fault gouge: Effect of
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 16, NO. B9, PAGES 19,319-19,337, SEPTEMBER 1, 21 Frictional restrengthening in simulated fault gouge: Effect of shear load perturbations Stephen L. Kamer and Chris
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 16, NO. B9, PAGES 19,319-19,337, SEPTEMBER 1, 21 Frictional restrengthening in simulated fault gouge: Effect of shear load perturbations Stephen L. Kamer and Chris
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI: /, J.-P. Ampuero, Institute of Geophysics, Seismology and Geodynamics ETH Honggerberg
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, 1 2 Earthquake nucleation on rate and state faults Aging and slip laws Jean-Paul Ampuero 3 Institute of Geophysics, ETH Zurich, Switzerland
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, 1 2 Earthquake nucleation on rate and state faults Aging and slip laws Jean-Paul Ampuero 3 Institute of Geophysics, ETH Zurich, Switzerland
A constitutive model for fault gouge deformation in dynamic rupture simulations
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.129/, A constitutive model for fault gouge deformation in dynamic rupture simulations Eric G. Daub and Jean M. Carlson Department of Physics, University
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:1.129/, A constitutive model for fault gouge deformation in dynamic rupture simulations Eric G. Daub and Jean M. Carlson Department of Physics, University
Megathrust earthquakes: How large? How destructive? How often? Jean-Philippe Avouac California Institute of Technology
 Megathrust earthquakes: How large? How destructive? How often? Jean-Philippe Avouac California Institute of Technology World seismicity (data source: USGS) and velocities relative to ITRF1997 (Sella et
Megathrust earthquakes: How large? How destructive? How often? Jean-Philippe Avouac California Institute of Technology World seismicity (data source: USGS) and velocities relative to ITRF1997 (Sella et
Chapter 2: Rock Friction. Jyr-Ching Hu, Dept. Geosciences National Taiwan University
 Chapter 2: Rock Friction Jyr-Ching Hu, Dept. Geosciences National Taiwan University Rock Friction Scholz, Christopher H., 1998. Earthquakes and Friction Laws. Nature. 1. Constitutive law of rock friction
Chapter 2: Rock Friction Jyr-Ching Hu, Dept. Geosciences National Taiwan University Rock Friction Scholz, Christopher H., 1998. Earthquakes and Friction Laws. Nature. 1. Constitutive law of rock friction
Rate and State-Dependent Friction in Earthquake Simulation
 Rate and State-Dependent Friction in Earthquake Simulation Zac Meadows UC Davis - Department of Physics Summer 2012 REU September 3, 2012 Abstract To better understand the spatial and temporal complexity
Rate and State-Dependent Friction in Earthquake Simulation Zac Meadows UC Davis - Department of Physics Summer 2012 REU September 3, 2012 Abstract To better understand the spatial and temporal complexity
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lectures & 3, 9/31 Aug 017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Discussion of Handin, JGR, 1969 and Chapter 1 Scholz, 00. Stress analysis and Mohr Circles Coulomb Failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lectures & 3, 9/31 Aug 017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Discussion of Handin, JGR, 1969 and Chapter 1 Scholz, 00. Stress analysis and Mohr Circles Coulomb Failure
Heterogeneous Coulomb stress perturbation during earthquake cycles in a 3D rate-and-state fault model
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L21306, doi:10.1029/2008gl035614, 2008 Heterogeneous Coulomb stress perturbation during earthquake cycles in a 3D rate-and-state fault
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L21306, doi:10.1029/2008gl035614, 2008 Heterogeneous Coulomb stress perturbation during earthquake cycles in a 3D rate-and-state fault
Nonsmooth dynamics of friction in modeling of earthquakes. Vladimir Ryabov Future University-Hakodate, Japan
 Nonsmooth dynamics of friction in modeling of earthquakes Vladimir Ryabov Future University-Hakodate, Japan Earthquakes are caused by friction between tectonic plates From: http://seismo.berkeley.edu/
Nonsmooth dynamics of friction in modeling of earthquakes Vladimir Ryabov Future University-Hakodate, Japan Earthquakes are caused by friction between tectonic plates From: http://seismo.berkeley.edu/
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 18, 16 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Earthquake Magnitude and Moment Brune Stress Drop Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws Scaling and
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 18, 16 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Earthquake Magnitude and Moment Brune Stress Drop Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws Scaling and
Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, 1 M. Lisa Manning, 1,2 and Jean M.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, 1 M. Lisa Manning, 1,2 and Jean M.
A viscoelastic damage rheology and rate- and state-dependent friction
 Geophys. J. Int. (2005) 161, 179 190 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2005.02583.x A viscoelastic damage rheology and rate- and state-dependent friction Vladimir Lyakhovsky, 1 Yehuda Ben-Zion 2 and Amotz Agnon
Geophys. J. Int. (2005) 161, 179 190 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2005.02583.x A viscoelastic damage rheology and rate- and state-dependent friction Vladimir Lyakhovsky, 1 Yehuda Ben-Zion 2 and Amotz Agnon
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
1.0. Shear Strength ( τ τ c )/ τ Fault Slip (w/d c ) Peak Strength (τp τ c)/ τ 0 1.2
 Evolution of contacting rock surfaces and a slip- and time-dependent fault constitutive law Hideo Aochi and Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Department of Earth and Planetary Physics, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
Evolution of contacting rock surfaces and a slip- and time-dependent fault constitutive law Hideo Aochi and Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Department of Earth and Planetary Physics, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
µ=µ 0 + a ln (V/V 0 ) + b ln(v θ/d c ),
 1 Long Term Friction: from Stick-Slip to Stable Sliding Christophe Voisin 1, François Renard 1,2 and Jean-Robert Grasso 1 1LGIT-CNRS-OSUG, Université Joseph Fourier, Grenoble, France 2 Physics of Geological
1 Long Term Friction: from Stick-Slip to Stable Sliding Christophe Voisin 1, François Renard 1,2 and Jean-Robert Grasso 1 1LGIT-CNRS-OSUG, Université Joseph Fourier, Grenoble, France 2 Physics of Geological
Frictional properties of olivine at high temperature with applications to the strength and dynamics of the oceanic lithosphere
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012jb009511, 2012 Frictional properties of olivine at high temperature with applications to the strength and dynamics of the oceanic lithosphere
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012jb009511, 2012 Frictional properties of olivine at high temperature with applications to the strength and dynamics of the oceanic lithosphere
The Influence of Brines and Temperature on the Frictional Properties of Laboratory Fault Gouge. Cody W. Bomberger ABSTRACT
 The Influence of Brines and Temperature on the Frictional Properties of Laboratory Fault Gouge Cody W. Bomberger ABSTRACT The frictional properties of gouge material within tectonic faults zones dictate
The Influence of Brines and Temperature on the Frictional Properties of Laboratory Fault Gouge Cody W. Bomberger ABSTRACT The frictional properties of gouge material within tectonic faults zones dictate
PUBLICATIONS. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth RESEARCH ARTICLE This article is a companion to Chen et al. (017), https://doi.org/10.100/ 017JB0146. Key Points: Microphysical constraints on
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth RESEARCH ARTICLE This article is a companion to Chen et al. (017), https://doi.org/10.100/ 017JB0146. Key Points: Microphysical constraints on
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 16, 9 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Energy Balance of dynamic rupture Crack tip stress field Frictional Rupture Fronts Meet in the lab (522
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 16, 9 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Energy Balance of dynamic rupture Crack tip stress field Frictional Rupture Fronts Meet in the lab (522
ON THE RATE OF FRICTIONAL HEALING AND THE CONSTITUTIVE LAW FOR TIME- AND SLIP-DEPENDENT FRICTION
 Int. J. Rock Mech. & Min. Sci. Vol. 34, No. 3-4, 1997 To cite this paper: Int. J. RockMech. &Min. Sci. 34:3-4, Paper No. 187 ON THE RATE OF FRICTIONAL HEALING AND THE CONSTITUTIVE LAW FOR TIME- AND SLIP-DEPENDENT
Int. J. Rock Mech. & Min. Sci. Vol. 34, No. 3-4, 1997 To cite this paper: Int. J. RockMech. &Min. Sci. 34:3-4, Paper No. 187 ON THE RATE OF FRICTIONAL HEALING AND THE CONSTITUTIVE LAW FOR TIME- AND SLIP-DEPENDENT
Slip-weakening behavior during the propagation of dynamic ruptures obeying rate- and state-dependent friction laws
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B8, 2373, doi:10.1029/2002jb002198, 2003 Slip-weakening behavior during the propagation of dynamic ruptures obeying rate- and state-dependent friction laws
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B8, 2373, doi:10.1029/2002jb002198, 2003 Slip-weakening behavior during the propagation of dynamic ruptures obeying rate- and state-dependent friction laws
Complex Earthquake Cycle Simulations Using a Two-Degree-of-Freedom Spring-Block Model with a Rate- and State-Friction Law
 Pure Appl. Geophys. 170 (2013), 745 765 Ó 2012 The Author(s) This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com DOI 10.1007/s00024-011-0450-8 Pure and Applied Geophysics Complex Earthquake
Pure Appl. Geophys. 170 (2013), 745 765 Ó 2012 The Author(s) This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com DOI 10.1007/s00024-011-0450-8 Pure and Applied Geophysics Complex Earthquake
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics
 Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Expansion of aftershock areas caused by propagating post-seismic sliding
 Geophys. J. Int. (2007) 168, 797 808 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03255.x Expansion of aftershock areas caused by propagating post-seismic sliding Naoyuki Kato Earthquake Research Institute, University
Geophys. J. Int. (2007) 168, 797 808 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03255.x Expansion of aftershock areas caused by propagating post-seismic sliding Naoyuki Kato Earthquake Research Institute, University
Intrinsic and apparent short-time limits for fault healing: Theory, observations, and implications for velocity-dependent friction
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jb004096, 2006 Intrinsic and apparent short-time limits for fault healing: Theory, observations, and implications for velocity-dependent friction
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jb004096, 2006 Intrinsic and apparent short-time limits for fault healing: Theory, observations, and implications for velocity-dependent friction
Brittle Deformation. Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm
 Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II
 Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II Project Representative Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo Authors Mitsuhiro
Development of a Predictive Simulation System for Crustal Activities in and around Japan - II Project Representative Mitsuhiro Matsu'ura Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo Authors Mitsuhiro
Simulation of earthquake rupture process and strong ground motion
 Simulation of earthquake rupture process and strong ground motion Takashi Miyatake (1) and Tomohiro Inoue (2) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Yayoi, Bunkyo, Tokyo, 113-0032, Japan
Simulation of earthquake rupture process and strong ground motion Takashi Miyatake (1) and Tomohiro Inoue (2) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Yayoi, Bunkyo, Tokyo, 113-0032, Japan
Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size?
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications for aftershock rates
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005154, 2008 Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005154, 2008 Variability of earthquake nucleation in continuum models of rate-and-state faults and implications
The critical slip distance for seismic and aseismic fault zones of finite width
 The critical slip distance for seismic and aseismic fault zones of finite width Chris Marone 1, Massimo Cocco, Eliza Richardson 1, and Elisa Tinti Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia, Rome,
The critical slip distance for seismic and aseismic fault zones of finite width Chris Marone 1, Massimo Cocco, Eliza Richardson 1, and Elisa Tinti Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia, Rome,
FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE. Kyle Withers Qian Yao
 FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE Kyle Withers Qian Yao Temperature Change Along Fault Mode II (plain strain) crack rupturing bilaterally at a constant speed v r Idealize earthquake ruptures as shear
FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE Kyle Withers Qian Yao Temperature Change Along Fault Mode II (plain strain) crack rupturing bilaterally at a constant speed v r Idealize earthquake ruptures as shear
The role of thermal pressurization and dilatancy in controlling the rate of fault slip
 The role of thermal pressurization and dilatancy in controlling the rate of fault slip Paul Segall Geophysics Department Stanford University Stanford, CA, 9435 Email: segall@stanford.edu Andrew M. Bradley
The role of thermal pressurization and dilatancy in controlling the rate of fault slip Paul Segall Geophysics Department Stanford University Stanford, CA, 9435 Email: segall@stanford.edu Andrew M. Bradley
Effect of the intermediate principal stress on fault strike and dip - theoretical analysis and experimental verification
 Effect of the intermediate principal stress on fault strike and dip - theoretical analysis and experimental verification B. Haimson University of Wisconsin, USA J. Rudnicki Northwestern University, USA
Effect of the intermediate principal stress on fault strike and dip - theoretical analysis and experimental verification B. Haimson University of Wisconsin, USA J. Rudnicki Northwestern University, USA
Source parameters II. Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop
 Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L24301, doi:10.1029/2008gl036249, 2008 Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L24301, doi:10.1029/2008gl036249, 2008 Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
Earthquake nucleation on rate and state faults Aging and slip laws
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005082, 2008 Earthquake nucleation on rate and state faults Aging and slip laws Jean-Paul Ampuero 1 and Allan M. Rubin 2 Received 30 March
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005082, 2008 Earthquake nucleation on rate and state faults Aging and slip laws Jean-Paul Ampuero 1 and Allan M. Rubin 2 Received 30 March
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09348 This section provides supporting information for Reches and Lockner Fault weakening and earthquake instability by powder lubrication. The present topics
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09348 This section provides supporting information for Reches and Lockner Fault weakening and earthquake instability by powder lubrication. The present topics
Earthquake stress drop and laboratory-inferred interseismic strength recovery
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln USGS Staff -- Published Research US Geological Survey 2001 Earthquake stress drop and laboratory-inferred interseismic strength
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln USGS Staff -- Published Research US Geological Survey 2001 Earthquake stress drop and laboratory-inferred interseismic strength
Scaling of Rock Friction Constitutive Parameters: The Effects of Surface Roughness and Cumulative Offset on Friction of Gabbro
 PAGEOPH, Vol. 143, No. 1/2/3 (1994) 0033-4553/94/030359-2751.50 + 0.20/0 9 1994 Birkh/iuser Verlag, Basel Scaling of Rock Friction Constitutive Parameters: The Effects of Surface Roughness and Cumulative
PAGEOPH, Vol. 143, No. 1/2/3 (1994) 0033-4553/94/030359-2751.50 + 0.20/0 9 1994 Birkh/iuser Verlag, Basel Scaling of Rock Friction Constitutive Parameters: The Effects of Surface Roughness and Cumulative
PUBLICATIONS. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. A friction to flow constitutive law and its application to a 2-D modeling of earthquakes
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: We propose a constitutive law describing transition from friction to flow The law merges a strength profile and a
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: We propose a constitutive law describing transition from friction to flow The law merges a strength profile and a
A PRESSURE VESSEL FOR TRUE-TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION & FLUID FLOW DURING FRICTIONAL SHEAR
 A PRESSURE VESSEL FOR TRUE-TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION & FLUID FLOW DURING FRICTIONAL SHEAR Chris Marone, Brett Carperter, Derek Elsworth, Igor Faoro, Matt Ikari, Matt Knuth, André Niemeijer, Demian Saffer, and
A PRESSURE VESSEL FOR TRUE-TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION & FLUID FLOW DURING FRICTIONAL SHEAR Chris Marone, Brett Carperter, Derek Elsworth, Igor Faoro, Matt Ikari, Matt Knuth, André Niemeijer, Demian Saffer, and
Interpretation of various slip modes on a plate boundary based on laboratory and numerical experiments
 Earth Planets Space, 56, 795 801, 2004 Interpretation of various slip modes on a plate boundary based on laboratory and numerical experiments Shingo Yoshida 1, Aitaro Kato 1,2, Naoyuki Kato 1, and Masao
Earth Planets Space, 56, 795 801, 2004 Interpretation of various slip modes on a plate boundary based on laboratory and numerical experiments Shingo Yoshida 1, Aitaro Kato 1,2, Naoyuki Kato 1, and Masao
In this article, we study linear and non-linear stability of the three state variables rate and state
 Nonlin. Processes Geophys. Discuss., doi:0./npg-0-, 0 Published: February 0 c Author(s) 0. CC-BY.0 License. 0 0 Linear and Non-linear Stability Analysis of the Rate and State Friction Model with Three
Nonlin. Processes Geophys. Discuss., doi:0./npg-0-, 0 Published: February 0 c Author(s) 0. CC-BY.0 License. 0 0 Linear and Non-linear Stability Analysis of the Rate and State Friction Model with Three
The effects of entrained debris on the basal sliding stability of a glacier
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: EARTH SURFACE, VOL. 118, 1 11, doi:1.12/jgrf.252, 213 The effects of entrained debris on the basal sliding stability of a glacier L. K. Zoet, 1,2 B. Carpenter, 3 M. Scuderi,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: EARTH SURFACE, VOL. 118, 1 11, doi:1.12/jgrf.252, 213 The effects of entrained debris on the basal sliding stability of a glacier L. K. Zoet, 1,2 B. Carpenter, 3 M. Scuderi,
Shear-induced dilatancy of fluid-saturated faults: Experiment and theory
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb006273, 2009 Shear-induced dilatancy of fluid-saturated faults: Experiment and theory Jon Samuelson, 1 Derek Elsworth,
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb006273, 2009 Shear-induced dilatancy of fluid-saturated faults: Experiment and theory Jon Samuelson, 1 Derek Elsworth,
Conceptual and physical clarification of rate and state friction: Frictional sliding as a thermally activated
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSCAL RESEARCH, VOL. 106, NO. B7, PAGES 13,347-13,380, JULY 10, 2001 Conceptual and physical clarification of rate and state friction: Frictional sliding as a thermally activated rheology
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSCAL RESEARCH, VOL. 106, NO. B7, PAGES 13,347-13,380, JULY 10, 2001 Conceptual and physical clarification of rate and state friction: Frictional sliding as a thermally activated rheology
Existence and Stability Analysis of Spring-Block Model Solutions with Rate and State Friction
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 36, 1785-1795 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Existence and Stability Analysis of Spring-Block Model Solutions with Rate and State Friction Kodwo Annan Department
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 7, 2013, no. 36, 1785-1795 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Existence and Stability Analysis of Spring-Block Model Solutions with Rate and State Friction Kodwo Annan Department
1/22/2015. High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics
 High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics Thanks: Amir Sagy Andrew Madden, David Lockner, Einat Aharonov Harry Green, Jay Finberg, Jefferson Chang, Shalev Siman Tov
High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics Thanks: Amir Sagy Andrew Madden, David Lockner, Einat Aharonov Harry Green, Jay Finberg, Jefferson Chang, Shalev Siman Tov
Foreshocks during the nucleation of stick-slip instability
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SOLID EARTH, VOL. 118, 1 16, doi:10.1002/jgrb.50232, 2013 Foreshocks during the nucleation of stick-slip instability Gregory C. McLaskey 1 and Brian D. Kilgore 1 Received
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SOLID EARTH, VOL. 118, 1 16, doi:10.1002/jgrb.50232, 2013 Foreshocks during the nucleation of stick-slip instability Gregory C. McLaskey 1 and Brian D. Kilgore 1 Received
Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.9/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, M. Lisa Manning, and Jean M. Carlson Abstract.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.9/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, M. Lisa Manning, and Jean M. Carlson Abstract.
A new hybrid numerical scheme for modelling elastodynamics in unbounded media with near-source heterogeneities
 A new hybrid numerical scheme for modelling elastodynamics in unbounded media with near-source heterogeneities Setare Hajarolasvadi Ahmed E. Elbanna https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bltx92tuwha MOTIVATION
A new hybrid numerical scheme for modelling elastodynamics in unbounded media with near-source heterogeneities Setare Hajarolasvadi Ahmed E. Elbanna https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bltx92tuwha MOTIVATION
Afterslip and aftershocks in the rate-and-state friction law
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005077, 2009 Afterslip and aftershocks in the rate-and-state friction law Agnès Helmstetter 1 and Bruce E. Shaw
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005077, 2009 Afterslip and aftershocks in the rate-and-state friction law Agnès Helmstetter 1 and Bruce E. Shaw
Pulse like, crack like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006388, 2010 Pulse like, crack like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G.
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006388, 2010 Pulse like, crack like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G.
Laboratory study of the frictional rheology of sheared till
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jf000815, 2008 Laboratory study of the frictional rheology of sheared till Andrew P. Rathbun, 1 Chris Marone, 1 Richard
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jf000815, 2008 Laboratory study of the frictional rheology of sheared till Andrew P. Rathbun, 1 Chris Marone, 1 Richard
Effects of shear velocity oscillations on stick-slip behavior in laboratory experiments
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2005jb004238, 2007 Effects of shear velocity oscillations on stick-slip behavior in laboratory experiments Heather M.
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2005jb004238, 2007 Effects of shear velocity oscillations on stick-slip behavior in laboratory experiments Heather M.
Microscopic elasticity and rate and state friction evolution laws
 Article Volume 13, umber 12 6 December 2012 Q12002, doi:10.1029/2012gc004393 ISS: 1525-2027 Microscopic elasticity and rate and state friction evolution laws orman H. Sleep Department of, Stanford University,
Article Volume 13, umber 12 6 December 2012 Q12002, doi:10.1029/2012gc004393 ISS: 1525-2027 Microscopic elasticity and rate and state friction evolution laws orman H. Sleep Department of, Stanford University,
Homework Problems. ( σ 11 + σ 22 ) 2. cos (θ /2), ( σ θθ σ rr ) 2. ( σ 22 σ 11 ) 2
 Engineering Sciences 47: Fracture Mechanics J. R. Rice, 1991 Homework Problems 1) Assuming that the stress field near a crack tip in a linear elastic solid is singular in the form σ ij = rλ Σ ij (θ), it
Engineering Sciences 47: Fracture Mechanics J. R. Rice, 1991 Homework Problems 1) Assuming that the stress field near a crack tip in a linear elastic solid is singular in the form σ ij = rλ Σ ij (θ), it
Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f
 Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f Material undergoes plastic deformation when stress exceeds yield stress σ 0 Permanent strain results from
Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f Material undergoes plastic deformation when stress exceeds yield stress σ 0 Permanent strain results from
The role of fault zone fabric and lithification state on frictional strength, constitutive behavior, and deformation microstructure
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008264, 2011 The role of fault zone fabric and lithification state on frictional strength, constitutive behavior, and deformation microstructure
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008264, 2011 The role of fault zone fabric and lithification state on frictional strength, constitutive behavior, and deformation microstructure
Spectral element modeling of spontaneous earthquake rupture on rate and state faults: Effect of velocity-strengthening friction at shallow depths
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005553, 2008 Spectral element modeling of spontaneous earthquake rupture on rate and state faults: Effect of velocity-strengthening friction
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jb005553, 2008 Spectral element modeling of spontaneous earthquake rupture on rate and state faults: Effect of velocity-strengthening friction
Frictional Properties of the Mount St. Helens Gouge
 Natural Resource Ecology and Management Publications Natural Resource Ecology and Management 2008 Frictional Properties of the Mount St. Helens Gouge Peter Lindsay Moore Iowa State University, pmoore@iastate.edu
Natural Resource Ecology and Management Publications Natural Resource Ecology and Management 2008 Frictional Properties of the Mount St. Helens Gouge Peter Lindsay Moore Iowa State University, pmoore@iastate.edu
This paper was prepared for presentation at the Americas Unconventional Resources Conference held in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA, 5 7 June 2012.
 SPE 155476 The Importance of Slow Slip on Faults During Hydraulic Fracturing Stimulation of Shale Gas Reservoirs Mark D. Zoback, SPE, Arjun Kohli, Indrajit Das and Mark McClure, SPE Stanford University
SPE 155476 The Importance of Slow Slip on Faults During Hydraulic Fracturing Stimulation of Shale Gas Reservoirs Mark D. Zoback, SPE, Arjun Kohli, Indrajit Das and Mark McClure, SPE Stanford University
On dynamic sliding with rate- and state-dependent friction laws
 Geophys. J. Int. (1999) 139, 671^678 On dynamic sliding with rate- and state-dependent friction laws Pascal Favreau, 1 Ioan R. Ionescu 2 and Michel Campillo 1 1 Laboratoire de Ge ophysique Interne et Tectonophysique,
Geophys. J. Int. (1999) 139, 671^678 On dynamic sliding with rate- and state-dependent friction laws Pascal Favreau, 1 Ioan R. Ionescu 2 and Michel Campillo 1 1 Laboratoire de Ge ophysique Interne et Tectonophysique,
Secondary Project Proposal
 Secondary Project Proposal Post-seismic deformation of Chi-chi earthquake Yunyue (Elita) Li 11:, Wednesday, June 2, 21 Li 2 Secondary project proposal Personal prospective MOTIVATION My interests for earthquake
Secondary Project Proposal Post-seismic deformation of Chi-chi earthquake Yunyue (Elita) Li 11:, Wednesday, June 2, 21 Li 2 Secondary project proposal Personal prospective MOTIVATION My interests for earthquake
