Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
|
|
|
- Charlotte York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 16, 9 Nov Energy Balance of dynamic rupture Crack tip stress field Frictional Rupture Fronts Meet in the lab (522 Deike) on Tuesday Nov. 14; See Problem Set #6 Exam 1 due tomorrow (10 Nov.)
2 Mode II crack propagation at speed Vr cohesive zone/slip weakening crack model for friction Shear Stress σ y σ o σ f f max scales as: f max = w/vr w = 7 24 Gu max r = 7 24 GD c w D c = 24 7 G w d c Cracked/Slipping zone Breakdown (cohesive) zone Intact, locked zone Slip
3 G is the fracture energy, Gc is the critical energy release rate for background see: L c is the crack length for unstable growth (and failure); it can be related to the critical patch size for frictional failure R c G is Shear modulus where C is a geometric constant and ν is poisson s ratio. For rupture propagation, Strength Excess S is an important parameter S = y 1 1 f N Propagating Rupture
4 Energy Balance: Specific fracture energy G c For a mode III crack, we can calculate a critical half length for crack extension note that G is shear modulus, sometimes written µ L c is of order 1-2 m for G c of 10 2 J/m 2. What about the stress concentration implied by such a model? How is the singularity resolved? (process zone? Irwin? ) θ See: Brittle Fracture Theory Predicts the Equation of Motion of Frictional Rupture Fronts, Ilya Svetlizky,David S. Kammer, Elsa Bayart, Gil Cohen, and Jay Fineberg, PRL 118, (2017) Classical shear cracks drive the onset of dry frictional motion, Svetlizky & Fineberg, Nature, See also: Johnson and Scholz, JGR, 1976.
5 Adhesive and Abrasive Wear: Fault gouge is wear material Chester et al., 2005 where T is gouge zone thickness, κ is a wear coefficient, D is slip, and h is material hardness This describes steady-state wear. But wear rate is generally higher during a run-in period. And what happens when the gouge zone thickness exceeds the surface roughness? We ll come back to this when we talk about fault growth and evolution.
6 Fault Growth and Development Fault gouge is wear material run in and steady-state wear rate Gouge Zone Thickness, T Fault offset, D This describes steady-state wear. But wear rate is generally higher during a run-in period.
7 Fault Growth and Development Fault gouge is wear material run in and steady-state wear rate Gouge Zone Thickness, T σ 2 > σ 1 σ 1 Fault offset, D This describes steady-state wear. But wear rate is generally higher during a run-in period.
8 Fault Growth and Development Fault gouge is wear material Gouge Zone Thickness, T run in and steady-state wear rate? Fault offset, D This describes steady-state wear. But wear rate is generally higher during a run-in period. And what happens when the gouge zone thickness exceeds the surface roughness?
9 Fault Growth and Development Fault gouge is wear material run in and steady-state wear rate Gouge Zone Thickness, T? Fault offset, D Scholz, 1987
10 Fault Growth and Development Fault Roughness Scholz, 1990
11 Scholz, 1990 Fault Growth and Development
12 Fault Growth and Development Cox and Scholz, JSG, 1988
13 Fault Growth and Development Fault zone width Tchalenko, GSA Bull., 1970
14 Fault zone roughness Ground (lab) surface Scholz, 1990
15 The critical slip distance for shear zones of finite width Fault zone of finite width; multiple, subparallel slip surfaces Surfaces obey rate and state friction Marone, C., Cocco, M., Richardson, E., and E. Tinti, 2009
16 Thermo-mechanics of faulting II San Andreas fault strength, heat flow. Consider: W f = τ v q If τ ~ 100 MPa and v is ~ 30 mm/year, then q is: 1e8 (N /m 2 ) 3e-2 (m/3e7s) = 1e-2 (J/s m 2 ) ~ 100 mw/m2. Problem of finding very low strength materials. Relates to the very broad question of the state of stress in the lithosphere? Byerlee s Law, Rangley experiments, Bore hole stress measurements, bore hole breakouts, earthquake focal mechanisms. Seismic stress drop vs. fault strength.
17 Fault Strength, State of Stress in the Lithosphere, and Earthquake Physics
18 Thermo-mechanics of faulting Fault strength, heat flow. Average Shear Stress Average slip velocity Consider shear heating: W f = τ v q If τ ~ 100 MPa and v is ~ 30 mm/year, then q is: 1e8 (N /m 2 ) 3e-2 (m/3e7s) = 1e-1 (J/s m 2 ) 100 mw/m 2
19 Fault Strength and State of Stress Data from Lachenbruch and Sass, 1980 Heat flow Stress orientations S A F e.g. Townend & Zoback, 2004;; Hickman & Zoback, 2004
20 Data from Lachenbruch and Sass, 1980 Fault Strength and State of Stress Heat flow Stress orientations Have been used to imply that the SAF is weak, µ 0.1. Inferred stress directions S A F σ 1 σ 1 S A F Predicted Observed e.g. Townend & Zoback, 2004;; Hickman & Zoback, 2004
21 SAFOD The San Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth Is the San Andreas anomalously weak?
22 SAF - Geology Based on Zoback et al., EOS, 2010
23 Frictional Strength, SAFOD Phase III Core Carpenter, Marone, and Saffer, Nature Geoscience, 2011 Carpenter, Saffer and Marone, Geology, 2012
24 Weak Fault in a Strong Crust Carpenter, Saffer, and Marone. Geology, 2012
25 Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Aki, Scaling law of seismic spectrum, JGR, 72, , Hanks, b Values and ω -γ seismic source models: implications for tectonic stress variations along active crustal fault zones and the estimation of high-frequency strong ground motion, JGR, 84, , Scaling and Self-Similarity of Earthquake Rupture: Implications for Rupture Dynamics and the Mode of Rupture Propagation 0 Self-similar: Are small earthquakes the same as large ones? Do small ones become large ones or are large eq s different from the start? 1 Geometric self-similarity: aspect ratio of rupture area 2 Physical self-similarity: stress drop, seismic strain, scaling of slip with rupture dimension 3 Observation of constant b-value over a wide range of inferred source dimension. 4 Same physical processes operate during shear rupture of very small (lab scale, mining induced seismicity) and very large earthquakes? 5 Expectation of scaling break if rupture physics/dynamics change in at a critical size (or slip velocity, etc.). Shimazaki result. (Fig. 4.12). Length-Moment scaling and transition at L 60km (Romanowicz, 1992; Scholz, 1994). 6 Gutenberg-Richter frequency-magnitude scaling, b-values. 7 G-R scaling, b-value data. Single-fault versus fault population. G-R versus characteristic earthquake model. 8 Crack vs. slip-pulse models
26 Earthquake Source Properties, Spectra, Scaling, Self-similarity Displacement and acceleration source spectra. Spectra: zero-frequency intercept (M o ), corner frequency (ω o or f c ), high frequency decay (ω γ ), maximum (observed, emitted) frequency f max ω -n ω-square model, ω -2 ω-cube model, ω -3 log u at R ω ο Far-field body-wave spectra and relation to source slip function log freq. (ω) Displacement waveform for P & S waves: In general, very complex. Ω(x, t) and Ω(ω) depend on slip function, azimuth to observer and relative importance of nucleation and stopping phases
27 Scaling and Self-Similarity Are small earthquakes the same as large ones? 1 Geometric self-similarity: rupture aspect ratio 2 Physical self-similarity: stress drop, seismic strain, scaling of slip with rupture dimension Circular ruptures (small) Hanks, 1977 Abercrombie & Leary, 1993
28 Earthquake Source Properties, Spectra, Scaling, Self-similarity ω -3 log u at R ω ο log freq. (ω) ω-cube model, ω -3 Similarity condition M o α L 3 ω o α L -1 Ω(0) α ω o -3 This defines a scaling law. Spectral curves differ by a constant factor at a given period (e.g., 20 s), but they have the same high-freq. asymptote This behavior is expected when the nucleation phase is responsible for the high-freq. asymptote --but consider problem of time domain implication for amplitude (M b decreases with M o )
29 Seismic Source Spectra. Saturation occurs for large events, particularly saturation of M s (T=20 s) Corner frequency, Brune Stress drop. Aki, 1967
30 Earthquake Source Properties, Spectra, Scaling, Self-similarity ω -2 log u at R ω ο ω-square model, ω -2 Two possible explanations log freq. (ω) 1)!Similarity condition (not-similarity) M o α L 2 ω o α L -1 Ω(0) α ω o -2 2) Have similarity condition in terms of nucleation, but high-freq. asymptote is produced by stopping phase if rupture stops very abruptly
31 Earthquake Source Properties, Spectra, Scaling, Self-similarity Displacement and acceleration source spectra. Spectra: zero-frequency intercept (M o ), corner frequency (ω o or f c ), high frequency decay (ω γ ), maximum (observed, emitted) frequency f max f max log u at R ω ο ω -n log a at R ω ο log freq. (ω) log freq. (ω) Aki, Scaling law of seismic spectrum, JGR, 72, , Hanks, b Values and ω -γ seismic source models: implications for tectonic stress variations along active crustal fault zones and the estimation of high-frequency strong ground motion, JGR, 84, , 1979.
32 Earthquake Source Properties, Spectra, Scaling, Self-similarity Source spectra for two events of equal stress drop: omega cube model Large and Small Eq L log u at R ω ο L ω -3 S ω ο S f max log freq. (ω) High-freq. spectral properties: produced by rupture growth, represent nucleation and enlargement log a at R ω ο L ω ο S log freq. (ω)
33 Source spectra for two events of equal stress drop: omega square model Large and Small Eq L log u at R ω ο L ω -2 S ω ο S L f max log freq. (ω) High-freq. spectral properties: produced by rupture growth, represent nucleation and enlargement log a at R ω ο L ω ο S S f max log freq. (ω)
34 Earthquake Source Properties, Spectra, Scaling, Self-similarity Relation between source (a) displacement (b) velocity (c) acceleration history and asymptotic behavior of spectrum
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 18, 16 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Earthquake Magnitude and Moment Brune Stress Drop Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws Scaling and
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 18, 16 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Earthquake Magnitude and Moment Brune Stress Drop Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws Scaling and
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 20, 30 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Aki, Scaling law
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 20, 30 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Aki, Scaling law
Source parameters II. Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop
 Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture Propagation: Evidence from Geological and Seismological Observations
 Euroconference of Rock Physics and Geomechanics: Natural hazards: thermo-hydro-mechanical processes in rocks Erice, Sicily, 25-30 September, 2007 Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture
Euroconference of Rock Physics and Geomechanics: Natural hazards: thermo-hydro-mechanical processes in rocks Erice, Sicily, 25-30 September, 2007 Scale Dependence in the Dynamics of Earthquake Rupture
friction friction a-b slow fast increases during sliding
 µ increases during sliding faster sliding --> stronger fault --> slows sliding leads to stable slip: no earthquakes can start velocity-strengthening friction slow fast µ velocity-strengthening friction
µ increases during sliding faster sliding --> stronger fault --> slows sliding leads to stable slip: no earthquakes can start velocity-strengthening friction slow fast µ velocity-strengthening friction
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lectures & 3, 9/31 Aug 017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Discussion of Handin, JGR, 1969 and Chapter 1 Scholz, 00. Stress analysis and Mohr Circles Coulomb Failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lectures & 3, 9/31 Aug 017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Discussion of Handin, JGR, 1969 and Chapter 1 Scholz, 00. Stress analysis and Mohr Circles Coulomb Failure
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip
 Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors
 Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors Chris Marone, The Pennsylvania State University John Leeman, Marco Scuderi, Elisa Tinti, Cristiano
Friction Constitutive Laws and. The Mechanics of Slow Earthquakes and the Spectrum of Fault Slip Behaviors Chris Marone, The Pennsylvania State University John Leeman, Marco Scuderi, Elisa Tinti, Cristiano
Di#erences in Earthquake Source and Ground Motion Characteristics between Surface and Buried Crustal Earthquakes
 Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. Univ. Tokyo Vol. 2+,**0 pp.,/3,00 Di#erences in Earthquake Source and Ground Motion Characteristics between Surface and Buried Crustal Earthquakes Paul Somerville* and Arben Pitarka
Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. Univ. Tokyo Vol. 2+,**0 pp.,/3,00 Di#erences in Earthquake Source and Ground Motion Characteristics between Surface and Buried Crustal Earthquakes Paul Somerville* and Arben Pitarka
The San Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth: Recent Site Characterization Studies and the 2.2-Km-Deep Pilot Hole
 The San Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth: Recent Site Characterization Studies and the 2.2-Km-Deep Pilot Hole Steve Hickman and Bill Ellsworth (USGS) Mark Zoback (Stanford University) and the Pre-EarthScope
The San Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth: Recent Site Characterization Studies and the 2.2-Km-Deep Pilot Hole Steve Hickman and Bill Ellsworth (USGS) Mark Zoback (Stanford University) and the Pre-EarthScope
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
Earthquake stress drop estimates: What are they telling us?
 Earthquake stress drop estimates: What are they telling us? Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego October 27, 2014 SCEC Community Stress Model Workshop Lots of data for big earthquakes (rupture dimensions,
Earthquake stress drop estimates: What are they telling us? Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego October 27, 2014 SCEC Community Stress Model Workshop Lots of data for big earthquakes (rupture dimensions,
1/22/2015. High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics
 High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics Thanks: Amir Sagy Andrew Madden, David Lockner, Einat Aharonov Harry Green, Jay Finberg, Jefferson Chang, Shalev Siman Tov
High velocity shear experiments with possible implications to earthquake physics Thanks: Amir Sagy Andrew Madden, David Lockner, Einat Aharonov Harry Green, Jay Finberg, Jefferson Chang, Shalev Siman Tov
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Surface and body forces Tensors, Mohr circles. Theoretical strength of materials Defects Stress concentrations Griffith failure
What allows seismic events to grow big?: Insights from fault roughness and b-value analysis in stick-slip experiments
 What allows seismic events to grow big?: Insights from fault roughness and b-value analysis in stick-slip experiments T. H. W. Goebel 1, G. Kwiatek 2, T. W. Becker 3, G. Dresen 2, E.E. Brodsky 1 1 UC Santa
What allows seismic events to grow big?: Insights from fault roughness and b-value analysis in stick-slip experiments T. H. W. Goebel 1, G. Kwiatek 2, T. W. Becker 3, G. Dresen 2, E.E. Brodsky 1 1 UC Santa
Earthquake nucleation. Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab
 Earthquake nucleation Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab How do earthquakes start? Do small and large earthquakes start differently? Predictive value of earthquake onset and foreshock sequences? Seismological
Earthquake nucleation Pablo Ampuero Caltech Seismolab How do earthquakes start? Do small and large earthquakes start differently? Predictive value of earthquake onset and foreshock sequences? Seismological
Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta. California Institute of Technology
 Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta California Institute of Technology Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip
Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip Behaviors: What We Have and What We Need Nadia Lapusta California Institute of Technology Modeling Approaches That Reproduce a Range of Fault Slip
FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE. Kyle Withers Qian Yao
 FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE Kyle Withers Qian Yao Temperature Change Along Fault Mode II (plain strain) crack rupturing bilaterally at a constant speed v r Idealize earthquake ruptures as shear
FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE Kyle Withers Qian Yao Temperature Change Along Fault Mode II (plain strain) crack rupturing bilaterally at a constant speed v r Idealize earthquake ruptures as shear
Earthquake Stress Drops in Southern California
 Earthquake Stress Drops in Southern California Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego September 11, 2009 Earthquake Research Institute Lots of data for big earthquakes (rupture dimensions, slip history,
Earthquake Stress Drops in Southern California Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego September 11, 2009 Earthquake Research Institute Lots of data for big earthquakes (rupture dimensions, slip history,
A mechanical model of the San Andreas fault and SAFOD Pilot Hole stress measurements
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L15S13, doi:10.1029/2004gl019521, 2004 A mechanical model of the San Andreas fault and SAFOD Pilot Hole stress measurements Jean Chéry Laboratoire Dynamique de la
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L15S13, doi:10.1029/2004gl019521, 2004 A mechanical model of the San Andreas fault and SAFOD Pilot Hole stress measurements Jean Chéry Laboratoire Dynamique de la
Fault Representation Methods for Spontaneous Dynamic Rupture Simulation. Luis A. Dalguer
 Fault Representation Methods for Spontaneous Dynamic Rupture Simulation Luis A. Dalguer Computational Seismology Group Swiss Seismological Service (SED) ETH-Zurich July 12-18, 2011 2 st QUEST Workshop,
Fault Representation Methods for Spontaneous Dynamic Rupture Simulation Luis A. Dalguer Computational Seismology Group Swiss Seismological Service (SED) ETH-Zurich July 12-18, 2011 2 st QUEST Workshop,
Regional tectonic stress near the San Andreas fault in central and southern California
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L15S11, doi:10.1029/2003gl018918, 2004 Regional tectonic stress near the San Andreas fault in central and southern California J. Townend School of Earth Sciences,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L15S11, doi:10.1029/2003gl018918, 2004 Regional tectonic stress near the San Andreas fault in central and southern California J. Townend School of Earth Sciences,
Frictional behavior of materials in the 3D SAFOD volume
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L05302, doi:10.1029/2008gl036660, 2009 Frictional behavior of materials in the 3D SAFOD volume B. M. Carpenter, 1 C. Marone, 1 and D.
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L05302, doi:10.1029/2008gl036660, 2009 Frictional behavior of materials in the 3D SAFOD volume B. M. Carpenter, 1 C. Marone, 1 and D.
Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs
 Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs Lindsey N. Meighan, Ted Urbancic and Adam Baig ESG, Kingston, Ontario Summary
Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs Lindsey N. Meighan, Ted Urbancic and Adam Baig ESG, Kingston, Ontario Summary
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Standard Solids and Fracture Fluids: Mechanical, Chemical Effects Effective Stress Dilatancy Hardening and Stability Mead, 1925
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Standard Solids and Fracture Fluids: Mechanical, Chemical Effects Effective Stress Dilatancy Hardening and Stability Mead, 1925
Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area. Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC
 Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC Constitutive law on the fault: Rate-and-state friction at low slip rates + Potential
Qualitative modeling of earthquakes and aseismic slip in the Tohoku-Oki area Nadia Lapusta, Caltech Hiroyuki Noda, JAMSTEC Constitutive law on the fault: Rate-and-state friction at low slip rates + Potential
Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures
 Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures (1) In terms of friction (2) In terms of fracture mechanics Scholz describes conditions for rupture propagation (i.e. instability) via energy
Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures (1) In terms of friction (2) In terms of fracture mechanics Scholz describes conditions for rupture propagation (i.e. instability) via energy
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ).
 Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
EXAMINATION ON CONSECUTIVE RUPTURING OF TWO CLOSE FAULTS BY DYNAMIC SIMULATION
 EXAMINATION ON CONSECUTIVE RUPTURING OF TWO CLOSE FAULTS BY DYNAMIC SIMULATION M. Muto 1, K. Dan 1, H. Torita 1, Y. Ohashi 1, and Y. Kase 2 1 Ohsaki Research Institute, Inc., Tokyo, Japan 2 National Institute
EXAMINATION ON CONSECUTIVE RUPTURING OF TWO CLOSE FAULTS BY DYNAMIC SIMULATION M. Muto 1, K. Dan 1, H. Torita 1, Y. Ohashi 1, and Y. Kase 2 1 Ohsaki Research Institute, Inc., Tokyo, Japan 2 National Institute
Using information about wave amplitudes to learn about the earthquake size.
 Earthquake Magnitudes and Moments Using information about wave amplitudes to learn about the earthquake size. Need to correct for decrease with distance M = log(a/t) + F(h,Δ) + C A is the amplitude of
Earthquake Magnitudes and Moments Using information about wave amplitudes to learn about the earthquake size. Need to correct for decrease with distance M = log(a/t) + F(h,Δ) + C A is the amplitude of
Inferring fault strength from earthquake rupture properties and the tectonic implications of high pore pressure faulting
 Earth Planets Space, 54, 1173 1179, 22 Inferring fault strength from earthquake rupture properties and the tectonic implications of high pore pressure faulting Stephen A. Miller Geophysics Institute, ETH-Zurich
Earth Planets Space, 54, 1173 1179, 22 Inferring fault strength from earthquake rupture properties and the tectonic implications of high pore pressure faulting Stephen A. Miller Geophysics Institute, ETH-Zurich
Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L24301, doi:10.1029/2008gl036249, 2008 Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L24301, doi:10.1029/2008gl036249, 2008 Depth variation of coseismic stress drop explains bimodal earthquake magnitude-frequency distribution
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 9, 21 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Rate and State Friction Velocity step test to measure RSF parameters SHS test to measure RSF parameters
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 9, 21 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Rate and State Friction Velocity step test to measure RSF parameters SHS test to measure RSF parameters
Potency-magnitude scaling relations for southern California earthquakes with 1.0 < M L < 7.0
 Geophys. J. Int. (2002) 148, F1 F5 FAST TRACK PAPER Potency-magnitude scaling relations for southern California earthquakes with 1.0 < M L < 7.0 Yehuda Ben-Zion 1, and Lupei Zhu 2 1 Department of Earth
Geophys. J. Int. (2002) 148, F1 F5 FAST TRACK PAPER Potency-magnitude scaling relations for southern California earthquakes with 1.0 < M L < 7.0 Yehuda Ben-Zion 1, and Lupei Zhu 2 1 Department of Earth
The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Christopher H. Scholz Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory and Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Columbia University 2nd edition CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Christopher H. Scholz Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory and Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Columbia University 2nd edition CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
Materials and Methods The deformation within the process zone of a propagating fault can be modeled using an elastic approximation.
 Materials and Methods The deformation within the process zone of a propagating fault can be modeled using an elastic approximation. In the process zone, stress amplitudes are poorly determined and much
Materials and Methods The deformation within the process zone of a propagating fault can be modeled using an elastic approximation. In the process zone, stress amplitudes are poorly determined and much
STUDYING THE IMPORTANT PARAMETERS IN EARTHQUAKE SIMULATION BASED ON STOCHASTIC FINITE FAULT MODELING
 STUDYING THE IMPORTANT PARAMETERS IN EARTHQUAKE SIMULATION BASED ON STOCHASTIC FINITE FAULT MODELING H. Moghaddam 1, N. Fanaie 2* and H. Hamzehloo 1 Professor, Dept. of civil Engineering, Sharif University
STUDYING THE IMPORTANT PARAMETERS IN EARTHQUAKE SIMULATION BASED ON STOCHASTIC FINITE FAULT MODELING H. Moghaddam 1, N. Fanaie 2* and H. Hamzehloo 1 Professor, Dept. of civil Engineering, Sharif University
Friction. Why friction? Because slip on faults is resisted by frictional forces.
 Friction Why friction? Because slip on faults is resisted by frictional forces. We first describe the results of laboratory friction experiments, and then discuss the implications of the friction constitutive
Friction Why friction? Because slip on faults is resisted by frictional forces. We first describe the results of laboratory friction experiments, and then discuss the implications of the friction constitutive
Utah State University. Ryan M. Lee Utah State University
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Physics Capstone Project Physics Student Research 12-22-2015 Correlations of Fault Rock Constitutive Properties Derived from Laboratory Retrieved Data of the North-Eastern
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Physics Capstone Project Physics Student Research 12-22-2015 Correlations of Fault Rock Constitutive Properties Derived from Laboratory Retrieved Data of the North-Eastern
Statistics of Earthquake Stress Drops on a Heterogeneous Fault in an Elastic Half-Space
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 99, No., pp. 7, June 9, doi:.7/ Statistics of Earthquake Stress Drops on a Heterogeneous Fault in an Elastic Half-Space by I. W. Bailey and Y. Ben-Zion
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 99, No., pp. 7, June 9, doi:.7/ Statistics of Earthquake Stress Drops on a Heterogeneous Fault in an Elastic Half-Space by I. W. Bailey and Y. Ben-Zion
The Frictional Regime
 The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
The Frictional Regime Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 1/25/2016 10:08 AM We Discuss The Frictional Regime Processes of Brittle Deformation
Mechanics of faulting
 Mechanics of faulting http://www.sanandre asfault.org Jyr-Ching Hu, Dept. Geosciences National Taiwan University Strengths of active thrust-belt wedges & their basal detachments: directly determined from
Mechanics of faulting http://www.sanandre asfault.org Jyr-Ching Hu, Dept. Geosciences National Taiwan University Strengths of active thrust-belt wedges & their basal detachments: directly determined from
Numerical study on multi-scaling earthquake rupture
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L266, doi:1.129/23gl1878, 24 Numerical study on multi-scaling earthquake rupture Hideo Aochi Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire, France Satoshi Ide
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L266, doi:1.129/23gl1878, 24 Numerical study on multi-scaling earthquake rupture Hideo Aochi Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire, France Satoshi Ide
JournalofGeophysicalResearch: SolidEarth
 JournalofGeophysicalResearch: SolidEarth RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Relations between source dimensions and corner frequencies are established Stress drop estimates are affected by differences in source
JournalofGeophysicalResearch: SolidEarth RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Relations between source dimensions and corner frequencies are established Stress drop estimates are affected by differences in source
Finite element modelling of fault stress triggering due to hydraulic fracturing
 Finite element modelling of fault stress triggering due to hydraulic fracturing Arsalan, Sattari and David, Eaton University of Calgary, Geoscience Department Summary In this study we aim to model fault
Finite element modelling of fault stress triggering due to hydraulic fracturing Arsalan, Sattari and David, Eaton University of Calgary, Geoscience Department Summary In this study we aim to model fault
PEAK AND ROOT-MEAN-SQUARE ACCELERATIONS RADIATED FROM CIRCULAR CRACKS AND STRESS-DROP ASSOCIATED WITH SEISMIC HIGH-FREQUENCY RADIATION
 PEAK AND ROOT-MEAN-SQUARE ACCELERATIONS RADIATED FROM CIRCULAR CRACKS AND STRESS-DROP ASSOCIATED WITH SEISMIC HIGH-FREQUENCY RADIATION Earthquake Research Institute, the University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
PEAK AND ROOT-MEAN-SQUARE ACCELERATIONS RADIATED FROM CIRCULAR CRACKS AND STRESS-DROP ASSOCIATED WITH SEISMIC HIGH-FREQUENCY RADIATION Earthquake Research Institute, the University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
Magnitude, scaling, and spectral signature of tensile microseisms
 Magnitude, scaling, and spectral signature of tensile microseisms David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Summary The spatial dimensions and rupture characteristics of microseismic
Magnitude, scaling, and spectral signature of tensile microseisms David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Summary The spatial dimensions and rupture characteristics of microseismic
Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f
 Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f Material undergoes plastic deformation when stress exceeds yield stress σ 0 Permanent strain results from
Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f Material undergoes plastic deformation when stress exceeds yield stress σ 0 Permanent strain results from
Numerical modeling of sliding contact
 Numerical modeling of sliding contact J.F. Molinari 1) Atomistic modeling of sliding contact; P. Spijker, G. Anciaux 2) Continuum modeling; D. Kammer, V. Yastrebov, P. Spijker pj ICTP/FANAS Conference
Numerical modeling of sliding contact J.F. Molinari 1) Atomistic modeling of sliding contact; P. Spijker, G. Anciaux 2) Continuum modeling; D. Kammer, V. Yastrebov, P. Spijker pj ICTP/FANAS Conference
When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress?
 When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress? How could you exert a non-zero shear stress on the ground? Hydrostatic Pressure (fluids)
When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress? How could you exert a non-zero shear stress on the ground? Hydrostatic Pressure (fluids)
Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size?
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
Scaling Laws. σ 1. σ = mean stress, which is needed to compute σ 0. η = percent strain energy released in eq. Introduction.
 Scaling Laws Introduction Scaling Laws or Relationships are the result of empirical observation. They describe how one physical parameter varies as a function of another physical parameter within a system.
Scaling Laws Introduction Scaling Laws or Relationships are the result of empirical observation. They describe how one physical parameter varies as a function of another physical parameter within a system.
Gutenberg-Richter Relationship: Magnitude vs. frequency of occurrence
 Quakes per year. Major = 7-7.9; Great = 8 or larger. Year Major quakes Great quakes 1969 15 1 1970 20 0 1971 19 1 1972 15 0 1973 13 0 1974 14 0 1975 14 1 1976 15 2 1977 11 2 1978 16 1 1979 13 0 1980 13
Quakes per year. Major = 7-7.9; Great = 8 or larger. Year Major quakes Great quakes 1969 15 1 1970 20 0 1971 19 1 1972 15 0 1973 13 0 1974 14 0 1975 14 1 1976 15 2 1977 11 2 1978 16 1 1979 13 0 1980 13
OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION 3 WHAT'S MISSING? 4 OBJECTIVES 5
 OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION 3 WHAT'S MISSING? 4 OBJECTIVES 5 DISTORTION OF SEISMIC SOURCE SPECTRUM 6 PRINCIPLE 7 SEISMIC SOURCE SPECTRUM 8 EFFECT OF RECORDING INSTRUMENTS 9 SEISMOMETERS 9 CORRECTION FOR FREQUENCY
OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION 3 WHAT'S MISSING? 4 OBJECTIVES 5 DISTORTION OF SEISMIC SOURCE SPECTRUM 6 PRINCIPLE 7 SEISMIC SOURCE SPECTRUM 8 EFFECT OF RECORDING INSTRUMENTS 9 SEISMOMETERS 9 CORRECTION FOR FREQUENCY
Internal Layers of the Earth
 Lecture #4 notes Geology 3950, Spring 2006; CR Stern Seismic waves, earthquake magnitudes and location, and internal earth structure (pages 28-95 in the 4 th edition and 28-32 and 50-106 in the 5 th edition)
Lecture #4 notes Geology 3950, Spring 2006; CR Stern Seismic waves, earthquake magnitudes and location, and internal earth structure (pages 28-95 in the 4 th edition and 28-32 and 50-106 in the 5 th edition)
Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, 1 M. Lisa Manning, 1,2 and Jean M.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, 1 M. Lisa Manning, 1,2 and Jean M.
Spectral Element simulation of rupture dynamics
 Spectral Element simulation of rupture dynamics J.-P. Vilotte & G. Festa Department of Seismology, Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, 75252 France ABSTRACT Numerical modeling is an important tool,
Spectral Element simulation of rupture dynamics J.-P. Vilotte & G. Festa Department of Seismology, Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, 75252 France ABSTRACT Numerical modeling is an important tool,
A constitutive scaling law and a unified comprehension for frictional slip failure, shear fracture of intact rock, and earthquake rupture
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B2, 2080, doi:10.1029/2000jb000123, 2003 A constitutive scaling law and a unified comprehension for frictional slip failure, shear fracture of intact rock,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B2, 2080, doi:10.1029/2000jb000123, 2003 A constitutive scaling law and a unified comprehension for frictional slip failure, shear fracture of intact rock,
Normal stress causes normal strain σ 22
 Normal stress causes normal strain blue box = before yellow box = after x 2 = Eɛ 22 ɛ 22 = E x 3 x 1 force is acting on the x2 face force is acting in the x2 direction Why do I draw this with equal stresses
Normal stress causes normal strain blue box = before yellow box = after x 2 = Eɛ 22 ɛ 22 = E x 3 x 1 force is acting on the x2 face force is acting in the x2 direction Why do I draw this with equal stresses
Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer. GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller
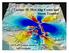 Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller Slow Slip Events From Kristine Larson What is a Slow Slip Event? Slip on a fault, like in an earthquake, BUT
Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller Slow Slip Events From Kristine Larson What is a Slow Slip Event? Slip on a fault, like in an earthquake, BUT
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law
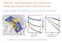 Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Research Themes in Stimulation Geomechanics. How do we optimize slickwater frac ing?
 Research Themes in Stimulation Geomechanics How do stress, fractures and rock properties affect the success of stimulation? How do pressure and stress (and formation properties) evolve during stimulation?
Research Themes in Stimulation Geomechanics How do stress, fractures and rock properties affect the success of stimulation? How do pressure and stress (and formation properties) evolve during stimulation?
Simulation of earthquake rupture process and strong ground motion
 Simulation of earthquake rupture process and strong ground motion Takashi Miyatake (1) and Tomohiro Inoue (2) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Yayoi, Bunkyo, Tokyo, 113-0032, Japan
Simulation of earthquake rupture process and strong ground motion Takashi Miyatake (1) and Tomohiro Inoue (2) (1) Earthquake Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Yayoi, Bunkyo, Tokyo, 113-0032, Japan
Weakness of the Intracontinental Strike-Slip Kunlun Fault and Implications for Tibetan Tectonics
 62 The Open Geology Journal, 2010, 4, 62-66 Open Access Weakness of the Intracontinental Strike-Slip Kunlun Fault and Implications for Tibetan Tectonics Weipeng Huang and Aiming Lin * Graduate School of
62 The Open Geology Journal, 2010, 4, 62-66 Open Access Weakness of the Intracontinental Strike-Slip Kunlun Fault and Implications for Tibetan Tectonics Weipeng Huang and Aiming Lin * Graduate School of
Brittle Deformation. Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm
 Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Lecture 6 Brittle Deformation Earth Structure (2 nd Edition), 2004 W.W. Norton & Co, New York Slide show by Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton, unless noted otherwise Brittle deformation EarthStructure (2 nd
Slip-weakening behavior during the propagation of dynamic ruptures obeying rate- and state-dependent friction laws
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B8, 2373, doi:10.1029/2002jb002198, 2003 Slip-weakening behavior during the propagation of dynamic ruptures obeying rate- and state-dependent friction laws
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B8, 2373, doi:10.1029/2002jb002198, 2003 Slip-weakening behavior during the propagation of dynamic ruptures obeying rate- and state-dependent friction laws
Instabilities and Dynamic Rupture in a Frictional Interface
 Instabilities and Dynamic Rupture in a Frictional Interface Laurent BAILLET LGIT (Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique) Grenoble France laurent.baillet@ujf-grenoble.fr http://www-lgit.obs.ujf-grenoble.fr/users/lbaillet/
Instabilities and Dynamic Rupture in a Frictional Interface Laurent BAILLET LGIT (Laboratoire de Géophysique Interne et Tectonophysique) Grenoble France laurent.baillet@ujf-grenoble.fr http://www-lgit.obs.ujf-grenoble.fr/users/lbaillet/
Overestimates of Earthquake Prediction Efficiency in a "Post-Prediction"
 Letter J. Phys. Earth, 41, 41-43, 1993 Overestimates of Earthquake Prediction Efficiency in a "Post-Prediction" State Shozo Matsumura National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention,
Letter J. Phys. Earth, 41, 41-43, 1993 Overestimates of Earthquake Prediction Efficiency in a "Post-Prediction" State Shozo Matsumura National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention,
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting 5 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Work of deformation, shear and volume strain Importance of volume change and diltancy rate (rate of volume strain with
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting 5 Sep. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Work of deformation, shear and volume strain Importance of volume change and diltancy rate (rate of volume strain with
An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth.
 An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth. Measuring an Earthquake s Size Magnitude and Moment Each can
An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth. Measuring an Earthquake s Size Magnitude and Moment Each can
Challenges in earthquake physics and source imaging
 Challenges in earthquake physics and source imaging Jean-Paul Ampuero and Nadia Lapusta (Caltech Seismolab) Main goals and current issues in earthquake dynamics The source imaging inverse problem Parallels
Challenges in earthquake physics and source imaging Jean-Paul Ampuero and Nadia Lapusta (Caltech Seismolab) Main goals and current issues in earthquake dynamics The source imaging inverse problem Parallels
On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent faults
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15303, doi:10.1029/2007gl030337, 2007 On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L15303, doi:10.1029/2007gl030337, 2007 On the nucleation of creep and the interaction between creep and seismic slip on rate- and state-dependent
Source Duration Scales with Magnitude Differently For Earthquakes on the San Andreas Fault and on Secondary Faults in Parkfield, CA
 Source Duration Scales with Magnitude Differently For Earthquakes on the San Andreas Fault and on Secondary Faults in Parkfield, CA Rebecca M. Harrington University of California, Los Angeles Dept. of
Source Duration Scales with Magnitude Differently For Earthquakes on the San Andreas Fault and on Secondary Faults in Parkfield, CA Rebecca M. Harrington University of California, Los Angeles Dept. of
LABORATORY-DERIVED FRICTION LAWS AND THEIR APPLICATION TO SEISMIC FAULTING
 Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1998. 26:643 96 Copyright c 1998 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved LABORATORY-DERIVED FRICTION LAWS AND THEIR APPLICATION TO SEISMIC FAULTING Chris Marone Department
Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1998. 26:643 96 Copyright c 1998 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved LABORATORY-DERIVED FRICTION LAWS AND THEIR APPLICATION TO SEISMIC FAULTING Chris Marone Department
Tectonics. Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting GNH7/GG09/GEOL4002 EARTHQUAKE SEISMOLOGY AND EARTHQUAKE HAZARD
 Tectonics Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting Plane strain 3 Strain occurs only in a plane. In the third direction strain is zero. 1 ε 2 = 0 3 2 Assumption of plane strain for faulting e.g., reverse fault:
Tectonics Lecture 12 Earthquake Faulting Plane strain 3 Strain occurs only in a plane. In the third direction strain is zero. 1 ε 2 = 0 3 2 Assumption of plane strain for faulting e.g., reverse fault:
Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.9/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, M. Lisa Manning, and Jean M. Carlson Abstract.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:.9/, Pulse-like, crack-like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G. Daub, M. Lisa Manning, and Jean M. Carlson Abstract.
Elastic Rebound Theory
 Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory Earthquakes occur when strain exceeds the strength of the rock and the rock fractures. The arrival of earthquakes waves is recorded by a seismograph. The amplitude of
Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory Earthquakes occur when strain exceeds the strength of the rock and the rock fractures. The arrival of earthquakes waves is recorded by a seismograph. The amplitude of
A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing
 A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing Jiyang Ye, Mirko Van Der Baan (Email: jiyang1@ualberta.ca, Mirko.VanderBaan@ualberta.ca)
A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing Jiyang Ye, Mirko Van Der Baan (Email: jiyang1@ualberta.ca, Mirko.VanderBaan@ualberta.ca)
Spatial and temporal stress drop variations in small earthquakes near Parkfield, California
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jb004395, 2007 Spatial and temporal stress drop variations in small earthquakes near Parkfield, California Bettina
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jb004395, 2007 Spatial and temporal stress drop variations in small earthquakes near Parkfield, California Bettina
Evidence for a strong San Andreas fault
 Evidence for a strong San Andreas fault Christopher H. Scholz Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Columbia University, Palisades, 10964, New York, USA ABSTRACT Stress measurements in deep boreholes have
Evidence for a strong San Andreas fault Christopher H. Scholz Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Columbia University, Palisades, 10964, New York, USA ABSTRACT Stress measurements in deep boreholes have
Microseismic Monitoring Shale Gas Plays: Advances in the Understanding of Hydraulic Fracturing 20 MAR 16 HANNAH CHITTENDEN
 Microseismic Monitoring Shale Gas Plays: Advances in the Understanding of Hydraulic Fracturing 20 MAR 16 HANNAH CHITTENDEN Introduction Early days: Microseismic monitoring has been around since the early
Microseismic Monitoring Shale Gas Plays: Advances in the Understanding of Hydraulic Fracturing 20 MAR 16 HANNAH CHITTENDEN Introduction Early days: Microseismic monitoring has been around since the early
Surface Rupture in Kinematic Ruptures Models for Hayward Fault Scenario Earthquakes
 Surface Rupture in Kinematic Ruptures Models for Hayward Fault Scenario Earthquakes Brad Aagaard May 21, 2009 Surface Rupture from Kinematic Rupture Models Objective Holistic approach to calculating surface
Surface Rupture in Kinematic Ruptures Models for Hayward Fault Scenario Earthquakes Brad Aagaard May 21, 2009 Surface Rupture from Kinematic Rupture Models Objective Holistic approach to calculating surface
Study of Rupture Directivity in a Foam Rubber Physical Model
 Progress Report Task 1D01 Study of Rupture Directivity in a Foam Rubber Physical Model Rasool Anooshehpoor and James N. Brune University of Nevada, Reno Seismological Laboratory (MS/174) Reno, Nevada 89557-0141
Progress Report Task 1D01 Study of Rupture Directivity in a Foam Rubber Physical Model Rasool Anooshehpoor and James N. Brune University of Nevada, Reno Seismological Laboratory (MS/174) Reno, Nevada 89557-0141
Dynamic Rupture, Fault Opening, and Near Fault Particle Motions along an Interface between Dissimilar Materials
 Dynamic Rupture, Fault Opening, and Near Fault Particle Motions along an Interface between Dissimilar Materials Baoping Shi 1, Yanheng Li 1, Jian Zhang 1 and James N. Brune 2 1 School of Earth Sciences,
Dynamic Rupture, Fault Opening, and Near Fault Particle Motions along an Interface between Dissimilar Materials Baoping Shi 1, Yanheng Li 1, Jian Zhang 1 and James N. Brune 2 1 School of Earth Sciences,
and fault roughness analysis in laboratory stick-slip experiments
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Publisher: GSA Journal: GEOL: Geology Article ID: Template What allows seismic events to grow big?: Insights from b-value and fault roughness analysis in laboratory stick-slip experiments
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Publisher: GSA Journal: GEOL: Geology Article ID: Template What allows seismic events to grow big?: Insights from b-value and fault roughness analysis in laboratory stick-slip experiments
SEISMIC SOURCES 1: FAULTING
 SEISMOLOGY Master Degree Programme in Physics - UNITS Physics of the Earth and of the Environment SEISMIC SOURCES 1: FAULTING FABIO ROMANELLI Department of Mathematics & Geosciences University of Trieste
SEISMOLOGY Master Degree Programme in Physics - UNITS Physics of the Earth and of the Environment SEISMIC SOURCES 1: FAULTING FABIO ROMANELLI Department of Mathematics & Geosciences University of Trieste
Elizabeth H. Hearn modified from W. Behr
 Reconciling postseismic and interseismic surface deformation around strike-slip faults: Earthquake-cycle models with finite ruptures and viscous shear zones Elizabeth H. Hearn hearn.liz@gmail.com modified
Reconciling postseismic and interseismic surface deformation around strike-slip faults: Earthquake-cycle models with finite ruptures and viscous shear zones Elizabeth H. Hearn hearn.liz@gmail.com modified
Fabric induced weakness of tectonic faults
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl041689, 2010 Fabric induced weakness of tectonic faults André Niemeijer, 1,2,3,4 Chris Marone, 2,3 and Derek Elsworth
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl041689, 2010 Fabric induced weakness of tectonic faults André Niemeijer, 1,2,3,4 Chris Marone, 2,3 and Derek Elsworth
Pulse like, crack like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006388, 2010 Pulse like, crack like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G.
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006388, 2010 Pulse like, crack like, and supershear earthquake ruptures with shear strain localization Eric G.
Properties of large ruptures and the dynamical influence of fluids on earthquakes and faulting
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. B9, 2182, doi:10.1029/2000jb000032, 2002 Properties of large ruptures and the dynamical influence of fluids on earthquakes and faulting S. A. Miller 1 Geology
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 107, NO. B9, 2182, doi:10.1029/2000jb000032, 2002 Properties of large ruptures and the dynamical influence of fluids on earthquakes and faulting S. A. Miller 1 Geology
HOMEWORK 3 Draft presentations due November 4 Oral presentations of Group problems, November 6, November 8
 HOMEWORK 3 Draft presentations due November 4 Oral presentations of Group problems, November 6, November 8 Group A1 Modeling marine magnetic anomalies Write a Matlab program to generate marine magnetic
HOMEWORK 3 Draft presentations due November 4 Oral presentations of Group problems, November 6, November 8 Group A1 Modeling marine magnetic anomalies Write a Matlab program to generate marine magnetic
Stress orientations at intermediate angles to the San Andreas Fault, California
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2004jb003239, 2004 Stress orientations at intermediate angles to the San Andreas Fault, California Jeanne L. Hardebeck and Andrew J. Michael U.S.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2004jb003239, 2004 Stress orientations at intermediate angles to the San Andreas Fault, California Jeanne L. Hardebeck and Andrew J. Michael U.S.
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2013) 193, 1691 1712 Advance Access publication 2013 March 26 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt074 Comparison of average stress drop measures for ruptures with heterogeneous
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2013) 193, 1691 1712 Advance Access publication 2013 March 26 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt074 Comparison of average stress drop measures for ruptures with heterogeneous
Broadband Strong Motion Simulation Based on a Dynamic Fault Rupture Model: Application to the 2000 Tottori, Japan earthquake
 Workshop on Numerical odeling of Earthquake Source Dynamics, Smolenice Castle, Slovak Republic Broadband Strong otion Simulation Based on a Dynamic Fault Rupture odel: Application to the 2000 Tottori,
Workshop on Numerical odeling of Earthquake Source Dynamics, Smolenice Castle, Slovak Republic Broadband Strong otion Simulation Based on a Dynamic Fault Rupture odel: Application to the 2000 Tottori,
Potential role of mantle-derived fluids in weakening the San Andreas Fault
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb006087, 2009 Potential role of mantle-derived fluids in weakening the San Andreas Fault Patrick M. Fulton 1,2 and
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb006087, 2009 Potential role of mantle-derived fluids in weakening the San Andreas Fault Patrick M. Fulton 1,2 and
Scaling of small repeating earthquakes explained by interaction of seismic and aseismic slip in a rate and state fault model
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb005749, 2009 Scaling of small repeating earthquakes explained by interaction of seismic and aseismic slip in a
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb005749, 2009 Scaling of small repeating earthquakes explained by interaction of seismic and aseismic slip in a
Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.002 Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.002 Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Apparent Slow Oceanic Transform Earthquakes Due to Source Mechanism Bias
 Apparent Slow Oceanic Transform Earthquakes Due to Source echanism Bias Kimberly Schramm and Seth Stein Kimberly Schramm 1 and Seth Stein Northwestern University INTRODUCTION Slow earthquakes, characterized
Apparent Slow Oceanic Transform Earthquakes Due to Source echanism Bias Kimberly Schramm and Seth Stein Kimberly Schramm 1 and Seth Stein Northwestern University INTRODUCTION Slow earthquakes, characterized
LECTURE #5: Plate Tectonics: Boundaries & Earthquake Science
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #5: Plate Tectonics: Boundaries & Earthquake Science Date: 23 January 2018 I. Reminder: Exam #1 is scheduled for Feb 1st one week from Thursday o
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #5: Plate Tectonics: Boundaries & Earthquake Science Date: 23 January 2018 I. Reminder: Exam #1 is scheduled for Feb 1st one week from Thursday o
Scaling Relations for Seismic Cycles on Mid-Ocean Ridge
 Scaling Relations for Seismic Cycles on Mid-Ocean Ridge Transform Faults Margaret S. Boettcher University of New Hampshire, Dept. of Earth Sciences, Durham, NH 03824 Jeffrey J. McGuire Woods Hole Oceanographic
Scaling Relations for Seismic Cycles on Mid-Ocean Ridge Transform Faults Margaret S. Boettcher University of New Hampshire, Dept. of Earth Sciences, Durham, NH 03824 Jeffrey J. McGuire Woods Hole Oceanographic
