A NOVEL TWO-DIMENSIONAL SPECTRAL/SPATIAL HYBRID CODE FOR OPTICAL CODE DIVISION MULTIPLE ACCESS SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Reynard Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A NOVEL TWO-DIMENSIONAL SPECTRAL/SPATIAL HYBRID CODE FOR OPTICAL CODE DIVISION MULTIPLE ACCESS SYSTEM RIMA. MATEM 1, S. A. ALJUNID, M. N JUNITA 3, C. B. M RASHIDI 4, ISRAA. SHIHAB AHMED 5 Advanced Communication Engineering Centre of Excellence School of Computer and Communication Engineering (ACE CoE -SCCE), Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP),Perlis, Malaysia, rymann90@hotmail.com, syedalwee@unimap.edu.my, junita.unimap@gmail.com, rashidibeson@unimap.edu.my, laithisraa@yahoo.com ABSTRACT A newly two-dimensional hybrid code based on Zero Cross Correlation (ZCC) and Multi Diagonal (MD) codes (D ZCC/MD) has been proposed for incoherent spectral/ spatial OCDMA system in this paper in order to supress MAI and mitigate PIIN. The D ZCC/MD keep the zero cross correlation property since the both of Zero Cross Correlation (ZCC) and Multi Diagonal (MD) codes have zero cross correlation property. Using the direct detection technique the proposed code is analysed where the performance of D ZCC/MD code is compared with existing D FCC/MDW and D DPDC. The analytical results prove that at low BER and high data D ZCC/MD can support more simultaneous user. Keywords: Optical Code Division Multiple Access (OCDMA), Multiple Access Interference (MAI), Zero Cross-Correlation Code (ZCC), Multi-Diagonal code (MD), Phase Induced Intensity Noise. 1. INTRODUCTION OCDMA (Optical Code Division Multiple Access) is a huge research area where it attracts many interesting research for decades. The importance of the system lies in the acquisition of certain characteristics that allow it to be interesting technique such as flexibility in high speed access network, high security, dynamic bandwidth assignment, large and effective bandwidth utilization [1]. OCDMA can be divided into five important schemes: frequency hopping [], [3], time spreading [4], [5], spectral amplitude coding (SAC) [6], [7] and spatial coding [8], [9]. Due to the ability of suppression of Multiple Access Interference (MAI) completely by the spectral coding and mitigation Phase Induced Intensity Noise (PIIN), the spectral amplitude coding (SAC- OCDMA) has attracted a more interest recently [10], [11]. OCDMA can be classified into coherent and incoherent categories. A coherent OCDMA system is costly due to the high cost of the light source as a mode-locked laser while an incoherent OCDMA is cheaper and more suitable in optical network [1]. OCDMA can be implemented in one-dimensional (1D)[13], [14], two-dimensional (D) [15], [16] or three-dimensional (3D) [17] for the main purpose to suppress Multiple Access Interference (MAI) and mitigation of Phase Induced Intensity Noise (PIIN) [18]. Many codes are introduced in two dimensional in order to overcome the obstacle of one dimensional as: -D diluted perfect difference (-D DPD) spectral/spatial code provided by Yeh et al., based on the 1-D PD code and the dilution method [19], [0], -D spectral/spatial code based on modified quadratic congruence (MQC) code developed by Yin, et al.[1], -D spectral/spatial modified double weight code optical code division multi-access system (D MDW) developed by Arief, A. R.and Aljunid, S. A [], D wavelength/time hybrid Flexible Eross Correlation/Modified Double Weight (FCC/MDW) provided by Nui [3], [4]. In the present paper we propose a new twodimensional hybrid ZCC/MD code established from the combination of 1D ZCC (Zero Cross Correlation) and 1D MD (Multi Diagonal) to recover the performance of the OCDMA system where the paper is arranged as follow: section focused on the D hybrid ZCC/MD code 704
2 construction. Section 3 presents system description. Section 4 presents the system performance where the numerical results and discussion are exhibited on the section 5. the last section gives the conclusion.. D HYBRID ZCC/MD CODE CONSTRUCTION Based on the combination of 1D MD code [7] and 1D ZCC code [5], the D-ZCC/MD code can be constructed. LetX x,x,x,.,x, Yy,y,y,.,y With k code weight of 1D-ZCC code and k code weight of 1D-MD code. Denoted that w is the code size of 1D-ZCC code and w is the code size of 1D-MD code, so the code length of X, Y are Mk w,n k w respectively. W w w represents the code size of D-ZCC/MD..1. 1D Zero Cross Correlation (ZCC) code The Zero Cross Correlation (ZCC) code for SAC OCDMA was developed by Anuar et al (009).[5] ZCC is designed with zero cross correlation property between its code words to improve the performance of SAC OCDMA system. ZCC is characterized by a matrix of KxL where K represents number of active users and L represents the minimum code length. The number of active user K and code length L are given as: Kw1 (1) Lww1 () The construction of the code is designed from the modified double weight (MDW) code [6] where the matrix is generated as follow with the basic ZCC code (w=1): ZCCw (3) 1 0 According to the following map, the increase of the number of users is occurred: ZCCw 0 Z (4) Z 0 ZCCw 3 0 Z (5) Z 0 The number of code weight can be increased by the general transformation below: Where: ZCC A B (6) C D A: is 1, ww 1 matrix of zeros. B: represents w replication of the matrix j0,1. C: contain of the duplication of the matrix from w1. D: is the diagonal pattern of m n with exchange column of zeros matrix m n. An example for the transformation code from w 1 w w3 as follow: ZCC A ZCC A C B (7) (8) ZCC (9) D B C D 705
3 .. 1D Multi Diagonal (MD) code One-dimensional Multi Diagonal (1D MD) was been developed by [7]. It is characterized by N(code length), w(code weight) and λ (in phase cross correlation) For the code sequence Xx,x,.,x, Y y,y,.,y. The cross correlation expression can be expressed by λ x y 1D MD (Multi Diagonal) possesses zero cross correlation λ 0. The matrix of 1D MD code consists of KxN where K is the number of user, Nis the code length. The choice of the weight value is free and N Kw. The 1D MD code can be designed as below: Step1: A sequence of diagonal matrix can be constructed using the value of the weight w and number of user K, according to these value the ii 1,,3,. K is the index of rows in each matrix and jj 1,,3,..,wwhere j is the number of diagonal matrix. Step: The MD sequences can be computed for each diagonal matrix using the equation below: S, i 1i,j even i for j odd (10) 1 K S,., S,., S,., (11) K 1 K Each element of the S, matrices represents the position of one in T, matrices with KxKdimensions. Where T, S,, T, S,,., T, S, (1) T, 0 1 Step3: , T, T, 0 1,., (13) The construction of the matrix of MD code of power KxN is based on the combination of diagonals matrices. In a matrix each row is a single code sequence. MD T, T, T, (14) a, a, a, a, a, a, MD a, a, a, a, a, a, (15) The following table give an example of MD code with K4, w3 Tablei: The MD Code With K 4, w3 i Code sequence The cross correlation of newly code can be obtained using four characteristics are given as follow: A Y X (16) A Y X (17) A Y X (18) A Y X (19) Where A (d), d (0,1,,3) has been given in [9] represents the characteristic matrices. Where parameters X and Y are the complementary of X 706
4 and Y respectively. The cross correlation of hybrid D ZCC/MD code A and A, is formulated as: a R g, h a (0) Where a depicts the i, j of A and a is the i, j of A,. TableII shows the cross correlation between any two codes A and A, of D Hybrid ZCC/MD code produced from the equation (0). Tableii: Cross Correlation Of D ZCC/MD Hybrid Code The cross correlation of A, and A, can be calculated as follows: R g, h a, a, g, h R R R R g0,h0 k k g0,h0 0 k k 0 0 g0,h0 0 0 k k 0 g0,h k k k k for g 0, h 0 0 otherwise (1) Based on the direct detection technique, D ZCC/MD is designed as illustrated in Figure1. It consists of w w pairs of transmitters and receivers, the star coupler to connect the transmitter and the receiver. Using the assigned codeword, the incoming data will be encoded and transmitted to the receiver via star coupler. At the receiver, the encoded data will be decoded through up one combiner and all codewords from different users are correlated.figure shows the construction of D ZCC/MD transmitter, it consists of incoherent light source (BLS), to send the data, an electrical to optical modulator (EOM) to modulate the signal coming from BLS, one splitter for the spectral encoding, two () Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) with the same number of grating but opposite arrangement for the spatial encoding. The incoming data from BLS will be converted to the optical signal through EOM with ON-OFF Keying format; this modulated data will pass through the FBG1 for the spectral encoding purpose according to X the spectral code sequence. The spectral components of optical pulse either matched to 1s of a code are filtered back and the other are filtered out. FBG is designed to compensate the delay of the set of FBG1 matched spectral components. These matched spectral components transmit to optical splitter where these are split into k equal parts to send it to the star coupler according to the code sequence of Y. At this phase, the optical signal is encoded in two dimensions. FBG1 FBG 3. SYSTEM DESCRIPTION To coupler1 Transmitter (0,0) Receiver (0,0) EOM To coupler Transmitter (0,1) Star coupler Receiver (0,0) light source Splitter Transmitter (M- 1,N-1) Receiver (M- 1,N-1) Information bit To couplern Figure : The Construction Of Transmitter Figure1: Block Diagram Of A D Hybrid ZCC/MD Spectral/Spatial OCDMA System Figure3 depicts the construction of the receiver where it is designed in order to suppress MAI and used as information bit recovery. It consists of one 707
5 combiner, one direct detection technique part and one integrator. The direct detection technique part in turn consists of two sets of Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG1 and FBG), two circulators and one Photo detector (PD). The incoming spatial code sequence Y from the star coupler are received and combined by the combiner. The spectral components which are matched to 1s of the spectral code sequence X are reflected back by FBG1. FBG with the same grating but opposite arrangement used to compensate the run-trip delay. The photo detectors (PD) convert the optical signals to electronic signals and then pass them to the integrator. τ () Where Sv consists the single sideband power spectral density. To simplify the analysis, four assumptions are made [9]: We defined Uv, i as follows: Uv, i uvv M i uv M i (3) FBG1 FBG From coupler1 From coupler Combiner LPF From couplern Figure3: The construction of the receiver. 4. SYSTEM PERFORMANCE According to the zero cross correlation property of the code D ZCC/MD, there is no overlapping in a spectra of different users, thus the effect of MAI have been removed. The effects of thermal noise, PIIN, and shot noise in the photo-detector have been considered in the analysis. The Gaussian approximation is employed to calculate the BER. The total noise photocurrent variance can be expressed as follow: i i i i BI τebi (1) Where e is the electron charge, I is the average photocurrent. B is the electrical bandwidth, T is the absolute temperature, K is Boltzmann's constant, R is the load resistance and τ is the coherence time of the light which expressed as: 708
6 TableIII: The D ZCC/MD code with (k 3,w 3,k,w 3) A, X X X X Y Y Y Y Where Uv, i is a unit step function defined as: 1 v 0 uv 0 v 0 The power spectral density (PSD) of the received signals can be written as (4) IR Gvdv k k dwr i, juv, idv dwr i, j (6) rv dk a,kuv, i (5) Where k and k are the code weights of spectral and spatial respectively, P is the effective source power at the receiver, N and M are the code lengths of spatial and spectral code sequences respectively, W is the number of active users, dk is the data bit of W user which can be 1 or 0 and a, is an element of the k user's codeword. depending on the cross correlation between A, and A, obtain the output currents of PD at receiver (0,0) is obtained as follows: Where η is the quantum efficiency of the photodiode, R is the responsivity of the photo-diode given by Rηe/hv and h is Plank's constant. Since, M w k and Ww w, then: I Phase Induced Intensity Noise (PIIN) can be calculated as: BI G vdv G vdv i BR G v dv (7) BR dkr Ui, j dv 709
7 BP R k v M k k dkr i, j B 0 (8) Consequently, the total noise where the probability of each user sending bit 1 is equal so: i noise i PIIN i shot i thermal (9) i noise BI τebi 4K bt n B (30) R L From the previous equations I noise can written as i noise i PIIN i shot i thermal i PIIN B R P srw k 1 vw i shot eb RP srw W (31) (3) i thermal 4K bt n B (33) R L i noise BR P srk1 vw ebrp srw W 4K bt n B R L (34) Table IV : Link parameters PD quantum R 0.75 efficiency Spectral width λ 30nm λ 3.75 of broadband light source Operating λ μm wavelength Electrical B 30MHz bandwidth Data R b 6Mbps transmission rate Receiver noise T n 300K temperature Receiver load R L 1030Ω resistor Boltzmann s K b W constant /K/Hz Electron charge e coulombs Light velocity C310 m/s 5. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION TableV exhibits the parameters used to analyze the performance of the D ZCC/MD code and obtain the numerical results. Note that the probability of sending bit 1 at any time for each user is 1/: i noise BR P srk1 ebrp srw vw W 4K bt n B R L (35) D ZCC/MD(M=6,N=3) D FCC/MDW (M=3,N=7) D ZCC/MD(M=3,N=7) D DPDC (M=91,N=3) 1D RD (N=9) 1D MDW (N=58) Finally, the average signal to noise ratio (SNR) can be calculated as BER SNR (36) from SNR, The BER can be expressed as follows: Number of users BER (37) Figure4: BER Against Number Of Users Where Data Rate Is Rb=1Gbps And Effective Power Is Psr=-10dbm Where erfc exp y dy (38) Figure4 shows the variation of BER versus the number of users of the codes D ZCC/MD (M=63, N=3) compared to D DPDC (M=91, N=3), D FCC/MDW (M=3, N=7), D ZCC/MD (M=3, 710
8 N=7), 1D RD (N=9) and 1D MDW (N=58) where effective power Psr equal to -10dBm and data rate Rb=1Gbps. It can be seen that D ZCC/MD exhibit the better performance than other codes. At BER equal to 10 9 the D ZCC/MD (M=3, N=7) can support until 10 user. indicates that the superior performance is coming from the ability of the code to fully to suppress the effect of the MAI and mitigate PIIN D ZCC/MD(M=63,N=3) D FCC/MDW (M=3,N=7) D ZCC/MD(M=3,N=7) D DPDC (M=91,N=3) 1D RD (N=9) 1D MDW (N=58) BER BER Number of users Figure5: BER Versus Number Of Users With Data Rate Is Rb=.5Gbps And Effective Power Is Psr=-10dbm Figure5 illustrates also the variation of the BER versus number of user of the same codes but with Psr=-10dBm and data rate Rb=.5Gbps. This figure confirms the observations given by the previous figure. It can be clearly seen that number of user is increased where for the D ZCC/MD (M=3, N=7) code can reach 315 user at BER equal to BER D ZCC/MD (M=63, N=3) (data rate=6 Mbps) -D FCC/MDW (M=3, N=7)(data rate=6mbps) -D DPDC (M=63, N=3)(data rate=6mbps) 1D RD (N=50)(data rate=6mbps) 1D MDW (N=58)(data rate=6mbps) effective received power Figure6: BER Versus Effective Power Psr When K=100 User And Data Rate Is Rb=6Mbps Figure6 shows the relation between the BER and the effective power in dbm when the number of user is equal to 100 and data rate equal to 6Mbps. The figure apparent that D ZCC/MD (M=3, N=7) is the best at high power and it has a minimum BER -4 comparing to the other codes. D ZCC/MD D ZCC/MD (M=63, N=3) -D FCC/MDW (M=3, N=7) -D DPDC (M=63, N=3) data bit rate x 10 9 Figure7: BER Versus Date Rate When The Effective Power Is Psr=-10dbm And The Number Of User Is K=100 User. Figure7 shows the variation of BER versus the data transmission rate of each user with similar code length when the number of user is 100 and the effective source power 10 dbm. At the BER equal to 10 9, the figure demonstrates that D ZCC/MD can accommodate the higher data transmission rate for each user with a similar code length is used compared to the other codes. 6. CONCLUSION The OCDMA is an interesting scheme due to characteristic such as: flexible bandwidth, asynchronous access, flexibility of implementation differential QOS and ability to support multimedia services. A newly two dimensional code has been proposed referred as D hybrid code for spectral/spatial OCDMA system. The construction of this code is based on the combination of 1D ZCC code and 1D MD code. The performance of this new code has been evaluated by using the analytical analysis. The proposed code has the MAI suppression property where the proposed system has a low BER. The proposed code represents the better performance compared to other codes so the system could robustly accommodate more users. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The author would like to acknowledge the support from Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) under Prof.Dr. Syed Alwee Aljunid, Department of Higher Education, Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia for the assistance with The grant. 711
9 REFERENCES [1] Abdullah, Amir Razif Arief Jamil, Syed Alwee Aljunid, Anuar Mat Safar, Junita Mohd Nordin, and R. Badlishah Ahmad. "Mitigation of multiple access interference using twodimensional modified double weight codes for optical code division multiple access systems." Optical Engineering 51, no. 6 (01): [] Fathallah, Habib, Leslie A. Rusch, and Sophie LaRochelle. "Passive optical fast frequencyhop CDMA communications system." Journal of Lightwave Technology 17, no. 3 (1999): 397. [3] Inaty, Elie, Hossam MH Shalaby, and Paul Fortier. "On the cutoff rates of a multiclass OFFH-CDMA system." IEEE transactions on communications 53, no. (005): [4] Chung, Fan RK, Jawad A. Salehi, and Victor K. Wei. "Optical orthogonal codes: design, analysis and applications." IEEE Transactions on Information theory 35, no. 3 (1989): [5] Weng, Chi-Shun, and Jingshown Wu. "Perfect difference codes for synchronous fiber-optic CDMA communication systems." Journal of Lightwave Technology 19, no. (001): 186. [6] Smith, Elwyn DJ, Richard J. Blaikie, and Desmond P. Taylor. "Performance enhancement of spectral-amplitude-coding optical CDMA using pulse-position modulation." IEEE Transactions on Communications 46, no. 9 (1998): [7] Abd, Thanaa Hussein, S. A. Aljunid, Hilal Adnan Fadhil, and N. M. Saad. "Design and simulation a new code with zero cross correlation for SAC-OCDMA networks." Australian J Basic and Appl Sci 6, no. 3 (01): [8] Kitayama, Ken-ichi. "Novel spatial spread spectrum based fiber optic CDMA networks for image transmission." IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 1, no. 4 (1994): Selected Areas in Communications, 1(4), (1994). [9] Yeh, Bih-Chyun, Cheing-Hong Lin, and Jingshown Wu. "Noncoherent spectral/spatial OCDMA system using two-dimensional hybrid codes." Journal of Optical Communications and Networking, no. 9 (010): [10] Rashidi, C. B. M., Mat Safar Anuar, and S. A. Aljunid. "Study of direct detection technique for zero cross correlation code in OCDMA." In Computer and Communication Engineering (ICCCE), 010 International Conference on, pp IEEE, 010. [11] Rashidi, C. B. M., S. A. Aljunid, F. Ghani, Hilal A. Fadhil, and M. S. Anuar. "Cardinality Enhancement Using Flexible Cross Correlation (FCC) Code for Spectral Amplitude Coding Optical Code Division Multiple Access Systems." Journal of Applied Sciences Research 8, no. 1 (01): [1] Huang, Jen-Fa, and Yao-Tang Chang. "Incoherent hybrid spectral polarization and amplitude coding implemented with specified orthogonal ternary code over balanced photodetectors." In Communication Networks and Services Research Conference, 006. CNSR 006. Proceedings of the 4th Annual, pp. 8- pp. IEEE, 006. [13] Wei, Zou, H. M. H. Shalaby, and H. Ghafouri- Shiraz. "Modified quadratic congruence codes for fiber Bragg-grating-based spectralamplitude-coding optical CDMA systems."journal of Lightwave Technology 19, no. 9 (001): [14] M.N.Junita. Development of New Code for Subcarrier Multiplexed-Optical Code Division Multiple Access System. 013 (Thesis) [15] Wan, Shengpeng, Xingdao He, and Jizhou Sun. "A novel D-OCDMA system with dynamic optimum decision threshold by estimating the number of active users." Optics Communications 8, no. 4 (009): [16] Yang, Chao-Chin, Jen-Fa Huang, and I-Min Chiu. "Performance analyses on hybrid MQC/M-sequence coding over frequency/spatial optical CDMA system." IEEE Transactions on communications 55, no. 1 (007): [17] Kadhim, Rasim Azeez, Hilal Adnan Fadhil, S. A. Aljunid, and Mohamad Shahrazel Razalli. "PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT OF A THREE DIMENSIONAL OCDMA SYSTEMS BASED ON A NEW CODE." Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology 81, no. 3 (015): 589. [18] Rasim Azeez Kadhim n, Hilal Adnan Fadhil, S.A. Aljunid, Mohamad Shahrazel Razalli. A new two dimensional spectral/spatial multidiagonal code for noncoherent optical code division multiple access (OCDMA) systems. journal homepage: 71
10 Optics Communications 39 (014) 8 33 [19] Yeh, Bih-Chyun, Cheing-Hong Lin, Chun- Liang Yang, and Jingshown Wu. "Noncoherent spectral/spatial optical CDMA system using -D diluted perfect difference codes." Journal of Lightwave Technology 7, no. 13 (009): [0] Yeh, Bih-Chyun, Cheing-Hong Lin, Chun- Liang Yang, and Jingshown Wu. "Noncoherent spectral/spatial optical CDMA system using -D diluted perfect difference codes." Journal of Lightwave Technology 7, no. 13 (009): [1] Yin, Hongxi, Le Ma, Hongbin Li, and Lixin Zhu. "A new family of D wavelength/time codes with large cardinality for incoherent spectral amplitude coding OCDMA networks and analysis of its performance." Photonic Network Communications 19, no. (010): [] Arief, Amir Razif, Syed Alwee Aljunid, M. S. Anuar, M. N. Junita, and R. B. Ahmad. "Cardinality enhancement of spectral/spatial modified double weight code optical code division multi-access system by PIIN suppression." Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics 14, no. 19 (013): [3] Keraf, N. Din, S. A. Aljunid, A. R. Arief, M. S. Anuar, C. B. M. Rashidi, P. Ehkan, and M. N. Nurol. "An optimal cardinality of Wavelength/Time incoherent OCDMA system using -D Hybrid FCC-MDW Code." In Electronic Design (ICED), 014 nd International Conference on, pp IEEE, 014. [4] N. Din Keraf, S. A. Aljunid, A. R. Arief, M. N. Nurol, M. S. Anuar, C. B. M. Rashidi, P. Ehkan Noise Mitigation for OCDMA System with Wavelength/Time D Hybrid Code. Proc. of 014 IEEE 5th International Conference on Photonics (ICP), Kuala Lumpur, -4 Sept [5] Anuar, M. S., Aljunid, S. A., Saad, N. M., & Hamzah, S. M. New design of spectral amplitude coding in OCDMA with zero crosscorrelation.optics Communications, 8(14), (009) [6] Aljunid, S. A., M. D. A. Samad, M. Othman, M. H. Hisham, A. H. Kasiman, and M. K. Abdullah. "Development of modified doubleweight code and its implementation in multirate transmissions." In Networks, 005. Jointly held with the 005 IEEE 7th Malaysia International Conference on Communication., th IEEE International Conference on, vol. 1, pp. 5-pp. IEEE,
Influence of Code Size Variation on the Performance of 2D Hybrid ZCC/MD in OCDMA System
 MATEC Web of Conferences 5, 68 (8) MUCET 7 https://doiorg/5/matecconf/8568 Influence of Code Size Variation on the Performance of D Hybrid ZCC/MD in OCDMA System Rima Matem,*, S A Aljunid, M N Junita,
MATEC Web of Conferences 5, 68 (8) MUCET 7 https://doiorg/5/matecconf/8568 Influence of Code Size Variation on the Performance of D Hybrid ZCC/MD in OCDMA System Rima Matem,*, S A Aljunid, M N Junita,
Research Article BER Analysis Using Beat Probability Method of 3D Optical CDMA Networks with Double Balanced Detection
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 2015, Article ID 456829, 6 pages http://dxdoiorg/101155/2015/456829 Research Article BER Analysis Using Beat Probability Method of 3D Optical CDMA Networks with
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 2015, Article ID 456829, 6 pages http://dxdoiorg/101155/2015/456829 Research Article BER Analysis Using Beat Probability Method of 3D Optical CDMA Networks with
Optoelectronic Applications. Injection Locked Oscillators. Injection Locked Oscillators. Q 2, ω 2. Q 1, ω 1
 Injection Locked Oscillators Injection Locked Oscillators Optoelectronic Applications Q, ω Q, ω E. Shumakher, J. Lasri,, B. Sheinman, G. Eisenstein, D. Ritter Electrical Engineering Dept. TECHNION Haifa
Injection Locked Oscillators Injection Locked Oscillators Optoelectronic Applications Q, ω Q, ω E. Shumakher, J. Lasri,, B. Sheinman, G. Eisenstein, D. Ritter Electrical Engineering Dept. TECHNION Haifa
Comunicações Ópticas Noise in photodetectors MIEEC EEC038. Henrique Salgado Receiver operation
 Comunicações Ópticas Noise in photodetectors 2007-2008 MIEEC EEC038 Henrique Salgado hsalgado@fe.up.pt Receiver operation Noise plays a fundamental role in design of an optical receiver Optical data link
Comunicações Ópticas Noise in photodetectors 2007-2008 MIEEC EEC038 Henrique Salgado hsalgado@fe.up.pt Receiver operation Noise plays a fundamental role in design of an optical receiver Optical data link
Application of high-precision temperature-controlled FBG f ilter and light source self-calibration technique in the BOTDR sensor system
 Application of high-precision temperature-controlled FBG f ilter and light source self-calibration technique in the BOTDR sensor system Jiacheng Hu ( ) 1,2, Fuchang Chen ( ) 1,2, Chengtao Zhang ( ) 1,2,
Application of high-precision temperature-controlled FBG f ilter and light source self-calibration technique in the BOTDR sensor system Jiacheng Hu ( ) 1,2, Fuchang Chen ( ) 1,2, Chengtao Zhang ( ) 1,2,
Direct-Sequence Spread-Spectrum
 Chapter 3 Direct-Sequence Spread-Spectrum In this chapter we consider direct-sequence spread-spectrum systems. Unlike frequency-hopping, a direct-sequence signal occupies the entire bandwidth continuously.
Chapter 3 Direct-Sequence Spread-Spectrum In this chapter we consider direct-sequence spread-spectrum systems. Unlike frequency-hopping, a direct-sequence signal occupies the entire bandwidth continuously.
Full polarization control for fiber optical quantum communication systems using polarization encoding
 Full polarization control for fiber optical quantum communication systems using polarization encoding G. B. Xavier, G. Vilela de Faria, G. P. Temporão and J. P. von der Weid* Pontifical Catholic University
Full polarization control for fiber optical quantum communication systems using polarization encoding G. B. Xavier, G. Vilela de Faria, G. P. Temporão and J. P. von der Weid* Pontifical Catholic University
ANALYSIS OF A PARTIAL DECORRELATOR IN A MULTI-CELL DS/CDMA SYSTEM
 ANAYSIS OF A PARTIA DECORREATOR IN A MUTI-CE DS/CDMA SYSTEM Mohammad Saquib ECE Department, SU Baton Rouge, A 70803-590 e-mail: saquib@winlab.rutgers.edu Roy Yates WINAB, Rutgers University Piscataway
ANAYSIS OF A PARTIA DECORREATOR IN A MUTI-CE DS/CDMA SYSTEM Mohammad Saquib ECE Department, SU Baton Rouge, A 70803-590 e-mail: saquib@winlab.rutgers.edu Roy Yates WINAB, Rutgers University Piscataway
Quantum Imaging Technologies: Quantum Laser Radar
 MURI 2005 Quantum Imaging: New Methods and Applications Year 3 Review / 17 November 2008 / UMBC, Baltimore, MD Quantum Imaging Technologies: Quantum Laser Radar Prem Kumar and Geraldo Barbosa EECS Department,
MURI 2005 Quantum Imaging: New Methods and Applications Year 3 Review / 17 November 2008 / UMBC, Baltimore, MD Quantum Imaging Technologies: Quantum Laser Radar Prem Kumar and Geraldo Barbosa EECS Department,
Optical solitons and its applications
 Physics 568 (Nonlinear optics) 04/30/007 Final report Optical solitons and its applications 04/30/007 1 1 Introduction to optical soliton. (temporal soliton) The optical pulses which propagate in the lossless
Physics 568 (Nonlinear optics) 04/30/007 Final report Optical solitons and its applications 04/30/007 1 1 Introduction to optical soliton. (temporal soliton) The optical pulses which propagate in the lossless
EE4512 Analog and Digital Communications Chapter 4. Chapter 4 Receiver Design
 Chapter 4 Receiver Design Chapter 4 Receiver Design Probability of Bit Error Pages 124-149 149 Probability of Bit Error The low pass filtered and sampled PAM signal results in an expression for the probability
Chapter 4 Receiver Design Chapter 4 Receiver Design Probability of Bit Error Pages 124-149 149 Probability of Bit Error The low pass filtered and sampled PAM signal results in an expression for the probability
Maximum Achievable Diversity for MIMO-OFDM Systems with Arbitrary. Spatial Correlation
 Maximum Achievable Diversity for MIMO-OFDM Systems with Arbitrary Spatial Correlation Ahmed K Sadek, Weifeng Su, and K J Ray Liu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Institute for Systems
Maximum Achievable Diversity for MIMO-OFDM Systems with Arbitrary Spatial Correlation Ahmed K Sadek, Weifeng Su, and K J Ray Liu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Institute for Systems
Computation of Bit-Error Rate of Coherent and Non-Coherent Detection M-Ary PSK With Gray Code in BFWA Systems
 Computation of Bit-Error Rate of Coherent and Non-Coherent Detection M-Ary PSK With Gray Code in BFWA Systems Department of Electrical Engineering, College of Engineering, Basrah University Basrah Iraq,
Computation of Bit-Error Rate of Coherent and Non-Coherent Detection M-Ary PSK With Gray Code in BFWA Systems Department of Electrical Engineering, College of Engineering, Basrah University Basrah Iraq,
Coherent Combining and Phase Locking of Fiber Lasers
 Coherent Combining and Phase Locking of Fiber Lasers Moti Fridman, Micha Nixon, Nir Davidson and Asher A. Friesem Weizmann Institute of Science, Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems, Rehovot 76100, Israel.
Coherent Combining and Phase Locking of Fiber Lasers Moti Fridman, Micha Nixon, Nir Davidson and Asher A. Friesem Weizmann Institute of Science, Dept. of Physics of Complex Systems, Rehovot 76100, Israel.
Electronic Compensation Technique to Mitigate Nonlinear Phase Noise
 > Journal of Lightwave Technology Electronic Compensation Technique to Mitigate onlinear Phase oise Keang-Po Ho, Member, IEEE, and Joseph M. Kahn, Fellow, IEEE Abstract onlinear phase noise, often called
> Journal of Lightwave Technology Electronic Compensation Technique to Mitigate onlinear Phase oise Keang-Po Ho, Member, IEEE, and Joseph M. Kahn, Fellow, IEEE Abstract onlinear phase noise, often called
Quantum Imaging Technologies: Quantum Laser Radar
 MURI 2005 Quantum Imaging: New Methods and Applications Year 4 Review / 13 November 2009 / Northwestern University, Evanston, IL Quantum Imaging Technologies: Quantum Laser Radar Prem Kumar and Geraldo
MURI 2005 Quantum Imaging: New Methods and Applications Year 4 Review / 13 November 2009 / Northwestern University, Evanston, IL Quantum Imaging Technologies: Quantum Laser Radar Prem Kumar and Geraldo
Fiber Gratings p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Bragg Diffraction p. 2 Photosensitivity p. 3 Fabrication Techniques p. 4 Single-Beam Internal Technique p.
 Preface p. xiii Fiber Gratings p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Bragg Diffraction p. 2 Photosensitivity p. 3 Fabrication Techniques p. 4 Single-Beam Internal Technique p. 4 Dual-Beam Holographic Technique p. 5
Preface p. xiii Fiber Gratings p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Bragg Diffraction p. 2 Photosensitivity p. 3 Fabrication Techniques p. 4 Single-Beam Internal Technique p. 4 Dual-Beam Holographic Technique p. 5
16.36 Communication Systems Engineering
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 16.36 Communication Systems Engineering Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 16.36: Communication
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 16.36 Communication Systems Engineering Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 16.36: Communication
Performance Analysis of Spread Spectrum CDMA systems
 1 Performance Analysis of Spread Spectrum CDMA systems 16:33:546 Wireless Communication Technologies Spring 5 Instructor: Dr. Narayan Mandayam Summary by Liang Xiao lxiao@winlab.rutgers.edu WINLAB, Department
1 Performance Analysis of Spread Spectrum CDMA systems 16:33:546 Wireless Communication Technologies Spring 5 Instructor: Dr. Narayan Mandayam Summary by Liang Xiao lxiao@winlab.rutgers.edu WINLAB, Department
Digital Band-pass Modulation PROF. MICHAEL TSAI 2011/11/10
 Digital Band-pass Modulation PROF. MICHAEL TSAI 211/11/1 Band-pass Signal Representation a t g t General form: 2πf c t + φ t g t = a t cos 2πf c t + φ t Envelope Phase Envelope is always non-negative,
Digital Band-pass Modulation PROF. MICHAEL TSAI 211/11/1 Band-pass Signal Representation a t g t General form: 2πf c t + φ t g t = a t cos 2πf c t + φ t Envelope Phase Envelope is always non-negative,
Photonic Communications Engineering Lecture. Dr. Demetris Geddis Department of Engineering Norfolk State University
 Photonic Communications Engineering Lecture Dr. Demetris Geddis Department of Engineering Norfolk State University Light Detectors How does this detector work? Image from visionweb.com Responds to range
Photonic Communications Engineering Lecture Dr. Demetris Geddis Department of Engineering Norfolk State University Light Detectors How does this detector work? Image from visionweb.com Responds to range
Keywords: Coupling length; Coupling ratio; Fiber coupler; Power transfer.
 OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF 1 X 4 WEAKLY COUPLED FIBERS Dedi Irawan 1*, Hartono, Rado Yendra 3, Ismu Kusumanto 1 1 Department of Industrial Engineering, Faculty of Science and Technology, UIN Suska Riau, Pekanbaru,
OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF 1 X 4 WEAKLY COUPLED FIBERS Dedi Irawan 1*, Hartono, Rado Yendra 3, Ismu Kusumanto 1 1 Department of Industrial Engineering, Faculty of Science and Technology, UIN Suska Riau, Pekanbaru,
Lecture 9. PMTs and Laser Noise. Lecture 9. Photon Counting. Photomultiplier Tubes (PMTs) Laser Phase Noise. Relative Intensity
 s and Laser Phase Phase Density ECE 185 Lasers and Modulators Lab - Spring 2018 1 Detectors Continuous Output Internal Photoelectron Flux Thermal Filtered External Current w(t) Sensor i(t) External System
s and Laser Phase Phase Density ECE 185 Lasers and Modulators Lab - Spring 2018 1 Detectors Continuous Output Internal Photoelectron Flux Thermal Filtered External Current w(t) Sensor i(t) External System
Residual Versus Suppressed-Carrier Coherent Communications
 TDA Progress Report -7 November 5, 996 Residual Versus Suppressed-Carrier Coherent Communications M. K. Simon and S. Million Communications and Systems Research Section This article addresses the issue
TDA Progress Report -7 November 5, 996 Residual Versus Suppressed-Carrier Coherent Communications M. K. Simon and S. Million Communications and Systems Research Section This article addresses the issue
Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a).
 7.1. Low-Coherence Interferometry (LCI) Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a). The light is split by the beam splitter (BS) and
7.1. Low-Coherence Interferometry (LCI) Let us consider a typical Michelson interferometer, where a broadband source is used for illumination (Fig. 1a). The light is split by the beam splitter (BS) and
Principles of Communications
 Principles of Communications Chapter V: Representation and Transmission of Baseband Digital Signal Yongchao Wang Email: ychwang@mail.xidian.edu.cn Xidian University State Key Lab. on ISN November 18, 2012
Principles of Communications Chapter V: Representation and Transmission of Baseband Digital Signal Yongchao Wang Email: ychwang@mail.xidian.edu.cn Xidian University State Key Lab. on ISN November 18, 2012
These outputs can be written in a more convenient form: with y(i) = Hc m (i) n(i) y(i) = (y(i); ; y K (i)) T ; c m (i) = (c m (i); ; c m K(i)) T and n
 Binary Codes for synchronous DS-CDMA Stefan Bruck, Ulrich Sorger Institute for Network- and Signal Theory Darmstadt University of Technology Merckstr. 25, 6428 Darmstadt, Germany Tel.: 49 65 629, Fax:
Binary Codes for synchronous DS-CDMA Stefan Bruck, Ulrich Sorger Institute for Network- and Signal Theory Darmstadt University of Technology Merckstr. 25, 6428 Darmstadt, Germany Tel.: 49 65 629, Fax:
When does vectored Multiple Access Channels (MAC) optimal power allocation converge to an FDMA solution?
 When does vectored Multiple Access Channels MAC optimal power allocation converge to an FDMA solution? Vincent Le Nir, Marc Moonen, Jan Verlinden, Mamoun Guenach Abstract Vectored Multiple Access Channels
When does vectored Multiple Access Channels MAC optimal power allocation converge to an FDMA solution? Vincent Le Nir, Marc Moonen, Jan Verlinden, Mamoun Guenach Abstract Vectored Multiple Access Channels
SNR i = 2E b 6N 3. Where
 Correlation Properties Of Binary Sequences Generated By The Logistic Map-Application To DS-CDMA *ZOUHAIR BEN JEMAA, **SAFYA BELGHITH *EPFL DSC LANOS ELE 5, 05 LAUSANNE **LABORATOIRE SYSCOM ENIT, 002 TUNIS
Correlation Properties Of Binary Sequences Generated By The Logistic Map-Application To DS-CDMA *ZOUHAIR BEN JEMAA, **SAFYA BELGHITH *EPFL DSC LANOS ELE 5, 05 LAUSANNE **LABORATOIRE SYSCOM ENIT, 002 TUNIS
Design of MMSE Multiuser Detectors using Random Matrix Techniques
 Design of MMSE Multiuser Detectors using Random Matrix Techniques Linbo Li and Antonia M Tulino and Sergio Verdú Department of Electrical Engineering Princeton University Princeton, New Jersey 08544 Email:
Design of MMSE Multiuser Detectors using Random Matrix Techniques Linbo Li and Antonia M Tulino and Sergio Verdú Department of Electrical Engineering Princeton University Princeton, New Jersey 08544 Email:
Spectra Power and Bandwidth of Fiber Bragg Grating Under Influence of Gradient Strain
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 4, 216: 333 338 Spectra Power and Bandwidth of Fiber Bragg Grating Under Influence of Gradient Strain Qinpeng LIU *, Xueguang QIAO, Zhen an JIA, and Haiwei FU Key Laboratory
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 4, 216: 333 338 Spectra Power and Bandwidth of Fiber Bragg Grating Under Influence of Gradient Strain Qinpeng LIU *, Xueguang QIAO, Zhen an JIA, and Haiwei FU Key Laboratory
Optical Component Characterization: A Linear Systems Approach
 Optical Component Characterization: A Linear Systems Approach Authors: Mark Froggatt, Brian Soller, Eric Moore, Matthew Wolfe Email: froggattm@lunatechnologies.com Luna Technologies, 2020 Kraft Drive,
Optical Component Characterization: A Linear Systems Approach Authors: Mark Froggatt, Brian Soller, Eric Moore, Matthew Wolfe Email: froggattm@lunatechnologies.com Luna Technologies, 2020 Kraft Drive,
Dark Soliton Fiber Laser
 Dark Soliton Fiber Laser H. Zhang, D. Y. Tang*, L. M. Zhao, and X. Wu School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798 *: edytang@ntu.edu.sg, corresponding
Dark Soliton Fiber Laser H. Zhang, D. Y. Tang*, L. M. Zhao, and X. Wu School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798 *: edytang@ntu.edu.sg, corresponding
Multi User Detection I
 January 12, 2005 Outline Overview Multiple Access Communication Motivation: What is MU Detection? Overview of DS/CDMA systems Concept and Codes used in CDMA CDMA Channels Models Synchronous and Asynchronous
January 12, 2005 Outline Overview Multiple Access Communication Motivation: What is MU Detection? Overview of DS/CDMA systems Concept and Codes used in CDMA CDMA Channels Models Synchronous and Asynchronous
Applications of Lattices in Telecommunications
 Applications of Lattices in Telecommunications Dept of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering Monash University amin.sakzad@monash.edu Oct. 2013 1 Sphere Decoder Algorithm Rotated Signal Constellations
Applications of Lattices in Telecommunications Dept of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering Monash University amin.sakzad@monash.edu Oct. 2013 1 Sphere Decoder Algorithm Rotated Signal Constellations
Observation of spectral enhancement in a soliton fiber laser with fiber Bragg grating
 Observation of spectral enhancement in a soliton fiber laser with fiber Bragg grating L. M. Zhao 1*, C. Lu 1, H. Y. Tam 2, D. Y. Tang 3, L. Xia 3, and P. Shum 3 1 Department of Electronic and Information
Observation of spectral enhancement in a soliton fiber laser with fiber Bragg grating L. M. Zhao 1*, C. Lu 1, H. Y. Tam 2, D. Y. Tang 3, L. Xia 3, and P. Shum 3 1 Department of Electronic and Information
Continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a locally generated local oscillator
 Continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a locally generated local oscillator Bing Qi, Pavel Lougovski, Raphael Pooser, Warren Grice, Miljko Bobrek, Charles Ci Wen Lim, and Philip G. Evans Quantum
Continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a locally generated local oscillator Bing Qi, Pavel Lougovski, Raphael Pooser, Warren Grice, Miljko Bobrek, Charles Ci Wen Lim, and Philip G. Evans Quantum
10. OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY
 1. OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a label-free (intrinsic contrast) technique that enables 3D imaging of tissues. The principle of its operation relies on low-coherence
1. OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a label-free (intrinsic contrast) technique that enables 3D imaging of tissues. The principle of its operation relies on low-coherence
System optimization of a long-range Brillouin-loss-based distributed fiber sensor
 System optimization of a long-range Brillouin-loss-based distributed fiber sensor Yongkang Dong, 1,2 Liang Chen, 1 and Xiaoyi Bao 1, * 1 Fiber Optics Group, Department of Physics, University of Ottawa,
System optimization of a long-range Brillouin-loss-based distributed fiber sensor Yongkang Dong, 1,2 Liang Chen, 1 and Xiaoyi Bao 1, * 1 Fiber Optics Group, Department of Physics, University of Ottawa,
PMD Compensator and PMD Emulator
 by Yu Mimura *, Kazuhiro Ikeda *, Tatsuya Hatano *, Takeshi Takagi *, Sugio Wako * and Hiroshi Matsuura * As a technology for increasing the capacity to meet the growing demand ABSTRACT for communications
by Yu Mimura *, Kazuhiro Ikeda *, Tatsuya Hatano *, Takeshi Takagi *, Sugio Wako * and Hiroshi Matsuura * As a technology for increasing the capacity to meet the growing demand ABSTRACT for communications
Deterministic secure communications using two-mode squeezed states
 Deterministic secure communications using twomode squeezed states Alberto M. Marino* and C. R. Stroud, Jr. The Institute of Optics, University of Rochester, Rochester, New York 467, USA Received 5 May
Deterministic secure communications using twomode squeezed states Alberto M. Marino* and C. R. Stroud, Jr. The Institute of Optics, University of Rochester, Rochester, New York 467, USA Received 5 May
Arbitrary and reconfigurable optics - new opportunities for integrated photonics
 Arbitrary and reconfigurable optics - new opportunities for integrated photonics David Miller, Stanford University For a copy of these slides, please e-mail dabm@ee.stanford.edu How to design any linear
Arbitrary and reconfigurable optics - new opportunities for integrated photonics David Miller, Stanford University For a copy of these slides, please e-mail dabm@ee.stanford.edu How to design any linear
Vector dark domain wall solitons in a fiber ring laser
 Vector dark domain wall solitons in a fiber ring laser H. Zhang, D. Y. Tang*, L. M. Zhao and R. J. Knize 1 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798
Vector dark domain wall solitons in a fiber ring laser H. Zhang, D. Y. Tang*, L. M. Zhao and R. J. Knize 1 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798
Performance of Brillouin Optical Time Domain Reflectometry with a Reference Brillouin Ring Laser
 913 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 46, 2015 Guest Editors: Peiyu Ren, Yancang Li, Huiping Song Copyright 2015, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-37-2; ISSN 2283-9216 The
913 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 46, 2015 Guest Editors: Peiyu Ren, Yancang Li, Huiping Song Copyright 2015, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-37-2; ISSN 2283-9216 The
OPTIMIZATION OF THE 1050 NM PUMP POWER AND FIBER LENGTH IN SINGLE-PASS AND DOUBLE-PASS THULIUM DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIERS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 14, 431 448, 29 OPTIMIZATION OF THE 15 NM PUMP POWER AND FIBER LENGTH IN SINGLE-PASS AND DOUBLE-PASS THULIUM DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIERS S. D. Emami and S. W. Harun
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 14, 431 448, 29 OPTIMIZATION OF THE 15 NM PUMP POWER AND FIBER LENGTH IN SINGLE-PASS AND DOUBLE-PASS THULIUM DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIERS S. D. Emami and S. W. Harun
홀로그램저장재료. National Creative Research Center for Active Plasmonics Applications Systems
 홀로그램저장재료 Holographic materials Material Reusable Processing Type of Exposure Spectral Resol. Max. diff. hologram (J/m2) sensitivity (lim./mm) efficiency Photographic emulsion Dichromated gelatin Photoresists
홀로그램저장재료 Holographic materials Material Reusable Processing Type of Exposure Spectral Resol. Max. diff. hologram (J/m2) sensitivity (lim./mm) efficiency Photographic emulsion Dichromated gelatin Photoresists
Nonlinear ultrafast fiber optic devices based on Carbon Nanotubes
 Nonlinear ultrafast fiber optic devices based on Carbon Nanotubes Guillermo E. Villanueva, Claudio J. Oton Michael B. Jakubinek, Benoit Simard,, Jaques Albert, Pere Pérez-Millán Outline Introduction CNT-coated
Nonlinear ultrafast fiber optic devices based on Carbon Nanotubes Guillermo E. Villanueva, Claudio J. Oton Michael B. Jakubinek, Benoit Simard,, Jaques Albert, Pere Pérez-Millán Outline Introduction CNT-coated
LIKELIHOOD RECEIVER FOR FH-MFSK MOBILE RADIO*
 LIKELIHOOD RECEIVER FOR FH-MFSK MOBILE RADIO* Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Viswanathan, R.; S.C. Gupta Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
LIKELIHOOD RECEIVER FOR FH-MFSK MOBILE RADIO* Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Viswanathan, R.; S.C. Gupta Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
BROADBAND MIMO SONAR SYSTEM: A THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH
 BROADBAND MIMO SONAR SYSTM: A THORTICAL AND XPRIMNTAL APPROACH Yan Pailhas a, Yvan Petillot a, Chris Capus a, Keith Brown a a Oceans Systems Lab., School of PS, Heriot Watt University, dinburgh, Scotland,
BROADBAND MIMO SONAR SYSTM: A THORTICAL AND XPRIMNTAL APPROACH Yan Pailhas a, Yvan Petillot a, Chris Capus a, Keith Brown a a Oceans Systems Lab., School of PS, Heriot Watt University, dinburgh, Scotland,
Optical sensor based on hybrid LPG/FBG in D-fiber for simultaneous refractive index and temperature measurement
 Optical sensor based on hybrid G/FBG in D-fiber for simultaneous refractive index and temperature measurement Xianfeng Chen*, Kaiming Zhou, Lin Zhang, Ian Bennion Photonics Research Group, Aston University,
Optical sensor based on hybrid G/FBG in D-fiber for simultaneous refractive index and temperature measurement Xianfeng Chen*, Kaiming Zhou, Lin Zhang, Ian Bennion Photonics Research Group, Aston University,
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2//e50054/dc Supplementary Materials for Two-photon quantum walk in a multimode fiber Hugo Defienne, Marco Barbieri, Ian A. Walmsley, Brian J. Smith, Sylvain Gigan
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2//e50054/dc Supplementary Materials for Two-photon quantum walk in a multimode fiber Hugo Defienne, Marco Barbieri, Ian A. Walmsley, Brian J. Smith, Sylvain Gigan
Optical Fiber Signal Degradation
 Optical Fiber Signal Degradation Effects Pulse Spreading Dispersion (Distortion) Causes the optical pulses to broaden as they travel along a fiber Overlap between neighboring pulses creates errors Resulting
Optical Fiber Signal Degradation Effects Pulse Spreading Dispersion (Distortion) Causes the optical pulses to broaden as they travel along a fiber Overlap between neighboring pulses creates errors Resulting
Adaptive Bit-Interleaved Coded OFDM over Time-Varying Channels
 Adaptive Bit-Interleaved Coded OFDM over Time-Varying Channels Jin Soo Choi, Chang Kyung Sung, Sung Hyun Moon, and Inkyu Lee School of Electrical Engineering Korea University Seoul, Korea Email:jinsoo@wireless.korea.ac.kr,
Adaptive Bit-Interleaved Coded OFDM over Time-Varying Channels Jin Soo Choi, Chang Kyung Sung, Sung Hyun Moon, and Inkyu Lee School of Electrical Engineering Korea University Seoul, Korea Email:jinsoo@wireless.korea.ac.kr,
New Coded Modulation for the Frequency Hoping OFDMA System.
 New Coded Modulation for the Frequency Hoping OFDMA System. Kreshchuk Alexey Potapov Vladimir Institute for Information Transmission Problems of Russian Academy of Science Thirteenth International Workshop
New Coded Modulation for the Frequency Hoping OFDMA System. Kreshchuk Alexey Potapov Vladimir Institute for Information Transmission Problems of Russian Academy of Science Thirteenth International Workshop
Estimation of Optical Link Length for Multi Haul Applications
 Estimation of Optical Link Length for Multi Haul Applications M V Raghavendra 1, P L H Vara Prasad 2 Research Scholar Department of Instrument Technology 1, Professor & Chairman (BOS) Department of Instrument
Estimation of Optical Link Length for Multi Haul Applications M V Raghavendra 1, P L H Vara Prasad 2 Research Scholar Department of Instrument Technology 1, Professor & Chairman (BOS) Department of Instrument
Low-coherence heterodyne photon correlation spectroscopy
 Low-coherence heterodyne photon correlation spectroscopy J.H. Johnson, S.L. Siefken, A. Schmidt, R. Corey, and P. Saulnier Department of Physics, Gustavus Adolphus College Saint Peter, MN 56082 ABSTRACT
Low-coherence heterodyne photon correlation spectroscopy J.H. Johnson, S.L. Siefken, A. Schmidt, R. Corey, and P. Saulnier Department of Physics, Gustavus Adolphus College Saint Peter, MN 56082 ABSTRACT
Blind Channel Identification in (2 1) Alamouti Coded Systems Based on Maximizing the Eigenvalue Spread of Cumulant Matrices
 Blind Channel Identification in (2 1) Alamouti Coded Systems Based on Maximizing the Eigenvalue Spread of Cumulant Matrices Héctor J. Pérez-Iglesias 1, Daniel Iglesia 1, Adriana Dapena 1, and Vicente Zarzoso
Blind Channel Identification in (2 1) Alamouti Coded Systems Based on Maximizing the Eigenvalue Spread of Cumulant Matrices Héctor J. Pérez-Iglesias 1, Daniel Iglesia 1, Adriana Dapena 1, and Vicente Zarzoso
Cooperative Communication with Feedback via Stochastic Approximation
 Cooperative Communication with Feedback via Stochastic Approximation Utsaw Kumar J Nicholas Laneman and Vijay Gupta Department of Electrical Engineering University of Notre Dame Email: {ukumar jnl vgupta}@ndedu
Cooperative Communication with Feedback via Stochastic Approximation Utsaw Kumar J Nicholas Laneman and Vijay Gupta Department of Electrical Engineering University of Notre Dame Email: {ukumar jnl vgupta}@ndedu
Gain dependence of measured spectra in coherent Brillouin optical time-domain analysis sensors
 Gain dependence of measured spectra in coherent Brillouin optical time-domain analysis sensors Jon Mariñelarena, Javier Urricelqui, Alayn Loayssa Universidad Pública de Navarra, Campus Arrosadía s/n, 316,
Gain dependence of measured spectra in coherent Brillouin optical time-domain analysis sensors Jon Mariñelarena, Javier Urricelqui, Alayn Loayssa Universidad Pública de Navarra, Campus Arrosadía s/n, 316,
A REDUCED COMPLEXITY TWO-DIMENSIONAL BCJR DETECTOR FOR HOLOGRAPHIC DATA STORAGE SYSTEMS WITH PIXEL MISALIGNMENT
 A REDUCED COMPLEXITY TWO-DIMENSIONAL BCJR DETECTOR FOR HOLOGRAPHIC DATA STORAGE SYSTEMS WITH PIXEL MISALIGNMENT 1 S. Iman Mossavat, 2 J.W.M.Bergmans 1 iman@nus.edu.sg 1 National University of Singapore,
A REDUCED COMPLEXITY TWO-DIMENSIONAL BCJR DETECTOR FOR HOLOGRAPHIC DATA STORAGE SYSTEMS WITH PIXEL MISALIGNMENT 1 S. Iman Mossavat, 2 J.W.M.Bergmans 1 iman@nus.edu.sg 1 National University of Singapore,
Generating Single Photons on Demand
 Vladan Vuletic Generating Single Photons on Demand I n optical signal transmission, binary signals are encoded in pulses of light traveling along optical fibers. An undesirable consequence is that if somebody
Vladan Vuletic Generating Single Photons on Demand I n optical signal transmission, binary signals are encoded in pulses of light traveling along optical fibers. An undesirable consequence is that if somebody
Linear and Nonlinear Iterative Multiuser Detection
 1 Linear and Nonlinear Iterative Multiuser Detection Alex Grant and Lars Rasmussen University of South Australia October 2011 Outline 1 Introduction 2 System Model 3 Multiuser Detection 4 Interference
1 Linear and Nonlinear Iterative Multiuser Detection Alex Grant and Lars Rasmussen University of South Australia October 2011 Outline 1 Introduction 2 System Model 3 Multiuser Detection 4 Interference
Quantum superpositions and correlations in coupled atomic-molecular BECs
 Quantum superpositions and correlations in coupled atomic-molecular BECs Karén Kheruntsyan and Peter Drummond Department of Physics, University of Queensland, Brisbane, AUSTRALIA Quantum superpositions
Quantum superpositions and correlations in coupled atomic-molecular BECs Karén Kheruntsyan and Peter Drummond Department of Physics, University of Queensland, Brisbane, AUSTRALIA Quantum superpositions
A Family of Nyquist Filters Based on Generalized Raised-Cosine Spectra
 Proc. Biennial Symp. Commun. (Kingston, Ont.), pp. 3-35, June 99 A Family of Nyquist Filters Based on Generalized Raised-Cosine Spectra Nader Sheikholeslami Peter Kabal Department of Electrical Engineering
Proc. Biennial Symp. Commun. (Kingston, Ont.), pp. 3-35, June 99 A Family of Nyquist Filters Based on Generalized Raised-Cosine Spectra Nader Sheikholeslami Peter Kabal Department of Electrical Engineering
Wavelength switchable flat-top all-fiber comb filter based on a double-loop Mach-Zehnder interferometer
 Wavelength switchable flat-top all-fiber comb filter based on a double-loop Mach-Zehnder interferometer Ai-Ping Luo, Zhi-Chao Luo,, Wen-Cheng Xu,, * and Hu Cui Laboratory of Photonic Information Technology,
Wavelength switchable flat-top all-fiber comb filter based on a double-loop Mach-Zehnder interferometer Ai-Ping Luo, Zhi-Chao Luo,, Wen-Cheng Xu,, * and Hu Cui Laboratory of Photonic Information Technology,
An Overview of Advanced LIGO Interferometry
 An Overview of Advanced LIGO Interferometry Luca Matone Columbia Experimental Gravity group (GECo) Jul 16-20, 2012 LIGO-G1200743 Day Topic References 1 2 3 4 5 Gravitational Waves, Michelson IFO, Fabry-Perot
An Overview of Advanced LIGO Interferometry Luca Matone Columbia Experimental Gravity group (GECo) Jul 16-20, 2012 LIGO-G1200743 Day Topic References 1 2 3 4 5 Gravitational Waves, Michelson IFO, Fabry-Perot
Optical spectral pulse shaping by combining two oppositely chirped fiber Bragg grating
 Optical spectral pulse shaping by combining two oppositely chirped fiber Bragg grating Miguel A. Preciado, Víctor García-Muñoz, Miguel A. Muriel ETSI Telecomunicación, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid
Optical spectral pulse shaping by combining two oppositely chirped fiber Bragg grating Miguel A. Preciado, Víctor García-Muñoz, Miguel A. Muriel ETSI Telecomunicación, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid
PART 2 : BALANCED HOMODYNE DETECTION
 PART 2 : BALANCED HOMODYNE DETECTION Michael G. Raymer Oregon Center for Optics, University of Oregon raymer@uoregon.edu 1 of 31 OUTLINE PART 1 1. Noise Properties of Photodetectors 2. Quantization of
PART 2 : BALANCED HOMODYNE DETECTION Michael G. Raymer Oregon Center for Optics, University of Oregon raymer@uoregon.edu 1 of 31 OUTLINE PART 1 1. Noise Properties of Photodetectors 2. Quantization of
Approximate Minimum Bit-Error Rate Multiuser Detection
 Approximate Minimum Bit-Error Rate Multiuser Detection Chen-Chu Yeh, Renato R. opes, and John R. Barry School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0250
Approximate Minimum Bit-Error Rate Multiuser Detection Chen-Chu Yeh, Renato R. opes, and John R. Barry School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0250
Implementation of Digital Chaotic Signal Generator Based on Reconfigurable LFSRs for Multiple Access Communications
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(7): 1691-1698, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 Implementation of Digital Chaotic Signal Generator Based on Reconfigurable LFSRs for Multiple Access Communications
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(7): 1691-1698, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 Implementation of Digital Chaotic Signal Generator Based on Reconfigurable LFSRs for Multiple Access Communications
Decoupling of CDMA Multiuser Detection via the Replica Method
 Decoupling of CDMA Multiuser Detection via the Replica Method Dongning Guo and Sergio Verdú Dept. of Electrical Engineering Princeton University Princeton, NJ 08544, USA email: {dguo,verdu}@princeton.edu
Decoupling of CDMA Multiuser Detection via the Replica Method Dongning Guo and Sergio Verdú Dept. of Electrical Engineering Princeton University Princeton, NJ 08544, USA email: {dguo,verdu}@princeton.edu
2062 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 28, NO. 14, JULY 15, /$ IEEE
 2062 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 28, NO. 14, JULY 15, 2010 Time-Domain Distributed Fiber Sensor With 1 cm Spatial Resolution Based on Brillouin Dynamic Grating Kwang Yong Song, Sanghoon Chin,
2062 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 28, NO. 14, JULY 15, 2010 Time-Domain Distributed Fiber Sensor With 1 cm Spatial Resolution Based on Brillouin Dynamic Grating Kwang Yong Song, Sanghoon Chin,
CS6956: Wireless and Mobile Networks Lecture Notes: 2/4/2015
 CS6956: Wireless and Mobile Networks Lecture Notes: 2/4/2015 [Most of the material for this lecture has been taken from the Wireless Communications & Networks book by Stallings (2 nd edition).] Effective
CS6956: Wireless and Mobile Networks Lecture Notes: 2/4/2015 [Most of the material for this lecture has been taken from the Wireless Communications & Networks book by Stallings (2 nd edition).] Effective
Advanced 3 G and 4 G Wireless Communication Prof. Aditya K Jagannathan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Advanced 3 G and 4 G Wireless Communication Prof. Aditya K Jagannathan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 19 Multi-User CDMA Uplink and Asynchronous CDMA
Advanced 3 G and 4 G Wireless Communication Prof. Aditya K Jagannathan Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 19 Multi-User CDMA Uplink and Asynchronous CDMA
Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results
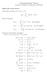 Signal and system theory Convolution of signals x(t) h(t) = y(t): Fourier Transform: Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results X(ω) = X(ω) = y(t) = X(ω) = j x(t) e jωt dt, 0 Properties
Signal and system theory Convolution of signals x(t) h(t) = y(t): Fourier Transform: Communication Theory Summary of Important Definitions and Results X(ω) = X(ω) = y(t) = X(ω) = j x(t) e jωt dt, 0 Properties
Propagation losses in optical fibers
 Chapter Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers 1-Fev-017 Propagation losses in optical fibers Charles Kao, Nobel Laureate (009) Courtesy of the Chinese University of Hong Kong S.O. Kasap, Optoelectronics
Chapter Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers 1-Fev-017 Propagation losses in optical fibers Charles Kao, Nobel Laureate (009) Courtesy of the Chinese University of Hong Kong S.O. Kasap, Optoelectronics
OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S
 OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S-108.3110 1 Course program 1. Introduction and Optical Fibers 2. Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fibers 3. Fiber-Optic Components I 4. Transmitters and Receivers 5. Fiber-Optic Measurements
OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS S-108.3110 1 Course program 1. Introduction and Optical Fibers 2. Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fibers 3. Fiber-Optic Components I 4. Transmitters and Receivers 5. Fiber-Optic Measurements
Performance Analysis of Physical Layer Network Coding
 Performance Analysis of Physical Layer Network Coding by Jinho Kim A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Electrical Engineering: Systems)
Performance Analysis of Physical Layer Network Coding by Jinho Kim A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Electrical Engineering: Systems)
Polarization division multiplexing system quality in the presence of polarization effects
 Opt Quant Electron (2009) 41:997 1006 DOI 10.1007/s11082-010-9412-0 Polarization division multiplexing system quality in the presence of polarization effects Krzysztof Perlicki Received: 6 January 2010
Opt Quant Electron (2009) 41:997 1006 DOI 10.1007/s11082-010-9412-0 Polarization division multiplexing system quality in the presence of polarization effects Krzysztof Perlicki Received: 6 January 2010
Design of a Polarization Maintaining Large Negative Dispersion PCF Using Rectangular Lattice
 Design of a Polarization Maintaining Large Negative Dispersion PCF Using Rectangular Lattice Sharafat Ali, Nasim Ahmed, Monirul Islam, S. A. Aljunid, R. B. Ahmad, H. Jaman, and S. Habib Abstract In this
Design of a Polarization Maintaining Large Negative Dispersion PCF Using Rectangular Lattice Sharafat Ali, Nasim Ahmed, Monirul Islam, S. A. Aljunid, R. B. Ahmad, H. Jaman, and S. Habib Abstract In this
EE485 Introduction to Photonics
 Pattern formed by fluorescence of quantum dots EE485 Introduction to Photonics Photon and Laser Basics 1. Photon properties 2. Laser basics 3. Characteristics of laser beams Reading: Pedrotti 3, Sec. 1.2,
Pattern formed by fluorescence of quantum dots EE485 Introduction to Photonics Photon and Laser Basics 1. Photon properties 2. Laser basics 3. Characteristics of laser beams Reading: Pedrotti 3, Sec. 1.2,
Estimation of the Capacity of Multipath Infrared Channels
 Estimation of the Capacity of Multipath Infrared Channels Jeffrey B. Carruthers Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Boston University jbc@bu.edu Sachin Padma Department of Electrical and
Estimation of the Capacity of Multipath Infrared Channels Jeffrey B. Carruthers Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Boston University jbc@bu.edu Sachin Padma Department of Electrical and
Design of Uniform Fiber Bragg grating using Transfer matrix method
 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research Vol, 3 Issue, 5 Design of Uniform Fiber Bragg grating using Transfer matrix method Deba Kumar Mahanta Department of Electrical Engineering, Assam
International Journal of Computational Engineering Research Vol, 3 Issue, 5 Design of Uniform Fiber Bragg grating using Transfer matrix method Deba Kumar Mahanta Department of Electrical Engineering, Assam
EM Channel Estimation and Data Detection for MIMO-CDMA Systems over Slow-Fading Channels
 EM Channel Estimation and Data Detection for MIMO-CDMA Systems over Slow-Fading Channels Ayman Assra 1, Walaa Hamouda 1, and Amr Youssef 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Concordia Institute
EM Channel Estimation and Data Detection for MIMO-CDMA Systems over Slow-Fading Channels Ayman Assra 1, Walaa Hamouda 1, and Amr Youssef 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Concordia Institute
Capacity Bounds for Power- and Band-Limited Wireless Infrared Channels Corrupted by Gaussian Noise
 40th Annual Allerton Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing, U.Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Oct. 2-4, 2002, Allerton House, Monticello, USA. Capacity Bounds for Power- and Band-Limited Wireless
40th Annual Allerton Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing, U.Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Oct. 2-4, 2002, Allerton House, Monticello, USA. Capacity Bounds for Power- and Band-Limited Wireless
Self-Phase Modulation in Optical Fiber Communications: Good or Bad?
 1/100 Self-Phase Modulation in Optical Fiber Communications: Good or Bad? Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Historical Introduction
1/100 Self-Phase Modulation in Optical Fiber Communications: Good or Bad? Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Historical Introduction
Results On Gas Detection and Concentration Estimation via Mid-IR-based Gas Detection System Analysis Model
 Results On Gas Detection and Concentration Estimation via Mid-IR-based Gas Detection System Analysis Model Yi Xin and Joel M. Morris Communications and Signal Processing Laboratory CSEE Dept/UMBC xin@umbc.edu,
Results On Gas Detection and Concentration Estimation via Mid-IR-based Gas Detection System Analysis Model Yi Xin and Joel M. Morris Communications and Signal Processing Laboratory CSEE Dept/UMBC xin@umbc.edu,
Approximately achieving the feedback interference channel capacity with point-to-point codes
 Approximately achieving the feedback interference channel capacity with point-to-point codes Joyson Sebastian*, Can Karakus*, Suhas Diggavi* Abstract Superposition codes with rate-splitting have been used
Approximately achieving the feedback interference channel capacity with point-to-point codes Joyson Sebastian*, Can Karakus*, Suhas Diggavi* Abstract Superposition codes with rate-splitting have been used
Random Matrices and Wireless Communications
 Random Matrices and Wireless Communications Jamie Evans Centre for Ultra-Broadband Information Networks (CUBIN) Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering University of Melbourne 3.5 1 3 0.8 2.5
Random Matrices and Wireless Communications Jamie Evans Centre for Ultra-Broadband Information Networks (CUBIN) Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering University of Melbourne 3.5 1 3 0.8 2.5
Flat Rayleigh fading. Assume a single tap model with G 0,m = G m. Assume G m is circ. symmetric Gaussian with E[ G m 2 ]=1.
![Flat Rayleigh fading. Assume a single tap model with G 0,m = G m. Assume G m is circ. symmetric Gaussian with E[ G m 2 ]=1. Flat Rayleigh fading. Assume a single tap model with G 0,m = G m. Assume G m is circ. symmetric Gaussian with E[ G m 2 ]=1.](/thumbs/75/71485687.jpg) Flat Rayleigh fading Assume a single tap model with G 0,m = G m. Assume G m is circ. symmetric Gaussian with E[ G m 2 ]=1. The magnitude is Rayleigh with f Gm ( g ) =2 g exp{ g 2 } ; g 0 f( g ) g R(G m
Flat Rayleigh fading Assume a single tap model with G 0,m = G m. Assume G m is circ. symmetric Gaussian with E[ G m 2 ]=1. The magnitude is Rayleigh with f Gm ( g ) =2 g exp{ g 2 } ; g 0 f( g ) g R(G m
First Name Last Name Title Date. Alexandra Stambaugh Slow Light on Chip Dec 8th Ring Resonators and Optofluidics
 Lecture 24 Semiconductor Detectors - Photodetectors Principle of the pn junction photodiode Absorption coefficient and photodiode materials Properties of semiconductor detectors The pin photodiodes Avalanche
Lecture 24 Semiconductor Detectors - Photodetectors Principle of the pn junction photodiode Absorption coefficient and photodiode materials Properties of semiconductor detectors The pin photodiodes Avalanche
Single-Mode Propagation ofmutual Temporal Coherence: Equivalence of Time and Frequency Measurements of Polarization Mode Dispersion
 r~3 HEWLETT ~~ PACKARD Single-Mode Propagation ofmutual Temporal Coherence: Equivalence of Time and Frequency Measurements of Polarization Mode Dispersion Brian Heffner Instruments and Photonics Laboratory
r~3 HEWLETT ~~ PACKARD Single-Mode Propagation ofmutual Temporal Coherence: Equivalence of Time and Frequency Measurements of Polarization Mode Dispersion Brian Heffner Instruments and Photonics Laboratory
Continuous-Model Communication Complexity with Application in Distributed Resource Allocation in Wireless Ad hoc Networks
 Continuous-Model Communication Complexity with Application in Distributed Resource Allocation in Wireless Ad hoc Networks Husheng Li 1 and Huaiyu Dai 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer
Continuous-Model Communication Complexity with Application in Distributed Resource Allocation in Wireless Ad hoc Networks Husheng Li 1 and Huaiyu Dai 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer
Onamethodtoimprove correlation properties of orthogonal polyphase spreading sequences
 Regular paper Onamethodtoimprove correlation properties of orthogonal polyphase spreading sequences Beata J. Wysocki and Tadeusz A. Wysocki Abstract In this paper, we propose a simple but efficient method
Regular paper Onamethodtoimprove correlation properties of orthogonal polyphase spreading sequences Beata J. Wysocki and Tadeusz A. Wysocki Abstract In this paper, we propose a simple but efficient method
Cooperative Diversity in CDMA over Nakagami m Fading Channels
 Cooperative Diversity in CDMA over Nakagami m Fading Channels Ali Moftah Ali Mehemed A Thesis in The Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
Cooperative Diversity in CDMA over Nakagami m Fading Channels Ali Moftah Ali Mehemed A Thesis in The Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
Lecture 4 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 4, Slide 1
 ecture 4 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion imitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
ecture 4 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion imitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
Step index planar waveguide
 N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
FBMC/OQAM transceivers for 5G mobile communication systems. François Rottenberg
 FBMC/OQAM transceivers for 5G mobile communication systems François Rottenberg Modulation Wikipedia definition: Process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal,
FBMC/OQAM transceivers for 5G mobile communication systems François Rottenberg Modulation Wikipedia definition: Process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal,
2001 Spectrometers. Instrument Machinery. Movies from this presentation can be access at
 2001 Spectrometers Instrument Machinery Movies from this presentation can be access at http://www.shsu.edu/~chm_tgc/sounds/sound.html Chp20: 1 Optical Instruments Instrument Components Components of various
2001 Spectrometers Instrument Machinery Movies from this presentation can be access at http://www.shsu.edu/~chm_tgc/sounds/sound.html Chp20: 1 Optical Instruments Instrument Components Components of various
Simultaneous Temperature and Strain Sensing for Cryogenic Applications Using Dual-Wavelength Fiber Bragg Gratings
 Simultaneous Temperature and Strain Sensing for Cryogenic Applications Using Dual-Wavelength Fiber Bragg Gratings Meng-Chou Wu *, William H. Prosser NASA, Langley Research Center, MS 231, Hampton, VA,
Simultaneous Temperature and Strain Sensing for Cryogenic Applications Using Dual-Wavelength Fiber Bragg Gratings Meng-Chou Wu *, William H. Prosser NASA, Langley Research Center, MS 231, Hampton, VA,
