Writing Exams: Writing Exams. Exam Review
|
|
|
- Aron Curtis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 riting Exms: riting Exms Exm Review riting Exms synhronous iruits += Res, yles n Stte ssignment Synhronous iruits Stte-Grph onstrution n Smll Prolems lso Multiple Outputs, n Hrer omintionl Prolem
2 riting Exms: riting Exms RLETON UNIVERSITY pril 28 Finl pril, 6 28; 9: hrs DURTION: 3 HOURS No. of Stuents: 22 Deprtment Nme & ourse Numer: Eletronis ELE 267 n ourse Instrutor(s) T.G.Ry n J. Knight Nme: Numer: Signture: UTHORIED MEMORND TURN OFF ell phones n personl ommunitions equipment n LEVE THEM T THE FRONT. Notes, ooks, n non-ommuniting lultor re llowe. Stuents MUST ount the numer of pges in this exmintion question pper efore eginning to write, n report ny isrepny immeitely to protor. This question pper hs pges. This exmintion pper My Not e tken from the exmintion room. In ition to this question pper, stuents require: n exmintion ooklet yes no x my request Sntron sheet yes no x 2% Plese nswer on the exmintion pper. If your nswer oes not fit, hek you re not oing long hr wy. You my sk for ooklet if you nee it. oolen If you use mp, inite in the spe unerneth it, for whih funtion it is. If you use lger, inite the rules use t the right sie of eh line. Espeilly for sorption, D2, Swp, onesus n other less ovious ones Mrks will e eute if you on t! D D mp of 2
3 riting Exms: riting Exms riting Exms Timing yourself: 3 hours, %.5 min for % or 5 min for %. /2 hour for lenup. Give Up: If you n t get it move on. RTFQ: Re The Foolish Question; re it gin DMN IT ht ws ske for? Just the stte tle? Then on t mke K-mps. Di it wnt iruit. Then rw it! Look for simple methos: Don t o ll lger questions y multiplying out. (++)(++)(+) = First look for simplifitions. re there three m spe for the nswer? Do you nee thirty? re you sure. Simplify t eh step: Right elow: +nything = Left elow: +nything = + nything Nose: += NO NO NO! F oes not equl its ul F = (++)(++)(+) = ++(+) = +++ = + = (+)(+) Tke ul Dist +nythng = (use simp twie) 3 += Exm Rey + = + = +
4 riting Exms: riting Exms riting Exms Timing yourself: 3 hours, %.5 min for % or 5 min for %. /2 hour for lenup. Give Up: If you n t get it move on. RTFQ: Re The Foolish Question; re it gin DMN IT ht ws ske for? Just the stte tle? Then on t mke K-mps. Di it wnt iruit. Then rw it! Look for simple methos: Don t o ll lger questions y multiplying out. (++)(++)(+)= First look for simplifitions. re there three m spe for the nswer? Do you nee thirty? No! see simplifition elow. Simplify t eh step: Right elow: +nything = Left elow: +nything = + nything F n F ul Nose: += F = (++)(++)(+) F ul = ++(+) = +++ = + (F ul ) ul = F = (+)(+) Tke ul Dist +nythng = (use simp twie) + =
5 ommon Mistkes: ommon Mistkes ommon Mistkes. Sying is the sme s 2. Sying n expression is equl to its ul. 3. Not using + = to simplify expressions efore using omplex rules. Not reuing using + E = + E. Simplifying n reuing first sves lger. 4. Sying + = Everyoy knows etter thn this, ut they still o it. 5. hen you tke ul, or generl Demorgn, o not put in the rkets in your he. ( + ) + DE ==> (+)(D +E) ( + ) + DE ==> (() + ) + (DE) ==> ((+))(D +E) 6. Not knowing D2. + =( + )( +) 7. Krnugh mp my not give the simplest iruit, ut it oes give the simplest Σ of Π iruit. Unless you mess up the irles 5
6 oolen lger: oolen lger oolen lger. hnge to Σ of Π ( + ) 2. Simplify D + 3. Tke the ul of F=( + )( + Y) + 4. Ftor + 5. Ftor + 6. Fin the ul of G=( + )( + ) + D 7. Ftor + D 8. onstrut simplest iruit with MUs + D + D 6
7 oolen lger: oolen lger oolen lger. hnge to Σ of Π ( + ) 2. Simplify D + + D + = rule += rule DeMorg rule += 3. Tke the ul of F=( + )( + Y) + 4. Ftor + 5. Ftor + F={( + )( + Y)} + rket NDs F ul ={()+(Y)} ( + )( + ) rule D2 ( +)( + ) rule D2 =( + )( +)( + ) rule D2 6. Fin the ul of G=( + )( + ) + D {( + )( + )} + D rket NDs G ul ={()+()}D ul =D rules =; x+=x 7. Ftor + D ( + )( + D) rule D2 8. onstrut with MUs + D + D =( + )( + )( + D)( + D) rule D2 + D D + D = =D 7
8 oolen lger: 8 oolen lger K-Mps; ommon Errors Mp of F Mp of G hek Your Mp Entries One vrile in the wrong squre, you re tost! Don t Tret Multiple Output Prolems Like Unrelte iruits Mp of F Mp of G 2 gtes, none shre 9 gtes, 3 shre hek for rp roun, Poor it of ftoring might lower gte ount. SHRE GTES Goo Fin iggest loops Poor n ier rp roun You fin two etter loops Using lger fter mp simplifition. Usully not help: K-mp gives the simplest Σ of Π iruit. three gtes + = ( + ) two gtes
9 oolen lger: oolen lger K-Mps; ommon Errors Do not onfuse 5-vrile mps n ul-output mps. 5-vrile use the lrgest irles, Try to enlrge irle y using oth mps. Multiple output Shring is very importnt to sve gtes Often (esp exms) some smller irles will give fewer gtes. shring lowers gte ount. lne these smller irles inrese letter ount. Multiple Output Mpping Rules Do Hlf-Mps First (Exept for PLs) No frien rule ll friens gone to rk sie rule Lst two rules re heuristis They help, ut ut not lwys, They o not reple ll thinking. 9
10 Multiple Outputs Detils: Multiple Outputs Detils Multiple Outputs Detils Exmple.-33 Fin the equtions with minimum logi Minimiztion with shring () Hlf Mps Look for hlf-mp irles (one letter terms) These o not require n ND gte. n n e irle without loss of potentil gte shring. No Friens (Lone )Rule (2) irle squres tht re on only one mp thus nnot e shre. No Friens, They ent To The Drk Sie, Rule (2) Fin squres tht nnot e usefully shre euse tht squre on other mps is lrey irle. irle them hlf-mp qurter-mp Lone Mp Y f No frien Y Lone Y Mp Y g Y
11 Multiple Outputs Detils: Multiple Outputs Detils No est Friens Rule Lonesome rule) (2) Loop squres tht pper on only one mp There is no wy to shre them. Loop them with s mny rothers, or s, s possile. No est friens Just rothers irle him with his rothers est irle y (fmily) No frien here Mp of Mp of No frien here No frien here Mp of Mp of Y
12 Multiple Outputs Detils: Multiple Outputs Detils My est Friens re Gone Rule. (They went over to the rk sie) (2) ith no est friens left, we nnot usefully shre loops. Loop these new frienless s with fmily. h one est frien Frien went to the rk sie Mp of Loop him with fmily Mp of est frien s gone est frien s gone Mp of Loop him His est frien is gone. Mp of Y 2
13 Multiple Outputs Detils: Multiple Outputs Detils Exmp.-33Fin the minimum Σ of Π Minimum numer of ND terms Poor Metho F Y G Y H Y etter Metho () irle hlf mps (none) Lrgest irles 7 ND terms (2) No Friens, ( s on only one mp) F Y G Y H Y Loop Frienless s, they will never shre Unfortuntely you hve hoies; severl wys to loop some squres F Y G Y hoies H Y hoies F Y G Y H Y 3
14 Fin the minimum Σ of Π(ont): Fin the minimum Σ of Π(ont) Fin the minimum Σ of Π(ont) hoies hoie () hosen irles re she Shows unneessry reunny hoie (2) hoie (3) hoies John s Solution 6 ND terms Tom s Solution 5 ND terms nie s Solution 5 ND terms F F Y F Y Y G Y G Y G Y F Y G Y H H H Y Y H Y Y 4
15 Design of Stte Grphs: Design of Stte Grphs Design of Stte Grphs Exmple.-34 or Mhine min sequene G- G- = got - = re Detet or with overlp. Output shoul lst for full lok yle. First tret s iniviul mhines:. Do the grph vertilly. re got got Fill in extr rrows got = = re re re re re Do the grph horizontlly. Do the min sequene first G- = got - got got got got Fill in extr rrows G- go for go for go for go for Mens Moore = got for 5
16 Design of Stte Grphs: or Moore Mhine Detet or with overlp. Mke the prout grph. The two grphs long the xes etermine where the rrows go. got - got G- = R = Design of Stte Grphs got - got got got got G- G = = = = = = R G got = got = got = 6
17 Design of Stte Grphs: or Mhine Detet or with overlp. omplete the prout grph. e sure eh stte hs two exit rrows. LUE got - G- = got Design of Stte Grphs got - got got got got G- = = = = = got got got = = = = = = 7
18 Design of Stte Grphs: Design of Stte Grphs or Mhine, lternte Solution Detet or with overlp. The t omes in serilly with the leftmost it first Output lsts for one whole lok yle. rrnge the sequenes long two xes. The xes show how fr long eh sequene one is. G- got - got - got - got got - got got got got got got got got got got got G- got - got - R got - got R = got - got R got got R got got got got R R got got R = got got 8
19 Prolems from De 96.: Prolems from De 96. Sketh the Output veforms D L Prolems from De 96. D Lth (inverte lok) Trnsprent when? Lthe when? L D Q D Flip-Flop ege triggere Q Equilivlent to gte D G L L D Lth Trnsprent when Lthe when 9
20 Prolems from De 96.: Lthes et from De 96. Exmple.-35 Sketh the Output veforms D L T T T Prolems from De 96. D Lth (inverte lok) Trnsprent when low Lthe when high L D Q D Flip-Flop Rising ege triggere Q D G L L T T T NOR gte D Lth Trnsprent when = Lthe when = 2
21 Prolems from De 96.: Prolems from De 96. Lthes et from De 96.Lthes et from De 96. Exmple.-36 Sketh the Output veforms D L T T T D Lth (inverte lok) Trnsprent when lok low Lthe when high L D Q D Flip-Flop Rising ege triggere Q D G L L T T T NOR gte D Lth Trnsprent when = Lthe when= 2
22 Prolems from De 96.: Lthes et. from De 96. Exmple.-37 Sketh the Output veforms R S E L R S L Prolems from De 96. Reset(L) - set(l) Lth Set output to when R= Set output = when RS= Store output when SR= F Synhronous Stte Grph x= x= x= z= x= z= LK Stte= Synhronous Stte Grph G x= x= z= x= LK x=/z= x=/z= Stte Stte Stte Show stte s well s 22
23 Prolems from De 96.: Lthes et. from De 96. Exmple.-38 Sketh the Output veforms R S E L R(L) S(L) L Prolems from De 96. Reset(L)-set(L) Lth Set output = when RS= Set output to when R= Store output when SR= Set ominnt F Synhronous Stte Grph x= x= x= z= x= z= Sketh the iruit. LK Stte Stte Stte Stte Stte= Stte only hnges on the lok ege Synhronous Stte Grph G x= x= = x= LK = Stte Stte Stte Show stte s well s Stte Stte Stte 23
24 Prolems from De 96.: Prolems from De 96. Summry So Fr T flip flop Q En LK R Re the question! ll of it! lwys hek for x + = Use this to simplify nywhere. lwys reue + x = + x Use nywhere exept for hzrs Too mny people sy x + = x Do not onfuse synhronous n synhronous. Synhronous Not othere y res. ssign sttes to reue logi. Not othere y hzrs. Don t try to ure them. 2. synhronous ssign sttes to e re free. Must not hve hzrs. To tell Moore from Mely in wor prolems LK. Moore Outputs Outputs will pper fter the next tive lok ege. 2. Mely Outputs Outputs will pper fter the input hnges Flip flops Smple D input just efore the lok.. Trnsfer this to the output just fter the lok. Q never hnges exept t lok eges T-flip flops Toggle Q fter every lok ege if - enle (provie it hs n enle) D LK D R D LK Q Input using output Moore Mely 24
25 Prolems from De 96.: Prolems from De 96. Must Do ith Finite-Stte Mhines. Rerrnge the stte tle into Krnugh mp orer.. hoose Moore or Mely outputs from esription. Mely output prolems hve wors like: The output eomes true s soon s the finl it in the sequene rrives. The output oes not hve to wit for the lok. hoose n output type most likely to reue the size of the iruit. Moore output prolems hve wors like: The output eomes true uring the next stte fter the finl input it is reeive. The output must not trnsfer ny glithes tht re on the input.. hnge sttes only t n tive lok ege. Often one when on timing igrms. NoNo. Rememer tht FSMs re multiple output mhines. th for shre gtes when you loop mps. Next-Stte Logi Output Logi Q 2 Q 2 Q 2 Q 2 Q 2 Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q D 2 D D Y Q D Q 25
26 Fin Res In synhronous Stte Fin Res In synhronous Stte Tles Exmple.4-.Fin Res ) Stte Tles for espile mhines Present Stte FG Next Stte F + G + For inputs: = = = = FG= FG= FG= FG= Fin Res In synhronous Stte ) irle stle sttes Present Stte FG Next Stte F + G + For inputs: = = = = FG= FG= FG= FG= ) Strting t stle sttes hnge one input, either or hek for oth F + n G + hnging. Present Stte FG Next Stte F + G + For inputs: = = = = FG= FG= 2 FG= FG= ) hek re Present Stte FG Next Stte F + G + For inputs: = = FG= FG= FG= FG= Re Strts t FG=, = hnges -> My en in FG=, = FG=, = Doule input hnges never hppen. Res tht on t strt in stle stte re who res unless prt of lrger pth. 26
27 Fin Res In synhronous Stte Fin Res In synhronous Stte Fin Res In synhronous Stte Tles (ont) Exmple.4-2.Fin Res ontinue ) Strting t stle sttes hnge one input, either or hek for oth F + n G + hnging. Present Stte FG Next Stte F + G + For inputs: = = = = FG= FG= FG= FG= 2 e) hek Re 2 Present Stte FG Next Stte F + G + For inputs: = = FG= FG= FG= Fixe thnks to Priti Re 2 Strts t FG=, = hnges -> ill en in FG=, = FG= Nonritil re f) If the first step is not re. hek for oth F + n G + hnging s trnsitions go own the olumn. Present Stte FG Next Stte F + G + For inputs: = = = = FG= 3 FG= FG= FG= g) hek Re 3 Present Stte FG Next Stte F + G + For inputs: = = FG= FG= FG= FG= Re 3 Strts t FG=, = hnges -> Re invoves FG=, = FG=, = FG=, = ill en in FG=, = Nonritil re etween trnsient sttes 27
28 Fin Res In synhronous Stte Fin Res In synhronous Stte Fining Nstys In synhronous Stte Tles Exmple.4-3.Fin Res ) Fin res irle stle sttes x + y + for inputs : x + y + for inputs : ) Y hek st re x + y + for inputs : Y ) ) Strting from stle sttes look for oule stte hnges x + y + for inputs : Y ritil. n en in three ifferent ifferent sttes Strt stte (=) En: one of stte (=) stte (=) stte (=) hek 2 n re x + y + for inputs : Y 2 Y 2 Rememer oule input hnges re not llowe. Res tht on t strt in stle stte re who res unless prt of lrger pth. e) No re: ) Not llowe input hnge ) Doesn t strt in stle stte ritil. n en in two ifferent sttes Strt stte (=) En: one of stte (=) stte (=) 28
29 Fin Res In synhronous Stte Fin Res In synhronous Stte Fining More Nstys In synhronous Stte Tles Exmple.4-4 Fin Nonritil Res One entry is hnge from previous stte tle. ) Fin nonritil res x + y + for inputs : Y hnge ) irle stle sttes x + y + for inputs : Y ) hek new re e) hek seonry pths x + y + for inputs : Re. x + y + for inputs : Y My go Y to three sttes. Strt in =-> ) Strting from stle sttes look for res x + y + for inputs : Y ut from ny stte we soon he k to. e will eventully reh stte (=). Nonritil Re. 29
30 Fin Res In synhronous Stte Fin Res In synhronous Stte Fining Still More Nstys Fin True yle Exmple.4-5 One whih osilltes until n input hnges.. ) Fin true yle ) irle stle sttes x + y + for inputs : x + y + for inputs : Y Y ) Look own olumns for yles x + y + for inputs : Y ) hek for other yles x + y + for inputs : Y Not yle eventully goes to yle No stle stte Osilltes until input hnges. 3
31 Fin Res In synhronous Stte Milly Diffiult Stte ssignments Exmple.4-6 ) ) Fin Re Free Stte ssignment Simultneous input hnges never hppen. synhronous Stte Tle irle Stle Sttes Next Stte for inputs x y: FG - - on t res re - Look t using - Next Stte for inputs x y: FG Fill in the on t res Fin Res In synhronous Stte ) Show llowe trnsitions ) Mke grph of Next Stte trnsitions. for inputs x y: Sme grph FG rwn ifferently - - Rerw grph nnot fit tringles on K-mp e) Grph trnsitions through - - eome trnsient sttes New grph with - use f) ssign Sttes Possile ssignment g) omplete tle Next stte for inputs x y: FG = = = = 3
32 Fin Res In synhronous Stte Fin Res In synhronous Stte nother Stte ssignments Exmple.4-7 ): synhronous Stte Tle; irle Stle Stes Fin Re Free Stte ssignment Simultneous input hnges never hppen. Present Next Stte Q + Q + 2 Output Stte Q Q 2 xy= xy= xy= xy= = F D D D F D D F F F D ): Drw Trnsitions Trnsitions tht must e 2 step ith ssignment () () F ): Look t two-step trnsitions Next Stte for inputs x y: F D Q Q 2 F D? F D F D n t fix D? F D D (2) F F F D? D ill not work Present Next Stte Q + + Q 2 Output Stte Q Q 2 xy= xy= xy= xy= = F D D D F D D F F F D ith ssignment (2) ): Look t two-step trnsitions orks Next Stte for inputs x y: Q Q 2 F D D D F D D F F F D D F F D e) ssign Sttes F () D (2) 32
Exam Review. John Knight Electronics Department, Carleton University March 2, 2009 ELEC 2607 A MIDTERM
 riting Exms: Exm Review riting Exms += riting Exms synhronous iruits Res, yles n Stte ssignment Synhronous iruits Stte-Grph onstrution n Smll Prolems lso Multiple Outputs, n Hrer omintionl Prolem riting
riting Exms: Exm Review riting Exms += riting Exms synhronous iruits Res, yles n Stte ssignment Synhronous iruits Stte-Grph onstrution n Smll Prolems lso Multiple Outputs, n Hrer omintionl Prolem riting
CARLETON UNIVERSITY. 1.0 Problems and Most Solutions, Sect B, 2005
 RLETON UNIVERSIT eprtment of Eletronis ELE 2607 Swithing iruits erury 28, 05; 0 pm.0 Prolems n Most Solutions, Set, 2005 Jn. 2, #8 n #0; Simplify, Prove Prolem. #8 Simplify + + + Reue to four letters (literls).
RLETON UNIVERSIT eprtment of Eletronis ELE 2607 Swithing iruits erury 28, 05; 0 pm.0 Prolems n Most Solutions, Set, 2005 Jn. 2, #8 n #0; Simplify, Prove Prolem. #8 Simplify + + + Reue to four letters (literls).
Project 6: Minigoals Towards Simplifying and Rewriting Expressions
 MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1. Given a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
 1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
Factorising FACTORISING.
 Ftorising FACTORISING www.mthletis.om.u Ftorising FACTORISING Ftorising is the opposite of expning. It is the proess of putting expressions into rkets rther thn expning them out. In this setion you will
Ftorising FACTORISING www.mthletis.om.u Ftorising FACTORISING Ftorising is the opposite of expning. It is the proess of putting expressions into rkets rther thn expning them out. In this setion you will
Counting Paths Between Vertices. Isomorphism of Graphs. Isomorphism of Graphs. Isomorphism of Graphs. Isomorphism of Graphs. Isomorphism of Graphs
 Isomorphism of Grphs Definition The simple grphs G 1 = (V 1, E 1 ) n G = (V, E ) re isomorphi if there is ijetion (n oneto-one n onto funtion) f from V 1 to V with the property tht n re jent in G 1 if
Isomorphism of Grphs Definition The simple grphs G 1 = (V 1, E 1 ) n G = (V, E ) re isomorphi if there is ijetion (n oneto-one n onto funtion) f from V 1 to V with the property tht n re jent in G 1 if
Digital Circuit Engineering
 Digitl Ciruit Engineering 5 INPUT MAPS (A) Loop squres with no friens, they n never shre. (B) Loop squres with no rothers, n simutneously loop their friens. Iterte: (A') Loop squres seperte from friens
Digitl Ciruit Engineering 5 INPUT MAPS (A) Loop squres with no friens, they n never shre. (B) Loop squres with no rothers, n simutneously loop their friens. Iterte: (A') Loop squres seperte from friens
Digital Circuit Engineering
 Digitl Ciruit Engineering 5 IN UT P MAPS (A) Loop squres with no friens, they n never shre. (B) Loop squres with no rothers, n simutneously loop their friens. Iterte: (A') Loop squres seperte from friens
Digitl Ciruit Engineering 5 IN UT P MAPS (A) Loop squres with no friens, they n never shre. (B) Loop squres with no rothers, n simutneously loop their friens. Iterte: (A') Loop squres seperte from friens
CS 2204 DIGITAL LOGIC & STATE MACHINE DESIGN SPRING 2014
 S 224 DIGITAL LOGI & STATE MAHINE DESIGN SPRING 214 DUE : Mrh 27, 214 HOMEWORK III READ : Relte portions of hpters VII n VIII ASSIGNMENT : There re three questions. Solve ll homework n exm prolems s shown
S 224 DIGITAL LOGI & STATE MAHINE DESIGN SPRING 214 DUE : Mrh 27, 214 HOMEWORK III READ : Relte portions of hpters VII n VIII ASSIGNMENT : There re three questions. Solve ll homework n exm prolems s shown
Lecture 6: Coding theory
 Leture 6: Coing theory Biology 429 Crl Bergstrom Ferury 4, 2008 Soures: This leture loosely follows Cover n Thoms Chpter 5 n Yeung Chpter 3. As usul, some of the text n equtions re tken iretly from those
Leture 6: Coing theory Biology 429 Crl Bergstrom Ferury 4, 2008 Soures: This leture loosely follows Cover n Thoms Chpter 5 n Yeung Chpter 3. As usul, some of the text n equtions re tken iretly from those
Equivalent fractions have the same value but they have different denominators. This means they have been divided into a different number of parts.
 Frtions equivlent frtions Equivlent frtions hve the sme vlue ut they hve ifferent enomintors. This mens they hve een ivie into ifferent numer of prts. Use the wll to fin the equivlent frtions: Wht frtions
Frtions equivlent frtions Equivlent frtions hve the sme vlue ut they hve ifferent enomintors. This mens they hve een ivie into ifferent numer of prts. Use the wll to fin the equivlent frtions: Wht frtions
Bridging the gap: GCSE AS Level
 Bridging the gp: GCSE AS Level CONTENTS Chpter Removing rckets pge Chpter Liner equtions Chpter Simultneous equtions 8 Chpter Fctors 0 Chpter Chnge the suject of the formul Chpter 6 Solving qudrtic equtions
Bridging the gp: GCSE AS Level CONTENTS Chpter Removing rckets pge Chpter Liner equtions Chpter Simultneous equtions 8 Chpter Fctors 0 Chpter Chnge the suject of the formul Chpter 6 Solving qudrtic equtions
Digital Circuit Engineering
 Digitl Ciruit Engineering DIGITAL VLSI Consensus, use Krnugh + + = + + + 2n Distriutive (X + A)(X + ) = X + A DESIGN Simplifition YX + X = X Generl DeMorgn Asorption Y + XY = X + Y F(,,... z,+,.,,) F(,,...
Digitl Ciruit Engineering DIGITAL VLSI Consensus, use Krnugh + + = + + + 2n Distriutive (X + A)(X + ) = X + A DESIGN Simplifition YX + X = X Generl DeMorgn Asorption Y + XY = X + Y F(,,... z,+,.,,) F(,,...
Instructions. An 8.5 x 11 Cheat Sheet may also be used as an aid for this test. MUST be original handwriting.
 ID: B CSE 2021 Computer Orgniztion Midterm Test (Fll 2009) Instrutions This is losed ook, 80 minutes exm. The MIPS referene sheet my e used s n id for this test. An 8.5 x 11 Chet Sheet my lso e used s
ID: B CSE 2021 Computer Orgniztion Midterm Test (Fll 2009) Instrutions This is losed ook, 80 minutes exm. The MIPS referene sheet my e used s n id for this test. An 8.5 x 11 Chet Sheet my lso e used s
Numbers and indices. 1.1 Fractions. GCSE C Example 1. Handy hint. Key point
 GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? IN THIS CHAPTER YOU WILL:
 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? 1 01 Squres, squre roots nd surds 1 02 Pythgors theorem 1 03 Finding the hypotenuse 1 04 Finding shorter side 1 05 Mixed prolems 1 06 Testing for right-ngled tringles
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? 1 01 Squres, squre roots nd surds 1 02 Pythgors theorem 1 03 Finding the hypotenuse 1 04 Finding shorter side 1 05 Mixed prolems 1 06 Testing for right-ngled tringles
System Validation (IN4387) November 2, 2012, 14:00-17:00
 System Vlidtion (IN4387) Novemer 2, 2012, 14:00-17:00 Importnt Notes. The exmintion omprises 5 question in 4 pges. Give omplete explntion nd do not onfine yourself to giving the finl nswer. Good luk! Exerise
System Vlidtion (IN4387) Novemer 2, 2012, 14:00-17:00 Importnt Notes. The exmintion omprises 5 question in 4 pges. Give omplete explntion nd do not onfine yourself to giving the finl nswer. Good luk! Exerise
Area and Perimeter. Area and Perimeter. Solutions. Curriculum Ready.
 Are n Perimeter Are n Perimeter Solutions Curriulum Rey www.mthletis.om How oes it work? Solutions Are n Perimeter Pge questions Are using unit squres Are = whole squres Are = 6 whole squres = units =
Are n Perimeter Are n Perimeter Solutions Curriulum Rey www.mthletis.om How oes it work? Solutions Are n Perimeter Pge questions Are using unit squres Are = whole squres Are = 6 whole squres = units =
CS 491G Combinatorial Optimization Lecture Notes
 CS 491G Comintoril Optimiztion Leture Notes Dvi Owen July 30, August 1 1 Mthings Figure 1: two possile mthings in simple grph. Definition 1 Given grph G = V, E, mthing is olletion of eges M suh tht e i,
CS 491G Comintoril Optimiztion Leture Notes Dvi Owen July 30, August 1 1 Mthings Figure 1: two possile mthings in simple grph. Definition 1 Given grph G = V, E, mthing is olletion of eges M suh tht e i,
The University of Nottingham SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE A LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER MACHINES AND THEIR LANGUAGES ANSWERS
 The University of ottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTR SCIC A LVL 2 MODUL, SPRIG SMSTR 2015 2016 MACHIS AD THIR LAGUAGS ASWRS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my omplete the front over of their nswer ook nd sign their
The University of ottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTR SCIC A LVL 2 MODUL, SPRIG SMSTR 2015 2016 MACHIS AD THIR LAGUAGS ASWRS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my omplete the front over of their nswer ook nd sign their
GM1 Consolidation Worksheet
 Cmridge Essentils Mthemtis Core 8 GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet 1 Clulte the size of eh ngle mrked y letter. Give resons for your nswers. or exmple, ngles on stright line dd up
Cmridge Essentils Mthemtis Core 8 GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet 1 Clulte the size of eh ngle mrked y letter. Give resons for your nswers. or exmple, ngles on stright line dd up
Solutions for HW9. Bipartite: put the red vertices in V 1 and the black in V 2. Not bipartite!
 Solutions for HW9 Exerise 28. () Drw C 6, W 6 K 6, n K 5,3. C 6 : W 6 : K 6 : K 5,3 : () Whih of the following re iprtite? Justify your nswer. Biprtite: put the re verties in V 1 n the lk in V 2. Biprtite:
Solutions for HW9 Exerise 28. () Drw C 6, W 6 K 6, n K 5,3. C 6 : W 6 : K 6 : K 5,3 : () Whih of the following re iprtite? Justify your nswer. Biprtite: put the re verties in V 1 n the lk in V 2. Biprtite:
Lesson 2.1 Inductive Reasoning
 Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
Lesson 2.1 Inductive Reasoning
 Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
2.4 Linear Inequalities and Interval Notation
 .4 Liner Inequlities nd Intervl Nottion We wnt to solve equtions tht hve n inequlity symol insted of n equl sign. There re four inequlity symols tht we will look t: Less thn , Less thn or
.4 Liner Inequlities nd Intervl Nottion We wnt to solve equtions tht hve n inequlity symol insted of n equl sign. There re four inequlity symols tht we will look t: Less thn , Less thn or
DeMorgan s Theorem. The dual DeMorgan D + E = D E D+E D E 1 D NOR D E. Slide 29 Modified; January 3, 2006 John Knight Digital Circuits p.
 DeMorgn s Theorem DeMorgn s Theorems, Simple orms DeMorgn s Theorem DeMorgn s Theorems, Simple orms DeMorgn The ul DeMorgn A + B = A B (DeM) D + E = D E (DeM2) Inverse The ul inverse A + B = A B D E =
DeMorgn s Theorem DeMorgn s Theorems, Simple orms DeMorgn s Theorem DeMorgn s Theorems, Simple orms DeMorgn The ul DeMorgn A + B = A B (DeM) D + E = D E (DeM2) Inverse The ul inverse A + B = A B D E =
Unit 4. Combinational Circuits
 Unit 4. Comintionl Ciruits Digitl Eletroni Ciruits (Ciruitos Eletrónios Digitles) E.T.S.I. Informáti Universidd de Sevill 5/10/2012 Jorge Jun 2010, 2011, 2012 You re free to opy, distriute
Unit 4. Comintionl Ciruits Digitl Eletroni Ciruits (Ciruitos Eletrónios Digitles) E.T.S.I. Informáti Universidd de Sevill 5/10/2012 Jorge Jun 2010, 2011, 2012 You re free to opy, distriute
18.06 Problem Set 4 Due Wednesday, Oct. 11, 2006 at 4:00 p.m. in 2-106
 8. Problem Set Due Wenesy, Ot., t : p.m. in - Problem Mony / Consier the eight vetors 5, 5, 5,..., () List ll of the one-element, linerly epenent sets forme from these. (b) Wht re the two-element, linerly
8. Problem Set Due Wenesy, Ot., t : p.m. in - Problem Mony / Consier the eight vetors 5, 5, 5,..., () List ll of the one-element, linerly epenent sets forme from these. (b) Wht re the two-element, linerly
I 3 2 = I I 4 = 2A
 ECE 210 Eletril Ciruit Anlysis University of llinois t Chigo 2.13 We re ske to use KCL to fin urrents 1 4. The key point in pplying KCL in this prolem is to strt with noe where only one of the urrents
ECE 210 Eletril Ciruit Anlysis University of llinois t Chigo 2.13 We re ske to use KCL to fin urrents 1 4. The key point in pplying KCL in this prolem is to strt with noe where only one of the urrents
Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q5 of Paper 2
 Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q of Pper The Bsis - The Trigonometry setion is ll out tringles. We will normlly e given some of the sides or ngles of tringle nd we use formule nd rules to find the others.
Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q of Pper The Bsis - The Trigonometry setion is ll out tringles. We will normlly e given some of the sides or ngles of tringle nd we use formule nd rules to find the others.
Fast Boolean Algebra
 Fst Boolen Alger ELEC 267 notes with the overurden removed A fst wy to lern enough to get the prel done honorly Printed; 3//5 Slide Modified; Jnury 3, 25 John Knight Digitl Circuits p. Fst Boolen Alger
Fst Boolen Alger ELEC 267 notes with the overurden removed A fst wy to lern enough to get the prel done honorly Printed; 3//5 Slide Modified; Jnury 3, 25 John Knight Digitl Circuits p. Fst Boolen Alger
Algebra 2 Semester 1 Practice Final
 Alger 2 Semester Prtie Finl Multiple Choie Ientify the hoie tht est ompletes the sttement or nswers the question. To whih set of numers oes the numer elong?. 2 5 integers rtionl numers irrtionl numers
Alger 2 Semester Prtie Finl Multiple Choie Ientify the hoie tht est ompletes the sttement or nswers the question. To whih set of numers oes the numer elong?. 2 5 integers rtionl numers irrtionl numers
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, November 14, 2018 Finite Automata II. Nickolas Rollick a b b. a b 4
 Intermedite Mth Circles Wednesdy, Novemer 14, 2018 Finite Automt II Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Regulr Lnguges Lst time, we were introduced to the ide of DFA (deterministic finite utomton), one
Intermedite Mth Circles Wednesdy, Novemer 14, 2018 Finite Automt II Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Regulr Lnguges Lst time, we were introduced to the ide of DFA (deterministic finite utomton), one
CS103B Handout 18 Winter 2007 February 28, 2007 Finite Automata
 CS103B ndout 18 Winter 2007 Ferury 28, 2007 Finite Automt Initil text y Mggie Johnson. Introduction Severl childrens gmes fit the following description: Pieces re set up on plying ord; dice re thrown or
CS103B ndout 18 Winter 2007 Ferury 28, 2007 Finite Automt Initil text y Mggie Johnson. Introduction Severl childrens gmes fit the following description: Pieces re set up on plying ord; dice re thrown or
EE 108A Lecture 2 (c) W. J. Dally and P. Levis 2
 EE08A Leture 2: Comintionl Logi Design EE 08A Leture 2 () 2005-2008 W. J. Dlly n P. Levis Announements Prof. Levis will hve no offie hours on Friy, Jn 8. Ls n setions hve een ssigne - see the we pge Register
EE08A Leture 2: Comintionl Logi Design EE 08A Leture 2 () 2005-2008 W. J. Dlly n P. Levis Announements Prof. Levis will hve no offie hours on Friy, Jn 8. Ls n setions hve een ssigne - see the we pge Register
SIMPLE NONLINEAR GRAPHS
 S i m p l e N o n l i n e r G r p h s SIMPLE NONLINEAR GRAPHS www.mthletis.om.u Simple SIMPLE Nonliner NONLINEAR Grphs GRAPHS Liner equtions hve the form = m+ where the power of (n ) is lws. The re lle
S i m p l e N o n l i n e r G r p h s SIMPLE NONLINEAR GRAPHS www.mthletis.om.u Simple SIMPLE Nonliner NONLINEAR Grphs GRAPHS Liner equtions hve the form = m+ where the power of (n ) is lws. The re lle
Total score: /100 points
 Points misse: Stuent's Nme: Totl sore: /100 points Est Tennessee Stte University Deprtment of Computer n Informtion Sienes CSCI 2710 (Trnoff) Disrete Strutures TEST 2 for Fll Semester, 2004 Re this efore
Points misse: Stuent's Nme: Totl sore: /100 points Est Tennessee Stte University Deprtment of Computer n Informtion Sienes CSCI 2710 (Trnoff) Disrete Strutures TEST 2 for Fll Semester, 2004 Re this efore
Surds and Indices. Surds and Indices. Curriculum Ready ACMNA: 233,
 Surs n Inies Surs n Inies Curriulum Rey ACMNA:, 6 www.mthletis.om Surs SURDS & & Inies INDICES Inies n surs re very losely relte. A numer uner (squre root sign) is lle sur if the squre root n t e simplifie.
Surs n Inies Surs n Inies Curriulum Rey ACMNA:, 6 www.mthletis.om Surs SURDS & & Inies INDICES Inies n surs re very losely relte. A numer uner (squre root sign) is lle sur if the squre root n t e simplifie.
For a, b, c, d positive if a b and. ac bd. Reciprocal relations for a and b positive. If a > b then a ab > b. then
 Slrs-7.2-ADV-.7 Improper Definite Integrls 27.. D.dox Pge of Improper Definite Integrls Before we strt the min topi we present relevnt lger nd it review. See Appendix J for more lger review. Inequlities:
Slrs-7.2-ADV-.7 Improper Definite Integrls 27.. D.dox Pge of Improper Definite Integrls Before we strt the min topi we present relevnt lger nd it review. See Appendix J for more lger review. Inequlities:
List all of the possible rational roots of each equation. Then find all solutions (both real and imaginary) of the equation. 1.
 Mth Anlysis CP WS 4.X- Section 4.-4.4 Review Complete ech question without the use of grphing clcultor.. Compre the mening of the words: roots, zeros nd fctors.. Determine whether - is root of 0. Show
Mth Anlysis CP WS 4.X- Section 4.-4.4 Review Complete ech question without the use of grphing clcultor.. Compre the mening of the words: roots, zeros nd fctors.. Determine whether - is root of 0. Show
NON-DETERMINISTIC FSA
 Tw o types of non-determinism: NON-DETERMINISTIC FS () Multiple strt-sttes; strt-sttes S Q. The lnguge L(M) ={x:x tkes M from some strt-stte to some finl-stte nd ll of x is proessed}. The string x = is
Tw o types of non-determinism: NON-DETERMINISTIC FS () Multiple strt-sttes; strt-sttes S Q. The lnguge L(M) ={x:x tkes M from some strt-stte to some finl-stte nd ll of x is proessed}. The string x = is
Scientific notation is a way of expressing really big numbers or really small numbers.
 Scientific Nottion (Stndrd form) Scientific nottion is wy of expressing relly big numbers or relly smll numbers. It is most often used in scientific clcultions where the nlysis must be very precise. Scientific
Scientific Nottion (Stndrd form) Scientific nottion is wy of expressing relly big numbers or relly smll numbers. It is most often used in scientific clcultions where the nlysis must be very precise. Scientific
CS 573 Automata Theory and Formal Languages
 Non-determinism Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Leture # 3 Septemer 6, 2 To hieve our gol, we need the onept of Non-deterministi Finite Automton with -moves (NFA) An NFA is tuple
Non-determinism Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Leture # 3 Septemer 6, 2 To hieve our gol, we need the onept of Non-deterministi Finite Automton with -moves (NFA) An NFA is tuple
Section 2.1 Special Right Triangles
 Se..1 Speil Rigt Tringles 49 Te --90 Tringle Setion.1 Speil Rigt Tringles Te --90 tringle (or just 0-60-90) is so nme euse of its ngle mesures. Te lengts of te sies, toug, ve very speifi pttern to tem
Se..1 Speil Rigt Tringles 49 Te --90 Tringle Setion.1 Speil Rigt Tringles Te --90 tringle (or just 0-60-90) is so nme euse of its ngle mesures. Te lengts of te sies, toug, ve very speifi pttern to tem
Regular expressions, Finite Automata, transition graphs are all the same!!
 CSI 3104 /Winter 2011: Introduction to Forml Lnguges Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Regulr expressions, Finite Automt, trnsition grphs re ll the sme!! Dr. Neji Zgui CSI3104-W11 1
CSI 3104 /Winter 2011: Introduction to Forml Lnguges Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Regulr expressions, Finite Automt, trnsition grphs re ll the sme!! Dr. Neji Zgui CSI3104-W11 1
Algebra Basics. Algebra Basics. Curriculum Ready ACMNA: 133, 175, 176, 177, 179.
 Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 33 75 76 77 79 www.mthletis.om Fill in the spes with nything you lredy know out Alger Creer Opportunities: Arhitets eletriins plumers et. use it to do importnt lultions. Give this
Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 33 75 76 77 79 www.mthletis.om Fill in the spes with nything you lredy know out Alger Creer Opportunities: Arhitets eletriins plumers et. use it to do importnt lultions. Give this
Homework 3 Solutions
 CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 3 Solutions 1. Give NFAs with the specified numer of sttes recognizing ech of the following lnguges. In ll cses, the lphet is Σ = {,1}.
CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 3 Solutions 1. Give NFAs with the specified numer of sttes recognizing ech of the following lnguges. In ll cses, the lphet is Σ = {,1}.
Section 2.3. Matrix Inverses
 Mtri lger Mtri nverses Setion.. Mtri nverses hree si opertions on mtries, ition, multiplition, n sutrtion, re nlogues for mtries of the sme opertions for numers. n this setion we introue the mtri nlogue
Mtri lger Mtri nverses Setion.. Mtri nverses hree si opertions on mtries, ition, multiplition, n sutrtion, re nlogues for mtries of the sme opertions for numers. n this setion we introue the mtri nlogue
Spacetime and the Quantum World Questions Fall 2010
 Spetime nd the Quntum World Questions Fll 2010 1. Cliker Questions from Clss: (1) In toss of two die, wht is the proility tht the sum of the outomes is 6? () P (x 1 + x 2 = 6) = 1 36 - out 3% () P (x 1
Spetime nd the Quntum World Questions Fll 2010 1. Cliker Questions from Clss: (1) In toss of two die, wht is the proility tht the sum of the outomes is 6? () P (x 1 + x 2 = 6) = 1 36 - out 3% () P (x 1
Introduction to Olympiad Inequalities
 Introdution to Olympid Inequlities Edutionl Studies Progrm HSSP Msshusetts Institute of Tehnology Snj Simonovikj Spring 207 Contents Wrm up nd Am-Gm inequlity 2. Elementry inequlities......................
Introdution to Olympid Inequlities Edutionl Studies Progrm HSSP Msshusetts Institute of Tehnology Snj Simonovikj Spring 207 Contents Wrm up nd Am-Gm inequlity 2. Elementry inequlities......................
Minimal DFA. minimal DFA for L starting from any other
 Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
I1 = I2 I1 = I2 + I3 I1 + I2 = I3 + I4 I 3
 2 The Prllel Circuit Electric Circuits: Figure 2- elow show ttery nd multiple resistors rrnged in prllel. Ech resistor receives portion of the current from the ttery sed on its resistnce. The split is
2 The Prllel Circuit Electric Circuits: Figure 2- elow show ttery nd multiple resistors rrnged in prllel. Ech resistor receives portion of the current from the ttery sed on its resistnce. The split is
Activities. 4.1 Pythagoras' Theorem 4.2 Spirals 4.3 Clinometers 4.4 Radar 4.5 Posting Parcels 4.6 Interlocking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes and Solutions
 MEP: Demonstrtion Projet UNIT 4: Trigonometry UNIT 4 Trigonometry tivities tivities 4. Pythgors' Theorem 4.2 Spirls 4.3 linometers 4.4 Rdr 4.5 Posting Prels 4.6 Interloking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes nd
MEP: Demonstrtion Projet UNIT 4: Trigonometry UNIT 4 Trigonometry tivities tivities 4. Pythgors' Theorem 4.2 Spirls 4.3 linometers 4.4 Rdr 4.5 Posting Prels 4.6 Interloking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes nd
CS 373, Spring Solutions to Mock midterm 1 (Based on first midterm in CS 273, Fall 2008.)
 CS 373, Spring 29. Solutions to Mock midterm (sed on first midterm in CS 273, Fll 28.) Prolem : Short nswer (8 points) The nswers to these prolems should e short nd not complicted. () If n NF M ccepts
CS 373, Spring 29. Solutions to Mock midterm (sed on first midterm in CS 273, Fll 28.) Prolem : Short nswer (8 points) The nswers to these prolems should e short nd not complicted. () If n NF M ccepts
Trigonometry and Constructive Geometry
 Trigonometry nd Construtive Geometry Trining prolems for M2 2018 term 1 Ted Szylowie tedszy@gmil.om 1 Leling geometril figures 1. Prtie writing Greek letters. αβγδɛθλµπψ 2. Lel the sides, ngles nd verties
Trigonometry nd Construtive Geometry Trining prolems for M2 2018 term 1 Ted Szylowie tedszy@gmil.om 1 Leling geometril figures 1. Prtie writing Greek letters. αβγδɛθλµπψ 2. Lel the sides, ngles nd verties
9.1 Day 1 Warm Up. Solve the equation = x x 2 = March 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythagorean Theorem 1
 9.1 Dy 1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 9.1 Dy 2 Wrm Up Use the Pythgoren
9.1 Dy 1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 9.1 Dy 2 Wrm Up Use the Pythgoren
6.5 Improper integrals
 Eerpt from "Clulus" 3 AoPS In. www.rtofprolemsolving.om 6.5. IMPROPER INTEGRALS 6.5 Improper integrls As we ve seen, we use the definite integrl R f to ompute the re of the region under the grph of y =
Eerpt from "Clulus" 3 AoPS In. www.rtofprolemsolving.om 6.5. IMPROPER INTEGRALS 6.5 Improper integrls As we ve seen, we use the definite integrl R f to ompute the re of the region under the grph of y =
Bases for Vector Spaces
 Bses for Vector Spces 2-26-25 A set is independent if, roughly speking, there is no redundncy in the set: You cn t uild ny vector in the set s liner comintion of the others A set spns if you cn uild everything
Bses for Vector Spces 2-26-25 A set is independent if, roughly speking, there is no redundncy in the set: You cn t uild ny vector in the set s liner comintion of the others A set spns if you cn uild everything
Proportions: A ratio is the quotient of two numbers. For example, 2 3
 Proportions: rtio is the quotient of two numers. For exmple, 2 3 is rtio of 2 n 3. n equlity of two rtios is proportion. For exmple, 3 7 = 15 is proportion. 45 If two sets of numers (none of whih is 0)
Proportions: rtio is the quotient of two numers. For exmple, 2 3 is rtio of 2 n 3. n equlity of two rtios is proportion. For exmple, 3 7 = 15 is proportion. 45 If two sets of numers (none of whih is 0)
= x x 2 = 25 2
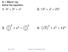 9.1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 7, 2016 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 9.1
9.1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 7, 2016 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 9.1
CS311 Computational Structures Regular Languages and Regular Grammars. Lecture 6
 CS311 Computtionl Strutures Regulr Lnguges nd Regulr Grmmrs Leture 6 1 Wht we know so fr: RLs re losed under produt, union nd * Every RL n e written s RE, nd every RE represents RL Every RL n e reognized
CS311 Computtionl Strutures Regulr Lnguges nd Regulr Grmmrs Leture 6 1 Wht we know so fr: RLs re losed under produt, union nd * Every RL n e written s RE, nd every RE represents RL Every RL n e reognized
CS 360 Exam 2 Fall 2014 Name
 CS 360 Exm 2 Fll 2014 Nme 1. The lsses shown elow efine singly-linke list n stk. Write three ifferent O(n)-time versions of the reverse_print metho s speifie elow. Eh version of the metho shoul output
CS 360 Exm 2 Fll 2014 Nme 1. The lsses shown elow efine singly-linke list n stk. Write three ifferent O(n)-time versions of the reverse_print metho s speifie elow. Eh version of the metho shoul output
Engr354: Digital Logic Circuits
 Engr354: Digitl Logi Ciruits Chpter 4: Logi Optimiztion Curtis Nelson Logi Optimiztion In hpter 4 you will lern out: Synthesis of logi funtions; Anlysis of logi iruits; Tehniques for deriving minimum-ost
Engr354: Digitl Logi Ciruits Chpter 4: Logi Optimiztion Curtis Nelson Logi Optimiztion In hpter 4 you will lern out: Synthesis of logi funtions; Anlysis of logi iruits; Tehniques for deriving minimum-ost
Geometry of the Circle - Chords and Angles. Geometry of the Circle. Chord and Angles. Curriculum Ready ACMMG: 272.
 Geometry of the irle - hords nd ngles Geometry of the irle hord nd ngles urriulum Redy MMG: 272 www.mthletis.om hords nd ngles HRS N NGLES The irle is si shpe nd so it n e found lmost nywhere. This setion
Geometry of the irle - hords nd ngles Geometry of the irle hord nd ngles urriulum Redy MMG: 272 www.mthletis.om hords nd ngles HRS N NGLES The irle is si shpe nd so it n e found lmost nywhere. This setion
p-adic Egyptian Fractions
 p-adic Egyptin Frctions Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Trditionl Egyptin Frctions nd Greedy Algorithm 2 3 Set-up 3 4 p-greedy Algorithm 5 5 p-egyptin Trditionl 10 6 Conclusion 1 Introduction An Egyptin frction
p-adic Egyptin Frctions Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Trditionl Egyptin Frctions nd Greedy Algorithm 2 3 Set-up 3 4 p-greedy Algorithm 5 5 p-egyptin Trditionl 10 6 Conclusion 1 Introduction An Egyptin frction
CIT 596 Theory of Computation 1. Graphs and Digraphs
 CIT 596 Theory of Computtion 1 A grph G = (V (G), E(G)) onsists of two finite sets: V (G), the vertex set of the grph, often enote y just V, whih is nonempty set of elements lle verties, n E(G), the ege
CIT 596 Theory of Computtion 1 A grph G = (V (G), E(G)) onsists of two finite sets: V (G), the vertex set of the grph, often enote y just V, whih is nonempty set of elements lle verties, n E(G), the ege
where the box contains a finite number of gates from the given collection. Examples of gates that are commonly used are the following: a b
 CS 294-2 9/11/04 Quntum Ciruit Model, Solovy-Kitev Theorem, BQP Fll 2004 Leture 4 1 Quntum Ciruit Model 1.1 Clssil Ciruits - Universl Gte Sets A lssil iruit implements multi-output oolen funtion f : {0,1}
CS 294-2 9/11/04 Quntum Ciruit Model, Solovy-Kitev Theorem, BQP Fll 2004 Leture 4 1 Quntum Ciruit Model 1.1 Clssil Ciruits - Universl Gte Sets A lssil iruit implements multi-output oolen funtion f : {0,1}
22: Union Find. CS 473u - Algorithms - Spring April 14, We want to maintain a collection of sets, under the operations of:
 22: Union Fin CS 473u - Algorithms - Spring 2005 April 14, 2005 1 Union-Fin We wnt to mintin olletion of sets, uner the opertions of: 1. MkeSet(x) - rete set tht ontins the single element x. 2. Fin(x)
22: Union Fin CS 473u - Algorithms - Spring 2005 April 14, 2005 1 Union-Fin We wnt to mintin olletion of sets, uner the opertions of: 1. MkeSet(x) - rete set tht ontins the single element x. 2. Fin(x)
Regular Language. Nonregular Languages The Pumping Lemma. The pumping lemma. Regular Language. The pumping lemma. Infinitely long words 3/17/15
 Regulr Lnguge Nonregulr Lnguges The Pumping Lemm Models of Comput=on Chpter 10 Recll, tht ny lnguge tht cn e descried y regulr expression is clled regulr lnguge In this lecture we will prove tht not ll
Regulr Lnguge Nonregulr Lnguges The Pumping Lemm Models of Comput=on Chpter 10 Recll, tht ny lnguge tht cn e descried y regulr expression is clled regulr lnguge In this lecture we will prove tht not ll
Chapter 4 State-Space Planning
 Leture slides for Automted Plnning: Theory nd Prtie Chpter 4 Stte-Spe Plnning Dn S. Nu CMSC 722, AI Plnning University of Mrylnd, Spring 2008 1 Motivtion Nerly ll plnning proedures re serh proedures Different
Leture slides for Automted Plnning: Theory nd Prtie Chpter 4 Stte-Spe Plnning Dn S. Nu CMSC 722, AI Plnning University of Mrylnd, Spring 2008 1 Motivtion Nerly ll plnning proedures re serh proedures Different
Section 1.3 Triangles
 Se 1.3 Tringles 21 Setion 1.3 Tringles LELING TRINGLE The line segments tht form tringle re lled the sides of the tringle. Eh pir of sides forms n ngle, lled n interior ngle, nd eh tringle hs three interior
Se 1.3 Tringles 21 Setion 1.3 Tringles LELING TRINGLE The line segments tht form tringle re lled the sides of the tringle. Eh pir of sides forms n ngle, lled n interior ngle, nd eh tringle hs three interior
How do we solve these things, especially when they get complicated? How do we know when a system has a solution, and when is it unique?
 XII. LINEAR ALGEBRA: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Tody we re going to tlk out solving systems of liner equtions. These re prolems tht give couple of equtions with couple of unknowns, like: 6= x + x 7=
XII. LINEAR ALGEBRA: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Tody we re going to tlk out solving systems of liner equtions. These re prolems tht give couple of equtions with couple of unknowns, like: 6= x + x 7=
Math Lecture 23
 Mth 8 - Lecture 3 Dyln Zwick Fll 3 In our lst lecture we delt with solutions to the system: x = Ax where A is n n n mtrix with n distinct eigenvlues. As promised, tody we will del with the question of
Mth 8 - Lecture 3 Dyln Zwick Fll 3 In our lst lecture we delt with solutions to the system: x = Ax where A is n n n mtrix with n distinct eigenvlues. As promised, tody we will del with the question of
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals
 AP Clulus BC Chpter 8: Integrtion Tehniques, L Hopitl s Rule nd Improper Integrls 8. Bsi Integrtion Rules In this setion we will review vrious integrtion strtegies. Strtegies: I. Seprte the integrnd into
AP Clulus BC Chpter 8: Integrtion Tehniques, L Hopitl s Rule nd Improper Integrls 8. Bsi Integrtion Rules In this setion we will review vrious integrtion strtegies. Strtegies: I. Seprte the integrnd into
CSE 332. Sorting. Data Abstractions. CSE 332: Data Abstractions. QuickSort Cutoff 1. Where We Are 2. Bounding The MAXIMUM Problem 4
 Am Blnk Leture 13 Winter 2016 CSE 332 CSE 332: Dt Astrtions Sorting Dt Astrtions QuikSort Cutoff 1 Where We Are 2 For smll n, the reursion is wste. The onstnts on quik/merge sort re higher thn the ones
Am Blnk Leture 13 Winter 2016 CSE 332 CSE 332: Dt Astrtions Sorting Dt Astrtions QuikSort Cutoff 1 Where We Are 2 For smll n, the reursion is wste. The onstnts on quik/merge sort re higher thn the ones
Logarithms LOGARITHMS.
 Logrithms LOGARITHMS www.mthletis.om.u Logrithms LOGARITHMS Logrithms re nother method to lulte nd work with eponents. Answer these questions, efore working through this unit. I used to think: In the
Logrithms LOGARITHMS www.mthletis.om.u Logrithms LOGARITHMS Logrithms re nother method to lulte nd work with eponents. Answer these questions, efore working through this unit. I used to think: In the
A Study on the Properties of Rational Triangles
 Interntionl Journl of Mthemtis Reserh. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 6, Numer (04), pp. 8-9 Interntionl Reserh Pulition House http://www.irphouse.om Study on the Properties of Rtionl Tringles M. Q. lm, M.R. Hssn
Interntionl Journl of Mthemtis Reserh. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 6, Numer (04), pp. 8-9 Interntionl Reserh Pulition House http://www.irphouse.om Study on the Properties of Rtionl Tringles M. Q. lm, M.R. Hssn
1 This diagram represents the energy change that occurs when a d electron in a transition metal ion is excited by visible light.
 1 This igrm represents the energy hnge tht ours when eletron in trnsition metl ion is exite y visile light. Give the eqution tht reltes the energy hnge ΔE to the Plnk onstnt, h, n the frequeny, v, of the
1 This igrm represents the energy hnge tht ours when eletron in trnsition metl ion is exite y visile light. Give the eqution tht reltes the energy hnge ΔE to the Plnk onstnt, h, n the frequeny, v, of the
Polynomials. Polynomials. Curriculum Ready ACMNA:
 Polynomils Polynomils Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 66 www.mthletis.om Polynomils POLYNOMIALS A polynomil is mthemtil expression with one vrile whose powers re neither negtive nor frtions. The power in eh expression
Polynomils Polynomils Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 66 www.mthletis.om Polynomils POLYNOMIALS A polynomil is mthemtil expression with one vrile whose powers re neither negtive nor frtions. The power in eh expression
Graph Theory. Simple Graph G = (V, E). V={a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,k} E={(a,b),(a,g),( a,h),(a,k),(b,c),(b,k),...,(h,k)}
 Grph Theory Simple Grph G = (V, E). V ={verties}, E={eges}. h k g f e V={,,,,e,f,g,h,k} E={(,),(,g),(,h),(,k),(,),(,k),...,(h,k)} E =16. 1 Grph or Multi-Grph We llow loops n multiple eges. G = (V, E.ψ)
Grph Theory Simple Grph G = (V, E). V ={verties}, E={eges}. h k g f e V={,,,,e,f,g,h,k} E={(,),(,g),(,h),(,k),(,),(,k),...,(h,k)} E =16. 1 Grph or Multi-Grph We llow loops n multiple eges. G = (V, E.ψ)
Lecture 2 : Propositions DRAFT
 CS/Mth 240: Introduction to Discrete Mthemtics 1/20/2010 Lecture 2 : Propositions Instructor: Dieter vn Melkeeek Scrie: Dlior Zelený DRAFT Lst time we nlyzed vrious mze solving lgorithms in order to illustrte
CS/Mth 240: Introduction to Discrete Mthemtics 1/20/2010 Lecture 2 : Propositions Instructor: Dieter vn Melkeeek Scrie: Dlior Zelený DRAFT Lst time we nlyzed vrious mze solving lgorithms in order to illustrte
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem
 Rep Voting Prdoxes Properties Arrow s Theorem Arrow s Impossiility Theorem Leture 12 Arrow s Impossiility Theorem Leture 12, Slide 1 Rep Voting Prdoxes Properties Arrow s Theorem Leture Overview 1 Rep
Rep Voting Prdoxes Properties Arrow s Theorem Arrow s Impossiility Theorem Leture 12 Arrow s Impossiility Theorem Leture 12, Slide 1 Rep Voting Prdoxes Properties Arrow s Theorem Leture Overview 1 Rep
Necessary and sucient conditions for some two. Abstract. Further we show that the necessary conditions for the existence of an OD(44 s 1 s 2 )
 Neessry n suient onitions for some two vrile orthogonl esigns in orer 44 C. Koukouvinos, M. Mitrouli y, n Jennifer Seerry z Deite to Professor Anne Penfol Street Astrt We give new lgorithm whih llows us
Neessry n suient onitions for some two vrile orthogonl esigns in orer 44 C. Koukouvinos, M. Mitrouli y, n Jennifer Seerry z Deite to Professor Anne Penfol Street Astrt We give new lgorithm whih llows us
Momentum and Energy Review
 Momentum n Energy Review Nme: Dte: 1. A 0.0600-kilogrm ll trveling t 60.0 meters per seon hits onrete wll. Wht spee must 0.0100-kilogrm ullet hve in orer to hit the wll with the sme mgnitue of momentum
Momentum n Energy Review Nme: Dte: 1. A 0.0600-kilogrm ll trveling t 60.0 meters per seon hits onrete wll. Wht spee must 0.0100-kilogrm ullet hve in orer to hit the wll with the sme mgnitue of momentum
Section 4: Integration ECO4112F 2011
 Reding: Ching Chpter Section : Integrtion ECOF Note: These notes do not fully cover the mteril in Ching, ut re ment to supplement your reding in Ching. Thus fr the optimistion you hve covered hs een sttic
Reding: Ching Chpter Section : Integrtion ECOF Note: These notes do not fully cover the mteril in Ching, ut re ment to supplement your reding in Ching. Thus fr the optimistion you hve covered hs een sttic
Comparing the Pre-image and Image of a Dilation
 hpter Summry Key Terms Postultes nd Theorems similr tringles (.1) inluded ngle (.2) inluded side (.2) geometri men (.) indiret mesurement (.6) ngle-ngle Similrity Theorem (.2) Side-Side-Side Similrity
hpter Summry Key Terms Postultes nd Theorems similr tringles (.1) inluded ngle (.2) inluded side (.2) geometri men (.) indiret mesurement (.6) ngle-ngle Similrity Theorem (.2) Side-Side-Side Similrity
Name Ima Sample ASU ID
 Nme Im Smple ASU ID 2468024680 CSE 355 Test 1, Fll 2016 30 Septemer 2016, 8:35-9:25.m., LSA 191 Regrding of Midterms If you elieve tht your grde hs not een dded up correctly, return the entire pper to
Nme Im Smple ASU ID 2468024680 CSE 355 Test 1, Fll 2016 30 Septemer 2016, 8:35-9:25.m., LSA 191 Regrding of Midterms If you elieve tht your grde hs not een dded up correctly, return the entire pper to
Computing data with spreadsheets. Enter the following into the corresponding cells: A1: n B1: triangle C1: sqrt
 Computing dt with spredsheets Exmple: Computing tringulr numers nd their squre roots. Rell, we showed 1 ` 2 ` `n npn ` 1q{2. Enter the following into the orresponding ells: A1: n B1: tringle C1: sqrt A2:
Computing dt with spredsheets Exmple: Computing tringulr numers nd their squre roots. Rell, we showed 1 ` 2 ` `n npn ` 1q{2. Enter the following into the orresponding ells: A1: n B1: tringle C1: sqrt A2:
Review of Gaussian Quadrature method
 Review of Gussin Qudrture method Nsser M. Asi Spring 006 compiled on Sundy Decemer 1, 017 t 09:1 PM 1 The prolem To find numericl vlue for the integrl of rel vlued function of rel vrile over specific rnge
Review of Gussin Qudrture method Nsser M. Asi Spring 006 compiled on Sundy Decemer 1, 017 t 09:1 PM 1 The prolem To find numericl vlue for the integrl of rel vlued function of rel vrile over specific rnge
CSE396 Prelim I Answer Key Spring 2017
 Nme nd St.ID#: CSE96 Prelim I Answer Key Spring 2017 (1) (24 pts.) Define A to e the lnguge of strings x {, } such tht x either egins with or ends with, ut not oth. Design DFA M such tht L(M) = A. A node-rc
Nme nd St.ID#: CSE96 Prelim I Answer Key Spring 2017 (1) (24 pts.) Define A to e the lnguge of strings x {, } such tht x either egins with or ends with, ut not oth. Design DFA M such tht L(M) = A. A node-rc
1 Nondeterministic Finite Automata
 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automt Suppose in life, whenever you hd choice, you could try oth possiilities nd live your life. At the end, you would go ck nd choose the one tht worked out the est. Then you
1 Nondeterministic Finite Automt Suppose in life, whenever you hd choice, you could try oth possiilities nd live your life. At the end, you would go ck nd choose the one tht worked out the est. Then you
Pythagoras Theorem PYTHAGORAS THEOREM.
 Pthgors Theorem PYTHAGORAS THEOREM www.mthletis.om.u How oes it work? Solutions Pthgors Theorem Pge 3 questions Right-ngle tringles D E x z Hotenuse is sie: F Hotenuse is sie: DF Q k j l Hotenuse is sie:
Pthgors Theorem PYTHAGORAS THEOREM www.mthletis.om.u How oes it work? Solutions Pthgors Theorem Pge 3 questions Right-ngle tringles D E x z Hotenuse is sie: F Hotenuse is sie: DF Q k j l Hotenuse is sie:
Lecture 6. CMOS Static & Dynamic Logic Gates. Static CMOS Circuit. PMOS Transistors in Series/Parallel Connection
 NMOS Trnsistors in Series/Prllel onnetion Leture 6 MOS Stti & ynmi Logi Gtes Trnsistors n e thought s swith ontrolled y its gte signl NMOS swith loses when swith ontrol input is high Peter heung eprtment
NMOS Trnsistors in Series/Prllel onnetion Leture 6 MOS Stti & ynmi Logi Gtes Trnsistors n e thought s swith ontrolled y its gte signl NMOS swith loses when swith ontrol input is high Peter heung eprtment
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computation. Lecture #31: What DFA s Can and Can t Do David Mix Barrington 9 April 2014
 CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computtion Lecture #31: Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Dvid Mix Brrington 9 April 2014 Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Deterministic Finite Automt Forml Definition of DFA s Exmples of DFA
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computtion Lecture #31: Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Dvid Mix Brrington 9 April 2014 Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Deterministic Finite Automt Forml Definition of DFA s Exmples of DFA
Lesson 2: The Pythagorean Theorem and Similar Triangles. A Brief Review of the Pythagorean Theorem.
 27 Lesson 2: The Pythgoren Theorem nd Similr Tringles A Brief Review of the Pythgoren Theorem. Rell tht n ngle whih mesures 90º is lled right ngle. If one of the ngles of tringle is right ngle, then we
27 Lesson 2: The Pythgoren Theorem nd Similr Tringles A Brief Review of the Pythgoren Theorem. Rell tht n ngle whih mesures 90º is lled right ngle. If one of the ngles of tringle is right ngle, then we
Year 10 Maths. Semester One Revision Booklet.
 Yer 0 Mths. Semester One Revision Booklet. Nme YEAR 0 MATHEMATICS REVISION BOOKLET AND STUDY SUGGESTIONS NAME: READ through ALL of this vie prior to strting your revision. It is essentil informtion. Chpters
Yer 0 Mths. Semester One Revision Booklet. Nme YEAR 0 MATHEMATICS REVISION BOOKLET AND STUDY SUGGESTIONS NAME: READ through ALL of this vie prior to strting your revision. It is essentil informtion. Chpters
Welcome. Balanced search trees. Balanced Search Trees. Inge Li Gørtz
 Welome nge Li Gørt. everse tehing n isussion of exerises: 02110 nge Li Gørt 3 tehing ssistnts 8.00-9.15 Group work 9.15-9.45 isussions of your solutions in lss 10.00-11.15 Leture 11.15-11.45 Work on exerises
Welome nge Li Gørt. everse tehing n isussion of exerises: 02110 nge Li Gørt 3 tehing ssistnts 8.00-9.15 Group work 9.15-9.45 isussions of your solutions in lss 10.00-11.15 Leture 11.15-11.45 Work on exerises
Interpreting Integrals and the Fundamental Theorem
 Interpreting Integrls nd the Fundmentl Theorem Tody, we go further in interpreting the mening of the definite integrl. Using Units to Aid Interprettion We lredy know tht if f(t) is the rte of chnge of
Interpreting Integrls nd the Fundmentl Theorem Tody, we go further in interpreting the mening of the definite integrl. Using Units to Aid Interprettion We lredy know tht if f(t) is the rte of chnge of
Lecture 11 Binary Decision Diagrams (BDDs)
 C 474A/57A Computer-Aie Logi Design Leture Binry Deision Digrms (BDDs) C 474/575 Susn Lyseky o 3 Boolen Logi untions Representtions untion n e represente in ierent wys ruth tle, eqution, K-mp, iruit, et
C 474A/57A Computer-Aie Logi Design Leture Binry Deision Digrms (BDDs) C 474/575 Susn Lyseky o 3 Boolen Logi untions Representtions untion n e represente in ierent wys ruth tle, eqution, K-mp, iruit, et
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Nme Dte hpter 9 Mintining Mthemtil Profiieny Simplify the epression. 1. 500. 189 3. 5 4. 4 3 5. 11 5 6. 8 Solve the proportion. 9 3 14 7. = 8. = 9. 1 7 5 4 = 4 10. 0 6 = 11. 7 4 10 = 1. 5 9 15 3 = 5 +
Nme Dte hpter 9 Mintining Mthemtil Profiieny Simplify the epression. 1. 500. 189 3. 5 4. 4 3 5. 11 5 6. 8 Solve the proportion. 9 3 14 7. = 8. = 9. 1 7 5 4 = 4 10. 0 6 = 11. 7 4 10 = 1. 5 9 15 3 = 5 +
