The Practice of Statistics Third Edition
|
|
|
- Suzan Paul
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Practice of Statistics Third Edition Chapter 6: Probability and Simulation: The Study of Randomness Copyright 2008 by W. H. Freeman & Company
2 Probability Rules True probability can only be found by many trials We need to describe probability mathematically. There are some facts that must be true for any assignment of probability. Probability is the long run proportion of repetitions on which an event occurs
3 In General Any probability is a number between zero and one. Zero means it never occurs, One means it always occurs The sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes must equal one. Some outcome must occur on every trial
4 In General Continued If two events have no outcome in common, the probability that one or the other occurs is the sum of the individual events. The probability that an event does not occur is 1 minus the probability that the event does occur.
5 So, in summary:
6 Set Notation A U B A union B. Means A or B. A B A intersection B. Means A and B. Ø Empty Event (No outcomes) A B = Ø. This means A intersect B is empty. A and B are disjoint. It can be helpful to draw a picture. These are called Venn Diagrams.
7 Event A and Event B are disjoint because they do not overlap. They have no outcomes in common. Their union consists of the empty set.
8 This is a Venn Diagram of Event A and the complement A c A U A c is S A A c is the Empty Set (Ø).
9 Distance Learning Age Group 18 to to to & over Probability Think of our rules: Each probability is between 0 and 1 Probabilities total 1 What is the probability that the student we draw is not in the traditional age range (18 23) for an undergraduate? P(not 18 to 23) = 1 P(18 to 23 years) = =.43 Events 30 to 39 years and 40 & over are disjoint because no student can be in each group. P(30 or over) = P(30 to 39) + P(40 & over) = =.26
10 Playing Dice There are 36 possible outcomes when throwing two dice. That means each outcome has probability 1/36. What is the probability of rolling a 5? So 1/36 + 1/36 + 1/36 + 1/36 = 4/36 = 1/9 =.111 What is the probability of rolling a seven? It is the most common outcome of throwing two dice. 6/36 = 1/6 =.167
11 The two previous examples show one way to assign probabilities to events: Assign a probability to every individual event and add the probabilities to find the probability of any event. The probabilities have to sum to 1.
12 Benford s Law Faked numbers in tax returns, payment records, invoices and other business documents often display patterns that are not present in legitimate records. The first digit of numbers in legitimate records follow a pattern called Benford s Law First Digit Prob Let s go over the probabilities carefully.
13 Examples Event A = {First digit is 1} Event B = {First digit is 6 or greater} P(A) = P(1) =.301 P(B) = P(6) + P(7) + P(8) +P(9) = =.222 So P(A U B) = P(A) + P(B) = =.523 Remember the addition rule only applies to disjoint events!!!!!!
14 What Does This Mean Usually applies to the first digits of the sizes of similar quantities, such as invoices. Auditors can detect fraud by comparing the probabilities with the first digit in records such as invoices paid by businesses.
15 Equally Likely Outcomes You would think that the first digits would all be equally likely to show (1/9) If that was the case P(B) = P(6) + P(7) + P(8) +P(9) = 4/9 =.444 But actually P(B) =.222 So a crook who fakes random data has too many first digits 6 or greater and too few 1s and 2s.
16 There is a pretty simple rule for equally likely outcomes: Most random phenomena do not have equally likely outcomes, so this rule is not really that important.
17 Assignment Exercise 6.44 Read Pages Watch:
Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes
 Chapter 6 Probability the study of randomness Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run, but has a regular and predictable pattern in the long
Chapter 6 Probability the study of randomness Probability- describes the pattern of chance outcomes Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run, but has a regular and predictable pattern in the long
Chapter 14. From Randomness to Probability. Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 From Randomness to Probability Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Dealing with Random Phenomena A random phenomenon is a situation in which we know what outcomes could happen,
Chapter 14 From Randomness to Probability Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Dealing with Random Phenomena A random phenomenon is a situation in which we know what outcomes could happen,
Lecture 6 Probability
 Lecture 6 Probability Example: When you toss a coin, there are only two possible outcomes, heads and tails. What if we toss a coin 4 times? Figure below shows the results of tossing a coin 5000 times twice.
Lecture 6 Probability Example: When you toss a coin, there are only two possible outcomes, heads and tails. What if we toss a coin 4 times? Figure below shows the results of tossing a coin 5000 times twice.
STA Module 4 Probability Concepts. Rev.F08 1
 STA 2023 Module 4 Probability Concepts Rev.F08 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Compute probabilities for experiments having equally likely outcomes. 2. Interpret
STA 2023 Module 4 Probability Concepts Rev.F08 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Compute probabilities for experiments having equally likely outcomes. 2. Interpret
3.2 Probability Rules
 3.2 Probability Rules The idea of probability rests on the fact that chance behavior is predictable in the long run. In the last section, we used simulation to imitate chance behavior. Do we always need
3.2 Probability Rules The idea of probability rests on the fact that chance behavior is predictable in the long run. In the last section, we used simulation to imitate chance behavior. Do we always need
Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness
 Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness 6.1 The Idea of Probability 6.2 Probability Models 6.3 General Probability Rules 1 Simple Question: If tossing a coin, what is the probability of the coin
Chapter 6: Probability The Study of Randomness 6.1 The Idea of Probability 6.2 Probability Models 6.3 General Probability Rules 1 Simple Question: If tossing a coin, what is the probability of the coin
MA : Introductory Probability
 MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
MA 320-001: Introductory Probability David Murrugarra Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky http://www.math.uky.edu/~dmu228/ma320/ Spring 2017 David Murrugarra (University of Kentucky) MA 320:
Lecture notes for probability. Math 124
 Lecture notes for probability Math 124 What is probability? Probabilities are ratios, expressed as fractions, decimals, or percents, determined by considering results or outcomes of experiments whose result
Lecture notes for probability Math 124 What is probability? Probabilities are ratios, expressed as fractions, decimals, or percents, determined by considering results or outcomes of experiments whose result
Chap 4 Probability p227 The probability of any outcome in a random phenomenon is the proportion of times the outcome would occur in a long series of
 Chap 4 Probability p227 The probability of any outcome in a random phenomenon is the proportion of times the outcome would occur in a long series of repetitions. (p229) That is, probability is a long-term
Chap 4 Probability p227 The probability of any outcome in a random phenomenon is the proportion of times the outcome would occur in a long series of repetitions. (p229) That is, probability is a long-term
Ch 14 Randomness and Probability
 Ch 14 Randomness and Probability We ll begin a new part: randomness and probability. This part contain 4 chapters: 14-17. Why we need to learn this part? Probability is not a portion of statistics. Instead
Ch 14 Randomness and Probability We ll begin a new part: randomness and probability. This part contain 4 chapters: 14-17. Why we need to learn this part? Probability is not a portion of statistics. Instead
Probability and Sample space
 Probability and Sample space We call a phenomenon random if individual outcomes are uncertain but there is a regular distribution of outcomes in a large number of repetitions. The probability of any outcome
Probability and Sample space We call a phenomenon random if individual outcomes are uncertain but there is a regular distribution of outcomes in a large number of repetitions. The probability of any outcome
Statistics 251: Statistical Methods
 Statistics 251: Statistical Methods Probability Module 3 2018 file:///volumes/users/r/renaes/documents/classes/lectures/251301/renae/markdown/master%20versions/module3.html#1 1/33 Terminology probability:
Statistics 251: Statistical Methods Probability Module 3 2018 file:///volumes/users/r/renaes/documents/classes/lectures/251301/renae/markdown/master%20versions/module3.html#1 1/33 Terminology probability:
Compound Events. The event E = E c (the complement of E) is the event consisting of those outcomes which are not in E.
 Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events for which it
Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events for which it
Math 243 Section 3.1 Introduction to Probability Lab
 Math 243 Section 3.1 Introduction to Probability Lab Overview Why Study Probability? Outcomes, Events, Sample Space, Trials Probabilities and Complements (not) Theoretical vs. Empirical Probability The
Math 243 Section 3.1 Introduction to Probability Lab Overview Why Study Probability? Outcomes, Events, Sample Space, Trials Probabilities and Complements (not) Theoretical vs. Empirical Probability The
AMS7: WEEK 2. CLASS 2
 AMS7: WEEK 2. CLASS 2 Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Friday April 10, 2015 Probability: Introduction Probability:
AMS7: WEEK 2. CLASS 2 Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Friday April 10, 2015 Probability: Introduction Probability:
Probability and Independence Terri Bittner, Ph.D.
 Probability and Independence Terri Bittner, Ph.D. The concept of independence is often confusing for students. This brief paper will cover the basics, and will explain the difference between independent
Probability and Independence Terri Bittner, Ph.D. The concept of independence is often confusing for students. This brief paper will cover the basics, and will explain the difference between independent
Chapter 15. Probability Rules! Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Probability Rules! Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. The General Addition Rule When two events A and B are disjoint, we can use the addition rule for disjoint events from Chapter
Chapter 15 Probability Rules! Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. The General Addition Rule When two events A and B are disjoint, we can use the addition rule for disjoint events from Chapter
4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio
 4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Wrong is right. Thelonious Monk 4.1 Three Definitions of
4 Lecture 4 Notes: Introduction to Probability. Probability Rules. Independence and Conditional Probability. Bayes Theorem. Risk and Odds Ratio Wrong is right. Thelonious Monk 4.1 Three Definitions of
Probability deals with modeling of random phenomena (phenomena or experiments whose outcomes may vary)
 Chapter 14 From Randomness to Probability How to measure a likelihood of an event? How likely is it to answer correctly one out of two true-false questions on a quiz? Is it more, less, or equally likely
Chapter 14 From Randomness to Probability How to measure a likelihood of an event? How likely is it to answer correctly one out of two true-false questions on a quiz? Is it more, less, or equally likely
UNIT 5 ~ Probability: What Are the Chances? 1
 UNIT 5 ~ Probability: What Are the Chances? 1 6.1: Simulation Simulation: The of chance behavior, based on a that accurately reflects the phenomenon under consideration. (ex 1) Suppose we are interested
UNIT 5 ~ Probability: What Are the Chances? 1 6.1: Simulation Simulation: The of chance behavior, based on a that accurately reflects the phenomenon under consideration. (ex 1) Suppose we are interested
I - Probability. What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring. 1classical probability. 2empirical probability. 3subjective probability
 What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring eg 1classical probability 2empirical probability 3subjective probability Section 2 - Probability (1) Probability - Terminology random (probability)
What is Probability? the chance of an event occuring eg 1classical probability 2empirical probability 3subjective probability Section 2 - Probability (1) Probability - Terminology random (probability)
Week 2. Section Texas A& M University. Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station 22 January-24 January 2019
 Week 2 Section 1.2-1.4 Texas A& M University Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station 22 January-24 January 2019 Oğuz Gezmiş (TAMU) Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Week2 1
Week 2 Section 1.2-1.4 Texas A& M University Department of Mathematics Texas A& M University, College Station 22 January-24 January 2019 Oğuz Gezmiş (TAMU) Topics in Contemporary Mathematics II Week2 1
(6, 1), (5, 2), (4, 3), (3, 4), (2, 5), (1, 6)
 Section 7.3: Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events
Section 7.3: Compound Events Because we are using the framework of set theory to analyze probability, we can use unions, intersections and complements to break complex events into compositions of events
The possible experimental outcomes: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 (Experimental outcomes are also known as sample points)
 Chapter 4 Introduction to Probability 1 4.1 Experiments, Counting Rules and Assigning Probabilities Example Rolling a dice you can get the values: S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} S is called the sample space. Experiment:
Chapter 4 Introduction to Probability 1 4.1 Experiments, Counting Rules and Assigning Probabilities Example Rolling a dice you can get the values: S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} S is called the sample space. Experiment:
Lecture Lecture 5
 Lecture 4 --- Lecture 5 A. Basic Concepts (4.1-4.2) 1. Experiment: A process of observing a phenomenon that has variation in its outcome. Examples: (E1). Rolling a die, (E2). Drawing a card form a shuffled
Lecture 4 --- Lecture 5 A. Basic Concepts (4.1-4.2) 1. Experiment: A process of observing a phenomenon that has variation in its outcome. Examples: (E1). Rolling a die, (E2). Drawing a card form a shuffled
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 2: Sets and Events Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: January 27, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Experiments and Events 3 Probabilistic Models
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning about Uncertainty Lecture 2: Sets and Events Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Last Compiled: January 27, 2017 Outline 1 Recap 2 Experiments and Events 3 Probabilistic Models
Notes 1 Autumn Sample space, events. S is the number of elements in the set S.)
 MAS 108 Probability I Notes 1 Autumn 2005 Sample space, events The general setting is: We perform an experiment which can have a number of different outcomes. The sample space is the set of all possible
MAS 108 Probability I Notes 1 Autumn 2005 Sample space, events The general setting is: We perform an experiment which can have a number of different outcomes. The sample space is the set of all possible
the time it takes until a radioactive substance undergoes a decay
 1 Probabilities 1.1 Experiments with randomness Wewillusethetermexperimentinaverygeneralwaytorefertosomeprocess that produces a random outcome. Examples: (Ask class for some first) Here are some discrete
1 Probabilities 1.1 Experiments with randomness Wewillusethetermexperimentinaverygeneralwaytorefertosomeprocess that produces a random outcome. Examples: (Ask class for some first) Here are some discrete
SET THEORY. Disproving an Alleged Set Property. Disproving an Alleged Set. Example 1 Solution CHAPTER 6
 CHAPTER 6 SET THEORY SECTION 6.3 Disproofs, Algebraic Proofs, and Boolean Algebras Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Disproving an Alleged
CHAPTER 6 SET THEORY SECTION 6.3 Disproofs, Algebraic Proofs, and Boolean Algebras Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Disproving an Alleged
Chapter 2 PROBABILITY SAMPLE SPACE
 Chapter 2 PROBABILITY Key words: Sample space, sample point, tree diagram, events, complement, union and intersection of an event, mutually exclusive events; Counting techniques: multiplication rule, permutation,
Chapter 2 PROBABILITY Key words: Sample space, sample point, tree diagram, events, complement, union and intersection of an event, mutually exclusive events; Counting techniques: multiplication rule, permutation,
1. Two useful probability results. Provide the reason for each step of the proofs. (a) Result: P(A ) + P(A ) = 1. = P(A ) + P(A ) < Axiom 3 >
 Textbook: D.C. Montgomery and G.C. Runger, Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2003. Chapter 2, Sections 2.3 2.5. 1. Two useful probability results. Provide the
Textbook: D.C. Montgomery and G.C. Runger, Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2003. Chapter 2, Sections 2.3 2.5. 1. Two useful probability results. Provide the
AP Statistics Ch 6 Probability: The Study of Randomness
 Ch 6.1 The Idea of Probability Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run but has a regular and predictable pattern in the long run. We call a phenomenon random if individual outcomes are uncertain
Ch 6.1 The Idea of Probability Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run but has a regular and predictable pattern in the long run. We call a phenomenon random if individual outcomes are uncertain
ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15. Lecture 2: Random Experiments. Prof. Vince Calhoun
 ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15 Lecture 2: Random Experiments Prof. Vince Calhoun Reading This class: Section 2.1-2.2 Next class: Section 2.3-2.4 Homework: Assignment 1: From the
ECE 340 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering M/W 3-4:15 Lecture 2: Random Experiments Prof. Vince Calhoun Reading This class: Section 2.1-2.2 Next class: Section 2.3-2.4 Homework: Assignment 1: From the
Example: Suppose we toss a quarter and observe whether it falls heads or tails, recording the result as 1 for heads and 0 for tails.
 Example: Suppose we toss a quarter and observe whether it falls heads or tails, recording the result as 1 for heads and 0 for tails. (In Mathematical language, the result of our toss is a random variable,
Example: Suppose we toss a quarter and observe whether it falls heads or tails, recording the result as 1 for heads and 0 for tails. (In Mathematical language, the result of our toss is a random variable,
Sample Space: Specify all possible outcomes from an experiment. Event: Specify a particular outcome or combination of outcomes.
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Probability 2.1 Probability Model Probability concerns about the chance of observing certain outcome resulting from an experiment. However, since chance is an abstraction of something
Chapter 2 Introduction to Probability 2.1 Probability Model Probability concerns about the chance of observing certain outcome resulting from an experiment. However, since chance is an abstraction of something
Fundamentals of Probability CE 311S
 Fundamentals of Probability CE 311S OUTLINE Review Elementary set theory Probability fundamentals: outcomes, sample spaces, events Outline ELEMENTARY SET THEORY Basic probability concepts can be cast in
Fundamentals of Probability CE 311S OUTLINE Review Elementary set theory Probability fundamentals: outcomes, sample spaces, events Outline ELEMENTARY SET THEORY Basic probability concepts can be cast in
Math 1313 Experiments, Events and Sample Spaces
 Math 1313 Experiments, Events and Sample Spaces At the end of this recording, you should be able to define and use the basic terminology used in defining experiments. Terminology The next main topic in
Math 1313 Experiments, Events and Sample Spaces At the end of this recording, you should be able to define and use the basic terminology used in defining experiments. Terminology The next main topic in
LING 473: Day 3. START THE RECORDING Assignment 1 Review Probability. University of Washington Linguistics 473: Computational Linguistics Fundamentals
 LING 473: Day 3 START THE RECORDING Assignment 1 Review Probability 1 Probability textbook: Resources Available Charles Grinstead and J. Laurie Snell Introduction to Probability - online on course website
LING 473: Day 3 START THE RECORDING Assignment 1 Review Probability 1 Probability textbook: Resources Available Charles Grinstead and J. Laurie Snell Introduction to Probability - online on course website
MATH 118 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 MATH 118 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Recommendations: 1. Take the Final Practice Exam and take note of questions 2. Use this study guide as you take the tests and cross off what you know well 3. Take the Practice
MATH 118 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Recommendations: 1. Take the Final Practice Exam and take note of questions 2. Use this study guide as you take the tests and cross off what you know well 3. Take the Practice
1.1 Introduction to Sets
 Math 166 Lecture Notes - S. Nite 8/29/2012 Page 1 of 5 1.1 Introduction to Sets Set Terminology and Notation A set is a well-defined collection of objects. The objects are called the elements and are usually
Math 166 Lecture Notes - S. Nite 8/29/2012 Page 1 of 5 1.1 Introduction to Sets Set Terminology and Notation A set is a well-defined collection of objects. The objects are called the elements and are usually
Chapter 5 : Probability. Exercise Sheet. SHilal. 1 P a g e
 1 P a g e experiment ( observing / measuring ) outcomes = results sample space = set of all outcomes events = subset of outcomes If we collect all outcomes we are forming a sample space If we collect some
1 P a g e experiment ( observing / measuring ) outcomes = results sample space = set of all outcomes events = subset of outcomes If we collect all outcomes we are forming a sample space If we collect some
Probability (Devore Chapter Two)
 Probability (Devore Chapter Two) 1016-345-01: Probability and Statistics for Engineers Fall 2012 Contents 0 Administrata 2 0.1 Outline....................................... 3 1 Axiomatic Probability 3
Probability (Devore Chapter Two) 1016-345-01: Probability and Statistics for Engineers Fall 2012 Contents 0 Administrata 2 0.1 Outline....................................... 3 1 Axiomatic Probability 3
Properties of Probability
 Econ 325 Notes on Probability 1 By Hiro Kasahara Properties of Probability In statistics, we consider random experiments, experiments for which the outcome is random, i.e., cannot be predicted with certainty.
Econ 325 Notes on Probability 1 By Hiro Kasahara Properties of Probability In statistics, we consider random experiments, experiments for which the outcome is random, i.e., cannot be predicted with certainty.
Probability and Applications
 Chapter 5 Probability and Applications 5.2 SOME USEFUL DEFINITIONS Random experiment: a process that has an unknown outcome or outcomes that are known only after the process is completed. Event: an outcome
Chapter 5 Probability and Applications 5.2 SOME USEFUL DEFINITIONS Random experiment: a process that has an unknown outcome or outcomes that are known only after the process is completed. Event: an outcome
Probability Theory and Applications
 Probability Theory and Applications Videos of the topics covered in this manual are available at the following links: Lesson 4 Probability I http://faculty.citadel.edu/silver/ba205/online course/lesson
Probability Theory and Applications Videos of the topics covered in this manual are available at the following links: Lesson 4 Probability I http://faculty.citadel.edu/silver/ba205/online course/lesson
Chapter 1 (Basic Probability)
 Chapter 1 (Basic Probability) What is probability? Consider the following experiments: 1. Count the number of arrival requests to a web server in a day. 2. Determine the execution time of a program. 3.
Chapter 1 (Basic Probability) What is probability? Consider the following experiments: 1. Count the number of arrival requests to a web server in a day. 2. Determine the execution time of a program. 3.
Bayes Theorem. Jan Kracík. Department of Applied Mathematics FEECS, VŠB - TU Ostrava
 Jan Kracík Department of Applied Mathematics FEECS, VŠB - TU Ostrava Introduction Bayes theorem fundamental theorem in probability theory named after reverend Thomas Bayes (1701 1761) discovered in Bayes
Jan Kracík Department of Applied Mathematics FEECS, VŠB - TU Ostrava Introduction Bayes theorem fundamental theorem in probability theory named after reverend Thomas Bayes (1701 1761) discovered in Bayes
Independence 1 2 P(H) = 1 4. On the other hand = P(F ) =
 Independence Previously we considered the following experiment: A card is drawn at random from a standard deck of cards. Let H be the event that a heart is drawn, let R be the event that a red card is
Independence Previously we considered the following experiment: A card is drawn at random from a standard deck of cards. Let H be the event that a heart is drawn, let R be the event that a red card is
PERMUTATIONS, COMBINATIONS AND DISCRETE PROBABILITY
 Friends, we continue the discussion with fundamentals of discrete probability in the second session of third chapter of our course in Discrete Mathematics. The conditional probability and Baye s theorem
Friends, we continue the discussion with fundamentals of discrete probability in the second session of third chapter of our course in Discrete Mathematics. The conditional probability and Baye s theorem
P (A) = P (B) = P (C) = P (D) =
 STAT 145 CHAPTER 12 - PROBABILITY - STUDENT VERSION The probability of a random event, is the proportion of times the event will occur in a large number of repititions. For example, when flipping a coin,
STAT 145 CHAPTER 12 - PROBABILITY - STUDENT VERSION The probability of a random event, is the proportion of times the event will occur in a large number of repititions. For example, when flipping a coin,
STP 226 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS
 STP 226 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS CHAPTER 5 Probability Theory - science of uncertainty 5.1 Probability Basics Equal-Likelihood Model Suppose an experiment has N possible outcomes, all equally likely. Then
STP 226 ELEMENTARY STATISTICS CHAPTER 5 Probability Theory - science of uncertainty 5.1 Probability Basics Equal-Likelihood Model Suppose an experiment has N possible outcomes, all equally likely. Then
Unit 7 Probability M2 13.1,2,4, 5,6
 + Unit 7 Probability M2 13.1,2,4, 5,6 7.1 Probability n Obj.: I will be able to determine the experimental and theoretical probabilities of an event, or its complement, occurring. n Vocabulary o Outcome
+ Unit 7 Probability M2 13.1,2,4, 5,6 7.1 Probability n Obj.: I will be able to determine the experimental and theoretical probabilities of an event, or its complement, occurring. n Vocabulary o Outcome
4. Probability of an event A for equally likely outcomes:
 University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 110A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Probability Probability: A measure of the chance that something will occur. 1. Random experiment:
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 110A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Probability Probability: A measure of the chance that something will occur. 1. Random experiment:
Information Science 2
 Information Science 2 Probability Theory: An Overview Week 12 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Agenda Terms and concepts from Week 11 Basic concepts of probability
Information Science 2 Probability Theory: An Overview Week 12 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Agenda Terms and concepts from Week 11 Basic concepts of probability
Name: Block: Unit 2 Inequalities
 Name: Block: Unit 2 Inequalities 2.1 Graphing and Writing Inequalities 2.2 Solving by Adding and Subtracting 2.3 Solving by Multiplying and Dividing 2.4 Solving Two Step and Multi Step Inequalities 2.5
Name: Block: Unit 2 Inequalities 2.1 Graphing and Writing Inequalities 2.2 Solving by Adding and Subtracting 2.3 Solving by Multiplying and Dividing 2.4 Solving Two Step and Multi Step Inequalities 2.5
STAT Chapter 3: Probability
 Basic Definitions STAT 515 --- Chapter 3: Probability Experiment: A process which leads to a single outcome (called a sample point) that cannot be predicted with certainty. Sample Space (of an experiment):
Basic Definitions STAT 515 --- Chapter 3: Probability Experiment: A process which leads to a single outcome (called a sample point) that cannot be predicted with certainty. Sample Space (of an experiment):
LECTURE 1. 1 Introduction. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
 LECTURE 1 1 Introduction The first part of our adventure is a highly selective review of probability theory, focusing especially on things that are most useful in statistics. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
LECTURE 1 1 Introduction The first part of our adventure is a highly selective review of probability theory, focusing especially on things that are most useful in statistics. 1.1 Sample spaces and events
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Note 14
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Note 14 Introduction One of the key properties of coin flips is independence: if you flip a fair coin ten times and get ten
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Note 14 Introduction One of the key properties of coin flips is independence: if you flip a fair coin ten times and get ten
Independence Solutions STAT-UB.0103 Statistics for Business Control and Regression Models
 Independence Solutions STAT-UB.003 Statistics for Business Control and Regression Models The Birthday Problem. A class has 70 students. What is the probability that at least two students have the same
Independence Solutions STAT-UB.003 Statistics for Business Control and Regression Models The Birthday Problem. A class has 70 students. What is the probability that at least two students have the same
Sets. Alice E. Fischer. CSCI 1166 Discrete Mathematics for Computing Spring, Outline Sets An Algebra on Sets Summary
 An Algebra on Alice E. Fischer CSCI 1166 Discrete Mathematics for Computing Spring, 2018 Alice E. Fischer... 1/37 An Algebra on 1 Definitions and Notation Venn Diagrams 2 An Algebra on 3 Alice E. Fischer...
An Algebra on Alice E. Fischer CSCI 1166 Discrete Mathematics for Computing Spring, 2018 Alice E. Fischer... 1/37 An Algebra on 1 Definitions and Notation Venn Diagrams 2 An Algebra on 3 Alice E. Fischer...
ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page α 2 θ 1 u 3. wear coat. θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ 1 = cold u 3 = brrr!
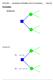 ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 2-01 Probability Decision trees u 1 u 2 α 2 θ 1 u 3 θ 2 u 4 Example 2.01 θ 1 = cold u 1 = snug! α 1 wear coat θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ
ENGI 4421 Introduction to Probability; Sets & Venn Diagrams Page 2-01 Probability Decision trees u 1 u 2 α 2 θ 1 u 3 θ 2 u 4 Example 2.01 θ 1 = cold u 1 = snug! α 1 wear coat θ 2 = warm u 2 = sweaty! θ
18.600: Lecture 3 What is probability?
 18.600: Lecture 3 What is probability? Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Formalizing probability Sample space DeMorgan s laws Axioms of probability Outline Formalizing probability Sample space DeMorgan s laws
18.600: Lecture 3 What is probability? Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Formalizing probability Sample space DeMorgan s laws Axioms of probability Outline Formalizing probability Sample space DeMorgan s laws
Discrete Random Variables. David Gerard Many slides borrowed from Linda Collins
 Discrete Random Variables David Gerard Many slides borrowed from Linda Collins 2017-09-28 1 Learning Objectives Random Variables Discrete random variables. Means of discrete random variables. Means of
Discrete Random Variables David Gerard Many slides borrowed from Linda Collins 2017-09-28 1 Learning Objectives Random Variables Discrete random variables. Means of discrete random variables. Means of
A B is shaded A B A B
 NION: Let and be subsets of a universal set. The union of sets and is the set of all elements in that belong to or to or to both, and is denoted. Symbolically: = {x x or x } EMMPLE: Let = {a, b, c, d,
NION: Let and be subsets of a universal set. The union of sets and is the set of all elements in that belong to or to or to both, and is denoted. Symbolically: = {x x or x } EMMPLE: Let = {a, b, c, d,
Introduction to Set Operations
 Introduction to Set Operations CIS008-2 Logic and Foundations of Mathematics David Goodwin david.goodwin@perisic.com 12:00, Friday 21 st October 2011 Outline 1 Recap 2 Introduction to sets 3 Class Exercises
Introduction to Set Operations CIS008-2 Logic and Foundations of Mathematics David Goodwin david.goodwin@perisic.com 12:00, Friday 21 st October 2011 Outline 1 Recap 2 Introduction to sets 3 Class Exercises
Proving simple set properties...
 Proving simple set properties... Part 1: Some examples of proofs over sets Fall 2013 Proving simple set properties... Fall 2013 1 / 17 Introduction Overview: Learning outcomes In this session we will...
Proving simple set properties... Part 1: Some examples of proofs over sets Fall 2013 Proving simple set properties... Fall 2013 1 / 17 Introduction Overview: Learning outcomes In this session we will...
Chapter 5: Probability in Our Daily Lives
 Chapter 5: in Our Daily Lives These notes reflect material from our text, Statistics: The Art and Science of Learning from Data, Third Edition, by Alan Agresti and Catherine Franklin, published by Pearson,
Chapter 5: in Our Daily Lives These notes reflect material from our text, Statistics: The Art and Science of Learning from Data, Third Edition, by Alan Agresti and Catherine Franklin, published by Pearson,
The enumeration of all possible outcomes of an experiment is called the sample space, denoted S. E.g.: S={head, tail}
 Random Experiment In random experiments, the result is unpredictable, unknown prior to its conduct, and can be one of several choices. Examples: The Experiment of tossing a coin (head, tail) The Experiment
Random Experiment In random experiments, the result is unpredictable, unknown prior to its conduct, and can be one of several choices. Examples: The Experiment of tossing a coin (head, tail) The Experiment
Probabilistic models
 Probabilistic models Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became
Probabilistic models Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became
2011 Pearson Education, Inc
 Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 3 Probability Contents 1. Events, Sample Spaces, and Probability 2. Unions and Intersections 3. Complementary Events 4. The Additive Rule and Mutually Exclusive
Statistics for Business and Economics Chapter 3 Probability Contents 1. Events, Sample Spaces, and Probability 2. Unions and Intersections 3. Complementary Events 4. The Additive Rule and Mutually Exclusive
Lecture 1. Chapter 1. (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 ( ). 1. What is Statistics?
 Lecture 1 (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 (2.1 --- 2.6). Chapter 1 1. What is Statistics? 2. Two definitions. (1). Population (2). Sample 3. The objective of statistics.
Lecture 1 (Part I) Material Covered in This Lecture: Chapter 1, Chapter 2 (2.1 --- 2.6). Chapter 1 1. What is Statistics? 2. Two definitions. (1). Population (2). Sample 3. The objective of statistics.
Chapter 1 Math Set: a collection of objects. For example, the set of whole numbers is W = {0, 1, 2, 3, }
 Chapter 1 Math 3201 1 Chapter 1: Set Theory: Organizing information into sets and subsets Graphically illustrating the relationships between sets and subsets using Venn diagrams Solving problems by using
Chapter 1 Math 3201 1 Chapter 1: Set Theory: Organizing information into sets and subsets Graphically illustrating the relationships between sets and subsets using Venn diagrams Solving problems by using
STAT 201 Chapter 5. Probability
 STAT 201 Chapter 5 Probability 1 2 Introduction to Probability Probability The way we quantify uncertainty. Subjective Probability A probability derived from an individual's personal judgment about whether
STAT 201 Chapter 5 Probability 1 2 Introduction to Probability Probability The way we quantify uncertainty. Subjective Probability A probability derived from an individual's personal judgment about whether
Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics
 Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics Lecture 2 Probability Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Ch. 3-1 3.1 Definition Random Experiment a process leading to an uncertain
Econ 325: Introduction to Empirical Economics Lecture 2 Probability Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Ch. 3-1 3.1 Definition Random Experiment a process leading to an uncertain
= A. Example 2. Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}, A = {4, 6, 7, 9, 10}, and B = {2, 6, 8, 9}. Draw the sets on a Venn diagram.
 MATH 109 Sets A mathematical set is a well-defined collection of objects A for which we can determine precisely whether or not any object belongs to A. Objects in a set are formally called elements of
MATH 109 Sets A mathematical set is a well-defined collection of objects A for which we can determine precisely whether or not any object belongs to A. Objects in a set are formally called elements of
MATH2206 Prob Stat/20.Jan Weekly Review 1-2
 MATH2206 Prob Stat/20.Jan.2017 Weekly Review 1-2 This week I explained the idea behind the formula of the well-known statistic standard deviation so that it is clear now why it is a measure of dispersion
MATH2206 Prob Stat/20.Jan.2017 Weekly Review 1-2 This week I explained the idea behind the formula of the well-known statistic standard deviation so that it is clear now why it is a measure of dispersion
Business Statistics. Lecture 3: Random Variables and the Normal Distribution
 Business Statistics Lecture 3: Random Variables and the Normal Distribution 1 Goals for this Lecture A little bit of probability Random variables The normal distribution 2 Probability vs. Statistics Probability:
Business Statistics Lecture 3: Random Variables and the Normal Distribution 1 Goals for this Lecture A little bit of probability Random variables The normal distribution 2 Probability vs. Statistics Probability:
Recap. The study of randomness and uncertainty Chances, odds, likelihood, expected, probably, on average,... PROBABILITY INFERENTIAL STATISTICS
 Recap. Probability (section 1.1) The study of randomness and uncertainty Chances, odds, likelihood, expected, probably, on average,... PROBABILITY Population Sample INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Today. Formulation
Recap. Probability (section 1.1) The study of randomness and uncertainty Chances, odds, likelihood, expected, probably, on average,... PROBABILITY Population Sample INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Today. Formulation
Math C067 Independence and Repeated Trials.
 Math C067 Independence and Repeated Trials. Richard Beigel February 7, 006 Socks. Bill s sock drawer contains 10 red socks, 0 green socks, and 30 blue socks. If Bill removes two socks from his drawer at
Math C067 Independence and Repeated Trials. Richard Beigel February 7, 006 Socks. Bill s sock drawer contains 10 red socks, 0 green socks, and 30 blue socks. If Bill removes two socks from his drawer at
1 Probability Theory. 1.1 Introduction
 1 Probability Theory Probability theory is used as a tool in statistics. It helps to evaluate the reliability of our conclusions about the population when we have only information about a sample. Probability
1 Probability Theory Probability theory is used as a tool in statistics. It helps to evaluate the reliability of our conclusions about the population when we have only information about a sample. Probability
Topic 3: Introduction to Probability
 Topic 3: Introduction to Probability 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Simple Definitions 3. Types of Probability 4. Theorems of Probability 5. Probabilities under conditions of statistically independent events
Topic 3: Introduction to Probability 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Simple Definitions 3. Types of Probability 4. Theorems of Probability 5. Probabilities under conditions of statistically independent events
SETS. Chapter Overview
 Chapter 1 SETS 1.1 Overview This chapter deals with the concept of a set, operations on sets.concept of sets will be useful in studying the relations and functions. 1.1.1 Set and their representations
Chapter 1 SETS 1.1 Overview This chapter deals with the concept of a set, operations on sets.concept of sets will be useful in studying the relations and functions. 1.1.1 Set and their representations
CIVL Why are we studying probability and statistics? Learning Objectives. Basic Laws and Axioms of Probability
 CIVL 3103 Basic Laws and Axioms of Probability Why are we studying probability and statistics? How can we quantify risks of decisions based on samples from a population? How should samples be selected
CIVL 3103 Basic Laws and Axioms of Probability Why are we studying probability and statistics? How can we quantify risks of decisions based on samples from a population? How should samples be selected
7.1 What is it and why should we care?
 Chapter 7 Probability In this section, we go over some simple concepts from probability theory. We integrate these with ideas from formal language theory in the next chapter. 7.1 What is it and why should
Chapter 7 Probability In this section, we go over some simple concepts from probability theory. We integrate these with ideas from formal language theory in the next chapter. 7.1 What is it and why should
Venn Diagrams; Probability Laws. Notes. Set Operations and Relations. Venn Diagram 2.1. Venn Diagrams; Probability Laws. Notes
 Lecture 2 s; Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 2.4 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models January 8, 2014 s; Whitney Huang Purdue University 2.1 Agenda s; 1 2 2.2 Intersection: the intersection
Lecture 2 s; Text: A Course in Probability by Weiss 2.4 STAT 225 Introduction to Probability Models January 8, 2014 s; Whitney Huang Purdue University 2.1 Agenda s; 1 2 2.2 Intersection: the intersection
STT When trying to evaluate the likelihood of random events we are using following wording.
 Introduction to Chapter 2. Probability. When trying to evaluate the likelihood of random events we are using following wording. Provide your own corresponding examples. Subjective probability. An individual
Introduction to Chapter 2. Probability. When trying to evaluate the likelihood of random events we are using following wording. Provide your own corresponding examples. Subjective probability. An individual
Section F Ratio and proportion
 Section F Ratio and proportion Ratio is a way of comparing two or more groups. For example, if something is split in a ratio 3 : 5 there are three parts of the first thing to every five parts of the second
Section F Ratio and proportion Ratio is a way of comparing two or more groups. For example, if something is split in a ratio 3 : 5 there are three parts of the first thing to every five parts of the second
6.2 Introduction to Probability. The Deal. Possible outcomes: STAT1010 Intro to probability. Definitions. Terms: What are the chances of?
 6.2 Introduction to Probability Terms: What are the chances of?! Personal probability (subjective) " Based on feeling or opinion. " Gut reaction.! Empirical probability (evidence based) " Based on experience
6.2 Introduction to Probability Terms: What are the chances of?! Personal probability (subjective) " Based on feeling or opinion. " Gut reaction.! Empirical probability (evidence based) " Based on experience
CISC 1100: Structures of Computer Science
 CISC 1100: Structures of Computer Science Chapter 2 Sets and Sequences Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Fall, 2010 CISC 1100/Fall, 2010/Chapter 2 1 / 49 Outline Sets Basic
CISC 1100: Structures of Computer Science Chapter 2 Sets and Sequences Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Fall, 2010 CISC 1100/Fall, 2010/Chapter 2 1 / 49 Outline Sets Basic
Chapter 7 Wednesday, May 26th
 Chapter 7 Wednesday, May 26 th Random event A random event is an event that the outcome is unpredictable. Example: There are 45 students in this class. What is the probability that if I select one student,
Chapter 7 Wednesday, May 26 th Random event A random event is an event that the outcome is unpredictable. Example: There are 45 students in this class. What is the probability that if I select one student,
MATH 120. Test 1 Spring, 2012 DO ALL ASSIGNED PROBLEMS. Things to particularly study
 MATH 120 Test 1 Spring, 2012 DO ALL ASSIGNED PROBLEMS Things to particularly study 1) Critical Thinking Basic strategies Be able to solve using the basic strategies, such as finding patterns, questioning,
MATH 120 Test 1 Spring, 2012 DO ALL ASSIGNED PROBLEMS Things to particularly study 1) Critical Thinking Basic strategies Be able to solve using the basic strategies, such as finding patterns, questioning,
Basic Set Concepts (2.1)
 1 Basic Set Concepts (2.1) I. Set A collection of objects whose contents can be clearly determined. Capitol letters usually name a set. Elements are the contents in a set. Sets can be described using words,
1 Basic Set Concepts (2.1) I. Set A collection of objects whose contents can be clearly determined. Capitol letters usually name a set. Elements are the contents in a set. Sets can be described using words,
Probability and Statistics Notes
 Probability and Statistics Notes Chapter One Jesse Crawford Department of Mathematics Tarleton State University (Tarleton State University) Chapter One Notes 1 / 71 Outline 1 A Sketch of Probability and
Probability and Statistics Notes Chapter One Jesse Crawford Department of Mathematics Tarleton State University (Tarleton State University) Chapter One Notes 1 / 71 Outline 1 A Sketch of Probability and
CISC 1100/1400 Structures of Comp. Sci./Discrete Structures Chapter 7 Probability. Outline. Terminology and background. Arthur G.
 CISC 1100/1400 Structures of Comp. Sci./Discrete Structures Chapter 7 Probability Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Copyright Arthur G. Werschulz, 2017.
CISC 1100/1400 Structures of Comp. Sci./Discrete Structures Chapter 7 Probability Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Copyright Arthur G. Werschulz, 2017.
Recitation 2: Probability
 Recitation 2: Probability Colin White, Kenny Marino January 23, 2018 Outline Facts about sets Definitions and facts about probability Random Variables and Joint Distributions Characteristics of distributions
Recitation 2: Probability Colin White, Kenny Marino January 23, 2018 Outline Facts about sets Definitions and facts about probability Random Variables and Joint Distributions Characteristics of distributions
MAT Mathematics in Today's World
 MAT 1000 Mathematics in Today's World Last Time We discussed the four rules that govern probabilities: 1. Probabilities are numbers between 0 and 1 2. The probability an event does not occur is 1 minus
MAT 1000 Mathematics in Today's World Last Time We discussed the four rules that govern probabilities: 1. Probabilities are numbers between 0 and 1 2. The probability an event does not occur is 1 minus
Topic 2 Probability. Basic probability Conditional probability and independence Bayes rule Basic reliability
 Topic 2 Probability Basic probability Conditional probability and independence Bayes rule Basic reliability Random process: a process whose outcome can not be predicted with certainty Examples: rolling
Topic 2 Probability Basic probability Conditional probability and independence Bayes rule Basic reliability Random process: a process whose outcome can not be predicted with certainty Examples: rolling
Probability (Devore Chapter Two)
 Probability (Devore Chapter Two) 1016-345-01: Probability and Statistics for Engineers Spring 2013 Contents 0 Preliminaries 3 0.1 Motivation..................................... 3 0.2 Administrata...................................
Probability (Devore Chapter Two) 1016-345-01: Probability and Statistics for Engineers Spring 2013 Contents 0 Preliminaries 3 0.1 Motivation..................................... 3 0.2 Administrata...................................
2.4. Conditional Probability
 2.4. Conditional Probability Objectives. Definition of conditional probability and multiplication rule Total probability Bayes Theorem Example 2.4.1. (#46 p.80 textbook) Suppose an individual is randomly
2.4. Conditional Probability Objectives. Definition of conditional probability and multiplication rule Total probability Bayes Theorem Example 2.4.1. (#46 p.80 textbook) Suppose an individual is randomly
Notes for Math 324, Part 12
 72 Notes for Math 324, Part 12 Chapter 12 Definition and main properties of probability 12.1 Sample space, events We run an experiment which can have several outcomes. The set consisting by all possible
72 Notes for Math 324, Part 12 Chapter 12 Definition and main properties of probability 12.1 Sample space, events We run an experiment which can have several outcomes. The set consisting by all possible
