1 (1 x) 4 by taking derivatives and rescaling appropriately. Conjecture what the general formula for the series for 1/(1 x) n.
|
|
|
- Eric Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 365 Wednesday 3/20/9 8.2 and 8.4 Exercise 35. Consider the recurrence relation a n =8a n 2 6a n 4 + F (n). (a) Write the associated homogeneous recursion relation and solve for its general solution {h n }. (b) For each of the following F (n), write the general form for the particular solution (don t solve for the unknowns). (i) F (n) =n 3 (ii) F (n) =n2 n (iii) F (n) =(n 2 2)( 2) n (iv) F (n) =2 (v) F (n) =( 2) n (vi) F (n) =n 2 4 n (vii) F (n) =n 4 2 n (c) Find the general solution to (d) Find the general solution to a n =8a n 2 6a n 4 +( 2) n. a n =8a n 2 6a n 4 + n 3. (e) Pick an example of appropriate initial conditions for the sequence in part (c), and solve for the corresponding specific solution. Check your answer by computing the first 6 terms of the sequence both recursively and using your closed formula. Exercise 36. (a) Explicitly compute the series for ( x) 3 and ( x) 4 by taking derivatives and rescaling appropriately. Conjecture what the general formula for the series for /( x) n. (b) Substitute y =3x into the series for y to get the series for. What is the series for 3x /( 4x)? What is the series for /( + x)? (c) Substitute y = x 3 into the series for y to get the series for. What is the series for x3 /( x 4 )? What is the series for /( 2x 3 )? d (d) Use the fact that dx (ln( x)) = to compute the series for ln( x). (Integrate, x and pick your +C to make it so that evaluating your series at x = 0 matches correctly with evaluating ln( x).)
2 Today: Section 8.2, continued. Last time: To solve recurrence relations, the best we can do is make educated guesses, according to what kind of relation we have. A linear homogeneous recurrence relation of degree k with constant coe cients is a recurrence relation of the form a n c a n ` c 2 a n 2 ` `c k a n k, where c,c 2,...,c k are real numbers, and c k 0. Solutions to this kind of relation come in the form r n,wherer is a root of the characteristic equation, which is obtained by plugging in r n, dividing through by r n k, and solving for 0: r k c r k c 2 r k 2 c k r c k 0. The roots of this equation are called the characteristic roots. Example from last time: plugging a n r n into the recursion relation gets which is true if and only if a n a n ` a n 2 ` a n 3 r n r n ` r n 2 ` r n 3, 0 r n ` r n r n 2 r n 3 r n 3 pr 3 ` r 2 r q which is true if and only if r 0 or 0 r 3 ` r 2 r looooooooooomooooooooooon characteristic equation pr ` q 2 pr q. The characteristic roots are r (with multiplicity ) and r 2 (with multiplicity 2).
3 Theorem: Solving linear homogeneous recurrences Let c,c 2,...,c k be real numbers. Suppose that the characteristic equation has roots r,r 2,...,r` with multiplicities m,m 2,...,m`. Then a sequence ta n u npn is a solution of the recurrence relation a n c a n ` c 2 a n 2 ` `c k a n k if and only if a n p pnqr n ` p 2 pnqr n 2 ` `p`pnqr ǹ, where p i pnq are polynomials in n of degree m i. Example: a n a n ` 5a n 2 a n 3 8a n 4 4a n 5. Characteristic equation: 0 r 5 r 4 5r 3 ` r 2 ` 8r ` 4 pr ` q 3 pr 2q 2. General solution: a n p 0 ` n ` 2 n 2 qp q n `p 0 ` nqp2q n. Non-homogeneous equations Suppose your recurrence is linear and constant coe cient in a i s, but is not homogeneous. In other words, it is in the form a n c a n ` c 2 a n 2 ` `c k a n k ` F pnq where F pnq is a function only in n (no a i s). The relation h n c h n ` c 2 h n 2 ` `c k h n k (so that a n h n ` F pnq) is called the associated homogeneous recurrence relation. Ex: a n 3a n ` 2n. F pnq 2n, Assoc. hom: h n 3h n. Ex: a n 5a n 6a n 2 ` 7 n. F pnq 7 n, Assoc. hom: h n 5h n 6h n 2. The following theorem says that if we can find one solution to a n, then the general solutions to h n will help us build all the rest of the solutions to a n.
4 Theorem: Solving non-homogeneous equations (a) If tâ n u npn is one solution of the non-homogeneous linear recurrence relation with constant coe cients a n c a n ` c 2 a n 2 ` `c k a n k ` F pnq, then every solution is of the form ta n â n ` h n u npn,where th n u npn is a solution of the associated homogeneous recurrence relation. (b) Finding â n : where Qpnq is a polynomial in n, and R is a constant, then there is a solution to a n of the form â n n m qpnqr n where degpqpnqq degpqpnqq, and m mult. of R in the characteristic equation (possibly 0). Ex: Find all solutions to a n 3a n ` 2n. What is the solution with a 3?. Break the sequence into two parts: homogeneous h n and a where m mult of R, andq n b 0 ` b n ` b 2 n 2 ` `b d n d Example: a n 4a n ` 3a n 2 8a n 3 ` 4 n Homog: h n 4h n ` 3h n 2 8h n 3 and F pnq 4 n. Char eq: 0 r 3 4r 2 3r ` 8 pr ` 2qpr 3q 2 Homog sol: h n p 2q n `p ` Particular solution guess: â n b4 n (gives b 32{3) General sol: a n p 2q n `p ` ` n.
5 . Break the sequence into two parts: homogeneous h n and a where m mult of R, andq n b 0 ` b n ` b 2 n 2 ` `b d n d Example: a n 4a n ` 3a n 2 8a n 3 ` n4 n Homog: h n 4h n ` 3h n 2 8h n 3 and F pnq n4 n. Char eq: 0 r 3 4r 2 3r ` 8 pr`2qpr 3q 2 Homog sol: h n p 2q n `p ` Particular solution guess: â n pb 0 ` b nq4 n (gives b 0 376{9 and b 63{3) General sol: a n p 2q n `p ` ` p nq4n.. Break the sequence into two parts: homogeneous h n and a where m mult of R, andq n b 0 ` b n ` b 2 n 2 ` `b d n d Example: a n 4a n ` 3a n 2 8a n 3 ` 3 n 2 Homog: h n 4h n ` 3h n 2 8h n 3 and F pnq 3 n. Char eq: 0 r 3 4r 2 3r ` 8 pr`2qpr 3q 2 Homog sol: h n p 2q n `p ` Particular solution guess: â n bn 3 n (gives b 3{2) General sol: a n p 2q n `p ` ` 3 2 n2 3 n.
6 . Break the sequence into two parts: homogeneous h n and a where m mult of R, andq n b 0 ` b n ` b 2 n 2 ` `b d n d Example: a n 4a n ` 3a n 2 8a n 3 ` n3 n Homog: h n 4h n ` 3h n 2 8h n 3 and F pnq 3 n. Char eq: 0 r 3 4r 2 3r ` 8 pr`2qpr 3q 2 Homog sol: h n p 2q n `p ` Particular solution guess: â n pb 0 ` b nqn 2 3 n (gives b 0 2{50 and b {0) General sol: a n p 2q n `p ` ` p 2 50 ` 0 nqn2 3 n. Section 8.4: Generating functions. Taylor series to know and love: nÿ ˆn ˆn p ` xq n x k ` k x ` x n n x ÿ x k ` x ` x 2 ` `x n x e x x k ` x ` x 2 ` x k {k! ` x ` x2 2 ` x3 3! Combining series: Let f pxq f pxq`gpxq ˆn x 2 ` `x n 2 a k x k and gpxq pa k`b k qx k and fpxqgpxq (finite) (finite) (infinite) ` (infinite) b k x k.then kÿ a i b k i x k.
7 Example: Compute the series for using p xq 2 x 8 xk. Approach : Use the multiplication rule, k kÿ b k x a i b k i x k, on a k x k p xq 2 x Here, a i b i for all i. So kÿ a i b k i k k x x x. kÿ k `. Thus p xq 2 pk ` qx k ` 2x ` 3x 2 ` 4x 3 `. Example: Compute the series for p xq 2 using x 8 xk. Approach 2: Use derivatives, noting that d dx Thus, x d dx p xq p qp xq 2 p q p xq 2. p xq 2 d dx p xq d x k dx d dx xk kx k (change summation: let j k ) pj ` qx j ` 2x ` 3x 2 ` 4x 3 `. j 0 You try: Exercise 36
Section 8.4: Generating functions.
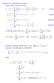 Section 8.4: Generating functions. Taylor series to know and love: nÿ ˆn ˆn p ` xq n x k ` k x ` x n n x ÿ x k ` x ` x 2 ` `x n x e x x k ` x ` x 2 ` x k {k! ` x ` x2 2 ` x3 3! Combining series: Let f
Section 8.4: Generating functions. Taylor series to know and love: nÿ ˆn ˆn p ` xq n x k ` k x ` x n n x ÿ x k ` x ` x 2 ` `x n x e x x k ` x ` x 2 ` x k {k! ` x ` x2 2 ` x3 3! Combining series: Let f
Math 365 Monday 3/25/19. 1 x n n 1. 1 x = X. a k x k (Considered formally, i.e. without consideration of convergence.)
 Recall: Also, for series we have f(x)+g(x) = Math 365 Monday 3/25/9 ( + x) n = e x = f(x) = nx X x k /k!, n x k, k and x n n x = X x k, x = X X a k x k and g(x) = X (a k + b k )x k and f(x)g(x) = x k X
Recall: Also, for series we have f(x)+g(x) = Math 365 Monday 3/25/9 ( + x) n = e x = f(x) = nx X x k /k!, n x k, k and x n n x = X x k, x = X X a k x k and g(x) = X (a k + b k )x k and f(x)g(x) = x k X
6.2 SOLVING EASY RECURRENCES
 Section 6.2 Solving Easy Recurrences 6.2.1 6.2 SOLVING EASY RECURRENCES We identify a type of recurrence that can be solved by special methods. def: A recurrence relation a n = f(a 0,..., a n 1 ) has degree
Section 6.2 Solving Easy Recurrences 6.2.1 6.2 SOLVING EASY RECURRENCES We identify a type of recurrence that can be solved by special methods. def: A recurrence relation a n = f(a 0,..., a n 1 ) has degree
Review of Power Series
 Review of Power Series MATH 365 Ordinary Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Introduction In addition to the techniques we have studied so far, we may use power
Review of Power Series MATH 365 Ordinary Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Introduction In addition to the techniques we have studied so far, we may use power
Some Review Problems for Exam 2: Solutions
 Math 5366 Fall 017 Some Review Problems for Exam : Solutions 1 Find the coefficient of x 15 in each of the following: 1 (a) (1 x) 6 Solution: 1 (1 x) = ( ) k + 5 x k 6 k ( ) ( ) 0 0 so the coefficient
Math 5366 Fall 017 Some Review Problems for Exam : Solutions 1 Find the coefficient of x 15 in each of the following: 1 (a) (1 x) 6 Solution: 1 (1 x) = ( ) k + 5 x k 6 k ( ) ( ) 0 0 so the coefficient
Defn: A linear recurrence relation has constant coefficients if the a i s are constant. Ch 14: 1, 4, 5, 10, 13, 18, 22, 24, 25 and
 7.4: linear homogeneous recurrence relation: Defn: A recurrence relation is linear if h n = a 1 (n)h n 1 + a (n)h n +... + a k (n)h n k + b(n) A recurrence relation has order k if a k 0 Ex: Derangement
7.4: linear homogeneous recurrence relation: Defn: A recurrence relation is linear if h n = a 1 (n)h n 1 + a (n)h n +... + a k (n)h n k + b(n) A recurrence relation has order k if a k 0 Ex: Derangement
Math123 Lecture 1. Dr. Robert C. Busby. Lecturer: Office: Korman 266 Phone :
 Lecturer: Math1 Lecture 1 Dr. Robert C. Busby Office: Korman 66 Phone : 15-895-1957 Email: rbusby@mcs.drexel.edu Course Web Site: http://www.mcs.drexel.edu/classes/calculus/math1_spring0/ (Links are case
Lecturer: Math1 Lecture 1 Dr. Robert C. Busby Office: Korman 66 Phone : 15-895-1957 Email: rbusby@mcs.drexel.edu Course Web Site: http://www.mcs.drexel.edu/classes/calculus/math1_spring0/ (Links are case
A SUMMARY OF RECURSION SOLVING TECHNIQUES
 A SUMMARY OF RECURSION SOLVING TECHNIQUES KIMMO ERIKSSON, KTH These notes are meant to be a complement to the material on recursion solving techniques in the textbook Discrete Mathematics by Biggs. In
A SUMMARY OF RECURSION SOLVING TECHNIQUES KIMMO ERIKSSON, KTH These notes are meant to be a complement to the material on recursion solving techniques in the textbook Discrete Mathematics by Biggs. In
July 21 Math 2254 sec 001 Summer 2015
 July 21 Math 2254 sec 001 Summer 2015 Section 8.8: Power Series Theorem: Let a n (x c) n have positive radius of convergence R, and let the function f be defined by this power series f (x) = a n (x c)
July 21 Math 2254 sec 001 Summer 2015 Section 8.8: Power Series Theorem: Let a n (x c) n have positive radius of convergence R, and let the function f be defined by this power series f (x) = a n (x c)
Math 253 Homework due Wednesday, March 9 SOLUTIONS
 Math 53 Homework due Wednesday, March 9 SOLUTIONS 1. Do Section 8.8, problems 11,, 15, 17 (these problems have to do with Taylor s Inequality, and they are very similar to what we did on the last homework.
Math 53 Homework due Wednesday, March 9 SOLUTIONS 1. Do Section 8.8, problems 11,, 15, 17 (these problems have to do with Taylor s Inequality, and they are very similar to what we did on the last homework.
17.2 Nonhomogeneous Linear Equations. 27 September 2007
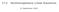 17.2 Nonhomogeneous Linear Equations 27 September 2007 Nonhomogeneous Linear Equations The differential equation to be studied is of the form ay (x) + by (x) + cy(x) = G(x) (1) where a 0, b, c are given
17.2 Nonhomogeneous Linear Equations 27 September 2007 Nonhomogeneous Linear Equations The differential equation to be studied is of the form ay (x) + by (x) + cy(x) = G(x) (1) where a 0, b, c are given
Elementary factoring algorithms
 Math 5330 Spring 018 Elementary factoring algorithms The RSA cryptosystem is founded on the idea that, in general, factoring is hard. Where as with Fermat s Little Theorem and some related ideas, one can
Math 5330 Spring 018 Elementary factoring algorithms The RSA cryptosystem is founded on the idea that, in general, factoring is hard. Where as with Fermat s Little Theorem and some related ideas, one can
Lecture 9: Taylor Series
 Math 8 Instructor: Padraic Bartlett Lecture 9: Taylor Series Week 9 Caltech 212 1 Taylor Polynomials and Series When we first introduced the idea of the derivative, one of the motivations we offered was
Math 8 Instructor: Padraic Bartlett Lecture 9: Taylor Series Week 9 Caltech 212 1 Taylor Polynomials and Series When we first introduced the idea of the derivative, one of the motivations we offered was
Problem Solving in Math (Math 43900) Fall 2013
 Problem Solving in Math (Math 43900) Fall 203 Week six (October ) problems recurrences Instructor: David Galvin Definition of a recurrence relation We met recurrences in the induction hand-out. Sometimes
Problem Solving in Math (Math 43900) Fall 203 Week six (October ) problems recurrences Instructor: David Galvin Definition of a recurrence relation We met recurrences in the induction hand-out. Sometimes
2t t dt.. So the distance is (t2 +6) 3/2
 Math 8, Solutions to Review for the Final Exam Question : The distance is 5 t t + dt To work that out, integrate by parts with u t +, so that t dt du The integral is t t + dt u du u 3/ (t +) 3/ So the
Math 8, Solutions to Review for the Final Exam Question : The distance is 5 t t + dt To work that out, integrate by parts with u t +, so that t dt du The integral is t t + dt u du u 3/ (t +) 3/ So the
7.3 Singular points and the method of Frobenius
 284 CHAPTER 7. POWER SERIES METHODS 7.3 Singular points and the method of Frobenius Note: or.5 lectures, 8.4 and 8.5 in [EP], 5.4 5.7 in [BD] While behaviour of ODEs at singular points is more complicated,
284 CHAPTER 7. POWER SERIES METHODS 7.3 Singular points and the method of Frobenius Note: or.5 lectures, 8.4 and 8.5 in [EP], 5.4 5.7 in [BD] While behaviour of ODEs at singular points is more complicated,
Math 2142 Homework 5 Part 1 Solutions
 Math 2142 Homework 5 Part 1 Solutions Problem 1. For the following homogeneous second order differential equations, give the general solution and the particular solution satisfying the given initial conditions.
Math 2142 Homework 5 Part 1 Solutions Problem 1. For the following homogeneous second order differential equations, give the general solution and the particular solution satisfying the given initial conditions.
MATH202 Introduction to Analysis (2007 Fall and 2008 Spring) Tutorial Note #12
 MATH0 Introduction to Analysis (007 Fall and 008 Spring) Tutorial Note #1 Limit (Part ) Recurrence Relation: Type 1: Monotone Sequence (Increasing/ Decreasing sequence) Theorem 1: Monotone Sequence Theorem
MATH0 Introduction to Analysis (007 Fall and 008 Spring) Tutorial Note #1 Limit (Part ) Recurrence Relation: Type 1: Monotone Sequence (Increasing/ Decreasing sequence) Theorem 1: Monotone Sequence Theorem
CHMC: Finite Fields 9/23/17
 CHMC: Finite Fields 9/23/17 1 Introduction This worksheet is an introduction to the fascinating subject of finite fields. Finite fields have many important applications in coding theory and cryptography,
CHMC: Finite Fields 9/23/17 1 Introduction This worksheet is an introduction to the fascinating subject of finite fields. Finite fields have many important applications in coding theory and cryptography,
Warm up: Recall that if you require real coe cients (not complex), polynomials always factor into degree 1 or 2 parts.
 Today: 6.3 Partial fractions Warm up: Recall that if you require real coe cients (not comple), polynomials always factor into degree or parts. For eample, 3 + +3 5=( )( + i)( ++i) =( {z } )( + + 5) {z
Today: 6.3 Partial fractions Warm up: Recall that if you require real coe cients (not comple), polynomials always factor into degree or parts. For eample, 3 + +3 5=( )( + i)( ++i) =( {z } )( + + 5) {z
Representation of Functions as Power Series
 Representation of Functions as Power Series Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Functions as Power Series Today / Introduction In this section and the next, we develop several techniques
Representation of Functions as Power Series Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Functions as Power Series Today / Introduction In this section and the next, we develop several techniques
Computing Taylor series
 TOPIC 9 Computing Taylor series Exercise 9.. Memorize the following x X e x cos x sin x X X X +x + x + x 3 +... xk +x + x + 6 x3 +... ( ) k (k)! xk ( ) k (k + )! xk+ x x +! x... For which values of x do
TOPIC 9 Computing Taylor series Exercise 9.. Memorize the following x X e x cos x sin x X X X +x + x + x 3 +... xk +x + x + 6 x3 +... ( ) k (k)! xk ( ) k (k + )! xk+ x x +! x... For which values of x do
Power Series and Analytic Function
 Dr Mansoor Alshehri King Saud University MATH204-Differential Equations Center of Excellence in Learning and Teaching 1 / 21 Some Reviews of Power Series Differentiation and Integration of a Power Series
Dr Mansoor Alshehri King Saud University MATH204-Differential Equations Center of Excellence in Learning and Teaching 1 / 21 Some Reviews of Power Series Differentiation and Integration of a Power Series
Math 475, Problem Set #8: Answers
 Math 475, Problem Set #8: Answers A. Brualdi, problem, parts (a), (b), and (d). (a): As n goes from to 6, the sum (call it h n ) takes on the values,, 8, 2, 55, and 44; we recognize these as Fibonacci
Math 475, Problem Set #8: Answers A. Brualdi, problem, parts (a), (b), and (d). (a): As n goes from to 6, the sum (call it h n ) takes on the values,, 8, 2, 55, and 44; we recognize these as Fibonacci
SYSTEMS OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS
 SYSTEMS OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS Widely used in the mathematical modeling of real world phenomena. We introduce some numerical methods for their solution. For better intuition, we examine systems of two
SYSTEMS OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS Widely used in the mathematical modeling of real world phenomena. We introduce some numerical methods for their solution. For better intuition, we examine systems of two
`an cos nπx. n 1. L `b
 4 Fourier Series A periodic function on a range p,q may be decomposed into a sum of sinusoidal (sine or cosine) functions. This can be written as follows gpxq 1 2 a ` ř8 `b (4.1) The aim of this chapter
4 Fourier Series A periodic function on a range p,q may be decomposed into a sum of sinusoidal (sine or cosine) functions. This can be written as follows gpxq 1 2 a ` ř8 `b (4.1) The aim of this chapter
Review for Exam 2. Review for Exam 2.
 Review for Exam 2. 5 or 6 problems. No multiple choice questions. No notes, no books, no calculators. Problems similar to homeworks. Exam covers: Regular-singular points (5.5). Euler differential equation
Review for Exam 2. 5 or 6 problems. No multiple choice questions. No notes, no books, no calculators. Problems similar to homeworks. Exam covers: Regular-singular points (5.5). Euler differential equation
Probability Generating Functions
 Probability Generating Functions Andreas Klappenecker Texas A&M University 2018 by Andreas Klappenecker. All rights reserved. 1 / 27 Probability Generating Functions Definition Let X be a discrete random
Probability Generating Functions Andreas Klappenecker Texas A&M University 2018 by Andreas Klappenecker. All rights reserved. 1 / 27 Probability Generating Functions Definition Let X be a discrete random
Section Example Determine the Maclaurin series of f (x) = e x and its the interval of convergence.
 Example Determine the Maclaurin series of f (x) = e x and its the interval of convergence. Example Determine the Maclaurin series of f (x) = e x and its the interval of convergence. f n (0)x n Recall from
Example Determine the Maclaurin series of f (x) = e x and its the interval of convergence. Example Determine the Maclaurin series of f (x) = e x and its the interval of convergence. f n (0)x n Recall from
Updated: January 16, 2016 Calculus II 7.4. Math 230. Calculus II. Brian Veitch Fall 2015 Northern Illinois University
 Math 30 Calculus II Brian Veitch Fall 015 Northern Illinois University Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions From algebra, we learned how to find common denominators so we can do something
Math 30 Calculus II Brian Veitch Fall 015 Northern Illinois University Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions From algebra, we learned how to find common denominators so we can do something
Introduction to Differential Equations
 Introduction to Differential Equations J. M. Veal, Ph. D. version 13.08.30 Contents 1 Introduction to Differential Equations 2 1.1 Definitions and Terminology.................... 2 1.2 Initial-Value Problems.......................
Introduction to Differential Equations J. M. Veal, Ph. D. version 13.08.30 Contents 1 Introduction to Differential Equations 2 1.1 Definitions and Terminology.................... 2 1.2 Initial-Value Problems.......................
Relevant sections from AMATH 351 Course Notes (Wainwright): Relevant sections from AMATH 351 Course Notes (Poulin and Ingalls):
 Lecture 5 Series solutions to DEs Relevant sections from AMATH 35 Course Notes (Wainwright):.4. Relevant sections from AMATH 35 Course Notes (Poulin and Ingalls): 2.-2.3 As mentioned earlier in this course,
Lecture 5 Series solutions to DEs Relevant sections from AMATH 35 Course Notes (Wainwright):.4. Relevant sections from AMATH 35 Course Notes (Poulin and Ingalls): 2.-2.3 As mentioned earlier in this course,
2 nd order Linear Homogeneous DEs with Non-Constant Coefficients
 Math 231, Wed 4-May-2011 -- Wed 4-May-2011 Wednesday, May 4th 2011 Topic:: DEs with Non-Constant Coeffs 2 nd order Linear Homogeneous DEs with Non-Constant Coefficients We consider linear 2 nd order homogeneous
Math 231, Wed 4-May-2011 -- Wed 4-May-2011 Wednesday, May 4th 2011 Topic:: DEs with Non-Constant Coeffs 2 nd order Linear Homogeneous DEs with Non-Constant Coefficients We consider linear 2 nd order homogeneous
Power Series Solutions We use power series to solve second order differential equations
 Objectives Power Series Solutions We use power series to solve second order differential equations We use power series expansions to find solutions to second order, linear, variable coefficient equations
Objectives Power Series Solutions We use power series to solve second order differential equations We use power series expansions to find solutions to second order, linear, variable coefficient equations
Notes for Recitation 14
 6.04/18.06J Mathematics for Computer Science October 7, 006 Tom Leighton and Ronitt Rubinfeld Notes for Recitation 14 Guessing a Particular Solution A general linear recurrence has the form: fn) = b 1
6.04/18.06J Mathematics for Computer Science October 7, 006 Tom Leighton and Ronitt Rubinfeld Notes for Recitation 14 Guessing a Particular Solution A general linear recurrence has the form: fn) = b 1
SOLUTIONS ABOUT ORDINARY POINTS
 238 CHAPTER 6 SERIES SOLUTIONS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS In Problems 23 and 24 use a substitution to shift the summation index so that the general term of given power series involves x k. 23. nc n x n2 n 24.
238 CHAPTER 6 SERIES SOLUTIONS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS In Problems 23 and 24 use a substitution to shift the summation index so that the general term of given power series involves x k. 23. nc n x n2 n 24.
Math 3313: Differential Equations Second-order ordinary differential equations
 Math 3313: Differential Equations Second-order ordinary differential equations Thomas W. Carr Department of Mathematics Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX Outline Mass-spring & Newton s 2nd law Properties
Math 3313: Differential Equations Second-order ordinary differential equations Thomas W. Carr Department of Mathematics Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX Outline Mass-spring & Newton s 2nd law Properties
CALCULUS JIA-MING (FRANK) LIOU
 CALCULUS JIA-MING (FRANK) LIOU Abstract. Contents. Power Series.. Polynomials and Formal Power Series.2. Radius of Convergence 2.3. Derivative and Antiderivative of Power Series 4.4. Power Series Expansion
CALCULUS JIA-MING (FRANK) LIOU Abstract. Contents. Power Series.. Polynomials and Formal Power Series.2. Radius of Convergence 2.3. Derivative and Antiderivative of Power Series 4.4. Power Series Expansion
Power series solutions for 2nd order linear ODE s (not necessarily with constant coefficients) a n z n. n=0
 Lecture 22 Power series solutions for 2nd order linear ODE s (not necessarily with constant coefficients) Recall a few facts about power series: a n z n This series in z is centered at z 0. Here z can
Lecture 22 Power series solutions for 2nd order linear ODE s (not necessarily with constant coefficients) Recall a few facts about power series: a n z n This series in z is centered at z 0. Here z can
DS-GA 3001: PROBLEM SESSION 2 SOLUTIONS VLADIMIR KOBZAR
 DS-GA 3: PROBLEM SESSION SOLUTIONS VLADIMIR KOBZAR Note: In this discussion we allude to the fact the dimension of a vector space is given by the number of basis vectors. We will shortly establish this
DS-GA 3: PROBLEM SESSION SOLUTIONS VLADIMIR KOBZAR Note: In this discussion we allude to the fact the dimension of a vector space is given by the number of basis vectors. We will shortly establish this
Asymptotic Analysis 1: Limits and Asymptotic Equality
 Asymptotic Analysis 1: Limits and Asymptotic Equality Andreas Klappenecker and Hyunyoung Lee Texas A&M University 1 / 15 Motivation In asymptotic analysis, our goal is to compare a function f pnq with
Asymptotic Analysis 1: Limits and Asymptotic Equality Andreas Klappenecker and Hyunyoung Lee Texas A&M University 1 / 15 Motivation In asymptotic analysis, our goal is to compare a function f pnq with
Power Series. Part 2 Differentiation & Integration; Multiplication of Power Series. J. Gonzalez-Zugasti, University of Massachusetts - Lowell
 Power Series Part 2 Differentiation & Integration; Multiplication of Power Series 1 Theorem 1 If a n x n converges absolutely for x < R, then a n f x n converges absolutely for any continuous function
Power Series Part 2 Differentiation & Integration; Multiplication of Power Series 1 Theorem 1 If a n x n converges absolutely for x < R, then a n f x n converges absolutely for any continuous function
#A22 INTEGERS 17 (2017) NEW CONGRUENCES FOR `-REGULAR OVERPARTITIONS
 #A22 INTEGERS 7 (207) NEW CONGRUENCES FOR `-REGULAR OVERPARTITIONS Shane Chern Department of Mathematics, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania shanechern@psu.edu Received: 0/6/6,
#A22 INTEGERS 7 (207) NEW CONGRUENCES FOR `-REGULAR OVERPARTITIONS Shane Chern Department of Mathematics, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania shanechern@psu.edu Received: 0/6/6,
DS-GA 1002: PREREQUISITES REVIEW SOLUTIONS VLADIMIR KOBZAR
 DS-GA 2: PEEQUISIES EVIEW SOLUIONS VLADIMI KOBZA he following is a selection of questions (drawn from Mr. Bernstein s notes) for reviewing the prerequisites for DS-GA 2. Questions from Ch, 8, 9 and 2 of
DS-GA 2: PEEQUISIES EVIEW SOLUIONS VLADIMI KOBZA he following is a selection of questions (drawn from Mr. Bernstein s notes) for reviewing the prerequisites for DS-GA 2. Questions from Ch, 8, 9 and 2 of
UNDETERMINED COEFFICIENTS SUPERPOSITION APPROACH *
 4.4 UNDETERMINED COEFFICIENTS SUPERPOSITION APPROACH 19 Discussion Problems 59. Two roots of a cubic auxiliary equation with real coeffi cients are m 1 1 and m i. What is the corresponding homogeneous
4.4 UNDETERMINED COEFFICIENTS SUPERPOSITION APPROACH 19 Discussion Problems 59. Two roots of a cubic auxiliary equation with real coeffi cients are m 1 1 and m i. What is the corresponding homogeneous
MB4018 Differential equations
 MB4018 Differential equations Part II http://www.staff.ul.ie/natalia/mb4018.html Prof. Natalia Kopteva Spring 2015 MB4018 (Spring 2015) Differential equations Part II 0 / 69 Section 1 Second-Order Linear
MB4018 Differential equations Part II http://www.staff.ul.ie/natalia/mb4018.html Prof. Natalia Kopteva Spring 2015 MB4018 (Spring 2015) Differential equations Part II 0 / 69 Section 1 Second-Order Linear
Exam 2 Solutions. x 1 x. x 4 The generating function for the problem is the fourth power of this, (1 x). 4
 Math 5366 Fall 015 Exam Solutions 1. (0 points) Find the appropriate generating function (in closed form) for each of the following problems. Do not find the coefficient of x n. (a) In how many ways can
Math 5366 Fall 015 Exam Solutions 1. (0 points) Find the appropriate generating function (in closed form) for each of the following problems. Do not find the coefficient of x n. (a) In how many ways can
1 Recursive Algorithms
 400 lecture note #8 [ 5.6-5.8] Recurrence Relations 1 Recursive Algorithms A recursive algorithm is an algorithm which invokes itself. A recursive algorithm looks at a problem backward -- the solution
400 lecture note #8 [ 5.6-5.8] Recurrence Relations 1 Recursive Algorithms A recursive algorithm is an algorithm which invokes itself. A recursive algorithm looks at a problem backward -- the solution
Constructing Taylor Series
 Constructing Taylor Series 8-8-200 The Taylor series for fx at x = c is fc + f cx c + f c 2! x c 2 + f c x c 3 + = 3! f n c x c n. By convention, f 0 = f. When c = 0, the series is called a Maclaurin series.
Constructing Taylor Series 8-8-200 The Taylor series for fx at x = c is fc + f cx c + f c 2! x c 2 + f c x c 3 + = 3! f n c x c n. By convention, f 0 = f. When c = 0, the series is called a Maclaurin series.
Math 126 Enhanced 10.3 Series with positive terms The University of Kansas 1 / 12
 Section 10.3 Convergence of series with positive terms 1. Integral test 2. Error estimates for the integral test 3. Comparison test 4. Limit comparison test (LCT) Math 126 Enhanced 10.3 Series with positive
Section 10.3 Convergence of series with positive terms 1. Integral test 2. Error estimates for the integral test 3. Comparison test 4. Limit comparison test (LCT) Math 126 Enhanced 10.3 Series with positive
Section 4.3. Polynomial Division; The Remainder Theorem and the Factor Theorem
 Section 4.3 Polynomial Division; The Remainder Theorem and the Factor Theorem Polynomial Long Division Let s compute 823 5 : Example of Long Division of Numbers Example of Long Division of Numbers Let
Section 4.3 Polynomial Division; The Remainder Theorem and the Factor Theorem Polynomial Long Division Let s compute 823 5 : Example of Long Division of Numbers Example of Long Division of Numbers Let
arxiv: v1 [math.ac] 3 Jan 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.ac] 3 Jan 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.ac] 3 Jan 2016](/thumbs/92/110827958.jpg) A new characterization of the invertibility of polynomial maps arxiv:1601.00332v1 [math.ac] 3 Jan 2016 ELŻBIETA ADAMUS Faculty of Applied Mathematics, AGH University of Science and Technology al. Mickiewicza
A new characterization of the invertibility of polynomial maps arxiv:1601.00332v1 [math.ac] 3 Jan 2016 ELŻBIETA ADAMUS Faculty of Applied Mathematics, AGH University of Science and Technology al. Mickiewicza
Lecture 4: Hardness Amplification: From Weak to Strong OWFs
 COM S 687 Introduction to Cryptography September 5, 2006 Lecture 4: Hardness Amplification: From Weak to Strong OWFs Instructor: Rafael Pass Scribe: Jed Liu Review In the previous lecture, we formalised
COM S 687 Introduction to Cryptography September 5, 2006 Lecture 4: Hardness Amplification: From Weak to Strong OWFs Instructor: Rafael Pass Scribe: Jed Liu Review In the previous lecture, we formalised
Solving Recurrence Relations 1. Guess and Math Induction Example: Find the solution for a n = 2a n 1 + 1, a 0 = 0 We can try finding each a n : a 0 =
 Solving Recurrence Relations 1. Guess and Math Induction Example: Find the solution for a n = 2a n 1 + 1, a 0 = 0 We can try finding each a n : a 0 = 0 a 1 = 2 0 + 1 = 1 a 2 = 2 1 + 1 = 3 a 3 = 2 3 + 1
Solving Recurrence Relations 1. Guess and Math Induction Example: Find the solution for a n = 2a n 1 + 1, a 0 = 0 We can try finding each a n : a 0 = 0 a 1 = 2 0 + 1 = 1 a 2 = 2 1 + 1 = 3 a 3 = 2 3 + 1
Continuous Random Variables
 MATH 38 Continuous Random Variables Dr. Neal, WKU Throughout, let Ω be a sample space with a defined probability measure P. Definition. A continuous random variable is a real-valued function X defined
MATH 38 Continuous Random Variables Dr. Neal, WKU Throughout, let Ω be a sample space with a defined probability measure P. Definition. A continuous random variable is a real-valued function X defined
1 Reductions from Maximum Matchings to Perfect Matchings
 15-451/651: Design & Analysis of Algorithms November 21, 2013 Lecture #26 last changed: December 3, 2013 When we first studied network flows, we saw how to find maximum cardinality matchings in bipartite
15-451/651: Design & Analysis of Algorithms November 21, 2013 Lecture #26 last changed: December 3, 2013 When we first studied network flows, we saw how to find maximum cardinality matchings in bipartite
LOWELL WEEKLY JOURNAL
 KY Y 872 K & q $ < 9 2 q 4 8 «7 K K K «> 2 26 8 5 4 4 7»» 2 & K q 4 [«5 «$6 q X «K «8K K88 K 7 ««$25 K Q ««q 8 K K Y & 7K /> Y 8«#»«Y 87 8 Y 4 KY «7««X & Y» K ) K K 5 KK K > K» Y Y 8 «KK > /» >» 8 K X
KY Y 872 K & q $ < 9 2 q 4 8 «7 K K K «> 2 26 8 5 4 4 7»» 2 & K q 4 [«5 «$6 q X «K «8K K88 K 7 ««$25 K Q ««q 8 K K Y & 7K /> Y 8«#»«Y 87 8 Y 4 KY «7««X & Y» K ) K K 5 KK K > K» Y Y 8 «KK > /» >» 8 K X
Elementary Differential Equations, Section 2 Prof. Loftin: Practice Test Problems for Test Find the radius of convergence of the power series
 Elementary Differential Equations, Section 2 Prof. Loftin: Practice Test Problems for Test 2 SOLUTIONS 1. Find the radius of convergence of the power series Show your work. x + x2 2 + x3 3 + x4 4 + + xn
Elementary Differential Equations, Section 2 Prof. Loftin: Practice Test Problems for Test 2 SOLUTIONS 1. Find the radius of convergence of the power series Show your work. x + x2 2 + x3 3 + x4 4 + + xn
Generating Functions of Partitions
 CHAPTER B Generating Functions of Partitions For a complex sequence {α n n 0,, 2, }, its generating function with a complex variable q is defined by A(q) : α n q n α n [q n ] A(q). When the sequence has
CHAPTER B Generating Functions of Partitions For a complex sequence {α n n 0,, 2, }, its generating function with a complex variable q is defined by A(q) : α n q n α n [q n ] A(q). When the sequence has
The Method of Frobenius
 The Method of Frobenius R. C. Trinity University Partial Differential Equations April 7, 2015 Motivating example Failure of the power series method Consider the ODE 2xy +y +y = 0. In standard form this
The Method of Frobenius R. C. Trinity University Partial Differential Equations April 7, 2015 Motivating example Failure of the power series method Consider the ODE 2xy +y +y = 0. In standard form this
Chapter Generating Functions
 Chapter 8.1.1-8.1.2. Generating Functions Prof. Tesler Math 184A Fall 2017 Prof. Tesler Ch. 8. Generating Functions Math 184A / Fall 2017 1 / 63 Ordinary Generating Functions (OGF) Let a n (n = 0, 1,...)
Chapter 8.1.1-8.1.2. Generating Functions Prof. Tesler Math 184A Fall 2017 Prof. Tesler Ch. 8. Generating Functions Math 184A / Fall 2017 1 / 63 Ordinary Generating Functions (OGF) Let a n (n = 0, 1,...)
PARTIAL FRACTIONS AND POLYNOMIAL LONG DIVISION. The basic aim of this note is to describe how to break rational functions into pieces.
 PARTIAL FRACTIONS AND POLYNOMIAL LONG DIVISION NOAH WHITE The basic aim of this note is to describe how to break rational functions into pieces. For example 2x + 3 = + x 3 x +. The point is that we don
PARTIAL FRACTIONS AND POLYNOMIAL LONG DIVISION NOAH WHITE The basic aim of this note is to describe how to break rational functions into pieces. For example 2x + 3 = + x 3 x +. The point is that we don
Tutorial 2 WANG PENG. Department of Systems Engineering and Engineering Management, The Chinese University of Hong Kong. September 28, 2017
 Tutorial 2 WANG PENG Department of Systems Engineering and Engineering Management, The Chinese University of Hong Kong September 28, 2017 WANG PENG (ENGG 2440B) Tutorial 2 September 28, 2017 1 / 17 Outline
Tutorial 2 WANG PENG Department of Systems Engineering and Engineering Management, The Chinese University of Hong Kong September 28, 2017 WANG PENG (ENGG 2440B) Tutorial 2 September 28, 2017 1 / 17 Outline
Learn how to use Desmos
 Learn how to use Desmos Maclaurin and Taylor series 1 Go to www.desmos.com. Create an account (click on bottom near top right of screen) Change the grid settings (click on the spanner) to 1 x 3, 1 y 12
Learn how to use Desmos Maclaurin and Taylor series 1 Go to www.desmos.com. Create an account (click on bottom near top right of screen) Change the grid settings (click on the spanner) to 1 x 3, 1 y 12
Definition: A sequence is a function from a subset of the integers (usually either the set
 Math 3336 Section 2.4 Sequences and Summations Sequences Geometric Progression Arithmetic Progression Recurrence Relation Fibonacci Sequence Summations Definition: A sequence is a function from a subset
Math 3336 Section 2.4 Sequences and Summations Sequences Geometric Progression Arithmetic Progression Recurrence Relation Fibonacci Sequence Summations Definition: A sequence is a function from a subset
Series Solutions Near a Regular Singular Point
 Series Solutions Near a Regular Singular Point MATH 365 Ordinary Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Background We will find a power series solution to the equation:
Series Solutions Near a Regular Singular Point MATH 365 Ordinary Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Background We will find a power series solution to the equation:
3.4 Introduction to power series
 3.4 Introduction to power series Definition 3.4.. A polynomial in the variable x is an expression of the form n a i x i = a 0 + a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n + a n x n i=0 or a n x n + a n x n + + a 2 x 2
3.4 Introduction to power series Definition 3.4.. A polynomial in the variable x is an expression of the form n a i x i = a 0 + a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n + a n x n i=0 or a n x n + a n x n + + a 2 x 2
Math 115 HW #10 Solutions
 Math 11 HW #10 Solutions 1. Suppose y 1 (t and y 2 (t are both solutions of the differential equation P (ty + Q(ty + R(ty = 0. Show that, for any constants C 1 and C 2, the function C 1 y 1 (t + C 2 y
Math 11 HW #10 Solutions 1. Suppose y 1 (t and y 2 (t are both solutions of the differential equation P (ty + Q(ty + R(ty = 0. Show that, for any constants C 1 and C 2, the function C 1 y 1 (t + C 2 y
Math 113 (Calculus 2) Exam 4
 Math 3 (Calculus ) Exam 4 November 0 November, 009 Sections 0, 3 7 Name Student ID Section Instructor In some cases a series may be seen to converge or diverge for more than one reason. For such problems
Math 3 (Calculus ) Exam 4 November 0 November, 009 Sections 0, 3 7 Name Student ID Section Instructor In some cases a series may be seen to converge or diverge for more than one reason. For such problems
Notes for Recitation 14
 6.04/18.06J Mathematics for Computer Science October 4, 006 Tom Leighton and Marten van Dijk Notes for Recitation 14 1 The Akra-Bazzi Theorem Theorem 1 (Akra-Bazzi, strong form). Suppose that: is defined
6.04/18.06J Mathematics for Computer Science October 4, 006 Tom Leighton and Marten van Dijk Notes for Recitation 14 1 The Akra-Bazzi Theorem Theorem 1 (Akra-Bazzi, strong form). Suppose that: is defined
Carolyn Abbott Tejas Bhojraj Zachary Carter Mohamed Abou Dbai Ed Dewey. Jale Dinler Di Fang Bingyang Hu Canberk Irimagzi Chris Janjigian
 Practice Final a Solutions (/7 Version) MATH (Lectures,, and 4) Fall 05. Name: Student ID#: Circle your TAs name: Carolyn Abbott Tejas Bhojraj achary Carter Mohamed Abou Dbai Ed Dewey Jale Dinler Di Fang
Practice Final a Solutions (/7 Version) MATH (Lectures,, and 4) Fall 05. Name: Student ID#: Circle your TAs name: Carolyn Abbott Tejas Bhojraj achary Carter Mohamed Abou Dbai Ed Dewey Jale Dinler Di Fang
Series Solutions of Linear ODEs
 Chapter 2 Series Solutions of Linear ODEs This Chapter is concerned with solutions of linear Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE). We will start by reviewing some basic concepts and solution methods for
Chapter 2 Series Solutions of Linear ODEs This Chapter is concerned with solutions of linear Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE). We will start by reviewing some basic concepts and solution methods for
MTH MTH Lecture 6. Yevgeniy Kovchegov Oregon State University
 MTH 306 0 MTH 306 - Lecture 6 Yevgeniy Kovchegov Oregon State University MTH 306 1 Topics Lines and planes. Systems of linear equations. Systematic elimination of unknowns. Coe cient matrix. Augmented
MTH 306 0 MTH 306 - Lecture 6 Yevgeniy Kovchegov Oregon State University MTH 306 1 Topics Lines and planes. Systems of linear equations. Systematic elimination of unknowns. Coe cient matrix. Augmented
MATH 103 Pre-Calculus Mathematics Test #3 Fall 2008 Dr. McCloskey Sample Solutions
 MATH 103 Pre-Calculus Mathematics Test #3 Fall 008 Dr. McCloskey Sample Solutions 1. Let P (x) = 3x 4 + x 3 x + and D(x) = x + x 1. Find polynomials Q(x) and R(x) such that P (x) = Q(x) D(x) + R(x). (That
MATH 103 Pre-Calculus Mathematics Test #3 Fall 008 Dr. McCloskey Sample Solutions 1. Let P (x) = 3x 4 + x 3 x + and D(x) = x + x 1. Find polynomials Q(x) and R(x) such that P (x) = Q(x) D(x) + R(x). (That
Infinite series, improper integrals, and Taylor series
 Chapter Infinite series, improper integrals, and Taylor series. Determine which of the following sequences converge or diverge (a) {e n } (b) {2 n } (c) {ne 2n } (d) { 2 n } (e) {n } (f) {ln(n)} 2.2 Which
Chapter Infinite series, improper integrals, and Taylor series. Determine which of the following sequences converge or diverge (a) {e n } (b) {2 n } (c) {ne 2n } (d) { 2 n } (e) {n } (f) {ln(n)} 2.2 Which
Legendre s Equation. PHYS Southern Illinois University. October 18, 2016
 Legendre s Equation PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University October 18, 2016 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Legendre s Equation October 18, 2016 1 / 11 Legendre s Equation Recall We are trying
Legendre s Equation PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University October 18, 2016 PHYS 500 - Southern Illinois University Legendre s Equation October 18, 2016 1 / 11 Legendre s Equation Recall We are trying
Math 5330 Spring Notes Prime Numbers
 Math 5330 Sring 208 Notes Prime Numbers The study of rime numbers is as old as mathematics itself. This set of notes has a bunch of facts about rimes, or related to rimes. Much of this stuff is old dating
Math 5330 Sring 208 Notes Prime Numbers The study of rime numbers is as old as mathematics itself. This set of notes has a bunch of facts about rimes, or related to rimes. Much of this stuff is old dating
Math 1B, lecture 15: Taylor Series
 Math B, lecture 5: Taylor Series Nathan Pflueger October 0 Introduction Taylor s theorem shows, in many cases, that the error associated with a Taylor approximation will eventually approach 0 as the degree
Math B, lecture 5: Taylor Series Nathan Pflueger October 0 Introduction Taylor s theorem shows, in many cases, that the error associated with a Taylor approximation will eventually approach 0 as the degree
6.4 BASIS AND DIMENSION (Review) DEF 1 Vectors v 1, v 2,, v k in a vector space V are said to form a basis for V if. (a) v 1,, v k span V and
 6.4 BASIS AND DIMENSION (Review) DEF 1 Vectors v 1, v 2,, v k in a vector space V are said to form a basis for V if (a) v 1,, v k span V and (b) v 1,, v k are linearly independent. HMHsueh 1 Natural Basis
6.4 BASIS AND DIMENSION (Review) DEF 1 Vectors v 1, v 2,, v k in a vector space V are said to form a basis for V if (a) v 1,, v k span V and (b) v 1,, v k are linearly independent. HMHsueh 1 Natural Basis
Math 112 Rahman. Week Taylor Series Suppose the function f has the following power series:
 Math Rahman Week 0.8-0.0 Taylor Series Suppose the function f has the following power series: fx) c 0 + c x a) + c x a) + c 3 x a) 3 + c n x a) n. ) Can we figure out what the coefficients are? Yes, yes
Math Rahman Week 0.8-0.0 Taylor Series Suppose the function f has the following power series: fx) c 0 + c x a) + c x a) + c 3 x a) 3 + c n x a) n. ) Can we figure out what the coefficients are? Yes, yes
Almost Conservation Laws for KdV and Cubic NLS. UROP Final Paper, Summer 2018
 Almost Conservation Laws for KdV and Cubic NLS UROP Final Paper, Summer 2018 Zixuan Xu Mentor: Ricardo Grande Izquierdo Project suggested by: Gigliola Staffilani Abstract In this paper, we explore the
Almost Conservation Laws for KdV and Cubic NLS UROP Final Paper, Summer 2018 Zixuan Xu Mentor: Ricardo Grande Izquierdo Project suggested by: Gigliola Staffilani Abstract In this paper, we explore the
Homework 1 Solutions Math 587
 Homework 1 Solutions Math 587 1) Find positive functions f(x),g(x), continuous on (0, ) so that f = O(g(x)) as x 0, but lim x 0 f(x)/g(x) does not exist. One can take f(x) = sin(1/x) and g(x) = 1, for
Homework 1 Solutions Math 587 1) Find positive functions f(x),g(x), continuous on (0, ) so that f = O(g(x)) as x 0, but lim x 0 f(x)/g(x) does not exist. One can take f(x) = sin(1/x) and g(x) = 1, for
PUTNAM TRAINING POLYNOMIALS. Exercises 1. Find a polynomial with integral coefficients whose zeros include
 PUTNAM TRAINING POLYNOMIALS (Last updated: December 11, 2017) Remark. This is a list of exercises on polynomials. Miguel A. Lerma Exercises 1. Find a polynomial with integral coefficients whose zeros include
PUTNAM TRAINING POLYNOMIALS (Last updated: December 11, 2017) Remark. This is a list of exercises on polynomials. Miguel A. Lerma Exercises 1. Find a polynomial with integral coefficients whose zeros include
Markov Chains. Andreas Klappenecker by Andreas Klappenecker. All rights reserved. Texas A&M University
 Markov Chains Andreas Klappenecker Texas A&M University 208 by Andreas Klappenecker. All rights reserved. / 58 Stochastic Processes A stochastic process X tx ptq: t P T u is a collection of random variables.
Markov Chains Andreas Klappenecker Texas A&M University 208 by Andreas Klappenecker. All rights reserved. / 58 Stochastic Processes A stochastic process X tx ptq: t P T u is a collection of random variables.
Solving Differential Equations Using Power Series
 LECTURE 25 Solving Differential Equations Using Power Series We are now going to employ power series to find solutions to differential equations of the form (25.) y + p(x)y + q(x)y = 0 where the functions
LECTURE 25 Solving Differential Equations Using Power Series We are now going to employ power series to find solutions to differential equations of the form (25.) y + p(x)y + q(x)y = 0 where the functions
Solving Differential Equations Using Power Series
 LECTURE 8 Solving Differential Equations Using Power Series We are now going to employ power series to find solutions to differential equations of the form () y + p(x)y + q(x)y = 0 where the functions
LECTURE 8 Solving Differential Equations Using Power Series We are now going to employ power series to find solutions to differential equations of the form () y + p(x)y + q(x)y = 0 where the functions
10. Noether Normalization and Hilbert s Nullstellensatz
 10. Noether Normalization and Hilbert s Nullstellensatz 91 10. Noether Normalization and Hilbert s Nullstellensatz In the last chapter we have gained much understanding for integral and finite ring extensions.
10. Noether Normalization and Hilbert s Nullstellensatz 91 10. Noether Normalization and Hilbert s Nullstellensatz In the last chapter we have gained much understanding for integral and finite ring extensions.
Chapter 5.2: Series solution near an ordinary point
 Chapter 5.2: Series solution near an ordinary point We now look at ODE s with polynomial coefficients of the form: P (x)y + Q(x)y + R(x)y = 0. Thus, we assume P (x), Q(x), R(x) are polynomials in x. Why?
Chapter 5.2: Series solution near an ordinary point We now look at ODE s with polynomial coefficients of the form: P (x)y + Q(x)y + R(x)y = 0. Thus, we assume P (x), Q(x), R(x) are polynomials in x. Why?
RECURSIVE ESTIMATION AND KALMAN FILTERING
 Chapter 3 RECURSIVE ESTIMATION AND KALMAN FILTERING 3. The Discrete Time Kalman Filter Consider the following estimation problem. Given the stochastic system with x k+ = Ax k + Gw k (3.) y k = Cx k + Hv
Chapter 3 RECURSIVE ESTIMATION AND KALMAN FILTERING 3. The Discrete Time Kalman Filter Consider the following estimation problem. Given the stochastic system with x k+ = Ax k + Gw k (3.) y k = Cx k + Hv
f (x) = k=0 f (0) = k=0 k=0 a k k(0) k 1 = a 1 a 1 = f (0). a k k(k 1)x k 2, k=2 a k k(k 1)(0) k 2 = 2a 2 a 2 = f (0) 2 a k k(k 1)(k 2)x k 3, k=3
 1 M 13-Lecture Contents: 1) Taylor Polynomials 2) Taylor Series Centered at x a 3) Applications of Taylor Polynomials Taylor Series The previous section served as motivation and gave some useful expansion.
1 M 13-Lecture Contents: 1) Taylor Polynomials 2) Taylor Series Centered at x a 3) Applications of Taylor Polynomials Taylor Series The previous section served as motivation and gave some useful expansion.
Introduction to Numerical Analysis
 Introduction to Numerical Analysis Lecture Notes for SI 507 Authors: S. Baskar and S. Sivaji Ganesh Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Powai, Mumbai 400 076. Contents 1 Mathematical
Introduction to Numerical Analysis Lecture Notes for SI 507 Authors: S. Baskar and S. Sivaji Ganesh Department of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Powai, Mumbai 400 076. Contents 1 Mathematical
Generating Functions
 Generating Functions Karen Ge May, 07 Abstract Generating functions gives us a global perspective when we need to study a local property. We define generating functions and present its applications in
Generating Functions Karen Ge May, 07 Abstract Generating functions gives us a global perspective when we need to study a local property. We define generating functions and present its applications in
MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 48
 official website http://uoft.me/mat137 MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 48 Today: Taylor Series Applications Next: Final Exams Important Taylor Series and their Radii of Convergence 1 1 x = e x = n=0 n=0 x n n!
official website http://uoft.me/mat137 MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 48 Today: Taylor Series Applications Next: Final Exams Important Taylor Series and their Radii of Convergence 1 1 x = e x = n=0 n=0 x n n!
Partial Fractions. (Do you see how to work it out? Substitute u = ax + b, so du = a dx.) For example, 1 dx = ln x 7 + C, x x (x 3)(x + 1) = a
 Partial Fractions 7-9-005 Partial fractions is the opposite of adding fractions over a common denominator. It applies to integrals of the form P(x) dx, wherep(x) and Q(x) are polynomials. Q(x) The idea
Partial Fractions 7-9-005 Partial fractions is the opposite of adding fractions over a common denominator. It applies to integrals of the form P(x) dx, wherep(x) and Q(x) are polynomials. Q(x) The idea
MATH 222 (Lectures 1,2, and 4) Fall 2015 Practice Midterm 2.1 Solutions. Carolyn Abbott Tejas Bhojraj Zachary Carter Mohamed Abou Dbai Ed Dewey
 MATH (Lectures,, and 4) Fall 05 Practice Midterm. Solutions Student ID#: Circle your TA s name from the following list. Carolyn Abbott Tejas Bhojraj Zachary Carter Mohamed Abou Dbai Ed Dewey Jale Dinler
MATH (Lectures,, and 4) Fall 05 Practice Midterm. Solutions Student ID#: Circle your TA s name from the following list. Carolyn Abbott Tejas Bhojraj Zachary Carter Mohamed Abou Dbai Ed Dewey Jale Dinler
Taylor series - Solutions
 Taylor series - Solutions. f(x) sin(x) sin(0) + x cos(0) + x x ( sin(0)) +!! ( cos(0)) + + x4 x5 (sin(0)) + 4! 5! 0 + x + 0 x x! + x5 5! x! + 0 + x5 (cos(0)) + x6 6! ( sin(0)) + x 7 7! + x9 9! 5! + 0 +
Taylor series - Solutions. f(x) sin(x) sin(0) + x cos(0) + x x ( sin(0)) +!! ( cos(0)) + + x4 x5 (sin(0)) + 4! 5! 0 + x + 0 x x! + x5 5! x! + 0 + x5 (cos(0)) + x6 6! ( sin(0)) + x 7 7! + x9 9! 5! + 0 +
Separation of Variables in Linear PDE: One-Dimensional Problems
 Separation of Variables in Linear PDE: One-Dimensional Problems Now we apply the theory of Hilbert spaces to linear differential equations with partial derivatives (PDE). We start with a particular example,
Separation of Variables in Linear PDE: One-Dimensional Problems Now we apply the theory of Hilbert spaces to linear differential equations with partial derivatives (PDE). We start with a particular example,
Difference Equation on Quintuple Products and Ramanujan s Partition Congruence p(11n +6) 0 (mod 11)
 International Mathematical Forum, 5, 2010, no 31, 1533-1539 Difference Equation on Quintuple Products and Ramanujan s Partition Congruence p(11n +6) 0 (mod 11) Qinglun Yan 1, Xiaona Fan and Jing Fu College
International Mathematical Forum, 5, 2010, no 31, 1533-1539 Difference Equation on Quintuple Products and Ramanujan s Partition Congruence p(11n +6) 0 (mod 11) Qinglun Yan 1, Xiaona Fan and Jing Fu College
Math 2602 Finite and Linear Math Fall 14. Homework 8: Core solutions
 Math 2602 Finite and Linear Math Fall 14 Homework 8: Core solutions Review exercises for Chapter 5 page 183 problems 25, 26a-26b, 29. Section 8.1 on page 252 problems 8, 9, 10, 13. Section 8.2 on page
Math 2602 Finite and Linear Math Fall 14 Homework 8: Core solutions Review exercises for Chapter 5 page 183 problems 25, 26a-26b, 29. Section 8.1 on page 252 problems 8, 9, 10, 13. Section 8.2 on page
Series Solutions. 8.1 Taylor Polynomials
 8 Series Solutions 8.1 Taylor Polynomials Polynomial functions, as we have seen, are well behaved. They are continuous everywhere, and have continuous derivatives of all orders everywhere. It also turns
8 Series Solutions 8.1 Taylor Polynomials Polynomial functions, as we have seen, are well behaved. They are continuous everywhere, and have continuous derivatives of all orders everywhere. It also turns
