An Improved Modeling of TDR Signal Propagation for Measuring Complex Dielectric Permittivity
|
|
|
- Regina Cannon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Jounal of Eath Siene, ol. 26, No. 6, p , Deembe 215 ISSN X Pinted in China DOI: 1.17/s An Impoved Modeling of TDR Signal Popagation fo Measuing Complex Dieleti Pemittivity Chih-Ping Lin 1, Sh-Hong Tang 2, Chun-Hung Lin 3, Chih-Chung Chung 4 1. Civil Engineeing, National Chiao Tung Univesity, Hsinhu 374, Taiwan, China 2. Infomation Management, St. May s Mediine, Nusing and Management College, Yilan 2653, Taiwan, China 3. Disaste Pevention and Wate Envionment Reseah Cente, National Chiao Tung Univesity, Hsinhu 374, Taiwan, China 4. Civil Engineeing, National Cental Univesity, hongli 321, Taiwan, China ABSTRACT: Time domain efletomety (TDR) is a measuement tehnique based upon tansmission line theoy. The solutions of tansmission line equations ae efomulated in tems of independent physial popeties, instead of oupled pe-unit-length iuit paametes. The omplete TDR esponse is effetively modeled by a non-unifom tansmission line using the non-eusive ABCD matix appoah. Appoahes to alibate line paametes and pefom TDR measuements based upon suh model ae intodued with an example on dieleti spetosopy. TDR modeling in tems of deoupled physial paametes and non-eusive algoithm allows moe onvenient alibation of line paametes and failitates intepetation of TDR measuements. KEY WORDS: time domain efletomety, tansmission line theoy, tansmission line measuements, dieleti measuements, spetosopy, soil measuements. INTRODUCTION Time domain efletomety (TDR) is a measuement tehnique based upon tansmission line theoy. The measuement utilizes able ada (a pulse-eeive devie fomally known as time domain efletomete, also abbeviated as TDR) and sensing waveguides. It has wide appliations anging fom defomation monitoing (Lin C-P et al., 29; Lin M W et al., 25; Dowding et al., 22, 1988), level measuement (Cataldo et al., 28a, b, 27; Di Sante, 25; Nemaih, 21), to measuement of dieleti pemittivity (Heimovaaa, 1994; Topp et al., 198; Clakson et al., 1977). The pulse geneato sends an eletomagneti pulse along a lead able and the sensing waveguide, whih then diets the eletomagneti wave into the mateial unde test o envionment to be monitoed. The sensing waveguide an be a oaxial able (e.g., fo monitoing of loalized shea defomation) o a speiallydesigned multi-onduto waveguide (e.g., fo monitoing of dieleti pemittivity, eletial ondutivity, and mateial level). Impedane hange ous when the measuement waveguide is subjeted to defomation o eletial popety of the suounding mateial hanges. Refletions fom the impedane hange ae eoded and used to intepet engineeing paametes. Despite damati developments in eletoni sensos, wieless ommuniation, and automati data aquisition Coesponding autho: plin@mail.ntu.edu.tw China Univesity of Geosienes and Spinge-elag Belin Heidelbeg 215 Manusipt eeived May 21, 215. Manusipt aepted Septembe 7, 215. systems in the aeas of instumentation tehnologies ove the past twenty yeas, efletomety method ompetes well due to its elevant pefomane haateistis, in tems of high flexibility, high sensitivity, lage appliation onditions as well as a distibuted detetion appoah. The deployment of TDR measuements anges fom shot able and sophistiated waveguides in the laboatoy to long able and ugged, unmathed waveguides in the field. The TDR measuement system is geneally a non-unifom tansmission line, onsisting of a lead able, onnetos and a sensing waveguide. The TDR esponse (measued efleted wavefom) is detemined by the length, oss-setional geomety, eletomagneti popeties of the insulating mateial, and esistivity of ondutos in eah unifom tansmission line setion. TDR typially measues one of the above physial popeties in the non-unifom line while the emaining ae alibated and kept onstant. Fo example, hange in oss-setional geomety of the sensing able is detemined fo slope monitoing using oaxial ables, length of etain unifom setion is detemined fo level measuement, and dieleti popety of the mateial in the sensing setion is detemined fo mateial haateization. A TDR esponse an be ompliated due to vaious phenomena, inluding dieleti dispesion (fequeny-dependent pemittivity), ondutive loss, esistive loss, as well as multiple efletions. Thee is a gowing demand fo modeling of TDR wavefom to bette undestand the measuement system and seve as the fowad model fo model-based invesion (Lin et al., 29; Cataldo et al., 28a; Lin, 23; Dowding et al., 22; Feng et al., 1999; Fiel and O, 1999; Heimovaaa, 1994; Yanuka et al., 1988). The TDR esponse an be modeled by finite element o Lin, C.-P., Tang, S.-H., Lin, C.-H., et al., 215. An Impoved Modeling of TDR Signal Popagation fo Measuing Complex Dieleti Pemittivity. Jounal of Eath Siene, 26(6): doi:1.17/s
2 828 Chih-Ping Lin, Sh-Hong Tang, Chun-Hung Lin and Chih-Chung Chung finite diffeene appoah (Bolvin and Chambael, 27; utilizes a moe effiient appoah based upon the tansmission line theoy (Paul, 1994; Ramo et al., 1994). Some onsideed multiple efletions but negleting dieleti dispesion (Yanuka et al., 1988), wheeas othes foused on dieleti dispesion (inluding ondutive loss) by minimizing impedane mismathes (Fiel and O, 1999; Heimovaaa, 1994). Moe eently, both multiple efletions and dieleti dispesion have been onsideed (Lin, 23; Feng et al., 1999). The effet of onduto esistane has mostly been negleted due to ompliation in fomulation and alibation of esistane fato. But its impotane and a moe ompehensive modeling of TDR wavefom have been eently pesented (Lin and Tang, 27; Lin et al., 27). In fomulating the solution of tansmission line equation, on the othe hand, most studies have unanimously utilized the lumped iuit model in tems of pe-unit-length esistane, ondutane, indutane, and apaitane. These lumped-iuit paametes ae all funtions of the physial popeties of the tansmission line (i.e., the oss-setional geomety and popety of ondutos and eletomagneti popety of the medium suounding the ondutos) and hene inte-oelated, obsuing the poess of system alibation and model-based invesion onsideing all wave phenomena. A deoupled paameteization of the tansmission line paametes has been epoted (Lin and Tang, 27). But it should be futhe genealized. The final solution of TDR measuement in a non-unifom tansmission line was deived as a eusive equation omputing in a bottom-up fashion in tems of satte funtion S11 (Feng et al., 1999) o input impedane (Lin, 23). Tansmission line paametes of diffeent setions ae tangled up in the eusive omputation, making it diffiult to sepaate leading setions fom the sensing waveguide and esulting in a omplex alibation poedue (Cataldo et al., 29). This pape is aimed to fomulate a moe geneal and non-eusive solution of tansmission line equation in tems of independent physial popeties and ompletely model TDR esponse aounting fo all wave phenomena inluding multiple efletion, dieleti dispesion, and onduto esistane. The alibation of system paametes and TDR measuement based upon suh model ae intodued with an example on dieleti spetosopy. 1 DECOUPLED FORMULATION OF TRANSMISSION LINE EQUATIONS The govening equations fo the tansmission line (i.e., the telegaph equations) in the phaso fom (i.e., in the fequeny domain) an be deived as d ( z) ( j2π fl) I( z) (1a) dz d() I z ( g j2π f) ( z) (1b) dz whee is the voltage between ondutos, I is the uent in the tansmission line, z is the position along the line, and f is the fequeny. The pe-unit-length paametes,, l, g, and, ae funtions of the oss-setional geomety of the tansmission Dowding et al., 22). But the majoity of the liteatue line and eletomagneti popeties of the media between ondutos. The eletomagneti popeties of a mateial is haateized by its dieleti pemittivity (), eletial ondutivity (), and magneti pemeability (). In geneal, these paametes ae funtions of fequeny. The dieleti pemittivity and magneti pemeability ae typially expessed elative to that of fee spae, =/ and =/, in whih is the elative pemittivity, is the elative pemeability, = F/m is the vauum pemittivity, and =4 1-7 H/m is the vauum pemeability. The pe-unit-length paametes Ramo et al. (1994) an be witten in genei foms fom as s ( f) (2a) l (2b) 2πf g (2) ( f) (2d) whee s () is the sufae esistivity of onduto, (m) is the geometi fato fo esistane, and (dimensionless) is the geometi fato fo indutane, ondutane, and apaitane. The sufae esistivity is a funtion of fequeny and an be appoximated by s = s 1-7 f 1/2 () fo good ondutos, whee s (s.5 ) is the haateisti of the onduto fo the skin effet. alues of s fo vaious typial ondutos an be found in Ramo et al. (1994). The genei foms of pe-unit-length paametes in Eq. (2) ae impotant fo deiving deoupled fomulation. The geneal solution of Eq. (1) an be witten as (Ramo et al., 1994) z e e z z (3a) z (3b) z e e I z whee + and ae the two unknown onstants in the geneal solution, is the popagation onstant, and is the haateisti impedane. The tems and an be witten as j2π flg j2π f (4a) j2πfl g j2πf (4b) Equation (4) an be found in most textbooks on eletomagneti waves. But the pe-unit-length paametes,, l, g, and an be analytially detemined fom oss-setional geomety only fo speial tansmission lines (i.e., oaxial lines). Futhemoe, these paametes ae not independent, as depited in (2). To deive the solution in tems of un-oupled paametes, substitute (2) into (4) j2πf 1 1 j s j2 f j2πf j2πf (5a)
3 An Impoved Modeling of TDR Signal Popagation fo Measuing Complex Dieleti Pemittivity 829 j2πf 1 1 js j2πf j2πf j2πf (5b) Binging out ommon fatos and letting ε jσ/2πfε =ε, Eq. (5) an be eaanged as j2πf 1 j s 2πf 1 1 s 1 j 2πf (6a) (6b) Bette-paameteized foms fo and an be futhe expessed as j2πf A (7a) v p A (7b) whee v is the speed of light, j /(2π f) is the omplex dieleti pemittivity, p is the geometi impedane defined as the haateisti impedane in fee spae, and A is the esistane oetion fato aounting fo the effet of able esistane. p and A an be witten out as 1 p (8a) s R A (1 j) (1 ) 7 j 2π 1 f f (8b) Notably, p is a funtion only of the geometi fato (), and A is a funtion of magneti pemeability (equal to 1. fo most mateials), the geometi fatos, and sufae esistivity. The esistane loss fato R (s -.5 ) is defined to epesent the ombined effet of geometi fatos and sufae esistivity. Equation (7) is the geneal fom fo popagation onstant and haateisti impedane in TDR modeling. If able esistane is ignoed (i.e., s =), A beomes 1. and and p have expessions idential to that deived in pevious studies (Lin, 23; Feng et al., 1999; Heimovaaa, 1994; Clakson et al., 1977). Futhemoe, the solution of the Telegaph equation is expessed in Eq. (7) in tems of independent physial paametes (geometi fato p, mateial popeties ε and, and esistane loss fato α R ), instead of oupled line paametes (, l, g, and ). Equation (7) is deived to expliitly sepaate effets of geometi haateisti (i.e., p ), mateial popety (i.e., ), and able esistane (i.e., ) on the popagation onstant and haateisti impedane. Sine A is fequeny dependent, R is defined as the ontolling paamete fo able esistane. Both p and R depend on waveguide dimensions ( and ). Although the geometi fatos ( and ) may be alulated theoetially fom pobe dimensions fo simple onfiguations (i.e., oaxial line), it is best and moe onvenient to dietly alibate p and R fom TDR measuements. Thus, the tansmission line is uniquely haateized by p,, and R. While length L, geometi fato p, mateial popeties ε and, and esistane loss fato α R epesent the physial paametes of a tansmission line, the popagation onstant () and haateisti impedane ( ) ae the two esultant paametes in the solution of the tansmission line equation. The popagation onstant ontols the speed and deay of a wave taveling along the line. Fo a line with setions of diffeent haateisti impedanes, efletion and tansmission of wave will ou at the setion intefaes. The phase shift of wave popagation is a ombined effet of L and, while the efletion magnitude is affeted by p and. Theefoe, all the physial paametes annot be uniquely detemined by invesion of the measued efleted wavefom alone. One of the thee paametes (L, p, ) needs to be known so that the othe two paametes and R an be detemined fom the measued TDR wavefom. This holds fo both system alibation and TDR measuements. Fo leading setions pio to the pobe, the exat values of (L, p, ) ae not neessay as long as they have the same effet on measued wavefom. Typially, L an be dietly estimated and p and an be alibated by mathing the measued wavefom. To peisely detemine the pobe geometi paametes L and p, mateials of known dieleti popety an be used to alibate L and p. Duing measuements, eithe one o two of the vaiables (L, p, ) ae vaiant and taget(s) of TDR measuements. Fo example, in level measuements, L is hanging while p and ae invaiant. It is also possible to simultaneously measue hanging L and while p emains onstant (Cataldo et al., 28a, b, 27). In mateial haateization, is to be measued while L and p of the pobe emains onstant. 2 NON-RECURSIE MODELING OF TDR MEASU- REMENTS Conside a TDR measuement system shown in Fig. 1 fo dieleti haateization of mateials. The mold is fist filled with mateials to be measued and the ental od with a onneto ap is then inseted to fom a oaxial ell. A long lead able is used to epesent possible field deployment, in whih the oaxial pobe is eplaed by a two-od o thee-od waveguide. Suh a TDR measuement system onsists of a lossy non-unifom tansmission line, whih an be modeled as a asade of unifom setions as shown in Fig. 2. The onneto ap shown in Fig. 1 is extemely thin; hene a minimum of two setions an be used to model the TDR measuement system, one fo the lead able and the othe fo the pobe setion. Additional setions an be added if the onneto ap is thik and ontains mismathes. Assuming =1 fo all setions, eah unifom tansmission line setion is haateized by thee independent paametes, p, ε, and α R, espetively epesenting the effet of oss-setional geomety, mateial popety, and line esistane loss. Theefoe, eah unifom setion is haateized by L i, p,i,,i, and R,i. Equations (3) and (7) epesent the geneal solution fo a unifom tansmission line. The unknown onstants in Eq. (3) an
4 83 Chih-Ping Lin, Sh-Hong Tang, Chun-Hung Lin and Chih-Chung Chung Figue 1. Configuations of the TDR measuement system and alibated paametes. Figue 2. Repesenting a non-unifom line as a asade of unifom setions, eah uniquely haateized by its setion length (L i ), geometi impedane ( p,i ), dieleti popety (,i ), and esistane loss fato ( R,i ). The effetive teminal input impedane in (z i ) is defined as the equivalent impedane when looking into the iuit at position z i. be detemined by applying bounday onditions. But fo non-unifom tansmission line as shown in Fig. 2, waves an be efleted and tansmitted at the intefaes of the setions, adding omplexity to the solution. Feng et al. (1999) and Lin (23) intodued a multi-setion wave popagation model based on the onept of input impedane, in whih the oveall input impedane of the measuement system is deived eusively in a bottom-up fashion stating fom the teminal impedane L (equal to in an open loop). ( z ) in n L ( z ) in n1, n ( z ) in n2, n1 () L, ntanh nln n, Ltanh nn l ( z ) tanh l ( z )tanh l in n1, n1 n1 n1 n, 1 in n1 n1 n1 ( z ) tanh l in 1,1 1 1 in,1,1 in( z 1)tanh 1 l 1 (9) whee the input impedane in (z i ) is defined as the equivalent impedane when looking into the iuit at position z i ;,i, i, and l i, ae the haateisti impedane, popagation onstant, and length of eah setion, espetively; and L is the teminal impedane. The whole eusive omputation has to be epeated fo eah wavefom simulation. A moe staightfowad appoah is utilized in this study to avoid epeating omputations in a model-based invesion and sum up effets fom all leading setions fo possible oveall alibation of line paametes. Seveal popagation maties have been intodued fo the satteing poblem (i.e., wave popagation in a non-unifom media) in geophysis and eletomagnetis, suh as the satteing matix, the tansfe matix, and the ABCD matix (Klein and Swift, 1977; Claebout, 1976; Potonotaios and Wing, 1967). In the ontext of two-pot measuement, Goiti and Slob (25) adopted the tansfe matix to expliitly sepaate the sample holde fom the tansition setions. Howeve, fo TDR modeling, the ABCD matix is found to be the simplest. It an be eadily explained in the ase of a unifom line. The voltage and uent at the two ends (z=, z=l) an be obtained fom Eq. (3) as
5 An Impoved Modeling of TDR Signal Popagation fo Measuing Complex Dieleti Pemittivity I l l e e l l l e e I l (1a) (1b) The elationship between the line voltage/uent at z= and the line voltage/uent at z=l an be obtained by equating + and in Eq. (1) as whee l sinh l osh l 1 I l sinh l osh l I os h l (11) l l e e (12a) 2 l l e e sin h l (12b) 2 Theefoe, + and ae eliminated by putting the solution Eq. (3) in the fom of Eq. (11). The 22 matix elating voltage and uent at two ends is alled the ABCD matix (). l sinh l l l osh A B 1 C D sinh osh (13) This epesentation elates the line voltage and uent at one end of line, z=, to the line voltage and uent at the othe end of the line, z=l. Fo a unifom tansmission line, the voltage and uent at the two ends (fou vaiables) an be solved by Eq. (11) and two bounday onditions. In geneal, the ABCD matix an elate the line voltages and uents of the two ends of any ith unifom setion of a non-unifom tansmission line by eplaing the l with l i in Eq. (13) z i z i 1 i I zi I zi 1 (14) The oveall ABCD matix () of the entie line is the matix that elates the voltages and uents at the two ends of the entie line. l I l I (15) whee an be obtained as the podut (in the appopiate ode) of the ABCD maties of the individual unifom setions as A B n n 1 1 C D (16) Now that the ABCD matix that elating the voltage and uent at the two ends has been obtained, teminal onstaints an be inopoated to solve fo teminal voltages and uents. At the soue end, z=, thee is an independent voltage soue S and a soue impedane S. The line is teminated at the load end, z=l, with a load impedane L. Thus, the bounday onditions (teminal onstaints) an be witten as () I() (17a) S S l () Il () (17b) L The fou unknowns (teminal voltages and uents) an be solved by fou equations, (15) to (17). The solution of patiula inteest is () in a TDR measuement. DB L L s L DBC A S (18) whee L is the load impedane, S is the soue impedane, S is the soue voltage, and A, B, C, and D ae fom Eq. (16). One the oveall ABCD (hain) matix of the entie line is obtained by use of Eq. (16), the sampling voltage an be omputed by Eq. (18). The solution aounts fo multiple efletions (by Eq. (16)) and able esistane (by Eq. (7)) and an aommodate dieleti dispesion and eletial ondutivity by fomulations in the fequeny domain. Sine all the above fomulations ae in the fequeny domain, the wavefom simulation would stat with a Fouie tansfom of the soue voltage signal. Equation (18) is then used to ompute the TDR esponse (i.e., sampling voltage) in the fequeny domain. And finally a Fouie invese tansfom of () gives the simulated TDR esponse in the time domain. 3 CALIBRATION OF TDR MEASUREMENT SYSTEM The sensing setion of a TDR measuement system is often times the last setion (n) shown in Fig. 2. Othe leading setion onsists of onnetos, leading able, and loal impedane mismathes within the TDR devie. To alibate the measuement system is equivalent to detemining L i, p,i,,i, and R,i fo i=1~n 1. As disussed ealie, it should be noted that diffeent ombinations of (L, p, ) an esult in the same TDR wavefom. One of the thee paametes (L, p, ) needs to be known o assumed so that the othe two paametes and R an be alibated fom the measued TDR wavefom. Calibation of these line paametes utilizes model-based invesion by wavefom mathing. The numbe of unknowns ineases with the numbe of unifom setions. When the numbe of setions is lage, the tansmission line maybe divided into seveal detahable subsetions and wavefoms ae measued by suessively adding up the subsetions. Line paametes of eah subsetion an then suessively alibated to avoid lage numbe of unknowns in the invesion. When n is lage, the alibation of the measuement system beomes a fomidable and tedious task. Futhemoe, it is often diffiult to detemine the appopiate numbe of setions (n) when paasiti efletions aused by loal impedane mismathes and impefet onnetos ae onsideed. An altenative effiient alibation poedue is devised heein based on the deoupled and non-eusive fomulation. The effets of all leading setions (i=1~n 1) may be summed up by a system ABCD matix, as shown in Fig. 3. And the sensing setion an be sepaated fom the system and teated as a new load
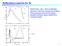
6 832 Chih-Ping Lin, Sh-Hong Tang, Chun-Hung Lin and Chih-Chung Chung Figue 3. The sensing setion is sepaated fom the system and teated as a load impedane in (z n-1 ); and the effets of all leading setions (i=1~n 1) ae summed up by a system ABCD matix. impedane L = in (z n-1 ). Equation (18) of the TDR esponse () is ewitten as in( zn 1) D B S in( zn 1) DBs in ( zn 1) C A in( zn 1) ( B/ D) in( zn 1) ( B/ D) s in( zn 1)( C / D) ( A/ D) (19) It should be noted that A, B, C, and D annot be uniquely detemined using only the efletion measuement without tansmission data. But all that ae needed fo TDR wavefom omputation ae the atios A/D, B/D, and C/D as indiated in Eq. (19). These atios an be alibated by shot-open-load (SOL) measuements (i.e., a measuement by shoting at the beginning of the sensing setion, a measuement by emoving the sensing setion, and a measuement of known dieleti pemittivity in the last sensing setion). Regadless the total numbe of setions, the atios A/D, B/D, and C/D ontain all popagation effets within the leading setions. 4 EXAMPLE-CALIBRATION AND MEASUREMENT BASED UPON TDR MODELING As an example shown in Fig. 1, the line paametes fo the leading able and the oaxial pobe need to be detemined befoe the system an be used fo measuing dieleti popety. The measuement ell was manufatued at the time when thee was no quik solution fo alibation of multiple impedane mismathes. It was puposely onstuted with an ulta thin ap to minimize impedane mismathes. Theefoe, the measuement system an be appoximated by a minimum of two setions, a lead able and the pobe setion. This measuement ell is by no means the best design fo soil measuement and thee wee no othe diet measuements (e.g., veto netwok analyze) available fo diet validation of the measued dieleti values. The following exeise is to demonstate dieleti measuement based upon TDR modeling using the new fomulation pesented. Line paametes fo the two unifom setions ae deoupled and epesented by distint physial paametes L, p,, and R, espetively epesenting length, geometi impedane, mateial popety, and line esistane, as illustated in Fig. 2. Sine only two setions ae involved in this exeise, the line paametes ae dietly alibated. The length of the lead able is dietly measued (i.e., L=1 m) and a mateial of S known dieleti popety (i.e., wate) in the pobe setion is used to obtain measued wavefom fo alibating the emaining paametes (i.e., eah setion has thee unknowns). Fo the example shown in Fig. 1, six unknown paametes ( p,, and R in the fist setion and L, p, and R in the seond setion) ae dietly alibated using one measued wavefom in tap wate. The dieleti pemittivity of wate is well known fom the liteatue (Klein and Swift, 1977) and the eletial ondutivity is dietly measued by a ondutivity mete. The devie used fo TDR measuement is a Tektonix 152C. TDR wavefom simulations and alibation of the system paametes by optimization wee implemented using Matlab. The alibated paametes ae listed in Fig. 1. The pedited wavefom using the alibated paametes mathes vey well with the measued wavefom, as shown in Fig. 4. Due to the lak of simple method to aount fo able esistane, the effet of able esistane was mostly negleted in dieleti haateization based on TDR. When ompaed with the pedited wavefom negleting able esistane ( R =), also shown in Fig. 4, signifiant effet of able esistane on the TDR wavefom is evealed. The esistane loss fato R affets the wavefom though the fequeny-dependent tem A. The ise time of the efleted pulse and the plateau of the step pulses inease as R ineases. The deoupled paameteization makes it easy to onside and alibate able esistane. This is extemely useful sine TDR is ineasingly used in the field Figue 4. Simulated and measued wavefom of tap wate with alibated paametes, whee measuing pobe is onneted to 1 m lead able.
7 An Impoved Modeling of TDR Signal Popagation fo Measuing Complex Dieleti Pemittivity 833 onditions whee long ables ae ommon. One the line paametes ae alibated, the TDR system in Fig. 1 an be used fo dieleti haateization of mateials. Thee diffeent soil samples wee pepaed at about the same volumeti wate ontent to demonstate the dieleti spetosopy of soils. Table 1 listed the soil type, bulk dy density (weight of soil patiles divided by the total volume), and volumeti wate ontent fo the thee samples. The appaent dieleti onstant fom time-domain tavel time analysis using the tangent line method is also listed in Table 1 to povide efeene data fo the following dieleti spetosopy. Afte the system alibation, the only unknown is. The omplex dieleti pemittivity an be dietly solved fo eah fequeny using Eq. (19). The esults ae shown in Fig. 5. The dieleti values at high fequenies ae lose to the appaent dieleti onstants listed in Table 1 as expeted. Figue 6 shows the pe dited wavefoms ompaed with the measued wavefoms. The exellent math between the simulated and measued wavefoms in Fig. 6 indiates that the model is eliable and auate fo the TDR measuement. Figue 5 shows simila dieleti pemittivity at fequenies geate than 1 MHz fo all soil types at about the same volumeti wate ontent, but distint dieleti elaxation phenomena an be obseved at lowe fequenies. Theefoe, the dieleti pemittivity at high fequenies an be used to estimate soil wate ontent, wheeas the dieleti dispesion at lowe fequeny is elated to patile size and wate-patile inteation. These measuements ae useful fo haateization of poous mateials. It is noted that measuements at fequeny geate than 2 MHz ae eoneous fo the high plastiity lay (bentonite). This is beause the lay is moe ondutive (lossy) and the signal to noise atio is downgaded at highe fequenies. The dieleti measuement may be altenatively onduted by Table 1 The bulk dy density (ρ d ), volumeti wate ontent (θ), and appaent dieleti onstant (K a ) of soil samples Soil type ρ d (g/m 3 ) θ K a Ottawa sand Silty sand Bentonite Figue 5. Real pat and imaginay pats of omplex dieleti pemittivity fo the thee soil samples. Im. Imaginay pat; Re. eal pat. Figue 6. Deoupling wave popagation model fo TDR wavefom simulation. onstaining the omplex dieleti pemittivity (f) via some mathematial model and pefoming invesion of the model paametes in the time domain by wavefom mathing. It is undestood that epesentation of the measuement system in Fig. 1 by two unifom segments is only an appoximation sine possible mismathes in the leading setion and finging effet due to geomety hange at the beginning of the sensing setion is negleted. Futhe impovements patiulaly at high fequenies may be ahieved by avoiding abupt geomety hange at the intefae between the leading setion and the sensing waveguide. Mismathes and finging effets within the leading setion an then be taken into aount by oveall alibation using Eq. (19) and SOL measuements. 5 CONCLUSION Time domain efletomety (TDR) is a measuement tehnique based upon tansmission line theoy. It is finding moe and moe appliations in engineeing measuements and monitoing in both laboatoy and field woks, diving the demand fo an auate TDR wave popagation model. In this study, the solutions of tansmission line equation wee efomulated in tems of independent physial popeties paameteized by geometi impedane ( p ), mateial popety ( and ), and esistane loss fato ( R ), instead of inte-elated iuit paametes (, l, g, and ). The deoupled paameteization of tansmission line equations allows moe onvenient alibation of line paametes and failitates intepetation of TDR measuements. When ombined with the ABCD matix appoah, the non-unifom tansmission line in a TDR measuement system an be effiiently modeled aounting fo multiple efletions, dieleti dispesion, ondutive loss, and able esistane all togethe. In patiula, the effet of able esistane whih was often ovelooked an have signifiant effet on the measued TDR wavefom. Effetive appoahes to alibate line paametes in a TDR system and pefom TDR measuements wee intodued. An example was given to demonstate dieleti spetosopy based upon TDR modeling. The exellent math between the simulated and measued wavefoms indiates that the model is eliable and auate. The intodued fomulation and modeling appoah povides a simple, yet theoetially sound foundation fo vaious engineeing measuements based on TDR.
8 834 Chih-Ping Lin, Sh-Hong Tang, Chun-Hung Lin and Chih-Chung Chung ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Funding fo this eseah was patly povided by the Envionmental Potetion Administation, Taiwan. REFERENCES CITED Bolvin H., Chambael, A., 27. Eletomagneti Wave Popagation in Polaizable Wet Media: Appliation to a TDR Pobe. Measuement Siene and Tehnology, 18: Cataldo, A., Catainui, L., Taione, L., et al., 29. A Combined TD-FD Method fo Enhaned Refletomety Measuements in Liquid Quality Monitoing. IEEE Tansations on Instumentation and Measuement, 58(1): Cataldo, A., Taione, L., Attivissimo, F., et al., 27. A TDR Method fo Real-time Monitoing of Liquids. IEEE Tansations on Instumentation and Measuement, 56(6): Cataldo, A., Taione, L., Attivissimo, F., et al., 28a. Simultaneous Measuement of Dieleti Popeties and Levels of Liquids Using a TDR Method. Measuement, 41(3): Cataldo, A., Taione, L., allone, M., et al., 28b. Unetainty Estimation in Simultaneous Measuements of Levels and Pemittivities of Liquids Using TDR Tehnique. IEEE Tansations on Instumentation and Measuement, 57(3): Claebout, J., Fundamentals of Geophysial Data Poessing. MGaw-Hill, New Yok Clakson, T. S., Glasse, L., Tuxwoth, R. W., et al., An Appeiation of Expeimental Fatos in Time-Domain Spetosopy. Advanes in Moleula Relaxation Poesses, 1(3): Di Sante, R., 25. Time Domain Refletomety-Based Liquid Level Senso. Review of Sientifi Instuments, 76(9): 9517 Dowding, C. H., Su, M. B., O Conno, K. M., Piniples of Time Domain Refletometomety Applied to Measuement of Rok Mass Defomation. Intenational Jounal of Rok Mehanis & Mining Sienes, 25(5): Dowding, C. H., Summes, J. A., Taflove, A., et al., 22. Eletomagneti Wave Popagation Model fo Diffeentiation of Geotehnial Distubanes along Buied Cables. Geotehnial Testing Jounal, 25(4): Feng, W., Lin, C.-P., Deshamps, R. J., et al., Theoetial Model of a Multisetion Time Domain Refletomety Measuement System. Wate Resoues Reseah, 35(8): Fiel, R., O, D., Fequeny Analysis of Time-Domain Refletomety (TDR) with Appliation to Dieleti Spetosopy of Soil Constituents. Geophysis, 64(3): Goiti, A. G., Slob, E. C., 25. A New Tool fo Auate S-Paametes Measuements and Pemittivity Reonstution. IEEE Tansations on Geosiene and Remote Sensing, 43(8): Heimovaaa, T. J., Fequeny Domain Analysis of Time Domain Refletomety Wavefoms: 1. Measuement of the Complex Dieleti Pemittivity of Soils. Wate Resoues Reseah, 3(2): Klein, L. A., Swift, C. T., An Impoved Model fo the Dieleti Constant of Sea Wate at Miowave Fequenies. IEEE Tansations on Antennas and Popagation, 25(1): Lin, C.-P., 23. Analysis of a Non-Unifom and Dispesive Time Domain Refletomety Measuement Systems with Appliation to the Dieleti Spetosopy of Soils. Wate Resoues Reseah, 39(1): 112 Lin, C.-P., Chung, C.-C., Tang, S. H., 27. Auate Time Domain Refletomety Measuement of Eletial Condutivity Aounting fo Cable Resistane and Reoding Time. Soil Siene Soiety of Ameia Jounal, 71(4): Lin, C.-P., Tang, S.-H., 27. Compehensive Wave Popagation Model to Impove TDR Intepetations fo Geotehnial Appliations. Geotehnial Testing Jounal, 3(2): 9 97 Lin, C.-P., Tang, S.-H., Lin, W.-C., et al., 29. Quantifiation of Cable Defomation with TDR: Impliations to Loalized Shea Defomation Monitoing. Jounal of Geotehnial and Geoenvionmental Engineeing, 135(1): Lin, M. W., Thadui, J., Abatan, A. O., 25. Development of an Eletial Time Domain Refletomety (ETDR) Distibuted Stain Senso. Measuement Siene and Tehnology, 16(7): Nemaih, C. P., 21. Time Domain Refletomety Liquid Level Sensos. IEEE Tansations on Instumentation and Measuement, 4(4): 4 44 Paul, C. R., Analysis of Multi-Conduto Tansmission Lines. John Wiley, New Yok Potonotaios, E. N., Wing, O., Analysis and Intinsi Popeties of the Geneal Non-Unifom Tansmission Line. IEEE Tansations on Miowave Theoy and Tehniques, 15: Ramo, S., Whinney, J. R., an Duze, T., Fields and Waves in Communiation Eletonis, 3d Ed.. John Wiley, New Yok Topp, G. C., Davis, J. L., Annan, A. P., 198. Eletomagneti Detemination of Soil Wate Content and Eletial Condutivity Measuement Using Time Domain Refletomety. Wate Resoues Reseah, 16(3): Yanuka, M., Topp, G. C., egelin, S., et al., Multiple Refletion and Attenuation of Time Domain Refletomety Pulses: Theoetial Consideations fo Appliations to Soil and Wate. Wate Resoues Reseah, 24(7):
Investigation of Magnitude and Phase Errors in Waveguide Samples for the Nicolson-Ross-Weir Permittivity Technique
 Univesity of New Hampshie Univesity of New Hampshie Sholas' Repositoy Maste's Theses and Capstones Student Sholaship Winte 016 Investigation of Magnitude and Phase Eos in Waveguide Samples fo the Niolson-Ross-Wei
Univesity of New Hampshie Univesity of New Hampshie Sholas' Repositoy Maste's Theses and Capstones Student Sholaship Winte 016 Investigation of Magnitude and Phase Eos in Waveguide Samples fo the Niolson-Ross-Wei
AVS fiziks. Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT-JAM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICAL SCIENCES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation. One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation. One example is to onside aousti adiation
COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE
 COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE To see how the piniple behind the analysis of vaiane method woks, let us onside the following simple expeiment. The means ( 1 and ) of
COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE To see how the piniple behind the analysis of vaiane method woks, let us onside the following simple expeiment. The means ( 1 and ) of
Generalized Vapor Pressure Prediction Consistent with Cubic Equations of State
 Genealized Vapo Pessue Pedition Consistent with Cubi Equations of State Laua L. Petasky and Mihael J. Misovih, Hope College, Holland, MI Intodution Equations of state may be used to alulate pue omponent
Genealized Vapo Pessue Pedition Consistent with Cubi Equations of State Laua L. Petasky and Mihael J. Misovih, Hope College, Holland, MI Intodution Equations of state may be used to alulate pue omponent
IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD
 Pogess In Eletomagnetis Reseah, PIER 58, 101 114, 006 IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD G.
Pogess In Eletomagnetis Reseah, PIER 58, 101 114, 006 IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD G.
Modeling of Vector Controlled Induction Motor in Different Reference Frames
 ISSN (Online) : 39-8753 ISSN (Pint) : 347-67 Intenational Jounal of Innovative Reseah in Siene, Engineeing and Tehnology Volume 3, Speial Issue 3, Mah 4 4 Intenational Confeene on Innovations in Engineeing
ISSN (Online) : 39-8753 ISSN (Pint) : 347-67 Intenational Jounal of Innovative Reseah in Siene, Engineeing and Tehnology Volume 3, Speial Issue 3, Mah 4 4 Intenational Confeene on Innovations in Engineeing
3D Modelling of Temperature Dependent Power Distribution During Microwave Annealing of Doped c-si
 IOSR Jounal of Eletial and Eletonis Engineeing (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 9, Issue 1 Ve. V (Feb. 2014), PP 46-51 3D Modelling of Tempeatue Dependent Powe Distibution Duing
IOSR Jounal of Eletial and Eletonis Engineeing (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 9, Issue 1 Ve. V (Feb. 2014), PP 46-51 3D Modelling of Tempeatue Dependent Powe Distibution Duing
Experiment 1 Electric field and electric potential
 Expeiment 1 Eleti field and eleti potential Pupose Map eleti equipotential lines and eleti field lines fo two-dimensional hage onfiguations. Equipment Thee sheets of ondutive papes with ondutive-ink eletodes,
Expeiment 1 Eleti field and eleti potential Pupose Map eleti equipotential lines and eleti field lines fo two-dimensional hage onfiguations. Equipment Thee sheets of ondutive papes with ondutive-ink eletodes,
PROPAGATION OF PHOTON IN RESTING AND MOVING MEDIUM. J. Zaleśny. Institute of Physics, Technical University of Szczecin, A b s t r a c t
 PROPGTION OF PHOTON IN RESTING ND MOVING MEDIUM J Zaleśny Institute of Physis, Tehnial Univesity of Szzein, l 30 70 Piastów 48, Szzein, Poland b s t a t The popagation of photon in a dieleti may be desibed
PROPGTION OF PHOTON IN RESTING ND MOVING MEDIUM J Zaleśny Institute of Physis, Tehnial Univesity of Szzein, l 30 70 Piastów 48, Szzein, Poland b s t a t The popagation of photon in a dieleti may be desibed
OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM
 OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM M. Hiaki, K. Takamasu and S. Ozono Depatment of Peision Engineeing, The Univesity of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan Abstat: In this pape, we popose
OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM M. Hiaki, K. Takamasu and S. Ozono Depatment of Peision Engineeing, The Univesity of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan Abstat: In this pape, we popose
Experiment I Voltage Variation and Control
 ELE303 Electicity Netwoks Expeiment I oltage aiation and ontol Objective To demonstate that the voltage diffeence between the sending end of a tansmission line and the load o eceiving end depends mainly
ELE303 Electicity Netwoks Expeiment I oltage aiation and ontol Objective To demonstate that the voltage diffeence between the sending end of a tansmission line and the load o eceiving end depends mainly
Physics 218, Spring March 2004
 Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
Vision Sensor. Vision. (Phase 1) pre-shaping. Actuator. Tactile Sensor. Vision. (Phase 2) shaping. Actuator. Tactile Sensor.
 Optimal Gasping using Visual and Tatile Feedbak Akio NAMIKI Masatoshi ISHIKAWA Depatment of Mathematial Engineeing and Infomation Physis Univesity of Tokyo Tokyo 3, Japan namik@k.t.u-tokyo.a.jp Abstat
Optimal Gasping using Visual and Tatile Feedbak Akio NAMIKI Masatoshi ISHIKAWA Depatment of Mathematial Engineeing and Infomation Physis Univesity of Tokyo Tokyo 3, Japan namik@k.t.u-tokyo.a.jp Abstat
From E.G. Haug Escape Velocity To the Golden Ratio at the Black Hole. Branko Zivlak, Novi Sad, May 2018
 Fom E.G. Haug Esape eloity To the Golden Ratio at the Blak Hole Banko Zivlak, bzivlak@gmail.om Novi Sad, May 018 Abstat Esape veloity fom the E.G. Haug has been heked. It is ompaed with obital veloity
Fom E.G. Haug Esape eloity To the Golden Ratio at the Blak Hole Banko Zivlak, bzivlak@gmail.om Novi Sad, May 018 Abstat Esape veloity fom the E.G. Haug has been heked. It is ompaed with obital veloity
Dissolution of Solid Particles in Liquids: A Shrinking Core Model
 Wold Aademy of Siene, Engineeing and Tehnology 5 9 Dissolution of Solid Patiles in Liquids: A Shining oe Model Wei-Lun Hsu, Mon-Jyh Lin, and Jyh-Ping Hsu Astat The dissolution of spheial patiles in liquids
Wold Aademy of Siene, Engineeing and Tehnology 5 9 Dissolution of Solid Patiles in Liquids: A Shining oe Model Wei-Lun Hsu, Mon-Jyh Lin, and Jyh-Ping Hsu Astat The dissolution of spheial patiles in liquids
not to be republished NCERT ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Chapter Eight MCQ I
 Chapte Eight ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES MCQ I 8 One equies ev of enegy to dissoiate a abon monoxide moleule into abon and oxygen atoms The minimum fequeny of the appopiate eletomagneti adiation to ahieve the
Chapte Eight ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES MCQ I 8 One equies ev of enegy to dissoiate a abon monoxide moleule into abon and oxygen atoms The minimum fequeny of the appopiate eletomagneti adiation to ahieve the
Photographing a time interval
 Potogaping a time inteval Benad Rotenstein and Ioan Damian Politennia Univesity of imisoaa Depatment of Pysis imisoaa Romania benad_otenstein@yaoo.om ijdamian@yaoo.om Abstat A metod of measuing time intevals
Potogaping a time inteval Benad Rotenstein and Ioan Damian Politennia Univesity of imisoaa Depatment of Pysis imisoaa Romania benad_otenstein@yaoo.om ijdamian@yaoo.om Abstat A metod of measuing time intevals
Red Shift and Blue Shift: A realistic approach
 Red Shift and Blue Shift: A ealisti appoah Benhad Rothenstein Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa, Physis Dept., Timisoaa, Romania E-mail: benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om Coina Nafonita Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa,
Red Shift and Blue Shift: A ealisti appoah Benhad Rothenstein Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa, Physis Dept., Timisoaa, Romania E-mail: benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om Coina Nafonita Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa,
An analytic calculation method on air gap flux in permanent magnet. brushless DC motor with ironless rotor
 Intenational Confeene on Enegy and Envionmental Potetion ICEEP 6 An analyti alulation method on ai gap flux in pemanent magnet bushless DC moto with ionless oto Xinghua Wang,Yaolong Sheng andshugang Zhao,,
Intenational Confeene on Enegy and Envionmental Potetion ICEEP 6 An analyti alulation method on ai gap flux in pemanent magnet bushless DC moto with ionless oto Xinghua Wang,Yaolong Sheng andshugang Zhao,,
Eddy Currents and Magnetic Calibrations in LDX using a Copper Plasma. D.P. Boyle, PPPL M.E. Mauel, D.T. Garnier, Columbia J.
 Eddy Cuents and Magneti Calibations in LDX using a Coppe Plasma D.P. Boyle PPPL M.E. Mauel D.T. Ganie Columbia J. Kesne MIT PSFC Coppe Plasma Oveview LDX Magnetis Goals Calibate magneti diagnostis positions
Eddy Cuents and Magneti Calibations in LDX using a Coppe Plasma D.P. Boyle PPPL M.E. Mauel D.T. Ganie Columbia J. Kesne MIT PSFC Coppe Plasma Oveview LDX Magnetis Goals Calibate magneti diagnostis positions
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation One example is to onside aousti adiation
Extra Examples for Chapter 1
 Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
Chapter 4. Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals
 Chapte 4 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals 1 Intodution Disete-time signals most ommonly ou as epesentations of sampled ontinuous-time signals. Unde easonable onstaints, a ontinuous-time signal an be
Chapte 4 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals 1 Intodution Disete-time signals most ommonly ou as epesentations of sampled ontinuous-time signals. Unde easonable onstaints, a ontinuous-time signal an be
THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON DROPWISE CONDENSATION IN PLATE HEAT EXCHANGERS
 Abstat THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON DROPWISE CONDENSATION IN PLATE HEAT EXCHANGERS V. Bendt, S. Zunft and H. Mülle-Steinhagen Geman Aeospae Cente (DLR), Stuttgat, Gemany This pape desibes the
Abstat THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON DROPWISE CONDENSATION IN PLATE HEAT EXCHANGERS V. Bendt, S. Zunft and H. Mülle-Steinhagen Geman Aeospae Cente (DLR), Stuttgat, Gemany This pape desibes the
Special Relativity in Acoustic and Electromagnetic Waves Without Phase Invariance and Lorentz Transformations 1. Introduction n k.
 Speial Relativit in Aousti and Eletomagneti Waves Without Phase Invaiane and Loentz Tansfomations Benhad Rothenstein bothenstein@gmail.om Abstat. Tansfomation equations fo the phsial quantities intodued
Speial Relativit in Aousti and Eletomagneti Waves Without Phase Invaiane and Loentz Tansfomations Benhad Rothenstein bothenstein@gmail.om Abstat. Tansfomation equations fo the phsial quantities intodued
The electrified interface.
 Physial and Intefaial Eletohemisty 3 Exess negative Eletode + + + Solution + + Potential elmholtz Laye s Letue 5 Eletode/solution Intefae Exess positive x a..6 nm istane L The eletified intefae. The intefae
Physial and Intefaial Eletohemisty 3 Exess negative Eletode + + + Solution + + Potential elmholtz Laye s Letue 5 Eletode/solution Intefae Exess positive x a..6 nm istane L The eletified intefae. The intefae
AN ELECTROMAGNETIC LAUNCH SYSTEM FOR UAVs
 Tehnial Sienes and Applied athematis AN ELECTROAGNETIC LAUNCH SYSTE FOR UAVs Lauian GHERAN Depatment of Eletonis and Infomatis, Faulty of Aeonautial anagement, Heni Coandă Ai Foe Aademy, Basov, Romania
Tehnial Sienes and Applied athematis AN ELECTROAGNETIC LAUNCH SYSTE FOR UAVs Lauian GHERAN Depatment of Eletonis and Infomatis, Faulty of Aeonautial anagement, Heni Coandă Ai Foe Aademy, Basov, Romania
Transmission Line Analysis of Beam Deflection in a BPM Stripline Kicker
 UCR-JC-126073 PREPRINT Tansmission ine Analysis of Beam Defletion in a BPM Stipline Kike Geoge J. Capoaso Yu Ju Chen Bian Poole This pape was pepaed fo submittal to the 1997 Patile Aeleato Confeene Vanouve,
UCR-JC-126073 PREPRINT Tansmission ine Analysis of Beam Defletion in a BPM Stipline Kike Geoge J. Capoaso Yu Ju Chen Bian Poole This pape was pepaed fo submittal to the 1997 Patile Aeleato Confeene Vanouve,
APPENDIX D COMPRESSIBILITY FACTOR EQUATIONS D.1 THE REDLICH KWONG EQUATION
 AENDIX D COMRESSIBILIY FACOR EQUAIONS D.1 HE REDLICH KWONG EQUAION he Redlih-Kwong equation is atually an equation of state. It was fomulated by Otto Redlih and Joseph N. S. Kwong in 1949 [Chemial Review
AENDIX D COMRESSIBILIY FACOR EQUAIONS D.1 HE REDLICH KWONG EQUAION he Redlih-Kwong equation is atually an equation of state. It was fomulated by Otto Redlih and Joseph N. S. Kwong in 1949 [Chemial Review
Macroelement Modelling of Laterally Loaded Piles and Pile-groups
 1 st Intenational Confeene on Natual Hazads & Infastutue 8-30 June, 016, Chania, Geee Maoelement Modelling of Lateally Loaded Piles and Pile-goups Nikos Geolymos 1 National Tehnial Univesity of Athens
1 st Intenational Confeene on Natual Hazads & Infastutue 8-30 June, 016, Chania, Geee Maoelement Modelling of Lateally Loaded Piles and Pile-goups Nikos Geolymos 1 National Tehnial Univesity of Athens
Non-Ideal Gas Behavior P.V.T Relationships for Liquid and Solid:
 hemodynamis Non-Ideal Gas Behavio.. Relationships fo Liquid and Solid: An equation of state may be solved fo any one of the thee quantities, o as a funtion of the othe two. If is onsideed a funtion of
hemodynamis Non-Ideal Gas Behavio.. Relationships fo Liquid and Solid: An equation of state may be solved fo any one of the thee quantities, o as a funtion of the othe two. If is onsideed a funtion of
PLEASE DO NOT REMOVE THIS PAGE
 Thank you fo downloading this doument fom the RMIT ReseahR Repositoy Citation: Davy, J, Mahn, J, Kaji, L, Waeing, R and Pease, J 205, 'Compaison of theoetial peditions of adiation effiieny with expeimental
Thank you fo downloading this doument fom the RMIT ReseahR Repositoy Citation: Davy, J, Mahn, J, Kaji, L, Waeing, R and Pease, J 205, 'Compaison of theoetial peditions of adiation effiieny with expeimental
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 303: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves. Fall 2007
 School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 8 Due on Oct. 19, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes.
School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 8 Due on Oct. 19, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes.
Electromagnetic Noise Source Approximation for Finite- Difference Time-Domain Modeling Using Near-Field Scanning and Particle Swarm Optimization
 Eletomagneti Noise Soue Appoximation fo Finite- Diffeene Time-Domain Modeling Using Nea-Field Sanning and Patile Swam Optimization Autho Siven, Ian, Lu, Junwei, Lewis, Andew Published 2010 Jounal Title
Eletomagneti Noise Soue Appoximation fo Finite- Diffeene Time-Domain Modeling Using Nea-Field Sanning and Patile Swam Optimization Autho Siven, Ian, Lu, Junwei, Lewis, Andew Published 2010 Jounal Title
Coupled Electromagnetic and Heat Transfer Simulations for RF Applicator Design for Efficient Heating of Materials
 Coupled Electomagnetic and Heat Tansfe Simulations fo RF Applicato Design fo Efficient Heating of Mateials Jeni Anto 1 and Raj C Thiagaajan 2 * 1 Reseache, Anna Univesity, Chennai, 2 ATOA Scientific Technologies
Coupled Electomagnetic and Heat Tansfe Simulations fo RF Applicato Design fo Efficient Heating of Mateials Jeni Anto 1 and Raj C Thiagaajan 2 * 1 Reseache, Anna Univesity, Chennai, 2 ATOA Scientific Technologies
On the indirect e ect in the Stokes±Helmert method of geoid determination
 Jounal of Geodesy (1999) 7: 87±9 On the indiet e et in the Stokes±Helmet method of geoid detemination L. E. SjoÈ beg, H. Nahavandhi oyal Institute of Tehnology, Depatment of Geodesy and Photogammety, S-100
Jounal of Geodesy (1999) 7: 87±9 On the indiet e et in the Stokes±Helmet method of geoid detemination L. E. SjoÈ beg, H. Nahavandhi oyal Institute of Tehnology, Depatment of Geodesy and Photogammety, S-100
Mass Transfer (Stoffaustausch)
 Mass Tansfe (Stoffaustaush) Examination 3. August 3 Name: Legi-N.: Edition Diffusion by E. L. Cussle: none nd 3 d Test Duation: minutes The following mateials ae not pemitted at you table and have to be
Mass Tansfe (Stoffaustaush) Examination 3. August 3 Name: Legi-N.: Edition Diffusion by E. L. Cussle: none nd 3 d Test Duation: minutes The following mateials ae not pemitted at you table and have to be
ATM Rate Based Traffic Control with Bode Principle
 4 Intenational Yuanwei Jounal Jing, of Hui Contol, Zeng, Automation, Qingshen Jing, and Systems, and Ping Yuan vol. 6, no., pp. 4-, Apil 8 AM Rate Based affi Contol with Bode Piniple Yuanwei Jing, Hui
4 Intenational Yuanwei Jounal Jing, of Hui Contol, Zeng, Automation, Qingshen Jing, and Systems, and Ping Yuan vol. 6, no., pp. 4-, Apil 8 AM Rate Based affi Contol with Bode Piniple Yuanwei Jing, Hui
Design of Brushless DC motor Drive System for Electric Vehicle Applications Yueying ZHU1,2, a, Xu CAO1,b,Shihai CUI1,2
 nd Intenational Confeene on Advanes in Mehanial Engineeing and Industial Infomatis (AMEII 016) Design of Bushless DC moto Dive System fo Eleti Vehile Appliations Yueying ZHU1,, a, Xu CAO1,b,Shihai CUI1,
nd Intenational Confeene on Advanes in Mehanial Engineeing and Industial Infomatis (AMEII 016) Design of Bushless DC moto Dive System fo Eleti Vehile Appliations Yueying ZHU1,, a, Xu CAO1,b,Shihai CUI1,
2 Parallel-Plate Transmission Line (Geometric Model) = c Assume it s a plane wave propagate in the z with polarization in y direction. d dz ~ ˆ.
 Tansmission ines 1 ntoution When the soue aiates in a ie aea, the eneg speas out. The aiate eneg is not guie an the tansmission of eneg though aiation is ineffiient. Dietive antenna oul have huge imensions
Tansmission ines 1 ntoution When the soue aiates in a ie aea, the eneg speas out. The aiate eneg is not guie an the tansmission of eneg though aiation is ineffiient. Dietive antenna oul have huge imensions
Suppose you have a bank account that earns interest at rate r, and you have made an initial deposit of X 0
 IOECONOMIC MODEL OF A FISHERY (ontinued) Dynami Maximum Eonomi Yield In ou deivation of maximum eonomi yield (MEY) we examined a system at equilibium and ou analysis made no distintion between pofits in
IOECONOMIC MODEL OF A FISHERY (ontinued) Dynami Maximum Eonomi Yield In ou deivation of maximum eonomi yield (MEY) we examined a system at equilibium and ou analysis made no distintion between pofits in
Electric Anisotropy, Magnetic Anisotropy, Uniaxial and Biaxial Materials, Bianisotropic Media (Definitions)
 leti nisotop agneti nisotop Uniaial and iaial ateials ianisotopi edia efinitions medium is alled eletiall anisotopi if tenso Note that and ae no longe paallel medium is magnetiall anisotopi if tenso Note
leti nisotop agneti nisotop Uniaial and iaial ateials ianisotopi edia efinitions medium is alled eletiall anisotopi if tenso Note that and ae no longe paallel medium is magnetiall anisotopi if tenso Note
Khmelnik S.I. Mathematical Model of Dust Whirl
 Khmelnik S.I. Mathematial Model of Dust Whil Abstat The question of the soue of enegy in a dust whil is onsideed. Atmosphei onditions annot be the sole soue of enegy, as suh dust whils exist on Mas, whee
Khmelnik S.I. Mathematial Model of Dust Whil Abstat The question of the soue of enegy in a dust whil is onsideed. Atmosphei onditions annot be the sole soue of enegy, as suh dust whils exist on Mas, whee
Natural Convection Heat Transfer Effects with Micro Finned Structures
 Natual Convetion Heat Tansfe Effets with Mio Finned Stutues Saad MAHMOUD, Raya AL-DADAH*, David ASPINWALL, Leung SOO * Coesponding autho: Tel.: ++44(0)114143513; Fax: ++44(0)114143958; Email:.k.aldadah@bham.a.uk
Natual Convetion Heat Tansfe Effets with Mio Finned Stutues Saad MAHMOUD, Raya AL-DADAH*, David ASPINWALL, Leung SOO * Coesponding autho: Tel.: ++44(0)114143513; Fax: ++44(0)114143958; Email:.k.aldadah@bham.a.uk
Gain-Scheduled Controller Design: An Analytic Framework Directly Incorporating Non-Equilibrium Plant Dynamics
 Gain-Sheduled Contolle Design: An Analyti Fameok Dietly Inopoating Non-Equilibium Plant Dynamis D.J.Leith W.E.Leithead Abstat Depatment of Eletoni & Eletial Engineeing, Univesity of Stathlyde, GLASGOW
Gain-Sheduled Contolle Design: An Analyti Fameok Dietly Inopoating Non-Equilibium Plant Dynamis D.J.Leith W.E.Leithead Abstat Depatment of Eletoni & Eletial Engineeing, Univesity of Stathlyde, GLASGOW
SKP-2 ALGORITHM: ON FORMING PART AND MACHINE CLUSTERS SEPARATELY
 Poeedings of the 1998 Paifi Confeene on Manufatuing, August 18-20, 1998, Bisbane, Queensland, Austalia SKP-2 ALGORITHM: ON FORMING PART AND MACHINE CLUSTERS SEPARATELY Susanto,S., Kennedy,R.D. and Pie,
Poeedings of the 1998 Paifi Confeene on Manufatuing, August 18-20, 1998, Bisbane, Queensland, Austalia SKP-2 ALGORITHM: ON FORMING PART AND MACHINE CLUSTERS SEPARATELY Susanto,S., Kennedy,R.D. and Pie,
(conservation of momentum)
 Dynamis of Binay Collisions Assumptions fo elasti ollisions: a) Eletially neutal moleules fo whih the foe between moleules depends only on the distane between thei entes. b) No intehange between tanslational
Dynamis of Binay Collisions Assumptions fo elasti ollisions: a) Eletially neutal moleules fo whih the foe between moleules depends only on the distane between thei entes. b) No intehange between tanslational
Mass Transfer. Dispersion. Lecture 13, , Dr. K. Wegner
 Mass Tansfe Dispesion Letue 3, 3..7, D. K. Wegne Dispesion to dispese to spead widely. Dispesion is the at o poess of dispesing, of distibuting one substane (small volume fation) in anothe (lage volume
Mass Tansfe Dispesion Letue 3, 3..7, D. K. Wegne Dispesion to dispese to spead widely. Dispesion is the at o poess of dispesing, of distibuting one substane (small volume fation) in anothe (lage volume
SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B. Calculations for Sample Cross-Section 2
 SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B Calulations fo Sample Coss-Setion. Use Input. Setion Popeties The popeties of Sample Coss-Setion ae shown in Figue and ae summaized below. Figue : Popeties of
SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B Calulations fo Sample Coss-Setion. Use Input. Setion Popeties The popeties of Sample Coss-Setion ae shown in Figue and ae summaized below. Figue : Popeties of
DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH 1. INTRODUCTION
 DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH Mugu B. RĂUŢ Coesponding autho: Mugu RĂUŢ, E-mail: m_b_aut@yahoo.om Abstat In this pape I popose a oetion to the well-known Newtonian gavitational
DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH Mugu B. RĂUŢ Coesponding autho: Mugu RĂUŢ, E-mail: m_b_aut@yahoo.om Abstat In this pape I popose a oetion to the well-known Newtonian gavitational
Discrete-Time Immersion and Invariance Adaptive Control of a Slider-crank Mechanism
 Pepints of the 9th Wold Congess he Intenational Fedeation of Automati Contol Cape own South Afia August -9 0 Disete-ime Immesion and Invaiane Adaptive Contol of a Slide-an Mehanism Yapa Yalçın Dept of
Pepints of the 9th Wold Congess he Intenational Fedeation of Automati Contol Cape own South Afia August -9 0 Disete-ime Immesion and Invaiane Adaptive Contol of a Slide-an Mehanism Yapa Yalçın Dept of
7.2.1 Basic relations for Torsion of Circular Members
 Section 7. 7. osion In this section, the geomety to be consideed is that of a long slende cicula ba and the load is one which twists the ba. Such poblems ae impotant in the analysis of twisting components,
Section 7. 7. osion In this section, the geomety to be consideed is that of a long slende cicula ba and the load is one which twists the ba. Such poblems ae impotant in the analysis of twisting components,
Reflectance spectra for Si
 Refletane speta fo Si Notie R and ε i and ε show onsideable stutues in the fom of peas and shouldes. These stutues aise fom the optial tansitions between alene bands to the ondution bands. 16 Miosopi Theoy:
Refletane speta fo Si Notie R and ε i and ε show onsideable stutues in the fom of peas and shouldes. These stutues aise fom the optial tansitions between alene bands to the ondution bands. 16 Miosopi Theoy:
Sensor and Simulation Notes. Note 525. Oct Lens Design for a Prolate-Spheroidal Impulse radiating Antenna (IRA)
 Senso and Simulation Notes Note 55 Oct 7 Lens Design fo a Polate-Spheoidal Impulse adiating Antenna (IRA) Sehat Altunc, Cal E. Baum, Chistos G. Chistodoulou and Edl Schamiloglu Univesity of New Mexico
Senso and Simulation Notes Note 55 Oct 7 Lens Design fo a Polate-Spheoidal Impulse adiating Antenna (IRA) Sehat Altunc, Cal E. Baum, Chistos G. Chistodoulou and Edl Schamiloglu Univesity of New Mexico
PHYS 110B - HW #7 Fall 2005, Solutions by David Pace Equations referenced as Eq. # are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased
 PHYS B - HW #7 Fall 5, Solutions by David Pae Equations efeened as Eq. # ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased [.] Poblem.4 fom Giffiths Show that Eq..4, V, t an be witten as Eq..44, V, t q t
PHYS B - HW #7 Fall 5, Solutions by David Pae Equations efeened as Eq. # ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased [.] Poblem.4 fom Giffiths Show that Eq..4, V, t an be witten as Eq..44, V, t q t
Permittivity of Human Skin in the Millimetre Wave Band
 Pemittivity of Human Skin in the Millimete Wave Band C. M. Alabaste, Canfield Univesity. E-mail: c.m.alabaste@mcs.canfield.ac.uk Abstact: The complex pemittivity of a human skin sample is measued ove the
Pemittivity of Human Skin in the Millimete Wave Band C. M. Alabaste, Canfield Univesity. E-mail: c.m.alabaste@mcs.canfield.ac.uk Abstact: The complex pemittivity of a human skin sample is measued ove the
Center for Advanced Studies in Measurement and Assessment. CASMA Research Report. Using G Theory to Examine Confounded Effects: The Problem of One
 Cente fo Advaned Studies in Measuement and Assessment CASMA Reseah Repot Numbe 51 Using G Theoy to Examine Confounded Effets: The Poblem of One Robet L. Bennan 1 Januay 017 1 Robet L. Bennan is E. F. Lindquist
Cente fo Advaned Studies in Measuement and Assessment CASMA Reseah Repot Numbe 51 Using G Theoy to Examine Confounded Effets: The Poblem of One Robet L. Bennan 1 Januay 017 1 Robet L. Bennan is E. F. Lindquist
A MATLAB Implementation of a Halton Sequence-Based GHK Simulator for Multinomial Probit Models *
 A MATLAB Implementation of a Halton Sequene-Based GHK Simulato fo Multinomial Pobit Models * Jose Miguel M. Abito Depatment of Eonomis National Uvesity of Singapoe Apil 005 * I would like to thank Kut
A MATLAB Implementation of a Halton Sequene-Based GHK Simulato fo Multinomial Pobit Models * Jose Miguel M. Abito Depatment of Eonomis National Uvesity of Singapoe Apil 005 * I would like to thank Kut
A near-perfect invisibility cloak constructed with homogeneous materials
 A nea-pefet invisibility loak onstuted with homogeneous mateials Wei Li, Jianguo Guan, * Zhigang Sun, Wei Wang, and Qingjie Zhang 1 State Key Lab of Advaned Tehnology fo Mateials Synthesis and Poessing,
A nea-pefet invisibility loak onstuted with homogeneous mateials Wei Li, Jianguo Guan, * Zhigang Sun, Wei Wang, and Qingjie Zhang 1 State Key Lab of Advaned Tehnology fo Mateials Synthesis and Poessing,
Central Coverage Bayes Prediction Intervals for the Generalized Pareto Distribution
 Statistics Reseach Lettes Vol. Iss., Novembe Cental Coveage Bayes Pediction Intevals fo the Genealized Paeto Distibution Gyan Pakash Depatment of Community Medicine S. N. Medical College, Aga, U. P., India
Statistics Reseach Lettes Vol. Iss., Novembe Cental Coveage Bayes Pediction Intevals fo the Genealized Paeto Distibution Gyan Pakash Depatment of Community Medicine S. N. Medical College, Aga, U. P., India
Time Dilation in Gravity Wells
 Time Dilation in Gavity Wells By Rihad R. Shiffman Digital Gaphis Asso. 038 Dunkik Ave. L.A., Ca. 9005 s@isi.edu This doument disusses the geneal elativisti effet of time dilation aused by a spheially
Time Dilation in Gavity Wells By Rihad R. Shiffman Digital Gaphis Asso. 038 Dunkik Ave. L.A., Ca. 9005 s@isi.edu This doument disusses the geneal elativisti effet of time dilation aused by a spheially
EKT 345 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING CHAPTER 2: PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES
 EKT 345 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING CHAPTER : PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES 1 Tansmission Lines A device used to tansfe enegy fom one point to anothe point efficiently Efficiently minimum loss, eflection and close
EKT 345 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING CHAPTER : PLANAR TRANSMISSION LINES 1 Tansmission Lines A device used to tansfe enegy fom one point to anothe point efficiently Efficiently minimum loss, eflection and close
The Research of AQI Index Changing Regularity Mainly in Tianjin Ziyu Guo
 nd Intenational Confeene on Eduation Tehnology, Management and Humanities Siene (ETMHS 06 The Reseah of AQI Index Changing Regulaity Mainly in Tianjin Ziyu Guo Shool of Institute of Eletial and Eletoni
nd Intenational Confeene on Eduation Tehnology, Management and Humanities Siene (ETMHS 06 The Reseah of AQI Index Changing Regulaity Mainly in Tianjin Ziyu Guo Shool of Institute of Eletial and Eletoni
Lecture 2 Date:
 Lectue 2 Date: 5.1.217 Definition of Some TL Paametes Examples of Tansmission Lines Tansmission Lines (contd.) Fo a lossless tansmission line the second ode diffeential equation fo phasos ae: LC 2 d I
Lectue 2 Date: 5.1.217 Definition of Some TL Paametes Examples of Tansmission Lines Tansmission Lines (contd.) Fo a lossless tansmission line the second ode diffeential equation fo phasos ae: LC 2 d I
A Distributed Sorting Framework for Ad Hoc Wireless Sensor Networks
 A Distibuted Soting Famewok fo Ad Ho Wieless Senso Netwoks Amitabha Ghosh Honeywell Tehnology Solutions Lab 151/1 Doaisanipalya, Banneghatta Road Bangaloe 560076, India Email: amitabha.ghosh@honeywell.om
A Distibuted Soting Famewok fo Ad Ho Wieless Senso Netwoks Amitabha Ghosh Honeywell Tehnology Solutions Lab 151/1 Doaisanipalya, Banneghatta Road Bangaloe 560076, India Email: amitabha.ghosh@honeywell.om
Electromagnetism. Christopher R Prior. ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
 letomagnetism Chistophe R Pio Fellow and Tuto in Mathematis Tinity College Oxfod ASTeC Intense Beams Goup Ruthefod Appleton Laboatoy Contents Maxwell s equations and Loentz Foe Law Motion of a haged patile
letomagnetism Chistophe R Pio Fellow and Tuto in Mathematis Tinity College Oxfod ASTeC Intense Beams Goup Ruthefod Appleton Laboatoy Contents Maxwell s equations and Loentz Foe Law Motion of a haged patile
Pulse Neutron Neutron (PNN) tool logging for porosity Some theoretical aspects
 Pulse Neuton Neuton (PNN) tool logging fo poosity Some theoetical aspects Intoduction Pehaps the most citicism of Pulse Neuton Neuon (PNN) logging methods has been chage that PNN is to sensitive to the
Pulse Neuton Neuton (PNN) tool logging fo poosity Some theoetical aspects Intoduction Pehaps the most citicism of Pulse Neuton Neuon (PNN) logging methods has been chage that PNN is to sensitive to the
PROCESSING QUALITY OF NEW POTATO CULTIVARS FOLLOWING PROLONGED STORAGE
 PRESSIG QUALITY F EW PTAT ULTIVARS FLLWIG PRLGED STRAGE Glenn E. Vogt J.R. Simplot o., aldwell, ID and Ei P. Eldedge and linton. Shok Malheu Expeiment Station egon State Univesity ntaio, R Intodution The
PRESSIG QUALITY F EW PTAT ULTIVARS FLLWIG PRLGED STRAGE Glenn E. Vogt J.R. Simplot o., aldwell, ID and Ei P. Eldedge and linton. Shok Malheu Expeiment Station egon State Univesity ntaio, R Intodution The
Absorption Rate into a Small Sphere for a Diffusing Particle Confined in a Large Sphere
 Applied Mathematics, 06, 7, 709-70 Published Online Apil 06 in SciRes. http://www.scip.og/jounal/am http://dx.doi.og/0.46/am.06.77065 Absoption Rate into a Small Sphee fo a Diffusing Paticle Confined in
Applied Mathematics, 06, 7, 709-70 Published Online Apil 06 in SciRes. http://www.scip.og/jounal/am http://dx.doi.og/0.46/am.06.77065 Absoption Rate into a Small Sphee fo a Diffusing Paticle Confined in
Ion-sound waves (electrostatic low frequency waves)
 OTHER TYPES of WAVES Ion-sound waves (eletostati low fequeny waves) ae longitudinal waves simila lassial sound in gas s kt k M B plasma sound is slow fo eletons, but fast fo ions Eleton density is in eah
OTHER TYPES of WAVES Ion-sound waves (eletostati low fequeny waves) ae longitudinal waves simila lassial sound in gas s kt k M B plasma sound is slow fo eletons, but fast fo ions Eleton density is in eah
Encapsulation theory: the transformation equations of absolute information hiding.
 1 Encapsulation theoy: the tansfomation equations of absolute infomation hiding. Edmund Kiwan * www.edmundkiwan.com Abstact This pape descibes how the potential coupling of a set vaies as the set is tansfomed,
1 Encapsulation theoy: the tansfomation equations of absolute infomation hiding. Edmund Kiwan * www.edmundkiwan.com Abstact This pape descibes how the potential coupling of a set vaies as the set is tansfomed,
Contact impedance of grounded and capacitive electrodes
 Abstact Contact impedance of gounded and capacitive electodes Andeas Hödt Institut fü Geophysik und extateestische Physik, TU Baunschweig The contact impedance of electodes detemines how much cuent can
Abstact Contact impedance of gounded and capacitive electodes Andeas Hödt Institut fü Geophysik und extateestische Physik, TU Baunschweig The contact impedance of electodes detemines how much cuent can
Study of the Endface Friction of the Revolving Vane Mechanism
 Pudue Univesity Pudue e-pubs Intenational Compesso Engineeing Confeene Shool of Mehanial Engineeing 010 Study of the Endfae Fition of the Revolving Vane Mehanism Alison Subiantoo Shool of Mehanial and
Pudue Univesity Pudue e-pubs Intenational Compesso Engineeing Confeene Shool of Mehanial Engineeing 010 Study of the Endfae Fition of the Revolving Vane Mehanism Alison Subiantoo Shool of Mehanial and
TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS IN THE SAW UNIT OF A KIND OF CIRCULAR SAW. NUMERICAL INVESTIGATIONS OF THE NATURAL FREQUENCIES AND MODE SHAPES
 TRIESKOVÉ A BEZTRIESKOVÉ OBRÁBANIE DREVA, 8(): 7 78, Zvolen, Tehniká univezita vo Zvolene, ISBN 978-8-8-85- 7 TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS IN THE SAW UNIT OF A KIND OF CIRCULAR SAW NUMERICAL INVESTIGATIONS OF
TRIESKOVÉ A BEZTRIESKOVÉ OBRÁBANIE DREVA, 8(): 7 78, Zvolen, Tehniká univezita vo Zvolene, ISBN 978-8-8-85- 7 TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS IN THE SAW UNIT OF A KIND OF CIRCULAR SAW NUMERICAL INVESTIGATIONS OF
Geometry of the homogeneous and isotropic spaces
 Geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces H. Sonoda Septembe 2000; last evised Octobe 2009 Abstact We summaize the aspects of the geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces which ae most elevant
Geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces H. Sonoda Septembe 2000; last evised Octobe 2009 Abstact We summaize the aspects of the geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces which ae most elevant
In electrostatics, the electric field E and its sources (charges) are related by Gauss s law: Surface
 Ampee s law n eletostatis, the eleti field E and its soues (hages) ae elated by Gauss s law: EdA i 4πQenl Sufae Why useful? When symmety applies, E an be easily omputed Similaly, in magnetism the magneti
Ampee s law n eletostatis, the eleti field E and its soues (hages) ae elated by Gauss s law: EdA i 4πQenl Sufae Why useful? When symmety applies, E an be easily omputed Similaly, in magnetism the magneti
arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018 arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018](/thumbs/90/103259092.jpg) Noname manusipt No. will be inseted by the edito Long-Range Longitudinal Eleti Wave in Vauum Radiated by Eleti Dipole: Pat I Altay Zhakatayev, Leila Tlebaldiyeva axiv:7.v4 [physis.lass-ph] 4 Jul 8 Reeived:
Noname manusipt No. will be inseted by the edito Long-Range Longitudinal Eleti Wave in Vauum Radiated by Eleti Dipole: Pat I Altay Zhakatayev, Leila Tlebaldiyeva axiv:7.v4 [physis.lass-ph] 4 Jul 8 Reeived:
ELASTIC ANALYSIS OF CIRCULAR SANDWICH PLATES WITH FGM FACE-SHEETS
 THE 9 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS ELASTIC ANALYSIS OF CIRCULAR SANDWICH PLATES WITH FGM FACE-SHEETS R. Sbulati *, S. R. Atashipou Depatment of Civil, Chemical and Envionmental Engineeing,
THE 9 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS ELASTIC ANALYSIS OF CIRCULAR SANDWICH PLATES WITH FGM FACE-SHEETS R. Sbulati *, S. R. Atashipou Depatment of Civil, Chemical and Envionmental Engineeing,
dp p v= = ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945).
 ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945). It is shown that at lage distanes fom the body, moving with a. veloity exeeding that of
ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945). It is shown that at lage distanes fom the body, moving with a. veloity exeeding that of
Planck Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gravitation
 Plank Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gavitation Espen Gaade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sienes Mah 0, 06 Abstat In this pape we ewite the gavitational onstant based on its elationship with the
Plank Quantization of Newton and Einstein Gavitation Espen Gaade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sienes Mah 0, 06 Abstat In this pape we ewite the gavitational onstant based on its elationship with the
Revised Newtonian Formula of Gravity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat Space-Time Transformed from Schwarzschild Solution
 Intenational Jounal of Astonomy and Astophysis,,, 6-8 http://dx.doi.og/.46/ijaa.. Published Online Mah (http://www.sip.og/jounal/ijaa) evised Newtonian Fomula of Gavity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat
Intenational Jounal of Astonomy and Astophysis,,, 6-8 http://dx.doi.og/.46/ijaa.. Published Online Mah (http://www.sip.og/jounal/ijaa) evised Newtonian Fomula of Gavity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat
A scaling-up methodology for co-rotating twin-screw extruders
 A scaling-up methodology fo co-otating twin-scew extudes A. Gaspa-Cunha, J. A. Covas Institute fo Polymes and Composites/I3N, Univesity of Minho, Guimaães 4800-058, Potugal Abstact. Scaling-up of co-otating
A scaling-up methodology fo co-otating twin-scew extudes A. Gaspa-Cunha, J. A. Covas Institute fo Polymes and Composites/I3N, Univesity of Minho, Guimaães 4800-058, Potugal Abstact. Scaling-up of co-otating
Correspondence Analysis & Related Methods
 Coespondene Analysis & Related Methods Oveview of CA and basi geometi onepts espondents, all eades of a etain newspape, osstabulated aoding to thei eduation goup and level of eading of the newspape Mihael
Coespondene Analysis & Related Methods Oveview of CA and basi geometi onepts espondents, all eades of a etain newspape, osstabulated aoding to thei eduation goup and level of eading of the newspape Mihael
Determine the Stress Calculating Mode of Sliding Failure of Soil Mass under the Push-Extend Multi-under-Reamed Pile
 Engineeing, 014, 6, 54-59 Published Online Apil 014 in SiRes. http://www.sip.og/jounal/eng http://dx.doi.og/10.436/eng.014.6509 Deteine the Stess Calulating Mode of Sliding Failue of Soil Mass unde the
Engineeing, 014, 6, 54-59 Published Online Apil 014 in SiRes. http://www.sip.og/jounal/eng http://dx.doi.og/10.436/eng.014.6509 Deteine the Stess Calulating Mode of Sliding Failue of Soil Mass unde the
8.022 (E&M) Lecture 13. What we learned about magnetism so far
 8.0 (E&M) Letue 13 Topis: B s ole in Mawell s equations Veto potential Biot-Savat law and its appliations What we leaned about magnetism so fa Magneti Field B Epeiments: uents in s geneate foes on hages
8.0 (E&M) Letue 13 Topis: B s ole in Mawell s equations Veto potential Biot-Savat law and its appliations What we leaned about magnetism so fa Magneti Field B Epeiments: uents in s geneate foes on hages
matschek (ccm2548) Ch17-h3 chiu (57890) 1
 matshek m2548) Ch17-h3 hiu 5789) 1 This pint-out should have 16 questions. Multiple-hoie questions may ontinue on the next olumn o page find all hoies efoe answeing. 1 1. points A student said, The eleti
matshek m2548) Ch17-h3 hiu 5789) 1 This pint-out should have 16 questions. Multiple-hoie questions may ontinue on the next olumn o page find all hoies efoe answeing. 1 1. points A student said, The eleti
COMPUTATIONS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS RADIATED FROM COMPLEX LIGHTNING CHANNELS
 Pogess In Electomagnetics Reseach, PIER 73, 93 105, 2007 COMPUTATIONS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS RADIATED FROM COMPLEX LIGHTNING CHANNELS T.-X. Song, Y.-H. Liu, and J.-M. Xiong School of Mechanical Engineeing
Pogess In Electomagnetics Reseach, PIER 73, 93 105, 2007 COMPUTATIONS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS RADIATED FROM COMPLEX LIGHTNING CHANNELS T.-X. Song, Y.-H. Liu, and J.-M. Xiong School of Mechanical Engineeing
Computational chemistry
 6 Computational hemisty The ental hallenge 6. The Hatee Fok fomalism 6. The Roothaan equations 6.3 Basis sets The fist appoah: semiempiial methods 6.4 The Hükel method evisited 6.5 Diffeential ovelap The
6 Computational hemisty The ental hallenge 6. The Hatee Fok fomalism 6. The Roothaan equations 6.3 Basis sets The fist appoah: semiempiial methods 6.4 The Hükel method evisited 6.5 Diffeential ovelap The
ASTR415: Problem Set #6
 ASTR45: Poblem Set #6 Cuan D. Muhlbege Univesity of Mayland (Dated: May 7, 27) Using existing implementations of the leapfog and Runge-Kutta methods fo solving coupled odinay diffeential equations, seveal
ASTR45: Poblem Set #6 Cuan D. Muhlbege Univesity of Mayland (Dated: May 7, 27) Using existing implementations of the leapfog and Runge-Kutta methods fo solving coupled odinay diffeential equations, seveal
Vibrational Modes and Instabilities of a Dust Particle Pair in a Complex Plasma
 > REPLACE THIS LINE WITH YOUR PAPER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (DOUBLE-CLICK HERE TO EDIT) < Vibational Modes and Instabilities of a Dust Patile Pai in a Comple Plasma K. Qiao, L. S. Matthews, and T. W. Hyde,
> REPLACE THIS LINE WITH YOUR PAPER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (DOUBLE-CLICK HERE TO EDIT) < Vibational Modes and Instabilities of a Dust Patile Pai in a Comple Plasma K. Qiao, L. S. Matthews, and T. W. Hyde,
A Theory of the Podkletnov Effect based on General Relativity: Anti-Gravity Force due to the Perturbed Non-Holonomic Background of Space
 July, 007 PROGRESS IN PHYSICS Volume 3 SPECIAL REPORT A Theoy of the Podkletnov Effet based on Geneal Relativity: Anti-Gavity Foe due to the Petubed Non-Holonomi Bakgound of Spae Dmiti Rabounski and Laissa
July, 007 PROGRESS IN PHYSICS Volume 3 SPECIAL REPORT A Theoy of the Podkletnov Effet based on Geneal Relativity: Anti-Gavity Foe due to the Petubed Non-Holonomi Bakgound of Spae Dmiti Rabounski and Laissa
A NEW VARIABLE STIFFNESS SPRING USING A PRESTRESSED MECHANISM
 Poceedings of the ASME 2010 Intenational Design Engineeing Technical Confeences & Computes and Infomation in Engineeing Confeence IDETC/CIE 2010 August 15-18, 2010, Monteal, Quebec, Canada DETC2010-28496
Poceedings of the ASME 2010 Intenational Design Engineeing Technical Confeences & Computes and Infomation in Engineeing Confeence IDETC/CIE 2010 August 15-18, 2010, Monteal, Quebec, Canada DETC2010-28496
Mass- and light-horizons, black holes' radii, the Schwartzschild metric and the Kerr metric
 006-010 Thiey De Mees Mass- and light-hoizons, blak holes' adii, the Shwatzshild meti and the Ke meti mpoved alulus. (using gavitomagnetism) T. De Mees - thieydm@pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes geneally ae
006-010 Thiey De Mees Mass- and light-hoizons, blak holes' adii, the Shwatzshild meti and the Ke meti mpoved alulus. (using gavitomagnetism) T. De Mees - thieydm@pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes geneally ae
Finite Difference Solution of Mixed Convective Heat Transfer Transient Flow along a Continuously Moving Cooled Plate
 Annals of Pue and Applied Mathematis Vol 7, No, 14, 18-6 ISSN: 79-87X (P), 79-888(online) Published on 7 August 14 eseahmathsiog Annals of Finite Diffeene Solution of Mixed Convetive Heat Tansfe Tansient
Annals of Pue and Applied Mathematis Vol 7, No, 14, 18-6 ISSN: 79-87X (P), 79-888(online) Published on 7 August 14 eseahmathsiog Annals of Finite Diffeene Solution of Mixed Convetive Heat Tansfe Tansient
Special relativity with clock synchronization
 Speial elativity with lok synhonization Benhad Rothenstein ), Stefan Popesu ) and Geoge J. Spi 3) ) Politehnia Univesity of Timisoaa, Physis Depatment, Timisoaa, Romania, benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om ) Siemens
Speial elativity with lok synhonization Benhad Rothenstein ), Stefan Popesu ) and Geoge J. Spi 3) ) Politehnia Univesity of Timisoaa, Physis Depatment, Timisoaa, Romania, benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om ) Siemens
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Department. Problem Set 10 Solutions. r s
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.033 Decembe 5, 003 Poblem Set 10 Solutions Poblem 1 M s y x test paticle The figue above depicts the geomety of the poblem. The position
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Physics Depatment Physics 8.033 Decembe 5, 003 Poblem Set 10 Solutions Poblem 1 M s y x test paticle The figue above depicts the geomety of the poblem. The position
MAGNETIC FIELD AROUND TWO SEPARATED MAGNETIZING COILS
 The 8 th Intenational Confeence of the Slovenian Society fo Non-Destuctive Testing»pplication of Contempoay Non-Destuctive Testing in Engineeing«Septembe 1-3, 5, Potoož, Slovenia, pp. 17-1 MGNETIC FIELD
The 8 th Intenational Confeence of the Slovenian Society fo Non-Destuctive Testing»pplication of Contempoay Non-Destuctive Testing in Engineeing«Septembe 1-3, 5, Potoož, Slovenia, pp. 17-1 MGNETIC FIELD
Confidence Intervals for the Squared Multiple Semipartial Correlation Coefficient. James Algina. University of Florida. H. J.
 Eet Size Conidene Inteval 1 Conidene Intevals o the Squaed Multiple Semipatial Coelation Coeiient by James Algina Univesity o Floida H. J. Keselman Univesity o Manitoba all D. Penield Univesity o Miami
Eet Size Conidene Inteval 1 Conidene Intevals o the Squaed Multiple Semipatial Coelation Coeiient by James Algina Univesity o Floida H. J. Keselman Univesity o Manitoba all D. Penield Univesity o Miami
Review: Electrostatics and Magnetostatics
 Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
