AC : RULE-BASED MODELING OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS AND COMPUTATION OF TRANSFER-FUNCTIONS WITH "MATLAB"
|
|
|
- Colleen Sherman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AC : RULE-BASED MODELING OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS AND COMPUTATION OF TRANSFER-FUNCTIONS WITH "MATLAB" Swami Karunamoorthy, St. Louis University Dr. Swami Karunamoorthy is the professor of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering at Saint Louis University. He is an Associate Fellow of AIAA, Fellow of ASME, and an active member of ASEE, AHS. He is also a Commissioner and Program Evaluator for ABET. His areas of interest are Engineering Education, Assessment, Vibrations, Linear system controls,composites, Helicopters, Aerospace Structures and Applied Aerodynamics. He has several publications on these areas. H. Mallikarjuna, St. Louis University Dr. Mallikarjuna H.S. is an associate professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Saint Louis University. His areas of interest are Circuits, Systems and Classical Control Systems. He is a member of IEEE and ASEE. American Society for Engineering Education, 007 Page.5.
2 RULE BASED MODELING OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS AND COMPUTATION OF TRANSFER-FUNCTIONS WITH MATLAB Abstract The dynamic systems are in general modeled by Newton s force method or Lagrange s energy method. In this paper a rule based procedure is given as an alternate method for simple linear systems. The resulting equations in matrix form can be used as input in the analytical computation of transfer functions with MATLAB software. Integration of rule based modeling of dynamic systems and analytical computation of transfer functions with MATLAB provides a viable pedagogical tool for undergraduate education in Linear System Control. Introduction Linear Vibrations and Linear System Control are relatively difficult courses in undergraduate curriculum for Aerospace, Mechanical as well as Electrical engineering students. The primary difficulty lies in developing the equations of motion from given physical system. In applying the Newton s force method, one should have good understanding of degree of freedom and free body diagram. In applying the energy method, one should have good understanding of kinetic energy, potential energy, and damping energy. Although some students have very good grasp of these principles, majority of the class have trouble in application of these concepts. The computation of transfer functions in analytical form requires the knowledge of partial fractions and Laplace Transforms. Manual computation of transfer functions is rather laborious for even some simple systems. MATLAB software can be easily used for this purpose and it is efficient in applying Laplace Transform in order to find the transfer function. Rules for Modeling. Degrees of Freedom: (a) Every degree of freedom [X i ] is associated with a mass [M i ]; (b) A degree of freedom without a real mass is associated with a virtual mass of zero magnitude (or zero-mass).. Stiffness Matrix: (a) Diagonal elements of the matrix [K ii ] are sum of the values of stiffness connected to each mass [M i ], including the zero-mass. (b) The Offdiagonal terms [Kij] are negative and equal to sum of the values of stiffness connected in between mass [M i ] and [M j ]. 3. Damping Matrix: (a) Diagonal elements of the matrix [C ii ] are sum of the values of damping connected to each mass [M i ], including the zero-mass. (b) The Offdiagonal terms [Cij] are negative and equal to sum of the values of damping connected in between mass [M i ] and [M j ]. Page.5.
3 4. Mass Matrix: (a) Diagonal elements of the matrix [M ii ] are the value of mass [M i ] that correspond to the degree of freedom [X i ]. However, the value of the zeromass is zero. (b) The Off-diagonal terms [Mij] are zero. Example : X X 3 In this example, there are two masses connected to a spring and three viscous dampers with two degrees of freedom. The values indicated at the mass, spring and damper represent the magnitude of each in their appropriate units. Now the matrices [M], [C], and [K] can be developed by applying the rules as shown below. Rule #: Degrees of Freedom This system has two degrees of freedom (X, X ) and each one is associated with a mass and the masses are real. Rule #: Stiffness Matrix Diagonal element K = (the value of all the stiffness connected to the mass with X as Diagonal element K = (the value of all the stiffness connected to the mass with X as Off-diagonal element K = - (the value of all the stiffness connected between the two masses) Off-diagonal element K = K = - (symmetry of the matrix) Rule #3: Damping Matrix Diagonal element C = 4 (the value of all the damping connected to the mass with X as Diagonal element C = 5 (the value of all the damping connected to the mass with X as Off-diagonal element C = -3 (the value of all the damping connected between the two masses) Off-diagonal element C = C = -3 (symmetry of the matrix) Page.5.3
4 Rule #4: Mass Matrix Diagonal elements M = and M = Off-diagonal elements M = M = 0 Now the mass, damping and stiffness matrices can be written as, M = ; [ C ] = ; [ ] [ K ] = Example : X X In this example, there is only one mass connected to a spring and damper with two degrees of freedom. While the Rule # requires that every degree of freedom is associated with a mass, the degree of freedom X is not associated with a mass. So, a virtual mass of zero magnitude (zero-mass) is introduced at the degree of freedom X as shown below. X X 0(zero) Page.5.4
5 Rule #: Degrees of Freedom This system has two degrees of freedom (X, X ). The degree of freedom X is associated with a virtual mass while the degree of freedom X is associated with a real mass. The virtual mass is shown with dashed line and its magnitude is zero. Rule #: Stiffness Matrix Diagonal element K = (the value of all the stiffness connected to the mass with X as Diagonal element K = (the value of all the stiffness connected to the mass with X as Off-diagonal element K = - (the value of all the stiffness connected between the two masses) Off-diagonal element K = K = - (symmetry of the matrix) Rule #3: Damping Matrix Diagonal element C = 0 ( the value of all the damping connected to the mass with X as Diagonal element C = (the value of all the damping connected to the mass with X as Off-diagonal element C = 0 (the value of all the damping connected between the two masses) Off-diagonal element C = C = 0 (symmetry of the matrix) Rule #4: Mass Matrix Diagonal elements M = 0 (zero-mass) and M = Off-diagonal elements M = M = 0 Now the mass, damping and stiffness matrices can be written as, [ M ] 0 0 = ; C = ; 0 [ ] [ K ] = General Solution The general equation of motion for a given system can be written as, [ M ]{ x} + [ C]{ x } + [ K]{ x} = { F() t } L et x (0) and x (0) be the initial conditions representing the initial displacement and initial velocity respectively. Applying the Laplace Transform, the above equation can be written as, [ ] + [ ] + [ ] { ()} = { ()} + [ ] + [ ] { (0)} + [ ]{ (0)} s M s C K x s F s s M C x M x Page.5.5
6 For zero initial conditions, { x() s } =[ Hs ()]{ Fs ()}; where the Transfer Function, [ ()] Hs = [ ] + [ ] + [ ] s M s C K This matrix equation for the transfer function can be evaluated in analytical form using the software, MATLAB. In general for multi degree of freedom, the transfer function can be expressed as, H ij = xi () s F () s j For example, if a system has two degrees of freedom with forcing function acting at each degree of freedom, the forcing function need to be applied one at a time in the evaluation of the transfer functions. Assuming F (t) is the only forcing function acting on the system and F (t)=0, H () () = x s ; H = x s () F() s F s Assuming F (t) is the only forcing function acting on the system and F (t)=0, H () () = x s ; H = x s () F () s F s Computation and Results This procedure can be easily programmed in MATLAB for finding the transfer function in closed form and the code is given below. MATLAB Code clc, clear all syms s dmat; fprintf( Enter the parameters of the system\n\n ) n = input ( order of the system := ); m = input ( M := ); c = input ( C := ); k = input ( K := ); for i = :n for j = :n dmat (i, j) = m(i,j) * s^+c(i,j)*s+k(i,j); end end h = inv (dmat); fprintf( \n Transfer Funtion: \n ) transfn(h) Page.5.6
7 Example-: The MATLAB template for Example- is given below: It can also be written as, (s + 5s+ ) (3s+ ) H() s = ; Δ (3s+ ) ( s + 4s+ ) Δ = s s + s + s+ 3 ( 3 4 3) Example- The results for Example- can be summarized as, ( s + s+ ) H() s = ; Δ= ss ( + ) Δ The MATLAB template of computation is given below. Page.5.7
8 Since the transfer function is computed in closed form, they can be readily used for further analysis in linear system control or in stability and control of aerospace vehicles. Conclusions Finding the transfer functions for a given dynamic system has been a difficult endeavor for most of the students in Aerospace, Mechanical as well as Electrical engineering programs. Rule based approach to develop the required mass, damping and stiffness matrices directly from the dynamic system eliminated the need for cumbersome procedure of deriving the equations of motion from first principles and then reducing them to required matrices. This approach is very well received by students and it is not in general available in existing text books. Applying the Laplace Transform to matrix equations of motion and extracting the transfer function by solving a series of partial fractions has been eliminated by using the MATLAB software. Since MATLAB is commonly used by most of the engineering students it would be appropriate to use for this purpose. Integrating the rule based approach and the application of MATLAB not only simplifies the process of obtaining the transfer functions, and also provides a valuable pedagogical tool to educate the engineering leaders of tomorrow. Page.5.8
9 Authors Biography Dr. Swami Karunamoorthy is the professor of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering at Saint Louis University. He is an Associate Fellow of AIAA, Fellow of ASME, and an active member of ASEE, AHS. He is also a Commissioner and Program Evaluator for ABET. His areas of interest are Engineering Education, Assessment, Vibrations, Linear System Controls, Composites, Helicopters, Aerospace Structures and Applied Aerodynamics. He has several publications on these areas. Dr. Mallikarjuna H.S. is an associate professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Saint Louis University. His areas of interest are Circuits, Systems, and Classical Controls. Page.5.9
A pragmatic approach to including complex natural modes of vibration in aeroelastic analysis
 A pragmatic approach to including complex natural modes of vibration in aeroelastic analysis International Aerospace Symposium of South Africa 14 to 16 September, 215 Stellenbosch, South Africa Louw van
A pragmatic approach to including complex natural modes of vibration in aeroelastic analysis International Aerospace Symposium of South Africa 14 to 16 September, 215 Stellenbosch, South Africa Louw van
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES
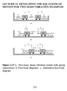 LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
Structural Dynamics Lecture 4. Outline of Lecture 4. Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems. Formulation of Equations of Motions. Undamped Eigenvibrations.
 Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Modification of a Sophomore Linear Systems Course to Reflect Modern Computing Strategies
 Session 3220 Modification of a Sophomore Linear Systems Course to Reflect Modern Computing Strategies Raymond G. Jacquot, Jerry C. Hamann, John E. McInroy Electrical Engineering Department, University
Session 3220 Modification of a Sophomore Linear Systems Course to Reflect Modern Computing Strategies Raymond G. Jacquot, Jerry C. Hamann, John E. McInroy Electrical Engineering Department, University
Advanced Vibrations. Elements of Analytical Dynamics. By: H. Ahmadian Lecture One
 Advanced Vibrations Lecture One Elements of Analytical Dynamics By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Elements of Analytical Dynamics Newton's laws were formulated for a single particle Can be extended to
Advanced Vibrations Lecture One Elements of Analytical Dynamics By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Elements of Analytical Dynamics Newton's laws were formulated for a single particle Can be extended to
Mechanical Vibration Analysis Using Maple
 Mechanical Vibration Analysis Using Maple WILLIAM F. SÁNCHEZ COSSIO Logic and Computation Group Theoretical and computational Physics Group Physics Engineering Program Sciences and Humanities School EAFIT
Mechanical Vibration Analysis Using Maple WILLIAM F. SÁNCHEZ COSSIO Logic and Computation Group Theoretical and computational Physics Group Physics Engineering Program Sciences and Humanities School EAFIT
AC : DEVELOPMENT OF VISUALIZATION TOOLS FOR ONE AND MULTIPLE DOF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS
 AC 2009-296: DEVELOPMENT OF VISUALIZATION TOOLS FOR ONE AND MULTIPLE DOF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS Jiang Zhou, Lamar University Jiang Zhou Ph. D in Mechanical Engineering of University of Maryland, Baltimore County
AC 2009-296: DEVELOPMENT OF VISUALIZATION TOOLS FOR ONE AND MULTIPLE DOF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS Jiang Zhou, Lamar University Jiang Zhou Ph. D in Mechanical Engineering of University of Maryland, Baltimore County
: TEACHING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH AN ENGINEERING FOCUS
 2006-915: TEACHING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH AN ENGINEERING FOCUS Stephen Pennell, University of Massachusetts-Lowell Stephen Pennell is a Professor in the Department of Mathematical Sciences at the
2006-915: TEACHING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH AN ENGINEERING FOCUS Stephen Pennell, University of Massachusetts-Lowell Stephen Pennell is a Professor in the Department of Mathematical Sciences at the
EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION
 1 EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION The course on Mechanical Vibration is an important part of the Mechanical Engineering undergraduate curriculum. It is necessary for the development
1 EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION The course on Mechanical Vibration is an important part of the Mechanical Engineering undergraduate curriculum. It is necessary for the development
Finite Element Modules for Demonstrating Critical Concepts in Engineering Vibration Course
 Finite Element Modules for Demonstrating Critical Concepts in Engineering Vibration Course Shengyong Zhang Assistant Professor of Mechanical Engineering College of Engineering and Technology Purdue University
Finite Element Modules for Demonstrating Critical Concepts in Engineering Vibration Course Shengyong Zhang Assistant Professor of Mechanical Engineering College of Engineering and Technology Purdue University
How Do You Teach Vibrations to Technology Students?
 Paper ID #9337 How Do You Teach Vibrations to Technology Students? Dr. M. Austin Creasy, Purdue University (Statewide Technology) Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Technology Purdue University
Paper ID #9337 How Do You Teach Vibrations to Technology Students? Dr. M. Austin Creasy, Purdue University (Statewide Technology) Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Technology Purdue University
The written qualifying (preliminary) examination covers the entire major field body of knowledge
 Dynamics The field of Dynamics embraces the study of forces and induced motions of rigid and deformable material systems within the limitations of classical (Newtonian) mechanics. The field is intended
Dynamics The field of Dynamics embraces the study of forces and induced motions of rigid and deformable material systems within the limitations of classical (Newtonian) mechanics. The field is intended
Dynamic Modelling of Mechanical Systems
 Dynamic Modelling of Mechanical Systems Dr. Bishakh Bhattacharya Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering g IIT Kanpur Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc - Funded by MHRD Hints of the Last Assignment
Dynamic Modelling of Mechanical Systems Dr. Bishakh Bhattacharya Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering g IIT Kanpur Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc - Funded by MHRD Hints of the Last Assignment
a) Find the equation of motion of the system and write it in matrix form.
 .003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
A Mass-Spring-Damper Model of a Bouncing Ball*
 Int. J. Engng Ed. Vol., No., pp. 393±41, 6 949-149X/91 $3.+. Printed in Great Britain. # 6 TEMPUS Publications. A Mass-Spring-Damper Model of a Bouncing Ball* MARK NAGURKA and SHUGUANG HUANG Department
Int. J. Engng Ed. Vol., No., pp. 393±41, 6 949-149X/91 $3.+. Printed in Great Britain. # 6 TEMPUS Publications. A Mass-Spring-Damper Model of a Bouncing Ball* MARK NAGURKA and SHUGUANG HUANG Department
Teaching Electromagnetic Fields with Computer Visualization
 Paper # 209, ENG 107 Teaching Electromagnetic Fields with Computer Visualization Yeqin Huang, Bill W. Yang, Robert Adams, Brian Howell, James Z. Zhang, and Kenneth Burbank Department of Engineering and
Paper # 209, ENG 107 Teaching Electromagnetic Fields with Computer Visualization Yeqin Huang, Bill W. Yang, Robert Adams, Brian Howell, James Z. Zhang, and Kenneth Burbank Department of Engineering and
Numerical Solution of Equation of Motion
 Class Notes: Earthquake Engineering, Ahmed Elgamal, September 25, 2001 (DRAFT) Numerical Solution of Equation of Motion Average Acceleration Method (Trapezoidal method) m a + c v + k d = f (t) In the above
Class Notes: Earthquake Engineering, Ahmed Elgamal, September 25, 2001 (DRAFT) Numerical Solution of Equation of Motion Average Acceleration Method (Trapezoidal method) m a + c v + k d = f (t) In the above
FREQUENCY DOMAIN FLUTTER ANALYSIS OF AIRCRAFT WING IN SUBSONIC FLOW
 FREQUENCY DOMAIN FLUTTER ANALYSIS OF AIRCRAFT WING IN SUBSONIC FLOW Ms.K.Niranjana 1, Mr.A.Daniel Antony 2 1 UG Student, Department of Aerospace Engineering, Karunya University, (India) 2 Assistant professor,
FREQUENCY DOMAIN FLUTTER ANALYSIS OF AIRCRAFT WING IN SUBSONIC FLOW Ms.K.Niranjana 1, Mr.A.Daniel Antony 2 1 UG Student, Department of Aerospace Engineering, Karunya University, (India) 2 Assistant professor,
MINIMAX DESIGN OF PREFILTERS FOR MANEUVERING FLEXIBLE STRUCTURES
 MINIMAX DESIGN OF PREFILTERS FOR MANEUVERING FLEXIBLE STRUCTURES Tarunraj Singh Yong-Lin Kuo Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering SUNY at Buffalo, Buffalo, New York 426 ABSTRACT This paper
MINIMAX DESIGN OF PREFILTERS FOR MANEUVERING FLEXIBLE STRUCTURES Tarunraj Singh Yong-Lin Kuo Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering SUNY at Buffalo, Buffalo, New York 426 ABSTRACT This paper
Introduction to Mechanical Vibration
 2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
Section 3.7: Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations
 Section 3.7: Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations Second order linear equations with constant coefficients serve as mathematical models for mechanical and electrical oscillations. For example, the motion
Section 3.7: Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations Second order linear equations with constant coefficients serve as mathematical models for mechanical and electrical oscillations. For example, the motion
13th IFAC Symposium on System Identification
 ESTIMATING PARAMETERS IN A LUMPED PARAMETER SYSTEM WITH FIRST PRINCIPLE MODELING AND DYNAMIC EXPERIMENTS RAdeCallafon UniversityofCalifornia,SanDiego Dept of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering 9500 Gilman
ESTIMATING PARAMETERS IN A LUMPED PARAMETER SYSTEM WITH FIRST PRINCIPLE MODELING AND DYNAMIC EXPERIMENTS RAdeCallafon UniversityofCalifornia,SanDiego Dept of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering 9500 Gilman
Problem 1: Find the Equation of Motion from the static equilibrium position for the following systems: 1) Assumptions
 Problem 1: Find the Equation of Motion from the static equilibrium position for the following systems: 1) Assumptions k 2 Wheels roll without friction k 1 Motion will not cause block to hit the supports
Problem 1: Find the Equation of Motion from the static equilibrium position for the following systems: 1) Assumptions k 2 Wheels roll without friction k 1 Motion will not cause block to hit the supports
Dynamic Analysis of Coupling Vehicle-Bridge System Using Finite Prism Method
 Dynamic Analysis of Coupling Vehicle-Bridge System Using Finite Prism Method A. T. Saeed and Zhongfu Xiang Abstract To investigate the transient responses of bridges under moving vehicles, Finite Prism
Dynamic Analysis of Coupling Vehicle-Bridge System Using Finite Prism Method A. T. Saeed and Zhongfu Xiang Abstract To investigate the transient responses of bridges under moving vehicles, Finite Prism
Vibration Analysis Experiment: mode shapes and frequency response of a scaled flexible three-story building & helicopter propeller
 MAE175a Vibration Analysis Experiment: mode shapes and frequency response of a scaled flexible three-story building & helicopter propeller Prof: Raymond de Callafon email: callafon@ucsd.edu TAs: Jeff Narkis,
MAE175a Vibration Analysis Experiment: mode shapes and frequency response of a scaled flexible three-story building & helicopter propeller Prof: Raymond de Callafon email: callafon@ucsd.edu TAs: Jeff Narkis,
Using web-based Java pplane applet to graph solutions of systems of differential equations
 Using web-based Java pplane applet to graph solutions of systems of differential equations Our class project for MA 341 involves using computer tools to analyse solutions of differential equations. This
Using web-based Java pplane applet to graph solutions of systems of differential equations Our class project for MA 341 involves using computer tools to analyse solutions of differential equations. This
Dynamic Systems. Modeling and Analysis. Hung V. Vu. Ramin S. Esfandiari. THE McGRAW-HILL COMPANIES, INC. California State University, Long Beach
 Dynamic Systems Modeling and Analysis Hung V. Vu California State University, Long Beach Ramin S. Esfandiari California State University, Long Beach THE McGRAW-HILL COMPANIES, INC. New York St. Louis San
Dynamic Systems Modeling and Analysis Hung V. Vu California State University, Long Beach Ramin S. Esfandiari California State University, Long Beach THE McGRAW-HILL COMPANIES, INC. New York St. Louis San
AN INTRODUCTION TO NUMERICAL METHODS USING MATHCAD. Mathcad Release 14. Khyruddin Akbar Ansari, Ph.D., P.E.
 AN INTRODUCTION TO NUMERICAL METHODS USING MATHCAD Mathcad Release 14 Khyruddin Akbar Ansari, Ph.D., P.E. Professor of Mechanical Engineering School of Engineering and Applied Science Gonzaga University
AN INTRODUCTION TO NUMERICAL METHODS USING MATHCAD Mathcad Release 14 Khyruddin Akbar Ansari, Ph.D., P.E. Professor of Mechanical Engineering School of Engineering and Applied Science Gonzaga University
41514 Dynamics of Machinery
 41514 Dynamics of Machinery Theory, Experiment, Phenomenology and Industrial Applications Ilmar (Iumár) Ferreira Santos 1. Course Structure 2. Objectives 3. Theoretical and Experimental Example 4. Industrial
41514 Dynamics of Machinery Theory, Experiment, Phenomenology and Industrial Applications Ilmar (Iumár) Ferreira Santos 1. Course Structure 2. Objectives 3. Theoretical and Experimental Example 4. Industrial
System Dynamics for Engineering Students Concepts and Applications
 System Dynamics for Engineering Students Concepts and Applications Nicolae Lobontiu University of Alaska Anchorage "Ж AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE
System Dynamics for Engineering Students Concepts and Applications Nicolae Lobontiu University of Alaska Anchorage "Ж AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE
Contents. Dynamics and control of mechanical systems. Focus on
 Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (01/08) Day 2 (03/08) Day 3 (05/08) Day 4 (07/08) Day 5 (09/08) Day 6 (11/08) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid bodies
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (01/08) Day 2 (03/08) Day 3 (05/08) Day 4 (07/08) Day 5 (09/08) Day 6 (11/08) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid bodies
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 4, Issue 07, 2016 ISSN (online):
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 4, Issue 07, 2016 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Analysis of Vibration Transmissibility on a System using Finite Element Analysis Rajesh
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 4, Issue 07, 2016 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Analysis of Vibration Transmissibility on a System using Finite Element Analysis Rajesh
Chapter 4 Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices
 Chapter 4 Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Section 5 Inverse of a Square Matrix Learning Objectives for Section 4.5 Inverse of a Square Matrix The student will be able to identify identity matrices
Chapter 4 Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Section 5 Inverse of a Square Matrix Learning Objectives for Section 4.5 Inverse of a Square Matrix The student will be able to identify identity matrices
Excel Spreadsheet in Mechanical Engineering Technology Education
 Excel Spreadsheet in Mechanical Engineering Technology Education Prof. Ti Lin, Liu Department of Manufacturing & Mechanical Engineering Technology Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, NY 14623
Excel Spreadsheet in Mechanical Engineering Technology Education Prof. Ti Lin, Liu Department of Manufacturing & Mechanical Engineering Technology Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, NY 14623
ANALYTICAL MECHANICS. LOUIS N. HAND and JANET D. FINCH CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS
 ANALYTICAL MECHANICS LOUIS N. HAND and JANET D. FINCH CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface xi 1 LAGRANGIAN MECHANICS l 1.1 Example and Review of Newton's Mechanics: A Block Sliding on an Inclined Plane 1
ANALYTICAL MECHANICS LOUIS N. HAND and JANET D. FINCH CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface xi 1 LAGRANGIAN MECHANICS l 1.1 Example and Review of Newton's Mechanics: A Block Sliding on an Inclined Plane 1
Developing a Virtual Model of a Second Order System to Simulation Real Laboratory Measurement Problems
 Proceedings of 24 IMECE: November 13-19, 24, Anaheim, CA 24 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and RD&D Expo Developing a Virtual Model of a Second Order System to Simulation Real Laboratory
Proceedings of 24 IMECE: November 13-19, 24, Anaheim, CA 24 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and RD&D Expo Developing a Virtual Model of a Second Order System to Simulation Real Laboratory
DYNAMICS OF A SPINNING MEMBRANE
 Preprint AAS 1-601 DYNAMICS OF A SPINNING MEMBRANE Jer-Nan Juang Chung-Han Hung and William K. Wilkie INTRODUCTION A novel approach is introduced to conduct dynamic analysis and system identification of
Preprint AAS 1-601 DYNAMICS OF A SPINNING MEMBRANE Jer-Nan Juang Chung-Han Hung and William K. Wilkie INTRODUCTION A novel approach is introduced to conduct dynamic analysis and system identification of
Piezoelectric Crystals Application on Landing Gears for Harvesting Energy
 Template Full Paper Aerospace Technology Congress11-12 October 2016, Solna, Stockholm Piezoelectric Crystals Application on Landing Gears for Harvesting Energy J. C. C.Pereira*, J.. P Silva** * Department
Template Full Paper Aerospace Technology Congress11-12 October 2016, Solna, Stockholm Piezoelectric Crystals Application on Landing Gears for Harvesting Energy J. C. C.Pereira*, J.. P Silva** * Department
Differential Equations and Linear Algebra Exercises. Department of Mathematics, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh EH14 4AS
 Differential Equations and Linear Algebra Exercises Department of Mathematics, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh EH14 4AS CHAPTER 1 Linear second order ODEs Exercises 1.1. (*) 1 The following differential
Differential Equations and Linear Algebra Exercises Department of Mathematics, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh EH14 4AS CHAPTER 1 Linear second order ODEs Exercises 1.1. (*) 1 The following differential
Differential Equations, Math 315 Midterm 2 Solutions
 Name: Section: Differential Equations, Math 35 Midterm 2 Solutions. A mass of 5 kg stretches a spring 0. m (meters). The mass is acted on by an external force of 0 sin(t/2)n (newtons) and moves in a medium
Name: Section: Differential Equations, Math 35 Midterm 2 Solutions. A mass of 5 kg stretches a spring 0. m (meters). The mass is acted on by an external force of 0 sin(t/2)n (newtons) and moves in a medium
AN ITERATIVE APPROACH TO VISCOUS DAMPING MATRIX IDENTIFICATION
 AN ITERATIVE APPROACH TO VISCOUS DAMPING MATRIX IDENTIFICATION Deborah F. Pilkey & Daniel J. Inman Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics Virginia Tech Blacksburg, VA 2406-029 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
AN ITERATIVE APPROACH TO VISCOUS DAMPING MATRIX IDENTIFICATION Deborah F. Pilkey & Daniel J. Inman Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics Virginia Tech Blacksburg, VA 2406-029 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
Computation Of Natural Frequencies Of Multi Degree Of Freedom System
 Computation Of Natural Frequencies Of Multi Degree Of Freedom System T. Ravi teja M.Tech (Robotics) S. Krishna chaitanya M.Tech Assistant professor Associate professor Narasaraopeta Engineering college
Computation Of Natural Frequencies Of Multi Degree Of Freedom System T. Ravi teja M.Tech (Robotics) S. Krishna chaitanya M.Tech Assistant professor Associate professor Narasaraopeta Engineering college
5.5 Exercises for This Chapter Two-Axle Vehicle on Cosine Track Two-Axle Vehicle on Generally Periodic Track...
 Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 The Basic Function of the Wheel/rail System.... 1 1.2 Significance of Dynamics on the Operation of Rail Vehicles... 2 1.3 On the History of Research in the Field of Railway
Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 The Basic Function of the Wheel/rail System.... 1 1.2 Significance of Dynamics on the Operation of Rail Vehicles... 2 1.3 On the History of Research in the Field of Railway
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems
 Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (03/05) - 05/05 Day 2 (07/05) Day 3 (09/05) Day 4 (11/05) Day 5 (14/05) Day 6 (16/05) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (03/05) - 05/05 Day 2 (07/05) Day 3 (09/05) Day 4 (11/05) Day 5 (14/05) Day 6 (16/05) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid
Math 330 (Section 7699 ): Fall 2015 Syllabus
 College of Staten Island, City University of New York (CUNY) Math 330 (Section 7699 ): Fall 2015 Syllabus Instructor: Joseph Maher Applied Mathematical Analysis I Office: 1S-222 Phone: (718) 982-3623 Email:
College of Staten Island, City University of New York (CUNY) Math 330 (Section 7699 ): Fall 2015 Syllabus Instructor: Joseph Maher Applied Mathematical Analysis I Office: 1S-222 Phone: (718) 982-3623 Email:
ANALYTICAL MODELING OF PLANETARY GEAR AND SENSITIVITY OF NATURAL FREQUENCIES
 ANALYTICAL MODELING OF PLANETARY GEAR AND SENSITIVITY OF NATURAL FREQUENCIES MAJID MEHRABI 1, DR. V.P.SINGH 2 1 Research Scholar, Department of Mechanical Engg. Department-PEC University of Technology
ANALYTICAL MODELING OF PLANETARY GEAR AND SENSITIVITY OF NATURAL FREQUENCIES MAJID MEHRABI 1, DR. V.P.SINGH 2 1 Research Scholar, Department of Mechanical Engg. Department-PEC University of Technology
Car Dynamics using Quarter Model and Passive Suspension, Part VI: Sprung-mass Step Response
 IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 17, Issue 2, Ver. 1 (Mar Apr. 2015), PP 65-74 www.iosrjournals.org Car Dynamics using Quarter Model and Passive
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 17, Issue 2, Ver. 1 (Mar Apr. 2015), PP 65-74 www.iosrjournals.org Car Dynamics using Quarter Model and Passive
Seminar 6: COUPLED HARMONIC OSCILLATORS
 Seminar 6: COUPLED HARMONIC OSCILLATORS 1. Lagrangian Equations of Motion Let consider a system consisting of two harmonic oscillators that are coupled together. As a model, we will use two particles attached
Seminar 6: COUPLED HARMONIC OSCILLATORS 1. Lagrangian Equations of Motion Let consider a system consisting of two harmonic oscillators that are coupled together. As a model, we will use two particles attached
AC : ASSESSING THE RELIABILITY OF SOME CLASSICAL MECHANICAL VIBRATION DESIGNS VIA SIMULATION SOFTWARE
 AC 011-14: ASSESSING THE RELIABILITY OF SOME CLASSICAL MECHANICAL VIBRATION DESIGNS VIA SIMULATION SOFTWARE Arnaldo Mazzei, Kettering University ARNALDO MAZZEI is a Professor of Mechanical Engineering
AC 011-14: ASSESSING THE RELIABILITY OF SOME CLASSICAL MECHANICAL VIBRATION DESIGNS VIA SIMULATION SOFTWARE Arnaldo Mazzei, Kettering University ARNALDO MAZZEI is a Professor of Mechanical Engineering
Structural Dynamics A Graduate Course in Aerospace Engineering
 Structural Dynamics A Graduate Course in Aerospace Engineering By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir The Science and Art of Structural Dynamics What do all the followings have in common? > A sport-utility
Structural Dynamics A Graduate Course in Aerospace Engineering By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir The Science and Art of Structural Dynamics What do all the followings have in common? > A sport-utility
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 5 Torsional Vibrations Lecture - 4 Transfer Matrix Approach
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 5 Torsional Vibrations Lecture - 4 Transfer Matrix Approach
Translational and Rotational Dynamics!
 Translational and Rotational Dynamics Robert Stengel Robotics and Intelligent Systems MAE 345, Princeton University, 217 Copyright 217 by Robert Stengel. All rights reserved. For educational use only.
Translational and Rotational Dynamics Robert Stengel Robotics and Intelligent Systems MAE 345, Princeton University, 217 Copyright 217 by Robert Stengel. All rights reserved. For educational use only.
Response Analysis for Multi Support Earthquake Excitation
 Chapter 5 Response Analysis for Multi Support Earthquake Excitation 5.1 Introduction It is very important to perform the dynamic analysis for the structure subjected to random/dynamic loadings. The dynamic
Chapter 5 Response Analysis for Multi Support Earthquake Excitation 5.1 Introduction It is very important to perform the dynamic analysis for the structure subjected to random/dynamic loadings. The dynamic
Follow links Class Use and other Permissions. For more information, send to:
 COPYRIGHT NOTICE: Stephen L. Campbell & Richard Haberman: Introduction to Differential Equations with Dynamical Systems is published by Princeton University Press and copyrighted, 2008, by Princeton University
COPYRIGHT NOTICE: Stephen L. Campbell & Richard Haberman: Introduction to Differential Equations with Dynamical Systems is published by Princeton University Press and copyrighted, 2008, by Princeton University
e jωt = cos(ωt) + jsin(ωt),
 This chapter introduces you to the most useful mechanical oscillator model, a mass-spring system with a single degree of freedom. Basic understanding of this system is the gateway to the understanding
This chapter introduces you to the most useful mechanical oscillator model, a mass-spring system with a single degree of freedom. Basic understanding of this system is the gateway to the understanding
ME scope Application Note 28
 App Note 8 www.vibetech.com 3/7/17 ME scope Application Note 8 Mathematics of a Mass-Spring-Damper System INTRODUCTION In this note, the capabilities of ME scope will be used to build a model of the mass-spring-damper
App Note 8 www.vibetech.com 3/7/17 ME scope Application Note 8 Mathematics of a Mass-Spring-Damper System INTRODUCTION In this note, the capabilities of ME scope will be used to build a model of the mass-spring-damper
Dynamic Response of Structures With Frequency Dependent Damping
 Dynamic Response of Structures With Frequency Dependent Damping Blanca Pascual & S Adhikari School of Engineering, Swansea University, Swansea, UK Email: S.Adhikari@swansea.ac.uk URL: http://engweb.swan.ac.uk/
Dynamic Response of Structures With Frequency Dependent Damping Blanca Pascual & S Adhikari School of Engineering, Swansea University, Swansea, UK Email: S.Adhikari@swansea.ac.uk URL: http://engweb.swan.ac.uk/
Dynamic Analysis on Vibration Isolation of Hypersonic Vehicle Internal Systems
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 1 (2013), pp. 55-60 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Dynamic Analysis on Vibration
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 1 (2013), pp. 55-60 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Dynamic Analysis on Vibration
Dynamics of Ocean Structures Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Dynamics of Ocean Structures Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 1 Lecture - 10 Methods of Writing Equation of Motion (Refer
Dynamics of Ocean Structures Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 1 Lecture - 10 Methods of Writing Equation of Motion (Refer
Vibration Mechanics. Linear Discrete Systems SPRINGER SCIENCE+BUSINESS MEDIA, B.V. M. Del Pedro and P. Pahud
 Vibration Mechanics Vibration Mechanics Linear Discrete Systems by M. Del Pedro and P. Pahud Swiss Federal Institute oftechnology, Lausanne, Switzerland SPRINGER SCIENCE+BUSINESS MEDIA, B.V. ISBN 978-94-010-5554-3
Vibration Mechanics Vibration Mechanics Linear Discrete Systems by M. Del Pedro and P. Pahud Swiss Federal Institute oftechnology, Lausanne, Switzerland SPRINGER SCIENCE+BUSINESS MEDIA, B.V. ISBN 978-94-010-5554-3
Vibrations Qualifying Exam Study Material
 Vibrations Qualifying Exam Study Material The candidate is expected to have a thorough understanding of engineering vibrations topics. These topics are listed below for clarification. Not all instructors
Vibrations Qualifying Exam Study Material The candidate is expected to have a thorough understanding of engineering vibrations topics. These topics are listed below for clarification. Not all instructors
Appendix A Prototypes Models
 Appendix A Prototypes Models This appendix describes the model of the prototypes used in Chap. 3. These mathematical models can also be found in the Student Handout by Quanser. A.1 The QUANSER SRV-02 Setup
Appendix A Prototypes Models This appendix describes the model of the prototypes used in Chap. 3. These mathematical models can also be found in the Student Handout by Quanser. A.1 The QUANSER SRV-02 Setup
CHAPTER 2 TRANSFER FUNCTION ANALYSIS
 . Introduction CHAPTER TRANSFER FUNCTION ANALYSIS The purpose of this chapter is to illustrate how to derive equations of motion for Multi Degree of Freedom (mdof) systems and how to solve for their transfer
. Introduction CHAPTER TRANSFER FUNCTION ANALYSIS The purpose of this chapter is to illustrate how to derive equations of motion for Multi Degree of Freedom (mdof) systems and how to solve for their transfer
MEC3403. Dynamics II. Introductory book. Faculty of Engineering and Surveying
 MEC3403 Dynamics II Faculty of Engineering and Surveying Introductory book Semester 2 2010 Published by University of Southern Queensland Toowoomba Queensland 4350 Australia http://www.usq.edu.au University
MEC3403 Dynamics II Faculty of Engineering and Surveying Introductory book Semester 2 2010 Published by University of Southern Queensland Toowoomba Queensland 4350 Australia http://www.usq.edu.au University
J. A. Jurado, S. Hernández, A. Baldomir, F. Nieto, School of Civil Engineering of the University of La Coruña.
 EACWE 5 Florence, Italy 19 th 23 rd July 2009 Flying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci Aeroelastic Analysis of Miradoiros Bridge in La Coruña (Spain) J. A. Jurado, S. Hernández, A. Baldomir, F. Nieto,
EACWE 5 Florence, Italy 19 th 23 rd July 2009 Flying Sphere image Museo Ideale L. Da Vinci Aeroelastic Analysis of Miradoiros Bridge in La Coruña (Spain) J. A. Jurado, S. Hernández, A. Baldomir, F. Nieto,
Module 4: Dynamic Vibration Absorbers and Vibration Isolator Lecture 19: Active DVA. The Lecture Contains: Development of an Active DVA
 The Lecture Contains: Development of an Active DVA Proof Mass Actutor Application of Active DVA file:///d /chitra/vibration_upload/lecture19/19_1.htm[6/25/2012 12:35:51 PM] In this section, we will consider
The Lecture Contains: Development of an Active DVA Proof Mass Actutor Application of Active DVA file:///d /chitra/vibration_upload/lecture19/19_1.htm[6/25/2012 12:35:51 PM] In this section, we will consider
Method of unsteady aerodynamic forces approximation for aeroservoelastic interactions
 Method of unsteady aerodynamic forces approximation for aeroservoelastic interactions Iulian Cotoi Ecole de Technologie Supérieure, 1100 Notre Dame O., Montréal, QC, Canada, H3C1K3 Ruxandra M. Botez Ecole
Method of unsteady aerodynamic forces approximation for aeroservoelastic interactions Iulian Cotoi Ecole de Technologie Supérieure, 1100 Notre Dame O., Montréal, QC, Canada, H3C1K3 Ruxandra M. Botez Ecole
The Development of Advanced Control Laboratories
 Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Rose-Hulman Scholar Graduate Theses - Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Spring 2-2015 The Development of Advanced Control Laboratories Matthew Randall Winter
Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Rose-Hulman Scholar Graduate Theses - Mechanical Engineering Mechanical Engineering Spring 2-2015 The Development of Advanced Control Laboratories Matthew Randall Winter
Damping Performance of Taut Cables with Passive Absorbers Incorporating Inerters
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Damping Performance of Taut Cables with Passive Absorbers Incorporating Inerters To cite this article: Jiannan Luo et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Damping Performance of Taut Cables with Passive Absorbers Incorporating Inerters To cite this article: Jiannan Luo et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Application of operational noise path analysis to systems with rotational degrees of freedom
 Application of operational noise path analysis to systems with rotational degrees of freedom D. Tcherniak Brüel & Kjær, Sound & Vibration Measurement A/S Skodsborgvej 307, DK-2850, Nærum, Denmark email:
Application of operational noise path analysis to systems with rotational degrees of freedom D. Tcherniak Brüel & Kjær, Sound & Vibration Measurement A/S Skodsborgvej 307, DK-2850, Nærum, Denmark email:
BMEN 398: MATLAB Module: Higher Order Differential Equations; SIMULINK Fall 2005 Updated 8/21/2005 Hart
 BMEN 398: MATLAB Module: Higher Order Differential Equations; SIMULINK Fall 2005 Updated 8/21/2005 Hart Higher Order ODEs: (Rao, 2002) Although we can now write MATLAB code to find numerical solutions
BMEN 398: MATLAB Module: Higher Order Differential Equations; SIMULINK Fall 2005 Updated 8/21/2005 Hart Higher Order ODEs: (Rao, 2002) Although we can now write MATLAB code to find numerical solutions
Car Dynamics using Quarter Model and Passive Suspension; Part V: Frequency Response Considering Driver-seat
 357 Car Dynamics using Quarter Model and Passive Suspension; Part V: Frequency Response Considering Driver-seat Galal Ali Hassaan Emeritus Professor, Department of Mechanical Design & Production, Faculty
357 Car Dynamics using Quarter Model and Passive Suspension; Part V: Frequency Response Considering Driver-seat Galal Ali Hassaan Emeritus Professor, Department of Mechanical Design & Production, Faculty
UNCERTAINTY MODELING VIA FREQUENCY DOMAIN MODEL VALIDATION
 AIAA 99-3959 UNCERTAINTY MODELING VIA FREQUENCY DOMAIN MODEL VALIDATION Martin R. Waszak, * NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia Dominick Andrisani II, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana
AIAA 99-3959 UNCERTAINTY MODELING VIA FREQUENCY DOMAIN MODEL VALIDATION Martin R. Waszak, * NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia Dominick Andrisani II, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana
Research Article On the Dynamics of the Furuta Pendulum
 Control Science and Engineering Volume, Article ID 583, 8 pages doi:.55//583 Research Article On the Dynamics of the Furuta Pendulum Benjamin Seth Cazzolato and Zebb Prime School of Mechanical Engineering,
Control Science and Engineering Volume, Article ID 583, 8 pages doi:.55//583 Research Article On the Dynamics of the Furuta Pendulum Benjamin Seth Cazzolato and Zebb Prime School of Mechanical Engineering,
CITY UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES
 CITY UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING MEng/BEng (Hons) AIR TRANSPORT ENGINEERING MEng/BEng (Hons) AIR TRANSPORT ENGINEERING BSc (Hons) AUTOMOTIVE AND
CITY UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING MEng/BEng (Hons) AIR TRANSPORT ENGINEERING MEng/BEng (Hons) AIR TRANSPORT ENGINEERING BSc (Hons) AUTOMOTIVE AND
High accuracy numerical and signal processing approaches to extract flutter derivatives
 High accuracy numerical and signal processing approaches to extract flutter derivatives *NakHyun Chun 1) and Hak-eun Lee 2) 1), 2) School of Civil, Environmental and Architectural Engineering, Korea University,
High accuracy numerical and signal processing approaches to extract flutter derivatives *NakHyun Chun 1) and Hak-eun Lee 2) 1), 2) School of Civil, Environmental and Architectural Engineering, Korea University,
Lecture 9: Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors in Classical Mechanics (See Section 3.12 in Boas)
 Lecture 9: Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors in Classical Mechanics (See Section 3 in Boas) As suggested in Lecture 8 the formalism of eigenvalues/eigenvectors has many applications in physics, especially in
Lecture 9: Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors in Classical Mechanics (See Section 3 in Boas) As suggested in Lecture 8 the formalism of eigenvalues/eigenvectors has many applications in physics, especially in
Software Verification
 EXAMPLE 6-6 LINK SUNY BUFFALO DAMPER WITH LINEAR VELOCITY EXPONENT PROBLEM DESCRIPTION This example comes from Section 5 of Scheller and Constantinou 1999 ( the SUNY Buffalo report ). It is a two-dimensional,
EXAMPLE 6-6 LINK SUNY BUFFALO DAMPER WITH LINEAR VELOCITY EXPONENT PROBLEM DESCRIPTION This example comes from Section 5 of Scheller and Constantinou 1999 ( the SUNY Buffalo report ). It is a two-dimensional,
International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational and Applied Sciences (IJETCAS)
 International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational
International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational
Fourier transforms of molecular vibrations
 Fourier transforms of molecular vibrations Part I: An Introduction to the Harmonic Oscillator and Fourier Transforms W. Tandy Grubbs, Department of Chemistry, Unit 827, Stetson University, DeLand, FL 32720
Fourier transforms of molecular vibrations Part I: An Introduction to the Harmonic Oscillator and Fourier Transforms W. Tandy Grubbs, Department of Chemistry, Unit 827, Stetson University, DeLand, FL 32720
Three year rotational plan for assessing student outcomes: EET
 Three year rotational plan for assessing student outcomes: EET Year 2015 ABET a, b, c, d, e ABET a, b, c, d, e 2016 ABET f, g, h, i, j, k ABET f, g, h, i, j, k 2017 EET a - e EET a - e 2018 ABET a, b,
Three year rotational plan for assessing student outcomes: EET Year 2015 ABET a, b, c, d, e ABET a, b, c, d, e 2016 ABET f, g, h, i, j, k ABET f, g, h, i, j, k 2017 EET a - e EET a - e 2018 ABET a, b,
In the presence of viscous damping, a more generalized form of the Lagrange s equation of motion can be written as
 2 MODELING Once the control target is identified, which includes the state variable to be controlled (ex. speed, position, temperature, flow rate, etc), and once the system drives are identified (ex. force,
2 MODELING Once the control target is identified, which includes the state variable to be controlled (ex. speed, position, temperature, flow rate, etc), and once the system drives are identified (ex. force,
NONLINEAR STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS USING FE METHODS
 NONLINEAR STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS USING FE METHODS Nonlinear Structural Dynamics Using FE Methods emphasizes fundamental mechanics principles and outlines a modern approach to understanding structural dynamics.
NONLINEAR STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS USING FE METHODS Nonlinear Structural Dynamics Using FE Methods emphasizes fundamental mechanics principles and outlines a modern approach to understanding structural dynamics.
Teaching Nanoscale Transport Phenomena
 Teaching Nanoscale Transport Phenomena Pamela Norris Professor Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Virginia Charlottesville, VA 22902 VIRGINIA 1 UVa MAE 612 Microscale Heat
Teaching Nanoscale Transport Phenomena Pamela Norris Professor Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of Virginia Charlottesville, VA 22902 VIRGINIA 1 UVa MAE 612 Microscale Heat
COMPLEX MODES IN LINEAR STOCHASTIC SYSTEMS
 Proceedings of VETOMAC-I October 25-27, 2, Bangalore, INDIA COMPLEX MODES IN LINEAR STOCHASTIC SYSTEMS S. Adhikari Cambridge University Engineering Department Trumpington Street Cambridge CB2 1PZ (U.K.)
Proceedings of VETOMAC-I October 25-27, 2, Bangalore, INDIA COMPLEX MODES IN LINEAR STOCHASTIC SYSTEMS S. Adhikari Cambridge University Engineering Department Trumpington Street Cambridge CB2 1PZ (U.K.)
AEROELASTIC ANALYSIS OF SPHERICAL SHELLS
 11th World Congress on Computational Mechanics (WCCM XI) 5th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM V) 6th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD VI) E. Oñate, J. Oliver
11th World Congress on Computational Mechanics (WCCM XI) 5th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM V) 6th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD VI) E. Oñate, J. Oliver
MECHANICS OF AERO-STRUCTURES
 MECHANICS OF AERO-STRUCTURES Mechanics of Aero-structures is a concise textbook for students of aircraft structures, which covers aircraft loads and maneuvers, as well as torsion and bending of singlecell,
MECHANICS OF AERO-STRUCTURES Mechanics of Aero-structures is a concise textbook for students of aircraft structures, which covers aircraft loads and maneuvers, as well as torsion and bending of singlecell,
The student will experimentally determine the parameters to represent the behavior of a damped oscillatory system of one degree of freedom.
 Practice 3 NAME STUDENT ID LAB GROUP PROFESSOR INSTRUCTOR Vibrations of systems of one degree of freedom with damping QUIZ 10% PARTICIPATION & PRESENTATION 5% INVESTIGATION 10% DESIGN PROBLEM 15% CALCULATIONS
Practice 3 NAME STUDENT ID LAB GROUP PROFESSOR INSTRUCTOR Vibrations of systems of one degree of freedom with damping QUIZ 10% PARTICIPATION & PRESENTATION 5% INVESTIGATION 10% DESIGN PROBLEM 15% CALCULATIONS
Computational Stiffness Method
 Computational Stiffness Method Hand calculations are central in the classical stiffness method. In that approach, the stiffness matrix is established column-by-column by setting the degrees of freedom
Computational Stiffness Method Hand calculations are central in the classical stiffness method. In that approach, the stiffness matrix is established column-by-column by setting the degrees of freedom
Theoretical Manual Theoretical background to the Strand7 finite element analysis system
 Theoretical Manual Theoretical background to the Strand7 finite element analysis system Edition 1 January 2005 Strand7 Release 2.3 2004-2005 Strand7 Pty Limited All rights reserved Contents Preface Chapter
Theoretical Manual Theoretical background to the Strand7 finite element analysis system Edition 1 January 2005 Strand7 Release 2.3 2004-2005 Strand7 Pty Limited All rights reserved Contents Preface Chapter
AA 242B / ME 242B: Mechanical Vibrations (Spring 2016)
 AA 242B / ME 242B: Mechanical Vibrations (Spring 206) Solution of Homework #3 Control Tab Figure : Schematic for the control tab. Inadequacy of a static-test A static-test for measuring θ would ideally
AA 242B / ME 242B: Mechanical Vibrations (Spring 206) Solution of Homework #3 Control Tab Figure : Schematic for the control tab. Inadequacy of a static-test A static-test for measuring θ would ideally
1439. Numerical simulation of the magnetic field and electromagnetic vibration analysis of the AC permanent-magnet synchronous motor
 1439. Numerical simulation of the magnetic field and electromagnetic vibration analysis of the AC permanent-magnet synchronous motor Bai-zhou Li 1, Yu Wang 2, Qi-chang Zhang 3 1, 2, 3 School of Mechanical
1439. Numerical simulation of the magnetic field and electromagnetic vibration analysis of the AC permanent-magnet synchronous motor Bai-zhou Li 1, Yu Wang 2, Qi-chang Zhang 3 1, 2, 3 School of Mechanical
In this lecture you will learn the following
 Module 9 : Forced Vibration with Harmonic Excitation; Undamped Systems and resonance; Viscously Damped Systems; Frequency Response Characteristics and Phase Lag; Systems with Base Excitation; Transmissibility
Module 9 : Forced Vibration with Harmonic Excitation; Undamped Systems and resonance; Viscously Damped Systems; Frequency Response Characteristics and Phase Lag; Systems with Base Excitation; Transmissibility
REVIEW. Hamilton s principle. based on FW-18. Variational statement of mechanics: (for conservative forces) action Equivalent to Newton s laws!
 Hamilton s principle Variational statement of mechanics: (for conservative forces) action Equivalent to Newton s laws! based on FW-18 REVIEW the particle takes the path that minimizes the integrated difference
Hamilton s principle Variational statement of mechanics: (for conservative forces) action Equivalent to Newton s laws! based on FW-18 REVIEW the particle takes the path that minimizes the integrated difference
θ α W Description of aero.m
 Description of aero.m Determination of the aerodynamic forces, moments and power by means of the blade element method; for known mean wind speed, induction factor etc. Simplifications: uniform flow (i.e.
Description of aero.m Determination of the aerodynamic forces, moments and power by means of the blade element method; for known mean wind speed, induction factor etc. Simplifications: uniform flow (i.e.
Constrained motion and generalized coordinates
 Constrained motion and generalized coordinates based on FW-13 Often, the motion of particles is restricted by constraints, and we want to: work only with independent degrees of freedom (coordinates) k
Constrained motion and generalized coordinates based on FW-13 Often, the motion of particles is restricted by constraints, and we want to: work only with independent degrees of freedom (coordinates) k
Numerical Methods for Engineers
 Numerical Methods for Engineers SEVENTH EDITION Steven C Chopra Berger Chair in Computing and Engineering Tufts University Raymond P. Canal Professor Emeritus of Civil Engineering of Michiaan University
Numerical Methods for Engineers SEVENTH EDITION Steven C Chopra Berger Chair in Computing and Engineering Tufts University Raymond P. Canal Professor Emeritus of Civil Engineering of Michiaan University
Reduction to the associated homogeneous system via a particular solution
 June PURDUE UNIVERSITY Study Guide for the Credit Exam in (MA 5) Linear Algebra This study guide describes briefly the course materials to be covered in MA 5. In order to be qualified for the credit, one
June PURDUE UNIVERSITY Study Guide for the Credit Exam in (MA 5) Linear Algebra This study guide describes briefly the course materials to be covered in MA 5. In order to be qualified for the credit, one
a. Follow the Start-Up Procedure in the laboratory manual. Note the safety rules.
 Lab #1 - Free Vibration Name: Date: Section / Group: Procedure Steps (from lab manual): a. Follow the Start-Up Procedure in the laboratory manual. Note the safety rules. b. Locate the various springs and
Lab #1 - Free Vibration Name: Date: Section / Group: Procedure Steps (from lab manual): a. Follow the Start-Up Procedure in the laboratory manual. Note the safety rules. b. Locate the various springs and
A NEW ANALYSIS APPROACH FOR MOTORCYCLE BRAKE SQUEAL NOISE AND ITS ADAPTATION
 SETC001 01 1850 A NEW ANALYSIS APPROACH FOR MOTORCYCLE BRAKE SQUEAL NOISE AND ITS ADAPTATION Hiroyuki Nakata, Kiyoshi Kobayashi, Masashi Kajita - Honda R&D Co., Ltd. - JAPAN C.H.Jerry CHUNG - MTS Systems
SETC001 01 1850 A NEW ANALYSIS APPROACH FOR MOTORCYCLE BRAKE SQUEAL NOISE AND ITS ADAPTATION Hiroyuki Nakata, Kiyoshi Kobayashi, Masashi Kajita - Honda R&D Co., Ltd. - JAPAN C.H.Jerry CHUNG - MTS Systems
