(b) The two pithballs have opposite electric charges positive for the first ball and negative for the second so they attract each other.
|
|
|
- Clarence Simon Owen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHY 309 L. Solutions for Problem set # 1. Question Q.4 at the end of chapter 12: (a) When a piece of glass is rubbed with a nylon cloth, some electrons move from the glass to the nylon. Since the electrons carry negative charges, this means that the nylon becomes negatively charged while the glass becomes positively charged. Subsequently, when the glass rod touches the first pith ball, the rod recovers some of its missing electrons by stealing them from the ball. In this way, some of the rod s positive electric charge gets transferred to the ball, so the first pith ball becomes positively charged. Likewise, when the nylon cloth touches the second pith ball, some of the nylon s extra electrons move to the ball. Thus, some of the nylon s negative charge is transferred to the ball, so the second ball becomes negatively charged. (b) The two pithballs have opposite electric charges positive for the first ball and negative for the second so they attract each other. Question Q.14 at the end of chapter 12: Initially, the pith ball has no net electric charge. Although the molecules of cellulose, lignin, etc., in the pith naturally contain both positively and negatively charged atoms, their charges cancel each other and the net charge is zero. Moreover, both types of charge are distributed uniformly throughout the pith, so every little piece of the ball is neutral and not just the whole ball. But when a charged rod is brought near the ball, the pith becomes polarized. Suppose the rod is positively charged as in figure 12.9 on page 242 of the textbook. This charge attract the negatively charged atoms in the pith so they move a tiny distance closer to the rod. On the other hand, the positively charged atoms in the pith are repelled by the rod s charge so they move a tiny distance away from the rod. Consequently, the two types of charges cancel each other only in the middle of the pith ball but not on its surface! On the side of the ball facing the rod the surface becomes negatively charged because the negatively charged atoms move in while the positively charged atoms move out. Similarly, on the other 1
2 side of the ball the surface becomes positively charged because the positive atoms move in while the negative atoms move out. Altogether, the net charge of the pith ball remains zero, but the side of the ball facing the rod acquires a negative charge while the opposite side gets an opposite positive charge. Consequently, the side of the ball facing the positively charged rod is attracted to it while the other side of the ball is repelled by the rod. But since the ball s side attracted to the rod is closer to it than the repelled side, the attractive force is stronger than the repulsive! Thus, the net force on the neutral pith ball is towards the charged rod. Now suppose the rod is negatively charged. In this case, the polarization of the pith works in the opposite direction: the positively charged atoms move a tiny distance towards the rod while the negatively charged atoms move a tiny distance away from it. Consequently, the surface of the pith ball facing the rod becomes positively charged which is attracted to the negatively charged rod while the surface on the other side of the ball becomes negatively charged and is repelled by the rod. The two charges are equal and opposite so the net charge of the ball is zero, but the forces between the two sides of the ball and the rod do not cancel. Instead, because of un-equal distances from the rod, the attractive force on the near side of the ball is stronger than the repulsive force on the far side, so the net force of the neutral pith ball is towards the charged rod, regardless of rod s charge being positive or negative! Thus, until the rod touches the pith ball, they attract each other because of the ball s polarization. But once they touch, some of the rod s charge is transferred to the ball. After that, the ball and the rod have like-sign charges both positive or both negative and they repel each other. Once the ball picks up enough net charge, this repulsive force becomes stronger than the attraction due to polarization, so the ball suddenly flies away from the rod. 2
3 Question Q.23 at the end of chapter 12: C A B D On this diagram, the red arrows are the electric fields of the positive charge +q only, the blue arrows are the electric fields of the negative charge q only, and the purple arrows are the net electric fields due to both charges. Problem E.8 at the end of chapter 12: The proton has positive charge +e = C while the electron has exactly opposite charge e. Like any other pair of opposite-sign electric charges, the electron and the proton attract each other with a Coulomb force F = k( e)(+e) r 2 = ke2 r 2 (1) where the indicates attractive rather than repulsive force, r is the distance between the two particles, and k = 1 4πε 0 = N m 2 /C 2. (2) In a hydrogen atom, the average distance between the electron and the proton is about r = 0.5 Å = m. At this distance, the numerical value of the attractive force is F = ke2 r 2 = (9 109 Nm 2 /C 2 )( C) 2 ( m) N. (3) This may not look like a big force, but please remember that the electron has has a very tiny mass m e kg. So the Coulomb force (3) gives it a tremendous acceleration a e = F/m e m/s 2, or 10,000 billion billion gees! 3
4 Problem E.10 at the end of chapter 12: A charge q in electric field E experiences an electrostatic force F = qe. (4) This is a vector equation, so for a positive charge q the force F has the same direction as the electric field E, while for a negative charge q the direction of the force F is opposite from the direction of the field E. The test charge in question q = +4µC is positive, so the electrostatic force acting on it has the same direction as the electric field. Since we know the direction of the force is downward, it follows that the direction of the electric field E is also downward. As to the magnitude E of the electric field, eq. (4) implies F = q E = E = F q, (5) hence E = 12 N C = N/C 3,000,000 V/m. (6) Problem E.12 at the end of chapter 12: The force on an electric charge q due to electric field E is F = qe. (4) This is a vector equation, so for a positive charge q the force F has the same direction as the electric field E, while for a negative charge q the direction of the force F is opposite from the direction of the field E. In this problem, the electric field E points to the right while the charge q is negative. Thus, the direction of the force F is opposite from the direction of E; in other words, the force on the charge is directed to the left. As to the magnitude of this force, F = q E = ( C) ( N/C) = N 0.25 N. (7) 4
5 Problem SP.1 at the end of chapter 12: Note: I am not sure the authors of this problem paid attention to significant figures, so I am calculating all the answers to 2 significant figures and then rounding them off to just 1 significant figure warranted by the problem data. (a) F AB = kq A q B r 2 AB = ( Nm 2 /C 2 )(+0.10 C)(+0.02 C) (2 m) 2 = N N. (8) (b) F CB = kq C q B r 2 CB = ( Nm 2 /C 2 )(+0.04 C)(+0.02 C) (1 m) 2 = N N. (9) (c) Since all 3 charges are positive, all forces between them are repulsive. Charge A sits left from charge B, so its force F AB pushes charge B to the right. On the other hand, charge C sits right from charge B, so its force F CB pushes charge B to the left. The net force on charge B is therefore F net onb = F AB F CB = N N = N N. (10) The magnitude of this force is mega Newtons, and its direction is to the left. (d) The net force on the test charge B is FonB net = q B E(B) (11) where E(B) is the electric field at point B created by all the charges except B itself. Given the net force obtained in part (c), this electric field is E(B) = Fnet onb q B = N C = V/m V/m. (12) In other words, the electric field created by charges A and C at point B has magnitude mega-volt per meter and direction to the left. 5
6 Note units: 1 V/m (Volt per meter) is the same as 1 N/C (Newton of force per Coulomb of charge). (e) In this part we change the value of the test charge B from q B = C to q B = 0.06 C but we don t change the charges A or C or the locations of any charges. Consequently, the electric field E(B) on the test charge B from the other charges A and C remains exactly as in part (d). Therefore, the force on the new test charge is simply FonnewB net = (new q B ) (old E(B)) = ( 0.06 C) ( V/m) = N N. (13) Note that the direction of this 8 mega Newton force is to the right rather than to the left. The non-textbook problem I is postponed to the next homework. 6
Chapter 18 Electric Force and Electric Fields. Sections
 Chapter 18 Electric Force and Electric Fields Sections 18.1 18.6 Objectives: After finishing this unit, you should be able to: Explain and demonstrate the First law of electrostatics and discuss charging
Chapter 18 Electric Force and Electric Fields Sections 18.1 18.6 Objectives: After finishing this unit, you should be able to: Explain and demonstrate the First law of electrostatics and discuss charging
Physics 12 ELECTROSTATICS
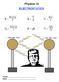 Physics 12 ELECTROSTATICS F = kq 1Q 2 r2 E = V d V = kq r E p = kq 1Q 2 r F = qe V = E p Q 1 000 000 Volts 1 000 000 Volts NAME: Block: Text References 3 rd Ed. Giancolli Pg. 416-30 4 th Ed. Giancolli
Physics 12 ELECTROSTATICS F = kq 1Q 2 r2 E = V d V = kq r E p = kq 1Q 2 r F = qe V = E p Q 1 000 000 Volts 1 000 000 Volts NAME: Block: Text References 3 rd Ed. Giancolli Pg. 416-30 4 th Ed. Giancolli
Electric Charge & Force Problems - 1 v Goodman & Zavorotniy
 The Atom Chapter Questions 1. Which part on an atom carries a positive charge? Which carries the negative charge? 2. How many types of electric charge are there? 3. When a neutral atom captures a free
The Atom Chapter Questions 1. Which part on an atom carries a positive charge? Which carries the negative charge? 2. How many types of electric charge are there? 3. When a neutral atom captures a free
Electric Charge & Force Problems - 1 v Goodman & Zavorotniy
 Electric Charge Chapter Questions 1. What happens to a plastic rod when it is rubbed with a piece of animal fur? What happens to the piece of fur? 2. How many types of electric charge are there? What are
Electric Charge Chapter Questions 1. What happens to a plastic rod when it is rubbed with a piece of animal fur? What happens to the piece of fur? 2. How many types of electric charge are there? What are
Electrostatics. Electrostatics - the study of electrical charges that can be collected and held in one place - charges at rest.
 Electrostatics Electrostatics - the study of electrical charges that can be collected and held in one place - charges at rest. Examples: BASIC IDEAS: Electricity begins inside the atom itself. An atom
Electrostatics Electrostatics - the study of electrical charges that can be collected and held in one place - charges at rest. Examples: BASIC IDEAS: Electricity begins inside the atom itself. An atom
Electrostatics Review A. A B. B C. C D. D
 Name: ate: 1. Which sketch best represents the charge distribution around a neutral electroscope when a positively charged strip is brought near, but does not touch, the electroscope? 4. In the diagram
Name: ate: 1. Which sketch best represents the charge distribution around a neutral electroscope when a positively charged strip is brought near, but does not touch, the electroscope? 4. In the diagram
c. They have electric charges that move freely d. Electrons are added to the rod a. charges are of unlike signs b. charges are of like signs
 Physics Review Chapter 17 & 18 Name: Date: Period: 1. What sentence best characterizes electron conductors? a. They have low mass density b. They have high tensile strength c. They have electric charges
Physics Review Chapter 17 & 18 Name: Date: Period: 1. What sentence best characterizes electron conductors? a. They have low mass density b. They have high tensile strength c. They have electric charges
ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS
 chapter ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) Section 18.1 The Origin of Electricity Section 18.2 Charged Objects and the
chapter ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) Section 18.1 The Origin of Electricity Section 18.2 Charged Objects and the
Electric Force and Field Chapter Questions
 Electric Force and Field Chapter Questions 1. What happens to a plastic rod when it is rubbed with a piece of animal fur? What happens to the piece of fur? 2. How many types of electric charge are there?
Electric Force and Field Chapter Questions 1. What happens to a plastic rod when it is rubbed with a piece of animal fur? What happens to the piece of fur? 2. How many types of electric charge are there?
Electric Fields Part 1: Coulomb s Law
 Electric Fields Part 1: Coulomb s Law F F Last modified: 07/02/2018 Contents Links Electric Charge & Coulomb s Law Electric Charge Coulomb s Law Example 1: Coulomb s Law Electric Field Electric Field Vector
Electric Fields Part 1: Coulomb s Law F F Last modified: 07/02/2018 Contents Links Electric Charge & Coulomb s Law Electric Charge Coulomb s Law Example 1: Coulomb s Law Electric Field Electric Field Vector
AP Physics 1 Electrostatics Practice Problems. Multiple Choice
 AP Physics 1 Electrostatics Practice Problems Multiple Choice 1. A plastic rod is rubbed with a piece of wool. During the process the plastic rod acquires a negative charge and the wool: (A) acquires an
AP Physics 1 Electrostatics Practice Problems Multiple Choice 1. A plastic rod is rubbed with a piece of wool. During the process the plastic rod acquires a negative charge and the wool: (A) acquires an
Chapter 20: Electric Fields and Forces Solutions
 Chapter 0: lectric Fields and Forces Solutions Questions: 5, 9, 13, 14, 0 xercises & Problems: 8, 14, 15, 6, 3, 43, 45, 58 Q0.5: When you take clothes out of the drier right after it stops, the clothes
Chapter 0: lectric Fields and Forces Solutions Questions: 5, 9, 13, 14, 0 xercises & Problems: 8, 14, 15, 6, 3, 43, 45, 58 Q0.5: When you take clothes out of the drier right after it stops, the clothes
r 2 and the charge on a proton is +e. We never see objects that have a charge which is not a whole number multiple of this number.
 Name: Physics Chapter 16 Study Guide ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Useful Information: e = 1.6"10 #19 C mass electron = 9.11"10 #31
Name: Physics Chapter 16 Study Guide ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Useful Information: e = 1.6"10 #19 C mass electron = 9.11"10 #31
C. Incorrect. Don t forget that the distance is squared in the Coulombs law formula.
 OAT Physics - Problem Drill 16: Electrostatics Question No. 1 of 10 1. The center of a balloon with 4x10 11 excess electrons is 30 centimeters away from a similar balloon with an equal excess of electrons.
OAT Physics - Problem Drill 16: Electrostatics Question No. 1 of 10 1. The center of a balloon with 4x10 11 excess electrons is 30 centimeters away from a similar balloon with an equal excess of electrons.
Electric Force and Electric Field Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1
 Electric Force and Electric Field Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1 Name Multiple Choice 1. A plastic rod is rubbed with a piece of wool. During the process the plastic rod acquires a negative charge
Electric Force and Electric Field Practice Problems PSI AP Physics 1 Name Multiple Choice 1. A plastic rod is rubbed with a piece of wool. During the process the plastic rod acquires a negative charge
Coulomb s Law. Phys102 Lecture 2. Key Points. Coulomb s Law The electric field (E is a vector!) References
 Phys102 Lecture 2 Phys102 Lecture 2-1 Coulomb s Law Key Points Coulomb s Law The electric field (E is a vector!) References SFU Ed: 21-5,6,7,8,9,10. 6 th Ed: 16-6,7,8,9,+. Phys102 Lecture 2 Phys102 Lecture
Phys102 Lecture 2 Phys102 Lecture 2-1 Coulomb s Law Key Points Coulomb s Law The electric field (E is a vector!) References SFU Ed: 21-5,6,7,8,9,10. 6 th Ed: 16-6,7,8,9,+. Phys102 Lecture 2 Phys102 Lecture
= C. on q 1 to the left. Using Coulomb s law, on q 2 to the right, and the charge q 2 exerts a force F 2 on 1 ( )
 Phsics Solutions to Chapter 5 5.. Model: Use the charge model. Solve: (a) In the process of charging b rubbing, electrons are removed from one material and transferred to the other because the are relativel
Phsics Solutions to Chapter 5 5.. Model: Use the charge model. Solve: (a) In the process of charging b rubbing, electrons are removed from one material and transferred to the other because the are relativel
Welcome to PHYS2002!
 Welcome to PHYS00! Physics I Done! We are now all experts in mechanics. Mechanics Mass M Interaction: mm F = G r 1 G = 6.67 10 Nm/ kg r M 11 1 We never said what mass is, only how it behaves. New Semester
Welcome to PHYS00! Physics I Done! We are now all experts in mechanics. Mechanics Mass M Interaction: mm F = G r 1 G = 6.67 10 Nm/ kg r M 11 1 We never said what mass is, only how it behaves. New Semester
Physics 1520, Fall 2011 Quiz 3, Form: A
 Physics 1520, Fall 2011 Quiz 3, Form: A Name: Date: Numeric answers must include units. Sketches must be labeled. All short-answer questions must include your reasoning, for full credit. A correct answer
Physics 1520, Fall 2011 Quiz 3, Form: A Name: Date: Numeric answers must include units. Sketches must be labeled. All short-answer questions must include your reasoning, for full credit. A correct answer
SPH 4U: Unit 3 - Electric and Magnetic Fields
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ SPH 4U: Unit 3 - Electric and Magnetic Fields Modified True/False (1 point each) Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to
Name: Class: _ Date: _ SPH 4U: Unit 3 - Electric and Magnetic Fields Modified True/False (1 point each) Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to
Electrostatics and Electric Potential - Outline
 Electrostatics and Electric Potential - Outline 1. Understand the basic properties of electric charge, including conservation of charge and that charges are quantized. 2. Differentiate between conductors
Electrostatics and Electric Potential - Outline 1. Understand the basic properties of electric charge, including conservation of charge and that charges are quantized. 2. Differentiate between conductors
Cutnell/Johnson Physics
 Cutnell/Johnson Physics Classroom Response System Questions Chapter 18 Electric Forces and Electric Fields Interactive Lecture Questions 18.1.1. A brass key has a net positive charge of +1.92 10 16 C.
Cutnell/Johnson Physics Classroom Response System Questions Chapter 18 Electric Forces and Electric Fields Interactive Lecture Questions 18.1.1. A brass key has a net positive charge of +1.92 10 16 C.
Chapter 23. Electric Fields
 Chapter 23 Electric Fields Electric Charges There are two kinds of electric charges Called positive and negative Negative charges are the type possessed by electrons Positive charges are the type possessed
Chapter 23 Electric Fields Electric Charges There are two kinds of electric charges Called positive and negative Negative charges are the type possessed by electrons Positive charges are the type possessed
IB-1 Physics Electrostatics Practice Questions. e +4e A. B. C. D.
 1. A plastic rod is rubbed with a cloth. At the end of the process, the rod is found to be positively charged and the cloth is found to be uncharged. This involves the movement of A. positive charge from
1. A plastic rod is rubbed with a cloth. At the end of the process, the rod is found to be positively charged and the cloth is found to be uncharged. This involves the movement of A. positive charge from
Electrostatics Electrostatics
 Electrostatics You will get a charge out of these questions... 1. A combination of four electrons and two protons would have a net charge of... d) 3.2 E 19 Coulombs c) +3.2 E 19 Coulombs b) 2 a) +2 2.
Electrostatics You will get a charge out of these questions... 1. A combination of four electrons and two protons would have a net charge of... d) 3.2 E 19 Coulombs c) +3.2 E 19 Coulombs b) 2 a) +2 2.
18.4 Coulomb's Law *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m52384 1 18.4 Coulomb's Law * Bobby Bailey Based on Coulomb's Law by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m52384 1 18.4 Coulomb's Law * Bobby Bailey Based on Coulomb's Law by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
Coulomb's Law * OpenStax. This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42308 1 Coulomb's Law * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract State Coulomb's law in terms of how
OpenStax-CNX module: m42308 1 Coulomb's Law * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract State Coulomb's law in terms of how
Electrostatics. Do Now: Describe the Concept of charge
 Electrostatics Do Now: Describe the Concept of charge Electrostatics The study of electrical charges that can be collected and held in one place Also referred to as static electricity Types of Charge:
Electrostatics Do Now: Describe the Concept of charge Electrostatics The study of electrical charges that can be collected and held in one place Also referred to as static electricity Types of Charge:
CHAPTER 15 PRE-TEST: ELECTRIC FORCE AND FIELDS
 Class: Date: CHAPTER 5 PRE-TEST: ELECTRIC FORCE AND FIELDS Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. What happens when a rubber rod is rubbed with
Class: Date: CHAPTER 5 PRE-TEST: ELECTRIC FORCE AND FIELDS Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. What happens when a rubber rod is rubbed with
Problem Set 2: Solutions
 University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 102 / LeClair Summer II 2012 Problem Set 2: Solutions 1. Two volley balls, mass 0.3 kg, tethered by nylon strings and charged with an electrostatic
University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 102 / LeClair Summer II 2012 Problem Set 2: Solutions 1. Two volley balls, mass 0.3 kg, tethered by nylon strings and charged with an electrostatic
Chapter Assignment Solutions
 Chapter 20-21 Assignment Solutions Table of Contents Page 558 #22, 24, 29, 31, 36, 37, 40, 43-48... 1 Lightning Worksheet (Transparency 20-4)... 4 Page 584 #42-46, 58-61, 66-69, 76-79, 84-86... 5 Chapter
Chapter 20-21 Assignment Solutions Table of Contents Page 558 #22, 24, 29, 31, 36, 37, 40, 43-48... 1 Lightning Worksheet (Transparency 20-4)... 4 Page 584 #42-46, 58-61, 66-69, 76-79, 84-86... 5 Chapter
Static Electricity Class Practice
 Static Electricity Class Practice 1. You are given 4 spheres that are electrically. If sphere 3 is positively, what are the charges of the other objects? 1 2 2 3 3 4 2. You have five spheres which are
Static Electricity Class Practice 1. You are given 4 spheres that are electrically. If sphere 3 is positively, what are the charges of the other objects? 1 2 2 3 3 4 2. You have five spheres which are
Section 1: Electric Fields
 PHY 132 Outline of Lecture Notes i Section 1: Electric Fields A property called charge is part of the basic nature of protons and electrons. Large scale objects become charged by gaining or losing electrons.
PHY 132 Outline of Lecture Notes i Section 1: Electric Fields A property called charge is part of the basic nature of protons and electrons. Large scale objects become charged by gaining or losing electrons.
Preview of Period 10: Electric Charge and Force
 Preview of Period 10: Electric Charge and Force 10.1 Electric Charge and Forces What happens when you place a negatively charged rod near an object? How do charges cause objects to move? 10.2 Conductors,
Preview of Period 10: Electric Charge and Force 10.1 Electric Charge and Forces What happens when you place a negatively charged rod near an object? How do charges cause objects to move? 10.2 Conductors,
PE q. F E = q. = kq 1q 2 d 2. Q = ne F e
 Chapters 32 & 33: Electrostatics NAME: Text: Chapter 32 Chapter 33 Think and Explain: 1-6, 8 Think and Explain: 1, 4, 5, 8, 10 Think and Solve: Think and Solve: 1-2 Vocabulary: electric forces, charge,
Chapters 32 & 33: Electrostatics NAME: Text: Chapter 32 Chapter 33 Think and Explain: 1-6, 8 Think and Explain: 1, 4, 5, 8, 10 Think and Solve: Think and Solve: 1-2 Vocabulary: electric forces, charge,
Exam 1--PHYS 102--S14
 Class: Date: Exam 1--PHYS 102--S14 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The magnitude of the charge on an electron is approximately: a. 10-23
Class: Date: Exam 1--PHYS 102--S14 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The magnitude of the charge on an electron is approximately: a. 10-23
5 10 C C
 Chapter solutions Q.. Reason: (a) Yes, the field would be zero at a point on the line between the two charges, closer to the 1 nc charge. (b) In this case the contributions from the two charges are in
Chapter solutions Q.. Reason: (a) Yes, the field would be zero at a point on the line between the two charges, closer to the 1 nc charge. (b) In this case the contributions from the two charges are in
Physics 2212 GJ Quiz #1 Solutions Fall 2015
 Physics 2212 GJ Quiz #1 Solutions Fall 2015 I. (14 points) A 2.0 µg dust particle, that has a charge of q = +3.0 nc, leaves the ground with an upward initial speed of v 0 = 1.0 m/s. It encounters a E =
Physics 2212 GJ Quiz #1 Solutions Fall 2015 I. (14 points) A 2.0 µg dust particle, that has a charge of q = +3.0 nc, leaves the ground with an upward initial speed of v 0 = 1.0 m/s. It encounters a E =
Lecture 2 [Chapter 21] Tuesday, Jan 17th
![Lecture 2 [Chapter 21] Tuesday, Jan 17th Lecture 2 [Chapter 21] Tuesday, Jan 17th](/thumbs/73/68267691.jpg) Lecture 2 [Chapter 21] Tuesday, Jan 17th Administrative Items Assignments this week: read Ch 21 and Ch 22 in the textbook complete Pre-Lecture Ch22 HW assignment complete Ch 21 HW assignment [Pre-Lecture
Lecture 2 [Chapter 21] Tuesday, Jan 17th Administrative Items Assignments this week: read Ch 21 and Ch 22 in the textbook complete Pre-Lecture Ch22 HW assignment complete Ch 21 HW assignment [Pre-Lecture
OUT OF BOOK QUESTION. Sphere Y is now moved away from X, as in Figure (b).
 X and Y are two uncharged metal spheres on insulating stands, and are in contact with each other. A positively charged rod R is brought close to X as shown in Figure (a). Sphere Y is now moved away from
X and Y are two uncharged metal spheres on insulating stands, and are in contact with each other. A positively charged rod R is brought close to X as shown in Figure (a). Sphere Y is now moved away from
Electric Force and Electric Field
 Electric Force and Electric Field Electrostatics Sources Outcomes Maxwell s Equation Stationary Charge Electric Force Gauss s Law Electric Field Electric Potential Capacitors Electric Forces and Electric
Electric Force and Electric Field Electrostatics Sources Outcomes Maxwell s Equation Stationary Charge Electric Force Gauss s Law Electric Field Electric Potential Capacitors Electric Forces and Electric
ELECTROSTATICS 3. P.Ravindran, PHY041: Electricity & Magnetism 15 January 2013: Electrostatics 3
 ELECTROSTATICS 3 q 0 Electro negativity ti it Rl Relative electro negativity ranking for some common materials from electron donating materials (+, glass) to electron accepting materials (, teflon) + +
ELECTROSTATICS 3 q 0 Electro negativity ti it Rl Relative electro negativity ranking for some common materials from electron donating materials (+, glass) to electron accepting materials (, teflon) + +
10th week Lectures March Chapter 12
 Electric charge. 10th week Lectures March 20. 2017. Chapter 12 Conductors and Insulators Coulomb law Electric field Electric Potential 3/20/2017 Physics 214 Spring 2017 1 Electric charge an atom has a
Electric charge. 10th week Lectures March 20. 2017. Chapter 12 Conductors and Insulators Coulomb law Electric field Electric Potential 3/20/2017 Physics 214 Spring 2017 1 Electric charge an atom has a
Ch. 16 and 17 Review Problems
 Ch. 16 and 17 Review Problems NAME 1) Is it possible for two negative charges to attract each other? A) Yes, they always attract. B) Yes, they will attract if they are close enough. C) Yes, they will attract
Ch. 16 and 17 Review Problems NAME 1) Is it possible for two negative charges to attract each other? A) Yes, they always attract. B) Yes, they will attract if they are close enough. C) Yes, they will attract
PHYSICS - Electrostatics
 PHYSICS - Electrostatics Electrostatics, or electricity at rest, involves electric charges, the forces between them, and their behavior in materials. 22.1 Electrical Forces and Charges The fundamental
PHYSICS - Electrostatics Electrostatics, or electricity at rest, involves electric charges, the forces between them, and their behavior in materials. 22.1 Electrical Forces and Charges The fundamental
ConcepTest PowerPoints
 ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
PH 202-1E Fall Electric Forces and Electric Fields. Lectures 1-4. Chapter 18 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 6 th edition)
 PH 202-1E Fall 2006 Electric Forces and Electric Fields Lectures 1-4 Chapter 18 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 6 th edition) 1 Electric Force and Electric Charge Qualitatively, a force is any push or pull
PH 202-1E Fall 2006 Electric Forces and Electric Fields Lectures 1-4 Chapter 18 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 6 th edition) 1 Electric Force and Electric Charge Qualitatively, a force is any push or pull
Electromagnetism Unit- Electrostatics Sub-Unit
 Electromagnetism Unit Electrostatics SubUnit 4.1.1 Elementary Charge Atomic Structure Review electrons nucleus two types of nucleons charge 0 charge Nucleons are not allowed to move around WITHIN matter
Electromagnetism Unit Electrostatics SubUnit 4.1.1 Elementary Charge Atomic Structure Review electrons nucleus two types of nucleons charge 0 charge Nucleons are not allowed to move around WITHIN matter
Chapter 19. Electric Charges, Forces and Electric Fields
 Chapter 19 Electric Charges, Forces and Electric Fields Agenda Atom History Induction Static Conductors Insulators Coulomb s Law Observation/ question Quiz The electrons in an atom are in a cloud surrounding
Chapter 19 Electric Charges, Forces and Electric Fields Agenda Atom History Induction Static Conductors Insulators Coulomb s Law Observation/ question Quiz The electrons in an atom are in a cloud surrounding
a. Since oppositely charged objects always attract each other, the rod and sphere will always experience a mutual attraction.
 3. REASONING AND SOLUTION When the charged insulating rod is brought near to (but not touching) the sphere, the free electrons in the sphere will move. If the rod is negatively charged, the free electrons
3. REASONING AND SOLUTION When the charged insulating rod is brought near to (but not touching) the sphere, the free electrons in the sphere will move. If the rod is negatively charged, the free electrons
Physics 11 Chapter 18: Electric Forces and Electric Fields
 Physics 11 Chapter 18: Electric Forces and Electric Fields Yesterday is not ours to recover, but tomorrow is ours to win or lose. Lyndon B. Johnson When I am anxious it is because I am living in the future.
Physics 11 Chapter 18: Electric Forces and Electric Fields Yesterday is not ours to recover, but tomorrow is ours to win or lose. Lyndon B. Johnson When I am anxious it is because I am living in the future.
ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS
 CHATER 18 ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS CONCETUAL QUESTIONS 1. REASONING AND SOLUTION In Figure 18.9, the grounding wire is removed first, followed by the rod, and the sphere is left with a positive
CHATER 18 ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS CONCETUAL QUESTIONS 1. REASONING AND SOLUTION In Figure 18.9, the grounding wire is removed first, followed by the rod, and the sphere is left with a positive
Chapter 23. Electric Force. A PowerPoint Presentation by Paul E. Tippens, Professor of Physics Southern Polytechnic State University
 Chapter 23. Electric Force A PowerPoint Presentation by Paul E. Tippens, Professor of Physics Southern Polytechnic State University 2007 Objectives: After finishing this unit, you should be able to: Explain
Chapter 23. Electric Force A PowerPoint Presentation by Paul E. Tippens, Professor of Physics Southern Polytechnic State University 2007 Objectives: After finishing this unit, you should be able to: Explain
Chapter 12 Electrostatic Phenomena
 Chapter 12 Electrostatic Phenomena 1. History Electric Charge The ancient Greeks noticed that if you rubbed amber (petrified tree resin) on fur, then the amber would have a property that it could attract
Chapter 12 Electrostatic Phenomena 1. History Electric Charge The ancient Greeks noticed that if you rubbed amber (petrified tree resin) on fur, then the amber would have a property that it could attract
Electromagnetism. Electricity Electromagnetism Magnetism Optics. In this course we are going to discuss the fundamental concepts of electromagnetism:
 Electromagnetism Electromagnetism is one of the fundamental forces in nature, and the the dominant force in a vast range of natural and technological phenomena The electromagnetic force is solely responsible
Electromagnetism Electromagnetism is one of the fundamental forces in nature, and the the dominant force in a vast range of natural and technological phenomena The electromagnetic force is solely responsible
A negatively charged object has more electrons than protons. A negatively charged object has more electrons than protons
 Electricity Electricity Describes all phenomena caused by positive and negative charges Electrical charge is caused by protons and electrons Electrons and protons are subatomic particles found in the atom
Electricity Electricity Describes all phenomena caused by positive and negative charges Electrical charge is caused by protons and electrons Electrons and protons are subatomic particles found in the atom
Electric Charge. Labs, Activities & Demonstrations: Notes: Unit: Electricity & Magnetism NGSS Standards: N/A
 Add Important Electric Charge Page: 44 NGSS Standards: N/A Electric Charge MA Curriculum Frameworks (006): 5.1, 5.4 AP Physics 1 Learning Objectives: 1.B.1.1, 1.B.1., 1.B..1, 1.B.3.1 Knowledge/Understanding
Add Important Electric Charge Page: 44 NGSS Standards: N/A Electric Charge MA Curriculum Frameworks (006): 5.1, 5.4 AP Physics 1 Learning Objectives: 1.B.1.1, 1.B.1., 1.B..1, 1.B.3.1 Knowledge/Understanding
Chapter 21 Electric Charge and Electric Field
 Chapter 21 Electric Charge and Electric Field 21-1 Static Electricity; Electric Charge and Its Conservation Objects can be charged by rubbing 21-1 Static Electricity; Electric Charge and Its Conservation
Chapter 21 Electric Charge and Electric Field 21-1 Static Electricity; Electric Charge and Its Conservation Objects can be charged by rubbing 21-1 Static Electricity; Electric Charge and Its Conservation
Polarization. Polarization is not necessarily a charge imbalance!
 Electrostatics Polarization Polarization is the separation of charge In a conductor, free electrons can move around the surface of the material, leaving one side positive and the other side negative. In
Electrostatics Polarization Polarization is the separation of charge In a conductor, free electrons can move around the surface of the material, leaving one side positive and the other side negative. In
Static Electricity Regents Chapter 20
 Chapter 20 Static Electricity part 1 Static Electricity Regents Chapter 20 Static vs. Current Two Kinds of Electric Charge: Positive Negative Common particles of the atom Protons Electrons Amount of charge
Chapter 20 Static Electricity part 1 Static Electricity Regents Chapter 20 Static vs. Current Two Kinds of Electric Charge: Positive Negative Common particles of the atom Protons Electrons Amount of charge
Chapter 20 Review Questions
 Chapter 20 Review Questions Name 20.1 I can define the basics of electrostatics, conservation and charge interactions 1. If an object is attracted by a positively charged rod, we can be sure that the body
Chapter 20 Review Questions Name 20.1 I can define the basics of electrostatics, conservation and charge interactions 1. If an object is attracted by a positively charged rod, we can be sure that the body
PH 222-2C Fall 2012 ELECTRIC CHARGE. Lecture 1. Chapter 21 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 222-2C Fall 2012 ELECTRIC CHARGE Lecture 1 Chapter 21 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 21 Electric Charge In this chapter we will introduce a new property of
PH 222-2C Fall 2012 ELECTRIC CHARGE Lecture 1 Chapter 21 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 21 Electric Charge In this chapter we will introduce a new property of
Chapters 21 and 22: Giancoli, 4 th Edition Electrostatics
 Chapters 21 and 22: Giancoli, 4 th Edition Electrostatics Electric Charges Coulomb s Law and Electric force The Electric Field Electric Field Lines Electric flux Gauss Law and applications of Gauss Law
Chapters 21 and 22: Giancoli, 4 th Edition Electrostatics Electric Charges Coulomb s Law and Electric force The Electric Field Electric Field Lines Electric flux Gauss Law and applications of Gauss Law
q C e C k (Equation 18.1) for the distance r, we obtain k (Equation 18.1), where Homework#1 3. REASONING
 Homework# 3. REASONING a. Since the objects are metallic and identical, the charges on each combine and produce a net charge that is shared equally by each object. Thus, each object ends up with one-fourth
Homework# 3. REASONING a. Since the objects are metallic and identical, the charges on each combine and produce a net charge that is shared equally by each object. Thus, each object ends up with one-fourth
INTRODUCTION TO BIOPHYSICS. II semester, week /2015
 INTRODUCTION TO BIOPHYSICS II semester, week 3 2014/2015 INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICITY Electricity phenomena associated with interaction between electrically charged objects PARTICLES AND ELECTRIC CHARGE
INTRODUCTION TO BIOPHYSICS II semester, week 3 2014/2015 INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICITY Electricity phenomena associated with interaction between electrically charged objects PARTICLES AND ELECTRIC CHARGE
Electrostatics. Electrostatics the study of electrical charges that can be collected and held in one place. Also referred to as Static Electricity
 Electrostatics 169 Electrostatics Electrostatics the study of electrical charges that can be collected and held in one place. Types of Charge Also referred to as Static Electricity Benjamin Franklin noticed
Electrostatics 169 Electrostatics Electrostatics the study of electrical charges that can be collected and held in one place. Types of Charge Also referred to as Static Electricity Benjamin Franklin noticed
Intro Video: n What is charge? n v=dvlpasdwxpy
 Electrostatics Intro Video: n What is charge? n https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=dvlpasdwxpy What is electrostatics? n Electrostatics or electricity at rest n Involves electric charges, the forces between
Electrostatics Intro Video: n What is charge? n https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=dvlpasdwxpy What is electrostatics? n Electrostatics or electricity at rest n Involves electric charges, the forces between
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the 1) A small sphere with a mass of 441 g is moving upward along the vertical +y-axis when it encounters
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the 1) A small sphere with a mass of 441 g is moving upward along the vertical +y-axis when it encounters
Physics 2B Electricity and Magnetism. Instructor: Prof Benjamin Grinstein UCSD
 Physics 2B Electricity and Magnetism Instructor: Prof Benjamin Grinstein UCSD week 1 Rank in order, from most positive to most negative, the charges q a to q e of these five systems. 1. q a = q b >
Physics 2B Electricity and Magnetism Instructor: Prof Benjamin Grinstein UCSD week 1 Rank in order, from most positive to most negative, the charges q a to q e of these five systems. 1. q a = q b >
Electric Charge and Electric Field AP Physics 4 Lecture Notes
 Electric Charge and Electric Field AP Physics 4 Lecture Notes Coulomb s Law The Electric Field Field Lines Electric Fields and Conductors Coulomb s law: Coulomb s Law Force (N) F F F k r F F F r Charge
Electric Charge and Electric Field AP Physics 4 Lecture Notes Coulomb s Law The Electric Field Field Lines Electric Fields and Conductors Coulomb s law: Coulomb s Law Force (N) F F F k r F F F r Charge
Ch 16: Electric Charge and Electric Field. Opposites attract by Paula Abdul
 Ch 16: Electric Charge and Electric Field Opposites attract by Paula Abdul Static Electricity A neutral object rubbed with another object can acquire a charge due to friction. It is said to posses a net
Ch 16: Electric Charge and Electric Field Opposites attract by Paula Abdul Static Electricity A neutral object rubbed with another object can acquire a charge due to friction. It is said to posses a net
Electrostatics: Coulomb's Law
 Electrostatics: Coulomb's Law Objective: To learn how excess charge is created and transferred. To measure the electrostatic force between two objects as a function of their electrical charges and their
Electrostatics: Coulomb's Law Objective: To learn how excess charge is created and transferred. To measure the electrostatic force between two objects as a function of their electrical charges and their
Electrostatics. 3) positive object: lack of electrons negative object: excess of electrons. Particle Mass Electric Charge. m e = 9.
 Electrostatics 1) electric charge: 2 types of electric charge: positive and negative 2) charging by friction: transfer of electrons from one object to another 3) positive object: lack of electrons negative
Electrostatics 1) electric charge: 2 types of electric charge: positive and negative 2) charging by friction: transfer of electrons from one object to another 3) positive object: lack of electrons negative
SOWETO/DIEPKLOOF P.O.BOX BOOYSENS 2016!!! " /7 #
 ! SOWETO/DIEPKLOOF P.O.BOX 39067 BOOYSENS 2016!!! " 011 9381666/7 # 011 9383603 email: sec@global.co.za Content Page Electrostatics: Summary of Relevant Theory 1 4 Worksheet 1: Multiple Choice Questions
! SOWETO/DIEPKLOOF P.O.BOX 39067 BOOYSENS 2016!!! " 011 9381666/7 # 011 9383603 email: sec@global.co.za Content Page Electrostatics: Summary of Relevant Theory 1 4 Worksheet 1: Multiple Choice Questions
PHYS102 - Superposition of Forces
 GoBack PHYS102 - of Forces Dr. Suess January 12, 2007 PHYS102 Introduction and Charge slide 1 PHYS102 Introduction and Charge slide 2 1. If you were in PHYS101 last semester, then please pick up your homework
GoBack PHYS102 - of Forces Dr. Suess January 12, 2007 PHYS102 Introduction and Charge slide 1 PHYS102 Introduction and Charge slide 2 1. If you were in PHYS101 last semester, then please pick up your homework
3/9/2016. Chapter 25 Electric Charges and Forces. Chapter 25 Preview. Chapter 25 Preview
 Chapter 25 Electric Charges and Forces Pickup PSE3e Photo from page 720, lightning (perhaps change the fonts and make this photo fill the entire slide) Chapter Goal: To describe electric phenomena in terms
Chapter 25 Electric Charges and Forces Pickup PSE3e Photo from page 720, lightning (perhaps change the fonts and make this photo fill the entire slide) Chapter Goal: To describe electric phenomena in terms
Ch 16 practice. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 16 practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What happens when a rubber rod is rubbed with a piece of fur, giving it a negative charge?
Ch 16 practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What happens when a rubber rod is rubbed with a piece of fur, giving it a negative charge?
(b: 5 pts) A thin plastic rod of length 4.5 m has been rubbed with a wool cloth, and has gained a net charge
 Problem 1 (25 pts). (a: 5 pts) student claimed that the formula for the electric field outside a cube of edge length L, carrying a uniformly distributed charge Q, at a distance x from the center of the
Problem 1 (25 pts). (a: 5 pts) student claimed that the formula for the electric field outside a cube of edge length L, carrying a uniformly distributed charge Q, at a distance x from the center of the
PHYSICS 30 ELECTRIC FIELDS ASSIGNMENT 1 55 MARKS
 For each of the following questions complete communication must be shown. Communication consists of an introduction to the physics of the situation, diagrams, word explanations and calculations in a well
For each of the following questions complete communication must be shown. Communication consists of an introduction to the physics of the situation, diagrams, word explanations and calculations in a well
Problem 1. What is the force between two small charged spheres that have charges of C and C and are placed 30 cm apart in air?
 5. NAME: Problem 1. What is the force between two small charged spheres that have charges of 2 10 7 C and 3 10 7 C and are placed 30 cm apart in air? 2. What is the value of charge of a body that carries
5. NAME: Problem 1. What is the force between two small charged spheres that have charges of 2 10 7 C and 3 10 7 C and are placed 30 cm apart in air? 2. What is the value of charge of a body that carries
To receive full credit, you must show your work (including calculations and formulas used).
 Page Score Problem : Problem 2: Problem 3: Problem 4: Problem 5: TOTAL: (25 pts) To receive full credit, you must show your work (including calculations and formulas used). If you do not wish your quiz
Page Score Problem : Problem 2: Problem 3: Problem 4: Problem 5: TOTAL: (25 pts) To receive full credit, you must show your work (including calculations and formulas used). If you do not wish your quiz
Semester 2 Physics (SF 026) Lecture: BP 3 by Yew Sze Fiona Website:
 Semester 2 Physics (SF 026) Lecture: BP 3 by Yew Sze Ling @ Fiona Website: http://yslphysics.weebly.com/ Chapter 1: Electrostatics The study of electric charges at rest, the forces between them and the
Semester 2 Physics (SF 026) Lecture: BP 3 by Yew Sze Ling @ Fiona Website: http://yslphysics.weebly.com/ Chapter 1: Electrostatics The study of electric charges at rest, the forces between them and the
Test Review FQ3eso_U5_3_Electric force
 Test Review FQ3eso_U5_3_Electric force Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1.- Two metal spheres, A and B, possess charges of 1.0 microcoulomb and
Test Review FQ3eso_U5_3_Electric force Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1.- Two metal spheres, A and B, possess charges of 1.0 microcoulomb and
Homework #1 Solutions version 3 6 problems
 Homework #1 Solutions version 6 problems Exercises 1. Charges A and lie 5 cm apart, on a line. Charge A is q A = + µc, and charge is q = mc. (e careful of the metrix prefixes!) (a) efore doing any calculation,
Homework #1 Solutions version 6 problems Exercises 1. Charges A and lie 5 cm apart, on a line. Charge A is q A = + µc, and charge is q = mc. (e careful of the metrix prefixes!) (a) efore doing any calculation,
HOMEWORK 1 SOLUTIONS
 HOMEWORK 1 SOLUTIONS CHAPTER 18 3. REASONING AND SOLUTION The total charge to be removed is 5.0 µc. The number of electrons corresponding to this charge is N = ( 5.0 10 6 C)/( 1.60 10 19 C) = 3.1 10 13
HOMEWORK 1 SOLUTIONS CHAPTER 18 3. REASONING AND SOLUTION The total charge to be removed is 5.0 µc. The number of electrons corresponding to this charge is N = ( 5.0 10 6 C)/( 1.60 10 19 C) = 3.1 10 13
Where, ε 0 = Permittivity of free space and = Nm 2 C 2 Therefore, force
 Exercises Question.: What is the force between two small charged spheres having charges of 2 0 7 C and 3 0 7 C placed 30 cm apart in air? Answer.: Repulsive force of magnitude 6 0 3 N Charge on the first
Exercises Question.: What is the force between two small charged spheres having charges of 2 0 7 C and 3 0 7 C placed 30 cm apart in air? Answer.: Repulsive force of magnitude 6 0 3 N Charge on the first
1. (a) With a understood to mean the magnitude of acceleration, Newton s second and third laws lead to. kg.
 1. (a) With a understood to mean the magnitude of acceleration, Newton s second and third laws lead to ma = ma m = 1 1 7 c63. 10 kghc70. m s h 90. ms (b) The magnitude of the (only) force on particle 1
1. (a) With a understood to mean the magnitude of acceleration, Newton s second and third laws lead to ma = ma m = 1 1 7 c63. 10 kghc70. m s h 90. ms (b) The magnitude of the (only) force on particle 1
Electricity Lecture Series
 Electricity Lecture Series Charges & Charging Applied Sciences Education Research Group (ASERG) Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARA email: drjjlanita@hotmail.com; drjjlanita@yahoo.com
Electricity Lecture Series Charges & Charging Applied Sciences Education Research Group (ASERG) Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARA email: drjjlanita@hotmail.com; drjjlanita@yahoo.com
Ch 5 Electric Charges, Fields
 Ch 5 Electric Charges, Fields Electrostatic Forces Forces between electric charges are responsible for binding atoms and molecules together to create solids and liquids--without electric forces, atoms
Ch 5 Electric Charges, Fields Electrostatic Forces Forces between electric charges are responsible for binding atoms and molecules together to create solids and liquids--without electric forces, atoms
Physics Worksheet Electrostatics, Electric Fields and Potential Section: Name: Electric Charges
 Electric Charges 1. The fundamental rule of all electrical phenomena is: Like charges, opposite charges 2. Thomson s cathode ray experiment proved that: _ 3. Millikan s oil drop experiment proved that:
Electric Charges 1. The fundamental rule of all electrical phenomena is: Like charges, opposite charges 2. Thomson s cathode ray experiment proved that: _ 3. Millikan s oil drop experiment proved that:
Coulomb s Law and Electric Fields
 Physics 102: Lecture 02 Coulomb s Law and Electric Fields Today we will get some practice using Coulomb s Law learn the concept of an Electric Field Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 1 Recall Coulomb s Law
Physics 102: Lecture 02 Coulomb s Law and Electric Fields Today we will get some practice using Coulomb s Law learn the concept of an Electric Field Physics 102: Lecture 2, Slide 1 Recall Coulomb s Law
Electric Charges & Electric Forces Chapter 20 Structure of atom
 Electric Charges & Electric Forces Chapter 20 Electric Charges & Electric Forces Chapter 20 Structure of atom Mass (kg) Charge (Coulombs) Proton 1.673X10-27 +1.60X10-19 Neutron 1.675X10-27 0 = + e Electron
Electric Charges & Electric Forces Chapter 20 Electric Charges & Electric Forces Chapter 20 Structure of atom Mass (kg) Charge (Coulombs) Proton 1.673X10-27 +1.60X10-19 Neutron 1.675X10-27 0 = + e Electron
PHYS 1444 Section 02. Lecture #3
 PHYS 1444 Section 0 Chapter 1 Electric Fields Electric Dipoles Lecture #3 Tuesday Jan 5, 011 Dr. Andrew Brandt Homework on Ch 1 is due 9pm Thursday, Jan. 7 1 Angle: After calculating magnitudes, take x+y
PHYS 1444 Section 0 Chapter 1 Electric Fields Electric Dipoles Lecture #3 Tuesday Jan 5, 011 Dr. Andrew Brandt Homework on Ch 1 is due 9pm Thursday, Jan. 7 1 Angle: After calculating magnitudes, take x+y
CPS lesson Electric Field ANSWER KEY
 CPS lesson Electric Field ANSWER KEY 1. A positively charged rod is brought near a conducting sphere on an insulated base. The opposite side of the sphere is briefly grounded. If the rod is now withdrawn,
CPS lesson Electric Field ANSWER KEY 1. A positively charged rod is brought near a conducting sphere on an insulated base. The opposite side of the sphere is briefly grounded. If the rod is now withdrawn,
ELECTROSTATICS. When two materials rub together the contact between their surfaces may cause: a) the surfaces to become hot and show wear and tear.
 1 ELECTROSTATICS Friction And Charge When two materials rub together the contact between their surfaces may cause: a) the surfaces to become hot and show wear and tear. b) the surfaces to become attracted
1 ELECTROSTATICS Friction And Charge When two materials rub together the contact between their surfaces may cause: a) the surfaces to become hot and show wear and tear. b) the surfaces to become attracted
Two. ( ) :. ; J.. v ( -I ) f - ) N. 1 o f.., J e. ( b) Like c a.,,9"s ref" ti. iocl, c, Qi' (f) .. i:1: ti,: f. c; (. c\... '1 t e-' r
 r (. Two + fes. ( ) :. ; J.. v ( -I ) ( b) N. 1 o f.., J e f - ) Like c a.,,9"s ref" ti iocl, c, Qi'.. i:1: ti,: f. c; (. ej Or (f) e e c\... '1 t e-' r......... e Electric charge and the structure of
r (. Two + fes. ( ) :. ; J.. v ( -I ) ( b) N. 1 o f.., J e f - ) Like c a.,,9"s ref" ti iocl, c, Qi'.. i:1: ti,: f. c; (. ej Or (f) e e c\... '1 t e-' r......... e Electric charge and the structure of
ConcepTest PowerPoints
 ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely
ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely
Bell Ringer: Define to the best of your ability the definition of:
 Bell Ringer: Define to the best of your ability the definition of: Potential Energy Electric Potential Energy Electric Circuit Current Voltage Resistance Coulomb Notes 7.1: Electrostatic Force This lesson
Bell Ringer: Define to the best of your ability the definition of: Potential Energy Electric Potential Energy Electric Circuit Current Voltage Resistance Coulomb Notes 7.1: Electrostatic Force This lesson
Physics 122 Unit 3 S1 Electrostatics Weebly.notebook. Unit 3. Section 1 Electrostatics
 Unit 3 Section 1 Electrostatics Electrostatics Electrostatics is the study of stationary electric charges. Only two types of electric charge have been discovered, positive and negative. proton (1.673 x
Unit 3 Section 1 Electrostatics Electrostatics Electrostatics is the study of stationary electric charges. Only two types of electric charge have been discovered, positive and negative. proton (1.673 x
Learning Outcomes from Last Time. Class 3. Learning Outcomes. What Causes Forces -Two Experiments. What Causes Forces -Two Experiments
 Learning Outcomes from Last Time Class 3 Electrostatic Forces Physics 106 Winter 2018 Press CTRL-L to view as a slide show. You should be able to answer these questions: What is science? What is physics?
Learning Outcomes from Last Time Class 3 Electrostatic Forces Physics 106 Winter 2018 Press CTRL-L to view as a slide show. You should be able to answer these questions: What is science? What is physics?
