Answer: Answer: 37! 3 How many five card hands are there that contain at least one club? Answer: How many one pair poker hands are there? Etc.
|
|
|
- Lucinda James
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Practice Final, M325K, 12/13/2014 PRINTED NAME: EID: No books, notes, calculators, or telephones are allowed. Every problem is worth an equal number of points. You must show your work; answers without substantiation do not count. Answers must appear in the box provided! No or the wrong answer in the answer box results in no credit! This does not aim nor claim to be exhaustive! Use this as a guide of what to study and not of what not to study! Do not expect to find every test problem listed here! The actual test will contain 7 10 problems very similar to those below. Pick 8 10 problems from the earlier tests and practice tests, including two story problems. Here are the earlier practice tests: Practice Test 1, 325K PRINTED NAME: EID: No books, notes, calculators, or telephones are allowed. Every problem is worth an equal number of points. You must show your work; answers without substantiation do not count. Answers must appear in the box provided! No or the wrong answer in the answer box results in no credit! This does not aim nor claim to be exhaustive! Use this as a guide of what to study and not of what not to study! Do not expect to find every test problem listed here! The actual test will contain 5 6 problems very similar to those below. How many arrangements are there of the letters SOCIOLOGICAL? ( ) In how many ways can you distribute 37 books on 4 shelves in such a way that no shelf is left empty? (The order of the books on any of the shelves does matter.) ( ) 36 37! 3 How many five card hands are there that contain at least one club? ( ) ( ) How many one pair poker hands are there? Etc. ( )( )( )( ) p. 28#8h How many two pairs poker hands are there? Etc. ( )( ) 2 ( )( ) A curious boy has to traverse 8 blocks going East and 6 blocks going North when walking from home to school. How many ways does he have to walk to school if he never walks South or West? ( ) ( ) = 6 8 Determine the coefficient of x 7 y 3 in the binomial expansion of (2x+3y) 10. ( )
2 Determine the number of integer solutions of x 1 +x 2 + +x 7 < 27, Z x i 2. ( ) 40+7 #{x 1 +x 2 + +x 7 < 27, Z x i 2} = 7 How many positive (x i 0) integer solutions are there to the pair of simultaneous equations ( ) 8 2 ( ) 34 3 x 1 + +x 7 = 37, x 1 +x 2 +x 3 = 6. The boss has 5 secretaries. She wishes to givem them X mas bonuses, but finds herself with 9 one dollar bills and 5 five dollar bills. a) In how many ways can she distribute these bills among the secretaries? b) In how many ways can she distribute them among the secretaries if every one of them must have at least one one dollar bill? ( )( ) a) 4 4 ( )( ) b) 4 4 Use truth tables or argue otherwise but cogently to show that [(p q) (q r)] (p r) is a logical implication. Consider the statement P: If 7 divides the product of two integers then it divides one of the factors. [7 m reads seven divides m and has negation 7 m.] a) Write P using quantifiers. P m,n Z 7 mn = 7 m 7 n. b) Compute (and simplify) the negation P. P m,n Z 7 mn 7 m 7 n. How many subsets of {1,2,3,...,15} contain at least one odd integer? Prove that for A,B,C,D U A C B D = A B C D. Write down a few laws of set theory. How many permutations of the alphabet contain the patterns BIG or ROUND? Let A,B U. Show that [A B = B A] [(A = ) (B = ) (A = B)] Consult Lecture 16
3 Of 52 monitored people by a TV rating company, 22 watch Reality Shows, 21 watch News, and 21 watch Soaps; 10 watch both Reality Shows and News, 10 watch Reality Shows and Soaps, and 10 watch both News and Soaps; 7 of then watch all three types of shows. How many viewers watch only Reality Shows? A Venn diagram shows that there are 9 of these. Practice Test 2, 325K PRINTED NAME: EID: No books, notes, calculators, or telephones are allowed. Every problem is worth an equal number of points. You must show your work; answers without substantiation do not count. Answers must appear in the box provided! No or the wrong answer in the answer box results in no credit! This does not aim nor claim to be exhaustive! Use this as a guide of what to study and not of what not to study! Do not expect to find every test problem listed here! Sigh. If you scramble the letters of the word SOCIOLOGICAL and then put them down randomly in linear order, what is the probability you will spell SOCIOLOGICAL? ( ) 1 What is the probability of getting a one pair hand in 5 card poker? ) ( (4 ) 4 3/ (52 ) A gambler rolls a fair die until a 6 comes up. What is the probability that he will need exactly 4 rolls? ( 5 ) 3 ( 1 6 6) 2% of all drivers at 11:00 PM are drunk. A drunk driver has a probability of 10% of causing an accident, while a sober driver has a probability of 1%. (These figures are made of whole cloth; I don t know what the real figures are; it would be good to know.) What is the probability that a driver causing an accident was drunk? 30% of all drivers drive while yapping on their cell phones. A driver on a cell phone has 1% probability of causing an accident, while a driver paying attention to the road only has a 0.1% probabability. (These figures are made of whole cloth; I don t know what the real figures are; it would be good to know.) What is the probability that a driver causing an accident was on his/her cell? Your friend was careful but still has a 4% chance of being pregnant (Event E). You buy her a pregancy test that has P[TP E] =.90 and P[TP E] =.10 (TP is the event the test shows positive). The test is positive. What is the probability p your friend is actually pregnant? [Give an answer of the form p = n/d, n,d integers.] p = 3 11 Prove that for every n {1,2,3...} n i=1 1 i(i+1) = n n+1. def def def Define recursively F 0 = 0, F 1 = 1, and F n+2 = F n +F n+1 for n 0. n Show that F i = F n+2 1 for n = 1,2,... i=0
4 How many different positive divisors does have? = has = 144 divisors Find the greatest common divisor of 462 and 3640 and write it as a linear combination of 462 and Hence gcd(3640,462)= 14 and 3640 = = ((3640,462)) = ((462,406)) 462 = = ((462,406))= ((406,56)) 406 = = ((406,56)) = ((56,14)) = ((14)). 14 = = ( ) = = ( ) = gcd(462,3640)= 14 = Show that 7 is irrational. Solution: Adapt lecture 15, replacing 2 by 7. a) Show: if p > 0 is a prime number and 0 < k < p then ( ) p p. k b) Show: if p > 0 is prime then n p =p n for all n 0. Solution: This is true by inspection for n = 0. For n > 0, by induction p ( ) p n p n = [(n 1)+1] p n = (n 1) k n k = ( ) p (n 1) p 1 k=1 k=0 ( p k ) (n 1) k + ( ) p (n 1) p n p = 1+qp+(n 1) p n = qp+[(n 1) p (n 1)] = p 0 IV) Find the positive generator of the ideal ((42,56,77)). Let a,b,n be strictly positive integers. Prove that n gcd(a,b) = gcd(an,bn). Set g def = gcd(a,b) and γ def = gcd(an,bn). g = xa+yb = ng ((an,bn)) = γ (ng). γ = ξan+ηbn = n (ξa+ηb) = n (kg) k = (ng) γ. Hence γ = ng.
5 III) The XYZ Company has a dinner for all its employees. A place setting costs $45, except for the women, who get an extra little vase with a flower for an additional $2. The company lays out a total of $1613 for this dinner. How may male and female employees does XYX company have? Solution: First, 1 = , and so 1613 = ( k 47) 45+(k ) 47, k Z. We want k Z so that both parentheses are positive: from = k = follows k = 789 and 1613 = Therefore XYZ company has 16 male and 19 female employees The farmer and his son fill the dry stock pond, which holds 224 liters, by filling their buckets, which hold 21 and 17 liters, respectively, with water, carrying them to the tank and dumping the water. When they are done, they argue about who did more work. They are sure that neither made more than twice the number of runs from spout to tank than the other. How many times did the son (with the 17 liter bucket) and the father (with the 21 liter bucket) make the run? Solution: First, 1 = , and so 224 = and 224 = (224 5 k 21) 17+(k ) 21, k Z. We want k Z so that both parentheses are positive: from 53.x = = k follows k = 53 and Therefore 224 = ( ) 17+( ) = ( ) 17+( ) 21 = = = 52.x Father makes 5 runs and the Son 7.
6 Let A,B be finite sets with A = m and B = n. (a) How many relations from A to B are there? (b) How many functions f : A B are there? (c) How many injective functions f : A B are there? (d) How many surjective functions f : A B are there? (a) 2 m n (b) n m (c) none if m > n, n!/(n m)! otherwise (d)n! S(m,n)
7 Practice Test 3, M325K PRINTED NAME: EID: No books, notes, calculators, or telephones are allowed. Every problem is worth an equal number of points. You must show your work; answers without substantiation do not count. Answers must appear in the box provided! No or the wrong answer in the answer box results in no credit! This does not aim nor claim to be exhaustive! Use this as a guide of what to study and not of what not to study! Do not expect to find every test problem listed here! Sigh. a) How many binary operations R : A A are there on A def = {a,b,c,d,e}? b) How many of them are commutative? c) have b for a neutral element? d) have a neutral element? Mother has enough cookie dough left for two decent size cookies that can t be told apart, and also has some M&M s left over: a white one, a red one, a blue one, a yellow one, and a pink one. In how many ways can she put the M&M s on the cookies so that each cookie receives at least one M&M? S(5,2) = 15 During the first six weeks in his senior year Brad sends out at least one resume per day, but no more than 60 in all. Show that there is a stretch of consecutive days during which he sends out precisely 23 resumes. The magician says Select seven distinct integers between 1 and 24 and denote by S the set of numbers you got. For every non void subset A S of your selection S compute the sum of the numbers in it and call it s(a). In other words s(a) def = i Ai. You will find that there are two distinct subsets A,A S with s(a) = s(a ). How does the magician know that? Solution: Your set S of seven integers between 1 and 2 has 119 non void subsets of size 5 or less. For any such subset A S we have 1 s(a) = 110. By the PHP there must be two subsets A,A S of size 5 or less with the same sum: S(A) = s(a ). On A def = {0,3,5,9,15} let be the relation defined by a b a b. (a) Draw the directed graph of. (b) Find the incidence matrix of. (c) Show that is a partial order on A. (d) Draw its Hasse diagram. (e) Toplogically sort (A, ) in two different ways and draw the resulting Hasse diagrams.
8 Let A,B be sets and f : A B a function. Show that f is injective if and only if f(a 1 A 2 ) = f(a 1 ) f(a 2 ) for any pair of subsets A 1,A 2 A. Solution: Consult Lecture 16. Let A,B be sets. In which cases is A B = B A? Prove your assertion! Solution: Consult Lecture 16. In summary, A B = B A if and only if A = or B = or A = B. Let A = m. (a) How many binary operations are there on A? (b) How many of them have a neutral element? (c) How many of them are commutative? (d) How many commutative ones have a neutral element? (a) m m m (b) m m (m 1) (m 1) (c) m m(m+1)/2 (d)m m m(m 1)/2 Let f,g : R R, f : x ax + b, g : x cx + d, where a,b,c,d are constants in R. What relationship(s) must these four constants satisfy in order that f g = g f? How are reflexivity etc. of the relation R A A reflected in the incidence matrix M(R)? Set A := {3,6,12,18,21} and define the relation R on A by arb a b. b) Show that R is a partial order. c) Find the incidence matrix of R. d) Display the directed graph and the Hasse diagram of R. e) Topologically order R. On Z define the relation by x y if x and y have the same remainder modulo 37. Show that is an equivalence relation.
9 Practice Final, M325K, 05/12/2011 PRINTED NAME: EID: No books, notes, calculators, or telephones are allowed. Every problem is worth an equal number of points. You must show your work; answers without substantiation do not count. Answers must appear in the box provided! No or the wrong answer in the answer box results in no credit! This does not aim nor claim to be exhaustive! Use this as a guide of what to study and not of what not to study! Do not expect to find every test problem listed here! Sigh. State the multinomial formula for (a+b+c) 10 : (a+b+c) 10 = (a+b+c) 10 = (b) How many summands are there in this sum? 0 i,j,k 10 i+j+k=10 ( ) n a i b j c k i,j,k ( ) 10+(3 1) There are = (3 1) ( ) 12 = 66 summands. 2 Write the converse, inverse, and contrapositive of the implication If the moon is made of yellow cheese then the pope is catholic. For this statement and its converse, inverse, and contrapositive determine its truth value. Truth value of If the moon is made of yellow cheese then the pope is catholic. : converse: truth value: contrapositive: truth value: inverse: truth value:
10 Let R 1, R 2 be relations on a set A. Prove or disprove the following a) If R 1 and R 2 both are reflexive then R 1 R 2 is reflexive. True False The reason: b) If R 1 and R 2 both are symmetric then R 1 R 2 is symmetric. True False The reason: c) If R 1 and R 2 both are antisymmetric then R 1 R 2 is antisymmetric. True False The reason: d) If R 1 and R 2 both are transitive then R 1 R 2 is transitive. True False The reason: How many (a) reflexive, (b) symmetric, (c) antisymmetric, (d) reflexive and symmetric, (e) symmetric and antisymmetric, (f) reflexive, symmetric, and non transitive, relations are there on a set of size n? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f). (a) Let A def = {1,2,3,4} and R def = {(1,1), (1,2), (2,3), (3,3), (3,4), (4,4)}. Find the relation matrix and the directed graph of R: M(R) =. Graph: (b) With A and R as in a), find two relation S,T on A such that S T yet R S = R T = {(1,1), (1,2), (1,4)}. On A def = {1,2,4,6,10,12} let be the relation defined by a b a b. (a) Draw the directed graph of and its incidence matrix. (b) Show that is a partial order on A. (c) Draw its Hasse diagram. (d) Toplogically sort (A, ) in two different ways and draw the resulting Hasse diagrams. How many equivalence relations are there on the set A def = {1,2,4,6,10,12}? As many as there are partitions. Consult lecture 23. There are 6 S(6, i) equivalence relations on A. i=1 On Z define the relation by x y if a and b have the same remainder modulo 37. Show that is an equivalence relation.
Math 230 Final Exam, Spring 2008
 c IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, May 15, 2008 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 230 Final Exam, Spring 2008 Conditions. 2 hours. No book, notes, calculator, cell phones, etc. Part
c IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, May 15, 2008 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 230 Final Exam, Spring 2008 Conditions. 2 hours. No book, notes, calculator, cell phones, etc. Part
STUDY GUIDE FOR THE WRECKONING. 1. Combinatorics. (1) How many (positive integer) divisors does 2940 have? What about 3150?
 STUDY GUIDE FOR THE WRECKONING. Combinatorics Go over combinatorics examples in the text. Review all the combinatorics problems from homework. Do at least a couple of extra problems given below. () How
STUDY GUIDE FOR THE WRECKONING. Combinatorics Go over combinatorics examples in the text. Review all the combinatorics problems from homework. Do at least a couple of extra problems given below. () How
Math 230 Final Exam, Spring 2009
 IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, May 13, 2009 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 230 Final Exam, Spring 2009 Conditions. 2 hours. No book, notes, calculator, cell phones, etc. Part
IIT Dept. Applied Mathematics, May 13, 2009 1 PRINT Last name: Signature: First name: Student ID: Math 230 Final Exam, Spring 2009 Conditions. 2 hours. No book, notes, calculator, cell phones, etc. Part
Logic. Facts (with proofs) CHAPTER 1. Definitions
 CHAPTER 1 Logic Definitions D1. Statements (propositions), compound statements. D2. Truth values for compound statements p q, p q, p q, p q. Truth tables. D3. Converse and contrapositive. D4. Tautologies
CHAPTER 1 Logic Definitions D1. Statements (propositions), compound statements. D2. Truth values for compound statements p q, p q, p q, p q. Truth tables. D3. Converse and contrapositive. D4. Tautologies
RED. Name: Instructor: Pace Nielsen Math 290 Section 1: Winter 2014 Final Exam
 RED Name: Instructor: Pace Nielsen Math 290 Section 1: Winter 2014 Final Exam Note that the first 10 questions are true-false. Mark A for true, B for false. Questions 11 through 20 are multiple choice
RED Name: Instructor: Pace Nielsen Math 290 Section 1: Winter 2014 Final Exam Note that the first 10 questions are true-false. Mark A for true, B for false. Questions 11 through 20 are multiple choice
1 Take-home exam and final exam study guide
 Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Fall 2013 1 Take-home exam and final exam study guide 1.1 Problems The following are some problems, some of which will appear on the final exam. 1.1.1 Number
Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Fall 2013 1 Take-home exam and final exam study guide 1.1 Problems The following are some problems, some of which will appear on the final exam. 1.1.1 Number
MATH 114 Fall 2004 Solutions to practice problems for Final Exam
 MATH 11 Fall 00 Solutions to practice problems for Final Exam Reminder: the final exam is on Monday, December 13 from 11am - 1am. Office hours: Thursday, December 9 from 1-5pm; Friday, December 10 from
MATH 11 Fall 00 Solutions to practice problems for Final Exam Reminder: the final exam is on Monday, December 13 from 11am - 1am. Office hours: Thursday, December 9 from 1-5pm; Friday, December 10 from
Math 205 April 28, 2009 Final Exam Review
 1 Definitions 1. Some question will ask you to statea a definition and/or give an example of a defined term. The terms are: subset proper subset intersection union power set cartesian product relation
1 Definitions 1. Some question will ask you to statea a definition and/or give an example of a defined term. The terms are: subset proper subset intersection union power set cartesian product relation
(1) Which of the following are propositions? If it is a proposition, determine its truth value: A propositional function, but not a proposition.
 Math 231 Exam Practice Problem Solutions WARNING: This is not a sample test. Problems on the exams may or may not be similar to these problems. These problems are just intended to focus your study of the
Math 231 Exam Practice Problem Solutions WARNING: This is not a sample test. Problems on the exams may or may not be similar to these problems. These problems are just intended to focus your study of the
Chapter 1. Sets and Numbers
 Chapter 1. Sets and Numbers 1. Sets A set is considered to be a collection of objects (elements). If A is a set and x is an element of the set A, we say x is a member of A or x belongs to A, and we write
Chapter 1. Sets and Numbers 1. Sets A set is considered to be a collection of objects (elements). If A is a set and x is an element of the set A, we say x is a member of A or x belongs to A, and we write
NORTHERN INDIA ENGINEERING COLLEGE, LKO D E P A R T M E N T O F M A T H E M A T I C S. B.TECH IIIrd SEMESTER QUESTION BANK ACADEMIC SESSION
 NORTHERN INDIA ENGINEERING COLLEGE, LKO D E P A R T M E N T O F M A T H E M A T I C S B.TECH IIIrd SEMESTER QUESTION BANK ACADEMIC SESSION 011-1 DISCRETE MATHEMATICS (EOE 038) 1. UNIT I (SET, RELATION,
NORTHERN INDIA ENGINEERING COLLEGE, LKO D E P A R T M E N T O F M A T H E M A T I C S B.TECH IIIrd SEMESTER QUESTION BANK ACADEMIC SESSION 011-1 DISCRETE MATHEMATICS (EOE 038) 1. UNIT I (SET, RELATION,
Final Exam Review. 2. Let A = {, { }}. What is the cardinality of A? Is
 1. Describe the elements of the set (Z Q) R N. Is this set countable or uncountable? Solution: The set is equal to {(x, y) x Z, y N} = Z N. Since the Cartesian product of two denumerable sets is denumerable,
1. Describe the elements of the set (Z Q) R N. Is this set countable or uncountable? Solution: The set is equal to {(x, y) x Z, y N} = Z N. Since the Cartesian product of two denumerable sets is denumerable,
REVIEW QUESTIONS. Chapter 1: Foundations: Sets, Logic, and Algorithms
 REVIEW QUESTIONS Chapter 1: Foundations: Sets, Logic, and Algorithms 1. Why can t a Venn diagram be used to prove a statement about sets? 2. Suppose S is a set with n elements. Explain why the power set
REVIEW QUESTIONS Chapter 1: Foundations: Sets, Logic, and Algorithms 1. Why can t a Venn diagram be used to prove a statement about sets? 2. Suppose S is a set with n elements. Explain why the power set
1. Consider the conditional E = p q r. Use de Morgan s laws to write simplified versions of the following : The negation of E : 5 points
 Introduction to Discrete Mathematics 3450:208 Test 1 1. Consider the conditional E = p q r. Use de Morgan s laws to write simplified versions of the following : The negation of E : The inverse of E : The
Introduction to Discrete Mathematics 3450:208 Test 1 1. Consider the conditional E = p q r. Use de Morgan s laws to write simplified versions of the following : The negation of E : The inverse of E : The
a + b = b + a and a b = b a. (a + b) + c = a + (b + c) and (a b) c = a (b c). a (b + c) = a b + a c and (a + b) c = a c + b c.
 Properties of the Integers The set of all integers is the set and the subset of Z given by Z = {, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, }, N = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, }, is the set of nonnegative integers (also called
Properties of the Integers The set of all integers is the set and the subset of Z given by Z = {, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, }, N = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, }, is the set of nonnegative integers (also called
Properties of the Integers
 Properties of the Integers The set of all integers is the set and the subset of Z given by Z = {, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, }, N = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, }, is the set of nonnegative integers (also called
Properties of the Integers The set of all integers is the set and the subset of Z given by Z = {, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, }, N = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, }, is the set of nonnegative integers (also called
DISCRETE STRUCTURES AMIN WITNO
 DISCRETE STRUCTURES AMIN WITNO p h i. w i t n o. c o m Discrete Structures Revision Notes and Problems Amin Witno Preface These notes were prepared for students as a revision workbook
DISCRETE STRUCTURES AMIN WITNO p h i. w i t n o. c o m Discrete Structures Revision Notes and Problems Amin Witno Preface These notes were prepared for students as a revision workbook
Notes for Math 290 using Introduction to Mathematical Proofs by Charles E. Roberts, Jr.
 Notes for Math 290 using Introduction to Mathematical Proofs by Charles E. Roberts, Jr. Chapter : Logic Topics:. Statements, Negation, and Compound Statements.2 Truth Tables and Logical Equivalences.3
Notes for Math 290 using Introduction to Mathematical Proofs by Charles E. Roberts, Jr. Chapter : Logic Topics:. Statements, Negation, and Compound Statements.2 Truth Tables and Logical Equivalences.3
Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts
 Meet #5 March/April 2005 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Average team score: 86.6 Average meet for the seasion: 95.9 Meet #5 March/April 2005 Category 1 Mystery Meet #5, March/April
Meet #5 March/April 2005 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Average team score: 86.6 Average meet for the seasion: 95.9 Meet #5 March/April 2005 Category 1 Mystery Meet #5, March/April
Mathematical Reasoning & Proofs
 Mathematical Reasoning & Proofs MAT 1362 Fall 2018 Alistair Savage Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Ottawa This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0
Mathematical Reasoning & Proofs MAT 1362 Fall 2018 Alistair Savage Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Ottawa This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0
Algebra 2 Pre-AP Summer Packet. PART I Solve the equation. Show all work on a separate sheet of paper. 1.) 5w 2 2w 5. 2.) 5b 4 2b 8. 6.
 Algebra 2 Pre-AP Summer Packet PART I Solve the equation. Show all work on a separate sheet of paper. 1.) 5w 2 2w 5 2.) 5b 4 2b 8.) 2z 6z 25 4.) 2c14 6 4c 5.) p5 25 4p 6.) 17 6r 25 r 12 r 2 r 5 r 7.) 2b
Algebra 2 Pre-AP Summer Packet PART I Solve the equation. Show all work on a separate sheet of paper. 1.) 5w 2 2w 5 2.) 5b 4 2b 8.) 2z 6z 25 4.) 2c14 6 4c 5.) p5 25 4p 6.) 17 6r 25 r 12 r 2 r 5 r 7.) 2b
Math 109 September 1, 2016
 Math 109 September 1, 2016 Question 1 Given that the proposition P Q is true. Which of the following must also be true? A. (not P ) or Q. B. (not Q) implies (not P ). C. Q implies P. D. A and B E. A, B,
Math 109 September 1, 2016 Question 1 Given that the proposition P Q is true. Which of the following must also be true? A. (not P ) or Q. B. (not Q) implies (not P ). C. Q implies P. D. A and B E. A, B,
Notation Index. gcd(a, b) (greatest common divisor) NT-16
 Notation Index (for all) B A (all functions) B A = B A (all functions) SF-18 (n) k (falling factorial) SF-9 a R b (binary relation) C(n,k) = n! k! (n k)! (binomial coefficient) SF-9 n! (n factorial) SF-9
Notation Index (for all) B A (all functions) B A = B A (all functions) SF-18 (n) k (falling factorial) SF-9 a R b (binary relation) C(n,k) = n! k! (n k)! (binomial coefficient) SF-9 n! (n factorial) SF-9
Name (please print) Mathematics Final Examination December 14, 2005 I. (4)
 Mathematics 513-00 Final Examination December 14, 005 I Use a direct argument to prove the following implication: The product of two odd integers is odd Let m and n be two odd integers Since they are odd,
Mathematics 513-00 Final Examination December 14, 005 I Use a direct argument to prove the following implication: The product of two odd integers is odd Let m and n be two odd integers Since they are odd,
Lecture Notes on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS. Eusebius Doedel
 Lecture Notes on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Eusebius Doedel c Eusebius J. Doedel, 009 Contents Logic. Introduction............................................................................... Basic logical
Lecture Notes on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Eusebius Doedel c Eusebius J. Doedel, 009 Contents Logic. Introduction............................................................................... Basic logical
8. Given a rational number r, prove that there exist coprime integers p and q, with q 0, so that r = p q. . For all n N, f n = an b n 2
 MATH 135: Randomized Exam Practice Problems These are the warm-up exercises and recommended problems taken from all the extra practice sets presented in random order. The challenge problems have not been
MATH 135: Randomized Exam Practice Problems These are the warm-up exercises and recommended problems taken from all the extra practice sets presented in random order. The challenge problems have not been
Chapter 2 PROBABILITY SAMPLE SPACE
 Chapter 2 PROBABILITY Key words: Sample space, sample point, tree diagram, events, complement, union and intersection of an event, mutually exclusive events; Counting techniques: multiplication rule, permutation,
Chapter 2 PROBABILITY Key words: Sample space, sample point, tree diagram, events, complement, union and intersection of an event, mutually exclusive events; Counting techniques: multiplication rule, permutation,
MATH 2200 Final LC Review
 MATH 2200 Final LC Review Thomas Goller April 25, 2013 1 Final LC Format The final learning celebration will consist of 12-15 claims to be proven or disproven. It will take place on Wednesday, May 1, from
MATH 2200 Final LC Review Thomas Goller April 25, 2013 1 Final LC Format The final learning celebration will consist of 12-15 claims to be proven or disproven. It will take place on Wednesday, May 1, from
WORKSHEET ON NUMBERS, MATH 215 FALL. We start our study of numbers with the integers: N = {1, 2, 3,...}
 WORKSHEET ON NUMBERS, MATH 215 FALL 18(WHYTE) We start our study of numbers with the integers: Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,... } and their subset of natural numbers: N = {1, 2, 3,...} For now we will not
WORKSHEET ON NUMBERS, MATH 215 FALL 18(WHYTE) We start our study of numbers with the integers: Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,... } and their subset of natural numbers: N = {1, 2, 3,...} For now we will not
2.6 Tools for Counting sample points
 2.6 Tools for Counting sample points When the number of simple events in S is too large, manual enumeration of every sample point in S is tedious or even impossible. (Example) If S contains N equiprobable
2.6 Tools for Counting sample points When the number of simple events in S is too large, manual enumeration of every sample point in S is tedious or even impossible. (Example) If S contains N equiprobable
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2016 Seshia and Walrand Midterm 1 Solutions
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2016 Seshia and Walrand Midterm 1 Solutions PRINT Your Name: Answer: Oski Bear SIGN Your Name: PRINT Your Student ID: CIRCLE your exam room: Dwinelle
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2016 Seshia and Walrand Midterm 1 Solutions PRINT Your Name: Answer: Oski Bear SIGN Your Name: PRINT Your Student ID: CIRCLE your exam room: Dwinelle
UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA DECEMBER EXAMINATIONS MATH 122: Logic and Foundations
 UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA DECEMBER EXAMINATIONS 2013 MATH 122: Logic and Foundations Instructor and section (check one): K. Mynhardt [A01] CRN 12132 G. MacGillivray [A02] CRN 12133 NAME: V00#: Duration: 3
UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA DECEMBER EXAMINATIONS 2013 MATH 122: Logic and Foundations Instructor and section (check one): K. Mynhardt [A01] CRN 12132 G. MacGillivray [A02] CRN 12133 NAME: V00#: Duration: 3
MTH202 Discrete Mathematics
 LATSEST MCQS FROM MIDTERM PAPERS 10 MAY 011 MC10040185 moaaz.pk@gmail.com Moaaz siddiq MTH0 Discrete Mathematics Question No. 1: If p= It is raining q = She will go to college "It is raining and she will
LATSEST MCQS FROM MIDTERM PAPERS 10 MAY 011 MC10040185 moaaz.pk@gmail.com Moaaz siddiq MTH0 Discrete Mathematics Question No. 1: If p= It is raining q = She will go to college "It is raining and she will
DISCRETE MATH: FINAL REVIEW
 DISCRETE MATH: FINAL REVIEW DR. DANIEL FREEMAN 1) a. Does 3 = {3}? b. Is 3 {3}? c. Is 3 {3}? c. Is {3} {3}? c. Is {3} {3}? d. Does {3} = {3, 3, 3, 3}? e. Is {x Z x > 0} {x R x > 0}? 1. Chapter 1 review
DISCRETE MATH: FINAL REVIEW DR. DANIEL FREEMAN 1) a. Does 3 = {3}? b. Is 3 {3}? c. Is 3 {3}? c. Is {3} {3}? c. Is {3} {3}? d. Does {3} = {3, 3, 3, 3}? e. Is {x Z x > 0} {x R x > 0}? 1. Chapter 1 review
Writing Assignment 2 Student Sample Questions
 Writing Assignment 2 Student Sample Questions 1. Let P and Q be statements. Then the statement (P = Q) ( P Q) is a tautology. 2. The statement If the sun rises from the west, then I ll get out of the bed.
Writing Assignment 2 Student Sample Questions 1. Let P and Q be statements. Then the statement (P = Q) ( P Q) is a tautology. 2. The statement If the sun rises from the west, then I ll get out of the bed.
Proofs. Chapter 2 P P Q Q
 Chapter Proofs In this chapter we develop three methods for proving a statement. To start let s suppose the statement is of the form P Q or if P, then Q. Direct: This method typically starts with P. Then,
Chapter Proofs In this chapter we develop three methods for proving a statement. To start let s suppose the statement is of the form P Q or if P, then Q. Direct: This method typically starts with P. Then,
Chapter 1 : The language of mathematics.
 MAT 200, Logic, Language and Proof, Fall 2015 Summary Chapter 1 : The language of mathematics. Definition. A proposition is a sentence which is either true or false. Truth table for the connective or :
MAT 200, Logic, Language and Proof, Fall 2015 Summary Chapter 1 : The language of mathematics. Definition. A proposition is a sentence which is either true or false. Truth table for the connective or :
Welcome to MAT 137! Course website:
 Welcome to MAT 137! Course website: http://uoft.me/ Read the course outline Office hours to be posted here Online forum: Piazza Precalculus review: http://uoft.me/precalc If you haven t gotten an email
Welcome to MAT 137! Course website: http://uoft.me/ Read the course outline Office hours to be posted here Online forum: Piazza Precalculus review: http://uoft.me/precalc If you haven t gotten an email
Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. You will have 75 minutes for the exam.
 Math 2603 Midterm 1 Spring 2018 Your Name Student ID # Section Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. You will have 75 minutes for the exam. Check that you have a complete exam. There are 5
Math 2603 Midterm 1 Spring 2018 Your Name Student ID # Section Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. You will have 75 minutes for the exam. Check that you have a complete exam. There are 5
Foundations of Mathematics MATH 220 FALL 2017 Lecture Notes
 Foundations of Mathematics MATH 220 FALL 2017 Lecture Notes These notes form a brief summary of what has been covered during the lectures. All the definitions must be memorized and understood. Statements
Foundations of Mathematics MATH 220 FALL 2017 Lecture Notes These notes form a brief summary of what has been covered during the lectures. All the definitions must be memorized and understood. Statements
Quantifiers. P. Danziger
 - 2 Quantifiers P. Danziger 1 Elementary Quantifiers (2.1) We wish to be able to use variables, such as x or n in logical statements. We do this by using the two quantifiers: 1. - There Exists 2. - For
- 2 Quantifiers P. Danziger 1 Elementary Quantifiers (2.1) We wish to be able to use variables, such as x or n in logical statements. We do this by using the two quantifiers: 1. - There Exists 2. - For
ALGEBRA. 1. Some elementary number theory 1.1. Primes and divisibility. We denote the collection of integers
 ALGEBRA CHRISTIAN REMLING 1. Some elementary number theory 1.1. Primes and divisibility. We denote the collection of integers by Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1,...}. Given a, b Z, we write a b if b = ac for some
ALGEBRA CHRISTIAN REMLING 1. Some elementary number theory 1.1. Primes and divisibility. We denote the collection of integers by Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1,...}. Given a, b Z, we write a b if b = ac for some
Discrete Structures for Computer Science: Counting, Recursion, and Probability
 Discrete Structures for Computer Science: Counting, Recursion, and Probability Michiel Smid School of Computer Science Carleton University Ottawa, Ontario Canada michiel@scs.carleton.ca December 18, 2017
Discrete Structures for Computer Science: Counting, Recursion, and Probability Michiel Smid School of Computer Science Carleton University Ottawa, Ontario Canada michiel@scs.carleton.ca December 18, 2017
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Concepts of Mathematics MATH 352
 Lecture Notes 1 Basic Concepts of Mathematics MATH 352 Ivan Avramidi New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology Socorro, NM 87801 June 3, 2004 Author: Ivan Avramidi; File: absmath.tex; Date: June 11,
Lecture Notes 1 Basic Concepts of Mathematics MATH 352 Ivan Avramidi New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology Socorro, NM 87801 June 3, 2004 Author: Ivan Avramidi; File: absmath.tex; Date: June 11,
Exam III Review Math-132 (Sections 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6, 8.1, 8.2, 8.3)
 1 Exam III Review Math-132 (Sections 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6, 8.1, 8.2, 8.3) On this exam, questions may come from any of the following topic areas: - Union and intersection of sets - Complement of
1 Exam III Review Math-132 (Sections 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6, 8.1, 8.2, 8.3) On this exam, questions may come from any of the following topic areas: - Union and intersection of sets - Complement of
IVA S STUDY GUIDE FOR THE DISCRETE FINAL EXAM - SELECTED SOLUTIONS. 1. Combinatorics
 IVA S STUDY GUIDE FOR THE DISCRETE FINAL EXAM - SELECTED SOLUTIONS Combinatorics Go over combinatorics examples in the text Review all the combinatorics problems from homewor Do at least a couple of extra
IVA S STUDY GUIDE FOR THE DISCRETE FINAL EXAM - SELECTED SOLUTIONS Combinatorics Go over combinatorics examples in the text Review all the combinatorics problems from homewor Do at least a couple of extra
Midterm 1. Your Exam Room: Name of Person Sitting on Your Left: Name of Person Sitting on Your Right: Name of Person Sitting in Front of You:
 CS70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory, Fall 2018 Midterm 1 8:00-10:00pm, 24 September Your First Name: SIGN Your Name: Your Last Name: Your Exam Room: Name of Person Sitting on Your Left: Name
CS70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory, Fall 2018 Midterm 1 8:00-10:00pm, 24 September Your First Name: SIGN Your Name: Your Last Name: Your Exam Room: Name of Person Sitting on Your Left: Name
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis
![UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis](/thumbs/85/92597132.jpg) UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 6 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 6 Notes Goals: CL Sections 3, 4; FN Section
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 6 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 6 Notes Goals: CL Sections 3, 4; FN Section
a. See the textbook for examples of proving logical equivalence using truth tables. b. There is a real number x for which f (x) < 0. (x 1) 2 > 0.
 For some problems, several sample proofs are given here. Problem 1. a. See the textbook for examples of proving logical equivalence using truth tables. b. There is a real number x for which f (x) < 0.
For some problems, several sample proofs are given here. Problem 1. a. See the textbook for examples of proving logical equivalence using truth tables. b. There is a real number x for which f (x) < 0.
Math 10 - Compilation of Sample Exam Questions + Answers
 Math 10 - Compilation of Sample Exam Questions + Sample Exam Question 1 We have a population of size N. Let p be the independent probability of a person in the population developing a disease. Answer the
Math 10 - Compilation of Sample Exam Questions + Sample Exam Question 1 We have a population of size N. Let p be the independent probability of a person in the population developing a disease. Answer the
Discrete mathematics
 Discrete mathematics Exercises. Introduction: sets and functions.. Let us consider the sets A = {x N x is even}, B = {x N x > 4}, and C = {x N x < 6}. What are the sets below? B \ C, A \ (B C, B C, (B
Discrete mathematics Exercises. Introduction: sets and functions.. Let us consider the sets A = {x N x is even}, B = {x N x > 4}, and C = {x N x < 6}. What are the sets below? B \ C, A \ (B C, B C, (B
1. Given the public RSA encryption key (e, n) = (5, 35), find the corresponding decryption key (d, n).
 MATH 135: Randomized Exam Practice Problems These are the warm-up exercises and recommended problems taken from all the extra practice sets presented in random order. The challenge problems have not been
MATH 135: Randomized Exam Practice Problems These are the warm-up exercises and recommended problems taken from all the extra practice sets presented in random order. The challenge problems have not been
1 The Basic Counting Principles
 1 The Basic Counting Principles The Multiplication Rule If an operation consists of k steps and the first step can be performed in n 1 ways, the second step can be performed in n ways [regardless of how
1 The Basic Counting Principles The Multiplication Rule If an operation consists of k steps and the first step can be performed in n 1 ways, the second step can be performed in n ways [regardless of how
CS Discrete Mathematics Dr. D. Manivannan (Mani)
 CS 275 - Discrete Mathematics Dr. D. Manivannan (Mani) Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Course Website: www.cs.uky.edu/~manivann/cs275 Notes based on Discrete Mathematics
CS 275 - Discrete Mathematics Dr. D. Manivannan (Mani) Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Course Website: www.cs.uky.edu/~manivann/cs275 Notes based on Discrete Mathematics
MATH 3330 ABSTRACT ALGEBRA SPRING Definition. A statement is a declarative sentence that is either true or false.
 MATH 3330 ABSTRACT ALGEBRA SPRING 2014 TANYA CHEN Dr. Gordon Heier Tuesday January 14, 2014 The Basics of Logic (Appendix) Definition. A statement is a declarative sentence that is either true or false.
MATH 3330 ABSTRACT ALGEBRA SPRING 2014 TANYA CHEN Dr. Gordon Heier Tuesday January 14, 2014 The Basics of Logic (Appendix) Definition. A statement is a declarative sentence that is either true or false.
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Summer 2014 James Cook Midterm 1
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Summer 2014 James Cook Midterm 1 Thursday July 17, 2014, 12:40pm-2:00pm. Instructions: Do not turn over this page until the proctor tells you to. Don t
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Summer 2014 James Cook Midterm 1 Thursday July 17, 2014, 12:40pm-2:00pm. Instructions: Do not turn over this page until the proctor tells you to. Don t
Exam Practice Problems
 Math 231 Exam Practice Problems WARNING: This is not a sample test. Problems on the exams may or may not be similar to these problems. These problems are just intended to focus your study of the topics.
Math 231 Exam Practice Problems WARNING: This is not a sample test. Problems on the exams may or may not be similar to these problems. These problems are just intended to focus your study of the topics.
Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 11
 Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 11 Andrew Nobel October 24, 2017 Basics of Counting Product Rule Product Rule: Suppose that the elements of a collection S can be specified by a sequence of k
Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 11 Andrew Nobel October 24, 2017 Basics of Counting Product Rule Product Rule: Suppose that the elements of a collection S can be specified by a sequence of k
WUCT121. Discrete Mathematics. Logic. Tutorial Exercises
 WUCT11 Discrete Mathematics Logic Tutorial Exercises 1 Logic Predicate Logic 3 Proofs 4 Set Theory 5 Relations and Functions WUCT11 Logic Tutorial Exercises 1 Section 1: Logic Question1 For each of the
WUCT11 Discrete Mathematics Logic Tutorial Exercises 1 Logic Predicate Logic 3 Proofs 4 Set Theory 5 Relations and Functions WUCT11 Logic Tutorial Exercises 1 Section 1: Logic Question1 For each of the
LECTURE NOTES DISCRETE MATHEMATICS. Eusebius Doedel
 LECTURE NOTES on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Eusebius Doedel 1 LOGIC Introduction. First we introduce some basic concepts needed in our discussion of logic. These will be covered in more detail later. A set is
LECTURE NOTES on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Eusebius Doedel 1 LOGIC Introduction. First we introduce some basic concepts needed in our discussion of logic. These will be covered in more detail later. A set is
Preparing for the CS 173 (A) Fall 2018 Midterm 1
 Preparing for the CS 173 (A) Fall 2018 Midterm 1 1 Basic information Midterm 1 is scheduled from 7:15-8:30 PM. We recommend you arrive early so that you can start exactly at 7:15. Exams will be collected
Preparing for the CS 173 (A) Fall 2018 Midterm 1 1 Basic information Midterm 1 is scheduled from 7:15-8:30 PM. We recommend you arrive early so that you can start exactly at 7:15. Exams will be collected
Proofs. Chapter 2 P P Q Q
 Chapter Proofs In this chapter we develop three methods for proving a statement. To start let s suppose the statement is of the form P Q or if P, then Q. Direct: This method typically starts with P. Then,
Chapter Proofs In this chapter we develop three methods for proving a statement. To start let s suppose the statement is of the form P Q or if P, then Q. Direct: This method typically starts with P. Then,
Relationships between elements of sets occur in many contexts. Every day we deal with
 C H A P T E R 9 Relations 9.1 Relations and Their Properties 9.2 n-ary Relations and Their Applications 9.3 Representing Relations 9.4 Closures of Relations 9.5 Equivalence Relations 9.6 Partial Orderings
C H A P T E R 9 Relations 9.1 Relations and Their Properties 9.2 n-ary Relations and Their Applications 9.3 Representing Relations 9.4 Closures of Relations 9.5 Equivalence Relations 9.6 Partial Orderings
CS1800 Discrete Structures Fall 2016 Profs. Gold & Schnyder April 25, CS1800 Discrete Structures Final
 CS1800 Discrete Structures Fall 2016 Profs. Gold & Schnyder April 25, 2017 CS1800 Discrete Structures Final Instructions: 1. The exam is closed book and closed notes. You may not use a calculator or any
CS1800 Discrete Structures Fall 2016 Profs. Gold & Schnyder April 25, 2017 CS1800 Discrete Structures Final Instructions: 1. The exam is closed book and closed notes. You may not use a calculator or any
Discrete Mathematics Exam File Spring Exam #1
 Discrete Mathematics Exam File Spring 2008 Exam #1 1.) Consider the sequence a n = 2n + 3. a.) Write out the first five terms of the sequence. b.) Determine a recursive formula for the sequence. 2.) Consider
Discrete Mathematics Exam File Spring 2008 Exam #1 1.) Consider the sequence a n = 2n + 3. a.) Write out the first five terms of the sequence. b.) Determine a recursive formula for the sequence. 2.) Consider
0 Sets and Induction. Sets
 0 Sets and Induction Sets A set is an unordered collection of objects, called elements or members of the set. A set is said to contain its elements. We write a A to denote that a is an element of the set
0 Sets and Induction Sets A set is an unordered collection of objects, called elements or members of the set. A set is said to contain its elements. We write a A to denote that a is an element of the set
McGill University Faculty of Science. Solutions to Practice Final Examination Math 240 Discrete Structures 1. Time: 3 hours Marked out of 60
 McGill University Faculty of Science Solutions to Practice Final Examination Math 40 Discrete Structures Time: hours Marked out of 60 Question. [6] Prove that the statement (p q) (q r) (p r) is a contradiction
McGill University Faculty of Science Solutions to Practice Final Examination Math 40 Discrete Structures Time: hours Marked out of 60 Question. [6] Prove that the statement (p q) (q r) (p r) is a contradiction
Computer Science Foundation Exam
 Computer Science Foundation Exam May 6, 2016 Section II A DISCRETE STRUCTURES NO books, notes, or calculators may be used, and you must work entirely on your own. SOLUTION Question Max Pts Category Passing
Computer Science Foundation Exam May 6, 2016 Section II A DISCRETE STRUCTURES NO books, notes, or calculators may be used, and you must work entirely on your own. SOLUTION Question Max Pts Category Passing
Cartesian Products and Relations
 Cartesian Products and Relations Definition (Cartesian product) If A and B are sets, the Cartesian product of A and B is the set A B = {(a, b) : (a A) and (b B)}. The following points are worth special
Cartesian Products and Relations Definition (Cartesian product) If A and B are sets, the Cartesian product of A and B is the set A B = {(a, b) : (a A) and (b B)}. The following points are worth special
Computer Science Foundation Exam
 Computer Science Foundation Exam August 2, 2002 Section II A DISCRETE STRUCTURES NO books, notes, or calculators may be used, and you must work entirely on your own. Name: SSN: In this section of the exam,
Computer Science Foundation Exam August 2, 2002 Section II A DISCRETE STRUCTURES NO books, notes, or calculators may be used, and you must work entirely on your own. Name: SSN: In this section of the exam,
Math Final Exam December 14, 2009 Page 1 of 5
 Math 201-803-Final Exam December 14, 2009 Page 1 of 5 (3) 1. Evaluate the expressions: (a) 10 C 4 (b) 10 P 4 (c) 15!4! 3!11! (4) 2. (a) In how many ways can a president, a vice president and a treasurer
Math 201-803-Final Exam December 14, 2009 Page 1 of 5 (3) 1. Evaluate the expressions: (a) 10 C 4 (b) 10 P 4 (c) 15!4! 3!11! (4) 2. (a) In how many ways can a president, a vice president and a treasurer
CS 360, Winter Morphology of Proof: An introduction to rigorous proof techniques
 CS 30, Winter 2011 Morphology of Proof: An introduction to rigorous proof techniques 1 Methodology of Proof An example Deep down, all theorems are of the form If A then B, though they may be expressed
CS 30, Winter 2011 Morphology of Proof: An introduction to rigorous proof techniques 1 Methodology of Proof An example Deep down, all theorems are of the form If A then B, though they may be expressed
Tutorial Obtain the principal disjunctive normal form and principal conjunction form of the statement
 Tutorial - 1 1. Obtain the principal disjunctive normal form and principal conjunction form of the statement Let S P P Q Q R P P Q Q R A: P Q Q R P Q R P Q Q R Q Q R A S Minterm Maxterm T T T F F T T T
Tutorial - 1 1. Obtain the principal disjunctive normal form and principal conjunction form of the statement Let S P P Q Q R P P Q Q R A: P Q Q R P Q R P Q Q R Q Q R A S Minterm Maxterm T T T F F T T T
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE ENGINEERING SUBJECT QUESTION BANK : MA6566 \ DISCRETE MATHEMATICS SEM / YEAR: V / III year CSE. UNIT I -
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE ENGINEERING SUBJECT QUESTION BANK : MA6566 \ DISCRETE MATHEMATICS SEM / YEAR: V / III year CSE. UNIT I -
Undergraduate Notes in Mathematics. Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics. Introductory Notes in Discrete Mathematics Solution Guide
 Undergraduate Notes in Mathematics Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics Introductory Notes in Discrete Mathematics Solution Guide Marcel B. Finan c All Rights Reserved 2015 Edition Contents
Undergraduate Notes in Mathematics Arkansas Tech University Department of Mathematics Introductory Notes in Discrete Mathematics Solution Guide Marcel B. Finan c All Rights Reserved 2015 Edition Contents
Executive Assessment. Executive Assessment Math Review. Section 1.0, Arithmetic, includes the following topics:
 Executive Assessment Math Review Although the following provides a review of some of the mathematical concepts of arithmetic and algebra, it is not intended to be a textbook. You should use this chapter
Executive Assessment Math Review Although the following provides a review of some of the mathematical concepts of arithmetic and algebra, it is not intended to be a textbook. You should use this chapter
Probabilistic models
 Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became the definitive formulation
Kolmogorov (Andrei Nikolaevich, 1903 1987) put forward an axiomatic system for probability theory. Foundations of the Calculus of Probabilities, published in 1933, immediately became the definitive formulation
7.11 A proof involving composition Variation in terminology... 88
 Contents Preface xi 1 Math review 1 1.1 Some sets............................. 1 1.2 Pairs of reals........................... 3 1.3 Exponentials and logs...................... 4 1.4 Some handy functions......................
Contents Preface xi 1 Math review 1 1.1 Some sets............................. 1 1.2 Pairs of reals........................... 3 1.3 Exponentials and logs...................... 4 1.4 Some handy functions......................
2007 Marywood Mathematics Contest
 007 Marywood Mathematics Contest Level II Sponsored by SEMI-GROUP The Student Mathematics Club of Marywood University February 4, 007 Directions:. This exam consists of 40 questions on 7 pages. Please
007 Marywood Mathematics Contest Level II Sponsored by SEMI-GROUP The Student Mathematics Club of Marywood University February 4, 007 Directions:. This exam consists of 40 questions on 7 pages. Please
Stat 225 Week 2, 8/27/12-8/31/12, Notes: Independence and Bayes Rule
 Stat 225 Week 2, 8/27/12-8/31/12, Notes: Independence and Bayes Rule The Fall 2012 Stat 225 T.A.s September 7, 2012 1 Monday, 8/27/12, Notes on Independence In general, a conditional probability will change
Stat 225 Week 2, 8/27/12-8/31/12, Notes: Independence and Bayes Rule The Fall 2012 Stat 225 T.A.s September 7, 2012 1 Monday, 8/27/12, Notes on Independence In general, a conditional probability will change
Give (one word answer) and Take (one mark in future):
 Star Sums: Give (one word answer) and Take (one mark in future): 1. If is a rational number, what is the condition on q so that the decimal representation of is terminating. 2. Find the (H.C.F X L.C.M)
Star Sums: Give (one word answer) and Take (one mark in future): 1. If is a rational number, what is the condition on q so that the decimal representation of is terminating. 2. Find the (H.C.F X L.C.M)
Number Theory and Divisibility
 Number Theory and Divisibility Recall the Natural Numbers: N = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, } Any Natural Number can be expressed as the product of two or more Natural Numbers: 2 x 12 = 24 3 x 8 = 24 6 x 4 = 24
Number Theory and Divisibility Recall the Natural Numbers: N = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, } Any Natural Number can be expressed as the product of two or more Natural Numbers: 2 x 12 = 24 3 x 8 = 24 6 x 4 = 24
February 2017 February 18, 2017
 February 017 February 18, 017 Combinatorics 1. Kelvin the Frog is going to roll three fair ten-sided dice with faces labelled 0, 1,,..., 9. First he rolls two dice, and finds the sum of the two rolls.
February 017 February 18, 017 Combinatorics 1. Kelvin the Frog is going to roll three fair ten-sided dice with faces labelled 0, 1,,..., 9. First he rolls two dice, and finds the sum of the two rolls.
Part IA Numbers and Sets
 Part IA Numbers and Sets Definitions Based on lectures by A. G. Thomason Notes taken by Dexter Chua Michaelmas 2014 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
Part IA Numbers and Sets Definitions Based on lectures by A. G. Thomason Notes taken by Dexter Chua Michaelmas 2014 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
About This Document. MTH299 - Examples Weeks 1-6; updated on January 5, 2018
 About This Document This is the examples document for MTH 299. Basically it is a loosely organized universe of questions (examples) that we think are interesting, helpful, useful for practice, and serve
About This Document This is the examples document for MTH 299. Basically it is a loosely organized universe of questions (examples) that we think are interesting, helpful, useful for practice, and serve
Solutions to Exercises (Sections )
 s to Exercises (Sections 1.1-1.10) Section 1.1 Exercise 1.1.1: Identifying propositions (a) Have a nice day. : Command, not a proposition. (b) The soup is cold. : Proposition. Negation: The soup is not
s to Exercises (Sections 1.1-1.10) Section 1.1 Exercise 1.1.1: Identifying propositions (a) Have a nice day. : Command, not a proposition. (b) The soup is cold. : Proposition. Negation: The soup is not
Contribution of Problems
 Exam topics 1. Basic structures: sets, lists, functions (a) Sets { }: write all elements, or define by condition (b) Set operations: A B, A B, A\B, A c (c) Lists ( ): Cartesian product A B (d) Functions
Exam topics 1. Basic structures: sets, lists, functions (a) Sets { }: write all elements, or define by condition (b) Set operations: A B, A B, A\B, A c (c) Lists ( ): Cartesian product A B (d) Functions
PUTNAM TRAINING NUMBER THEORY. Exercises 1. Show that the sum of two consecutive primes is never twice a prime.
 PUTNAM TRAINING NUMBER THEORY (Last updated: December 11, 2017) Remark. This is a list of exercises on Number Theory. Miguel A. Lerma Exercises 1. Show that the sum of two consecutive primes is never twice
PUTNAM TRAINING NUMBER THEORY (Last updated: December 11, 2017) Remark. This is a list of exercises on Number Theory. Miguel A. Lerma Exercises 1. Show that the sum of two consecutive primes is never twice
Discrete Mathematics (CS503)
 Discrete Mathematics (CS503) Module I Suggested Questions Day 1, 2 1. Translate the following statement into propositional logic using the propositions provided: You can upgrade your operating system only
Discrete Mathematics (CS503) Module I Suggested Questions Day 1, 2 1. Translate the following statement into propositional logic using the propositions provided: You can upgrade your operating system only
Chapter 8 Sequences, Series, and Probability
 Chapter 8 Sequences, Series, and Probability Overview 8.1 Sequences and Series 8.2 Arithmetic Sequences and Partial Sums 8.3 Geometric Sequences and Partial Sums 8.5 The Binomial Theorem 8.6 Counting Principles
Chapter 8 Sequences, Series, and Probability Overview 8.1 Sequences and Series 8.2 Arithmetic Sequences and Partial Sums 8.3 Geometric Sequences and Partial Sums 8.5 The Binomial Theorem 8.6 Counting Principles
University of California, San Diego Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE 20. Solutions to Midterm Exam Winter 2018
 University of California, San Diego Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE 20 Solutions to Midterm Exam Winter 2018 Problem 1 (30 points) a. The boolean function f(p, q) = (q p) ( q p) is specified
University of California, San Diego Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE 20 Solutions to Midterm Exam Winter 2018 Problem 1 (30 points) a. The boolean function f(p, q) = (q p) ( q p) is specified
Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 10
 Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 10 Andrew Nobel October 17, 2017 Mathematical Induction Given: Propositional function P (n) with domain N + Basis step: Show that P (1) is true Inductive step:
Introduction to Decision Sciences Lecture 10 Andrew Nobel October 17, 2017 Mathematical Induction Given: Propositional function P (n) with domain N + Basis step: Show that P (1) is true Inductive step:
4) Solve for this system using your graphing
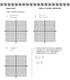 Algebra Unit 5 HW Day 1 SOLVING GRAPHICALLY Graph the following systems: 1) x 2y 12 y 2x 6 2) y x 2 6x 2y 10 ) x y 9 4) Solve for this system using your graphing x calculator. [You will still need to put
Algebra Unit 5 HW Day 1 SOLVING GRAPHICALLY Graph the following systems: 1) x 2y 12 y 2x 6 2) y x 2 6x 2y 10 ) x y 9 4) Solve for this system using your graphing x calculator. [You will still need to put
CS 250/251 Discrete Structures I and II Section 005 Fall/Winter Professor York
 CS 250/251 Discrete Structures I and II Section 005 Fall/Winter 2013-2014 Professor York Practice Quiz March 10, 2014 CALCULATORS ALLOWED, SHOW ALL YOUR WORK 1. Construct the power set of the set A = {1,2,3}
CS 250/251 Discrete Structures I and II Section 005 Fall/Winter 2013-2014 Professor York Practice Quiz March 10, 2014 CALCULATORS ALLOWED, SHOW ALL YOUR WORK 1. Construct the power set of the set A = {1,2,3}
Chapter VI. Relations. Assumptions are the termites of relationships. Henry Winkler
 Chapter VI Relations Assumptions are the termites of relationships. Henry Winkler Studying relationships between objects can yield important information about the objects themselves. In the real numbers,
Chapter VI Relations Assumptions are the termites of relationships. Henry Winkler Studying relationships between objects can yield important information about the objects themselves. In the real numbers,
Reading 11 : Relations and Functions
 CS/Math 240: Introduction to Discrete Mathematics Fall 2015 Reading 11 : Relations and Functions Instructor: Beck Hasti and Gautam Prakriya In reading 3, we described a correspondence between predicates
CS/Math 240: Introduction to Discrete Mathematics Fall 2015 Reading 11 : Relations and Functions Instructor: Beck Hasti and Gautam Prakriya In reading 3, we described a correspondence between predicates
Multiple Choice Questions for Review
 Equivalence and Order Multiple Choice Questions for Review In each case there is one correct answer (given at the end of the problem set). Try to work the problem first without looking at the answer. Understand
Equivalence and Order Multiple Choice Questions for Review In each case there is one correct answer (given at the end of the problem set). Try to work the problem first without looking at the answer. Understand
2030 LECTURES. R. Craigen. Inclusion/Exclusion and Relations
 2030 LECTURES R. Craigen Inclusion/Exclusion and Relations The Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion 7 ROS enumerates the union of disjoint sets. What if sets overlap? Some 17 out of 30 students in a class
2030 LECTURES R. Craigen Inclusion/Exclusion and Relations The Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion 7 ROS enumerates the union of disjoint sets. What if sets overlap? Some 17 out of 30 students in a class
2 Elementary number theory
 2 Elementary number theory 2.1 Introduction Elementary number theory is concerned with properties of the integers. Hence we shall be interested in the following sets: The set if integers {... 2, 1,0,1,2,3,...},
2 Elementary number theory 2.1 Introduction Elementary number theory is concerned with properties of the integers. Hence we shall be interested in the following sets: The set if integers {... 2, 1,0,1,2,3,...},
8 th Grade Exam Scoring Format: 3 points per correct response -1 each wrong response 0 for blank answers
 Pellissippi State Middle School Mathematics Competition 8 th Grade Exam Scoring Format: 3 points per correct response -1 each wrong response 0 for blank answers Directions: For each multiple-choice problem
Pellissippi State Middle School Mathematics Competition 8 th Grade Exam Scoring Format: 3 points per correct response -1 each wrong response 0 for blank answers Directions: For each multiple-choice problem
