1. Here is a distribution. y p(y) A.(5) Draw a graph of this distribution. Solution:
|
|
|
- Roy Hubbard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISQS 5347 Final Exam. Instructions: Open book. No loose leaf notes. No electronic devices. Put all answers on the paper provided to ou. Points (out of 200) are in parentheses. 1. Here is a distribution. p() A.(5) Draw a graph of this distribution. p_ B.(5) Calculate E(Y) for this distribution. E(Y) = = = C.(10) Explain the meaning of the ou calculated in 1.B. using the Law of Large Numbers. Refer ver specificall to (i) the distribution shown above, and (ii) the number calculated in 1.B. in our answer. If data values Y 1,, Y n are produced as iid from the distribution shown above, and the average is Y = (Y 1 + Y Y n )/n is calculated, then Y will be approximatel equal to 1.9. For larger n, the approximation is better.
2 2. Suppose Y ~ U(0, θ ), the uniform distribution with unknown upper limit θ. 2.A.(5) Draw a graph of this distribution. Annotate both axes. p() 1/θ 0 θ/2 θ 2.B.(5) Explain wh E(Y) = θ/2 using the graph of 2.A. and the point of balance concept. See the graph. The densit function, if it were a cardboard cut-out, would balance at the value θ/2. If the point were higher than θ/2 it would fall to the left; if it were lower than θ/2 it would fall to the right. 2.C.(10) Using the fact that E(Y) = θ/2, demonstrate that θˆ= 2Y is an unbiased estimator of θ. Use (i) the definition of unbiasedness and (ii) linearit and/or additivit properties of expectation for each logical step of our demonstration. B definition of unbiasedness, θˆ is an unbiased estimator of θ if E(θˆ) = θ. So let s calculate E(θˆ): E(θˆ) = E(2Y) (b substitution) = 2E(Y) (b the linearit propert of expectation) = 2(θ/2) (using the fact that E(Y) = θ/2) = θ (b algebra). Thus, E(θˆ) = θ, which implies that θˆ is an unbiased estimator of θ.
3 3. Twent-five students will be asked, what is our favorite beverage? The will be asked to choose between Soda, Coffee, and Tea. A hpothetical realization of the data could look like 1 = Coffee, 2 = Coffee, 3 = Soda, 4 = Tea,, 25 = Soda, but man other realizations are also possible. 3.A.(10) Give a model for how the data Y 1, Y 2,, Y 25 will appear, in the absence of an other information about the students. Be as specific as ou can. Solution. A good model is Y 1, Y 2,, Y 25 ~ iid p(). Here, p() has the following form: p() Soda π 1 Coffee π 2 Tea π 3 Total: 1.00
4 3.B.(15) Suppose data on student US citizenship, X, either Yes or No, is available. A hpothetical realization of the data in this case could look like (x 1, 1 ) = (No, Coffee), (x 2, 2 ) = (Yes, Coffee), (x 3, 3 ) = (No, Soda), (x 4, 4 ) = (No, Tea),, (x 25, 25 ) = (Yes, Soda), but man other realizations are also possible. Give a regression model for how the data Y 1, Y 2,, Y 25 will appear, given the data X 1 =x 1, X 2 =x 2, X 25 =x 25. Be as specific as ou can. Solution. A good model is Y 1 X 1 = x 1, Y 2 X 2 = x 2,, Y 25 X 25 = x 25 ~ ind p( x). Here, p( x) has the following form: Soda Coffee p( X =Yes) π 1,es π 2,es π 3,es Tea Total: 1.00 Soda Coffee Tea p( X =No) π 1,no π 2,no π 3,no Total: (15) Nature favors continuit over discontinuit describes conditional distributions that produce data. Use the example Y = average dail food expense and X = annual income. Draw and annotate graphs of conditional distributions p( x) that clearl show what nature favors continuit over discontinuit means in this example.
5 densit Food Expense In the graph, the solid and dashed lines are distributions of food expense for people whose incomes differ ver little, eg, the solid line might be the food expense distribution for people with Income=30,000 and the dashed line might be the food expense distribution for people with Income = 31,000. These distributions differ ver little, demonstrating the idea that Nature favors continuit over discontinuit. The dotted line, on the other hand, shows a hpothetical food expense distribution for people with Income = 100,000. So the distributions differ greatl when the X differs greatl, but the distributions are similar when the X values are similar. 5.(25) Suppose Y 1, Y 2,, Y n ~ iid p(), where p() is a non-normal distribution with finite variance. Let S denote the sum of the Y s, S = Y 1 +Y 2 + +Y n. The Central Limit Theorem states that S has an approximatel normal distribution. Describe a simulation stud that demonstrates that the sum, S, of n=100 values produced as iid from the Poisson distribution with λ = 1, has an approximate normal distribution. Structure our answer as follows:
6 Step 1:. Step 2:. Use the concept of a q-q plot in our answer. Do not write R code. Instead, just sa what ou are doing at each step. Be ver clear in stating what result of our simulation stud and q-q plot will show that S has approximatel a normal distribution. Step 1: Generate 100 random numbers from the Poisson distribution with λ = 1, Y 1,,Y 100. Step 2: Calculate the sum, S= Y 1 + Y Y 100. Step 3: Repeat steps 1 and 2 100,000 times, getting values S 1, S 2,,S ,each a sum of 100 numbers. Step 4: Plot the sums S 1, S 2,,S using a q-q plot. If the q-q plot is approximatel a straight line, then this will demonstrate that the distribution of S is approximatel a normal distribution. 6.(25) If data Y 1, Y 2,, Y 100 are produced as iid from the N(0,1) distribution, then Y = (Y 1 + Y Y 100 )/100 is also a random variable. You know from probabilit theor that the standard deviation of Y is σ/ 100 = 1/10 = 0.1. Describe, step b step, a simulation stud that shows that the standard deviation of the average Y = (Y 1 + Y Y 100 )/100 is approximatel 0.1. There must be no calculation of 1/10 = 0.1 in our simulation stud. Instead, state what in the simulation will give the value of approximatel 0.1, demonstrating that the standard deviation of Y is 0.1. Structure our answer as follows: Step 1:. Step 2:. (more steps until done) Do not write R code. Instead, just sa what ou are doing at each step. Be ver clear in stating what result of our simulation stud will show that the standard deviation of Y = (Y 1 + Y Y 100 )/100 is approximatel 0.1. Step 1: Generate 100 random numbers from the N(0,1), Y 1,,Y 100. Step 2: Calculate the average, Y = (Y 1 + Y Y 100 )/100.
7 Step 3: Repeat steps 1 and 2100,000 times, getting values Y 1, Y 2,, Y , each an average of 100 numbers. Step 4: Calculate the standard deviation of the 100,000 values in Step 3. This number will be approximatel (15) A test of a restricted data-producing model gives a likelihood ratio chi-square statistic of 21.2 and a corresponding p-value p = The probabilit 0.02 can be understood loosel as 2 out of 100. Explain what 2 out of 100 means here; specificall, what does 2 refer to, and what does 100 refer to? In our answer include all of the following terms: (i) restricted data-producing model, (ii) repeated samples, (iii) random likelihood ratio chi square statistic, (4) If the data are produced b the restricted data-producing model, then each sample will ield a random likelihood ratio chi square statistic. In 100 such repeated samples, approximatel 2 out of 100 will produce a likelihood ratio chi square statistic that is greater then Man statistical procedures assume normalit of the distributions p() that are assumed to produce the data. But real data that we can analze are never produced b normal distributions. Consider our example Y = a person s claimed average dail food expense. 8.A.(5) Explain wh the p() that produces these Y data values must be a discrete distribution. The data we analzed were rounded to the nearest dollar. Hence the cannot fill a continuum. But no matter how the are collected no data we humans can analze can possibl fill a continuum due to finiteness of our measuring instruments. 8.B.(5) Explain wh the p() that produces these Y data values must be a skewed (non-smmetric) distribution. The distribution is bounded below b 0 but unbounded at the high end. Thus there is a possibilit to observe an occasional extremel large value, but no possibilit to observe an occasional extremel small value. 9.(5) An R command is x = seq(0, 10,.01) What is x? The list of values 0.00, 0.01, 0.02,, 9.99,
8 Multiple choice R questions. (Four points each) 10. What does the R function rnorm(100) do? A. Generates 100 normall distributed data values. B. Computes the densit of the normal distribution at = 100. C. Finds the q-q plot from the normal distribution with 100 data values. D. Graphs the normal densit function from 0 to Which R command allows ou to read data into the program? A. read.data B. data.read C. all.in D. read.csv 12. Which R command draws a scatterplot of data pairs (x, )? A. scatter(x,) B. plot(x,) C. pairs(x,) D. all(x,) 13. Wh are data generated from R s computer random number generators independent? A. Because that is the wa computer random number generators work. B. Because the are from the same distribution. C. Because the are identicall distributed. D. Because the data depend on R s random number generator seed value. 14. Which command generates a sample from the bootstrap distribution of the data in the R list? A. bootstrap(,length(), replace=t) B. bootstrap(, length(), replace=f) C. sample(, length()), replace =T) D. sample(, length()), replace =F) 15. Which R function does Baesian analsis? A. RBaes B. BaesR C. MCMCRegress D. MaxLik 16. Wh is == used in R? A. to allow roundoff errors B. to compare different quantities C. to force items to be equal even when the are not D. to generate random numbers
9 17. What does tpe=h do in the plot function? A. increases the height of the plot B. makes the plot a needle plot C. makes the plot character a square rather than a circle D. connects the points with straight lines 18. What is the purpose of jitter in R, as in plot(jitter(x), jitter())? A. To make the distribution look more normal B. To make the relationship closer to linear C. To keep points from being plotted on top of each other D. To solve the log likelihood function for the maximum likelihood estimates 19. Data frames, lists, fitted models, and matrices are examples of in R. A. objects B. variables C. observations D. functions
Open book, but no loose leaf notes and no electronic devices. Points (out of 200) are in parentheses. Put all answers on the paper provided to you.
 ISQS 5347 Final Exam Spring 2017 Open book, but no loose leaf notes and no electronic devices. Points (out of 200) are in parentheses. Put all answers on the paper provided to you. 1. Recall the commute
ISQS 5347 Final Exam Spring 2017 Open book, but no loose leaf notes and no electronic devices. Points (out of 200) are in parentheses. Put all answers on the paper provided to you. 1. Recall the commute
Quiz 1. Name: Instructions: Closed book, notes, and no electronic devices.
 Quiz 1. Name: Instructions: Closed book, notes, and no electronic devices. 1. What is the difference between a deterministic model and a probabilistic model? (Two or three sentences only). 2. What is the
Quiz 1. Name: Instructions: Closed book, notes, and no electronic devices. 1. What is the difference between a deterministic model and a probabilistic model? (Two or three sentences only). 2. What is the
ISQS 5349 Final Exam, Spring 2017.
 ISQS 5349 Final Exam, Spring 7. Instructions: Put all answers on paper other than this exam. If you do not have paper, some will be provided to you. The exam is OPEN BOOKS, OPEN NOTES, but NO ELECTRONIC
ISQS 5349 Final Exam, Spring 7. Instructions: Put all answers on paper other than this exam. If you do not have paper, some will be provided to you. The exam is OPEN BOOKS, OPEN NOTES, but NO ELECTRONIC
0.24 adults 2. (c) Prove that, regardless of the possible values of and, the covariance between X and Y is equal to zero. Show all work.
 1 A socioeconomic stud analzes two discrete random variables in a certain population of households = number of adult residents and = number of child residents It is found that their joint probabilit mass
1 A socioeconomic stud analzes two discrete random variables in a certain population of households = number of adult residents and = number of child residents It is found that their joint probabilit mass
Quiz 1. Name: Instructions: Closed book, notes, and no electronic devices.
 Quiz 1. Name: Instructions: Closed book, notes, and no electronic devices. 1.(10) What is usually true about a parameter of a model? A. It is a known number B. It is determined by the data C. It is an
Quiz 1. Name: Instructions: Closed book, notes, and no electronic devices. 1.(10) What is usually true about a parameter of a model? A. It is a known number B. It is determined by the data C. It is an
t s time we revisit our friend, the equation of a line: y = mx + b
 CH PARALLEL AND PERPENDICULAR LINES Introduction I t s time we revisit our friend, the equation of a line: mx + b SLOPE -INTERCEPT To be precise, b is not the -intercept; b is the -coordinate of the -intercept.
CH PARALLEL AND PERPENDICULAR LINES Introduction I t s time we revisit our friend, the equation of a line: mx + b SLOPE -INTERCEPT To be precise, b is not the -intercept; b is the -coordinate of the -intercept.
MATH 2070 Test 3 (Sections , , & )
 Multiple Choice: Use a # pencil and completel fill in each bubble on our scantron to indicate the answer to each question. Each question has one correct answer. If ou indicate more than one answer, or
Multiple Choice: Use a # pencil and completel fill in each bubble on our scantron to indicate the answer to each question. Each question has one correct answer. If ou indicate more than one answer, or
Chapter 6. Exploring Data: Relationships
 Chapter 6 Exploring Data: Relationships For All Practical Purposes: Effective Teaching A characteristic of an effective instructor is fairness and consistenc in grading and evaluating student performance.
Chapter 6 Exploring Data: Relationships For All Practical Purposes: Effective Teaching A characteristic of an effective instructor is fairness and consistenc in grading and evaluating student performance.
Experimental Uncertainty Review. Abstract. References. Measurement Uncertainties and Uncertainty Propagation
 Experimental Uncertaint Review Abstract This is intended as a brief summar of the basic elements of uncertaint analsis, and a hand reference for laborator use. It provides some elementar "rules-of-thumb"
Experimental Uncertaint Review Abstract This is intended as a brief summar of the basic elements of uncertaint analsis, and a hand reference for laborator use. It provides some elementar "rules-of-thumb"
Math Sec 4 CST Topic 7. Statistics. i.e: Add up all values and divide by the total number of values.
 Measures of Central Tendency Statistics 1) Mean: The of all data values Mean= x = x 1+x 2 +x 3 + +x n n i.e: Add up all values and divide by the total number of values. 2) Mode: Most data value 3) Median:
Measures of Central Tendency Statistics 1) Mean: The of all data values Mean= x = x 1+x 2 +x 3 + +x n n i.e: Add up all values and divide by the total number of values. 2) Mode: Most data value 3) Median:
MATH 021 UNIT 1 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS
 MATH 01 UNIT 1 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS General Instructions You will notice that most of the homework assignments for a section have more than one part. Usuall, the part (A) questions ask for eplanations,
MATH 01 UNIT 1 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS General Instructions You will notice that most of the homework assignments for a section have more than one part. Usuall, the part (A) questions ask for eplanations,
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Algebra - nd Semester Final Exam Review Part Name: Hour: Date: Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which of the following is the inverse of the
Algebra - nd Semester Final Exam Review Part Name: Hour: Date: Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which of the following is the inverse of the
Quoting from the document I suggested you read (http://courses.ttu.edu/isqs5349 westfall/images/5349/practiceproblems_discussion.
 Spring 14, ISQS 5349 Midterm 1. Instructions: Closed book, notes and no electronic devices. Put all answers on scratch paper provided. Points (out of 100) are in parentheses. 1. (20) Define regression
Spring 14, ISQS 5349 Midterm 1. Instructions: Closed book, notes and no electronic devices. Put all answers on scratch paper provided. Points (out of 100) are in parentheses. 1. (20) Define regression
Mathematical Notation Math Introduction to Applied Statistics
 Mathematical Notation Math 113 - Introduction to Applied Statistics Name : Use Word or WordPerfect to recreate the following documents. Each article is worth 10 points and can be printed and given to the
Mathematical Notation Math 113 - Introduction to Applied Statistics Name : Use Word or WordPerfect to recreate the following documents. Each article is worth 10 points and can be printed and given to the
Regular Physics - Notes Ch. 1
 Regular Phsics - Notes Ch. 1 What is Phsics? the stud of matter and energ and their relationships; the stud of the basic phsical laws of nature which are often stated in simple mathematical equations.
Regular Phsics - Notes Ch. 1 What is Phsics? the stud of matter and energ and their relationships; the stud of the basic phsical laws of nature which are often stated in simple mathematical equations.
1. Graph Real Numbers on a Number Line
 (Chapters and ) A. Real Numbers and Expressions The set of real numbers consists of all rational and irrational numbers. Rational numbers can be expressed as fractions, and irrational numbers can not be
(Chapters and ) A. Real Numbers and Expressions The set of real numbers consists of all rational and irrational numbers. Rational numbers can be expressed as fractions, and irrational numbers can not be
Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning: Homework 2 MLE, MAP and Naive Bayes
 10-715 Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning: Homework 2 MLE, MAP and Naive Baes Released: Wednesda, September 12, 2018 Due: 11:59 p.m. Wednesda, September 19, 2018 Instructions Late homework polic:
10-715 Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning: Homework 2 MLE, MAP and Naive Baes Released: Wednesda, September 12, 2018 Due: 11:59 p.m. Wednesda, September 19, 2018 Instructions Late homework polic:
ACCELERATED ALGEBRA ONE SEMESTER ONE REVIEW. Systems. Families of Statistics Equations. Models 16% 24% 26% 12% 21% 3. Solve for y.
 ACCELERATED ALGEBRA ONE SEMESTER ONE REVIEW NAME: The midterm assessment assesses the following topics. Solving Linear Systems Families of Statistics Equations Models and Matrices Functions 16% 24% 26%
ACCELERATED ALGEBRA ONE SEMESTER ONE REVIEW NAME: The midterm assessment assesses the following topics. Solving Linear Systems Families of Statistics Equations Models and Matrices Functions 16% 24% 26%
CONTINUOUS SPATIAL DATA ANALYSIS
 CONTINUOUS SPATIAL DATA ANALSIS 1. Overview of Spatial Stochastic Processes The ke difference between continuous spatial data and point patterns is that there is now assumed to be a meaningful value, s
CONTINUOUS SPATIAL DATA ANALSIS 1. Overview of Spatial Stochastic Processes The ke difference between continuous spatial data and point patterns is that there is now assumed to be a meaningful value, s
Second Semester Exam Review
 Second Semester Exam Review Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. What is the solution of the equation? 1. a. 36 b. 2 c. 2 d. What is the solution
Second Semester Exam Review Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. What is the solution of the equation? 1. a. 36 b. 2 c. 2 d. What is the solution
Data transformation. Core: Data analysis. Chapter 5
 Chapter 5 5 Core: Data analsis Data transformation ISBN 978--7-56757-3 Jones et al. 6 66 Core Chapter 5 Data transformation 5A Introduction You first encountered data transformation in Chapter where ou
Chapter 5 5 Core: Data analsis Data transformation ISBN 978--7-56757-3 Jones et al. 6 66 Core Chapter 5 Data transformation 5A Introduction You first encountered data transformation in Chapter where ou
Math 369 Exam #1 Practice Problems
 Math 69 Exam # Practice Problems Find the set of solutions of the following sstem of linear equations Show enough work to make our steps clear x + + z + 4w x 4z 6w x + 5 + 7z + w Answer: We solve b forming
Math 69 Exam # Practice Problems Find the set of solutions of the following sstem of linear equations Show enough work to make our steps clear x + + z + 4w x 4z 6w x + 5 + 7z + w Answer: We solve b forming
4.3 Exercises. local maximum or minimum. The second derivative is. e 1 x 2x 1. f x x 2 e 1 x 1 x 2 e 1 x 2x x 4
 SECTION 4.3 HOW DERIVATIVES AFFECT THE SHAPE OF A GRAPH 297 local maimum or minimum. The second derivative is f 2 e 2 e 2 4 e 2 4 Since e and 4, we have f when and when 2 f. So the curve is concave downward
SECTION 4.3 HOW DERIVATIVES AFFECT THE SHAPE OF A GRAPH 297 local maimum or minimum. The second derivative is f 2 e 2 e 2 4 e 2 4 Since e and 4, we have f when and when 2 f. So the curve is concave downward
CHAPTER 1 Functions, Graphs, and Limits
 CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula... Section. Graphs of Equations...8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope... Mid-Chapter Quiz Solutions... Section.
CHAPTER Functions, Graphs, and Limits Section. The Cartesian Plane and the Distance Formula... Section. Graphs of Equations...8 Section. Lines in the Plane and Slope... Mid-Chapter Quiz Solutions... Section.
MATH Line integrals III Fall The fundamental theorem of line integrals. In general C
 MATH 255 Line integrals III Fall 216 In general 1. The fundamental theorem of line integrals v T ds depends on the curve between the starting point and the ending point. onsider two was to get from (1,
MATH 255 Line integrals III Fall 216 In general 1. The fundamental theorem of line integrals v T ds depends on the curve between the starting point and the ending point. onsider two was to get from (1,
Instructions: Closed book, notes, and no electronic devices. Points (out of 200) in parentheses
 ISQS 5349 Final Spring 2011 Instructions: Closed book, notes, and no electronic devices. Points (out of 200) in parentheses 1. (10) What is the definition of a regression model that we have used throughout
ISQS 5349 Final Spring 2011 Instructions: Closed book, notes, and no electronic devices. Points (out of 200) in parentheses 1. (10) What is the definition of a regression model that we have used throughout
STAT 3900/4950 MIDTERM TWO Name: Spring, 2015 (print: first last ) Covered topics: Two-way ANOVA, ANCOVA, SLR, MLR and correlation analysis
 STAT 3900/4950 MIDTERM TWO Name: Spring, 205 (print: first last ) Covered topics: Two-way ANOVA, ANCOVA, SLR, MLR and correlation analysis Instructions: You may use your books, notes, and SPSS/SAS. NO
STAT 3900/4950 MIDTERM TWO Name: Spring, 205 (print: first last ) Covered topics: Two-way ANOVA, ANCOVA, SLR, MLR and correlation analysis Instructions: You may use your books, notes, and SPSS/SAS. NO
Inequalities and Multiplication
 Lesson 3-6 Inequalities and Multiplication BIG IDEA Multipling each side of an inequalit b a positive number keeps the direction of the inequalit; multipling each side b a negative number reverses the
Lesson 3-6 Inequalities and Multiplication BIG IDEA Multipling each side of an inequalit b a positive number keeps the direction of the inequalit; multipling each side b a negative number reverses the
Biostatistics in Research Practice - Regression I
 Biostatistics in Research Practice - Regression I Simon Crouch 30th Januar 2007 In scientific studies, we often wish to model the relationships between observed variables over a sample of different subjects.
Biostatistics in Research Practice - Regression I Simon Crouch 30th Januar 2007 In scientific studies, we often wish to model the relationships between observed variables over a sample of different subjects.
Functions. Introduction CHAPTER OUTLINE
 Functions,00 P,000 00 0 970 97 980 98 990 99 000 00 00 Figure Standard and Poor s Inde with dividends reinvested (credit "bull": modification of work b Praitno Hadinata; credit "graph": modification of
Functions,00 P,000 00 0 970 97 980 98 990 99 000 00 00 Figure Standard and Poor s Inde with dividends reinvested (credit "bull": modification of work b Praitno Hadinata; credit "graph": modification of
February 11, JEL Classification: C72, D43, D44 Keywords: Discontinuous games, Bertrand game, Toehold, First- and Second- Price Auctions
 Eistence of Mied Strateg Equilibria in a Class of Discontinuous Games with Unbounded Strateg Sets. Gian Luigi Albano and Aleander Matros Department of Economics and ELSE Universit College London Februar
Eistence of Mied Strateg Equilibria in a Class of Discontinuous Games with Unbounded Strateg Sets. Gian Luigi Albano and Aleander Matros Department of Economics and ELSE Universit College London Februar
NCC Precalculus Partnership Program Final Examination, 2004
 NCC Precalculus Partnership Program Final Eamination, 2004 Part I: Answer onl 20 of the 25 questions below. Each question is worth 2 points. Place our answers on the answer sheet provided. Write the word
NCC Precalculus Partnership Program Final Eamination, 2004 Part I: Answer onl 20 of the 25 questions below. Each question is worth 2 points. Place our answers on the answer sheet provided. Write the word
6348 Final, Fall 14. Closed book, closed notes, no electronic devices. Points (out of 200) in parentheses.
 6348 Final, Fall 14. Closed book, closed notes, no electronic devices. Points (out of 200) in parentheses. 0 11 1 1.(5) Give the result of the following matrix multiplication: 1 10 1 Solution: 0 1 1 2
6348 Final, Fall 14. Closed book, closed notes, no electronic devices. Points (out of 200) in parentheses. 0 11 1 1.(5) Give the result of the following matrix multiplication: 1 10 1 Solution: 0 1 1 2
In everyday speech, a continuous. Limits and Continuity. Critical Thinking Exercises
 062 Chapter Introduction to Calculus Critical Thinking Eercises Make Sense? In Eercises 74 77, determine whether each statement makes sense or does not make sense, and eplain our reasoning. 74. I evaluated
062 Chapter Introduction to Calculus Critical Thinking Eercises Make Sense? In Eercises 74 77, determine whether each statement makes sense or does not make sense, and eplain our reasoning. 74. I evaluated
M(t) = 1 t. (1 t), 6 M (0) = 20 P (95. X i 110) i=1
 Math 66/566 - Midterm Solutions NOTE: These solutions are for both the 66 and 566 exam. The problems are the same until questions and 5. 1. The moment generating function of a random variable X is M(t)
Math 66/566 - Midterm Solutions NOTE: These solutions are for both the 66 and 566 exam. The problems are the same until questions and 5. 1. The moment generating function of a random variable X is M(t)
Math 116 First Midterm October 9, 2017
 On m honor, as a student, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work. Initials: Do not write in this area Your Initials Onl: Math 116 First Midterm October 9, 217 Your U-M
On m honor, as a student, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work. Initials: Do not write in this area Your Initials Onl: Math 116 First Midterm October 9, 217 Your U-M
Math 107: Calculus II, Spring 2015: Midterm Exam II Monday, April Give your name, TA and section number:
 Math 7: Calculus II, Spring 25: Midterm Exam II Monda, April 3 25 Give our name, TA and section number: Name: TA: Section number:. There are 5 questions for a total of points. The value of each part of
Math 7: Calculus II, Spring 25: Midterm Exam II Monda, April 3 25 Give our name, TA and section number: Name: TA: Section number:. There are 5 questions for a total of points. The value of each part of
CSE 546 Midterm Exam, Fall 2014
 CSE 546 Midterm Eam, Fall 2014 1. Personal info: Name: UW NetID: Student ID: 2. There should be 14 numbered pages in this eam (including this cover sheet). 3. You can use an material ou brought: an book,
CSE 546 Midterm Eam, Fall 2014 1. Personal info: Name: UW NetID: Student ID: 2. There should be 14 numbered pages in this eam (including this cover sheet). 3. You can use an material ou brought: an book,
ISQS 5349 Spring 2013 Final Exam
 ISQS 5349 Spring 2013 Final Exam Name: General Instructions: Closed books, notes, no electronic devices. Points (out of 200) are in parentheses. Put written answers on separate paper; multiple choices
ISQS 5349 Spring 2013 Final Exam Name: General Instructions: Closed books, notes, no electronic devices. Points (out of 200) are in parentheses. Put written answers on separate paper; multiple choices
FSA Algebra I End-of-Course Review Packet
 FSA Algebra I End-of-Course Review Packet Table of Contents MAFS.912.N-RN.1.2 EOC Practice... 3 MAFS.912.N-RN.2.3 EOC Practice... 5 MAFS.912.N-RN.1.1 EOC Practice... 8 MAFS.912.S-ID.1.1 EOC Practice...
FSA Algebra I End-of-Course Review Packet Table of Contents MAFS.912.N-RN.1.2 EOC Practice... 3 MAFS.912.N-RN.2.3 EOC Practice... 5 MAFS.912.N-RN.1.1 EOC Practice... 8 MAFS.912.S-ID.1.1 EOC Practice...
Finding Limits Graphically and Numerically. An Introduction to Limits
 8 CHAPTER Limits and Their Properties Section Finding Limits Graphicall and Numericall Estimate a it using a numerical or graphical approach Learn different was that a it can fail to eist Stud and use
8 CHAPTER Limits and Their Properties Section Finding Limits Graphicall and Numericall Estimate a it using a numerical or graphical approach Learn different was that a it can fail to eist Stud and use
Functions. Introduction
 Functions,00 P,000 00 0 70 7 80 8 0 000 00 00 Figure Standard and Poor s Inde with dividends reinvested (credit "bull": modification of work b Praitno Hadinata; credit "graph": modification of work b MeasuringWorth)
Functions,00 P,000 00 0 70 7 80 8 0 000 00 00 Figure Standard and Poor s Inde with dividends reinvested (credit "bull": modification of work b Praitno Hadinata; credit "graph": modification of work b MeasuringWorth)
1.2 Relations. 20 Relations and Functions
 0 Relations and Functions. Relations From one point of view, all of Precalculus can be thought of as studing sets of points in the plane. With the Cartesian Plane now fresh in our memor we can discuss
0 Relations and Functions. Relations From one point of view, all of Precalculus can be thought of as studing sets of points in the plane. With the Cartesian Plane now fresh in our memor we can discuss
Linear Transformations
 inear Transformations 6 The main objects of stud in an course in linear algebra are linear functions: Definition A function : V! W is linear if V and W are vector spaces and (ru + sv) r(u)+s(v) for all
inear Transformations 6 The main objects of stud in an course in linear algebra are linear functions: Definition A function : V! W is linear if V and W are vector spaces and (ru + sv) r(u)+s(v) for all
UNIVERSITY OF DUBLIN TRINITY COLLEGE. Faculty of Engineering, Mathematics and Science. School of Computer Science & Statistics
 UNIVERSI OF DUBLIN RINI COLLEGE Facult of Engineering, Mathematics and Science School of Comuter Science & Statistics BA (Mod) Maths, SM rinit erm 04 SF and JS S35 Probabilit and heoretical Statistics
UNIVERSI OF DUBLIN RINI COLLEGE Facult of Engineering, Mathematics and Science School of Comuter Science & Statistics BA (Mod) Maths, SM rinit erm 04 SF and JS S35 Probabilit and heoretical Statistics
Properties of Limits
 33460_003qd //04 :3 PM Page 59 SECTION 3 Evaluating Limits Analticall 59 Section 3 Evaluating Limits Analticall Evaluate a it using properties of its Develop and use a strateg for finding its Evaluate
33460_003qd //04 :3 PM Page 59 SECTION 3 Evaluating Limits Analticall 59 Section 3 Evaluating Limits Analticall Evaluate a it using properties of its Develop and use a strateg for finding its Evaluate
Saturday X-tra X-Sheet: 8. Inverses and Functions
 Saturda X-tra X-Sheet: 8 Inverses and Functions Ke Concepts In this session we will ocus on summarising what ou need to know about: How to ind an inverse. How to sketch the inverse o a graph. How to restrict
Saturda X-tra X-Sheet: 8 Inverses and Functions Ke Concepts In this session we will ocus on summarising what ou need to know about: How to ind an inverse. How to sketch the inverse o a graph. How to restrict
Trusses - Method of Sections
 Trusses - Method of Sections ME 202 Methods of Truss Analsis Method of joints (previous notes) Method of sections (these notes) 2 MOS - Concepts Separate the structure into two parts (sections) b cutting
Trusses - Method of Sections ME 202 Methods of Truss Analsis Method of joints (previous notes) Method of sections (these notes) 2 MOS - Concepts Separate the structure into two parts (sections) b cutting
Chapter 11 Exponential and Logarithmic Function
 Chapter Eponential and Logarithmic Function - Page 69.. Real Eponents. a m a n a mn. (a m ) n a mn. a b m a b m m, when b 0 Graphing Calculator Eploration Page 700 Check for Understanding. The quantities
Chapter Eponential and Logarithmic Function - Page 69.. Real Eponents. a m a n a mn. (a m ) n a mn. a b m a b m m, when b 0 Graphing Calculator Eploration Page 700 Check for Understanding. The quantities
1 ** The performance objectives highlighted in italics have been identified as core to an Algebra II course.
 Strand One: Number Sense and Operations Every student should understand and use all concepts and skills from the pervious grade levels. The standards are designed so that new learning builds on preceding
Strand One: Number Sense and Operations Every student should understand and use all concepts and skills from the pervious grade levels. The standards are designed so that new learning builds on preceding
3.7 InveRSe FUnCTIOnS
 CHAPTER functions learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Verif inverse functions. Determine the domain and range of an inverse function, and restrict the domain of a function to make it one-to-one.
CHAPTER functions learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Verif inverse functions. Determine the domain and range of an inverse function, and restrict the domain of a function to make it one-to-one.
Finding Limits Graphically and Numerically. An Introduction to Limits
 60_00.qd //0 :05 PM Page 8 8 CHAPTER Limits and Their Properties Section. Finding Limits Graphicall and Numericall Estimate a it using a numerical or graphical approach. Learn different was that a it can
60_00.qd //0 :05 PM Page 8 8 CHAPTER Limits and Their Properties Section. Finding Limits Graphicall and Numericall Estimate a it using a numerical or graphical approach. Learn different was that a it can
Constant Acceleration
 Constant Acceleration Ch. in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: ) Write the definition of acceleration, either in words or as an equation ) Create an equation for the movement of an object
Constant Acceleration Ch. in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: ) Write the definition of acceleration, either in words or as an equation ) Create an equation for the movement of an object
Lesson 1 Homework Practice
 Lesson 1 Homework Practice Scatter Plots Interpret each scatter plot. 1. Games Won 1 8 6 4 2 1 2 3 4 5 Average Game Attendance 2. Car Value (% cost new) 1 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 2 4 6 8 1 Car Age (r) 3. Pumpkin
Lesson 1 Homework Practice Scatter Plots Interpret each scatter plot. 1. Games Won 1 8 6 4 2 1 2 3 4 5 Average Game Attendance 2. Car Value (% cost new) 1 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 2 4 6 8 1 Car Age (r) 3. Pumpkin
CCSD Practice Proficiency Exam Fall 2010
 Fall 00. In the diagram below, line m is parallel to line n. m n 60 x. Brock borrows $,000 from his father and repays the money after years, plus 5% simple interest. How much interest does Brock pay on
Fall 00. In the diagram below, line m is parallel to line n. m n 60 x. Brock borrows $,000 from his father and repays the money after years, plus 5% simple interest. How much interest does Brock pay on
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science December 2013 Final Examination STA442H1F/2101HF Methods of Applied Statistics Jerry Brunner Duration - 3 hours Aids: Calculator Model(s): Any calculator
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science December 2013 Final Examination STA442H1F/2101HF Methods of Applied Statistics Jerry Brunner Duration - 3 hours Aids: Calculator Model(s): Any calculator
Copyright, 2008, R.E. Kass, E.N. Brown, and U. Eden REPRODUCTION OR CIRCULATION REQUIRES PERMISSION OF THE AUTHORS
 Copright, 8, RE Kass, EN Brown, and U Eden REPRODUCTION OR CIRCULATION REQUIRES PERMISSION OF THE AUTHORS Chapter 6 Random Vectors and Multivariate Distributions 6 Random Vectors In Section?? we etended
Copright, 8, RE Kass, EN Brown, and U Eden REPRODUCTION OR CIRCULATION REQUIRES PERMISSION OF THE AUTHORS Chapter 6 Random Vectors and Multivariate Distributions 6 Random Vectors In Section?? we etended
Fall 07 ISQS 6348 Midterm Solutions
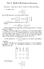 Fall 07 ISQS 648 Midterm Solutions Instructions: Open notes, no books. Points out of 00 in parentheses. 1. A random vector X = 4 X 1 X X has the following mean vector and covariance matrix: E(X) = 4 1
Fall 07 ISQS 648 Midterm Solutions Instructions: Open notes, no books. Points out of 00 in parentheses. 1. A random vector X = 4 X 1 X X has the following mean vector and covariance matrix: E(X) = 4 1
Math 1040 Final Exam Form A Introduction to Statistics Fall Semester 2010
 Math 1040 Final Exam Form A Introduction to Statistics Fall Semester 2010 Instructor Name Time Limit: 120 minutes Any calculator is okay. Necessary tables and formulas are attached to the back of the exam.
Math 1040 Final Exam Form A Introduction to Statistics Fall Semester 2010 Instructor Name Time Limit: 120 minutes Any calculator is okay. Necessary tables and formulas are attached to the back of the exam.
Psych 230. Psychological Measurement and Statistics
 Psych 230 Psychological Measurement and Statistics Pedro Wolf December 9, 2009 This Time. Non-Parametric statistics Chi-Square test One-way Two-way Statistical Testing 1. Decide which test to use 2. State
Psych 230 Psychological Measurement and Statistics Pedro Wolf December 9, 2009 This Time. Non-Parametric statistics Chi-Square test One-way Two-way Statistical Testing 1. Decide which test to use 2. State
15.2 Graphing Logarithmic
 _ - - - - - - Locker LESSON 5. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the graphs of f () = b and f () = log b
_ - - - - - - Locker LESSON 5. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the graphs of f () = b and f () = log b
Algebra I Exam Review
 Name Algebra I Exam Review Assigned on Assignment 1/17 Final Exam Practice Units 1 and Problems 1-4 1/18 Final Exam Practice Units and 4 Problems 5-5 1/19 Practice Final Exam Multiple Choice 1-16 1/ Practice
Name Algebra I Exam Review Assigned on Assignment 1/17 Final Exam Practice Units 1 and Problems 1-4 1/18 Final Exam Practice Units and 4 Problems 5-5 1/19 Practice Final Exam Multiple Choice 1-16 1/ Practice
Short Answer Questions: Answer on your separate blank paper. Points are given in parentheses.
 ISQS 6348 Final exam solutions. Name: Open book and notes, but no electronic devices. Answer short answer questions on separate blank paper. Answer multiple choice on this exam sheet. Put your name on
ISQS 6348 Final exam solutions. Name: Open book and notes, but no electronic devices. Answer short answer questions on separate blank paper. Answer multiple choice on this exam sheet. Put your name on
ALGEBRA 2/TRIGONOMETRY
 ALGEBRA 2/TRIGONOMETRY The Universit of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION ALGEBRA 2/TRIGONOMETRY Wednesda, August 18, 2010 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., onl Student Name: School Name: Print our
ALGEBRA 2/TRIGONOMETRY The Universit of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION ALGEBRA 2/TRIGONOMETRY Wednesda, August 18, 2010 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., onl Student Name: School Name: Print our
Linear and Nonlinear Systems of Equations. The Method of Substitution. Equation 1 Equation 2. Check (2, 1) in Equation 1 and Equation 2: 2x y 5?
 3330_070.qd 96 /5/05 Chapter 7 7. 9:39 AM Page 96 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations What ou should learn Use the method of substitution to solve sstems of linear
3330_070.qd 96 /5/05 Chapter 7 7. 9:39 AM Page 96 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations What ou should learn Use the method of substitution to solve sstems of linear
Learning Objective: We will construct and interpret scatterplots (G8M6L4)
 Learning Objective: We will construct and interpret scatterplots (G8ML) Concept Development: A Scatter Plot is a graph of numerical data on two variables. Eamples: -- The number of hours ou stud for a
Learning Objective: We will construct and interpret scatterplots (G8ML) Concept Development: A Scatter Plot is a graph of numerical data on two variables. Eamples: -- The number of hours ou stud for a
Linear regression Class 25, Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan Bloom
 1 Learning Goals Linear regression Class 25, 18.05 Jerem Orloff and Jonathan Bloom 1. Be able to use the method of least squares to fit a line to bivariate data. 2. Be able to give a formula for the total
1 Learning Goals Linear regression Class 25, 18.05 Jerem Orloff and Jonathan Bloom 1. Be able to use the method of least squares to fit a line to bivariate data. 2. Be able to give a formula for the total
Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Academic Standards Mathematics
 ALGEBRA 1 Standard 1 Operations with Real Numbers Students simplify and compare expressions. They use rational exponents, and simplify square roots. A1.1.1 A1.1.2 A1.1.3 A1.1.4 A1.1.5 Compare real number
ALGEBRA 1 Standard 1 Operations with Real Numbers Students simplify and compare expressions. They use rational exponents, and simplify square roots. A1.1.1 A1.1.2 A1.1.3 A1.1.4 A1.1.5 Compare real number
Final Exam. Name: Solution:
 Final Exam. Name: Instructions. Answer all questions on the exam. Open books, open notes, but no electronic devices. The first 13 problems are worth 5 points each. The rest are worth 1 point each. HW1.
Final Exam. Name: Instructions. Answer all questions on the exam. Open books, open notes, but no electronic devices. The first 13 problems are worth 5 points each. The rest are worth 1 point each. HW1.
Symmetry Arguments and the Role They Play in Using Gauss Law
 Smmetr Arguments and the Role The la in Using Gauss Law K. M. Westerberg (9/2005) Smmetr plas a ver important role in science in general, and phsics in particular. Arguments based on smmetr can often simplif
Smmetr Arguments and the Role The la in Using Gauss Law K. M. Westerberg (9/2005) Smmetr plas a ver important role in science in general, and phsics in particular. Arguments based on smmetr can often simplif
1.5. Analyzing Graphs of Functions. The Graph of a Function. What you should learn. Why you should learn it. 54 Chapter 1 Functions and Their Graphs
 0_005.qd /7/05 8: AM Page 5 5 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions What ou should learn Use the Vertical Line Test for functions. Find the zeros of functions. Determine intervals
0_005.qd /7/05 8: AM Page 5 5 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs.5 Analzing Graphs of Functions What ou should learn Use the Vertical Line Test for functions. Find the zeros of functions. Determine intervals
9-1. The Function with Equation y = ax 2. Vocabulary. Graphing y = x 2. Lesson
 Chapter 9 Lesson 9-1 The Function with Equation = a BIG IDEA The graph of an quadratic function with equation = a, with a 0, is a parabola with verte at the origin. Vocabular parabola refl ection-smmetric
Chapter 9 Lesson 9-1 The Function with Equation = a BIG IDEA The graph of an quadratic function with equation = a, with a 0, is a parabola with verte at the origin. Vocabular parabola refl ection-smmetric
Math Released Item Algebra 1. Solve the Equation VH046614
 Math Released Item 2017 Algebra 1 Solve the Equation VH046614 Anchor Set A1 A8 With Annotations Prompt Rubric VH046614 Rubric Score Description 3 Student response includes the following 3 elements. Reasoning
Math Released Item 2017 Algebra 1 Solve the Equation VH046614 Anchor Set A1 A8 With Annotations Prompt Rubric VH046614 Rubric Score Description 3 Student response includes the following 3 elements. Reasoning
Math 121. Practice Problems from Chapter 4 Fall 2016
 Math 11. Practice Problems from Chapter Fall 01 1 Inverse Functions 1. The graph of a function f is given below. On same graph sketch the inverse function of f; notice that f goes through the points (0,
Math 11. Practice Problems from Chapter Fall 01 1 Inverse Functions 1. The graph of a function f is given below. On same graph sketch the inverse function of f; notice that f goes through the points (0,
MAE 323: Chapter 4. Plane Stress and Plane Strain. The Stress Equilibrium Equation
 The Stress Equilibrium Equation As we mentioned in Chapter 2, using the Galerkin formulation and a choice of shape functions, we can derive a discretized form of most differential equations. In Structural
The Stress Equilibrium Equation As we mentioned in Chapter 2, using the Galerkin formulation and a choice of shape functions, we can derive a discretized form of most differential equations. In Structural
6. This sum can be rewritten as 4( ). We then recall the formula n =
 . c = 9b = 3 b = 3 a 3 = a = = 6.. (3,, ) = 3 + + 3 = 9 + + 3 = 6 6. 3. We see that this is equal to. 3 = ( +.) 3. Using the fact that (x + ) 3 = x 3 + 3x + 3x + and replacing x with., we find that. 3
. c = 9b = 3 b = 3 a 3 = a = = 6.. (3,, ) = 3 + + 3 = 9 + + 3 = 6 6. 3. We see that this is equal to. 3 = ( +.) 3. Using the fact that (x + ) 3 = x 3 + 3x + 3x + and replacing x with., we find that. 3
Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Levels 6-8 Calculator not allowed
 Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Levels 6-8 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your school
Mathematics Second Practice Test 1 Levels 6-8 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your school
MATH 1710 College Algebra Final Exam Review
 MATH 7 College Algebra Final Eam Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. ) There were 80 people at a pla. The admission price was $
MATH 7 College Algebra Final Eam Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. ) There were 80 people at a pla. The admission price was $
36-720: Latent Class Models
 36-720: Latent Class Models Brian Junker October 17, 2007 Latent Class Models and Simpson s Paradox Latent Class Model for a Table of Counts An Intuitive E-M Algorithm for Fitting Latent Class Models Deriving
36-720: Latent Class Models Brian Junker October 17, 2007 Latent Class Models and Simpson s Paradox Latent Class Model for a Table of Counts An Intuitive E-M Algorithm for Fitting Latent Class Models Deriving
Worksheet #1. A little review.
 Worksheet #1. A little review. I. Set up BUT DO NOT EVALUATE definite integrals for each of the following. 1. The area between the curves = 1 and = 3. Solution. The first thing we should ask ourselves
Worksheet #1. A little review. I. Set up BUT DO NOT EVALUATE definite integrals for each of the following. 1. The area between the curves = 1 and = 3. Solution. The first thing we should ask ourselves
Inference about the Slope and Intercept
 Inference about the Slope and Intercept Recall, we have established that the least square estimates and 0 are linear combinations of the Y i s. Further, we have showed that the are unbiased and have the
Inference about the Slope and Intercept Recall, we have established that the least square estimates and 0 are linear combinations of the Y i s. Further, we have showed that the are unbiased and have the
Objectives To solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula To find the number of solutions of a quadratic equation
 9-6 The Quadratic Formula and the Discriminant Content Standards A.REI..a Use the method of completing the square to transform an quadratic equation in into an equation of the form ( p) 5 q... Derive the
9-6 The Quadratic Formula and the Discriminant Content Standards A.REI..a Use the method of completing the square to transform an quadratic equation in into an equation of the form ( p) 5 q... Derive the
Math 2930 Worksheet Equilibria and Stability
 Math 2930 Worksheet Equilibria and Stabilit Week 3 September 7, 2017 Question 1. (a) Let C be the temperature (in Fahrenheit) of a cup of coffee that is cooling off to room temperature. Which of the following
Math 2930 Worksheet Equilibria and Stabilit Week 3 September 7, 2017 Question 1. (a) Let C be the temperature (in Fahrenheit) of a cup of coffee that is cooling off to room temperature. Which of the following
STATISTICS AND BUSINESS MATHEMATICS B.com-1 Private Annual Examination 2015
 B.com-1 STATISTICS AND BUSINESS MATHEMATICS B.com-1 Private Annual Examination 2015 Compiled & Solved By: JAHANGEER KHAN (SECTION A) Q.1 (a): Find the distance between the points (1, 2), (4, 5). SOLUTION
B.com-1 STATISTICS AND BUSINESS MATHEMATICS B.com-1 Private Annual Examination 2015 Compiled & Solved By: JAHANGEER KHAN (SECTION A) Q.1 (a): Find the distance between the points (1, 2), (4, 5). SOLUTION
Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to:
 1 Chaptter 7:: CORRELATIION Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the concept of relationship between variables Discuss the use of the statistical tests to determine correlation
1 Chaptter 7:: CORRELATIION Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the concept of relationship between variables Discuss the use of the statistical tests to determine correlation
Algebra II Notes Unit Six: Polynomials Syllabus Objectives: 6.2 The student will simplify polynomial expressions.
 Algebra II Notes Unit Si: Polnomials Sllabus Objectives: 6. The student will simplif polnomial epressions. Review: Properties of Eponents (Allow students to come up with these on their own.) Let a and
Algebra II Notes Unit Si: Polnomials Sllabus Objectives: 6. The student will simplif polnomial epressions. Review: Properties of Eponents (Allow students to come up with these on their own.) Let a and
From the help desk: It s all about the sampling
 The Stata Journal (2002) 2, Number 2, pp. 90 20 From the help desk: It s all about the sampling Allen McDowell Stata Corporation amcdowell@stata.com Jeff Pitblado Stata Corporation jsp@stata.com Abstract.
The Stata Journal (2002) 2, Number 2, pp. 90 20 From the help desk: It s all about the sampling Allen McDowell Stata Corporation amcdowell@stata.com Jeff Pitblado Stata Corporation jsp@stata.com Abstract.
1.2 Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus
 1. Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1. FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1. 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function. Find the domain of a function given
1. Functions and Their Properties PreCalculus 1. FUNCTIONS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Learning Targets for 1. 1. Determine whether a set of numbers or a graph is a function. Find the domain of a function given
15.2 Graphing Logarithmic
 Name Class Date 15. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a log b ( h) + k where b > 0 and b 1 related to the graph of f () = log b? Resource Locker A.5.A Determine
Name Class Date 15. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a log b ( h) + k where b > 0 and b 1 related to the graph of f () = log b? Resource Locker A.5.A Determine
PHSY133 Lab 5 Atomic Spectra
 Instructional Goals: PHSY133 Lab 5 Goal: Investigate the wavelengths of light produced b atoms. Background Reading: Background reading for this lab can be found in our class notes and Chapter 5 of our
Instructional Goals: PHSY133 Lab 5 Goal: Investigate the wavelengths of light produced b atoms. Background Reading: Background reading for this lab can be found in our class notes and Chapter 5 of our
3.0 PROBABILITY, RANDOM VARIABLES AND RANDOM PROCESSES
 3.0 PROBABILITY, RANDOM VARIABLES AND RANDOM PROCESSES 3.1 Introduction In this chapter we will review the concepts of probabilit, rom variables rom processes. We begin b reviewing some of the definitions
3.0 PROBABILITY, RANDOM VARIABLES AND RANDOM PROCESSES 3.1 Introduction In this chapter we will review the concepts of probabilit, rom variables rom processes. We begin b reviewing some of the definitions
Ch. 4 Review College Algebra Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Ch. Review College Algebra Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the functions are inverses of each other. 3 5 +
Ch. Review College Algebra Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the functions are inverses of each other. 3 5 +
Let X denote a random variable, and z = h(x) a function of x. Consider the
 EE385 Class Notes 11/13/01 John Stensb Chapter 5 Moments and Conditional Statistics Let denote a random variable, and z = h(x) a function of x. Consider the transformation Z = h(). We saw that we could
EE385 Class Notes 11/13/01 John Stensb Chapter 5 Moments and Conditional Statistics Let denote a random variable, and z = h(x) a function of x. Consider the transformation Z = h(). We saw that we could
Functions and Graphs TERMINOLOGY
 5 Functions and Graphs TERMINOLOGY Arc of a curve: Part or a section of a curve between two points Asmptote: A line towards which a curve approaches but never touches Cartesian coordinates: Named after
5 Functions and Graphs TERMINOLOGY Arc of a curve: Part or a section of a curve between two points Asmptote: A line towards which a curve approaches but never touches Cartesian coordinates: Named after
) = 12(7)
 Chapter 6 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc (p. 89). ( ) + 9 = (7) + 9 = (7) 7 + 8 = 8 7 + 8 = 7 + 8 = 7 8 = 9. 8 + 0 = 8 + 0 = 00 + 0 = 0 + 0 = 0 + 60 = 0 = 06. 7 + 6 + (0 ) = 7 + 6 + (0 6) = 7 + 6
Chapter 6 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc (p. 89). ( ) + 9 = (7) + 9 = (7) 7 + 8 = 8 7 + 8 = 7 + 8 = 7 8 = 9. 8 + 0 = 8 + 0 = 00 + 0 = 0 + 0 = 0 + 60 = 0 = 06. 7 + 6 + (0 ) = 7 + 6 + (0 6) = 7 + 6
Probability Theory Refresher
 Machine Learning WS24 Module IN264 Sheet 2 Page Machine Learning Worksheet 2 Probabilit Theor Refresher Basic Probabilit Problem : A secret government agenc has developed a scanner which determines whether
Machine Learning WS24 Module IN264 Sheet 2 Page Machine Learning Worksheet 2 Probabilit Theor Refresher Basic Probabilit Problem : A secret government agenc has developed a scanner which determines whether
ECON 497 Midterm Spring
 ECON 497 Midterm Spring 2009 1 ECON 497: Economic Research and Forecasting Name: Spring 2009 Bellas Midterm You have three hours and twenty minutes to complete this exam. Answer all questions and explain
ECON 497 Midterm Spring 2009 1 ECON 497: Economic Research and Forecasting Name: Spring 2009 Bellas Midterm You have three hours and twenty minutes to complete this exam. Answer all questions and explain
Letter STUDENT NUMBER FURTHER MATHEMATICS. Written examination 2. Day Date
 Victorian Certificate of Education Year SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER FURTHER MATHEMATICS Written examination 2 Section A Core Section B Modules Day Date Reading time:
Victorian Certificate of Education Year SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Letter STUDENT NUMBER FURTHER MATHEMATICS Written examination 2 Section A Core Section B Modules Day Date Reading time:
5.6 RATIOnAl FUnCTIOnS. Using Arrow notation. learning ObjeCTIveS
 CHAPTER PolNomiAl ANd rational functions learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Use arrow notation. Solve applied problems involving rational functions. Find the domains of rational functions. Identif
CHAPTER PolNomiAl ANd rational functions learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Use arrow notation. Solve applied problems involving rational functions. Find the domains of rational functions. Identif
3. A boat that costs $4000 decreases in value by 17% per year. How much will the boat be worth after 6 years?
 Algebra Stud Guide 1. Write a recursive formula for the sequence.,, 50, 50,.... Given that u = 3, u = 1, and u = 5u + u where n 3, what is the fifth term of the sequence? [A] 57 [B] 63 [C] 307 [D] 1649
Algebra Stud Guide 1. Write a recursive formula for the sequence.,, 50, 50,.... Given that u = 3, u = 1, and u = 5u + u where n 3, what is the fifth term of the sequence? [A] 57 [B] 63 [C] 307 [D] 1649
