To calculate the distribution of the seismic moment at a site, we assume that on a
|
|
|
- Ernest Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 KAGAN : EARTHQUAKE SLIP DISTRIBUTION X - 1 Appendix A: Seismic Moment Distribution at a Site To calculate the distribution of the seismic moment at a site, we assume that on a fault zone of total length L the rate of earthquake with moment M 0 = N m (m = 7) or greater and rupture length L 0 = 37.5 km is equal to α 0 (see section 4.3). The complementary moment function is then = α 0L 0 L C 1 1 x 1/d φ(x)dx, M (A1) φ(x) is defined by equations (4), (5), (6), and (7) and C 1 1 is a normalizing coefficient. Similar to the moment-frequency relation, the function shows the number of fractures caused by an earthquake with moment M at a fault site. For the characteristic distribution, = α 0L 0 L ξd βd(m 0/M) ξ (M 0 /M xc ) ξ ] = 0 M > M xc, (A2) ξ = (βd 1)/d. Using equation 7 of Kagan 2002b], we can convert (A2) = 1 β ξd Ṁ 0 M β 0 M β 1 xc βd(m 0 /M) ξ (M 0 /M xc ) ξ ] (A3) Ṁ0 is the seismic moment rate on L 0.
2 X - 2 KAGAN : EARTHQUAKE SLIP DISTRIBUTION = α 0L 0 βη p L ξ (M 0 /M) ξ (M 0 /M xp ) ξ ] M xp > M M 0, = 0 M M xp, (A4) η p is defined by η p = M β xp M β xp M β 0, (A5) Alternately, = 1 β ξd Ṁ 0 M β 0 M β 1 xp (M 0 /M) ξ (M 0 /M xp ) ξ ] M xp > M M 0. (A6) If βd = 1, equations (A2) (A4) need to be modified. For the characteristic distribution, = α 0L 0 1 log(m L xc/m)] = 0 M > M xc, (A7) = α 0L 0 βη p L log(m xp /M) M xp > M M 0, = 0 M M xp, (A8)
3 KAGAN : EARTHQUAKE SLIP DISTRIBUTION X - 3 Appendix B: Slip Distribution The distribution density of the average slip is obtained from υ(m) (see equations (18) and (23)), as f(u) υ u d/(d 1)] u 1/(d 1). (B1) Inserting in (B1) appropriate expressions for seismic moment distribution and integrating to obtain a cumulative function, we obtain the following formula for the complementary function of displacement: Ψ(u) = C 1 f(x)dx. u (B2) To simplify the equations, we normalize the displacement by dividing them by u 0 = 1.87 m; u x is the slip corresponding to the maximum earthquake (normalized by dividing it by u 0 ). For the characteristic distribution, Ψ(u) = βd u ζ u ζ xc βd u ζ 0 u ζ xc, u xc > u u 0, Ψ(u) = 0 u u xc, (B3) ζ = βd 1 d 1 ; (B4) hence ζ 0 for d 1/β. For the truncated Pareto distribution of the seismic moment, Ψ(u) = u ζ u ζ xp u ζ 0 u ζ xp, u xp > u u 0, Ψ(u) = 0 u u xp. (B5)
4 X - 4 KAGAN : EARTHQUAKE SLIP DISTRIBUTION Ψ(u) = C 1 C g { Γ 1 βd 1, ( ) ] d/(d 1) u d + ( u ) (1 βd)/(d 1) exp ( u ) d/(d 1) ]}, (B6) Γ(a, x) is the incomplete gamma function Abramowitz and Stegun, 1972, p. 260] x P (x, a) = (Γ(a)) 1 e t t a 1 dt, a > 0, (B7) Γ(a) is the gamma function Abramowitz and Stegun, 1972, p. 260]. 0 C 1 ( = β d 1 βd ) ( u0 ) (1 βd)/(d 1) exp ( u0 ) d/(1 d) ], (B8) C g = C 1 Γ 1 βd 1, ( ) ] d/(1 d) u 0 d + βd. βd 1 (B9) If βd = 1, equations (B3), (B5), and (B6) need to be modified. For the characteristic distribution, Ψ(u) = d 1+log u xc log u d 1+log u xc log u 0, u xc > u u 0, Ψ(u) = 0 u u xc. (B10) Ψ(u) = log u xp log u log u xp log u 0, u xp > u u 0, Ψ(u) = 0 for u u xp. (B11) ( ) / ( ) u u0 Ψ(u) = E 1 E 1 u u 0, (B12) E 1 (z) is an exponential integral Abramowitz and Stegun, 1972, p. 228] E 1 (z) = t 1 e t dt. (B13) z We calculate this integral using the mathematica package Wolfram, 1999].
5 KAGAN : EARTHQUAKE SLIP DISTRIBUTION X - 5 Appendix C: Cumulative Slip Distribution at a Site The cumulative distribution of the total slip at a site can be expressed as follows: For the characteristic distribution of the seismic moment tensor, Φ(u) = C 2 u 1 ζ 1 u 1 ζ xc 1, u xc > u 1, Φ(u) = 1 u u xc, (C1) ζ = βd 1 d 1, (C2) see (B4) and C 2 = β 1 uζ 1 xc 1 βu ζ 1. (C3) xc For the truncated Pareto distribution of the seismic moment tensor, Φ(u) = u1 ζ 1 u 1 ζ xp 1, u xp > u 1, Φ(u) = 1 u u xp. (C4) see (B7) for the definition of the P function. Φ(u) = P 1 P 2 1 P 2, (C5) ( ( u ) ) d/(1 d) P 1 = P, 1 β, (C6) ( ( 1 ) ) d/(1 d) P 2 = P, 1 β, (C7)
Seismic moment distribution revisited: II. Moment conservation principle
 Geophys. J. Int. (2002) 149, 731 754 Seismic moment distribution revisited: II. Moment conservation principle Yan Y. Kagan Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles,
Geophys. J. Int. (2002) 149, 731 754 Seismic moment distribution revisited: II. Moment conservation principle Yan Y. Kagan Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles,
Forecasting Earthquakes
 Forecasting Earthquakes Lecture 9 Earthquake Recurrence ) Long-term prediction - Elastic Rebound Theory Stress Stress & strain accumulation 0 0 4 F slow accumulation of stress & strain that deforms rock
Forecasting Earthquakes Lecture 9 Earthquake Recurrence ) Long-term prediction - Elastic Rebound Theory Stress Stress & strain accumulation 0 0 4 F slow accumulation of stress & strain that deforms rock
science specialties. size distribution, scaling of geometric parameters with by earthquakes in plate boundary zones and zones of distributed fault.
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, PostScript le created: May 16, 2011 EARTHQUAKE SLIP DISTRIBUTION: A STATISTICAL MODEL Yan Y. Kagan 1 1 Department of Earth and Space Sciences,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, PostScript le created: May 16, 2011 EARTHQUAKE SLIP DISTRIBUTION: A STATISTICAL MODEL Yan Y. Kagan 1 1 Department of Earth and Space Sciences,
On an asymptotic series of Ramanujan
 Ramanujan J (2009) 20: 179 188 DOI 10.1007/s11139-009-9169-x On an asymptotic series of Ramanujan Yaming Yu Received: 22 May 2008 / Accepted: 1 April 2009 / Published online: 12 August 2009 The Author(s)
Ramanujan J (2009) 20: 179 188 DOI 10.1007/s11139-009-9169-x On an asymptotic series of Ramanujan Yaming Yu Received: 22 May 2008 / Accepted: 1 April 2009 / Published online: 12 August 2009 The Author(s)
Asymptotic Variance Formulas, Gamma Functions, and Order Statistics
 Statistical Models and Methods for Lifetime Data, Second Edition by Jerald F. Lawless Copyright 2003 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. APPENDIX Β Asymptotic Variance Formulas, Gamma Functions, and Order Statistics
Statistical Models and Methods for Lifetime Data, Second Edition by Jerald F. Lawless Copyright 2003 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. APPENDIX Β Asymptotic Variance Formulas, Gamma Functions, and Order Statistics
6 Source Characterization
 6 Source Characterization Source characterization describes the rate at which earthquakes of a given magnitude, and dimensions (length and width) occur at a given location. For each seismic source, the
6 Source Characterization Source characterization describes the rate at which earthquakes of a given magnitude, and dimensions (length and width) occur at a given location. For each seismic source, the
Oceanic Transform Fault Seismicity Earthquakes of a Different Kind
 University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping 4-2009 Oceanic Transform Fault Seismicity Earthquakes
University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping 4-2009 Oceanic Transform Fault Seismicity Earthquakes
Partial Differential Equations, Winter 2015
 Partial Differential Equations, Winter 215 Homework #2 Due: Thursday, February 12th, 215 1. (Chapter 2.1) Solve u xx + u xt 2u tt =, u(x, ) = φ(x), u t (x, ) = ψ(x). Hint: Factor the operator as we did
Partial Differential Equations, Winter 215 Homework #2 Due: Thursday, February 12th, 215 1. (Chapter 2.1) Solve u xx + u xt 2u tt =, u(x, ) = φ(x), u t (x, ) = ψ(x). Hint: Factor the operator as we did
An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth.
 An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth. Measuring an Earthquake s Size Magnitude and Moment Each can
An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth. Measuring an Earthquake s Size Magnitude and Moment Each can
Inversion of Earthquake Rupture Process:Theory and Applications
 Inversion of Earthquake Rupture Process:Theory and Applications Yun-tai CHEN 12 * Yong ZHANG 12 Li-sheng XU 2 1School of the Earth and Space Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100871 2Institute of Geophysics,
Inversion of Earthquake Rupture Process:Theory and Applications Yun-tai CHEN 12 * Yong ZHANG 12 Li-sheng XU 2 1School of the Earth and Space Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100871 2Institute of Geophysics,
Source parameters II. Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop
 Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE. Kyle Withers Qian Yao
 FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE Kyle Withers Qian Yao Temperature Change Along Fault Mode II (plain strain) crack rupturing bilaterally at a constant speed v r Idealize earthquake ruptures as shear
FRICTIONAL HEATING DURING AN EARTHQUAKE Kyle Withers Qian Yao Temperature Change Along Fault Mode II (plain strain) crack rupturing bilaterally at a constant speed v r Idealize earthquake ruptures as shear
PostScript file created: June 11, 2011; time 985 minutes RANDOM STRESS AND OMORI S LAW. Yan Y. Kagan
 PostScript file created: June 11, 2011; time 985 minutes RANDOM STRESS AND OMORI S LAW Yan Y. Kagan Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, California 90095-1567,
PostScript file created: June 11, 2011; time 985 minutes RANDOM STRESS AND OMORI S LAW Yan Y. Kagan Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, California 90095-1567,
AN OVERVIEW AND GUIDELINES FOR PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPPING
 CO 2 TRACCS INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP Bucharest, 2 September, 2012 AN OVERVIEW AND GUIDELINES FOR PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPPING M. Semih YÜCEMEN Department of Civil Engineering and Earthquake Studies
CO 2 TRACCS INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP Bucharest, 2 September, 2012 AN OVERVIEW AND GUIDELINES FOR PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPPING M. Semih YÜCEMEN Department of Civil Engineering and Earthquake Studies
CS Lecture 19. Exponential Families & Expectation Propagation
 CS 6347 Lecture 19 Exponential Families & Expectation Propagation Discrete State Spaces We have been focusing on the case of MRFs over discrete state spaces Probability distributions over discrete spaces
CS 6347 Lecture 19 Exponential Families & Expectation Propagation Discrete State Spaces We have been focusing on the case of MRFs over discrete state spaces Probability distributions over discrete spaces
Dynamic Earthquake Triggering Due to Stress from Surface Wave Particle Displacement
 Emily Morton Geop 523: Theoretical Seismology 29 April 2011 Introduction Dynamic Earthquake Triggering Due to Stress from Surface Wave Particle Displacement Earthquakes can be triggered by other earthquakes.
Emily Morton Geop 523: Theoretical Seismology 29 April 2011 Introduction Dynamic Earthquake Triggering Due to Stress from Surface Wave Particle Displacement Earthquakes can be triggered by other earthquakes.
Spatio-temporal variation in slip rate on the plate boundary off Sanriku, northeastern Japan, estimated from small repeating earthquakes
 Spatio-temporal variation in slip rate on the plate boundary off Sanriku, northeastern Japan, estimated from small repeating earthquakes T. Matsuzawa, N. Uchida, T. Igarashi *, N. Umino, and A. Hasegawa
Spatio-temporal variation in slip rate on the plate boundary off Sanriku, northeastern Japan, estimated from small repeating earthquakes T. Matsuzawa, N. Uchida, T. Igarashi *, N. Umino, and A. Hasegawa
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11492 Figure S1 Short-period Seismic Energy Release Pattern Imaged by F-net. (a) Locations of broadband seismograph stations in Japanese F-net used for the 0.5-2.0 Hz P wave back-projection
doi:10.1038/nature11492 Figure S1 Short-period Seismic Energy Release Pattern Imaged by F-net. (a) Locations of broadband seismograph stations in Japanese F-net used for the 0.5-2.0 Hz P wave back-projection
Y. Y. Kagan and L. Knopoff Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California, Los Angeles, California 90024, USA
 Geophys. J. R. astr. SOC. (1987) 88, 723-731 Random stress and earthquake statistics: time dependence Y. Y. Kagan and L. Knopoff Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California,
Geophys. J. R. astr. SOC. (1987) 88, 723-731 Random stress and earthquake statistics: time dependence Y. Y. Kagan and L. Knopoff Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, University of California,
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 20, 30 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Aki, Scaling law
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 20, 30 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws. Aki, Scaling law
Manila subduction zone
 Manila subduction zone Andrew T.S. Lin SSC TI Team Member Taiwan SSHAC Level 3 PSHA Study Workshop #3, June 19 23, 2017 Taipei, Taiwan 1 1 Manila subduction zone Hazard Contribution Geometry Setting interface
Manila subduction zone Andrew T.S. Lin SSC TI Team Member Taiwan SSHAC Level 3 PSHA Study Workshop #3, June 19 23, 2017 Taipei, Taiwan 1 1 Manila subduction zone Hazard Contribution Geometry Setting interface
Scaling Laws. σ 1. σ = mean stress, which is needed to compute σ 0. η = percent strain energy released in eq. Introduction.
 Scaling Laws Introduction Scaling Laws or Relationships are the result of empirical observation. They describe how one physical parameter varies as a function of another physical parameter within a system.
Scaling Laws Introduction Scaling Laws or Relationships are the result of empirical observation. They describe how one physical parameter varies as a function of another physical parameter within a system.
ON A GENERALIZATION OF THE GUMBEL DISTRIBUTION
 ON A GENERALIZATION OF THE GUMBEL DISTRIBUTION S. Adeyemi Department of Mathematics Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife. Nigeria.0005 e-mail:shollerss00@yahoo.co.uk Abstract A simple generalization of
ON A GENERALIZATION OF THE GUMBEL DISTRIBUTION S. Adeyemi Department of Mathematics Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife. Nigeria.0005 e-mail:shollerss00@yahoo.co.uk Abstract A simple generalization of
Derivation of Table 2 in Okada (1992)
 Derivation of Table 2 in Okada (1992) [ I ] Derivation of Eqs.(4) through (6) Eq.(1) of Okada (1992) can be rewritten, where is the displacement at due to a j-th direction single force of unit magnitude
Derivation of Table 2 in Okada (1992) [ I ] Derivation of Eqs.(4) through (6) Eq.(1) of Okada (1992) can be rewritten, where is the displacement at due to a j-th direction single force of unit magnitude
Finite element modelling of fault stress triggering due to hydraulic fracturing
 Finite element modelling of fault stress triggering due to hydraulic fracturing Arsalan, Sattari and David, Eaton University of Calgary, Geoscience Department Summary In this study we aim to model fault
Finite element modelling of fault stress triggering due to hydraulic fracturing Arsalan, Sattari and David, Eaton University of Calgary, Geoscience Department Summary In this study we aim to model fault
Earthquakes. Forces Within Eartth. Faults form when the forces acting on rock exceed the rock s strength.
 Earthquakes Vocabulary: Stress Strain Elastic Deformation Plastic Deformation Fault Seismic Wave Primary Wave Secondary Wave Focus Epicenter Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish
Earthquakes Vocabulary: Stress Strain Elastic Deformation Plastic Deformation Fault Seismic Wave Primary Wave Secondary Wave Focus Epicenter Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish
WP2: Framework for Seismic Hazard Analysis of Spatially Distributed Systems
 Systemic Seismic Vulnerability and Risk Analysis for Buildings, Lifeline Networks and Infrastructures Safety Gain WP2: Framework for Seismic Hazard Analysis of Spatially Distributed Systems Graeme Weatherill,
Systemic Seismic Vulnerability and Risk Analysis for Buildings, Lifeline Networks and Infrastructures Safety Gain WP2: Framework for Seismic Hazard Analysis of Spatially Distributed Systems Graeme Weatherill,
F n = F n 1 + F n 2. F(z) = n= z z 2. (A.3)
 Appendix A MATTERS OF TECHNIQUE A.1 Transform Methods Laplace transforms for continuum systems Generating function for discrete systems This method is demonstrated for the Fibonacci sequence F n = F n
Appendix A MATTERS OF TECHNIQUE A.1 Transform Methods Laplace transforms for continuum systems Generating function for discrete systems This method is demonstrated for the Fibonacci sequence F n = F n
Martina Nardon and Paolo Pianca
 Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Venice WORKING PAPER SERIES Martina Nardon and Paolo Pianca Simulation techniques for generalized Gaussian densities Working Paper n. 145/26 November 26
Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Venice WORKING PAPER SERIES Martina Nardon and Paolo Pianca Simulation techniques for generalized Gaussian densities Working Paper n. 145/26 November 26
Short-Term Properties of Earthquake Catalogs and Models of Earthquake Source
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 94, No. 4, pp. 1207 1228, August 2004 Short-Term Properties of Earthquake Catalogs and Models of Earthquake Source by Yan Y. Kagan Abstract I review
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 94, No. 4, pp. 1207 1228, August 2004 Short-Term Properties of Earthquake Catalogs and Models of Earthquake Source by Yan Y. Kagan Abstract I review
PROBABILISTIC SURFACE FAULT DISPLACEMENT HAZARD ANALYSIS (PFDHA) DATA FOR STRIKE SLIP FAULTS
 PROBABILISTIC SURFACE FAULT DISPLACEMENT HAZARD ANALYSIS (PFDHA) DATA FOR STRIKE SLIP FAULTS PEER SURFACE FAULT DISPLACEMENT HAZARD WORKSHOP U.C. Berkeley May 20-21, 2009 Timothy Dawson California Geological
PROBABILISTIC SURFACE FAULT DISPLACEMENT HAZARD ANALYSIS (PFDHA) DATA FOR STRIKE SLIP FAULTS PEER SURFACE FAULT DISPLACEMENT HAZARD WORKSHOP U.C. Berkeley May 20-21, 2009 Timothy Dawson California Geological
. Then Φ is a diffeomorphism from (0, ) onto (0, 1)
 1 + 5..0: uv i Set F s, t s α 1 t β 1 e s+t and Φu, v. Then Φ is a u1 v diffeomorphism from 0, 0, 1 onto 0,, and JΦu, v u. Hence, ΓαΓβ F s, t dsdt F Φu, vjφu, v dudv 0, 0, 0,1 u α+β 1 e u v α 1 1 v β 1
1 + 5..0: uv i Set F s, t s α 1 t β 1 e s+t and Φu, v. Then Φ is a u1 v diffeomorphism from 0, 0, 1 onto 0,, and JΦu, v u. Hence, ΓαΓβ F s, t dsdt F Φu, vjφu, v dudv 0, 0, 0,1 u α+β 1 e u v α 1 1 v β 1
ST5215: Advanced Statistical Theory
 Department of Statistics & Applied Probability Monday, September 26, 2011 Lecture 10: Exponential families and Sufficient statistics Exponential Families Exponential families are important parametric families
Department of Statistics & Applied Probability Monday, September 26, 2011 Lecture 10: Exponential families and Sufficient statistics Exponential Families Exponential families are important parametric families
Review 1: STAT Mark Carpenter, Ph.D. Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics and Statistics. August 25, 2015
 Review : STAT 36 Mark Carpenter, Ph.D. Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics and Statistics August 25, 25 Support of a Random Variable The support of a random variable, which is usually denoted
Review : STAT 36 Mark Carpenter, Ph.D. Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics and Statistics August 25, 25 Support of a Random Variable The support of a random variable, which is usually denoted
A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR
 A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR Annemarie CHRISTOPHERSEN 1 And Euan G C SMITH 2 SUMMARY This paper considers the distribution of aftershocks in space, abundance, magnitude and time. Investigations
A GLOBAL MODEL FOR AFTERSHOCK BEHAVIOUR Annemarie CHRISTOPHERSEN 1 And Euan G C SMITH 2 SUMMARY This paper considers the distribution of aftershocks in space, abundance, magnitude and time. Investigations
Elastic rebound theory
 Elastic rebound theory Focus epicenter - wave propagation Dip-Slip Fault - Normal Normal Fault vertical motion due to tensional stress Hanging wall moves down, relative to the footwall Opal Mountain, Mojave
Elastic rebound theory Focus epicenter - wave propagation Dip-Slip Fault - Normal Normal Fault vertical motion due to tensional stress Hanging wall moves down, relative to the footwall Opal Mountain, Mojave
Earthquake predictability measurement: information score and error diagram
 Earthquake predictability measurement: information score and error diagram Yan Y. Kagan Department of Earth and Space Sciences University of California, Los Angeles, California, USA August, 00 Abstract
Earthquake predictability measurement: information score and error diagram Yan Y. Kagan Department of Earth and Space Sciences University of California, Los Angeles, California, USA August, 00 Abstract
5.4.3 Centre of stiffness and elastic displacements of the diaphragm
 5.4.3 Centre of stiffness and elastic displacements of the diaphragm The current paragraph examines the special case of orthogonal columns in parallel arrangement. The general case is examined in Appendix
5.4.3 Centre of stiffness and elastic displacements of the diaphragm The current paragraph examines the special case of orthogonal columns in parallel arrangement. The general case is examined in Appendix
Numerical explorations of a forward-backward diffusion equation
 Numerical explorations of a forward-backward diffusion equation Newton Institute KIT Programme Pauline Lafitte 1 C. Mascia 2 1 SIMPAF - INRIA & U. Lille 1, France 2 Univ. La Sapienza, Roma, Italy September
Numerical explorations of a forward-backward diffusion equation Newton Institute KIT Programme Pauline Lafitte 1 C. Mascia 2 1 SIMPAF - INRIA & U. Lille 1, France 2 Univ. La Sapienza, Roma, Italy September
Method of Moments. which we usually denote by X or sometimes by X n to emphasize that there are n observations.
 Method of Moments Definition. If {X 1,..., X n } is a sample from a population, then the empirical k-th moment of this sample is defined to be X k 1 + + Xk n n Example. For a sample {X 1, X, X 3 } the
Method of Moments Definition. If {X 1,..., X n } is a sample from a population, then the empirical k-th moment of this sample is defined to be X k 1 + + Xk n n Example. For a sample {X 1, X, X 3 } the
PostScript file created: December 21, 2011; time 1069 minutes TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE: A SURPRISE? Yan Y. Kagan and David D. Jackson
 PostScript file created: December 21, 2011; time 1069 minutes TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE: A SURPRISE? Yan Y. Kagan and David D. Jackson Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles,
PostScript file created: December 21, 2011; time 1069 minutes TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE: A SURPRISE? Yan Y. Kagan and David D. Jackson Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles,
Preliminary slip model of M9 Tohoku earthquake from strongmotion stations in Japan - an extreme application of ISOLA code.
 Preliminary slip model of M9 Tohoku earthquake from strongmotion stations in Japan - an extreme application of ISOLA code. J. Zahradnik 1), F. Gallovic 1), E. Sokos 2) G-A. Tselentis 2) 1) Charles University
Preliminary slip model of M9 Tohoku earthquake from strongmotion stations in Japan - an extreme application of ISOLA code. J. Zahradnik 1), F. Gallovic 1), E. Sokos 2) G-A. Tselentis 2) 1) Charles University
earthquake virtual
 Activity: Elasticity of the crust Elasticity of the crust. The earth s crust is slightly elastic, it can be stretched or compressed. Without this elasticity all movements along faults would be slow and
Activity: Elasticity of the crust Elasticity of the crust. The earth s crust is slightly elastic, it can be stretched or compressed. Without this elasticity all movements along faults would be slow and
MFM Practitioner Module: Quantitiative Risk Management. John Dodson. October 14, 2015
 MFM Practitioner Module: Quantitiative Risk Management October 14, 2015 The n-block maxima 1 is a random variable defined as M n max (X 1,..., X n ) for i.i.d. random variables X i with distribution function
MFM Practitioner Module: Quantitiative Risk Management October 14, 2015 The n-block maxima 1 is a random variable defined as M n max (X 1,..., X n ) for i.i.d. random variables X i with distribution function
ANALYSIS OF THE CORRELATION BETWEEN INSTRUMENTAL INTENSITIES OF STRONG EARTHQUAKE GROUND MOTION
 ANALYSIS OF THE CORRELATION BETWEEN INSTRUMENTAL INTENSITIES OF STRONG EARTHQUAKE GROUND MOTION J.Enrique Martinez-Rueda 1, Evdokia Tsantali 1 1 Civil Engineering & Geology Division School of Environment
ANALYSIS OF THE CORRELATION BETWEEN INSTRUMENTAL INTENSITIES OF STRONG EARTHQUAKE GROUND MOTION J.Enrique Martinez-Rueda 1, Evdokia Tsantali 1 1 Civil Engineering & Geology Division School of Environment
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Overview Milestones in continuum mechanics Concepts of modulus and stiffness. Stress-strain relations Elasticity Surface and body
Shape of the return probability density function and extreme value statistics
 Shape of the return probability density function and extreme value statistics 13/09/03 Int. Workshop on Risk and Regulation, Budapest Overview I aim to elucidate a relation between one field of research
Shape of the return probability density function and extreme value statistics 13/09/03 Int. Workshop on Risk and Regulation, Budapest Overview I aim to elucidate a relation between one field of research
Probability Distributions Columns (a) through (d)
 Discrete Probability Distributions Columns (a) through (d) Probability Mass Distribution Description Notes Notation or Density Function --------------------(PMF or PDF)-------------------- (a) (b) (c)
Discrete Probability Distributions Columns (a) through (d) Probability Mass Distribution Description Notes Notation or Density Function --------------------(PMF or PDF)-------------------- (a) (b) (c)
Notes on a skew-symmetric inverse double Weibull distribution
 Journal of the Korean Data & Information Science Society 2009, 20(2), 459 465 한국데이터정보과학회지 Notes on a skew-symmetric inverse double Weibull distribution Jungsoo Woo 1 Department of Statistics, Yeungnam
Journal of the Korean Data & Information Science Society 2009, 20(2), 459 465 한국데이터정보과학회지 Notes on a skew-symmetric inverse double Weibull distribution Jungsoo Woo 1 Department of Statistics, Yeungnam
Fracking and Earthquakes What s the Risk? Alastair Muir, President Muir&Associates Consulting
 Fracking and Earthquakes What s the Risk? Alastair Muir, President Muir&Associates Consulting Who am I? Big data since 1979 Hydraulic Fracturing Induced Earthquakes Earthquake Prediction Since my first
Fracking and Earthquakes What s the Risk? Alastair Muir, President Muir&Associates Consulting Who am I? Big data since 1979 Hydraulic Fracturing Induced Earthquakes Earthquake Prediction Since my first
Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs
 Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs Lindsey N. Meighan, Ted Urbancic and Adam Baig ESG, Kingston, Ontario Summary
Seismic Efficiency, Overshoot and Enhanced Dynamic Weaking of Fractures Associated with Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoirs Lindsey N. Meighan, Ted Urbancic and Adam Baig ESG, Kingston, Ontario Summary
University of Lisbon, Portugal
 Development and comparative study of two near-exact approximations to the distribution of the product of an odd number of independent Beta random variables Luís M. Grilo a,, Carlos A. Coelho b, a Dep.
Development and comparative study of two near-exact approximations to the distribution of the product of an odd number of independent Beta random variables Luís M. Grilo a,, Carlos A. Coelho b, a Dep.
Simulating Uniform- and Triangular- Based Double Power Method Distributions
 Journal of Statistical and Econometric Methods, vol.6, no.1, 2017, 1-44 ISSN: 1792-6602 (print), 1792-6939 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2017 Simulating Uniform- and Triangular- Based Double Power Method Distributions
Journal of Statistical and Econometric Methods, vol.6, no.1, 2017, 1-44 ISSN: 1792-6602 (print), 1792-6939 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2017 Simulating Uniform- and Triangular- Based Double Power Method Distributions
arxiv: v2 [physics.geo-ph] 21 Jul 2012
![arxiv: v2 [physics.geo-ph] 21 Jul 2012 arxiv: v2 [physics.geo-ph] 21 Jul 2012](/thumbs/90/104139209.jpg) PostScript file created: November 1, 2018; time 148 minutes TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE: A SURPRISE? Yan Y. Kagan and David D. Jackson arxiv:1112.5217v2 [physics.geo-ph] 21 Jul 2012 Department of Earth and Space
PostScript file created: November 1, 2018; time 148 minutes TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE: A SURPRISE? Yan Y. Kagan and David D. Jackson arxiv:1112.5217v2 [physics.geo-ph] 21 Jul 2012 Department of Earth and Space
which is a group homomorphism, such that if W V U, then
 4. Sheaves Definition 4.1. Let X be a topological space. A presheaf of groups F on X is a a function which assigns to every open set U X a group F(U) and to every inclusion V U a restriction map, ρ UV
4. Sheaves Definition 4.1. Let X be a topological space. A presheaf of groups F on X is a a function which assigns to every open set U X a group F(U) and to every inclusion V U a restriction map, ρ UV
Theoretical Seismology (GEOP 523) Seismic Sources
 Theoretical Seismology GEOP 523 Seismic Sources Rick Aster April 25, 2011 Up to this point, we have been mostly concerned with homogeneous solutions to the wave equation, gx, t 2 g t 2 c2 2 g = 0. 1 In
Theoretical Seismology GEOP 523 Seismic Sources Rick Aster April 25, 2011 Up to this point, we have been mostly concerned with homogeneous solutions to the wave equation, gx, t 2 g t 2 c2 2 g = 0. 1 In
3D Finite Element Modeling of fault-slip triggering caused by porepressure
 3D Finite Element Modeling of fault-slip triggering caused by porepressure changes Arsalan Sattari and David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Suary We present a 3D model using a
3D Finite Element Modeling of fault-slip triggering caused by porepressure changes Arsalan Sattari and David W. Eaton Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary Suary We present a 3D model using a
Solution. (i) Find a minimal sufficient statistic for (θ, β) and give your justification. X i=1. By the factorization theorem, ( n
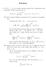 Solution 1. Let (X 1,..., X n ) be a simple random sample from a distribution with probability density function given by f(x;, β) = 1 ( ) 1 β x β, 0 x, > 0, β < 1. β (i) Find a minimal sufficient statistic
Solution 1. Let (X 1,..., X n ) be a simple random sample from a distribution with probability density function given by f(x;, β) = 1 ( ) 1 β x β, 0 x, > 0, β < 1. β (i) Find a minimal sufficient statistic
Approximating the Conway-Maxwell-Poisson normalizing constant
 Filomat 30:4 016, 953 960 DOI 10.98/FIL1604953S Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Approximating the Conway-Maxwell-Poisson
Filomat 30:4 016, 953 960 DOI 10.98/FIL1604953S Published by Faculty of Sciences and Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Approximating the Conway-Maxwell-Poisson
Quiz 6. 1) The measure of the time between two peaks of a sine wave is called the. A) period B) wavelength C) amplitude.
 Quiz 6 1) The measure of the time between two peaks of a sine wave is called the A) period B) wavelength C) amplitude Amplitude (m) Motion of one point Time (s) Hint: look at the units of the axis. Quiz
Quiz 6 1) The measure of the time between two peaks of a sine wave is called the A) period B) wavelength C) amplitude Amplitude (m) Motion of one point Time (s) Hint: look at the units of the axis. Quiz
Supplement to A Hierarchical Approach for Fitting Curves to Response Time Measurements
 Supplement to A Hierarchical Approach for Fitting Curves to Response Time Measurements Jeffrey N. Rouder Francis Tuerlinckx Paul L. Speckman Jun Lu & Pablo Gomez May 4 008 1 The Weibull regression model
Supplement to A Hierarchical Approach for Fitting Curves to Response Time Measurements Jeffrey N. Rouder Francis Tuerlinckx Paul L. Speckman Jun Lu & Pablo Gomez May 4 008 1 The Weibull regression model
Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.002 Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.002 Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Physics 351, Spring 2018, Homework #9. Due at start of class, Friday, March 30, 2018
 Physics 351, Spring 218, Homework #9. Due at start of class, Friday, March 3, 218 Please write your name on the LAST PAGE of your homework submission, so that we don t notice whose paper we re grading
Physics 351, Spring 218, Homework #9. Due at start of class, Friday, March 3, 218 Please write your name on the LAST PAGE of your homework submission, so that we don t notice whose paper we re grading
Stable Limit Laws for Marginal Probabilities from MCMC Streams: Acceleration of Convergence
 Stable Limit Laws for Marginal Probabilities from MCMC Streams: Acceleration of Convergence Robert L. Wolpert Institute of Statistics and Decision Sciences Duke University, Durham NC 778-5 - Revised April,
Stable Limit Laws for Marginal Probabilities from MCMC Streams: Acceleration of Convergence Robert L. Wolpert Institute of Statistics and Decision Sciences Duke University, Durham NC 778-5 - Revised April,
Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures
 Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures (1) In terms of friction (2) In terms of fracture mechanics Scholz describes conditions for rupture propagation (i.e. instability) via energy
Two ways to think about the dynamics of earthquake ruptures (1) In terms of friction (2) In terms of fracture mechanics Scholz describes conditions for rupture propagation (i.e. instability) via energy
Kinematics of the Southern California Fault System Constrained by GPS Measurements
 Title Page Kinematics of the Southern California Fault System Constrained by GPS Measurements Brendan Meade and Bradford Hager Three basic questions Large historical earthquakes One basic question How
Title Page Kinematics of the Southern California Fault System Constrained by GPS Measurements Brendan Meade and Bradford Hager Three basic questions Large historical earthquakes One basic question How
Fric%onal Hea%ng During an Earthquake. Te-Yang Geodynamics HW3 (Group G)
 Fric%onal Hea%ng During an Earthquake Te-Yang Yeh @ Geodynamics HW3 (Group G) [San Andreas], 2015 Common misconception Some people might think that most of energy generated by an earthquake is released
Fric%onal Hea%ng During an Earthquake Te-Yang Yeh @ Geodynamics HW3 (Group G) [San Andreas], 2015 Common misconception Some people might think that most of energy generated by an earthquake is released
Earthquake Focal Mechanisms and Waveform Modeling
 Earthquake Focal Mechanisms and Waveform Modeling Rengin Gök Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory USA RELEMR Workshop İstanbul 2008 Gudmundar E. Sigvaldason The Dynamic Earth, USGS The size of the event
Earthquake Focal Mechanisms and Waveform Modeling Rengin Gök Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory USA RELEMR Workshop İstanbul 2008 Gudmundar E. Sigvaldason The Dynamic Earth, USGS The size of the event
Are faults fractals?
 Are faults fractals? Alexandra Käßner Technical university Bergakademie Freiberg Abstract A universal scaling law would be imperative to understand the processes of the evolution of faults. Searching for
Are faults fractals? Alexandra Käßner Technical university Bergakademie Freiberg Abstract A universal scaling law would be imperative to understand the processes of the evolution of faults. Searching for
Seismic Hazard Assessment for Specified Area
 ESTIATION OF AXIU REGIONAL AGNITUDE m At present there is no generally accepted method for estimating the value of the imum regional magnitude m. The methods for evaluating m fall into two main categories:
ESTIATION OF AXIU REGIONAL AGNITUDE m At present there is no generally accepted method for estimating the value of the imum regional magnitude m. The methods for evaluating m fall into two main categories:
Continuous Random Variables and Continuous Distributions
 Continuous Random Variables and Continuous Distributions Continuous Random Variables and Continuous Distributions Expectation & Variance of Continuous Random Variables ( 5.2) The Uniform Random Variable
Continuous Random Variables and Continuous Distributions Continuous Random Variables and Continuous Distributions Expectation & Variance of Continuous Random Variables ( 5.2) The Uniform Random Variable
Simulation. Li Zhao, SJTU. Spring, Li Zhao Simulation 1 / 19
 Simulation Li Zhao, SJTU Spring, 2017 Li Zhao Simulation 1 / 19 Introduction Simulation consists of drawing from a density, calculating a statistic for each draw, and averaging the results. Simulation
Simulation Li Zhao, SJTU Spring, 2017 Li Zhao Simulation 1 / 19 Introduction Simulation consists of drawing from a density, calculating a statistic for each draw, and averaging the results. Simulation
A Closer Look At Body Wave Magnitude & Introduction To Moment Magnitude
 A Closer Look At Body Wave Magnitude & Introduction To Moment Magnitude Previously we have learned the mechanics of calculating earthquake magnitudes with several magnitude scales: Duration Magnitude,
A Closer Look At Body Wave Magnitude & Introduction To Moment Magnitude Previously we have learned the mechanics of calculating earthquake magnitudes with several magnitude scales: Duration Magnitude,
log 4 0.7m log m Seismic Analysis of Structures by TK Dutta, Civil Department, IIT Delhi, New Delhi. Module 1 Seismology Exercise Problems :
 Seismic Analysis of Structures by TK Dutta, Civil Department, IIT Delhi, New Delhi. Module Seismology Exercise Problems :.4. Estimate the probabilities of surface rupture length, rupture area and maximum
Seismic Analysis of Structures by TK Dutta, Civil Department, IIT Delhi, New Delhi. Module Seismology Exercise Problems :.4. Estimate the probabilities of surface rupture length, rupture area and maximum
Contents. I Basic Methods 13
 Preface xiii 1 Introduction 1 I Basic Methods 13 2 Convergent and Divergent Series 15 2.1 Introduction... 15 2.1.1 Power series: First steps... 15 2.1.2 Further practical aspects... 17 2.2 Differential
Preface xiii 1 Introduction 1 I Basic Methods 13 2 Convergent and Divergent Series 15 2.1 Introduction... 15 2.1.1 Power series: First steps... 15 2.1.2 Further practical aspects... 17 2.2 Differential
Earthquakes and How to Measure Them
 Earthquakes and How to Measure Them Earth Systems Georgia Performance Standards: SES2c. Relate certain geologic hazards to plate tectonic settings. Created by: Christy Dion Paulding County High School
Earthquakes and How to Measure Them Earth Systems Georgia Performance Standards: SES2c. Relate certain geologic hazards to plate tectonic settings. Created by: Christy Dion Paulding County High School
Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock
 Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock Bradford H. Hager Director, Earth Resources Laboratory and Cecil and Ida Green Professor Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
Integrating Lab and Numerical Experiments to Investigate Fractured Rock Bradford H. Hager Director, Earth Resources Laboratory and Cecil and Ida Green Professor Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
Tectonic Seismogenic Index of Geothermal Reservoirs
 Tectonic Seismogenic Index of Geothermal Reservoirs C. Dinske 1, F. Wenzel 2 and S.A. Shapiro 1 1 Freie Universität Berlin 2 KIT Karlsruhe November 27, 2012 Introduction M max reservoir location -2.0 Barnett
Tectonic Seismogenic Index of Geothermal Reservoirs C. Dinske 1, F. Wenzel 2 and S.A. Shapiro 1 1 Freie Universität Berlin 2 KIT Karlsruhe November 27, 2012 Introduction M max reservoir location -2.0 Barnett
A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing
 A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing Jiyang Ye, Mirko Van Der Baan (Email: jiyang1@ualberta.ca, Mirko.VanderBaan@ualberta.ca)
A review of friction laws and their application for simulation of microseismicity prior to hydraulic fracturing Jiyang Ye, Mirko Van Der Baan (Email: jiyang1@ualberta.ca, Mirko.VanderBaan@ualberta.ca)
Accelerating energy release prior to large events in simulated earthquake cycles: implications for earthquake forecasting
 Accelerating energy release prior to large events in simulated earthquake cycles: implications for earthquake forecasting Peter Mora and David Place QUAKES, Department of Earth Sciences, The University
Accelerating energy release prior to large events in simulated earthquake cycles: implications for earthquake forecasting Peter Mora and David Place QUAKES, Department of Earth Sciences, The University
Apparent Breaks in Scaling in the Earthquake Cumulative Frequency-Magnitude Distribution: Fact or Artifact?
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 90, 1, pp. 86 97, February 2000 Apparent Breaks in Scaling in the Earthquake Cumulative Frequency-Magnitude Distribution: Fact or Artifact? by Ian Main
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 90, 1, pp. 86 97, February 2000 Apparent Breaks in Scaling in the Earthquake Cumulative Frequency-Magnitude Distribution: Fact or Artifact? by Ian Main
ON A NESTED BOUNDARY-LAYER PROBLEM. X. Liang. R. Wong. Dedicated to Professor Philippe G. Ciarlet on the occasion of his 70th birthday
 COMMUNICATIONS ON doi:.3934/cpaa.9.8.49 PURE AND APPLIED ANALYSIS Volume 8, Number, January 9 pp. 49 433 ON A NESTED BOUNDARY-LAYER PROBLEM X. Liang Department of Mathematics, Massachusetts Institute of
COMMUNICATIONS ON doi:.3934/cpaa.9.8.49 PURE AND APPLIED ANALYSIS Volume 8, Number, January 9 pp. 49 433 ON A NESTED BOUNDARY-LAYER PROBLEM X. Liang Department of Mathematics, Massachusetts Institute of
PostScript file created: March 27, 2012; time 1137 minutes TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE: A SURPRISE? Yan Y. Kagan and David D. Jackson
 PostScript file created: March 27, 2012; time 1137 minutes TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE: A SURPRISE? Yan Y. Kagan and David D. Jackson Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles,
PostScript file created: March 27, 2012; time 1137 minutes TOHOKU EARTHQUAKE: A SURPRISE? Yan Y. Kagan and David D. Jackson Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles,
. D CR Nomenclature D 1
 . D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
. D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
KUMAMOTO EARTHQUAKE (review)
 1 平成 28 年熊本地震 KUMAMOTO EARTHQUAKE (review) Miroslav Hallo 1 ミロスラヴハロー 1 Charles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Czech Republic, チェコ Overview 2 Shallow earthquake sequence in central Kyushu
1 平成 28 年熊本地震 KUMAMOTO EARTHQUAKE (review) Miroslav Hallo 1 ミロスラヴハロー 1 Charles University, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Czech Republic, チェコ Overview 2 Shallow earthquake sequence in central Kyushu
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 18, 16 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Earthquake Magnitude and Moment Brune Stress Drop Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws Scaling and
Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Lecture 18, 16 Nov. 2017 www.geosc.psu.edu/courses/geosc508 Earthquake Magnitude and Moment Brune Stress Drop Seismic Spectra & Earthquake Scaling laws Scaling and
PostScript le created: August 6, 2006 time 839 minutes
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, PostScript le created: August 6, 2006 time 839 minutes Earthquake predictability measurement: information score and error diagram Yan Y. Kagan
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, PostScript le created: August 6, 2006 time 839 minutes Earthquake predictability measurement: information score and error diagram Yan Y. Kagan
On the W ± and Z 0 Masses
 On the W ± and Z Masses Kenneth Dalton e-mail: kxdalton@yahoo.com Abstract Scalar and vector fields are coupled in a gauge invariant manner, such as to form massive vector fields. In this, there is no
On the W ± and Z Masses Kenneth Dalton e-mail: kxdalton@yahoo.com Abstract Scalar and vector fields are coupled in a gauge invariant manner, such as to form massive vector fields. In this, there is no
Contribution of HPC to the mitigation of natural risks. B. Feignier. CEA-DAM Ile de France Département Analyse, Surveillance, Environnement
 Contribution of HPC to the mitigation of natural risks B. Feignier CEA-DAM Ile de France Département Analyse, Surveillance, Environnement Introduction Over the last 40 years, the increase in computational
Contribution of HPC to the mitigation of natural risks B. Feignier CEA-DAM Ile de France Département Analyse, Surveillance, Environnement Introduction Over the last 40 years, the increase in computational
Gutenberg-Richter Relationship: Magnitude vs. frequency of occurrence
 Quakes per year. Major = 7-7.9; Great = 8 or larger. Year Major quakes Great quakes 1969 15 1 1970 20 0 1971 19 1 1972 15 0 1973 13 0 1974 14 0 1975 14 1 1976 15 2 1977 11 2 1978 16 1 1979 13 0 1980 13
Quakes per year. Major = 7-7.9; Great = 8 or larger. Year Major quakes Great quakes 1969 15 1 1970 20 0 1971 19 1 1972 15 0 1973 13 0 1974 14 0 1975 14 1 1976 15 2 1977 11 2 1978 16 1 1979 13 0 1980 13
As usual, these notes are intended for use by class participants only, and are not for circulation. Week 6: Lectures 11, 12
 As usual, these notes are intended for use by class participants only, and are not for circulation Week 6: Lectures, The Dirac equation and algebra March 5, 0 The Lagrange density for the Dirac equation
As usual, these notes are intended for use by class participants only, and are not for circulation Week 6: Lectures, The Dirac equation and algebra March 5, 0 The Lagrange density for the Dirac equation
Scaling Relations for Seismic Cycles on Mid-Ocean Ridge
 Scaling Relations for Seismic Cycles on Mid-Ocean Ridge Transform Faults Margaret S. Boettcher University of New Hampshire, Dept. of Earth Sciences, Durham, NH 03824 Jeffrey J. McGuire Woods Hole Oceanographic
Scaling Relations for Seismic Cycles on Mid-Ocean Ridge Transform Faults Margaret S. Boettcher University of New Hampshire, Dept. of Earth Sciences, Durham, NH 03824 Jeffrey J. McGuire Woods Hole Oceanographic
Case Study 2: 2014 Iquique Sequence
 Case Study 2: 2014 Iquique Sequence Overview Mw 8.2 earthquake on 1 April 2014 at 11:08:43 UTC Pictures of damage Seismicity maps Foreshock seismicity -> Main shock -> Aftershock 1 April 2014 11:08:43
Case Study 2: 2014 Iquique Sequence Overview Mw 8.2 earthquake on 1 April 2014 at 11:08:43 UTC Pictures of damage Seismicity maps Foreshock seismicity -> Main shock -> Aftershock 1 April 2014 11:08:43
Continued Fractions for Special Functions: Handbook and Software
 Continued Fractions for Special Functions: Handbook and Software Team: A. Cuyt, V.B. Petersen, J. Van Deun, H. Waadeland, F. Backeljauw, S. Becuwe, M. Colman, W.B. Jones Universiteit Antwerpen Sør-Trøndelag
Continued Fractions for Special Functions: Handbook and Software Team: A. Cuyt, V.B. Petersen, J. Van Deun, H. Waadeland, F. Backeljauw, S. Becuwe, M. Colman, W.B. Jones Universiteit Antwerpen Sør-Trøndelag
Using information about wave amplitudes to learn about the earthquake size.
 Earthquake Magnitudes and Moments Using information about wave amplitudes to learn about the earthquake size. Need to correct for decrease with distance M = log(a/t) + F(h,Δ) + C A is the amplitude of
Earthquake Magnitudes and Moments Using information about wave amplitudes to learn about the earthquake size. Need to correct for decrease with distance M = log(a/t) + F(h,Δ) + C A is the amplitude of
Earthquakes and How to Measure Them
 Earthquakes and How to Measure Them Earth Systems Georgia Performance Standards: SES2c. Relate certain geologic hazards to plate tectonic settings. Created by: Christy Dion Paulding County High School
Earthquakes and How to Measure Them Earth Systems Georgia Performance Standards: SES2c. Relate certain geologic hazards to plate tectonic settings. Created by: Christy Dion Paulding County High School
Procedure for Probabilistic Tsunami Hazard Assessment for Incomplete and Uncertain Data
 Procedure for Probabilistic Tsunami Hazard Assessment for Incomplete and Uncertain Data A. Kijko (1), A. Smit (1), G.A. Papadopoulos (2), 1. University of Pretoria Natural Hazard Centre University of Pretoria,
Procedure for Probabilistic Tsunami Hazard Assessment for Incomplete and Uncertain Data A. Kijko (1), A. Smit (1), G.A. Papadopoulos (2), 1. University of Pretoria Natural Hazard Centre University of Pretoria,
Hybrid Back-Projection: Theory and Future Direction of Seismic Array Analysis
 Hybrid Back-Proection: Theory and Future Direction of Seismic Array Analysis YAGI Yui (Univ. of Tsukuba) Collaborators: FUKAHATA Yukitoshi (DPRI, Kyoto University) KASAHARA Amato, NAKAO Atsushi, EZAKI
Hybrid Back-Proection: Theory and Future Direction of Seismic Array Analysis YAGI Yui (Univ. of Tsukuba) Collaborators: FUKAHATA Yukitoshi (DPRI, Kyoto University) KASAHARA Amato, NAKAO Atsushi, EZAKI
of other regional earthquakes (e.g. Zoback and Zoback, 1980). I also want to find out
 4. Focal Mechanism Solutions A way to investigate source properties of the 2001 sequence is to attempt finding well-constrained focal mechanism solutions to determine if they are consistent with those
4. Focal Mechanism Solutions A way to investigate source properties of the 2001 sequence is to attempt finding well-constrained focal mechanism solutions to determine if they are consistent with those
Is there evidence of log-periodicities in the tail of the distribution of seismic moments?
 Is there evidence of log-periodicities in the tail of the distribution of seismic moments? Luísa Canto e Castro Sandra Dias CEAUL, Department of Statistics University of Lisbon, Portugal CEAUL, Department
Is there evidence of log-periodicities in the tail of the distribution of seismic moments? Luísa Canto e Castro Sandra Dias CEAUL, Department of Statistics University of Lisbon, Portugal CEAUL, Department
