CS Lecture 19. Exponential Families & Expectation Propagation
|
|
|
- Malcolm Paul Smith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS 6347 Lecture 19 Exponential Families & Expectation Propagation
2 Discrete State Spaces We have been focusing on the case of MRFs over discrete state spaces Probability distributions over discrete spaces correspond to vectors of probabilities for each element in the space such that the vector sums to one The partition function is simply a sum over all of the possible values for each variable Entropy of the distribution is nonnegative and is also computed by summing over the state space 2
3 Continuous State Spaces p x = 1 Z C ψ C xc For continuous state spaces, the partition function is now an integral The entropy becomes Z = න C ψ C xc dx H x = න p x log p(x) dx 3
4 Differential Entropy H x = න p x log p(x) dx This is called the differential entropy It is not always greater than or equal to zero Easy to construct such distributions: Let q x be the uniform distribution over the interval [a, b], what is the entropy of q(x)? 4
5 Differential Entropy H x = න p x log p(x) dx This is called the differential entropy It is not always greater than or equal to zero Easy to construct such distributions: Let q x be the uniform distribution over the interval [a, b], what is the entropy of q(x)? b 1 H q = න a b a log 1 b a dx = log(b a) 5
6 KL Divergence d(q p = න q x log q x p(x) dx The KL-divergence is still nonnegative, even though it contains the differential entropy This means that all of the observations that we made for finite state spaces will carry over to the continuous case The EM algorithm, mean-field methods, etc. Most importantly log Z H q + න q C x C log ψ C x C dx C C 6
7 Continuous State Spaces Examples of probability distributions over continuous state spaces The uniform distribution over the interval [a, b] q x = 1 x a,b b a The multivariate normal distribution with mean μ and covariance matrix Σ q x = 1 2π k det(σ) exp 1 2 x μ T Σ 1 (x μ) 7
8 Continuous State Spaces What makes continuous distributions so difficult to deal with? They may not be compactly representable Families of continuous distributions need not be closed under marginalization The marginal distributions of multivariate normal distributions are (multivariate) normal distributions Integration problems of interest (e.g., the partition function or marginal distributions) may not have closed form solutions Integrals may also not exist! 8
9 The Exponential Family p x θ = h x exp θ, φ(x) log Z(θ) A distribution is a member of the exponential family if its probability density function can be expressed as above for some choice of parameters θ and potential functions φ(x) We are only interested in models for which Z(θ) is finite The family of log-linear models that we have been focusing on in the discrete case belong to the exponential family 9
10 The Exponential Family p x θ = h x exp θ, φ(x) log Z(θ) As in the discrete case, there is not necessarily a unique way to express a distribution in this form We say that the representation is minimal if there does not exist a vector a 0 such that a, φ(x) = constant In this case, there is a unique parameter vector associated with each member of the family The φ are called sufficient statistics for the distribution 10
11 The Multivariate Normal q x μ, Σ = 1 Z exp 1 2 x μ T Σ 1 x μ The multivariate normal distribution is a member of the exponential family q x θ = 1 Z(θ) exp i θ i x i + θ ij x i x j The mean and the covariance matrix (must be positive semidefinite) are sufficient statistics of the multivariate normal distribution i j 11
12 The Exponential Family Many of the discrete distributions that you have seen before are members of the exponential family Binomial, Poisson, Bernoulli, Gamma, Beta, Laplace, Categorical, etc. The exponential family, while not the most general parametric family, is one of the easiest to work with and captures a variety of different distributions 12
13 Continuous Bethe Approximation Recall that, from the nonnegativity of the KL-divergence log Z H q + න q C x C log ψ C x C dx C for any probability distribution q C We can make the same approximations that we did in the discrete case to approximate Z(θ) in the continuous case 13
14 Continuous Bethe Approximation max τ T H B τ + C න τ C x C log ψ c x c dx C where τ C (x C ) H B τ = න τ i x i log τ i (x i ) dx i න τ C x C log ς i C τ i x i i V and T is a vector of locally consistent marginals C dx C This approximation is exact on trees 14
15 Continuous Belief Propagation p x = 1 Z i V φ i (x i ) i,j E ψ ij (x i, x j ) The messages passed by belief propagation are m ij x j න φ i x i ψ ij x i, x j k N i j m ki (x i ) dx i Depending on the functional form of the potential functions, the message update may not have a closed form solution We can t necessarily compute the correct marginal distributions/partition function even in the case of a tree! 15
16 Gaussian Belief Propagation When p(x) is a multivariate normal distribution, the message updates can be computed in closed form In this case, max-product and sum-product are equivalent Note that computing the mode of a multivariate normal is equivalent to solving a linear system of equations Called Gaussian belief propagation or GaBP Does not converge for all multivariate normal The messages can have a non-positive definite inverse covariance matrix 16
17 Properties of Exponential Families Exponential families are Closed under multiplication Not closed under marginalization Easy to get mixtures of Gaussians when a model has both discrete and continuous variables Let p(x, y) be such that x R n and y {1,, k} such that p(x y) is normally distributed and p y is multinomially distributed p(x) is then a Gaussian mixture (mixtures of exponential family distributions are not generally in the exponential family) 17
18 Properties of Exponential Families Derivatives of the log-partition function correspond to expectations of the sufficient statistics So do second derivatives 2 θ k θ l log Z θ = θ log Z(θ) = න p x θ φ(x)dx න p x θ φ x k φ x l dx න p x θ φ x k dx න p x θ φ x l dx 18
19 KL-Divergence and Exponential Families Minimizing KL divergence is equivalent to moment matching Let q x θ = h x exp θ, φ(x) log Z(θ) and let p(x) be an arbitrary distribution d(p q = න p(x) log p(x) q(x θ) dx This KL divergence is minimized (as a function of θ) when න p x φ x k dx = න q x θ φ x k dx 19
20 Expectation Propagation Key idea: given p x = 1 Z ς C ψ C (x C ) approximate it by a simpler distribution p x p x = 1 Z ς C ψ C (x C ) We could just replace each factor with a member of some exponential family that best describes it, but this can result in a poor approximation unless each ψ C is essentially a member of the exponential family already Instead, we construct the approximating distribution by performing a series of optimizations 20
21 Expectation Propagation Initialize the approximate distribution p x = 1 Z ς C ψ C (x C ) so that each ψ C (x C ) is a member of some exponential family Repeat until convergence For each C Let p C x = p x ψ C x C Set q = argmin q d( p \C ψ C q) where the minimization is over all exponential families q of the chosen form Set ψ C x C = q x p \C (x) 21
22 Expectation Propagation This is one approach used to handle continuous distributions in practice Other methods include discretization/sampling methods that approximate BP messages and then sample to compute the message updates Nonparametric BP Particle BP Stochastic BP 22
13: Variational inference II
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 13: Variational inference II Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Ronghuo Zheng, Zhiting Hu, Yuntian Deng 1 Introduction We started to talk about variational
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 13: Variational inference II Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Ronghuo Zheng, Zhiting Hu, Yuntian Deng 1 Introduction We started to talk about variational
Probabilistic Graphical Models. Theory of Variational Inference: Inner and Outer Approximation. Lecture 15, March 4, 2013
 School of Computer Science Probabilistic Graphical Models Theory of Variational Inference: Inner and Outer Approximation Junming Yin Lecture 15, March 4, 2013 Reading: W & J Book Chapters 1 Roadmap Two
School of Computer Science Probabilistic Graphical Models Theory of Variational Inference: Inner and Outer Approximation Junming Yin Lecture 15, March 4, 2013 Reading: W & J Book Chapters 1 Roadmap Two
14 : Theory of Variational Inference: Inner and Outer Approximation
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2017 14 : Theory of Variational Inference: Inner and Outer Approximation Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Maria Ryskina, Yen-Chia Hsu 1 Introduction
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2017 14 : Theory of Variational Inference: Inner and Outer Approximation Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Maria Ryskina, Yen-Chia Hsu 1 Introduction
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 Probabilistic Graphical Models Brown University CSCI 2950-P, Spring 2013 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 12: Gaussian Belief Propagation, State Space Models and Kalman Filters Guest Kalman Filter Lecture by
Probabilistic Graphical Models Brown University CSCI 2950-P, Spring 2013 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 12: Gaussian Belief Propagation, State Space Models and Kalman Filters Guest Kalman Filter Lecture by
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 School of Computer Science Probabilistic Graphical Models Variational Inference II: Mean Field Method and Variational Principle Junming Yin Lecture 15, March 7, 2012 X 1 X 1 X 1 X 1 X 2 X 3 X 2 X 2 X 3
School of Computer Science Probabilistic Graphical Models Variational Inference II: Mean Field Method and Variational Principle Junming Yin Lecture 15, March 7, 2012 X 1 X 1 X 1 X 1 X 2 X 3 X 2 X 2 X 3
Chapter 5 continued. Chapter 5 sections
 Chapter 5 sections Discrete univariate distributions: 5.2 Bernoulli and Binomial distributions Just skim 5.3 Hypergeometric distributions 5.4 Poisson distributions Just skim 5.5 Negative Binomial distributions
Chapter 5 sections Discrete univariate distributions: 5.2 Bernoulli and Binomial distributions Just skim 5.3 Hypergeometric distributions 5.4 Poisson distributions Just skim 5.5 Negative Binomial distributions
Expectation Propagation Algorithm
 Expectation Propagation Algorithm 1 Shuang Wang School of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Oklahoma, Tulsa, OK, 74135 Email: {shuangwang}@ou.edu This note contains three parts. First,
Expectation Propagation Algorithm 1 Shuang Wang School of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Oklahoma, Tulsa, OK, 74135 Email: {shuangwang}@ou.edu This note contains three parts. First,
ST5215: Advanced Statistical Theory
 Department of Statistics & Applied Probability Monday, September 26, 2011 Lecture 10: Exponential families and Sufficient statistics Exponential Families Exponential families are important parametric families
Department of Statistics & Applied Probability Monday, September 26, 2011 Lecture 10: Exponential families and Sufficient statistics Exponential Families Exponential families are important parametric families
Information Geometric view of Belief Propagation
 Information Geometric view of Belief Propagation Yunshu Liu 2013-10-17 References: [1]. Shiro Ikeda, Toshiyuki Tanaka and Shun-ichi Amari, Stochastic reasoning, Free energy and Information Geometry, Neural
Information Geometric view of Belief Propagation Yunshu Liu 2013-10-17 References: [1]. Shiro Ikeda, Toshiyuki Tanaka and Shun-ichi Amari, Stochastic reasoning, Free energy and Information Geometry, Neural
14 : Theory of Variational Inference: Inner and Outer Approximation
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 14 : Theory of Variational Inference: Inner and Outer Approximation Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Yu-Hsin Kuo, Amos Ng 1 Introduction Last lecture
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 14 : Theory of Variational Inference: Inner and Outer Approximation Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Yu-Hsin Kuo, Amos Ng 1 Introduction Last lecture
Structured Variational Inference
 Structured Variational Inference Sargur srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics 1. Structured Variational Approximations 1. The Mean Field Approximation 1. The Mean Field Energy 2. Maximizing the energy functional:
Structured Variational Inference Sargur srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics 1. Structured Variational Approximations 1. The Mean Field Approximation 1. The Mean Field Energy 2. Maximizing the energy functional:
Probabilistic and Bayesian Machine Learning
 Probabilistic and Bayesian Machine Learning Day 4: Expectation and Belief Propagation Yee Whye Teh ywteh@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit University College London http://www.gatsby.ucl.ac.uk/
Probabilistic and Bayesian Machine Learning Day 4: Expectation and Belief Propagation Yee Whye Teh ywteh@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit University College London http://www.gatsby.ucl.ac.uk/
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 School of Computer Science Probabilistic Graphical Models Variational Inference IV: Variational Principle II Junming Yin Lecture 17, March 21, 2012 X 1 X 1 X 1 X 1 X 2 X 3 X 2 X 2 X 3 X 3 Reading: X 4
School of Computer Science Probabilistic Graphical Models Variational Inference IV: Variational Principle II Junming Yin Lecture 17, March 21, 2012 X 1 X 1 X 1 X 1 X 2 X 3 X 2 X 2 X 3 X 3 Reading: X 4
13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation and Mean Field
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2012 13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation and Mean Field Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Peter Schulam and William Wang 1 Introduction
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2012 13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation and Mean Field Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Peter Schulam and William Wang 1 Introduction
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 11 CRFs, Exponential Family CS/CNS/EE 155 Andreas Krause Announcements Homework 2 due today Project milestones due next Monday (Nov 9) About half the work should
Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 11 CRFs, Exponential Family CS/CNS/EE 155 Andreas Krause Announcements Homework 2 due today Project milestones due next Monday (Nov 9) About half the work should
Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning
 Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning CS 584: Big Data Analytics Material adapted from Radford Neal s tutorial (http://ftp.cs.utoronto.ca/pub/radford/bayes-tut.pdf), Zoubin Ghahramni (http://hunch.net/~coms-4771/zoubin_ghahramani_bayesian_learning.pdf),
Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning CS 584: Big Data Analytics Material adapted from Radford Neal s tutorial (http://ftp.cs.utoronto.ca/pub/radford/bayes-tut.pdf), Zoubin Ghahramni (http://hunch.net/~coms-4771/zoubin_ghahramani_bayesian_learning.pdf),
Bayesian Machine Learning - Lecture 7
 Bayesian Machine Learning - Lecture 7 Guido Sanguinetti Institute for Adaptive and Neural Computation School of Informatics University of Edinburgh gsanguin@inf.ed.ac.uk March 4, 2015 Today s lecture 1
Bayesian Machine Learning - Lecture 7 Guido Sanguinetti Institute for Adaptive and Neural Computation School of Informatics University of Edinburgh gsanguin@inf.ed.ac.uk March 4, 2015 Today s lecture 1
Probabilistic Graphical Models for Image Analysis - Lecture 4
 Probabilistic Graphical Models for Image Analysis - Lecture 4 Stefan Bauer 12 October 2018 Max Planck ETH Center for Learning Systems Overview 1. Repetition 2. α-divergence 3. Variational Inference 4.
Probabilistic Graphical Models for Image Analysis - Lecture 4 Stefan Bauer 12 October 2018 Max Planck ETH Center for Learning Systems Overview 1. Repetition 2. α-divergence 3. Variational Inference 4.
Expectation Propagation in Factor Graphs: A Tutorial
 DRAFT: Version 0.1, 28 October 2005. Do not distribute. Expectation Propagation in Factor Graphs: A Tutorial Charles Sutton October 28, 2005 Abstract Expectation propagation is an important variational
DRAFT: Version 0.1, 28 October 2005. Do not distribute. Expectation Propagation in Factor Graphs: A Tutorial Charles Sutton October 28, 2005 Abstract Expectation propagation is an important variational
CS Lecture 13. More Maximum Likelihood
 CS 6347 Lecture 13 More Maxiu Likelihood Recap Last tie: Introduction to axiu likelihood estiation MLE for Bayesian networks Optial CPTs correspond to epirical counts Today: MLE for CRFs 2 Maxiu Likelihood
CS 6347 Lecture 13 More Maxiu Likelihood Recap Last tie: Introduction to axiu likelihood estiation MLE for Bayesian networks Optial CPTs correspond to epirical counts Today: MLE for CRFs 2 Maxiu Likelihood
Machine learning - HT Maximum Likelihood
 Machine learning - HT 2016 3. Maximum Likelihood Varun Kanade University of Oxford January 27, 2016 Outline Probabilistic Framework Formulate linear regression in the language of probability Introduce
Machine learning - HT 2016 3. Maximum Likelihood Varun Kanade University of Oxford January 27, 2016 Outline Probabilistic Framework Formulate linear regression in the language of probability Introduce
Lecture 13 : Variational Inference: Mean Field Approximation
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2017 Lecture 13 : Variational Inference: Mean Field Approximation Lecturer: Willie Neiswanger Scribes: Xupeng Tong, Minxing Liu 1 Problem Setup 1.1
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2017 Lecture 13 : Variational Inference: Mean Field Approximation Lecturer: Willie Neiswanger Scribes: Xupeng Tong, Minxing Liu 1 Problem Setup 1.1
17 Variational Inference
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.438 Algorithms for Inference Fall 2014 17 Variational Inference Prompted by loopy graphs for which exact
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.438 Algorithms for Inference Fall 2014 17 Variational Inference Prompted by loopy graphs for which exact
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 7 Approximate
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 7 Approximate
Chapter 5. Chapter 5 sections
 1 / 43 sections Discrete univariate distributions: 5.2 Bernoulli and Binomial distributions Just skim 5.3 Hypergeometric distributions 5.4 Poisson distributions Just skim 5.5 Negative Binomial distributions
1 / 43 sections Discrete univariate distributions: 5.2 Bernoulli and Binomial distributions Just skim 5.3 Hypergeometric distributions 5.4 Poisson distributions Just skim 5.5 Negative Binomial distributions
Junction Tree, BP and Variational Methods
 Junction Tree, BP and Variational Methods Adrian Weller MLSALT4 Lecture Feb 21, 2018 With thanks to David Sontag (MIT) and Tony Jebara (Columbia) for use of many slides and illustrations For more information,
Junction Tree, BP and Variational Methods Adrian Weller MLSALT4 Lecture Feb 21, 2018 With thanks to David Sontag (MIT) and Tony Jebara (Columbia) for use of many slides and illustrations For more information,
Bayesian Learning. HT2015: SC4 Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning. Maximum Likelihood Principle. The Bayesian Learning Framework
 HT5: SC4 Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning Dino Sejdinovic Department of Statistics Oxford http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~sejdinov/sdmml.html Maximum Likelihood Principle A generative model for
HT5: SC4 Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning Dino Sejdinovic Department of Statistics Oxford http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~sejdinov/sdmml.html Maximum Likelihood Principle A generative model for
EE/Stats 376A: Homework 7 Solutions Due on Friday March 17, 5 pm
 EE/Stats 376A: Homework 7 Solutions Due on Friday March 17, 5 pm 1. Feedback does not increase the capacity. Consider a channel with feedback. We assume that all the recieved outputs are sent back immediately
EE/Stats 376A: Homework 7 Solutions Due on Friday March 17, 5 pm 1. Feedback does not increase the capacity. Consider a channel with feedback. We assume that all the recieved outputs are sent back immediately
Lecture 6: Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM)
 Helsinki Institute for Information Technology Lecture 6: Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM) Pedram Daee 3.11.2015 Outline Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM) Models Model families and parameters Parameter learning
Helsinki Institute for Information Technology Lecture 6: Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM) Pedram Daee 3.11.2015 Outline Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM) Models Model families and parameters Parameter learning
Variational Inference (11/04/13)
 STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Variational Inference (11/04/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: Matt Dickenson, Alireza Samany, Tracy Schifeling 1 Introduction In this lecture we will further
STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Variational Inference (11/04/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: Matt Dickenson, Alireza Samany, Tracy Schifeling 1 Introduction In this lecture we will further
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Parametric Distributions Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation: or? Recall Curve Fitting Binary Variables
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Parametric Distributions Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation: or? Recall Curve Fitting Binary Variables
Parametric Inference Maximum Likelihood Inference Exponential Families Expectation Maximization (EM) Bayesian Inference Statistical Decison Theory
 Statistical Inference Parametric Inference Maximum Likelihood Inference Exponential Families Expectation Maximization (EM) Bayesian Inference Statistical Decison Theory IP, José Bioucas Dias, IST, 2007
Statistical Inference Parametric Inference Maximum Likelihood Inference Exponential Families Expectation Maximization (EM) Bayesian Inference Statistical Decison Theory IP, José Bioucas Dias, IST, 2007
PMR Learning as Inference
 Outline PMR Learning as Inference Probabilistic Modelling and Reasoning Amos Storkey Modelling 2 The Exponential Family 3 Bayesian Sets School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh Amos Storkey PMR Learning
Outline PMR Learning as Inference Probabilistic Modelling and Reasoning Amos Storkey Modelling 2 The Exponential Family 3 Bayesian Sets School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh Amos Storkey PMR Learning
Inference and Representation
 Inference and Representation David Sontag New York University Lecture 5, Sept. 30, 2014 David Sontag (NYU) Inference and Representation Lecture 5, Sept. 30, 2014 1 / 16 Today s lecture 1 Running-time of
Inference and Representation David Sontag New York University Lecture 5, Sept. 30, 2014 David Sontag (NYU) Inference and Representation Lecture 5, Sept. 30, 2014 1 / 16 Today s lecture 1 Running-time of
LECTURE 11: EXPONENTIAL FAMILY AND GENERALIZED LINEAR MODELS
 LECTURE : EXPONENTIAL FAMILY AND GENERALIZED LINEAR MODELS HANI GOODARZI AND SINA JAFARPOUR. EXPONENTIAL FAMILY. Exponential family comprises a set of flexible distribution ranging both continuous and
LECTURE : EXPONENTIAL FAMILY AND GENERALIZED LINEAR MODELS HANI GOODARZI AND SINA JAFARPOUR. EXPONENTIAL FAMILY. Exponential family comprises a set of flexible distribution ranging both continuous and
Graphical Models and Kernel Methods
 Graphical Models and Kernel Methods Jerry Zhu Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison, USA MLSS June 17, 2014 1 / 123 Outline Graphical Models Probabilistic Inference Directed vs.
Graphical Models and Kernel Methods Jerry Zhu Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison, USA MLSS June 17, 2014 1 / 123 Outline Graphical Models Probabilistic Inference Directed vs.
Unsupervised Learning
 Unsupervised Learning Bayesian Model Comparison Zoubin Ghahramani zoubin@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit, and MSc in Intelligent Systems, Dept Computer Science University College
Unsupervised Learning Bayesian Model Comparison Zoubin Ghahramani zoubin@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit, and MSc in Intelligent Systems, Dept Computer Science University College
Probability Distributions
 Probability Distributions Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science Pohang University of Science and Technology, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr 1 / 25 Outline Summarize the main properties of some of
Probability Distributions Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science Pohang University of Science and Technology, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr 1 / 25 Outline Summarize the main properties of some of
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 School of Computer Science Probabilistic Graphical Models Variational Inference III: Variational Principle I Junming Yin Lecture 16, March 19, 2012 X 1 X 1 X 1 X 1 X 2 X 3 X 2 X 2 X 3 X 3 Reading: X 4
School of Computer Science Probabilistic Graphical Models Variational Inference III: Variational Principle I Junming Yin Lecture 16, March 19, 2012 X 1 X 1 X 1 X 1 X 2 X 3 X 2 X 2 X 3 X 3 Reading: X 4
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning Introduction to Probabilistic Methods Varun Chandola Computer Science & Engineering State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA chandola@buffalo.edu Chandola@UB
Introduction to Machine Learning Introduction to Probabilistic Methods Varun Chandola Computer Science & Engineering State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA chandola@buffalo.edu Chandola@UB
Minimizing D(Q,P) def = Q(h)
 Inference Lecture 20: Variational Metods Kevin Murpy 29 November 2004 Inference means computing P( i v), were are te idden variables v are te visible variables. For discrete (eg binary) idden nodes, exact
Inference Lecture 20: Variational Metods Kevin Murpy 29 November 2004 Inference means computing P( i v), were are te idden variables v are te visible variables. For discrete (eg binary) idden nodes, exact
13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Rajarshi Das, Zhengzhong Liu, Dishan Gupta 1 Introduction
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Rajarshi Das, Zhengzhong Liu, Dishan Gupta 1 Introduction
Stat 521A Lecture 18 1
 Stat 521A Lecture 18 1 Outline Cts and discrete variables (14.1) Gaussian networks (14.2) Conditional Gaussian networks (14.3) Non-linear Gaussian networks (14.4) Sampling (14.5) 2 Hybrid networks A hybrid
Stat 521A Lecture 18 1 Outline Cts and discrete variables (14.1) Gaussian networks (14.2) Conditional Gaussian networks (14.3) Non-linear Gaussian networks (14.4) Sampling (14.5) 2 Hybrid networks A hybrid
Lecture 9: PGM Learning
 13 Oct 2014 Intro. to Stats. Machine Learning COMP SCI 4401/7401 Table of Contents I Learning parameters in MRFs 1 Learning parameters in MRFs Inference and Learning Given parameters (of potentials) and
13 Oct 2014 Intro. to Stats. Machine Learning COMP SCI 4401/7401 Table of Contents I Learning parameters in MRFs 1 Learning parameters in MRFs Inference and Learning Given parameters (of potentials) and
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 Probabilistic Graphical Models Brown University CSCI 295-P, Spring 213 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 11: Inference & Learning Overview, Gaussian Graphical Models Some figures courtesy Michael Jordan s draft
Probabilistic Graphical Models Brown University CSCI 295-P, Spring 213 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 11: Inference & Learning Overview, Gaussian Graphical Models Some figures courtesy Michael Jordan s draft
Introduction to Machine Learning
 What does this mean? Outline Contents Introduction to Machine Learning Introduction to Probabilistic Methods Varun Chandola December 26, 2017 1 Introduction to Probability 1 2 Random Variables 3 3 Bayes
What does this mean? Outline Contents Introduction to Machine Learning Introduction to Probabilistic Methods Varun Chandola December 26, 2017 1 Introduction to Probability 1 2 Random Variables 3 3 Bayes
Probability and Estimation. Alan Moses
 Probability and Estimation Alan Moses Random variables and probability A random variable is like a variable in algebra (e.g., y=e x ), but where at least part of the variability is taken to be stochastic.
Probability and Estimation Alan Moses Random variables and probability A random variable is like a variable in algebra (e.g., y=e x ), but where at least part of the variability is taken to be stochastic.
Discrete Markov Random Fields the Inference story. Pradeep Ravikumar
 Discrete Markov Random Fields the Inference story Pradeep Ravikumar Graphical Models, The History How to model stochastic processes of the world? I want to model the world, and I like graphs... 2 Mid to
Discrete Markov Random Fields the Inference story Pradeep Ravikumar Graphical Models, The History How to model stochastic processes of the world? I want to model the world, and I like graphs... 2 Mid to
Classical and Bayesian inference
 Classical and Bayesian inference AMS 132 January 18, 2018 Claudia Wehrhahn (UCSC) Classical and Bayesian inference January 18, 2018 1 / 9 Sampling from a Bernoulli Distribution Theorem (Beta-Bernoulli
Classical and Bayesian inference AMS 132 January 18, 2018 Claudia Wehrhahn (UCSC) Classical and Bayesian inference January 18, 2018 1 / 9 Sampling from a Bernoulli Distribution Theorem (Beta-Bernoulli
1 Bayesian Linear Regression (BLR)
 Statistical Techniques in Robotics (STR, S15) Lecture#10 (Wednesday, February 11) Lecturer: Byron Boots Gaussian Properties, Bayesian Linear Regression 1 Bayesian Linear Regression (BLR) In linear regression,
Statistical Techniques in Robotics (STR, S15) Lecture#10 (Wednesday, February 11) Lecturer: Byron Boots Gaussian Properties, Bayesian Linear Regression 1 Bayesian Linear Regression (BLR) In linear regression,
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 9: Variational Inference Relaxations Volkan Cevher, Matthias Seeger Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne 24/10/2011 (EPFL) Graphical Models 24/10/2011 1 / 15
Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 9: Variational Inference Relaxations Volkan Cevher, Matthias Seeger Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne 24/10/2011 (EPFL) Graphical Models 24/10/2011 1 / 15
Advanced Machine Learning & Perception
 Advanced Machine Learning & Perception Instructor: Tony Jebara Topic 6 Standard Kernels Unusual Input Spaces for Kernels String Kernels Probabilistic Kernels Fisher Kernels Probability Product Kernels
Advanced Machine Learning & Perception Instructor: Tony Jebara Topic 6 Standard Kernels Unusual Input Spaces for Kernels String Kernels Probabilistic Kernels Fisher Kernels Probability Product Kernels
Latent Variable Models and EM algorithm
 Latent Variable Models and EM algorithm SC4/SM4 Data Mining and Machine Learning, Hilary Term 2017 Dino Sejdinovic 3.1 Clustering and Mixture Modelling K-means and hierarchical clustering are non-probabilistic
Latent Variable Models and EM algorithm SC4/SM4 Data Mining and Machine Learning, Hilary Term 2017 Dino Sejdinovic 3.1 Clustering and Mixture Modelling K-means and hierarchical clustering are non-probabilistic
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning Brown University CSCI 1950-F, Spring 2012 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 20: Expectation Maximization Algorithm EM for Mixture Models Many figures courtesy Kevin Murphy s
Introduction to Machine Learning Brown University CSCI 1950-F, Spring 2012 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 20: Expectation Maximization Algorithm EM for Mixture Models Many figures courtesy Kevin Murphy s
Expectation propagation for symbol detection in large-scale MIMO communications
 Expectation propagation for symbol detection in large-scale MIMO communications Pablo M. Olmos olmos@tsc.uc3m.es Joint work with Javier Céspedes (UC3M) Matilde Sánchez-Fernández (UC3M) and Fernando Pérez-Cruz
Expectation propagation for symbol detection in large-scale MIMO communications Pablo M. Olmos olmos@tsc.uc3m.es Joint work with Javier Céspedes (UC3M) Matilde Sánchez-Fernández (UC3M) and Fernando Pérez-Cruz
14 : Mean Field Assumption
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2018 14 : Mean Field Assumption Lecturer: Kayhan Batmanghelich Scribes: Yao-Hung Hubert Tsai 1 Inferential Problems Can be categorized into three aspects:
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2018 14 : Mean Field Assumption Lecturer: Kayhan Batmanghelich Scribes: Yao-Hung Hubert Tsai 1 Inferential Problems Can be categorized into three aspects:
Gaussian processes. Chuong B. Do (updated by Honglak Lee) November 22, 2008
 Gaussian processes Chuong B Do (updated by Honglak Lee) November 22, 2008 Many of the classical machine learning algorithms that we talked about during the first half of this course fit the following pattern:
Gaussian processes Chuong B Do (updated by Honglak Lee) November 22, 2008 Many of the classical machine learning algorithms that we talked about during the first half of this course fit the following pattern:
CS 591, Lecture 2 Data Analytics: Theory and Applications Boston University
 CS 591, Lecture 2 Data Analytics: Theory and Applications Boston University Charalampos E. Tsourakakis January 25rd, 2017 Probability Theory The theory of probability is a system for making better guesses.
CS 591, Lecture 2 Data Analytics: Theory and Applications Boston University Charalampos E. Tsourakakis January 25rd, 2017 Probability Theory The theory of probability is a system for making better guesses.
Information geometry for bivariate distribution control
 Information geometry for bivariate distribution control C.T.J.Dodson + Hong Wang Mathematics + Control Systems Centre, University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology Optimal control of stochastic
Information geometry for bivariate distribution control C.T.J.Dodson + Hong Wang Mathematics + Control Systems Centre, University of Manchester Institute of Science and Technology Optimal control of stochastic
Stat 5101 Lecture Notes
 Stat 5101 Lecture Notes Charles J. Geyer Copyright 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001 by Charles J. Geyer May 7, 2001 ii Stat 5101 (Geyer) Course Notes Contents 1 Random Variables and Change of Variables 1 1.1 Random
Stat 5101 Lecture Notes Charles J. Geyer Copyright 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001 by Charles J. Geyer May 7, 2001 ii Stat 5101 (Geyer) Course Notes Contents 1 Random Variables and Change of Variables 1 1.1 Random
Exponential Family and Maximum Likelihood, Gaussian Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm. by Korbinian Schwinger
 Exponential Family and Maximum Likelihood, Gaussian Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm by Korbinian Schwinger Overview Exponential Family Maximum Likelihood The EM Algorithm Gaussian Mixture Models Exponential
Exponential Family and Maximum Likelihood, Gaussian Mixture Models and the EM Algorithm by Korbinian Schwinger Overview Exponential Family Maximum Likelihood The EM Algorithm Gaussian Mixture Models Exponential
CMPE 58K Bayesian Statistics and Machine Learning Lecture 5
 CMPE 58K Bayesian Statistics and Machine Learning Lecture 5 Multivariate distributions: Gaussian, Bernoulli, Probability tables Department of Computer Engineering, Boğaziçi University, Istanbul, Turkey
CMPE 58K Bayesian Statistics and Machine Learning Lecture 5 Multivariate distributions: Gaussian, Bernoulli, Probability tables Department of Computer Engineering, Boğaziçi University, Istanbul, Turkey
Introduction to graphical models: Lecture III
 Introduction to graphical models: Lecture III Martin Wainwright UC Berkeley Departments of Statistics, and EECS Martin Wainwright (UC Berkeley) Some introductory lectures January 2013 1 / 25 Introduction
Introduction to graphical models: Lecture III Martin Wainwright UC Berkeley Departments of Statistics, and EECS Martin Wainwright (UC Berkeley) Some introductory lectures January 2013 1 / 25 Introduction
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Bishop Chapter 2: Probability Distributions
 Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Chapter 2: Probability Distributions Cécile Amblard Alex Kläser Jakob Verbeek October 11, 27 Probability Distributions: General Density Estimation: given a finite
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Chapter 2: Probability Distributions Cécile Amblard Alex Kläser Jakob Verbeek October 11, 27 Probability Distributions: General Density Estimation: given a finite
Part 1: Expectation Propagation
 Chalmers Machine Learning Summer School Approximate message passing and biomedicine Part 1: Expectation Propagation Tom Heskes Machine Learning Group, Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Radboud
Chalmers Machine Learning Summer School Approximate message passing and biomedicine Part 1: Expectation Propagation Tom Heskes Machine Learning Group, Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Radboud
12 : Variational Inference I
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 12 : Variational Inference I Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Fattaneh Jabbari, Eric Lei, Evan Shapiro 1 Introduction Probabilistic inference is one of
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 12 : Variational Inference I Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Fattaneh Jabbari, Eric Lei, Evan Shapiro 1 Introduction Probabilistic inference is one of
Quantitative Biology II Lecture 4: Variational Methods
 10 th March 2015 Quantitative Biology II Lecture 4: Variational Methods Gurinder Singh Mickey Atwal Center for Quantitative Biology Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Image credit: Mike West Summary Approximate
10 th March 2015 Quantitative Biology II Lecture 4: Variational Methods Gurinder Singh Mickey Atwal Center for Quantitative Biology Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Image credit: Mike West Summary Approximate
Recitation 9: Loopy BP
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.438 Algorithms For Inference Fall 204 Recitation 9: Loopy BP General Comments. In terms of implementation,
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.438 Algorithms For Inference Fall 204 Recitation 9: Loopy BP General Comments. In terms of implementation,
CS839: Probabilistic Graphical Models. Lecture 7: Learning Fully Observed BNs. Theo Rekatsinas
 CS839: Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 7: Learning Fully Observed BNs Theo Rekatsinas 1 Exponential family: a basic building block For a numeric random variable X p(x ) =h(x)exp T T (x) A( ) = 1
CS839: Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 7: Learning Fully Observed BNs Theo Rekatsinas 1 Exponential family: a basic building block For a numeric random variable X p(x ) =h(x)exp T T (x) A( ) = 1
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 11 Project
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 11 Project
Lecture 18 Generalized Belief Propagation and Free Energy Approximations
 Lecture 18, Generalized Belief Propagation and Free Energy Approximations 1 Lecture 18 Generalized Belief Propagation and Free Energy Approximations In this lecture we talked about graphical models and
Lecture 18, Generalized Belief Propagation and Free Energy Approximations 1 Lecture 18 Generalized Belief Propagation and Free Energy Approximations In this lecture we talked about graphical models and
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS. J. Elder CSE 6390/PSYC 6225 Computational Modeling of Visual Perception
 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Credits 2 These slides were sourced and/or modified from: Christopher Bishop, Microsoft UK Parametric Distributions 3 Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation:
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Credits 2 These slides were sourced and/or modified from: Christopher Bishop, Microsoft UK Parametric Distributions 3 Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation:
Foundations of Nonparametric Bayesian Methods
 1 / 27 Foundations of Nonparametric Bayesian Methods Part II: Models on the Simplex Peter Orbanz http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/porbanz/npb-tutorial.html 2 / 27 Tutorial Overview Part I: Basics Part II: Models
1 / 27 Foundations of Nonparametric Bayesian Methods Part II: Models on the Simplex Peter Orbanz http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/porbanz/npb-tutorial.html 2 / 27 Tutorial Overview Part I: Basics Part II: Models
5. Conditional Distributions
 1 of 12 7/16/2009 5:36 AM Virtual Laboratories > 3. Distributions > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 5. Conditional Distributions Basic Theory As usual, we start with a random experiment with probability measure P on an
1 of 12 7/16/2009 5:36 AM Virtual Laboratories > 3. Distributions > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 5. Conditional Distributions Basic Theory As usual, we start with a random experiment with probability measure P on an
Variational Scoring of Graphical Model Structures
 Variational Scoring of Graphical Model Structures Matthew J. Beal Work with Zoubin Ghahramani & Carl Rasmussen, Toronto. 15th September 2003 Overview Bayesian model selection Approximations using Variational
Variational Scoring of Graphical Model Structures Matthew J. Beal Work with Zoubin Ghahramani & Carl Rasmussen, Toronto. 15th September 2003 Overview Bayesian model selection Approximations using Variational
NPFL108 Bayesian inference. Introduction. Filip Jurčíček. Institute of Formal and Applied Linguistics Charles University in Prague Czech Republic
 NPFL108 Bayesian inference Introduction Filip Jurčíček Institute of Formal and Applied Linguistics Charles University in Prague Czech Republic Home page: http://ufal.mff.cuni.cz/~jurcicek Version: 21/02/2014
NPFL108 Bayesian inference Introduction Filip Jurčíček Institute of Formal and Applied Linguistics Charles University in Prague Czech Republic Home page: http://ufal.mff.cuni.cz/~jurcicek Version: 21/02/2014
Chapter 6 Expectation and Conditional Expectation. Lectures Definition 6.1. Two random variables defined on a probability space are said to be
 Chapter 6 Expectation and Conditional Expectation Lectures 24-30 In this chapter, we introduce expected value or the mean of a random variable. First we define expectation for discrete random variables
Chapter 6 Expectation and Conditional Expectation Lectures 24-30 In this chapter, we introduce expected value or the mean of a random variable. First we define expectation for discrete random variables
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder. Canberra February June 2017
 Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2017 (Many figures from C. M. Bishop, "Pattern Recognition and ") 1of 679 Part XIX
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 2017 (Many figures from C. M. Bishop, "Pattern Recognition and ") 1of 679 Part XIX
Stat 5101 Notes: Brand Name Distributions
 Stat 5101 Notes: Brand Name Distributions Charles J. Geyer September 5, 2012 Contents 1 Discrete Uniform Distribution 2 2 General Discrete Uniform Distribution 2 3 Uniform Distribution 3 4 General Uniform
Stat 5101 Notes: Brand Name Distributions Charles J. Geyer September 5, 2012 Contents 1 Discrete Uniform Distribution 2 2 General Discrete Uniform Distribution 2 3 Uniform Distribution 3 4 General Uniform
Estimation and Maintenance of Measurement Rates for Multiple Extended Target Tracking
 FUSION 2012, Singapore 118) Estimation and Maintenance of Measurement Rates for Multiple Extended Target Tracking Karl Granström*, Umut Orguner** *Division of Automatic Control Department of Electrical
FUSION 2012, Singapore 118) Estimation and Maintenance of Measurement Rates for Multiple Extended Target Tracking Karl Granström*, Umut Orguner** *Division of Automatic Control Department of Electrical
Message-Passing Algorithms for GMRFs and Non-Linear Optimization
 Message-Passing Algorithms for GMRFs and Non-Linear Optimization Jason Johnson Joint Work with Dmitry Malioutov, Venkat Chandrasekaran and Alan Willsky Stochastic Systems Group, MIT NIPS Workshop: Approximate
Message-Passing Algorithms for GMRFs and Non-Linear Optimization Jason Johnson Joint Work with Dmitry Malioutov, Venkat Chandrasekaran and Alan Willsky Stochastic Systems Group, MIT NIPS Workshop: Approximate
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Probabilities Marc Toussaint University of Stuttgart Winter 2018/19 Motivation: AI systems need to reason about what they know, or not know. Uncertainty may have so many sources:
Artificial Intelligence Probabilities Marc Toussaint University of Stuttgart Winter 2018/19 Motivation: AI systems need to reason about what they know, or not know. Uncertainty may have so many sources:
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5
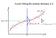 Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Pattern Recognition. Parameter Estimation of Probability Density Functions
 Pattern Recognition Parameter Estimation of Probability Density Functions Classification Problem (Review) The classification problem is to assign an arbitrary feature vector x F to one of c classes. The
Pattern Recognition Parameter Estimation of Probability Density Functions Classification Problem (Review) The classification problem is to assign an arbitrary feature vector x F to one of c classes. The
Lecture 21: Minimax Theory
 Lecture : Minimax Theory Akshay Krishnamurthy akshay@cs.umass.edu November 8, 07 Recap In the first part of the course, we spent the majority of our time studying risk minimization. We found many ways
Lecture : Minimax Theory Akshay Krishnamurthy akshay@cs.umass.edu November 8, 07 Recap In the first part of the course, we spent the majority of our time studying risk minimization. We found many ways
Variational Learning : From exponential families to multilinear systems
 Variational Learning : From exponential families to multilinear systems Ananth Ranganathan th February 005 Abstract This note aims to give a general overview of variational inference on graphical models.
Variational Learning : From exponential families to multilinear systems Ananth Ranganathan th February 005 Abstract This note aims to give a general overview of variational inference on graphical models.
The Particle Filter. PD Dr. Rudolph Triebel Computer Vision Group. Machine Learning for Computer Vision
 The Particle Filter Non-parametric implementation of Bayes filter Represents the belief (posterior) random state samples. by a set of This representation is approximate. Can represent distributions that
The Particle Filter Non-parametric implementation of Bayes filter Represents the belief (posterior) random state samples. by a set of This representation is approximate. Can represent distributions that
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics
 Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 3 October 29, 2012 Silvia Masciocchi, GSI Darmstadt s.masciocchi@gsi.de Winter Semester 2012 / 13 Outline Reminder: Probability density function Cumulative
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 3 October 29, 2012 Silvia Masciocchi, GSI Darmstadt s.masciocchi@gsi.de Winter Semester 2012 / 13 Outline Reminder: Probability density function Cumulative
Part IA Probability. Definitions. Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua. Lent 2015
 Part IA Probability Definitions Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
Part IA Probability Definitions Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
Inference as Optimization
 Inference as Optimization Sargur Srihari srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics in Inference as Optimization Overview Exact Inference revisited The Energy Functional Optimizing the Energy Functional 2 Exact
Inference as Optimization Sargur Srihari srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 Topics in Inference as Optimization Overview Exact Inference revisited The Energy Functional Optimizing the Energy Functional 2 Exact
The Expectation Maximization or EM algorithm
 The Expectation Maximization or EM algorithm Carl Edward Rasmussen November 15th, 2017 Carl Edward Rasmussen The EM algorithm November 15th, 2017 1 / 11 Contents notation, objective the lower bound functional,
The Expectation Maximization or EM algorithm Carl Edward Rasmussen November 15th, 2017 Carl Edward Rasmussen The EM algorithm November 15th, 2017 1 / 11 Contents notation, objective the lower bound functional,
Multiple Random Variables
 Multiple Random Variables This Version: July 30, 2015 Multiple Random Variables 2 Now we consider models with more than one r.v. These are called multivariate models For instance: height and weight An
Multiple Random Variables This Version: July 30, 2015 Multiple Random Variables 2 Now we consider models with more than one r.v. These are called multivariate models For instance: height and weight An
CSC 2541: Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning
 CSC 2541: Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning Radford M. Neal, University of Toronto, 2011 Lecture 10 Alternatives to Monte Carlo Computation Since about 1990, Markov chain Monte Carlo has been the dominant
CSC 2541: Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning Radford M. Neal, University of Toronto, 2011 Lecture 10 Alternatives to Monte Carlo Computation Since about 1990, Markov chain Monte Carlo has been the dominant
Formulas for probability theory and linear models SF2941
 Formulas for probability theory and linear models SF2941 These pages + Appendix 2 of Gut) are permitted as assistance at the exam. 11 maj 2008 Selected formulae of probability Bivariate probability Transforms
Formulas for probability theory and linear models SF2941 These pages + Appendix 2 of Gut) are permitted as assistance at the exam. 11 maj 2008 Selected formulae of probability Bivariate probability Transforms
Data Mining Techniques
 Data Mining Techniques CS 6220 - Section 2 - Spring 2017 Lecture 6 Jan-Willem van de Meent (credit: Yijun Zhao, Chris Bishop, Andrew Moore, Hastie et al.) Project Project Deadlines 3 Feb: Form teams of
Data Mining Techniques CS 6220 - Section 2 - Spring 2017 Lecture 6 Jan-Willem van de Meent (credit: Yijun Zhao, Chris Bishop, Andrew Moore, Hastie et al.) Project Project Deadlines 3 Feb: Form teams of
Variational algorithms for marginal MAP
 Variational algorithms for marginal MAP Alexander Ihler UC Irvine CIOG Workshop November 2011 Variational algorithms for marginal MAP Alexander Ihler UC Irvine CIOG Workshop November 2011 Work with Qiang
Variational algorithms for marginal MAP Alexander Ihler UC Irvine CIOG Workshop November 2011 Variational algorithms for marginal MAP Alexander Ihler UC Irvine CIOG Workshop November 2011 Work with Qiang
Non-Parametric Bayes
 Non-Parametric Bayes Mark Schmidt UBC Machine Learning Reading Group January 2016 Current Hot Topics in Machine Learning Bayesian learning includes: Gaussian processes. Approximate inference. Bayesian
Non-Parametric Bayes Mark Schmidt UBC Machine Learning Reading Group January 2016 Current Hot Topics in Machine Learning Bayesian learning includes: Gaussian processes. Approximate inference. Bayesian
Introduction to Probability and Statistics (Continued)
 Introduction to Probability and Statistics (Continued) Prof. icholas Zabaras Center for Informatics and Computational Science https://cics.nd.edu/ University of otre Dame otre Dame, Indiana, USA Email:
Introduction to Probability and Statistics (Continued) Prof. icholas Zabaras Center for Informatics and Computational Science https://cics.nd.edu/ University of otre Dame otre Dame, Indiana, USA Email:
Goodness of Fit Test and Test of Independence by Entropy
 Journal of Mathematical Extension Vol. 3, No. 2 (2009), 43-59 Goodness of Fit Test and Test of Independence by Entropy M. Sharifdoost Islamic Azad University Science & Research Branch, Tehran N. Nematollahi
Journal of Mathematical Extension Vol. 3, No. 2 (2009), 43-59 Goodness of Fit Test and Test of Independence by Entropy M. Sharifdoost Islamic Azad University Science & Research Branch, Tehran N. Nematollahi
Lecture 5: Moment Generating Functions
 Lecture 5: Moment Generating Functions IB Paper 7: Probability and Statistics Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge February 28th, 2018 Rasmussen (CUED) Lecture 5: Moment
Lecture 5: Moment Generating Functions IB Paper 7: Probability and Statistics Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge February 28th, 2018 Rasmussen (CUED) Lecture 5: Moment
