MIMO and Mode Division Multiplexing in Multimode Fibers
|
|
|
- Lisa Wilkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MIMO and Mode Division Multiplexing in Multimode Fibers Kumar Appaiah Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Tutorial: National Conference on Communications 2017, Chennai 1
2 Prerequisites Basic EE, physics Maxwell s equations Linear system theory, communication theory Optics, reflection, refraction etc. 2
3 Outline Introduction Basic optical fiber concepts Propagation characteristics MIMO, MDM in multimode fibers Recent trends, adoption, future Summary 3
4 Introduction Optical fibers: waveguides that carry EM waves High bandwidths, long distance carrying abilities Challenges: alignment, dispersion, nonlinearities Insert picture here 4
5 Electromagnetic spectrum Frequency (Hz) Gamma-rays Wavelength 0.1 Å X-rays 1Å 0.1 nm 1 nm 400 nm 10 nm Ultraviolet Visible Near IR 100 nm 1000 nm 1 µm 500 nm 600 nm Infra-red 10 µm MHz Thermal IR Far IR 100 µm 1000 µm 1 mm 700 nm 500 MHz UHF Microwaves Radar 1 cm 10 cm VHF Radio, TV 1 m 100 MHz 50 MHz FM VHF AM 10 m 100 m Long-waves 1000 m 5
6 Optical fibre Guided medium High bandwidth Large bandwidth-length product Examples: Long undersea links Medium haul links Short links: data centres, vehicles 6
7 Maxwell s equations E = B t H = D t (1) (2) D = 0 (3) B = 0 (4) where D = ϵe, B = μh. 7
8 Maxwell s equations Take curl of equation (1) Identity: ( E) = μ t ( H) = μϵ 2 E t 2 ( E) = ( E) 2 E Using E = 0, we get the wave equations (repeated for H): 2 E = μϵ 2 E t 2 2 H = μϵ 2 H t 2 8
9 Waveguide equations Using cylindrical coordinate system: E(r, ϕ, z) = E 0 (r, ϕ)e j(ωt βz) H(r, ϕ, z) = H 0 (r, ϕ)e j(ωt βz) β: z-component of propagation vector, determined by the boundary conditions. Substitute above in the curl equations. Use in cylindrical coordinates: 1 1 rêr ê ϕ rêz A = det r ϕ z A r A ϕ A z 9
10 Waveguide equations 1 E z r ( ϕ + jrβe ϕ ) = jωμh r jβe r + E z r = jωμh ϕ 1 r ( r (re ϕ) E r ϕ ) = jμωh z 1 H z r ( ϕ + jrβh ϕ ) = jωμe r jβh r + H z r = jωμe ϕ 1 r ( r (rh ϕ) H r ϕ ) = jμωe z Six fields are coupled, eliminate to keep only H z and E z. 10
11 Waveguide equations E r = j q 2 ( β E z r + μω r H z ϕ ) E ϕ = j β E z q 2 ( r ϕ μω H z r ) H r = j q 2 ( β H z r ϵω r E z ϕ ) H ϕ = j β H z q 2 ( r ϕ + ϵω E z r ) We now substitute the above into 2 E = μϵ 2 E t 2, to get 2 E z r r E z r + 1 r 2 2 E z ϕ 2 + q2 E z = 0 where q 2 = ω 2 μϵ β 2. 11
12 Waveguide equations Separation of variables: let s see if this works: E z = AF 1 (r)f 2 (ϕ)f 3 (z)f 4 (t) where F 3 (z)f 4 (t) = e j(ωt βz) by prior assumption. By symmetry, we also have F 2 (ϕ) = e jνϕ. Finally, for F 1 (z), we have: 2 E z r r E z r + 1 r 2 2 E z ϕ 2 + q2 E z = 0 2 F 1 r r F 1 r + ( q2 ν2 r 2 ) F 1 = 0 Solution of above differential equation: Bessel functions (Please refer) 12
13 Boundary conditions Boundary conditions lead to Bessel functions J ν, K ν. 1. The field can t be at the centre. 2. The field has to die far away from the centre (cladding). Solution with boundary conditions: E z (r < a) = AJ ν (ur)e jνϕ e j(ωt βz) H z (r < a) = BJ ν (ur)e jνϕ e j(ωt βz) E z (r > a) = CK ν (wr)e jνϕ e j(ωt βz) H z (r > a) = DK ν (wr)e jνϕ e j(ωt βz) where u 2 = k 2 1 β 2, w 2 = β 2 k 2 2. We need F 1 to be real everywhere. So, u 2 0, v 2 0 k 2 β k 1. 13
14 Boundary conditions At the core-cladding interface, E ϕ, E z, H ϕ, H z must be continuous. AJ ν (ua) = CK ν (ua) BJ ν (ua) = DK ν (wa) Similarly, E ϕ, H ϕ can be found from E z, H z, and the continuity condition may be obtained as 1 u 2 [ Ajνβ a J ν(ua) BωμuJ ν(ua) ] = 1 w 2 [ Cjνβ a K ν(wa) DωμwK ν(wa) ] 1 u 2 [ Bjνβ a J ν(ua) + Aωϵ 1 uj ν(ua) ] = 1 w 2 [ Djνβ a K ν(wa) + Cωϵ 2 wk ν(wa) ] 14
15 Boundary conditions Consolidating above equation, we get det J ν (ua) 0 K ν (wa) 0 βν au J jωμ βν ν(ua) 2 u J ν(ua) aw K jωμ ν(wa) 2 w K ν(wa) 0 J ν (ua) 0 K ν (wa) jωϵ 1 u J ν(ua) βν au 2 J ν(ua) jωϵ 2 w K ν(wa) βν aw 2 K ν(wa) = 0 J ν(ua) ( uj ν (ua) + K ν(wa) k 2 1J ν(ua) wk ν (wa)) ( uj ν (ua) + k2 2K ν(wa) wk ν (wa) ) = ( 2 βν a ) Solving above for β gives us the values of β that correspond to the propagating modes of the fibre. 1 ( u w 2 ) 2 15
16 Fibre modes Inspecting the equation for ν = 0, we get J 0(ua) ( uj 0 (ua) + K 0(wa) k 2 1J 0(ua) wk 0 (wa)) ( uj 0 (ua) + k2 2K 0(wa) wk 0 (wa) ) = 0 which implies that J 0(ua) ( uj 0 (ua) + K 0(wa) wk 0 (wa)) = 0 TE modes k or 2 1J 0(ua) ( uj 0 (ua) + k2 2K 0(wa) wk 0 (wa) ) TM modes = 0 Proof that these are TE/TM: homework. For ν 1, solution is more complex. 16
17 Fibre modes Convenience substitutions: Normalized frequency or V-number, defined by: 2 2 2πa 2πa V 2 = (u 2 + w 2 )a 2 = (n ( λ 2 1 n 2 2) = NA 2 ) ( λ ) Normalized propagation constant b, defined as: b = a2 w 2 V 2 = (β/k)2 n 2 2 n 2 1 n
18 Linearly polarized modes In the weakly guiding case (i.e. Δ << 1 or n 1 n 2 << 1), several mode pairs are almost degenerate. That is, HE ν+1,m and EH ν 1,m are very similar. Similar is the case for TE 0m, TM 0m and HE 2m. So, only four field components need to be considered, instead of six. Linearly polarized modes: Simplification 1. LP 0m is derived from HE 1m mode 2. LP 1m is derived from HE 2m, TE 0m and TM 0m modes 3. LP νm for ν 2 is derived from an HE ν+1,m and an EH ν 1,m mode 18
19 Fibre modes
20 Ideal modes Ideal modes have specific field distributions Different modes may have different propagation constants Orthonormal: overlap integral zero Provide spatial degrees of freedom 20
21 Ideal modes are orthogonal E p q (x, y)e pq (x, y)dxdy = 0 if p p or q q = 1 if p = p and q = q Any arbitrary pattern propagating in the fiber can be represented as the linear combination of ideal modes. Since each mode can be in x polarized or in y polarized, pattern E(x, y) propagating inside fiber (supporting M spatial modes) can be written as E 2M 1 = [a x 1 a x 2 a x M a y 1 a y 2 a y M] T 21
22 Types of fiber Criterion Single-mode Few-mode Multimode Core diameter < 10 μm < 14 μm 50 μm Alignment tolerance 0.5 μm 0.5 μm >3 μm Data rate limits 100 Gb/s-km > 200 Gb/s-km 2 Gb/s-km Length scales km km 10 m - a few km Materials Silica Silica Silica, plastic 22
23 Comparison of SMF and MMF Single Mode Fiber Multimode Fiber SMF: no modal dispersion MMF: easier to couple Tradeoff: bandwidth-length product 23
24 Modal Dispersion Detector Ideal MMF t Laser t 24
25 Modal Dispersion Different modes travel at different speeds Different have different spatial distributions Modes detected at the photodetector retain individual propagation delays Pulse spreading: dispersion, limits data rates Conventional MMFs: BW-length product below 1 Gb/s km 25
26 Selective excitation of modes Detector SLM IM Pattern Ideal MMF t Laser t Computer 26
27 Intermodal coupling SLM IM Pattern Imperfect MMF Detector t Laser t Computer 27
28 Multiplexing using fiber modes Idea: Shape inputs to match each mode shape Shape outputs to match each mode shape Ideal fiber: spatial multiplexing! Issue: Intermodal coupling mixes the signal 28
29 Handling mode mixing Mode mixing: linear or nonlinear? Coherent or incoherent? Depends on what? Fiber length? What else? Complexity of implementation? 29
30 Next topics Incoherent multiplexing techniques Coherent multiplexing techniques Mode generation, shaping DSP implementation issues 30
31 Incoherent systems Incoherent in laser Like amplitude modulation 31
32 Incoherent multiplexing Stuart: dispersive multiplexing Offset coupling based solutions Mode group diversity multiplexing Issues and limitations 32
33 Incoherent multiplexing Laser Source 1 Intensity Modulator 1 Detector 1 Detector 2 Laser Source 2 Intensity Modulator 2 Mode Multiplexer Mode De-Multiplexer Laser Source M Intensity Modulator M Detector M 33
34 Mode group diversity multiplexing Idea: Modes with close β values travel together, so use them to multiplex Intermodal mixing: linear methods help reduce cross-talk 34
35 Coherent multiplexing Coherent: laser + polarization recovered at receiver Requires PLL (optical/electrical) or homodyne Improves receiver sensitivity Price: requires balanced detection Modulator Modulator POL MUX POL DEMUX Quadrature Optical Hybrid Balanced Detectors Digital Signal Processor Laser Local Oscillator 35
36 PSK and DPSK
37 PSK: Phase noise
38 Photonic Lantern Isolated SMFs New Cladding FMF The SMF ends act as spatial filter Different locations of SMFs causes coupling to different modes Post-processing required to separate modes 38
39 Free space coupling SMF Phase Plate Beam Splitters SMF FMF Mirror Phase Plate Lens 1 Lens 2 SMF 39
40 Free space coupling Mirror 1 SMF Periscope FMF SMF Mirror 2 Lens 1 Lens 2 SMF 40
41 Latest trends NEC Labs: 1.05 Petabit/s with multicore fiber Infinera: Advanced modulation, multiplexing Bell Labs: Several SDM experiments New fibers: OM4 (100GBASE over 150 metres) OM5 + SWDM: Further increase in data rates 41
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 07
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 07 Analysis of Wave-Model of Light Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 07 Analysis of Wave-Model of Light Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of
Lecture 3 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 3, Slide 1
 Lecture 3 Optical fibers as waveguides Maxwell s equations The wave equation Fiber modes Phase velocity, group velocity Dispersion Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 3, Slide 1 Maxwell s equations in
Lecture 3 Optical fibers as waveguides Maxwell s equations The wave equation Fiber modes Phase velocity, group velocity Dispersion Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 3, Slide 1 Maxwell s equations in
4. Integrated Photonics. (or optoelectronics on a flatland)
 4. Integrated Photonics (or optoelectronics on a flatland) 1 x Benefits of integration in Electronics: Are we experiencing a similar transformation in Photonics? Mach-Zehnder modulator made from Indium
4. Integrated Photonics (or optoelectronics on a flatland) 1 x Benefits of integration in Electronics: Are we experiencing a similar transformation in Photonics? Mach-Zehnder modulator made from Indium
Optical Fiber. Chapter 1. n 1 n 2 n 2. index. index
 Chapter 1 Optical Fiber An optical ber consists of cylindrical dielectric material surrounded by another cylindrical dielectric material with a lower index of refraction. Figure 1.1 shows that the transistion
Chapter 1 Optical Fiber An optical ber consists of cylindrical dielectric material surrounded by another cylindrical dielectric material with a lower index of refraction. Figure 1.1 shows that the transistion
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements Homework #4 is assigned, due March 25 th Start discussion
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements Homework #4 is assigned, due March 25 th Start discussion
MODE THEORY FOR STEP INDEX MULTI-MODE FIBERS. Evgeny Klavir. Ryerson University Electrical And Computer Engineering
 MODE THEORY FOR STEP INDEX MULTI-MODE FIBERS Evgeny Klavir Ryerson University Electrical And Computer Engineering eklavir@ee.ryerson.ca ABSTRACT Cladding n = n This project consider modal theory for step
MODE THEORY FOR STEP INDEX MULTI-MODE FIBERS Evgeny Klavir Ryerson University Electrical And Computer Engineering eklavir@ee.ryerson.ca ABSTRACT Cladding n = n This project consider modal theory for step
UNIT 1. By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Electronics & Communication Engineering Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun
 UNIT 1 By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Electronics & Communication Engineering Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun Syllabus Introduction: Demand of Information Age, Block Diagram
UNIT 1 By: Ajay Kumar Gautam Asst. Prof. Electronics & Communication Engineering Dev Bhoomi Institute of Technology & Engineering, Dehradun Syllabus Introduction: Demand of Information Age, Block Diagram
Propagation losses in optical fibers
 Chapter Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers 1-Fev-017 Propagation losses in optical fibers Charles Kao, Nobel Laureate (009) Courtesy of the Chinese University of Hong Kong S.O. Kasap, Optoelectronics
Chapter Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers 1-Fev-017 Propagation losses in optical fibers Charles Kao, Nobel Laureate (009) Courtesy of the Chinese University of Hong Kong S.O. Kasap, Optoelectronics
Cylindrical Dielectric Waveguides
 03/02/2017 Cylindrical Dielectric Waveguides Integrated Optics Prof. Elias N. Glytsis School of Electrical & Computer Engineering National Technical University of Athens Geometry of a Single Core Layer
03/02/2017 Cylindrical Dielectric Waveguides Integrated Optics Prof. Elias N. Glytsis School of Electrical & Computer Engineering National Technical University of Athens Geometry of a Single Core Layer
Light Waves and Polarization
 Light Waves and Polarization Xavier Fernando Ryerson Communications Lab http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~fernando The Nature of Light There are three theories explain the nature of light: Quantum Theory Light
Light Waves and Polarization Xavier Fernando Ryerson Communications Lab http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~fernando The Nature of Light There are three theories explain the nature of light: Quantum Theory Light
Traceable Encircled Flux measurements for multimode fibre components and systems
 Traceable Encircled Flux measurements for multimode fibre components and systems J. Morel / N.Castagna CCPR WG-SP Workshop / 19.09.2016 Outline 1. Introduction to the problematic of multimode fibres 2.
Traceable Encircled Flux measurements for multimode fibre components and systems J. Morel / N.Castagna CCPR WG-SP Workshop / 19.09.2016 Outline 1. Introduction to the problematic of multimode fibres 2.
Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers. 高錕 Charles Kao
 Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers 高錕 Charles Kao 1 Planar Dielectric Slab Waveguide Symmetric Planar Slab Waveguide n 1 area : core, n 2 area : cladding a light ray can undergo TIR at the n 1 /n
Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers 高錕 Charles Kao 1 Planar Dielectric Slab Waveguide Symmetric Planar Slab Waveguide n 1 area : core, n 2 area : cladding a light ray can undergo TIR at the n 1 /n
Optical fibers. Weak guidance approximation in cylindrical waveguides
 Optical fibers Weak guidance approximation in cylindrical waveguides Propagation equation with symmetry of revolution r With cylindrical coordinates : r ( r,θ) 1 ψ( r,θ) 1 ψ( r,θ) ψ + + r r + r θ [ ( )
Optical fibers Weak guidance approximation in cylindrical waveguides Propagation equation with symmetry of revolution r With cylindrical coordinates : r ( r,θ) 1 ψ( r,θ) 1 ψ( r,θ) ψ + + r r + r θ [ ( )
Transporting Data on the Orbital Angular Momentum of Light. Leslie A. Rusch Canada Research Chair Communications Systems Enabling the Cloud
 Transporting Data on the Orbital Angular Momentum of Light Leslie A. Rusch Canada Research Chair Communications Systems Enabling the Cloud FOR FURTHER READING 2 Outline Motivation overcoming the Shannon
Transporting Data on the Orbital Angular Momentum of Light Leslie A. Rusch Canada Research Chair Communications Systems Enabling the Cloud FOR FURTHER READING 2 Outline Motivation overcoming the Shannon
OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS
 L21-1 OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS Free-Space Propagation: Similar to radiowaves (but more absorption by clouds, haze) Same expressions: antenna gain, effective area, power received Examples: TV controllers,
L21-1 OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS Free-Space Propagation: Similar to radiowaves (but more absorption by clouds, haze) Same expressions: antenna gain, effective area, power received Examples: TV controllers,
Step index planar waveguide
 N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
Optical Fiber Signal Degradation
 Optical Fiber Signal Degradation Effects Pulse Spreading Dispersion (Distortion) Causes the optical pulses to broaden as they travel along a fiber Overlap between neighboring pulses creates errors Resulting
Optical Fiber Signal Degradation Effects Pulse Spreading Dispersion (Distortion) Causes the optical pulses to broaden as they travel along a fiber Overlap between neighboring pulses creates errors Resulting
Optical Fiber Concept
 Optical Fiber Concept Optical fibers are light pipes Communications signals can be transmitted over these hair-thin strands of glass or plastic Concept is a century old But only used commercially for the
Optical Fiber Concept Optical fibers are light pipes Communications signals can be transmitted over these hair-thin strands of glass or plastic Concept is a century old But only used commercially for the
Optics, Optoelectronics and Photonics
 Optics, Optoelectronics and Photonics Engineering Principles and Applications Alan Billings Emeritus Professor, University of Western Australia New York London Toronto Sydney Tokyo Singapore v Contents
Optics, Optoelectronics and Photonics Engineering Principles and Applications Alan Billings Emeritus Professor, University of Western Australia New York London Toronto Sydney Tokyo Singapore v Contents
Numerical Analysis of Low-order Modes in Thermally Diffused Expanded Core (TEC) Fibers
 Proceedings of the 4th WSEAS Int. Conference on Electromagnetics, Wireless and Optical Communications, Venice, Italy, November 2-22, 26 26 Numerical Analysis of Low-order Modes in Thermally Diffused Expanded
Proceedings of the 4th WSEAS Int. Conference on Electromagnetics, Wireless and Optical Communications, Venice, Italy, November 2-22, 26 26 Numerical Analysis of Low-order Modes in Thermally Diffused Expanded
Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1)
 EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
Lect. 15: Optical Fiber
 3-dimentioanl dielectric waveguide? planar waveguide circular waveguide optical fiber Optical Fiber: Circular dielectric waveguide made of silica (SiO ) y y n n 1 n Cladding Core r z Fiber axis SiO :Ge
3-dimentioanl dielectric waveguide? planar waveguide circular waveguide optical fiber Optical Fiber: Circular dielectric waveguide made of silica (SiO ) y y n n 1 n Cladding Core r z Fiber axis SiO :Ge
Lecture 4 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 4, Slide 1
 ecture 4 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion imitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
ecture 4 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion imitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
QUESTION BANK IN PHYSICS
 QUESTION BANK IN PHYSICS LASERS. Name some properties, which make laser light different from ordinary light. () {JUN 5. The output power of a given laser is mw and the emitted wavelength is 630nm. Calculate
QUESTION BANK IN PHYSICS LASERS. Name some properties, which make laser light different from ordinary light. () {JUN 5. The output power of a given laser is mw and the emitted wavelength is 630nm. Calculate
Mode-Field Diameter (MFD)
 Mode-Field Diameter (MFD) Important parameter determined from mode-field distribution of fundamental LP 01 mode. Characterized by various models Main consideration: how to approximate the electric field
Mode-Field Diameter (MFD) Important parameter determined from mode-field distribution of fundamental LP 01 mode. Characterized by various models Main consideration: how to approximate the electric field
What is a mode in few mode fibers?: Proposal of MIMOfree mode division multiplexing using true eigenmodes
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.13, No.18, 1 1 What is a mode in few mode fibers?: Proposal of MIMOfree mode division multiplexing using true eigenmodes Yasuo Kokubun 1a), Tatsuhiko Watanabe, Seiya
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.13, No.18, 1 1 What is a mode in few mode fibers?: Proposal of MIMOfree mode division multiplexing using true eigenmodes Yasuo Kokubun 1a), Tatsuhiko Watanabe, Seiya
Orbital Angular Momentum (OAM) based Mode Division Multiplexing (MDM) over a km-length Fiber
 Orbital Angular Momentum (OAM) based Mode Division Multiplexing (MDM) over a km-length Fiber N. Bozinovic, S. Ramachandran, Y. Yue, Y. Ren, A.E. Willner, M. Tur, P. Kristensen ECOC, September 20 th 2012
Orbital Angular Momentum (OAM) based Mode Division Multiplexing (MDM) over a km-length Fiber N. Bozinovic, S. Ramachandran, Y. Yue, Y. Ren, A.E. Willner, M. Tur, P. Kristensen ECOC, September 20 th 2012
ECE 604, Lecture 17. October 30, In this lecture, we will cover the following topics: Reflection and Transmission Single Interface Case
 ECE 604, Lecture 17 October 30, 2018 In this lecture, we will cover the following topics: Duality Principle Reflection and Transmission Single Interface Case Interesting Physical Phenomena: Total Internal
ECE 604, Lecture 17 October 30, 2018 In this lecture, we will cover the following topics: Duality Principle Reflection and Transmission Single Interface Case Interesting Physical Phenomena: Total Internal
A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging. Outline
 A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging Outline General Goals Linear Imaging Systems An Example, The Pin Hole Camera Radiations and Their Interactions with Matter Coherent vs. Incoherent Imaging Length
A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging Outline General Goals Linear Imaging Systems An Example, The Pin Hole Camera Radiations and Their Interactions with Matter Coherent vs. Incoherent Imaging Length
Analysis of Single Mode Step Index Fibres using Finite Element Method. * 1 Courage Mudzingwa, 2 Action Nechibvute,
 Analysis of Single Mode Step Index Fibres using Finite Element Method. * 1 Courage Mudzingwa, 2 Action Nechibvute, 1,2 Physics Department, Midlands State University, P/Bag 9055, Gweru, Zimbabwe Abstract
Analysis of Single Mode Step Index Fibres using Finite Element Method. * 1 Courage Mudzingwa, 2 Action Nechibvute, 1,2 Physics Department, Midlands State University, P/Bag 9055, Gweru, Zimbabwe Abstract
Quasi-Optical Design and Analysis (MBI) Créidhe O Sullivan, J.Anthony Murphy, Marcin Gradziel, Neil Trappe, Tully Peacocke & graduate students
 Quasi-Optical Design and Analysis (MBI) Créidhe O Sullivan, J.Anthony Murphy, Marcin Gradziel, Neil Trappe, Tully Peacocke & graduate students Outline Corrugated Horns Analysis Techniques MBI/MODAL 2 Analysis
Quasi-Optical Design and Analysis (MBI) Créidhe O Sullivan, J.Anthony Murphy, Marcin Gradziel, Neil Trappe, Tully Peacocke & graduate students Outline Corrugated Horns Analysis Techniques MBI/MODAL 2 Analysis
MCQs E M WAVES. Physics Without Fear.
 MCQs E M WAVES Physics Without Fear Electromagnetic Waves At A Glance Ampere s law B. dl = μ 0 I relates magnetic fields due to current sources. Maxwell argued that this law is incomplete as it does not
MCQs E M WAVES Physics Without Fear Electromagnetic Waves At A Glance Ampere s law B. dl = μ 0 I relates magnetic fields due to current sources. Maxwell argued that this law is incomplete as it does not
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2//e50054/dc Supplementary Materials for Two-photon quantum walk in a multimode fiber Hugo Defienne, Marco Barbieri, Ian A. Walmsley, Brian J. Smith, Sylvain Gigan
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2//e50054/dc Supplementary Materials for Two-photon quantum walk in a multimode fiber Hugo Defienne, Marco Barbieri, Ian A. Walmsley, Brian J. Smith, Sylvain Gigan
Phys 531 Lecture 27 6 December 2005
 Phys 531 Lecture 27 6 December 2005 Final Review Last time: introduction to quantum field theory Like QM, but field is quantum variable rather than x, p for particle Understand photons, noise, weird quantum
Phys 531 Lecture 27 6 December 2005 Final Review Last time: introduction to quantum field theory Like QM, but field is quantum variable rather than x, p for particle Understand photons, noise, weird quantum
Polarization Mode Dispersion
 Unit-7: Polarization Mode Dispersion https://sites.google.com/a/faculty.muet.edu.pk/abdullatif Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro 1 Goos Hänchen Shift The Goos-Hänchen effect is a phenomenon
Unit-7: Polarization Mode Dispersion https://sites.google.com/a/faculty.muet.edu.pk/abdullatif Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro 1 Goos Hänchen Shift The Goos-Hänchen effect is a phenomenon
Schemes to generate entangled photon pairs via spontaneous parametric down conversion
 Schemes to generate entangled photon pairs via spontaneous parametric down conversion Atsushi Yabushita Department of Electrophysics National Chiao-Tung University? Outline Introduction Optical parametric
Schemes to generate entangled photon pairs via spontaneous parametric down conversion Atsushi Yabushita Department of Electrophysics National Chiao-Tung University? Outline Introduction Optical parametric
Summary of Beam Optics
 Summary of Beam Optics Gaussian beams, waves with limited spatial extension perpendicular to propagation direction, Gaussian beam is solution of paraxial Helmholtz equation, Gaussian beam has parabolic
Summary of Beam Optics Gaussian beams, waves with limited spatial extension perpendicular to propagation direction, Gaussian beam is solution of paraxial Helmholtz equation, Gaussian beam has parabolic
>> D-5006 CWDM components for 40 G and 100 G Transceivers
 >> D-5006 CWDM components for 40 G and 100 G Transceivers Introduction In this White paper the principals of Cube s Thin Film Filter design and their performance with regard to construction tolerances
>> D-5006 CWDM components for 40 G and 100 G Transceivers Introduction In this White paper the principals of Cube s Thin Film Filter design and their performance with regard to construction tolerances
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 15. Optical Sources-LASER
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 15 Optical Sources-LASER Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 15 Optical Sources-LASER Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
Experimental Investigation of Nonlinear Eects in Multi-mode Optical Fibers
 Lehigh University Lehigh Preserve Theses and Dissertations 2016 Experimental Investigation of Nonlinear Eects in Multi-mode Optical Fibers Mina Esmaeelpour Lehigh University Follow this and additional
Lehigh University Lehigh Preserve Theses and Dissertations 2016 Experimental Investigation of Nonlinear Eects in Multi-mode Optical Fibers Mina Esmaeelpour Lehigh University Follow this and additional
Computational Electromagnetics and Applications Professor Krish Sankaran Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Lab Tour 4
 Computational Electromagnetics and Applications Professor Krish Sankaran Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Lab Tour 4 So now we are going to do a different kind of experiment, now in a little bit in
Computational Electromagnetics and Applications Professor Krish Sankaran Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Lab Tour 4 So now we are going to do a different kind of experiment, now in a little bit in
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
 Document downloaded from: http://hdl.handle.net/151/64933 This paper must be cited as: Gasulla Mestre, I.; Kahn, JM. (15). Performance of Direct-Detection Mode-Group-Division Multiplexing using Fused Fiber
Document downloaded from: http://hdl.handle.net/151/64933 This paper must be cited as: Gasulla Mestre, I.; Kahn, JM. (15). Performance of Direct-Detection Mode-Group-Division Multiplexing using Fused Fiber
Dielectric Slab Waveguide
 Chapter Dielectric Slab Waveguide We will start off examining the waveguide properties of a slab of dielectric shown in Fig... d n n x z n Figure.: Cross-sectional view of a slab waveguide. { n, x < d/
Chapter Dielectric Slab Waveguide We will start off examining the waveguide properties of a slab of dielectric shown in Fig... d n n x z n Figure.: Cross-sectional view of a slab waveguide. { n, x < d/
0.4 s 0.8 s 1.5 s. 2.5 s. 2. A beam of light from a ray box spreads out as shown in the diagram and strikes a plane mirror.
 1. ship is fitted with echo-sounding equipment. pulse of sound is sent downwards from the ship at a speed of 1500 m/s. The seabed is 600m below the ship. How long will it take the pulse of sound to return
1. ship is fitted with echo-sounding equipment. pulse of sound is sent downwards from the ship at a speed of 1500 m/s. The seabed is 600m below the ship. How long will it take the pulse of sound to return
Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fiber. Dr. Mohammad Faisal Assistant Professor Dept. of EEE, BUET
 Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fiber Dr. Mohammad Faisal Assistant Professor Dept. of EEE, BUET Fiber Nonlinearities The response of any dielectric material to the light becomes nonlinear for intense electromagnetic
Nonlinear Effects in Optical Fiber Dr. Mohammad Faisal Assistant Professor Dept. of EEE, BUET Fiber Nonlinearities The response of any dielectric material to the light becomes nonlinear for intense electromagnetic
Optical Fibre Communication Systems
 Optical Fibre Communication Systems Lecture 2: Nature of Light and Light Propagation Professor Z Ghassemlooy Northumbria Communications Laboratory Faculty of Engineering and Environment The University
Optical Fibre Communication Systems Lecture 2: Nature of Light and Light Propagation Professor Z Ghassemlooy Northumbria Communications Laboratory Faculty of Engineering and Environment The University
1 Optical Fibers supplementary notes
 1 Optical Fibers supplementary notes Optical fibers are cylindrical dielectric waveguides. Their operation, in analogy with dielectric slab waveguides, depends on total internal reflections from the boundary
1 Optical Fibers supplementary notes Optical fibers are cylindrical dielectric waveguides. Their operation, in analogy with dielectric slab waveguides, depends on total internal reflections from the boundary
arxiv: v2 [physics.optics] 11 Jan 2015
![arxiv: v2 [physics.optics] 11 Jan 2015 arxiv: v2 [physics.optics] 11 Jan 2015](/thumbs/84/90829415.jpg) Slow light with electromagnetically induced transparency in cylindrical waveguide arxiv:42.5742v2 [physics.optics] Jan 25 Agus Muhamad Hatta,, 2, Ali A. Kamli, Ola A. Al-Hagan, 3 and Sergey A. Moiseev
Slow light with electromagnetically induced transparency in cylindrical waveguide arxiv:42.5742v2 [physics.optics] Jan 25 Agus Muhamad Hatta,, 2, Ali A. Kamli, Ola A. Al-Hagan, 3 and Sergey A. Moiseev
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT
 POLARIZATION OF LIGHT OVERALL GOALS The Polarization of Light lab strongly emphasizes connecting mathematical formalism with measurable results. It is not your job to understand every aspect of the theory,
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT OVERALL GOALS The Polarization of Light lab strongly emphasizes connecting mathematical formalism with measurable results. It is not your job to understand every aspect of the theory,
10. OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY
 1. OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a label-free (intrinsic contrast) technique that enables 3D imaging of tissues. The principle of its operation relies on low-coherence
1. OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a label-free (intrinsic contrast) technique that enables 3D imaging of tissues. The principle of its operation relies on low-coherence
Optical/IR Observational Astronomy Telescopes I: Optical Principles. David Buckley, SAAO. 24 Feb 2012 NASSP OT1: Telescopes I-1
 David Buckley, SAAO 24 Feb 2012 NASSP OT1: Telescopes I-1 1 What Do Telescopes Do? They collect light They form images of distant objects The images are analyzed by instruments The human eye Photographic
David Buckley, SAAO 24 Feb 2012 NASSP OT1: Telescopes I-1 1 What Do Telescopes Do? They collect light They form images of distant objects The images are analyzed by instruments The human eye Photographic
CHEM6416 Theory of Molecular Spectroscopy 2013Jan Spectroscopy frequency dependence of the interaction of light with matter
 CHEM6416 Theory of Molecular Spectroscopy 2013Jan22 1 1. Spectroscopy frequency dependence of the interaction of light with matter 1.1. Absorption (excitation), emission, diffraction, scattering, refraction
CHEM6416 Theory of Molecular Spectroscopy 2013Jan22 1 1. Spectroscopy frequency dependence of the interaction of light with matter 1.1. Absorption (excitation), emission, diffraction, scattering, refraction
Lasers and Electro-optics
 Lasers and Electro-optics Second Edition CHRISTOPHER C. DAVIS University of Maryland III ^0 CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface to the Second Edition page xv 1 Electromagnetic waves, light, and lasers 1
Lasers and Electro-optics Second Edition CHRISTOPHER C. DAVIS University of Maryland III ^0 CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface to the Second Edition page xv 1 Electromagnetic waves, light, and lasers 1
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Electromagnetic Waves Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Electromagnetism Geometric optics overlooks the wave nature of light. Light inconsistent with longitudinal
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Electromagnetic Waves Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Electromagnetism Geometric optics overlooks the wave nature of light. Light inconsistent with longitudinal
GUIDED MICROWAVES AND OPTICAL WAVES
 Chapter 1 GUIDED MICROWAVES AND OPTICAL WAVES 1.1 Introduction In communication engineering, the carrier frequency has been steadily increasing for the obvious reason that a carrier wave with a higher
Chapter 1 GUIDED MICROWAVES AND OPTICAL WAVES 1.1 Introduction In communication engineering, the carrier frequency has been steadily increasing for the obvious reason that a carrier wave with a higher
ECE 107: Electromagnetism
 ECE 107: Electromagnetism Notes Set 1 Instructor: Prof. Vitaliy Lomakin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego, CA 92093 1 Introduction (1) atom Electromagnetism
ECE 107: Electromagnetism Notes Set 1 Instructor: Prof. Vitaliy Lomakin Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, San Diego, CA 92093 1 Introduction (1) atom Electromagnetism
Electromagnetic Waves
 4/15/12 Chapter 26: Properties of Light Field Induction Ok, so a changing magnetic field causes a current (Faraday s law) Why do we have currents in the first place? electric fields of the charges Changing
4/15/12 Chapter 26: Properties of Light Field Induction Ok, so a changing magnetic field causes a current (Faraday s law) Why do we have currents in the first place? electric fields of the charges Changing
Mansoor Sheik-Bahae. Class meeting times: Mondays, Wednesdays 17:30-18:45 am; Physics and Astronomy, Room 184
 Mansoor Sheik-Bahae Office: Physics & Astronomy Rm. 1109 (North Wing) Phone: 277-2080 E-mail: msb@unm.edu To see me in my office, please make an appointment (call or email). Class meeting times: Mondays,
Mansoor Sheik-Bahae Office: Physics & Astronomy Rm. 1109 (North Wing) Phone: 277-2080 E-mail: msb@unm.edu To see me in my office, please make an appointment (call or email). Class meeting times: Mondays,
Optical Spectroscopy of Advanced Materials
 Phys 590B Condensed Matter Physics: Experimental Methods Optical Spectroscopy of Advanced Materials Basic optics, nonlinear and ultrafast optics Jigang Wang Department of Physics, Iowa State University
Phys 590B Condensed Matter Physics: Experimental Methods Optical Spectroscopy of Advanced Materials Basic optics, nonlinear and ultrafast optics Jigang Wang Department of Physics, Iowa State University
Solitons. Nonlinear pulses and beams
 Solitons Nonlinear pulses and beams Nail N. Akhmediev and Adrian Ankiewicz Optical Sciences Centre The Australian National University Canberra Australia m CHAPMAN & HALL London Weinheim New York Tokyo
Solitons Nonlinear pulses and beams Nail N. Akhmediev and Adrian Ankiewicz Optical Sciences Centre The Australian National University Canberra Australia m CHAPMAN & HALL London Weinheim New York Tokyo
STUDY OF DISPERSION CURVES IN M-TYPE TRIPLE CLAD SINGLE MODE OPTICAL FIBER
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (IJECET) ISSN ISSN 0976 6464(Print)
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (IJECET) ISSN ISSN 0976 6464(Print)
Alka Sharma Department of Physics, J. N. P. G. College Lucknow University, Lucknow, India
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 78-4861.Volume 8, Issue 4 Ver. II (Jul. - Aug. 016), PP 87-91 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis Of Waveguide Whose Guiding Region Filled With Dielectric Material
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 78-4861.Volume 8, Issue 4 Ver. II (Jul. - Aug. 016), PP 87-91 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis Of Waveguide Whose Guiding Region Filled With Dielectric Material
Homework 1. Property LASER Incandescent Bulb
 Homework 1 Solution: a) LASER light is spectrally pure, single wavelength, and they are coherent, i.e. all the photons are in phase. As a result, the beam of a laser light tends to stay as beam, and not
Homework 1 Solution: a) LASER light is spectrally pure, single wavelength, and they are coherent, i.e. all the photons are in phase. As a result, the beam of a laser light tends to stay as beam, and not
Introduction to optical waveguide modes
 Chap. Introduction to optical waveguide modes PHILIPPE LALANNE (IOGS nd année) Chapter Introduction to optical waveguide modes The optical waveguide is the fundamental element that interconnects the various
Chap. Introduction to optical waveguide modes PHILIPPE LALANNE (IOGS nd année) Chapter Introduction to optical waveguide modes The optical waveguide is the fundamental element that interconnects the various
PART 2 : BALANCED HOMODYNE DETECTION
 PART 2 : BALANCED HOMODYNE DETECTION Michael G. Raymer Oregon Center for Optics, University of Oregon raymer@uoregon.edu 1 of 31 OUTLINE PART 1 1. Noise Properties of Photodetectors 2. Quantization of
PART 2 : BALANCED HOMODYNE DETECTION Michael G. Raymer Oregon Center for Optics, University of Oregon raymer@uoregon.edu 1 of 31 OUTLINE PART 1 1. Noise Properties of Photodetectors 2. Quantization of
Demonstration of true-eigenmode propagation in few-mode fibers by selective LP mode excitation and near-field observation
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.15, No.10, 1 12 Demonstration of true-eigenmode propagation in few-mode fibers by selective LP mode excitation and near-field observation Takuto Yamaguchi 1,4, Seiya
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.15, No.10, 1 12 Demonstration of true-eigenmode propagation in few-mode fibers by selective LP mode excitation and near-field observation Takuto Yamaguchi 1,4, Seiya
Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory. ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy
 Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy The three major branches of optics Geometrical Optics Light travels as straight rays Physical Optics Light can be
Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy The three major branches of optics Geometrical Optics Light travels as straight rays Physical Optics Light can be
Fundamentals of fiber waveguide modes
 SMR 189 - Winter College on Fibre Optics, Fibre Lasers and Sensors 1-3 February 007 Fundamentals of fiber waveguide modes (second part) K. Thyagarajan Physics Department IIT Delhi New Delhi, India Fundamentals
SMR 189 - Winter College on Fibre Optics, Fibre Lasers and Sensors 1-3 February 007 Fundamentals of fiber waveguide modes (second part) K. Thyagarajan Physics Department IIT Delhi New Delhi, India Fundamentals
Lecture 16 Light transmission and optical detectors
 Lecture 6 Light transmission and optical detectors Charged particle traversing through a material can generate signal in form of light via electromagnetic interactions with orbital electrons of the atoms
Lecture 6 Light transmission and optical detectors Charged particle traversing through a material can generate signal in form of light via electromagnetic interactions with orbital electrons of the atoms
Raman Amplification for Telecom Optical Networks. Dominique Bayart Alcatel Lucent Bell Labs France, Research Center of Villarceaux
 Raman Amplification for Telecom Optical Networks Dominique Bayart Alcatel Lucent Bell Labs France, Research Center of Villarceaux Training day www.brighter.eu project Cork, June 20th 2008 Outline of the
Raman Amplification for Telecom Optical Networks Dominique Bayart Alcatel Lucent Bell Labs France, Research Center of Villarceaux Training day www.brighter.eu project Cork, June 20th 2008 Outline of the
EE485 Introduction to Photonics. Introduction
 EE485 Introduction to Photonics Introduction Nature of Light They could but make the best of it and went around with woebegone faces, sadly complaining that on Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays, they must
EE485 Introduction to Photonics Introduction Nature of Light They could but make the best of it and went around with woebegone faces, sadly complaining that on Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays, they must
Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310
 Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310 Deadline for submission: 12-Nov-2013 e-mail the answers in one pdf file to vikashp@ifi.uio.no Part I: Multiple choice questions Multiple choice geometrical optics
Mandatory Assignment 2013 INF-GEO4310 Deadline for submission: 12-Nov-2013 e-mail the answers in one pdf file to vikashp@ifi.uio.no Part I: Multiple choice questions Multiple choice geometrical optics
DEVELOPMENT OF HIGH-POWER PICOSECOND FIBER-BASED ULTRAVIOLET SOURCE
 MSc in Photonics Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) Universitat de Barcelona (UB) Institut de Ciències Fotòniques (ICFO) PHOTONICSBCN http://www.photonicsbcn.eu
MSc in Photonics Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) Universitat de Barcelona (UB) Institut de Ciències Fotòniques (ICFO) PHOTONICSBCN http://www.photonicsbcn.eu
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics. Final Exam. April 16, 2007.
 Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Final Exam April 16, 2007 Exam Type: D (Close-book + two double-sided aid sheets + a non-programmable
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Final Exam April 16, 2007 Exam Type: D (Close-book + two double-sided aid sheets + a non-programmable
Imaging Chain. Imaging Chain. Imaging Chain. 1. Light source. 2. Object interactions. 3. Propagation & Collection: optics (lenses & mirrors)
 1. Light source λ [nm] sunset blue sky 2. Object interactions 3. Propagation & Collection: optics (lenses & mirrors) 1 Optics: Lenses Objects Images Optics: Mirrors Object Image 4. Detector or Sensor Photographic
1. Light source λ [nm] sunset blue sky 2. Object interactions 3. Propagation & Collection: optics (lenses & mirrors) 1 Optics: Lenses Objects Images Optics: Mirrors Object Image 4. Detector or Sensor Photographic
OPTICAL FIBRES IN ASTRONOMY (OP-006) Course Overview
 OPTICAL FIBRES IN ASTRONOMY (OP-006) Course Overview The course, based on practical experience and containing several examples of real instruments, is focused on the application of optical fibres in Astronomy.
OPTICAL FIBRES IN ASTRONOMY (OP-006) Course Overview The course, based on practical experience and containing several examples of real instruments, is focused on the application of optical fibres in Astronomy.
Study of Propagating Modes and Reflectivity in Bragg Filters with AlxGa1-xN/GaN Material Composition
 Study of Propagating Modes and Reflectivity in Bragg Filters with AlxGa1-xN/GaN Material Composition Sourangsu Banerji Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, RCC Institute of Information
Study of Propagating Modes and Reflectivity in Bragg Filters with AlxGa1-xN/GaN Material Composition Sourangsu Banerji Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, RCC Institute of Information
F. Elohim Becerra Chavez
 F. Elohim Becerra Chavez Email:fbecerra@unm.edu Office: P&A 19 Phone: 505 277-2673 Lectures: Tuesday and Thursday, 9:30-10:45 P&A Room 184. Textbook: Laser Electronics (3rd Edition) by Joseph T. Verdeyen.
F. Elohim Becerra Chavez Email:fbecerra@unm.edu Office: P&A 19 Phone: 505 277-2673 Lectures: Tuesday and Thursday, 9:30-10:45 P&A Room 184. Textbook: Laser Electronics (3rd Edition) by Joseph T. Verdeyen.
Optical Fibres - Dispersion Part 1
 ECE 455 Lecture 05 1 Otical Fibres - Disersion Part 1 Stavros Iezekiel Deartment of Electrical and Comuter Engineering University of Cyrus HMY 445 Lecture 05 Fall Semester 016 ECE 455 Lecture 05 Otical
ECE 455 Lecture 05 1 Otical Fibres - Disersion Part 1 Stavros Iezekiel Deartment of Electrical and Comuter Engineering University of Cyrus HMY 445 Lecture 05 Fall Semester 016 ECE 455 Lecture 05 Otical
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
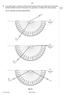 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
Scalar electromagnetic integral equations
 Scalar electromagnetic integral equations Uday K Khankhoje Abstract This brief note derives the two dimensional scalar electromagnetic integral equation starting from Maxwell s equations, and shows how
Scalar electromagnetic integral equations Uday K Khankhoje Abstract This brief note derives the two dimensional scalar electromagnetic integral equation starting from Maxwell s equations, and shows how
1.3 Sinusoidal Steady State
 1.3 Sinusoidal Steady State Electromagnetics applications can be divided into two broad classes: Time-domain: Excitation is not sinusoidal (pulsed, broadband, etc.) Ultrawideband communications Pulsed
1.3 Sinusoidal Steady State Electromagnetics applications can be divided into two broad classes: Time-domain: Excitation is not sinusoidal (pulsed, broadband, etc.) Ultrawideband communications Pulsed
Physics 3323, Fall 2014 Problem Set 13 due Friday, Dec 5, 2014
 Physics 333, Fall 014 Problem Set 13 due Friday, Dec 5, 014 Reading: Finish Griffiths Ch. 9, and 10..1, 10.3, and 11.1.1-1. Reflecting on polarizations Griffiths 9.15 (3rd ed.: 9.14). In writing (9.76)
Physics 333, Fall 014 Problem Set 13 due Friday, Dec 5, 014 Reading: Finish Griffiths Ch. 9, and 10..1, 10.3, and 11.1.1-1. Reflecting on polarizations Griffiths 9.15 (3rd ed.: 9.14). In writing (9.76)
Electricity & Optics
 Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 26 Chapter 33 sec. 1-4 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Interference of Light Interference phenomena are a consequence of the wave-like nature of light Electric
Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 26 Chapter 33 sec. 1-4 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Interference of Light Interference phenomena are a consequence of the wave-like nature of light Electric
Theory of Optical Waveguide
 Theor of Optical Waveguide Class: Integrated Photonic Devices Time: Fri. 8:am ~ :am. Classroom: 資電 6 Lecturer: Prof. 李明昌 (Ming-Chang Lee Reflection and Refraction at an Interface (TE n kˆi H i E i θ θ
Theor of Optical Waveguide Class: Integrated Photonic Devices Time: Fri. 8:am ~ :am. Classroom: 資電 6 Lecturer: Prof. 李明昌 (Ming-Chang Lee Reflection and Refraction at an Interface (TE n kˆi H i E i θ θ
GRATING CLASSIFICATION
 GRATING CLASSIFICATION SURFACE-RELIEF GRATING TYPES GRATING CLASSIFICATION Transmission or Reflection Classification based on Regime DIFFRACTION BY GRATINGS Acousto-Optics Diffractive Optics Integrated
GRATING CLASSIFICATION SURFACE-RELIEF GRATING TYPES GRATING CLASSIFICATION Transmission or Reflection Classification based on Regime DIFFRACTION BY GRATINGS Acousto-Optics Diffractive Optics Integrated
Nanoscale Energy Conversion and Information Processing Devices - NanoNice - Photoacoustic response in mesoscopic systems
 Nanoscale Energy Conversion and Information Processing Devices - NanoNice - Photoacoustic response in mesoscopic systems Photonics group W. Claeys, S. Dilhair, S. Grauby, JM. Rampnoux, L. Patino Lopez,
Nanoscale Energy Conversion and Information Processing Devices - NanoNice - Photoacoustic response in mesoscopic systems Photonics group W. Claeys, S. Dilhair, S. Grauby, JM. Rampnoux, L. Patino Lopez,
High energy X-ray vortex generation using inverse Compton scattering
 22nd International Spin Symposium 9/28/216 High energy X-ray vortex generation using inverse Compton scattering Yoshitaka Taira National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST),
22nd International Spin Symposium 9/28/216 High energy X-ray vortex generation using inverse Compton scattering Yoshitaka Taira National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST),
requency generation spectroscopy Rahul N
 requency generation spectroscopy Rahul N 2-11-2013 Sum frequency generation spectroscopy Sum frequency generation spectroscopy (SFG) is a technique used to analyze surfaces and interfaces. SFG was first
requency generation spectroscopy Rahul N 2-11-2013 Sum frequency generation spectroscopy Sum frequency generation spectroscopy (SFG) is a technique used to analyze surfaces and interfaces. SFG was first
F. Elohim Becerra Chavez
 F. Elohim Becerra Chavez Email:fbecerra@unm.edu Office: P&A 19 Phone: 505 277-2673 Lectures: Monday and Wednesday, 5:30-6:45 pm P&A Room 184. Textbook: Many good ones (see webpage) Lectures follow order
F. Elohim Becerra Chavez Email:fbecerra@unm.edu Office: P&A 19 Phone: 505 277-2673 Lectures: Monday and Wednesday, 5:30-6:45 pm P&A Room 184. Textbook: Many good ones (see webpage) Lectures follow order
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 17.
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 17 Optical Sources- Introduction to LASER Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar,
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 17 Optical Sources- Introduction to LASER Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar,
Optical solitons and its applications
 Physics 568 (Nonlinear optics) 04/30/007 Final report Optical solitons and its applications 04/30/007 1 1 Introduction to optical soliton. (temporal soliton) The optical pulses which propagate in the lossless
Physics 568 (Nonlinear optics) 04/30/007 Final report Optical solitons and its applications 04/30/007 1 1 Introduction to optical soliton. (temporal soliton) The optical pulses which propagate in the lossless
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 25 Propagation of Light Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones Midterm Exam: Date: Wednesday, March 6 th Time: 8:00 10:00 pm Room: PHYS 203 Material: French, chapters
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 25 Propagation of Light Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones Midterm Exam: Date: Wednesday, March 6 th Time: 8:00 10:00 pm Room: PHYS 203 Material: French, chapters
Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves Units of Chapter 31 Changing Electric Fields Produce Magnetic Fields; Ampère s Law and Displacement Current Gauss s Law for Magnetism Maxwell s
Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves Units of Chapter 31 Changing Electric Fields Produce Magnetic Fields; Ampère s Law and Displacement Current Gauss s Law for Magnetism Maxwell s
in Electromagnetics Numerical Method Introduction to Electromagnetics I Lecturer: Charusluk Viphavakit, PhD
 2141418 Numerical Method in Electromagnetics Introduction to Electromagnetics I Lecturer: Charusluk Viphavakit, PhD ISE, Chulalongkorn University, 2 nd /2018 Email: charusluk.v@chula.ac.th Website: Light
2141418 Numerical Method in Electromagnetics Introduction to Electromagnetics I Lecturer: Charusluk Viphavakit, PhD ISE, Chulalongkorn University, 2 nd /2018 Email: charusluk.v@chula.ac.th Website: Light
Dispersion Information for Photonic Fiber Modes from CUDOS Simulations
 July 14, 005 ARDB Note Dispersion Information for Photonic Fiber Modes from CUDOS Simulations Robert J. Noble Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University 575 Sand Hill Road, Menlo Park, California
July 14, 005 ARDB Note Dispersion Information for Photonic Fiber Modes from CUDOS Simulations Robert J. Noble Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University 575 Sand Hill Road, Menlo Park, California
Is the speed of light in free-space always c? Miles Padgett FRS Kelvin Chair of Natural Philosophy
 Is the speed of light in free-space always c? Miles Padgett FRS Kelvin Chair of Natural Philosophy 1 What s the speed of light in free space? Always? The team www.physics.gla.ac.uk/optics Jacqui Romero
Is the speed of light in free-space always c? Miles Padgett FRS Kelvin Chair of Natural Philosophy 1 What s the speed of light in free space? Always? The team www.physics.gla.ac.uk/optics Jacqui Romero
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall 2016 YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT.
 CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
Class XII Chapter 8 Electromagnetic Waves Physics
 Question 8.1: Figure 8.6 shows a capacitor made of two circular plates each of radius 12 cm, and separated by 5.0 cm. The capacitor is being charged by an external source (not shown in the figure). The
Question 8.1: Figure 8.6 shows a capacitor made of two circular plates each of radius 12 cm, and separated by 5.0 cm. The capacitor is being charged by an external source (not shown in the figure). The
Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves Units of Chapter 31 Changing Electric Fields Produce Magnetic Fields; Ampère s Law and Displacement Current Gauss s Law for Magnetism Maxwell s
Chapter 31 Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves Units of Chapter 31 Changing Electric Fields Produce Magnetic Fields; Ampère s Law and Displacement Current Gauss s Law for Magnetism Maxwell s
