Quasi-Optical Design and Analysis (MBI) Créidhe O Sullivan, J.Anthony Murphy, Marcin Gradziel, Neil Trappe, Tully Peacocke & graduate students
|
|
|
- Andrea Copeland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quasi-Optical Design and Analysis (MBI) Créidhe O Sullivan, J.Anthony Murphy, Marcin Gradziel, Neil Trappe, Tully Peacocke & graduate students
2 Outline Corrugated Horns Analysis Techniques MBI/MODAL 2
3 Analysis Techniques: Horns Principle of reciprocity: consider horns as emitters Horns must satisfy strict criteria with regard to cross-polarisation and sidelobe level (e.g. PLANCK) Corrugated horns designed to propagate HE 11 mode PSB waveguide polypropylene filter cap 2b 2a bolometer cavity z 3 L
4 Hybrid Mode (Surface Impedance) Model Treat corrugated walls as surface with different average impedance in the z and φ directions Hybrid modes (HE/EH modes) are natural eigenmodes of the system, efficient description of system with few modes and no scattering Hybrid modes propagate independently through waveguide filter and conical horns Assume several corrugations per wavelength (>3) 4
5 Dispersion characteristics for modes of azimuthal order 1 in a corrugated waveguide 10 8 r 1 /r o = 0.6 βr 1 6 EH 11 HE 11 HE EH 12 HE kr 1 Finite bandwidth for fundamental mode Fall off in horn gain (on-axis efficiency) at high frequencies 5
6 Intuitive, fast computationally Gives high- and low-frequency cut-off for hybrid modes Simple analytical expression, convenient as input to quasioptical software Bessel function approximation to a scalar horn normalised intensity (db) E-Plane H-Plane truncated Bessel Gaussian beam But 6-50 off-axis angle (degrees) It s approximate, especially when there are few corrugations per λ takes no account of profiling of horn
7 Mode Matching (Scattering Matrix) Model PLANCK and QUaD both use cylindrically symmetric horns which transmit both orthogonal polarisations profiled horns & multimoded for non-polarised PLANCK channels r o r 1 7 corrugated waveguide Electromagnetic mode-matching technique regards the corrugated structure as a sequence of smooth-walled cylindrical waveguide sections each of which can support a set of TE and TM modes. At each junction power is scattered between the guide modes.
8 Mode Matching (Scattering Matrix) Model 8 Rectangular-circular transitions, profiles etc.
9 Far field intensity at 150GHz 150 GHz Far-Field Intensity Intensity (db) Intensity(dB) E Plane H Plane -10 exp result - H plane -15 exp result - E plane Theta(degrees) off-axis angle (deg) 9
10 normalised intensity (db) measurements SCATTER prediction off-axis angle (degrees) 100 GHz Broadband beams exp result Broadband Intensity Approximate Model Total Intensity GHz +/-30%
11 primarymirror Gaussian focal plane secondary mirror SCATTER angle (degrees) angle (degrees) Gaussian vs mode-matching description of a PLANCK horn
12 Phase centre 12
13 Analysis Techniques Coherent Field Analysis Incoherent Field Analysis Approximate Source Field Boundary Element Methods Method of Moments Finite Difference Techniques Diffraction Integrals Modal Analysis Geometrical Optics (ray tracing) Physical Optics Kirchhoff Rayleigh Rayleigh Sommerfeld Sommerfeld 1 2 Debye (Plane Waves) Gaussian Modes Gabor Modes Geometrical Theory of Diffraction Physical Theory Diffraction Aperture Field Method Projected Aperture Method Boundary Wave Analysis Equivalence Theorem Hermite Functions Laguerre Functions S. Withington 13 Stationary Phase Gabor Modes (ZEMAX) Plane Waves (GLAD) Gaussian Beam Modes (MODAL) Physical Optics (MODAL, GRASP)
14 secondary mirror primary mirror HDPE lenses cryostat window 14 focal plane
15 15 Gaussian intensity distribution remains Gaussian at every point along its path of propagation through an optical system Only the width of the Gaussian and its phase radius of curvature change R(z) W(z) W o Z Gaussian Beam Modes + = 2 o 2 o 2 1 ) ( W z W z W π λ + = z W z z R λ π 2 o 1 ) (
16 R. May 1 Standing wave effect between two conical horns -limited mode description coupling between horns with no standing waves included Dr. N. Trappe 16 Power coupling between TE11 modes in single-moded corrugated horns as a function of distance
17 Far-Field Beam Patterns on-axis Care must be taken with fast beams off-axis 17
18 MBI Beam Combiner D=200mm 2A=50mm ν = 90 GHz λ/d 1 for a baseline D 200mm 2a = 25mm λ / D 2 samples per fringe on the focal plane equivalent focal length of 3000mm 4a = 50mm 18
19 19
20 200mm mm
21 Diffraction Analysis The beams from corrugated horns of diameter 2a = 50mm and axial length 130 mm have waist w o a = 1 π + λr a distance Δz = 1+ π ( a) λr ( a) behind the horn aperture. R = = 102.3mm 7.67mm L=130mm R = 132.4mm w o Δz 2a aperture w = 16.1mm 2a 21
22 Diffraction Analysis A phase-flattening lens can be used to move the beam waist to the mouth of the horn The equivalent focal length of the system is f = 3000mm therefore the beam width at the output (focal) plane is: w λf out = π ( d = f ) = mm w o. (First fringe is at 50mm) 22
23 But truncation is a problem in this system 23
24 beam radius concave convex distance from secondary 2a = 10mm detectors 24
25 sky corrugated horns secondary mirror cassegrain beam combiner primary mirror detector plane P. Timbie, G. Tucker, A. Khorotkov & the MBI collaboration 25
26 26
27 MODAL 27 M. Gradziel & G. Curran
28 28
29 physical optics Gaussian beam modes 29
30 30 Summary Corrugated horns Gaussian approximation may not always reproduce the main beam A Bessel function is an excellent description of a scalar horn (phase centre) Electromagnetic mode-matching techniques are used especially for shaped & multimoded horns. Propagation through optics GBM for beam sizes Zemax extremely useful, lenses, optimisation etc. but must take care with certain steps GRASP as benchmark but no lenses, slow for optimisation etc.
31 31
Modeling the quasi-optical performance of CMB astronomical interferometers
 Modeling the quasi-optical performance of CMB astronomical interferometers Gareth S. Curran* a, Marcin L. Gradziel b, Créidhe O Sullivan b, J. Anthony Murphy b, Andrei Korotkov c, Siddharth Malu d, Peter
Modeling the quasi-optical performance of CMB astronomical interferometers Gareth S. Curran* a, Marcin L. Gradziel b, Créidhe O Sullivan b, J. Anthony Murphy b, Andrei Korotkov c, Siddharth Malu d, Peter
Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics
 Keqian Zhang Dejie Li Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics Second Edition With 280 Figures and 13 Tables 4u Springer Basic Electromagnetic Theory 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations 1 1.1.1
Keqian Zhang Dejie Li Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics Second Edition With 280 Figures and 13 Tables 4u Springer Basic Electromagnetic Theory 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations 1 1.1.1
Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics
 Keqian Zhang Dejie Li Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics Translated by authors With 259 Figures Springer Contents 1 Basic Electromagnetic Theory 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations 1 1.1.1
Keqian Zhang Dejie Li Electromagnetic Theory for Microwaves and Optoelectronics Translated by authors With 259 Figures Springer Contents 1 Basic Electromagnetic Theory 1 1.1 Maxwell's Equations 1 1.1.1
Part I. The Quad-Ridged Flared Horn
 9 Part I The Quad-Ridged Flared Horn 10 Chapter 2 Key Requirements of Radio Telescope Feeds Almost all of today s radio telescopes operating above 0.5 GHz use reflector antennas consisting of one or more
9 Part I The Quad-Ridged Flared Horn 10 Chapter 2 Key Requirements of Radio Telescope Feeds Almost all of today s radio telescopes operating above 0.5 GHz use reflector antennas consisting of one or more
feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field matching
 CHAPTER-2 MATCHED FEED FOR OFFSET REFLECTOR ANTENNA The primary objective of this chapter is to discuss the basic concept of matched feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field
CHAPTER-2 MATCHED FEED FOR OFFSET REFLECTOR ANTENNA The primary objective of this chapter is to discuss the basic concept of matched feed. The fundamental principle of the matched feed depends on the field
IMPLEMENTATION OF A QUASI-OPTICAL FREE-SPACE S-PARAMETERS MEASUREMENT SYSTEM
 IMPLEMENTATION OF A QUASI-OPTICAL FREE-SPACE S-PARAMETERS MEASUREMENT SYSTEM B. Maffei, S. Legg, M. Robinson, F. Ozturk, M. W. Ng, P. Schemmel and G. Pisano. JBCA, School of Physics and Astronomy, The
IMPLEMENTATION OF A QUASI-OPTICAL FREE-SPACE S-PARAMETERS MEASUREMENT SYSTEM B. Maffei, S. Legg, M. Robinson, F. Ozturk, M. W. Ng, P. Schemmel and G. Pisano. JBCA, School of Physics and Astronomy, The
The Einstein Polarization Interferometer for Cosmology (EPIC)
 The Einstein Polarization Interferometer for Cosmology (EPIC) Greg Tucker Brown University for the EPIC collaboration 25 October 2006 BPol Satellite Workshop 1 EPIC Mission Concept Study Team Brown University
The Einstein Polarization Interferometer for Cosmology (EPIC) Greg Tucker Brown University for the EPIC collaboration 25 October 2006 BPol Satellite Workshop 1 EPIC Mission Concept Study Team Brown University
The Millimeter-Wave Bolometric Interferometer (MBI) Greg Tucker Brown University
 The Millimeter-Wave Bolometric Interferometer (MBI) Greg Tucker Brown University Brown University Greg Tucker Jaiseung Kim Andrei Korotkov Jerry Vinokurov MBI Collaboration University of Wisconsin Madison
The Millimeter-Wave Bolometric Interferometer (MBI) Greg Tucker Brown University Brown University Greg Tucker Jaiseung Kim Andrei Korotkov Jerry Vinokurov MBI Collaboration University of Wisconsin Madison
3.5 Cavities Cavity modes and ABCD-matrix analysis 206 CHAPTER 3. ULTRASHORT SOURCES I - FUNDAMENTALS
 206 CHAPTER 3. ULTRASHORT SOURCES I - FUNDAMENTALS which is a special case of Eq. (3.30. Note that this treatment of dispersion is equivalent to solving the differential equation (1.94 for an incremental
206 CHAPTER 3. ULTRASHORT SOURCES I - FUNDAMENTALS which is a special case of Eq. (3.30. Note that this treatment of dispersion is equivalent to solving the differential equation (1.94 for an incremental
Laser Optics-II. ME 677: Laser Material Processing Instructor: Ramesh Singh 1
 Laser Optics-II 1 Outline Absorption Modes Irradiance Reflectivity/Absorption Absorption coefficient will vary with the same effects as the reflectivity For opaque materials: reflectivity = 1 - absorptivity
Laser Optics-II 1 Outline Absorption Modes Irradiance Reflectivity/Absorption Absorption coefficient will vary with the same effects as the reflectivity For opaque materials: reflectivity = 1 - absorptivity
Final Design and Testing of the 94 GHz Quasi-Optical-Feed for the EarthCARE S Cloud Profiling Radar
 Final Design and Testing of the 94 GHz Quasi-Optical-Feed for the EarthCARE S Cloud Profiling Radar J. Hartmann #, Chr. Hartwanger #, R. Wylde +, C. Cappellin*, H. Horie x # Astrium GmbH - Satellites,
Final Design and Testing of the 94 GHz Quasi-Optical-Feed for the EarthCARE S Cloud Profiling Radar J. Hartmann #, Chr. Hartwanger #, R. Wylde +, C. Cappellin*, H. Horie x # Astrium GmbH - Satellites,
Quasi-optical beam waveguide analysis using frame based Gaussian beam expansion
 Thirteenth international Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology, Harvard University, March 2002. Quasi-optical beam waveguide analysis using frame based Gaussian beam expansion Torsten Bondw and Stig
Thirteenth international Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology, Harvard University, March 2002. Quasi-optical beam waveguide analysis using frame based Gaussian beam expansion Torsten Bondw and Stig
all dimensions are mm the minus means meniscus lens f 2
 TEM Gauss-beam described with ray-optics. F.A. van Goor, University of Twente, Enschede The Netherlands. fred@uttnqe.utwente.nl December 8, 994 as significantly modified by C. Nelson - 26 Example of an
TEM Gauss-beam described with ray-optics. F.A. van Goor, University of Twente, Enschede The Netherlands. fred@uttnqe.utwente.nl December 8, 994 as significantly modified by C. Nelson - 26 Example of an
FEASIBILITY STUDY FOR THE FOCALISATION OF THE NEW 40m RADIOTELESCOPE OF CENTRO ASTRONÓMICO DE YEBES
 Thirteenth international Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology, Harvard University, March 2002. FEASIBILITY STUDY FOR THE FOCALISATION OF THE NEW 40m RADIOTELESCOPE OF CENTRO ASTRONÓMICO DE YEBES E.
Thirteenth international Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology, Harvard University, March 2002. FEASIBILITY STUDY FOR THE FOCALISATION OF THE NEW 40m RADIOTELESCOPE OF CENTRO ASTRONÓMICO DE YEBES E.
21. Propagation of Gaussian beams
 1. Propagation of Gaussian beams How to propagate a Gaussian beam Rayleigh range and confocal parameter Transmission through a circular aperture Focusing a Gaussian beam Depth of field Gaussian beams and
1. Propagation of Gaussian beams How to propagate a Gaussian beam Rayleigh range and confocal parameter Transmission through a circular aperture Focusing a Gaussian beam Depth of field Gaussian beams and
The Effect of Dust on Lensed and non-lensed Connectors. Dr. Michael A. Kadar-Kallen Broadband Network Solutions, TE Connectivity
 The Effect of Dust on Lensed and non-lensed Connectors Dr. Michael A. Kadar-Kallen Broadband Network Solutions, TE Connectivity Presentation for inemi at OFC: March 3, 015 Outline as discussed with the
The Effect of Dust on Lensed and non-lensed Connectors Dr. Michael A. Kadar-Kallen Broadband Network Solutions, TE Connectivity Presentation for inemi at OFC: March 3, 015 Outline as discussed with the
LC circuit: Energy stored. This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters
 Disclaimer: Chapter 29 Alternating-Current Circuits (1) This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters 29-33. LC circuit: Energy stored LC
Disclaimer: Chapter 29 Alternating-Current Circuits (1) This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters 29-33. LC circuit: Energy stored LC
Optics, Optoelectronics and Photonics
 Optics, Optoelectronics and Photonics Engineering Principles and Applications Alan Billings Emeritus Professor, University of Western Australia New York London Toronto Sydney Tokyo Singapore v Contents
Optics, Optoelectronics and Photonics Engineering Principles and Applications Alan Billings Emeritus Professor, University of Western Australia New York London Toronto Sydney Tokyo Singapore v Contents
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS
 PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS C. A. Bennett University of North Carolina At Asheville WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS Preface 1 The Physics of Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICAL OPTICS C. A. Bennett University of North Carolina At Asheville WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS Preface 1 The Physics of Waves 1 1.1 Introduction
Gaussian Beam Mode Analysis of Imaging Arrays
 Gaussian Beam Mode Analysis of Imaging Arrays J.A. Murphy, St. Patrick's College, Maynooth, Co.Kildare, Ireland & Stafford Withington, Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge CB3 OHE, UK Abstract In this paper
Gaussian Beam Mode Analysis of Imaging Arrays J.A. Murphy, St. Patrick's College, Maynooth, Co.Kildare, Ireland & Stafford Withington, Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge CB3 OHE, UK Abstract In this paper
Revisiting the ALMA Band 1 Optics Design P. Zorzi 1, D. Henke 2, S. Claude 2, P. Mena 1, L. Bronfman 3, and J. May 3
 Revisiting the ALMA Band 1 Optics Design P. Zorzi 1, D. Henke 2, S. Claude 2, P. Mena 1, L. Bronfman 3, and J. May 3 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile 2 NRC
Revisiting the ALMA Band 1 Optics Design P. Zorzi 1, D. Henke 2, S. Claude 2, P. Mena 1, L. Bronfman 3, and J. May 3 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile 2 NRC
3.1 The Plane Mirror Resonator 3.2 The Spherical Mirror Resonator 3.3 Gaussian modes and resonance frequencies 3.4 The Unstable Resonator
 Quantum Electronics Laser Physics Chapter 3 The Optical Resonator 3.1 The Plane Mirror Resonator 3. The Spherical Mirror Resonator 3.3 Gaussian modes and resonance frequencies 3.4 The Unstable Resonator
Quantum Electronics Laser Physics Chapter 3 The Optical Resonator 3.1 The Plane Mirror Resonator 3. The Spherical Mirror Resonator 3.3 Gaussian modes and resonance frequencies 3.4 The Unstable Resonator
Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light
 CHAPTER 6 Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light We present a method to efficiently sort orbital angular momentum (OAM) states of light using two static optical elements. The optical
CHAPTER 6 Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light We present a method to efficiently sort orbital angular momentum (OAM) states of light using two static optical elements. The optical
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. ECE426F Optical Engineering. Final Exam. Dec. 17, 2003.
 Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE426F Optical Engineering Final Exam Dec. 17, 2003 Exam Type: D (Close-book + one 2-sided aid sheet + a non-programmable calculator)
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE426F Optical Engineering Final Exam Dec. 17, 2003 Exam Type: D (Close-book + one 2-sided aid sheet + a non-programmable calculator)
Chapter 2 Basic Optics
 Chapter Basic Optics.1 Introduction In this chapter we will discuss the basic concepts associated with polarization, diffraction, and interference of a light wave. The concepts developed in this chapter
Chapter Basic Optics.1 Introduction In this chapter we will discuss the basic concepts associated with polarization, diffraction, and interference of a light wave. The concepts developed in this chapter
PHY410 Optics Exam #3
 PHY410 Optics Exam #3 NAME: 1 2 Multiple Choice Section - 5 pts each 1. A continuous He-Ne laser beam (632.8 nm) is chopped, using a spinning aperture, into 500 nanosecond pulses. Compute the resultant
PHY410 Optics Exam #3 NAME: 1 2 Multiple Choice Section - 5 pts each 1. A continuous He-Ne laser beam (632.8 nm) is chopped, using a spinning aperture, into 500 nanosecond pulses. Compute the resultant
Department of Physics Preliminary Exam January 2 5, 2013
 Department of Physics Preliminary Exam January 2 5, 2013 Day 2: Electricity, Magnetism and Optics Thursday, January 3, 2013 9:00 a.m. 12:00 p.m. Instructions: 1. Write the answer to each question on a
Department of Physics Preliminary Exam January 2 5, 2013 Day 2: Electricity, Magnetism and Optics Thursday, January 3, 2013 9:00 a.m. 12:00 p.m. Instructions: 1. Write the answer to each question on a
Modeling microlenses by use of vectorial field rays and diffraction integrals
 Modeling microlenses by use of vectorial field rays and diffraction integrals Miguel A. Alvarez-Cabanillas, Fang Xu, and Yeshaiahu Fainman A nonparaxial vector-field method is used to describe the behavior
Modeling microlenses by use of vectorial field rays and diffraction integrals Miguel A. Alvarez-Cabanillas, Fang Xu, and Yeshaiahu Fainman A nonparaxial vector-field method is used to describe the behavior
S. Blair September 27,
 S. Blair September 7, 010 54 4.3. Optical Resonators With Spherical Mirrors Laser resonators have the same characteristics as Fabry-Perot etalons. A laser resonator supports longitudinal modes of a discrete
S. Blair September 7, 010 54 4.3. Optical Resonators With Spherical Mirrors Laser resonators have the same characteristics as Fabry-Perot etalons. A laser resonator supports longitudinal modes of a discrete
Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1)
 EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION
 October 4-6, 2007 - Chiinu, Rep.Moldova USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION Ionu- P. NICA, Valeriu Gh. DAVID, /tefan URSACHE Gh. Asachi Technical University Iai, Faculty
October 4-6, 2007 - Chiinu, Rep.Moldova USAGE OF NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDS OPTIMIZATION Ionu- P. NICA, Valeriu Gh. DAVID, /tefan URSACHE Gh. Asachi Technical University Iai, Faculty
Appendix 3 Change Record
 ALMA Project ALMA Front End Optics Design Report Band 3 Optics Measurement Doc # : FEND-4.2..-35-B-REP Date: 27-9-26 Version: A Status: Released Page: 1 of 75 Prepared By: Name(s) and Signature(s) Organization
ALMA Project ALMA Front End Optics Design Report Band 3 Optics Measurement Doc # : FEND-4.2..-35-B-REP Date: 27-9-26 Version: A Status: Released Page: 1 of 75 Prepared By: Name(s) and Signature(s) Organization
Simulation of laser propagation in plasma chamber including nonlinearities by utilization of VirtualLab 5 software
 Simulation of laser propagation in plasma chamber including nonlinearities by utilization of VirtualLab 5 software DESY Summer Student Programme, 2012 Anusorn Lueangaramwong Chiang Mai University, Thailand
Simulation of laser propagation in plasma chamber including nonlinearities by utilization of VirtualLab 5 software DESY Summer Student Programme, 2012 Anusorn Lueangaramwong Chiang Mai University, Thailand
Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory. ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy
 Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy The three major branches of optics Geometrical Optics Light travels as straight rays Physical Optics Light can be
Interference, Diffraction and Fourier Theory ATI 2014 Lecture 02! Keller and Kenworthy The three major branches of optics Geometrical Optics Light travels as straight rays Physical Optics Light can be
Gaussian Beam Analysis of Relay Optics for the SEQUOIA Focal Plane Array
 15th International Symposium on Space Terahert Technology Gaussian Beam Analysis of Relay Optics for the SEQUOIA Focal Plane Array Gopal Narayananl Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts,
15th International Symposium on Space Terahert Technology Gaussian Beam Analysis of Relay Optics for the SEQUOIA Focal Plane Array Gopal Narayananl Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts,
Design of an off set optics with high polarization purity and large Focal plane Area for CMB polarization observations
 Designofanoff setopticswith highpolarizationpurityandlargefocal planearea forcmbpolarizationobservations P.Bolli %,E.Carretti *,A.Navarrini % % OsservatorioAstronomicodiCagliari INAF Loc.PoggiodeiPini,Strada54
Designofanoff setopticswith highpolarizationpurityandlargefocal planearea forcmbpolarizationobservations P.Bolli %,E.Carretti *,A.Navarrini % % OsservatorioAstronomicodiCagliari INAF Loc.PoggiodeiPini,Strada54
Vector diffraction theory of refraction of light by a spherical surface
 S. Guha and G. D. Gillen Vol. 4, No. 1/January 007/J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1 Vector diffraction theory of refraction of light by a spherical surface Shekhar Guha and Glen D. Gillen* Materials and Manufacturing
S. Guha and G. D. Gillen Vol. 4, No. 1/January 007/J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1 Vector diffraction theory of refraction of light by a spherical surface Shekhar Guha and Glen D. Gillen* Materials and Manufacturing
Optics for Engineers Chapter 9
 Optics for Engineers Chapter 9 Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Nov. 202 Gaussian Beams Applications Many Laser Beams Minimum Uncertainty Simple Equations Good Approximation Extensible (e.g.
Optics for Engineers Chapter 9 Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Nov. 202 Gaussian Beams Applications Many Laser Beams Minimum Uncertainty Simple Equations Good Approximation Extensible (e.g.
A family of closed form expressions for the scalar field of strongly focused
 Scalar field of non-paraxial Gaussian beams Z. Ulanowski and I. K. Ludlow Department of Physical Sciences University of Hertfordshire Hatfield Herts AL1 9AB UK. A family of closed form expressions for
Scalar field of non-paraxial Gaussian beams Z. Ulanowski and I. K. Ludlow Department of Physical Sciences University of Hertfordshire Hatfield Herts AL1 9AB UK. A family of closed form expressions for
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements Homework #4 is assigned, due March 25 th Start discussion
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements Homework #4 is assigned, due March 25 th Start discussion
Astronomy 203 practice final examination
 Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Cylindrical Dielectric Waveguides
 03/02/2017 Cylindrical Dielectric Waveguides Integrated Optics Prof. Elias N. Glytsis School of Electrical & Computer Engineering National Technical University of Athens Geometry of a Single Core Layer
03/02/2017 Cylindrical Dielectric Waveguides Integrated Optics Prof. Elias N. Glytsis School of Electrical & Computer Engineering National Technical University of Athens Geometry of a Single Core Layer
Electromagnetic Implosion Using a Lens
 Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 516 July 2006 Electromagnetic Implosion Using a Lens Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque New Mexico 87131
Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 516 July 2006 Electromagnetic Implosion Using a Lens Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque New Mexico 87131
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 1 O P T I C S 1. Define resolving power of a telescope & microscope and give the expression for its resolving power. 2. Explain briefly the formation of mirage in deserts. 3. The radii of curvature of
1 O P T I C S 1. Define resolving power of a telescope & microscope and give the expression for its resolving power. 2. Explain briefly the formation of mirage in deserts. 3. The radii of curvature of
Fourier Optics - Exam #1 Review
 Fourier Optics - Exam #1 Review Ch. 2 2-D Linear Systems A. Fourier Transforms, theorems. - handout --> your note sheet B. Linear Systems C. Applications of above - sampled data and the DFT (supplement
Fourier Optics - Exam #1 Review Ch. 2 2-D Linear Systems A. Fourier Transforms, theorems. - handout --> your note sheet B. Linear Systems C. Applications of above - sampled data and the DFT (supplement
Optics for Engineers Chapter 9
 Optics for Engineers Chapter 9 Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Mar. 204 Gaussian Beams Applications Many Laser Beams Minimum Uncertainty Simple Equations Good Approximation Extensible (e.g.
Optics for Engineers Chapter 9 Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Mar. 204 Gaussian Beams Applications Many Laser Beams Minimum Uncertainty Simple Equations Good Approximation Extensible (e.g.
Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light
 Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light Lecture aims to explain: 1. Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications 2. Interference of two one dimensional electromagnetic waves 3. Typical
Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light Lecture aims to explain: 1. Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications 2. Interference of two one dimensional electromagnetic waves 3. Typical
A REVISED PROPOSAL FOR A FEED SYSTEM FOR THE VLBA ANTENNA P. J. NAPIER 1/11/82 INTRODUCTION
 A REVISED PROPOSAL FOR A FEED SYSTEM FOR THE VLBA ANTENNA P. J. NAPIER 1/11/82 INTRODUCTION In a previous report a concept for a feed system for the VLBA antenna was presented. Further study of the problem
A REVISED PROPOSAL FOR A FEED SYSTEM FOR THE VLBA ANTENNA P. J. NAPIER 1/11/82 INTRODUCTION In a previous report a concept for a feed system for the VLBA antenna was presented. Further study of the problem
LECTURE 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) Equation Section 18
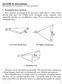 LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) quation Section 18 1 Rectangular horn antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave band (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. The diagram shows the concave mirror of a Cassegrain reflecting telescope, together with the eyepiece lens. Complete the diagram of the telescope and mark on it the focal
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. The diagram shows the concave mirror of a Cassegrain reflecting telescope, together with the eyepiece lens. Complete the diagram of the telescope and mark on it the focal
Novel Features of Computational EM and Particle-in-Cell Simulations. Shahid Ahmed. Illinois Institute of Technology
 Novel Features of Computational EM and Particle-in-Cell Simulations Shahid Ahmed Illinois Institute of Technology Outline Part-I EM Structure Motivation Method Modes, Radiation Leakage and HOM Damper Conclusions
Novel Features of Computational EM and Particle-in-Cell Simulations Shahid Ahmed Illinois Institute of Technology Outline Part-I EM Structure Motivation Method Modes, Radiation Leakage and HOM Damper Conclusions
Application of nondiffracting beams to wireless optical communications
 Application of nondiffracting beams to wireless optical communications V. Kollárová a, T. Medřík a, R. Čelechovský a, Z. Bouchal a O. Wilfert* b, Z. Kolka b a Faculty of Science, Palacký University, 17.
Application of nondiffracting beams to wireless optical communications V. Kollárová a, T. Medřík a, R. Čelechovský a, Z. Bouchal a O. Wilfert* b, Z. Kolka b a Faculty of Science, Palacký University, 17.
Focal shift in vector beams
 Focal shift in vector beams Pamela L. Greene The Institute of Optics, University of Rochester, Rochester, New York 1467-186 pgreene@optics.rochester.edu Dennis G. Hall The Institute of Optics and The Rochester
Focal shift in vector beams Pamela L. Greene The Institute of Optics, University of Rochester, Rochester, New York 1467-186 pgreene@optics.rochester.edu Dennis G. Hall The Institute of Optics and The Rochester
Describe the forces and torques exerted on an electric dipole in a field.
 Learning Outcomes - PHYS 2015 Electric charges and forces: Describe the electrical nature of matter; Explain how an object can be charged; Distinguish between electrical conductors and insulators and the
Learning Outcomes - PHYS 2015 Electric charges and forces: Describe the electrical nature of matter; Explain how an object can be charged; Distinguish between electrical conductors and insulators and the
Fourier transform = F. Introduction to Fourier Optics, J. Goodman Fundamentals of Photonics, B. Saleh &M. Teich. x y x y x y
 Fourier transform Introduction to Fourier Optics, J. Goodman Fundamentals of Photonics, B. Saleh &M. Teich f( x, y) FT g( f, f ) f( x, y) IFT g( f, f ) x x y y + 1 { g( f, ) } x fy { π } f( x, y) = g(
Fourier transform Introduction to Fourier Optics, J. Goodman Fundamentals of Photonics, B. Saleh &M. Teich f( x, y) FT g( f, f ) f( x, y) IFT g( f, f ) x x y y + 1 { g( f, ) } x fy { π } f( x, y) = g(
EE485 Introduction to Photonics
 Pattern formed by fluorescence of quantum dots EE485 Introduction to Photonics Photon and Laser Basics 1. Photon properties 2. Laser basics 3. Characteristics of laser beams Reading: Pedrotti 3, Sec. 1.2,
Pattern formed by fluorescence of quantum dots EE485 Introduction to Photonics Photon and Laser Basics 1. Photon properties 2. Laser basics 3. Characteristics of laser beams Reading: Pedrotti 3, Sec. 1.2,
Concave mirrors. Which of the following ray tracings is correct? A: only 1 B: only 2 C: only 3 D: all E: 2& 3
 Concave mirrors Which of the following ray tracings is correct? A: only 1 B: only 2 C: only 3 D: all E: 2& 3 1 2 3 c F Point C: geometrical center of the mirror, F: focal point 2 Concave mirrors Which
Concave mirrors Which of the following ray tracings is correct? A: only 1 B: only 2 C: only 3 D: all E: 2& 3 1 2 3 c F Point C: geometrical center of the mirror, F: focal point 2 Concave mirrors Which
ULTRASONIC INSPECTION, MATERIAL NOISE AND. Mehmet Bilgen and James H. Center for NDE Iowa State University Ames, IA 50011
 ULTRASONIC INSPECTION, MATERIAL NOISE AND SURFACE ROUGHNESS Mehmet Bilgen and James H. Center for NDE Iowa State University Ames, IA 511 Rose Peter B. Nagy Department of Welding Engineering Ohio State
ULTRASONIC INSPECTION, MATERIAL NOISE AND SURFACE ROUGHNESS Mehmet Bilgen and James H. Center for NDE Iowa State University Ames, IA 511 Rose Peter B. Nagy Department of Welding Engineering Ohio State
Step index planar waveguide
 N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
N. Dubreuil S. Lebrun Exam without document Pocket calculator permitted Duration of the exam: 2 hours The exam takes the form of a multiple choice test. Annexes are given at the end of the text. **********************************************************************************
1 Longitudinal modes of a laser cavity
 Adrian Down May 01, 2006 1 Longitudinal modes of a laser cavity 1.1 Resonant modes For the moment, imagine a laser cavity as a set of plane mirrors separated by a distance d. We will return to the specific
Adrian Down May 01, 2006 1 Longitudinal modes of a laser cavity 1.1 Resonant modes For the moment, imagine a laser cavity as a set of plane mirrors separated by a distance d. We will return to the specific
Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light
 Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications Diffraction in everyday life Diffraction in applications Spectroscopy: physics, chemistry, medicine,
Lecture 11: Introduction to diffraction of light Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications Diffraction in everyday life Diffraction in applications Spectroscopy: physics, chemistry, medicine,
Supplementary Materials for
 wwwsciencemagorg/cgi/content/full/scienceaaa3035/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Spatially structured photons that travel in free space slower than the speed of light Daniel Giovannini, Jacquiline Romero,
wwwsciencemagorg/cgi/content/full/scienceaaa3035/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Spatially structured photons that travel in free space slower than the speed of light Daniel Giovannini, Jacquiline Romero,
Module Labworks Optics Abbe School of Photonics Contact person Supervisors
 Module Labworks Optics Abbe School of Photonics, Friedrich-Schiller-Universität, Physikalisch-Astronomische-Fakultät, Max-Wien-Platz 1, 07743 Jena, Germany Phone: +49 3641 947 960 Fax: +49 3641 947 962
Module Labworks Optics Abbe School of Photonics, Friedrich-Schiller-Universität, Physikalisch-Astronomische-Fakultät, Max-Wien-Platz 1, 07743 Jena, Germany Phone: +49 3641 947 960 Fax: +49 3641 947 962
Lecture notes 5: Diffraction
 Lecture notes 5: Diffraction Let us now consider how light reacts to being confined to a given aperture. The resolution of an aperture is restricted due to the wave nature of light: as light passes through
Lecture notes 5: Diffraction Let us now consider how light reacts to being confined to a given aperture. The resolution of an aperture is restricted due to the wave nature of light: as light passes through
UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS
 UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS 1) Define electric potential and potential difference. 2) Name few applications of gauss law in electrostatics. 3) State point form of Ohm s Law. 4) State Divergence Theorem.
UNIT I ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS 1) Define electric potential and potential difference. 2) Name few applications of gauss law in electrostatics. 3) State point form of Ohm s Law. 4) State Divergence Theorem.
Nature of Light Part 2
 Nature of Light Part 2 Fresnel Coefficients From Helmholts equation see imaging conditions for Single lens 4F system Diffraction ranges Rayleigh Range Diffraction limited resolution Interference Newton
Nature of Light Part 2 Fresnel Coefficients From Helmholts equation see imaging conditions for Single lens 4F system Diffraction ranges Rayleigh Range Diffraction limited resolution Interference Newton
P5 Revision Questions
 P5 Revision Questions Part 2 Question 1 How can microwaves be used to communicate? Answer 1 Sent from transmitter, received and amplified by satellite in space, re-transmitted back to earth and picked
P5 Revision Questions Part 2 Question 1 How can microwaves be used to communicate? Answer 1 Sent from transmitter, received and amplified by satellite in space, re-transmitted back to earth and picked
1 ESO's Compact Laser Guide Star Unit Ottobeuren, Germany Beam optics!
 1 ESO's Compact Laser Guide Star Unit Ottobeuren, Germany www.eso.org Introduction Characteristics Beam optics! ABCD matrices 2 Background! A paraxial wave has wavefronts whose normals are paraxial rays.!!
1 ESO's Compact Laser Guide Star Unit Ottobeuren, Germany www.eso.org Introduction Characteristics Beam optics! ABCD matrices 2 Background! A paraxial wave has wavefronts whose normals are paraxial rays.!!
Crash Course on Optics I & II. COST Action IC1101 OPTICWISE 4 th Training School
 Crash Course on Optics I & II COST Action IC1101 OPTICWISE 4 th Training School Introductory Concepts Fermat s principle Snell s law Total internal refraction Dispersion Aberrations Interference and Diffraction
Crash Course on Optics I & II COST Action IC1101 OPTICWISE 4 th Training School Introductory Concepts Fermat s principle Snell s law Total internal refraction Dispersion Aberrations Interference and Diffraction
LECTURE 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.)
 LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) 1 Rectangular Horn Antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave bands (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high gain, low VSWR (with
LCTUR 18: Horn Antennas (Rectangular horn antennas. Circular apertures.) 1 Rectangular Horn Antennas Horn antennas are popular in the microwave bands (above 1 GHz). Horns provide high gain, low VSWR (with
b) Derive the charge-current continuity equation for free charge-density (, ) and free current-density (, ) from Maxwell s microscopic equations.
 Fall 205 Written Comprehensive Exam Opti 50 System of units: MKSA 2Pts a) The charge-current continuity equation is written (, )+ (, ) =0. Explain in a few sentences the physical meaning of the equation
Fall 205 Written Comprehensive Exam Opti 50 System of units: MKSA 2Pts a) The charge-current continuity equation is written (, )+ (, ) =0. Explain in a few sentences the physical meaning of the equation
LIST OF TOPICS BASIC LASER PHYSICS. Preface xiii Units and Notation xv List of Symbols xvii
 ate LIST OF TOPICS Preface xiii Units and Notation xv List of Symbols xvii BASIC LASER PHYSICS Chapter 1 An Introduction to Lasers 1.1 What Is a Laser? 2 1.2 Atomic Energy Levels and Spontaneous Emission
ate LIST OF TOPICS Preface xiii Units and Notation xv List of Symbols xvii BASIC LASER PHYSICS Chapter 1 An Introduction to Lasers 1.1 What Is a Laser? 2 1.2 Atomic Energy Levels and Spontaneous Emission
Free-Electron Lasers
 Introduction to Free-Electron Lasers Neil Thompson ASTeC Outline Introduction: What is a Free-Electron Laser? How does an FEL work? Choosing the required parameters Laser Resonators for FELs FEL Output
Introduction to Free-Electron Lasers Neil Thompson ASTeC Outline Introduction: What is a Free-Electron Laser? How does an FEL work? Choosing the required parameters Laser Resonators for FELs FEL Output
Offset Spheroidal Mirrors for Gaussian Beam Optics in ZEMAX
 Offset Spheroidal Mirrors for Gaussian Beam Optics in ZEMAX Antony A. Stark and Urs Graf Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, University of Cologne aas@cfa.harvard.edu 1 October 2013 This memorandum
Offset Spheroidal Mirrors for Gaussian Beam Optics in ZEMAX Antony A. Stark and Urs Graf Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, University of Cologne aas@cfa.harvard.edu 1 October 2013 This memorandum
Optical Systems Program of Studies Version 1.0 April 2012
 Optical Systems Program of Studies Version 1.0 April 2012 Standard1 Essential Understand Optical experimental methodology, data analysis, interpretation, and presentation strategies Essential Understandings:
Optical Systems Program of Studies Version 1.0 April 2012 Standard1 Essential Understand Optical experimental methodology, data analysis, interpretation, and presentation strategies Essential Understandings:
The Einstein Polarization Interferometer for Cosmology (EPIC)
 The Einstein Polarization Interferometer for Cosmology (EPIC) Peter Timbie UW-Madison for the EPIC collaboration Brown, Cardiff, Illinois, Ireland-Maynooth, LLNL, Manchester, Richmond, UCSD, Wisconsin,
The Einstein Polarization Interferometer for Cosmology (EPIC) Peter Timbie UW-Madison for the EPIC collaboration Brown, Cardiff, Illinois, Ireland-Maynooth, LLNL, Manchester, Richmond, UCSD, Wisconsin,
1 Lectures 10 and 11: resonance cavities
 1 1 Lectures 10 and 11: resonance cavities We now analyze cavities that consist of a waveguide of length h, terminated by perfectly conducting plates at both ends. The coordinate system is oriented such
1 1 Lectures 10 and 11: resonance cavities We now analyze cavities that consist of a waveguide of length h, terminated by perfectly conducting plates at both ends. The coordinate system is oriented such
Lasers and Electro-optics
 Lasers and Electro-optics Second Edition CHRISTOPHER C. DAVIS University of Maryland III ^0 CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface to the Second Edition page xv 1 Electromagnetic waves, light, and lasers 1
Lasers and Electro-optics Second Edition CHRISTOPHER C. DAVIS University of Maryland III ^0 CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface to the Second Edition page xv 1 Electromagnetic waves, light, and lasers 1
Copyright 1966, by the author(s). All rights reserved.
 Copyright 1966, by the author(s). All rights reserved. Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are
Copyright 1966, by the author(s). All rights reserved. Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are
Quasi-Optical Filters
 Quasi-Optical Filters Peter Ade Cardiff School of Physics and Astronomy, Cardiff University, Queens Buildings, The Parade, Cardiff, CF24 3AA Peter.Ade@astro.cf.ac.uk Abstract: We describe the current state-of-art
Quasi-Optical Filters Peter Ade Cardiff School of Physics and Astronomy, Cardiff University, Queens Buildings, The Parade, Cardiff, CF24 3AA Peter.Ade@astro.cf.ac.uk Abstract: We describe the current state-of-art
PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM. Student Number. The last two pages of the exam have some equations and some physical constants.
 PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM Name Student Number CHECK ONE: Instructor 1 10:00 Instructor 2 1:00 Note that problems 1-19 are worth 2 points each, while problem 20 is worth 15 points and problems 21 and
PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM Name Student Number CHECK ONE: Instructor 1 10:00 Instructor 2 1:00 Note that problems 1-19 are worth 2 points each, while problem 20 is worth 15 points and problems 21 and
Classical Electrodynamics
 Classical Electrodynamics Third Edition John David Jackson Professor Emeritus of Physics, University of California, Berkeley JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. Contents Introduction and Survey 1 I.1 Maxwell Equations
Classical Electrodynamics Third Edition John David Jackson Professor Emeritus of Physics, University of California, Berkeley JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. Contents Introduction and Survey 1 I.1 Maxwell Equations
MIMO and Mode Division Multiplexing in Multimode Fibers
 MIMO and Mode Division Multiplexing in Multimode Fibers Kumar Appaiah Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay akumar@ee.iitb.ac.in Tutorial: National Conference on Communications
MIMO and Mode Division Multiplexing in Multimode Fibers Kumar Appaiah Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay akumar@ee.iitb.ac.in Tutorial: National Conference on Communications
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON. Answer all questions in Section A and two and only two questions in. Section B.
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS2023W1 SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2009/10 WAVE PHYSICS Duration: 120 MINS Answer all questions in Section A and two and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries 1/3
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS2023W1 SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2009/10 WAVE PHYSICS Duration: 120 MINS Answer all questions in Section A and two and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries 1/3
2.71. Final examination. 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET
 2.71 Final examination 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH YOUR SOLUTION SHEET(S) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
2.71 Final examination 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH YOUR SOLUTION SHEET(S) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Course Secretary: Christine Berber O3.095, phone x-6351,
 IMPRS: Ultrafast Source Technologies Franz X. Kärtner (Umit Demirbas) & Thorsten Uphues, Bldg. 99, O3.097 & Room 6/3 Email & phone: franz.kaertner@cfel.de, 040 8998 6350 thorsten.uphues@cfel.de, 040 8998
IMPRS: Ultrafast Source Technologies Franz X. Kärtner (Umit Demirbas) & Thorsten Uphues, Bldg. 99, O3.097 & Room 6/3 Email & phone: franz.kaertner@cfel.de, 040 8998 6350 thorsten.uphues@cfel.de, 040 8998
3. How long will a radioactive isotope, whose half-life is T years, take for its activity to reduce to 1/8 th of its initial value?
 No. of printed pages:5 INDIAN SCHOOL SOHAR SECOND TERM EXAM- 2014 PHYSICS THEY CLASS: XII MARKS:70 DATE: 1 /12/2014 TIME:3hrs General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. There are 26 questions
No. of printed pages:5 INDIAN SCHOOL SOHAR SECOND TERM EXAM- 2014 PHYSICS THEY CLASS: XII MARKS:70 DATE: 1 /12/2014 TIME:3hrs General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. There are 26 questions
Focusing of light. Colin Sheppard Division of Bioengineering and Department of Biological Sciences National University of Singapore
 Focusing of light Colin Sheppard Division of Bioengineering and Department of Biological Sciences National University of Singapore E-mail: colin@nus.edu.sg Tight focusing of light Microscopy Laser micromachining
Focusing of light Colin Sheppard Division of Bioengineering and Department of Biological Sciences National University of Singapore E-mail: colin@nus.edu.sg Tight focusing of light Microscopy Laser micromachining
Modeling of the propagation of Bessel beams in a uniaxial crystal at different positions of the crystal axis
 Modeling of the propagation of Bessel beams in a uniaxial crystal at different positions of the crystal axis Krasnov A.P. Samara State Aerospace University Abstract. The numerical study of the propagation
Modeling of the propagation of Bessel beams in a uniaxial crystal at different positions of the crystal axis Krasnov A.P. Samara State Aerospace University Abstract. The numerical study of the propagation
High-Gradient, Millimeter Wave Accelerating Structure
 DPF2015-337 August 31, 2015 High-Gradient, Millimeter Wave Accelerating Structure S.V. Kuzikov 1,2, A.A. Vikharev 1,3, N.Yu. Peskov 1 1 Institute of Applied Physics, 46 Ulyanova Str., Nizhny Novgorod,
DPF2015-337 August 31, 2015 High-Gradient, Millimeter Wave Accelerating Structure S.V. Kuzikov 1,2, A.A. Vikharev 1,3, N.Yu. Peskov 1 1 Institute of Applied Physics, 46 Ulyanova Str., Nizhny Novgorod,
Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers. 高錕 Charles Kao
 Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers 高錕 Charles Kao 1 Planar Dielectric Slab Waveguide Symmetric Planar Slab Waveguide n 1 area : core, n 2 area : cladding a light ray can undergo TIR at the n 1 /n
Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers 高錕 Charles Kao 1 Planar Dielectric Slab Waveguide Symmetric Planar Slab Waveguide n 1 area : core, n 2 area : cladding a light ray can undergo TIR at the n 1 /n
Chapter Ray Optics and Optical Instrument
 Chapter Ray Optics and Optical Instrument Q1. Focal length of a convex lens of refractive index 1.5 is 2 cm. Focal length of the lens when immersed in a liquid of refractive index of 1.25 will be [1988]
Chapter Ray Optics and Optical Instrument Q1. Focal length of a convex lens of refractive index 1.5 is 2 cm. Focal length of the lens when immersed in a liquid of refractive index of 1.25 will be [1988]
Massimiliano Casaletti * and Stefano Maci Department of Information Engineering, University of Siena, Via Roma 56, Siena 53100, Italy
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 28, 245 257, 213 APERTURE BEAM EXPANSION BY USING A SPECTRAL 2D-GPOF METHOD Massimiliano Casaletti * and Stefano Maci Department of Information Engineering,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 28, 245 257, 213 APERTURE BEAM EXPANSION BY USING A SPECTRAL 2D-GPOF METHOD Massimiliano Casaletti * and Stefano Maci Department of Information Engineering,
Quantum Electronics Laser Physics PS Theory of the Laser Oscillation
 Quantum Electronics Laser Physics PS407 6. Theory of the Laser Oscillation 1 I. Laser oscillator: Overview Laser is an optical oscillator. Resonant optical amplifier whose output is fed back into its input
Quantum Electronics Laser Physics PS407 6. Theory of the Laser Oscillation 1 I. Laser oscillator: Overview Laser is an optical oscillator. Resonant optical amplifier whose output is fed back into its input
Tutorial: Ray matrices, gaussian beams, and ABCD.app
 Tutorial: Ray matrices, gaussian beams, and ABCD.app Prof. Daniel Côté Daniel.Cote@crulrg.ulaval.ca April 30, 2013 1 Introduc on This document is a companion guide to ABCD.app and serves as a refresher
Tutorial: Ray matrices, gaussian beams, and ABCD.app Prof. Daniel Côté Daniel.Cote@crulrg.ulaval.ca April 30, 2013 1 Introduc on This document is a companion guide to ABCD.app and serves as a refresher
SMR WINTER COLLEGE QUANTUM AND CLASSICAL ASPECTS INFORMATION OPTICS. The Origins of Light s angular Momentum
 SMR.1738-8 WINTER COLLEGE on QUANTUM AND CLASSICAL ASPECTS of INFORMATION OPTICS 30 January - 10 February 2006 The Origins of Light s angular Momentum Miles PADGETT University of Glasgow Dept. of Physics
SMR.1738-8 WINTER COLLEGE on QUANTUM AND CLASSICAL ASPECTS of INFORMATION OPTICS 30 January - 10 February 2006 The Origins of Light s angular Momentum Miles PADGETT University of Glasgow Dept. of Physics
Fourier transform = F. Introduction to Fourier Optics, J. Goodman Fundamentals of Photonics, B. Saleh &M. Teich. x y x y x y
 Fourier transform Introduction to Fourier Optics, J. Goodman Fundamentals of Photonics, B. Saleh &M. Teich f( x, y) FT g( f, f ) f( x, y) IFT g( f, f ) x x y y + 1 { g( f, ) } x fy { π } f( x, y) = g(
Fourier transform Introduction to Fourier Optics, J. Goodman Fundamentals of Photonics, B. Saleh &M. Teich f( x, y) FT g( f, f ) f( x, y) IFT g( f, f ) x x y y + 1 { g( f, ) } x fy { π } f( x, y) = g(
Week 7: Interference
 Week 7: Interference Superposition: Till now we have mostly discusssed single waves. While discussing group velocity we did talk briefly about superposing more than one wave. We will now focus on superposition
Week 7: Interference Superposition: Till now we have mostly discusssed single waves. While discussing group velocity we did talk briefly about superposing more than one wave. We will now focus on superposition
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN AHMEDABAD REGION 50 SURE SHOT QUESTIONS (LONG ANSWER TYPE)
 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN AHMEDABAD REGION 50 SURE SHOT QUESTIONS (LONG ANSWER TYPE) 1. Define electric field intensity and electric dipole moment. Derive expression for electric field intensity at
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN AHMEDABAD REGION 50 SURE SHOT QUESTIONS (LONG ANSWER TYPE) 1. Define electric field intensity and electric dipole moment. Derive expression for electric field intensity at
DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY. Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University
 DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University 1995 ELSEVIER Amsterdam Lausanne New York Oxford Shannon Tokyo CONTENTS Preface to the first
DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University 1995 ELSEVIER Amsterdam Lausanne New York Oxford Shannon Tokyo CONTENTS Preface to the first
