LTL Translation Improvements in Spot
|
|
|
- Lorena Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LTL Trnsltion Improvements in Spot Alexndre Duret-Lutz VECoS'11 16 September 2011 Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 1 / 19
2 Context High-level model M Does the model M veries the property ϕ? LTL property ϕ M = ϕ or counterexmple Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 2 / 19
3 Automt-Theoretic LTL Model Checking High-level model M Stte-spce genertion Stte-spce utomton A M Synchronized product L (A M A ϕ ) = L (A M ) L (A ϕ ) Product Automton A M A ϕ Emptiness check L (A M A ϕ )? = LTL property ϕ LTL trnsltion Negted property utomton A ϕ M = ϕ or counterexmple Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 2 / 19
4 Automt-Theoretic LTL Model Checking High-level model M Stte-spce genertion Stte-spce utomton A M Synchronized product L (A M A ϕ ) = L (A M ) L (A ϕ ) Product Automton A M A ϕ Emptiness check L (A M A ϕ )? = LTL property ϕ LTL trnsltion Negted property utomton A ϕ M = ϕ or counterexmple Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 2 / 19
5 Automt-Theoretic LTL Model Checking High-level model M On-the-y genertion of stte-spce utomton A M On-the-y synchronized product L (A M A ϕ ) = L (A M ) L (A ϕ ) Emptiness check L (A M A ϕ )? = LTL property ϕ LTL trnsltion Negted property utomton A ϕ M = ϕ or counterexmple Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 2 / 19
6 Automt-Theoretic LTL Model Checking High-level model M Custom Model Checker On-the-y genertion of stte-spce utomton A M SPOT On-the-y synchronized product L (A M A ϕ ) = L (A M ) L (A ϕ ) Emptiness check L (A M A ϕ )? = LTL property ϕ LTL trnsltion Negted property utomton A ϕ M = ϕ or counterexmple Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 2 / 19
7 Let's Tlk bout the LTL Trnsltion We trnslte LTL to generlized Büchi utomt with trnsition-bsed cceptnce. Most people prefer non-generlized Büchi utomt with stte cceptnce. Our trnsltion is competitive, thnks to: A simple tbleu construction tht use BDD for simplictions Two techniques to improve determinism Severl LTL rewriting rules tht ese the trnsltion (not shown) Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 3 / 19
8 Trnsition-bsed Generlized Acceptnce Conditions 1 Introduction 2 Trnsition-bsed Generlized Acceptnce Conditions 3 Trnslting LTL into (TG)BA eciently 4 Conclusion Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 4 / 19
9 Dierent Kinds of Büchi Automt (G F G F b) Trnsition-bsed Generlized Generlized Büchi Automton Büchi Automton Büchi Automton ā āb ā b 3 1 b āb 1 b b 2 b b ā b ā b 2 3 b b b b ā b āb Sme expressive power. Converting BA to GBA, or GBA to TGBA, is trivil. The opposite direction requires degenerliztion. (T)GBA occur nturlly when trnslting LTL. Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 5 / 19
10 Trnslting LTL into (TG)BA eciently 1 Introduction 2 Trnsition-bsed Generlized Acceptnce Conditions 3 Trnslting LTL into (TG)BA eciently Gols: Size nd Speed Core Trnsltion: Tbleu using BDDs Improving Determinism with BDDs nd WDBA Results 4 Conclusion Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 6 / 19
11 Trnsltion of Litterture Formuls Cumulted sizes of utomt for 188 formuls from the litterture Products with rndom stte-spce of 200 sttes Σ A ϕ Σ A M A ϕ st. tr. st. tr. BA Spin (A 9) LTL2BA Modell ( 1) Spot Spot det Spot WDBA TGBA Spot Spot det Spot WDBA A = 15min timeout = bogus trnsltion Produce more deterministic ut. WDBA minimiztion when pplicble Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 7 / 19
12 Rozier & Vrdi's Sclbility Experiment (1/2) An LTL formul C n tht cn be encoded by n2 n -stte utomton. K. Y. Rozier nd M. Y. Vrdi. LTL stisbility checking. In Proc. of SPIN'07, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 8 / 19
13 Rozier & Vrdi's Sclbility Experiment (1/2) An LTL formul C n tht cn be encoded by n2 n -stte utomton. E.g. C 3 = (( (G( (X( X( X )))))) (( b) X( b X b)) (G(( b) (X((X X b) ((( ) (b X X X b) (( b) (X X X b))) U ))))) (G(( b) (X((X X b) ((b ( ) X X X b) U( (( ) ( b) (X((X X b) ((( ) (b X X X b) (( b) X X X b)) U ))))))))))) K. Y. Rozier nd M. Y. Vrdi. LTL stisbility checking. In Proc. of SPIN'07, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 8 / 19
14 Rozier & Vrdi's Sclbility Experiment (1/2) An LTL formul C n tht cn be encoded by n2 n -stte utomton. E.g. C 3 = (( (G( (X( X( X )))))) (( b) X( b X b)) (G(( b) (X((X X b) ((( ) (b X X X b) (( b) (X X X b))) U ))))) (G(( b) (X((X X b) ((b ( ) X X X b) U( (( ) ( b) (X((X X b) ((( ) (b X X X b) (( b) X X X b)) U ))))))))))) b ā b ā b b ā b ā b b āb ā b b āb āb āb b āb āb b āb ā b b āb ā b b ā b K. Y. Rozier nd M. Y. Vrdi. LTL stisbility checking. In Proc. of SPIN'07, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 8 / 19
15 Rozier & Vrdi's Sclbility Experiment (2/2) 100s 80s 60s 40s 20s 0s spot-0.4 spot-0.5 ltl2b-1.1 C 6 C 8 C 10 C 12 C 14 Time to trnslte C n into BA Other explicit trnsltors re o the chrt: Modell took nerly 6 minutes to compute C 4 nd rn out of memory on C 5. Spin took more thn 11 hours to trnslte C 1 into 33-stte utomton with 447 trnsitions (insted of 2 sttes nd 2 trnsitions). Mny trnsitions hving unstisble gurds such s ((!b) && () && (b)). All experiments done on n Intel Core2 with 8GB of RAM. Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 9 / 19
16 Tbleu Construction for LTL (X ) (b U ) 1 Lbel the initil stte by the formul to trnslte J.-M. Couvreur. On-the-y veriction of liner temporl logic. In Proc. of FM'99, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 10 / 19
17 Tbleu Construction for LTL (X ) (b U ) 1 Lbel the initil stte by the formul to trnslte 2 Rewrite ech stte lbel ϕ s β i X ψ i i Boolen formul LTL formul Since f U g = g (f X(f U g)) we hve: (X ) (b U ) = ( X ) (b (X ) X(b U )) J.-M. Couvreur. On-the-y veriction of liner temporl logic. In Proc. of FM'99, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 10 / 19
18 Tbleu Construction for LTL (X ) (b U ) 1 Lbel the initil stte by the formul to trnslte 2 Rewrite ech stte lbel ϕ s β i X ψ i i Since f U g = g (f X(f U g)) we hve: (X ) (b U ) = ( X ) (b X( (b U ))) J.-M. Couvreur. On-the-y veriction of liner temporl logic. In Proc. of FM'99, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 10 / 19
19 Tbleu Construction for LTL (X ) (b U ) b (b U ) 1 Lbel the initil stte by the formul to trnslte 2 Rewrite ech stte lbel ϕ s β i X ψ i i Then connect ϕ to ech ψ i using β i s lbel Since f U g = g (f X(f U g)) we hve: (X ) (b U ) = ( X ) (b X( (b U ))) J.-M. Couvreur. On-the-y veriction of liner temporl logic. In Proc. of FM'99, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 10 / 19
20 Tbleu Construction for LTL (X ) (b U ) b (b U ) 1 Lbel the initil stte by the formul to trnslte 2 Rewrite ech stte lbel ϕ s β i X ψ i i Then connect ϕ to ech ψ i using β i s lbel Since f U g = g (f X(f U g)) we hve: (X ) (b U ) = ( X ) (b X( (b U ))) = X J.-M. Couvreur. On-the-y veriction of liner temporl logic. In Proc. of FM'99, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 10 / 19
21 Tbleu Construction for LTL (X ) (b U ) b (b U ) 1 Lbel the initil stte by the formul to trnslte 2 Rewrite ech stte lbel ϕ s β i X ψ i i Then connect ϕ to ech ψ i using β i s lbel Since f U g = g (f X(f U g)) we hve: (X ) (b U ) = ( X ) (b X( (b U ))) = X ; = X J.-M. Couvreur. On-the-y veriction of liner temporl logic. In Proc. of FM'99, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 10 / 19
22 Tbleu Construction for LTL (X ) (b U ) b (b U ) 1 Lbel the initil stte by the formul to trnslte 2 Rewrite ech stte lbel ϕ s β i X ψ i i Then connect ϕ to ech ψ i using β i s lbel Since f U g = g (f X(f U g)) we hve: (X ) (b U ) = ( X ) (b X( (b U ))) = X ; = X ; (b U ) = ( (b X(b U ))) J.-M. Couvreur. On-the-y veriction of liner temporl logic. In Proc. of FM'99, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 10 / 19
23 Tbleu Construction for LTL (X ) (b U ) b (b U ) b b U 1 Lbel the initil stte by the formul to trnslte 2 Rewrite ech stte lbel ϕ s β i X ψ i i Then connect ϕ to ech ψ i using β i s lbel Since f U g = g (f X(f U g)) we hve: (X ) (b U ) = ( X ) (b X( (b U ))) = X ; = X ; (b U ) = b X (b U ) J.-M. Couvreur. On-the-y veriction of liner temporl logic. In Proc. of FM'99, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 10 / 19
24 Tbleu Construction for LTL (X ) (b U ) b (b U ) b b U b 1 Lbel the initil stte by the formul to trnslte 2 Rewrite ech stte lbel ϕ s β i X ψ i i Then connect ϕ to ech ψ i using β i s lbel Since f U g = g (f X(f U g)) we hve: (X ) (b U ) = ( X ) (b X( (b U ))) = X ; = X ; (b U ) = b X (b U ) b U = ( X ) (b X (b U )) J.-M. Couvreur. On-the-y veriction of liner temporl logic. In Proc. of FM'99, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 10 / 19
25 Tbleu Construction for LTL (X ) (b U ) b;p (b U ) b U b;p b;p 1 Lbel the initil stte by the formul to trnslte 2 Rewrite ( ech stte lbel ϕ s β i X ψ i ) P γ ij i j Then connect ϕ to ech ψ i using β i s lbel nd {P γ ij } j s promises Since f U g = g (f X(f U g) P g ) we hve: (X ) (b U ) = ( X ) (b X( (b U )) P ) = X ; = X ; (b U ) = b X (b U ) P b U = ( X ) (b X (b U ) P ) J.-M. Couvreur. On-the-y veriction of liner temporl logic. In Proc. of FM'99, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 10 / 19
26 Tbleu Construction for LTL (X ) (b U ) 1 Lbel the initil stte by the formul to trnslte b 2 Rewrite ( ech stte lbel ϕ s (b U ) β i X ψ i ) P γ ij b i j Then connect ϕ to ech ψ i using b U β i s lbel nd {P γ ij } j s promises b 3 Crete Büchi cceptnce sets complementing ech promise Since f U g = g (f X(f U g) P g ) we hve: (X ) (b U ) = ( X ) (b X( (b U )) P ) = X ; = X ; (b U ) = b X (b U ) P b U = ( X ) (b X (b U ) P ) J.-M. Couvreur. On-the-y veriction of liner temporl logic. In Proc. of FM'99, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 10 / 19
27 Implementing the Trnsltion with BDDs (1/2) r( ) = r( ) = r(p) = Vr[p] r( p) = Vr[p] r(f g) = r(f ) r(g) r(f g) = r(f ) r(g) r( (f g)) = r( f ) r( g) r( (f g)) = r( f ) r( g) r(x f ) = Next[f ] r( X f ) = Next[ f ] r(f U g) = r(g) (r(f ) Next[f U g] P[g]) r( (f U g)) = r( g) (r( f ) Next[ (f U g)]) Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 11 / 19
28 Implementing the Trnsltion using BDDs (2/2) r((x ) (b U )) = r(x ) r(b U ) = Next[] (r( ) (P[ ] r(b) Next[b U ])) = Next[] ( Vr[] (P[ ] Vr[b] Next[b U ])) Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 12 / 19
29 Implementing the Trnsltion using BDDs (2/2) r((x ) (b U )) = r(x ) r(b U ) = Next[] (r( ) (P[ ] r(b) Next[b U ])) = Next[] ( Vr[] (P[ ] Vr[b] Next[b U ])) This BDD is then mssged into n irredundnt sum of products: = ( Vr[] Next[]) (Vr[b] Next[] Next[b U ] P[ ]) S. Minto. Fst genertion of irredundnt sum-of-products forms from binry decision digrms. In Proc. of SASIMI'92, pp Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 12 / 19
30 Implementing the Trnsltion using BDDs (2/2) r((x ) (b U )) = r(x ) r(b U ) = Next[] (r( ) (P[ ] r(b) Next[b U ])) = Next[] ( Vr[] (P[ ] Vr[b] Next[b U ])) This BDD is then mssged into n irredundnt sum of products: = ( Vr[] Next[]) (Vr[b] Next[] Next[b U ] P[ ]) S. Minto. Fst genertion of irredundnt sum-of-products forms from binry decision digrms. In Proc. of SASIMI'92, pp Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 12 / 19
31 BDD Gins (1/3): Automtic Simplictions Trivil simplictions of ded brnches: Less trivil simplictions: e.g. (( U b) (b U c)). Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 13 / 19
32 BDD Gins (1/3): Automtic Simplictions Trivil simplictions of ded brnches: A trnsition lbeled by cnnot exist Less trivil simplictions: e.g. (( U b) (b U c)). Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 13 / 19
33 BDD Gins (1/3): Automtic Simplictions Trivil simplictions of ded brnches: A trnsition lbeled by cnnot exist Less trivil simplictions: e.g. (( U b) (b U c)). Tbleu rules give four immedite successors: ( ) ( b) ( c) ( ) ( b) ( c) X (b U c) ( b) ( c) (X ( U b)) ( b) ( c) (X ( U b)) X (b U c) BDD rewritings give two successors: Vr[b] ( Vr[] Next[ ( U b)]) Vr[c] ( Vr[b] Next[ (b U c)]) Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 13 / 19
34 BDD Gins (1/3): Automtic Simplictions Trivil simplictions of ded brnches: A trnsition lbeled by cnnot exist Less trivil simplictions: e.g. (( U b) (b U c)). Tbleu rules give four immedite successors: ( ) ( b) ( c) ( ) ( b) ( c) X (b U c) ( b) ( c) (X ( U b)) ( b) ( c) (X ( U b)) X (b U c) BDD rewritings give two successors: Vr[b] ( Vr[] Next[ ( U b)]) Vr[c] ( Vr[b] Next[ (b U c)]) = Vr[b] Vr[c] ( Vr[] Next[ ( U b)]) Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 13 / 19
35 BDD Gins (2/3): Automtic Quotienting BDD rewritings give us n equivlence reltion between LTL formuls. r(g F ) =((Next[F ] P[]) Vr[]) Next[G F ] r(f G F ) =((Next[F ] P[]) Vr[]) Next[G F ] G F (F ) G F G F Could we produce something more deterministic? Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 14 / 19
36 BDD Gin (3/3): Improving Determinism Let's improve the determinism of the previous construction by checking how dierent vrible ssignments inuence destintions: r(g F ) = ((Next[F ] P[]) Vr[]) Next[G F ] r(g F ) Vr[] = Vr[] Next[G F ] r(g F ) Vr[] = Vr[] Next[F ] P[] Next[G F ] G F (F ) G F G F Experiment on 188 LTL formuls from the literture pplied to rndom grphs: 0.4% less sttes, 25% less trnsitions in product. Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 15 / 19
37 Temporl Hierrchy Rectivity G F pi F G q i Recurrence G F p Persistence F G p Obligtion G pi F q i Sfety G p Gurntee F p Z. Mnn nd A. Pnueli. A hierrchy of temporl properties. In Proc. of PODC'90, pp ACM Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 16 / 19
38 Temporl Hierrchy Deterministic Büchi Automt Rectivity G F pi F G q i Wek Büchi Automt Recurrence G F p Persistence F G p Obligtion G pi F q i Wek Det. Büchi Aut. (WDBA) Sfety G p Gurntee F p I. ƒerná nd R. Pelánek. Relting hierrchy of temporl properties to model checking. In Proc. of MFCS'03, vol of LNCS, pp Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 16 / 19
39 Deling with Obligtion Properties 118 out of the 188 formuls (62%) re obligtions properties WDBA cn be minimized in sme wy s DFAs (Löding; 2001) Dx et l. (2007) show how to minimize ny utomton tht cn be expressed s WDBA. In Spot this lgorithm tkes TGBA nd outputs WDBA when the minimiztion is pplicble Although converting to miniml WDBA incurs determiniztion, the number of sttes seldom increses C. Löding. Ecient minimiztion of deterministic wek ω-utomt. Informtion Processing Letters, 79(3):105109, 2001 C. Dx, J. Eisinger, nd F. Kledtke. Mechnizing the powerset construction for restricted clsses of ω-utomt. In Proc. of ATVA'07, vol of LNCS. Springer Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 17 / 19
40 Trnsltion of Litterture Formuls Cumulted sizes of utomt for 188 formuls from the litterture Products with rndom stte-spce of 200 sttes Σ A ϕ Σ A M A ϕ st. tr. st. tr. BA Spin (A 9) LTL2BA Modell ( 1) Spot Spot det Spot WDBA TGBA Spot Spot det Spot WDBA A = 15min timeout = bogus trnsltion Produce more deterministic ut. WDBA minimiztion when pplicble Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 18 / 19
41 Conclusion LTL trnsltion The core trnsltion is ecient nd simple to implement Four tricks: Supporting the wek until opertor (not shown). Choosing pproprite rewriting rules (not shown). Using BDD is importnt (for speed nd determinism) Buiding WDBA when possible is often good ide Try it on-line: Wht's Cooking Support for PSL (Property Speciction Lnguge) Essentilly: LTL + rtionl opertors. { 1[*]; init; busy[=2]; done } []-> (!init U bell) Simultion-bsed reductions (for TGBA) Alexndre Duret-Lutz LTL Trnsltion Improvements 19 / 19
Lecture 9: LTL and Büchi Automata
 Lecture 9: LTL nd Büchi Automt 1 LTL Property Ptterns Quite often the requirements of system follow some simple ptterns. Sometimes we wnt to specify tht property should only hold in certin context, clled
Lecture 9: LTL nd Büchi Automt 1 LTL Property Ptterns Quite often the requirements of system follow some simple ptterns. Sometimes we wnt to specify tht property should only hold in certin context, clled
CS 267: Automated Verification. Lecture 8: Automata Theoretic Model Checking. Instructor: Tevfik Bultan
 CS 267: Automted Verifiction Lecture 8: Automt Theoretic Model Checking Instructor: Tevfik Bultn LTL Properties Büchi utomt [Vrdi nd Wolper LICS 86] Büchi utomt: Finite stte utomt tht ccept infinite strings
CS 267: Automted Verifiction Lecture 8: Automt Theoretic Model Checking Instructor: Tevfik Bultn LTL Properties Büchi utomt [Vrdi nd Wolper LICS 86] Büchi utomt: Finite stte utomt tht ccept infinite strings
From LTL to Symbolically Represented Deterministic Automata
 Motivtion nd Prolem Setting Determinizing Non-Confluent Automt Det. vi Automt Hierrchy From LTL to Symoliclly Represented Deterministic Automt Andres Morgenstern Klus Schneider Sven Lmerti Mnuel Gesell
Motivtion nd Prolem Setting Determinizing Non-Confluent Automt Det. vi Automt Hierrchy From LTL to Symoliclly Represented Deterministic Automt Andres Morgenstern Klus Schneider Sven Lmerti Mnuel Gesell
Deterministic Finite Automata
 Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd J. Rot Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences Version: fll 2016 J. Rot Version: fll 2016 Tlen en Automten 1 / 21 Outline Finite Automt Finite
Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd J. Rot Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences Version: fll 2016 J. Rot Version: fll 2016 Tlen en Automten 1 / 21 Outline Finite Automt Finite
Java II Finite Automata I
 Jv II Finite Automt I Bernd Kiefer Bernd.Kiefer@dfki.de Deutsches Forschungszentrum für künstliche Intelligenz Finite Automt I p.1/13 Processing Regulr Expressions We lredy lerned out Jv s regulr expression
Jv II Finite Automt I Bernd Kiefer Bernd.Kiefer@dfki.de Deutsches Forschungszentrum für künstliche Intelligenz Finite Automt I p.1/13 Processing Regulr Expressions We lredy lerned out Jv s regulr expression
Strong Bisimulation. Overview. References. Actions Labeled transition system Transition semantics Simulation Bisimulation
 Strong Bisimultion Overview Actions Lbeled trnsition system Trnsition semntics Simultion Bisimultion References Robin Milner, Communiction nd Concurrency Robin Milner, Communicting nd Mobil Systems 32
Strong Bisimultion Overview Actions Lbeled trnsition system Trnsition semntics Simultion Bisimultion References Robin Milner, Communiction nd Concurrency Robin Milner, Communicting nd Mobil Systems 32
Is There a Best Büchi Automaton for Explicit Model Checking?
 Is There Best Büchi Automton for Explicit Model Checking? Frntišek Blhoudek Msryk University Brno, Czech Republic xblhoud@fi.muni.cz Alexndre Duret-Lutz LRDE, EPITA Le Kremlin-Bicêtre, Frnce dl@lrde.epit.fr
Is There Best Büchi Automton for Explicit Model Checking? Frntišek Blhoudek Msryk University Brno, Czech Republic xblhoud@fi.muni.cz Alexndre Duret-Lutz LRDE, EPITA Le Kremlin-Bicêtre, Frnce dl@lrde.epit.fr
LTL Translation Improvements in Spot
 A. LRDE / EPITA 14-16 rue Voltire, 94276 Le Kremlin-Bicêtre Cedex Frnce dl@lrde.epit.fr Spot is lirry of model-checking lgorithms. This pper focuses on the module trnslting LTL formulæ into utomt. We discuss
A. LRDE / EPITA 14-16 rue Voltire, 94276 Le Kremlin-Bicêtre Cedex Frnce dl@lrde.epit.fr Spot is lirry of model-checking lgorithms. This pper focuses on the module trnslting LTL formulæ into utomt. We discuss
Good-for-Games Automata versus Deterministic Automata.
 Good-for-Gmes Automt versus Deterministic Automt. Denis Kuperberg 1,2 Mich l Skrzypczk 1 1 University of Wrsw 2 IRIT/ONERA (Toulouse) Séminire MoVe 12/02/2015 LIF, Luminy Introduction Deterministic utomt
Good-for-Gmes Automt versus Deterministic Automt. Denis Kuperberg 1,2 Mich l Skrzypczk 1 1 University of Wrsw 2 IRIT/ONERA (Toulouse) Séminire MoVe 12/02/2015 LIF, Luminy Introduction Deterministic utomt
Non-Deterministic Finite Automata. Fall 2018 Costas Busch - RPI 1
 Non-Deterministic Finite Automt Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet ={} q q2 1 q 0 q 3 Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 2 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet
Non-Deterministic Finite Automt Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet ={} q q2 1 q 0 q 3 Fll 2018 Costs Busch - RPI 2 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet
Software Engineering using Formal Methods
 Softwre Engineering using Forml Methods Propositionl nd (Liner) Temporl Logic Wolfgng Ahrendt 13th Septemer 2016 SEFM: Liner Temporl Logic /GU 160913 1 / 60 Recpitultion: FormlistionFormlistion: Syntx,
Softwre Engineering using Forml Methods Propositionl nd (Liner) Temporl Logic Wolfgng Ahrendt 13th Septemer 2016 SEFM: Liner Temporl Logic /GU 160913 1 / 60 Recpitultion: FormlistionFormlistion: Syntx,
More on automata. Michael George. March 24 April 7, 2014
 More on utomt Michel George Mrch 24 April 7, 2014 1 Automt constructions Now tht we hve forml model of mchine, it is useful to mke some generl constructions. 1.1 DFA Union / Product construction Suppose
More on utomt Michel George Mrch 24 April 7, 2014 1 Automt constructions Now tht we hve forml model of mchine, it is useful to mke some generl constructions. 1.1 DFA Union / Product construction Suppose
On Determinisation of History-Deterministic Automata.
 On Deterministion of History-Deterministic Automt. Denis Kupererg Mich l Skrzypczk University of Wrsw YR-ICALP 2014 Copenhgen Introduction Deterministic utomt re centrl tool in utomt theory: Polynomil
On Deterministion of History-Deterministic Automt. Denis Kupererg Mich l Skrzypczk University of Wrsw YR-ICALP 2014 Copenhgen Introduction Deterministic utomt re centrl tool in utomt theory: Polynomil
Probabilistic Model Checking Michaelmas Term Dr. Dave Parker. Department of Computer Science University of Oxford
 Probbilistic Model Checking Michelms Term 2011 Dr. Dve Prker Deprtment of Computer Science University of Oxford Long-run properties Lst lecture: regulr sfety properties e.g. messge filure never occurs
Probbilistic Model Checking Michelms Term 2011 Dr. Dve Prker Deprtment of Computer Science University of Oxford Long-run properties Lst lecture: regulr sfety properties e.g. messge filure never occurs
CSCI 340: Computational Models. Kleene s Theorem. Department of Computer Science
 CSCI 340: Computtionl Models Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7 Deprtment of Computer Science Unifiction In 1954, Kleene presented (nd proved) theorem which (in our version) sttes tht if lnguge cn e defined y ny
CSCI 340: Computtionl Models Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7 Deprtment of Computer Science Unifiction In 1954, Kleene presented (nd proved) theorem which (in our version) sttes tht if lnguge cn e defined y ny
a,b a 1 a 2 a 3 a,b 1 a,b a,b 2 3 a,b a,b a 2 a,b CS Determinisitic Finite Automata 1
 CS4 45- Determinisitic Finite Automt -: Genertors vs. Checkers Regulr expressions re one wy to specify forml lnguge String Genertor Genertes strings in the lnguge Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) re nother
CS4 45- Determinisitic Finite Automt -: Genertors vs. Checkers Regulr expressions re one wy to specify forml lnguge String Genertor Genertes strings in the lnguge Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) re nother
Finite Automata. Informatics 2A: Lecture 3. John Longley. 22 September School of Informatics University of Edinburgh
 Lnguges nd Automt Finite Automt Informtics 2A: Lecture 3 John Longley School of Informtics University of Edinburgh jrl@inf.ed.c.uk 22 September 2017 1 / 30 Lnguges nd Automt 1 Lnguges nd Automt Wht is
Lnguges nd Automt Finite Automt Informtics 2A: Lecture 3 John Longley School of Informtics University of Edinburgh jrl@inf.ed.c.uk 22 September 2017 1 / 30 Lnguges nd Automt 1 Lnguges nd Automt Wht is
Relating logic to formal languages
 Relting logic to forml lnguges Kml Lody The Institute of Mthemticl Sciences, Chenni October 2018 Reding 1. Howrd Strubing: Forml lnguges, finite utomt nd circuit complexity, birkhäuser. 2. Wolfgng Thoms:
Relting logic to forml lnguges Kml Lody The Institute of Mthemticl Sciences, Chenni October 2018 Reding 1. Howrd Strubing: Forml lnguges, finite utomt nd circuit complexity, birkhäuser. 2. Wolfgng Thoms:
Theory of Computation Regular Languages. (NTU EE) Regular Languages Fall / 38
 Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges (NTU EE) Regulr Lnguges Fll 2017 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of Finite Automt A finite utomton hs finite set of control
Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges (NTU EE) Regulr Lnguges Fll 2017 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of Finite Automt A finite utomton hs finite set of control
AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES. Definition 1.5: Finite Automaton
 25. Finite Automt AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES A system of computtion tht only hs finite numer of possile sttes cn e modeled using finite utomton A finite utomton is often illustrted s stte digrm d d d. d q
25. Finite Automt AUTOMATA AND LANGUAGES A system of computtion tht only hs finite numer of possile sttes cn e modeled using finite utomton A finite utomton is often illustrted s stte digrm d d d. d q
Chapter 2 Finite Automata
 Chpter 2 Finite Automt 28 2.1 Introduction Finite utomt: first model of the notion of effective procedure. (They lso hve mny other pplictions). The concept of finite utomton cn e derived y exmining wht
Chpter 2 Finite Automt 28 2.1 Introduction Finite utomt: first model of the notion of effective procedure. (They lso hve mny other pplictions). The concept of finite utomton cn e derived y exmining wht
Theory of Computation Regular Languages
 Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges Bow-Yw Wng Acdemi Sinic Spring 2012 Bow-Yw Wng (Acdemi Sinic) Regulr Lnguges Spring 2012 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of
Theory of Computtion Regulr Lnguges Bow-Yw Wng Acdemi Sinic Spring 2012 Bow-Yw Wng (Acdemi Sinic) Regulr Lnguges Spring 2012 1 / 38 Schemtic of Finite Automt control 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 Figure: Schemtic of
Non Deterministic Automata. Linz: Nondeterministic Finite Accepters, page 51
 Non Deterministic Automt Linz: Nondeterministic Finite Accepters, pge 51 1 Nondeterministic Finite Accepter (NFA) Alphbet ={} q 1 q2 q 0 q 3 2 Nondeterministic Finite Accepter (NFA) Alphbet ={} Two choices
Non Deterministic Automt Linz: Nondeterministic Finite Accepters, pge 51 1 Nondeterministic Finite Accepter (NFA) Alphbet ={} q 1 q2 q 0 q 3 2 Nondeterministic Finite Accepter (NFA) Alphbet ={} Two choices
Finite Automata. Informatics 2A: Lecture 3. Mary Cryan. 21 September School of Informatics University of Edinburgh
 Finite Automt Informtics 2A: Lecture 3 Mry Cryn School of Informtics University of Edinburgh mcryn@inf.ed.c.uk 21 September 2018 1 / 30 Lnguges nd Automt Wht is lnguge? Finite utomt: recp Some forml definitions
Finite Automt Informtics 2A: Lecture 3 Mry Cryn School of Informtics University of Edinburgh mcryn@inf.ed.c.uk 21 September 2018 1 / 30 Lnguges nd Automt Wht is lnguge? Finite utomt: recp Some forml definitions
Learning Moore Machines from Input-Output Traces
 Lerning Moore Mchines from Input-Output Trces Georgios Gintmidis 1 nd Stvros Tripkis 1,2 1 Alto University, Finlnd 2 UC Berkeley, USA Motivtion: lerning models from blck boxes Inputs? Lerner Forml Model
Lerning Moore Mchines from Input-Output Trces Georgios Gintmidis 1 nd Stvros Tripkis 1,2 1 Alto University, Finlnd 2 UC Berkeley, USA Motivtion: lerning models from blck boxes Inputs? Lerner Forml Model
Designing finite automata II
 Designing finite utomt II Prolem: Design DFA A such tht L(A) consists of ll strings of nd which re of length 3n, for n = 0, 1, 2, (1) Determine wht to rememer out the input string Assign stte to ech of
Designing finite utomt II Prolem: Design DFA A such tht L(A) consists of ll strings of nd which re of length 3n, for n = 0, 1, 2, (1) Determine wht to rememer out the input string Assign stte to ech of
Minimal DFA. minimal DFA for L starting from any other
 Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Extending Automated Compositional Verification to the Full Class of Omega-Regular Languages
 Extending Automted Compositionl Verifiction to the Full Clss of Omeg-Regulr Lnguges Azdeh Frzn 1, Yu-Fng Chen 2, Edmund M. Clrke 1, Yih-Kuen Tsy 2, nd Bow-Yw Wng 3 1 Crnegie Mellon University 2 Ntionl
Extending Automted Compositionl Verifiction to the Full Clss of Omeg-Regulr Lnguges Azdeh Frzn 1, Yu-Fng Chen 2, Edmund M. Clrke 1, Yih-Kuen Tsy 2, nd Bow-Yw Wng 3 1 Crnegie Mellon University 2 Ntionl
1 Nondeterministic Finite Automata
 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automt Suppose in life, whenever you hd choice, you could try oth possiilities nd live your life. At the end, you would go ck nd choose the one tht worked out the est. Then you
1 Nondeterministic Finite Automt Suppose in life, whenever you hd choice, you could try oth possiilities nd live your life. At the end, you would go ck nd choose the one tht worked out the est. Then you
CS103B Handout 18 Winter 2007 February 28, 2007 Finite Automata
 CS103B ndout 18 Winter 2007 Ferury 28, 2007 Finite Automt Initil text y Mggie Johnson. Introduction Severl childrens gmes fit the following description: Pieces re set up on plying ord; dice re thrown or
CS103B ndout 18 Winter 2007 Ferury 28, 2007 Finite Automt Initil text y Mggie Johnson. Introduction Severl childrens gmes fit the following description: Pieces re set up on plying ord; dice re thrown or
FABER Formal Languages, Automata and Models of Computation
 DVA337 FABER Forml Lnguges, Automt nd Models of Computtion Lecture 5 chool of Innovtion, Design nd Engineering Mälrdlen University 2015 1 Recp of lecture 4 y definition suset construction DFA NFA stte
DVA337 FABER Forml Lnguges, Automt nd Models of Computtion Lecture 5 chool of Innovtion, Design nd Engineering Mälrdlen University 2015 1 Recp of lecture 4 y definition suset construction DFA NFA stte
Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automata and Finite-State Transducers. Mehryar Mohri Courant Institute and Google Research
 Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automt nd Finite-Stte Trnsducers Mehryr Mohri Cournt Institute nd Google Reserch mohri@cims.nyu.com Preliminries Finite lphet Σ, empty string. Set of ll strings over
Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automt nd Finite-Stte Trnsducers Mehryr Mohri Cournt Institute nd Google Reserch mohri@cims.nyu.com Preliminries Finite lphet Σ, empty string. Set of ll strings over
Anatomy of a Deterministic Finite Automaton. Deterministic Finite Automata. A machine so simple that you can understand it in less than one minute
 Victor Admchik Dnny Sletor Gret Theoreticl Ides In Computer Science CS 5-25 Spring 2 Lecture 2 Mr 3, 2 Crnegie Mellon University Deterministic Finite Automt Finite Automt A mchine so simple tht you cn
Victor Admchik Dnny Sletor Gret Theoreticl Ides In Computer Science CS 5-25 Spring 2 Lecture 2 Mr 3, 2 Crnegie Mellon University Deterministic Finite Automt Finite Automt A mchine so simple tht you cn
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. DFAs, and NFAs, and Regexps (Oh my!)
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges DFAs, nd NFAs, nd Regexps (Oh my!) CMSC330 Spring 2018 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges DFAs, nd NFAs, nd Regexps (Oh my!) CMSC330 Spring 2018 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018
 Finite Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 10 An Bove April 23rd 2018 Recp: Regulr Lnguges We cn convert between FA nd RE; Hence both FA nd RE ccept/generte regulr lnguges; More
Finite Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 10 An Bove April 23rd 2018 Recp: Regulr Lnguges We cn convert between FA nd RE; Hence both FA nd RE ccept/generte regulr lnguges; More
NFA DFA Example 3 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Equivalence of DFAs and NFAs. Equivalence of DFAs and NFAs (cont.
 NFA DFA Exmple 3 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges NFA {B,D,E {A,E {C,D {E Finite Automt, con't. R = { {A,E, {B,D,E, {C,D, {E 2 Equivlence of DFAs nd NFAs Any string from {A to either {D or {CD
NFA DFA Exmple 3 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges NFA {B,D,E {A,E {C,D {E Finite Automt, con't. R = { {A,E, {B,D,E, {C,D, {E 2 Equivlence of DFAs nd NFAs Any string from {A to either {D or {CD
Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automata and Finite-State Transducers
 Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automt nd Finite-Stte Trnsducers Eugene Weinstein Google, NYU Cournt Institute eugenew@cs.nyu.edu Slide Credit: Mehryr Mohri Preliminries Finite lphet, empty string.
Speech Recognition Lecture 2: Finite Automt nd Finite-Stte Trnsducers Eugene Weinstein Google, NYU Cournt Institute eugenew@cs.nyu.edu Slide Credit: Mehryr Mohri Preliminries Finite lphet, empty string.
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring Regular Languages. Equivalences between Finite automata and REs. Haniel Barbosa
 CS:4330 Theory of Computtion Spring 208 Regulr Lnguges Equivlences between Finite utomt nd REs Hniel Brbos Redings for this lecture Chpter of [Sipser 996], 3rd edition. Section.3. Finite utomt nd regulr
CS:4330 Theory of Computtion Spring 208 Regulr Lnguges Equivlences between Finite utomt nd REs Hniel Brbos Redings for this lecture Chpter of [Sipser 996], 3rd edition. Section.3. Finite utomt nd regulr
Automata Theory 101. Introduction. Outline. Introduction Finite Automata Regular Expressions ω-automata. Ralf Huuck.
 Outline Automt Theory 101 Rlf Huuck Introduction Finite Automt Regulr Expressions ω-automt Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 1 Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 2 Acknowledgement Some slides re sed on Wolfgng Thoms excellent
Outline Automt Theory 101 Rlf Huuck Introduction Finite Automt Regulr Expressions ω-automt Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 1 Session 1 2006 Rlf Huuck 2 Acknowledgement Some slides re sed on Wolfgng Thoms excellent
Formal Methods in Software Engineering
 Forml Methods in Softwre Engineering Lecture 09 orgniztionl issues Prof. Dr. Joel Greenyer Decemer 9, 2014 Written Exm The written exm will tke plce on Mrch 4 th, 2015 The exm will tke 60 minutes nd strt
Forml Methods in Softwre Engineering Lecture 09 orgniztionl issues Prof. Dr. Joel Greenyer Decemer 9, 2014 Written Exm The written exm will tke plce on Mrch 4 th, 2015 The exm will tke 60 minutes nd strt
Non-Deterministic Finite Automata
 Non-Deterministic Finite Automt http://users.comlb.ox.c.uk/luke. ong/teching/moc/nf2up.pdf 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet ={} q1 q2 2 Alphbet ={} Two choices q1 q2 3 Alphbet ={} Two choices
Non-Deterministic Finite Automt http://users.comlb.ox.c.uk/luke. ong/teching/moc/nf2up.pdf 1 Nondeterministic Finite Automton (NFA) Alphbet ={} q1 q2 2 Alphbet ={} Two choices q1 q2 3 Alphbet ={} Two choices
Fundamentals of Computer Science
 Fundmentls of Computer Science Chpter 3: NFA nd DFA equivlence Regulr expressions Henrik Björklund Umeå University Jnury 23, 2014 NFA nd DFA equivlence As we shll see, it turns out tht NFA nd DFA re equivlent,
Fundmentls of Computer Science Chpter 3: NFA nd DFA equivlence Regulr expressions Henrik Björklund Umeå University Jnury 23, 2014 NFA nd DFA equivlence As we shll see, it turns out tht NFA nd DFA re equivlent,
CS415 Compilers. Lexical Analysis and. These slides are based on slides copyrighted by Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Linda Torczon at Rice University
 CS415 Compilers Lexicl Anlysis nd These slides re sed on slides copyrighted y Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Lind Torczon t Rice University First Progrmming Project Instruction Scheduling Project hs een posted
CS415 Compilers Lexicl Anlysis nd These slides re sed on slides copyrighted y Keith Cooper, Ken Kennedy & Lind Torczon t Rice University First Progrmming Project Instruction Scheduling Project hs een posted
Assignment 1 Automata, Languages, and Computability. 1 Finite State Automata and Regular Languages
 Deprtment of Computer Science, Austrlin Ntionl University COMP2600 Forml Methods for Softwre Engineering Semester 2, 206 Assignment Automt, Lnguges, nd Computility Smple Solutions Finite Stte Automt nd
Deprtment of Computer Science, Austrlin Ntionl University COMP2600 Forml Methods for Softwre Engineering Semester 2, 206 Assignment Automt, Lnguges, nd Computility Smple Solutions Finite Stte Automt nd
Introduction to ω-autamata
 Fridy 25 th Jnury, 2013 Outline From finite word utomt ω-regulr lnguge ω-utomt Nondeterministic Models Deterministic Models Two Lower Bounds Conclusion Discussion Synthesis Preliminry From finite word
Fridy 25 th Jnury, 2013 Outline From finite word utomt ω-regulr lnguge ω-utomt Nondeterministic Models Deterministic Models Two Lower Bounds Conclusion Discussion Synthesis Preliminry From finite word
Nondeterminism and Nodeterministic Automata
 Nondeterminism nd Nodeterministic Automt 61 Nondeterminism nd Nondeterministic Automt The computtionl mchine models tht we lerned in the clss re deterministic in the sense tht the next move is uniquely
Nondeterminism nd Nodeterministic Automt 61 Nondeterminism nd Nondeterministic Automt The computtionl mchine models tht we lerned in the clss re deterministic in the sense tht the next move is uniquely
Worked out examples Finite Automata
 Worked out exmples Finite Automt Exmple Design Finite Stte Automton which reds inry string nd ccepts only those tht end with. Since we re in the topic of Non Deterministic Finite Automt (NFA), we will
Worked out exmples Finite Automt Exmple Design Finite Stte Automton which reds inry string nd ccepts only those tht end with. Since we re in the topic of Non Deterministic Finite Automt (NFA), we will
1. For each of the following theorems, give a two or three sentence sketch of how the proof goes or why it is not true.
 York University CSE 2 Unit 3. DFA Clsses Converting etween DFA, NFA, Regulr Expressions, nd Extended Regulr Expressions Instructor: Jeff Edmonds Don t chet y looking t these nswers premturely.. For ech
York University CSE 2 Unit 3. DFA Clsses Converting etween DFA, NFA, Regulr Expressions, nd Extended Regulr Expressions Instructor: Jeff Edmonds Don t chet y looking t these nswers premturely.. For ech
Finite Automata-cont d
 Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Lecture # 6 Finite Automt-cont d The Pumping Lemm WEB SITE: http://ingwe.inghmton.edu/ ~lnder/cs573.html Septemer 18, 2000 Exmple 1 Consider L = {ww
Automt Theory nd Forml Lnguges Professor Leslie Lnder Lecture # 6 Finite Automt-cont d The Pumping Lemm WEB SITE: http://ingwe.inghmton.edu/ ~lnder/cs573.html Septemer 18, 2000 Exmple 1 Consider L = {ww
Automata, Games, and Verification
 Automt, Gmes, nd Verifiction Prof. Bernd Finkbeiner, Ph.D. Srlnd University Summer Term 2015 Lecture Notes by Bernd Finkbeiner, Felix Klein, Tobis Slzmnn These lecture notes re working document nd my contin
Automt, Gmes, nd Verifiction Prof. Bernd Finkbeiner, Ph.D. Srlnd University Summer Term 2015 Lecture Notes by Bernd Finkbeiner, Felix Klein, Tobis Slzmnn These lecture notes re working document nd my contin
Let's start with an example:
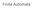 Finite Automt Let's strt with n exmple: Here you see leled circles tht re sttes, nd leled rrows tht re trnsitions. One of the sttes is mrked "strt". One of the sttes hs doule circle; this is terminl stte
Finite Automt Let's strt with n exmple: Here you see leled circles tht re sttes, nd leled rrows tht re trnsitions. One of the sttes is mrked "strt". One of the sttes hs doule circle; this is terminl stte
Chapter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automata. Formal Language, chapter 5, slide 1
 Chpter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automt Forml Lnguge, chpter 5, slide 1 1 A DFA hs exctly one trnsition from every stte on every symol in the lphet. By relxing this requirement we get relted ut more
Chpter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automt Forml Lnguge, chpter 5, slide 1 1 A DFA hs exctly one trnsition from every stte on every symol in the lphet. By relxing this requirement we get relted ut more
State Minimization for DFAs
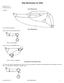 Stte Minimiztion for DFAs Red K & S 2.7 Do Homework 10. Consider: Stte Minimiztion 4 5 Is this miniml mchine? Step (1): Get rid of unrechle sttes. Stte Minimiztion 6, Stte is unrechle. Step (2): Get rid
Stte Minimiztion for DFAs Red K & S 2.7 Do Homework 10. Consider: Stte Minimiztion 4 5 Is this miniml mchine? Step (1): Get rid of unrechle sttes. Stte Minimiztion 6, Stte is unrechle. Step (2): Get rid
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computation. Lecture #31: What DFA s Can and Can t Do David Mix Barrington 9 April 2014
 CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computtion Lecture #31: Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Dvid Mix Brrington 9 April 2014 Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Deterministic Finite Automt Forml Definition of DFA s Exmples of DFA
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computtion Lecture #31: Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Dvid Mix Brrington 9 April 2014 Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Deterministic Finite Automt Forml Definition of DFA s Exmples of DFA
Model Reduction of Finite State Machines by Contraction
 Model Reduction of Finite Stte Mchines y Contrction Alessndro Giu Dip. di Ingegneri Elettric ed Elettronic, Università di Cgliri, Pizz d Armi, 09123 Cgliri, Itly Phone: +39-070-675-5892 Fx: +39-070-675-5900
Model Reduction of Finite Stte Mchines y Contrction Alessndro Giu Dip. di Ingegneri Elettric ed Elettronic, Università di Cgliri, Pizz d Armi, 09123 Cgliri, Itly Phone: +39-070-675-5892 Fx: +39-070-675-5900
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 CMSC 330 1 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 CMSC 330 1 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt (DFA) Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic
Regular languages refresher
 Regulr lnguges refresher 1 Regulr lnguges refresher Forml lnguges Alphet = finite set of letters Word = sequene of letter Lnguge = set of words Regulr lnguges defined equivlently y Regulr expressions Finite-stte
Regulr lnguges refresher 1 Regulr lnguges refresher Forml lnguges Alphet = finite set of letters Word = sequene of letter Lnguge = set of words Regulr lnguges defined equivlently y Regulr expressions Finite-stte
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2007
 CS 188: Artificil Intelligence Spring 2007 Lecture 3: Queue-Bsed Serch 1/23/2007 Srini Nrynn UC Berkeley Mny slides over the course dpted from Dn Klein, Sturt Russell or Andrew Moore Announcements Assignment
CS 188: Artificil Intelligence Spring 2007 Lecture 3: Queue-Bsed Serch 1/23/2007 Srini Nrynn UC Berkeley Mny slides over the course dpted from Dn Klein, Sturt Russell or Andrew Moore Announcements Assignment
The Value 1 Problem for Probabilistic Automata
 The Vlue 1 Prolem for Proilistic Automt Bruxelles Nthnël Fijlkow LIAFA, Université Denis Diderot - Pris 7, Frnce Institute of Informtics, Wrsw University, Polnd nth@lif.univ-pris-diderot.fr June 20th,
The Vlue 1 Prolem for Proilistic Automt Bruxelles Nthnël Fijlkow LIAFA, Université Denis Diderot - Pris 7, Frnce Institute of Informtics, Wrsw University, Polnd nth@lif.univ-pris-diderot.fr June 20th,
Formal Languages and Automata
 Moile Computing nd Softwre Engineering p. 1/5 Forml Lnguges nd Automt Chpter 2 Finite Automt Chun-Ming Liu cmliu@csie.ntut.edu.tw Deprtment of Computer Science nd Informtion Engineering Ntionl Tipei University
Moile Computing nd Softwre Engineering p. 1/5 Forml Lnguges nd Automt Chpter 2 Finite Automt Chun-Ming Liu cmliu@csie.ntut.edu.tw Deprtment of Computer Science nd Informtion Engineering Ntionl Tipei University
CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter Final Exam (solutions) SOLUTIONS
 CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter 2003 - Finl Exm (solutions) SOLUTIONS 1. (Logic) Use truth tles to prove the following logicl equivlences: () p q (p p) (q q) () p q (p q) (p q) () p q p q p p q q (q q) (p p)
CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter 2003 - Finl Exm (solutions) SOLUTIONS 1. (Logic) Use truth tles to prove the following logicl equivlences: () p q (p p) (q q) () p q (p q) (p q) () p q p q p p q q (q q) (p p)
NFAs and Regular Expressions. NFA-ε, continued. Recall. Last class: Today: Fun:
 CMPU 240 Lnguge Theory nd Computtion Spring 2019 NFAs nd Regulr Expressions Lst clss: Introduced nondeterministic finite utomt with -trnsitions Tody: Prove n NFA- is no more powerful thn n NFA Introduce
CMPU 240 Lnguge Theory nd Computtion Spring 2019 NFAs nd Regulr Expressions Lst clss: Introduced nondeterministic finite utomt with -trnsitions Tody: Prove n NFA- is no more powerful thn n NFA Introduce
Coalgebra, Lecture 15: Equations for Deterministic Automata
 Colger, Lecture 15: Equtions for Deterministic Automt Julin Slmnc (nd Jurrin Rot) Decemer 19, 2016 In this lecture, we will study the concept of equtions for deterministic utomt. The notes re self contined
Colger, Lecture 15: Equtions for Deterministic Automt Julin Slmnc (nd Jurrin Rot) Decemer 19, 2016 In this lecture, we will study the concept of equtions for deterministic utomt. The notes re self contined
Types of Finite Automata. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Comparing DFAs and NFAs. Comparing DFAs and NFAs (cont.) Finite Automata 2
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
Non Deterministic Automata. Formal Languages and Automata - Yonsei CS 1
 Non Deterministic Automt Forml Lnguges nd Automt - Yonsei CS 1 Nondeterministic Finite Accepter (NFA) We llow set of possible moves insted of A unique move. Alphbet = {} Two choices q 1 q2 Forml Lnguges
Non Deterministic Automt Forml Lnguges nd Automt - Yonsei CS 1 Nondeterministic Finite Accepter (NFA) We llow set of possible moves insted of A unique move. Alphbet = {} Two choices q 1 q2 Forml Lnguges
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, November 14, 2018 Finite Automata II. Nickolas Rollick a b b. a b 4
 Intermedite Mth Circles Wednesdy, Novemer 14, 2018 Finite Automt II Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Regulr Lnguges Lst time, we were introduced to the ide of DFA (deterministic finite utomton), one
Intermedite Mth Circles Wednesdy, Novemer 14, 2018 Finite Automt II Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Regulr Lnguges Lst time, we were introduced to the ide of DFA (deterministic finite utomton), one
Convert the NFA into DFA
 Convert the NF into F For ech NF we cn find F ccepting the sme lnguge. The numer of sttes of the F could e exponentil in the numer of sttes of the NF, ut in prctice this worst cse occurs rrely. lgorithm:
Convert the NF into F For ech NF we cn find F ccepting the sme lnguge. The numer of sttes of the F could e exponentil in the numer of sttes of the NF, ut in prctice this worst cse occurs rrely. lgorithm:
Tutorial Automata and formal Languages
 Tutoril Automt nd forml Lnguges Notes for to the tutoril in the summer term 2017 Sestin Küpper, Christine Mik 8. August 2017 1 Introduction: Nottions nd sic Definitions At the eginning of the tutoril we
Tutoril Automt nd forml Lnguges Notes for to the tutoril in the summer term 2017 Sestin Küpper, Christine Mik 8. August 2017 1 Introduction: Nottions nd sic Definitions At the eginning of the tutoril we
Lecture 08: Feb. 08, 2019
 4CS4-6:Theory of Computtion(Closure on Reg. Lngs., regex to NDFA, DFA to regex) Prof. K.R. Chowdhry Lecture 08: Fe. 08, 2019 : Professor of CS Disclimer: These notes hve not een sujected to the usul scrutiny
4CS4-6:Theory of Computtion(Closure on Reg. Lngs., regex to NDFA, DFA to regex) Prof. K.R. Chowdhry Lecture 08: Fe. 08, 2019 : Professor of CS Disclimer: These notes hve not een sujected to the usul scrutiny
Non-deterministic Finite Automata
 Non-deterministic Finite Automt From Regulr Expressions to NFA- Eliminting non-determinism Rdoud University Nijmegen Non-deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd J. Rot Institute for Computing nd Informtion
Non-deterministic Finite Automt From Regulr Expressions to NFA- Eliminting non-determinism Rdoud University Nijmegen Non-deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd J. Rot Institute for Computing nd Informtion
Automata and Languages
 Automt nd Lnguges Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering Lb. The University of Aizu Jpn Grmmr Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
Automt nd Lnguges Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering Lb. The University of Aizu Jpn Grmmr Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
CS667 Lecture 6: Monte Carlo Integration 02/10/05
 CS667 Lecture 6: Monte Crlo Integrtion 02/10/05 Venkt Krishnrj Lecturer: Steve Mrschner 1 Ide The min ide of Monte Crlo Integrtion is tht we cn estimte the vlue of n integrl by looking t lrge number of
CS667 Lecture 6: Monte Crlo Integrtion 02/10/05 Venkt Krishnrj Lecturer: Steve Mrschner 1 Ide The min ide of Monte Crlo Integrtion is tht we cn estimte the vlue of n integrl by looking t lrge number of
How to simulate Turing machines by invertible one-dimensional cellular automata
 How to simulte Turing mchines by invertible one-dimensionl cellulr utomt Jen-Christophe Dubcq Déprtement de Mthémtiques et d Informtique, École Normle Supérieure de Lyon, 46, llée d Itlie, 69364 Lyon Cedex
How to simulte Turing mchines by invertible one-dimensionl cellulr utomt Jen-Christophe Dubcq Déprtement de Mthémtiques et d Informtique, École Normle Supérieure de Lyon, 46, llée d Itlie, 69364 Lyon Cedex
CS 275 Automata and Formal Language Theory
 CS 275 Automt nd Forml Lnguge Theory Course Notes Prt II: The Recognition Problem (II) Chpter II.6.: Push Down Automt Remrk: This mteril is no longer tught nd not directly exm relevnt Anton Setzer (Bsed
CS 275 Automt nd Forml Lnguge Theory Course Notes Prt II: The Recognition Problem (II) Chpter II.6.: Push Down Automt Remrk: This mteril is no longer tught nd not directly exm relevnt Anton Setzer (Bsed
Lecture 09: Myhill-Nerode Theorem
 CS 373: Theory of Computtion Mdhusudn Prthsrthy Lecture 09: Myhill-Nerode Theorem 16 Ferury 2010 In this lecture, we will see tht every lnguge hs unique miniml DFA We will see this fct from two perspectives
CS 373: Theory of Computtion Mdhusudn Prthsrthy Lecture 09: Myhill-Nerode Theorem 16 Ferury 2010 In this lecture, we will see tht every lnguge hs unique miniml DFA We will see this fct from two perspectives
Typeness for ω-regular Automata
 Interntionl Journl of Foundtions of Computer Science c World Scientific Pulishing Compny Typeness for ω-regulr Automt Orn Kupfermn School of Engineering nd Computer Science Herew University, Jeruslem 91904,
Interntionl Journl of Foundtions of Computer Science c World Scientific Pulishing Compny Typeness for ω-regulr Automt Orn Kupfermn School of Engineering nd Computer Science Herew University, Jeruslem 91904,
CHAPTER 1 Regular Languages. Contents. definitions, examples, designing, regular operations. Non-deterministic Finite Automata (NFA)
 Finite Automt (FA or DFA) CHAPTER Regulr Lnguges Contents definitions, exmples, designing, regulr opertions Non-deterministic Finite Automt (NFA) definitions, equivlence of NFAs DFAs, closure under regulr
Finite Automt (FA or DFA) CHAPTER Regulr Lnguges Contents definitions, exmples, designing, regulr opertions Non-deterministic Finite Automt (NFA) definitions, equivlence of NFAs DFAs, closure under regulr
A tutorial on sequential functions
 A tutoril on sequentil functions Jen-Éric Pin LIAFA, CNRS nd University Pris 7 30 Jnury 2006, CWI, Amsterdm Outline (1) Sequentil functions (2) A chrcteriztion of sequentil trnsducers (3) Miniml sequentil
A tutoril on sequentil functions Jen-Éric Pin LIAFA, CNRS nd University Pris 7 30 Jnury 2006, CWI, Amsterdm Outline (1) Sequentil functions (2) A chrcteriztion of sequentil trnsducers (3) Miniml sequentil
Synchronizing Automata with Random Inputs
 Synchronizing Automt with Rndom Inputs Vldimir Gusev Url Federl University, Ekterinurg, Russi 9 August, 14 Vldimir Gusev (UrFU) Synchronizing Automt with Rndom Input 9 August, 14 1 / 13 Introduction Synchronizing
Synchronizing Automt with Rndom Inputs Vldimir Gusev Url Federl University, Ekterinurg, Russi 9 August, 14 Vldimir Gusev (UrFU) Synchronizing Automt with Rndom Input 9 August, 14 1 / 13 Introduction Synchronizing
Formal Language and Automata Theory (CS21004)
 Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge nd Automt Theory (CS21004) Khrgpur Khrgpur Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Tle of Contents Forml Lnguge nd Automt Khrgpur 1 2 3 Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge
Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge nd Automt Theory (CS21004) Khrgpur Khrgpur Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Tle of Contents Forml Lnguge nd Automt Khrgpur 1 2 3 Khrgpur Forml Lnguge nd Automt Forml Lnguge
Refined interfaces for compositional verification
 Refined interfces for compositionl verifiction Frédéric Lng INRI Rhône-lpes http://www.inrilpes.fr/vsy Motivtion Enumertive verifiction of concurrent systems Prllel composition of synchronous processes
Refined interfces for compositionl verifiction Frédéric Lng INRI Rhône-lpes http://www.inrilpes.fr/vsy Motivtion Enumertive verifiction of concurrent systems Prllel composition of synchronous processes
Types of Finite Automata. CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Comparing DFAs and NFAs. NFA for (a b)*abb.
 CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
CMSC 330: Orgniztion of Progrmming Lnguges Finite Automt 2 Types of Finite Automt Deterministic Finite Automt () Exctly one sequence of steps for ech string All exmples so fr Nondeterministic Finite Automt
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 20: Complexity V (Polynomial-Time Reducibility)
 CS5371 Theory of Computtion Lecture 20: Complexity V (Polynomil-Time Reducibility) Objectives Polynomil Time Reducibility Prove Cook-Levin Theorem Polynomil Time Reducibility Previously, we lernt tht if
CS5371 Theory of Computtion Lecture 20: Complexity V (Polynomil-Time Reducibility) Objectives Polynomil Time Reducibility Prove Cook-Levin Theorem Polynomil Time Reducibility Previously, we lernt tht if
Non-deterministic Finite Automata
 Non-deterministic Finite Automt Eliminting non-determinism Rdoud University Nijmegen Non-deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd T. vn Lrhoven Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences Intelligent
Non-deterministic Finite Automt Eliminting non-determinism Rdoud University Nijmegen Non-deterministic Finite Automt H. Geuvers nd T. vn Lrhoven Institute for Computing nd Informtion Sciences Intelligent
Nondeterministic Biautomata and Their Descriptional Complexity
 Nondeterministic Biutomt nd Their Descriptionl Complexity Mrkus Holzer nd Sestin Jkoi Institut für Informtik Justus-Lieig-Universität Arndtstr. 2, 35392 Gießen, Germny 23. Theorietg Automten und Formle
Nondeterministic Biutomt nd Their Descriptionl Complexity Mrkus Holzer nd Sestin Jkoi Institut für Informtik Justus-Lieig-Universität Arndtstr. 2, 35392 Gießen, Germny 23. Theorietg Automten und Formle
4 Deterministic Büchi Automata
 Bernd Finkeiner Dte: April 26, 2011 Automt, Gmes nd Verifiction: Lecture 3 4 Deterministic Büchi Automt Theorem 1 The lnguge ( + ) ω is not recognizle y deterministic Büchi utomton. Assume tht L is recognized
Bernd Finkeiner Dte: April 26, 2011 Automt, Gmes nd Verifiction: Lecture 3 4 Deterministic Büchi Automt Theorem 1 The lnguge ( + ) ω is not recognizle y deterministic Büchi utomton. Assume tht L is recognized
CHAPTER 1 Regular Languages. Contents
 Finite Automt (FA or DFA) CHAPTE 1 egulr Lnguges Contents definitions, exmples, designing, regulr opertions Non-deterministic Finite Automt (NFA) definitions, euivlence of NFAs nd DFAs, closure under regulr
Finite Automt (FA or DFA) CHAPTE 1 egulr Lnguges Contents definitions, exmples, designing, regulr opertions Non-deterministic Finite Automt (NFA) definitions, euivlence of NFAs nd DFAs, closure under regulr
Formal languages, automata, and theory of computation
 Mälrdlen University TEN1 DVA337 2015 School of Innovtion, Design nd Engineering Forml lnguges, utomt, nd theory of computtion Thursdy, Novemer 5, 14:10-18:30 Techer: Dniel Hedin, phone 021-107052 The exm
Mälrdlen University TEN1 DVA337 2015 School of Innovtion, Design nd Engineering Forml lnguges, utomt, nd theory of computtion Thursdy, Novemer 5, 14:10-18:30 Techer: Dniel Hedin, phone 021-107052 The exm
CDM Automata on Infinite Words
 CDM Automt on Infinite Words 1 Infinite Words Klus Sutner Crnegie Mellon Universlity 60-omeg 2017/12/15 23:19 Deterministic Lnguges Muller nd Rin Automt Towrds Infinity 3 Infinite Words 4 As mtter of principle,
CDM Automt on Infinite Words 1 Infinite Words Klus Sutner Crnegie Mellon Universlity 60-omeg 2017/12/15 23:19 Deterministic Lnguges Muller nd Rin Automt Towrds Infinity 3 Infinite Words 4 As mtter of principle,
Converting Regular Expressions to Discrete Finite Automata: A Tutorial
 Converting Regulr Expressions to Discrete Finite Automt: A Tutoril Dvid Christinsen 2013-01-03 This is tutoril on how to convert regulr expressions to nondeterministic finite utomt (NFA) nd how to convert
Converting Regulr Expressions to Discrete Finite Automt: A Tutoril Dvid Christinsen 2013-01-03 This is tutoril on how to convert regulr expressions to nondeterministic finite utomt (NFA) nd how to convert
Myhill-Nerode Theorem
 Overview Myhill-Nerode Theorem Correspondence etween DA s nd MN reltions Cnonicl DA for L Computing cnonicl DFA Myhill-Nerode Theorem Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute
Overview Myhill-Nerode Theorem Correspondence etween DA s nd MN reltions Cnonicl DA for L Computing cnonicl DFA Myhill-Nerode Theorem Deepk D Souz Deprtment of Computer Science nd Automtion Indin Institute
COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS
 CST.2011.2.1 COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS Prt IA Tuesdy 7 June 2011 1.30 to 4.30 COMPUTER SCIENCE Pper 2 Answer one question from ech of Sections A, B nd C, nd two questions from Section D. Submit the nswers
CST.2011.2.1 COMPUTER SCIENCE TRIPOS Prt IA Tuesdy 7 June 2011 1.30 to 4.30 COMPUTER SCIENCE Pper 2 Answer one question from ech of Sections A, B nd C, nd two questions from Section D. Submit the nswers
Reinforcement Learning
 Reinforcement Lerning Tom Mitchell, Mchine Lerning, chpter 13 Outline Introduction Comprison with inductive lerning Mrkov Decision Processes: the model Optiml policy: The tsk Q Lerning: Q function Algorithm
Reinforcement Lerning Tom Mitchell, Mchine Lerning, chpter 13 Outline Introduction Comprison with inductive lerning Mrkov Decision Processes: the model Optiml policy: The tsk Q Lerning: Q function Algorithm
automata for formal methods: little steps towards perfection
 utomt for forml methods: little steps towrds perfection Frntišek Blhoudek phd thesis corrected version (September 25, 2018) Fculty of Informtics Msryk University Brno Mrch 2018 Acknowledgements I will
utomt for forml methods: little steps towrds perfection Frntišek Blhoudek phd thesis corrected version (September 25, 2018) Fculty of Informtics Msryk University Brno Mrch 2018 Acknowledgements I will
Grammar. Languages. Content 5/10/16. Automata and Languages. Regular Languages. Regular Languages
 5//6 Grmmr Automt nd Lnguges Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
5//6 Grmmr Automt nd Lnguges Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
Lecture 6 Regular Grammars
 Lecture 6 Regulr Grmmrs COT 4420 Theory of Computtion Section 3.3 Grmmr A grmmr G is defined s qudruple G = (V, T, S, P) V is finite set of vribles T is finite set of terminl symbols S V is specil vrible
Lecture 6 Regulr Grmmrs COT 4420 Theory of Computtion Section 3.3 Grmmr A grmmr G is defined s qudruple G = (V, T, S, P) V is finite set of vribles T is finite set of terminl symbols S V is specil vrible
Compiler Design. Fall Lexical Analysis. Sample Exercises and Solutions. Prof. Pedro C. Diniz
 University of Southern Cliforni Computer Science Deprtment Compiler Design Fll Lexicl Anlysis Smple Exercises nd Solutions Prof. Pedro C. Diniz USC / Informtion Sciences Institute 4676 Admirlty Wy, Suite
University of Southern Cliforni Computer Science Deprtment Compiler Design Fll Lexicl Anlysis Smple Exercises nd Solutions Prof. Pedro C. Diniz USC / Informtion Sciences Institute 4676 Admirlty Wy, Suite
Hybrid Control and Switched Systems. Lecture #2 How to describe a hybrid system? Formal models for hybrid system
 Hyrid Control nd Switched Systems Lecture #2 How to descrie hyrid system? Forml models for hyrid system João P. Hespnh University of Cliforni t Snt Brr Summry. Forml models for hyrid systems: Finite utomt
Hyrid Control nd Switched Systems Lecture #2 How to descrie hyrid system? Forml models for hyrid system João P. Hespnh University of Cliforni t Snt Brr Summry. Forml models for hyrid systems: Finite utomt
Regular expressions, Finite Automata, transition graphs are all the same!!
 CSI 3104 /Winter 2011: Introduction to Forml Lnguges Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Regulr expressions, Finite Automt, trnsition grphs re ll the sme!! Dr. Neji Zgui CSI3104-W11 1
CSI 3104 /Winter 2011: Introduction to Forml Lnguges Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Chpter 7: Kleene s Theorem Regulr expressions, Finite Automt, trnsition grphs re ll the sme!! Dr. Neji Zgui CSI3104-W11 1
CS 373, Spring Solutions to Mock midterm 1 (Based on first midterm in CS 273, Fall 2008.)
 CS 373, Spring 29. Solutions to Mock midterm (sed on first midterm in CS 273, Fll 28.) Prolem : Short nswer (8 points) The nswers to these prolems should e short nd not complicted. () If n NF M ccepts
CS 373, Spring 29. Solutions to Mock midterm (sed on first midterm in CS 273, Fll 28.) Prolem : Short nswer (8 points) The nswers to these prolems should e short nd not complicted. () If n NF M ccepts
