Formation of Cooper Pairs as a Consequence of Exchange Interaction
|
|
|
- Esther Richard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stanislav Dolgopolov omation of Coope Pais as a Consequene of xhange Inteation Abstat: Analyzing the exhange enegy of two ondution eletons in a ystal at many-body appoah we find that the exhange enegy may be negative and, thus, the singlet state may be favoable. A full ovelap in the eal spae of the wave funtions of two ondution eletons leads to a deepe exhange enegy. hus the exhange inteation auses a bond between two ondution eletons in the eal spae. he singlet bond is possible beause the singlet eletons ae in aveage lose to positive ions than single eletons. If ondution eletons, befoe the paiing, ae put on the emi sufae in the momentum spae, then evey pai may exist pemanently in time. he motion of ondution eletons in the ystal may pevent the fomation of Coope pais, beause the kineti enegy of the motion is usually lage than the binding enegy in the pai. Condution eletons as standing waves have zeo momenta, hene thei momenta ae synhonous; theefoe the fomation of Coope pais is moe pobable than in ase of non-zeo momenta. he appoah of standing waves explains the invese isotope effet and many othe fats about supeondutos. Consideing the eletoni pais as bosons we find that a futhe neessay ondition fo supeondutivity is a non-zeo tempeatue of the ose-instein-condensation. Keywods: Coope pai; exhange inteation; Pauli xlusion Piniple; singlet state; supeondutivity; standing wave; ose-instein-condensation.. Intodution and motivation. he knowledge of oot auses of supeondutivity SC would explain many mysteious fats about all lasses of supeondutos. Howeve, a unified solution emains still an open question, uent theoies ae not univesal and explain many effets ambiguously []. he mainsteam theoies assume that SC is a esult of the eleton paiing at a mean-field appoximation, the spin odeing plays a pat fo the pai fomation [], [3], [4]. vey spin odeing is elated with the exhange inteation, whih influenes the total enegy of the eletons inteating with evey patile of the ystal. Moeove the exhange inteation may in itself ause binding states in quantum systems at a many-body appoah [5], [6]. heefoe the many-body appoah is moe appopiate to define the eleton states than the meanfield appoximation, and the ole of the exhange inteation seems to be uially impotant fo the pai fomation. In the wok is shown that the Pauli xlusion Piniple and its assoiated exhange inteation may in piniple lead to binding states of ondution eletons, whih unde etain onditions beome supeonduting.. omation of supeonduting pais. Nomally the spins of ondution eletons in a ystal ae unodeed beause the themal flutuations and own motion of eletons destoy the spin odeing. hus the spin of evey ondution eleton e is andom to spins of all othe eletons. his state of eleton e is designated as unpaied o single. If the spins of eletons e, e fom a singlet in thei ovelap aea in the eal spae, then the state of the eletons is designated as paied. vey unpaied ondution eleton has its auate spatial wave funtion desibing the position of the eleton in the ystal. Knowing the auate wave funtions of unpaied eletons e, e we an ompute thei exhange enegy. If two eletons e,e fom a singlet, then thei oveall position-spae wave funtion, is symmeti:,. whee, ae auate wave funtions of unpaied e,e ;, ae adius-vetos of e,e. he sum of the diet and exhange enegies D+J we find substituting, fom q.. into the integal with an oveall enegy opeato Oˆ, : D J, Oˆ,, Oˆ, Oˆ, If the exhange inteation of eletons e, e is vey weak, then thei spins emain unpaied and fully andom. In this ase the exhange enegy is negligible and the oveall enegy of the unpaied eletons is equal to the diet tem D as it should be fo the unpaied eletons with auate wave funtions, :., D Oˆ,.3
2 he exhange enegy J fom q.. is J Oˆ,.4 If the exhange inteation of eletons e, e is not negligible, then thei exhange tem J is not zeo. A singlet state of e, e is favoable, if thei exhange enegy J is negative [7]. J takes into aount the modifiation of the initially unpaied wave funtions esulting fom the paiing. his wave funtion modifiation influenes all inteations of e, e in the ystal; hene we must ompute the exhange enegy J fo Oˆ, as a sum of all inteations of e, e inluding thei kineti enegy, epulsion of e, e fom evey ondution eleton and attation of e, e to evey ion. If two eletons fom a tiplet, then thei oveall position-spae wave funtion is antisymmeti. he tiplet state of e, e is favoable, if thei exhange enegy J is positive. We assume that, have an ovelap in the eal spae and ontain simila atom obitals fo sample s- obitals; momenta of e, e along the ystal ae equal o zeo. In this ase, ae not othogonal as obitals of the gound state in H -moleule o in Helium atom; hene the ovelap integal appeaing in q..4 is not zeo:.5 he wave funtions of ondution eletons fade out slowly with the distane and an ove many points of lattie, thus the wave funtions of many eletons may ovelap in a shaed eal spae, so we onside at fist the limiting ase that, almost oinide in the eal spae, i.e.:.6 elow we will see that this assumption is tue beause a maximal ovelap in the eal spae of two paied wave funtions is enegetially favoable in ompaison to a patial ovelap. Using q..6 and non-othogonality of, in q..5 we an use fo q..4:, Substituting q..7 into.4 we obtain:.7 J Oˆ,.8 We see that q..8 is equal to q..3, i.e. in the ase of the full ovelap of non-othogonal wave funtions, the exhange enegy of two singlet eletons is equal to the oveall enegy of two initially unpaied eletons: J,.9 We may define that the eleton enegy outside of the ystal is zeo. hen the eleton enegy, inside the ystal should be negative, othewise the states of single eletons in the ystal ae instable. hus the exhange enegy J of e, e is also negative and the paied state is favoable in ompaison to the unpaied state. his onlusion has a lea physial meaning. he exhange tem takes into aount that the aveage distane between two singlet eletons deeases [8], [9], what ineases the epulsion between eletons. Conside a small aea aound one of ions in the ovelap aea of e, e in the eal spae; due to the xlusion Piniple two singlet eletons ae loated in this small aea with a pobability highe than two eletons with paallel spins, beause the eletons with paallel spins avoid eah othe and annot be put into a small aea i.e. the pobability that is little. If two eletons ae unpaied, then thei spins ae equipobably paallel o antipaallel, hene the eletons avoid eah othe, but do it weake than the eletons with paallel spins. hus the pobability to obseve in this small aea two unpaied eletons is lage than this pobability fo two eletons with paallel spins, and smalle than this pobability fo a singlet. heefoe the singlet eletons ae in aveage lose to the ion than two unpaied eletons. In simple wods two singlet eletons ae
3 lose to eah othe, the ions ae loated somewhee between eletons, theefoe the singlet eletons ae unavoidably lose to ions. he exhange tem takes into aount this deease in distane between eletons and ions. Conside that the ovelap aea of e, e in the eal spae is negligible i.e. integal is small, then the exhange enegy in q..4 is negligible. In this ase thee is no advantage of the singlet state, sine the eletons ae sepaated in the eal spae. hus the lage the ovelap, the geate the enegy advantage of the paiing. Consequently two paied wave funtions tend to a full oinidene in the eal spae and emain togethe in equilibium. hus the assumption in q..6 is justified. inally two eleton waves stay togethe beause the singlet state with a full ovelap in the eal spae edues thei total enegy. It is possible to show that the singlet paiing of some ondution eletons is favoable fo the whole ystal. We define all pats of the oveall enegy of two unpaied ondution eletons, :. he kineti enegies of eletons e and e, K e, K e ;. he potential enegy of epulsion of eleton e fom all ondution eletons in the ystal, P e, e ; 3. he potential enegy of epulsion of eleton e fom all ondution eletons in the ystal, P e, e ; 4. We must oet double ounting the epulsion between e, e, so we subtat the potential enegy of epulsion between eletons e, e, P e, e ; 5. he potential enegy of attation of eleton e to all ions in the ystal, P e, I ; 6. he potential enegy of attation of eleton e to all ions in the ystal, P e, I. he exhange enegy of e, e in q..9 is a sum of the points -6: J, K e K e P e, e P e, e P e, e P e, I P e, I. he points -6 ae a list of the ystal enegy tems, whih ontain the paied eletons e, e. If the ystal has many singlet pais, then the enegy of eah pai e, e ontains the points -6 howeve, we must again oet double i i ounting the epulsion between eletons of diffeent pais. he total enegy of the many-body ystal ontains additional enegy tems: 7. he kineti enegies of single ondution eletons; 8. he potential enegy of epulsion between single ondution eletons; 9. he potential enegy of attation of single ondution eletons to ions;. he potential enegy of epulsion between ions. he points - ae a full list of all ystal enegy tems. he single, emaining unpaied, eletons don t hange thei states; hene the ystal enegy tems in the points 7- emain unhanged. In the points -6 the oveall enegy of evey singlet pai e, e is lowe than the enegy of two unpaied eletons e, e i i i i due to the negative exhange enegy J. hus the singlet paiing of some ondution eletons inevitably leads to the enegy loweing of the whole ystal, the maosopi state an exist. One an obtain the same esult by exploing the many-body ystal Hamiltonian H... and the total ystal wave n funtion as a podut of nomalized auate wave funtions of evey single [] and paied eleton: ystal... i i i i... m m m m... H... n... i i i i... m m m m... Whee: i i, i i nomalized auate wave funtions of paied eletons; m m, m m auate wave funtions of unpaied eletons;... n adius-vetos of all eletons and ions. he Hamiltonian H... is a sum of opeatos fo enegies: n. he kineti enegies of paied and single ondution eletons;. he potential enegy of epulsion between all ondution eletons paied and single; 3. he potential enegy of attation to ions of all ondution eletons paied and single; 4. he potential enegy of epulsion between ions. All onlusions fom qs.-. ae valid if the eletons e, e ae two equal unning loh waves []:, t, t u exp i t i k.. nomalized 3
4 Howeve, it is a ae event that the momenta k of two unning waves ae equal pemanently in time. he momenta of eletons may be pemanently equal if befoe paiing eah eleton is a standing wave, whih is a sum of two equipobable loh waves popagating in opposite dietions:, t, t u exp i t i k u exp i t i k.3 he total momentum of eah eleton as standing wave is zeo, hene the momenta of eletons ae synhonous, so the paiing is possible despite the fat that the kineti enegy of eletons may be lage than thei paiing enegy. he oveall enegy of two unpaied eletons, is usually not abitaily small; onsequently the exhange enegy J in q..9 is also not abitaily small. he sign of the exhange tem J is elated with the sign of the enegy inement esulting fom the paiing. his enegy inement is elated with wave funtion modifiations and is not neessaily negligible if J is not negligible; theefoe the binding enegy in the singlet pai is also not negligible: Oˆ, Oˆ, A J.4 Whee, ae nomalized auate wave funtions of e, e afte paiing; A is a positive mateial onstant. Sine the binding paiing enegy is not abitaily weak, the unpaied nomal state of e, e is instable. Howeve, the paied state of e, e is pemanent in time only if extenal enegies tempeatue, adiation, magneti field ae weake than. he binding enegy is oughly elated to a paiing tempeatue *: k *. If the wave funtions of two ondution eletons in the ystal fo sample two s-eletons pemanently oinide in the eal spae and fom a pemanent singlet, then the eletons ae simila to the eletons in the gound state of Helium. he diffeene is that in the ystal the wave funtions ove many ions and the pai an move in an extenal potential, sine all ystal aeas ae equipotential fo the pai. In the gound state of Helium the singlet state is favoable despite the fat that the epulsion of eletons is maximal; the inease in attation of the singlet s-eletons to the Helium nuleus exeeds the inease in epulsion and in kineti enegy. he eletoni pai is stable like a valene bond in multi-atom systems, so the pai doesn t fom/lose any bonds in the ystal and doesn t absob/adiate any hemial enegy. vey standing wave is limited in the eal spae, theefoe a stable singlet of two standing waves an be onsideed as a zeo-spin boson. osons an fom the ose-instein-condensate C below a etain tempeatue C. If all eletoni pais ae in the C gound state, then the exitation enegy of evey pai is oughly elated to k C, whih is not zeo if the bosoni density is not zeo. If all extenal influenes ae weake than k C, then the pais emain in the C gound state and annot absob/adiate any enegy in the ystal; as a esult the total enegy and momentum of all pais don t dissipate, the pais flutuate without esistane despite the fat that the single eletons wee standing waves befoe paiing. hus the paiing of ondution eletons and C of the pais lead to the zeo esistivity likewise woks the supefluidity in Helium-4; the paiing enegy of eletons k * in Helium-4 is huge, wheeas k C is small. In an extenal magneti field H the ystal obtains an additional enegy density w,5 H ; the enegy of the singlet eletons splits. If the magneti enegy split H is weake than the binding enegy k * and exitation enegy k C, then the pai flutuates in the field H as a fee patile with a hage -e and zeo spin. Consequently thee ae no obstales to edistibute the non-dissipative flutuations of the pais into non-dissipative uents ompensating the additional magneti enegy w Meissne effet. If the binding enegy pe one eleton in q..4 is lage than the insulating band gap g of the ystal, then eletons an leave the valene band at a tempeatue *, hene the eletons may pai up despite the band gap. A doping in the ystal may edue the band gap and, thus, give ise to SC. his doping effet is obsevable in upates [], in ion-based supeondutos [3], in semiondutos [4]. A neessay ondition fo SC in metals is that the eletons, befoe paiing, ae lose to the emi sufae in the momentum spae. We show this assuming that the paiing ous when the enegy of the single eleton has a etain value λ. If the themal enegy doesn t exeed the binding enegy in q..4, then the onentation of the pais is not zeo and in the enegy spetum of single eletons ous a gap aound the value λ. he gap is thin, sine is usually small and the density of eletons with lose enegies is limited by the xlusion Piniple. If λ is notably less than the emi level, then thee ae single eletons with the enegy lage than λ. hese single eletons may dop to the level λ due to enegy flutuations and may, thus, fom new pais. he onentation of the paied eletons is limited by the thin gap aound λ ; theefoe the new pais eplae the aleady existing pais, whih lose the paied state. hus eah eleton is not pemanently paied, but it beomes peiodially unpaied. Duing evey swithing of states the eleton absobs/loses enegy, in the unpaied state the eleton is esistive, theefoe the momentum of the eleton and of the pai dissipates. hus the state with λ < annot keep a supeuent, despite the fat that the paiing is possible. If λ = then evey pai may exist pemanently in time, beause below a tempeatue the 4
5 single eletons annot oveome the enegy gap and annot eah the paiing level λ = ; as a esult the new pais don t aise and don t eplae the existing pais. Hene the swithing of states doesn t ou and the total momentum of the pais doesn t dissipate. hus the supeonduting paiing ous only fo single eletons in an enegy gap with as the uppe limit. Only suh pemanent pais ae supeonduting. At a tempeatue above the themal enegy is suffiient to satte single eletons though the enegy gap to the paiing level λ, theefoe new pais may aise and eplae the existing ones, the state beomes dissipative. 3. Paiing of standing waves. We found that the binding enegy in the singlet pai e, e is maximal if the ovelap integal is maximal, i.e. the wave funtions oinide in the eal spae. he enegy gap of supeondutos has ode of magnitude -3 ev, the emi level has ode of magnitude a few ev. Consequently the eleton motion an split the pai in the eal spae. he enegy of vey slow eletons is usually muh lowe than the emi level; hene the slow eletons annot fom supeonduting pais. wo eletons an fom a pai if thei momenta ae synhonous, but it is a ae event fo unning waves. he eletons as standing waves have zeo-momenta, hene thei momenta may be synhonous and the paiing is possible despite a lage kineti enegy. A standing wave ous as a esult of efletions of a unning wave fom a peiodi potential. he ondition of the standing wave in a ystal is the agg ondition [5]: n 3. Whee: n intege; length of the loh wave in q..; one of lattie paametes. Unde agg ondition the eleton beomes a set of standing waves with a zeo total momentum [6]. At n= in q. 3. the length of the standing wave is maximal:. A ystal has some values,, et. depending on the ystal axis and, thus, some values. ah value is linked to the enegy : h / m h 8 m 3. Whee m is the inetial mass of fee eleton. Not all mateials have ondution eletons with shot values λ= and with its assoiated. If the emi level of a ystal is low, then λ values ae lage than shot values and eleton enegies ae lowe than oesponding ; so the states with shot λ= ae empty and shot standing waves don t ou. In some metals is lose to it is equivalent that λ =. Pobably in some ystals the fomation of pais is possible at n lage than in q. 3.. o sample at n= the length of standing waves is λ =. vey at of the paiing is enegetially favoable; hene the enegy is emitted. hus the momentum of eah pai ineases fom zeo to a value p m.5. his momentum p should be added to the momenta of paied eletons in the momentum spae. heefoe the kineti enegies of eletons fom diffeent pais ae not equal, but distibuted into a spetum with the width. o instane, if the kineti enegy of nomal eletons was befoe paiing, then afte the paiing the kineti enegy beomes +. So the spetum of paied eletons is above the spetum of single eletons in the momentum spae. Note: the same onlusion follows fom the exhange enegy: the exhange tem fo kineti enegy is positive, i.e. the kineti enegy gows by paiing, wheeas the total enegy falls the same elation is valid fo all singlet bonds in hemisty. hus the paied eletons an ovelap with nomal eletons in the eal spae. he density of paied eletons is S, whee S is the density of states of ondution eletons. he spetum of nomal eletons obtains a oesponding gap - aound the value λ=, ae limits of the gap. he gap is not negligible if the themal enegy is insuffiient to destoy the pais. As shown above a neessay ondition fo SC is that is the uppe limit of the gap: =. he enegy gap is -, whee the gap bottom should be below λ= othewise new pais aise and eplae the existing ones, enegy dissipates. he density of the singlet eletons N s is limited by the enegy gap: N s S d 3.3 hus the enegies and states of single eletons below the gap - stay unhanged as assumed fo q... he eletons befoe supeonduting paiing must be lose to the emi sufae, i.e. the value must be lose to i.e.. eally, the enegy gap is muh less than ; theefoe if is signifiantly less than, then the uppe gap limit is also less than ; as shown above this ase is not supeonduting beause the pais ae not pemanent in time. o this eason Au, Ag, Cu whee signifiantly [7] ae not supeondutos. If 5
6 is signifiantly lage than, then thee ae no eletons with and the gap doesn t ou. o this eason in some stutues with a low a doping may aise the aie density and its assoiated up to the level whih is onstant, if doesn't hange. hus the doping may lead to SC, ineases. If the ystal is ovedoped, then is too lage;, vanishes. his doping effet explains the dome fom of phase diagams of supeondutos [8]. A double dome fom is possible due to the fat that the ystal has some lattie paametes depending on the ystal stutue. hus a lage value suppesses. If, then oesponds to the paiing enegy in q..4; howeve, the doping influenes on both maximum is not always pinned exatly to. and, so the - We an speify the enegy C k C is a mateial speifi onstant as a minimum themal enegy, whih is neessay to satte single eletons fom the bottom of the supeonduting gap to the paiing level, whee new pais aise and eplae the old ones. So we know about the tuning: if 3.4 C k C k if if and and hus Ck is an enegy aea between the SC - gap bottom and λ=. A gowing loses ontinuously the aea Ck by putting thee single nomal eletons. At = the aea Ck is oveed by single eletons. Knowing the density of single states S λ aound the SC-gap, we an alulate and C - paamete in Ck. he paiing enegy in q..4 is to find by investigating the wave funtion modifiations esulting fom the singlet paiing and leading onsistently to expeimental -values. he SC - gap bottom is to find fom qs 3.5, 3.6: C k if if C k he single-eleton-distibution on the SC-gap bottom is the emi-dia funtion f λ,. he single-eletononentation N at just below is: N S f, d S d 3.9 exp k At = the single-eleton-onentation N is: N S d 3. New pais don t aise at, so N is independent of. Hene N=N and q. 3.9 is equal to q. 3.: S d S d 3. exp k is alulable fom qs 3.7 o 3.8, λ= is known fom ystal stutue; hene, knowing S λ, we an alulate fom q. 3.. C paamete in Ck we find fom and using Ck = λ= -. Calulations with q. 3. show:,5 A. o emi liquids S λ is popotional to, then C depends slightly on the level and. Substituting the anges =.5-3 ev and =. - 5 K into q. 3. we find λ= and the ange C units;. C depends on the S λ -slope aound the level : the lage ds/d λ, the smalle C. On the zone edge λ= ds/d λ,5 may be lage than the -slope, theefoe C may be smalle than by a few units, i.e. C 3-7. hese C - values ae onsistent with expeiments. he isotope substitution is a way to tune by tuning to λ= based on the fat that depends on the effetive mass of eleton m* and eleton density N [9], wheeas λ= in q. 3. depends only on the lattie paamete. h 8m * 3N /3 3. 6
7 he isotope effet is a onsequene that the enegy of phonons is popotional to M -,5 M - mass of ion. he deease in M aises the enegy of phonons; theefoe the eleton-ion inteation and its assoiated efletion of eletons fom ions may intensify. his intensifiation is equivalent to the inease in the effetive mass m* and, thus, to the deease in, wheeas is almost unhanged. If the initial value is lage than λ= it is usual fo metals, then the deease in M pulls down lose to λ= ; hene gows the isotope oeffiient α>. If the initial value is less than λ=, then the deease in M pulls down away fom λ= ; hene may vanish α<. One an onlude that in ase the isotope effet may be weak α <,5. hus the diffeent values and sign of α [] ae a esult of the diffeent initial positions to λ=. Othe ways to tune by tuning to λ= ae: eleti field [] sine depends on the eletoni density; film thikness [], [3], [4], [5] sine the mutual of layeed stutues depends on laye thiknesses; the high pessue [6], [7], [8] sine depends on the distane between atoms. A futhe sample of the tuning is the alkali metals Li, Na, K, b, Cs. Only Lithium is supeonduto at ambient pessue [9] and only Lithium has =3,9 ev alulated by q. 3. in b-stutue, =3,49 Å elatively lose to 3, ev [3] at ambient tempeatue. he next andidate in supeondutos afte Lithium is Cesium: =,33 ev alulated by q. 3. in b-stutue, 6,4 3 5,3,,54 ev alulated by q. 3.; Cesium is eally supeonduto unde high pessue [3]. he high pessue ineases the density of ions, so m* ises and dops to ; theefoe gows both in Li and in Cs. he othe alkali metals ae not supeondutos and thei values ae lage than moe signifiantly than in Li and in Cs table. We note that and ineases both ae equally popotional to and., hene without the modifiation of m* an isotopi -edution able. Compaison of enegies and λ= fo alkali metals. λ= ae alulated by q. 3. fo lattie paametes and in b ystals. Lage -values ae not onsideed, sine they oespond to smalle λ= values. o Li is used the expeimental value at ambient tempeatue; fo othe alkali metals ae used values alulated by q. 3. oesponding oughly to the expeimental values. - fo fo fo fo ev ev ev ev ev Li Na K b Cs he desibed appoah explains the ombined isotope and high pessue effet in lithium [3]. In lithium-6 the high pessue and light isotope pull below the level λ=, so stats to diminish at a etain pessue p. In heavy lithium-7 emains above λ= at p, hene the ineasing pessue ontinues to pull down towad λ= ; ontinues to gow. As a esult the sign of d /dp above the pessue p is diffeent fo 6 Li and 7 Li. A pefet onduto annot fom the Coope pais, beause the eletons pass though the lattie without efletion, the standing waves don t aise, the eletoni wave pakets ae unlimited in the eal spae, hene a oelation of wave funtions in aodane with q.. is impossible beause of a finite speed of eleton-eleton inteation; so the exhange enegy and tends to zeo. hus the exhange enegy and the assoiated paiing enegy should be elated with the stength of the eleton-ion efletion via the potential enegy of eletons in q... A deepe potential enegy of eletons leads to a deepe J in q.. and, thus, to a stonge paiing enegy in q..4. On the othe hand, a deepe potential enegy means a deepe potential on eah ion, whih inteats/eflets ondution eletons moe stongly. So the singlet bond is stonge if the efletion of the unpaied eletons is stonge; hene may also be lage, but unde the ondition that is kept. he desibed appoah is onsistent with the fat that the high tempeatue supeondutos ae layeed stutues and poo ondutos in the nomal state. In some layeed stutues is possible to ombine two pooly ompatible things: a lage effetive mass m* elated to the stong eleton-ion inteation/efletion and a lage up to the value λ=. his is beause in thin films is lage than in bulk [33], wheeas the eleton efletion and m* in-plane may emain almost unhanged. In a 3-dimensional stutue is diffiult to ombine a lage m* > 5 m and a few ev. hus in quasi -dimensional systems an be highe. he paiing enegy in the poposed model is elated athe to the lattie potential than to the aie density. his enables SC at elatively low aie densities. A sample is supeonduting bismuth at ambient pessue, a semimetal with a low
8 aie density, N 3 7 /m 3 [34]. of bismuth is 5 mev, hene oesponding λ = h m m. hus in bismuth ae woking the long values of =.5 λ.39-8 m i.e. 8, 9 and simila. hese long standing waves exist only due to the high ystal puity, whee the eletoni mean fee path is muh lage than λ. hus SCpais emege fom the long standing waves on the emi level. Sine the eleton's waves ae long ange, the mean distane between eletons in one pai may be lage than the eleton's wave length λ -8 m, so the paiing is possible at a aie density less than λ -3 8 /m 3. o emi metals we an estimate the elation between C-tempeatue and paiing tempeatue, C /*. / 3 Assuming N S and 3.5 k *, using the well-known equations S m 3/ / fo s /3 emi liquid and N 3.35 N / m k fo bosoni gas we obtain: * C /3 C s 3.3 s o emi metals usually >>, hene C >* and SC depends athe on * than on C, i.e. =*< C. o stongly oelated systems may be ode of magnitude, so C may define SC, i.e. = C <*. If the paiing tempeatue * is lage than C i.e. *> C, then at above C the eletoni pais may be pemanent but non-supeonduting. he non-supeonduting pais ae obseved in [35]. Conside is lose to the SC-gap bottom and notable below λ= that is possible, fo example, in undedoped upates. hen the gap - in q. 3.3 is small and the singlet density N s is also small. Hene the oesponding C may be lowe than the paiing tempeatue *, beause * depends athe on the lattie potential than on N s. If the C is a neessay ondition fo SC and C <*, then = C ; so is also lowe than *. hus at between and * thee ae pemanent pais without SC. his may be elated with the pseudogap in some supeondutos. 4. Conlusion and disussion. he above agumentation shows that the exhange inteation may in itself ause the eletoni paiing in a ystal. hus the non-zeo paiing binding enegy is a esult of the Pauli xlusion Piniple. uthe neessay onditions fo SC: the pemaneny in time of evey eletoni pai povided with paiing of standing waves on the emi sufae; the non-zeo tempeatue of the C gound state of the eletoni pais. he appoah of the exhange enegy is lealy appliable when the waves, ontain s-obitals, beause the s-obitals envelop eah ion and the singlet paiing leads to a onvegene of eletons to ions. In ase of p-, d-, f- obitals the desibed appoah woks if the obitals envelop neaest neighbo ions. In this ase the singlet paiing depends on the obital oientation and on fatos influening the distane between ions pessue, doping et. he appoah of standing waves is elated with the agg-efletion, whih may fom diffation pattens in the ystal. his explains why the hage density ode pe-exists the supeondutivity in upates [36], [37], [38]. ollowing the poposed appoah we an define main ways to a highe in new supeondutos: A. he value should be tunable lose to λ= i.e. λ is tunable to shot. he tuning is possible by doping, pessue, film thikness, eleti field et.. he mateial should have a lage value m*, sine m* is elated to deepe lattie potentials in q.. ausing a deepe exhange enegy. Howeve, the ondition = λ= should be kept. A possible way to ombine lage values and m* is the low dimensionality; C. he mateial should be homogeneous miosopially, beause impuities/defets suppess by satteing the egula standing waves and values and. he appoah of standing waves is not appliable to systems with heavy femions, whee is muh smalle than λ=. ut in this ase the kineti enegy of eletons on the emi sufae may be smalle than the binding enegy in the pai; hene the pai may aise and exist pemanently in time ausing SC. One an wite oughly fo naow band systems: C k 4. heefoe a tuning of down may ause a highe in systems with heavy femions obseved in [39]. 5. efeenes. [] J.. Hish, M.. Maple,. Masiglio, Supeonduting mateials lasses: Intodution and oveview, Physia C, Vol [] adeen, John; Coope, Leon; Shieffe, J.. heoy of Supeondutivity. Physial eview 85:
9 [3]. Moiya, K. Ueda, Spin flutuations and high tempeatue supeondutivity, Advanes in Physis, Vol. 49, Issue 5 [4] P.W. Andeson, et al, Phys. ev. Lett. 58, [5].I. leaney,. leaney, letiity and Magnetism, Volume, hid dition, Oxfod Univesity Pess, Chaptes 5.8; 6 3 [6] Masatsugu Suzuki, Itsuko S. Suzuki, Letue note on solid state physis Supeexhange inteation, Chaptes.;., Depatment of Physis, State Univesity of New Yok at inghamton, August 8, 7, evised May 8, 9 [7] Van Vlek, J. H.: he heoy of leti and Magneti Suseptibilities, Oxfod, Claendon Pess, p [8] David J. Giffiths, Intodution to Quantum Mehanis nd dition, Peason diation Limited, pp. 7-4 [9] Stöh, J. and Siegmann, H. C., Magnetism: om undamentals to Nanosale Dynamis, Spinge Velag elin Heidelbeg, Vol. 5, pp [] Stöh, J. and Siegmann, H. C., Magnetism: om undamentals to Nanosale Dynamis, Spinge Velag elin Heidelbeg, Vol. 5, pp [] obet L. Spoull, Moden Physis, Mosow, Nauka, 8.5, p [] P. A. Lee, N. Nagaosa, X.-G. Wen, Doping a Mott insulato: Physis of high-tempeatue supeondutivity. ev. Mod. Phys. 78, 7 6 [3] Hideo Hosono et al, Si. ehnol. Adv. Mate [4]. ustaet, Supeondutivity in doped semiondutos, Physia C 54, [5] obet L. Spoull, Moden Physis, Mosow, Nauka, 8.5, eq [6] obet L. Spoull, Moden Physis, Mosow, Nauka, 8.5, p [7] obet L. Spoull, Moden Physis, Mosow, Nauka, 9.4, p. 9, table [8] Md. Atiku ahman et al. A eview on Cupate ased Supeonduting Mateials Inluding Chaateistis and Appliations. Ameian Jounal of Physis and Appliations. Vol. 3, No., pp [9] obet L. Spoull, Moden Physis, Mosow, Nauka, 9.4, p [] Manzoo A. Malik, ilal A. Malik, Isotope ffet as a Pobe of the ole of Phonons in Conventional and High empeatue Supeondutos, Ameian Jounal of Condensed Matte Physis, 3:67-7 [] Yen-Hsiang Lin, J. Nelson, A.M. Goldman, Physia C 54, [] A. ydman, Physia C 39, 89 3 [3] D.. Haviland, Y. Liu, and A.M. Goldman, Phys. ev. Lett. 6, [4] Yen-Hsiang Lin, J. Nelson, A.M. Goldman, Physia C 54, [5] A. Goza, I. ozovi, High empeatue Intefae Supeondutivity, Physia C, Vol. 5 5, p [6] J.J. Hamlin, Supeondutivity in the metalli elements at high pessues, Physia C 54, [7] Yoshihio Kubozono et al. Supeondutivity in aomati hydoabons, Physia C, Vol. 54, p [8] M Debessai et al, Pessue-indued supeondutivity in euopium metal, J. Phys.: Conf. se [9] uoiniemi J, et al. Supeondutivity in lithium below.4 mk at ambient pessue. Natue 44774:87 7 [3] obet L. Spoull, Moden Physis, Mosow, Nauka, 9.4, p. 9, table [3] Wittig, J. Pessue-indued supeondutivity in esium and yttium, Phys. ev. Lett. 4, [3] Anne Maie J. Shaeffe et al. High pessue supeonduting phase diagam of 6Li: anomalous isotope effets in dense lithium, axiv: [33] V. D. Dymnikov, emi enegy of eletons in a thin metalli plate, Physis of the Solid State, Volume 53, Issue 5, pp 9-97 [34] Om Pakash et al, videne fo bulk supeondutivity in pue bismuth single ystals at ambient pessue, Siene 7 Jan 6;35563: [35] G. Cheng at al, leton Paiing without Supeondutivity, Natue 5, 96-99, 5 [36] J. Chang et al, Natue Physis, 8, [37] M. ujita et al, J. Phys. So. Jpn. 8, 7 [38]. eg et al, Phys. ev. Lett. 99, 73 7 [39] Yi, M et al, andwidth and leton Coelation-uned Supeondutivity in b.8 e Se -z S z, Physial eview Lettes, Volume 5, Issue 5, id
Extra Examples for Chapter 1
 Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
Exta Examples fo Chapte 1 Example 1: Conenti ylinde visomete is a devie used to measue the visosity of liquids. A liquid of unknown visosity is filling the small gap between two onenti ylindes, one is
Non-Ideal Gas Behavior P.V.T Relationships for Liquid and Solid:
 hemodynamis Non-Ideal Gas Behavio.. Relationships fo Liquid and Solid: An equation of state may be solved fo any one of the thee quantities, o as a funtion of the othe two. If is onsideed a funtion of
hemodynamis Non-Ideal Gas Behavio.. Relationships fo Liquid and Solid: An equation of state may be solved fo any one of the thee quantities, o as a funtion of the othe two. If is onsideed a funtion of
AVS fiziks. Institute for NET/JRF, GATE, IIT-JAM, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PHYSICAL SCIENCES
 ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOLUTIONS GATE- Q. An insulating sphee of adius a aies a hage density a os ; a. The leading ode tem fo the eleti field at a distane d, fa away fom the hage distibution, is popotional
From E.G. Haug Escape Velocity To the Golden Ratio at the Black Hole. Branko Zivlak, Novi Sad, May 2018
 Fom E.G. Haug Esape eloity To the Golden Ratio at the Blak Hole Banko Zivlak, bzivlak@gmail.om Novi Sad, May 018 Abstat Esape veloity fom the E.G. Haug has been heked. It is ompaed with obital veloity
Fom E.G. Haug Esape eloity To the Golden Ratio at the Blak Hole Banko Zivlak, bzivlak@gmail.om Novi Sad, May 018 Abstat Esape veloity fom the E.G. Haug has been heked. It is ompaed with obital veloity
Experiment 1 Electric field and electric potential
 Expeiment 1 Eleti field and eleti potential Pupose Map eleti equipotential lines and eleti field lines fo two-dimensional hage onfiguations. Equipment Thee sheets of ondutive papes with ondutive-ink eletodes,
Expeiment 1 Eleti field and eleti potential Pupose Map eleti equipotential lines and eleti field lines fo two-dimensional hage onfiguations. Equipment Thee sheets of ondutive papes with ondutive-ink eletodes,
Answers to Coursebook questions Chapter 2.11
 Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
Answes to Couseook questions Chapte 11 1 he net foe on the satellite is F = G Mm and this plays the ole of the entipetal foe on the satellite, ie mv mv Equating the two gives π Fo iula motion we have that
Physics 218, Spring March 2004
 Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
Today in Physis 8: eleti dipole adiation II The fa field Veto potential fo an osillating eleti dipole Radiated fields and intensity fo an osillating eleti dipole Total satteing oss setion of a dieleti
A Relativistic BCS Theory of S-Wave Superconductivity
 A Relativisti BCS Theoy of S-Wave Supeondutivity Damien BERTRAND Jan GOVAERTS John MENDY UC-FYNU / Supeondutivity Goup ouvain-la-neuve - June 4 Outline Ginzbug-andau fundamentals Oiginal theoy Covaiant
A Relativisti BCS Theoy of S-Wave Supeondutivity Damien BERTRAND Jan GOVAERTS John MENDY UC-FYNU / Supeondutivity Goup ouvain-la-neuve - June 4 Outline Ginzbug-andau fundamentals Oiginal theoy Covaiant
Reflectance spectra for Si
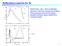 Refletane speta fo Si Notie R and ε i and ε show onsideable stutues in the fom of peas and shouldes. These stutues aise fom the optial tansitions between alene bands to the ondution bands. 16 Miosopi Theoy:
Refletane speta fo Si Notie R and ε i and ε show onsideable stutues in the fom of peas and shouldes. These stutues aise fom the optial tansitions between alene bands to the ondution bands. 16 Miosopi Theoy:
dp p v= = ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945).
 ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945). It is shown that at lage distanes fom the body, moving with a. veloity exeeding that of
ON SHOCK WAVES AT LARGE DISTANCES FROM THE PLACE OF THEIR ORIGIN By Lev D. Landau J. Phys. U.S.S.R. 9, 496 (1945). It is shown that at lage distanes fom the body, moving with a. veloity exeeding that of
Khmelnik S.I. Mathematical Model of Dust Whirl
 Khmelnik S.I. Mathematial Model of Dust Whil Abstat The question of the soue of enegy in a dust whil is onsideed. Atmosphei onditions annot be the sole soue of enegy, as suh dust whils exist on Mas, whee
Khmelnik S.I. Mathematial Model of Dust Whil Abstat The question of the soue of enegy in a dust whil is onsideed. Atmosphei onditions annot be the sole soue of enegy, as suh dust whils exist on Mas, whee
PROPAGATION OF PHOTON IN RESTING AND MOVING MEDIUM. J. Zaleśny. Institute of Physics, Technical University of Szczecin, A b s t r a c t
 PROPGTION OF PHOTON IN RESTING ND MOVING MEDIUM J Zaleśny Institute of Physis, Tehnial Univesity of Szzein, l 30 70 Piastów 48, Szzein, Poland b s t a t The popagation of photon in a dieleti may be desibed
PROPGTION OF PHOTON IN RESTING ND MOVING MEDIUM J Zaleśny Institute of Physis, Tehnial Univesity of Szzein, l 30 70 Piastów 48, Szzein, Poland b s t a t The popagation of photon in a dieleti may be desibed
not to be republished NCERT ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Chapter Eight MCQ I
 Chapte Eight ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES MCQ I 8 One equies ev of enegy to dissoiate a abon monoxide moleule into abon and oxygen atoms The minimum fequeny of the appopiate eletomagneti adiation to ahieve the
Chapte Eight ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES MCQ I 8 One equies ev of enegy to dissoiate a abon monoxide moleule into abon and oxygen atoms The minimum fequeny of the appopiate eletomagneti adiation to ahieve the
Chapter 4. Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals
 Chapte 4 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals 1 Intodution Disete-time signals most ommonly ou as epesentations of sampled ontinuous-time signals. Unde easonable onstaints, a ontinuous-time signal an be
Chapte 4 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals 1 Intodution Disete-time signals most ommonly ou as epesentations of sampled ontinuous-time signals. Unde easonable onstaints, a ontinuous-time signal an be
Red Shift and Blue Shift: A realistic approach
 Red Shift and Blue Shift: A ealisti appoah Benhad Rothenstein Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa, Physis Dept., Timisoaa, Romania E-mail: benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om Coina Nafonita Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa,
Red Shift and Blue Shift: A ealisti appoah Benhad Rothenstein Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa, Physis Dept., Timisoaa, Romania E-mail: benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om Coina Nafonita Politehnia Uniesity of Timisoaa,
In electrostatics, the electric field E and its sources (charges) are related by Gauss s law: Surface
 Ampee s law n eletostatis, the eleti field E and its soues (hages) ae elated by Gauss s law: EdA i 4πQenl Sufae Why useful? When symmety applies, E an be easily omputed Similaly, in magnetism the magneti
Ampee s law n eletostatis, the eleti field E and its soues (hages) ae elated by Gauss s law: EdA i 4πQenl Sufae Why useful? When symmety applies, E an be easily omputed Similaly, in magnetism the magneti
Suppose you have a bank account that earns interest at rate r, and you have made an initial deposit of X 0
 IOECONOMIC MODEL OF A FISHERY (ontinued) Dynami Maximum Eonomi Yield In ou deivation of maximum eonomi yield (MEY) we examined a system at equilibium and ou analysis made no distintion between pofits in
IOECONOMIC MODEL OF A FISHERY (ontinued) Dynami Maximum Eonomi Yield In ou deivation of maximum eonomi yield (MEY) we examined a system at equilibium and ou analysis made no distintion between pofits in
Photographing a time interval
 Potogaping a time inteval Benad Rotenstein and Ioan Damian Politennia Univesity of imisoaa Depatment of Pysis imisoaa Romania benad_otenstein@yaoo.om ijdamian@yaoo.om Abstat A metod of measuing time intevals
Potogaping a time inteval Benad Rotenstein and Ioan Damian Politennia Univesity of imisoaa Depatment of Pysis imisoaa Romania benad_otenstein@yaoo.om ijdamian@yaoo.om Abstat A metod of measuing time intevals
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation. One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation. One example is to onside aousti adiation
matschek (ccm2548) Ch17-h3 chiu (57890) 1
 matshek m2548) Ch17-h3 hiu 5789) 1 This pint-out should have 16 questions. Multiple-hoie questions may ontinue on the next olumn o page find all hoies efoe answeing. 1 1. points A student said, The eleti
matshek m2548) Ch17-h3 hiu 5789) 1 This pint-out should have 16 questions. Multiple-hoie questions may ontinue on the next olumn o page find all hoies efoe answeing. 1 1. points A student said, The eleti
Mass Transfer (Stoffaustausch)
 Mass Tansfe (Stoffaustaush) Examination 3. August 3 Name: Legi-N.: Edition Diffusion by E. L. Cussle: none nd 3 d Test Duation: minutes The following mateials ae not pemitted at you table and have to be
Mass Tansfe (Stoffaustaush) Examination 3. August 3 Name: Legi-N.: Edition Diffusion by E. L. Cussle: none nd 3 d Test Duation: minutes The following mateials ae not pemitted at you table and have to be
COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE
 COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE To see how the piniple behind the analysis of vaiane method woks, let us onside the following simple expeiment. The means ( 1 and ) of
COMPARING MORE THAN TWO POPULATION MEANS: AN ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE To see how the piniple behind the analysis of vaiane method woks, let us onside the following simple expeiment. The means ( 1 and ) of
(conservation of momentum)
 Dynamis of Binay Collisions Assumptions fo elasti ollisions: a) Eletially neutal moleules fo whih the foe between moleules depends only on the distane between thei entes. b) No intehange between tanslational
Dynamis of Binay Collisions Assumptions fo elasti ollisions: a) Eletially neutal moleules fo whih the foe between moleules depends only on the distane between thei entes. b) No intehange between tanslational
Review for the previous lecture
 Review fo the pevious letue Definition: sample spae, event, opeations (union, intesetion, omplementay), disjoint, paiwise disjoint Theoem: ommutatitivity, assoiativity, distibution law, DeMogan s law Pobability
Review fo the pevious letue Definition: sample spae, event, opeations (union, intesetion, omplementay), disjoint, paiwise disjoint Theoem: ommutatitivity, assoiativity, distibution law, DeMogan s law Pobability
THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON DROPWISE CONDENSATION IN PLATE HEAT EXCHANGERS
 Abstat THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON DROPWISE CONDENSATION IN PLATE HEAT EXCHANGERS V. Bendt, S. Zunft and H. Mülle-Steinhagen Geman Aeospae Cente (DLR), Stuttgat, Gemany This pape desibes the
Abstat THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON DROPWISE CONDENSATION IN PLATE HEAT EXCHANGERS V. Bendt, S. Zunft and H. Mülle-Steinhagen Geman Aeospae Cente (DLR), Stuttgat, Gemany This pape desibes the
PHYS 110B - HW #7 Fall 2005, Solutions by David Pace Equations referenced as Eq. # are from Griffiths Problem statements are paraphrased
 PHYS B - HW #7 Fall 5, Solutions by David Pae Equations efeened as Eq. # ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased [.] Poblem.4 fom Giffiths Show that Eq..4, V, t an be witten as Eq..44, V, t q t
PHYS B - HW #7 Fall 5, Solutions by David Pae Equations efeened as Eq. # ae fom Giffiths Poblem statements ae paaphased [.] Poblem.4 fom Giffiths Show that Eq..4, V, t an be witten as Eq..44, V, t q t
Eddy Currents and Magnetic Calibrations in LDX using a Copper Plasma. D.P. Boyle, PPPL M.E. Mauel, D.T. Garnier, Columbia J.
 Eddy Cuents and Magneti Calibations in LDX using a Coppe Plasma D.P. Boyle PPPL M.E. Mauel D.T. Ganie Columbia J. Kesne MIT PSFC Coppe Plasma Oveview LDX Magnetis Goals Calibate magneti diagnostis positions
Eddy Cuents and Magneti Calibations in LDX using a Coppe Plasma D.P. Boyle PPPL M.E. Mauel D.T. Ganie Columbia J. Kesne MIT PSFC Coppe Plasma Oveview LDX Magnetis Goals Calibate magneti diagnostis positions
Generalized Vapor Pressure Prediction Consistent with Cubic Equations of State
 Genealized Vapo Pessue Pedition Consistent with Cubi Equations of State Laua L. Petasky and Mihael J. Misovih, Hope College, Holland, MI Intodution Equations of state may be used to alulate pue omponent
Genealized Vapo Pessue Pedition Consistent with Cubi Equations of State Laua L. Petasky and Mihael J. Misovih, Hope College, Holland, MI Intodution Equations of state may be used to alulate pue omponent
Mass- and light-horizons, black holes' radii, the Schwartzschild metric and the Kerr metric
 006-010 Thiey De Mees Mass- and light-hoizons, blak holes' adii, the Shwatzshild meti and the Ke meti mpoved alulus. (using gavitomagnetism) T. De Mees - thieydm@pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes geneally ae
006-010 Thiey De Mees Mass- and light-hoizons, blak holes' adii, the Shwatzshild meti and the Ke meti mpoved alulus. (using gavitomagnetism) T. De Mees - thieydm@pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes geneally ae
Mass Transfer. Dispersion. Lecture 13, , Dr. K. Wegner
 Mass Tansfe Dispesion Letue 3, 3..7, D. K. Wegne Dispesion to dispese to spead widely. Dispesion is the at o poess of dispesing, of distibuting one substane (small volume fation) in anothe (lage volume
Mass Tansfe Dispesion Letue 3, 3..7, D. K. Wegne Dispesion to dispese to spead widely. Dispesion is the at o poess of dispesing, of distibuting one substane (small volume fation) in anothe (lage volume
The Research of AQI Index Changing Regularity Mainly in Tianjin Ziyu Guo
 nd Intenational Confeene on Eduation Tehnology, Management and Humanities Siene (ETMHS 06 The Reseah of AQI Index Changing Regulaity Mainly in Tianjin Ziyu Guo Shool of Institute of Eletial and Eletoni
nd Intenational Confeene on Eduation Tehnology, Management and Humanities Siene (ETMHS 06 The Reseah of AQI Index Changing Regulaity Mainly in Tianjin Ziyu Guo Shool of Institute of Eletial and Eletoni
2. Equation of generalized Dynamics. Let rectangular right hand coordinate triple is fixed in three-dimensional Euclidian space.
 Genealized Dynamis about Foes Ating on Chage Moving in Capaito and Solenoid. J.G. Klyushin, Ph. D. Aademy of Civil Aviation, hai of applied mathematis; e-mail: klyushin@shaping.og; mail: Intenational Club
Genealized Dynamis about Foes Ating on Chage Moving in Capaito and Solenoid. J.G. Klyushin, Ph. D. Aademy of Civil Aviation, hai of applied mathematis; e-mail: klyushin@shaping.og; mail: Intenational Club
Nuclear and Particle Physics - Lecture 20 The shell model
 1 Intoduction Nuclea and Paticle Physics - Lectue 0 The shell model It is appaent that the semi-empiical mass fomula does a good job of descibing tends but not the non-smooth behaviou of the binding enegy.
1 Intoduction Nuclea and Paticle Physics - Lectue 0 The shell model It is appaent that the semi-empiical mass fomula does a good job of descibing tends but not the non-smooth behaviou of the binding enegy.
11) A thin, uniform rod of mass M is supported by two vertical strings, as shown below.
 Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
Time Dilation in Gravity Wells
 Time Dilation in Gavity Wells By Rihad R. Shiffman Digital Gaphis Asso. 038 Dunkik Ave. L.A., Ca. 9005 s@isi.edu This doument disusses the geneal elativisti effet of time dilation aused by a spheially
Time Dilation in Gavity Wells By Rihad R. Shiffman Digital Gaphis Asso. 038 Dunkik Ave. L.A., Ca. 9005 s@isi.edu This doument disusses the geneal elativisti effet of time dilation aused by a spheially
Molecular Energy Changes During a Reaction
 Reation Kinetis Moleula Enegy Changes Duing a Reation Chemial Enegy of Speies E xn E* +BP E* P+B Moleules above this enegy level (defined somewhat abitaily) ae alled ativated omplexes Poduts Reatants Pogession
Reation Kinetis Moleula Enegy Changes Duing a Reation Chemial Enegy of Speies E xn E* +BP E* P+B Moleules above this enegy level (defined somewhat abitaily) ae alled ativated omplexes Poduts Reatants Pogession
arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018
![arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018 arxiv: v4 [physics.class-ph] 14 Jul 2018](/thumbs/90/103259092.jpg) Noname manusipt No. will be inseted by the edito Long-Range Longitudinal Eleti Wave in Vauum Radiated by Eleti Dipole: Pat I Altay Zhakatayev, Leila Tlebaldiyeva axiv:7.v4 [physis.lass-ph] 4 Jul 8 Reeived:
Noname manusipt No. will be inseted by the edito Long-Range Longitudinal Eleti Wave in Vauum Radiated by Eleti Dipole: Pat I Altay Zhakatayev, Leila Tlebaldiyeva axiv:7.v4 [physis.lass-ph] 4 Jul 8 Reeived:
IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD
 Pogess In Eletomagnetis Reseah, PIER 58, 101 114, 006 IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD G.
Pogess In Eletomagnetis Reseah, PIER 58, 101 114, 006 IMPLEMENTATION OF MUR S ABSORBING BOUNDARIES WITH PERIODIC STRUCTURES TO SPEED UP THE DESIGN PROCESS USING FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN METHOD G.
8.022 (E&M) Lecture 13. What we learned about magnetism so far
 8.0 (E&M) Letue 13 Topis: B s ole in Mawell s equations Veto potential Biot-Savat law and its appliations What we leaned about magnetism so fa Magneti Field B Epeiments: uents in s geneate foes on hages
8.0 (E&M) Letue 13 Topis: B s ole in Mawell s equations Veto potential Biot-Savat law and its appliations What we leaned about magnetism so fa Magneti Field B Epeiments: uents in s geneate foes on hages
4) Magnetic confinement of plasma
 4) Magneti onfineent of plasa Due to the shielding in the plasa, thee is alost no ontol with eleti fields. A ontol is possible with agneti fields, as patiles ae bound to the field lines. This is alled
4) Magneti onfineent of plasa Due to the shielding in the plasa, thee is alost no ontol with eleti fields. A ontol is possible with agneti fields, as patiles ae bound to the field lines. This is alled
OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM
 OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM M. Hiaki, K. Takamasu and S. Ozono Depatment of Peision Engineeing, The Univesity of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan Abstat: In this pape, we popose
OBSTACLE DETECTION USING RING BEAM SYSTEM M. Hiaki, K. Takamasu and S. Ozono Depatment of Peision Engineeing, The Univesity of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan Abstat: In this pape, we popose
Value Distribution of L-Functions with Rational Moving Targets
 Advanes in Pue Mathematis 3 3 79-73 Pulished Online Deeme 3 (http://wwwsipog/jounal/apm) http://dxdoiog/436/apm33998 Value Distiution of -Funtions wh ational Moving agets Matthew Cadwell Zhuan Ye * ntelligent
Advanes in Pue Mathematis 3 3 79-73 Pulished Online Deeme 3 (http://wwwsipog/jounal/apm) http://dxdoiog/436/apm33998 Value Distiution of -Funtions wh ational Moving agets Matthew Cadwell Zhuan Ye * ntelligent
An analytic calculation method on air gap flux in permanent magnet. brushless DC motor with ironless rotor
 Intenational Confeene on Enegy and Envionmental Potetion ICEEP 6 An analyti alulation method on ai gap flux in pemanent magnet bushless DC moto with ionless oto Xinghua Wang,Yaolong Sheng andshugang Zhao,,
Intenational Confeene on Enegy and Envionmental Potetion ICEEP 6 An analyti alulation method on ai gap flux in pemanent magnet bushless DC moto with ionless oto Xinghua Wang,Yaolong Sheng andshugang Zhao,,
Question 1: The dipole
 Septembe, 08 Conell Univesity, Depatment of Physics PHYS 337, Advance E&M, HW #, due: 9/5/08, :5 AM Question : The dipole Conside a system as discussed in class and shown in Fig.. in Heald & Maion.. Wite
Septembe, 08 Conell Univesity, Depatment of Physics PHYS 337, Advance E&M, HW #, due: 9/5/08, :5 AM Question : The dipole Conside a system as discussed in class and shown in Fig.. in Heald & Maion.. Wite
Classical Approach to the Theory of Elementary Particles
 Classial Appoah to the Theoy of Elementay Patiles By Yui N. Keilman Abstat: Pesented hee is an attempt to modify /extend lassial eletodynamis (CED) in ode to enable the lassial appoah (the appoah based
Classial Appoah to the Theoy of Elementay Patiles By Yui N. Keilman Abstat: Pesented hee is an attempt to modify /extend lassial eletodynamis (CED) in ode to enable the lassial appoah (the appoah based
? this lecture. ? next lecture. What we have learned so far. a Q E F = q E a. F = q v B a. a Q in motion B. db/dt E. de/dt B.
 PHY 249 Lectue Notes Chapte 32: Page 1 of 12 What we have leaned so fa a a F q a a in motion F q v a a d/ Ae thee othe "static" chages that can make -field? this lectue d/? next lectue da dl Cuve Cuve
PHY 249 Lectue Notes Chapte 32: Page 1 of 12 What we have leaned so fa a a F q a a in motion F q v a a d/ Ae thee othe "static" chages that can make -field? this lectue d/? next lectue da dl Cuve Cuve
Lecture 8 - Gauss s Law
 Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Lectue 8 - Gauss s Law A Puzzle... Example Calculate the potential enegy, pe ion, fo an infinite 1D ionic cystal with sepaation a; that is, a ow of equally spaced chages of magnitude e and altenating sign.
Partition Functions. Chris Clark July 18, 2006
 Patition Functions Chis Clak July 18, 2006 1 Intoduction Patition functions ae useful because it is easy to deive expectation values of paametes of the system fom them. Below is a list of the mao examples.
Patition Functions Chis Clak July 18, 2006 1 Intoduction Patition functions ae useful because it is easy to deive expectation values of paametes of the system fom them. Below is a list of the mao examples.
The electrified interface.
 Physial and Intefaial Eletohemisty 3 Exess negative Eletode + + + Solution + + Potential elmholtz Laye s Letue 5 Eletode/solution Intefae Exess positive x a..6 nm istane L The eletified intefae. The intefae
Physial and Intefaial Eletohemisty 3 Exess negative Eletode + + + Solution + + Potential elmholtz Laye s Letue 5 Eletode/solution Intefae Exess positive x a..6 nm istane L The eletified intefae. The intefae
Dissolution of Solid Particles in Liquids: A Shrinking Core Model
 Wold Aademy of Siene, Engineeing and Tehnology 5 9 Dissolution of Solid Patiles in Liquids: A Shining oe Model Wei-Lun Hsu, Mon-Jyh Lin, and Jyh-Ping Hsu Astat The dissolution of spheial patiles in liquids
Wold Aademy of Siene, Engineeing and Tehnology 5 9 Dissolution of Solid Patiles in Liquids: A Shining oe Model Wei-Lun Hsu, Mon-Jyh Lin, and Jyh-Ping Hsu Astat The dissolution of spheial patiles in liquids
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation
 1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation One example is to onside aousti adiation
1 Fundamental Solutions to the Wave Equation Physial insight in the sound geneation mehanism an be gained by onsideing simple analytial solutions to the wave equation One example is to onside aousti adiation
Diffraction from Crystals Shape Factor
 Letue 3 Diffation fom Cystals Shape Fato - Fultz & Howe, Chap. 5 - Williams & Cate, Chap. 7 - Reime, Chap. 7 Satteed wave: Shape Fato Cystal size effet k F k ep i k Shape fato: S k ep ik z Unit ell (/w
Letue 3 Diffation fom Cystals Shape Fato - Fultz & Howe, Chap. 5 - Williams & Cate, Chap. 7 - Reime, Chap. 7 Satteed wave: Shape Fato Cystal size effet k F k ep i k Shape fato: S k ep ik z Unit ell (/w
The Radii of Baryons
 Jounal Heading Yea; Vol. (No.): page ange DOI: 0.592/j.xxx.xxxxxxxx.xx The Radii of Bayons Maio Evealdo de Souza Depatmento de Físia, Univesidade Fedeal de Segipe, São Cistovão, 4900-000, Bazil Astat Consideing
Jounal Heading Yea; Vol. (No.): page ange DOI: 0.592/j.xxx.xxxxxxxx.xx The Radii of Bayons Maio Evealdo de Souza Depatmento de Físia, Univesidade Fedeal de Segipe, São Cistovão, 4900-000, Bazil Astat Consideing
F g. = G mm. m 1. = 7.0 kg m 2. = 5.5 kg r = 0.60 m G = N m 2 kg 2 = = N
 Chapte answes Heinemann Physics 4e Section. Woked example: Ty youself.. GRAVITATIONAL ATTRACTION BETWEEN SMALL OBJECTS Two bowling balls ae sitting next to each othe on a shelf so that the centes of the
Chapte answes Heinemann Physics 4e Section. Woked example: Ty youself.. GRAVITATIONAL ATTRACTION BETWEEN SMALL OBJECTS Two bowling balls ae sitting next to each othe on a shelf so that the centes of the
DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH 1. INTRODUCTION
 DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH Mugu B. RĂUŢ Coesponding autho: Mugu RĂUŢ, E-mail: m_b_aut@yahoo.om Abstat In this pape I popose a oetion to the well-known Newtonian gavitational
DARK MATTER AND THE DYNAMICS OF GALAXIES: A NEWTONIAN APPROACH Mugu B. RĂUŢ Coesponding autho: Mugu RĂUŢ, E-mail: m_b_aut@yahoo.om Abstat In this pape I popose a oetion to the well-known Newtonian gavitational
The Kerr-metric, mass- and light-horizons, and black holes' radii.
 006 Thiey De Mees The Ke-meti, mass- and light-hoizons, and blak holes' adii. (using the Analogue Maxwell theoy) T. De Mees - thieydm @ pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes an geneally be defined as stella objets
006 Thiey De Mees The Ke-meti, mass- and light-hoizons, and blak holes' adii. (using the Analogue Maxwell theoy) T. De Mees - thieydm @ pandoa.be Abstat Blak holes an geneally be defined as stella objets
Revised Newtonian Formula of Gravity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat Space-Time Transformed from Schwarzschild Solution
 Intenational Jounal of Astonomy and Astophysis,,, 6-8 http://dx.doi.og/.46/ijaa.. Published Online Mah (http://www.sip.og/jounal/ijaa) evised Newtonian Fomula of Gavity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat
Intenational Jounal of Astonomy and Astophysis,,, 6-8 http://dx.doi.og/.46/ijaa.. Published Online Mah (http://www.sip.og/jounal/ijaa) evised Newtonian Fomula of Gavity and Equation of Cosmology in Flat
Physics 505 Homework No. 9 Solutions S9-1
 Physics 505 Homewok No 9 s S9-1 1 As pomised, hee is the tick fo summing the matix elements fo the Stak effect fo the gound state of the hydogen atom Recall, we need to calculate the coection to the gound
Physics 505 Homewok No 9 s S9-1 1 As pomised, hee is the tick fo summing the matix elements fo the Stak effect fo the gound state of the hydogen atom Recall, we need to calculate the coection to the gound
Journal of Theoretics
 Jounal of Theoetis Volume 6-1, Feb-Mah 4 An Altenative Exlanation of the Cosmologial Redshift by the Tahyon Plasma Field in Integalati Sae Takaaki Musha musha@jda-tdi.go.j, musha@jg.ejnet.ne.j MRI, -11-7-61,
Jounal of Theoetis Volume 6-1, Feb-Mah 4 An Altenative Exlanation of the Cosmologial Redshift by the Tahyon Plasma Field in Integalati Sae Takaaki Musha musha@jda-tdi.go.j, musha@jg.ejnet.ne.j MRI, -11-7-61,
FI 2201 Electromagnetism
 FI 2201 Electomagnetism Alexande A. Iskanda, Ph.D. Physics of Magnetism and Photonics Reseach Goup Electodynamics ELETROMOTIVE FORE AND FARADAY S LAW 1 Ohm s Law To make a cuent flow, we have to push the
FI 2201 Electomagnetism Alexande A. Iskanda, Ph.D. Physics of Magnetism and Photonics Reseach Goup Electodynamics ELETROMOTIVE FORE AND FARADAY S LAW 1 Ohm s Law To make a cuent flow, we have to push the
Rydberg-Rydberg Interactions
 Rydbeg-Rydbeg Inteactions F. Robicheaux Aubun Univesity Rydbeg gas goes to plasma Dipole blockade Coheent pocesses in fozen Rydbeg gases (expts) Theoetical investigation of an excitation hopping though
Rydbeg-Rydbeg Inteactions F. Robicheaux Aubun Univesity Rydbeg gas goes to plasma Dipole blockade Coheent pocesses in fozen Rydbeg gases (expts) Theoetical investigation of an excitation hopping though
AN ELECTROMAGNETIC LAUNCH SYSTEM FOR UAVs
 Tehnial Sienes and Applied athematis AN ELECTROAGNETIC LAUNCH SYSTE FOR UAVs Lauian GHERAN Depatment of Eletonis and Infomatis, Faulty of Aeonautial anagement, Heni Coandă Ai Foe Aademy, Basov, Romania
Tehnial Sienes and Applied athematis AN ELECTROAGNETIC LAUNCH SYSTE FOR UAVs Lauian GHERAN Depatment of Eletonis and Infomatis, Faulty of Aeonautial anagement, Heni Coandă Ai Foe Aademy, Basov, Romania
Diffusion and Transport. 10. Friction and the Langevin Equation. Langevin Equation. f d. f ext. f () t f () t. Then Newton s second law is ma f f f t.
 Diffusion and Tanspot 10. Fiction and the Langevin Equation Now let s elate the phenomena of ownian motion and diffusion to the concept of fiction, i.e., the esistance to movement that the paticle in the
Diffusion and Tanspot 10. Fiction and the Langevin Equation Now let s elate the phenomena of ownian motion and diffusion to the concept of fiction, i.e., the esistance to movement that the paticle in the
3D Modelling of Temperature Dependent Power Distribution During Microwave Annealing of Doped c-si
 IOSR Jounal of Eletial and Eletonis Engineeing (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 9, Issue 1 Ve. V (Feb. 2014), PP 46-51 3D Modelling of Tempeatue Dependent Powe Distibution Duing
IOSR Jounal of Eletial and Eletonis Engineeing (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 9, Issue 1 Ve. V (Feb. 2014), PP 46-51 3D Modelling of Tempeatue Dependent Powe Distibution Duing
Electric Field, Potential Energy, & Voltage
 Slide 1 / 66 lectic Field, Potential negy, & oltage Wok Slide 2 / 66 Q+ Q+ The foce changes as chages move towads each othe since the foce depends on the distance between the chages. s these two chages
Slide 1 / 66 lectic Field, Potential negy, & oltage Wok Slide 2 / 66 Q+ Q+ The foce changes as chages move towads each othe since the foce depends on the distance between the chages. s these two chages
Determination of Local Structure in Disordered Systems by SAXS. Outline
 Detemination of Loal Stutue in Disodeed Systems by SAXS Andé ten Elshof MESA + Institute fo Nanotehnology Univesity of Twente Enshede the Nethelands Email: j.e.tenelshof@utwente.nl Outline. Intodution
Detemination of Loal Stutue in Disodeed Systems by SAXS Andé ten Elshof MESA + Institute fo Nanotehnology Univesity of Twente Enshede the Nethelands Email: j.e.tenelshof@utwente.nl Outline. Intodution
Special relativity with clock synchronization
 Speial elativity with lok synhonization Benhad Rothenstein ), Stefan Popesu ) and Geoge J. Spi 3) ) Politehnia Univesity of Timisoaa, Physis Depatment, Timisoaa, Romania, benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om ) Siemens
Speial elativity with lok synhonization Benhad Rothenstein ), Stefan Popesu ) and Geoge J. Spi 3) ) Politehnia Univesity of Timisoaa, Physis Depatment, Timisoaa, Romania, benhad_othenstein@yahoo.om ) Siemens
Physics 2B Chapter 22 Notes - Magnetic Field Spring 2018
 Physics B Chapte Notes - Magnetic Field Sping 018 Magnetic Field fom a Long Staight Cuent-Caying Wie In Chapte 11 we looked at Isaac Newton s Law of Gavitation, which established that a gavitational field
Physics B Chapte Notes - Magnetic Field Sping 018 Magnetic Field fom a Long Staight Cuent-Caying Wie In Chapte 11 we looked at Isaac Newton s Law of Gavitation, which established that a gavitational field
B. Spherical Wave Propagation
 11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
11/8/007 Spheical Wave Popagation notes 1/1 B. Spheical Wave Popagation Evey antenna launches a spheical wave, thus its powe density educes as a function of 1, whee is the distance fom the antenna. We
SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B. Calculations for Sample Cross-Section 2
 SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B Calulations fo Sample Coss-Setion. Use Input. Setion Popeties The popeties of Sample Coss-Setion ae shown in Figue and ae summaized below. Figue : Popeties of
SAMPLE LABORATORY SESSION FOR JAVA MODULE B Calulations fo Sample Coss-Setion. Use Input. Setion Popeties The popeties of Sample Coss-Setion ae shown in Figue and ae summaized below. Figue : Popeties of
Physics 11 Chapter 20: Electric Fields and Forces
 Physics Chapte 0: Electic Fields and Foces Yesteday is not ous to ecove, but tomoow is ous to win o lose. Lyndon B. Johnson When I am anxious it is because I am living in the futue. When I am depessed
Physics Chapte 0: Electic Fields and Foces Yesteday is not ous to ecove, but tomoow is ous to win o lose. Lyndon B. Johnson When I am anxious it is because I am living in the futue. When I am depessed
APPENDIX D COMPRESSIBILITY FACTOR EQUATIONS D.1 THE REDLICH KWONG EQUATION
 AENDIX D COMRESSIBILIY FACOR EQUAIONS D.1 HE REDLICH KWONG EQUAION he Redlih-Kwong equation is atually an equation of state. It was fomulated by Otto Redlih and Joseph N. S. Kwong in 1949 [Chemial Review
AENDIX D COMRESSIBILIY FACOR EQUAIONS D.1 HE REDLICH KWONG EQUAION he Redlih-Kwong equation is atually an equation of state. It was fomulated by Otto Redlih and Joseph N. S. Kwong in 1949 [Chemial Review
Vibrational Modes and Instabilities of a Dust Particle Pair in a Complex Plasma
 > REPLACE THIS LINE WITH YOUR PAPER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (DOUBLE-CLICK HERE TO EDIT) < Vibational Modes and Instabilities of a Dust Patile Pai in a Comple Plasma K. Qiao, L. S. Matthews, and T. W. Hyde,
> REPLACE THIS LINE WITH YOUR PAPER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (DOUBLE-CLICK HERE TO EDIT) < Vibational Modes and Instabilities of a Dust Patile Pai in a Comple Plasma K. Qiao, L. S. Matthews, and T. W. Hyde,
On a quantity that is analogous to potential and a theorem that relates to it
 Su une quantité analogue au potential et su un théoème y elatif C R Acad Sci 7 (87) 34-39 On a quantity that is analogous to potential and a theoem that elates to it By R CLAUSIUS Tanslated by D H Delphenich
Su une quantité analogue au potential et su un théoème y elatif C R Acad Sci 7 (87) 34-39 On a quantity that is analogous to potential and a theoem that elates to it By R CLAUSIUS Tanslated by D H Delphenich
The Planck Mass Particle Finally Discovered! The True God Particle! Good bye to the Point Particle Hypothesis!
 The Plank Mass Patile Finally Disoveed! The Tue God Patile! Good bye to the Point Patile Hypothesis! Espen Gaade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sienes Septembe, 06 Abstat In this pape we suggest that
The Plank Mass Patile Finally Disoveed! The Tue God Patile! Good bye to the Point Patile Hypothesis! Espen Gaade Haug Nowegian Univesity of Life Sienes Septembe, 06 Abstat In this pape we suggest that
Section 11. Timescales Radiation transport in stars
 Section 11 Timescales 11.1 Radiation tanspot in stas Deep inside stas the adiation eld is vey close to black body. Fo a black-body distibution the photon numbe density at tempeatue T is given by n = 2
Section 11 Timescales 11.1 Radiation tanspot in stas Deep inside stas the adiation eld is vey close to black body. Fo a black-body distibution the photon numbe density at tempeatue T is given by n = 2
Numerical Modeling in Biomedical Systems
 Numeial Modeling in Biomedial Systems BME 15:35 Letue 7 9/6/17 Nonlinea Systems Dunn Chapte 5 Nonlinea equations Root finding Baketing methods Open methods Gaphial Bisetion False Position Newton s method
Numeial Modeling in Biomedial Systems BME 15:35 Letue 7 9/6/17 Nonlinea Systems Dunn Chapte 5 Nonlinea equations Root finding Baketing methods Open methods Gaphial Bisetion False Position Newton s method
Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In Chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics, i.e., we descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity, and acceleation without any insights
Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In Chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics, i.e., we descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity, and acceleation without any insights
Voltage ( = Electric Potential )
 V-1 of 10 Voltage ( = lectic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage
V-1 of 10 Voltage ( = lectic Potential ) An electic chage altes the space aound it. Thoughout the space aound evey chage is a vecto thing called the electic field. Also filling the space aound evey chage
Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics i.e. descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity and acceleation without any insights as to
Chapte 5 Foce and Motion In chaptes 2 and 4 we have studied kinematics i.e. descibed the motion of objects using paametes such as the position vecto, velocity and acceleation without any insights as to
Photon, Charged Particle and Anti-charged Particle
 Adv. Studies Teo. Pys., Vol. 3, 9, no. 11, 41-419 Poton, Caged Patile and Anti-aged Patile Cen Sen nian Dept. of Pys., (National) Hua Qiao Univ. Quanzou, Fujian, P.. Cina ensennian@yaoo.om.n Abstat: Based
Adv. Studies Teo. Pys., Vol. 3, 9, no. 11, 41-419 Poton, Caged Patile and Anti-aged Patile Cen Sen nian Dept. of Pys., (National) Hua Qiao Univ. Quanzou, Fujian, P.. Cina ensennian@yaoo.om.n Abstat: Based
EM-2. 1 Coulomb s law, electric field, potential field, superposition q. Electric field of a point charge (1)
 EM- Coulomb s law, electic field, potential field, supeposition q ' Electic field of a point chage ( ') E( ) kq, whee k / 4 () ' Foce of q on a test chage e at position is ee( ) Electic potential O kq
EM- Coulomb s law, electic field, potential field, supeposition q ' Electic field of a point chage ( ') E( ) kq, whee k / 4 () ' Foce of q on a test chage e at position is ee( ) Electic potential O kq
Determine the Stress Calculating Mode of Sliding Failure of Soil Mass under the Push-Extend Multi-under-Reamed Pile
 Engineeing, 014, 6, 54-59 Published Online Apil 014 in SiRes. http://www.sip.og/jounal/eng http://dx.doi.og/10.436/eng.014.6509 Deteine the Stess Calulating Mode of Sliding Failue of Soil Mass unde the
Engineeing, 014, 6, 54-59 Published Online Apil 014 in SiRes. http://www.sip.og/jounal/eng http://dx.doi.og/10.436/eng.014.6509 Deteine the Stess Calulating Mode of Sliding Failue of Soil Mass unde the
The second law of thermodynamics - II.
 Januay 21, 2013 The second law of themodynamics - II. Asaf Pe e 1 1. The Schottky defect At absolute zeo tempeatue, the atoms of a solid ae odeed completely egulaly on a cystal lattice. As the tempeatue
Januay 21, 2013 The second law of themodynamics - II. Asaf Pe e 1 1. The Schottky defect At absolute zeo tempeatue, the atoms of a solid ae odeed completely egulaly on a cystal lattice. As the tempeatue
Germán Sierra Instituto de Física Teórica CSIC-UAM, Madrid, Spain
 Gemán Siea Instituto de Física Teóica CSIC-UAM, Madid, Spain Wo in pogess done in collaboation with J. Lins and S. Y. Zhao (Univ. Queensland, Austalia) and M. Ibañez (IFT, Madid) Taled pesented at the
Gemán Siea Instituto de Física Teóica CSIC-UAM, Madid, Spain Wo in pogess done in collaboation with J. Lins and S. Y. Zhao (Univ. Queensland, Austalia) and M. Ibañez (IFT, Madid) Taled pesented at the
13. Adiabatic Invariants and Action-Angle Variables Michael Fowler
 3 Adiabatic Invaiants and Action-Angle Vaiables Michael Fowle Adiabatic Invaiants Imagine a paticle in one dimension oscillating back and foth in some potential he potential doesn t have to be hamonic,
3 Adiabatic Invaiants and Action-Angle Vaiables Michael Fowle Adiabatic Invaiants Imagine a paticle in one dimension oscillating back and foth in some potential he potential doesn t have to be hamonic,
ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION. 1. Introduction. 1 r r. r k for every set E A, E \ {0},
 ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION E. J. IONASCU and A. A. STANCU Abstact. We ae inteested in constucting concete independent events in puely atomic pobability
ON INDEPENDENT SETS IN PURELY ATOMIC PROBABILITY SPACES WITH GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION E. J. IONASCU and A. A. STANCU Abstact. We ae inteested in constucting concete independent events in puely atomic pobability
ASTR415: Problem Set #6
 ASTR45: Poblem Set #6 Cuan D. Muhlbege Univesity of Mayland (Dated: May 7, 27) Using existing implementations of the leapfog and Runge-Kutta methods fo solving coupled odinay diffeential equations, seveal
ASTR45: Poblem Set #6 Cuan D. Muhlbege Univesity of Mayland (Dated: May 7, 27) Using existing implementations of the leapfog and Runge-Kutta methods fo solving coupled odinay diffeential equations, seveal
Investigation of Magnitude and Phase Errors in Waveguide Samples for the Nicolson-Ross-Weir Permittivity Technique
 Univesity of New Hampshie Univesity of New Hampshie Sholas' Repositoy Maste's Theses and Capstones Student Sholaship Winte 016 Investigation of Magnitude and Phase Eos in Waveguide Samples fo the Niolson-Ross-Wei
Univesity of New Hampshie Univesity of New Hampshie Sholas' Repositoy Maste's Theses and Capstones Student Sholaship Winte 016 Investigation of Magnitude and Phase Eos in Waveguide Samples fo the Niolson-Ross-Wei
763620SS STATISTICAL PHYSICS Solutions 2 Autumn 2012
 763620SS STATISTICAL PHYSICS Solutions 2 Autumn 2012 1. Continuous Random Walk Conside a continuous one-dimensional andom walk. Let w(s i ds i be the pobability that the length of the i th displacement
763620SS STATISTICAL PHYSICS Solutions 2 Autumn 2012 1. Continuous Random Walk Conside a continuous one-dimensional andom walk. Let w(s i ds i be the pobability that the length of the i th displacement
molecules ISSN
 Moleules 7, 1, 9-9 Full Pape moleules ISSN 1-9 http://www.mdpi.og Modeling of Aetylene Pyolysis unde Steel Vauum Cabuizing Conditions in a Tubula Flow Reato Rafi Ullah Khan *, Siegfied Bajoh, Fank Gaf
Moleules 7, 1, 9-9 Full Pape moleules ISSN 1-9 http://www.mdpi.og Modeling of Aetylene Pyolysis unde Steel Vauum Cabuizing Conditions in a Tubula Flow Reato Rafi Ullah Khan *, Siegfied Bajoh, Fank Gaf
Anisotropic 2-D Wavelet Packets and Rectangular Tiling: Theory and Algorithms
 Anisotopi -D Wavelet Pakets and Retangula Tiling: Theoy and Algoithms Dan Xu and Minh N. Do Depatment of Eletial and Compute Engineeing and Bekman Institute Univesity of Illinois at Ubana-Champaign Email:
Anisotopi -D Wavelet Pakets and Retangula Tiling: Theoy and Algoithms Dan Xu and Minh N. Do Depatment of Eletial and Compute Engineeing and Bekman Institute Univesity of Illinois at Ubana-Champaign Email:
Uniform Circular Motion
 Unifom Cicula Motion Intoduction Ealie we defined acceleation as being the change in velocity with time: a = v t Until now we have only talked about changes in the magnitude of the acceleation: the speeding
Unifom Cicula Motion Intoduction Ealie we defined acceleation as being the change in velocity with time: a = v t Until now we have only talked about changes in the magnitude of the acceleation: the speeding
Pulse Neutron Neutron (PNN) tool logging for porosity Some theoretical aspects
 Pulse Neuton Neuton (PNN) tool logging fo poosity Some theoetical aspects Intoduction Pehaps the most citicism of Pulse Neuton Neuon (PNN) logging methods has been chage that PNN is to sensitive to the
Pulse Neuton Neuton (PNN) tool logging fo poosity Some theoetical aspects Intoduction Pehaps the most citicism of Pulse Neuton Neuon (PNN) logging methods has been chage that PNN is to sensitive to the
Flux. Area Vector. Flux of Electric Field. Gauss s Law
 Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
Gauss s Law Flux Flux in Physics is used to two distinct ways. The fist meaning is the ate of flow, such as the amount of wate flowing in a ive, i.e. volume pe unit aea pe unit time. O, fo light, it is
On the indirect e ect in the Stokes±Helmert method of geoid determination
 Jounal of Geodesy (1999) 7: 87±9 On the indiet e et in the Stokes±Helmet method of geoid detemination L. E. SjoÈ beg, H. Nahavandhi oyal Institute of Tehnology, Depatment of Geodesy and Photogammety, S-100
Jounal of Geodesy (1999) 7: 87±9 On the indiet e et in the Stokes±Helmet method of geoid detemination L. E. SjoÈ beg, H. Nahavandhi oyal Institute of Tehnology, Depatment of Geodesy and Photogammety, S-100
Ion-sound waves (electrostatic low frequency waves)
 OTHER TYPES of WAVES Ion-sound waves (eletostati low fequeny waves) ae longitudinal waves simila lassial sound in gas s kt k M B plasma sound is slow fo eletons, but fast fo ions Eleton density is in eah
OTHER TYPES of WAVES Ion-sound waves (eletostati low fequeny waves) ae longitudinal waves simila lassial sound in gas s kt k M B plasma sound is slow fo eletons, but fast fo ions Eleton density is in eah
Electrostatics (Electric Charges and Field) #2 2010
 Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Electic Field: The concept of electic field explains the action at a distance foce between two chaged paticles. Evey chage poduces a field aound it so that any othe chaged paticle expeiences a foce when
Collision Frequency of Adsorbed Particles
 Bulg. J. Phys. 40 (2013) 214 218 Collision Fequency of Adsobed Paticles N.S. Peev Geogi Nadjakov Institute of Solid State Physics, Bulgaian Academy of Sciences, 72 Tzaigadsko Chaussee Blvd., 1784 Sofia,
Bulg. J. Phys. 40 (2013) 214 218 Collision Fequency of Adsobed Paticles N.S. Peev Geogi Nadjakov Institute of Solid State Physics, Bulgaian Academy of Sciences, 72 Tzaigadsko Chaussee Blvd., 1784 Sofia,
Thermodynamic derivations of conditions for chemical equilibrium and of Onsager reciprocal relations for chemical reactors
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 121, NUMBER 6 8 AUGUST 2004 Themodynami deivations of onditions fo hemial equilibium and of Onsage eipoal elations fo hemial eatos Gian Paolo Beetta a) Univesità di Besia,
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 121, NUMBER 6 8 AUGUST 2004 Themodynami deivations of onditions fo hemial equilibium and of Onsage eipoal elations fo hemial eatos Gian Paolo Beetta a) Univesità di Besia,
