USA Mathematical Talent Search Solutions to Problem 4/4/16
|
|
|
- Branden Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4/4/1. Find, with proof, all integers n such that there is a solution in nonnegative real numbers (x, y, z) to the system of equations 2x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = n and x + 4y + 5z = 2. Credit This problem was created by USAMTS Director Richard Rusczyk. Comments There are a variety of solutions to this problem. Zhou Fan and Nathan Pflueger present algebraic approaches. Lawrence Chan considers a geometric interpretation of the problem, and Richard McCutchen uses vectors. Solution 1 by: Zhou Fan (11/NJ) Let x = x 1, 4y = y 1, and 5z = z 1. Then x 1 + y 1 + z 1 = 2 and 2 9 x2 1 + can find bounds for n as follows: For the upper bound, we note: 1 y z2 1 = n. We n = 2 9 x y z (x2 1 + y z 2 1) 25 (x 1 + y 1 + z 1 ) 2 = We can obtain equality when (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) = (0, 0, 2). For the lower bound, we note that = 2, so we can let (x , y 1, z 1 ) = ( a, + b, + c) where a + b + c = 0. Then n = 2 9 x y z2 1 = 2 ( ) a + 1 ( ) b + ( ) c = 2 9 a a b b + 25 c c = 2 9 a b c
2 We can obtain equality when a, b, c = 0 and thus (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) = ( , , ). We note that the ranges of values of x 1, y 1, and z 1 are all continuous intervals since the original x, y, z can be any nonnegative real numbers. Thus, we can have a continuous change between (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) = ( 207, 184, 575) and (x , y 1, z 1 ) = (0, 0, 0), so n can take any real value between and. Thus, if n is restricted to the integers, then n can be any integer 25 between 8 and 12 inclusive. Solution 2 by: Nathan Pflueger (12/WA) We shall show that all integers n, 8 n 12, there exist nonnegative reals (x, y, z) such that 2x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = n and x + 4y + 5z = 2, and these are the only integers n with this characteristic. Define f(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + z 2, for any nonnegative reals x, y, z, satisfying x + 4y + 5z = 2. Note that f(x, y, z) = a carries both the implication that 2x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = a as well as x + 4y + 5z = 2, f only being defined on its given domain. LEMMA: If f(x 1, y 1, z 1 ) = a 1, and f(x 2, y 2, z 2 ) = a 2, then for all a between a 1 and a 2, there exist x, y, z such that f(x, y, z) = a. PROOF: Define the function g(t) = f(x 1 + (x 2 x 1 )t, y 1 + (y 2 y 1 )t, z 1 + (z 2 z 1 )t). The arguments given for f lie between the (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and (x 2, y 2, z 2 ), so they are nonnegative, and they satisfy x + 4y + 5z = 2, so g is defined for all t [0, 1]. g expands out to a polynomial function of t, so it is continuous. Since g(0) = a 1 and g(1) = a 2, for all a between a 1 and a 2 there is some t [0, 1] such that g(t) = a, and thus some (x, y, z) such that f(x, y, z) = a. By the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality, (x y 4 + z 5 ) 2 (2x 2 + y 2 + z 2 )( ) = f(x, y, z), so f(x, y, z) (x + 4y + 2 5z)2 = 22 the equality condition of Cauchy, we find that f( 9, 4, 115) = = 529. By applying By the trivial ineqality and the fact that < 2 <, f(x, y, z) = (x)2 + 1 (4y) (5z)2 15 ((x)2 +(4y) 2 +(5z) 2 ). Since x, y, z > 0 and due to the expansion of (a +b+c) 2, this is in turn less than or equal to (x + 4y z)2 = = 174. Thus we have 25 f(x, y, z) 174. The equality case is achievable; f(0, 0, 2) = Thus we have determined that f(x, y, z), and there exist x, y, z satisfying 25 both equality cases. Therefore, by the lemma, for any integer n [ 529, 174 ], there exist nonnegative reals (x, y, z) such that f(x, y, z) = n. = 7, and = 12 24, so all possible integer values of n are the integers from 8 to 12.
3 Solution by: Lawrence Chan (11/IL) There is an interesting geometric solution to this problem. We begin by noting that 2x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = n is an ellipsoid and x + 4y + 5z = 2 is a plane. If the ellipsoid becomes too small, it will not be able to touch the plane. If it becomes too big, its intersection with the plane will be outside the set of triples of positive reals. We will begin by finding the lower bound. Since we want to find the point where the ellipsoid just touches the plane, we want to find n such that the ellipsoid is tangent to the plane. To simplify things, we will rearrange variables and define new variables. We will define Our equation then becomes 2x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = n ( 2x) 2 + ( y) 2 + ( z) 2 = n u := 2x v := y w := z u 2 + v 2 + w 2 = n which is a sphere centered at (0,0,0) with radius n. We will also change the variables in the equation of the plane to get u + 4 v + 5 w = 2 2 If a plane is tangent to a sphere centered at the origin, the distance from the plane to the origin is equal to the radius of the sphere. Thus, n = 2 (0) + 4 (0) + 5 (0) 2 ( 2 ) 2 + ( 4 ) 2 + ( 5 ) 2 n = 22 n We want the the first n that works, so our lower bound is n = 8. To find the upper bound, we check the axes since those are the farthest reaching (in other words, we let x and
4 y equal 0 to find the upper bound by z, and we do this for each of the three variables). We want to find the largest n such that n = 2 checking z axis 5 n 12.9 n = 2 checking y axis 4 n n = 2 checking x axis 2 n The highest n that still works is 12, so our answer is as follows: n= {x : x Z and 8 x 12} Solution 4 by: Richard McCutchen (10/MD) A change of variables will make this problem a bit easier. Let x = u/ 2, y = v/, and z = w/ ; the new variables u, v, and w are nonnegative iff x, y, and z are. Our two equations become u 2 + v 2 + w 2 = n, (1) u + 4 v + 5 w = 2. (2) 2 Introduce a rectangular uvw coordinate system; we consider only the region where u, v, w 0 (henceforth the first octant). (1) asserts that the distance from (u, v, w) to the origin is n, while (2) asserts that (u, v, w) is on a plane (call it P) that does not depend on n. Thus, if we can determine at what distances the first-octant points on P lie from the origin, we ll know for which values of n the system is solvable. For convenience, let a = 2, 4, 5 and b = u, v, w. We can then rewrite (1) and (2) as b = n, (1 ) a b = 2. (2 )
5 It is also useful to know that a = : 2, 4, ( ) 5 2 ( ) 2 ( ) = = =. The first-octant point of P nearest the origin The Cauchy-Schwartz Inequality on vectors states that ( a b) a b, () where a and b are as above. I d like to use this to obtain a lower bound on the distance from points b on P from the origin; this distance is b. Since b is on P, we can substitute for the left side using (2 ), and we already know what a is: 2 b b 2/. (4) This is interesting. There is, in fact, a point of P in the first octant that lies at a distance of 2/ from the origin. It is b = (2/) a. This point lies on P because (2/) a a = (2/) a 2 = 2, and b = (2/) a = 2/. The first-octant point of P furthest from the origin What first-octant point of P is furthest from the origin? To find this out, I would like to prove a lemma. Lemma. Let A = A 1 A 2... A k be a polygon lying in -space, and let P be a point in - space. Of all the points on or inside A, the point furthest from P is one of the vertices A i. (If multiple points on or inside A tie for furthest, they are all vertices of A.) Proof. Let Q be any point of A other than a vertex; I will prove that there is a point of A further from P than Q. There must be a line segment UV lying on or inside A and having Q as its midpoint. (If Q is on a side of A, take a short segment along this side. Otherwise, any sufficiently short segment with midpoint Q and in the plane of A will do.) Let w = QV = UQ. Suppose w P Q 0. Then V is further from P than Q is, because P V 2 = P Q+ w 2 = ( P Q+ w) ( P Q+ w) = P Q 2 + w 2 +2P Q w > P Q 2 +2P Q w P Q 2. (The last inequality follows because w P Q 0.) If w P Q < 0, the proof is similar; U is further from P than Q is. Either way, we have proved the lemma.
6 It should be clear that the intersection of the fixed plane P with the first octant is a triangle (call it T ) with one vertex on each axis. Using (2), these vertices are ( 2 ) ( ) ( ) 2, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, A quick calculator approximation shows that (0, 0, 2 /5) is the furthest from the origin among these three. The lemma then says that (0, 0, 2 /5) is furthest from the origin among all points of T. Of course, the distance is 2 /5. Putting it together So, we know that, of the points of the triangle T, (2/) a ( a was the messy vector from a while ago) is the closest to the origin at a distance of 2, and (0, 0, 2 /5) is the furthest from the origin at a distance of 2 /5. Now, back to the system u 2 + v 2 + w 2 = n, (1) u + 4 v + 5 w = 2. (2) 2 (2) says that (u, v, w) is on or inside T. (1) says that (u, v, w) is at a distance n from the origin. Thus, the system is solvable for a given n iff T has a point n units from the origin. Thus, if n could be a real number, it could range from (2/ ) 2 = 529/ 7.78 to (2 /5) 2 = 174/25 = Since n must be an integer, the system is solvable for 8 n 12.
USA Mathematical Talent Search Round 4 Solutions Year 20 Academic Year
 1/4/20. Consider a sequence {a n } with a 1 = 2 and a n = a2 n 1 a n 2 for all n 3. If we know that a 2 and a 5 are positive integers and a 5 2009, then what are the possible values of a 5? Since a 1 and
1/4/20. Consider a sequence {a n } with a 1 = 2 and a n = a2 n 1 a n 2 for all n 3. If we know that a 2 and a 5 are positive integers and a 5 2009, then what are the possible values of a 5? Since a 1 and
1. Vectors and Matrices
 E. 8.02 Exercises. Vectors and Matrices A. Vectors Definition. A direction is just a unit vector. The direction of A is defined by dir A = A, (A 0); A it is the unit vector lying along A and pointed like
E. 8.02 Exercises. Vectors and Matrices A. Vectors Definition. A direction is just a unit vector. The direction of A is defined by dir A = A, (A 0); A it is the unit vector lying along A and pointed like
11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System
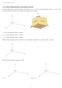 11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System In three dimensions, a point has three coordinates: (x,y,z). The normal orientation of the x, y, and z-axes is shown below. The three axes divide the region into
11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System In three dimensions, a point has three coordinates: (x,y,z). The normal orientation of the x, y, and z-axes is shown below. The three axes divide the region into
USA Mathematical Talent Search Solutions to Problem 5/3/16
 Solutions to Problem 5//16 5//16. Consider an isosceles triangle ABC with side lengths AB = AC = 10 2 and BC = 10. Construct semicircles P, Q, and R with diameters AB, AC, BC respectively, such that the
Solutions to Problem 5//16 5//16. Consider an isosceles triangle ABC with side lengths AB = AC = 10 2 and BC = 10. Construct semicircles P, Q, and R with diameters AB, AC, BC respectively, such that the
BMT 2018 Team Test Solutions March 18, 2018
 . A circle with radius is inscribed in a right triangle with hypotenuse 4 as shown below. What is the area of the triangle? Note that the diagram is not to scale. 4 Answer: 9 Solution : We wish to use
. A circle with radius is inscribed in a right triangle with hypotenuse 4 as shown below. What is the area of the triangle? Note that the diagram is not to scale. 4 Answer: 9 Solution : We wish to use
IYGB. Special Paper U. Time: 3 hours 30 minutes. Created by T. Madas. Created by T. Madas
 IYGB Special Paper U Time: 3 hours 30 minutes Candidates may NOT use any calculator Information for Candidates This practice paper follows the Advanced Level Mathematics Core Syllabus Booklets of Mathematical
IYGB Special Paper U Time: 3 hours 30 minutes Candidates may NOT use any calculator Information for Candidates This practice paper follows the Advanced Level Mathematics Core Syllabus Booklets of Mathematical
USA Mathematical Talent Search Round 1 Solutions Year 27 Academic Year
 1/1/27. Fill in the spaces of the grid to the right with positive integers so that in each 2 2 square with top left number a, top right number b, bottom left number c, and bottom right number d, either
1/1/27. Fill in the spaces of the grid to the right with positive integers so that in each 2 2 square with top left number a, top right number b, bottom left number c, and bottom right number d, either
The Lemniscate of Bernoulli, without Formulas
 The Lemniscate of ernoulli, without Formulas rseniy V. kopyan ariv:1003.3078v [math.h] 4 May 014 bstract In this paper, we give purely geometrical proofs of the well-known properties of the lemniscate
The Lemniscate of ernoulli, without Formulas rseniy V. kopyan ariv:1003.3078v [math.h] 4 May 014 bstract In this paper, we give purely geometrical proofs of the well-known properties of the lemniscate
Sums of Squares (FNS 195-S) Fall 2014
 Sums of Squares (FNS 195-S) Fall 014 Record of What We Did Drew Armstrong Vectors When we tried to apply Cartesian coordinates in 3 dimensions we ran into some difficulty tryiing to describe lines and
Sums of Squares (FNS 195-S) Fall 014 Record of What We Did Drew Armstrong Vectors When we tried to apply Cartesian coordinates in 3 dimensions we ran into some difficulty tryiing to describe lines and
Example 1: Finding angle measures: I ll do one: We ll do one together: You try one: ML and MN are tangent to circle O. Find the value of x
 Ch 1: Circles 1 1 Tangent Lines 1 Chords and Arcs 1 3 Inscribed Angles 1 4 Angle Measures and Segment Lengths 1 5 Circles in the coordinate plane 1 1 Tangent Lines Focused Learning Target: I will be able
Ch 1: Circles 1 1 Tangent Lines 1 Chords and Arcs 1 3 Inscribed Angles 1 4 Angle Measures and Segment Lengths 1 5 Circles in the coordinate plane 1 1 Tangent Lines Focused Learning Target: I will be able
CS 6820 Fall 2014 Lectures, October 3-20, 2014
 Analysis of Algorithms Linear Programming Notes CS 6820 Fall 2014 Lectures, October 3-20, 2014 1 Linear programming The linear programming (LP) problem is the following optimization problem. We are given
Analysis of Algorithms Linear Programming Notes CS 6820 Fall 2014 Lectures, October 3-20, 2014 1 Linear programming The linear programming (LP) problem is the following optimization problem. We are given
Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations.
 1. Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations. x + y = 5, z = 4 Choose the correct description. A. The circle with center (0,0, 4)
1. Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations. x + y = 5, z = 4 Choose the correct description. A. The circle with center (0,0, 4)
P1 Chapter 6 :: Circles
 P1 Chapter 6 :: Circles jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 11 th August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
P1 Chapter 6 :: Circles jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 11 th August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free at: www.drfrostmaths.com/homework
A2 HW Imaginary Numbers
 Name: A2 HW Imaginary Numbers Rewrite the following in terms of i and in simplest form: 1) 100 2) 289 3) 15 4) 4 81 5) 5 12 6) -8 72 Rewrite the following as a radical: 7) 12i 8) 20i Solve for x in simplest
Name: A2 HW Imaginary Numbers Rewrite the following in terms of i and in simplest form: 1) 100 2) 289 3) 15 4) 4 81 5) 5 12 6) -8 72 Rewrite the following as a radical: 7) 12i 8) 20i Solve for x in simplest
Integration. Tuesday, December 3, 13
 4 Integration 4.3 Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals Objectives n Understand the definition of a Riemann sum. n Evaluate a definite integral using properties of definite integrals. 3 Riemann Sums 4 Riemann
4 Integration 4.3 Riemann Sums and Definite Integrals Objectives n Understand the definition of a Riemann sum. n Evaluate a definite integral using properties of definite integrals. 3 Riemann Sums 4 Riemann
POINTS, LINES, DISTANCES
 POINTS, LINES, DISTANCES NIKOS APOSTOLAKIS Examples/Exercises: (1) Find the equation of the line that passes through (4, 5), (4, ) () Find the equation of the line that passes through the points (1, ),
POINTS, LINES, DISTANCES NIKOS APOSTOLAKIS Examples/Exercises: (1) Find the equation of the line that passes through (4, 5), (4, ) () Find the equation of the line that passes through the points (1, ),
Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 2007
 Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 007 Questions will be set on the following and related topics. Algebra: Sets, operations on sets. Prime numbers, factorisation of integers
Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 007 Questions will be set on the following and related topics. Algebra: Sets, operations on sets. Prime numbers, factorisation of integers
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
EGMO 2016, Day 1 Solutions. Problem 1. Let n be an odd positive integer, and let x1, x2,..., xn be non-negative real numbers.
 EGMO 2016, Day 1 Solutions Problem 1. Let n be an odd positive integer, and let x1, x2,..., xn be non-negative real numbers. Show that min (x2i + x2i+1 ) max (2xj xj+1 ), j=1,...,n i=1,...,n where xn+1
EGMO 2016, Day 1 Solutions Problem 1. Let n be an odd positive integer, and let x1, x2,..., xn be non-negative real numbers. Show that min (x2i + x2i+1 ) max (2xj xj+1 ), j=1,...,n i=1,...,n where xn+1
Lines, parabolas, distances and inequalities an enrichment class
 Lines, parabolas, distances and inequalities an enrichment class Finbarr Holland 1. Lines in the plane A line is a particular kind of subset of the plane R 2 = R R, and can be described as the set of ordered
Lines, parabolas, distances and inequalities an enrichment class Finbarr Holland 1. Lines in the plane A line is a particular kind of subset of the plane R 2 = R R, and can be described as the set of ordered
Supplementary File: Proof of Proposition 1
 Supplementary File: Proof of Proposition 1 Tong Tong Wu and Kenneth Lange The expected loss E ( Y f(x) ɛ ) can be written as [ ] E [E ( Y f(x) ɛ X)] = E p (X) v f(x) ɛ X, where p (x) = Pr(Y = v X = x).
Supplementary File: Proof of Proposition 1 Tong Tong Wu and Kenneth Lange The expected loss E ( Y f(x) ɛ ) can be written as [ ] E [E ( Y f(x) ɛ X)] = E p (X) v f(x) ɛ X, where p (x) = Pr(Y = v X = x).
UNDERSTANDING RULER AND COMPASS CONSTRUCTIONS WITH FIELD THEORY
 UNDERSTANDING RULER AND COMPASS CONSTRUCTIONS WITH FIELD THEORY ISAAC M. DAVIS Abstract. By associating a subfield of R to a set of points P 0 R 2, geometric properties of ruler and compass constructions
UNDERSTANDING RULER AND COMPASS CONSTRUCTIONS WITH FIELD THEORY ISAAC M. DAVIS Abstract. By associating a subfield of R to a set of points P 0 R 2, geometric properties of ruler and compass constructions
Circle Chains Inside a Circular Segment
 Forum eometricorum Volume 9 (009) 73 79. FRUM EM ISSN 534-78 ircle hains Inside a ircular Segment iovanni Lucca bstract. We consider a generic circles chain that can be drawn inside a circular segment
Forum eometricorum Volume 9 (009) 73 79. FRUM EM ISSN 534-78 ircle hains Inside a ircular Segment iovanni Lucca bstract. We consider a generic circles chain that can be drawn inside a circular segment
UNIT 3 CIRCLES AND VOLUME Lesson 1: Introducing Circles Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: performing operations with fractions understanding slope, both algebraically and graphically understanding the relationship of
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: performing operations with fractions understanding slope, both algebraically and graphically understanding the relationship of
a. Define a function called an inner product on pairs of points x = (x 1, x 2,..., x n ) and y = (y 1, y 2,..., y n ) in R n by
 Real Analysis Homework 1 Solutions 1. Show that R n with the usual euclidean distance is a metric space. Items a-c will guide you through the proof. a. Define a function called an inner product on pairs
Real Analysis Homework 1 Solutions 1. Show that R n with the usual euclidean distance is a metric space. Items a-c will guide you through the proof. a. Define a function called an inner product on pairs
Correlation of 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Algebra I and Geometry to Moving with Math SUMS Moving with Math SUMS Algebra 1
 Correlation of 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Algebra I and Geometry to Moving with Math SUMS Moving with Math SUMS Algebra 1 ALGEBRA I A.1 Mathematical process standards. The student
Correlation of 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Algebra I and Geometry to Moving with Math SUMS Moving with Math SUMS Algebra 1 ALGEBRA I A.1 Mathematical process standards. The student
Complex numbers, the exponential function, and factorization over C
 Complex numbers, the exponential function, and factorization over C 1 Complex Numbers Recall that for every non-zero real number x, its square x 2 = x x is always positive. Consequently, R does not contain
Complex numbers, the exponential function, and factorization over C 1 Complex Numbers Recall that for every non-zero real number x, its square x 2 = x x is always positive. Consequently, R does not contain
Mathematics (MEI) Advanced Subsidiary GCE Core 1 (4751) May 2010
 Link to past paper on OCR website: http://www.mei.org.uk/files/papers/c110ju_ergh.pdf These solutions are for your personal use only. DO NOT photocopy or pass on to third parties. If you are a school or
Link to past paper on OCR website: http://www.mei.org.uk/files/papers/c110ju_ergh.pdf These solutions are for your personal use only. DO NOT photocopy or pass on to third parties. If you are a school or
TWO THEOREMS ON THE FOCUS-SHARING ELLIPSES: A THREE-DIMENSIONAL VIEW
 TWO THEOREMS ON THE FOCUS-SHARING ELLIPSES: A THREE-DIMENSIONAL VIEW ILYA I. BOGDANOV Abstract. Consider three ellipses each two of which share a common focus. The radical axes of the pairs of these ellipses
TWO THEOREMS ON THE FOCUS-SHARING ELLIPSES: A THREE-DIMENSIONAL VIEW ILYA I. BOGDANOV Abstract. Consider three ellipses each two of which share a common focus. The radical axes of the pairs of these ellipses
Solutions to the February problems.
 Solutions to the February problems. 348. (b) Suppose that f(x) is a real-valued function defined for real values of x. Suppose that both f(x) 3x and f(x) x 3 are increasing functions. Must f(x) x x also
Solutions to the February problems. 348. (b) Suppose that f(x) is a real-valued function defined for real values of x. Suppose that both f(x) 3x and f(x) x 3 are increasing functions. Must f(x) x x also
= 1 2x. x 2 a ) 0 (mod p n ), (x 2 + 2a + a2. x a ) 2
 8. p-adic numbers 8.1. Motivation: Solving x 2 a (mod p n ). Take an odd prime p, and ( an) integer a coprime to p. Then, as we know, x 2 a (mod p) has a solution x Z iff = 1. In this case we can suppose
8. p-adic numbers 8.1. Motivation: Solving x 2 a (mod p n ). Take an odd prime p, and ( an) integer a coprime to p. Then, as we know, x 2 a (mod p) has a solution x Z iff = 1. In this case we can suppose
1 Take-home exam and final exam study guide
 Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Fall 2013 1 Take-home exam and final exam study guide 1.1 Problems The following are some problems, some of which will appear on the final exam. 1.1.1 Number
Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Fall 2013 1 Take-home exam and final exam study guide 1.1 Problems The following are some problems, some of which will appear on the final exam. 1.1.1 Number
MAT1035 Analytic Geometry
 MAT1035 Analytic Geometry Lecture Notes R.A. Sabri Kaan Gürbüzer Dokuz Eylül University 2016 2 Contents 1 Review of Trigonometry 5 2 Polar Coordinates 7 3 Vectors in R n 9 3.1 Located Vectors..............................................
MAT1035 Analytic Geometry Lecture Notes R.A. Sabri Kaan Gürbüzer Dokuz Eylül University 2016 2 Contents 1 Review of Trigonometry 5 2 Polar Coordinates 7 3 Vectors in R n 9 3.1 Located Vectors..............................................
y 2 . = x 1y 1 + x 2 y x + + x n y n 2 7 = 1(2) + 3(7) 5(4) = 3. x x = x x x2 n.
 6.. Length, Angle, and Orthogonality In this section, we discuss the defintion of length and angle for vectors and define what it means for two vectors to be orthogonal. Then, we see that linear systems
6.. Length, Angle, and Orthogonality In this section, we discuss the defintion of length and angle for vectors and define what it means for two vectors to be orthogonal. Then, we see that linear systems
SOLUTIONS TO ADDITIONAL EXERCISES FOR II.1 AND II.2
 SOLUTIONS TO ADDITIONAL EXERCISES FOR II.1 AND II.2 Here are the solutions to the additional exercises in betsepexercises.pdf. B1. Let y and z be distinct points of L; we claim that x, y and z are not
SOLUTIONS TO ADDITIONAL EXERCISES FOR II.1 AND II.2 Here are the solutions to the additional exercises in betsepexercises.pdf. B1. Let y and z be distinct points of L; we claim that x, y and z are not
CHAPTER 2: CONVEX SETS AND CONCAVE FUNCTIONS. W. Erwin Diewert January 31, 2008.
 1 ECONOMICS 594: LECTURE NOTES CHAPTER 2: CONVEX SETS AND CONCAVE FUNCTIONS W. Erwin Diewert January 31, 2008. 1. Introduction Many economic problems have the following structure: (i) a linear function
1 ECONOMICS 594: LECTURE NOTES CHAPTER 2: CONVEX SETS AND CONCAVE FUNCTIONS W. Erwin Diewert January 31, 2008. 1. Introduction Many economic problems have the following structure: (i) a linear function
The Graphs of Polynomial Functions
 Section 4.3 The Graphs of Polynomial Functions Objective 1: Understanding the Definition of a Polynomial Function Definition Polynomial Function n n 1 n 2 The function f() x = anx + an 1x + an 2x + L +
Section 4.3 The Graphs of Polynomial Functions Objective 1: Understanding the Definition of a Polynomial Function Definition Polynomial Function n n 1 n 2 The function f() x = anx + an 1x + an 2x + L +
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS
 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AS level Mathematics Core mathematics 1 C1 2015-2016 Name: Page C1 workbook contents Indices and Surds Simultaneous equations Quadratics Inequalities Graphs Arithmetic series
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AS level Mathematics Core mathematics 1 C1 2015-2016 Name: Page C1 workbook contents Indices and Surds Simultaneous equations Quadratics Inequalities Graphs Arithmetic series
Test Corrections for Unit 1 Test
 MUST READ DIRECTIONS: Read the directions located on www.koltymath.weebly.com to understand how to properly do test corrections. Ask for clarification from your teacher if there are parts that you are
MUST READ DIRECTIONS: Read the directions located on www.koltymath.weebly.com to understand how to properly do test corrections. Ask for clarification from your teacher if there are parts that you are
For all questions, answer choice E. NOTA" means none of the above answers is correct.
 For all questions, answer choice " means none of the above answers is correct. 1. The sum of the integers 1 through n can be modeled by a quadratic polynomial. What is the product of the non-zero coefficients
For all questions, answer choice " means none of the above answers is correct. 1. The sum of the integers 1 through n can be modeled by a quadratic polynomial. What is the product of the non-zero coefficients
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1
 OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1 (37) If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? Solution: Complete
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1 (37) If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? Solution: Complete
Scope and Sequence: National Curriculum Mathematics from Haese Mathematics (7 10A)
 Scope and Sequence: National Curriculum Mathematics from Haese Mathematics (7 10A) Updated 06/05/16 http://www.haesemathematics.com.au/ Note: Exercises in red text indicate material in the 10A textbook
Scope and Sequence: National Curriculum Mathematics from Haese Mathematics (7 10A) Updated 06/05/16 http://www.haesemathematics.com.au/ Note: Exercises in red text indicate material in the 10A textbook
Vector Calculus. Lecture Notes
 Vector Calculus Lecture Notes Adolfo J. Rumbos c Draft date November 23, 211 2 Contents 1 Motivation for the course 5 2 Euclidean Space 7 2.1 Definition of n Dimensional Euclidean Space........... 7 2.2
Vector Calculus Lecture Notes Adolfo J. Rumbos c Draft date November 23, 211 2 Contents 1 Motivation for the course 5 2 Euclidean Space 7 2.1 Definition of n Dimensional Euclidean Space........... 7 2.2
Notes on Complex Analysis
 Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
Michael Papadimitrakis Notes on Complex Analysis Department of Mathematics University of Crete Contents The complex plane.. The complex plane...................................2 Argument and polar representation.........................
Copyright 2018 UC Regents and ALEKS Corporation. ALEKS is a registered trademark of ALEKS Corporation. 2/10
 Prep for Calculus This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (281 topics + 125 additional topics) Real
Prep for Calculus This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (281 topics + 125 additional topics) Real
Detailed objectives are given in each of the sections listed below. 1. Cartesian Space Coordinates. 2. Displacements, Forces, Velocities and Vectors
 Unit 1 Vectors In this unit, we introduce vectors, vector operations, and equations of lines and planes. Note: Unit 1 is based on Chapter 12 of the textbook, Salas and Hille s Calculus: Several Variables,
Unit 1 Vectors In this unit, we introduce vectors, vector operations, and equations of lines and planes. Note: Unit 1 is based on Chapter 12 of the textbook, Salas and Hille s Calculus: Several Variables,
Solutions 2017 AB Exam
 1. Solve for x : x 2 = 4 x. Solutions 2017 AB Exam Texas A&M High School Math Contest October 21, 2017 ANSWER: x = 3 Solution: x 2 = 4 x x 2 = 16 8x + x 2 x 2 9x + 18 = 0 (x 6)(x 3) = 0 x = 6, 3 but x
1. Solve for x : x 2 = 4 x. Solutions 2017 AB Exam Texas A&M High School Math Contest October 21, 2017 ANSWER: x = 3 Solution: x 2 = 4 x x 2 = 16 8x + x 2 x 2 9x + 18 = 0 (x 6)(x 3) = 0 x = 6, 3 but x
Jim Lambers MAT 610 Summer Session Lecture 2 Notes
 Jim Lambers MAT 610 Summer Session 2009-10 Lecture 2 Notes These notes correspond to Sections 2.2-2.4 in the text. Vector Norms Given vectors x and y of length one, which are simply scalars x and y, the
Jim Lambers MAT 610 Summer Session 2009-10 Lecture 2 Notes These notes correspond to Sections 2.2-2.4 in the text. Vector Norms Given vectors x and y of length one, which are simply scalars x and y, the
Projection Theorem 1
 Projection Theorem 1 Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality Lemma. (Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality) For all x, y in an inner product space, [ xy, ] x y. Equality holds if and only if x y or y θ. Proof. If y θ, the inequality
Projection Theorem 1 Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality Lemma. (Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality) For all x, y in an inner product space, [ xy, ] x y. Equality holds if and only if x y or y θ. Proof. If y θ, the inequality
HMMT November 2013 Saturday 9 November 2013
 . [5] Evaluate + 5 + 8 + + 0. 75 There are 0 HMMT November 0 Saturday 9 November 0 Guts Round = 4 terms with average +0, so their sum is 7 0 = 75.. [5] Two fair six-sided dice are rolled. What is the probability
. [5] Evaluate + 5 + 8 + + 0. 75 There are 0 HMMT November 0 Saturday 9 November 0 Guts Round = 4 terms with average +0, so their sum is 7 0 = 75.. [5] Two fair six-sided dice are rolled. What is the probability
UNC Charlotte Super Competition - Comprehensive test March 2, 2015
 March 2, 2015 1. triangle is inscribed in a semi-circle of radius r as shown in the figure: θ The area of the triangle is () r 2 sin 2θ () πr 2 sin θ () r sin θ cos θ () πr 2 /4 (E) πr 2 /2 2. triangle
March 2, 2015 1. triangle is inscribed in a semi-circle of radius r as shown in the figure: θ The area of the triangle is () r 2 sin 2θ () πr 2 sin θ () r sin θ cos θ () πr 2 /4 (E) πr 2 /2 2. triangle
27th Russian Mathematics Olympiad
 27th Russian Mathematics Olympiad 10 April 2001 (Communicated by Fedor Petrov) 9 FORM 1. The integers from 1 to 999999 are partioned into two groups: those integers for which the nearest perfect square
27th Russian Mathematics Olympiad 10 April 2001 (Communicated by Fedor Petrov) 9 FORM 1. The integers from 1 to 999999 are partioned into two groups: those integers for which the nearest perfect square
3. Vector spaces 3.1 Linear dependence and independence 3.2 Basis and dimension. 5. Extreme points and basic feasible solutions
 A. LINEAR ALGEBRA. CONVEX SETS 1. Matrices and vectors 1.1 Matrix operations 1.2 The rank of a matrix 2. Systems of linear equations 2.1 Basic solutions 3. Vector spaces 3.1 Linear dependence and independence
A. LINEAR ALGEBRA. CONVEX SETS 1. Matrices and vectors 1.1 Matrix operations 1.2 The rank of a matrix 2. Systems of linear equations 2.1 Basic solutions 3. Vector spaces 3.1 Linear dependence and independence
Solution to Homework 1
 Solution to Homework 1 Olena Bormashenko September, 0 Section 1.1:, 5b)d), 7b)f), 8a)b), ; Section 1.:, 5, 7, 9, 10, b)c), 1, 15b), 3 Section 1.1. In each of the following cases, find a point that is two-thirds
Solution to Homework 1 Olena Bormashenko September, 0 Section 1.1:, 5b)d), 7b)f), 8a)b), ; Section 1.:, 5, 7, 9, 10, b)c), 1, 15b), 3 Section 1.1. In each of the following cases, find a point that is two-thirds
Definitions and Properties of R N
 Definitions and Properties of R N R N as a set As a set R n is simply the set of all ordered n-tuples (x 1,, x N ), called vectors. We usually denote the vector (x 1,, x N ), (y 1,, y N ), by x, y, or
Definitions and Properties of R N R N as a set As a set R n is simply the set of all ordered n-tuples (x 1,, x N ), called vectors. We usually denote the vector (x 1,, x N ), (y 1,, y N ), by x, y, or
Linear Algebra. Alvin Lin. August December 2017
 Linear Algebra Alvin Lin August 207 - December 207 Linear Algebra The study of linear algebra is about two basic things. We study vector spaces and structure preserving maps between vector spaces. A vector
Linear Algebra Alvin Lin August 207 - December 207 Linear Algebra The study of linear algebra is about two basic things. We study vector spaces and structure preserving maps between vector spaces. A vector
1 The Real Number System
 1 The Real Number System The rational numbers are beautiful, but are not big enough for various purposes, and the set R of real numbers was constructed in the late nineteenth century, as a kind of an envelope
1 The Real Number System The rational numbers are beautiful, but are not big enough for various purposes, and the set R of real numbers was constructed in the late nineteenth century, as a kind of an envelope
Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review
 Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review c Trinity College 1 A note to the students from the lecturer: This course will be moving rather quickly, and it will be in your own best interests to
Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review c Trinity College 1 A note to the students from the lecturer: This course will be moving rather quickly, and it will be in your own best interests to
RPS SECONDARY MATH CURRICULUM. Unit 4 - Polynomials
 Unit 4 - Polynomials 4 weeks Overview: By introducing the basic concept of complex number, the form of complex numbers and basic operations with complex numbers, Unit 4 starts to lay the foundation for
Unit 4 - Polynomials 4 weeks Overview: By introducing the basic concept of complex number, the form of complex numbers and basic operations with complex numbers, Unit 4 starts to lay the foundation for
Tennessee s State Mathematics Standards Precalculus
 Tennessee s State Mathematics Standards Precalculus Domain Cluster Standard Number Expressions (N-NE) Represent, interpret, compare, and simplify number expressions 1. Use the laws of exponents and logarithms
Tennessee s State Mathematics Standards Precalculus Domain Cluster Standard Number Expressions (N-NE) Represent, interpret, compare, and simplify number expressions 1. Use the laws of exponents and logarithms
Math Review for AP Calculus
 Math Review for AP Calculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Math Review for AP Calculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Math Prep for Statics
 Math Prep for Statics This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
Math Prep for Statics This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
UNCC 2001 Algebra II
 UNCC 2001 Algebra II March 5, 2001 1. Compute the sum of the roots of x 2 5x + 6 = 0. (A) 3 (B) 7/2 (C) 4 (D) 9/2 (E) 5 (E) The sum of the roots of the quadratic ax 2 + bx + c = 0 is b/a which, for this
UNCC 2001 Algebra II March 5, 2001 1. Compute the sum of the roots of x 2 5x + 6 = 0. (A) 3 (B) 7/2 (C) 4 (D) 9/2 (E) 5 (E) The sum of the roots of the quadratic ax 2 + bx + c = 0 is b/a which, for this
Optimization and Optimal Control in Banach Spaces
 Optimization and Optimal Control in Banach Spaces Bernhard Schmitzer October 19, 2017 1 Convex non-smooth optimization with proximal operators Remark 1.1 (Motivation). Convex optimization: easier to solve,
Optimization and Optimal Control in Banach Spaces Bernhard Schmitzer October 19, 2017 1 Convex non-smooth optimization with proximal operators Remark 1.1 (Motivation). Convex optimization: easier to solve,
MATH 117 LECTURE NOTES
 MATH 117 LECTURE NOTES XIN ZHOU Abstract. This is the set of lecture notes for Math 117 during Fall quarter of 2017 at UC Santa Barbara. The lectures follow closely the textbook [1]. Contents 1. The set
MATH 117 LECTURE NOTES XIN ZHOU Abstract. This is the set of lecture notes for Math 117 during Fall quarter of 2017 at UC Santa Barbara. The lectures follow closely the textbook [1]. Contents 1. The set
Vectors, dot product, and cross product
 MTH 201 Multivariable calculus and differential equations Practice problems Vectors, dot product, and cross product 1. Find the component form and length of vector P Q with the following initial point
MTH 201 Multivariable calculus and differential equations Practice problems Vectors, dot product, and cross product 1. Find the component form and length of vector P Q with the following initial point
Mathematics (MEI) Advanced Subsidiary GCE Core 1 (4751) June 2010
 Link to past paper on OCR website: www.ocr.org.uk The above link takes you to OCR s website. From there you click QUALIFICATIONS, QUALIFICATIONS BY TYPE, AS/A LEVEL GCE, MATHEMATICS (MEI), VIEW ALL DOCUMENTS,
Link to past paper on OCR website: www.ocr.org.uk The above link takes you to OCR s website. From there you click QUALIFICATIONS, QUALIFICATIONS BY TYPE, AS/A LEVEL GCE, MATHEMATICS (MEI), VIEW ALL DOCUMENTS,
2010 Fermat Contest (Grade 11)
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 010 Fermat Contest (Grade 11) Thursday, February 5, 010
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 010 Fermat Contest (Grade 11) Thursday, February 5, 010
RPS SECONDARY MATH CURRICULUM. Unit 5 - Polynomials
 Unit 5 - Polynomials 4 weeks Overview: By introducing the basic concept of complex number, the form of complex numbers and basic operations with complex numbers, Unit 5 starts to lay the foundation for
Unit 5 - Polynomials 4 weeks Overview: By introducing the basic concept of complex number, the form of complex numbers and basic operations with complex numbers, Unit 5 starts to lay the foundation for
1 Convexity explains SVMs
 1 Convexity explains SVMs The convex hull of a set is the collection of linear combinations of points in the set where the coefficients are nonnegative and sum to one. Two sets are linearly separable if
1 Convexity explains SVMs The convex hull of a set is the collection of linear combinations of points in the set where the coefficients are nonnegative and sum to one. Two sets are linearly separable if
BUILT YOU. ACT Pathway. for
 BUILT for YOU 2016 2017 Think Through Math s is built to equip students with the skills and conceptual understandings of high school level mathematics necessary for success in college. This pathway progresses
BUILT for YOU 2016 2017 Think Through Math s is built to equip students with the skills and conceptual understandings of high school level mathematics necessary for success in college. This pathway progresses
H2 MATHS SET D PAPER 1
 H Maths Set D Paper H MATHS Exam papers with worked solutions SET D PAPER Compiled by THE MATHS CAFE P a g e b The curve y ax c x 3 points, and, H Maths Set D Paper has a stationary point at x 3. It also
H Maths Set D Paper H MATHS Exam papers with worked solutions SET D PAPER Compiled by THE MATHS CAFE P a g e b The curve y ax c x 3 points, and, H Maths Set D Paper has a stationary point at x 3. It also
2018 LEHIGH UNIVERSITY HIGH SCHOOL MATH CONTEST
 08 LEHIGH UNIVERSITY HIGH SCHOOL MATH CONTEST. A right triangle has hypotenuse 9 and one leg. What is the length of the other leg?. Don is /3 of the way through his run. After running another / mile, he
08 LEHIGH UNIVERSITY HIGH SCHOOL MATH CONTEST. A right triangle has hypotenuse 9 and one leg. What is the length of the other leg?. Don is /3 of the way through his run. After running another / mile, he
Math Day at the Beach 2016
 Multiple Choice Write your name and school and mark your answers on the answer sheet. You have 30 minutes to work on these problems. No calculator is allowed. 1. What is the median of the following five
Multiple Choice Write your name and school and mark your answers on the answer sheet. You have 30 minutes to work on these problems. No calculator is allowed. 1. What is the median of the following five
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012
 Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
VOYAGER INSIDE ALGEBRA CORRELATED TO THE NEW JERSEY STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES AND CCSS.
 We NJ Can STUDENT Early Learning LEARNING Curriculum OBJECTIVES PreK Grades 8 12 VOYAGER INSIDE ALGEBRA CORRELATED TO THE NEW JERSEY STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES AND CCSS www.voyagersopris.com/insidealgebra
We NJ Can STUDENT Early Learning LEARNING Curriculum OBJECTIVES PreK Grades 8 12 VOYAGER INSIDE ALGEBRA CORRELATED TO THE NEW JERSEY STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES AND CCSS www.voyagersopris.com/insidealgebra
Introduction to Proofs
 Real Analysis Preview May 2014 Properties of R n Recall Oftentimes in multivariable calculus, we looked at properties of vectors in R n. If we were given vectors x =< x 1, x 2,, x n > and y =< y1, y 2,,
Real Analysis Preview May 2014 Properties of R n Recall Oftentimes in multivariable calculus, we looked at properties of vectors in R n. If we were given vectors x =< x 1, x 2,, x n > and y =< y1, y 2,,
CCSS Math- Algebra. Domain: Algebra Seeing Structure in Expressions A-SSE. Pacing Guide. Standard: Interpret the structure of expressions.
 1 Domain: Algebra Seeing Structure in Expressions A-SSE Standard: Interpret the structure of expressions. H.S. A-SSE.1a. Interpret expressions that represent a quantity in terms of its context. Content:
1 Domain: Algebra Seeing Structure in Expressions A-SSE Standard: Interpret the structure of expressions. H.S. A-SSE.1a. Interpret expressions that represent a quantity in terms of its context. Content:
OSTROWSKI S THEOREM FOR Q(i)
 OSTROWSKI S THEOREM FOR Q(i) KEITH CONRAD We will extend Ostrowki s theorem from Q to the quadratic field Q(i). On Q, every nonarchimedean absolute value is equivalent to the p-adic absolute value for
OSTROWSKI S THEOREM FOR Q(i) KEITH CONRAD We will extend Ostrowki s theorem from Q to the quadratic field Q(i). On Q, every nonarchimedean absolute value is equivalent to the p-adic absolute value for
UNC Charlotte 2005 Comprehensive March 7, 2005
 March 7, 2005 1 The numbers x and y satisfy 2 x = 15 and 15 y = 32 What is the value xy? (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 (E) none of A, B, C or D 2 Suppose x, y, z, and w are real numbers satisfying x/y = 4/7,
March 7, 2005 1 The numbers x and y satisfy 2 x = 15 and 15 y = 32 What is the value xy? (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 (E) none of A, B, C or D 2 Suppose x, y, z, and w are real numbers satisfying x/y = 4/7,
Game Theory and Algorithms Lecture 7: PPAD and Fixed-Point Theorems
 Game Theory and Algorithms Lecture 7: PPAD and Fixed-Point Theorems March 17, 2011 Summary: The ultimate goal of this lecture is to finally prove Nash s theorem. First, we introduce and prove Sperner s
Game Theory and Algorithms Lecture 7: PPAD and Fixed-Point Theorems March 17, 2011 Summary: The ultimate goal of this lecture is to finally prove Nash s theorem. First, we introduce and prove Sperner s
The Art of Dumbassing Brian Hamrick July 2, 2010
 The Art of Dumbassing Brian Hamrick July, Introduction The field of inequalities is far from trivial. Many techniques, including Cauchy, Hölder, isolated fudging, Jensen, and smoothing exist and lead to
The Art of Dumbassing Brian Hamrick July, Introduction The field of inequalities is far from trivial. Many techniques, including Cauchy, Hölder, isolated fudging, Jensen, and smoothing exist and lead to
Math 1120 Calculus, sections 1 and 2 Test 1
 February 11, 2015 Name The problems count as marked. The total number of points available is 150. Throughout this test, show your work. Using a calculator to circumvent ideas discussed in class will generally
February 11, 2015 Name The problems count as marked. The total number of points available is 150. Throughout this test, show your work. Using a calculator to circumvent ideas discussed in class will generally
Problems for Putnam Training
 Problems for Putnam Training 1 Number theory Problem 1.1. Prove that for each positive integer n, the number is not prime. 10 1010n + 10 10n + 10 n 1 Problem 1.2. Show that for any positive integer n,
Problems for Putnam Training 1 Number theory Problem 1.1. Prove that for each positive integer n, the number is not prime. 10 1010n + 10 10n + 10 n 1 Problem 1.2. Show that for any positive integer n,
39.1 Absolute maxima/minima
 Module 13 : Maxima, Minima Saddle Points, Constrained maxima minima Lecture 39 : Absolute maxima / minima [Section 39.1] Objectives In this section you will learn the following : The notion of absolute
Module 13 : Maxima, Minima Saddle Points, Constrained maxima minima Lecture 39 : Absolute maxima / minima [Section 39.1] Objectives In this section you will learn the following : The notion of absolute
12-neighbour packings of unit balls in E 3
 12-neighbour packings of unit balls in E 3 Károly Böröczky Department of Geometry Eötvös Loránd University Pázmány Péter sétány 1/c H-1117 Budapest Hungary László Szabó Institute of Informatics and Economics
12-neighbour packings of unit balls in E 3 Károly Böröczky Department of Geometry Eötvös Loránd University Pázmány Péter sétány 1/c H-1117 Budapest Hungary László Szabó Institute of Informatics and Economics
Bell Quiz 2-3. Determine the end behavior of the graph using limit notation. Find a function with the given zeros , 2. 5 pts possible.
 Bell Quiz 2-3 2 pts Determine the end behavior of the graph using limit notation. 5 2 1. g( ) = 8 + 13 7 3 pts Find a function with the given zeros. 4. -1, 2 5 pts possible Ch 2A Big Ideas 1 Questions
Bell Quiz 2-3 2 pts Determine the end behavior of the graph using limit notation. 5 2 1. g( ) = 8 + 13 7 3 pts Find a function with the given zeros. 4. -1, 2 5 pts possible Ch 2A Big Ideas 1 Questions
The Advantage Testing Foundation Solutions
 The Advantage Testing Foundation 2016 Problem 1 Let T be a triangle with side lengths 3, 4, and 5. If P is a point in or on T, what is the greatest possible sum of the distances from P to each of the three
The Advantage Testing Foundation 2016 Problem 1 Let T be a triangle with side lengths 3, 4, and 5. If P is a point in or on T, what is the greatest possible sum of the distances from P to each of the three
Exhaustion: From Eudoxus to Archimedes
 Exhaustion: From Eudoxus to Archimedes Franz Lemmermeyer April 22, 2005 Abstract Disclaimer: Eventually, I plan to polish this and use my own diagrams; so far, most of it is lifted from the web. Exhaustion
Exhaustion: From Eudoxus to Archimedes Franz Lemmermeyer April 22, 2005 Abstract Disclaimer: Eventually, I plan to polish this and use my own diagrams; so far, most of it is lifted from the web. Exhaustion
From Calculus II: An infinite series is an expression of the form
 MATH 3333 INTERMEDIATE ANALYSIS BLECHER NOTES 75 8. Infinite series of numbers From Calculus II: An infinite series is an expression of the form = a m + a m+ + a m+2 + ( ) Let us call this expression (*).
MATH 3333 INTERMEDIATE ANALYSIS BLECHER NOTES 75 8. Infinite series of numbers From Calculus II: An infinite series is an expression of the form = a m + a m+ + a m+2 + ( ) Let us call this expression (*).
EUCLIDEAN SPACES AND VECTORS
 EUCLIDEAN SPACES AND VECTORS PAUL L. BAILEY 1. Introduction Our ultimate goal is to apply the techniques of calculus to higher dimensions. We begin by discussing what mathematical concepts describe these
EUCLIDEAN SPACES AND VECTORS PAUL L. BAILEY 1. Introduction Our ultimate goal is to apply the techniques of calculus to higher dimensions. We begin by discussing what mathematical concepts describe these
Prep for College Algebra
 Prep for College Algebra This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (219 topics + 85 additional topics)
Prep for College Algebra This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (219 topics + 85 additional topics)
Area and Integration
 Area and Integration Professor Richard Blecksmith richard@math.niu.edu Dept. of Mathematical Sciences Northern Illinois University http://math.niu.edu/ richard/math229. Two Fundamental Problems of Calculus
Area and Integration Professor Richard Blecksmith richard@math.niu.edu Dept. of Mathematical Sciences Northern Illinois University http://math.niu.edu/ richard/math229. Two Fundamental Problems of Calculus
arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 10 Dec 2009
![arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 10 Dec 2009 arxiv: v1 [math.nt] 10 Dec 2009](/thumbs/96/128277757.jpg) Ford circles, continued fractions, and best approximation of the second kind arxiv:092.997v [math.nt] 0 Dec 2009 Ian Short Centre for Mathematical Sciences Wilberforce Road Cambridge CB3 0WB United Kingdom
Ford circles, continued fractions, and best approximation of the second kind arxiv:092.997v [math.nt] 0 Dec 2009 Ian Short Centre for Mathematical Sciences Wilberforce Road Cambridge CB3 0WB United Kingdom
River Dell Regional School District. Pre-Calculus Curriculum
 River Dell Regional School District Pre-Calculus Curriculum 2015 Mr. Patrick Fletcher Superintendent River Dell Regional Schools Ms. Lorraine Brooks Principal River Dell High School Mr. Richard Freedman
River Dell Regional School District Pre-Calculus Curriculum 2015 Mr. Patrick Fletcher Superintendent River Dell Regional Schools Ms. Lorraine Brooks Principal River Dell High School Mr. Richard Freedman
Core Mathematics C12
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level Centre Number Candidate Number Core Mathematics C12 Advanced Subsidiary Tuesday 10 January 2017 Morning Time: 2 hours
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level Centre Number Candidate Number Core Mathematics C12 Advanced Subsidiary Tuesday 10 January 2017 Morning Time: 2 hours
Mathematics High School Algebra
 Mathematics High School Algebra Expressions. An expression is a record of a computation with numbers, symbols that represent numbers, arithmetic operations, exponentiation, and, at more advanced levels,
Mathematics High School Algebra Expressions. An expression is a record of a computation with numbers, symbols that represent numbers, arithmetic operations, exponentiation, and, at more advanced levels,
Prep for College Algebra with Trigonometry
 Prep for College Algebra with Trigonometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (246 topics +
Prep for College Algebra with Trigonometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (246 topics +
= 10 such triples. If it is 5, there is = 1 such triple. Therefore, there are a total of = 46 such triples.
 . Two externally tangent unit circles are constructed inside square ABCD, one tangent to AB and AD, the other to BC and CD. Compute the length of AB. Answer: + Solution: Observe that the diagonal of the
. Two externally tangent unit circles are constructed inside square ABCD, one tangent to AB and AD, the other to BC and CD. Compute the length of AB. Answer: + Solution: Observe that the diagonal of the
