Topics include Newton s laws, pressure, work, average velocity, kinetic energy, momentum and conservation of momentum, work-energy theorem
|
|
|
- Dustin Todd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 3: Safety Overall: Topics include Newton s laws, pressure, work, average velocity, kinetic energy, momentum and conservation of momentum, work-energy theorem Sections 1-2: These two sections introduce safety and safety features in automobiles. Section 1 can be skipped over or the quiz be used as a short introduction to safety. Very little time needs to be spent on the first section and can easily be combined with section 2. The investigation in section 2 has students sending a clay model down a ramp without seatbelts, then with narrow and then wide seatbelts. This introduces the idea of pressure and reinforces Newton s 1 st law. Section 3: Students use eggs and flower to understand how stopping distance changes the amount of force an object experiences. This is a high-interest lab that introduces Kinetic Energy and the work-energy theorem and reinforces Newton s second law. Section 4: This section deals with Newton s 1 st and 2 nd law in a new way. Even though our kids have a lot of exposure to Newton s laws at this point they typically are unable to hypothesize motion in a rear end collision. This is a valuable and fun lab. - 5 Section 6 Section 7 Must-Dos: Scientific Practices: It is important to recognize that scientific practices are a key part of the investigative process in this book even though they are not always specifically drawn out in a manner you may be used to. Your students will be responsible for understanding experimental design and must be able to create hypotheses, identify variables and constants, interpret qualitative and quantitative data, and make conclusions that justify what has been learned. Ensure that your instruction explicitly focuses on these practices in all the sections you teach. You can expect that district and state assessments will contain questions relating to scientific practices Learning Outcomes, Pitfalls, Misconceptions by Section Section 1: Accidents pitfalls: Identify and evaluate safety features in selected automobiles Compare and contrast safety features in selected automobiles Identify safety features for other modes of transportation (in-line skates, skateboards, motorcycles) Very little time needs to be spent on this section. Have the students take the quiz as a warm up in class and spend a few minutes discussing each question. Make copies of the table for the students to save time. misconceptions:
2 After reading the Physics Talk, students seem to think that having a solid steering column is a safety feature. The quiz can be passed over in section Section 2: Safety and Seatbelts Explain Newton s first law of motion Identify the three collisions in every accident Compare the effectiveness of various wide and narrow seat belts Express the relationship between pressure, force, and area pitfalls: Have a student assistant make the clay models ahead of time. Some modeling clay is too hard and significant injury might not be visible. Play Dough is an option but it will dry out over time. Also, the wire may make an indentation in the model that is difficult to remove, making students think that all seatbelts cause the same amount of damage. misconceptions: This section discusses pressure and designing a safer seatbelt. Emphasize that the force each seat belt exerted to stop the passenger was the same, but the results were different. To help students differentiate force from pressure, have the students stand on two feet, then one, then their toes. Correlate pressure they felt with the amount of contact. The force remained constant but as area decreased pressure increased. Section 3: Why Air Bags? Model an airbag Relate the energy of a moving object to the work required to stop the object Demonstrate an understanding about the relationship between the force of an impact and the stopping distance The flour in this lab can be messy. Have the students use a Petri dish and a ruler to get the flour level, then place the Petri dish into a container. Some teachers have had eggs taken from the class. Account for each group s eggs at the end of the activity.
3 Misconceptions: Students think that stopping distance is decreased when an airbag deploys because they confuse traveling distance and stopping distance. Emphasize that an airbag increases the distance over which a person s head stops compared to a dashboard, even though the distance the person s head travels through the air prior to hitting an object is less when an airbag deploys (fix the phrasing on this). The egg hitting the sheet is a good example to return to when discussing stopping distance. Some students confuse work with force. Remind students that the amount of work done on both eggs was the same, since the total work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. Both eggs had the same KE since they were dropped from the same height. Students struggle with the idea that for a given force, the stopping distance is proportional to the speed squared. (d=v 2 /2a). If a vehicle triples its speed from 10 to 30 m/s, the stopping distance will be 9 times greater than before. Section 4: Newton s Second law of Motion: The Rear-End Collision Evaluate, from simulated collisions, the effect of rear-end collisions on the neck muscles Describe the causes of whiplash injuries Provide examples of Newton s first and second laws of motion in automobile crashes Analyze the role of safety devices in preventing whiplash injury Have a student assistant fold the templates (see the blackline masters) ahead of time and try them out on the carts to be sure they are the correct width. Make the clay figures ahead of time to save money. Students will struggle with seeing how much the neck bends in a rear end collision. Be sure to use wire that is strong enough to hold the head but is still able to bend. After each collision the wire needs to be straightened and the head re-fastened securely. Remind students of things that need to remain constant: target car beginning at same spot, resetting the wire between each trial, etc. Misconceptions: Students believe that a head moves backward in a rear end collision, when in fact it remains at rest and the rest of the body moves forward.
4 Below are some videos of older and newer cars involved in rear end collisions. These can be helpful when discussing the results of your investigation Have students take the whiplash quiz found in the Physics to Go together on whiteboards. Section 5: Momentum: Concentrating on Collisions Apply the definition of momentum Conduct analysis of the momentum of pairs of objects involved in onedimensional collisions. In order to see momentum being conserved, it is important to use carts with very little friction and also to emphasize to students to observe just before and just after the collision. Understand and apply the law of conservation of momentum to collisions. Measure the momentum before and after a moving mass strikes a stationary mass in a head-on collision Use tracks to make sure the collisions will occur at the center of the carts. Tape the weights into the carts. Tape an index card to the side of each cart so the velocimeter will more easily detect the motion of the carts before and after the collision. Make a copy of the data tables for the kids to save time. For the 6 collision types, provide a table with the Type of Collision, the Before sketch and the After sketch. Model how to fill in each column. Provide carts for the kids to use if they struggle with visualizing the collisions. When calculating momentum before and after, have students create a T-chart to separate each object s individual momentum. There will be a lot of variation on the data collected. Be sure to discuss sources of error, unbalanced forces from the environment, and difficulties in working with models.
5 Section 7: Impulse and Momentum: Crumple Zone Learning Outcomes: Design a device that is able to absorb the energy of a collision and reduce the net force on an object in an automobile. Describe collisions and crumple zones in terms of momentum, impulse, and force. Use a motion probe to determine the velocity of moving vehicles. Compare the change of momentum of a model vehicle before a collision with the impulse applied during a collision. Explore ways of using cushions to increase the time that a force acts during a primary collision. ***this section to be completed as the school year progresses*** Misconceptions:
Physics Talk FORCES AFFECTING COLLISIONS
 Chapter 3 Safety Physics Talk FORCES AFFECTING COLLISIONS By examining the different crumple zones designed by other teams in your class, you can get an insight into the physics of collisions. Probably
Chapter 3 Safety Physics Talk FORCES AFFECTING COLLISIONS By examining the different crumple zones designed by other teams in your class, you can get an insight into the physics of collisions. Probably
Egg Crash! Designing a Collision Safety Device
 TEACHER LESSON Key question(s) How do people survive major collisions? How does physics explain the effectiveness of seat belts and airbags? Crash Course Definitions impulse: product of force and time
TEACHER LESSON Key question(s) How do people survive major collisions? How does physics explain the effectiveness of seat belts and airbags? Crash Course Definitions impulse: product of force and time
Activity 4. Life (and Death) before Seat Belts. What Do You Think? For You To Do GOALS
 Activity 4 Life (and Death) before Seat Belts Activity 4 Life (and Death) before Seat Belts GOALS In this activity you will: Understand Newton s First Law of Motion. Understand the role of safety belts.
Activity 4 Life (and Death) before Seat Belts Activity 4 Life (and Death) before Seat Belts GOALS In this activity you will: Understand Newton s First Law of Motion. Understand the role of safety belts.
FORCE AND MOTION SEPUP UNIT OVERVIEW
 FORCE AND MOTION SEPUP UNIT OVERVIEW Listed below is a summary of the activities in this unit. Note that the total teaching time is listed as 26-32 periods of approximately 50 minutes (approximately 5-6
FORCE AND MOTION SEPUP UNIT OVERVIEW Listed below is a summary of the activities in this unit. Note that the total teaching time is listed as 26-32 periods of approximately 50 minutes (approximately 5-6
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS
 SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS FORCES L (P.123-129) Galileo s View of Force & Motion Prior to the 1600s, early scientists held a simplistic view of motion. They noticed that moving objects would spontaneously
SPH3U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS FORCES L (P.123-129) Galileo s View of Force & Motion Prior to the 1600s, early scientists held a simplistic view of motion. They noticed that moving objects would spontaneously
Physics 18 Spring 2011 Homework 3 Wednesday February 2, 2011
 Physics 18 Spring 2011 Homework 3 Wednesday February 2, 2011 Make sure your name is on your homework, and please box your final answer. Because we will be giving partial credit, be sure to attempt all
Physics 18 Spring 2011 Homework 3 Wednesday February 2, 2011 Make sure your name is on your homework, and please box your final answer. Because we will be giving partial credit, be sure to attempt all
3 Using Newton s Laws
 3 Using Newton s Laws What You ll Learn how Newton's first law explains what happens in a car crash how Newton's second law explains the effects of air resistance 4(A), 4(C), 4(D), 4(E) Before You Read
3 Using Newton s Laws What You ll Learn how Newton's first law explains what happens in a car crash how Newton's second law explains the effects of air resistance 4(A), 4(C), 4(D), 4(E) Before You Read
AQA Physics P2 Topic 1. Motion
 AQA Physics P2 Topic 1 Motion Distance / Time graphs Horizontal lines mean the object is stationary. Straight sloping lines mean the object is travelling at a constant speed. The steeper the slope, the
AQA Physics P2 Topic 1 Motion Distance / Time graphs Horizontal lines mean the object is stationary. Straight sloping lines mean the object is travelling at a constant speed. The steeper the slope, the
Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. UCVTS AIT Physics
 Newton s First Law of Motion - Inertia Aristotle (384-322 BC) on Motion (4 th century BC) Natural Motion It was thought to be either straight up or straight down a rock would fall, smoke would rise. Circular
Newton s First Law of Motion - Inertia Aristotle (384-322 BC) on Motion (4 th century BC) Natural Motion It was thought to be either straight up or straight down a rock would fall, smoke would rise. Circular
Momentum and Impulse
 analyse impulse, and momentum transfer, in collisions between objects moving along a straight line; Momentum The momentum (p) of a body is the product of its mass and velocity. P = mv. The unit is kilogram
analyse impulse, and momentum transfer, in collisions between objects moving along a straight line; Momentum The momentum (p) of a body is the product of its mass and velocity. P = mv. The unit is kilogram
Chapter 2: FORCE and MOTION
 Chapter 2: FORCE and MOTION Linear Motion Linear motion is the movement of an object along a straight line. Distance The distance traveled by an object is the total length that is traveled by that object.
Chapter 2: FORCE and MOTION Linear Motion Linear motion is the movement of an object along a straight line. Distance The distance traveled by an object is the total length that is traveled by that object.
Forces and Newton s Laws
 chapter 3 Forces and Newton s Laws section 3 Using Newton s Laws Before You Read Imagine riding on a sled, or in a wagon, or perhaps a school bus that stops quickly or suddenly. What happens to your body
chapter 3 Forces and Newton s Laws section 3 Using Newton s Laws Before You Read Imagine riding on a sled, or in a wagon, or perhaps a school bus that stops quickly or suddenly. What happens to your body
Written homework #5 due on Monday Online homework #5 due on Tuesday. Answer keys posted on course web site SPARK grades uploaded Average = 74.
 Homework Written homework #5 due on Monday Online homework #5 due on Tuesday Exam 1 Answer keys posted on course web site SPARK grades uploaded Average = 74.3% 1 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
Homework Written homework #5 due on Monday Online homework #5 due on Tuesday Exam 1 Answer keys posted on course web site SPARK grades uploaded Average = 74.3% 1 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
The Laws of Motion. Before You Read. Science Journal
 The Laws of Motion Before You Read Before you read the chapter, use the What I know column to list three things you know about motion. Then list three questions you have about motion in the What I want
The Laws of Motion Before You Read Before you read the chapter, use the What I know column to list three things you know about motion. Then list three questions you have about motion in the What I want
LAB 7: COLLISIONS AND MOMENTUM - NEWTON'S THIRD LAW
 109 Name Date Partners LAB 7: COLLISIONS AND MOMENTUM - NEWTON'S THIRD LAW OBJECTIVES In any system of bodies which act on each other, action and reaction, estimated by momentum gained and lost, balance
109 Name Date Partners LAB 7: COLLISIONS AND MOMENTUM - NEWTON'S THIRD LAW OBJECTIVES In any system of bodies which act on each other, action and reaction, estimated by momentum gained and lost, balance
Thanks. You Might Also Like. I look forward helping you focus your instruction and save time prepping.
 Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Connect Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
LAB 7: COLLISIONS & MOMENTUM - NEWTON'S THIRD LAW
 115 Name Date Partners LAB 7: COLLISIONS & MOMENTUM - NEWTON'S THIRD LAW OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW In any system of bodies which act on each other, action and reaction, estimated by momentum gained and lost,
115 Name Date Partners LAB 7: COLLISIONS & MOMENTUM - NEWTON'S THIRD LAW OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW In any system of bodies which act on each other, action and reaction, estimated by momentum gained and lost,
It would be appropriate to pull out your phone or planner and write these dates down.
 Upcoming dates 11/11 (A) + 11/12 (B): Virtual Collision Lab 11/13 (A) + 11/14 (B): Momentum and Impulse Quiz and Collision Lab 11/17 (A) + 11/18 (B): Momentum and Impulse Vocabulary Quiz and Test Review
Upcoming dates 11/11 (A) + 11/12 (B): Virtual Collision Lab 11/13 (A) + 11/14 (B): Momentum and Impulse Quiz and Collision Lab 11/17 (A) + 11/18 (B): Momentum and Impulse Vocabulary Quiz and Test Review
EGG CRASH! DESIGNING A COLLISION SAFETY DEVICE
 T E AC H E R L E S S O N EGG CRASH! DESIGNING A COLLISION SAFETY DEVICE DEFINITIONS momentum: the inertia of moving objects; product of the mass and the velocity of an object (p = mv) impulse: product
T E AC H E R L E S S O N EGG CRASH! DESIGNING A COLLISION SAFETY DEVICE DEFINITIONS momentum: the inertia of moving objects; product of the mass and the velocity of an object (p = mv) impulse: product
Show all workings for questions that involve multiple choice.
 Assignment 2 Unit 2 Newton s Laws (Outcomes 325-5, 325-8) Name: Multiple Choice: Show all workings for questions that involve multiple choice. 1 Which choice represents a NON-INERTIAL frame of reference?
Assignment 2 Unit 2 Newton s Laws (Outcomes 325-5, 325-8) Name: Multiple Choice: Show all workings for questions that involve multiple choice. 1 Which choice represents a NON-INERTIAL frame of reference?
Choosing a Safe Vehicle Challenge: Analysis: Measuring Speed Challenge: Analysis: Reflection:
 Activity 73: Choosing a Safe Vehicle Challenge: Which vehicle do you think is safer? 1. Compare the features you listed in the data evidence section to the features listed on the worksheet. a. How are
Activity 73: Choosing a Safe Vehicle Challenge: Which vehicle do you think is safer? 1. Compare the features you listed in the data evidence section to the features listed on the worksheet. a. How are
UbD Unit. Unit Cover Page. Key Words: Newton s Laws, friction, impulse, momentum, rotational loads, centripetal force
 UbD Unit Unit Cover Page Unit Title: Laws of Motion Grade Level: 12th Subject/Topic: Laws of Motion Key Words: Newton s Laws, friction, impulse, momentum, rotational loads, centripetal force Standards/Indicators:
UbD Unit Unit Cover Page Unit Title: Laws of Motion Grade Level: 12th Subject/Topic: Laws of Motion Key Words: Newton s Laws, friction, impulse, momentum, rotational loads, centripetal force Standards/Indicators:
Unit 8. Unit 8 - MTM. Outcomes. What does the word momentum mean to you?
 Outcomes Unit 8 THE MOMENTUM TRANSFER MODEL (MTM) I M P U L S E A N D M O M E N T U M Unit 8 - MTM P A R T 1 F O R C E S C H A N G E M O M E N T U M P A R T 2 M O M E N T U M I S C O N S E R V E D What
Outcomes Unit 8 THE MOMENTUM TRANSFER MODEL (MTM) I M P U L S E A N D M O M E N T U M Unit 8 - MTM P A R T 1 F O R C E S C H A N G E M O M E N T U M P A R T 2 M O M E N T U M I S C O N S E R V E D What
Vocabulary. The mass of an object multiplied by its speed or velocity. The product of force x time that causes a change in momentum.
 Vocabulary Term Definition The mass of an object multiplied by its speed or. Kg m s The units for momentum. Impulse The product of force x time that causes a change in momentum. N s The units for impulse.
Vocabulary Term Definition The mass of an object multiplied by its speed or. Kg m s The units for momentum. Impulse The product of force x time that causes a change in momentum. N s The units for impulse.
A moving object can have a large momentum if it has a, a, or both. Momentum is a quantity so it needs
 Moe said a lot of things Name Hour and Moe meant em! Chapter 8 Notes 8.1 Momentum We can define momentum as in motion UNITS: A moving object can have a large momentum if it has a, a, or both. Momentum
Moe said a lot of things Name Hour and Moe meant em! Chapter 8 Notes 8.1 Momentum We can define momentum as in motion UNITS: A moving object can have a large momentum if it has a, a, or both. Momentum
COLLISIONS AND MOMENTUM - NEWTON'S THIRD LAW
 July 18 Collisions and Momentum Newton s Third Law 1 Name Date Partners COLLISIONS AND MOMENTUM - NEWTON'S THIRD LAW In any system of bodies which act on each other, action and reaction, estimated by momentum
July 18 Collisions and Momentum Newton s Third Law 1 Name Date Partners COLLISIONS AND MOMENTUM - NEWTON'S THIRD LAW In any system of bodies which act on each other, action and reaction, estimated by momentum
Q1. (a) The diagram shows a car being driven at 14 rn/s. The driver has forgotten to clear a thick layer of snow from the roof.
 Q1. (a) The diagram shows a car being driven at 14 rn/s. The driver has forgotten to clear a thick layer of snow from the roof. Which of the following has the smallest momentum? Draw a circle around your
Q1. (a) The diagram shows a car being driven at 14 rn/s. The driver has forgotten to clear a thick layer of snow from the roof. Which of the following has the smallest momentum? Draw a circle around your
Negative Acceleration: Braking Your Automobile
 Chapter 1 Driving the Roads SECTION 5 Negative Acceleration: Braking Your Automobile Section Overview This section addresses the distance traveled during negative acceleration as a function of the initial
Chapter 1 Driving the Roads SECTION 5 Negative Acceleration: Braking Your Automobile Section Overview This section addresses the distance traveled during negative acceleration as a function of the initial
Physics 2048 Test 3 Dr. Jeff Saul Spring 2001
 Physics 248 Test 3 Dr. Jeff Saul Spring 21 Name: Table: Date: READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE YOU BEGIN Before you start the test, WRITE YOUR NAME ON EVERY PAGE OF THE EXAM. Calculators are permitted, but
Physics 248 Test 3 Dr. Jeff Saul Spring 21 Name: Table: Date: READ THESE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE YOU BEGIN Before you start the test, WRITE YOUR NAME ON EVERY PAGE OF THE EXAM. Calculators are permitted, but
Evaluation copy 10A. Impulse and Momentum. Experiment INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES MATERIALS PRE-LAB QUESTIONS
 Impulse and Momentum Experiment 10A INTRODUCTION You are no doubt familiar with everyday uses of the term momentum; e.g., a sports team that has begun to exert superiority over an opponent is said to have
Impulse and Momentum Experiment 10A INTRODUCTION You are no doubt familiar with everyday uses of the term momentum; e.g., a sports team that has begun to exert superiority over an opponent is said to have
Plus. Active Physics. Calculating Momentum. What Do You Think Now? Checking Up
 Section 5 Momentum: Concentrating on Collisions In the same way, vehicles have different momenta depending on their mass and velocity. An 18-wheel tractor trailer has a large momentum even if it is moving
Section 5 Momentum: Concentrating on Collisions In the same way, vehicles have different momenta depending on their mass and velocity. An 18-wheel tractor trailer has a large momentum even if it is moving
Client Profile: Master Electrician
 4Q1 - Quiz on Obtaining, Evaluating, and Communicating Information 4Q2 - Quiz 2 on Big Ideas of Impulse Learning Target Name: Period: Date: Client Profile: Master Electrician Interview Notes: Adaliah,
4Q1 - Quiz on Obtaining, Evaluating, and Communicating Information 4Q2 - Quiz 2 on Big Ideas of Impulse Learning Target Name: Period: Date: Client Profile: Master Electrician Interview Notes: Adaliah,
Mark scheme. 1 Forces and motion 1. Practical work. 1 Forces and motion 1
 Forces and motion Mark scheme Forces and motion Practical work States a similarity, e.g. both experiments measure the fastest speed States a difference, e.g. one experiment takes readings using a data
Forces and motion Mark scheme Forces and motion Practical work States a similarity, e.g. both experiments measure the fastest speed States a difference, e.g. one experiment takes readings using a data
Impulse,Momentum, CM Practice Questions
 Name: Date: 1. A 12.0-kilogram cart is moving at a speed of 0.25 meter per second. After the speed of the cart is tripled, the inertia of the cart will be A. unchanged B. one-third as great C. three times
Name: Date: 1. A 12.0-kilogram cart is moving at a speed of 0.25 meter per second. After the speed of the cart is tripled, the inertia of the cart will be A. unchanged B. one-third as great C. three times
Figure 5.1: Force is the only action that has the ability to change motion. Without force, the motion of an object cannot be started or changed.
 5.1 Newton s First Law Sir Isaac Newton, an English physicist and mathematician, was one of the most brilliant scientists in history. Before the age of thirty he had made many important discoveries in
5.1 Newton s First Law Sir Isaac Newton, an English physicist and mathematician, was one of the most brilliant scientists in history. Before the age of thirty he had made many important discoveries in
HSC Physics Module 8.4. Moving About
 HSC Physics Module 8.4 Moving About 8.4 Moving About (30 indicative hours) Contextual outline Increased access to transport is a feature of today s society. Most people access some form of transport for
HSC Physics Module 8.4 Moving About 8.4 Moving About (30 indicative hours) Contextual outline Increased access to transport is a feature of today s society. Most people access some form of transport for
Unit 8. Unit 8 - MTM. Outcomes. Momentum. Solve this problem. What does the word momentum mean to you?
 Outcomes Unit 8 THE MOMENTUM TRANSFER MODEL (MTM) I M P U L S E A N D M O M E N T U M What does the word momentum mean to you? Unit 8 - MTM P A R T 1 F O R C E S C H A N G E M O M E N T U M The home team
Outcomes Unit 8 THE MOMENTUM TRANSFER MODEL (MTM) I M P U L S E A N D M O M E N T U M What does the word momentum mean to you? Unit 8 - MTM P A R T 1 F O R C E S C H A N G E M O M E N T U M The home team
Improving Safety Features during a Head on Collision inside a Car Cabin
 Improving Safety Features during a Head on Collision inside a Car Cabin Harinarayan Vishwakarma Abstract The core theme of this research is directed towards the idea of providing more safety features inside
Improving Safety Features during a Head on Collision inside a Car Cabin Harinarayan Vishwakarma Abstract The core theme of this research is directed towards the idea of providing more safety features inside
LAB 7: COLLISIONS AND MOMENTUM - NEWTON'S THIRD LAW
 Lab 7 Collisions and Momentum Newton s Third Law 73 Name Date Partners LAB 7: COLLISIONS AND MOMENTUM - NEWTON'S THIRD LAW In any system of bodies which act on each other, action and reaction, estimated
Lab 7 Collisions and Momentum Newton s Third Law 73 Name Date Partners LAB 7: COLLISIONS AND MOMENTUM - NEWTON'S THIRD LAW In any system of bodies which act on each other, action and reaction, estimated
Standard(s): 2.5 TA: Independence Level: % Assistance, coaching, prompting:
 Name: Class: Date: / / Momentum Quiz Review KEY Introductory Physics (670) 1. What unit is momentum measured with? kilograms meters per second 2. Decide if the objects below have momentum or not. Write
Name: Class: Date: / / Momentum Quiz Review KEY Introductory Physics (670) 1. What unit is momentum measured with? kilograms meters per second 2. Decide if the objects below have momentum or not. Write
Objectives: Identify the factors that affect an object s momentum Identify the factors that affect how much an object s momentum changes?
 Momentum is conserved for all collisions as long as external forces don t interfere. Objectives: Identify the factors that affect an object s momentum Identify the factors that affect how much an object
Momentum is conserved for all collisions as long as external forces don t interfere. Objectives: Identify the factors that affect an object s momentum Identify the factors that affect how much an object
Standard(s): 2.5 TA: Independence Level: % Assistance, coaching, prompting:
 Name: Class: Date: / / Momentum Quiz Review Introductory Physics (670) 1. What unit is momentum measured with? 2. Decide if the objects below have momentum or not. Write yes if the underlined object has
Name: Class: Date: / / Momentum Quiz Review Introductory Physics (670) 1. What unit is momentum measured with? 2. Decide if the objects below have momentum or not. Write yes if the underlined object has
Chapter 9: Circular Motion
 Text: Chapter 9 Think and Explain: 1-5, 7-9, 11 Think and Solve: --- Chapter 9: Circular Motion NAME: Vocabulary: rotation, revolution, axis, centripetal, centrifugal, tangential speed, Hertz, rpm, rotational
Text: Chapter 9 Think and Explain: 1-5, 7-9, 11 Think and Solve: --- Chapter 9: Circular Motion NAME: Vocabulary: rotation, revolution, axis, centripetal, centrifugal, tangential speed, Hertz, rpm, rotational
Part I Review Unit Review Name Momentum and Impulse
 Part I Review Unit Review Name Momentum and Impulse 1. A 5.00-kilogram block slides along a horizontal, frictionless surface at 10.0 meters per second for 4.00 seconds. The magnitude of the block's momentum
Part I Review Unit Review Name Momentum and Impulse 1. A 5.00-kilogram block slides along a horizontal, frictionless surface at 10.0 meters per second for 4.00 seconds. The magnitude of the block's momentum
Show all workings for questions that involve calculations. No marks will be given for correct answers that are not supported by calculations.
 Assignment 8 Unit 2 Newton s Laws (Outcomes 325-5, 325-8) Name: Multiple Choice: Show all workings for questions that involve calculations. No marks will be given for correct answers that are not supported
Assignment 8 Unit 2 Newton s Laws (Outcomes 325-5, 325-8) Name: Multiple Choice: Show all workings for questions that involve calculations. No marks will be given for correct answers that are not supported
Unit D Energy-Analysis Questions
 Unit D Energy-Analysis Questions Activity 53-Home Energy Use 1. How do Climates of the two home locations influence the energy used in the homes? 2. In the context of this activity, what does the term
Unit D Energy-Analysis Questions Activity 53-Home Energy Use 1. How do Climates of the two home locations influence the energy used in the homes? 2. In the context of this activity, what does the term
SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS
 SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ENERGY & MOMENTUM L Momentum & Impulse (P.222-227) Momentum & Impulse The driver of this race car walked away from the crash without a scratch. Luck had little to do with this
SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS ENERGY & MOMENTUM L Momentum & Impulse (P.222-227) Momentum & Impulse The driver of this race car walked away from the crash without a scratch. Luck had little to do with this
Chapter 4: Newton s laws of motion
 Chapter 4: Newton s laws of motion Objectives: What are forces? How do we identify them? Drawing free-body diagrams. Relating forces and motion. Solving force and motion problems. What is a force? Forces
Chapter 4: Newton s laws of motion Objectives: What are forces? How do we identify them? Drawing free-body diagrams. Relating forces and motion. Solving force and motion problems. What is a force? Forces
What are two forms of Potential Energy that we commonly use? Explain Conservation of Energy and how we utilize it for problem-solving technics.
 Bell Ringer: Define Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy, and Work. What are two forms of Potential Energy that we commonly use? Explain Conservation of Energy and how we utilize it for problem-solving technics.
Bell Ringer: Define Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy, and Work. What are two forms of Potential Energy that we commonly use? Explain Conservation of Energy and how we utilize it for problem-solving technics.
PHYSICS 30 MOMENTUM AND IMPULSE ASSIGNMENT 4 VERSION:0 55 MARKS
 Clearly communicate your understanding of the physics principles that you are going to solve a question and how those principles apply to the problem at hand. You may communicate this understanding through
Clearly communicate your understanding of the physics principles that you are going to solve a question and how those principles apply to the problem at hand. You may communicate this understanding through
UNIT 2 ONE-DIMENSIONAL FORCES AND MOTION. Objectives. To devise a method for applying a constant force to an object.
 UNIT 2 ONE-DIMENSIONAL FORCES AND MOTION Objectives To devise a method for applying a constant force to an object. To devise a scale for measuring force. To understand the relationship between force and
UNIT 2 ONE-DIMENSIONAL FORCES AND MOTION Objectives To devise a method for applying a constant force to an object. To devise a scale for measuring force. To understand the relationship between force and
Momentum is a property of moving matter. Momentum describes the tendency of objects to keep going in the same direction with the same speed.
 Warm-up A mosquito collides head-on with a car traveling 60 mph. How do you think the size of the force that car exerts on the mosquito compares to the size of the force that mosquito exerts on car? 12.1
Warm-up A mosquito collides head-on with a car traveling 60 mph. How do you think the size of the force that car exerts on the mosquito compares to the size of the force that mosquito exerts on car? 12.1
Why constant (or straight line) motion? Remember, if an object turns at a constant speed it is accelerating.
 Newton s 1st Law Newton s 1st Law of Motion - An object in constant motion will continue in constant motion or an object at rest will stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Unbalanced force
Newton s 1st Law Newton s 1st Law of Motion - An object in constant motion will continue in constant motion or an object at rest will stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Unbalanced force
Block 7-Momentum and Collision Day 1 odd 11/18 even 11/19 Day 2 odd 11/20 even 11/30 Day 3 odd 12/1 even 12/2 Day 4 odd 12/3 even 12/4 Due Day
 Block 7-Momentum and Collision Day 1 odd 11/18 even 11/19 Day 2 odd 11/20 even 11/30 Day 3 odd 12/1 even 12/2 Day 4 odd 12/3 even 12/4 Due Day https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o87qlo3gzma comets asteroids
Block 7-Momentum and Collision Day 1 odd 11/18 even 11/19 Day 2 odd 11/20 even 11/30 Day 3 odd 12/1 even 12/2 Day 4 odd 12/3 even 12/4 Due Day https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o87qlo3gzma comets asteroids
LAB PHYSICS MIDTERM EXAMINATION STUDY GUIDE
 Freehold Regional High School District 2011-12 LAB PHYSICS MIDTERM EXAMINATION STUDY GUIDE About the Exam The Lab Physics Midterm Examination consists of 32 multiple choice questions designed to assess
Freehold Regional High School District 2011-12 LAB PHYSICS MIDTERM EXAMINATION STUDY GUIDE About the Exam The Lab Physics Midterm Examination consists of 32 multiple choice questions designed to assess
Energy& Momentum ~Learning Guide Name:
 Energy& Momentum ~Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the
Energy& Momentum ~Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The Pre-Reading is marked, based on effort, completeness, and neatness (not accuracy). The rest of the
Life (and Fewer Deaths) after Seat Belts
 Activity 5 Life (and Fewer Deaths) after Seat Belts Activity 5 Life (and Fewer Deaths) after Seat Belts GOALS In this activity you will: Understand the role of safety belts. Compare the effectiveness of
Activity 5 Life (and Fewer Deaths) after Seat Belts Activity 5 Life (and Fewer Deaths) after Seat Belts GOALS In this activity you will: Understand the role of safety belts. Compare the effectiveness of
Bellringer Day In your opinion, what are the five most important lab safety rules?
 Bellringer Day 01 1. In your opinion, what are the five most important lab safety rules? Lab Safety Video Lab Safety Map See if you can identify the lab safety equipment around the room. You can discuss
Bellringer Day 01 1. In your opinion, what are the five most important lab safety rules? Lab Safety Video Lab Safety Map See if you can identify the lab safety equipment around the room. You can discuss
CHAPTER 6 TEST. Directions: Show work on problems. Choose correct answer when available and place next to the question number.
 CHAPTER 6 TEST Directions: Show work on problems. Choose correct answer when available and place next to the question number. 1. What is inertia? A. the amount of matter in an object B. the force of gravity
CHAPTER 6 TEST Directions: Show work on problems. Choose correct answer when available and place next to the question number. 1. What is inertia? A. the amount of matter in an object B. the force of gravity
Section 2. Gravitational Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy: What Goes Up and What Comes Down. What Do You See? What Do You Think?
 Thrills and Chills Section Gravitational Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy: What Goes Up and What Comes Down Florida Next Generation Sunshine State Standards: Additional Benchmarks met in Section SC.91.N..4
Thrills and Chills Section Gravitational Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy: What Goes Up and What Comes Down Florida Next Generation Sunshine State Standards: Additional Benchmarks met in Section SC.91.N..4
Lab/Demo 5 Periodic Motion and Momentum PHYS 1800
 Lab/Demo 5 Periodic Motion and Momentum PHYS 1800 Objectives: Learn to recognize and describe periodic motion. Develop some intuition for the principle of conservation of energy in periodic systems. Use
Lab/Demo 5 Periodic Motion and Momentum PHYS 1800 Objectives: Learn to recognize and describe periodic motion. Develop some intuition for the principle of conservation of energy in periodic systems. Use
Lesson 11: Newton s Third Law: Quantitative
 11.1 Observe and Find a Pattern Lesson 11: Newton s Third Law: Quantitative The goal of this experiment is to determine a mathematical relationship between the force that object A exerts on object B and
11.1 Observe and Find a Pattern Lesson 11: Newton s Third Law: Quantitative The goal of this experiment is to determine a mathematical relationship between the force that object A exerts on object B and
Preview. Momentum and Collisions Section 1. Section 1 Momentum and Impulse. Section 2 Conservation of Momentum
 Momentum and Collisions Section 1 Preview Section 1 Momentum and Impulse Section 2 Conservation of Momentum Section 3 Elastic and Inelastic Collisions Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Momentum
Momentum and Collisions Section 1 Preview Section 1 Momentum and Impulse Section 2 Conservation of Momentum Section 3 Elastic and Inelastic Collisions Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Momentum
CONSERVATION of MOMENTUM
 1 CONSERVATION of MOMENTUM Purpose: Understand conservation of momentum and energy in elastic and inelastic collisions. Examine the concept of impulse in a real-life situation. Apparatus: Pasco track,
1 CONSERVATION of MOMENTUM Purpose: Understand conservation of momentum and energy in elastic and inelastic collisions. Examine the concept of impulse in a real-life situation. Apparatus: Pasco track,
KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS
 Measuring 74 40- to 2-3 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R AT O R Y Students use a cart, ramp, and track to measure the time it takes for a cart to roll 100 centimeters. They then calculate
Measuring 74 40- to 2-3 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R AT O R Y Students use a cart, ramp, and track to measure the time it takes for a cart to roll 100 centimeters. They then calculate
Sir Isaac Newton ( ) One of the world s greatest scientists Developed the 3 Laws of Motion
 Motion and Forces Sir Isaac Newton (1643 1727) One of the world s greatest scientists Developed the 3 Laws of Motion Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law Law of Inertia 2 nd Law Force = Mass x Acceleration
Motion and Forces Sir Isaac Newton (1643 1727) One of the world s greatest scientists Developed the 3 Laws of Motion Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law Law of Inertia 2 nd Law Force = Mass x Acceleration
Lesson Plan Chapter 4
 CHAPTER 4 Forces and the Laws of Motion 10/21/13-11/1/13 Chapter Opener Tapping Prior Knowledge, TE Review previously learned concepts and check for preconceptions about the chapter content. Discovery
CHAPTER 4 Forces and the Laws of Motion 10/21/13-11/1/13 Chapter Opener Tapping Prior Knowledge, TE Review previously learned concepts and check for preconceptions about the chapter content. Discovery
14300 Dynamics Carts w/o Hoops Teachers Instructions
 14300 Dynamics Carts w/o Hoops Teachers Instructions Required Accessories o (2) Table stops (wooden bars) o (4) C-Clamps o (2) Recording Timers (#15210 or #15215) o (5) Bricks or Books (or other identical
14300 Dynamics Carts w/o Hoops Teachers Instructions Required Accessories o (2) Table stops (wooden bars) o (4) C-Clamps o (2) Recording Timers (#15210 or #15215) o (5) Bricks or Books (or other identical
Solution Figure 2(a) shows the situation. Since there is no net force acting on the system, momentum is conserved. Thus,
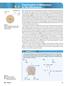 large rock Mars 5.4 small fragments to Earth Figure 1 The two-dimensional nature of the collision between a rock and the surface of Mars Conservation of Momentum in Two Dimensions How could a chunk of
large rock Mars 5.4 small fragments to Earth Figure 1 The two-dimensional nature of the collision between a rock and the surface of Mars Conservation of Momentum in Two Dimensions How could a chunk of
Conservation of Momentum in One Dimension
 Conservation of Momentum in One Dimension 5.2 Imagine standing at rest on skates on essentially frictionless ice, and throwing a basketball forward (Figure 1). As the ball moves in one direction, you move
Conservation of Momentum in One Dimension 5.2 Imagine standing at rest on skates on essentially frictionless ice, and throwing a basketball forward (Figure 1). As the ball moves in one direction, you move
Forces, Momentum, Work and Energy
 Adult Basic Education Science Forces, Momentum, Work and Energy Prerequisite: Physics 2104A Credit Value: 1 Physics Concentration Physics 1104 Physics 2104A Physics 2104C Physics 3104A Physics 3104B Physics
Adult Basic Education Science Forces, Momentum, Work and Energy Prerequisite: Physics 2104A Credit Value: 1 Physics Concentration Physics 1104 Physics 2104A Physics 2104C Physics 3104A Physics 3104B Physics
Calculating Average Speed and Comparing Kinetic and Potential Energy
 Calculating Average Speed and Comparing Kinetic and Potential Energy Author: Matthew Kurth Grade Level: pre-ap 6 th grade Science (45 minute class) Sources: CPO Science (Force and Motion) o Curriculum
Calculating Average Speed and Comparing Kinetic and Potential Energy Author: Matthew Kurth Grade Level: pre-ap 6 th grade Science (45 minute class) Sources: CPO Science (Force and Motion) o Curriculum
Activity P11: Collision Impulse and Momentum (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor)
 Name Class Date Activity P11: Collision Impulse and Momentum (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Newton s Laws P11 Impulse.DS P14 Collision P14_COLL.SWS
Name Class Date Activity P11: Collision Impulse and Momentum (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) Newton s Laws P11 Impulse.DS P14 Collision P14_COLL.SWS
Lab 8 Impulse and Momentum
 b Lab 8 Impulse and Momentum Physics 211 Lab What You Need To Know: The Physics Today we will deal with two physical concepts: impulse and momentum. For both, it turns out to be harder to say what they
b Lab 8 Impulse and Momentum Physics 211 Lab What You Need To Know: The Physics Today we will deal with two physical concepts: impulse and momentum. For both, it turns out to be harder to say what they
PRELAB: COLLISIONS Collisions, p. 1/15
 PRELAB: COLLISIONS Collisions, p. 1/15 1. What is your Prediction 1-7 when the truck is accelerating? Explain the reasoning behind your prediction. 2. If you set up the force probes according to the instructions
PRELAB: COLLISIONS Collisions, p. 1/15 1. What is your Prediction 1-7 when the truck is accelerating? Explain the reasoning behind your prediction. 2. If you set up the force probes according to the instructions
Unit 5: Momentum. Vocabulary: momentum, impulse, center of mass, conservation of momentum, elastic collision, inelastic collision.
 Text: Chapter 9 Unit 5: Momentum NAME: Problems (p. 229-240) #1: 18, 20, 27, 31, 37 (momentum & impulse) #2: 40, 42, 45, 46, 100 (conservation of momentum) #3: 49, 103, 123, 129 (collisions) Vocabulary:
Text: Chapter 9 Unit 5: Momentum NAME: Problems (p. 229-240) #1: 18, 20, 27, 31, 37 (momentum & impulse) #2: 40, 42, 45, 46, 100 (conservation of momentum) #3: 49, 103, 123, 129 (collisions) Vocabulary:
Evaluation copy. Momentum: A Crash Lesson. computer OBJECTIVES MATERIALS
 Momentum: A Crash Lesson Computer 38 An object s momentum depends on both its mass and its velocity. Momentum can be expressed by the formula p = mv where p = momentum (in g m/s), m = mass (in g), and
Momentum: A Crash Lesson Computer 38 An object s momentum depends on both its mass and its velocity. Momentum can be expressed by the formula p = mv where p = momentum (in g m/s), m = mass (in g), and
Extra Circular Motion Questions
 Extra Circular Motion Questions Elissa is at an amusement park and is driving a go-cart around a challenging track. Not being the best driver in the world, Elissa spends the first 10 minutes of her go-cart
Extra Circular Motion Questions Elissa is at an amusement park and is driving a go-cart around a challenging track. Not being the best driver in the world, Elissa spends the first 10 minutes of her go-cart
P5 Momentum Collision Calculations
 P5 Momentum Collision Calculations Question Practice Name: Class: Date: Time: 88 minutes Marks: 88 marks Comments: PHYSICS ONLY Page of 24 (a) How can the momentum of an object be calculated? (2) (b) In
P5 Momentum Collision Calculations Question Practice Name: Class: Date: Time: 88 minutes Marks: 88 marks Comments: PHYSICS ONLY Page of 24 (a) How can the momentum of an object be calculated? (2) (b) In
Chapter5 SUMMARY. Key Equations
 Chapter5 SUMMARY Key Expectations define and describe the concepts and units related to momentum (momentum, impulse, elastic collisions, inelastic collisions) (5.1, 5.2, 5.3) analyze, with the aid of vector
Chapter5 SUMMARY Key Expectations define and describe the concepts and units related to momentum (momentum, impulse, elastic collisions, inelastic collisions) (5.1, 5.2, 5.3) analyze, with the aid of vector
AP Physics II Summer Packet
 Name: AP Physics II Summer Packet Date: Period: Complete this packet over the summer, it is to be turned it within the first week of school. Show all work were needed. Feel free to use additional scratch
Name: AP Physics II Summer Packet Date: Period: Complete this packet over the summer, it is to be turned it within the first week of school. Show all work were needed. Feel free to use additional scratch
Lab 8 Impulse and Momentum
 b Lab 8 Impulse and Momentum What You Need To Know: The Physics There are many concepts in physics that are defined purely by an equation and not by a description. In some cases, this is a source of much
b Lab 8 Impulse and Momentum What You Need To Know: The Physics There are many concepts in physics that are defined purely by an equation and not by a description. In some cases, this is a source of much
Science 20. Unit B: Changes in Motion. Assignment Booklet B2
 Science 20 Unit B: Changes in Motion Assignment Booklet B2 FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY Summary Teacher s Comments Chapter 2 Assignment Total Possible Marks 36 Your Mark Science 20 Unit B: Changes in Motion
Science 20 Unit B: Changes in Motion Assignment Booklet B2 FOR TEACHER S USE ONLY Summary Teacher s Comments Chapter 2 Assignment Total Possible Marks 36 Your Mark Science 20 Unit B: Changes in Motion
PHYSICS 220 LAB #5: COLLISIONS
 Name: Partners: PHYSICS 220 LAB #5: COLLISIONS A large pickup truck and a small car, both moving at the same speed, are about to collide head on. If they get stuck together, which way will the wreckage
Name: Partners: PHYSICS 220 LAB #5: COLLISIONS A large pickup truck and a small car, both moving at the same speed, are about to collide head on. If they get stuck together, which way will the wreckage
Newton s Laws of Motion
 3 Newton s Laws of Motion Key Concept Newton s laws of motion describe the relationship between forces and the motion of an object. What You Will Learn Newton s first law of motion states that the motion
3 Newton s Laws of Motion Key Concept Newton s laws of motion describe the relationship between forces and the motion of an object. What You Will Learn Newton s first law of motion states that the motion
Physics Curriculum Map school year
 Physics Curriculum Map- 2014-2015 school year. Quarter Page 1 2-6 2 7-9 3 10-12 4 13-16 This map is a result of surveys and the physics committee- we will implement for the 2013 school year. Please keep
Physics Curriculum Map- 2014-2015 school year. Quarter Page 1 2-6 2 7-9 3 10-12 4 13-16 This map is a result of surveys and the physics committee- we will implement for the 2013 school year. Please keep
UNIT 2G. Momentum & It s Conservation
 Name: Date:_ UNIT 2G Momentum & It s Conservation Momentum & Newton s 2 nd Law of Motion Newton s 2 nd Law states When an unbalanced force acts upon a body, it accelerates that body in the direction of
Name: Date:_ UNIT 2G Momentum & It s Conservation Momentum & Newton s 2 nd Law of Motion Newton s 2 nd Law states When an unbalanced force acts upon a body, it accelerates that body in the direction of
Newton s Second Law: Push or Pull
 Chapter 2 Physics in Action SECTION 3 Newton s Second Law: Push or Pull Section Overview Students observe how acceleration is directly proportional to the force applied and inversely proportional to an
Chapter 2 Physics in Action SECTION 3 Newton s Second Law: Push or Pull Section Overview Students observe how acceleration is directly proportional to the force applied and inversely proportional to an
Measuring Momentum: Using distance moved after impact to estimate velocity
 Case File 6 Measuring Momentum: Using distance moved after impact to estimate velocity Explore how the speed of an impacting vehicle causes a stationary object to move. Police Report Last Tuesday night,
Case File 6 Measuring Momentum: Using distance moved after impact to estimate velocity Explore how the speed of an impacting vehicle causes a stationary object to move. Police Report Last Tuesday night,
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions
 Elastic and Inelastic Collisions - TA Version Physics Topics If necessary, review the following topics and relevant textbook sections from Serway / Jewett Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 9th Ed.
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions - TA Version Physics Topics If necessary, review the following topics and relevant textbook sections from Serway / Jewett Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 9th Ed.
Physics. Impulse & Momentum
 Physics Impulse & Momentum Warm up - Write down everything you know about impulse and momentum. Objectives Students will learn the definitions and equations for impulse, momentum, elastic and inelastic
Physics Impulse & Momentum Warm up - Write down everything you know about impulse and momentum. Objectives Students will learn the definitions and equations for impulse, momentum, elastic and inelastic
AP Physics 1 Momentum
 AP Physics 1 Momentum 2017-07-20 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section Momentum Impulse-Momentum Equation The Momentum of a System of Objects Conservation of Momentum
AP Physics 1 Momentum 2017-07-20 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section Momentum Impulse-Momentum Equation The Momentum of a System of Objects Conservation of Momentum
(a) (i) The toy has a mass of 0.15 kg and moves forward with a velocity of 0.08 m/s. How is the momentum of the toy calculated?
 MOMENTUM Q1. The diagram shows an air-driven toy. When the electric motor is switched on the fan rotates. The fan pushes air backwards making the toy move forwards. The toy has a mass of 0.15 kg and moves
MOMENTUM Q1. The diagram shows an air-driven toy. When the electric motor is switched on the fan rotates. The fan pushes air backwards making the toy move forwards. The toy has a mass of 0.15 kg and moves
Friction. Friction is a force that resists the motion of objects or surfaces. Many kinds of friction exist.
 Friction Friction is a force that resists the motion of objects or surfaces. Many kinds of friction exist. Friction Friction depends on both of the surfaces in contact. When the hockey puck slides on
Friction Friction is a force that resists the motion of objects or surfaces. Many kinds of friction exist. Friction Friction depends on both of the surfaces in contact. When the hockey puck slides on
9 Momentum and Its Conservation 2 Conservation of Momentum MAINIDEA
 9 Momentum and Its Conservation 2 Conservation of Momentum MAINIDEA Write the Main Idea for this section. REVIEW VOCABULARY Recall and write the definition of the Review Vocabulary term. NEW VOCABULARY
9 Momentum and Its Conservation 2 Conservation of Momentum MAINIDEA Write the Main Idea for this section. REVIEW VOCABULARY Recall and write the definition of the Review Vocabulary term. NEW VOCABULARY
AP PHYSICS C Mechanics - SUMMER ASSIGNMENT FOR
 AP PHYSICS C Mechanics - SUMMER ASSIGNMENT FOR 2018-2019 Dear Student: The AP physics course you have signed up for is designed to prepare you for a superior performance on the AP test. To complete material
AP PHYSICS C Mechanics - SUMMER ASSIGNMENT FOR 2018-2019 Dear Student: The AP physics course you have signed up for is designed to prepare you for a superior performance on the AP test. To complete material
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES. Duration of resource: 12 Minutes. Year of Production: Stock code: VEA12054
 ADDITIONAL RESOURCES Any type of motion means a force is at work it is one of the most fundamental concepts in physics, and has formed the basis of the work of many pioneering scientists, including Isaac
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES Any type of motion means a force is at work it is one of the most fundamental concepts in physics, and has formed the basis of the work of many pioneering scientists, including Isaac
IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences 0654 Unit 18: Forces and motion
 IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences 0654 Unit 18: Forces and motion Recommended Prior Knowledge Students should have a basic knowledge of the effects of balanced and unbalanced forces. They should have good graphing
IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences 0654 Unit 18: Forces and motion Recommended Prior Knowledge Students should have a basic knowledge of the effects of balanced and unbalanced forces. They should have good graphing
Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces
 Table of Contents Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces Section 1: Describing Motion Section 2: Acceleration Section 3: Motion and Forces 1 Motion Are distance and time important in describing running
Table of Contents Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces Section 1: Describing Motion Section 2: Acceleration Section 3: Motion and Forces 1 Motion Are distance and time important in describing running
