Today. Clicker Question. Announcements: Today: SETI loose ends Atoms and Nuclei. Clicker question. Clicker Question
|
|
|
- Kenneth Richard Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Announcements: Today HW#9 is due Friday April 16 at 8:00 am Exam #3 Thurs. April 29 Final Exam will be on CAPA Today: SETI loose ends Atoms and Nuclei If the Sun suddenly became a black hole, what would happen to the Earth s orbit? A). The Earth would start a spiral into the Sun B). The Earth would fly off out of the solar system C). Depending of the mass of the Sun, the Earth s orbit would approximately double or be approximately half of what it is now D). The Earth would join all the other plants at the same radius from the black hole E). Nothing ISP209s10 Lecture ISP209s10 Lecture If the Sun suddenly became a black hole, what would happen to the Earth s orbit? A). The Earth would start a spiral into the Sun B). The Earth would fly off out of the solar system C). Depending of the mass of the Sun, the Earth s orbit would approximately double or be approximately half of what it is now D). The Earth would join all the other plants at the same radius from the black hole E). Nothing Clicker question True or False. In principle, it is only possible for extremely large Masses to form a black hole. A) True B) False ISP209s10 Lecture ISP209s10 Lecture 23-4-
2 Clicker question True or False. In principle, it is only possible for extremely large Masses to form a black hole. A) True B) False Given any mass M, if you squish it down to a sufficiently small radius ( Schwartzchild radius ), the escape velocity becomes equal to c, which signals that a black hole has formed. ISP209s10 Lecture Drake Equation # civilizations in Milky Way = N* f p n e f l f i f c f L N number of stars in the Milky Way (200 billion) F p fraction of stars with planets (0.2 to 0.4) n e number of planets where life may exist per star (1 to 5) f l fraction where life begins (0-1) f i fraction of life that develops intelligence (0-1) f c fraction of intelligent life that develops communication (0-1) f L fraction of a star s life when intelligent life survives (0-1) The red factors are complete guesses, so the final answer can be billions or zero! Some critics say this makes the Drake Equation meaningless. Others say it still helps identify key factors. ISP209s10 Lecture Drake Equation # civilizations in Milky Way = N* f p n e f l f i f c f L N number of stars in the Milky Way (200 billion) F p fraction of stars with planets (0.5) n e number of planets where life may exist per star (2) f l fraction where life begins (1) f i fraction of life that develops intelligence (0.2) f c fraction of intelligent life that develops communication (1) f L fraction of a star s life when intelligent life survives (3x10-7 ) Drake s guesses are shown in blue. His final answer is ~ 10,000 ISP209s10 Lecture Fermi s Question: Where is Everybody? Nobel-winning physicist who was famous for back of the envelope estimates. Much like Drake, he estimated there should be many intelligent civilizations in our universe. Why then, haven t we made contact? Fermi came up with 3 possible answers: 1) Interstellar travel is impossible 2) Interstellar travel is possible, but not worth the effort 3) Civilizations don t survive long enough to develop interstellar travel ISP209s10 Lecture 23-8-
3 Search for Extra Terrestrial Intelligence (SETI) We have been broadcasting EM signals (radio/tv) into space unintentionally for ~ 100 years Recently (1970 s), we have sent intentional signals to a star cluster 27,000 light-years away We also have been listening for radio signals from intelligent civilizations (SETI institute) About 10% of stars within 40,000 light-years have been searched with no luck. They re either using too weak signals, or a different frequency range, or not transmitting EM signals, or maybe they re not there! ISP209s10 Lecture Want to help SETI make 1st contact? go to and download the software you find there. Your computer will search for extraterrestrial signals by crunching data from SETI s telescopes when you are not using it. Watch Film => ISP209s10 Lecture From Large to Small Atomic Nuclei Atoms Atomic Nucleus A Proton Nucleus at center of atom discovered by the backscattering of!-particles (which are much heavier than electrons) off gold atoms (1911) Contradicted the previous plum pudding model Electrons embedded in a positive charge background like raisins in pudding Made of nuclei and electrons. Size: 10-9 m Made of neutrons and protons. Size: m ISP209s10 Lecture Made of quarks. -Atomic # (aka Proton Number) Z determines the element Size: Neutron # N m -Mass # (aka atomic mass A = N + Z) A neutron has ddu quarks. ISP209s10 Lecture
4 The Nucleus The nucleus contains more than 99.95% of an atom s mass, but only 1E-15 of its volume! The nucleons are held together by the strong force, even though the protons repel each other very strongly. Mass Number Atomic Number (or Proton Number) Element Neutron Number ISP209s10 Lecture The Chart of the Nuclides: A Map of All Known and Possible Nuclei Atomic Nuclei and Elements The number of protons determine the element (oxygen). The number of neutrons+protons determines the atomic mass (16 as shown). This nucleus is 16 O. ISP209s10 Lecture Radioactivity A radioactive nucleus is unstable: Alpha Decay 238 Pu " 234 U + 4 He Beta Decay Gamma Decay 152 Dy* " 152 Dy +! Fission 238 Pu heated by its own radioactivity. 248 Cm " 144 Ce Sr n (spontaneous) 1 n U " 141 Ba + 92 Kr n (induced) ISP209s10 Lecture Why are some nuclei unstable? Two fundamental tendencies in nature: Move toward higher entropy Move toward lower potential energy For most nuclear processes the change in entropy is ~0. Therefore, energy dominates. Total Energy per Mass Unit 6 Li 56 Fe Mass Number 238 U ISP209s10 Lecture
5 Alpha Decay as a Quantum Tunneling Event The alpha particle is like a ball that is contained in a box (the nucleus). QM tells us the wave function of the ball in non-zero outside The box. There is a finite probability you find the ball outside the box as if it tunneled thru the wall. ISP209s10 Lecture Half-Life and Radioactive Decay Law Radioactive decay is a quantum phenomena. Can t say when one given nucleus will decay. Only averages. Find a exponential decay law Amount at time t Original Amount N = N 0 e -" t Decay constant (different for each Type of nucleus) ISP209s10 Lecture Half-Life and Radioactive Decay Law Radioactive decay is a quantum phenomena. Can t say when one given nucleus will decay. Only averages. A more useful form: ( t 1/2 = ln(2)/# ~.693/#) ISP209s10 Lecture Sample Problem Suppose we find a sample of material that has 43.5% of the expected original amount. The half-life of the material is 23.0 days. What is the best estimate for the age of the sample? ( t t 1 / 2 ) ( t 23.0 d) N & 1 # N & 1 # = $! ' = = $! N0 % 2 " N0 % 2 " - ln = ln +,! t = ' % ( 1/ 2) & t $ " 23.0 d # ( 23.0 d)( ln 0.435) ln ( 1/ 2) * ' t $ ( = % ln(1/ 2) 23.0 " ) & d # = 27.6 d Math tip: ln(x y ) = yln(x) ISP209s10 Lecture
6 Radioisotope Dating 14 C is an isotope of carbon that is produced continually by the interaction of cosmic rays with 14 N in the atmosphere: 1 n + 14 N " 14 C + 1 H An organism establishes an equilibrium with 14 C by breathing in 14 CO 2. After death, no new 14 C is absorbed, so it decays away with a half-life of 5730 years. ISP209s10 Lecture Examples of Radioactive Dating 14 C (half-life = 5730 y) is used to date archeological objects. Normal living material has a certain amount of 14 C, which is produced in the atmosphere. 40 K (half-life = 1.25 By) is used to date rocks. It decays 10% of the time to 40 Ar which is not naturally found in most rocks. 238 U (half-life = 4.5 By) is used to date the Earth, the Sun, and other stars. This is one of the ways we estimate that the Earth is 4.5 By old. ISP209s10 Lecture Suppose that fresh tuna contains a certain amount of an isotope that has a half-life of 10 years. Once canned the radioactive isotope decays and is not replaced. If we find a tuna can that has half the expected amount of the nucleus, how old is it? A). We can not tell B). 1 year C). 10 years D). 20 years E).! year Suppose that fresh tuna contains a certain amount of an isotope that has a half-life of 10 years. Once canned the radioactive isotope decays and is not replaced. If we find a tuna can that has half the expected amount of the nucleus, how old is it? A). We can not tell B). 1 year C). 10 years t 1/2 = time for 1/2 of the nuclei to decay D). 20 years E).! year ISP209s10 Lecture ISP209s10 Lecture
7 After three half-lives, what fraction of a radioactive material is left? A). 1/2 B). (1/2) (1/2) (1/2) = 1/8 C). (1/2) (1/2) = 1/4 D). (1/2) (1/2) (1/2) (1/2) (1/2) (1/2) = 1/64 E). 2 3 = 8 After three half-lives, what fraction of a radioactive material is left? A). 1/2 B). (1/2) (1/2) (1/2) = 1/8 C). (1/2) (1/2) = 1/4 D). (1/2) (1/2) (1/2) (1/2) (1/2) (1/2) = 1/64 E). 2 3 = 8 3 half-lives means the Amount has been cut By 1/2 three times. ISP209s10 Lecture ISP209s10 Lecture The equation for fraction remaining is A & 1 # f = = $! B % 2 " Which letter in the above equation is the half-life? A). A B). B C). C C ISP209s10 Lecture The equation for fraction remaining is A & 1 # f = = $! B % 2 " Which letter in the above equation is the half-life? A). A B). B C). C C ISP209s10 Lecture
8 DATA: Take the half-life of 14-C to be 6000 years. If we find a sample of old bone that has (1/16) the normal amount of 14-C found in living bone, how old is the bone? A) years B). 12,000 years C). 18,000 years D). 24,000 years E). (1/6000) 4 years ISP209s10 Lecture DATA: Take the half-life of 14-C to be 6000 years. If we find a sample of old bone that has (1/16) the normal amount of 14-C found in living bone, how old is the bone? A) years B). 12,000 years C). 18,000 years D). 24,000 years E). (1/6000) 4 years You could have used the equation: Equivalently, you could notice that 1/16 = 1/2 x 1/2 x 1/2 x 1/2 => 4 half-lives have elapsed. 4 x 6000 = 24,000 years ISP209s10 Lecture Applications: Nuclear Power A nuclear reactor is a fancy way of generating heat to produce steam. The rest works like a traditional power plant. All nuclear plants produce fissile material as part of their operation. This had led to concerns about proliferation of this material, which could be used for a dirty bomb or possibly to make a nuclear weapon. Nuclear plants produce radioactive wastes which must be stored safely, possibly for tens of thousands of years. Fission Chain Reaction This process repeats continuously. Nuclear Reactor: Stays at criticality. Nuclear Weapon: Reaction goes supercritical. ISP209s10 Lecture ISP209s10 Lecture Nuclear plants do not produce greenhouse gases.
9 Example of use Nuclear Medicine Radiolabelled compounds can be injected into the body for diagnostic purposes. Similarly, compounds can be attached to tumors to kill them (but leaves them in place). X-rays, CT scans, PET scans. Average Dose per Year We are constantly exposed to small amounts of radiation. As long as the damage is not too great our natural repair mechanisms fix the damage: Source Dose (mrem/year) Radon 200 Medical/Dental X-Rays 40 Internal Sources 40 Other Natural Sources 60 Consumer Products ~11 Roger Ressmeyer/Corbis ISP209s10 Lecture ISP209s10 Lecture Average Dose per Year (continued) Source Dose (mrem/year) Nuclear Medicine ~15 Fallout from weapons testing ~2 Nuclear Power ~0.4 Coal Power ~1.2 Total (U.S. Average) ~360 Smoking one pack per day Smoking two packs per day ISP209s10 Lecture RISK Average Loss of Life Expectancy (days) Being male 2800 Being unmarried 2000 Smoking cigarettes (1 pack/day) 1600 Coal Mining 1100 Cancer lb overweight 900; 15 lb overweight 450 Driving a car (risk of accidents) 200 Alcohol 130 Homicide 90 Drowning 40 Diet drinks, one per day for life 2 Power generated by all nuclear 1.5 (Union Concerned Scientists) Hurricanes and tornadoes 1 ISP209s10 Lecture Airline crashes 1
4.4 Atomic structure Notes
 4.4 Atomic structure Notes Ionising radiation is hazardous but can be very useful. Although radioactivity was discovered over a century ago, it took many nuclear physicists several decades to understand
4.4 Atomic structure Notes Ionising radiation is hazardous but can be very useful. Although radioactivity was discovered over a century ago, it took many nuclear physicists several decades to understand
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 21. Nuclear Chemistry. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 21, Inc. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Energy: Chemical vs. Chemical energy is associated with making and breaking chemical bonds. energy is enormous in comparison.
Lecture Presentation Chapter 21, Inc. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Energy: Chemical vs. Chemical energy is associated with making and breaking chemical bonds. energy is enormous in comparison.
P4 Quick Revision Questions
 P4 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only P3 for AQA GCSE examination 2018 onwards Question 1... of 50 What are the components of an atom, their location and their charge?
P4 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only P3 for AQA GCSE examination 2018 onwards Question 1... of 50 What are the components of an atom, their location and their charge?
The basic structure of an atom is a positively charged nucleus composed of both protons and neutrons surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
 4.4 Atomic structure Ionising radiation is hazardous but can be very useful. Although radioactivity was discovered over a century ago, it took many nuclear physicists several decades to understand the
4.4 Atomic structure Ionising radiation is hazardous but can be very useful. Although radioactivity was discovered over a century ago, it took many nuclear physicists several decades to understand the
Chapter 10. Table of Contents. Section 1 What Is Radioactivity? Section 2 Nuclear Fission and Fusion. Section 3 Nuclear Radiation Today
 Nuclear Chemistry Table of Contents Section 1 What Is Radioactivity? Section 2 Nuclear Fission and Fusion Section 3 Nuclear Radiation Today Section 1 What Is Radioactivity? Bellringer Before studying about
Nuclear Chemistry Table of Contents Section 1 What Is Radioactivity? Section 2 Nuclear Fission and Fusion Section 3 Nuclear Radiation Today Section 1 What Is Radioactivity? Bellringer Before studying about
Friday, 05/06/16 6) HW QUIZ MONDAY Learning Target (NEW)
 Friday, 05/06/16 1) Warm-up: If you start with 100g of a radioactive substance, how much will be left after 3 half-lives? 2) Review HW & Nuclear Notes 3) Complete Modeling Energy Investigation 4) Complete:
Friday, 05/06/16 1) Warm-up: If you start with 100g of a radioactive substance, how much will be left after 3 half-lives? 2) Review HW & Nuclear Notes 3) Complete Modeling Energy Investigation 4) Complete:
4.4.1 Atoms and isotopes The structure of an atom Mass number, atomic number and isotopes. Content
 4.4 Atomic structure Ionising radiation is hazardous but can be very useful. Although radioactivity was discovered over a century ago, it took many nuclear physicists several decades to understand the
4.4 Atomic structure Ionising radiation is hazardous but can be very useful. Although radioactivity was discovered over a century ago, it took many nuclear physicists several decades to understand the
Exam #3. Final Exam. Exam 3 review. How do we measure properties of a star? A detailed outline of study topics is here:
 Exam #3 Exam #3 is Thursday 4/9 in this room You can bring page of notes (front and back) Bring your calculator and a # pencil Exam 3 covers material from 4/1 onward (only 8 lectures) Consequently, no
Exam #3 Exam #3 is Thursday 4/9 in this room You can bring page of notes (front and back) Bring your calculator and a # pencil Exam 3 covers material from 4/1 onward (only 8 lectures) Consequently, no
Ch Radioactivity. Henry Becquerel, using U-238, discovered the radioactive nature of elements in 1896.
 Ch. 10 - Radioactivity Henry Becquerel, using U-238, discovered the radioactive nature of elements in 1896. Radioactivity the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus emits charged particles and energy
Ch. 10 - Radioactivity Henry Becquerel, using U-238, discovered the radioactive nature of elements in 1896. Radioactivity the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus emits charged particles and energy
Core Questions Physics unit 4 - Atomic Structure
 Core Questions Physics unit 4 - Atomic Structure No. Question Answer 1 What did scientists think about atoms before the discovery of the They were tiny spheres that could not be broken up electron? 2 Which
Core Questions Physics unit 4 - Atomic Structure No. Question Answer 1 What did scientists think about atoms before the discovery of the They were tiny spheres that could not be broken up electron? 2 Which
Unit 3: Chemistry in Society Nuclear Chemistry Summary Notes
 St Ninian s High School Chemistry Department National 5 Chemistry Unit 3: Chemistry in Society Nuclear Chemistry Summary Notes Name Learning Outcomes After completing this topic you should be able to :
St Ninian s High School Chemistry Department National 5 Chemistry Unit 3: Chemistry in Society Nuclear Chemistry Summary Notes Name Learning Outcomes After completing this topic you should be able to :
Ch 17 Radioactivity & Nuc. Chemistry Study Guide Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON
 Ch 17 Radioactivity & Nuc. Chemistry Study Guide Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON Name No-Calculators Allowed /65 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
Ch 17 Radioactivity & Nuc. Chemistry Study Guide Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON Name No-Calculators Allowed /65 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
Radioactivity. L 38 Modern Physics [4] Hazards of radiation. Nuclear Reactions and E = mc 2 Einstein: a little mass goes a long way
![Radioactivity. L 38 Modern Physics [4] Hazards of radiation. Nuclear Reactions and E = mc 2 Einstein: a little mass goes a long way Radioactivity. L 38 Modern Physics [4] Hazards of radiation. Nuclear Reactions and E = mc 2 Einstein: a little mass goes a long way](/thumbs/80/81251381.jpg) L 38 Modern Physics [4] Nuclear physics what s inside the nucleus and what holds it together what is radioactivity, halflife carbon dating Nuclear energy nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear reactors
L 38 Modern Physics [4] Nuclear physics what s inside the nucleus and what holds it together what is radioactivity, halflife carbon dating Nuclear energy nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear reactors
A Nuclear Power Plant
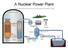 A Nuclear Power Plant Fallout from Chernobyl The question that all countries asked in 1986, and continue to ask to this day: Could it happen here? Radioactivity Np Pu+ 239 239 0 93 94 1 Beta decay the
A Nuclear Power Plant Fallout from Chernobyl The question that all countries asked in 1986, and continue to ask to this day: Could it happen here? Radioactivity Np Pu+ 239 239 0 93 94 1 Beta decay the
Chapter 10. Section 10.1 What is Radioactivity?
 Chapter 10 Section 10.1 What is Radioactivity? What happens when an element undergoes radioactive decay? How does radiation affect the nucleus of an unstable isotope? How do scientists predict when an
Chapter 10 Section 10.1 What is Radioactivity? What happens when an element undergoes radioactive decay? How does radiation affect the nucleus of an unstable isotope? How do scientists predict when an
P7 Radioactivity. Student Book answers. P7.1 Atoms and radiation. Question Answer Marks Guidance
 P7. Atoms and radiation a radiation from U consists = particles, radiation from lamp = electromagnetic waves, radiation from U is ionising, radiation from lamp is non-ionising b radioactive atoms have
P7. Atoms and radiation a radiation from U consists = particles, radiation from lamp = electromagnetic waves, radiation from U is ionising, radiation from lamp is non-ionising b radioactive atoms have
Nuclear Chemistry Unit
 Nuclear Chemistry Unit January 28th HW Due Thurs. 1/30 Read pages 284 291 Define: Radioactivity Nuclear Radiation Alpha Particle Beta Particle Gamma Ray Half-Life Answer: -Questions 1-3 -Write the symbols
Nuclear Chemistry Unit January 28th HW Due Thurs. 1/30 Read pages 284 291 Define: Radioactivity Nuclear Radiation Alpha Particle Beta Particle Gamma Ray Half-Life Answer: -Questions 1-3 -Write the symbols
Radioactivity One of the pieces of evidence for the fact that atoms are made of smaller particles came from the work of Marie Curie
 1 Nuclear Chemistry Radioactivity 2 One of the pieces of evidence for the fact that atoms are made of smaller particles came from the work of Marie Curie (1876-1934). She discovered radioactivity or radioactive
1 Nuclear Chemistry Radioactivity 2 One of the pieces of evidence for the fact that atoms are made of smaller particles came from the work of Marie Curie (1876-1934). She discovered radioactivity or radioactive
Science 10 Radioactivity Review v3
 Class: Date: Science 10 Radioactivity Review v3 Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. An atom
Class: Date: Science 10 Radioactivity Review v3 Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. An atom
Unit 12: Nuclear Chemistry
 Unit 12: Nuclear Chemistry 1. Stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation.
Unit 12: Nuclear Chemistry 1. Stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation.
Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 30. Nuclear Physics. Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 30 Nuclear Physics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Atomic Nuclei Rutherford s discovery of the atomic nucleus caused scientists
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 30 Nuclear Physics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Atomic Nuclei Rutherford s discovery of the atomic nucleus caused scientists
Atomic Structure and Radioactivity
 Atomic Structure and Radioactivity Models of the atom know: Plum pudding model of the atom and Rutherford and Marsden s alpha experiments, being able to explain why the evidence from the scattering experiment
Atomic Structure and Radioactivity Models of the atom know: Plum pudding model of the atom and Rutherford and Marsden s alpha experiments, being able to explain why the evidence from the scattering experiment
β and γ decays, Radiation Therapies and Diagnostic, Fusion and Fission Final Exam Surveys New material Example of β-decay Beta decay Y + e # Y'+e +
 β and γ decays, Radiation Therapies and Diagnostic, Fusion and Fission Last Lecture: Radioactivity, Nuclear decay Radiation damage This lecture: nuclear physics in medicine and fusion and fission Final
β and γ decays, Radiation Therapies and Diagnostic, Fusion and Fission Last Lecture: Radioactivity, Nuclear decay Radiation damage This lecture: nuclear physics in medicine and fusion and fission Final
2 Energy from the Nucleus
 CHAPTER 4 2 Energy from the Nucleus SECTION Atomic Energy BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is nuclear fission? What is nuclear fusion? What
CHAPTER 4 2 Energy from the Nucleus SECTION Atomic Energy BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is nuclear fission? What is nuclear fusion? What
Year 9 AQA GCSE Physics Revision Booklet
 Year 9 AQA GCSE Physics Revision Booklet Atomic Structure and Radioactivity Models of the atom know: Plum pudding model of the atom and Rutherford and Marsden s alpha experiments, being able to explain
Year 9 AQA GCSE Physics Revision Booklet Atomic Structure and Radioactivity Models of the atom know: Plum pudding model of the atom and Rutherford and Marsden s alpha experiments, being able to explain
The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation
 The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation Announcements: First midterm is 7:30pm on Sept 26, 2013 Will post a past midterm exam from 2011 today. We are covering Chapter 3 today. (Started on Wednesday)
The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation Announcements: First midterm is 7:30pm on Sept 26, 2013 Will post a past midterm exam from 2011 today. We are covering Chapter 3 today. (Started on Wednesday)
IGCSE Physics 0625 notes: unit 5 Atomic Physics: Revised on 01 December
 IGCSE Physics 0625 notes: unit 5 Atomic Physics: Revised on 01 December 2011 1 TOPIC 5 ATOMIC PHYSICS Radioactivity or radioactive decay: 1. It is the process in which certain unstable atomic nuclei (plural
IGCSE Physics 0625 notes: unit 5 Atomic Physics: Revised on 01 December 2011 1 TOPIC 5 ATOMIC PHYSICS Radioactivity or radioactive decay: 1. It is the process in which certain unstable atomic nuclei (plural
Nuclear processes: Vocabulary: Radioactive decay Isotope Alpha particle Beta particle Transmutation Strong Nuclear Force Fusion fission
 Nuclear processes: Students will develop models to illustrate the changes in the composition of the nucleus of the atom and the energy released during the processes of fission, fusion, and radioactive
Nuclear processes: Students will develop models to illustrate the changes in the composition of the nucleus of the atom and the energy released during the processes of fission, fusion, and radioactive
There are no stable isotopes of elements above atomic number 83.
 Nuclear Chemistry Stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation. All
Nuclear Chemistry Stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation. All
21/11/ /11/2017 Atomic Structure AQA Physics topic 4
 Atomic Structure AQA Physics topic 4 4.1 Atoms and Isotopes The structure of the atom ELECTRON negative, mass nearly nothing The nucleus is around 10,000 times smaller then the atom! NEUTRON neutral, same
Atomic Structure AQA Physics topic 4 4.1 Atoms and Isotopes The structure of the atom ELECTRON negative, mass nearly nothing The nucleus is around 10,000 times smaller then the atom! NEUTRON neutral, same
NUCLEAR ENERGY! DAY 1: (RADIATION, FISSION, FUSION)
 NUCLEAR ENERGY! DAY 1: (RADIATION, FISSION, FUSION) Nucleus Stability Stability of the nucleus depends on the nuclear forces that act between protons and neutrons Protons repel each other Protons attract
NUCLEAR ENERGY! DAY 1: (RADIATION, FISSION, FUSION) Nucleus Stability Stability of the nucleus depends on the nuclear forces that act between protons and neutrons Protons repel each other Protons attract
Physics 219 Help Session. Date: Wed 12/07, Time: 6:00-8:00 pm. Location: Physics 331
 Lecture 25-1 Physics 219 Help Session Date: Wed 12/07, 2016. Time: 6:00-8:00 pm Location: Physics 331 Lecture 25-2 Final Exam Dec. 14. 2016. 1:00-3:00pm in Phys. 112 Bring your ID card, your calculator
Lecture 25-1 Physics 219 Help Session Date: Wed 12/07, 2016. Time: 6:00-8:00 pm Location: Physics 331 Lecture 25-2 Final Exam Dec. 14. 2016. 1:00-3:00pm in Phys. 112 Bring your ID card, your calculator
Isotopes. An isotope is an atom of the same element (same number of protons) that varies in the number of neutrons.
 Nuclear Chemistry Isotopes An isotope is an atom of the same element (same number of protons) that varies in the number of neutrons. Most elements have several isotopes Some are unstable and emit radiation
Nuclear Chemistry Isotopes An isotope is an atom of the same element (same number of protons) that varies in the number of neutrons. Most elements have several isotopes Some are unstable and emit radiation
Isotopes. An isotope is an atoms of the same element (same number of protons) that vary in the number of neutrons.
 Nuclear Chemistry Isotopes An isotope is an atoms of the same element (same number of protons) that vary in the number of neutrons. Most elements have several isotopes Some are unstable and emit radiation
Nuclear Chemistry Isotopes An isotope is an atoms of the same element (same number of protons) that vary in the number of neutrons. Most elements have several isotopes Some are unstable and emit radiation
Unit 5 Physical Science Radioactivity Answer Key
 Unit 5 Physical Science Radioactivity Answer Key Page 198 1. True 2. False: The higher the frequency is, the higher the energy is. 3. True 4. False: Energy increases as frequency increases. 5. False: The
Unit 5 Physical Science Radioactivity Answer Key Page 198 1. True 2. False: The higher the frequency is, the higher the energy is. 3. True 4. False: Energy increases as frequency increases. 5. False: The
RADIOACTIVITY & HALF-LIFE Part 3
 RADIOACTIVITY & HALF-LIFE Part 3 Half-Life Half-life: is the rate of decay for a radioactive isotope. is the time required for half of an original quantity of an element to decay. is constant and independent
RADIOACTIVITY & HALF-LIFE Part 3 Half-Life Half-life: is the rate of decay for a radioactive isotope. is the time required for half of an original quantity of an element to decay. is constant and independent
L 36 Modern Physics :006 FINAL EXAM. Nuclear reactions: E = mc 2. Radioactivity. Hazards of radiation. Biological effects of nuclear radiation
 9:006 FINAL EXAM The final exam is on Monday MAY 7:30 AM - 9:30 AM in W90 CB The FE is not cumulative, and will cover lectures 3 through 36. (50 questions) The last regular lecture (Lec. 36) will be given
9:006 FINAL EXAM The final exam is on Monday MAY 7:30 AM - 9:30 AM in W90 CB The FE is not cumulative, and will cover lectures 3 through 36. (50 questions) The last regular lecture (Lec. 36) will be given
Nuclear processes: Vocabulary: Radioactive decay Isotope Alpha particle Beta particle Transmutation Strong Nuclear Force Fusion Fission
 Nuclear processes: Students will develop models to illustrate the changes in the composition of the nucleus of the atom and the energy released during the processes of fission, fusion, and radioactive
Nuclear processes: Students will develop models to illustrate the changes in the composition of the nucleus of the atom and the energy released during the processes of fission, fusion, and radioactive
Nonrenewable Energy: Nuclear. Energy Part 2
 Nonrenewable Energy: Nuclear Energy Part 2 What do you know about Nuclear Chemistry? http://ed.ted.com/lessons/radioactivity-expect-the-unexpected-steveweatherall I. Radiation Radiation = any movement
Nonrenewable Energy: Nuclear Energy Part 2 What do you know about Nuclear Chemistry? http://ed.ted.com/lessons/radioactivity-expect-the-unexpected-steveweatherall I. Radiation Radiation = any movement
The Electromagnetic Spectrum. 7.1 Atomic Theory and Radioactive Decay. Isotopes. 19K, 19K, 19K Representing Isotopes
 7.1 Atomic Theory and Radioactive Decay Natural background radiation exists all around us. Radioactivity is the release of high energy particles or waves When atoms lose high energy particles and waves,
7.1 Atomic Theory and Radioactive Decay Natural background radiation exists all around us. Radioactivity is the release of high energy particles or waves When atoms lose high energy particles and waves,
Chemistry Unit 5 Exam Study Guide Nuclear Chemistry
 Chemistry Unit 5 Exam Study Guide Nuclear Chemistry Define the following vocabulary terms: Radioactivity Radiation Alpha Particle Beta Particle Gamma Ray Transmutation Half-life Nuclear Decay Nuclear Fission
Chemistry Unit 5 Exam Study Guide Nuclear Chemistry Define the following vocabulary terms: Radioactivity Radiation Alpha Particle Beta Particle Gamma Ray Transmutation Half-life Nuclear Decay Nuclear Fission
L 36 Atomic and Nuclear Physics-4. Radioactivity. Nuclear reactions: E = mc 2. Hazards of radiation. Biological effects of nuclear radiation
 L 36 Atomic and Nuclear Physics- Nuclear physics what s inside the nucleus and what holds it together what is radioactivity, half-life carbon dating Nuclear energy nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear
L 36 Atomic and Nuclear Physics- Nuclear physics what s inside the nucleus and what holds it together what is radioactivity, half-life carbon dating Nuclear energy nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear
Radioactivity is the emission of high energy released when the of atoms change. Radioactivity can be or.
 Chapter 19 1 RADIOACTIVITY Radioactivity is the emission of high energy released when the of atoms change. Radioactivity can be or. TYPES OF RADIATION OR EMITTED ENERGY IN NUCLEAR CHANGES Radiation is
Chapter 19 1 RADIOACTIVITY Radioactivity is the emission of high energy released when the of atoms change. Radioactivity can be or. TYPES OF RADIATION OR EMITTED ENERGY IN NUCLEAR CHANGES Radiation is
Alta Chemistry CHAPTER 25. Nuclear Chemistry: Radiation, Radioactivity & its Applications
 CHAPTER 25 Nuclear Chemistry: Radiation, Radioactivity & its Applications Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Chemistry deals with changes in the nucleus The nucleus of an atom contains Protons Positively Charged
CHAPTER 25 Nuclear Chemistry: Radiation, Radioactivity & its Applications Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Chemistry deals with changes in the nucleus The nucleus of an atom contains Protons Positively Charged
RADIOACTIVITY. An atom consists of protons, neutrons and electrons.
 RADIOACTIVITY An atom consists of protons, neutrons and electrons. - Protons and neutrons are inside the nucleus - Electrons revolve around the nucleus in specific orbits ATOMIC NUMBER: - Total number
RADIOACTIVITY An atom consists of protons, neutrons and electrons. - Protons and neutrons are inside the nucleus - Electrons revolve around the nucleus in specific orbits ATOMIC NUMBER: - Total number
Unit 13: Nuclear Practice Packet Regents Chemistry: Practice Packet: Unit 13 Nuclear Chemistry
 Unit 13: Nuclear Practice Packet Regents Chemistry: Practice Packet: Unit 13 Nuclear Chemistry 1 Unit 13: Nuclear Practice Packet Lesson 1: Radioactive Decay Objective: Construct nuclear equations for
Unit 13: Nuclear Practice Packet Regents Chemistry: Practice Packet: Unit 13 Nuclear Chemistry 1 Unit 13: Nuclear Practice Packet Lesson 1: Radioactive Decay Objective: Construct nuclear equations for
Revision checklist. Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it!
 Radioactivity a Atomic models Describe the structure of an atom (in terms of nucleus and electrons). State where most of the mass of an atom is found. State the sizes of atoms and small molecules. Describe
Radioactivity a Atomic models Describe the structure of an atom (in terms of nucleus and electrons). State where most of the mass of an atom is found. State the sizes of atoms and small molecules. Describe
Nuclear fission is used in nuclear power stations to generate electricity. Nuclear fusion happens naturally in stars.
 1 (a) Nuclear fission is used in nuclear power stations to generate electricity. Nuclear fusion happens naturally in stars. (i) Explain briefly the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion.
1 (a) Nuclear fission is used in nuclear power stations to generate electricity. Nuclear fusion happens naturally in stars. (i) Explain briefly the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion.
Unit 6 Nuclear Radiation Parent Guide. What is radioactivity and why are things radioactive?
 Unit 6 Nuclear Radiation Parent Guide What is radioactivity and why are things radioactive? The nucleus of an atom is comprised of subatomic particles called protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive
Unit 6 Nuclear Radiation Parent Guide What is radioactivity and why are things radioactive? The nucleus of an atom is comprised of subatomic particles called protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive
Notes: Unit 14 Nuclear Chemistry
 Name: Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Notes: Unit 14 Nuclear Chemistry www.mrpalermo.com Name: KEY IDEAS: Stability of isotopes is based in the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most
Name: Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Notes: Unit 14 Nuclear Chemistry www.mrpalermo.com Name: KEY IDEAS: Stability of isotopes is based in the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most
Unit 13: Nuclear Chemistry
 Name Unit 13: Nuclear Chemistry Skills: 1. Review Atomic Structure 2. Determining Nuclear Stability 3. Naming and Drawing Hydrocarbons 4. Using N + O to Write Decay Equations Period 5. Solve Various Half
Name Unit 13: Nuclear Chemistry Skills: 1. Review Atomic Structure 2. Determining Nuclear Stability 3. Naming and Drawing Hydrocarbons 4. Using N + O to Write Decay Equations Period 5. Solve Various Half
Name: Class: Date: SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided.
 CHAPTER 21 REVIEW Nuclear Chemistry SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Based on the information about the three elementary particles in the text, which has
CHAPTER 21 REVIEW Nuclear Chemistry SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. Based on the information about the three elementary particles in the text, which has
Chapter 4: Atomic structure
 Chapter : Atomic structure Lesson.1 Atomic structure 1 88 electrons 2 92 protons, 238 92 = 16 neutrons 3 The number of electrons is the same; the number of protons is the same; the number of neutrons is
Chapter : Atomic structure Lesson.1 Atomic structure 1 88 electrons 2 92 protons, 238 92 = 16 neutrons 3 The number of electrons is the same; the number of protons is the same; the number of neutrons is
[2] State in what form the energy is released in such a reaction.... [1]
![[2] State in what form the energy is released in such a reaction.... [1] [2] State in what form the energy is released in such a reaction.... [1]](/thumbs/87/96058923.jpg) (a) The following nuclear reaction occurs when a slow-moving neutron is absorbed by an isotope of uranium-35. 0n + 35 9 U 4 56 Ba + 9 36Kr + 3 0 n Explain how this reaction is able to produce energy....
(a) The following nuclear reaction occurs when a slow-moving neutron is absorbed by an isotope of uranium-35. 0n + 35 9 U 4 56 Ba + 9 36Kr + 3 0 n Explain how this reaction is able to produce energy....
Nuclear power plants can generate large amounts of electricity.
 7.3 Nuclear Reactions Nuclear fission and fusion are processes that involve extremely large amounts of energy. Fission = the splitting of nuclei Fusion = the joining of nuclei Nuclear power plants can
7.3 Nuclear Reactions Nuclear fission and fusion are processes that involve extremely large amounts of energy. Fission = the splitting of nuclei Fusion = the joining of nuclei Nuclear power plants can
Atomic Structure & Nuclear Chemistry Unit 3 Notes
 Atomic Structure & Nuclear Chemistry Unit 3 Notes Academic Chemistry Name 52 24 Cr Mass Number Symbol Atomic Number Unit #3 Test Date You can never learn less, you can only learn more. R. Buckminster Fuller
Atomic Structure & Nuclear Chemistry Unit 3 Notes Academic Chemistry Name 52 24 Cr Mass Number Symbol Atomic Number Unit #3 Test Date You can never learn less, you can only learn more. R. Buckminster Fuller
Nuclear Radiation. Natural Radioactivity. A person working with radioisotopes wears protective clothing and gloves and stands behind a shield.
 Nuclear Radiation Natural Radioactivity A person working with radioisotopes wears protective clothing and gloves and stands behind a shield. 1 Radioactive Isotopes A radioactive isotope has an unstable
Nuclear Radiation Natural Radioactivity A person working with radioisotopes wears protective clothing and gloves and stands behind a shield. 1 Radioactive Isotopes A radioactive isotope has an unstable
Atomic Theory. Contribution to Modern Atomic Theory
 Alief High School Chemistry STAAR Review Reporting Category 2: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry C.6.A Understand the experimental design and conclusions used in the development of modern atomic theory,
Alief High School Chemistry STAAR Review Reporting Category 2: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry C.6.A Understand the experimental design and conclusions used in the development of modern atomic theory,
UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
 UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY student version www.toppr.com Contents (a) Types of Radiation (b) Properties of Radiation (c) Dangers of Radiation (d) Rates of radioactive decay (e) Nuclear
UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY student version www.toppr.com Contents (a) Types of Radiation (b) Properties of Radiation (c) Dangers of Radiation (d) Rates of radioactive decay (e) Nuclear
Chapter 20: Phenomena. Chapter 20: The Nucleus: A Chemist s View. Nuclear Decay. Nuclear Decay. Nuclear Decay. Nuclear Decay
 Chapter 20: Phenomena Phenomena: Below is a list of stable isotopes of different elements. Examine the data and see what patterns you can identify. The mass of a electron is 0.00055 u, the mass of a proton
Chapter 20: Phenomena Phenomena: Below is a list of stable isotopes of different elements. Examine the data and see what patterns you can identify. The mass of a electron is 0.00055 u, the mass of a proton
Nuclear Chemistry. Proposal: build a nuclear power plant in Broome County. List the pros & cons
 Nuclear Chemistry Proposal: build a nuclear power plant in Broome County. List the pros & cons 1 Nuclear Chemistry Friend or Fiend 2 The Nucleus What is in the nucleus? How big is it vs. the atom? How
Nuclear Chemistry Proposal: build a nuclear power plant in Broome County. List the pros & cons 1 Nuclear Chemistry Friend or Fiend 2 The Nucleus What is in the nucleus? How big is it vs. the atom? How
Nuclear fission and fusion are processes that involve extremely large amounts of energy.
 Nuclear Reactions & Energy Nuclear fission and fusion are processes that involve extremely large amounts of energy. Fission = the splitting of a large nucleus into two smaller nuclei, subatomic particles
Nuclear Reactions & Energy Nuclear fission and fusion are processes that involve extremely large amounts of energy. Fission = the splitting of a large nucleus into two smaller nuclei, subatomic particles
Atomic & Nuclear Physics
 Atomic & Nuclear Physics Life and Atoms Every time you breathe you are taking in atoms. Oxygen atoms to be exact. These atoms react with the blood and are carried to every cell in your body for various
Atomic & Nuclear Physics Life and Atoms Every time you breathe you are taking in atoms. Oxygen atoms to be exact. These atoms react with the blood and are carried to every cell in your body for various
Ch 22 Radioactivity Nuclear Chemistry
 AMHS AP Chemistry Name Period S T A T I O N 1 Q U I Z O N P E O P L E Match the people with the following ideas. Each name may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a) Albert Einstein b) Marie Curie
AMHS AP Chemistry Name Period S T A T I O N 1 Q U I Z O N P E O P L E Match the people with the following ideas. Each name may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a) Albert Einstein b) Marie Curie
PARTICLE RELATIVE MASS RELATIVE CHARGE. proton 1 +1
 Q1. (a) Atoms are made up of three types of particle called protons, neutrons and electrons. Complete the table below to show the relative mass and charge of a neutron and an electron. The relative mass
Q1. (a) Atoms are made up of three types of particle called protons, neutrons and electrons. Complete the table below to show the relative mass and charge of a neutron and an electron. The relative mass
UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
 UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY teacher version www.toppr.com Contents (a) Types of Radiation (b) Properties of Radiation (c) Dangers of Radiation (d) Rates of radioactive decay (e) Nuclear
UNIT 10 RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY teacher version www.toppr.com Contents (a) Types of Radiation (b) Properties of Radiation (c) Dangers of Radiation (d) Rates of radioactive decay (e) Nuclear
Radioisotopes. alpha. Unstable isotope. stable. beta. gamma
 Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Chemistry Nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons Strong forces (nuclear force) hold nucleus together Protons in nucleus have electrostatic repulsion however, strong
Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Chemistry Nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons Strong forces (nuclear force) hold nucleus together Protons in nucleus have electrostatic repulsion however, strong
Nuclear Physics. Radioactivity. # protons = # neutrons. Strong Nuclear Force. Checkpoint 4/17/2013. A Z Nucleus = Protons+ Neutrons
 Marie Curie 1867-1934 Radioactivity Spontaneous emission of radiation from the nucleus of an unstable isotope. Antoine Henri Becquerel 1852-1908 Wilhelm Roentgen 1845-1923 Nuclear Physics A Z Nucleus =
Marie Curie 1867-1934 Radioactivity Spontaneous emission of radiation from the nucleus of an unstable isotope. Antoine Henri Becquerel 1852-1908 Wilhelm Roentgen 1845-1923 Nuclear Physics A Z Nucleus =
Part 12- Physics Paper 1 Atomic Structure Application Questions Triple Science
 Part 12- Physics Paper 1 Atomic Structure Application Questions Triple Science Internal energy and energy transfers Internal energy and energy transfers Changes of state and the particle model Particle
Part 12- Physics Paper 1 Atomic Structure Application Questions Triple Science Internal energy and energy transfers Internal energy and energy transfers Changes of state and the particle model Particle
Physics 180B Test Points. a. 3/2c b. c c. 15/16c d. 24/25c
 Physics 180B Test 4-120 Points Name Answer 10 of the 13 Multiple Choice questions. Cross off 3 questions. 1. A rocket is traveling toward the earth at 3/4c when it ejects a missile forward at 3/4c relative
Physics 180B Test 4-120 Points Name Answer 10 of the 13 Multiple Choice questions. Cross off 3 questions. 1. A rocket is traveling toward the earth at 3/4c when it ejects a missile forward at 3/4c relative
Differentiating Chemical Reactions from Nuclear Reactions
 Differentiating Chemical Reactions from Nuclear Reactions 1 CHEMICAL Occurs when bonds are broken or formed. Atoms remained unchanged, though may be rearranged. Involves valence electrons Small energy
Differentiating Chemical Reactions from Nuclear Reactions 1 CHEMICAL Occurs when bonds are broken or formed. Atoms remained unchanged, though may be rearranged. Involves valence electrons Small energy
Isotopes Atoms of an element (same # p+) that differ in their number of neutrons
 Isotopes Atoms of an element (same # p+) that differ in their number of neutrons Radio-isotopes Isotope of an element that is UNSTABLE. They spontaneously emit particles (energy) in order to achieve a
Isotopes Atoms of an element (same # p+) that differ in their number of neutrons Radio-isotopes Isotope of an element that is UNSTABLE. They spontaneously emit particles (energy) in order to achieve a
Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity.
 Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity. A. Differentiate among alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. B. Differentiate between fission and fusion. C. Explain the process
Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity. A. Differentiate among alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. B. Differentiate between fission and fusion. C. Explain the process
Regents review Nuclear Chemistry
 2011-2012 1. Given the nuclear equation: 14 7N + X 16 8O + 2 1H What is particle X? A) an alpha particle B) a beta particle C) a deuteron D) a triton 2. The nucleus of a radium-226 atom is unstable, which
2011-2012 1. Given the nuclear equation: 14 7N + X 16 8O + 2 1H What is particle X? A) an alpha particle B) a beta particle C) a deuteron D) a triton 2. The nucleus of a radium-226 atom is unstable, which
Q1. Describe, in as much detail as you can, the life history of a star like our Sun
 Q1. Describe, in as much detail as you can, the life history of a star like our Sun..................................... (Total 6 marks) Q2. The energy radiated by a main sequence star like the Sun is
Q1. Describe, in as much detail as you can, the life history of a star like our Sun..................................... (Total 6 marks) Q2. The energy radiated by a main sequence star like the Sun is
Section 3: Nuclear Radiation Today
 : Nuclear Radiation Today Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Where is Radiation? Beneficial Uses of Nuclear Radiation Risks of Nuclear Radiation Nuclear Power Key Ideas Where are we exposed to radiation? What
: Nuclear Radiation Today Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Where is Radiation? Beneficial Uses of Nuclear Radiation Risks of Nuclear Radiation Nuclear Power Key Ideas Where are we exposed to radiation? What
Chapter 21
 Chapter 21 http://youtu.be/kwasz59f8ga Nuclear reactions involve the nucleus The nucleus opens, and protons and neutrons are rearranged. The opening of the nucleus releases a tremendous amount of energy
Chapter 21 http://youtu.be/kwasz59f8ga Nuclear reactions involve the nucleus The nucleus opens, and protons and neutrons are rearranged. The opening of the nucleus releases a tremendous amount of energy
Homework 06. Nuclear
 HW06 - Nuclear Started: Mar 22 at 11:05am Quiz Instruc!ons Homework 06 Nuclear Question 1 How does a nuclear reaction differ from a chemical reaction? In a nuclear reaction, the elements change identities
HW06 - Nuclear Started: Mar 22 at 11:05am Quiz Instruc!ons Homework 06 Nuclear Question 1 How does a nuclear reaction differ from a chemical reaction? In a nuclear reaction, the elements change identities
What happens during nuclear decay? During nuclear decay, atoms of one element can change into atoms of a different element altogether.
 When Henri Becquerel placed uranium salts on a photographic plate and then developed the plate, he found a foggy image. The image was caused by rays that had not been observed before. For his discovery
When Henri Becquerel placed uranium salts on a photographic plate and then developed the plate, he found a foggy image. The image was caused by rays that had not been observed before. For his discovery
By Tim, John, Shane, Owen
 By Tim, John, Shane, Owen A few refreshers Atoms of the same element, which always have an identical number of protons, that have different numbers of neutrons, is an isotope. Protons and neutrons are
By Tim, John, Shane, Owen A few refreshers Atoms of the same element, which always have an identical number of protons, that have different numbers of neutrons, is an isotope. Protons and neutrons are
Aim:How can we determine the particles emitted from radioactive
 Aim:How can we determine the particles emitted from radioactive decay? Nuclear Stability: The larger (more massive) a nucleus is, the harder it is for it to stay together. Natural transmutation (natural
Aim:How can we determine the particles emitted from radioactive decay? Nuclear Stability: The larger (more massive) a nucleus is, the harder it is for it to stay together. Natural transmutation (natural
10.1 RADIOACTIVE DECAY
 10.1 RADIOACTIVE DECAY When Henri Becquerel placed uranium salts on a photographic plate and then developed the plate, he found a foggy image. The image was caused by rays that had not been observed before.
10.1 RADIOACTIVE DECAY When Henri Becquerel placed uranium salts on a photographic plate and then developed the plate, he found a foggy image. The image was caused by rays that had not been observed before.
The detector and counter are used in an experiment to show that a radioactive source gives out alpha and beta radiation only.
 ATOMS AND NUCLEAR RADIATION PART II Q1. The detector and counter are used in an experiment to show that a radioactive source gives out alpha and beta radiation only. Two different types of absorber are
ATOMS AND NUCLEAR RADIATION PART II Q1. The detector and counter are used in an experiment to show that a radioactive source gives out alpha and beta radiation only. Two different types of absorber are
Lecture Outlines Chapter 32. Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 32 Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker 2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in
Lecture Outlines Chapter 32 Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker 2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in
Table O: Symbols Used in Nuclear Chemistry
 Packet 12: NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY STABLITY OF NUCLEI Most nuclei are stable and don t change. They are found within the belt of stability. Some nuclei are unstable and break down spontaneously giving off rays
Packet 12: NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY STABLITY OF NUCLEI Most nuclei are stable and don t change. They are found within the belt of stability. Some nuclei are unstable and break down spontaneously giving off rays
Nuclear Reactions and E = mc 2. L 38 Modern Physics [4] Hazards of radiation. Radiation sickness. Biological effects of nuclear radiation
![Nuclear Reactions and E = mc 2. L 38 Modern Physics [4] Hazards of radiation. Radiation sickness. Biological effects of nuclear radiation Nuclear Reactions and E = mc 2. L 38 Modern Physics [4] Hazards of radiation. Radiation sickness. Biological effects of nuclear radiation](/thumbs/77/76435546.jpg) L 38 Modern Physics [4] Nuclear physics what s s inside the nucleus and what holds it together what is radioactivity, halflife carbon dating Nuclear energy nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear reactors
L 38 Modern Physics [4] Nuclear physics what s s inside the nucleus and what holds it together what is radioactivity, halflife carbon dating Nuclear energy nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear reactors
Chapter 18. Nuclear Chemistry
 Chapter 18 Nuclear Chemistry The energy of the sun comes from nuclear reactions. Solar flares are an indication of fusion reactions occurring at a temperature of millions of degrees. Introduction to General,
Chapter 18 Nuclear Chemistry The energy of the sun comes from nuclear reactions. Solar flares are an indication of fusion reactions occurring at a temperature of millions of degrees. Introduction to General,
Review A Z. a particle. proton. neutron. electron e -1. positron. e +1. Mass Number Atomic Number. Element Symbol
 Nuclear Chemistry 1 Review Atomic number (Z) = number of protons in nucleus Mass number (A) = number of protons + number of neutrons = atomic number (Z) + number of neutrons Mass Number Atomic Number A
Nuclear Chemistry 1 Review Atomic number (Z) = number of protons in nucleus Mass number (A) = number of protons + number of neutrons = atomic number (Z) + number of neutrons Mass Number Atomic Number A
Nuclear Chemistry. Nuclear Terminology
 Nuclear Chemistry Up to now, we have been concerned mainly with the electrons in the elements the nucleus has just been a positively charged things that attracts electrons The nucleus may also undergo
Nuclear Chemistry Up to now, we have been concerned mainly with the electrons in the elements the nucleus has just been a positively charged things that attracts electrons The nucleus may also undergo
and have low penetrating power) Alpha particles are released through alpha decay. Beta Particles: An electron that comes from a nucleus through
 TOPIC 13: Nuclear Chemistry 1. When the atomic nucleus of one element is changed into the nucleus of a different element, the reaction is called transmutation. Stability of a Nucleus: Any element containing
TOPIC 13: Nuclear Chemistry 1. When the atomic nucleus of one element is changed into the nucleus of a different element, the reaction is called transmutation. Stability of a Nucleus: Any element containing
Name Date Class. alpha particle radioactivity gamma ray radioisotope beta particles radiation X-ray radioactive decay
 Name Date _ Class _ Nuclear Chemistry Section.1 Nuclear Radiation In your textbook, read about the terms used to describe nuclear changes. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
Name Date _ Class _ Nuclear Chemistry Section.1 Nuclear Radiation In your textbook, read about the terms used to describe nuclear changes. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
Nuclear Chemistry. Technology Strategies for Success PO Box 1485 East Northport, NY (631) NYS-PREP
 Nuclear Chemistry Technology Strategies for Success PO Box 1485 East Northport, NY 11725 (631)734-0115 1-888-NYS-PREP techstrategies@gmail.com Nuclear Chemistry Table of Contents 1.0 Nuclear Chemistry...3
Nuclear Chemistry Technology Strategies for Success PO Box 1485 East Northport, NY 11725 (631)734-0115 1-888-NYS-PREP techstrategies@gmail.com Nuclear Chemistry Table of Contents 1.0 Nuclear Chemistry...3
Nuclear Chemistry Review Packet
 Name Date Nuclear Chemistry Review Packet 1. The ratio of stability is (1) proton : neutron (2) neutron : proton (3) proton : positron (4) beta : proton 2. Which nuclear reaction is classified as alpha
Name Date Nuclear Chemistry Review Packet 1. The ratio of stability is (1) proton : neutron (2) neutron : proton (3) proton : positron (4) beta : proton 2. Which nuclear reaction is classified as alpha
Chapter 11 Nuclear Chemistry
 Chapter 11 Nuclear Chemistry 11.1 Nuclear Reactions Nuclear reactions involve the particles located in the nucleus of the atom: The nucleus contains: An atom is characterized by: X A Z - Z the gives the
Chapter 11 Nuclear Chemistry 11.1 Nuclear Reactions Nuclear reactions involve the particles located in the nucleus of the atom: The nucleus contains: An atom is characterized by: X A Z - Z the gives the
Nuclear Physics Part 2: Radioactive Decay
 Nuclear Physics Part 2: Radioactive Decay Last modified: 17/10/2017 Part A: Decay Reactions What is a Decay? Alpha Decay Definition Q-value Example Not Every Alpha Decay is Possible Beta Decay β rays are
Nuclear Physics Part 2: Radioactive Decay Last modified: 17/10/2017 Part A: Decay Reactions What is a Decay? Alpha Decay Definition Q-value Example Not Every Alpha Decay is Possible Beta Decay β rays are
Recap I Lecture 41 Matthias Liepe, 2012
 Recap I Lecture 41 Matthias Liepe, 01 Recap II Nuclear Physics The nucleus Radioactive decay Fission Fusion Particle Physics: What is the Higgs? Today: Nuclear Physics: The Nucleus Positive charge and
Recap I Lecture 41 Matthias Liepe, 01 Recap II Nuclear Physics The nucleus Radioactive decay Fission Fusion Particle Physics: What is the Higgs? Today: Nuclear Physics: The Nucleus Positive charge and
In order to get the G.C.S.E. grade you are capable of, you must make your own revision notes using your Physics notebook.
 In order to get the G.C.S.E. grade you are capable of, you must make your own revision notes using your Physics notebook. When summarising notes, use different colours and draw diagrams/pictures. If you
In order to get the G.C.S.E. grade you are capable of, you must make your own revision notes using your Physics notebook. When summarising notes, use different colours and draw diagrams/pictures. If you
Chapter 30 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity
 Chapter 30 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity 30.1 Structure and Properties of the Nucleus Nucleus is made of protons and neutrons Proton has positive charge: Neutron is electrically neutral: 30.1 Structure
Chapter 30 Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity 30.1 Structure and Properties of the Nucleus Nucleus is made of protons and neutrons Proton has positive charge: Neutron is electrically neutral: 30.1 Structure
LECTURE 26 RADIATION AND RADIOACTIVITY
 LECTURE 26 RADIATION AND RADIOACTIVITY 30.4 Radiation and radioactivity Decay series Nuclear radiation is a form of ionizing radiation 30.5 Nuclear decay and half-lives Activity Radioactive dating Radiocarbon
LECTURE 26 RADIATION AND RADIOACTIVITY 30.4 Radiation and radioactivity Decay series Nuclear radiation is a form of ionizing radiation 30.5 Nuclear decay and half-lives Activity Radioactive dating Radiocarbon
Chapter 21 Nuclear Chemistry
 Chapter 21 Nuclear Chemistry The Nucleus Remember that the nucleus is comprised of the two nucleons, protons and neutrons. The number of protons is the atomic number. The number of protons and neutrons
Chapter 21 Nuclear Chemistry The Nucleus Remember that the nucleus is comprised of the two nucleons, protons and neutrons. The number of protons is the atomic number. The number of protons and neutrons
