RADIOACTIVITY. An atom consists of protons, neutrons and electrons.
|
|
|
- Gilbert Copeland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RADIOACTIVITY An atom consists of protons, neutrons and electrons. - Protons and neutrons are inside the nucleus - Electrons revolve around the nucleus in specific orbits ATOMIC NUMBER: - Total number of protons on the nucleus symbol is Z MASS NUMBER - Total number of nucleons (sum of protons and neutrons) in the nucleus symbol is A It is represented by Z X A. ISOTOPES: Atoms of the same element having same atomic number but different mass number (e.g) 1 H 1. 1H 2. 1H 3. There are two kinds of isotopes. - Stable isotopes number of neutrons is nearly equal to number of protons. - Unstable or radioactive isotopes number of neutrons is much more than number of protons. ISOBARS Atoms of different elements having same mass number A but different atomic number Z (e.g) 6 C 14. 7N 14. If the number of protons and neutrons get interchanged inside the nucleus, they are called mirror isobars.
2 (e.g) 11 Na Mg 23. ISOTONES: Atoms having different number of protons but same number of neutrons are called isotones. RADIO ACTIVITY Isotopes of nearly all elements of atomic number >82 are radioactive because number of neutrons >> number of protons. Any physical change (such as change in temperature and pressure) or chemical change (such as excessive heating, freezing, action of strong electric and magnetic fields, chemical treatment, oxidation etc.) does not change the nature of radiation because the effect is felt only in the orbital electrons and not in the nucleus. Radioactivity is the process of spontaneous emission of alpha, beta or gamma radiations from the nucleus of atoms during the decay. Read the diagrams given in page 282: fig 12.4, 12.5 Properties of alpha particles Ionising power is maximum Penetrating power is very less Properties of beta particles Ionising power is less than alpha particle Penetrating power is more than alpha Properties of gamma particles Ionising power is minimum Penetrating power is very large
3 CHANGES WIHIN NUCLEUS IN ALPHA, BETA AND GAMMA EMISSION ALPHA EMISSION: If a nucleus X emits an alpha particle, a new element is formed which has mass number (A - 4) and atomic number equal to (Z 2). THIS IS EXPRESSED BY: (example) BETA EMISSION: If a nucleus X emits a beta particle, the number of nucleons remains same, but the number of neutrons is decreased by one and the number of protons id increased by one. (OR) By the emission of a beta particle, the mass number A does not change but the atomic number is increased by one.
4 GAMMA EMISSION: There is no change in the mass number and atomic number in gamma emission. USES OF RADIOACTIVITY: Radio isotopes isotopes whose atomic number < 82 are called radio isotopes. Uses in Medical Scientific Industrial fields (important: be specific when you are asked to write the benefits) Sources of harmful radiations: Radioactive fallout Nuclear waste Other sources (including cosmic radiation and X rays) Safety precautions Safety measures while establishing a power plant Safety measures while handling radioactive materials Safety measures in safe disposal of radioactive waste Any two points to be read
5 BACKGROUND RADIATIONS: Internal source potassium (K-40) present inside the body External source cosmic rays (radon-222) NUCLEAR FISSION AND FUSION Nuclear fission: heavy nucleus split into two light nuclei by bombarding with slow moving neutrons Radioactive decay nuclear fission 1. It is a self-process it does not occur by itself 2. The rate of decay cannot be controlled can be controlled Nuclear fusion: process by which two light nuclei combine to form a new nucleus Nuclear fission nuclear fusion 1. Splits into two nearly equal fragments two light nuclei combine To form a heavy nucleus 2. Reaction possible at ordinary reaction possible at very Temperature and pressure high temperature Any two differences is enough
Unit 3: Chemistry in Society Nuclear Chemistry Summary Notes
 St Ninian s High School Chemistry Department National 5 Chemistry Unit 3: Chemistry in Society Nuclear Chemistry Summary Notes Name Learning Outcomes After completing this topic you should be able to :
St Ninian s High School Chemistry Department National 5 Chemistry Unit 3: Chemistry in Society Nuclear Chemistry Summary Notes Name Learning Outcomes After completing this topic you should be able to :
Chapter 25. Nuclear Chemistry. Types of Radiation
 Chapter 25 Nuclear Chemistry Chemical Reactions 1. Bonds are broken and formed 2. Atoms may rearrange, but remain unchanged 3. Involve only valence electrons 4. Small energy changes 5. Reaction rate is
Chapter 25 Nuclear Chemistry Chemical Reactions 1. Bonds are broken and formed 2. Atoms may rearrange, but remain unchanged 3. Involve only valence electrons 4. Small energy changes 5. Reaction rate is
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Radioactivity Test Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Radioactive s have unstable a. electrons. c. protons. b. nuclei.
Radioactivity Test Review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Radioactive s have unstable a. electrons. c. protons. b. nuclei.
Year 11 Physics booklet Topic 1 Atomic structure and radioactivity Name:
 Year 11 Physics booklet Topic 1 Atomic structure and radioactivity Name: Atomic structure and radioactivity Give a definition for each of these key words: Atom Isotope Proton Neutron Electron Atomic nucleus
Year 11 Physics booklet Topic 1 Atomic structure and radioactivity Name: Atomic structure and radioactivity Give a definition for each of these key words: Atom Isotope Proton Neutron Electron Atomic nucleus
Unit 12: Nuclear Chemistry
 Unit 12: Nuclear Chemistry 1. Stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation.
Unit 12: Nuclear Chemistry 1. Stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation.
PHYSICS A2 UNIT 2 SECTION 1: RADIOACTIVITY & NUCLEAR ENERGY
 PHYSICS A2 UNIT 2 SECTION 1: RADIOACTIVITY & NUCLEAR ENERGY THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS / NUCLEAR RADIUS & DENSITY / PROPERTIES OF NUCLEAR RADIATION / INTENSITY & BACKGROUND RADIATION / EXPONENTIAL LAW OF DECAY
PHYSICS A2 UNIT 2 SECTION 1: RADIOACTIVITY & NUCLEAR ENERGY THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS / NUCLEAR RADIUS & DENSITY / PROPERTIES OF NUCLEAR RADIATION / INTENSITY & BACKGROUND RADIATION / EXPONENTIAL LAW OF DECAY
6-4 Atomic structure Physics
 6-4 Atomic structure Physics.0 Figure shows a helium atom. Figure. Use the words in the box to label the diagram. electron neutron proton.2 An alpha particle is the same as the nucleus of a helium atom.
6-4 Atomic structure Physics.0 Figure shows a helium atom. Figure. Use the words in the box to label the diagram. electron neutron proton.2 An alpha particle is the same as the nucleus of a helium atom.
UNIT 13: NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
 UNIT 13: NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY REVIEW: ISOTOPE NOTATION An isotope notation is written as Z A X, where X is the element, A is the mass number (sum of protons and neutrons), and Z is the atomic number. For
UNIT 13: NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY REVIEW: ISOTOPE NOTATION An isotope notation is written as Z A X, where X is the element, A is the mass number (sum of protons and neutrons), and Z is the atomic number. For
Nuclear Physics. Chapter 43. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman
 Chapter 43 Nuclear Physics PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 43 To understand some key properties
Chapter 43 Nuclear Physics PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 43 To understand some key properties
Isotopes Atoms of an element (same # p+) that differ in their number of neutrons
 Isotopes Atoms of an element (same # p+) that differ in their number of neutrons Radio-isotopes Isotope of an element that is UNSTABLE. They spontaneously emit particles (energy) in order to achieve a
Isotopes Atoms of an element (same # p+) that differ in their number of neutrons Radio-isotopes Isotope of an element that is UNSTABLE. They spontaneously emit particles (energy) in order to achieve a
Part 12- Physics Paper 1 Atomic Structure Application Questions Triple Science
 Part 12- Physics Paper 1 Atomic Structure Application Questions Triple Science Internal energy and energy transfers Internal energy and energy transfers Changes of state and the particle model Particle
Part 12- Physics Paper 1 Atomic Structure Application Questions Triple Science Internal energy and energy transfers Internal energy and energy transfers Changes of state and the particle model Particle
Nuclear Energy. Nuclear Structure and Radioactivity
 Nuclear Energy Nuclear Structure and Radioactivity I. Review - Periodic Table A. Atomic Number: The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom B. Atomic Mass: The sum of the mass of protons, neutrons
Nuclear Energy Nuclear Structure and Radioactivity I. Review - Periodic Table A. Atomic Number: The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom B. Atomic Mass: The sum of the mass of protons, neutrons
and have low penetrating power) Alpha particles are released through alpha decay. Beta Particles: An electron that comes from a nucleus through
 TOPIC 13: Nuclear Chemistry 1. When the atomic nucleus of one element is changed into the nucleus of a different element, the reaction is called transmutation. Stability of a Nucleus: Any element containing
TOPIC 13: Nuclear Chemistry 1. When the atomic nucleus of one element is changed into the nucleus of a different element, the reaction is called transmutation. Stability of a Nucleus: Any element containing
Question Bank. Nuclear Physics
 Nuclear Physics 1. State one difference between a chemical change and a nuclear change. Ans. A chemical change takes place due to transfer/sharing of orbital electrons of atoms of different elements, whereas
Nuclear Physics 1. State one difference between a chemical change and a nuclear change. Ans. A chemical change takes place due to transfer/sharing of orbital electrons of atoms of different elements, whereas
Isotopes and Radioactive Decay
 NAME PERIOD DATE CHAPTER 4 NOTES: ISOTOPES Isotopes and Radioactive Decay ISOTOPES: Atoms that contain the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Isotopes containing more neutrons have
NAME PERIOD DATE CHAPTER 4 NOTES: ISOTOPES Isotopes and Radioactive Decay ISOTOPES: Atoms that contain the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Isotopes containing more neutrons have
Nuclear Chemistry. Mass Defect. E=mc 2. Radioactivity. Types of Radiation. Other Nuclear Particles. Nuclear Reactions vs. Normal Chemical Changes
 1 Nuclear Chemistry Mass Defect 4 Some of the mass can be converted into energy Shown by a very famous equation! E=mc 2 Energy Mass Speed of light Radioactivity 2 Types of Radiation 5 One of the pieces
1 Nuclear Chemistry Mass Defect 4 Some of the mass can be converted into energy Shown by a very famous equation! E=mc 2 Energy Mass Speed of light Radioactivity 2 Types of Radiation 5 One of the pieces
Nuclear Reactions Homework Unit 13 - Topic 4
 Nuclear Reactions Homework Unit 13 - Topic 4 Use the laws of conservation of mass number and charge to determine the identity of X in the equations below. Refer to a periodic table as needed. 222 a. Rn
Nuclear Reactions Homework Unit 13 - Topic 4 Use the laws of conservation of mass number and charge to determine the identity of X in the equations below. Refer to a periodic table as needed. 222 a. Rn
Chapter 21. Preview. Lesson Starter Objectives Mass Defect and Nuclear Stability Nucleons and Nuclear Stability Nuclear Reactions
 Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Mass Defect and Nuclear Stability Nucleons and Nuclear Stability Nuclear Reactions Section 1 The Nucleus Lesson Starter Nuclear reactions result in much larger energy
Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Mass Defect and Nuclear Stability Nucleons and Nuclear Stability Nuclear Reactions Section 1 The Nucleus Lesson Starter Nuclear reactions result in much larger energy
SCIENCE 10: (7.1) ATOMIC THEORY, ISOTOPES AND RADIOACTIVE DECAY Name: Date: Block: (Textbook Reference pp in BC Science 10) into an
 SCIENCE 10: (7.1) ATOMIC THEORY, ISOTOPES AND RADIOACTIVE DECAY Name: Date: Block: (Textbook Reference pp. 286-301 in BC Science 10) Natural background radiation: It has the ability to interact with an
SCIENCE 10: (7.1) ATOMIC THEORY, ISOTOPES AND RADIOACTIVE DECAY Name: Date: Block: (Textbook Reference pp. 286-301 in BC Science 10) Natural background radiation: It has the ability to interact with an
Unit 1 Test A Atomic Theory & Nuclear Decay 1. Which of these BEST describes any two atoms of the same element? a. same number of protons
 1. Which of these BEST describes any two atoms of the same element? same number of protons same number of chemical bonds same number of neutrons same number of particles in the nucleus Self Assessment
1. Which of these BEST describes any two atoms of the same element? same number of protons same number of chemical bonds same number of neutrons same number of particles in the nucleus Self Assessment
Radioactivity. (b) Fig shows two samples of the same radioactive substance. The substance emits β-particles. Fig. 12.1
 112 (a) What is meant by radioactive decay? Radioactivity [2] (b) Fig. 12.1 shows two samples of the same radioactive substance. The substance emits β-particles. Fig. 12.1 Put a tick alongside any of the
112 (a) What is meant by radioactive decay? Radioactivity [2] (b) Fig. 12.1 shows two samples of the same radioactive substance. The substance emits β-particles. Fig. 12.1 Put a tick alongside any of the
Chapter 22 - Nuclear Chemistry
 Chapter - Nuclear Chemistry - The Nucleus I. Introduction A. Nucleons. Neutrons and protons B. Nuclides. Atoms identified by the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus 8 a. radium-8 or 88 Ra II.
Chapter - Nuclear Chemistry - The Nucleus I. Introduction A. Nucleons. Neutrons and protons B. Nuclides. Atoms identified by the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus 8 a. radium-8 or 88 Ra II.
Friday, 05/06/16 6) HW QUIZ MONDAY Learning Target (NEW)
 Friday, 05/06/16 1) Warm-up: If you start with 100g of a radioactive substance, how much will be left after 3 half-lives? 2) Review HW & Nuclear Notes 3) Complete Modeling Energy Investigation 4) Complete:
Friday, 05/06/16 1) Warm-up: If you start with 100g of a radioactive substance, how much will be left after 3 half-lives? 2) Review HW & Nuclear Notes 3) Complete Modeling Energy Investigation 4) Complete:
Unit 2 Exam - Atomic Structure and Nuclear
 1. The atomic number of an atom is always equal to the total number of. neutrons in the nucleus. protons in the nucleus 5. The mass number of an atom is equal to the number of. neutrons, only. protons,
1. The atomic number of an atom is always equal to the total number of. neutrons in the nucleus. protons in the nucleus 5. The mass number of an atom is equal to the number of. neutrons, only. protons,
There are no stable isotopes of elements above atomic number 83.
 Nuclear Chemistry Stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation. All
Nuclear Chemistry Stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation. All
RADIOACTIVITY: spontaneous disintegration of the nucleus of certain atoms accompanied by the emission (release) of particles and/or energy
 RADIOACTIVITY: spontaneous disintegration of the nucleus of certain atoms accompanied by the emission (release) of particles and/or energy ~ TRANSMUTATION: the change of one element into another due to
RADIOACTIVITY: spontaneous disintegration of the nucleus of certain atoms accompanied by the emission (release) of particles and/or energy ~ TRANSMUTATION: the change of one element into another due to
SAVE PAPER AND INK!!!
 SAVE PAPER AND INK!!! When you print out the notes on PowerPoint, print "Handouts" instead of "Slides" in the print setup. Also, turn off the backgrounds (Tools>Options>Print>UNcheck "Background Printing")!
SAVE PAPER AND INK!!! When you print out the notes on PowerPoint, print "Handouts" instead of "Slides" in the print setup. Also, turn off the backgrounds (Tools>Options>Print>UNcheck "Background Printing")!
Nonrenewable Energy: Nuclear. Energy Part 2
 Nonrenewable Energy: Nuclear Energy Part 2 What do you know about Nuclear Chemistry? http://ed.ted.com/lessons/radioactivity-expect-the-unexpected-steveweatherall I. Radiation Radiation = any movement
Nonrenewable Energy: Nuclear Energy Part 2 What do you know about Nuclear Chemistry? http://ed.ted.com/lessons/radioactivity-expect-the-unexpected-steveweatherall I. Radiation Radiation = any movement
6-4 Atomic structure Trilogy
 6-4 Atomic structure Trilogy.0 Figure shows a helium atom. Figure. Use the words in the box to label the diagram. electron neutron proton [2 marks].2 An alpha particle is the same as the nucleus of a helium
6-4 Atomic structure Trilogy.0 Figure shows a helium atom. Figure. Use the words in the box to label the diagram. electron neutron proton [2 marks].2 An alpha particle is the same as the nucleus of a helium
The diagram below shows a radioactive isotope going through several half-lives as it decays.
 By what process do most stars release energy? A. Electromagnetic induction resulting from strong magnetic fields B. Radioactivity in the interior of the star C. Nuclear fusion in the interior of the star
By what process do most stars release energy? A. Electromagnetic induction resulting from strong magnetic fields B. Radioactivity in the interior of the star C. Nuclear fusion in the interior of the star
 Radioactive Decay What is Radioactivity? http://explorecuriocity.org/explore/articleid/3033 http://explorecuriocity.org/explore/articleid/3035 http://explorecuriocity.org/explore/articleid/2160 Quick Review
Radioactive Decay What is Radioactivity? http://explorecuriocity.org/explore/articleid/3033 http://explorecuriocity.org/explore/articleid/3035 http://explorecuriocity.org/explore/articleid/2160 Quick Review
RADIOACTIVITY. Nature of Radioactive Emissions
 1 RADIOACTIVITY Radioactivity is the spontaneous emissions from the nucleus of certain atoms, of either alpha, beta or gamma radiation. These radiations are emitted when the nuclei of the radioactive substance
1 RADIOACTIVITY Radioactivity is the spontaneous emissions from the nucleus of certain atoms, of either alpha, beta or gamma radiation. These radiations are emitted when the nuclei of the radioactive substance
Unit 6 Nuclear Radiation Parent Guide. What is radioactivity and why are things radioactive?
 Unit 6 Nuclear Radiation Parent Guide What is radioactivity and why are things radioactive? The nucleus of an atom is comprised of subatomic particles called protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive
Unit 6 Nuclear Radiation Parent Guide What is radioactivity and why are things radioactive? The nucleus of an atom is comprised of subatomic particles called protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive
Thursday, April 23, 15. Nuclear Physics
 Nuclear Physics Some Properties of Nuclei! All nuclei are composed of protons and neutrons! Exception is ordinary hydrogen with just a proton! The atomic number, Z, equals the number of protons in the
Nuclear Physics Some Properties of Nuclei! All nuclei are composed of protons and neutrons! Exception is ordinary hydrogen with just a proton! The atomic number, Z, equals the number of protons in the
Atoms have two separate parts. The nucleus and the electron cloud.
 Name Ch. 5 - Atomic Structure Pre-AP Modern Atomic Theory All atoms are made of three subatomic (smaller than the atom) particles: the protons, the electrons and the neutrons. (P.E.N. s) There are particles
Name Ch. 5 - Atomic Structure Pre-AP Modern Atomic Theory All atoms are made of three subatomic (smaller than the atom) particles: the protons, the electrons and the neutrons. (P.E.N. s) There are particles
Nuclear Study Packet. 1. What subatomic particles are involved in nuclear reactions? 2. What subatomic particles are involved in chemical reactions?
 Name Period Nuclear Study Packet Set 1 1. What subatomic particles are involved in nuclear reactions? 2. What subatomic particles are involved in chemical reactions? 3. If an atom undergoes a reaction
Name Period Nuclear Study Packet Set 1 1. What subatomic particles are involved in nuclear reactions? 2. What subatomic particles are involved in chemical reactions? 3. If an atom undergoes a reaction
Chapter 7 Review. Block: Date:
 Science 10 Chapter 7 Review Name: KEY Block: Date: 1. Radioactivity is the release of high-energy particles and rays from a substance as a result of changes in the nuclei of its atoms.. _Natural background
Science 10 Chapter 7 Review Name: KEY Block: Date: 1. Radioactivity is the release of high-energy particles and rays from a substance as a result of changes in the nuclei of its atoms.. _Natural background
CHAPTER 1 RADIATION AND RADIOACTIVITY
 CHAPTER 1 RADIATION AND RADIOACTIVITY 1 Atomic Model Atomic Structure Atomic Number Mass Number Isotope [Mass Number][HKCEE] If the nucleus of an atom is represented by the symbol 214 83 X, it means that
CHAPTER 1 RADIATION AND RADIOACTIVITY 1 Atomic Model Atomic Structure Atomic Number Mass Number Isotope [Mass Number][HKCEE] If the nucleus of an atom is represented by the symbol 214 83 X, it means that
Atoms and Nuclear Chemistry. Atoms Isotopes Calculating Average Atomic Mass Radioactivity
 Atoms and Nuclear Chemistry Atoms Isotopes Calculating Average Atomic Mass Radioactivity Atoms An atom is the smallest particle of an element that has all of the properties of that element. Composition
Atoms and Nuclear Chemistry Atoms Isotopes Calculating Average Atomic Mass Radioactivity Atoms An atom is the smallest particle of an element that has all of the properties of that element. Composition
The basic structure of an atom is a positively charged nucleus composed of both protons and neutrons surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
 4.4 Atomic structure Ionising radiation is hazardous but can be very useful. Although radioactivity was discovered over a century ago, it took many nuclear physicists several decades to understand the
4.4 Atomic structure Ionising radiation is hazardous but can be very useful. Although radioactivity was discovered over a century ago, it took many nuclear physicists several decades to understand the
Revision checklist. Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it!
 Radioactivity a Atomic models Describe the structure of an atom (in terms of nucleus and electrons). State where most of the mass of an atom is found. State the sizes of atoms and small molecules. Describe
Radioactivity a Atomic models Describe the structure of an atom (in terms of nucleus and electrons). State where most of the mass of an atom is found. State the sizes of atoms and small molecules. Describe
RADIOACTIVITY: spontaneous disintegration of the nucleus of certain atoms accompanied by the emission (release) of particles and/or energy
 RADIOACTIVITY: spontaneous disintegration of the nucleus of certain atoms accompanied by the emission (release) of particles and/or energy ~ TRANSMUTATION: the change of one element into another due to
RADIOACTIVITY: spontaneous disintegration of the nucleus of certain atoms accompanied by the emission (release) of particles and/or energy ~ TRANSMUTATION: the change of one element into another due to
CONCEPT MAP ATOMS. Atoms. 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model. 6. Hydrogen spectrum
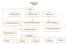 CONCEPT MAP ATOMS Atoms 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model 4.Emission line spectra 2a. Alpha scattering experiment 3a. Bohr s postulates 6. Hydrogen spectrum 8. De Broglie s explanation 5.Absorption
CONCEPT MAP ATOMS Atoms 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model 4.Emission line spectra 2a. Alpha scattering experiment 3a. Bohr s postulates 6. Hydrogen spectrum 8. De Broglie s explanation 5.Absorption
Nuclear Chemistry Review Packet
 Name Date Nuclear Chemistry Review Packet 1. The ratio of stability is (1) proton : neutron (2) neutron : proton (3) proton : positron (4) beta : proton 2. Which nuclear reaction is classified as alpha
Name Date Nuclear Chemistry Review Packet 1. The ratio of stability is (1) proton : neutron (2) neutron : proton (3) proton : positron (4) beta : proton 2. Which nuclear reaction is classified as alpha
NOTES: 25.2 Nuclear Stability and Radioactive Decay
 NOTES: 25.2 Nuclear Stability and Radioactive Decay Why does the nucleus stay together? STRONG NUCLEAR FORCE Short range, attractive force that acts among nuclear particles Nuclear particles attract one
NOTES: 25.2 Nuclear Stability and Radioactive Decay Why does the nucleus stay together? STRONG NUCLEAR FORCE Short range, attractive force that acts among nuclear particles Nuclear particles attract one
Basic Nuclear Theory. Lecture 1 The Atom and Nuclear Stability
 Basic Nuclear Theory Lecture 1 The Atom and Nuclear Stability Introduction Nuclear power is made possible by energy emitted from either nuclear fission or nuclear fusion. Current nuclear power plants utilize
Basic Nuclear Theory Lecture 1 The Atom and Nuclear Stability Introduction Nuclear power is made possible by energy emitted from either nuclear fission or nuclear fusion. Current nuclear power plants utilize
2. With the help of diagram explain the Edison s discovery of thermionic emission. Mention the observations and the conclusion.
 Work Sheet - 1 1. Explain the following terms i) Bound Electrons ii) Conduction/free electrons iii) Work function iv) Thermionic emission 2. With the help of diagram explain the Edison s discovery of thermionic
Work Sheet - 1 1. Explain the following terms i) Bound Electrons ii) Conduction/free electrons iii) Work function iv) Thermionic emission 2. With the help of diagram explain the Edison s discovery of thermionic
Card #1/28. Card #2/28. Science Revision P2. Science Revision P2. Science Revision P2. Card #4/28. Topic: F = ma. Topic: Resultant Forces
 Card #1/28 Card #2/28 Topic: Resultant Forces Topic: F = ma Topic: Distance-TIme Graphs Card #3/28 Card #4/28 Topic: Velocity-Time Graphs Card #2/28 Card #1/28 Card #4/28 Card #3/28 Card #5/28 Card #6/28
Card #1/28 Card #2/28 Topic: Resultant Forces Topic: F = ma Topic: Distance-TIme Graphs Card #3/28 Card #4/28 Topic: Velocity-Time Graphs Card #2/28 Card #1/28 Card #4/28 Card #3/28 Card #5/28 Card #6/28
Radioactive Decay 1 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2016
 Radioactive Decay 1 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Radioactive Decay 2 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What is radiation? 3 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2016 The term radiation (also known as nuclear radiation) refers to
Radioactive Decay 1 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Radioactive Decay 2 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What is radiation? 3 of 20 Boardworks Ltd 2016 The term radiation (also known as nuclear radiation) refers to
Table O: Symbols Used in Nuclear Chemistry
 Packet 12: NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY STABLITY OF NUCLEI Most nuclei are stable and don t change. They are found within the belt of stability. Some nuclei are unstable and break down spontaneously giving off rays
Packet 12: NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY STABLITY OF NUCLEI Most nuclei are stable and don t change. They are found within the belt of stability. Some nuclei are unstable and break down spontaneously giving off rays
7.1 Atomic Theory and Radioactive Decay
 7.1 Atomic Theory and Radioactive Decay exists all around us. This radiation consists of high energy particles or waves being emitted from a variety of materials. is the release of high energy particles
7.1 Atomic Theory and Radioactive Decay exists all around us. This radiation consists of high energy particles or waves being emitted from a variety of materials. is the release of high energy particles
NUCLEI, RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR REACTIONS
 NUCLEI, RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR REACTIONS VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Q-1. Which of the two is bigger 1 kwh or 1 MeV? Q-2. What should be the approximate minimum energy of a gamma ray photon for pair
NUCLEI, RADIOACTIVITY AND NUCLEAR REACTIONS VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Q-1. Which of the two is bigger 1 kwh or 1 MeV? Q-2. What should be the approximate minimum energy of a gamma ray photon for pair
Notes: Unit 13 Nuclear Chemistry
 Name: Regents Chemistry: Notes: Unit 13 Nuclear Chemistry Name: KEY IDEAS: Stability of isotopes is based in the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are
Name: Regents Chemistry: Notes: Unit 13 Nuclear Chemistry Name: KEY IDEAS: Stability of isotopes is based in the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are
Name Date Class NUCLEAR RADIATION. alpha particle beta particle gamma ray
 25.1 NUCLEAR RADIATION Section Review Objectives Explain how an unstable nucleus releases energy Describe the three main types of nuclear radiation Vocabulary radioisotopes radioactivity radiation alpha
25.1 NUCLEAR RADIATION Section Review Objectives Explain how an unstable nucleus releases energy Describe the three main types of nuclear radiation Vocabulary radioisotopes radioactivity radiation alpha
4.4.1 Atoms and isotopes The structure of an atom Mass number, atomic number and isotopes. Content
 4.4 Atomic structure Ionising radiation is hazardous but can be very useful. Although radioactivity was discovered over a century ago, it took many nuclear physicists several decades to understand the
4.4 Atomic structure Ionising radiation is hazardous but can be very useful. Although radioactivity was discovered over a century ago, it took many nuclear physicists several decades to understand the
Unit 1 Atomic Structure
 Unit 1 Atomic Structure Defining the Atom I. Atomic Theory A. Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the same element are chemically alike 3. Individual
Unit 1 Atomic Structure Defining the Atom I. Atomic Theory A. Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the same element are chemically alike 3. Individual
5 Atomic Physics. 1 of the isotope remains. 1 minute, 4. Atomic Physics. 1. Radioactivity 2. The nuclear atom
 5 Atomic Physics 1. Radioactivity 2. The nuclear atom 1. In a fission reactor, which particle causes a Uranium-235 nucleus to split? A. alpha-particle B. gamma ray C. neutron D. proton 2. A radioactive
5 Atomic Physics 1. Radioactivity 2. The nuclear atom 1. In a fission reactor, which particle causes a Uranium-235 nucleus to split? A. alpha-particle B. gamma ray C. neutron D. proton 2. A radioactive
There are 82 protons in a lead nucleus. Why doesn t the lead nucleus burst apart?
 Question 32.1 The Nucleus There are 82 protons in a lead nucleus. Why doesn t the lead nucleus burst apart? a) Coulomb repulsive force doesn t act inside the nucleus b) gravity overpowers the Coulomb repulsive
Question 32.1 The Nucleus There are 82 protons in a lead nucleus. Why doesn t the lead nucleus burst apart? a) Coulomb repulsive force doesn t act inside the nucleus b) gravity overpowers the Coulomb repulsive
Part 12- Physics Paper 1 Atomic Structure Application Questions Combined Science
 Part 12- Physics Paper 1 Atomic Structure Application Questions Combined Science Internal energy and energy transfers Internal energy and energy transfers Changes of state and the particle model Particle
Part 12- Physics Paper 1 Atomic Structure Application Questions Combined Science Internal energy and energy transfers Internal energy and energy transfers Changes of state and the particle model Particle
Chapter 37. Nuclear Chemistry. Copyright (c) 2011 by Michael A. Janusa, PhD. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 37 Nuclear Chemistry Copyright (c) 2 by Michael A. Janusa, PhD. All rights reserved. 37. Radioactivity Radioactive decay is the process in which a nucleus spontaneously disintegrates, giving off
Chapter 37 Nuclear Chemistry Copyright (c) 2 by Michael A. Janusa, PhD. All rights reserved. 37. Radioactivity Radioactive decay is the process in which a nucleus spontaneously disintegrates, giving off
Name: Nuclear Practice Test Ms. DeSerio
 Name: Nuclear Practice Test Ms. DeSerio 1. Which nuclear emission has the greatest mass and the least penetrating power? 1) an alpha particle 2) a beta particle 3) a neutron 4) a positron 2. The nucleus
Name: Nuclear Practice Test Ms. DeSerio 1. Which nuclear emission has the greatest mass and the least penetrating power? 1) an alpha particle 2) a beta particle 3) a neutron 4) a positron 2. The nucleus
Unit 1 Atomic Structure
 Unit 1 Atomic Structure 3-1 The Atom: From Philosophical Idea to Scientific Theory I. Atomic Theory A. Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the
Unit 1 Atomic Structure 3-1 The Atom: From Philosophical Idea to Scientific Theory I. Atomic Theory A. Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the
 The previous images display some of our hopes and fears associated with nuclear radiation. We know the images, and some of the uses, but what is Nuclear Radiation and where does it come from? Nuclide In
The previous images display some of our hopes and fears associated with nuclear radiation. We know the images, and some of the uses, but what is Nuclear Radiation and where does it come from? Nuclide In
Section 3: Nuclear Radiation Today
 : Nuclear Radiation Today Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Where is Radiation? Beneficial Uses of Nuclear Radiation Risks of Nuclear Radiation Nuclear Power Key Ideas Where are we exposed to radiation? What
: Nuclear Radiation Today Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Where is Radiation? Beneficial Uses of Nuclear Radiation Risks of Nuclear Radiation Nuclear Power Key Ideas Where are we exposed to radiation? What
Nuclear Physics Questions. 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of?
 Nuclear Physics Questions 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of? 2. What is the definition of the atomic number? What is its symbol?
Nuclear Physics Questions 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of? 2. What is the definition of the atomic number? What is its symbol?
the properties of that element
 Name Date Due Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table: Unit Objective Study Guide Part 1 Directions: Write your answers to the following questions in the space provided. For problem solving, all of the
Name Date Due Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table: Unit Objective Study Guide Part 1 Directions: Write your answers to the following questions in the space provided. For problem solving, all of the
Key Question: What role did the study of radioactivity play in learning more about atoms?
 Name Chemistry Essential question: How were the parts of the atom determined? Key Question: What role did the study of radioactivity play in learning more about atoms? Vocabulary: alpha particle fusion
Name Chemistry Essential question: How were the parts of the atom determined? Key Question: What role did the study of radioactivity play in learning more about atoms? Vocabulary: alpha particle fusion
Chemistry 19 Prep Test - Nuclear Processes
 Chapter 9 Prep-Test Chemistry 9 Prep Test - Nuclear Processes Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which of the illustrations above
Chapter 9 Prep-Test Chemistry 9 Prep Test - Nuclear Processes Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which of the illustrations above
Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity.
 Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity. A. Differentiate among alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. B. Differentiate between fission and fusion. C. Explain the process
Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity. A. Differentiate among alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. B. Differentiate between fission and fusion. C. Explain the process
Multiple Choice Questions
 Nuclear Physics & Nuclear Reactions Practice Problems PSI AP Physics B 1. The atomic nucleus consists of: (A) Electrons (B) Protons (C)Protons and electrons (D) Protons and neutrons (E) Neutrons and electrons
Nuclear Physics & Nuclear Reactions Practice Problems PSI AP Physics B 1. The atomic nucleus consists of: (A) Electrons (B) Protons (C)Protons and electrons (D) Protons and neutrons (E) Neutrons and electrons
Nuclear Chemistry. Chapter 24
 Nuclear Chemistry Chapter 24 Radioactivity Radioisotopes are isotopes that have an unstable nucleus. They emit radiation to attain more stable atomic configurations in a process called radioactive decay.
Nuclear Chemistry Chapter 24 Radioactivity Radioisotopes are isotopes that have an unstable nucleus. They emit radiation to attain more stable atomic configurations in a process called radioactive decay.
Nuclear Radiation. Natural Radioactivity. A person working with radioisotopes wears protective clothing and gloves and stands behind a shield.
 Nuclear Radiation Natural Radioactivity A person working with radioisotopes wears protective clothing and gloves and stands behind a shield. 1 Radioactive Isotopes A radioactive isotope has an unstable
Nuclear Radiation Natural Radioactivity A person working with radioisotopes wears protective clothing and gloves and stands behind a shield. 1 Radioactive Isotopes A radioactive isotope has an unstable
Chapter 10. Table of Contents. Section 1 What Is Radioactivity? Section 2 Nuclear Fission and Fusion. Section 3 Nuclear Radiation Today
 Nuclear Chemistry Table of Contents Section 1 What Is Radioactivity? Section 2 Nuclear Fission and Fusion Section 3 Nuclear Radiation Today Section 1 What Is Radioactivity? Bellringer Before studying about
Nuclear Chemistry Table of Contents Section 1 What Is Radioactivity? Section 2 Nuclear Fission and Fusion Section 3 Nuclear Radiation Today Section 1 What Is Radioactivity? Bellringer Before studying about
25.1. Nuclear Radiation
 Nuclear Radiation Marie Curie was a Polish scientist whose research led to many discoveries about radiation and radioactive elements. In 1934 she died from leukemia caused by her long-term exposure to
Nuclear Radiation Marie Curie was a Polish scientist whose research led to many discoveries about radiation and radioactive elements. In 1934 she died from leukemia caused by her long-term exposure to
H 1. Nuclear Physics. Nuclear Physics. 1. Parts of Atom. A. Nuclear Structure. 2b. Nomenclature. 2. Isotopes. AstroPhysics Notes
 AstroPhysics Notes Nuclear Physics Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Nuclear Physics A. Nuclear Structure B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions Updated: 0Feb07 Rough draft A. Nuclear Structure. Parts of Atom. Parts of
AstroPhysics Notes Nuclear Physics Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Nuclear Physics A. Nuclear Structure B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions Updated: 0Feb07 Rough draft A. Nuclear Structure. Parts of Atom. Parts of
Chemistry 132 NT. Nuclear Chemistry. Not everything that can be counted counts, and not everything that counts can be counted.
 Chemistry 132 NT Not everything that can be counted counts, and not everything that counts can be counted. Albert Einstein 1 Chem 132 NT Nuclear Chemistry Module 1 Radioactivity and Nuclear Bombardment
Chemistry 132 NT Not everything that can be counted counts, and not everything that counts can be counted. Albert Einstein 1 Chem 132 NT Nuclear Chemistry Module 1 Radioactivity and Nuclear Bombardment
 CHAPTER 19 THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS NUCLEAR STRUCTURE The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons. A protonis a positively charged particle having mass 1.6726 x 10(-27) kg and charge 1.6 x 10(-19) coulomb.
CHAPTER 19 THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS NUCLEAR STRUCTURE The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons. A protonis a positively charged particle having mass 1.6726 x 10(-27) kg and charge 1.6 x 10(-19) coulomb.
D) g. 2. In which pair do the particles have approximately the same mass?
 1. A student constructs a model for comparing the masses of subatomic particles. The student selects a small, metal sphere with a mass of gram to represent an electron. A sphere with which mass would be
1. A student constructs a model for comparing the masses of subatomic particles. The student selects a small, metal sphere with a mass of gram to represent an electron. A sphere with which mass would be
From Last Time. Stronger than coulomb force, But much shorter range than coulomb force.
 From Last Time Nucleus is small, tightly bound system of protons & neutrons. Proton number determines the element. Different isotopes have different # neutrons. Some isotopes unstable, radioactively decay
From Last Time Nucleus is small, tightly bound system of protons & neutrons. Proton number determines the element. Different isotopes have different # neutrons. Some isotopes unstable, radioactively decay
: When electrons bombarded surface of certain materials, invisible rays were emitted
 Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Reactions 1. Occur when nuclei emit particles and/or rays. 2. Atoms are often converted into atoms of another element. 3. May involve protons, neutrons, and electrons 4. Associated
Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Reactions 1. Occur when nuclei emit particles and/or rays. 2. Atoms are often converted into atoms of another element. 3. May involve protons, neutrons, and electrons 4. Associated
Journal 14. What is so dangerous about nuclear energy?
 Journal 14 What is so dangerous about nuclear energy? Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Chemistry Bravo 15,000 kilotons Discovery of Radiation Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen had discovered X rays Pierre & Marie Curie
Journal 14 What is so dangerous about nuclear energy? Nuclear Chemistry Nuclear Chemistry Bravo 15,000 kilotons Discovery of Radiation Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen had discovered X rays Pierre & Marie Curie
4 Nuclear Stability And Instability
 4 Nuclear Stability nd Instability Figure 4.1 Plot of N vs. Each black dot in Figure 4.1 represents a stable nuclide. Where more than one dot appears for a particular atomic number, those dots represent
4 Nuclear Stability nd Instability Figure 4.1 Plot of N vs. Each black dot in Figure 4.1 represents a stable nuclide. Where more than one dot appears for a particular atomic number, those dots represent
Nuclear forces and Radioactivity. Two forces are at work inside the nucleus of an atom
 Nuclear forces and Radioactivity Two forces are at work inside the nucleus of an atom Forces act in opposing directions Electrostatic repulsion: pushes protons apart Strong nuclear force: pulls protons
Nuclear forces and Radioactivity Two forces are at work inside the nucleus of an atom Forces act in opposing directions Electrostatic repulsion: pushes protons apart Strong nuclear force: pulls protons
Name: COMBINED SCIENCE Topics 4, 5 & 6 LEARNING OUTCOMES. Maintain a record of your progress Use the booklet to guide revision
 Name: COMBINED SCIENCE Topics 4, 5 & 6 LEARNING OUTCOMES Maintain a record of your progress Use the booklet to guide revision Close the Gap Contemporary record of the Topics / Learning outcomes that I
Name: COMBINED SCIENCE Topics 4, 5 & 6 LEARNING OUTCOMES Maintain a record of your progress Use the booklet to guide revision Close the Gap Contemporary record of the Topics / Learning outcomes that I
H 1. Nuclear Physics. Nuclear Physics. 1. Parts of Atom. 2. Isotopes. AstroPhysics Notes. Dr. Bill Pezzaglia. Rough draft. A.
 AstroPhysics Notes Tom Lehrer: Elements Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Nuclear Physics Updated: 0Feb Rough draft Nuclear Physics A. Nuclear Structure A. Nuclear Structure B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions. Parts
AstroPhysics Notes Tom Lehrer: Elements Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Nuclear Physics Updated: 0Feb Rough draft Nuclear Physics A. Nuclear Structure A. Nuclear Structure B. Nuclear Decay C. Nuclear Reactions. Parts
P7 Radioactivity. Student Book answers. P7.1 Atoms and radiation. Question Answer Marks Guidance
 P7. Atoms and radiation a radiation from U consists = particles, radiation from lamp = electromagnetic waves, radiation from U is ionising, radiation from lamp is non-ionising b radioactive atoms have
P7. Atoms and radiation a radiation from U consists = particles, radiation from lamp = electromagnetic waves, radiation from U is ionising, radiation from lamp is non-ionising b radioactive atoms have
IGCSE Physics 0625 notes: unit 5 Atomic Physics: Revised on 01 December
 IGCSE Physics 0625 notes: unit 5 Atomic Physics: Revised on 01 December 2011 1 TOPIC 5 ATOMIC PHYSICS Radioactivity or radioactive decay: 1. It is the process in which certain unstable atomic nuclei (plural
IGCSE Physics 0625 notes: unit 5 Atomic Physics: Revised on 01 December 2011 1 TOPIC 5 ATOMIC PHYSICS Radioactivity or radioactive decay: 1. It is the process in which certain unstable atomic nuclei (plural
By Tim, John, Shane, Owen
 By Tim, John, Shane, Owen A few refreshers Atoms of the same element, which always have an identical number of protons, that have different numbers of neutrons, is an isotope. Protons and neutrons are
By Tim, John, Shane, Owen A few refreshers Atoms of the same element, which always have an identical number of protons, that have different numbers of neutrons, is an isotope. Protons and neutrons are
Chapter 21
 Chapter 21 http://youtu.be/kwasz59f8ga Nuclear reactions involve the nucleus The nucleus opens, and protons and neutrons are rearranged. The opening of the nucleus releases a tremendous amount of energy
Chapter 21 http://youtu.be/kwasz59f8ga Nuclear reactions involve the nucleus The nucleus opens, and protons and neutrons are rearranged. The opening of the nucleus releases a tremendous amount of energy
Nuclear Medicine Treatments and Clinical Applications
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 243- LECTURE 4 Nuclear Medicine Treatments and Clinical Applications DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM References "Advancing Nuclear Medicine Through Innovation". Committee on State
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 243- LECTURE 4 Nuclear Medicine Treatments and Clinical Applications DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM References "Advancing Nuclear Medicine Through Innovation". Committee on State
Slide 1 / 57. Nuclear Physics & Nuclear Reactions Practice Problems
 Slide 1 / 57 Nuclear Physics & Nuclear Reactions Practice Problems Slide 2 / 57 Multiple Choice Slide 3 / 57 1 The atomic nucleus consists of: A B C D E Electrons Protons Protons and electrons Protons
Slide 1 / 57 Nuclear Physics & Nuclear Reactions Practice Problems Slide 2 / 57 Multiple Choice Slide 3 / 57 1 The atomic nucleus consists of: A B C D E Electrons Protons Protons and electrons Protons
Nuclear Chemistry Lecture Notes: I Radioactive Decay A. Type of decay: See table. B. Predicting Atomic Stability
 Nuclear Chemistry Lecture Notes: I Radioactive Decay A. Type of decay: See table Type Symbol Charge Mass (AMU) Effect on Atomic # Alpha α +2 4 decrease by 2 Beta β- -1 0 increase electron by 1 Beta β+
Nuclear Chemistry Lecture Notes: I Radioactive Decay A. Type of decay: See table Type Symbol Charge Mass (AMU) Effect on Atomic # Alpha α +2 4 decrease by 2 Beta β- -1 0 increase electron by 1 Beta β+
Radioactivity pp Topic 9: Nuclear Physics Ch. 10. Radioactivity. Radioactivity
 Topic 9: Nuclear Physics Ch. 10 pp.244-249 results from radioactive decay, which is the process in which unstable atomic nuclei transform and emit radiation. has existed longer than the human race. Unstable
Topic 9: Nuclear Physics Ch. 10 pp.244-249 results from radioactive decay, which is the process in which unstable atomic nuclei transform and emit radiation. has existed longer than the human race. Unstable
Chapter 12: Nuclear Reaction
 Chapter 12: Nuclear Reaction A nuclear reaction occurs when a nucleus is unstable or is being bombarded by a nuclear particle. The product of a nuclear reaction is a new nuclide with an emission of a nuclear
Chapter 12: Nuclear Reaction A nuclear reaction occurs when a nucleus is unstable or is being bombarded by a nuclear particle. The product of a nuclear reaction is a new nuclide with an emission of a nuclear
Particles involved proton neutron electron positron gamma ray 1
 TOPIC : Nuclear and radiation chemistry Nuclide - an atom with a particular mass number and atomic number Isotopes - nuclides with the same atomic number (Z) but different mass numbers (A) Notation A Element
TOPIC : Nuclear and radiation chemistry Nuclide - an atom with a particular mass number and atomic number Isotopes - nuclides with the same atomic number (Z) but different mass numbers (A) Notation A Element
Chemistry 500: Chemistry in Modern Living. Topic 5: The Fires of Nuclear Fission. Atomic Structure, Nuclear Fission and Fusion, and Nuclear.
 Chemistry 500: Chemistry in Modern Living 1 Topic 5: The Fires of Nuclear Fission Atomic Structure, Nuclear Fission and Fusion, and Nuclear Weapons Chemistry in Context, 2 nd Edition: Chapter 8, Pages
Chemistry 500: Chemistry in Modern Living 1 Topic 5: The Fires of Nuclear Fission Atomic Structure, Nuclear Fission and Fusion, and Nuclear Weapons Chemistry in Context, 2 nd Edition: Chapter 8, Pages
HOMEWORK 22-1 (pp )
 CHAPTER 22 HOMEWORK 22-1 (pp. 701 702) Define. 1. nucleons 2. nuclide 3. mass defect 4. nuclear binding energy Solve. Use masses of 1.0087 amu for the neutron, 1.00728 amu for the proton, and 5.486 x 10
CHAPTER 22 HOMEWORK 22-1 (pp. 701 702) Define. 1. nucleons 2. nuclide 3. mass defect 4. nuclear binding energy Solve. Use masses of 1.0087 amu for the neutron, 1.00728 amu for the proton, and 5.486 x 10
3 Types of Nuclear Decay Processes
 3 Types of Nuclear Decay Processes Radioactivity is the spontaneous decay of an unstable nucleus The radioactive decay of a nucleus may result from the emission of some particle from the nucleus. The emitted
3 Types of Nuclear Decay Processes Radioactivity is the spontaneous decay of an unstable nucleus The radioactive decay of a nucleus may result from the emission of some particle from the nucleus. The emitted
21/11/ /11/2017 Atomic Structure AQA Physics topic 4
 Atomic Structure AQA Physics topic 4 4.1 Atoms and Isotopes The structure of the atom ELECTRON negative, mass nearly nothing The nucleus is around 10,000 times smaller then the atom! NEUTRON neutral, same
Atomic Structure AQA Physics topic 4 4.1 Atoms and Isotopes The structure of the atom ELECTRON negative, mass nearly nothing The nucleus is around 10,000 times smaller then the atom! NEUTRON neutral, same
Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Pakistan Online tuition Online Tutor Pakistan. NUCLEAR PHYSICS: Chapter 19
 Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Pakistan Online tuition Online Tutor Pakistan NUCLEAR PHYSICS: Chapter 19 Nuclear Physics: Branch of physics that deals with the study of the nucleus is called nuclear physics.
Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Pakistan Online tuition Online Tutor Pakistan NUCLEAR PHYSICS: Chapter 19 Nuclear Physics: Branch of physics that deals with the study of the nucleus is called nuclear physics.
