SILVER OAK COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
|
|
|
- Merryl Booker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BE - SEMESTER IV MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION SUMMER 2015 SUBJECT: MECHANICAL MEASUREMENT & METROLOGY ( ) DATE: TIME:11:00 am to 12:30 pm TOTAL MARKS:40 Q.1 (a) Explain errors and its classification. (b) Define the following terms. (i) Threshold (ii) Accuracy (iii) Linearity (iv) Hysteresis (v) Resolution Q.2 (a) Describe with sketch the construction and working of a micrometer. Explain how least count is found and reading is taken. [6] (b) Explain working principle of Linear Variable Differential Transformer [6] (LVDT) and advantages disadvantage of LVDT. (c) Explain any one Limit Gauges for measurement. [3] Q.2 (a) Explain the construction and use of sine bar with neat sketch [6] (b) Describe with neat sketch working of piezoelectric accelerometer. [6] (c) What are the angle gauges? Explain it with neat sketch. [3] Q.3 (a) Explain pitch measurement Methods. [6] (b) Describe the construction and working of Resistance Temperature Detector [6] (RTD) with its advantages and disadvantages. (c) State and explain three laws of Thermocouple. [3] Q.3 (a) Describe with sketch the construction and use of Gear Tooth Vernier Caliper. Derive equation for measurement. [6] (b) Explain Total Radiation Pyrometer. [6] (c) Differentiate between Resistance thermometer and thermister. [3] ****************************************************************************************************
2 BE - SEMESTER IV MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION SUMMER 2015 SUBJECT: Engineering Economics and Management ( ) DATE: TIME: 11:00 am to 12:30 pm TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Discuss the levels of management. [04] (b) Differentiate between Micro-economics and Macro-economics. [03] (c) List down the principles of organizing. [03] Q.2 (a) Explain the determinants of demand. [05] (b) Explain Maslow s need hierarchy theory with the help of a diagram. [05] (c) How is the function of staffing important in management? [05] Q.2 (a) Define elasticity. Explain price elasticity of demand in detail. [05] (b) Explain the following concepts of cost: 1. Opportunity cost 2. Fixed and variable cost [05] 3. Average cost (c) Explain the functions of financial management. [05] Q.3 (a) Define marketing management? Explain marketing mix (4Ps) in detail. [08] (b) What is production? Discuss the factors of production in detail. [07] Q.3 (a) Write short notes on: 1. Matrix Organization Structure [08] 2. Line and Staff Organization Structure (b) Explain Henry Fayol s principles of administrative management. [07] ****************************************************************************************************
3 B.E. Semester- (IV) MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION Summer 2015 SUBJECT: Complex Variables And Numerical Methods ( ) Date: TIME:11:00A.M. to 12:45P.M. Total Marks: 40 Q.1 (a) Find real root of x 3 +x-1= 0 (upto 3 decimal places) using Newton-Raphson Method. 3 (b) Evaluate dx 1 0 x with n=6 by using Simpson s 3/8 rule and hence calculate log2. Q.2 (a) Find the real root of xe x -2 = 0 which lies between 0.8 and 0.9 up to 3 decimal places using Regula Falsi method. (b) Solve the following system of equations by using Gauss-Seidel method correct up to two decimal places: 20x+2y+z= 30, x-40y+3z = -75, 2x - y+10z=30. (c) 6 2 Evaluate the integral ( 1 x 2 ) 3 / dx by Gaussian formula for n =3. 2 Q.2 (a) Find the real root of equation x 3 +4x 2-10=0 using Bisection Method. (b) Solve the following system of equation using Gauss Elimination method with Partial Pivoting: x+y +z =7, 3x+3y+4z = 24, 2x +y+3z= (c) Evaluate 2 x 1 dx 1 0 using four strips by simpson s 3 1 rule. Q.3 (a) What is analytic function? Show that 3 (b) Show that 3 2 f z z is analytic everywhere. u x, y 2x x 3xy is harmonic and Find a harmonic conjugate v ( x, y). (c) 1 dy Use the Euler method to find y (1.4) given that xy 2, y(1) 1 dx. Q.3 (a) 2 3 Evaluate dominant eigenvalue of matrix using power method. 5 4 (b) 2 Solve the equation z 5 i z 8 i 0 (c) Apply Runge-Kutta method of fourth order to calculate y (0.2) given y y ( 0) 1 taking h=0.1. 2, x y ********************************************************************************
4 BE - SEMESTER IV MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION SUMMER 2015 SUBJECT: FLUID MECHANICS ( ) DATE: TIME: 11:00 am to 12:30 pm TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Define the following: 1. Streak line 2. Stream line 3. Path line (b) The pressure difference Δp in a pipe of diameter D and length l due to viscous flow depends on the velocity V, viscosity µ and density ρ. Using Buckingham s π- theorem, obtain an expression for Δp. [3] [7] Q.2 (a) Define: Density, Cohesion, Geometric Similarity, Specific Gravity, Specific Volume. (b) Calculate the dynamic viscosity of oil, which is used for lubrication between a rectangular plate of size 1.0 m 0.8 m and an inclined plane with angle of inclination 25. The mass of the rectangular plate is 20 kg and it slides down the inclined plane with a uniform velocity of 0.5 m/s. the thickness of oil film is 2 mm. (c) A 1:15 scale model of an airplane, the model tested in water (density 998 Kg/m 3 and viscosity 0.02 poise). The pressure drop in model is 6 KN/m 2. The density and viscosity of air 1.23 Kg/m 3 and poise respectively. Calculate pressure drop in the prototype. Q.2 (a) Derive Pascal s law using proper notations? (b) Define continuum and capillary effect. Derive expression for capillary rise for a tube? (c) In a geometrically similar model of spillway the discharge per meter length and force are 1/6 m 3 /s and 2 N. if the scale of the model is 1/36. Find the discharge per meter length of the prototype. Q.3 (a) Velocity components of a fluid flow are given as u=(6xy 2 + t), v= (3yz+t 2 +5), w=(z+3ty) where x, y, z are given in meters and time t in seconds. Determine [6]
5 velocity vector at point P (4,1,2) at time t=4s. Also determine the magnitude of velocity and acceleration of the flow for given location and time. (b) Derive Euler s equation along a stream line and from it obtain the Bernoulli s equation. Clearly mention the assumptions used. (c) Define the following : 1. Uniform and non uniform flow 2. Stream tube 3. Laminar and Turbulent flow 4. Steady and unsteady flow Q.3 (a) Derive the continuity equation for three dimensional Cartesian coordinates. Simplify it for two dimensional, steady and incompressible flows. (b) A horizontal venturi meter of 200mm 100mm is used to measure the discharge of an oil of specific gravity The mercury manometer is used for the purpose. If the discharge is 100 liters per second and if the coefficient of discharge of the venturi meter is 0.97, find the difference of mercury level in between two limbs of manometer. (c) Differentiate between: 1. Eulerian approach and Lagrangian approach 2.Rotational Flow and Irrotational flow [4] [6] [4] ****************************************************************************************************
6 BE - SEMESTER IV MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION SUMMER 2015 MACHINE DESIGN & INDUSTRIAL DRAFTING ( ) DATE: 13/03/2015 TIME: 11:00AM TO 12:45PM TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Define fit. Describe various types of fits in brief. [3] (b) Explain hole basis system and shaft basis system of fits. [3] (c) How surface roughness is calculated using formulas? Indicate [4] machining symbol showing direction of lay in terms of geometric tolerances. Q.2 (a) Square key is stronger against crushing than rectangular key. Justify [05] the statement. (b) What do you mean by couplings? How couplings are classified? [04] (c) A steel spindle transmits 4kW at 800 rpm. The angular deflection [06] should not exceed 0.25 per meter of the spindle. If the modulus of rigidity for the material of the spindle is N/mm 2. Find the diameter of spindle and shear stress induced in the spindle. Q.2 (a) Explain different types of keys with its applications. [05] (b) Explain the Design of muff coupling. [03] (c) A belt driven C.I pulley of 0.9 m diameter overhangs the bearing by 0.2 [07] m as shown in figure-1. The pulley is driven from the bottom by a belt. The angles of lap and tension on tight side are 180 and 2600 N respectively. The weight of pulley is 600 N. Assume co-efficient of friction between pulley and belt is Shaft is made up of 30C8. σ yt = 400 N/mm², σ ut = 500 N/mm² Determine the shaft diameter according to ASME code. Take Ks=1.0, Kb=1.5.
7 Figure-1 Q.3 (a) Define theories of failures. (b) It is required to design a cotter joint to connect two steel rods of equal [10] diameter. Each rod is subjected to an axial tensile load of 50 kn. The permissible stresses are 67 MPa in tension, 34 MPa in shear and 134 Mpa in crushing for all parts. Calculate following dimension, i) Diameter of spigot, ii) thickness of cotter, iii) Diameter of socket collar, iv) Thickness of socket collar, v) Width of cotter. Q.3 (a) A bell crank lever is to be designed to raise a load of 5kN at the short [7] arm end. The arm lengths are 150mm and 500mm. The permissible stresses for lever pin materials in shear and tension are 60 MPa and 90 Mpa respectively. The bearing pressure intensity on the pin is to be limited to 12 MPa. Assume the lever cross-section as t 4t and length of fulcrum pin as 1.25 times pin diameter. Design the lever from above data. (b) Design a knuckle joint to connect two mild steel bars under a tensile [8] load of 25 kn. The allowable stresses are 65 MPa in tension, 50 MPa in shear and 83 MPa in crushing. ****************************************************************************************************
8 BE - SEMESTER IV MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION SUMMER 2015 SUBJECT: MANUFACTURING PROCESSES-II ( ) DATE: TIME: 11:00AM TO 12:30PM TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Define following terms 1. Mould 2. Cavity 3. Pattern 4. Chaplets 5. Core print 6. Break Even Point (b) What type of allowances is generally incorporated into a casting pattern? Discuss shrinkage and distortion allowances. (c) Determine the permeability number if 2000 cc of air takes 80 sec. to pass through a standard specimen (4.45cm height and 4.45cm dia) and the manometer indicate an air pressure reading of 5 gm/cm 2. (3) (4) (3) Q.2 (a) Explain with neat sketches types of gating systems used in casting process. (5) (b) Explain investment casting process. (7) (c) Explain the properties of moldings sand (any two). (3) Q.2 (a) Describe casting defects stating their causes and remedies. (5) (b) Explain die casting process. (7) (c) Draw the neat sketch of sweep and match plate pattern. (3) Q.3 (a) Explain the principle of rolling process. Classify rolling mill and explain any (6) one in detail. (b) Write short note on wire drawing. (5) (c) Define: slab, bloom, billet and ingot. (4) Q.3 (a) Explain with sketch the difference between direct and indirect extrusion. (5) (b) Differentiate between hot working and cold working. (6) (c) Explain elastic and plastic deformation process briefly. (4) ******************************ALL THE BEST*********************************
9 BE - SEMESTER IV MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION SUMMER 2015 SUBJECT: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS ( ) DATE: TIME: 11:00 am to 12:30 pm TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Define Thermodynamic system. Also explain different thermodynamic [7] systems with appropriate examples. (b) Differentiate between Intensive and Extensive properties of system. [3] Q.2 (a) Prove that Energy A Property of System [4] (b) In a steam power cycle, the dry and saturated steam is supplied at 15 bar. If [6] the Condenser pressure is 0.4 bar, calculate the Carnot and Rankine cycle Efficiencies neglecting the pump work. (c) Write comparison of Carnot and Rankine cycle. Q.2 (a) Explain following terms: Flow work, critical point, triple point. [3] (b) The mass flow rate of steam into a steam turbine is 1.5Kg/s and heat [6] transfer from the turbine is 8.5KW. The steam is entering in the turbine at the pressure of 2 MPa, temperature 350 C, velocity 50m/s, elevation 6m and is leaving the turbine at a pressure of 0.1 MPa, quality of 100% velocity of 200m/s, elevation of 3m. Determine the power output of turbine. (c) Explain P-V and T-s diagram for Diesel cycle. Derive the formula for the [6] efficiency of the cycle. Q.3 (a) Write steady flow energy equation in case of Nozzle, Diffuser and Turbine. [6] (b) In a steam power station, steam flows steadily through a 0.2 m diameter pipeline from the boiler to the turbine. At the boiler end, the steam conditions are found to be: p=4 MPa, t= 400 deg C, h= kj/kg and v= m3/kg. At the turbine end the condition are found to be: p= 3.5 MPa, t=392 deg C, h= kj/kg & v= m3/kg. There is a heat loss of 8.5 kj/kg from the pipe line. Calculate the steam flow rate. (c) Prove that Energy is a point function of a system undergoing change of [4] state.
10 Q.3 (a) What is meant by thermodynamic equilibrium? How goes it differ from thermal equilibrium. (b) Carnot cycle is not practical. Justify. [3] (c) A Carnot engine receives 4000 KJ as heat addition at 337 c and rejects [7] energy at triple point of water. Calculate (1) thermal efficiency (2) The net work output in KJ If the efficiency of an irreversible engine is 70 % of Carnot engine. Find the % change in heat rejected for the same input and fluid temperature. ****************************************************************************************************
11 BE - SEMESTER IV MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION SUMMER 2015 SUBJECT: KINEMATIC OF MACHINES ( ) DATE: TIME: 11:00 am to 12:30 pm TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Classify cams and followers in detail. [4] (b) Define: [3] i) Contact Ratio ii) Module iii) Circular Pitch (c) Explain the difference between interference and undercut with neat sketch. [3] Q.2 (a) Define the following terms: [7] 1. Link 2. Locked Chain 3. Higher Pair 4. Ternary Joint 5. Degrees of freedom 6. Constrained Motion 7. Quaternary Link. (b) Define the following terms as applied to cam with a neat sketch :- (a)base circle, (b) Pitch circle, (c) Pressure angle, and (d) Trace Point (e) Pitch Curve. (c) Explain the following terms [3] (1) Resistant body (2) D.O.F (3) link Q.2 (a) Sketch and describe the working of Beam Engine. (b) Explain types of motions [3] (1) Completely constrained motion; (2) Incompletely constrained motion; (3) Successfully constrained motion (c) A cam is to give the following motion to a knife-edged follower: [7] 1. Outstroke during 60 of cam rotation; 2. Dwell for the next 30 of cam rotation; 3. Return stroke during next 60 of cam rotation and 4. Dwell for the remaining 210 of cam rotation. The stroke of the follower is 40 mm and the minimum radius of the cam is 50 mm. The follower moves with uniform velocity during both the outstroke and return strokes. Draw the profile of the cam when the axis of the follower passes through the axis of the cam shaft,
12 Q.3 (a) Explain Compound gear train with neat sketch in detail. [6] (b) An epicyclic gear train as shown in fig. has a sun wheel S of 30 teeth and two [9] planet wheels P of 50 teeth. The planet wheel mesh with the internal teeth of a fixed annular A. The driving shaft carrying the sun wheel transmits 4 KW at 300 rpm. The driven shaft is connected to an arm which carries the planet wheel. Determine the speed of the driven shaft. Q.3 (a) Derive an Expression for Length of Path of contact of Gears. [7] (b) Determine the minimum number of teeth required on a pinion, in order to [8] avoid interference which is to gear with, 1. A wheel to give a gear ratio of 3 to 1; and 2. An equal wheel. The pressure angle is 20 and a standard addendum of 1 module for the wheel may be assumed. ****************************************************************************************************
AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14
 AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14 III SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY-2013 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY-I Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What
AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14 III SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY-2013 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY-I Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What
SILVER OAK COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ADITYA SILVER OAK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 SUBJECT: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (2131905) (ME) DATE: 11-08-2017 TIME: 10:00 am to 11:30 am TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Answer following questions in short/brief: 1. Energy of an isolated system is always
SUBJECT: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (2131905) (ME) DATE: 11-08-2017 TIME: 10:00 am to 11:30 am TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Answer following questions in short/brief: 1. Energy of an isolated system is always
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK : AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING.
 Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : Mechanics of Fluids : A00 : II-I- B. Tech Year : 0 0 Course Coordinator
Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : Mechanics of Fluids : A00 : II-I- B. Tech Year : 0 0 Course Coordinator
ME3560 Tentative Schedule Spring 2019
 ME3560 Tentative Schedule Spring 2019 Week Number Date Lecture Topics Covered Prior to Lecture Read Section Assignment Prep Problems for Prep Probs. Must be Solved by 1 Monday 1/7/2019 1 Introduction to
ME3560 Tentative Schedule Spring 2019 Week Number Date Lecture Topics Covered Prior to Lecture Read Section Assignment Prep Problems for Prep Probs. Must be Solved by 1 Monday 1/7/2019 1 Introduction to
R09. d water surface. Prove that the depth of pressure is equal to p +.
 Code No:A109210105 R09 SET-1 B.Tech II Year - I Semester Examinations, December 2011 FLUID MECHANICS (CIVIL ENGINEERING) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any five questions All questions carry equal
Code No:A109210105 R09 SET-1 B.Tech II Year - I Semester Examinations, December 2011 FLUID MECHANICS (CIVIL ENGINEERING) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any five questions All questions carry equal
Civil Services Examination-1989
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission.
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission.
ME3560 Tentative Schedule Fall 2018
 ME3560 Tentative Schedule Fall 2018 Week Number 1 Wednesday 8/29/2018 1 Date Lecture Topics Covered Introduction to course, syllabus and class policies. Math Review. Differentiation. Prior to Lecture Read
ME3560 Tentative Schedule Fall 2018 Week Number 1 Wednesday 8/29/2018 1 Date Lecture Topics Covered Introduction to course, syllabus and class policies. Math Review. Differentiation. Prior to Lecture Read
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
UNIT I FLUID PROPERTIES AND STATICS
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Fluid Mechanics (16CE106) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & I-Sem Course & Branch:
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Fluid Mechanics (16CE106) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & I-Sem Course & Branch:
2014 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 R10 SET - 1 II. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 MEHNIS OF MTERILS (ivil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 nswer any FIVE Questions ll Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
R10 SET - 1 II. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 MEHNIS OF MTERILS (ivil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 nswer any FIVE Questions ll Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
PES Institute of Technology
 PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
(Following Paper ID and Roll No. to be filled in your Answer Book) I I I I I. B.Tech. SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION,
 - Printed Pages - 6 TME - 201 (Following Paper ID and Roll No. to be filled in your Answer Book) I I I I I Roll No. B.Tech. SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION, 2005-2006 '-" Time: 3 Hours oa:::::t U') om (D om
- Printed Pages - 6 TME - 201 (Following Paper ID and Roll No. to be filled in your Answer Book) I I I I I Roll No. B.Tech. SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION, 2005-2006 '-" Time: 3 Hours oa:::::t U') om (D om
 CE 6303 MECHANICS OF FLUIDS L T P C QUESTION BANK 3 0 0 3 UNIT I FLUID PROPERTIES AND FLUID STATICS PART - A 1. Define fluid and fluid mechanics. 2. Define real and ideal fluids. 3. Define mass density
CE 6303 MECHANICS OF FLUIDS L T P C QUESTION BANK 3 0 0 3 UNIT I FLUID PROPERTIES AND FLUID STATICS PART - A 1. Define fluid and fluid mechanics. 2. Define real and ideal fluids. 3. Define mass density
PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY
 PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011 COURSE NAME: Mechanical Engineering Science CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: JUNE 28 TIME: DURATION:
PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011 COURSE NAME: Mechanical Engineering Science CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: JUNE 28 TIME: DURATION:
S.E. (Mech.) (First Sem.) EXAMINATION, (Common to Mech/Sandwich) FLUID MECHANICS (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 8 Seat No. [4262]-113 S.E. (Mech.) (First Sem.) EXAMINATION, 2012 (Common to Mech/Sandwich) FLUID MECHANICS (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 8 Seat No. [4262]-113 S.E. (Mech.) (First Sem.) EXAMINATION, 2012 (Common to Mech/Sandwich) FLUID MECHANICS (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum
UNIVERSITY POLYTECHNIC B.I.T., MESRA, RANCHI
 COURSE STRUCTURE Diploma in Technology (W.E.F. 2011 Batch Students) SEMESTER IV (Total Unit 7.5) Mechanical Course Theory Unit Course Sessional Unit Code Code DAE 4001 Thermal Engineering 1.0 DAE 4002
COURSE STRUCTURE Diploma in Technology (W.E.F. 2011 Batch Students) SEMESTER IV (Total Unit 7.5) Mechanical Course Theory Unit Course Sessional Unit Code Code DAE 4001 Thermal Engineering 1.0 DAE 4002
Fluid Mechanics Answer Key of Objective & Conventional Questions
 019 MPROVEMENT Mechanical Engineering Fluid Mechanics Answer Key of Objective & Conventional Questions 1 Fluid Properties 1. (c). (b) 3. (c) 4. (576) 5. (3.61)(3.50 to 3.75) 6. (0.058)(0.05 to 0.06) 7.
019 MPROVEMENT Mechanical Engineering Fluid Mechanics Answer Key of Objective & Conventional Questions 1 Fluid Properties 1. (c). (b) 3. (c) 4. (576) 5. (3.61)(3.50 to 3.75) 6. (0.058)(0.05 to 0.06) 7.
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS
 SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics
![PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics](/thumbs/92/109382806.jpg) Page1 PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [2910601] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics 1. Differentiate between Scalar and Vector quantity. Write S.I.
Page1 PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [2910601] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics 1. Differentiate between Scalar and Vector quantity. Write S.I.
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
Figure 3: Problem 7. (a) 0.9 m (b) 1.8 m (c) 2.7 m (d) 3.6 m
 1. For the manometer shown in figure 1, if the absolute pressure at point A is 1.013 10 5 Pa, the absolute pressure at point B is (ρ water =10 3 kg/m 3, ρ Hg =13.56 10 3 kg/m 3, ρ oil = 800kg/m 3 ): (a)
1. For the manometer shown in figure 1, if the absolute pressure at point A is 1.013 10 5 Pa, the absolute pressure at point B is (ρ water =10 3 kg/m 3, ρ Hg =13.56 10 3 kg/m 3, ρ oil = 800kg/m 3 ): (a)
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
[5] Stress and Strain
![[5] Stress and Strain [5] Stress and Strain](/thumbs/95/123344550.jpg) [5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
[5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
Levers. 558 A Textbook of Machine Design
 558 A Textbook of Machine Design C H A P T E R 15 Levers 1. Introduction.. Application of Levers in Engineering Practice.. Design of a Lever. 4. Hand Lever. 5. Foot Lever. 6. Cranked Lever. 7. Lever for
558 A Textbook of Machine Design C H A P T E R 15 Levers 1. Introduction.. Application of Levers in Engineering Practice.. Design of a Lever. 4. Hand Lever. 5. Foot Lever. 6. Cranked Lever. 7. Lever for
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SEMESTER: III SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A
 DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 009 Mechanical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 009 Mechanical
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) PART-A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
Topic wise Tests. Complex Variables, Numerical Methods and Probability and Statistics.
 ME-01 ME-02 ME-03 ME-04 GEM-1 GEM-2 GMC 1 Mechanics) GHT 1 Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
ME-01 ME-02 ME-03 ME-04 GEM-1 GEM-2 GMC 1 Mechanics) GHT 1 Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
Set 2 (d) 150 C (a) 0.45 (d) can be positive, negative or zero (C) 8.5 J/K (a) 0.1
 Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
Lesson 6 Review of fundamentals: Fluid flow
 Lesson 6 Review of fundamentals: Fluid flow The specific objective of this lesson is to conduct a brief review of the fundamentals of fluid flow and present: A general equation for conservation of mass
Lesson 6 Review of fundamentals: Fluid flow The specific objective of this lesson is to conduct a brief review of the fundamentals of fluid flow and present: A general equation for conservation of mass
D e s i g n o f R i v e t e d J o i n t s, C o t t e r & K n u c k l e J o i n t s
 D e s i g n o f R i v e t e d J o i n t s, C o t t e r & K n u c k l e J o i n t s 1. Design of various types of riveted joints under different static loading conditions, eccentrically loaded riveted joints.
D e s i g n o f R i v e t e d J o i n t s, C o t t e r & K n u c k l e J o i n t s 1. Design of various types of riveted joints under different static loading conditions, eccentrically loaded riveted joints.
FE Fluids Review March 23, 2012 Steve Burian (Civil & Environmental Engineering)
 Topic: Fluid Properties 1. If 6 m 3 of oil weighs 47 kn, calculate its specific weight, density, and specific gravity. 2. 10.0 L of an incompressible liquid exert a force of 20 N at the earth s surface.
Topic: Fluid Properties 1. If 6 m 3 of oil weighs 47 kn, calculate its specific weight, density, and specific gravity. 2. 10.0 L of an incompressible liquid exert a force of 20 N at the earth s surface.
General Aptitude (GA) Set-1. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are.
 GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-1 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Going by the that many hands make light work, the school involved all the students in the task. The words that best fill the blanks
GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-1 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Going by the that many hands make light work, the school involved all the students in the task. The words that best fill the blanks
Public Service Commission, West Bengal
 Public Service Commission, West Bengal Syllabus for the Written Test for recruitment to the posts of ASSISTANT ENGINEER (Agri - Mechanical) in West Bengal Service of Agricultural Engineers Mechanical Engineering
Public Service Commission, West Bengal Syllabus for the Written Test for recruitment to the posts of ASSISTANT ENGINEER (Agri - Mechanical) in West Bengal Service of Agricultural Engineers Mechanical Engineering
Set 1. a. 100 kj/kg b. 110 kj/kg c. 140 kj/kg d. 150 kj/kg
 Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
ACE Engineering College
 ACE Engineering College Ankushapur (V), Ghatkesar (M), R.R.Dist 501 301. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * MECHANICS OF FLUIDS & HYDRAULIC
ACE Engineering College Ankushapur (V), Ghatkesar (M), R.R.Dist 501 301. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * MECHANICS OF FLUIDS & HYDRAULIC
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy
 Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
SSC JE MECHANICAL Paper Pattern & Syllabus
 SSC JE MECHANICAL 2017-18 Paper Pattern & Syllabus About Us Transformation of education and training has begun. Our task is to bring redress, establish, quality. Open the doors of opportunity, enable a
SSC JE MECHANICAL 2017-18 Paper Pattern & Syllabus About Us Transformation of education and training has begun. Our task is to bring redress, establish, quality. Open the doors of opportunity, enable a
CIVIL DEPARTMENT MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES- ASSIGNMENT NO 1. Brach: CE YEAR:
 MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES- ASSIGNMENT NO 1 SEMESTER: V 1) Find the least moment of Inertia about the centroidal axes X-X and Y-Y of an unequal angle section 125 mm 75 mm 10 mm as shown in figure 2) Determine
MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES- ASSIGNMENT NO 1 SEMESTER: V 1) Find the least moment of Inertia about the centroidal axes X-X and Y-Y of an unequal angle section 125 mm 75 mm 10 mm as shown in figure 2) Determine
SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA
 SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA (Declared as Deemed-to-be University under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956, Vide notification No.F.9.9/92-U-3 dated 26 th May 1993 of the Govt. of
SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA (Declared as Deemed-to-be University under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956, Vide notification No.F.9.9/92-U-3 dated 26 th May 1993 of the Govt. of
GATE 2009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper
 GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper. For a matrix [M]= x [M]. The value of x is given by GATE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 009 (ME) GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper Q. No. 0 Carry One
GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper. For a matrix [M]= x [M]. The value of x is given by GATE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 009 (ME) GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper Q. No. 0 Carry One
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. Candidates should attempt
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. Candidates should attempt
3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No.
 *17304* 17304 14115 3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All questions are compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full
*17304* 17304 14115 3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All questions are compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full
Q.1 a) any six of the following 6x2= 12. i) Define - ( Each term 01 mark)
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
V/ t = 0 p/ t = 0 ρ/ t = 0. V/ s = 0 p/ s = 0 ρ/ s = 0
 UNIT III FLOW THROUGH PIPES 1. List the types of fluid flow. Steady and unsteady flow Uniform and non-uniform flow Laminar and Turbulent flow Compressible and incompressible flow Rotational and ir-rotational
UNIT III FLOW THROUGH PIPES 1. List the types of fluid flow. Steady and unsteady flow Uniform and non-uniform flow Laminar and Turbulent flow Compressible and incompressible flow Rotational and ir-rotational
2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 R10 SET - 1 II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
R10 SET - 1 II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Only for Reference Page 1 of 18
 Only for Reference www.civilpddc2013.weebly.com Page 1 of 18 Seat No.: Enrolment No. GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY PDDC - SEMESTER II EXAMINATION WINTER 2013 Subject Code: X20603 Date: 26-12-2013 Subject
Only for Reference www.civilpddc2013.weebly.com Page 1 of 18 Seat No.: Enrolment No. GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY PDDC - SEMESTER II EXAMINATION WINTER 2013 Subject Code: X20603 Date: 26-12-2013 Subject
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK III SEMESTER CE 8302 FLUID MECHANICS Regulation 2017 Academic Year 2018 19 Prepared by Mrs.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK III SEMESTER CE 8302 FLUID MECHANICS Regulation 2017 Academic Year 2018 19 Prepared by Mrs.
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
UNIT II Fig (1) Fig (1)
 UNIVERSITY OF PUNE [4362]-116 S.E.(Mechanical / Automobile) Examination 2013 (2008 pattern) THEY OF MACHINES -1 [Total No. of Questions: 12] [Total No. of Printed pages: 7] [Time: 4 Hours] [Max. Marks:
UNIVERSITY OF PUNE [4362]-116 S.E.(Mechanical / Automobile) Examination 2013 (2008 pattern) THEY OF MACHINES -1 [Total No. of Questions: 12] [Total No. of Printed pages: 7] [Time: 4 Hours] [Max. Marks:
1 FLUIDS AND THEIR PROPERTIES
 FLUID MECHANICS CONTENTS CHAPTER DESCRIPTION PAGE NO 1 FLUIDS AND THEIR PROPERTIES PART A NOTES 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Fluids 1.3 Newton s Law of Viscosity 1.4 The Continuum Concept of a Fluid 1.5 Types
FLUID MECHANICS CONTENTS CHAPTER DESCRIPTION PAGE NO 1 FLUIDS AND THEIR PROPERTIES PART A NOTES 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Fluids 1.3 Newton s Law of Viscosity 1.4 The Continuum Concept of a Fluid 1.5 Types
Detailed Outline, M E 320 Fluid Flow, Spring Semester 2015
 Detailed Outline, M E 320 Fluid Flow, Spring Semester 2015 I. Introduction (Chapters 1 and 2) A. What is Fluid Mechanics? 1. What is a fluid? 2. What is mechanics? B. Classification of Fluid Flows 1. Viscous
Detailed Outline, M E 320 Fluid Flow, Spring Semester 2015 I. Introduction (Chapters 1 and 2) A. What is Fluid Mechanics? 1. What is a fluid? 2. What is mechanics? B. Classification of Fluid Flows 1. Viscous
EXPERIMENT No.1 FLOW MEASUREMENT BY ORIFICEMETER
 EXPERIMENT No.1 FLOW MEASUREMENT BY ORIFICEMETER 1.1 AIM: To determine the co-efficient of discharge of the orifice meter 1.2 EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED: Orifice meter test rig, Stopwatch 1.3 PREPARATION 1.3.1
EXPERIMENT No.1 FLOW MEASUREMENT BY ORIFICEMETER 1.1 AIM: To determine the co-efficient of discharge of the orifice meter 1.2 EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED: Orifice meter test rig, Stopwatch 1.3 PREPARATION 1.3.1
Elements of Mechanical Engineering
 2011 Elements of Mechanical Engineering AMRAT PATEL Asst. Professor 1/17/2011 Smt Shantaben Haribhai Gajera Charitable Trust, Surat LAXMI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, SARIGAM BE I, Sem I (Section: A, B & C)
2011 Elements of Mechanical Engineering AMRAT PATEL Asst. Professor 1/17/2011 Smt Shantaben Haribhai Gajera Charitable Trust, Surat LAXMI INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, SARIGAM BE I, Sem I (Section: A, B & C)
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ
 BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ Year/Sem : III/V Sub.Code/Title: ME6504- METROLOGY & MEASUREMENTS UNIT-I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT PART-A 1. Define
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE, NATTRAMPALLI. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FAQ Year/Sem : III/V Sub.Code/Title: ME6504- METROLOGY & MEASUREMENTS UNIT-I CONCEPT OF MEASUREMENT PART-A 1. Define
Fluid Mechanics. du dy
 FLUID MECHANICS Technical English - I 1 th week Fluid Mechanics FLUID STATICS FLUID DYNAMICS Fluid Statics or Hydrostatics is the study of fluids at rest. The main equation required for this is Newton's
FLUID MECHANICS Technical English - I 1 th week Fluid Mechanics FLUID STATICS FLUID DYNAMICS Fluid Statics or Hydrostatics is the study of fluids at rest. The main equation required for this is Newton's
Downloaded from Downloaded from / 1
 PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
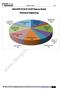 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS-II
 Set No. 1 Code No: R32035 R10 DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS-II Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75. All Questions carry equal marks (Data books may be allowed) 1 a) Explain about classification of bearings. 5 b)
Set No. 1 Code No: R32035 R10 DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS-II Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75. All Questions carry equal marks (Data books may be allowed) 1 a) Explain about classification of bearings. 5 b)
ENGINEERING FLUID MECHANICS. CHAPTER 1 Properties of Fluids
 CHAPTER 1 Properties of Fluids ENGINEERING FLUID MECHANICS 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Development of Fluid Mechanics 1.3 Units of Measurement (SI units) 1.4 Mass, Density, Specific Weight, Specific Volume, Specific
CHAPTER 1 Properties of Fluids ENGINEERING FLUID MECHANICS 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Development of Fluid Mechanics 1.3 Units of Measurement (SI units) 1.4 Mass, Density, Specific Weight, Specific Volume, Specific
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05010302 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, February 2008 ENGINEERING MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Metallurgy & Material Technology, Production Engineering,
Code No: R05010302 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, February 2008 ENGINEERING MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Metallurgy & Material Technology, Production Engineering,
Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1
 Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1 1. Given that the determinant of the matrix 2 6 0 the matrix 4 12 8 is 2 0 4 1 3 0 2 6 4 1 0 2 is 12, the determinant of (A) 96 (B) 24 (C) 24 (D) 96 2. x sin x Lt 1 cosx
Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1 1. Given that the determinant of the matrix 2 6 0 the matrix 4 12 8 is 2 0 4 1 3 0 2 6 4 1 0 2 is 12, the determinant of (A) 96 (B) 24 (C) 24 (D) 96 2. x sin x Lt 1 cosx
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : STRENGTH OF MATERIALS II Course Code : A404 Class : II B. Tech II Semester Section
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : STRENGTH OF MATERIALS II Course Code : A404 Class : II B. Tech II Semester Section
THEORY OF MACHINES I
 THEORY OF MACHINES I (Kinematics of Machines) (In SI Units) For BE/B.Tech. 3rd YEAR (Strictly as per the latest syllabus prescribed by U.P.T.U., U.P.) By Dr. R.K. BANSAL B.Sc. Engg. (Mech.), M.Tech., Hons.
THEORY OF MACHINES I (Kinematics of Machines) (In SI Units) For BE/B.Tech. 3rd YEAR (Strictly as per the latest syllabus prescribed by U.P.T.U., U.P.) By Dr. R.K. BANSAL B.Sc. Engg. (Mech.), M.Tech., Hons.
Chapter 8 Acceleration in Mechanisms
 Chapter 8 Acceleration in Mechanisms 1 2 8.2. Acceleration Diagram for a Link Example 8.1 3 The crank of a slider crank mechanism rotates cw at a constant speed of 300 rpm. The crank is 150 mm & the ConRod
Chapter 8 Acceleration in Mechanisms 1 2 8.2. Acceleration Diagram for a Link Example 8.1 3 The crank of a slider crank mechanism rotates cw at a constant speed of 300 rpm. The crank is 150 mm & the ConRod
If there is convective heat transfer from outer surface to fluid maintained at T W.
 Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING BRANCH: MECHANICAL YEAR / SEMESTER: I / II UNIT 1 PART- A 1. State Newton's three laws of motion? 2.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING BRANCH: MECHANICAL YEAR / SEMESTER: I / II UNIT 1 PART- A 1. State Newton's three laws of motion? 2.
cos(θ)sin(θ) Alternative Exercise Correct Correct θ = 0 skiladæmi 10 Part A Part B Part C Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, November 11, 2015
 skiladæmi 10 Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, November 11, 015 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due Grading Policy Alternative Exercise 1115 A bar with cross sectional
skiladæmi 10 Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, November 11, 015 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due Grading Policy Alternative Exercise 1115 A bar with cross sectional
ENGR 1100 Introduction to Mechanical Engineering
 ENGR 1100 Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Mech. Engineering Objectives Newton s Laws of Motion Free Body Diagram Transmissibility Forces and Moments as vectors Parallel Vectors (addition/subtraction)
ENGR 1100 Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Mech. Engineering Objectives Newton s Laws of Motion Free Body Diagram Transmissibility Forces and Moments as vectors Parallel Vectors (addition/subtraction)
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING. (Dr.VPR Nagar, Manimangalam, Tambaram) Chennai
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (Dr.VPR Nagar, Manimangalam, Tambaram) Chennai - 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING III YEAR V SEMESTER ME6504 ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING (Dr.VPR Nagar, Manimangalam, Tambaram) Chennai - 601 301 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING III YEAR V SEMESTER ME6504 ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND MEASUREMENTS QUESTION
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
STRESS. Bar. ! Stress. ! Average Normal Stress in an Axially Loaded. ! Average Shear Stress. ! Allowable Stress. ! Design of Simple Connections
 STRESS! Stress Evisdom! verage Normal Stress in an xially Loaded ar! verage Shear Stress! llowable Stress! Design of Simple onnections 1 Equilibrium of a Deformable ody ody Force w F R x w(s). D s y Support
STRESS! Stress Evisdom! verage Normal Stress in an xially Loaded ar! verage Shear Stress! llowable Stress! Design of Simple onnections 1 Equilibrium of a Deformable ody ody Force w F R x w(s). D s y Support
PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
 Unit - I Chapter - PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS Solutions of Examples for Practice Example.9 : Given data : u = y y, = 8 Poise = 0.8 Pa-s To find : Shear stress. Step - : Calculate the shear stress at various
Unit - I Chapter - PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS Solutions of Examples for Practice Example.9 : Given data : u = y y, = 8 Poise = 0.8 Pa-s To find : Shear stress. Step - : Calculate the shear stress at various
Simple Stresses in Machine Parts
 Simple Stresses in Machine Parts 87 C H A P T E R 4 Simple Stresses in Machine Parts 1. Introduction.. Load. 3. Stress. 4. Strain. 5. Tensile Stress and Strain. 6. Compressive Stress and Strain. 7. Young's
Simple Stresses in Machine Parts 87 C H A P T E R 4 Simple Stresses in Machine Parts 1. Introduction.. Load. 3. Stress. 4. Strain. 5. Tensile Stress and Strain. 6. Compressive Stress and Strain. 7. Young's
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
Sliding Contact Bearings
 Sliding Contact Bearings Classification of Bearings 1. According to the direction of load to be supported. The bearings under this group are classified as: (a) Radial bearings (b) Thrust bearings. In radial
Sliding Contact Bearings Classification of Bearings 1. According to the direction of load to be supported. The bearings under this group are classified as: (a) Radial bearings (b) Thrust bearings. In radial
CE MECHANICS OF FLUIDS
 CE60 - MECHANICS OF FLUIDS (FOR III SEMESTER) UNIT II FLUID STATICS & KINEMATICS PREPARED BY R.SURYA, M.E Assistant Professor DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SRI VIDYA COLLEGE
CE60 - MECHANICS OF FLUIDS (FOR III SEMESTER) UNIT II FLUID STATICS & KINEMATICS PREPARED BY R.SURYA, M.E Assistant Professor DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SRI VIDYA COLLEGE
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
: APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
Sample Question Paper
 Scheme I Sample Question Paper Program Name : Mechanical Engineering Program Group Program Code : AE/ME/PG/PT/FG Semester : Third Course Title : Strength of Materials Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Instructions:
Scheme I Sample Question Paper Program Name : Mechanical Engineering Program Group Program Code : AE/ME/PG/PT/FG Semester : Third Course Title : Strength of Materials Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Instructions:
Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at C of the beam shown in Fig. 1 4a.
 E X M P L E 1.1 Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at of the beam shown in Fig. 1 a. 70 N/m m 6 m Fig. 1 Support Reactions. This problem can be solved in the most direct
E X M P L E 1.1 Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at of the beam shown in Fig. 1 a. 70 N/m m 6 m Fig. 1 Support Reactions. This problem can be solved in the most direct
MULTIPLE-CHOICE PROBLEMS:(Two marks per answer) (Circle the Letter Beside the Most Correct Answer in the Questions Below.)
 MULTIPLE-CHOICE PROLEMS:(Two marks per answer) (Circle the Letter eside the Most Correct Answer in the Questions elow.) 1. The absolute viscosity µ of a fluid is primarily a function of: a. Density. b.
MULTIPLE-CHOICE PROLEMS:(Two marks per answer) (Circle the Letter eside the Most Correct Answer in the Questions elow.) 1. The absolute viscosity µ of a fluid is primarily a function of: a. Density. b.
1. Choose answer and indicate by writing only the corresponding capital letter (A, B, C, D) as the case may be).
 1. Choose answer and indicate by writing only the corresponding capital letter (A, B, C, D) as the case may be). 1.1 The manufacturing area of a plat is divided into four quadrants. Four machines have
1. Choose answer and indicate by writing only the corresponding capital letter (A, B, C, D) as the case may be). 1.1 The manufacturing area of a plat is divided into four quadrants. Four machines have
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION
 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION 1-1 The Fluid. 1-2 Dimensions. 1-3 Units. 1-4 Fluid Properties. 1 1-1 The Fluid: It is the substance that deforms continuously when subjected to a shear stress. Matter Solid Fluid
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION 1-1 The Fluid. 1-2 Dimensions. 1-3 Units. 1-4 Fluid Properties. 1 1-1 The Fluid: It is the substance that deforms continuously when subjected to a shear stress. Matter Solid Fluid
18.Define the term modulus of resilience. May/June Define Principal Stress. 20. Define Hydrostatic Pressure.
 CE6306 STREGNTH OF MATERIALS Question Bank Unit-I STRESS, STRAIN, DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART-A 1. Define Poison s Ratio May/June 2009 2. What is thermal stress? May/June 2009 3. Estimate the load carried
CE6306 STREGNTH OF MATERIALS Question Bank Unit-I STRESS, STRAIN, DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART-A 1. Define Poison s Ratio May/June 2009 2. What is thermal stress? May/June 2009 3. Estimate the load carried
Subject-wise Tests. Tests will be activated at 6:00 pm on scheduled day
 Subject-wise Tests Tests will be activated at 6:00 pm on scheduled day Test No Test-01 Test-02 SM-1 Economic development in India since independence with emphasis on Andhra Pradesh + Science & Technology
Subject-wise Tests Tests will be activated at 6:00 pm on scheduled day Test No Test-01 Test-02 SM-1 Economic development in India since independence with emphasis on Andhra Pradesh + Science & Technology
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS)
 BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
NAME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: Law of Sines:
 NME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: EXM 3 PST PROBLEMS (LESSONS 21 TO 28) 100 points Thursday, November 16, 2017, 7pm to 9:30, Room 200 You are allowed to use a calculator and drawing equipment, only.
NME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: EXM 3 PST PROBLEMS (LESSONS 21 TO 28) 100 points Thursday, November 16, 2017, 7pm to 9:30, Room 200 You are allowed to use a calculator and drawing equipment, only.
Tuesday, February 11, Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
UNIT 3 Friction and Belt Drives 06ME54. Structure
 UNIT 3 Friction and Belt Drives 06ME54 Structure Definitions Types of Friction Laws of friction Friction in Pivot and Collar Bearings Belt Drives Flat Belt Drives Ratio of Belt Tensions Centrifugal Tension
UNIT 3 Friction and Belt Drives 06ME54 Structure Definitions Types of Friction Laws of friction Friction in Pivot and Collar Bearings Belt Drives Flat Belt Drives Ratio of Belt Tensions Centrifugal Tension
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 DYNAMICALLY EQUIVALENT SYSTEM. Structure. Objectives. 4.1 Introduction
 UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
Principles Of Engineering. Part A
 Principles Of Engineering Final Examination Part A Fall 2007 Student Name: Date: Class Period: Total Points: /40 Converted Score: /50 Page 1 of 11 Directions: Circle the letter of the response that best
Principles Of Engineering Final Examination Part A Fall 2007 Student Name: Date: Class Period: Total Points: /40 Converted Score: /50 Page 1 of 11 Directions: Circle the letter of the response that best
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I 3 credit hour. Basic Equations in fluid Dynamics
 COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I 3 credit hour Basic Equations in fluid Dynamics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Description of Fluid
COURSE NUMBER: ME 321 Fluid Mechanics I 3 credit hour Basic Equations in fluid Dynamics Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 Description of Fluid
Benha University College of Engineering at Benha Questions For Corrective Final Examination Subject: Fluid Mechanics M 201 May 24/ 2016
 Benha University College of Engineering at Benha Questions For Corrective Final Examination Subject: Fluid Mechanics M 01 May 4/ 016 Second year Mech. Time :180 min. Examiner:Dr.Mohamed Elsharnoby Attempt
Benha University College of Engineering at Benha Questions For Corrective Final Examination Subject: Fluid Mechanics M 01 May 4/ 016 Second year Mech. Time :180 min. Examiner:Dr.Mohamed Elsharnoby Attempt
MM303 FLUID MECHANICS I PROBLEM SET 1 (CHAPTER 2) FALL v=by 2 =-6 (1/2) 2 = -3/2 m/s
 MM303 FLUID MECHANICS I PROBLEM SET 1 (CHAPTER ) FALL 018 1) For the velocity fields given below, determine: i) Whether the flow field is one-, two-, or three-dimensional, and why. ii) Whether the flow
MM303 FLUID MECHANICS I PROBLEM SET 1 (CHAPTER ) FALL 018 1) For the velocity fields given below, determine: i) Whether the flow field is one-, two-, or three-dimensional, and why. ii) Whether the flow
Heat and Mass Transfer Prof. S.P. Sukhatme Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Heat and Mass Transfer Prof. S.P. Sukhatme Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. 18 Forced Convection-1 Welcome. We now begin our study of forced convection
Heat and Mass Transfer Prof. S.P. Sukhatme Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. 18 Forced Convection-1 Welcome. We now begin our study of forced convection
Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics
 Sixth Edition Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics International Student Version BRUCE R. MUNSON DONALD F. YOUNG Department of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics THEODORE H. OKIISHI Department
Sixth Edition Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics International Student Version BRUCE R. MUNSON DONALD F. YOUNG Department of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics THEODORE H. OKIISHI Department
