Radiative forcing of fine ash and volcanic sulphate aerosol. sulphate aerosol after a very large Northern hemisphere mid-latitude eruption
|
|
|
- Harry Kenneth Caldwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Radiative forcing of fine ash and volcanic sulphate aerosol after a very large Northern hemisphere mid-latitude eruption Ulrike Niemeier (1), Claudia Timmreck (1), Sebastian Rast (1), Marco Giorgetta (1), Hans-F Graf (2), Stephen Self (3) 1) Max Plack Institute for Meteorology, Bundesstr. 53, D Hamburg, Germany ( ulrike.niemeier@zmaw.de) 2) Centre Atmospheric Sciences, University Cambridge, Downing Place, Cambridge CB2 3EN, Unitgdomed Kingdom 3) Department of Earth Science, Open University, Milton Keynes IUGG, July 2007
2 Outline Introduction The Model Pinatubo Yellowstone Conclusions
3 Introduction History of simulation of volcanic eruptions at MPI-MET Interactive simulation of ash and sulfate processes necessary Volcano Module for ECHAM5 see also talk of C.Timmreck after coffee break
4 GCM ECHAM5 Global Circulation Model Spectral dynamical core Semi-implicit leapfrog time differencing Prognostic equations for vorticity, divergence, pressure and temperature Flux-form semi-lagrangian transport of passive tracers Micro-physical prognostic equations for water vapour, water, and ice SW radiation scheme; 4 spectral bands LW radiation scheme; 16 spectral bands
5 GCM ECHAM5 Adiabatic processes Winds Temperature Humidity Cloud species Diffusion Radiation Cumulus convection Stratiform precipitation Friction Sensible heat flux Evaporation Ground roughness Ground temperature Snow Ground humidity Model processes Model variables Snow melt
6 Aerosol Model HAM Aerosol micro physics 7 log-normal modes Aerosol mass and number are transported as tracers Contains: Sulfate, OC, BC, Dust, DMS, Sea Salt Composition of internally mixed mode modified by aerosol dynamics, themodynamical and cloud processes Stratospheric sulfate chemistry for volcano study
7 Ash Module Ash independent from HAM - own module Dry deposition Wet deposition Sedimentation SW-LW radiative effects One mode only HAM used for sulfate chemistry Extension of HAM toward the stratosphere
8 Interactive eruption in ECHAM5 Fine Ash and SO2 is injected into the Stratosphere at 50 and 30 hpa Only 5% of the total errupted ash Other parts coagulate in wet aggregates Mean Radius of fine ash: 10µm
9 Simulations Pinatubo eruption Ash - number and mass: 468 Mt at 50hPa for 3 hours SO2: 17 Mt at 30hPa for 3 hours Yellowstone Erruption 100 times Pinatubo Ash - number and mass: Mt at 50hPa for 10 days SO2: 1700 Mt at 30hPa for 10 days SO2 conversion follows parameterization after Bekki (1996)
10 Pinatubo: Fine Ash and SO2 at 50hPa
11 Pinatubo: Fine ash wetdeposition [kg/m2]
12 Pinatubo: Measurements Ash deposition [mm] (Wiesner et al, 2004)
13 Comparison with Satellite Data Ash [Mt] days ECHAM Satellite days Comparison of the global mass of fine ash in the size range 1µm to 15µm in ECHAM to retrieval results of Guo et al (2004) Ash [Mt]
14 ECHAM5/HAM T63 L31 and L47 Ash mass Monthly mean values one month after eruption: L31 left and L47 right at 50 hpa
15 Yellowstone Erruption eruption time: 1st of June for 10 days 100 times Pinatubo Ash - number and mass: Mt at 50hPa for 10 days SO2: 1700 Mt at 30hPa for 10 days SO2 conversion follows parameterization after Bekki (1996)
16
17 Yellowstone: Ash [1.e-9 kg/kg]; monthly mean July August December
18 Yellowstone: Ash fall out [kg/m2] in the first month dry dep. wet dep. sedimentation
19 Yellowstone: SO2 [1.e-9 kg/kg]; monthly mean After Bekki (1996): OH is limited; SO2 lifetime prescribed; OH concentration set to zero in the stratosphere
20 Yellowstone: Sulfate [1.e-9 kg/kg]; monthly mean July August December
21 Yellowstone: SW heating rate [K/d] of Sulfate July August December
22 Yellowstone: Temperature responce [K] to LW effect of sulfate in June; monthly mean
23 Summary Summary We developed a interactive volcanic ash modul for ECHAM5/HAM Aerosol model HAM was extended to stratosphere including sulfate chemistry Comparison of Pinatubo eruption to measurement Showed first results of a super volcano eruption Radiative effect of ash and lw effect of sulfate still missing Effect on meteorological parameters not extremely strong Next steps Include coupling with LW and SW radiation Include gas phase chemistry, especially for calculation of the OH chemistry
24 Thank you
AEROCOM-Workshop,Paris, June 2-3, model. Øyvind Seland; Alf Kirkevåg
 An AGCM operated at University of Oslo (UiO) Norway Øyvind Seland; Alf Kirkevåg AEROCOM-Workshop,Paris, June 2-3, 2003 by Kirkevåg; Jón Egill Kristjánsson; ; Trond Iversen Basic: NCAR-CCM3.2 CCM3.2 (Kiehl,et
An AGCM operated at University of Oslo (UiO) Norway Øyvind Seland; Alf Kirkevåg AEROCOM-Workshop,Paris, June 2-3, 2003 by Kirkevåg; Jón Egill Kristjánsson; ; Trond Iversen Basic: NCAR-CCM3.2 CCM3.2 (Kiehl,et
Do large tropical volcanic eruptions influence the Southern Annular Mode?
 SPARC GA, Queenstown, NZ, January 14, 2014 Do large tropical volcanic eruptions influence the Southern Annular Mode? Kirstin Krüger 1,2, Matt Toohey 2, Doreen Metzner 2,3 ( 1 UiO, Oslo, Norway; 2 GEOMAR,
SPARC GA, Queenstown, NZ, January 14, 2014 Do large tropical volcanic eruptions influence the Southern Annular Mode? Kirstin Krüger 1,2, Matt Toohey 2, Doreen Metzner 2,3 ( 1 UiO, Oslo, Norway; 2 GEOMAR,
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
Atmospheric Processes
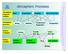 Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
CHAPTER 8. AEROSOLS 8.1 SOURCES AND SINKS OF AEROSOLS
 1 CHAPTER 8 AEROSOLS Aerosols in the atmosphere have several important environmental effects They are a respiratory health hazard at the high concentrations found in urban environments They scatter and
1 CHAPTER 8 AEROSOLS Aerosols in the atmosphere have several important environmental effects They are a respiratory health hazard at the high concentrations found in urban environments They scatter and
A Global Atmospheric Model. Joe Tribbia NCAR Turbulence Summer School July 2008
 A Global Atmospheric Model Joe Tribbia NCAR Turbulence Summer School July 2008 Outline Broad overview of what is in a global climate/weather model of the atmosphere Spectral dynamical core Some results-climate
A Global Atmospheric Model Joe Tribbia NCAR Turbulence Summer School July 2008 Outline Broad overview of what is in a global climate/weather model of the atmosphere Spectral dynamical core Some results-climate
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric sulfate burdens
 Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric sulfate burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric sulfate burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric
NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING Part II
 TOPIC #12 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING Part II (p 72 in Class Notes) Today we will focus on the third main driver of NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING: 1) ATRONOMICAL FORCING 2) SOLAR FORCING 3) VOLCANIC FORCING VOLCANIC
TOPIC #12 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING Part II (p 72 in Class Notes) Today we will focus on the third main driver of NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING: 1) ATRONOMICAL FORCING 2) SOLAR FORCING 3) VOLCANIC FORCING VOLCANIC
Volcanic sulfate deposition to Greenland and Antarctica: A modeling sensitivity study
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 8, 4788 48, doi:.2/jgrd.5428, 23 Volcanic sulfate deposition to Greenland and Antarctica: A modeling sensitivity study Matthew Toohey, Kirstin Krüger,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: ATMOSPHERES, VOL. 8, 4788 48, doi:.2/jgrd.5428, 23 Volcanic sulfate deposition to Greenland and Antarctica: A modeling sensitivity study Matthew Toohey, Kirstin Krüger,
FORCING ANTHROPOGENIC
 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING Earth-Sun orbital relationships, changing landsea distribution (due to plate tectonics), solar variability & VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS vs. ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING Human-Enhanced GH Effect,
NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING Earth-Sun orbital relationships, changing landsea distribution (due to plate tectonics), solar variability & VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS vs. ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING Human-Enhanced GH Effect,
Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site: Lecture 27 Dec
 Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Climate Natural Variations Feedback Mechanisms Lecture 27 Dec 4 2018 1 Climate
Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Climate Natural Variations Feedback Mechanisms Lecture 27 Dec 4 2018 1 Climate
A possible joint WCRP SPARC SSiRC/AeroCom initiative on stratospheric sulfur
 A possible joint WCRP SPARC SSiRC/AeroCom initiative on stratospheric sulfur Claudia Timmreck and the SSiRC team AeroCom workshop, Hamburg, 23. 9. 2013 Stratospheric Sulfur and Climate Climate Volcanic
A possible joint WCRP SPARC SSiRC/AeroCom initiative on stratospheric sulfur Claudia Timmreck and the SSiRC team AeroCom workshop, Hamburg, 23. 9. 2013 Stratospheric Sulfur and Climate Climate Volcanic
Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs
 Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs Ulrike Lohmann ETH Zurich Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science Reading, 13.11.2006 Acknowledgements: Sylvaine Ferrachat, Corinna Hoose, Erich Roeckner,
Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs Ulrike Lohmann ETH Zurich Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science Reading, 13.11.2006 Acknowledgements: Sylvaine Ferrachat, Corinna Hoose, Erich Roeckner,
Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI
 Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Assessment Schedule 2017 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of processes in the atmosphere system (91414)
 NCEA Level 3 Earth and Space Science (91414) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of processes in the atmosphere system (91414) Evidence Statement
NCEA Level 3 Earth and Space Science (91414) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Earth and Space Science: Demonstrate understanding of processes in the atmosphere system (91414) Evidence Statement
Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002
 Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002 Soon-Ung Park, Jae-In Jeong* Center for Atmospheric and Environmental Modeling *School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Seoul National
Direct radiative forcing due to aerosols in Asia during March 2002 Soon-Ung Park, Jae-In Jeong* Center for Atmospheric and Environmental Modeling *School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Seoul National
Model Systems at MPI-M. Marco Giorgetta
 Model Systems at MPI-M Marco Giorgetta Content What is a model in climate research as used here for IPCC? What is a model? Components of the climate system Climate models What is inside? Climate models
Model Systems at MPI-M Marco Giorgetta Content What is a model in climate research as used here for IPCC? What is a model? Components of the climate system Climate models What is inside? Climate models
Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation
 Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation 8 March, 2011 Jonathon Wright Department of Applied Mathematics & Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge
Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation 8 March, 2011 Jonathon Wright Department of Applied Mathematics & Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge
Effects of stratospheric sulfate aerosol geo-engineering on cirrus clouds
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053797, 2012 Effects of stratospheric sulfate aerosol geo-engineering on cirrus clouds Miriam Kuebbeler, 1 Ulrike Lohmann, 1 and Johann Feichter
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053797, 2012 Effects of stratospheric sulfate aerosol geo-engineering on cirrus clouds Miriam Kuebbeler, 1 Ulrike Lohmann, 1 and Johann Feichter
Deutscher Wetterdienst
 Deutscher Wetterdienst Modelling the Volcanic Ash Episode: Experiences with COSMO-ART Detlev Majewski (FE1) Bernhard Vogel, Heike Vogel (KIT) Thomas Hanisch, Jochen Förstner (FE13), Ulrich Pflüger (FE15)
Deutscher Wetterdienst Modelling the Volcanic Ash Episode: Experiences with COSMO-ART Detlev Majewski (FE1) Bernhard Vogel, Heike Vogel (KIT) Thomas Hanisch, Jochen Förstner (FE13), Ulrich Pflüger (FE15)
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric burdens
 Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric and
Stratospheric sulfate geoengineering has limited efficacy and increases tropospheric burdens Jason English PhD Candidate Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, and Department of Atmospheric and
Atmospheric modeling in the Climate System. Joe Tribbia NCAR.ESSL.CGD.AMP
 Atmospheric modeling in the Climate System Joe Tribbia NCAR.ESSL.CGD.AMP The climate represents a coupled system consisting of an atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and cryosphere What is CCSM? Bio Geochemistry
Atmospheric modeling in the Climate System Joe Tribbia NCAR.ESSL.CGD.AMP The climate represents a coupled system consisting of an atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and cryosphere What is CCSM? Bio Geochemistry
Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate
 Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Climate of the Ocean Lecture 7: The Monash Simple Climate Model Dr. Claudia Frauen Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde (IOW) claudia.frauen@io-warnemuende.de Outline: Motivation The GREB
Aerosol size-dependent below-cloud scavenging by rain and snow in the ECHAM5-HAM
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 4653 4675, 29 www.atmos-chem-phys.net/9/4653/29/ Author(s) 29. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3. License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Aerosol
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 4653 4675, 29 www.atmos-chem-phys.net/9/4653/29/ Author(s) 29. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3. License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Aerosol
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate
 Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Aerosols AP sizes AP types Sources Sinks Amount and lifetime Aerosol radiative effects. Aerosols. Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21
 Aerosols Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21 Aerosols: Definition Definition of an aerosol: disperse system with air as carrier gas and a solid or liquid or a mixture of both as disperse phases. Aerosol particles
Aerosols Trude Storelvmo Aerosols 1 / 21 Aerosols: Definition Definition of an aerosol: disperse system with air as carrier gas and a solid or liquid or a mixture of both as disperse phases. Aerosol particles
Aerosol modeling with WRF/Chem
 Aerosol modeling with WRF/Chem Jan Kazil University of Colorado / NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory WRF/Chem Tutorial, 3 August 2015 (WRF/Chem 3.7) Part I - Introduction Overview of... Aerosol Aerosol
Aerosol modeling with WRF/Chem Jan Kazil University of Colorado / NOAA Earth System Research Laboratory WRF/Chem Tutorial, 3 August 2015 (WRF/Chem 3.7) Part I - Introduction Overview of... Aerosol Aerosol
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales. John Houghton. C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth
 Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 21 Climate 21.1 Factors That Affect Climate Factors That Affect Climate Latitude As latitude increases, the intensity of solar energy decreases. The
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 21 Climate 21.1 Factors That Affect Climate Factors That Affect Climate Latitude As latitude increases, the intensity of solar energy decreases. The
Climate forcing volcanic eruptions: future extreme event occurrence likelihoods
 Climate Change and Extreme Events: Managing Tail Risks Workshop 2 3 February 2010 Washington DC Climate forcing volcanic eruptions: future extreme event occurrence likelihoods Willy Aspinall with apologies
Climate Change and Extreme Events: Managing Tail Risks Workshop 2 3 February 2010 Washington DC Climate forcing volcanic eruptions: future extreme event occurrence likelihoods Willy Aspinall with apologies
Lecture 8. The Holocene and Recent Climate Change
 Lecture 8 The Holocene and Recent Climate Change Recovery from the last ice age About 15,000 years ago, the earth began to warm and the huge ice sheets covering much of North America and Eurasia began
Lecture 8 The Holocene and Recent Climate Change Recovery from the last ice age About 15,000 years ago, the earth began to warm and the huge ice sheets covering much of North America and Eurasia began
2. Outline of the MRI-EPS
 2. Outline of the MRI-EPS The MRI-EPS includes BGM cycle system running on the MRI supercomputer system, which is developed by using the operational one-month forecasting system by the Climate Prediction
2. Outline of the MRI-EPS The MRI-EPS includes BGM cycle system running on the MRI supercomputer system, which is developed by using the operational one-month forecasting system by the Climate Prediction
What is PRECIS? The Physical Parameters Boundary Conditions Why the Mediterranean Basin? The Sulfur Cycle & Aerosols Aerosols Impacts Data Analysis
 What is PRECIS? The Physical Parameters Boundary Conditions Why the Mediterranean Basin? The Sulfur Cycle & Aerosols Aerosols Impacts Data Analysis Sulfur Cycle Validation Future Scenarios Conclusions
What is PRECIS? The Physical Parameters Boundary Conditions Why the Mediterranean Basin? The Sulfur Cycle & Aerosols Aerosols Impacts Data Analysis Sulfur Cycle Validation Future Scenarios Conclusions
The water vapour channels of SEVIRI (Meteosat). An introduction
 The water vapour channels of SEVIRI (Meteosat). An introduction jose.prieto@eumetsat.int Cachoeira P. July 2006 Formats 1.5 1 Objectives 2 Describe the characteristics of WV channels on board of SEVIRI
The water vapour channels of SEVIRI (Meteosat). An introduction jose.prieto@eumetsat.int Cachoeira P. July 2006 Formats 1.5 1 Objectives 2 Describe the characteristics of WV channels on board of SEVIRI
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 21 Climate 21.1 Factors That Affect Climate Factors That Affect Climate Latitude As latitude increases, the intensity of solar energy decreases. The
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 21 Climate 21.1 Factors That Affect Climate Factors That Affect Climate Latitude As latitude increases, the intensity of solar energy decreases. The
Wrap up of TOPIC # 13 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING: Volcanic Eruptions (pp 71-74)
 Wrap up of TOPIC # 13 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING: Volcanic Eruptions (pp 71-74) How the Climatic Effect Occurs.... through the ENERGY BALANCE of course! p 71 Mt Merapi Latitude: 7 32'30"S Indonesia's Mount
Wrap up of TOPIC # 13 NATURAL CLIMATIC FORCING: Volcanic Eruptions (pp 71-74) How the Climatic Effect Occurs.... through the ENERGY BALANCE of course! p 71 Mt Merapi Latitude: 7 32'30"S Indonesia's Mount
Global transport of POPs: the role of aerosol particles
 Global transport of POPs: the role of aerosol particles Sunling Gong Air Quality Research Division Persistent Organic Pollutants Organic chemical compounds and mixtures that include industrial chemicals
Global transport of POPs: the role of aerosol particles Sunling Gong Air Quality Research Division Persistent Organic Pollutants Organic chemical compounds and mixtures that include industrial chemicals
Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data
 Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data Why Is Lindzen and Choi (2009) Criticized? Zhiyu Wang Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah March 9, 2010 / Earth Climate System Outline 1 Introduction
Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data Why Is Lindzen and Choi (2009) Criticized? Zhiyu Wang Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah March 9, 2010 / Earth Climate System Outline 1 Introduction
UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions
 UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions Nicolas Bellouin UKCA Training Workshop, Cambridge, 8 January 2015 University of Reading 2014 n.bellouin@reading.ac.uk Lecture summary Why care about aerosol-radiation
UKCA_RADAER Aerosol-radiation interactions Nicolas Bellouin UKCA Training Workshop, Cambridge, 8 January 2015 University of Reading 2014 n.bellouin@reading.ac.uk Lecture summary Why care about aerosol-radiation
Factors That Affect Climate
 Factors That Affect Climate Factors That Affect Climate Latitude As latitude (horizontal lines) increases, the intensity of solar energy decreases. The tropical zone is between the tropic of Cancer and
Factors That Affect Climate Factors That Affect Climate Latitude As latitude (horizontal lines) increases, the intensity of solar energy decreases. The tropical zone is between the tropic of Cancer and
Stable Water Isotope Cycle
 Regional Atmospheric Modelling of the Stable Water Isotope Cycle SIMS workshop, Vienna Mars 2004. Kristof Sturm 1,3 Georg Hoffmann 2, Bärbel Langmann 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut für Meteorologie, Hamburg 2
Regional Atmospheric Modelling of the Stable Water Isotope Cycle SIMS workshop, Vienna Mars 2004. Kristof Sturm 1,3 Georg Hoffmann 2, Bärbel Langmann 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut für Meteorologie, Hamburg 2
Impacts of aerosols in the CORDEX-Europe domain using the regional aerosol-climate model REMO-HAM
 Impacts of aerosols in the CORDEX-Europe domain using the regional aerosol-climate model REMO-HAM Armelle Reca C. Remedio (1), Claas Teichmann (1,2), Joni-Pekka Pietikäinen (3), Natalia Sudarchikova (1),
Impacts of aerosols in the CORDEX-Europe domain using the regional aerosol-climate model REMO-HAM Armelle Reca C. Remedio (1), Claas Teichmann (1,2), Joni-Pekka Pietikäinen (3), Natalia Sudarchikova (1),
Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~
 2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
2015/11/16 TCC Seminar JMA Introduction to Climate ~ Part I ~ Shuhei MAEDA (MRI/JMA) Climate Research Department Meteorological Research Institute (MRI/JMA) 1 Outline of the lecture 1. Climate System (
Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle
 Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle Source: Sulfate aerosols are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception
Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle Source: Sulfate aerosols are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception
Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction
 1 Supplementary Material Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction N. S. Keenlyside 1, Hui Ding 2, and M. Latif 2,3 1 Geophysical Institute and Bjerknes Centre, University
1 Supplementary Material Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction N. S. Keenlyside 1, Hui Ding 2, and M. Latif 2,3 1 Geophysical Institute and Bjerknes Centre, University
How good are our models?
 direct Estimates of regional and global forcing: ^ How good are our models? Bill Collins with Andrew Conley, David Fillmore, and Phil Rasch National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Models
direct Estimates of regional and global forcing: ^ How good are our models? Bill Collins with Andrew Conley, David Fillmore, and Phil Rasch National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Models
A global modeler looks at regional climate modeling. Zippy:Regional_Climate_01:Regional_Climate_01.frame
 A global modeler looks at regional climate modeling I come in peace. Global climate models, 1 All global climate models must include representations of the ocean, sea ice, and the vegetated land surface,
A global modeler looks at regional climate modeling I come in peace. Global climate models, 1 All global climate models must include representations of the ocean, sea ice, and the vegetated land surface,
Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds
 Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds Ulrike Lohmann Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, N. S., Canada Contributions from Johann Feichter, Johannes Hendricks,
Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds Ulrike Lohmann Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, N. S., Canada Contributions from Johann Feichter, Johannes Hendricks,
Thursday Nov 6 th SIT WITH YOUR GROUP TODAY Topic # 11 Natural Climatic Forcing Part II ANNOUNCEMENTS
 Thursday Nov 6 th SIT WITH YOUR GROUP TODAY Topic # 11 Natural Climatic Forcing Part II ANNOUNCEMENTS NO CLASS next Tuesday Nov 11 (Veteran s Day) but don t forget that RQ-7 is DUE before Midnight that
Thursday Nov 6 th SIT WITH YOUR GROUP TODAY Topic # 11 Natural Climatic Forcing Part II ANNOUNCEMENTS NO CLASS next Tuesday Nov 11 (Veteran s Day) but don t forget that RQ-7 is DUE before Midnight that
A climate model study of indirect radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulfate aerosols
 A climate model study of indirect radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulfate aerosols A. Jones, D.L. Roberts & A. Slingo Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Meteorological Office, London
A climate model study of indirect radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulfate aerosols A. Jones, D.L. Roberts & A. Slingo Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Meteorological Office, London
ERA report series. 1 The ERA-Interim archive. ERA-Interim ERA-40. Version 1.0 ERA-15
 ERA report series ERA-15 ERA-40 ERA-Interim 1 The ERA-Interim archive Version 1.0 Paul Berrisford, Dick Dee, Keith Fielding, Manuel Fuentes, Per Kållberg, Shinya Kobayashi and Sakari Uppala Series: ERA
ERA report series ERA-15 ERA-40 ERA-Interim 1 The ERA-Interim archive Version 1.0 Paul Berrisford, Dick Dee, Keith Fielding, Manuel Fuentes, Per Kållberg, Shinya Kobayashi and Sakari Uppala Series: ERA
Fundamentals of Weather and Climate
 Fundamentals of Weather and Climate ROBIN McILVEEN Environmental Science Division Institute of Environmental and Biological Sciences Lancaster University CHAPMAN & HALL London Glasgow Weinheim New York
Fundamentals of Weather and Climate ROBIN McILVEEN Environmental Science Division Institute of Environmental and Biological Sciences Lancaster University CHAPMAN & HALL London Glasgow Weinheim New York
(2010), Aerosol size confines climate response to volcanic supereruptions,
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl045464, 2010 Aerosol size confines climate response to volcanic super eruptions Claudia Timmreck, 1 Hans F. Graf, 2 Stephan J. Lorenz, 1 Ulrike
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl045464, 2010 Aerosol size confines climate response to volcanic super eruptions Claudia Timmreck, 1 Hans F. Graf, 2 Stephan J. Lorenz, 1 Ulrike
Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle
 Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle Irina N. Sokolik School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA,
Atmospheric Aerosol in High Latitudes: Linkages to Radiative Energy Balance and Hydrological Cycle Irina N. Sokolik School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, GA,
Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future. Basic Concepts
 Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future Basic Concepts Weather instantaneous or synoptic measurements Climate time / space average Weather - the state of the air and atmosphere at a particular
Northern New England Climate: Past, Present, and Future Basic Concepts Weather instantaneous or synoptic measurements Climate time / space average Weather - the state of the air and atmosphere at a particular
Recent anthropogenic increases in SO2 from Asia have minimal impact on stratospheric aerosol
 !1 Recent anthropogenic increases in SO2 from Asia have minimal impact on stratospheric aerosol Ryan R. Neely III (NCAR/ASP), O. Brian Toon, Susan Solomon, Karen H. Rosenlof, John S Daniel, J. English,
!1 Recent anthropogenic increases in SO2 from Asia have minimal impact on stratospheric aerosol Ryan R. Neely III (NCAR/ASP), O. Brian Toon, Susan Solomon, Karen H. Rosenlof, John S Daniel, J. English,
The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes
 1of 18 The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes Vivek Arora Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis Meteorological Service of Canada Outline 2of 18
1of 18 The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes Vivek Arora Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis Meteorological Service of Canada Outline 2of 18
Bacteria and fungal spores in the global climate model ECHAM5-HAM
 Bacteria and fungal spores in the global climate model ECHAM5-HAM Ana Sesartic, ETH Zurich, Switzerland Acknowledgements: Ulrike Lohmann, Trude Storelvmo, Sylvaine Ferrachat, Tanja Dallafior, Declan O'Donnell,
Bacteria and fungal spores in the global climate model ECHAM5-HAM Ana Sesartic, ETH Zurich, Switzerland Acknowledgements: Ulrike Lohmann, Trude Storelvmo, Sylvaine Ferrachat, Tanja Dallafior, Declan O'Donnell,
Operational and research activities at ECMWF now and in the future
 Operational and research activities at ECMWF now and in the future Sarah Keeley Education Officer Erland Källén Director of Research ECMWF An independent intergovernmental organisation established in 1975
Operational and research activities at ECMWF now and in the future Sarah Keeley Education Officer Erland Källén Director of Research ECMWF An independent intergovernmental organisation established in 1975
Climate impacts of ice nucleation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012jd017950, 2012 Climate impacts of ice nucleation A. Gettelman, 1,2 X. Liu, 3 D. Barahona, 4,5 U. Lohmann, 2 and C. Chen 1 Received 16 April 2012;
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012jd017950, 2012 Climate impacts of ice nucleation A. Gettelman, 1,2 X. Liu, 3 D. Barahona, 4,5 U. Lohmann, 2 and C. Chen 1 Received 16 April 2012;
Introduction to Climate Change
 Ch 19 Climate Change Introduction to Climate Change Throughout time, the earth's climate has always been changing produced ice ages Hence, climate variations have been noted in the past what physical processes
Ch 19 Climate Change Introduction to Climate Change Throughout time, the earth's climate has always been changing produced ice ages Hence, climate variations have been noted in the past what physical processes
Prof. Simon Tett, Chair of Earth System Dynamics & Modelling: The University of Edinburgh
 SAGES Scottish Alliance for Geoscience, Environment & Society Modelling Climate Change Prof. Simon Tett, Chair of Earth System Dynamics & Modelling: The University of Edinburgh Climate Modelling Climate
SAGES Scottish Alliance for Geoscience, Environment & Society Modelling Climate Change Prof. Simon Tett, Chair of Earth System Dynamics & Modelling: The University of Edinburgh Climate Modelling Climate
IMPACT OF SOIL FREEZING ON THE CONTINENTAL-SCALE SEASONAL CYCLE SIMULATED BY A GENERAL CIRCULATION MODEL
 IMPACT OF SOIL FREEZING ON THE CONTINENTAL-SCALE SEASONAL CYCLE SIMULATED BY A GENERAL CIRCULATION MODEL Kumiko Takata 1, Masahide Kimoto 2 1. Domestic Research Fellow, National Institute of Environmental
IMPACT OF SOIL FREEZING ON THE CONTINENTAL-SCALE SEASONAL CYCLE SIMULATED BY A GENERAL CIRCULATION MODEL Kumiko Takata 1, Masahide Kimoto 2 1. Domestic Research Fellow, National Institute of Environmental
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 )
 3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Basic information on CO 2 with regard to environmental issues Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is a significant greenhouse gas that has strong absorption bands in the infrared region and
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Basic information on CO 2 with regard to environmental issues Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is a significant greenhouse gas that has strong absorption bands in the infrared region and
Physical and Optical Properties of the Stratospheric Aerosol Layer
 Physical and Optical Properties of the Stratospheric Aerosol Layer Patrick Hamill Department of Physics and Astronomy San Jose State University San Jose, California Justification for this Talk Much debate
Physical and Optical Properties of the Stratospheric Aerosol Layer Patrick Hamill Department of Physics and Astronomy San Jose State University San Jose, California Justification for this Talk Much debate
!"#$%&'()*+,-./ I!"#$%&
 www.climatechange.cn Q = O OMMU P ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH Vol.4, No.2 March, 2 8!"673-79 (28) 2--6 &'()*+,-./ I & NIO == N N=&' =NMMMUN O= &'()*+, =RNMSRR = NCAR! GCM CAM3. &'()*+,-&'()*+,
www.climatechange.cn Q = O OMMU P ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH Vol.4, No.2 March, 2 8!"673-79 (28) 2--6 &'()*+,-./ I & NIO == N N=&' =NMMMUN O= &'()*+, =RNMSRR = NCAR! GCM CAM3. &'()*+,-&'()*+,
Modelling and data assimilation of hazardous volcanic ash plumes in the chemical-transport model MOCAGE
 Modelling and data assimilation of hazardous volcanic ash plumes in the chemical-transport model MOCAGE Bojan Sic, Laaziz El Amraoui, Matthieu Plu CNRM/Météo-France 2 Introduction Model MOCAGE of Météo-France
Modelling and data assimilation of hazardous volcanic ash plumes in the chemical-transport model MOCAGE Bojan Sic, Laaziz El Amraoui, Matthieu Plu CNRM/Météo-France 2 Introduction Model MOCAGE of Météo-France
Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions
 Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions William K. M. Lau NASA/GSFC Co-authors: K. M. Kim, M. Chin, P. Colarco, A. DaSilva Atmospheric loading of Saharan dust Annual emission
Saharan Dust Induced Radiation-Cloud-Precipitation-Dynamics Interactions William K. M. Lau NASA/GSFC Co-authors: K. M. Kim, M. Chin, P. Colarco, A. DaSilva Atmospheric loading of Saharan dust Annual emission
Supplemental Material for Transient climate impacts for scenarios of aerosol emissions from Asia: a story of coal versus gas
 Supplemental Material for Transient climate impacts for scenarios of aerosol emissions from Asia: a story of coal versus gas B. S. Grandey, H. Cheng, and C. Wang December 22, 2015 List of Tables 1 Annual
Supplemental Material for Transient climate impacts for scenarios of aerosol emissions from Asia: a story of coal versus gas B. S. Grandey, H. Cheng, and C. Wang December 22, 2015 List of Tables 1 Annual
The atmospheric response to solar irradiance variations: Simulations with HAMMONIA
 The atmospheric response to solar irradiance variations: Simulations with HAMMONIA Hauke Schmidt, Marco A. Giorgetta Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg, Germany Guy P. Brasseur National Center
The atmospheric response to solar irradiance variations: Simulations with HAMMONIA Hauke Schmidt, Marco A. Giorgetta Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg, Germany Guy P. Brasseur National Center
The initial dispersal and radiative forcing of a Northern Hemisphere mid-latitude super volcano: a model study
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 6, 35 49, 2006 SRef-ID: 1680-7324/acp/2006-6-35 European Geosciences Union Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics The initial dispersal and radiative forcing of a Northern Hemisphere mid-latitude
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 6, 35 49, 2006 SRef-ID: 1680-7324/acp/2006-6-35 European Geosciences Union Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics The initial dispersal and radiative forcing of a Northern Hemisphere mid-latitude
Clouds on Mars Cloud Classification
 Lecture Ch. 8 Cloud Classification Descriptive approach to clouds Drop Growth and Precipitation Processes Microphysical characterization of clouds Complex (i.e. Real) Clouds Examples Curry and Webster,
Lecture Ch. 8 Cloud Classification Descriptive approach to clouds Drop Growth and Precipitation Processes Microphysical characterization of clouds Complex (i.e. Real) Clouds Examples Curry and Webster,
WACCM: The High-Top Model
 WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
WACCM: The High-Top Model WACCM top Michael Mills CAM top WACCM Liaison mmills@ucar.edu (303) 497-1425 http://bb.cgd.ucar.edu/ 40 km Ozone Layer Jarvis, Bridging the Atmospheric Divide, Science, 293, 2218,
Aerosols and climate. Rob Wood, Atmospheric Sciences
 Aerosols and climate Rob Wood, Atmospheric Sciences What are aerosols? Solid or liquid particles suspended in air Sizes range from a few nm to a few thousand nm Huge range of masses Where do aerosols come
Aerosols and climate Rob Wood, Atmospheric Sciences What are aerosols? Solid or liquid particles suspended in air Sizes range from a few nm to a few thousand nm Huge range of masses Where do aerosols come
Cloud parameterization and cloud prediction scheme in Eta numerical weather model
 Cloud parameterization and cloud prediction scheme in Eta numerical weather model Belgrade, 10th September, 2018 Ivan Ristić, CEO at Weather2 Ivana Kordić, meteorologist at Weather2 Introduction Models
Cloud parameterization and cloud prediction scheme in Eta numerical weather model Belgrade, 10th September, 2018 Ivan Ristić, CEO at Weather2 Ivana Kordić, meteorologist at Weather2 Introduction Models
CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION
 i CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION 1 1.1 MIXING RATIO 1 1.2 NUMBER DENSITY 2 1.3 PARTIAL PRESSURE 6 PROBLEMS 10 1.1 Fog formation 10 1.2 Phase partitioning of water in cloud 10 1.3 The ozone
i CONTENTS 1 MEASURES OF ATMOSPHERIC COMPOSITION 1 1.1 MIXING RATIO 1 1.2 NUMBER DENSITY 2 1.3 PARTIAL PRESSURE 6 PROBLEMS 10 1.1 Fog formation 10 1.2 Phase partitioning of water in cloud 10 1.3 The ozone
ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions
 ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions Themes: 1. Parametrization of microphysics 2. Representing sub-grid cloud variability 3. Constraining cloud and precipitation
ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions Themes: 1. Parametrization of microphysics 2. Representing sub-grid cloud variability 3. Constraining cloud and precipitation
Progress on Application of Modal Aerosol Dynamics to CAM
 Progress on Application of Modal Aerosol Dynamics to CAM Xiaohong Liu, Steve Ghan, Richard Easter, Rahul Zaveri, Yun Qian (Pacific Northwest National Laboratory) Jean-Francois Lamarque, Peter Hess, Natalie
Progress on Application of Modal Aerosol Dynamics to CAM Xiaohong Liu, Steve Ghan, Richard Easter, Rahul Zaveri, Yun Qian (Pacific Northwest National Laboratory) Jean-Francois Lamarque, Peter Hess, Natalie
Questions we would like to learn (scattered through the whole lecture)
 Climate Impacts on the Baltic Sea: From Science to Policy Bornholm, July 2009 (Paleo) Climate Modelling Eduardo Zorita GK SS Research Centre, Geesthacht, Germany Questions we would like to learn (scattered
Climate Impacts on the Baltic Sea: From Science to Policy Bornholm, July 2009 (Paleo) Climate Modelling Eduardo Zorita GK SS Research Centre, Geesthacht, Germany Questions we would like to learn (scattered
CESM1.0/WACCM4 with CARMA3.0 Microphysics. Michael Mills Charles Bardeen
 CESM1.0/WACCM4 with CARMA3.0 Microphysics Michael Mills Charles Bardeen CAM/CARMA (C. Bardeen) CARMA Sectional Microphysics Fortran 90 Embeddable Shared with NASA Goddard CAM/CARMA Clouds & Aerosols Integrated
CESM1.0/WACCM4 with CARMA3.0 Microphysics Michael Mills Charles Bardeen CAM/CARMA (C. Bardeen) CARMA Sectional Microphysics Fortran 90 Embeddable Shared with NASA Goddard CAM/CARMA Clouds & Aerosols Integrated
Temperature (T) degrees Celsius ( o C) arbitrary scale from 0 o C at melting point of ice to 100 o C at boiling point of water Also (Kelvin, K) = o C
 1 2 3 4 Temperature (T) degrees Celsius ( o C) arbitrary scale from 0 o C at melting point of ice to 100 o C at boiling point of water Also (Kelvin, K) = o C plus 273.15 0 K is absolute zero, the minimum
1 2 3 4 Temperature (T) degrees Celsius ( o C) arbitrary scale from 0 o C at melting point of ice to 100 o C at boiling point of water Also (Kelvin, K) = o C plus 273.15 0 K is absolute zero, the minimum
Impacts of historical ozone changes on climate in GFDL-CM3
 Impacts of historical ozone changes on climate in GFDL-CM3 Larry Horowitz (GFDL) with: Vaishali Naik (GFDL), Pu Lin (CICS), and M. Daniel Schwarzkopf (GFDL) WMO (2014) Figure ADM 5-1 1 Response of tropospheric
Impacts of historical ozone changes on climate in GFDL-CM3 Larry Horowitz (GFDL) with: Vaishali Naik (GFDL), Pu Lin (CICS), and M. Daniel Schwarzkopf (GFDL) WMO (2014) Figure ADM 5-1 1 Response of tropospheric
Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models. Richard Forbes
 Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models Richard Forbes (ECMWF) with thanks to Peter Bechtold and Martin Köhler RMetS National Meeting on Clouds and Precipitation, 16 Nov
Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models Richard Forbes (ECMWF) with thanks to Peter Bechtold and Martin Köhler RMetS National Meeting on Clouds and Precipitation, 16 Nov
What are Aerosols? Suspension of very small solid particles or liquid droplets Radii typically in the range of 10nm to
 What are Aerosols? Suspension of very small solid particles or liquid droplets Radii typically in the range of 10nm to 10µm Concentrations decrease exponentially with height N(z) = N(0)exp(-z/H) Long-lived
What are Aerosols? Suspension of very small solid particles or liquid droplets Radii typically in the range of 10nm to 10µm Concentrations decrease exponentially with height N(z) = N(0)exp(-z/H) Long-lived
Decreasing trend of tropical cyclone frequency in 228-year high-resolution AGCM simulations
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053360, 2012 Decreasing trend of tropical cyclone frequency in 228-year high-resolution AGCM simulations Masato Sugi 1,2 and Jun Yoshimura 2 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053360, 2012 Decreasing trend of tropical cyclone frequency in 228-year high-resolution AGCM simulations Masato Sugi 1,2 and Jun Yoshimura 2 Received
The Structure and Motion of the Atmosphere OCEA 101
 The Structure and Motion of the Atmosphere OCEA 101 Why should you care? - the atmosphere is the primary driving force for the ocean circulation. - the atmosphere controls geographical variations in ocean
The Structure and Motion of the Atmosphere OCEA 101 Why should you care? - the atmosphere is the primary driving force for the ocean circulation. - the atmosphere controls geographical variations in ocean
Introduction to atmospheric dispersion modelling. M.Sofiev
 Introduction to atmospheric dispersion modelling M.Sofiev Content Main parts of the atmosphere Basic terms atmospheric tracer temporal and spatial scales life time in the atmosphere life cycle of atmospheric
Introduction to atmospheric dispersion modelling M.Sofiev Content Main parts of the atmosphere Basic terms atmospheric tracer temporal and spatial scales life time in the atmosphere life cycle of atmospheric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1857 Figure S1a shows significant inter-annual variability in seasonal SPA data with multi-decadal periods exhibiting positive and negative SPAs. A similar
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1857 Figure S1a shows significant inter-annual variability in seasonal SPA data with multi-decadal periods exhibiting positive and negative SPAs. A similar
Impact of Solar and Sulfate Geoengineering on Surface Ozone
 Impact of Solar and Sulfate Geoengineering on Surface Ozone Lili Xia 1, Peer J. Nowack 2, Simone Tilmes 3 and Alan Robock 1 1 Department of Environmental Sciences, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ
Impact of Solar and Sulfate Geoengineering on Surface Ozone Lili Xia 1, Peer J. Nowack 2, Simone Tilmes 3 and Alan Robock 1 1 Department of Environmental Sciences, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ
GEO1010 tirsdag
 GEO1010 tirsdag 31.08.2010 Jørn Kristiansen; jornk@met.no I dag: Først litt repetisjon Stråling (kap. 4) Atmosfærens sirkulasjon (kap. 6) Latitudinal Geographic Zones Figure 1.12 jkl TØRR ATMOSFÆRE Temperature
GEO1010 tirsdag 31.08.2010 Jørn Kristiansen; jornk@met.no I dag: Først litt repetisjon Stråling (kap. 4) Atmosfærens sirkulasjon (kap. 6) Latitudinal Geographic Zones Figure 1.12 jkl TØRR ATMOSFÆRE Temperature
2. Fargo, North Dakota receives more snow than Charleston, South Carolina.
 2015 National Tournament Division B Meteorology Section 1: Weather versus Climate Chose the answer that best answers the question 1. The sky is partly cloudy this morning in Lincoln, Nebraska. 2. Fargo,
2015 National Tournament Division B Meteorology Section 1: Weather versus Climate Chose the answer that best answers the question 1. The sky is partly cloudy this morning in Lincoln, Nebraska. 2. Fargo,
JRA-55 Product Users' Handbook
 Climate Prediction Division Global Environment and Marine Department Japan Meteorological Agency September 2013 Change record Version Date Remarks 1.0 30 September 2013 First version 2.0 3 March 2014 Corrected
Climate Prediction Division Global Environment and Marine Department Japan Meteorological Agency September 2013 Change record Version Date Remarks 1.0 30 September 2013 First version 2.0 3 March 2014 Corrected
Climate change with an iris-effect. Thorsten Mauritsen and Bjorn Stevens Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg
 Climate change with an iris-effect! Thorsten Mauritsen and Bjorn Stevens Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg AR4 Temperature anomaly ( C) w.r.t. 1961 1990 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 } AR4 CMIP3 } Observations
Climate change with an iris-effect! Thorsten Mauritsen and Bjorn Stevens Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg AR4 Temperature anomaly ( C) w.r.t. 1961 1990 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 } AR4 CMIP3 } Observations
CHAPTER 6 Modeling of Stratospheric Aerosols
 CHAPTER 6 Modeling of Stratospheric Aerosols Lead Authors: Debra Weisenstein Slimane Bekki Authors: Michael Mills Giovanni Pitari Claudia Timmreck Contributors: Mian Chin Mark Hervig Fok-Yan Leung Beiping
CHAPTER 6 Modeling of Stratospheric Aerosols Lead Authors: Debra Weisenstein Slimane Bekki Authors: Michael Mills Giovanni Pitari Claudia Timmreck Contributors: Mian Chin Mark Hervig Fok-Yan Leung Beiping
Satellite Observations of Greenhouse Gases
 Satellite Observations of Greenhouse Gases Richard Engelen European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Outline Introduction Data assimilation vs. retrievals 4D-Var data assimilation Observations
Satellite Observations of Greenhouse Gases Richard Engelen European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts Outline Introduction Data assimilation vs. retrievals 4D-Var data assimilation Observations
REVISION OF THE STATEMENT OF GUIDANCE FOR GLOBAL NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION. (Submitted by Dr. J. Eyre)
 WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION Distr.: RESTRICTED CBS/OPAG-IOS (ODRRGOS-5)/Doc.5, Add.5 (11.VI.2002) COMMISSION FOR BASIC SYSTEMS OPEN PROGRAMME AREA GROUP ON INTEGRATED OBSERVING SYSTEMS ITEM: 4 EXPERT
WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION Distr.: RESTRICTED CBS/OPAG-IOS (ODRRGOS-5)/Doc.5, Add.5 (11.VI.2002) COMMISSION FOR BASIC SYSTEMS OPEN PROGRAMME AREA GROUP ON INTEGRATED OBSERVING SYSTEMS ITEM: 4 EXPERT
Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration
 Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration Climatological and hydrological field work Figure 1: Estimate of the Earth s annual and global mean energy balance. Over the long term, the incoming
Radiation, Sensible Heat Flux and Evapotranspiration Climatological and hydrological field work Figure 1: Estimate of the Earth s annual and global mean energy balance. Over the long term, the incoming
The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation Analysis of the Resolved Wave Forcing
 The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation Analysis of the Resolved Wave Forcing Thomas Krismer, Marco Giorgetta Max Planck Institute for Meteorology Hamburg Introduction 1) The Quasi Biennial Oscillation is driven
The Quasi-Biennial Oscillation Analysis of the Resolved Wave Forcing Thomas Krismer, Marco Giorgetta Max Planck Institute for Meteorology Hamburg Introduction 1) The Quasi Biennial Oscillation is driven
The early 20th century warming in the Arctic A possible mechanism
 The early 20th century warming in the Arctic A possible mechanism Lennart Bengtsson Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg, Germany ESSC, University of Reading, UK Thanks to Vladimir Semenov and
The early 20th century warming in the Arctic A possible mechanism Lennart Bengtsson Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg, Germany ESSC, University of Reading, UK Thanks to Vladimir Semenov and
