Notes for Use of the Cpx-Plag-Ol Thermobar Workbook Last Updated:
|
|
|
- Rudolph Osborn Mason
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Notes for Use of the Cpx-Plag-Ol Thermobar Workbook Last Updated: Cpx-Plag-Ol Thermobar is an Excel workbook that can be used to calculate crystallization pressures and temperatures for clinopyroxene- and plagioclaseliquid composition pairs. For clinopyroxene, the calculations utilize the models of Putirka et al. (1996, 2003) and Putirka (2005). The workbook also allows for calculation of a clinopyroxene saturation surface, using the models of Putirka (1999) (i.e., the worksheet calculates a clinopyroxene saturation temperature, and nominal equilibrium clinopyroxene composition, for a given input liquid composition and input pressure). In addition, the workbook contains several olivine-liquid thermometers. The workbook is set up so that data entry is performed in the following worksheets Cpx & Liq Input, Plag & Liq Input and Ol & Liq Input. You will need to input clinopyroxene, plagioclase and/or olivine compositions as weight % values. You will also need to input weight % values for nominal equilibrium liquid compositions; for these latter values, whole rock or glass compositions might be used, or perhaps a whole rock composition adjusted for the addition or subtraction of phenocryst phases. Once the appropriate data are entered all results can be viewed in the first few columns of the three worksheets: Cpx P-T Results, Plag P-T Results, and Ol Temp Results. This workbook differs somewhat in format compared to earlier spreadsheets: the various worksheet pairs ( -Input & -Results ) are linked, hence, there is no longer a need to cut and paste results from one spreadsheet to another. Some notes regarding the application of these models follow. General Instructions: 1) Input weight % data for nominal liquid and mineral compositions using the - Input worksheets, then read the results in the worksheets labeled - Results. The individual Input worksheets are color-coded: gray = input, or calculations that are not a function of P and/or T calculations. colors = results columns. Cut-and-paste operations will delete these formats, but will not affect P-T calculations ( paste special values only will preserve the formats). 2) To enter additional data, enter weight % s in the appropriate columns and then use the fill down command for ALL columns in the -Results worksheets. Caveats: 1) If you receive a circular reference error while using P-T Calcs, make sure that in the Tools-Preferences-Calculation window (in Excel) the Iteration box is checked, or that your spreadsheet preferences are otherwise set up to handle iterative calculations.
2 2) For clinopyroxene P-T calculations, if Excel returns the error: #NUM! one very likely reason is that your clinopyroxene composition was such that a jadeite component could not be calculated (this will happen if either Na or octahedral Al are too low in the analysis/calculation). Clinopyroxene calculations: In contrast to the models of Putirka et al. (1996) the model results labeled Am. Min apply to a wider range of liquid compositions (basalt dacite) as well as hydrous liquid compositions. The 1996 models, though, might be more precise for dry basaltic bulk compositions. Tests of equilibrium: The predicted clinopyroxene components in Cpx P-T Results (columns N U) and the clinopyroxene saturation temperature, Cpx sat in column L are predicted using the models of Putirka (1999) and make use of the input liquid composition, and the estimate of P in column D. These models collectively comprise a saturation surface for clinopyroxene calibrated using experiments performed on a range of silicate liquids. As the Jd component is to a significant extent a function of pressure, prediction of this component is necessarily circular, but most other components, though still P-dependent, should be useful as a test to whether a suitable liquid composition has been selected for a given clinopyroxene. The argument is as follows: If the input liquid composition were at the predicted pressure then (a) at what T would clinopyroxene crystallize (the saturation T, in column L)? and (b) what would be the equilibrium composition of the clinopyroxene (the output of columns N U)? The hope is that if the liquid and clinopyroxene compositions represent an equilibrium pair, then the T of saturation should approach that of the crystallization T (L compared to C or F). Similarly, clinopyroxene components calculated from the observed phenocryst phases (columns W AD) should approach values calculated from the assumption of equilibrium (columns N U). To avoid circularity altogether, one may enter some nominal P value as input into column M (which by default will be the pressure given in column D, from the Am. Min., 2003 paper). Olivine and cpx crystallization temperatures need not match, but the Fe-Mg exchange model of Putirka et al. (1996), and olivine (see below) can be used to compare olivine crystallization conditions to those calculated from cpx. Some whole rock liquid compositions that appear not to be liquids (due to cumulus olivine) can still sometimes be used by adding or subtracting an appropriate amount of olivine to bring Fe-Mg exchange ratios to anticipated equilibrium values. One can then, for example, check whether the amount of olivine removed matches modal proportions (although there are some obvious complications to this approach). In summary, adjusting cumulate whole rock compositions until either (a) olivine-liquid K D (Fe-Mg) exchange values approach 0.3 (Roeder and Emslie, 1971), or (b) cpx K D (Fe-Mg) approaches 0.27 (or values predicted from
3 equation 3.3 in Table 3 of Putirka (1999); see also column T of Cpx P-T Results), might at times be useful. The clinopyroxene component calculation scheme follows a normative procedure adapted from Lindsley (1983); cations are calculated on the basis of 6 oxygens (see Klein, 2002). Fe 3+ is calculated using models of Lindsley (1983) and Droop (1987) (see columns AH AI in Cpx P-T Results) but Fe 3+ measurements by McGuire et al (1989) indicate that such values are of limited usefulness. A check of clinopyroxene cation sums (column AF), and a check that K in clinopyroxene is very close to zero, are probably the best means to evaluate the quality of clinopyroxene analyses. Plagioclase Thermobarometers These calculations are based on the models of Putirka (2005). Be aware that plag-liquid hygrometers are not very effective at predicting H 2 O for samples not used for calibration. Olivine Temperatures: An new olivine-melt thermometer is provided (in column D of Ol Temp Results); it was calibrated in an attempt to provide a single olivine + liquid thermometer that could be applied to both hydrous and anhydrous bulk compositions. I have also added several other olivine theremometers, some of which will yield a single T for a given bulk composition (e.g., Beattie, 1993). Olivine temperature estimates are sensitive to f(o2), and so using cells D5 and J5 in the Ol Temp Results spreadsheet, it is possible to adjust f(o2) conditions. Since the calculations are iterative, please note that adjusting log units in cell J5 will not yield a precisely a whole number log unit difference in calculated f(o 2 ). Olivine temperatures for the various models in this spreadsheet are compared using 635 experimental data whose experimental conditions range from o C, and 0-70 kbar. In these experiments, liquid (glass) compositions range from wt. % SiO 2, and 107 of these experiments were performed on hydrous bulk compositions. All models predict T s that are too high for the o C range, hence statistics for all models are compared for the 614 experimental data conducted between in the o C (Tables 1, 2). For anhydrous data, the models of Beattie (1993) and Model 3 are the most precise, though Model 3 yields much better slope and intercept values for the regression line (T-predicted vs. T-measured). The Beattie (1993) model over-predicts T for 96% of the 107 hydrous experiments (by a coincidental average of 107 o C), as can be seen below in Table 2 (Difference of Means = Mean of predicted values Mean of observed values). The Langmuir et al. (1992) model provides the least systematic offset for the hydrous data, but with a 25% cost in SEE compared to Model 3. Table 1 T(C) Calculated vs. T(C) Measured Anhydrous and Hydrous data Anhydrous data only
4 T(C) = ; n = 614 T(C) = ; n = 507 R 2 SEE Slope Intercept R 2 SEE Slope Intercept Difference of Means Beattie (1993) Langmuir et al. (1992) Ford et al. (1983) (Mg-model) Model Table 2 T(C) Calculated vs. T(C) Measured Hydrous data only T(C) = ; n = 107 R 2 SEE Slope Intercept Difference of Means Beattie (1993) Langmuir et al. (1992) Ford et al. (1983) (Mg-model) Model Some References Beattie, P. (1993) Olivine-melt and orthopyroxene-melt equilibria, Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 115, Droop, G.T.R. (1987) A general equation for estimating Fe 3+ concentrations in ferromagnesian silicates and oxides from microprobe analyses, using stoichiometric criteria, Mineralogical Magazine. 51, Ford, C.E., Russell, D.G., Craven, J.A. and Fisk-, M.R. (1983) Olivine-liquid equilibria; temperature, pressure and composition dependence of the crystal/ liquid cation partition coefficients for Mg, Fe 2+, Ca and Mn, Journal of Petrology, 24, Langmuir, C.H., E.M. Klein, and T. Plank (1992) Petrological systematics of mid-ocean ridge basalts: Constraints on melt generation beneath ocean ridges, in Mantle Flow and Melt Generation at Mid-Ocean Ridges, Geophys. Monogr., Ser.71, J.P. Morgan, D.K. Blackman, and J.M. Sinton, eds., p , AGU, Washington, D.C. Lindsley, D. H. (1983) Pyroxene thermometry, American Mineralogist, 68, McGuire, A.V., Dyar, M.D. and Ward, K. (1989) Neglected Fe 3+ /Fe 2+ ratios a study of Fe 3+ content of megacrysts from alkali basalts. Geology, 17, Putirka, K. (1997) Magma Transport at Hawaii: Inferences based on igneous thermobarometry, Geology, 25, Putirka, K. (1999) Clinopyroxene + liquid equilibria. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 135, Putirka, K. (2005) Igneous thermometers and barometers based on
5 plagioclase +liquid equilibria: Test of some existing models and new calibrations, American Mineralogist, v. 90, p Putirka, K., Johnson, M., Kinzler, R., Longhi, J. and Walker, D. (1996) Thermobarometry of mafic igneous rocks based on clinopyroxene-liquid equilibria, 0-30 kb, Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 123, Putirka, K., Mikaelian, H., Ryerson, F. J., and Shaw, H. (2003) New clinopyroxene-liquid thermobarometers for mafic, evolved and volatile-bearing lava compositions, with applications to lavas from Tibet and the Snake River Plain, ID, American Mineralogist, 88, Roeder, P.L. and Emslie, R.F. (1970) Olivine-liquid equilibrium. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 29, Please note that these Excel worksheets were not originally designed for distribution, but having received a large number of requests, I have tried to put together something useful. I would still greatly appreciate any feedback from you if you have suggestions for improvement or added clarity. Thank you for your interest in this work. Cheers, Keith Putirka Keith Putirka California State University, Fresno Dept. of Earth & Environmental Sciences 2576 E. San Ramon Ave., MS/ST 24 Fresno, CA, kputirka@csufresno.edu office tele: lab tele: dept. tele: fax:
LAB 9: ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS, CUMULATES AND MELT SOURCES
 Geology 316 (Petrology) (03/26/2012) Name LAB 9: ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS, CUMULATES AND MELT SOURCES INTRODUCTION Ultramafic rocks are igneous rocks containing less than 10% felsic minerals (quartz + feldspars
Geology 316 (Petrology) (03/26/2012) Name LAB 9: ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS, CUMULATES AND MELT SOURCES INTRODUCTION Ultramafic rocks are igneous rocks containing less than 10% felsic minerals (quartz + feldspars
Trace Elements. Today s lecture
 Trace Elements 300 Ni 200 ppm 100 0 300 Zr 200 100 0 40 50 60 70 80 SiO 2 wt. % Updates: M&M due date: Tuesday Today s lecture Topics: Trace element compositions Trace element behavior Partitioning Spider(
Trace Elements 300 Ni 200 ppm 100 0 300 Zr 200 100 0 40 50 60 70 80 SiO 2 wt. % Updates: M&M due date: Tuesday Today s lecture Topics: Trace element compositions Trace element behavior Partitioning Spider(
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40
 GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40 QUIZ 3 1) Name two geologic features that provide physical evidence for the mineralogy of the earth s mantle (2 pts) Ophiolites,
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40 QUIZ 3 1) Name two geologic features that provide physical evidence for the mineralogy of the earth s mantle (2 pts) Ophiolites,
12 Chemistry (Mg,Fe) 2 SiO 4 Olivine is forms what is called an isomorphous solid solution series that ranges between two end members: Forsterite Mg
 11 Olivine Structure Olivine is a common green or brown rock forming minerals which consists of a solid-solution series between Forsterite (Fo) and Fayalite (Fa). It is an orthorhombic orthosilicate with
11 Olivine Structure Olivine is a common green or brown rock forming minerals which consists of a solid-solution series between Forsterite (Fo) and Fayalite (Fa). It is an orthorhombic orthosilicate with
Partial melting of mantle peridotite
 Partial melting of mantle peridotite 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 (TºC) Depth (km) 50 100 150 Plag lherzolite (ol-opx-cpx-pl) Spinel lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-sp) Garnet lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-gar) Graphite Diamond
Partial melting of mantle peridotite 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 (TºC) Depth (km) 50 100 150 Plag lherzolite (ol-opx-cpx-pl) Spinel lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-sp) Garnet lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-gar) Graphite Diamond
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2016 Score / 58. Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10
 GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name KEY Spring 2016 Score / 58 Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10 1) Name two things that petrologists want to know about magmas (1 pt) Formation, source, composition,
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name KEY Spring 2016 Score / 58 Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10 1) Name two things that petrologists want to know about magmas (1 pt) Formation, source, composition,
The application of olivine geothermometry to infer crystallization temperatures of parental liquids: Implications for the temperature of MORB magmas
 Chemical Geology 241 (2007) 207 233 www.elsevier.com/locate/chemgeo The application of olivine geothermometry to infer crystallization temperatures of parental liquids: Implications for the temperature
Chemical Geology 241 (2007) 207 233 www.elsevier.com/locate/chemgeo The application of olivine geothermometry to infer crystallization temperatures of parental liquids: Implications for the temperature
DIFFERENTIATION OF MAGMAS BY FRACTIONAL CRYSTALLIZATION THE M&M MAGMA CHAMBER
 Geol 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2009 Name DIFFERENTIATION OF MAGMAS BY FRACTIONAL CRYSTALLIZATION THE M&M MAGMA CHAMBER Objective: This exercise is intended to improve understanding
Geol 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2009 Name DIFFERENTIATION OF MAGMAS BY FRACTIONAL CRYSTALLIZATION THE M&M MAGMA CHAMBER Objective: This exercise is intended to improve understanding
WORKING WITH ELECTRON MICROPROBE DATA FROM A HIGH PRESSURE EXPERIMENT CALCULATING MINERAL FORMULAS, UNIT CELL CONTENT, AND GEOTHERMOMETRY
 WORKING WITH ELECTRON MICROPROBE DATA FROM A HIGH PRESSURE EXPERIMENT CALCULATING MINERAL FORMULAS, UNIT CELL CONTENT, AND GEOTHERMOMETRY Brandon E. Schwab Department of Geology Humboldt State University
WORKING WITH ELECTRON MICROPROBE DATA FROM A HIGH PRESSURE EXPERIMENT CALCULATING MINERAL FORMULAS, UNIT CELL CONTENT, AND GEOTHERMOMETRY Brandon E. Schwab Department of Geology Humboldt State University
LAB 6: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS
 GEOLOGY 17.01: Mineralogy LAB 6: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS Part 2: Minerals in Gabbroic Rocks Learning Objectives: Students will be able to identify the most common silicate minerals in gabbroic
GEOLOGY 17.01: Mineralogy LAB 6: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS Part 2: Minerals in Gabbroic Rocks Learning Objectives: Students will be able to identify the most common silicate minerals in gabbroic
Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts
 Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts Lherzolite Basalt Factors controlling magma composition Composition of the source Partial melting process Fractional crystallization Crustal
Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts Lherzolite Basalt Factors controlling magma composition Composition of the source Partial melting process Fractional crystallization Crustal
Chapter 6: The Phase Rule and One and Two-Component Systems aka Phase Equilibria
 Chapter 6: The Phase Rule and One and Two-Component Systems aka Phase Equilibria Makaopuhi Lava Lake Magma samples recovered from various depths beneath solid crust From Wright and Okamura, (1977) USGS
Chapter 6: The Phase Rule and One and Two-Component Systems aka Phase Equilibria Makaopuhi Lava Lake Magma samples recovered from various depths beneath solid crust From Wright and Okamura, (1977) USGS
Chapter 9: Trace Elements
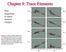 Chapter 9: Trace Elements Note magnitude of major element changes Figure 8.2. Harker variation diagram for 310 analyzed volcanic rocks from Crater Lake (Mt. Mazama), Oregon Cascades. Data compiled by Rick
Chapter 9: Trace Elements Note magnitude of major element changes Figure 8.2. Harker variation diagram for 310 analyzed volcanic rocks from Crater Lake (Mt. Mazama), Oregon Cascades. Data compiled by Rick
Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr
 Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr Basalt with the mode: Table 9.2. Conversion from mode to weight percent Mineral Mode Density Wt prop Wt% ol 15 3.6 54 0.18 cpx 33 3.4 112.2 0.37 plag 51 2.7 137.7
Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr Basalt with the mode: Table 9.2. Conversion from mode to weight percent Mineral Mode Density Wt prop Wt% ol 15 3.6 54 0.18 cpx 33 3.4 112.2 0.37 plag 51 2.7 137.7
Chapter 9: Trace Elements
 Lecture 13 Introduction to Trace Elements Wednesday, March 9, 2005 Chapter 9: Trace Elements Note magnitude of major element changes Figure 8-2. Harker variation diagram for 310 analyzed volcanic rocks
Lecture 13 Introduction to Trace Elements Wednesday, March 9, 2005 Chapter 9: Trace Elements Note magnitude of major element changes Figure 8-2. Harker variation diagram for 310 analyzed volcanic rocks
Lecture 14: A brief review
 Lecture 14: A brief review A few updates for the remainder of the course Report for the lab on pelite metamorphism - Lab 3 Needs to be handed in before Tuesday the 14 th of March at 17:00. My most important
Lecture 14: A brief review A few updates for the remainder of the course Report for the lab on pelite metamorphism - Lab 3 Needs to be handed in before Tuesday the 14 th of March at 17:00. My most important
Chapter IV MINERAL CHEMISTRY
 Chapter IV MINERAL CHEMISTRY Chapter-IV MINERAL CHEMISTRY 4.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter, chemical analyses of different minerals present in various rocks of Mashhad granitoid plutons have been presented.
Chapter IV MINERAL CHEMISTRY Chapter-IV MINERAL CHEMISTRY 4.1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter, chemical analyses of different minerals present in various rocks of Mashhad granitoid plutons have been presented.
C = 3: Ternary Systems: Example 1: Ternary Eutectic
 Phase Equilibrium C = 3: Ternary Systems: Example 1: Ternary Eutectic Adding components, becomes increasingly difficult to depict 1-C: P - T diagrams easy 2-C: isobaric T-X, isothermal P-X 3-C:?? Still
Phase Equilibrium C = 3: Ternary Systems: Example 1: Ternary Eutectic Adding components, becomes increasingly difficult to depict 1-C: P - T diagrams easy 2-C: isobaric T-X, isothermal P-X 3-C:?? Still
Lecture 36. Igneous geochemistry
 Lecture 36 Igneous geochemistry Reading - White Chapter 7 Today 1. Overview 2. solid-melt distribution coefficients Igneous geochemistry The chemistry of igneous systems provides clues to a number of important
Lecture 36 Igneous geochemistry Reading - White Chapter 7 Today 1. Overview 2. solid-melt distribution coefficients Igneous geochemistry The chemistry of igneous systems provides clues to a number of important
Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism
 Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism Monday, May 2 nd 2005 Subduction Related Magmatism Activity along arcuate volcanic chains along subduction zones Distinctly different from the mainly basaltic provinces
Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism Monday, May 2 nd 2005 Subduction Related Magmatism Activity along arcuate volcanic chains along subduction zones Distinctly different from the mainly basaltic provinces
GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology. Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments
 GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments Factors controlling Magma production Source rock composition Amount of fluids, especially H 2 O Pressure (Depth)
GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments Factors controlling Magma production Source rock composition Amount of fluids, especially H 2 O Pressure (Depth)
Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington
 Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington S. C. Kuehn and P. R. Hooper, Department of Geology, Washington State University, Pullman, WA A. E. Eggers and C. Kerrick, Department of Geology,
Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington S. C. Kuehn and P. R. Hooper, Department of Geology, Washington State University, Pullman, WA A. E. Eggers and C. Kerrick, Department of Geology,
Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization
 Wirth Magmatic Differentiation Using M&M s 1 HANDOUT Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization Objective The objective of this exercise is to gain first-hand knowledge of the process of magmatic
Wirth Magmatic Differentiation Using M&M s 1 HANDOUT Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization Objective The objective of this exercise is to gain first-hand knowledge of the process of magmatic
GEOLOGY. Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02
 GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and. MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout)
 Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and 20 MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout) Chain silicate eg Diopside Mg and Fe ions link SiO 3 chains The chain runs up and down
Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and 20 MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout) Chain silicate eg Diopside Mg and Fe ions link SiO 3 chains The chain runs up and down
Mineral chemistry of submarine lavas from Hilo Ridge, Hawaii: implications for magmatic processes within Hawaiian rift zones
 Contrib Mineral Petrol (1999) 135: 355±372 Ó Springer-Verlag 1999 Huai-Jen Yang á Frederick A. Frey David A. Clague á Michael O. Garcia Mineral chemistry of submarine lavas from Hilo Ridge, Hawaii: implications
Contrib Mineral Petrol (1999) 135: 355±372 Ó Springer-Verlag 1999 Huai-Jen Yang á Frederick A. Frey David A. Clague á Michael O. Garcia Mineral chemistry of submarine lavas from Hilo Ridge, Hawaii: implications
A - METHOD. GSA Data Repository
 GSA Data Repository 2018133 Ganne et al., 2018, Deep into magma plumbing systems: Interrogating the crystal cargo of volcanic deposits: Geology, https://doi.org/10.1130/g39857.1. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
GSA Data Repository 2018133 Ganne et al., 2018, Deep into magma plumbing systems: Interrogating the crystal cargo of volcanic deposits: Geology, https://doi.org/10.1130/g39857.1. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
Petrolog v. 3. Manual. January 2011
 Petrolog v. 3 Manual January 2011 The latest version of Petrolog and this manual can be downloaded from the Petrolog home page at http://petrolog.web.ru Leonid Danyushevsky L.Dan@utas.edu.au Pavel Plechov
Petrolog v. 3 Manual January 2011 The latest version of Petrolog and this manual can be downloaded from the Petrolog home page at http://petrolog.web.ru Leonid Danyushevsky L.Dan@utas.edu.au Pavel Plechov
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100
 Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
*Revision 2 for Manuscript 5783* A Review and Update of Mantle Thermobarometry for Primitive Arc Magmas
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 *Revision 2 for Manuscript 5783* A Review and Update of Mantle Thermobarometry for Primitive Arc Magmas Christy B. Till School of Earth &
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 *Revision 2 for Manuscript 5783* A Review and Update of Mantle Thermobarometry for Primitive Arc Magmas Christy B. Till School of Earth &
Classification of Igneous Rocks
 Classification of Igneous Rocks Textures: Glassy- no crystals formed Aphanitic- crystals too small to see by eye Phaneritic- can see the constituent minerals Fine grained- < 1 mm diameter Medium grained-
Classification of Igneous Rocks Textures: Glassy- no crystals formed Aphanitic- crystals too small to see by eye Phaneritic- can see the constituent minerals Fine grained- < 1 mm diameter Medium grained-
Slow cooling of the lowermost oceanic crust at the fastspreading
 GSA Data Repository 2016030 Slow cooling of the lowermost oceanic crust at the fastspreading East Pacific Rise Kathrin Faak and Kathryn M. Gillis Model parameters and input conditions for the diffusion
GSA Data Repository 2016030 Slow cooling of the lowermost oceanic crust at the fastspreading East Pacific Rise Kathrin Faak and Kathryn M. Gillis Model parameters and input conditions for the diffusion
Electronic Appendix A: Supplementary material to accompany the manuscript, Fe 3+ / Fe in Mariana Arc basalts and primary fo 2.
 Electronic Appendix A: Supplementary material to accompany the manuscript, Fe 3+ / Fe in Mariana Arc basalts and primary fo 2. Screening for olivine interference in Fe-µ-XANES spectra When collecting Fe-µ-XANES
Electronic Appendix A: Supplementary material to accompany the manuscript, Fe 3+ / Fe in Mariana Arc basalts and primary fo 2. Screening for olivine interference in Fe-µ-XANES spectra When collecting Fe-µ-XANES
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization Modified from Karl Wirth, rev. July 2011
 M&M s Magma Chamber 1 Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization Modified from Karl Wirth, rev. July 2011 Objective The objective of this exercise is to gain first-hand knowledge of the process
M&M s Magma Chamber 1 Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization Modified from Karl Wirth, rev. July 2011 Objective The objective of this exercise is to gain first-hand knowledge of the process
a listing of all of the references for data incorporated into our database of olivine-liquid pairs from the literature.
 Supplementary Material to the paper Fe-Mg partitioning between olivine and high-magnesian melts and the nature of Hawaiian parental liquids by A.K. Matzen, M.B. Baker, J.R. Beckett, and E.M. Stolper In
Supplementary Material to the paper Fe-Mg partitioning between olivine and high-magnesian melts and the nature of Hawaiian parental liquids by A.K. Matzen, M.B. Baker, J.R. Beckett, and E.M. Stolper In
Metal saturation in the upper mantle
 Vol 449 27 September 2007 Metal saturation in the upper mantle A. Rohrbach, C. Ballhaus, U. Golla Schindler, P. Ulmer,V.S. Kamenetsky, D.V. Kuzmin NS seminar 2007.10.25 The uppermost mantle is oxidized.
Vol 449 27 September 2007 Metal saturation in the upper mantle A. Rohrbach, C. Ballhaus, U. Golla Schindler, P. Ulmer,V.S. Kamenetsky, D.V. Kuzmin NS seminar 2007.10.25 The uppermost mantle is oxidized.
Straddling the tholeiitic/calc-alkaline transition: the effects of modest amounts of water on magmatic differentiation at Newberry Volcano, Oregon
 Straddling the tholeiitic/calc-alkaline transition: the effects of modest amounts of water on magmatic differentiation at Newberry Volcano, Oregon The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available.
Straddling the tholeiitic/calc-alkaline transition: the effects of modest amounts of water on magmatic differentiation at Newberry Volcano, Oregon The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available.
PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS
 PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS PLATE TECTONICS TO IGNEOUS ROCKS Internal Heat Seafloor Spreading/Plate Tectonics Volcanism Plate Boundary Intra-plate (hot spot) Divergent Convergent Igneous
PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS PLATE TECTONICS TO IGNEOUS ROCKS Internal Heat Seafloor Spreading/Plate Tectonics Volcanism Plate Boundary Intra-plate (hot spot) Divergent Convergent Igneous
III-1 MANGANESE PARTITIONING DURING HYDROUS MELTING OF PERIDOTITE. J. Brian Balta. Paul D. Asimow. Jed L. Mosenfelder
 III-1 MANGANESE PARTITIONING DURING HYDROUS MELTING OF PERIDOTITE By J. Brian Balta Paul D. Asimow Jed L. Mosenfelder III-2 ABSTRACT Manganese contents and the iron/manganese ratio of igneous rocks have
III-1 MANGANESE PARTITIONING DURING HYDROUS MELTING OF PERIDOTITE By J. Brian Balta Paul D. Asimow Jed L. Mosenfelder III-2 ABSTRACT Manganese contents and the iron/manganese ratio of igneous rocks have
Earth Science 232 Petrography
 Earth Science 232 Petrography Course notes by Shaun Frape and Alec Blyth Winter 2002 1 Petrology - Introduction Some Definitions Petra Greek for rock Logos Greek for disclosure or explanation Petrology
Earth Science 232 Petrography Course notes by Shaun Frape and Alec Blyth Winter 2002 1 Petrology - Introduction Some Definitions Petra Greek for rock Logos Greek for disclosure or explanation Petrology
Melting Behavior of Simplified Lherzolite in the System CaO-MgO-Al 2 O 3 -SiO 2 -Na 2 O from 7 to 35 kbar
 Melting Behavior of Simplified Lherzolite in the System --Al 2 O 3 - -Na 2 O from 7 to 35 kbar by MICHAEL J. WALTER* AND DEAN C. PRESNALL Center for Lithospheric Studies, University of Texas at Dallas,
Melting Behavior of Simplified Lherzolite in the System --Al 2 O 3 - -Na 2 O from 7 to 35 kbar by MICHAEL J. WALTER* AND DEAN C. PRESNALL Center for Lithospheric Studies, University of Texas at Dallas,
GEOL3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks G. Mattioli, Dept. of Geosciences, Univ. of Arkansas, Spring 2008
 GEOL3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks G. Mattioli, Dept. of Geosciences, Univ. of Arkansas, Spring 2008 Homework Assignment 3 Calculation of CIPW Norm Due in Class February 13, 2008 Problem
GEOL3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks G. Mattioli, Dept. of Geosciences, Univ. of Arkansas, Spring 2008 Homework Assignment 3 Calculation of CIPW Norm Due in Class February 13, 2008 Problem
EAS 4550: Geochemistry Problem Set 4 Solutions Due Sept. 27, 2017
 1. Interaction parameters for the enstatite diopside solid solution have been determined as follows: WH-En = 34.0 kj/mol, WH-Di = 24.74 kj/mol (assume WV and WS are 0). (a) Use the asymmetric solution
1. Interaction parameters for the enstatite diopside solid solution have been determined as follows: WH-En = 34.0 kj/mol, WH-Di = 24.74 kj/mol (assume WV and WS are 0). (a) Use the asymmetric solution
amphibole PART 3 Pyroxene: augite CHAIN SILICATES
 amphibole PART 3 Pyroxene: augite CHAIN SILICATES CHAIN SILICATES = INOSILICATES inos = chains Basic structural group: Si 2 O 6 (each tetrahedra shared two corners) Simple or double chains linked by cations
amphibole PART 3 Pyroxene: augite CHAIN SILICATES CHAIN SILICATES = INOSILICATES inos = chains Basic structural group: Si 2 O 6 (each tetrahedra shared two corners) Simple or double chains linked by cations
Ultramafic rocks. Types of Ultramafic Rocks. Spinel lherzolite xenolith
 Ultramafic rocks Definition: Color Index > 90, i.e., less than 10% felsic minerals. Not to be confused with Ultrabasic Rocks which are rocks with
Ultramafic rocks Definition: Color Index > 90, i.e., less than 10% felsic minerals. Not to be confused with Ultrabasic Rocks which are rocks with
How 2 nd half labs will work
 How 2 nd half labs will work Continue to use your mineral identification skills Learn to describe, classify, interpret rock hand samples: Igneous sedimentary metamorphic volcanic plutonic (1 week) (1 wk)
How 2 nd half labs will work Continue to use your mineral identification skills Learn to describe, classify, interpret rock hand samples: Igneous sedimentary metamorphic volcanic plutonic (1 week) (1 wk)
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools -
 High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
1 - C Systems. The system H 2 O. Heat an ice at 1 atm from-5 to 120 o C. Heat vs. Temperature
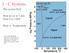 1 - C Systems The system H 2 O Heat an ice at 1 atm from-5 to 120 o C Heat vs. Temperature Fig. 6.7. After Bridgman (1911) Proc. Amer. Acad. Arts and Sci., 5, 441-513; (1936) J. Chem. Phys., 3, 597-605;
1 - C Systems The system H 2 O Heat an ice at 1 atm from-5 to 120 o C Heat vs. Temperature Fig. 6.7. After Bridgman (1911) Proc. Amer. Acad. Arts and Sci., 5, 441-513; (1936) J. Chem. Phys., 3, 597-605;
GSA DATA REPOSITORY
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013019 Supplemental information for The Solidus of Alkaline Carbonatite in the Deep Mantle Konstantin D. Litasov, Anton Shatskiy, Eiji Ohtani, and Gregory M. Yaxley EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013019 Supplemental information for The Solidus of Alkaline Carbonatite in the Deep Mantle Konstantin D. Litasov, Anton Shatskiy, Eiji Ohtani, and Gregory M. Yaxley EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
- low FeO*/MgO is controlled by the reaction relation oliv + liq! opx.
 Mantle melting trend to high-sio 2 - low FeO*/MgO is controlled by the reaction relation oliv + liq! opx. 4 3 2 1 Ol+Opx +Cpx+Sp +liq 79-35g 82-66 87S35 85-44 85-41c -ol +opx Mantle melting/reaction 0
Mantle melting trend to high-sio 2 - low FeO*/MgO is controlled by the reaction relation oliv + liq! opx. 4 3 2 1 Ol+Opx +Cpx+Sp +liq 79-35g 82-66 87S35 85-44 85-41c -ol +opx Mantle melting/reaction 0
Common non-silicate planetary minerals
 Common non-silicate planetary minerals Many of the non-silicate minerals are simple oxides. Corundum Al2O3 Al2+3 O3-2 Rutile Ti2O3 Ti2+3 O3-2 Ilmenite FeTiO3 Fe+3Ti+3O3-2 Hematite Fe2O3 Fe2+3 O3-2 Families
Common non-silicate planetary minerals Many of the non-silicate minerals are simple oxides. Corundum Al2O3 Al2+3 O3-2 Rutile Ti2O3 Ti2+3 O3-2 Ilmenite FeTiO3 Fe+3Ti+3O3-2 Hematite Fe2O3 Fe2+3 O3-2 Families
Name Petrology Spring 2006 Igneous rocks lab Part II Hand samples of igneous rocks Due Tuesday 3/7
 Igneous rocks lab Part II Hand samples of igneous rocks Due Tuesday 3/7 1. Use the color index and density of the rock to establish whether it is felsic, intermediate, mafic, or ultramafic. 2. Determine
Igneous rocks lab Part II Hand samples of igneous rocks Due Tuesday 3/7 1. Use the color index and density of the rock to establish whether it is felsic, intermediate, mafic, or ultramafic. 2. Determine
Melts of garnet lherzolite: experiments, models and comparison to melts of pyroxenite and carbonated lherzolite
 Contrib Mineral Petrol (2013) 166:887 910 DOI 10.1007/s00410-013-0899-9 ORIGINAL PAPER Melts of garnet lherzolite: experiments, models and comparison to melts of pyroxenite and carbonated lherzolite Timothy
Contrib Mineral Petrol (2013) 166:887 910 DOI 10.1007/s00410-013-0899-9 ORIGINAL PAPER Melts of garnet lherzolite: experiments, models and comparison to melts of pyroxenite and carbonated lherzolite Timothy
Mineral Chemistry and Geothermobarometry of Alkali Basalts from the Elmadağ Volcanic Complex, Ankara (Central Anatolia, Turkey)
 Mineral Chemistry and Geothermobarometry of Alkali Basalts from the Elmadağ Volcanic Complex, Ankara (Central Anatolia, Turkey) KÜRŞAD ASAN Geological Engineering Department Selçuk University Alaeddin
Mineral Chemistry and Geothermobarometry of Alkali Basalts from the Elmadağ Volcanic Complex, Ankara (Central Anatolia, Turkey) KÜRŞAD ASAN Geological Engineering Department Selçuk University Alaeddin
Chapter 4 8/27/2013. Igneous Rocks. and Intrusive Igneous Activity. Introduction. The Properties and Behavior of Magma and Lava
 Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Magma Formation and Behavior
 Magma Formation and Behavior Questions What causes mantle rock to melt, resulting in magma formation? Why is magma formation restricted to specific plate tectonic settings? Why are mafic (basaltic) magmas
Magma Formation and Behavior Questions What causes mantle rock to melt, resulting in magma formation? Why is magma formation restricted to specific plate tectonic settings? Why are mafic (basaltic) magmas
Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
Most mafic magmas come from the upper mantle and lower crust. This handout will address five questions:
 Geology 101 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate
Geology 101 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate
Igneous Rocks of the Convergent Margins
 Page 1 of 10 EENS 2120 Petrology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tulane University Igneous Rocks of the This document last updated on 08-Feb-2011 The convergent plate margins are the most intense areas of active
Page 1 of 10 EENS 2120 Petrology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tulane University Igneous Rocks of the This document last updated on 08-Feb-2011 The convergent plate margins are the most intense areas of active
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 GSA Data Repository 080 Schorn et al., 08, Thermal buffering in the orogenic crust: Geology, https://doi.org/0.30/g4046.. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 3 PHASE DIAGRAM MODELING 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 3 4 Phase diagrams
GSA Data Repository 080 Schorn et al., 08, Thermal buffering in the orogenic crust: Geology, https://doi.org/0.30/g4046.. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 3 PHASE DIAGRAM MODELING 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 3 4 Phase diagrams
Anderson RN, Uyeda S, Miyashiro A. (1976) Geophysical and geochemical constraints
 REFERENCES RELEVANT TO PERIDOTITE PARTIAL MELTING IN THE MANTLE WEDGE Anderson RN, Uyeda S, Miyashiro A. (1976) Geophysical and geochemical constraints at converging plate boundaries - I: Dehydration in
REFERENCES RELEVANT TO PERIDOTITE PARTIAL MELTING IN THE MANTLE WEDGE Anderson RN, Uyeda S, Miyashiro A. (1976) Geophysical and geochemical constraints at converging plate boundaries - I: Dehydration in
INTRODUCTION ROCK COLOR
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS Instructions: Some rocks that you would be working with may have sharp edges and corners, therefore, be careful when working with them! When you are
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS Instructions: Some rocks that you would be working with may have sharp edges and corners, therefore, be careful when working with them! When you are
A ESTIMATION OF THE PHYSICAL PARAMETERS OF MAGMA CRYSTALLIZATION FOR SANTORPNI LAVA USING THERMODYNAMIC METHODS
 Senior Thesis A ESTIMATION OF THE PHYSICAL PARAMETERS OF MAGMA CRYSTALLIZATION FOR SANTORPNI LAVA USING THERMODYNAMIC METHODS Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Bachelor
Senior Thesis A ESTIMATION OF THE PHYSICAL PARAMETERS OF MAGMA CRYSTALLIZATION FOR SANTORPNI LAVA USING THERMODYNAMIC METHODS Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Bachelor
6. IGNEOUS ROCKS AND VOLCANIC HAZARDS
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS AND VOLCANIC HAZARDS Instructions: Refer to Laboratory 5 in your lab book on pages 129-152 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 6. IGNEOUS ROCKS AND VOLCANIC HAZARDS Instructions: Refer to Laboratory 5 in your lab book on pages 129-152 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will
Most mafic magmas come from the upper mantle and lower crust. This handout will address five questions:
 IDS 102 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate those
IDS 102 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate those
Phase Equilibrium. Phase Rule. Phase Diagram
 Phase Equilibrium Phase Rule Phase Diagram Makaopuhi Lava Lake Magma samples recovered from various depths beneath solid crust From Wright and Okamura, (1977) USGS Prof. Paper, 1004. Makaopuhi Lava Lake
Phase Equilibrium Phase Rule Phase Diagram Makaopuhi Lava Lake Magma samples recovered from various depths beneath solid crust From Wright and Okamura, (1977) USGS Prof. Paper, 1004. Makaopuhi Lava Lake
Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks
 Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly recognize
Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly recognize
Larsen, H.C., Duncan, R.A., Allan, J.F., Brooks, K. (Eds.), 1999 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol.
 Larsen, H.C., Duncan, R.A., Allan, J.F., Brooks, K. (Eds.), 1999 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 163 9. LOW-PRESSURE MELTING STUDIES OF BASALT AND BASALTIC ANDESITE
Larsen, H.C., Duncan, R.A., Allan, J.F., Brooks, K. (Eds.), 1999 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 163 9. LOW-PRESSURE MELTING STUDIES OF BASALT AND BASALTIC ANDESITE
Melts of garnet lherzolite: experiments, models and comparison to melts of pyroxenite and carbonated lherzolite
 Melts of garnet lherzolite: experiments, models and comparison to melts of pyroxenite and carbonated lherzolite The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Melts of garnet lherzolite: experiments, models and comparison to melts of pyroxenite and carbonated lherzolite The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
ESS103A Igneous Petrology
 Welcome to ESS103A Igneous Petrology Please pick up handouts Plan for today: Who are we? What is this class about? What is the structure of this course? How does the scientific method work? Who are we?
Welcome to ESS103A Igneous Petrology Please pick up handouts Plan for today: Who are we? What is this class about? What is the structure of this course? How does the scientific method work? Who are we?
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Lecture 24 Hawaii. Hawaii
 Lecture 24 Hawaii Friday, April 22 nd 2005 Hawaii The Hawaiian Islands, in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, are volcanic islands at the end of a long chain of submerged volcanoes. These volcanoes get progressively
Lecture 24 Hawaii Friday, April 22 nd 2005 Hawaii The Hawaiian Islands, in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, are volcanic islands at the end of a long chain of submerged volcanoes. These volcanoes get progressively
Clara S. Tsang Senior Integrative Exercise March 10, 2008
 Do secondary magma chambers exist in Mauna Loa s Southwest Rift Zone? - A Petrologic and Geochemical Analysis of Xenoliths Clara S. Tsang Senior Integrative Exercise March 10, 2008 Advisors: Cam Davidson,
Do secondary magma chambers exist in Mauna Loa s Southwest Rift Zone? - A Petrologic and Geochemical Analysis of Xenoliths Clara S. Tsang Senior Integrative Exercise March 10, 2008 Advisors: Cam Davidson,
The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us?
 The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us? Mantle metasomatism Physical and chemical processes that are implemented during the flow of magmas and / or fluids within
The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us? Mantle metasomatism Physical and chemical processes that are implemented during the flow of magmas and / or fluids within
Metamorphic Petrology GLY 712 Geothermo-barometry
 Metamorphic Petrology GLY 712 Geothermo-barometry What is thermobarometry? Thermobarometry is concerned with estimating or inferring the temperatures and pressures at which a rock formed and/or subsequently
Metamorphic Petrology GLY 712 Geothermo-barometry What is thermobarometry? Thermobarometry is concerned with estimating or inferring the temperatures and pressures at which a rock formed and/or subsequently
Metamorphic Petrology GLY 262 P-T and T-X phase diagrams
 Metamorphic Petrology GLY 262 P-T and T-X phase diagrams How do we estimate P-T conditions? Inverse modelling: (1) Look at our rock, identify the mineral assemblage and determine the compositions of the
Metamorphic Petrology GLY 262 P-T and T-X phase diagrams How do we estimate P-T conditions? Inverse modelling: (1) Look at our rock, identify the mineral assemblage and determine the compositions of the
Earth Science Rocks! Using Earth Science Activities to Engage Students as Scientists
 Earth Science Rocks! Using Earth Science Activities to Engage Students as Scientists Missy Holzer, Roberta Johnson, Richard Jones, Russell Kohrs, Joe Monaco, John Moore, Michael Passow, Wendy Van Norden
Earth Science Rocks! Using Earth Science Activities to Engage Students as Scientists Missy Holzer, Roberta Johnson, Richard Jones, Russell Kohrs, Joe Monaco, John Moore, Michael Passow, Wendy Van Norden
doi: /nature09369
 doi:10.1038/nature09369 Supplementary Figure S1 Scanning electron microscope images of experimental charges with vapour and vapour phase quench. Experimental runs are in the order of added water concentration
doi:10.1038/nature09369 Supplementary Figure S1 Scanning electron microscope images of experimental charges with vapour and vapour phase quench. Experimental runs are in the order of added water concentration
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes
 Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
"Grimsvotn: Pressure ofcrystallization and Magma Chamber Depth"
 "Grimsvotn: Pressure ofcrystallization and Magma Chamber Depth" Senior Thesis Submitted in partial fulfillment ofthe requirements for the Bachelor of Science Degree At The Ohio State University By: Kyle
"Grimsvotn: Pressure ofcrystallization and Magma Chamber Depth" Senior Thesis Submitted in partial fulfillment ofthe requirements for the Bachelor of Science Degree At The Ohio State University By: Kyle
AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY
 NORDIC VOLCANOLOGICAL INSTITUTE 78 01 UNIVERSITY OF!CELANO PARTITIONING OF Cr, Mn, Co AND Ni BETWEEN OLIVINE AND BASALTIC LIQUID: AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY by Heikki Makipaa This is a preliminary report from
NORDIC VOLCANOLOGICAL INSTITUTE 78 01 UNIVERSITY OF!CELANO PARTITIONING OF Cr, Mn, Co AND Ni BETWEEN OLIVINE AND BASALTIC LIQUID: AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY by Heikki Makipaa This is a preliminary report from
Plate tectonics, rock cycle
 Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Origin of Basaltic Magma. Geology 346- Petrology
 Origin of Basaltic Magma Geology 346- Petrology 2 principal types of basalt in the ocean basins Tholeiitic Basalt and Alkaline Basalt Table 10-1 Common petrographic differences between tholeiitic and alkaline
Origin of Basaltic Magma Geology 346- Petrology 2 principal types of basalt in the ocean basins Tholeiitic Basalt and Alkaline Basalt Table 10-1 Common petrographic differences between tholeiitic and alkaline
Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks
 Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - 1 Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly
Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - 1 Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly
Magma Formation and Behavior
 Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
GRADUATE THESIS PROPOSAL EARTH SCIENCES 6300
 GRADUATE THESIS PROPOSAL EARTH SCIENCES 6300 LAST NAME: KELTIE FIRST NAME: ERIN STUDENT NUMBER: B00597303 DEGREE PROGRAMME: M.SC SUPERVISOR(S): DR. JAMES BRENAN TITLE OF PROPOSAL: AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION
GRADUATE THESIS PROPOSAL EARTH SCIENCES 6300 LAST NAME: KELTIE FIRST NAME: ERIN STUDENT NUMBER: B00597303 DEGREE PROGRAMME: M.SC SUPERVISOR(S): DR. JAMES BRENAN TITLE OF PROPOSAL: AN EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION
Harzburgite melting with and without H 2 O: Experimental data and predictive modeling
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003jb002566, 2004 Harzburgite ing with and without H 2 O: Experimental data and predictive modeling Stephen W. Parman and Timothy L. Grove Department
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003jb002566, 2004 Harzburgite ing with and without H 2 O: Experimental data and predictive modeling Stephen W. Parman and Timothy L. Grove Department
TWO COMPONENT (BINARY) PHASE DIAGRAMS. Experimental Determination of 2-Component Phase Diagrams
 Page 1 of 12 EENS 211 Earth Materials Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson TWO COMPONENT (BINARY) PHASE DIAGRAMS This document last updated on 08-Oct-2003 Experimental Determination of 2-Component
Page 1 of 12 EENS 211 Earth Materials Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson TWO COMPONENT (BINARY) PHASE DIAGRAMS This document last updated on 08-Oct-2003 Experimental Determination of 2-Component
Revision 1. Parameterized lattice strain models for REE. partitioning between amphibole and silicate melt
 1 2 3 Revision 1 Parameterized lattice strain models for REE partitioning between amphibole and silicate melt 4 5 Kei Shimizu 1*, Yan Liang 1, Chenguang Sun 2, Colin R. M. Jackson 3, and Alberto E. Saal
1 2 3 Revision 1 Parameterized lattice strain models for REE partitioning between amphibole and silicate melt 4 5 Kei Shimizu 1*, Yan Liang 1, Chenguang Sun 2, Colin R. M. Jackson 3, and Alberto E. Saal
PETROGENESIS OF A SERIES OF MAFIC SHEETS WITHIN THE VINALHAVEN PLUTON, VINALHAVEN ISLAND, MAINE
 PETROGENESIS OF A SERIES OF MAFIC SHEETS WITHIN THE VINALHAVEN PLUTON, VINALHAVEN ISLAND, MAINE DANIEL HAWKINS Western Kentucky University Research Advisor: Andrew Wulff INTRODUCTION Round Point, in the
PETROGENESIS OF A SERIES OF MAFIC SHEETS WITHIN THE VINALHAVEN PLUTON, VINALHAVEN ISLAND, MAINE DANIEL HAWKINS Western Kentucky University Research Advisor: Andrew Wulff INTRODUCTION Round Point, in the
J. Mangas and F.J. Perez-Torrado. Departamento de Física. Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria Las Palmas de Gran Canaria.
 Magmatic processes in the oceanic lithosphere: characterization of the ultramafic and mafic materials from the Holocene volcanic centers of Bandama and La Caldera de Pinos de Gáldar (Gran Canaria, Canary
Magmatic processes in the oceanic lithosphere: characterization of the ultramafic and mafic materials from the Holocene volcanic centers of Bandama and La Caldera de Pinos de Gáldar (Gran Canaria, Canary
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Ambient and excess mantle temperatures, olivine thermometry, and active vs. passive upwelling
 Chemical Geology 241 (2007) 177 206 www.elsevier.com/locate/chemgeo Ambient and excess mantle temperatures, olivine thermometry, and active vs. passive upwelling Keith D. Putirka a,, Michael Perfit b,
Chemical Geology 241 (2007) 177 206 www.elsevier.com/locate/chemgeo Ambient and excess mantle temperatures, olivine thermometry, and active vs. passive upwelling Keith D. Putirka a,, Michael Perfit b,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Mineral Stability and Phase Diagrams Introduction
 1 of 10 10/10/2002 2:50 PM Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Geology 211 Tulane University Mineralogy and Phase Diagrams Introduction This document last updated on 10-Oct-2002 As we discussed previously, there are
1 of 10 10/10/2002 2:50 PM Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Geology 211 Tulane University Mineralogy and Phase Diagrams Introduction This document last updated on 10-Oct-2002 As we discussed previously, there are
Technical Note: Calculation of stoichiometry from EMP data for apatite and other phases with
 1 REVISION 1 2 3 Technical Note: Calculation of stoichiometry from EMP data for apatite and other phases with mixing on monovalent anion sites 4 Richard A. Ketcham 1 5 1 Jackson School of Geosciences,
1 REVISION 1 2 3 Technical Note: Calculation of stoichiometry from EMP data for apatite and other phases with mixing on monovalent anion sites 4 Richard A. Ketcham 1 5 1 Jackson School of Geosciences,
LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types Date: 13 February 2018 I. Exam I grades are posted on the class website (link at the bottom
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types Date: 13 February 2018 I. Exam I grades are posted on the class website (link at the bottom
