Schultenite, a new mineral, from South-West Africcu
|
|
|
- Arline Shelton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 149 Schultenite, a new mineral, from South-West Africcu ]~y L. J. SI,~cE~, ~I.A., Sc.D., F.R.S. With a chemicm analysis by E. D. ~[otr~*~axx, ~I.A. Mineral Department, British Museum (Natural tiistory). [Road November 2, 1926.] ARON A. DE SCHULTEN, x a political refugee from Finland, worked B during the latter part of his life in the chemical laboratories of the Sorbonne in Paris. There he prepared in a crystallized form numl)er of minerals and compounds analogous to them. These were determined crystallographlcally and compared in isonlorphous series. For example, having obtained crystals of artificial monetite, ~" CatIPQ, he then proceeded to prepare the corresponding compounds in which strontium, barimn, or lead take the place of calcium, and arsenic the place of phosphorus, s In this series he determined the crystallographic constants and optical data for CaHPO4, SrHPOI, BaKPQ, 1)bHPO4, SrHAsO4, and I)bHAsO~. Crystals of CaHAsO 4 were also obtained, but they were too small tbr measurement. Any of these compounds might be expected to occur in nature, but hitherto only monetite has been found as a mineral. His 'mongtite ars~ni~e de plomb' is the,subject of the present note, and for ig, as a mineral, the name schultenite is suggested. :Baron Schulten presented to the British Musemn collection in 1898 a small set of his artificial products, but unfortunately these include none of his monetite series. 1 August Benjamin Friherro af Schuit6n ( ) ; obituary notice, Min. ]~Iag., 1913, vol. 16, p A. de Schulten, Reproductioll artifieielle de la mon6tite. Bull. See. Frang. ~lin., 1901, vol. 24, pp llecherches sur le phosphate dicalcique. Reproduction artificielle de l't brushite. Reproduction de la mon(idte par un nouveau procdd6. Ibid., 1903, vol. 26, pp a A. de Schulten, Reproduction artifieiolle de mondtites de baryum, de plomb et de strontium et do monstites ars6nidcs de plomb et de strontium. Ibid., 190~, vol. 27~ pp (hioadtite arsdui.de de plomb, p. 113.) L2
2 150 I,. J. SPENCER ON TMs compound, lead hydrogen orthoarsenate, PbHAsQ, is the 'lead arsenate' of commerce, and was first prepared by J. J. ]3erzelius in It is used as an insecticide, especially in America in sprays for fruit-trees; and being practically insoluble in water it is no doubt responsible for the retention of arsenic in apples. H. Goguel 1 in 1895 obtained monoc]inic crystals on which he determined some of the characters under the microscope. Later, in 1916, C. C. McDonnell and C. M. Smith, 2 in a detailed study of the several forms of lead arsenate, also gave some of the microscopic characters. As yet only a single specimen representing the new mineral is known. but doubtless there are others in collections amongst the rich series of crystallized material that has come from the locality. This specimen [B.M. 1926, 205] was acquired in 1926 for the British Museum collection from ~[r. Wilhelm Muncher of Munich, and was labelled ' Lanarkite : Tsumeb, Otavi, South-West Africa'. Although the mineral was incorrectly labelled lanarkite, there can be no doubt about the locality, for the specimen is very typical of the pseudomorphous crusts that have been found in abundance at Tsumeb. The lead chloro-arsenate (mimetite) is common at this locality. The specimen shows a base of large (2 cm. across) crystals of yellowish anglesite which are altered on the surface and along cracks to bayldonite. l~esting on the anglesite were tabular crystals probably of chessylite, and hexagonal prisms and rods no doubt representing mimetite ; both of these are now completely changed to bayldonite. The bayldonite (a basic arsenate of lead and copper) is yellowish-green in the interior, and bluish-green and minutely crystalline on the surface. The new mineral rests on these pseudomorphs, and is somewhat intermixed with bayldonite. The schultenite has the form of thin crystal plates which are perfectly transparent, clear, and colourless, and with a brilliant vitreous to almost adamantine lustre. The largest plates measure 1 cm. across with a thickness of 1 mm., and the smallest is about 1 ram. across. The material is brittle and easily crushed to a white powder; hardness 289 The crystals are monoclinic (holohedra]) with the elements : a : b : c : 1 : , fi = 84 ~ 36", 1 It. Goguel~ Contribution ~ l'~tude des ars6niates e~ des antimoniates cristallis~s pr6par6s par voie humide. Mdm. Soc. Sci. Bordeaux~ 1895~ vol. 1~ pp (Orthoars6niate diplombique~ p. 135.) C. C. McDonnell and C. 1~. Smith, Journ. Amer. Chem. Soc.~ 1916~ vol. 38~ p A summary of the chemical literature is there given.
3 SCHULTENITE, A INIgW ]~IINERAL, I~ROM SOUTH-WEST AFIqICA. I~I as calculated from the measured angles co, el, and bl given in the following table. A few other measured angles are also added for comparison with the calculated angles, sufficient to show that good results were obtained. ~ean. Limibs. ano. Calculated. cp = (001) :(lu)... 45~ 45~176 9 * cl = (001) :(130) * bl = (010):(130) ~ * bp = (010) :(111) ~ 16' ce = (001):(011) st--(ff11):(221) The complete list of sixteen forms and ~heir angles is, however, given in a form of table (. i58), which, it is bei{eved, combines tim advantages both of the arrangement in zones of interracial angles (as adopted by Miller, Dana, ttintze, and Groth) and of the ~ and p (longitude and latitude) angles employed in two-circle goniometry (as advocated by Goldsehmidt). For monoclinic crystals the polar distances p are more conveniently taken from the fixed b-axis (the axis of symmetry), rather than from the arbitrary c-axis as done by Goldschmidt. The angle between any two faces lying in a zone containing one of the axial planes is at once given by the difference between two angles in the table. Such a table of angles can be quickly checked by placing a transparent stereographic net over tile projection (fig. 3). The crystals are all flattened parallel to the plane of symmetry b (010), parallel to which there is a good cleavage. The usual habit is rhombshaped (fig. 1), with much the appearance of crystals of gypsum. A small (1 ram.) crystal of this type, which was mounted on the goniometer, is completely developed on all sides. Less often the pyramidfaces ) are partly or sometimes completely cut out by the basal plane c (001) (fig. 2). The prolninent prism is /(130), and n(140)is usually present as narrow faces, but m (110) is only rarely represented. Small clino-dome faces e t011) sometimes border the basal plane when the latter is present. Except for 2(111), all the pyramid-faces are quite small. The faces b (010) are prominently striated parallel to their intersection with the prism-faces; and when c(001) is present they also bear less prominent striations parallel to and close to the edge b/s. The prism-faces are faintly striated vertically. The basal plane and the pyramids are perfectly smooth, and give single sharp images when not confused by sub-parallel growth of the crystals. The determination of the optical constants presented some difficulty and unfortunately is not complete. The crystals are very thin and brittle, and the thicker and better crystals on the single specimen
4 152 L.J. SPENCER ON could not be sacrificed for cutting oriented plates and prisms. Measurements of the extinction-angle on the plane of symmetry gave readings varying from 19 ~ to 28 ~ to the prism-edge in the acute angle fi, the mean being 24 ~. Owing to the high refraction, the optic axes do not emerge into air through b(010), and it was consequently at first thought that the optic axial plane was parallel to the plane of symmetry (as previously described for the artiticial crystals): One optic axis is, however, visible through /)(111). A small fragment broken approximately perpendicular to the plane of symmetry and the cleavage, and giving straight extinction, showed a wide-angle biaxial figure of positive sign with the optic axial plane perl~endicular to the plane of symmetry. The angle was estimated under the microscope with a micrometer scale as 2Ea = 185 ~ By immersing a crystal in a trough of methylene iodide it was possible to observe the obtuse angle through b (010), and on the Fuess axial angle apparatus this was measured as 2go :6 ~ 84/ for sodium-light. Taking fl as 1"9097 and for methylene iodide n = 1.742, this gives : 2V~ ~ 14:' and 2E~ = 186 ~ 88' (Na). The optical orientation of the crystals is: optic axial plane perpendicular to the plane of symmetry and lying in the obtuse angle fi ; a(bxo)'= b, fi:c = --24 ~, 7(Bx~):c = +66~ sign positive. These directions are plotted on the stere0graphic projection (fig. 8). Refractive indices were determined by the prism method of minhnnm deviation through the natural prism given by the faces /(130)(130), the refracting angle on the crystal employed being measured as 42 ~ 22 t. In such a prism the path of the light is symmetrical through the prism in the direction of the axis of symmetry ; and the vibration-directions fi and ~/ lie in the plane of symmetry, though not parallel and perpendicular to the refracting edge of the prism. The use of natural prisms of orthorhombic crystals in this connexion is well recognized, when the vibration-directions are p~rallcl and perpendicular to the refracting edge; but for monoclinic crystals I have not been able to find any mention of this method in the text-books on crystallography and crystal-optics. With white light the schultenite prism gave two long and widely separated spectra, indicating high dispersion and strong birefringence. The crystal used was small and readings could not be obtained for lithium- and thallium-light. The values determined for sodium-light are : fl = 1"9097 and 7 = 1"9765 (Na). Calculated from fl, 7, and 2V, the value of a is 1"8903.
5 SCIIULTENIT:E~ A.NEW MINEI~AL~ ]:'1~.05[ SOUTH~WEST AFRICA. 153 h o b,~olo l D. '~140 ~ 2.~ 713o "-. \I/ ~ 2 i o F~(4. 1. Fro. 2. FI~. 3. Crystals and Stereogral)hic Projection of Schul~enite. Forms of Schultenite aqul the normal angles of each to the three axial planes. Angle to..,,.._ ~orm~. ~00) ~ <01,)). c (001~. b(010) ~ 0' ~ 0' c(001) ~ 0' h,~lo) m(llo) I k(120) ,0 30 l , 1 (130) _ ~ (140) e (011) "~4: labs.(101)] ~_,.tbs. (1_02)~ [~bs. (101)] ,) 'Labs. (~01)] ~-- w'323) i,v(111) I v(~ _ ~(121) ") i-- r (122" ~ q~:lll)... ]' i s(:)ll)... ] (221) The question of the crystallographic orientation must now be considered, since the one here adopted differs from that of Schulten for the artificial crystals, tie gave the elements as a : b 9 c = : 1 : 0"8704, fl = 84 ~ 23', and the forms recorded by him were gl(010), m(ll0),
6 154 L. Z. S~ENCXR ON e 1 (011), b89 (ill), and b 1 (i12). Groth ~ adopts Schulten's orientation but letters the forms bmqo~i respectively. The difference amounts only to an interchange of the a and c axes ; but to get the crystals into parallel position one must be rotated through 8489 ~ and then turned over (180 ~ about the new c-axis~ The first and last indices of the forms must also be interchanged, but this affects only some of the forms. The following tabular comparison shows the differences, and at the same time shows that Schulten's measured angles (except those on which the calculations are based) are in closer agreement with my values than with his own calculated values. Sehulten. Spencer. Angle. Obs. Calc. Angle. Calc. (0105 : (1105 5d~ ~ 20' * (010) : (011) 54 ~ 26' (011) : ( * (110): ( (011) : (i10) * (]10) :(011) (010):(011) ~ C' (010):(110) (010) :(i11) (010) :(ill) 60 1 (010) : (i12) ~ (010) : (211) (1105:(i11) (011) :(i11) (i12) :(i11) (211): (]11) On the natural crystals now described the zone chosen by Schulten for the prism-zone is frequently not developed (fig. 1), and when it is present [b e cj the prism-faces e are always small. Further, it is to be noted that the orientation here adopted is the same as the earlier one shown in the figure of H. Goguel (1895), whose paper is not mentioned by Schulten and was apparently unknown to him. There remains the question of the optical orientation, which has been given incorrectly by previous authors for the artificial crystals. Goguel and Schulten both state that the optic axial plane is parallel to the plane of symmetry (this has been dealt with above). Goguel measured under the microscope the angle fi as 83 ~ 24', and McDonnell and Smith (1916) give the corresponding value 84~ but both these authors give the extinction as being in the obtuse (not acute) angle fl, their values to the prism-edge being +21 ~ to 22 ~ (for n~ [i.e. fl~) and +29 ~ respectively. Schulten gives the extinction-angle as 38 ~ in the obtuse angle, which in the second orientation is equivalent to 3289 ~ in the acute angle ft. The statement of obtuse for acute angle is evidently a slip, and the variation 21 ~ to 3289 ~ (compare 19 ~ to 28 ~ above) may perhaps be due to dispersion. 1 p. Groth, Chem. Kryst.~ 1908, vol. 2, p. 822.
7 SCtIULTENITE~ A HEW 5II~EI~AL, FROM SOUTH-WEST AFRICA. 155 It may be mentioned that the data recorded above for the natural crystals were all determined before the identity of the mineral with the artificial crystals was established by ~r. Mountain's analysis. The substance could not be identified from the crystallographic data alone, since a copy of Fedorov's ' Tables for Crystallo-chemical Analysis' was not available. PseudomorThs of anglesite after schultenite(?).--another specimen [B.M. 1922, 388] from Tsun~eh, acquired from ~Ir. W. Maucher in 1922, was labelled 'Anglesite pseudomorphous after a monoclinic mineral (lanarkite? or gypsum?) '. This shows lath-shaped tabular crystals up to 189 cm. long which are completely changed to an aggregate of small crystals of anglesite and stained with a later thin deposit of bayldonite. Most of the pseudo-crystals are merely hollow Crusts, and, consisting of an aggregate of anglesite crystals, the form is not always distinct. Terminated crystals, however, show a form suggestive of fig. 1, and it is possible that these are really pseudomorphs of anglesite after schultenite. Chemical Analysis of Sc7~ultenite. The total weight of available material was gram. The crystal fragments were collected by Dr. Spencer and contained only a minute trace of bayldonite, the copper of which was not sufficient to determine. A specific gravity1 determination by the pyknometer method gave a corrected value of The analysis was made on 0"2917 gram. The water was determined as loss of weight on heating to incipient fusion. The residual powder was dissolved in a small quantity of dilute nitric acid and the lead was precipitated as lead sulphate. Subsequently the arsenic was estimated as sulphide after prolonged reduction by hydrogen sulphide. The analysis gave the following results : l~iolec, ratios. Calculated. PbO As20~... ~ I This corresponds with the formula 2PbO. As205. H20 or PbHAsQ. i Specific gravity of the artificial crystals (Schulten, 1904), (NcDonall and Smith, 1916).
Biaxial Minerals This document last updated on 27-Oct-2014
 1 of 18 10/27/2014 1:10 PM EENS 2110 Tulane University Biaxial Minerals Mineralogy Prof. Stephen A. Nelson This document last updated on 27-Oct-2014 All minerals that crystallize in the orthorhombic, monoclinic,
1 of 18 10/27/2014 1:10 PM EENS 2110 Tulane University Biaxial Minerals Mineralogy Prof. Stephen A. Nelson This document last updated on 27-Oct-2014 All minerals that crystallize in the orthorhombic, monoclinic,
Sapphirine crystals from Blinkwater, ~ rans~ aal.
 277 S r ) Sapphirine crystals from Blinkwater, ~ rans~ aal. By EDGAR D. MOUNT.~.IN, M.A. Professor of Geology and Mineralogy, Rtmdes University College, Grahamstown, South Africa. [Read January 26, 1939.]
277 S r ) Sapphirine crystals from Blinkwater, ~ rans~ aal. By EDGAR D. MOUNT.~.IN, M.A. Professor of Geology and Mineralogy, Rtmdes University College, Grahamstown, South Africa. [Read January 26, 1939.]
Prismatic cleavage and steep rhombohedral form in s-quartz.
 259 Prismatic cleavage and steep rhombohedral form in s-quartz. By JULIEN DRUGM*~, M.Sc., PhD. [Read November 3, 1938.] (l) AN EXAMPLE OF ~-QUARTZ SHOWING GOOD :PRISMATIC CLEAVAGES. S is well known, quartz
259 Prismatic cleavage and steep rhombohedral form in s-quartz. By JULIEN DRUGM*~, M.Sc., PhD. [Read November 3, 1938.] (l) AN EXAMPLE OF ~-QUARTZ SHOWING GOOD :PRISMATIC CLEAVAGES. S is well known, quartz
Irregularly developed crystals of Zircon (sp. gr. 4"0) from Ceylon.
 43 S Irregularly developed crystals of Zircon (sp. gr. 4"0) from Ceylon. By L. J. SPx~oE~, ~r.a., F.O.S. Assistant in the Mineral Department of the British Museum. [Read Ma~ch 92, 190;.] OME small isolated
43 S Irregularly developed crystals of Zircon (sp. gr. 4"0) from Ceylon. By L. J. SPx~oE~, ~r.a., F.O.S. Assistant in the Mineral Department of the British Museum. [Read Ma~ch 92, 190;.] OME small isolated
OLIVINES, PYROXENES, AND AMPHIBOLES PLEOCHROISM, INTERFERENCE COLORS AND EXTINCTION ANGLES
 GLY 4200C Lab Exercise 12 Pleochroism OLIVINES, PYROXENES, AND AMPHIBOLES PLEOCHROISM, INTERFERENCE COLORS AND EXTINCTION ANGLES When minerals are viewed under PP they may show color. Many minerals are
GLY 4200C Lab Exercise 12 Pleochroism OLIVINES, PYROXENES, AND AMPHIBOLES PLEOCHROISM, INTERFERENCE COLORS AND EXTINCTION ANGLES When minerals are viewed under PP they may show color. Many minerals are
Introduction to Crystallography and Mineral Crystal Systems by Mike and Darcy Howard Part 6: The Hexagonal System
 Introduction to Crystallography and Mineral Crystal Systems by Mike and Darcy Howard Part 6: The Hexagonal System Now we will consider the only crystal system that has 4 crystallographic axes! You will
Introduction to Crystallography and Mineral Crystal Systems by Mike and Darcy Howard Part 6: The Hexagonal System Now we will consider the only crystal system that has 4 crystallographic axes! You will
Tnn AuERTcAN M rnerar,ocrsr
 Tnn AuERTcAN M rnerar,ocrsr JOURNAI, OF THE MINERA].OGIC.AL SOCIETY OF AMERICA Vor,. 16 APRIL, 1931 No.4 SCHAIRERITE, A NEW MINERAL FROM SEARLES LAKE, CALIFORNIA Wrr,r,ra.ur F. Fosuac, U. S. Nati,onal
Tnn AuERTcAN M rnerar,ocrsr JOURNAI, OF THE MINERA].OGIC.AL SOCIETY OF AMERICA Vor,. 16 APRIL, 1931 No.4 SCHAIRERITE, A NEW MINERAL FROM SEARLES LAKE, CALIFORNIA Wrr,r,ra.ur F. Fosuac, U. S. Nati,onal
INTRODUCTION TO THE PETROGRAPHIC MICROSCOPE AND RELIEF, BECKE LINE, AND OBLIQUE ILLUMINATION
 GLY 4200C LAB EXERCISE 10 INTRODUCTION TO THE PETROGRAPHIC MICROSCOPE AND RELIEF, BECKE LINE, AND OBLIQUE ILLUMINATION Locate all of the following microscope parts. Refer to Figure1 1) Eyepiece (note the
GLY 4200C LAB EXERCISE 10 INTRODUCTION TO THE PETROGRAPHIC MICROSCOPE AND RELIEF, BECKE LINE, AND OBLIQUE ILLUMINATION Locate all of the following microscope parts. Refer to Figure1 1) Eyepiece (note the
8 th Earth Science Chapter 3 Minerals Name
 Section 1 Minerals: 8 th Earth Science Chapter 3 Minerals Name Mineral About different minerals are found on Earth, but they all share four characteristics. 1.All minerals are formed by processes. These
Section 1 Minerals: 8 th Earth Science Chapter 3 Minerals Name Mineral About different minerals are found on Earth, but they all share four characteristics. 1.All minerals are formed by processes. These
CRYSTAL MEASUREMENT AND AXIAL RATIO LABORATORY
 CRYSTAL MEASUREMENT AND AXIAL RATIO LABORATORY George R. McCormick Department of Geology The University of Iowa Iowa City, Iowa 52242 george_mccormick@uiowa.edu Goals of the Exercise This exercise is designed
CRYSTAL MEASUREMENT AND AXIAL RATIO LABORATORY George R. McCormick Department of Geology The University of Iowa Iowa City, Iowa 52242 george_mccormick@uiowa.edu Goals of the Exercise This exercise is designed
EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS MINERALS LAB 1 HANDOUT
 EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS MINERALS LAB 1 HANDOUT Sources: Cornell EAS302 lab, UMass Lowell 89.301 Mineralogy, LHRIC.org The Petrographic Microscope As you know, light is an electromagnetic
EESC 4701: Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology IGNEOUS MINERALS LAB 1 HANDOUT Sources: Cornell EAS302 lab, UMass Lowell 89.301 Mineralogy, LHRIC.org The Petrographic Microscope As you know, light is an electromagnetic
Interference Figures. Biaxial Interference Figures. Acute Bisectrix Figure. Biaxial Minerals
 Interference Figures Biaxial inerals Biaxial Interference Figures Figures are obtained the same way as uniaxial figures The appearance of the figure is dependant on the orientation of the mineral grain
Interference Figures Biaxial inerals Biaxial Interference Figures Figures are obtained the same way as uniaxial figures The appearance of the figure is dependant on the orientation of the mineral grain
Chapter 4 Minerals Sec. 4.1 What is a Mineral?
 Chapter 4 Minerals Sec. 4.1 What is a Mineral? Minerals Earth s crust is composed of about 3000 minerals. Besides forming rocks and shaping Earth s surface, some minerals have helped to develop civilization.
Chapter 4 Minerals Sec. 4.1 What is a Mineral? Minerals Earth s crust is composed of about 3000 minerals. Besides forming rocks and shaping Earth s surface, some minerals have helped to develop civilization.
THE MINERALOGICAL MAGAZINE
 THE MINERALOGICAL MAGAZINE AND JOURNAL OF THE MINERALOGICAL SOCIETY No. 238 September, 1957 Vol. XXXI GStzenite and combeite, two new silicates from the Belgian Congo. By TR. G. SA~AMA and KAI HYT(gNEN,
THE MINERALOGICAL MAGAZINE AND JOURNAL OF THE MINERALOGICAL SOCIETY No. 238 September, 1957 Vol. XXXI GStzenite and combeite, two new silicates from the Belgian Congo. By TR. G. SA~AMA and KAI HYT(gNEN,
AUGELITE FROM MONO COUNTY, CALIFORNIA. Dwrcnr M. LBulroN, Stanford, Llniaersity, California.
 AUGELITE FROM MONO COUNTY, CALIFORNIA Dwrcnr M. LBulroN, Stanford, Llniaersity, California. Augelite, basic aluminum phosphate, was discovered in the andalusite orebody of the l\{ono County Mine of Champion
AUGELITE FROM MONO COUNTY, CALIFORNIA Dwrcnr M. LBulroN, Stanford, Llniaersity, California. Augelite, basic aluminum phosphate, was discovered in the andalusite orebody of the l\{ono County Mine of Champion
Plagioclases from Sultan Hamud, Kenya.
 682 Plagioclases from Sultan Hamud, Kenya. By P. M. GhM~, B.Se. Department of Mineralogy, British Museum. [Read March 31, 1949.] HE plagioclase which forms the subject of this investigation was T presented
682 Plagioclases from Sultan Hamud, Kenya. By P. M. GhM~, B.Se. Department of Mineralogy, British Museum. [Read March 31, 1949.] HE plagioclase which forms the subject of this investigation was T presented
Fun with Asbestos 1. Table 1: Asbestos Minerals. Mineral Asbestos Variety Mineral Group Comments. monoclinic amphibole. monoclinic amphibole
 1 Fun with Asbestos 1 WARNING: DO NOT OPEN BOTTLES CONTAINING ASBESTOS. Asbestos may cause lung damage. Do not breathe fibers. The crocidolite (blue asbestos) is considered most hazardous, but the other
1 Fun with Asbestos 1 WARNING: DO NOT OPEN BOTTLES CONTAINING ASBESTOS. Asbestos may cause lung damage. Do not breathe fibers. The crocidolite (blue asbestos) is considered most hazardous, but the other
And the study of mineral the branch in geology is termed as mineralogy. (Refer Slide Time: 0:29)
 Earth Sciences for Civil Engineering Professor Javed N Malik Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Module 2 Lecture No 6 Rock-Forming Minerals and their Properties (Part-2)
Earth Sciences for Civil Engineering Professor Javed N Malik Department of Earth Sciences Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Module 2 Lecture No 6 Rock-Forming Minerals and their Properties (Part-2)
Appendix B6. SEM observations, experiment 2. Coating stage pre Ca(OH) 2 addition
 Appendix B6 Appendix B6 SEM observations, experiment 2 Coating stage pre Ca(OH) 2 addition Column Column A Major Fe Zn sulphate Habit and morphology coating with desiccation cracks, variable thickness
Appendix B6 Appendix B6 SEM observations, experiment 2 Coating stage pre Ca(OH) 2 addition Column Column A Major Fe Zn sulphate Habit and morphology coating with desiccation cracks, variable thickness
Last Time. GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy. Polymorphs & Polymorphism. Other Crystal Structures. Other Crystal Structures. This Week s Agenda
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA Last Time GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy 1. Polymorphs and Polymorphism 2. Pseudomorphs and other definitions 3. Crystal Habit Lecture 7: Optical Mineralogy (two day lecture?)
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA Last Time GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy 1. Polymorphs and Polymorphism 2. Pseudomorphs and other definitions 3. Crystal Habit Lecture 7: Optical Mineralogy (two day lecture?)
Solids / Crystal Structure
 The first crystal analysis proved that in the typical inorganic salt, NaCl, there is no molecular grouping. The inference that the structure consists of alternate ions of sodium and chlorine was an obvious
The first crystal analysis proved that in the typical inorganic salt, NaCl, there is no molecular grouping. The inference that the structure consists of alternate ions of sodium and chlorine was an obvious
Fro. 2. Fibrous brucite in vein of chrysotile asbestos, Asbestos, Quebec. Pr,ern I. Frc. 1. Photograph of fibrous brucite from Asbestos, Quebec.
 Pr,ern I Frc. 1. Photograph of fibrous brucite from Asbestos, Quebec. sbe stos Fro. 2. Fibrous brucite in vein of chrysotile asbestos, Asbestos, Quebec. Frc. 3. Sketch of photograph in Fig. 2, to show
Pr,ern I Frc. 1. Photograph of fibrous brucite from Asbestos, Quebec. sbe stos Fro. 2. Fibrous brucite in vein of chrysotile asbestos, Asbestos, Quebec. Frc. 3. Sketch of photograph in Fig. 2, to show
FIG. I.--Upper side, showing pittings. (Two-fifths actual size.)
 THE FRANCEVILLE (EL PASO COUNTY, COLORADO) METEORITE. THIS meteorite was bought by Professor F. W. Cragin, of Colorado College, Colorado Springs, Colo., from Mr. David Anderson and wife of Colorado Springs.
THE FRANCEVILLE (EL PASO COUNTY, COLORADO) METEORITE. THIS meteorite was bought by Professor F. W. Cragin, of Colorado College, Colorado Springs, Colo., from Mr. David Anderson and wife of Colorado Springs.
Rocks and Minerals. Tillery, Chapter 19. Solid Earth Materials
 Rocks and Minerals Tillery, Chapter 19 Science 330 Summer 2007 No other planet in the solar system has the unique combination of fluids of Earth. Earth has a surface that is mostly covered with liquid
Rocks and Minerals Tillery, Chapter 19 Science 330 Summer 2007 No other planet in the solar system has the unique combination of fluids of Earth. Earth has a surface that is mostly covered with liquid
ESS 439 Igneous Petrology/Optical Mineralogy
 1 Lab # 3: Biaxial minerals ESS 439 Igneous Petrology/Optical Mineralogy In this laboratory session we will introduce the concepts of the Biaxial Indicatrix, Optic Axes, Vibration Directions and Ray Paths,
1 Lab # 3: Biaxial minerals ESS 439 Igneous Petrology/Optical Mineralogy In this laboratory session we will introduce the concepts of the Biaxial Indicatrix, Optic Axes, Vibration Directions and Ray Paths,
2 THE NATURE OF MATTER
 2 THE NATURE OF MATTER I. Tick ( ) the most appropriate answer. 1. Gases have (a) infinite free surfaces (b) two free surfaces (c) one free surface (d) no free surfaces 2. Solids have (a) definite volume,
2 THE NATURE OF MATTER I. Tick ( ) the most appropriate answer. 1. Gases have (a) infinite free surfaces (b) two free surfaces (c) one free surface (d) no free surfaces 2. Solids have (a) definite volume,
Crystallographic Calculations
 Page 1 of 7 EENS 2110 Tulane University Mineralogy Prof. Stephen A. Nelson This page last updated on 07-Sep-2010 Crystallographic calculations involve the following: 1. Miller Indices (hkl) 2. Axial ratios
Page 1 of 7 EENS 2110 Tulane University Mineralogy Prof. Stephen A. Nelson This page last updated on 07-Sep-2010 Crystallographic calculations involve the following: 1. Miller Indices (hkl) 2. Axial ratios
The Crystal Structure of Sodium Pentafluorodistannate(II), NaSn2Fs*
 1104 Acta Cryst. (1964). 17, 1104 The Crystal Structure of Sodium Pentafluorodistannate(II), NaSn2Fs* :BY ROBERT R. MCDONALD,'~ ALLEN C. I~RSON, AND Do~ T. CROMER University of California, Los Alamos Scientific
1104 Acta Cryst. (1964). 17, 1104 The Crystal Structure of Sodium Pentafluorodistannate(II), NaSn2Fs* :BY ROBERT R. MCDONALD,'~ ALLEN C. I~RSON, AND Do~ T. CROMER University of California, Los Alamos Scientific
SOME RECENT ACCESSIONS TO THE MINERAL COLLEC-
 SOME RECENT ACCESSIONS TO THE MINERAL COLLEC- TIONS OF THE UNITED STATES NATIONAL MUSELT^I. By William F. Foshag, Assistant Curator in charge of Mineral Collections, United States National Museum. During
SOME RECENT ACCESSIONS TO THE MINERAL COLLEC- TIONS OF THE UNITED STATES NATIONAL MUSELT^I. By William F. Foshag, Assistant Curator in charge of Mineral Collections, United States National Museum. During
NMR Shifts. I Introduction and tensor/crystal symmetry.
 NMR Shifts. I Introduction and tensor/crystal symmetry. These notes were developed for my group as introduction to NMR shifts and notation. 1) Basic shift definitions and notation: For nonmagnetic materials,
NMR Shifts. I Introduction and tensor/crystal symmetry. These notes were developed for my group as introduction to NMR shifts and notation. 1) Basic shift definitions and notation: For nonmagnetic materials,
IVAR OFTEDAL and P. CHR. SÆBO
 NORSK GEOLOGISK TIDSSKRIFT 45 CONTRIBUTIONS TO THE MINERALOGY OF NORWAY No. 30. Minerals from Nordmarkite Druses BY IVAR OFTEDAL and P. CHR. SÆBO (Institutt for geologi, Blindern, Oslo 3) Abstract. Crystals
NORSK GEOLOGISK TIDSSKRIFT 45 CONTRIBUTIONS TO THE MINERALOGY OF NORWAY No. 30. Minerals from Nordmarkite Druses BY IVAR OFTEDAL and P. CHR. SÆBO (Institutt for geologi, Blindern, Oslo 3) Abstract. Crystals
GY-343 Petrology Petrographic Microscope Laboratory
 Introduction to the Petrographic Microscope In this laboratory you will be using the petrographic microscope to analyze thin sections of various types of igneous rocks. You will be assigned a thin section
Introduction to the Petrographic Microscope In this laboratory you will be using the petrographic microscope to analyze thin sections of various types of igneous rocks. You will be assigned a thin section
INTRODUCTION TO MINERALOGY 15
 INTRODUCTION TO MINERALOGY 15 Silicates vs. phosphates, and sulphates Electronegativities: Si 1.8 P 2.1 S 2.5 Typical occurences: Accessory in igneous rocks, large masses in pegmatites, also biomineral
INTRODUCTION TO MINERALOGY 15 Silicates vs. phosphates, and sulphates Electronegativities: Si 1.8 P 2.1 S 2.5 Typical occurences: Accessory in igneous rocks, large masses in pegmatites, also biomineral
Minerals: Building Blocks of Rocks Chapter 2. Based on: Earth Science, 10e
 Minerals: Building Blocks of Rocks Chapter 2 Based on: Earth Science, 10e Minerals: the building blocks of rocks Definition of a mineral Solid Inorganic Natural Crystalline Structure - Possess an orderly
Minerals: Building Blocks of Rocks Chapter 2 Based on: Earth Science, 10e Minerals: the building blocks of rocks Definition of a mineral Solid Inorganic Natural Crystalline Structure - Possess an orderly
GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy Lecture 7b: Optical Mineralogy Instructor: Dr. Douglas Haywick Last Time 1. Properties of light 2. Minerals and light transmission Light
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy Lecture 7b: Optical Mineralogy Instructor: Dr. Douglas Haywick Last Time 1. Properties of light 2. Minerals and light transmission Light
Symmetry Crystallography
 Crystallography Motif: the fundamental part of a symmetric design that, when repeated, creates the whole pattern In 3-D, translation defines operations which move the motif into infinitely repeating patterns
Crystallography Motif: the fundamental part of a symmetric design that, when repeated, creates the whole pattern In 3-D, translation defines operations which move the motif into infinitely repeating patterns
NOTE ON DETERMINATION OF OPTIC AXIAL ANGLE AND EXTINCTION ANGLE IN PIGEONITES. F. J. TunNrn, [Jniters'ity oj Otago, Dunedin, I{ew Zealond.
 NOTE ON DETERMINATION OF OPTIC AXIAL ANGLE AND EXTINCTION ANGLE IN PIGEONITES F. J. TunNrn, [Jniters'ity oj Otago, Dunedin, I{ew Zealond. During the past decade the work of several petrologists on the
NOTE ON DETERMINATION OF OPTIC AXIAL ANGLE AND EXTINCTION ANGLE IN PIGEONITES F. J. TunNrn, [Jniters'ity oj Otago, Dunedin, I{ew Zealond. During the past decade the work of several petrologists on the
NATIONAL 5 CHEMISTRY
 Farr High School NATIONAL 5 CHEMISTRY Unit 1 Chemical Changes and Structure Question Booklet 1 Rates of Reaction 1. Explain how the following would affect the rate of the reaction between 1.0 g of magnesium
Farr High School NATIONAL 5 CHEMISTRY Unit 1 Chemical Changes and Structure Question Booklet 1 Rates of Reaction 1. Explain how the following would affect the rate of the reaction between 1.0 g of magnesium
7.2 Chemical Bonding. Ionic Bonding Electron Transfer between a Metal and a Non-Metal
 7.2 Chemical Bonding The physical forces that join or connect atoms together are called chemical bonds. As previously stated, this bonding is associated with electron interactions between atoms. This has
7.2 Chemical Bonding The physical forces that join or connect atoms together are called chemical bonds. As previously stated, this bonding is associated with electron interactions between atoms. This has
ENVI.2030L - Minerals
 ENVI.2030L - Minerals Name I. Minerals Minerals are crystalline solids - the particles (atoms) that make-up the solid have a regular arrangement. In glasses, on the other hand, the atoms are not arranged
ENVI.2030L - Minerals Name I. Minerals Minerals are crystalline solids - the particles (atoms) that make-up the solid have a regular arrangement. In glasses, on the other hand, the atoms are not arranged
UNIT I SOLID STATE PHYSICS
 UNIT I SOLID STATE PHYSICS CHAPTER 1 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE 1.1 INTRODUCTION When two atoms are brought together, two kinds of forces: attraction and repulsion come into play. The force of attraction increases
UNIT I SOLID STATE PHYSICS CHAPTER 1 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE 1.1 INTRODUCTION When two atoms are brought together, two kinds of forces: attraction and repulsion come into play. The force of attraction increases
Orthoclase Feldspar Smith College Mineralogy, Fall 20XX
 Orthoclase Feldspar Smith College Mineralogy, Fall 20XX Abstract A sample of orthoclase feldspar with composition of K (0.737) Na (0.22218) Ca (- 0.0012)Al (1.0018) Si (3.0095) O (8.00) was collected on
Orthoclase Feldspar Smith College Mineralogy, Fall 20XX Abstract A sample of orthoclase feldspar with composition of K (0.737) Na (0.22218) Ca (- 0.0012)Al (1.0018) Si (3.0095) O (8.00) was collected on
564 R. B. FERGUSON AND M. A. PEACOCK
 MEASUREMENT OF THE THREE PRINCIPAL INDICES OF REFRACTION IN MICACEOUS MINERALS BY IMMERSION ON A TILTING STAGE R. B. FBncusoN AND M. A. Poacocx, []niaersity oj Toronto, Toronto, Canada. Assfitacr An accurate
MEASUREMENT OF THE THREE PRINCIPAL INDICES OF REFRACTION IN MICACEOUS MINERALS BY IMMERSION ON A TILTING STAGE R. B. FBncusoN AND M. A. Poacocx, []niaersity oj Toronto, Toronto, Canada. Assfitacr An accurate
A mineral is a- In order for a substance to be called a mineral, it must have of the characteristics described in this definition.
 Section 1 Minerals Minerals A mineral is a- In order for a substance to be called a mineral, it must have of the characteristics described in this definition. Inorganic A mineral must be inorganic, or
Section 1 Minerals Minerals A mineral is a- In order for a substance to be called a mineral, it must have of the characteristics described in this definition. Inorganic A mineral must be inorganic, or
ST. FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL
 ST. FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY SPECIMEN PAPER NAME: FORM 3 CLASS: TIME: 2 hrs Directions to Candidates: Answer ALL Questions in Section 1 and Section 2. Write your answers
ST. FRANCIS SECONDARY SCHOOL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY SPECIMEN PAPER NAME: FORM 3 CLASS: TIME: 2 hrs Directions to Candidates: Answer ALL Questions in Section 1 and Section 2. Write your answers
QUARTZ CRYSTALS OCCURRING IN GYPSUM
 JOURNAL MINERALOGICAL SOCIETY OF AMEMCA 19 DOUBLY TERMINATED QUARTZ CRYSTALS OCCURRING IN GYPSUM W. A. T.qnn, University of Missouri'. The specimens upon which this brief description is based were obtained
JOURNAL MINERALOGICAL SOCIETY OF AMEMCA 19 DOUBLY TERMINATED QUARTZ CRYSTALS OCCURRING IN GYPSUM W. A. T.qnn, University of Missouri'. The specimens upon which this brief description is based were obtained
Phenacite and other minerals from Ge~zan East Africa.
 178 Phenacite and other minerals from Ge~zan East Africa. By L. J. SeE~CER, M.A., F.G.S. Assistant in the Mineral Department of the British Museum. [Read March 15, 1905.] X SMALL collection of minerals,
178 Phenacite and other minerals from Ge~zan East Africa. By L. J. SeE~CER, M.A., F.G.S. Assistant in the Mineral Department of the British Museum. [Read March 15, 1905.] X SMALL collection of minerals,
GEOL. 40 ELEMENTARY MINERALOGY
 CRYSTAL DESCRIPTION AND CALCULATION A. INTRODUCTION This exercise develops the framework necessary for describing a crystal. In essence we shall discuss how we fix the position of any crystallographic
CRYSTAL DESCRIPTION AND CALCULATION A. INTRODUCTION This exercise develops the framework necessary for describing a crystal. In essence we shall discuss how we fix the position of any crystallographic
Unit 2: Atomic Structure Additional Practice
 Name: Unit 2: Atomic Structure Additional Practice Period: 1. Which particles have approximately the same mass? an electron and an alpha particle an electron and a proton a neutron and an alpha particle
Name: Unit 2: Atomic Structure Additional Practice Period: 1. Which particles have approximately the same mass? an electron and an alpha particle an electron and a proton a neutron and an alpha particle
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4437/5H London Examinations IGCSE Science (Double Award) Chemistry Paper 5H Higher Tier Tuesday 16 November 2010 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4437/5H London Examinations IGCSE Science (Double Award) Chemistry Paper 5H Higher Tier Tuesday 16 November 2010 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
Solid Type of solid Type of particle Attractive forces between particles Na P 4 MgO SO 3
 QUESTION (2011:2) Complete the table below by stating the type of solid, the type of particle present, and the bonding (attractive forces) between particles in the solid state. Solid Type of solid Type
QUESTION (2011:2) Complete the table below by stating the type of solid, the type of particle present, and the bonding (attractive forces) between particles in the solid state. Solid Type of solid Type
Section B: Some Essential Background Chemistry
 Section B: Some Essential Background Chemistry Soluble and insoluble salts The importance of knowing whether a salt is soluble or insoluble in water You will remember that acids react with carbonates to
Section B: Some Essential Background Chemistry Soluble and insoluble salts The importance of knowing whether a salt is soluble or insoluble in water You will remember that acids react with carbonates to
Minerals II: Physical Properties and Crystal Forms. From:
 Minerals II: Physical Properties and Crystal Forms From: http://webmineral.com/data/rhodochrosite.shtml The Physical Properties of Minerals Color Streak Luster Hardness External Crystal Form Cleavage The
Minerals II: Physical Properties and Crystal Forms From: http://webmineral.com/data/rhodochrosite.shtml The Physical Properties of Minerals Color Streak Luster Hardness External Crystal Form Cleavage The
CHAPTER 1: Chemistry, An Introduction
 CHAPTER 1: Chemistry, An Introduction science: the study of nature to explain what one observes 1.4 THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD: How Chemists Think Applying the Scientific Method 1. Make an observation, and
CHAPTER 1: Chemistry, An Introduction science: the study of nature to explain what one observes 1.4 THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD: How Chemists Think Applying the Scientific Method 1. Make an observation, and
Weathering: the disintegration, or breakdown of rock material
 Weathering: the disintegration, or breakdown of rock material Mechanical Weathering: no change in chemical composition--just disintegration into smaller pieces Chemical Weathering: breakdown as a result
Weathering: the disintegration, or breakdown of rock material Mechanical Weathering: no change in chemical composition--just disintegration into smaller pieces Chemical Weathering: breakdown as a result
CHAPTER 3: MATTER. Active Learning Questions: 1-6, 9, 13-14; End-of-Chapter Questions: 1-18, 20, 24-32, 38-42, 44, 49-52, 55-56, 61-64
 CHAPTER 3: MATTER Active Learning Questions: 1-6, 9, 13-14; End-of-Chapter Questions: 1-18, 20, 24-32, 38-42, 44, 49-52, 55-56, 61-64 3.1 MATTER Matter: Anything that has mass and occupies volume We study
CHAPTER 3: MATTER Active Learning Questions: 1-6, 9, 13-14; End-of-Chapter Questions: 1-18, 20, 24-32, 38-42, 44, 49-52, 55-56, 61-64 3.1 MATTER Matter: Anything that has mass and occupies volume We study
Symmetry. 2-D Symmetry. 2-D Symmetry. Symmetry. EESC 2100: Mineralogy 1. Symmetry Elements 1. Rotation. Symmetry Elements 1. Rotation.
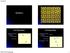 Symmetry a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation Operation Motif = the symbol for a two-fold rotation EESC 2100: Mineralogy 1 a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation
Symmetry a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation Operation Motif = the symbol for a two-fold rotation EESC 2100: Mineralogy 1 a. Two-fold rotation = 30 o /2 rotation
Chapter 1: Matter, Energy, and the Origins of the Universe
 Chapter 1: Matter, Energy, and the Origins of the Universe Problems: 1.1-1.40, 1.43-1.98 science: study of nature that results in a logical explanation of the observations chemistry: study of matter, its
Chapter 1: Matter, Energy, and the Origins of the Universe Problems: 1.1-1.40, 1.43-1.98 science: study of nature that results in a logical explanation of the observations chemistry: study of matter, its
PETROGENESIS OF ANGLE-PLATED QUARTZ AND ASSOCIATED VOID- FILLING CALCITE, EAGLE AND PHENIX DAM SITE, COLUMBUS, GA
 PETROGENESIS OF ANGLE-PLATED QUARTZ AND ASSOCIATED VOID- FILLING CALCITE, EAGLE AND PHENIX DAM SITE, COLUMBUS, GA Information supplemental to: GEOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR CONSTRUCTING A RAFTING AND KAYAKING
PETROGENESIS OF ANGLE-PLATED QUARTZ AND ASSOCIATED VOID- FILLING CALCITE, EAGLE AND PHENIX DAM SITE, COLUMBUS, GA Information supplemental to: GEOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR CONSTRUCTING A RAFTING AND KAYAKING
DIELECTRIC CONSTANTS OF CRYSTALS III BY D. A. A. S. NARAYANA RAO
 DIELECTRIC CONSTANTS OF CRYSTALS III BY D. A. A. S. NARAYANA RAO (Department of Physic, Andhra University, Waltair) Received May 25, 1949 (Communicated by Prof. S. Bhagavantam, F.A.sc.) 1. INTRODUCTION
DIELECTRIC CONSTANTS OF CRYSTALS III BY D. A. A. S. NARAYANA RAO (Department of Physic, Andhra University, Waltair) Received May 25, 1949 (Communicated by Prof. S. Bhagavantam, F.A.sc.) 1. INTRODUCTION
CHAPTER 3. Crystallography
 CHAPTER 3 Crystallography Atomic Structure Atoms are made of Protons: mass 1.00728 amu, +1 positive charge Neutrons: mass of 1.00867 amu, neutral Electrons: mass of 0.00055 amu, -1 negative charge (1 amu
CHAPTER 3 Crystallography Atomic Structure Atoms are made of Protons: mass 1.00728 amu, +1 positive charge Neutrons: mass of 1.00867 amu, neutral Electrons: mass of 0.00055 amu, -1 negative charge (1 amu
Name Date Class MATTER AND CHANGE. SECTION 2.1 PROPERTIES OF MATTER (pages 39 42)
 2 MATTER AND CHANGE SECTION 2.1 PROPERTIES OF MATTER (pages 39 42) This section helps you distinguish extensive from intensive properties and identify substances by their properties. It teaches you how
2 MATTER AND CHANGE SECTION 2.1 PROPERTIES OF MATTER (pages 39 42) This section helps you distinguish extensive from intensive properties and identify substances by their properties. It teaches you how
Conical extinction curves: a new universal stage technique 1
 853 Conical extinction curves: a new universal stage technique 1 By N. JOEL, M.Sc., Ph.D., A.Inst.P. Centro de Investigaciones de Cristalografia, Instituto de Fisica y Matem~ticas, Universidad de Chile,
853 Conical extinction curves: a new universal stage technique 1 By N. JOEL, M.Sc., Ph.D., A.Inst.P. Centro de Investigaciones de Cristalografia, Instituto de Fisica y Matem~ticas, Universidad de Chile,
GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy Lecture 7a: Optical Mineralogy (two day lecture) Instructor: Dr. Douglas Haywick This Week s Agenda 1. Properties of light 2. Minerals and
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 302: Crystallography & Mineralogy Lecture 7a: Optical Mineralogy (two day lecture) Instructor: Dr. Douglas Haywick This Week s Agenda 1. Properties of light 2. Minerals and
Optical Mineralogy in a Nutshell
 Optical Mineralogy in a Nutshell Use of the petrographic microscope Slides borrowed/adapted from Jane Selverstone (University of New Mexico) and John Winter (Whitman College) Why use the petrographic microscope?
Optical Mineralogy in a Nutshell Use of the petrographic microscope Slides borrowed/adapted from Jane Selverstone (University of New Mexico) and John Winter (Whitman College) Why use the petrographic microscope?
Chapter 1. Matter. 1.1 What is Chemistry. 1.2 The Scientific Method:
 Chapter 1. Matter 1.1 What is Chemistry CHEMISTRY The study of the structure, composition, properties and reactions of matter and the energy changes associated with matter. In other words the study of
Chapter 1. Matter 1.1 What is Chemistry CHEMISTRY The study of the structure, composition, properties and reactions of matter and the energy changes associated with matter. In other words the study of
Earth Materials Lab 2 - Lattices and the Unit Cell
 Earth Materials Lab 2 - Lattices and the Unit Cell Unit Cell Minerals are crystallographic solids and therefore are made of atoms arranged into lattices. The average size hand specimen is made of more
Earth Materials Lab 2 - Lattices and the Unit Cell Unit Cell Minerals are crystallographic solids and therefore are made of atoms arranged into lattices. The average size hand specimen is made of more
Name Class Date. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. When working with this Lab Report file, remember to save often.
 Name Class Date Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Virtual Lab Identifying Elements When working with this Lab Report file, remember to save often. PROBLEM Chemistry is often used to
Name Class Date Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Virtual Lab Identifying Elements When working with this Lab Report file, remember to save often. PROBLEM Chemistry is often used to
Geology Topics Minerals
 Geology Topics Minerals RED SLIDE: These are notes that are very important and should be recorded in your science journal. BLACK SLIDE: Pay attention, follow directions, complete projects as described
Geology Topics Minerals RED SLIDE: These are notes that are very important and should be recorded in your science journal. BLACK SLIDE: Pay attention, follow directions, complete projects as described
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2008 69451 Weinheim, Germany Supporting Information Unmasking Representative Structures of TMP-Active Hauser and Turbo Hauser Bases Pablo García-Álvarez, David V. Graham,
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2008 69451 Weinheim, Germany Supporting Information Unmasking Representative Structures of TMP-Active Hauser and Turbo Hauser Bases Pablo García-Álvarez, David V. Graham,
LAB 1: OPTICAL PROPERTIES AND THE PLM #1 Orthoscopic Light
 GEOLOGY 17.01: Mineralogy LAB 1: OPTICAL PROPERTIES AND THE PLM #1 Orthoscopic Light Learning Objectives: Students will be able to describe optical properties of minerals in planepolarized and cross-polarized
GEOLOGY 17.01: Mineralogy LAB 1: OPTICAL PROPERTIES AND THE PLM #1 Orthoscopic Light Learning Objectives: Students will be able to describe optical properties of minerals in planepolarized and cross-polarized
The table shows the results of some tests carried out on three solutions, A, B and C. Hydrochloric acid is added. Solution
 1 Chemical tests can be used to identify compounds. The table shows the results of some tests carried out on three solutions, A, B and C. Solution Flame Test Hydrochloric acid is added Sodium hydroxide
1 Chemical tests can be used to identify compounds. The table shows the results of some tests carried out on three solutions, A, B and C. Solution Flame Test Hydrochloric acid is added Sodium hydroxide
GOZO COLLEGE BOYS SECONDARY SCHOOL
 GOZO COLLEGE BOYS SECONDARY SCHOOL Embracing Diversity Half Yearly Exams 2013-2014 FORM 4 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min Name: Class: Useful Data: One Faraday is equivalent to 96500 C. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 H 1
GOZO COLLEGE BOYS SECONDARY SCHOOL Embracing Diversity Half Yearly Exams 2013-2014 FORM 4 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min Name: Class: Useful Data: One Faraday is equivalent to 96500 C. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 H 1
1. A Covalent bonding B Polar covalent bonding C Metallic bonding D Hydrogen bonding E Ionic bonding F London dispersion forces
 Higher (National 6) Unit 1: Chemical changes and structure 1c Bonding and structure Problem sheets 1. A Covalent bonding B Polar covalent bonding C Metallic bonding D Hydrogen bonding E Ionic bonding F
Higher (National 6) Unit 1: Chemical changes and structure 1c Bonding and structure Problem sheets 1. A Covalent bonding B Polar covalent bonding C Metallic bonding D Hydrogen bonding E Ionic bonding F
St. Xavier s College Mumbai
 St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for B.Sc I st Semester Courses in Geology (June 2016 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.1.01 - Introduction to Mineralogy and Crystallography o
St. Xavier s College Mumbai Syllabus for B.Sc I st Semester Courses in Geology (June 2016 onwards) Contents: Theory Syllabus for Courses: o S.Geo.1.01 - Introduction to Mineralogy and Crystallography o
SPECTROSCOPIC STUDY OF LUMINESCENCE PATTERNS IN DIAMOND BY ANNA MANI. Received August 21, 1944 (Communicated by Sir C. V. Raman, Kt., F.R.S., N.L.
 SPECTROSCOPIC STUDY OF LUMINESCENCE PATTERNS IN DIAMOND BY ANNA MANI (From the Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore) Received August 21, 1944 (Communicated by Sir C. V. Raman,
SPECTROSCOPIC STUDY OF LUMINESCENCE PATTERNS IN DIAMOND BY ANNA MANI (From the Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore) Received August 21, 1944 (Communicated by Sir C. V. Raman,
This Lab will not be marked so make sure to get anything you are unsure about checked by your TA!
 Lab One. Microscope Refresher and Advanced Microscope Techniques Learning Goals. After this Lab, you should be able: Demonstrate the operation of the petrographic microscope in plane and crossed polarized
Lab One. Microscope Refresher and Advanced Microscope Techniques Learning Goals. After this Lab, you should be able: Demonstrate the operation of the petrographic microscope in plane and crossed polarized
Elements. Chem101 - Lecture 2. Elements. Elements. Elements. Elements. Atoms and Molecules
 Chem101 - Lecture 2 Atoms and Molecules Elements Elements are pure substances containing only one kind of atom (homoatomic). There are at last count 114 elements. (Your book indicates 112.). - 88 of these
Chem101 - Lecture 2 Atoms and Molecules Elements Elements are pure substances containing only one kind of atom (homoatomic). There are at last count 114 elements. (Your book indicates 112.). - 88 of these
ESS 439 Lab 2 Examine Optical Properties of Minerals
 ESS 439 Lab 2 Examine Optical Properties of Minerals The optical properties depend on the manner that visible light is transmitted through the crystal, and thus are dependent on mineral s Crystal Structure
ESS 439 Lab 2 Examine Optical Properties of Minerals The optical properties depend on the manner that visible light is transmitted through the crystal, and thus are dependent on mineral s Crystal Structure
100% ionic compounds do not exist but predominantly ionic compounds are formed when metals combine with non-metals.
 2.21 Ionic Bonding 100% ionic compounds do not exist but predominantly ionic compounds are formed when metals combine with non-metals. Forming ions Metal atoms lose electrons to form +ve ions. Non-metal
2.21 Ionic Bonding 100% ionic compounds do not exist but predominantly ionic compounds are formed when metals combine with non-metals. Forming ions Metal atoms lose electrons to form +ve ions. Non-metal
May 09, Ksp.notebook. Ksp = [Li + ] [F + ] Find the Ksp for the above reaction.
![May 09, Ksp.notebook. Ksp = [Li + ] [F + ] Find the Ksp for the above reaction. May 09, Ksp.notebook. Ksp = [Li + ] [F + ] Find the Ksp for the above reaction.](/thumbs/85/92550924.jpg) example: Constant Product K sp Solubility Product Constant Some compounds dissolve in water Some compounds dissolve better than others The more that a compound can dissolve, the more soluble the compound
example: Constant Product K sp Solubility Product Constant Some compounds dissolve in water Some compounds dissolve better than others The more that a compound can dissolve, the more soluble the compound
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. The asymmetric unit in para-iodio-phenylalanine crystal. The 50% probability ellipsoid representation was prepared using the Mercury Software. Colors are as
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. The asymmetric unit in para-iodio-phenylalanine crystal. The 50% probability ellipsoid representation was prepared using the Mercury Software. Colors are as
305 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, AND MINERALS
 DATE DUE: Name: Instructor: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, AND MINERALS Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC VOCABULARY where APPLICABLE!
DATE DUE: Name: Instructor: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, AND MINERALS Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC VOCABULARY where APPLICABLE!
Crystallography basics
 Crystallography basics 1 ? 2 Family of planes (hkl) - Family of plane: parallel planes and equally spaced. The indices correspond to the plane closer to the origin which intersects the cell at a/h, b/k
Crystallography basics 1 ? 2 Family of planes (hkl) - Family of plane: parallel planes and equally spaced. The indices correspond to the plane closer to the origin which intersects the cell at a/h, b/k
Basics of crystallography
 Basics of crystallography 1 Family of planes (hkl) - Family of plane: parallel planes and equally spaced. The indices correspond to the plane closer to the origin which intersects the cell at a/h, b/k
Basics of crystallography 1 Family of planes (hkl) - Family of plane: parallel planes and equally spaced. The indices correspond to the plane closer to the origin which intersects the cell at a/h, b/k
sodium carbonate. sodium hydrogencarbonate. sodium nitrate. D sodium sulfate. (Total for Question 9 = mark)
 1 ompound X is an anhydrous, white solid which decomposes on heating to form a white solid residue, a colourless gas, and a colourless vapour which condenses to a colourless liquid. ompound X is sodium
1 ompound X is an anhydrous, white solid which decomposes on heating to form a white solid residue, a colourless gas, and a colourless vapour which condenses to a colourless liquid. ompound X is sodium
Chem 161. Dr. Jasmine Bryant
 Chem 161 Dr. Jasmine Bryant Chapter 1: Matter, Energy, and the Origins of the Universe Problems: 1.1-1.10, 1.14-1.22, 1.24-1.93, 1.96 Science: study of nature that results in a logical explanation of the
Chem 161 Dr. Jasmine Bryant Chapter 1: Matter, Energy, and the Origins of the Universe Problems: 1.1-1.10, 1.14-1.22, 1.24-1.93, 1.96 Science: study of nature that results in a logical explanation of the
Draw one line from each solution to the ph value of the solution. Solution ph value of the solution
 1 The ph scale is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. (a) Draw one line from each solution to the ph value of the solution. Solution ph value of the solution 5 Acid 7 9 Neutral 11 13
1 The ph scale is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. (a) Draw one line from each solution to the ph value of the solution. Solution ph value of the solution 5 Acid 7 9 Neutral 11 13
Lab 3: Minerals and the rock cycle. Rocks are divided into three major categories on the basis of their origin:
 Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 3: Minerals and the rock cycle Rocks are divided into three major categories on the basis of their origin: Igneous rocks (from the Latin word, ignis = fire) are composed of minerals
Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 3: Minerals and the rock cycle Rocks are divided into three major categories on the basis of their origin: Igneous rocks (from the Latin word, ignis = fire) are composed of minerals
Crystal Chem Crystallography
 Crystal Chem Crystallography Chemistry behind minerals and how they are assembled Bonding properties and ideas governing how atoms go together Mineral assembly precipitation/ crystallization and defects
Crystal Chem Crystallography Chemistry behind minerals and how they are assembled Bonding properties and ideas governing how atoms go together Mineral assembly precipitation/ crystallization and defects
Phosphoric acid is made by reacting phosphate rock with sulfuric acid. Only three of the methods shown below will increase the rate of this reaction.
 Q. The picture shows a lump of phosphate rock. Rob Lavinsky, irocks.com CC-BY-SA-3.0 [CC-BY-SA-3.0], via Wikimedia Commons Phosphoric acid is made by reacting phosphate rock with sulfuric acid. Only three
Q. The picture shows a lump of phosphate rock. Rob Lavinsky, irocks.com CC-BY-SA-3.0 [CC-BY-SA-3.0], via Wikimedia Commons Phosphoric acid is made by reacting phosphate rock with sulfuric acid. Only three
Lab 7: Metathesis Reactions. Pre-lab: Pages Post-Lab: Pages 164
 Lab 7: Metathesis Reactions Pre-lab: Pages 159-160 Post-Lab: Pages 164 Lab Objectives Careful observation and detailed description of chemical reactions in solution Inferring from observation and from
Lab 7: Metathesis Reactions Pre-lab: Pages 159-160 Post-Lab: Pages 164 Lab Objectives Careful observation and detailed description of chemical reactions in solution Inferring from observation and from
Flushing Out the Moles in Lab: The Reaction of Calcium Chloride with Carbonate Salts
 Flushing Out the Moles in Lab: The Reaction of Calcium Chloride with Carbonate Salts Pre-lab Assignment: Reading: 1. Chapter sections 3.3, 3.4, 3.7 and 4.2 in your course text. 2. This lab handout. Questions:
Flushing Out the Moles in Lab: The Reaction of Calcium Chloride with Carbonate Salts Pre-lab Assignment: Reading: 1. Chapter sections 3.3, 3.4, 3.7 and 4.2 in your course text. 2. This lab handout. Questions:
Mineralogy Problem Set Crystal Systems, Crystal Classes
 Mineralogy Problem Set Crystal Systems, Crystal Classes (1) For each of the three accompanying plane patterns: (a) Use a ruler to draw solid lines to show where there are mirror planes on the pattern.
Mineralogy Problem Set Crystal Systems, Crystal Classes (1) For each of the three accompanying plane patterns: (a) Use a ruler to draw solid lines to show where there are mirror planes on the pattern.
CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC NOTES : CRISTOBALITE, STEPHANITE, NATROLITE Josnrrr Munnocu, Uniaersity of CatiJorni,a, Los Angeles.
 CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC NOTES : CRISTOBALITE, STEPHANITE, NATROLITE Josnrrr Munnocu, Uniaersity of CatiJorni,a, Los Angeles. ABSTRAcT cristobalite crystals with cubic habit are reported from Two Rivers, california.
CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC NOTES : CRISTOBALITE, STEPHANITE, NATROLITE Josnrrr Munnocu, Uniaersity of CatiJorni,a, Los Angeles. ABSTRAcT cristobalite crystals with cubic habit are reported from Two Rivers, california.
KENYA NATIONAL EXAMINATION COUNCIL REVISION MOCK EXAMS 2016 TOP NATIONAL SCHOOLS KAPSABET BOYS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 TIME: 2 HOURS
 KENYA NATIONAL EXAMINATION COUNCIL REVISION MOCK EXAMS 2016 TOP NATIONAL SCHOOLS KAPSABET BOYS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 TIME: 2 HOURS SCHOOLS NET KENYA Osiligi House, Opposite KCB, Ground Floor Off Magadi Road,
KENYA NATIONAL EXAMINATION COUNCIL REVISION MOCK EXAMS 2016 TOP NATIONAL SCHOOLS KAPSABET BOYS CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 TIME: 2 HOURS SCHOOLS NET KENYA Osiligi House, Opposite KCB, Ground Floor Off Magadi Road,
305 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, AND MINERALS
 DATE DUE: Name: Instructor: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, AND MINERALS Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC VOCABULARY where APPLICABLE!
DATE DUE: Name: Instructor: Ms. Terry J. Boroughs Geology 305 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, AND MINERALS Instructions: Read each question carefully before selecting the BEST answer. Use GEOLOGIC VOCABULARY where APPLICABLE!
The structure of liquids and glasses. The lattice and unit cell in 1D. The structure of crystalline materials. Describing condensed phase structures
 Describing condensed phase structures Describing the structure of an isolated small molecule is easy to do Just specify the bond distances and angles How do we describe the structure of a condensed phase?
Describing condensed phase structures Describing the structure of an isolated small molecule is easy to do Just specify the bond distances and angles How do we describe the structure of a condensed phase?
The Study of Minerals (Chapter 1) Introduction to Mineral Identification THE SILICATE MINERALS
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: The Study of Minerals (Chapter 1) Introduction to Mineral Identification THE SILICATE MINERALS For this assignment you will require: a streak
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: The Study of Minerals (Chapter 1) Introduction to Mineral Identification THE SILICATE MINERALS For this assignment you will require: a streak
Periodic Table Practice 11/29
 Periodic Table Practice 11/29 1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) the number of electron shells D) the
Periodic Table Practice 11/29 1. The arrangement of the elements from left to right in Period 4 on the Periodic Table is based on A) atomic mass B) atomic number C) the number of electron shells D) the
