Seismic Hazard & Risk Assessment
|
|
|
- Blanche Glenn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Seismic Hazard & Risk Assessment
2 HAZARD ASSESSMENT INVENTORY OF ELEMENTS AT RISK VULNERABILITIES RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY AND SOFTWARE LOSS RESULTS Event Local Site Effects: Attenuation of Seismic Energy
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 Basic Steps in Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis Seismic source characterization Estimation of source seismicity parameters (recurrence) parameters and probabilistic model Selection of ground motion attenuation models Treatment of Epistemic Uncertainties with Logic Tree Models Quantification of the seismic hazard
11
12 Basic steps in probabilistic seismic hazard analysis Seismic source characterization Estimation of seismicity (recurrence) parameters for each source Selection of ground motion attenuation models Quantification of the seismic hazard Faults (line sources) F 1 SOURCE MODELS F 2 log(n) RECURRENCE pga, S a, A i GROUND MOTION ATTENUATION Area source M distance SEISMIC HAZARD MAP Probability of exceedance SEISMIC HAZARD CURVES Acceleration
13 Earthquake Probability Estimation Poissonian ( Time Independent ) No memory -- probability is independent of past (recent) earthquake history Time Dependent ( Predictable ) Considers the time elapsed since the last event in estimating the probability of future events. Stress Transfer ( Migration ) Occurrence of earthquake on one fault has an impact on the probability of occurrence on another fault
14
15 SOURCE CHARACTERIZATION
16 Active faults of eastern Marmara region during the last century (Akyuz et al., 2000) The recent high-resolution bathymetric map obtained from the survey of the Ifremer RV Le Suroit vessel that indicates a single, thoroughgoing strike-slip fault system (LePichon et al., 2001)
17 (A)Simplified tectonic map of eastern Mediterranean region, (B) Seismotectonic map of the Marmara Sea Region ( Yaltırak, 2002)
18 The Earthquake Catalog Development of one catalog from several catalogs Declustering Use of the catalog Calculation of the Gutenberg-Richter a and b values for the background Assignment of major earthquakes to the segments in the fault segmentation model
19 The long-term seismicity of the Marmara region (Seismicity between 32 AD 1983 taken from Ambraseys and Finkel, 1991)
20 Association of major earthquakes between 1500-present with the segmentation proposed
21 The sequence of earthquakes in the 18 th century (after Hubert-Ferrari, 2000).
22 The seismic activity of the Marmara region with M>3 events from Jan 1, 1990 to August 16, 1999 The seismic activity of the Marmara region with M>3 events from August 17, 1999 to present
23 Fault segmentation model developed for this study
24 Source Zonation Scheme
25 RECURRENCE RELATIONSHIPS
26 The earthquake recurrence models for the fault segments Poisson model characteristic earthquake recurrence is assumed, probability of occurrence of the characteristic event does not change in time the annual rate is calculated as: R = 1 / mean recurrence interval Time dependent (Renewal model) the probability of occurrence of the characteristic event increases as a function of the time elapsed since the last characteristic event, a lognormal distribution with a coefficient of variation of 0.5 is assumed to represent the earthquake probability density distribution. the annual rate is calculated as: R eff = -ln(1 P cond ) / T
27 MAGNITUDE AND FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION 1. Truncated Gutenberg-Richter distribution logn(m)=a-bm Richter (1958) N: The number of earthquakes per year with a magnitude equal to or greater than M. N is associated with a given area and time period. a ve b: Constants for the seismic zone. 2. Characteristic Distribution a.assess magnitude of potential earthquakes (segmentation, floating) b. Calculate recurrence of earthquake (Wells ve Coppersmith, 1994) = moment of char earthquake/moment rate of fault = rigidity*area*displacement/rigidity*area*slip rate rigidity modulus (resistance to shearing motion we use in U.S. is 3.0 X 10exp11 gm/cm*s*s(dynes/cm*cm) Gutenberg-Richter Characteristic Log (no of eq >=M) Magnitude (M) Magnitude (M)
28 Gutenberg-Richter Distribution Richter (1958) logn=a-bm N: The number of earthquakes per year with a magnitude equal to or greater than M. N is associated with a given area and time period. a ve b: Constants for the seismic zone. The constant a is the logarithm of the number of earthquakes with magnitude equal to or greater than zero. The constant b is the slope of the distribution and controls the relative proportion of large to small earthquakes.
29 Recurrence Relationships
30 Cascading It is well known that, even though segments can be mapped separately at the surface, they could combine and be a single structure at depth, or a rupture on one segment could trigger ruptures on others in a cascade model. So two scenarios are envisioned: 1. faults rupture independently, producing characteristic-size earthquakes, or 2. fault segments rupture together as a cascade, producing earthquakes of M>7. The Cascade assumption increases the Maximum Magnitude but reduces the rate of occurrence of the more moderate events. Previous rupturing cycles around the Marmara Sea indicate that, on average, one out of three ruptures were multiple segments. The probabilistic results based on cascade models provided about the same earthquake hazard levels obtained from noncascading models.
31 ATTENUATION MODELS
32 PGA =f (Magnitude, Distance, Fault type, Site condition)
33
34 Boore, Joyner, Fumal (1997) Based on Western North America data Distance measure is closest distance to surface projection of rupture Strike-slip and reverse faults Site conditions based on shear-wave velocity in upper 30 m of soil PSA from 0 to 2.0 seconds ln(y) = b 1 + b 2 (M-6) + b 3 (M-6) 2 + b 5 lnr + b V ln (V S / V A )
35 Campbell 1997 Based on worldwide data Horizontal and vertical components Distance measure is shortest distance to seismogenic rupture Strike-slip and reverse faults Hard rock, soft rock (620 m/sec), and firm soil site conditions PSA from 0.05 to 4 sec ln(a H ) = M ln[r SEIS 2 + (0 149e 0.67M ) 2 ] 1/2 + [ ln(R SEIS ) M]F + [ ln(r SEIS )] S SR + [ ln(r SEIS )] S HR + ε
36 Sadigh, 1997 Based on California data Horizontal and vertical components Distance measure is closest to rupture Strike-slip and reverse faults Rock and deep soil site conditions PSA to 4.0 seconds ln(y) = C 1 + C 2 M + C 3 (8,5-M) C 4 ln[r rup + exp(c 5 +C 6 M)] + C7ln(r rup +2)
37
38
39
40
41 QUANTIFICATION OF THE EARTHQUAKE HAZARD
42 Fault line Fault line SITE Source area Source area 1- SOURCES 2- RECURRENCE Log(Num.Eqs.>M)..... Magnitude M. 3- ATTENUATION 4- PROBABILITY Ground motion Distance M3 >M2 >M1 M3 M2 M1 Prob. of exceedance Ground motion Steps of probabilistic seismic hazard analysis (1) definition of earthquake sources, (2) earthquake recurrence characteristics for each source, (3) attenuation of ground motions with magnitude and distance, and (4) ground motions for specified probability of exceedance levels (calculated by summing probabilities over all the sources, magnitudes, and distances).
43 The Earthquake Hazard The ground motion parameters used in the quantification of the earthquake hazard are the peak ground acceleration (PGA) and the spectral accelerations (SA) for natural periods of 0.2 and 1.0 seconds. The ground motions are determined for soft rock (NEHRP B/C boundary) conditions (Vs = 760m/s). The results are presented as iso-intensity contour maps for 10% probability of exceedence in 50 years.
44 Sa S MS Sa=S M1 / T S M1 0.4 S MS T 0 T S 1.0 Period Standard Shape of the Response Spectrum (NEHRP 1997)
45 Time Dependent, Characteristic, PGA, %10-50
46 Time Dependent, Characteristic, SA (0.2), %10-50
47 Time Dependent, Characteristic, SA (1.0), %10-50
48 SITE-DEPENDENT HAZARD
49
50
51 The NEHRP-based Soil Classification Map of Istanbul
52 The earthquake hazard results are converted to site-dependent values to reflect the local site effects in Istanbul. For this reason, spectral response acceleration values obtained for NEHRP site class B/C boundary (Vs= 760 m/sec) are adjusted using Fa factors for short period and Fv factors for long period site-correction defined in the 1997 NEHRP Provisions (NEHRP 1997). Fa, the short period site-correction defined in the 1997 NEHRP Provisions (NEHRP 1997) Fv, the long period site correction defined in the 1994 and 1997 NEHRP Provisions (NEHRP 1997)
53 Site dependent seismic hazard assessment Site dependent SA (T=0.2 s) map at NEHRP B/C boundary site class for 10% probability of exceedence in 50 years
54 Site dependent seismic hazard assessment Site dependent SA (T=1.0 s) map at NEHRP B/C boundary site class for 10% probability of exceedence in 50 years
55 Deterministic Seismic Hazard Mw=7.5 scenario earthquake for Istanbul and vicinity
56 Site dependent deterministic intensity distribution
57 Site-dependent deterministic SA(T=0.2 sec) values in units of g
58 Site-dependent deterministic SA(T=1.0 sec) values in units of g
59 Earthquake Hazard Analysis ADAPAZARI T=0.2sn deki spektral ivmeler (%40/50) T=1.0sn deki spektral ivmeler (%40/50) ÜNİFORM TEHLİKE DAVRANIŞ SPEKTRUMU Spektral Davranış İvmesi, Sİ Sahaya özel EBİ veya 0.4Sms Sahaya özel EBİ veya 0.4Sms Periyot, sn Her bir hücre için elde edilen eş tehlike spektrumu Site Response Analysis
60 Deterministic Seismic Hazard Estimation of Peak Ground Velocity (PGV) and Intensity
61 Peak Ground Velocity Based on HAZUS99 recommendations PGV has been calculated from SA at T=1.0 using the following formula. where PGV is the peak ground velocity in inches per second and S A1 is the spectral acceleration in units of g, at T=1.0sec.
62 Intensity Based Deterministic Earthquake Hazard The relationships between PGA, PGV and Modified Mercalli Intensity of Walid et al. (1999)
63 Risk Assessment
64 ELEMENTS AT RISK Buildings Lifeline Systems Built Environment Population Socio-Economic Activities
65
66
67
68
69
70
71 Area plot for vulnerability curves
72
73
74 Line plot for vulnerability curves
75 KOERILoss Intensity Based Loss Estimation Algorithm
76 KOERILoss Spectral displacement Based Loss Estimation Algorithm
77
78 Classification of Building Data Structural systems category I = 1 : RC frame building I = 2 : Masonry building I = 3 : Shear wall building (Tunnel formwork system) I = 4 : Pre-fabricated building Number of building stories category J = 1 : 1 4 stories (including basement) J = 2 : 5 8 stories (including basement) J = 3 : > 8 stories (including basement) - Construction Year category K = 1 : Construction year: pre-1979 (included) K = 2 : Construction year: post-1980
79 Classification of Structural Damage S: Slight damage M: Moderate damage E: Extensive damage C: Complete damage Classification of Casualties Severity 1 Severity 2 Severity 3 Severity 4
80 BUILDING INVENTORIES Building Inventory based on aerial photos prepared by İki Nokta Data prepared by State Statistics Institute (SSI)
81
82 DEMOGRAPHIC DATA
83 Total Extensive Damage Distribution
84 Casualty Distribution for Severity Level 4
85 Shelter Need Distribution
86 The main dialog of the KOERILoss
87 Integration of KOERILoss and MapInfo features
88 Integration of KOERILoss and MapInfo Graphics
89 Output of the Analysis Buildings Damage Loss Direct Economic Loss Number of Casualties In terms of Geo-cells (Grids) Subdistricts (Mahalle) Districts (İlçe)
90 Moderate Damage Distribution of Mid-Rise Pre-1980 R/C Buildings
91 Extensive Damage Distribution of Mid-Rise Pre-1980 R/C Buildings
92 Complete Damage Distribution of Mid-Rise Pre-1980 R/C Buildings
93 Extensive Damage Distribution of Low-Rise Pre-1980 Masonry Buildings
94 Lifeline Systems
95
96
97
98
99 Intensity Based Life Line Damage Assessment
100 Transportation system: Earthquake Vulnerability and Damage Road damages consist of the surface damages and collapse of the neighboring slopes or retaining walls. Also collapsed underpasses or buildings can block the traffic even if the motorway is not damaged. According to ATC 25, the ratio of damage of local roads during an earthquake are given as %2 for MMI V, %4 for MMI VI, %11 for MMI VII, and %32 for MMI VIII
101 Water and Wastewater Transmission Systems According to ATC 25, the ratio of damage of water transmission lines during an earthquake are given as %0 for MMI V, 1% for MMI VI, 4% for MMI VII, and 12% for MMI VIII. According to ATC 25, the ratio of damage of wastewater transmission lines during an earthquake are given as 0% for MMI V, 2% for MMI VI, 40% for MMI VII, and 100% for MMI VIII
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS. Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1
 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 Seismic Hazard Analysis Deterministic procedures Probabilistic procedures USGS hazard
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 Seismic Hazard Analysis Deterministic procedures Probabilistic procedures USGS hazard
Overview of Seismic PHSA Approaches with Emphasis on the Management of Uncertainties
 H4.SMR/1645-29 "2nd Workshop on Earthquake Engineering for Nuclear Facilities: Uncertainties in Seismic Hazard" 14-25 February 2005 Overview of Seismic PHSA Approaches with Emphasis on the Management of
H4.SMR/1645-29 "2nd Workshop on Earthquake Engineering for Nuclear Facilities: Uncertainties in Seismic Hazard" 14-25 February 2005 Overview of Seismic PHSA Approaches with Emphasis on the Management of
Development of U. S. National Seismic Hazard Maps and Implementation in the International Building Code
 Development of U. S. National Seismic Hazard Maps and Implementation in the International Building Code Mark D. Petersen (U.S. Geological Survey) http://earthquake.usgs.gov/hazmaps/ Seismic hazard analysis
Development of U. S. National Seismic Hazard Maps and Implementation in the International Building Code Mark D. Petersen (U.S. Geological Survey) http://earthquake.usgs.gov/hazmaps/ Seismic hazard analysis
7 Ground Motion Models
 7 Ground Motion Models 7.1 Introduction Ground motion equations are often called attenution relations but they describe much more than just the attenutation of the ground motion; they describe the probability
7 Ground Motion Models 7.1 Introduction Ground motion equations are often called attenution relations but they describe much more than just the attenutation of the ground motion; they describe the probability
AN OVERVIEW AND GUIDELINES FOR PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPPING
 CO 2 TRACCS INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP Bucharest, 2 September, 2012 AN OVERVIEW AND GUIDELINES FOR PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPPING M. Semih YÜCEMEN Department of Civil Engineering and Earthquake Studies
CO 2 TRACCS INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP Bucharest, 2 September, 2012 AN OVERVIEW AND GUIDELINES FOR PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPPING M. Semih YÜCEMEN Department of Civil Engineering and Earthquake Studies
Definitions. Seismic Risk, R (Σεισμική διακινδύνευση) = risk of damage of a structure
 SEISMIC HAZARD Definitions Seismic Risk, R (Σεισμική διακινδύνευση) = risk of damage of a structure Seismic Hazard, Η (Σεισμικός κίνδυνος) = expected intensity of ground motion at a site Vulnerability,
SEISMIC HAZARD Definitions Seismic Risk, R (Σεισμική διακινδύνευση) = risk of damage of a structure Seismic Hazard, Η (Σεισμικός κίνδυνος) = expected intensity of ground motion at a site Vulnerability,
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN
 EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN Dr Ilaria Mosca 1 and Dr Natalya Silacheva 2 1 British Geological Survey, Edinburgh (UK) imosca@nerc.ac.uk 2 Institute of Seismology, Almaty (Kazakhstan) silacheva_nat@mail.ru
EARTHQUAKE HAZARD ASSESSMENT IN KAZAKHSTAN Dr Ilaria Mosca 1 and Dr Natalya Silacheva 2 1 British Geological Survey, Edinburgh (UK) imosca@nerc.ac.uk 2 Institute of Seismology, Almaty (Kazakhstan) silacheva_nat@mail.ru
Project 17 Development of Next-Generation Seismic Design Value Maps
 Project 17 Development of Next-Generation Seismic Design Value Maps Geo Structures 2016 16 February 2016 R.O. Hamburger, SE, SECB www.sgh.com Some History Prior to 1988 - maps provided broad seismic zones
Project 17 Development of Next-Generation Seismic Design Value Maps Geo Structures 2016 16 February 2016 R.O. Hamburger, SE, SECB www.sgh.com Some History Prior to 1988 - maps provided broad seismic zones
WP2: Framework for Seismic Hazard Analysis of Spatially Distributed Systems
 Systemic Seismic Vulnerability and Risk Analysis for Buildings, Lifeline Networks and Infrastructures Safety Gain WP2: Framework for Seismic Hazard Analysis of Spatially Distributed Systems Graeme Weatherill,
Systemic Seismic Vulnerability and Risk Analysis for Buildings, Lifeline Networks and Infrastructures Safety Gain WP2: Framework for Seismic Hazard Analysis of Spatially Distributed Systems Graeme Weatherill,
PSHA results for the BSHAP region
 NATO Science for Peace and Security Programme CLOSING CONFERENCE OF THE NATO SfP 983054 (BSHAP) PROJECT Harmonization of Seismic Hazard Maps for the Western Balkan Countries October 23, 2011 Ankara, Turkey
NATO Science for Peace and Security Programme CLOSING CONFERENCE OF THE NATO SfP 983054 (BSHAP) PROJECT Harmonization of Seismic Hazard Maps for the Western Balkan Countries October 23, 2011 Ankara, Turkey
Regional Workshop on Essential Knowledge of Site Evaluation Report for Nuclear Power Plants.
 Regional Workshop on Essential Knowledge of Site Evaluation Report for Nuclear Power Plants. Development of seismotectonic models Ramon Secanell Kuala Lumpur, 26-30 August 2013 Overview of Presentation
Regional Workshop on Essential Knowledge of Site Evaluation Report for Nuclear Power Plants. Development of seismotectonic models Ramon Secanell Kuala Lumpur, 26-30 August 2013 Overview of Presentation
THE RESPONSE SPECTRUM
 (NBCC 25) Gail M. The Canadian Society for Civil Engineering, Vancouver Section THE RESPONSE SPECTRUM Seismic Hazard Analysis to obtain Uniform Hazard Response Spectrum (NBCC 25) Gail M. Department of
(NBCC 25) Gail M. The Canadian Society for Civil Engineering, Vancouver Section THE RESPONSE SPECTRUM Seismic Hazard Analysis to obtain Uniform Hazard Response Spectrum (NBCC 25) Gail M. Department of
Current Landscape of Spatial Decision Support Systems (SDSS) and Software Applications for Earthquake Disaster Management in Turkey
 Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Current Landscape of Spatial Decision Support Systems (SDSS) and Software Applications for Earthquake Disaster Management in Turkey
Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Current Landscape of Spatial Decision Support Systems (SDSS) and Software Applications for Earthquake Disaster Management in Turkey
Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design
 Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design *Jun-Kyoung Kim 1), Soung-Hoon Wee 2) and Seong-Hwa Yoo 2) 1) Department of Fire Protection and Disaster Prevention, Semyoung University,
Uniform Hazard Spectrum(UHS) for performance based seismic design *Jun-Kyoung Kim 1), Soung-Hoon Wee 2) and Seong-Hwa Yoo 2) 1) Department of Fire Protection and Disaster Prevention, Semyoung University,
Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering
 Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Humboldt Fellow, JSPS Fellow, BOYSCAST Fellow Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in
Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Humboldt Fellow, JSPS Fellow, BOYSCAST Fellow Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in
EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM THE NORTHRIDGE EARTHQUAKE FOR SITE- SPECIFIC AMPLIFICATION FACTORS USED IN US BUILDING CODES
 EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM THE NORTHRIDGE EARTHQUAKE FOR SITE- SPECIFIC AMPLIFICATION FACTORS USED IN US BUILDING CODES Roger D BORCHERDT And Thomas E FUMAL SUMMARY Site-specific amplification factors, F
EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE FROM THE NORTHRIDGE EARTHQUAKE FOR SITE- SPECIFIC AMPLIFICATION FACTORS USED IN US BUILDING CODES Roger D BORCHERDT And Thomas E FUMAL SUMMARY Site-specific amplification factors, F
RESPONSE SPECTRA RECOMMENDED FOR AUSTRALIA
 RESPONSE SPECTRA RECOMMENDED FOR AUSTRALIA Malcolm Somerville, Kevin McCue and Cvetan Sinadinovski Australian Geological Survey Organisation, Canberra SUMMARY Response spectra suitable for intraplate regions
RESPONSE SPECTRA RECOMMENDED FOR AUSTRALIA Malcolm Somerville, Kevin McCue and Cvetan Sinadinovski Australian Geological Survey Organisation, Canberra SUMMARY Response spectra suitable for intraplate regions
Module 7 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS (Lectures 33 to 36)
 Lecture 35 Topics Module 7 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS (Lectures 33 to 36) 7.4.4 Predictive Relationships 7.4.5 Temporal Uncertainty 7.4.6 Poisson Model 7.4.7 Other Models 7.4.8 Model Applicability 7.4.9 Probability
Lecture 35 Topics Module 7 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS (Lectures 33 to 36) 7.4.4 Predictive Relationships 7.4.5 Temporal Uncertainty 7.4.6 Poisson Model 7.4.7 Other Models 7.4.8 Model Applicability 7.4.9 Probability
Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering
 Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Humboldt Fellow, JSPS Fellow, BOYSCAST Fellow Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in
Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Humboldt Fellow, JSPS Fellow, BOYSCAST Fellow Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS
 SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 This topic addresses deterministic and probabilistic seismic hazard analysis, ground
SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS Instructional Material Complementing FEMA 451, Design Examples Seismic Hazard Analysis 5a - 1 This topic addresses deterministic and probabilistic seismic hazard analysis, ground
Commentary Appendix A DEVELOPMENT OF MAXIMUM CONSIDERED EARTHQUAKE GROUND MOTION MAPS FIGURES THROUGH
 Commentary Appendix A DEVELOPMENT OF MAXIMUM CONSIDERED EARTHQUAKE GROUND MOTION MAPS FIGURES 3.3-1 THROUGH 3.3-14 BACKGROUND The maps used in the Provisions through 1994 provided the A a (effective peak
Commentary Appendix A DEVELOPMENT OF MAXIMUM CONSIDERED EARTHQUAKE GROUND MOTION MAPS FIGURES 3.3-1 THROUGH 3.3-14 BACKGROUND The maps used in the Provisions through 1994 provided the A a (effective peak
6 Source Characterization
 6 Source Characterization Source characterization describes the rate at which earthquakes of a given magnitude, and dimensions (length and width) occur at a given location. For each seismic source, the
6 Source Characterization Source characterization describes the rate at which earthquakes of a given magnitude, and dimensions (length and width) occur at a given location. For each seismic source, the
5. Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis
 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA) proposed by C.A. Cornell (1968) used to determine the design earthquake for all locations in USA. PSHA gives a relative quantification i of the design earthquake,
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA) proposed by C.A. Cornell (1968) used to determine the design earthquake for all locations in USA. PSHA gives a relative quantification i of the design earthquake,
Spatial Cross-correlation Models for Vector Intensity Measures (PGA, Ia, PGV and Sa s) Considering Regional Site Conditions
 Spatial Cross-correlation Models for Vector Intensity Measures (PGA, Ia, PGV and Sa s) Considering Regional Site Conditions Gang Wang and Wenqi Du Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Hong
Spatial Cross-correlation Models for Vector Intensity Measures (PGA, Ia, PGV and Sa s) Considering Regional Site Conditions Gang Wang and Wenqi Du Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Hong
Downtown Anchorage Seismic Risk Assessment & Land Use Regulations to Mitigate Seismic Risk
 Prepared for: The Municipality of Anchorage Planning Department and the Geotechnical Advisory Commission Downtown Anchorage Seismic Risk Assessment & Land Use Regulations to Mitigate Seismic Risk Prepared
Prepared for: The Municipality of Anchorage Planning Department and the Geotechnical Advisory Commission Downtown Anchorage Seismic Risk Assessment & Land Use Regulations to Mitigate Seismic Risk Prepared
log 4 0.7m log m Seismic Analysis of Structures by TK Dutta, Civil Department, IIT Delhi, New Delhi. Module 1 Seismology Exercise Problems :
 Seismic Analysis of Structures by TK Dutta, Civil Department, IIT Delhi, New Delhi. Module Seismology Exercise Problems :.4. Estimate the probabilities of surface rupture length, rupture area and maximum
Seismic Analysis of Structures by TK Dutta, Civil Department, IIT Delhi, New Delhi. Module Seismology Exercise Problems :.4. Estimate the probabilities of surface rupture length, rupture area and maximum
Deterministic Seismic Hazard Assessment of Quetta, Pakistan
 Deterministic Seismic Hazard Assessment of Quetta, Pakistan M.A. Shah Micro Seismic Studies Programme, Islamabad, Pakistan Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Islamabad, Pakistan M.
Deterministic Seismic Hazard Assessment of Quetta, Pakistan M.A. Shah Micro Seismic Studies Programme, Islamabad, Pakistan Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Islamabad, Pakistan M.
Ground-Motion Attenuation Relationships for Subduction- Zone Earthquakes in Northern Taiwan
 Ground-Motion Attenuation Relationships for Subduction- Zone Earthquakes in Northern Taiwan Lin, P.S., Lee, C.T. Bulletin of the Seismology Society of America (2008) Presenter: Yang Pei-Xin Adviser: Lee
Ground-Motion Attenuation Relationships for Subduction- Zone Earthquakes in Northern Taiwan Lin, P.S., Lee, C.T. Bulletin of the Seismology Society of America (2008) Presenter: Yang Pei-Xin Adviser: Lee
Understanding Seismic Hazard Needs for Infrastructure Risk Analysis: Lessons from SYNER-G
 Systemic Seismic Vulnerability and Risk Analysis for Buildings, Lifeline Networks and Infrastructures Safety Gain Understanding Seismic Hazard Needs for Infrastructure Risk Analysis: Lessons from SYNER-G
Systemic Seismic Vulnerability and Risk Analysis for Buildings, Lifeline Networks and Infrastructures Safety Gain Understanding Seismic Hazard Needs for Infrastructure Risk Analysis: Lessons from SYNER-G
Arthur Frankel, William Stephenson, David Carver, Jack Odum, Robert Williams, and Susan Rhea U.S. Geological Survey
 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Maps for Seattle: 3D Sedimentary Basin Effects, Nonlinear Site Response, and Uncertainties from Random Velocity Variations Arthur Frankel, William Stephenson, David Carver,
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Maps for Seattle: 3D Sedimentary Basin Effects, Nonlinear Site Response, and Uncertainties from Random Velocity Variations Arthur Frankel, William Stephenson, David Carver,
Naturgefahren Erdbebenrisiko. Seismische Gefährdungsanalyse. Evaluation of earthquake hazard
 Naturgefahren Erdbebenrisiko Nachdiplomkurs in angewandten Erdwissenschaft 15-19 Mai 2000 Seismische Gefährdungsanalyse ------------------------------------------- Evaluation of earthquake hazard Souad
Naturgefahren Erdbebenrisiko Nachdiplomkurs in angewandten Erdwissenschaft 15-19 Mai 2000 Seismische Gefährdungsanalyse ------------------------------------------- Evaluation of earthquake hazard Souad
Assessment and Mitigation of Ground Motion Hazards from Induced Seismicity. Gail M. Atkinson
 Assessment and Mitigation of Ground Motion Hazards from Induced Seismicity Gail M. Atkinson (with acknowledgement to many collaborators, especially Ghofrani and Assatourians) NSERC/TransAlta/Nanometrics
Assessment and Mitigation of Ground Motion Hazards from Induced Seismicity Gail M. Atkinson (with acknowledgement to many collaborators, especially Ghofrani and Assatourians) NSERC/TransAlta/Nanometrics
Incorporating simulated Hikurangi subduction interface spectra into probabilistic hazard calculations for Wellington
 Incorporating simulated Hikurangi subduction interface spectra into probabilistic hazard calculations for Wellington G.H. McVerry & C. Holden GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New Zealand. 2014 NZSEE Conference
Incorporating simulated Hikurangi subduction interface spectra into probabilistic hazard calculations for Wellington G.H. McVerry & C. Holden GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New Zealand. 2014 NZSEE Conference
PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM OBSERVED STRONG-MOTION RECORDS
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 3488 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 3488 PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MAPS AT GROUND SURFACE IN JAPAN BASED ON SITE EFFECTS ESTIMATED FROM
Preliminary probabilistic seismic hazard assessment for the Nuclear Power Plant Bohunice (Slovakia) site
 Preliminary probabilistic seismic hazard assessment for the Nuclear Power Plant Bohunice (Slovakia) site P. Labák, A. Bystrická & P. Moczo Geophysical Institute, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Dúbravská cesta
Preliminary probabilistic seismic hazard assessment for the Nuclear Power Plant Bohunice (Slovakia) site P. Labák, A. Bystrická & P. Moczo Geophysical Institute, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Dúbravská cesta
Model Uncertainties of the 2002 Update of California Seismic Hazard Maps
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 95, No. 6, pp. 24 257, December 25, doi: 1.1785/12517 Model Uncertainties of the 22 Update of California Seismic Hazard Maps by Tianqing Cao, Mark
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol. 95, No. 6, pp. 24 257, December 25, doi: 1.1785/12517 Model Uncertainties of the 22 Update of California Seismic Hazard Maps by Tianqing Cao, Mark
Application of a GIS for Earthquake Hazard Assessment and Risk Mitigation in Vietnam
 Application of a GIS for Earthquake Hazard Assessment and Risk Mitigation in Vietnam Nguyen Hong Phuong Earthquake Information and Tsunami Warning Centre, VAST OUTLINE Introduction Fault Source Model and
Application of a GIS for Earthquake Hazard Assessment and Risk Mitigation in Vietnam Nguyen Hong Phuong Earthquake Information and Tsunami Warning Centre, VAST OUTLINE Introduction Fault Source Model and
Site specific seismic hazard assessment a case study of Guanyin offshore wind farm 場址特定地震危害度評估 - 以觀音離岸風力發電廠為例
 Site specific seismic hazard assessment a case study of Guanyin offshore wind farm 場址特定地震危害度評估 - 以觀音離岸風力發電廠為例 Supervisor : Dr. Chyi-Tyi Lee and Dr. Kuo-Fong Ma Speaker : Jia-Cian Gao 2018/04/26 1 1. A
Site specific seismic hazard assessment a case study of Guanyin offshore wind farm 場址特定地震危害度評估 - 以觀音離岸風力發電廠為例 Supervisor : Dr. Chyi-Tyi Lee and Dr. Kuo-Fong Ma Speaker : Jia-Cian Gao 2018/04/26 1 1. A
(Seismological Research Letters, July/August 2005, Vol.76 (4): )
 (Seismological Research Letters, July/August 2005, Vol.76 (4):466-471) Comment on How Can Seismic Hazard around the New Madrid Seismic Zone Be Similar to that in California? by Arthur Frankel Zhenming
(Seismological Research Letters, July/August 2005, Vol.76 (4):466-471) Comment on How Can Seismic Hazard around the New Madrid Seismic Zone Be Similar to that in California? by Arthur Frankel Zhenming
Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard.
 Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard. T. Dhu, D. Robinson, C. Sinadinovski, T. Jones, A. Jones & J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, Australia.
Probabilistic Earthquake Risk Assessment of Newcastle and Lake Macquarie Part 1 Seismic Hazard. T. Dhu, D. Robinson, C. Sinadinovski, T. Jones, A. Jones & J. Schneider Geoscience Australia, Canberra, Australia.
PROJECT SITE. Ione St. VICINITY MAP. Sutter. Creek. Jackson. Newman Ridge Quarry Project Amador County, California. Scale in Miles. Old. Rd.
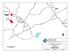 124 Old Hwy. Ione Michigan Bar Irish Hill Ione Sutter Creek Ridge PROJECT SITE Dutschke Mile Dr. 124 Sutter Loch Lane Res. Old Five Stockton Castle Oaks Golf Club Marlette Ione St. 124 Charles Howard Park
124 Old Hwy. Ione Michigan Bar Irish Hill Ione Sutter Creek Ridge PROJECT SITE Dutschke Mile Dr. 124 Sutter Loch Lane Res. Old Five Stockton Castle Oaks Golf Club Marlette Ione St. 124 Charles Howard Park
Japan Seismic Hazard Information Station
 Japan Seismic Hazard Information Station (J-SHIS) Hiroyuki Fujiwara National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention (NIED) Background of the Project Headquarters for Earthquake Research
Japan Seismic Hazard Information Station (J-SHIS) Hiroyuki Fujiwara National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Prevention (NIED) Background of the Project Headquarters for Earthquake Research
Ground Motion Prediction Equations: Past, Present, and Future
 Ground Motion Prediction Equations: Past, Present, and Future The 2014 William B. Joyner Lecture David M. Boore As presented at the SMIP15 meeting, Davis, California, 22 October 2015 The William B. Joyner
Ground Motion Prediction Equations: Past, Present, and Future The 2014 William B. Joyner Lecture David M. Boore As presented at the SMIP15 meeting, Davis, California, 22 October 2015 The William B. Joyner
Uncertainties in a probabilistic model for seismic hazard analysis in Japan
 Uncertainties in a probabilistic model for seismic hazard analysis in Japan T. Annaka* and H. Yashiro* * Tokyo Electric Power Services Co., Ltd., Japan ** The Tokio Marine and Fire Insurance Co., Ltd.,
Uncertainties in a probabilistic model for seismic hazard analysis in Japan T. Annaka* and H. Yashiro* * Tokyo Electric Power Services Co., Ltd., Japan ** The Tokio Marine and Fire Insurance Co., Ltd.,
Occurrence of negative epsilon in seismic hazard analysis deaggregation, and its impact on target spectra computation
 Occurrence of negative epsilon in seismic hazard analysis deaggregation, and its impact on target spectra computation Lynne S. Burks 1 and Jack W. Baker Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Occurrence of negative epsilon in seismic hazard analysis deaggregation, and its impact on target spectra computation Lynne S. Burks 1 and Jack W. Baker Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
DCPP Seismic FAQ s Geosciences Department 08/04/2011 GM1) What magnitude earthquake is DCPP designed for?
 GM1) What magnitude earthquake is DCPP designed for? The new design ground motions for DCPP were developed after the discovery of the Hosgri fault. In 1977, the largest magnitude of the Hosgri fault was
GM1) What magnitude earthquake is DCPP designed for? The new design ground motions for DCPP were developed after the discovery of the Hosgri fault. In 1977, the largest magnitude of the Hosgri fault was
PROBABILISTIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT OF FAULT DISPLACEMENTS
 PROBABILISTIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT OF FAULT DISPLACEMENTS R. Sigbjörnsson, 1 J.Th. Snæbjörnsson, 2 S.M. Higgins, 3 S. Ólafsson 3 and B. Halldórsson 3 ABSTRACT: 1 Professor, EERC, School of Engineering and
PROBABILISTIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT OF FAULT DISPLACEMENTS R. Sigbjörnsson, 1 J.Th. Snæbjörnsson, 2 S.M. Higgins, 3 S. Ólafsson 3 and B. Halldórsson 3 ABSTRACT: 1 Professor, EERC, School of Engineering and
Spatial variation of maximum considered and design basis earthquakes in peninsular India
 Spatial variation of maximum considered and design basis earthquakes in peninsular India Kishor Jaiswal and Ravi Sinha* Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai 400
Spatial variation of maximum considered and design basis earthquakes in peninsular India Kishor Jaiswal and Ravi Sinha* Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai 400
ROSE SCHOOL AN INVESTIGATIVE STUDY ON THE MODELLING OF EARTHQUAKE HAZARD FOR LOSS ASSESSMENT
 I.U.S.S. Istituto Universitario di Studi Superiori Università degli Studi di Pavia EUROPEAN SCHOOL FOR ADVANCED STUDIES IN REDUCTION OF SEISMIC RISK ROSE SCHOOL AN INVESTIGATIVE STUDY ON THE MODELLING
I.U.S.S. Istituto Universitario di Studi Superiori Università degli Studi di Pavia EUROPEAN SCHOOL FOR ADVANCED STUDIES IN REDUCTION OF SEISMIC RISK ROSE SCHOOL AN INVESTIGATIVE STUDY ON THE MODELLING
PACIFIC EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING RESEARCH CENTER
 PACIFIC EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING RESEARCH CENTER Identification of Site Parameters that Improve Predictions of Site Amplification Ellen M. Rathje Sara Navidi Department of Civil, Architectural, and Environmental
PACIFIC EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING RESEARCH CENTER Identification of Site Parameters that Improve Predictions of Site Amplification Ellen M. Rathje Sara Navidi Department of Civil, Architectural, and Environmental
2C09 Design for seismic and climate changes
 2C09 Design for seismic and climate changes Lecture 10: Characterisation of seismic motion Aurel Stratan, Politehnica University of Timisoara 07/04/2017 European Erasmus Mundus Master Course Sustainable
2C09 Design for seismic and climate changes Lecture 10: Characterisation of seismic motion Aurel Stratan, Politehnica University of Timisoara 07/04/2017 European Erasmus Mundus Master Course Sustainable
Analysis Of Earthquake Records of Istanbul Earthquake Rapid Response System Stations Related to the Determination of Site Fundamental Frequency
 Analysis Of Earthquake Records of Istanbul Earthquake Rapid Response System Stations Related to the Determination of Site Fundamental Frequency A. C. Zulfikar, H. Alcik & E. Cakti Bogazici University,Kandilli
Analysis Of Earthquake Records of Istanbul Earthquake Rapid Response System Stations Related to the Determination of Site Fundamental Frequency A. C. Zulfikar, H. Alcik & E. Cakti Bogazici University,Kandilli
A NEW PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MODEL FOR NEW ZEALAND
 A NEW PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MODEL FOR NEW ZEALAND Mark W STIRLING 1 SUMMARY The Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences (GNS) has developed a new seismic hazard model for New Zealand that incorporates
A NEW PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD MODEL FOR NEW ZEALAND Mark W STIRLING 1 SUMMARY The Institute of Geological and Nuclear Sciences (GNS) has developed a new seismic hazard model for New Zealand that incorporates
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis of Nepal considering Uniform Density Model
 Proceedings of IOE Graduate Conference, 2016 pp. 115 122 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis of Nepal considering Uniform Density Model Sunita Ghimire 1, Hari Ram Parajuli 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering,
Proceedings of IOE Graduate Conference, 2016 pp. 115 122 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis of Nepal considering Uniform Density Model Sunita Ghimire 1, Hari Ram Parajuli 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering,
IGC. 50 th INDIAN GEOTECHNICAL CONFERENCE PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS FOR WARANGAL CONSIDERING SINGLE SEISMOGENIC ZONING
 50 th IGC 50 th INDIAN GEOTECHNICAL CONFERENCE 17 th 19 th DECEMBER 2015, Pune, Maharashtra, India Venue: College of Engineering (Estd. 1854), Pune, India PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS FOR WARANGAL
50 th IGC 50 th INDIAN GEOTECHNICAL CONFERENCE 17 th 19 th DECEMBER 2015, Pune, Maharashtra, India Venue: College of Engineering (Estd. 1854), Pune, India PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS FOR WARANGAL
PROBABILITY-BASED DESIGN EARTHQUAKE LOAD CONSIDERING ACTIVE FAULT
 PROBABILITY-BASED DESIGN EARTHUAKE LOAD CONSIDERING ACTIVE FAULT Jun KANDA And Ichiro SATOH SUMMARY The probability-based structural design can provide a specific safety performance demand for the earthquake
PROBABILITY-BASED DESIGN EARTHUAKE LOAD CONSIDERING ACTIVE FAULT Jun KANDA And Ichiro SATOH SUMMARY The probability-based structural design can provide a specific safety performance demand for the earthquake
Shaking Hazard Compatible Methodology for Probabilistic Assessment of Fault Displacement Hazard
 Surface Fault Displacement Hazard Workshop PEER, Berkeley, May 20-21, 2009 Shaking Hazard Compatible Methodology for Probabilistic Assessment of Fault Displacement Hazard Maria Todorovska Civil & Environmental
Surface Fault Displacement Hazard Workshop PEER, Berkeley, May 20-21, 2009 Shaking Hazard Compatible Methodology for Probabilistic Assessment of Fault Displacement Hazard Maria Todorovska Civil & Environmental
Actual practices of seismic strong motion estimation at NPP sites
 ANSN Regional Workshop on Site Selection and Evaluation for Nuclear Power Plants June 2010, Hanoi Vietnam IAEA/ISSC Actual practices of seismic strong motion estimation at NPP sites Yoshi. FUKUSHIMA (JNES)
ANSN Regional Workshop on Site Selection and Evaluation for Nuclear Power Plants June 2010, Hanoi Vietnam IAEA/ISSC Actual practices of seismic strong motion estimation at NPP sites Yoshi. FUKUSHIMA (JNES)
Development of Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis for International Sites, Challenges and Guidelines
 Development of Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis for International Sites, Challenges and Guidelines ABSTRACT Dr. Antonio Fernandez Ares Paul C. Rizzo Associates, Inc. 500 Penn Center Boulevard, Suite
Development of Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis for International Sites, Challenges and Guidelines ABSTRACT Dr. Antonio Fernandez Ares Paul C. Rizzo Associates, Inc. 500 Penn Center Boulevard, Suite
Borah Peak Earthquake HAZUS Scenario Project Executive Summary Idaho Bureau of Homeland Security Idaho Geological Survey Western States Seismic
 Borah Peak Earthquake HAZUS Scenario Project Executive Summary Idaho Bureau of Homeland Security Idaho Geological Survey Western States Seismic Policy Council 12/30/2008 The HAZUS-MH analysis of the Borah
Borah Peak Earthquake HAZUS Scenario Project Executive Summary Idaho Bureau of Homeland Security Idaho Geological Survey Western States Seismic Policy Council 12/30/2008 The HAZUS-MH analysis of the Borah
DIRECT HAZARD ANALYSIS OF INELASTIC RESPONSE SPECTRA
 DIRECT HAZARD ANALYSIS OF INELASTIC RESPONSE SPECTRA ABSTRACT Y. Bozorgnia, M. Hachem, and K.W. Campbell Associate Director, PEER, University of California, Berkeley, California, USA Senior Associate,
DIRECT HAZARD ANALYSIS OF INELASTIC RESPONSE SPECTRA ABSTRACT Y. Bozorgnia, M. Hachem, and K.W. Campbell Associate Director, PEER, University of California, Berkeley, California, USA Senior Associate,
CHARACTERIZING SPATIAL CROSS-CORRELATION BETWEEN GROUND- MOTION SPECTRAL ACCELERATIONS AT MULTIPLE PERIODS. Nirmal Jayaram 1 and Jack W.
 Proceedings of the 9th U.S. National and 10th Canadian Conference on Earthquake Engineering Compte Rendu de la 9ième Conférence Nationale Américaine et 10ième Conférence Canadienne de Génie Parasismique
Proceedings of the 9th U.S. National and 10th Canadian Conference on Earthquake Engineering Compte Rendu de la 9ième Conférence Nationale Américaine et 10ième Conférence Canadienne de Génie Parasismique
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Maps in Dam Foundation
 Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Maps in Dam Foundation by Hideaki Kawasaki 1, Masafumi Kondo 2, Akira Nakamura 3, Kenji Inagaki 4 ABSTRACT Because Japan is one of the world s most earthquake prone countries,
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Maps in Dam Foundation by Hideaki Kawasaki 1, Masafumi Kondo 2, Akira Nakamura 3, Kenji Inagaki 4 ABSTRACT Because Japan is one of the world s most earthquake prone countries,
2 Approaches To Developing Design Ground Motions
 2 Approaches To Developing Design Ground Motions There are two basic approaches to developing design ground motions that are commonly used in practice: deterministic and probabilistic. While both approaches
2 Approaches To Developing Design Ground Motions There are two basic approaches to developing design ground motions that are commonly used in practice: deterministic and probabilistic. While both approaches
CHARACTERIZATION OF EARTHQUAKE SHAKING EFFECTS
 1. Introduction CHARACTERIZATION OF EARTHQUAKE SHAKING EFFECTS This section presents information on engineering seismology and engineering characterization of earthquakes. The key references for this module
1. Introduction CHARACTERIZATION OF EARTHQUAKE SHAKING EFFECTS This section presents information on engineering seismology and engineering characterization of earthquakes. The key references for this module
UPDATE OF THE PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF SEISMIC DESIGN GROUND MOTIONS AT THE LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL LABORATORY
 F I N A L R E P O R T UPDATE OF THE PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF SEISMIC DESIGN GROUND MOTIONS AT THE LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL LABORATORY Prepared for Los Alamos National Laboratory
F I N A L R E P O R T UPDATE OF THE PROBABILISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ANALYSIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF SEISMIC DESIGN GROUND MOTIONS AT THE LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL LABORATORY Prepared for Los Alamos National Laboratory
Vertical to Horizontal (V/H) Ratios for Large Megathrust Subduction Zone Earthquakes
 Vertical to Horizontal (V/H) Ratios for Large Megathrust Subduction Zone Earthquakes N.J. Gregor Consultant, Oakland, California, USA N.A. Abrahamson University of California, Berkeley, USA K.O. Addo BC
Vertical to Horizontal (V/H) Ratios for Large Megathrust Subduction Zone Earthquakes N.J. Gregor Consultant, Oakland, California, USA N.A. Abrahamson University of California, Berkeley, USA K.O. Addo BC
NEXT GENERATION ATTENUATION (NGA) EMPIRICAL GROUND MOTION MODELS: CAN THEY BE USED IN EUROPE?
 First European Conference on Earthquake Engineering and Seismology (a joint event of the 13 th ECEE & 30 th General Assembly of the ESC) Geneva, Switzerland, 3-8 September 2006 Paper Number: 458 NEXT GENERATION
First European Conference on Earthquake Engineering and Seismology (a joint event of the 13 th ECEE & 30 th General Assembly of the ESC) Geneva, Switzerland, 3-8 September 2006 Paper Number: 458 NEXT GENERATION
A. Akinci 1, M. Murru 1, R. Console 2, G. Falcone 1, S. Pucci 1 1. Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia, Rome, Italy 2
 Earthquake Forecasting Models and their Impact on the Ground Motion Hazard in the Marmara Region, Turkey A. Akinci 1, M. Murru 1, R. Console 2, G. Falcone 1, S. Pucci 1 1 Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica
Earthquake Forecasting Models and their Impact on the Ground Motion Hazard in the Marmara Region, Turkey A. Akinci 1, M. Murru 1, R. Console 2, G. Falcone 1, S. Pucci 1 1 Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica
L. Danciu, D. Giardini, J. Wößner Swiss Seismological Service ETH-Zurich Switzerland
 BUILDING CAPACITIES FOR ELABORATION OF NDPs AND NAs OF THE EUROCODES IN THE BALKAN REGION Experience on the field of seismic hazard zonation SHARE Project L. Danciu, D. Giardini, J. Wößner Swiss Seismological
BUILDING CAPACITIES FOR ELABORATION OF NDPs AND NAs OF THE EUROCODES IN THE BALKAN REGION Experience on the field of seismic hazard zonation SHARE Project L. Danciu, D. Giardini, J. Wößner Swiss Seismological
Evaluation of Acceleration Time-Histories for Design of Nuclear Facilities at Kalpakkam (India)
 Evaluation of Acceleration Time-Histories for Design of Nuclear Facilities at Kalpakkam (India) L. Kanagarathinam, G. R. Dodagoudar & A. Boominathan Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai SUMMARY:
Evaluation of Acceleration Time-Histories for Design of Nuclear Facilities at Kalpakkam (India) L. Kanagarathinam, G. R. Dodagoudar & A. Boominathan Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai SUMMARY:
Section Forces Within Earth. 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes
 Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
SEISMIC RISK ANALYSIS OF L AQUILA GAS DISTRIBUTION NETWORK Paper ID. 2999
 SEISMIC RISK ANALYSIS OF L AQUILA GAS DISTRIBUTION NETWORK Paper ID. 2999 Simona Esposito, Iunio Iervolino Department of Structural Engineering, University of Naples Federico II A gas distribution system
SEISMIC RISK ANALYSIS OF L AQUILA GAS DISTRIBUTION NETWORK Paper ID. 2999 Simona Esposito, Iunio Iervolino Department of Structural Engineering, University of Naples Federico II A gas distribution system
EARTHQUAKE CLUSTERS, SMALL EARTHQUAKES
 EARTHQUAKE CLUSTERS, SMALL EARTHQUAKES AND THEIR TREATMENT FOR HAZARD ESTIMATION Gary Gibson and Amy Brown RMIT University, Melbourne Seismology Research Centre, Bundoora AUTHORS Gary Gibson wrote his
EARTHQUAKE CLUSTERS, SMALL EARTHQUAKES AND THEIR TREATMENT FOR HAZARD ESTIMATION Gary Gibson and Amy Brown RMIT University, Melbourne Seismology Research Centre, Bundoora AUTHORS Gary Gibson wrote his
THE USE OF INPUT ENERGY FOR SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT WITH DIFFERENT DUCTILITY LEVEL
 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, Paper No. 8 THE USE OF INPUT ENERGY FOR SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT WITH DIFFERENT DUCTILITY LEVEL Mao-Sheng GONG And Li-Li
th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, Paper No. 8 THE USE OF INPUT ENERGY FOR SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT WITH DIFFERENT DUCTILITY LEVEL Mao-Sheng GONG And Li-Li
Unique Site Conditions and Response Analysis Challenges in the Central and Eastern U.S.
 Unique Site Conditions and Response Analysis Challenges in the Central and Eastern U.S. James R. Martin, C. Guney Olgun, & Morgan Eddy Civil and Environmental Engineering World Institute for Disaster Risk
Unique Site Conditions and Response Analysis Challenges in the Central and Eastern U.S. James R. Martin, C. Guney Olgun, & Morgan Eddy Civil and Environmental Engineering World Institute for Disaster Risk
Overview of National Seismic Hazard Maps for the next National Building Code
 Overview of National Seismic Hazard Maps for the next National Building Code John Adams Earthquakes Canada Geological Survey of Canada Copyright. Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, 2004 CSCE Workshop
Overview of National Seismic Hazard Maps for the next National Building Code John Adams Earthquakes Canada Geological Survey of Canada Copyright. Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, 2004 CSCE Workshop
ENGINEERING GROUND MOTION PARAMETERS ATTENUATION RELATIONSHIPS FOR GREECE
 ENGINEERING GROUND MOTION PARAMETERS ATTENUATION RELATIONSHIPS FOR GREECE Laurentiu Danciu and G-Akis Tselentis 1 SUMMARY Engineering ground motion parameters can be used to describe the damage potential
ENGINEERING GROUND MOTION PARAMETERS ATTENUATION RELATIONSHIPS FOR GREECE Laurentiu Danciu and G-Akis Tselentis 1 SUMMARY Engineering ground motion parameters can be used to describe the damage potential
Estimation of Seismic Hazard Using PSHA in and around National Capital Region (NCR) of India
 Geosciences 2017, 7(4): 109-116 DOI: 10.5923/j.geo.20170704.01 Estimation of Seismic Hazard Using PSHA in and around National Capital Region (NCR) of India S. Sarkar, D. Shanker * Department of Earthquake
Geosciences 2017, 7(4): 109-116 DOI: 10.5923/j.geo.20170704.01 Estimation of Seismic Hazard Using PSHA in and around National Capital Region (NCR) of India S. Sarkar, D. Shanker * Department of Earthquake
Scientific Research on the Cascadia Subduction Zone that Will Help Improve Seismic Hazard Maps, Building Codes, and Other Risk-Mitigation Measures
 Scientific Research on the Cascadia Subduction Zone that Will Help Improve Seismic Hazard Maps, Building Codes, and Other Risk-Mitigation Measures Art Frankel U.S. Geological Survey Seattle, WA GeoPrisms-Earthscope
Scientific Research on the Cascadia Subduction Zone that Will Help Improve Seismic Hazard Maps, Building Codes, and Other Risk-Mitigation Measures Art Frankel U.S. Geological Survey Seattle, WA GeoPrisms-Earthscope
Spatial Correlation of Ground Motions in Seismic Hazard Assessment
 Spatial Correlation of Ground Motions in Seismic Hazard Assessment Taojun Liu tliu82@uwo.ca Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering University of Western Ontario London, Ontario, Canada 1 Outline
Spatial Correlation of Ground Motions in Seismic Hazard Assessment Taojun Liu tliu82@uwo.ca Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering University of Western Ontario London, Ontario, Canada 1 Outline
Preview Mode: ON Earthquake Risk in Stable, Intraplate Regions: the Case. of Perth, Australia. Historical Seismicity in the Perth Region
 Preview Mode: ON Earthquake Risk in Stable, Intraplate Regions: the Case Editor s note: There is often a tendency to discount earthquake risk in of Perth, Australia 02.2010 AIRCurrents regions where earthquakes
Preview Mode: ON Earthquake Risk in Stable, Intraplate Regions: the Case Editor s note: There is often a tendency to discount earthquake risk in of Perth, Australia 02.2010 AIRCurrents regions where earthquakes
Introduction to Strong Motion Seismology. Norm Abrahamson Pacific Gas & Electric Company SSA/EERI Tutorial 4/21/06
 Introduction to Strong Motion Seismology Norm Abrahamson Pacific Gas & Electric Company SSA/EERI Tutorial 4/21/06 Probabilistic Methods Deterministic Approach Select a small number of individual earthquake
Introduction to Strong Motion Seismology Norm Abrahamson Pacific Gas & Electric Company SSA/EERI Tutorial 4/21/06 Probabilistic Methods Deterministic Approach Select a small number of individual earthquake
I N T R O D U C T I O N T O P R O B A B I L I S T I C S E I S M I C H A Z A R D A N A LY S I S
 I N T R O D U C T I O N T O P R O B A B I L I S T I C S E I S M I C H A Z A R D A N A LY S I S J A C K W. B A K E R Copyright 2015 Jack W. Baker Preferred citation for this document: Baker, Jack W. (2015)
I N T R O D U C T I O N T O P R O B A B I L I S T I C S E I S M I C H A Z A R D A N A LY S I S J A C K W. B A K E R Copyright 2015 Jack W. Baker Preferred citation for this document: Baker, Jack W. (2015)
Comparisons of Ground Motions from the 1999 Chi-Chi Earthquake with Empirical Predictions Largely Based on Data from California
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 9, 5, pp. 7, October 00 Comparisons of Ground Motions from the 999 Chi-Chi Earthquake with Empirical Predictions Largely Based on Data from California
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 9, 5, pp. 7, October 00 Comparisons of Ground Motions from the 999 Chi-Chi Earthquake with Empirical Predictions Largely Based on Data from California
Preliminary Earthquake Risk Management Strategy Plan of Eskisehir, Turkey by using GIS
 Preliminary Earthquake Risk Management Strategy Plan of Eskisehir, Turkey by using GIS Metin Altan, Ferah Özturk and Can Ayday Space and Satellite Sciences Research Institute Anadolu University, TURKEY
Preliminary Earthquake Risk Management Strategy Plan of Eskisehir, Turkey by using GIS Metin Altan, Ferah Özturk and Can Ayday Space and Satellite Sciences Research Institute Anadolu University, TURKEY
Professor Terje Haukaas University of British Columbia, Vancouver terje.civil.ubc.ca. Earthquakes
 Earthquakes In 1963 research concluded that sea floors and continents drift horizontally and soon after, in 1968, the term plate tectonics was established. This represented a paradigm shift in geology
Earthquakes In 1963 research concluded that sea floors and continents drift horizontally and soon after, in 1968, the term plate tectonics was established. This represented a paradigm shift in geology
PROPOSED CHANGE TO THE 2012 BUILDING CODE O. REG. 332/12 AS AMENDED
 Ministry of Municipal Affairs PROPOSED CHANGE TO THE 2012 BUILDING CODE O. REG. 332/12 AS AMENDED CHANGE NUMBER: SOURCE: B-04-01-15 Ontario-NBC CODE REFERENCE: Division B / 4.1.8.2. Division B / 4.1.8.4.
Ministry of Municipal Affairs PROPOSED CHANGE TO THE 2012 BUILDING CODE O. REG. 332/12 AS AMENDED CHANGE NUMBER: SOURCE: B-04-01-15 Ontario-NBC CODE REFERENCE: Division B / 4.1.8.2. Division B / 4.1.8.4.
CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY
 32 CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY 3.1 GENERAL In 1910, the seismological society of America identified the three groups of earthquake problems, the associated ground motions and the effect on structures. Indeed
32 CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY 3.1 GENERAL In 1910, the seismological society of America identified the three groups of earthquake problems, the associated ground motions and the effect on structures. Indeed
PROBABILISTIC PERFORMANCE-BASED SEISMIC DEMAND MODEL FOR R/C FRAME BUILDINGS
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 1547 PROBABILISTIC PERFORMANCE-BASED SEISMIC DEMAND MODEL FOR R/C FRAME BUILDINGS Srdjan JANKOVIC 1 and
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 1547 PROBABILISTIC PERFORMANCE-BASED SEISMIC DEMAND MODEL FOR R/C FRAME BUILDINGS Srdjan JANKOVIC 1 and
I N T R O D U C T I O N T O P R O B A B I L I S T I C S E I S M I C H A Z A R D A N A LY S I S
 I N T R O D U C T I O N T O P R O B A B I L I S T I C S E I S M I C H A Z A R D A N A LY S I S J A C K W. B A K E R Copyright 2013 Jack W. Baker Preferred citation for this document: Baker, Jack W. (2013)
I N T R O D U C T I O N T O P R O B A B I L I S T I C S E I S M I C H A Z A R D A N A LY S I S J A C K W. B A K E R Copyright 2013 Jack W. Baker Preferred citation for this document: Baker, Jack W. (2013)
NEODETERMINISTIC SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT. Seismic hazard in Asia Trieste 4-8 December 2006
 H4.SMR/1882-2 Seismic Hazard in Asia 4-8 December 2006 Neodeterministic Hazard Assessment G.F. Panza 1, 2 1 Department of Earth Sciences University of Trieste 2 ICTP SAND Group, Trieste NEODETERMINISTIC
H4.SMR/1882-2 Seismic Hazard in Asia 4-8 December 2006 Neodeterministic Hazard Assessment G.F. Panza 1, 2 1 Department of Earth Sciences University of Trieste 2 ICTP SAND Group, Trieste NEODETERMINISTIC
SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT AND SITE-DEPENDENT RESPONSE SPECTRA PARAMETERS OF THE CURRENT SEISMIC DESIGN CODE IN ALBANIA
 SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT AND SITE-DEPENDENT RESPONSE SPECTRA PARAMETERS OF THE CURRENT SEISMIC DESIGN CODE IN ALBANIA Ll. Duni & N. Kuka Institute of Seismology, Academy of Sciences, Tirana, Albania ABSTRACT:
SEISMIC HAZARD ASSESSMENT AND SITE-DEPENDENT RESPONSE SPECTRA PARAMETERS OF THE CURRENT SEISMIC DESIGN CODE IN ALBANIA Ll. Duni & N. Kuka Institute of Seismology, Academy of Sciences, Tirana, Albania ABSTRACT:
Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard. Earthquake Environment
 Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard Ultimately what we want is a seismic intensity measure that will allow us to quantify effect of an earthquake on a structure. S a
Part 2 - Engineering Characterization of Earthquakes and Seismic Hazard Ultimately what we want is a seismic intensity measure that will allow us to quantify effect of an earthquake on a structure. S a
Updated NGA-West2 Ground Motion Prediction Equations for Active Tectonic Regions Worldwide
 Updated NGA-West2 Ground Motion Prediction Equations for Active Tectonic Regions Worldwide Kenneth W. Campbell 1 and Yousef Bozorgnia 2 1. Corresponding Author. Vice President, EQECAT, Inc., 1130 NW 161st
Updated NGA-West2 Ground Motion Prediction Equations for Active Tectonic Regions Worldwide Kenneth W. Campbell 1 and Yousef Bozorgnia 2 1. Corresponding Author. Vice President, EQECAT, Inc., 1130 NW 161st
THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR
 JURNAL KEJURUTERAAN AWAM (JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING) Vol. 15 No. 2, 2002 THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR Assoc. Prof. Dr. Azlan Adnan Hendriyawan Structural Earthquake
JURNAL KEJURUTERAAN AWAM (JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING) Vol. 15 No. 2, 2002 THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR Assoc. Prof. Dr. Azlan Adnan Hendriyawan Structural Earthquake
DEVELOPMENT OF DESIGN RESPONSE SPECTRAL SHAPES FOR CENTRAL AND EASTERN U.S. (CEUS) AND WESTERN U.S. (WUS) ROCK SITE CONDITIONS*
 DEVELOPMENT OF DESIGN RESPONSE SPECTRAL SHAPES FOR CENTRAL AND EASTERN U.S. (CEUS) AND WESTERN U.S. (WUS) ROCK SITE CONDITIONS* 1 INTRODUCTION W. J. Silva, R.R. Youngs, and I.M. Idriss In developing response
DEVELOPMENT OF DESIGN RESPONSE SPECTRAL SHAPES FOR CENTRAL AND EASTERN U.S. (CEUS) AND WESTERN U.S. (WUS) ROCK SITE CONDITIONS* 1 INTRODUCTION W. J. Silva, R.R. Youngs, and I.M. Idriss In developing response
CAMPBELL-BOZORGNIA NEXT GENERATION ATTENUATION (NGA) RELATIONS FOR PGA, PGV AND SPECTRAL ACCELERATION: A PROGRESS REPORT
 Proceedings of the 8 th U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering April 18-22, 2006, San Francisco, California, USA Paper No. 906 CAMPBELL-BOZORGNIA NEXT GENERATION ATTENUATION (NGA) RELATIONS
Proceedings of the 8 th U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering April 18-22, 2006, San Francisco, California, USA Paper No. 906 CAMPBELL-BOZORGNIA NEXT GENERATION ATTENUATION (NGA) RELATIONS
Geo-Marine Letters Volume 36, 2016, electronic supplementary material
 1 Geo-Marine Letters Volume 36, 016, electronic supplementary material Submarine landslides offshore Vancouver Island along the northern Cascadia margin, British Columbia: why preconditioning is likely
1 Geo-Marine Letters Volume 36, 016, electronic supplementary material Submarine landslides offshore Vancouver Island along the northern Cascadia margin, British Columbia: why preconditioning is likely
An Approach for Seismic Design in Malaysia following the Principles of Eurocode 8
 An Approach for Seismic Design in Malaysia following the Principles of Eurocode 8 by Dr J. W. Pappin, Ms. P. H. I. Yim and Mr. C. H. R. Koo 1. INTRODUCTION Eurocode 8 is a useful document providing systematic
An Approach for Seismic Design in Malaysia following the Principles of Eurocode 8 by Dr J. W. Pappin, Ms. P. H. I. Yim and Mr. C. H. R. Koo 1. INTRODUCTION Eurocode 8 is a useful document providing systematic
