Recent advances in the analysis of volatiles and fluid-mobile elements in melt inclusions by Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS)
|
|
|
- Quentin Anthony
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Edinburgh Research Explorer Recent advances in the analysis of volatiles and fluid-mobile elements in melt inclusions by Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Citation for published version: De Hoog, C-J & Hinton, R 2015, 'Recent advances in the analysis of volatiles and fluid-mobile elements in melt inclusions by Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS)' ECROFI XXII, Leeds, United Kingdom, 27/06/15-29/06/15,. Link: Link to publication record in Edinburgh Research Explorer Document Version: Peer reviewed version General rights Copyright for the publications made accessible via the Edinburgh Research Explorer is retained by the author(s) and / or other copyright owners and it is a condition of accessing these publications that users recognise and abide by the legal requirements associated with these rights. Take down policy The University of Edinburgh has made every reasonable effort to ensure that Edinburgh Research Explorer content complies with UK legislation. If you believe that the public display of this file breaches copyright please contact openaccess@ed.ac.uk providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. Download date: 10. Jan. 2019
2 European Current Research On Fluid Inclusions (ECROFI-XXIII), Recent Advances in the Analysis of Volatiles and Fluid-Mobile Elements in Melt Inclusions by Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Jan C. M. De Hoog, R. W. Hinton & EIMF Edinburgh Ion Microprobe Facility, School of GeoSciences, University of Edinburgh, Introduction Melt inclusions are micrometre-sized pockets of melt trapped in crystals while they crystallise from magma. The crystal host acts as a robust container, shielding the melt inclusion from late stage volcanic processes such as eruption, crystallisation and degassing. Hence, melt inclusions may provide a wealth of information about pre-eruptive conditions of the magma, in particular the volatile species H 2O, CO 2, S, Cl and F, which are often lost from the magma during its evolution and eruption. Several analytical techniques are capable of determining volatile concentrations in melt inclusions at the high spatial resolution needed ( micrometre), but few are as versatile as Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS or ionprobe). This technique is capable not only of determining elemental concentrations of most volatiles down to ppm level, but also isotopic ratios of these species. In addition, many elements can be analysed simultaneously with volatiles, including fluid-mobile elements such as lithium and boron. The SIMS technique works by sputtering small amounts of material of the sample surface using a high-energy focused ion beam, typically composed of 16 O - or 133 Cs +. This sputtered material is accelerated into a mass spectrometer and ion intensities are counted using an electron multiplier or Faraday cup. Multi-collector detection is also possible. The analysis pit is typically ca µm wide and several µm deep (Fig. 1). Sample requirements are modest, most importantly a flat surface and compatibility with high vacuum (10-9 mbar). As every analytical technique, SIMS has its limitations, the most critical one being the need of well-characterised and matrix-matched calibration standards. The following sections will briefly discuss the analytical details of different volatile and fluid-mobile elements as currently employed by the Edinburgh Ion Microprobe Facility (EIMF). This NERCsupported facility hosts two ion microprobes each with their own strengths, a small geometry Cameca IMS 4f and a large geometry, highresolution Cameca IMS Figure 1. Secondary electron image showing the pits created by the two stages of SIMS analysis conducted on a zircon-hosted melt inclusion. The largest oval represents the pit generated by the boron isotope analysis, the smaller oval is the pit generated by the trace element analysis. DM = daughter mineral (magnetite). H 2O Water is typically the most abundant volatile in melt inclusions and provides key information about pre-eruptive volatile contents, magma storage depths, volcanic gas emissions and water content of the magma source [e.g., 1]. It can be measured in silicate glasses as 1 H or 16 O 1 H. Of all volatiles, good vacuum conditions are most critical for water analyses (<10-9 mbar). Therefore, where possible samples are mounted in indium, which has superior outgassing properties compared to more commonly used epoxy resins. At EIMF, H 2O is generally measured using the Cameca IMS 4f using a 16 O- primary beam and collecting H + ions. This allows it to be measured at the same time as light volatile elements and trace elements up to z = The Cameca IMS 4f is preferred due to its fast peak switching capability and excellent vacuum control, including an eight-sample air lock and a cryogenic pump.
3 H 2 O wt% (FTIR) Counts per second European Current Research On Fluid Inclusions (ECROFI-XXIII), During analysis of silicate glasses, ion intensities are commonly counted relative to that of 30 Si and corrected for the amount of SiO 2 in the sample (determined independently by, e.g., electron microprobe, EPMA). Working curves are calculated by measuring several standard reference materials and plotting known H 2O/SiO 2 vs measured 1 H/ 30 Si. Doing that, a strong matrix-induced bias is observed between s (SiO 2 ca. 50 wt%) and s (SiO 2 ca. 70 wt%). This effect, rather fortuitously, scales with the amount of SiO 2 in the sample. Omitting the SiO 2 correction for H 2O analyses results in working curves that are very similar for s and s (Fig. 2), and can therefore be used for intermediate melt inclusion compositions (SiO 2 = wt.%). Our analytical protocol and extensive collection of glasses with known H 2O contents allows water concentrations in nearly all natural silicate glasses with H 2O contents from wt% H 2O to be determined with an accuracy of ca. 10% H 2 O = 3.76± H/ 30 Si r² = H 2 O = 3.323± H/ 30 Si r² = H/ 30 Si Figure 2. Typical working curves for water in and glasses as measured in positive ion mode using the Cameca IMS 4f. Note on the x- axis is plotted 1 H/ 30 Si to correct for matrix-induced fractionation; without this correction the equation would have been 1 H/ 30 Si SiO 2 (wt.%). CO 2 CO 2 is for volcanologist a volatile species as important as H 2O and usually measured in conjunction. At EIMF C is generally measured in positive ion mode like other trace elements and H 2O, using either the Cameca IMS 4f or the Due to potential interference of 24 Mg 2+ on the 12 C + signal this species needs to be measured at high mass resolution of ca to allow interference-free measurement. This is particularly important for ic and intermediate melt compositions. Only in rhyolitic and granitic systems where MgO<0.5 wt.% can the measurements be done using low mass resolution, but still requires peak stripping of 24 Mg 2+ signals based on measured 25 Mg 2+ signals Mg C Mass M40 standard 2200 ppm CO wt.% H 2 O 6.1 wt.% MgO 7.5 ppm B BH/B= BH + Figure 3. Typical mass spectrum for ic glass in the 12 C mass region. Note that even though 24 Mg 2+ and 12 C are not fully resolved at M/ΔM=1200, the Mg signal is negligible at the centre of the 12 C peak at mass Using a higher resolution would lead to unnecessary loss of C sensitivity. The 11 BH peak is fully resolved. In contrast to H 2O, most carbon contamination does not come from the vacuum but from the sample surface. Therefore a stringent precleaning routine by rastering the ionbeam for several minutes prior to data collection is vital. Adopting this approach we routinely achieve ~1 cps 12 C backgrounds even on Mg-rich materials, equivalent to ca. 10 ppm CO 2. Several well-characterised sets of calibration standards obtained by EIMF over the last few years have shown that little matrix effect exist between ic and rhyolitic glasses (Fig. 4), allowing measurement of nearly all natural silicate glasses with 20 ppm - 1 wt.% CO 2 with an accuracy of ca. 10%. Halogens (F, Cl) Halogens are preferably measured in negative ion mode but can be measured in positive ion mode, which allows simultaneous analysis with H 2O and light fluid-mobile elements (Li, B ± CO 2). Detection limits are at the low ppm level.
4 CO 2 ppm (FTIR) European Current Research On Fluid Inclusions (ECROFI-XXIII), CO 2 = 183± ( 12 C/ 30 Si) SiO 2 r² = Stable isotopes SIMS is particularly well-suited for measuring isotope ratios due to its production of very stable ion beams over long time periods. The rewards of developing the stable isotope systems for H, C and S will be high, as these may provide detailed information about volatile sources and degassing processes that are difficult to obtain otherwise [e.g., 3] CO 2 = 171± ( 12 C/ 30 Si) SiO 2 r² = C/ 30 Si SiO 2 (wt.%) Figure 4. Working curves for CO 2 in and glasses. Matrix-induced bias is negligible. Note that the highest concentration CO 2 standard (1.03 wt.%) is not shown but has been included in the calibration. The main issue is the availability of reliable standards, particularly for F, as for many glass standards values in the literature vary by up to a factor two. A considerable matrix effect is apparent between ic and rhyolitic glasses but quantification of this awaits better characterised standards, and is less of an issue in negative ion mode due to much higher ionisation yields. In positive ion mode, the estimated difference in relative ion yield for F and Cl (relative to Si) between s and s is about a factor 2, which limits the accuracy to no better than about 25%. Sulfur Sulfur is an important volatile as it produces sulfate aerosols in the stratosphere following large volcanic eruptions, which induces significant, but short-lived, climatic effects [2]. In melt inclusions it is often present in high enough concentrations that it can be measured by EPMA and therefore demand at EIMF has not been high. Due to interference of O 2 molecular species it can only be measured at high mass resolution, preferably in negative ion mode using a 133 Cs + primary beam on the Cameca IMS It is therefore not routinely measured with the other volatiles, which are predominantly measured in positive ion mode using the Cameca IMS 4f. However, it can be measured simultaneously with C and halogens in negative ion mode. However, progress for the measurement of these stable isotope system has been hampered by difficulties in obtaining calibration standards with a large enough compositional range to cover that of natural samples. Therefore, matrix-induced isotope fractionation effects have not been fully assessed. Synthesising standards, as has been successfully done for volatile concentrations, has been less successful as it has proven difficult to obtain isotopically homogenous glasses in large enough quantities to allow analysis by independent techniques. Natural glasses may be better suited, but sourcing samples with sufficiently high volatile concentrations has so far been largely unsuccessful. Preliminary results in the literature suggested limited matrix-induced fractionation for sulfur isotopes [4], but this awaits further verification by other labs. Boron One of the more successful stable isotope systems is that of boron. Boron occurs in nature as two isotopes, 10 B and 11 B in a ratio of about 1:4. Boron isotopes are strongly fractionated at the Earth s surface and therefore provide an excellent tracer of recycling of crustal material in subduction zones and the Earth s mantle, as well as hydrothermal processes [e.g., 5]. At EIMF are measured preferably using the Cameca IMS 1270 in positive ion mode. Due to the Cameca IMS 1270 s large geometry, even at its lowest resolution all potentially interfering species (such as 10 B 1 H and 9 Be 1 H) are fully resolved. Boron isotope ratios can be measured on materials with as little as 1 ppm B to a precision of ca. 1 permil (1σ) in 30 minutes using mono-collection mode and an electron multiplier detector. For concentrations of 10 ppm or higher we can achieve <0.5 precision in 15 minutes.
5 European Current Research On Fluid Inclusions (ECROFI-XXIII), As isotope ratios measured by SIMS typically show significant instrumental mass fractionation, particularly for light elements, measured isotope ratios are corrected using measurements of reference glasses with known isotopic composition (Fig. 5). Many stable isotope systems show significant matrixdependent isotope fractionation but for boron isotopes it is negligible, as a diverse range of glass standards with SiO 2 ranging from wt% fall within 1.5 permil of the certified values. The largest source of uncertainty is the apparent heterogeneity of some of the reference materials. 11 B/ 10 B reference y = x B/ 10 B measured Figure 5. Typical working curve for boron isotopes in silicate glasses with B contents ranging from ppm and with SiO 2 contents between wt%. Error bars represent 2s uncertainties. Instrumental mass fractionation in this example is Lithium Lithium occurs in nature as two isotopes, 6 Li and 7 Li in a ratio of about 1:12. Geochemically, it provides much the same information as boron, but is more prone to kinetic fractionation [6]. Analytical conditions are virtually identical to those of boron isotopes described above. However, SIMS analysis of lithium isotopes suffers from significant matrix-dependent isotope fractionation even within single mineral species [7]. This is in part mitigated by the availability of a diverse suite of glass standards with SiO 2 ranging from wt%. Lithium ionises more efficiently than B, so precision is about two times better at equal concentration, but accuracy is somewhat less due to uncertainty associated with matrix-induced fractionation. Summary The analysis at EIMF of H 2O and CO 2 concentrations in melt inclusions is now routine with good sets of calibration standards and well-tested analytical protocols. The same can be said about boron and lithium isotope ratios. Halogen concentrations are still somewhat challenging, but recently more standard material has become available and these are now being tested as well as cross-calibrated with other materials. Stable isotope analysis of H, C and S still awaits reliable standard material, which is actively being worked on. Work in other labs suggest that matrix-induced fractionation is limited for S isotopes, so this is probably the most promising application in the short term. Web site See the Edinburgh Ion Microprobe Facility web site at for more information, instrument access, sample preparation, etc. References [1] Wallace P.J. Volatiles in subduction zone magmas: concentrations and fluxes based on melt inclusion and volcanic gas data, J Volcanol Geotherm Res 140, pp , [2] Pollack et al. Volcanic explosions and climate change: a theoretical assessment, J Geophys Res 81, pp , [3] Shaw A. et al. Hydrogen isotopes in Mariana arc melt inclusions: Implications for subduction dehydration and the deep-earth water cycle, Earth Planet Sci Lett 275, pp , [4] Mandeville C. et al. Sulfur isotope variation in ic melt inclusions from Krakatau revealed by a newly developed secondary ion mass spectrometry technique for silicate glasses, AGU Fall Meeting, abstract #V13F-07, [5] Jones R. et al. Temporal variations in the influence of the subducting slab on Central Andean arc magmas related to flat-slab subduction: evidence from boron isotopes, Earth Planet Sci Lett 408, pp , [6] Marschall H.R. et al. "The lithium isotopic composition of orogenic eclogites and deep subducted slabs," Earth Planet Sci Lett 262, pp , [7] Bell et al. Lithium isotope analysis of olivine by SIMS: Calibration of a matrix effect and application to magmatic phenocrysts, Chem Geol 258, pp. 5-16, 2009.
LAACHER SEE REVISITED: HIGH SPATIAL RESOLUTION ZIRCON DATING IMPLIES RAPID FORMATION OF A ZONED MAGMA CHAMBER -
 LAACHER SEE REVISITED: HIGH SPATIAL RESOLUTION ZIRCON DATING IMPLIES RAPID FORMATION OF A ZONED MAGMA CHAMBER - DATA REPOSITORY ANALYTICAL PROCEDURES Ion microprobe U-Th measurements Th-U dating was performed
LAACHER SEE REVISITED: HIGH SPATIAL RESOLUTION ZIRCON DATING IMPLIES RAPID FORMATION OF A ZONED MAGMA CHAMBER - DATA REPOSITORY ANALYTICAL PROCEDURES Ion microprobe U-Th measurements Th-U dating was performed
Treatment of Data. Methods of determining analytical error -Counting statistics -Reproducibility of reference materials -Homogeneity of sample
 Treatment of Data Methods of determining analytical error -Counting statistics -Reproducibility of reference materials -Homogeneity of sample Detection Limits Assessment of analytical quality -Analytical
Treatment of Data Methods of determining analytical error -Counting statistics -Reproducibility of reference materials -Homogeneity of sample Detection Limits Assessment of analytical quality -Analytical
TECHNIC A L WORK ING GROUP ITWG GUIDELINE ON SECONDARY ION MASS SPECTROMETRY (SIMS)
 NUCLE A R FORENSIC S INTERN ATION A L TECHNIC A L WORK ING GROUP ITWG GUIDELINE ON SECONDARY ION MASS SPECTROMETRY (SIMS) EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) is used for elemental
NUCLE A R FORENSIC S INTERN ATION A L TECHNIC A L WORK ING GROUP ITWG GUIDELINE ON SECONDARY ION MASS SPECTROMETRY (SIMS) EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) is used for elemental
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Tables Major element compositions of host and daughter crystals: Table 1 reports composition for host-olivine. No daughter olivine has been found. The number for
Supplementary Information Supplementary Tables Major element compositions of host and daughter crystals: Table 1 reports composition for host-olivine. No daughter olivine has been found. The number for
Observations Regarding Automated SEM and SIMS Analysis of Minerals. Kristofor Ingeneri. April 22, 2009
 Observations Regarding Automated SEM and SIMS Analysis of Minerals Kristofor Ingeneri April 22, 2009 Forensic Geoscience A field of inquiry that utilizes techniques developed in the geosciences (geology,
Observations Regarding Automated SEM and SIMS Analysis of Minerals Kristofor Ingeneri April 22, 2009 Forensic Geoscience A field of inquiry that utilizes techniques developed in the geosciences (geology,
3.2 Ga detrital uraninite in the Witwatersrand Basin, South. Africa: Evidence of a reducing Archean atmosphere
 GSA Data Repository 2018085 https://doi.org/10.1130/g39957.1 1 2 3 4 3.2 Ga detrital uraninite in the Witwatersrand Basin, South Africa: Evidence of a reducing Archean atmosphere Ian Burron 1, Giuliana
GSA Data Repository 2018085 https://doi.org/10.1130/g39957.1 1 2 3 4 3.2 Ga detrital uraninite in the Witwatersrand Basin, South Africa: Evidence of a reducing Archean atmosphere Ian Burron 1, Giuliana
CO 2 quantification in magmatic systems
 CO 2 quantification in magmatic systems Innovative coupling of X-ray micro-tomography, in-situ microanalysis and thermodynamic modelling By Laura Créon Créon et al. (2018) Problematics 7 years work to
CO 2 quantification in magmatic systems Innovative coupling of X-ray micro-tomography, in-situ microanalysis and thermodynamic modelling By Laura Créon Créon et al. (2018) Problematics 7 years work to
Kent and Cooper, 2018, How well do zircons record the thermal evolution of magmatic systems?: Geology,
 GSA Data Repository 2018024 Kent and Cooper, 2018, How well do zircons record the thermal evolution of magmatic systems?: Geology, https://doi.org/10.1130/g39690.1. Supplemental Text Modelling methodology
GSA Data Repository 2018024 Kent and Cooper, 2018, How well do zircons record the thermal evolution of magmatic systems?: Geology, https://doi.org/10.1130/g39690.1. Supplemental Text Modelling methodology
Cosmochemical application of High Precision Multi-collector SIMS
 Cosmochemical application of High Precision Multi-collector SIMS Oxygen Three Isotopes in Chondrules Early Solar System Chronology of Refractory Inclusions Noriko Kita Wisc-SIMS Laboratory, University
Cosmochemical application of High Precision Multi-collector SIMS Oxygen Three Isotopes in Chondrules Early Solar System Chronology of Refractory Inclusions Noriko Kita Wisc-SIMS Laboratory, University
published sources and U-Pb geochronology performed in this study. We analyzed six
 Data Repository: Uba, Strecker, and Schmitt U-Pb radiometric dating The age controls for the stable isotopic records presented here are from both published sources and U-Pb geochronology performed in this
Data Repository: Uba, Strecker, and Schmitt U-Pb radiometric dating The age controls for the stable isotopic records presented here are from both published sources and U-Pb geochronology performed in this
Fluids, melts, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones
 cosmic rays Fluids, s, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones 10 Be volcanic front N, O 10 Be ocean water + CO 2 tracing petrologic and geotectonic processes (trace)
cosmic rays Fluids, s, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones 10 Be volcanic front N, O 10 Be ocean water + CO 2 tracing petrologic and geotectonic processes (trace)
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow Citation for published version: Attal, M 2009, 'GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow' Nature Geoscience, vol. 2, no. 11,
Edinburgh Research Explorer GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow Citation for published version: Attal, M 2009, 'GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow' Nature Geoscience, vol. 2, no. 11,
EPMA IMAGES. Figure 9. Energy-dispersive spectra of spot mineral analyses in sample 89GGR-33A for locations 1-5 in Figure 8.
 EPMA IMAGES The attached images and mineral data can be used to supplement an instrument-based lab, or serve as the basis for lab that can be completed without an instrument. Please provide credit for
EPMA IMAGES The attached images and mineral data can be used to supplement an instrument-based lab, or serve as the basis for lab that can be completed without an instrument. Please provide credit for
Defining quality standards for the analysis of solid samples
 Defining quality standards for the analysis of solid samples Thermo Scientific Element GD Plus Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometer Redefine your quality standards for the elemental analysis of solid samples
Defining quality standards for the analysis of solid samples Thermo Scientific Element GD Plus Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometer Redefine your quality standards for the elemental analysis of solid samples
Metcalf and Buck. GSA Data Repository
 GSA Data Repository 2015035 Metcalf and Buck Figure DR1. Secondary ionization mass-spectrometry U-Pb zircon geochronology plots for data collected on two samples of Wilson Ridge plutonic rocks. Data presented
GSA Data Repository 2015035 Metcalf and Buck Figure DR1. Secondary ionization mass-spectrometry U-Pb zircon geochronology plots for data collected on two samples of Wilson Ridge plutonic rocks. Data presented
Volatile solubility models and their application to magma storage and transport in the mantle and he crust. Julie Roberge ESIA-Ticoman, IPN Mexico
 Volatile solubility models and their application to magma storage and transport in the mantle and he crust Julie Roberge ESIA-Ticoman, IPN Mexico Melt Inclusions What are they? How to use them volatiles
Volatile solubility models and their application to magma storage and transport in the mantle and he crust Julie Roberge ESIA-Ticoman, IPN Mexico Melt Inclusions What are they? How to use them volatiles
N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0
 N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0 is initial number of parents, D* is number of radiogenic daughter atoms, and λ is the decay
N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0 is initial number of parents, D* is number of radiogenic daughter atoms, and λ is the decay
ESS 312 Geochemistry Simulating Earth degassing using radionuclides
 ESS 312 Geochemistry Simulating Earth degassing using radionuclides CHEMICAL AND ISOTOPIC EVOLUTION OF A TWO-RESERVOIR SYSTEM In lectures we discussed radioactive decay and build-up of a daughter isotope
ESS 312 Geochemistry Simulating Earth degassing using radionuclides CHEMICAL AND ISOTOPIC EVOLUTION OF A TWO-RESERVOIR SYSTEM In lectures we discussed radioactive decay and build-up of a daughter isotope
Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
FIB - SIMS. Focussed Ion Beam Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry.
 FIB - SIMS Focussed Ion Beam Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry Outline Introduction to Hiden Analytical Introduction to SIMS FIB-SIMS - Introduction and key features FIB-SIMS - Applications data Hiden SIMS
FIB - SIMS Focussed Ion Beam Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry Outline Introduction to Hiden Analytical Introduction to SIMS FIB-SIMS - Introduction and key features FIB-SIMS - Applications data Hiden SIMS
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Thomas Sky
 1 Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Thomas Sky Depth (µm) 2 Characterization of solar cells 0,0 1E16 1E17 1E18 1E19 1E20 0,2 0,4 0,6 0,8 1,0 1,2 P Concentration (cm -3 ) Characterization Optimization
1 Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Thomas Sky Depth (µm) 2 Characterization of solar cells 0,0 1E16 1E17 1E18 1E19 1E20 0,2 0,4 0,6 0,8 1,0 1,2 P Concentration (cm -3 ) Characterization Optimization
Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Dr. Nilanjan Chatterjee
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dr. Nilanjan Chatterjee Electron Probe Micro-Analysis (EPMA) Imaging and micrometer-scale chemical compositional analysis of solids Signals produced in The Electron
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dr. Nilanjan Chatterjee Electron Probe Micro-Analysis (EPMA) Imaging and micrometer-scale chemical compositional analysis of solids Signals produced in The Electron
Thermo Scientific ELEMENT GD PLUS Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometer. Defining quality standards for the analysis of solid samples
 Thermo Scientific ELEMENT GD PLUS Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometer Defining quality standards for the analysis of solid samples Redefine your quality standards for the elemental analysis of solid samples
Thermo Scientific ELEMENT GD PLUS Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometer Defining quality standards for the analysis of solid samples Redefine your quality standards for the elemental analysis of solid samples
What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay. Harvard University
 What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay Harvard University The mantle zoo Hofmann, 1997 187 Os/ 188 Os 0.168 0.156 0.144 0.132 EM1 Hawaii Pitcairn DMM peridotites Shield Basalts
What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay Harvard University The mantle zoo Hofmann, 1997 187 Os/ 188 Os 0.168 0.156 0.144 0.132 EM1 Hawaii Pitcairn DMM peridotites Shield Basalts
TRACE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF DIAMOND BY LAM ICPMS: STANDARDISATION, RESULTS AND DIRECTIONS
 TRACE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF DIAMOND BY LAM ICPMS: STANDARDISATION, RESULTS AND DIRECTIONS W.L. Griffin 1, 3, Sonal Rege 1, Rondi M. Davies 1, 2, Simon Jackson 1, Suzanne Y. O Reilly 1 1.ARC National Key
TRACE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF DIAMOND BY LAM ICPMS: STANDARDISATION, RESULTS AND DIRECTIONS W.L. Griffin 1, 3, Sonal Rege 1, Rondi M. Davies 1, 2, Simon Jackson 1, Suzanne Y. O Reilly 1 1.ARC National Key
Breeding et al., Data Repository Material Figure DR1. Athens. Study Area
 Breeding, Ague, and Brocker 1 Figure DR1 21 o 24 Greece o A 38 o Athens Tinos 37 o Syros Attic-Cycladic Blueschist Belt Syros Kampos B Study Area Ermoupoli N Vari Unit Cycladic HP-LT Unit Marble horizons
Breeding, Ague, and Brocker 1 Figure DR1 21 o 24 Greece o A 38 o Athens Tinos 37 o Syros Attic-Cycladic Blueschist Belt Syros Kampos B Study Area Ermoupoli N Vari Unit Cycladic HP-LT Unit Marble horizons
Characterization of Secondary Emission Materials for Micro-Channel Plates. S. Jokela, I. Veryovkin, A. Zinovev
 Characterization of Secondary Emission Materials for Micro-Channel Plates S. Jokela, I. Veryovkin, A. Zinovev Secondary Electron Yield Testing Technique We have incorporated XPS, UPS, Ar-ion sputtering,
Characterization of Secondary Emission Materials for Micro-Channel Plates S. Jokela, I. Veryovkin, A. Zinovev Secondary Electron Yield Testing Technique We have incorporated XPS, UPS, Ar-ion sputtering,
Record of ancient Martian hydrosphere preserved in zircon from a Martian meteoritie
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NGEO2231 Record of ancient Martian hydrosphere preserved in zircon from a Martian meteoritie A. A. Nemchin 1,2, M. Humayun 3, M. J. Whitehouse 1, R. H. Hewins 4,5,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NGEO2231 Record of ancient Martian hydrosphere preserved in zircon from a Martian meteoritie A. A. Nemchin 1,2, M. Humayun 3, M. J. Whitehouse 1, R. H. Hewins 4,5,
Overview of the KAHT system. Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland
 Overview of the KAHT system Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland Tonga-Kermadec-New Zealand Arc Developed on the Pacific - Australian convergent margin Mainly intraoceanic except
Overview of the KAHT system Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland Tonga-Kermadec-New Zealand Arc Developed on the Pacific - Australian convergent margin Mainly intraoceanic except
Application of NanoSIMS on Organo Mineral Structures
 Application of NanoSIMS on Organo Mineral Structures Carmen Höschen*, Carsten W. Mueller, Katja Heister, Johann Lugmeier and Ingrid Kögel-Knabner Lehrstuhl für Bodenkunde, TU München, 85350 Freising-Weihenstephan,
Application of NanoSIMS on Organo Mineral Structures Carmen Höschen*, Carsten W. Mueller, Katja Heister, Johann Lugmeier and Ingrid Kögel-Knabner Lehrstuhl für Bodenkunde, TU München, 85350 Freising-Weihenstephan,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Crustal thickness control on Sr/Y signatures of recent arc magmas: an Earth scale perspective Massimo Chiaradia Section of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Geneva,
Supplementary Information Crustal thickness control on Sr/Y signatures of recent arc magmas: an Earth scale perspective Massimo Chiaradia Section of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Geneva,
Petrology and Geochronology of Iran Tepe volcano, Eastern Rhodopes, Bulgaria: Age relationship with the Ada Tepe gold deposit. (preliminary data)
 Petrology and Geochronology of Iran Tepe volcano, Eastern Rhodopes, Bulgaria: Age relationship with the Ada Tepe gold deposit. (preliminary data) Peter Kibarov, Peter Marchev, Maria Ovtcharova, Raya Raycheva,
Petrology and Geochronology of Iran Tepe volcano, Eastern Rhodopes, Bulgaria: Age relationship with the Ada Tepe gold deposit. (preliminary data) Peter Kibarov, Peter Marchev, Maria Ovtcharova, Raya Raycheva,
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Constitution of Magmas. Magmas. Gas Law. Composition. Atomic Structure of Magma. Structural Model. PV = nrt H 2 O + O -2 = 2(OH) -
 Constitution of Magmas Magmas Best, Ch. 8 Hot molten rock T = 700-1200 degrees C Composed of ions or complexes Phase Homogeneous Separable part of the system With an interface Composition Most components
Constitution of Magmas Magmas Best, Ch. 8 Hot molten rock T = 700-1200 degrees C Composed of ions or complexes Phase Homogeneous Separable part of the system With an interface Composition Most components
Magma reservoir dynamics at Toba caldera, Indonesia, recorded by oxygen isotope zoning in quartz. Supplementary Information
 Magma reservoir dynamics at Toba caldera, Indonesia, recorded by oxygen isotope zoning in quartz David A. Budd, Valentin R. Troll, Frances M. Deegan, Ester M. Jolis, Victoria C. Smith, Martin J. Whitehouse,
Magma reservoir dynamics at Toba caldera, Indonesia, recorded by oxygen isotope zoning in quartz David A. Budd, Valentin R. Troll, Frances M. Deegan, Ester M. Jolis, Victoria C. Smith, Martin J. Whitehouse,
Th) ) dating of micro-baddeleyite
 U-Pb (and U-ThU Th) ) dating of micro-baddeleyite 30 μm Axel K. Schmitt UCLA SIMS, NSF National Ion Microprobe Facility Collaborators: T. Mark Harrison (UCLA) Kevin Chamberlain (University of Wyoming)
U-Pb (and U-ThU Th) ) dating of micro-baddeleyite 30 μm Axel K. Schmitt UCLA SIMS, NSF National Ion Microprobe Facility Collaborators: T. Mark Harrison (UCLA) Kevin Chamberlain (University of Wyoming)
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism
 Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism Monday, May 2 nd 2005 Subduction Related Magmatism Activity along arcuate volcanic chains along subduction zones Distinctly different from the mainly basaltic provinces
Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism Monday, May 2 nd 2005 Subduction Related Magmatism Activity along arcuate volcanic chains along subduction zones Distinctly different from the mainly basaltic provinces
V. B. NAUMOV 1, V. A. KOVALENKER 2 and V. L. RUSINOV 2
 CHEMICAL COMPOSITION, TRACE ELEMENTS, AND VOLATILE COMPONENTS OF MELTS: EVIDENCE FROM INCLUSIONS IN THE MINERALS OF NEOVOLCANITES FROM THE CENTRAL AND EASTERN SLOVAKIA V. B. NAUMOV 1, V. A. KOVALENKER
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION, TRACE ELEMENTS, AND VOLATILE COMPONENTS OF MELTS: EVIDENCE FROM INCLUSIONS IN THE MINERALS OF NEOVOLCANITES FROM THE CENTRAL AND EASTERN SLOVAKIA V. B. NAUMOV 1, V. A. KOVALENKER
APPENDICES. Appendix 1
 Corthouts, T.L., Lageson, D.R., and Shaw, C.A., 2016, Polyphase deformation, dynamic metamorphism and metasomatism of Mount Everest s summit limestone, east central Himalaya, Nepal/Tibet: Lithosphere,
Corthouts, T.L., Lageson, D.R., and Shaw, C.A., 2016, Polyphase deformation, dynamic metamorphism and metasomatism of Mount Everest s summit limestone, east central Himalaya, Nepal/Tibet: Lithosphere,
Use of PV 25 in the PV Industry: Strengths and Weaknesses. Larry Wang, Ph.D. Evans Analytical Group Sunnyvale, CA, USA
 Use of PV 25 in the PV Industry: Strengths and Weaknesses Larry Wang, Ph.D. Evans Analytical Group Sunnyvale, CA, USA lwang@eaglabs.com B, P, C and O in PV Si Boron, phosphorus, carbon and oxygen are the
Use of PV 25 in the PV Industry: Strengths and Weaknesses Larry Wang, Ph.D. Evans Analytical Group Sunnyvale, CA, USA lwang@eaglabs.com B, P, C and O in PV Si Boron, phosphorus, carbon and oxygen are the
High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools -
 High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
What can noble gases really say about mantle. 2) Extent of mantle degassing
 What can noble gases really say about mantle convection and the deep Earth volatile cycles? 1) Constraints on mass flow 1) Constraints on mass flow 2) Extent of mantle degassing Outline: -Noble gas geochemistry
What can noble gases really say about mantle convection and the deep Earth volatile cycles? 1) Constraints on mass flow 1) Constraints on mass flow 2) Extent of mantle degassing Outline: -Noble gas geochemistry
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1142021/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Remnants of the Early Solar System Water Enriched in Heavy Oxygen Isotopes Naoya Sakamoto, Yusuke Seto, Shoichi Itoh, Kiyoshi
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1142021/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Remnants of the Early Solar System Water Enriched in Heavy Oxygen Isotopes Naoya Sakamoto, Yusuke Seto, Shoichi Itoh, Kiyoshi
The Martian Sedimentary Mass: Constraints on its Composition, Age and Size. Scott McLennan Department of Geosciences, SUNY Stony Brook
 The Martian Sedimentary Mass: Constraints on its Composition, Age and Size Scott McLennan Department of Geosciences, SUNY Stony Brook Exploring Mars Habitability Lisbon 14 June, 2011 Martian Crustal Chemistry
The Martian Sedimentary Mass: Constraints on its Composition, Age and Size Scott McLennan Department of Geosciences, SUNY Stony Brook Exploring Mars Habitability Lisbon 14 June, 2011 Martian Crustal Chemistry
Towards SHRIMP SI: Developments in Stable Isotope Analysis with SHRIMP
 Towards SHRIMP SI: Developments in Stable Isotope Analysis with SHRIMP Trevor Ireland Research School of Earth Sciences The Australian National University Acknowledgments Ryan Ickert, Joe Hiess Peter Holden,
Towards SHRIMP SI: Developments in Stable Isotope Analysis with SHRIMP Trevor Ireland Research School of Earth Sciences The Australian National University Acknowledgments Ryan Ickert, Joe Hiess Peter Holden,
Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington
 Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington S. C. Kuehn and P. R. Hooper, Department of Geology, Washington State University, Pullman, WA A. E. Eggers and C. Kerrick, Department of Geology,
Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington S. C. Kuehn and P. R. Hooper, Department of Geology, Washington State University, Pullman, WA A. E. Eggers and C. Kerrick, Department of Geology,
GSA DATA REPOSITORY
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013019 Supplemental information for The Solidus of Alkaline Carbonatite in the Deep Mantle Konstantin D. Litasov, Anton Shatskiy, Eiji Ohtani, and Gregory M. Yaxley EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013019 Supplemental information for The Solidus of Alkaline Carbonatite in the Deep Mantle Konstantin D. Litasov, Anton Shatskiy, Eiji Ohtani, and Gregory M. Yaxley EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS)
 Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) ELEC-L3211 Postgraduate Course in Micro and Nanosciences Department of Micro and Nanosciences Personal motivation and experience on SIMS Offers the possibility to
Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) ELEC-L3211 Postgraduate Course in Micro and Nanosciences Department of Micro and Nanosciences Personal motivation and experience on SIMS Offers the possibility to
Uncertainty in Measurement of Isotope Ratios by Multi-Collector Mass Spectrometry
 1 IAEA-CN-184/168 Uncertainty in Measurement of Isotope Ratios by Multi-Collector Mass Spectrometry R. Williams Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Livermore, California U.S.A. williams141@llnl.gov
1 IAEA-CN-184/168 Uncertainty in Measurement of Isotope Ratios by Multi-Collector Mass Spectrometry R. Williams Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Livermore, California U.S.A. williams141@llnl.gov
Supplementary Information. Analytics
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013192 S. Kutterolf et al. Supplementary Information Analytics Table DR1: Summary of Nicaraguan tephra properties. Eruption ages and erupted magma masses from Kutterolf et al. (2007,
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013192 S. Kutterolf et al. Supplementary Information Analytics Table DR1: Summary of Nicaraguan tephra properties. Eruption ages and erupted magma masses from Kutterolf et al. (2007,
Trace Elements - Definitions
 Trace Elements - Definitions Elements that are not stoichiometric constituents in phases in the system of interest For example, IG/MET systems would have different trace elements than aqueous systems Do
Trace Elements - Definitions Elements that are not stoichiometric constituents in phases in the system of interest For example, IG/MET systems would have different trace elements than aqueous systems Do
Original Paper Fission Gas Bubbles Characterisation in Irradiated UO 2 Fuel by SEM, EPMA and SIMS
 Microchim Acta 155, 183 187 (2006) DOI 10.1007/s00604-006-0540-y Original Paper Fission Gas Bubbles Characterisation in Irradiated UO 2 Fuel by SEM, EPMA and SIMS Jérôme Lamontagne, Lionel Desgranges,
Microchim Acta 155, 183 187 (2006) DOI 10.1007/s00604-006-0540-y Original Paper Fission Gas Bubbles Characterisation in Irradiated UO 2 Fuel by SEM, EPMA and SIMS Jérôme Lamontagne, Lionel Desgranges,
Volatiles (H, C, N, F, S, Cl) in the lunar mantle, crust, and regolith: What questions remain and where to go next?
 Volatiles (H, C, N, F, S, Cl) in the lunar mantle, crust, and regolith: What questions remain and where to go next? Francis M. McCubbin & Charles K. Shearer Motivation behind this work 100, In Revision,
Volatiles (H, C, N, F, S, Cl) in the lunar mantle, crust, and regolith: What questions remain and where to go next? Francis M. McCubbin & Charles K. Shearer Motivation behind this work 100, In Revision,
Lecture 3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Dr. Shwan Omar
 Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones
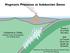 Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography Univ. of Rhode Island Thanks to Terry Plank Erik Hauri GVP: Liz Cottrell Simon Carn Jennifer Jay Ed Venzke Subduction
Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography Univ. of Rhode Island Thanks to Terry Plank Erik Hauri GVP: Liz Cottrell Simon Carn Jennifer Jay Ed Venzke Subduction
Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS)
 Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) Lasse Vines 1 Secondary ion mass spectrometry O Zn 10000 O 2 Counts/sec 1000 100 Li Na K Cr ZnO 10 ZnO 2 1 0 20 40 60 80 100 Mass (AMU) 10 21 10 20 Si 07 Ge 0.3 Atomic
Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) Lasse Vines 1 Secondary ion mass spectrometry O Zn 10000 O 2 Counts/sec 1000 100 Li Na K Cr ZnO 10 ZnO 2 1 0 20 40 60 80 100 Mass (AMU) 10 21 10 20 Si 07 Ge 0.3 Atomic
Nu Plasma II - Collector Configuration
 Nu Plasma II - Collector Configuration Nu Plasma II - Collector Configuration U-Th-Pb mass array 238U 232Th 207Pb 206Pb 208Pb 202Hg 204Pb, 204Hg Peak Alignment/Coincidence 238 U 232 Th 208 Pb 207 Pb 206
Nu Plasma II - Collector Configuration Nu Plasma II - Collector Configuration U-Th-Pb mass array 238U 232Th 207Pb 206Pb 208Pb 202Hg 204Pb, 204Hg Peak Alignment/Coincidence 238 U 232 Th 208 Pb 207 Pb 206
Electron Microprobe Analysis 1 Nilanjan Chatterjee, Ph.D. Principal Research Scientist
 12.141 Electron Microprobe Analysis 1 Nilanjan Chatterjee, Ph.D. Principal Research Scientist Massachusetts Institute of Technology Electron Microprobe Facility Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
12.141 Electron Microprobe Analysis 1 Nilanjan Chatterjee, Ph.D. Principal Research Scientist Massachusetts Institute of Technology Electron Microprobe Facility Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
Electron Microprobe Analysis 1 Nilanjan Chatterjee, Ph.D. Principal Research Scientist
 12.141 Electron Microprobe Analysis 1 Nilanjan Chatterjee, Ph.D. Principal Research Scientist Massachusetts Institute of Technology Electron Microprobe Facility Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
12.141 Electron Microprobe Analysis 1 Nilanjan Chatterjee, Ph.D. Principal Research Scientist Massachusetts Institute of Technology Electron Microprobe Facility Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
GEOLOGY. Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02
 GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
Additional Analytical Methods. Detrital zircon samples were collected from nine fine-, medium-, and coarse-grained
 GSA Data Repository 2016214 Leary, R.J., DeCelles, P.G., Quade, J., Gehrels, G.E., and Waanders, G., 2016, The Liuqu Conglomerate, southern Tibet: Early Miocene basin development related to deformation
GSA Data Repository 2016214 Leary, R.J., DeCelles, P.G., Quade, J., Gehrels, G.E., and Waanders, G., 2016, The Liuqu Conglomerate, southern Tibet: Early Miocene basin development related to deformation
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer The ns and nd Rydberg states of O-2 described by Hund's case (e) Citation for published version: Lefebvre-Brion, H & Ridley, T 2005, 'The ns and nd Rydberg states of O-2 described
Edinburgh Research Explorer The ns and nd Rydberg states of O-2 described by Hund's case (e) Citation for published version: Lefebvre-Brion, H & Ridley, T 2005, 'The ns and nd Rydberg states of O-2 described
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Nonlinear Scattering-based Imaging in Elastic Media Citation for published version: Ravasi, M & Curtis, A 213, 'Nonlinear Scattering-based Imaging in Elastic Media' Paper presented
Edinburgh Research Explorer Nonlinear Scattering-based Imaging in Elastic Media Citation for published version: Ravasi, M & Curtis, A 213, 'Nonlinear Scattering-based Imaging in Elastic Media' Paper presented
Lecture 38. Igneous geochemistry. Read White Chapter 7 if you haven t already
 Lecture 38 Igneous geochemistry Read White Chapter 7 if you haven t already Today. Magma mixing/afc 2. Spot light on using the Rare Earth Elements (REE) to constrain mantle sources and conditions of petrogenesis
Lecture 38 Igneous geochemistry Read White Chapter 7 if you haven t already Today. Magma mixing/afc 2. Spot light on using the Rare Earth Elements (REE) to constrain mantle sources and conditions of petrogenesis
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Evolution of the Slave Province and Abitibi Subprovince Based on U-Pb Dating and Hf Isotopic Composition of Zircon
 Evolution of the Slave Province and Abitibi Subprovince Based on U-Pb Dating and Hf Isotopic Composition of Zircon John W.F. Ketchum 1, Wouter Bleeker 2, William L. Griffin 1, Suzanne Y. O Reilly 1, Norman
Evolution of the Slave Province and Abitibi Subprovince Based on U-Pb Dating and Hf Isotopic Composition of Zircon John W.F. Ketchum 1, Wouter Bleeker 2, William L. Griffin 1, Suzanne Y. O Reilly 1, Norman
High-T T heating stage: : application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools -
 High-T T heating stage: : application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
High-T T heating stage: : application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
Petrology. Petrology: the study of rocks, especially aspects such as physical, chemical, spatial and chronoligic. Associated fields include:
 Petrology Petrology: the study of rocks, especially aspects such as physical, chemical, spatial and chronoligic. Associated fields include: Petrography: study of description and classification of rocks
Petrology Petrology: the study of rocks, especially aspects such as physical, chemical, spatial and chronoligic. Associated fields include: Petrography: study of description and classification of rocks
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The mantle under the crust (about 2,890 km deep) is composed mostly of silicate rocks rich in magnesium and iron. The elements of the crust have
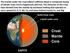 The mantle under the crust (about 2,890 km deep) is composed mostly of silicate rocks rich in magnesium and iron. The elements of the crust have derived from the mantle by fractional melting that operates
The mantle under the crust (about 2,890 km deep) is composed mostly of silicate rocks rich in magnesium and iron. The elements of the crust have derived from the mantle by fractional melting that operates
vacuum analysis plasma diagnostics surface science gas analysis
 Hiden EQP Systems High Sensitivity Mass and Energy Analysers for Monitoring, Control and Characterisation of Ions, Neutrals and Radicals in Plasma. vacuum analysis surface science gas analysis plasma diagnostics
Hiden EQP Systems High Sensitivity Mass and Energy Analysers for Monitoring, Control and Characterisation of Ions, Neutrals and Radicals in Plasma. vacuum analysis surface science gas analysis plasma diagnostics
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11021 Sample Description Tuff beds and granular iron formation Tuff beds were identified in the basal Frere Formation in diamond drill-core from drill hole TDH26
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11021 Sample Description Tuff beds and granular iron formation Tuff beds were identified in the basal Frere Formation in diamond drill-core from drill hole TDH26
SR Allen, RS Fiske, Y Tamura Sumisu methods
 SR Allen, RS Fiske, Y Tamura Sumisu methods FTIR water contents from melt inclusions Quartz-hosted melt inclusions were analyzed for H 2 O and CO 2 by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) at
SR Allen, RS Fiske, Y Tamura Sumisu methods FTIR water contents from melt inclusions Quartz-hosted melt inclusions were analyzed for H 2 O and CO 2 by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) at
Prelude to a Supervolcano: REU Investigations in the Miocene volcanic field of the southern Black Mountains, Arizona
 Prelude to a Supervolcano: REU Investigations in the Miocene volcanic field of the southern Black Mountains, Arizona Lily Claiborne Nick Lang Calvin Miller Susanne McDowell Charles Ferguson Warner Cribb
Prelude to a Supervolcano: REU Investigations in the Miocene volcanic field of the southern Black Mountains, Arizona Lily Claiborne Nick Lang Calvin Miller Susanne McDowell Charles Ferguson Warner Cribb
Paper Reference. Friday 16 January 2009 Morning Time: 1 hour
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 6241/01 Edexcel GCE Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit Test 1 Friday 16 January 2009 Morning Time: 1 hour Materials required for examination Nil Candidates may
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 6241/01 Edexcel GCE Chemistry Advanced Subsidiary Unit Test 1 Friday 16 January 2009 Morning Time: 1 hour Materials required for examination Nil Candidates may
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
The Claviature of Gas Analysis
 The Claviature of Gas Analysis Mass spectrometric gas analysis for quality assurance of gases and gas mixtures High purity and special gases are becoming increasingly important in the development of modern
The Claviature of Gas Analysis Mass spectrometric gas analysis for quality assurance of gases and gas mixtures High purity and special gases are becoming increasingly important in the development of modern
CO 2 sequestration via direct mineral carbonation of Mg-silicates. Natalie Johnson GCEP Symposium 4 October 2011
 CO 2 sequestration via direct mineral carbonation of Mg-silicates Natalie Johnson GCEP Symposium 4 October 2011 CO 2 release/year (Gt) 2 CCS: Part of climate change mitigation Projection based on current
CO 2 sequestration via direct mineral carbonation of Mg-silicates Natalie Johnson GCEP Symposium 4 October 2011 CO 2 release/year (Gt) 2 CCS: Part of climate change mitigation Projection based on current
Supplementary Information for: Giant Kiruna-type deposits form by. efficient flotation of magmatic magnetite suspensions
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2015206 1 2 Supplementary Information for: Giant Kiruna-type deposits form by efficient flotation of magmatic magnetite suspensions 3 4 Jaayke L. Knipping, Laura D. Bilenker, Adam C.
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2015206 1 2 Supplementary Information for: Giant Kiruna-type deposits form by efficient flotation of magmatic magnetite suspensions 3 4 Jaayke L. Knipping, Laura D. Bilenker, Adam C.
Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE
 Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE Reading this week: Should have been White Ch 10 and 11!! 7- Nov Differentiation of the Earth, Core formation W 10.6.6, 11.4 9- Nov Moon, crust, mantle, atmosphere
Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE Reading this week: Should have been White Ch 10 and 11!! 7- Nov Differentiation of the Earth, Core formation W 10.6.6, 11.4 9- Nov Moon, crust, mantle, atmosphere
Radiometric Measurements of Environmental Radioactivity Beta Counting, Alpha and Gamma Spectrometry
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jan 31, 2018 Radiometric Measurements of Environmental Radioactivity Beta Counting, Alpha and Gamma Spectrometry Nielsen, Sven Poul Publication date: 2013 Link back to
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jan 31, 2018 Radiometric Measurements of Environmental Radioactivity Beta Counting, Alpha and Gamma Spectrometry Nielsen, Sven Poul Publication date: 2013 Link back to
LATE ARCHAEAN FELSIC ALKALINE MAGMATISM: GEOLOGY, GEOCHEMISTRY, AND TECTONIC SETTING
 LATE ARCHAEAN FELSIC ALKALINE MAGMATISM: GEOLOGY, GEOCHEMISTRY, AND TECTONIC SETTING ZOZULYA DMITRY 1, EBY NELSON 2 1 - Geological Institute Kola Science Centre RAS, Apatity, Russia 2 - Department of Environmental,
LATE ARCHAEAN FELSIC ALKALINE MAGMATISM: GEOLOGY, GEOCHEMISTRY, AND TECTONIC SETTING ZOZULYA DMITRY 1, EBY NELSON 2 1 - Geological Institute Kola Science Centre RAS, Apatity, Russia 2 - Department of Environmental,
IRMS. perspective. Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry.
 IRMS perspective Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry www.nu-ins.com Perspective The Nu Instruments Perspective geometry forms the basis for two state of the art IRMS instruments. Designed for flexibility,
IRMS perspective Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry www.nu-ins.com Perspective The Nu Instruments Perspective geometry forms the basis for two state of the art IRMS instruments. Designed for flexibility,
Chemical Geology 264 (2009) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Chemical Geology. journal homepage:
 Chemical Geology 264 (2009) 43 57 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Chemical Geology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chemgeo High precision SIMS oxygen isotope analysis and the effect
Chemical Geology 264 (2009) 43 57 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Chemical Geology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chemgeo High precision SIMS oxygen isotope analysis and the effect
Partitioning of chlorine between H 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt of Mt. Etna
 Partitioning of chlorine between H 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt of Mt. Etna Oliver Beermann Jan Stelling XXVII. (14.) Arbeitstagung DGK, Arbeitskreis Nichtkristalline und Partiellkristalline Strukturen
Partitioning of chlorine between H 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt of Mt. Etna Oliver Beermann Jan Stelling XXVII. (14.) Arbeitstagung DGK, Arbeitskreis Nichtkristalline und Partiellkristalline Strukturen
Water Rock Interaction [WRI 14] Chemical weathering of granitic rocks: experimental approach and Pb-Li isotopes tracing
![Water Rock Interaction [WRI 14] Chemical weathering of granitic rocks: experimental approach and Pb-Li isotopes tracing Water Rock Interaction [WRI 14] Chemical weathering of granitic rocks: experimental approach and Pb-Li isotopes tracing](/thumbs/86/94595506.jpg) Author manuscript, published in "Procedia Earth and Planetary Science (2013) 1-4" Water Rock Interaction [WRI 14] Chemical weathering of granitic rocks: experimental approach and Pb-Li isotopes tracing
Author manuscript, published in "Procedia Earth and Planetary Science (2013) 1-4" Water Rock Interaction [WRI 14] Chemical weathering of granitic rocks: experimental approach and Pb-Li isotopes tracing
The Composition of the Continental Crust
 The Composition of the Continental Crust Roberta L. Rudnick Geochemistry Laboratory Department of Geology University of Maryland Apollo 17 view of Earth Rationale: Why is studying crust composition important?
The Composition of the Continental Crust Roberta L. Rudnick Geochemistry Laboratory Department of Geology University of Maryland Apollo 17 view of Earth Rationale: Why is studying crust composition important?
Supplementary information. Carn, S. A., Fioletov, V., McLinden, C., Li, C. & Krotkov, N. A.
 Supplementary information Carn, S. A., Fioletov, V., McLinden, C., Li, C. & Krotkov, N. A. A decade of global volcanic SO 2 emissions measured from space. Sci. Rep. Supplementary Table 1 The complete volcanic
Supplementary information Carn, S. A., Fioletov, V., McLinden, C., Li, C. & Krotkov, N. A. A decade of global volcanic SO 2 emissions measured from space. Sci. Rep. Supplementary Table 1 The complete volcanic
Introduction to SIMS Basic principles Components Techniques Drawbacks Figures of Merit Variations Resources
 Introduction to SIMS Basic principles Components Techniques Drawbacks Figures of Merit Variations Resources New technique for surface chemical analysis. SIMS examines the mass of ions, instead of energy
Introduction to SIMS Basic principles Components Techniques Drawbacks Figures of Merit Variations Resources New technique for surface chemical analysis. SIMS examines the mass of ions, instead of energy
Secular Archaean. Pronounced secular trends from. However, also. Cr, intermediate to felsic magmas, and
 Secular Archaean Pronounced secular trends from 1. early sodic granites (TTGs) 2. later potassic granites However, also 1. LILE- & LREE-enriched, high MgO, Mg#, Ni, Cr, intermediate to felsic magmas, and
Secular Archaean Pronounced secular trends from 1. early sodic granites (TTGs) 2. later potassic granites However, also 1. LILE- & LREE-enriched, high MgO, Mg#, Ni, Cr, intermediate to felsic magmas, and
Lithogeochemistry Using a Portable X-Ray Fluorescence (pxrf) Spectrometer and Preliminary Results From the Eagle Ford Shale
 Lithogeochemistry Using a Portable X-Ray Fluorescence (pxrf) Spectrometer and Preliminary Results From the Eagle Ford Shale Dr. Mark T. Ford and John M. Dabney EFCREO Student Driven Research Symposium
Lithogeochemistry Using a Portable X-Ray Fluorescence (pxrf) Spectrometer and Preliminary Results From the Eagle Ford Shale Dr. Mark T. Ford and John M. Dabney EFCREO Student Driven Research Symposium
Q. WANG, Q-K. XIA, S. Y. O REILLY, W. L. GRIFFIN, E. E. BEYER AND H. K. BRUECKNER
 Pressure- and stress-induced fabric transition in olivine from peridotites in the Western Gneiss Region (Norway): implications for mantle seismic anisotropy Q. WANG, Q-K. XIA, S. Y. O REILLY, W. L. GRIFFIN,
Pressure- and stress-induced fabric transition in olivine from peridotites in the Western Gneiss Region (Norway): implications for mantle seismic anisotropy Q. WANG, Q-K. XIA, S. Y. O REILLY, W. L. GRIFFIN,
QUANTITATIVE ENERGY-DISPERSIVE ELECTRON PROBE X-RAY MICROANALYSIS OF INDIVIDUAL PARTICLES
 QUANTITATIVE ENERGY-DISPERSIVE ELECTRON PROBE X-RAY MICROANALYSIS OF INDIVIDUAL PARTICLES 287 Chul-Un Ro Department of Chemistry, Inha University 253, Yonghyun-dong, Nam-gu, Incheon 402-751, Korea ABSTRACT
QUANTITATIVE ENERGY-DISPERSIVE ELECTRON PROBE X-RAY MICROANALYSIS OF INDIVIDUAL PARTICLES 287 Chul-Un Ro Department of Chemistry, Inha University 253, Yonghyun-dong, Nam-gu, Incheon 402-751, Korea ABSTRACT
PERSPECTIVE STABLE ISOTOPE RATIO MS
 Nu Plasma II Multi-Collector ICP-MS Aspect HR Stable Isotope Ratio MS PERSPECTIVE STABLE ISOTOPE RATIO MS Astrum Glow Discharge MS Nu Plasma 1700 Multi-Collector ICP-MS Panorama HR Stable Isotope Ratio
Nu Plasma II Multi-Collector ICP-MS Aspect HR Stable Isotope Ratio MS PERSPECTIVE STABLE ISOTOPE RATIO MS Astrum Glow Discharge MS Nu Plasma 1700 Multi-Collector ICP-MS Panorama HR Stable Isotope Ratio
X Rays & Crystals. Characterizing Mineral Chemistry & Structure. J.D. Price
 X Rays & Crystals Characterizing Mineral Chemistry & Structure J.D. Price Light - electromagnetic spectrum Wave behavior vs. particle behavior If atoms are on the 10-10 m scale, we need to use sufficiently
X Rays & Crystals Characterizing Mineral Chemistry & Structure J.D. Price Light - electromagnetic spectrum Wave behavior vs. particle behavior If atoms are on the 10-10 m scale, we need to use sufficiently
WATER IN THE EARTH S MANTLE:
 WATER IN THE EARTH S MANTLE: NATHALIE BOLFAN-CASANOVA LABORATOIRE MAGMAS ET VOLCANS => Heterogeneous distribution of water in the mantle > 10000 pmm wt H2O ~ 10000 pmm wt H2O ~ 1000 pmm wt H2O On what
WATER IN THE EARTH S MANTLE: NATHALIE BOLFAN-CASANOVA LABORATOIRE MAGMAS ET VOLCANS => Heterogeneous distribution of water in the mantle > 10000 pmm wt H2O ~ 10000 pmm wt H2O ~ 1000 pmm wt H2O On what
All work was carried out at the Advanced Analytical Centre, at James Cook
 Appendix LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of monazite All work was carried out at the Advanced Analytical Centre, at James Cook University (Townsville, Australia). We used a Coherent GeolasPro 193 nm ArF Excimer
Appendix LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of monazite All work was carried out at the Advanced Analytical Centre, at James Cook University (Townsville, Australia). We used a Coherent GeolasPro 193 nm ArF Excimer
Accelerator Mass Spectroscopy
 Accelerator Mass Spectroscopy Accelerator Mass Spectroscopy (AMS) is a highly sensitive technique that is useful in isotopic analysis of specific elements in small samples (1mg or less of sample containing
Accelerator Mass Spectroscopy Accelerator Mass Spectroscopy (AMS) is a highly sensitive technique that is useful in isotopic analysis of specific elements in small samples (1mg or less of sample containing
ICP-MS. plasma 17OO. High Resolution Multi-Collector ICP-MS.
 ICP-MS plasma 17OO High Resolution Multi-Collector ICP-MS www.nu-ins.com Plasma 1700 & Sapphire 1700 Plasma 1700: Large Geometry Multi-Collector Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer For more information
ICP-MS plasma 17OO High Resolution Multi-Collector ICP-MS www.nu-ins.com Plasma 1700 & Sapphire 1700 Plasma 1700: Large Geometry Multi-Collector Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer For more information
