Quantitative Geography Analysis on Spatial Structure of A-grade Tourist Attractions in China
|
|
|
- Alaina Paul
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Jan., 2015 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.6 No.1 J. Resour. Ecol (1) DOI: /j.issn x Article Quantitative Geography Analysis on Spatial Structure of A-grade Tourist Attractions in China PAN Jinghu 1 *, LI Junfeng 1 and CONG Yibo 2 1 College of Geography and Environmental Science, Northwest Normal University, Lanzhou , China; 2 College of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou , China Abstract: Tourist attraction is a very important carrier of tourism activities. A-grade tourist attraction is a national standard of comprehensive evaluation about tourist attractions quality and grade in China. In this paper, spatial structure of 2424 national A-grade tourist attractions are investigated by using GIS and quantitative analysis methods, such as nearest neighbor index (NNI), quadrat analysis, Gini coefficient and hot spot clustering. Spatial accessibility of all A-grade tourist attractions was calculated using cost weighted distance method and ArcGIS software. Service range of each tourist attraction at 4A grade and above in China was delimitated based on the cost allocation method. Results show that China s A-grade tourist attractions present aggregate distribution characteristics on the whole, and cultural attractions aggregate distribution is higher than of natural tourist attractions. Above-4A grade quality attractions aggregate distribution is lower than the Below-4A grade tourist attractions; cultural Above-4A grade are significantly greater than the cultural Below-4A grade tourist attractions. A-grade tourist attractions in China s eight districts are aggregate. The spatial distribution uniformity is low. Affected by the degree of economic development and tourism resources endowment, the service range of Above-4A grade attractions is big in West, small in East, big in North, and small in South. First-order hot spots areas were mainly concentrated in the east side of the line formed by Deqen-Alxa Left Banner. The second-order hot spot areas were composed of 11 regions, while the third-order hot spot areas include Beijing, Tianjin, Central Plains and the Yangtze River Delta. Key words: spatial structure; spatial accessibility; tourist attractions; GIS; China 1 Introduction Tourist attraction is an indispensable carrier of tourist activities, which has an important special status in the tourism activities (Guo et al. 2012). Spatial structure of tourist attractions refers to natural attractions and cultural attractions on the spatial correlation and combinations. It is the complex of node (spots), channel (communication) and domain (region) (Xie and Wu 2008), which is a hotspot of research on tourism spatial structure. Spatial structure of tourist attractions not only includes the combination of distribution pattern, grade and quantity, but also caused the spatial behavior of tourists directly, which has a profound impact on the tourist attractions development speed, scale, efficiency, temporal-spatial arrangement, and the nature, extent, and development strategy of tourism regional spatial competition (Weaver 1998; Andreas 2004; Li and Wu 2012). Researches of tourism spatial structure began in the 1960 s, mainly focusing on the spatial analysis and determination research of tourist source market, while on tourist spatial structure is less. Wilson (1967) proposed statistical theory based on tourist spatial distribution model. Miossec (1976) analyzed the evolution process of the destination tourism by using the spatial dynamic method. Dredge (1999) proposed three kinds of spatial structure model about tourism destinations. Sophie and Romain (2009) come to a conclusion that the accessibility have influence on tourism spatial structure and the economic structure. Chinese scholars have been more concerned about the spatial structure of tourist attractions that are mainly concentrated in: the accessibility and transportation of tourist attractions (Jin et al. 2009; Pan and Cong 2012), spatial distribution Received: Accepted: Foundation: National Natural Science Foundation of China (No , ). * Corresponding author: PAN Jinghu. panjh_nwnu@nwnu.edu.cn.
2 PAN Jinghu, et al.: Quantitative Geography Analysis on Spatial Structure of A-grade Tourist Attractions in China 13 Grade 5A-grade 4A-grade 3A-grade 2A-grade 1A-grade Natural tourist attractions Type Cultural tourist attractions Fig.1 Distribution of A-grade tourist attractions characteristics (Yuan et al. 2010; Ma et al. 2013), the spatial structure evolution model (Mao et al. 2011) and spatial structure optimization (Wang and Li 2010). For methods, most researches use Pattern Analysis (Zhang et al. 2011), Lorentz curve and Gini Coefficient (Wei and Chen 2012), varied coefficient and equilibrium degree coefficient (Jin and Xu 2012), fractal (Cui and Sun 2011), etc. On the whole, the studies on spatial structure of tourist attractions evolved from qualitative analysis to the combination of GIS spatial analysis and mathematical statistics method, from the static description to the dynamic research of tourist attractions distribution, and from the spatial pattern description to the spatial structure optimization study. The study scope focused on the provinces, cities, or urban agglomeration in Eastern and Central China, and nationwide comprehensive research is relatively scarce. The intuitive and effective methods to perform the spatial distribution characters of tourist attractions are insufficient. A-grade tourist attraction is a unique quality grade division and evaluation system issued by China National Tourism Administration, which released firstly in Nowadays, A-grade tourist attraction has become a national standard to evaluate the quality and class of tourist attraction comprehensively. This paper adopt the GIS spatial measurement analysis method, quadrat analysis, nearest neighbor distance index, Gini Coefficient and hot spot detection, to analyze spatial structure and distribution characteristics of A-grade tourist attractions in China, which aims to provide a scientific reference for quality tourism resources, spatial structure optimization and regional joint development of attractions. 2 Data and research method 2.1 Data sources and processing China National Tourism Administration issued A-grade Tourist Attractions Directory on its website ( cnta.gov.cn/). Released on the Directory, we merged the repeating spots for updating. By the end of 2012, there are 2424 A-grade tourist attractions in China (Fig. 1). The number of 5A-grade tourist attractions is 127, 4A-grade tourist attractions is 926, 3A-grade tourist attractions is 443, 2A-grade tourist attractions is 815, and 1A-grade tourist attractions is 113. Regions such as Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan present special geographical and social barriers and use inconsistent statistical procedures, were not included in the present study. According to the nature of the tourism resources, we divide tourist attractions into two types, natural and cultural, for the convenience of analysis. There are 1108 natural tourist attractions, which including natural tourist attractions, forest parks, nature reserves, rural village, etc. Cultural tourist attractions total 1316, including historical and cultural sites, ancient architectures and gardens, sports halls, museums, amusement parks, theme parks, resorts, etc. We marked the attractions location by ArcGIS9.3 software. The coordinates of A-grade tourist attractions obtained from Google Maps ( ditu.google.cn/), and the attractions with larger areas take their centroidal coordinates as attractions coordinates. We divided all A grade tourist attractions into two grades: 4A and 5A (abbreviation for Above-4A ) and, below 4A (abbreviation for Below-4A ). The Above-4A grade tourist attractions can fully reflect the degree and protection status of the dominated tourism resources; at the same time, this sub-classification also reflects the current tourism development situation and service ability of a region. Traffic data digitized from 1:4,500,000 Chinese Traffic Map by Chinese borders vector data were obtained from the National Geometrics Center of China at a scale of 1:4,000,000. The graphic data unified projection to Albers equal-area conic projection system by ArcGIS9.3. All data are stored in a geographical database.
3 14 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.6 No.1, Point pattern analysis Nearest Neighbor Index (NNI) NNI is result of the average distance of the nearest neighbor points divided by the average distance of the random distribution model, to describe deviation degree of the random distribution (Yan et al. 2009): ( d ) N min i= 1 NNI = 0.5 Sqrt A / N ij N ( ) In Formula (1), min (d ij ) is the distance between point and its nearest neighbor point, N is the total number of tourist attraction, A is total area of the study area Quadrat analysis We use a set of quadrats covered on the study area and make overlay analysis. Then we count the sample number on each quadrat. After statistics the number of samples and its frequency with m points, compared with completely random process to determine the spatial distribution characteristics of point mode. The results generally judged by the Variance Mean Ratio (VMR) (Cox and Lewis 1966): VMR=VAR/Mean (2) In Formula (2), VAR = (1) 2 px ( px) 2 n i i i i, Mean n 1 = Σx/m (Mao and Li 2004). Among them, p i is quadrat frequency with i points, x i is the point number in each quadrat, n is the quadrat number, m is the total points. In a Poisson distribution, VMR = 1. When VMR< 1, the object of study has an obvious uniform distribution trend. When VMR> 1, the object has a tendency to concentrate distribution. The more number of quadrats, the smaller the Mean. VAR is smaller and falling faster than Mean, so VMR value becomes smaller, but will not change the type of distribution. Quadrat size determined by the rules of thumb (Mao and Li 2004), namely the quadrat size should be twice the average area of each point Gini coefficient and distribution uniformity degree Gini Coefficient is used to depict the distribution of spatial elements, which can judge distribution of tourist attractions in the study area. In theory, the Gini coefficient is between 0 and 1, the greater the value is, the higher the concentration is. The following is the calculating formula (Yitzhaki 1983): n P ln P i i i= 1 G = (3) ln N In Formula (3), G is the Gini Coefficient, P i is the number of A-grade tourist attractions in the i partition of the A-grade tourist attractions total number in the proportion. N is the number of partitions. C = 1 G (Qi and Wang 2013), which is distribution uniformity Hot spot clustering Hot spots performed lots of spots get together on the space (Getis and Ord 1992), namely is the area with larger density. This paper adopt the Closest Distance Hierarchical Clustering Method (Lance and Williams 1967), which according to the nearest distance of each tourist attraction i, defining a accumulative unit, limit distance or threshold value, and the minimum number of each accumulative unit; then compared accumulative unit with every bit of the nearest distance. When the nearest distance of one point is less than the limit distance, it will be included in the unit. According to the method, original point data will clustering in several ellipse region, named the first order hot area. Similarly, the first order hot area clustering in several ellipse region, named the second order hot area. The second order hot area should go next and so on. 2.3 Partition of tourist attractions in service scope based on the accessibility The accessibility is defined as the average value of trip distance, starting from tourist attraction to its adjacent areas within a certain period of time (Morris et al. 1978; Geurs and Wee 2004; Wang et al. 2011). This paper uses the cost weighted distance method to calculate the shortest weighted distance. The distance is from each grid to a certain objective grid for raster data (Jin et al. 2009). The orthogonal grid with certain accuracy is used to divide research area into raster images. Attribute value of each raster represents its cost. This paper defines the cost as the degree of time consumption required through the raster. In order to improve computational accuracy as much as possible, this paper selected the raster with an area of 1 km 1 km, and set up the reference of time cost value as the minutes required approximately for traveling 1 km on average. The equation was: cost (time cost) = (1/v) 60 (where v represents setting speed of various types of spatial objects). Different land surface types have different schedule types and travel speeds. According to railway mileages and speed standards at different grades of China, and the Technical Standard of Highway Engineering of the People s Republic of China (JTGB ), the various travelling speeds are set as follows: the road network consists of highway, national trunk highway, provincial highway, ordinary road, and railway, with the average travelling speeds of 120, 90, 80, 60, and 120 km h -1, respectively. Land areas except for roads are supposed isotropic, which meant it is able to travel on the land towards any directions. Traveling methods were restricted, mainly referring to on foot. The cost value can be seen in Table 1. By adding road maps and basic geographic maps into ArcGIS as basic maps, with the help of Google Maps, we have obtained the location of A-grade tourist attractions and established a new point shapefile in ArcGIS (ESRI 2006). Obviously, given that a large number of A-grade tourist
4 PAN Jinghu, et al.: Quantitative Geography Analysis on Spatial Structure of A-grade Tourist Attractions in China 15 Table 1 Velocity and time cost of the spatial objects. Spatial objects Velocity (km h -1 ) Time cost (min) National Provincial Ordinary Railway Highway trunk Land highway road highway attractions, we take 4A grade and above attractions which have the most high quality as the analysis object to explore accessibility. Using ArcGIS Cost Weighted, we have calculated the cost time of 4A grade and above attractions based on cumulative cost, and have then calculated the area of the accessibility of tourist attractions. Based on the accessibility of tourist attractions, we partition each service scope of 4A grade and above attractions. Partition standard is if the cost time of any grid to the tourist attraction i less than the time of the grid to any other attractions, then the grid is service scope of attraction i. And by this analogy, service scope of attractions i is composed of a series of consecutive grids for this domain. In addition, the boundaries of the service scope to two tourist attractions cost the same time. 3 Results and analysis 3.1 Distribution characteristics of tourist attractions Analysis of NNI results With the aid of ArcGIS9.3, we calculated the nearest neighbor distance index (NNI) of tourist attractions based on Formula (1). Results are shown in Table 2. The analysis results proceeded with rectangular and circular correction to eliminate the influence of boundary effects. If, for example, all A-grade tourist attractions are taken, the value of NNI without correction is , with rectangular correction is , and with circular correction is Obviously, the results between correction and without correction are inconsequential. In other words, the boundary effects have little spatial effect to the study of Chinese A-grade tourist attractions distribution, can be ignored. Generally recognized (Li et al. 2008) that NNI 0.5 is aggregate distribution and NNI 1.5 is uniform distribution; 0.5<NNI 0.8 is aggregate - random distribution; 0.8<NNI<1.2 is random distribution; 1.2 NNI <1.5 is random - uniform distribution. As the Table 2 shows, the spatial distribution of all types of A-grade tourist attractions on the whole showed aggregate distribution characteristics. Noteworthy, the Z test value is highly significant. Classification: overall, the aggregate distribution of above-4a attractions is lower than below-4a attractions, while above-4a cultural tourist attractions are obviously more fit the aggregate than below 4A cultural tourist attractions Analysis of Quadrat results There are 2424 A-grade tourist attractions in the database, so on average every km 2 area has one A-grade tourist attraction. According to the Rule of Thumb, each quadrat area should be km 2, so this paper uses the size of km km quadrats to analysis distribution patterns of all A-grade tourist attractions (Fig.2). Overlay analysis was carried out on the quadrats with the national boundary, there are 1009 quadrats across A-grade tourist attractions Fig. 2 Quadrats of A-grade tourist attractions distribution. Table 2 Nearest neighbor distance index of tourist attractions distribution. Type Number of samples Average nearest distance (m) Expected nearest distance (m) NNI Z test value All A-grade Above 4A Below 4A Natural A-grade Above 4A Below 4A Cultural A-grade Above 4A Below 4A
5 16 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.6 No.1, 2015 Table 3 VMR of quadrat analysis of A-grade tourist attractions distribution. Type All Natural Cultural A-grade Above 4A Below 4A the country, but lots of them are located on the quadrat boundaries. In order to eliminate the influence of boundary effect, we deleted these quadrats. This left 708 quadrats and 1937 A-grade attractions within quadrats; 487 A-grade attractions are not covered by quadrats. Next, the number of A-grade attractions in each quadrat was counted and quadrat frequency variance and quadrat average frequency calculated. According to Formula (2), we can get the VMR. The quadrat side length of Above-4A grade attractions is km; quadrat side length of Below-4A grade attractions is km. Results shown in Table 3. As Table 3 showed, on the whole, VMR of all A-grade attractions is (slightly greater than 1), so we can put it up as aggregate distribution. In analyzing different grades, we find that the Above-4A grade attractions is closer to the aggregate than the Below-4A grade attractions. Namely: high quality tourism resources tend to fit aggregated distribution. This phenomenon is more evident in cultural A-grade attractions; the VMR of Above-4A grade attractions as high as 5.191, much higher than Below-4A grade tourist attractions. Points of view, on the whole cultural attractions concentrate higher than the natural tourist attractions. But for the Below-4A grade attractions, the distribution of the natural A-grade attractions is more clustered than cultural attractions. The above conclusions are consistent with the NNI results Analysis of Gini Coefficient and Distribution Uniformity Degree According to the eight major comprehensive district theory which is proposed by Zhao and Chen (1999), we analyzed the Gini Coefficient based on statistics the number of the A-grade attractions in 8 districts to determine its distribution uniformity, the concrete results shown in Fig. 3 and Table 4. Fig. 3 and Table 4 show that A-grade tourist attractions Gini Coefficient was 0.888, and the distribution uniformity degree: It shows that A-grade tourist attractions in China s 8 districts are concentrated and the distribution uniformity degree is low. Specifically, the assemble region of A-grade tourist attractions are distributed in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, the North and Southwest China. Those regions are higher than uniform distribution proportions; the others are lower than the uniform distribution proportion. On the one hand, regional economic development level has a notable influence at the distribution of tourist attractions in so much as the degree of economic development will not only affect the infrastructure and traffic conditions which is tourist attractions rely on, but also tourist market. On the other hand, the regional tourism resources endowment is also an important influence factor. In terms of the assembled distribution of A-grade tourist attractions, the nearby tourist resources and tourist market structure tend to have a certain degree of similarity. In such situations there is the danger All Above 4A Below 4A All natural Natural above 4A Natural below 4A All cultural Cultural above 4A Cultural below 4A C Gini Fig. 3 Gini coefficient and distribution uniformity degree of A-grade tourist attractions. Table 4 Spatial distribution of A-grade tourist attractions. Region All Natural attractions Cultural attractions A-grade Above 4A Below 4A A-grade Above 4A Below 4A A-grade Above 4A Below 4A Northeast China North China Shanxi, Shaanxi and Inner Mongolia Middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Southeast China Southeast China Northwest China Qinghai-Tibet Total
6 PAN Jinghu, et al.: Quantitative Geography Analysis on Spatial Structure of A-grade Tourist Attractions in China 17 that this excessive concentration might lead to inter-site competition or trigger internal friction something to be vigorously avoided. We suggest the solution is to carry out effective optimization or integration. From the perspective of the grading and classification of tourist attractions, the difference of Gini Coefficient and distribution uniformity degree in large area is negligible. It is noteworthy that relatively, the Above-4A grade tourist attractions are more concentrated than the Below-4A grade tourist attractions in the 8 districts distribution. 3.2 Hot spot detection We adopt the Closest Distance Hierarchical Clustering Method to detect the hot spot distribution of A-grade tourist attractions in China. The result is shown in Fig. 4. It can be seen directly that: (1) On the whole, the first order hot area of A-grade tourist attractions are distributed across the country, but mainly concentrated in the east side of Deqen County Alxa Left Banner line. There are 11 second order hotspot areas: Beijing-Tianjin, Shanghai-Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Shandong peninsula, Chengdu-Chongqing, central Hubei province, eastern and southern Liaoning province, northern Jiangxi province, southern Anhui province, central Henan province, the junction of Shanxi, Henan and Hebei provinces. Third order hotspot areas consist of Beijing- Tianjin-Hebei, the Central Plains and the Yangtze River Delta. (2) Comparison between the natural and cultural tourist attractions, natural tourist attraction have 4 second order hot spot area, namely, Yangtze River Delta, the junction of Shandong, Henan and Jiangsu, central Jiangsu-North Jiangxi, central Shanxi-northern Henan. Second order hotspot areas of cultural tourist attraction number six: Attraction Natural attraction Cultural attraction Above 4A grade Below 4A grade Natural above 4A grade Cultural above 4A grade Natural below 4A grade Cultural below 4A grade First order Second order Third order Fig. 4 Spatial hotspot detection of tourist attractions distribution.
7 18 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.6 No.1, km Accessibility (min) Tourist attractions above-4a grade Service range Fig. 5 Accessibility of tourist attractions. Fig. 6 Service range of tourist attractions above-4a grade. Beijing-Tianjin, the boundary of Shandong and Henan, north Henan-central Shaanxi plain, Yangtze River Delta, Chengdu-Chongqing, the junction of Hubei, Hunan and Jiangxi. Third order hotspot area distribution of natural tourist attraction and all A-grade tourist attraction is roughly the same, while cultural tourist attractions to the westward including most of the Shaanxi, Gansu and Sichuan area. (3) Comparison between the Above-4A grade and Below-4A grade: there are 3 second order hotspot areas of Above-4A grade tourist attractions. The biggest one is from central Jilin to southwestern Henan. The other two pieces are Shandong-Henan and Yangtze River Delta. These areas are core areas of quality tourism resource in China. The second order hot areas of Below-4A attractions are widely dispersed. The distribution of third order hotspot area of Above-4A grade is almost similar to and comparable with all A-grade tourist attractions. The third order hotspot area of Below-4A grade tourist attractions is towards to southwest, viz. the Sichuan Basin. It is worth noting that the distribution of second and third order hotspot areas of Above-4A grade and Below-4A grade tourist attractions form large overlapping areas in the Middle East. There are fewer areas of first order hotspot areas in the western region, reflecting the regional distribution imbalance of A-grade tourist attractions. 3.3 Service range measurement We divided A-grade tourist attractions accessibility into 10 time segments: 15min, 30min, 45min, 1h, 1.5h, 2h, 3h, 5h and 8h, for the standard (Fig. 5). Considering A-grade tourist attractions are numerous, and the high quality of 4A grade and above attractions, we took 4A grade and above tourist attractions as the analysis object to explore accessibility. We divided service range of the A grade and above tourist attractions which are followed the principle of the shortest possible time to tourist attractions (Fig. 6). As a result of our intense analysis of the service range of attractions, we conclude that the service range of Above- 4A grade tourist attractions is greater in the West and South and smaller in the East and North of China. The reason is that the tourist attractions are clustered in the eastern China where there has been more economic development, and central China where there has been better tourism resources endowment. In contrast, to the East, western China suffers from a lack of tourist attractions. There is an inverse relationship between accessibility (Fig. 5) and the service range of regions with poor spatial accessibility. The service range of high quality tourist attractions on the East coast and in North China is small compared with those in other regions with poor spatial accessibility. However, one should note that there is significant difference in the service range between each tourist attraction. The largest service range is Héytgah Folk Cultural Tourism Scenic Spot in Xinjiang, which covers km 2. This is almost equal in size to the combined area of five of China s eastern provinces: Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Shandong, Fujian and Anhui. On the other hand, the minimal service range is Beihai-Jingshan park in Beijing, which covers only 3.82 km 2 ; a times difference. Other examples of service ranges with more than km 2 are: Tashilhunpo Monastery of in Shigatse, Tibet; Kuche Palace in Xinjiang; Meri Snow Mountain in Diqing, Yunnan; Mount Qomolangma National Nature Reserve in Shigatse, Tibet; and Xiangsi Lake in Mongolian Autonomous Prefecture of Bayingolin, Xinjiang.
8 PAN Jinghu, et al.: Quantitative Geography Analysis on Spatial Structure of A-grade Tourist Attractions in China 19 4 Conclusion and discussion In this paper, we introduced the GIS spatial analysis and measurement method of geography and a preliminary analysis of the spatial structure of A-grade tourist attractions in China, providing a new way for tourism spatial structure research. Main conclusions are as follows: (1) China s A-grade tourist attractions present an aggregate distribution characteristics on the whole, and NNI = < 1. Cultural attractions aggregate distribution is higher than of natural tourist attractions; Above-4A grade quality attractions aggregate distribution is lower than the Below-4A grade scenic spot; cultural Above-4A grade are significantly greater than the cultural Below-4A grade scenic spot. (2) China s A-grade tourist attractions in China s eight districts are aggregate. The spatial distribution uniformity is 0.112, which is low; the Gini Coefficient is The difference between the Gini Coefficient and the distribution uniformity is very small in these 8 districts. More than half of the A-grade tourist attractions are concentrated in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and North China. (3) Affected by the degree of economic development and tourism resources endowment, the service scope of Above- 4A grade attractions is big in West, small in East, big in North, and small in South. This correlates with spatial structure and traffic accessibility. China s A-grade tourist attractions are distributed nonuniformly, while they characterized high concentration degree in individual region. According to the core-periphery theory (Friedman 1966), several core tourism regions are suggested to plan in the high concentration zones. On the one hand, we should drive the development of the tourist attractions at the edge, which relying on the advantage of highly concentrated core region tourist attractions. So we can expand the depth of tourism development and the hinterland, make tourism layout keep balance gradually in regions. On the other hand, many tourist attractions in close geographic proximity face fierce internal competition - which has typically led to the cutthroat operating due to the homogeneity. The government and managers need innovation of competition pattern, implements the linkage development, and makes the heterogeneous tourism products, aims at obtained in the development of more space. Limited to the difficulty of data acquisition, this paper does not consider the effect of air and shipping. Neither does the paper take the uneven distribution of population and economic factors such as GDP into account. We appreciate that other factors may have influenced the spatial distribution of tourist attractions. We therefore make a provisional recommendation that the conclusion we have made be seriously considered but also further more in depth studies be undertaken. References Andreas P Exploring the evolution of tourism resorts. Annals of Tourism Research, 31(1): Cox D R, Lewis P A W The Statistical Analysis of Series of Events. London: Methuen. Cui D H, Sun Y Fractal-dimension-based study on optimization of spatial structure of Huzhou tourism scenic system. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 31(3): (in Chinese) Dredge D Destination place planning and design. Annals of Tourism Research, 26(4): ESRI ArcGIS Desktop Developer Help. ESRI Press. Friedman J R Regional development policy: a case study of Venezuela. Cambridge: MIT Press. Getis A, Ord J K The analysis of spatia1 association by the use of distance statistics. Geographica1 Analysis, 24(1): Geurs K,Wee B Accessibility evaluation of land-use and transport strategies review and research directions. Journal of Transport Geography, 12(2): Guo Q E, Zhong Y X, Li J X, et al The research on the spatial structure of A-grade tourist districts in Poyang Lake Eco-Economic Zone. Journal of Jiangxi Normal University (Natural Science), 36(6): (in Chinese) Jin C, Lu Y Q, Zhang L, et al An analysis of accessibility of tourist attractions based on land traffic net work: A case study of Nanjing. Geographical Research, 28(1): (in Chinese) Jin C, Xu J Quantitative study on diversity of tourism spot distribution in Jiangsu Province. Areal Research and Development, 31(6): (in Chinese) Lance G N, Williams W T A general theory of classificatory sorting strategies. I. Hierarchical systems. The Computer Journal, 9(4): Li X L, Liu Z B, Zhao J Space distribution type of residential area in Shiyang River Basin. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University(Natural Science Edition), 29(4): (in Chinese) Li Z X, Wu G X Evolution model and spatial structure for tourism resources in Luoyang City. Areal Research and Development,31(4): (in Chinese) Ma L, Ma Y F, Lin Z H A comparative study of the spatial structure of 100 tourism attractions. Resources Science, 35(2): (in Chinese) Mao X G, Song J P, Yu W Space structure and its evolution of A-grade tourist attractions in Beijing. Economic Geography, 31(8): (in Chinese) Mao Z Y, Li L Spatial Pattern: Measure and Application. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) Miossec J M Elements pourune Theorie de l Escape Touristique. In : Les Chasiers der Tourisme Centre des Hautes Etudes Touristique, Aix-en- Provence. Serie C: 36. (in French) Morris J M, Dumble P L, Wigan M R Accessibility indicators for transport planning. Transportation Research A, 13(2) : Pan J H, Cong Y B Spatial accessibility of scenic spot at 4A grade and above in China. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 32(11): (in Chinese) Qi X, Wang X Study on the spatial structures of tourist attractions in Chengyu Economic Zone. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 29(1): (in Chinese) Sophie M, Romain P Can the high speed rail reinforce tourism attractiveness? The case of the high speed rail between Perpignan (France) and Barcelona (Spain). Technovation, 29(9): Wang H, Li Y Z A study on spatial structure of scenic areas in Dalian city and its optimization. Areal Research And Development, 29(1): (in Chinese) Wang Z B,Xu J G,Fang C L, et al The study on county accessibility in China: Characteristics and effects on population agglomeration. Journal of Geographical Science, 21(1): Weaver D B Peripheries of the periphery: Tourism in Tobago and
9 20 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.6 No.1, 2015 Barbuda. Annals of Tourism Research, 25(2): Wei W, Chen J H Research on spatial structure of scenic spot in Zhejiang province based on geographic mathematics method. Tourism Research, 4(3): (in Chinese) Wilson A G A statistical theory of spatial distribution models. Transportation Research, 1(1): Xie Z H, Wu B H Tourism spatial structure of resources-based attractions in China. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 28(6): (in Chinese) Yan Q W, Bian Z F, Wang Z A spatial analysis on patterns of settlements distribution in Xuzhou. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 34(5): (in Chinese) Yitzhaki S On the extension of the Gini Index. International Economic Review, 24(3): Yuan J, Yu R L, Liu C L, et al Research on spatial structure of national A-grade tourist districts of Wuhan Metropolitan Area. Economic Geography, 30(2): (in Chinese) Zhang Y P, Wu J S, Huang X L, et al A study on the tourism spatial structure over the west coast of the Taiwan Strait Economic Zone. Resources Science, 33(9): (in Chinese) Zhao J, Chen C K Chinese Geography. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 382. (in Chinese) 基于计量地理分析的中国 A 级旅游景点 ( 区 ) 空间结构研究 潘竟虎 1, 李俊峰 1 2, 从忆波 1 西北师范大学地理与环境科学学院, 兰州 ; 2 兰州大学资源环境学院, 兰州 摘要 : 以 2012 年底中国 2424 个 A 级景区 ( 点 ) 为研究对象, 采用 GIS 空间分析和计量地理方法 ( 最近邻指数 样方分析 基尼系数和热点聚类等 ), 对 A 级旅游景点的空间结构特征进行了分析 ; 利用栅格成本加权距离算法计算了景点的空间可达性 ; 借助耗费分配方法划分了 4A 级及以上景点的服务范围 结果表明 : 总体上, 中国 A 级景点的空间分布呈现聚集分布的特点, 人文类景点的聚集度高于自然类景点 ;4A 级及以上景点的聚集度低于 4A 级以下景点 ;4A 级及以上人文类景点的聚集度高于 4A 级以下人文类景点 A 级旅游景点在中国八大地理分区中的分布也呈现集中分布状态, 空间分布的均匀度较低 受经济发展水平和旅游资源禀赋的影响,4A 级及以上景点的服务范围表现为西部 > 东部, 北方 > 南方的特征 景点的一级热点区主要集中分布在德庆 - 阿拉善左旗一线的东侧 ; 二级热点区由 11 个区域组成 ; 三级热点区则主要由京津 - 中原 - 长三角组成 关键词 : 空间结构 ; 空间可达性 ; 旅游景点 ;GIS; 中国
Analysis of the Tourism Locations of Chinese Provinces and Autonomous Regions: An Analysis Based on Cities
 Chinese Journal of Urban and Environmental Studies Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) 1450004 (9 pages) World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S2345748114500043 Analysis of the Tourism Locations of Chinese
Chinese Journal of Urban and Environmental Studies Vol. 2, No. 1 (2014) 1450004 (9 pages) World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S2345748114500043 Analysis of the Tourism Locations of Chinese
Analysis for Regional Differences and Influence Factor of Rural Income in China
 Modern Economy, 2012, 3, 578-583 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/me.2012.35076 Published Online September 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/me) Analysis for Regional Differences and Influence Factor of Rural
Modern Economy, 2012, 3, 578-583 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/me.2012.35076 Published Online September 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/me) Analysis for Regional Differences and Influence Factor of Rural
Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Pattern Evolution of Fishery Geographic Agglomeration in China
 2016 International Conference on Education, Management Science and Economics (ICEMSE-16) Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Pattern Evolution of Fishery Geographic Agglomeration in China
2016 International Conference on Education, Management Science and Economics (ICEMSE-16) Analysis of Spatial-Temporal Characteristics and Pattern Evolution of Fishery Geographic Agglomeration in China
A Numerical Simulation Analysis of (Hukou) Labour Mobility Restrictions in China
 A Numerical Simulation Analysis of (Hukou) Labour Mobility Restrictions in China John Whalley Department of Economics, The University of Western Ontario and Shunming Zhang Department of Finance, School
A Numerical Simulation Analysis of (Hukou) Labour Mobility Restrictions in China John Whalley Department of Economics, The University of Western Ontario and Shunming Zhang Department of Finance, School
Variance Analysis of Regional Per Capita Income Based on Principal Component Analysis and Cluster Analysis
 0 rd International Conference on Social Science (ICSS 0) ISBN: --0-0- Variance Analysis of Regional Per Capita Income Based on Principal Component Analysis and Cluster Analysis Yun HU,*, Ruo-Yu WANG, Ping-Ping
0 rd International Conference on Social Science (ICSS 0) ISBN: --0-0- Variance Analysis of Regional Per Capita Income Based on Principal Component Analysis and Cluster Analysis Yun HU,*, Ruo-Yu WANG, Ping-Ping
Sampling Scheme for 2003 General Social Survey of China
 Sampling Scheme for 2003 General Social Survey of China 1. Sampling Unit This survey uses a five-stage stratified sampling scheme with unequal probabilities. The sampling units at each stage are as follows:
Sampling Scheme for 2003 General Social Survey of China 1. Sampling Unit This survey uses a five-stage stratified sampling scheme with unequal probabilities. The sampling units at each stage are as follows:
Design, Development and Application of Northeast Asia Resources and Environment Scientific Expedition Data Platform
 September, 2011 J. Resour. Ecol. 2011 2(3) 266-271 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-764x.2011.03.010 www.jorae.cn Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.2 No.3 NE Asia Design, Development and Application of Northeast
September, 2011 J. Resour. Ecol. 2011 2(3) 266-271 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-764x.2011.03.010 www.jorae.cn Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.2 No.3 NE Asia Design, Development and Application of Northeast
2012 Typhoon Activity Prediction
 2012 Typhoon Activity Prediction Published by Shanghai Typhoon Institute of China Meteorological Administration 4 May 2012 Prediction of 2012 Northwest Pacific Basin and South China Sea Tropical Cyclone
2012 Typhoon Activity Prediction Published by Shanghai Typhoon Institute of China Meteorological Administration 4 May 2012 Prediction of 2012 Northwest Pacific Basin and South China Sea Tropical Cyclone
A Study on Dynamics and Problems of Residential Suburbanization in Xi an
 Nanyang Technological University From the SelectedWorks of Man LUO Spring April 2, 2014 A Study on Dynamics and Problems of Residential Suburbanization in Xi an Man LUO Available at: https://works.bepress.com/man_luo/1/
Nanyang Technological University From the SelectedWorks of Man LUO Spring April 2, 2014 A Study on Dynamics and Problems of Residential Suburbanization in Xi an Man LUO Available at: https://works.bepress.com/man_luo/1/
The Impact of Tianjin-Baoding Intercity Railway on the Traffic Pattern of the Jing-Jin-Ji Urban Agglomeration QI Lei1,a*,GUO Jing2
 3rd International Conference on Management, Education Technology and Sports Science (METSS 2016) The Impact of Tianjin-Baoding Intercity Railway on the Traffic Pattern of the Jing-Jin-Ji Urban Agglomeration
3rd International Conference on Management, Education Technology and Sports Science (METSS 2016) The Impact of Tianjin-Baoding Intercity Railway on the Traffic Pattern of the Jing-Jin-Ji Urban Agglomeration
Spatial Differentiation of Rural Touristization and Its Determinants in China: A Geo-detector-based Case Study of Yesanpo Scenic Area
 Nov., 2016 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 7 No.6 J. Resour. Ecol. 2016 7(6) 464-471 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2016.06.006 www.jorae.cn Spatial Differentiation of Rural Touristization and Its
Nov., 2016 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 7 No.6 J. Resour. Ecol. 2016 7(6) 464-471 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2016.06.006 www.jorae.cn Spatial Differentiation of Rural Touristization and Its
Extraction and Dynamic Spatial-Temporal Changes of Grassland Deterioration Research Hot Regions in China
 July, 2017 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 8 No.4 J. Resour. Ecol. 2017 8(4) 352-358 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2017.04.006 www.jorae.cn Extraction and Dynamic Spatial-Temporal Changes of Grassland
July, 2017 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 8 No.4 J. Resour. Ecol. 2017 8(4) 352-358 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2017.04.006 www.jorae.cn Extraction and Dynamic Spatial-Temporal Changes of Grassland
A Spatial Econometric Approach to Model the Growth of Tourism Flows to China Cities
 April 15, 2010 AAG 2010 Conference, Washington DC A Spatial Econometric Approach to Model the Growth of Tourism Flows to China Cities Yang Yang University of Florida Kevin. K.F. Wong The Hong Kong Polytechnic
April 15, 2010 AAG 2010 Conference, Washington DC A Spatial Econometric Approach to Model the Growth of Tourism Flows to China Cities Yang Yang University of Florida Kevin. K.F. Wong The Hong Kong Polytechnic
INTERNATIONAL EXPERIENCE IN INNOVATIONS IN METRO RAIL. Gerald Ollivier Transport Cluster Leader Singapore, World Bank
 INTERNATIONAL EXPERIENCE IN INNOVATIONS IN METRO RAIL Gerald Ollivier Transport Cluster Leader Singapore, World Bank Innovation 1: Density Aligned with Transit From Serge Salat London s Jobs densities
INTERNATIONAL EXPERIENCE IN INNOVATIONS IN METRO RAIL Gerald Ollivier Transport Cluster Leader Singapore, World Bank Innovation 1: Density Aligned with Transit From Serge Salat London s Jobs densities
Galileo Galilei ( ) Title page of Galileo's Dialogue concerning the two chief world systems, published in Florence in February 1632.
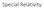 Special Relativity Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) Title page of Galileo's Dialogue concerning the two chief world systems, published in Florence in February 1632. 2 Galilean Transformation z z!!! r ' = r
Special Relativity Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) Title page of Galileo's Dialogue concerning the two chief world systems, published in Florence in February 1632. 2 Galilean Transformation z z!!! r ' = r
Study on Spatial Structure Dynamic Evolution of Tourism Economic Zone along Wuhan-Guangzhou HSR
 Open Access Library Journal 2017, Volume 4, e4045 ISSN Online: 2333-9721 ISSN Print: 2333-9705 Study on Spatial Structure Dynamic Evolution of Tourism Economic Zone along Wuhan-Guangzhou HSR Chun Liu 1,2
Open Access Library Journal 2017, Volume 4, e4045 ISSN Online: 2333-9721 ISSN Print: 2333-9705 Study on Spatial Structure Dynamic Evolution of Tourism Economic Zone along Wuhan-Guangzhou HSR Chun Liu 1,2
Quantitative Measurement of Urban Expansion and Its Driving Factors in Qingdao: An Empirical Analysis Based on County Unit Data
 May, 2015 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.6 o.3 J. Resour. Ecol. 2015 6 (3) 172-179 DOI:10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2015.03.006 www.jorae.cn Article Quantitative Measurement of Urban Expansion and Its
May, 2015 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.6 o.3 J. Resour. Ecol. 2015 6 (3) 172-179 DOI:10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2015.03.006 www.jorae.cn Article Quantitative Measurement of Urban Expansion and Its
Source mechanism solution
 Source mechanism solution Contents Source mechanism solution 1 1. A general introduction 1 2. A step-by-step guide 1 Step-1: Prepare data files 1 Step-2: Start GeoTaos or GeoTaos_Map 2 Step-3: Convert
Source mechanism solution Contents Source mechanism solution 1 1. A general introduction 1 2. A step-by-step guide 1 Step-1: Prepare data files 1 Step-2: Start GeoTaos or GeoTaos_Map 2 Step-3: Convert
Remote Sensing Applications in Agricultural Statistics at China NBS. Yu Xinhua Department of Rural Surveys, National Bureau of Statistics(NBS)
 Remote Sensing Applications in Agricultural Statistics at China NBS Yu Xinhua Department of Rural Surveys, National Bureau of Statistics(NBS) Outline Introduction Remote Sensing Measurement Area Frame
Remote Sensing Applications in Agricultural Statistics at China NBS Yu Xinhua Department of Rural Surveys, National Bureau of Statistics(NBS) Outline Introduction Remote Sensing Measurement Area Frame
Area Classification of Surrounding Parking Facility Based on Land Use Functionality
 Open Journal of Applied Sciences, 0,, 80-85 Published Online July 0 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojapps http://dx.doi.org/0.4/ojapps.0.709 Area Classification of Surrounding Parking Facility
Open Journal of Applied Sciences, 0,, 80-85 Published Online July 0 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojapps http://dx.doi.org/0.4/ojapps.0.709 Area Classification of Surrounding Parking Facility
2012 AP Calculus BC 模拟试卷
 0 AP Calculus BC 模拟试卷 北京新东方罗勇 luoyong@df.cn 0-3- 说明 : 请严格按照实际考试时间进行模拟, 考试时间共 95 分钟 Multiple-Choice section A 部分 : 无计算器 B 部分 : 有计算器 Free-response section A 部分 : 有计算器 B 部分 : 无计算器 总计 45 题 /05 分钟 8 题,55 分钟
0 AP Calculus BC 模拟试卷 北京新东方罗勇 luoyong@df.cn 0-3- 说明 : 请严格按照实际考试时间进行模拟, 考试时间共 95 分钟 Multiple-Choice section A 部分 : 无计算器 B 部分 : 有计算器 Free-response section A 部分 : 有计算器 B 部分 : 无计算器 总计 45 题 /05 分钟 8 题,55 分钟
A Study on Differences of China s Regional Economic Development Level Based on Cluster Analysis
 MATEC Web of Conferences 22, 0 5 022 ( 2015) DOI: 10.1051/ matec conf / 201 5 220 5 022 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2015 A Study on Differences of China s Regional Economic Development
MATEC Web of Conferences 22, 0 5 022 ( 2015) DOI: 10.1051/ matec conf / 201 5 220 5 022 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2015 A Study on Differences of China s Regional Economic Development
Factors Driving the Expansion of Construction Land: A Panel Data Study of Districts and Counties in Ningbo City, China
 July, 2018 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 9 No.4 J. Resour. Ecol. 2018 9(4) 365-373 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2018.04.004 www.jorae.cn Factors Driving the Expansion of Construction Land: A Panel
July, 2018 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 9 No.4 J. Resour. Ecol. 2018 9(4) 365-373 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2018.04.004 www.jorae.cn Factors Driving the Expansion of Construction Land: A Panel
Quantitative Assessment of Seismic Mortality Risks in China
 March, 2011 J. Resour. Ecol. 2011 2(1) 83-90 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-764x.2011.01.012 www.jorae.cn Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.2 No.1 Article Quantitative Assessment of Seismic Mortality Risks
March, 2011 J. Resour. Ecol. 2011 2(1) 83-90 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-764x.2011.01.012 www.jorae.cn Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.2 No.1 Article Quantitative Assessment of Seismic Mortality Risks
Sustainable Cities and Communities based on Indicators on Urbanization 地理国情监测技术. Prof. Dr. John W. Z. SHI The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
 IAEG- SDGs WG on Geospatial Information, 1 st Expert Group Meeting 12-14 Dec 2016 Mexico City Measure 地理国情监测技术 Sustainable Cities and Communities 专业 based on Indicators on Urbanization Prof. Dr. John W.
IAEG- SDGs WG on Geospatial Information, 1 st Expert Group Meeting 12-14 Dec 2016 Mexico City Measure 地理国情监测技术 Sustainable Cities and Communities 专业 based on Indicators on Urbanization Prof. Dr. John W.
The Agglomeration Characteristics of Blue Economic Zone of Shandong Peninsula. Fuhui Jing 1, a, Lina Chang 2,b,Hong Wang3,c
 3rd International Conference on Education, Management, Arts, Economics and Social Science (ICEMAESS 2015) The Agglomeration Characteristics of Blue Economic Zone of Shandong Peninsula Fuhui Jing 1, a,
3rd International Conference on Education, Management, Arts, Economics and Social Science (ICEMAESS 2015) The Agglomeration Characteristics of Blue Economic Zone of Shandong Peninsula Fuhui Jing 1, a,
Road & Railway Network Density Dataset at 1 km over the Belt and Road and Surround Region
 Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery. 2017, 1(4): 402-407 DOI:10.3974/geodp.2017.04.03 www.geodoi.ac.cn 2017 GCdataPR Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository Road & Railway Network Density
Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery. 2017, 1(4): 402-407 DOI:10.3974/geodp.2017.04.03 www.geodoi.ac.cn 2017 GCdataPR Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository Road & Railway Network Density
Sustainable tourism development monitor: university as a driver for sustainable tourism based on experience and lessons from China ---
 Sustainable tourism development monitor: university as a driver for sustainable tourism based on experience and lessons from China --- THE SCHOOL OF TOURISM MANAGEMENT SUN YAT- SEN UNIVERSITY XU HONGGANG
Sustainable tourism development monitor: university as a driver for sustainable tourism based on experience and lessons from China --- THE SCHOOL OF TOURISM MANAGEMENT SUN YAT- SEN UNIVERSITY XU HONGGANG
The dynamic N1-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA 报告人 : 沈胤
 The dynamic N1-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA 报告人 : 沈胤 2016.12.26 研究背景 RNA 甲基化作为表观遗传学研究的重要内容之一, 是指发生在 RNA 分子上不同位置的甲基化修饰现象 RNA 甲基化在调控基因表达 剪接 RNA 编辑 RNA 稳定性 控制 mrna 寿命和降解等方面可能扮演重要角色
The dynamic N1-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA 报告人 : 沈胤 2016.12.26 研究背景 RNA 甲基化作为表观遗传学研究的重要内容之一, 是指发生在 RNA 分子上不同位置的甲基化修饰现象 RNA 甲基化在调控基因表达 剪接 RNA 编辑 RNA 稳定性 控制 mrna 寿命和降解等方面可能扮演重要角色
Technological Progress, Industrial Transformation and Regional Development
 23/11/2012,RSA. London, UK Technological Progress, Industrial Transformation and Regional Development A Case Study of Yangtze River Delta Zhen Feng School of Architecture and Urban Planning, Nanjing University
23/11/2012,RSA. London, UK Technological Progress, Industrial Transformation and Regional Development A Case Study of Yangtze River Delta Zhen Feng School of Architecture and Urban Planning, Nanjing University
DISTRIBUTION AND DIURNAL VARIATION OF WARM-SEASON SHORT-DURATION HEAVY RAINFALL IN RELATION TO THE MCSS IN CHINA
 3 DISTRIBUTION AND DIURNAL VARIATION OF WARM-SEASON SHORT-DURATION HEAVY RAINFALL IN RELATION TO THE MCSS IN CHINA Jiong Chen 1, Yongguang Zheng 1*, Xiaoling Zhang 1, Peijun Zhu 2 1 National Meteorological
3 DISTRIBUTION AND DIURNAL VARIATION OF WARM-SEASON SHORT-DURATION HEAVY RAINFALL IN RELATION TO THE MCSS IN CHINA Jiong Chen 1, Yongguang Zheng 1*, Xiaoling Zhang 1, Peijun Zhu 2 1 National Meteorological
Land Use Regionalization of Rural Settlements in China
 Chin. Geogra. Sci. 2013 Vol. 23 No. 4 pp. 421 434 Springer Science Press doi: 10.1007/s11769-013-0592-y www.springerlink.com/content/1002-0063 Land Use Regionalization of Rural Settlements in China SONG
Chin. Geogra. Sci. 2013 Vol. 23 No. 4 pp. 421 434 Springer Science Press doi: 10.1007/s11769-013-0592-y www.springerlink.com/content/1002-0063 Land Use Regionalization of Rural Settlements in China SONG
Journal of Asian Business Strategy ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN FOREIGN TRADE AND REGIONAL DISPARITY IN CHINA IN THE POST-REFORM ERA
 2016 Asian Economic and Social Society. All rights reserved ISSN (P): 2309-8295, ISSN (E): 2225-4226 Volume 6, Issue 3, 2016, pp. 50-62 Journal of Asian Business Strategy http://aessweb.com/journal-detail.php?id=5006
2016 Asian Economic and Social Society. All rights reserved ISSN (P): 2309-8295, ISSN (E): 2225-4226 Volume 6, Issue 3, 2016, pp. 50-62 Journal of Asian Business Strategy http://aessweb.com/journal-detail.php?id=5006
C.V. of Dr. Xueguang Ma
 C.V. of Dr. Xueguang Ma Xueguang Ma Ph.D, Associate Professor Director, Institute of Land Resources Management, Ocean University of China(OUC) Director, Sino-Australian Joint Research Centre for Coastal
C.V. of Dr. Xueguang Ma Xueguang Ma Ph.D, Associate Professor Director, Institute of Land Resources Management, Ocean University of China(OUC) Director, Sino-Australian Joint Research Centre for Coastal
China s River Chiefs and Other Protected River Systems in the World 中国河长制与世界河流保护地体系
 China s River Chiefs and Other Protected River Systems in the World 中国河长制与世界河流保护地体系 Dr. Li Peng 李鹏 Yunnan University, China Aldo Leopold Wilderness Research Institute, U.S.A content 1. China s River Chiefs
China s River Chiefs and Other Protected River Systems in the World 中国河长制与世界河流保护地体系 Dr. Li Peng 李鹏 Yunnan University, China Aldo Leopold Wilderness Research Institute, U.S.A content 1. China s River Chiefs
A Case Study of Regional Dynamics of China 中国区域动态案例研究
 A Case Study of Regional Dynamics of China 中国区域动态案例研究 Shuming Bao Spatial Data Center & China Data Center University of Michigan 1:00 PM - 2:00 PM, Tue, Feb 6, 2018 EST USA A Case Study of Regional Dynamics
A Case Study of Regional Dynamics of China 中国区域动态案例研究 Shuming Bao Spatial Data Center & China Data Center University of Michigan 1:00 PM - 2:00 PM, Tue, Feb 6, 2018 EST USA A Case Study of Regional Dynamics
YIFEI SUN. Department of Geography California State University Northridge, CA Tel: (818) (o)
 YIFEI SUN Department of Geography California State University Northridge, CA 91330-8249 Tel: (818) 677-3529 (o) Email: yifei.sun@csun.edu EDUCATION Ph.D. in Geography, 2001. State University of New York
YIFEI SUN Department of Geography California State University Northridge, CA 91330-8249 Tel: (818) 677-3529 (o) Email: yifei.sun@csun.edu EDUCATION Ph.D. in Geography, 2001. State University of New York
Rigorous back analysis of shear strength parameters of landslide slip
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 1459 1464 Rigorous back analysis of shear strength parameters of landslide slip Ke ZHANG 1, Ping CAO 1, Rui BAO 1,2 1. School of Resources and Safety Engineering,
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 1459 1464 Rigorous back analysis of shear strength parameters of landslide slip Ke ZHANG 1, Ping CAO 1, Rui BAO 1,2 1. School of Resources and Safety Engineering,
上海激光电子伽玛源 (SLEGS) 样机的实验介绍
 上海激光电子伽玛源 (SLEGS) 样机的实验介绍 Pan Qiangyan for SLEGS collaborators 一. 引言二. 装置布局三. 实验及其结果四. 结论 一, 引言 为建设 SLEGS 光束线提供参考和研制依据, 中科院上海应用物理研究所于 2005 年成立了以徐望研究员为组长的 SLEGS 小组, 开展 SLEGS 样机的实验工作 ; 在中科院知识创新工程方向性项目 (
上海激光电子伽玛源 (SLEGS) 样机的实验介绍 Pan Qiangyan for SLEGS collaborators 一. 引言二. 装置布局三. 实验及其结果四. 结论 一, 引言 为建设 SLEGS 光束线提供参考和研制依据, 中科院上海应用物理研究所于 2005 年成立了以徐望研究员为组长的 SLEGS 小组, 开展 SLEGS 样机的实验工作 ; 在中科院知识创新工程方向性项目 (
RAIL-INDUCED TRAFFIC IN CHINA
 NAN HE, Ph.D. 1 (Corresponding author) E-mail: honny_he@hotmail.com JITAO LI, Ph.D. Candidate 1 E-mail: to_lijao@djtu.edu.cn YU WANG, Ph.D. 1 E-mail: wangyudjtu@163.com CAIWEN MA, Ph.D. 1 E-mail: macaiwen@djtu.edu.cn
NAN HE, Ph.D. 1 (Corresponding author) E-mail: honny_he@hotmail.com JITAO LI, Ph.D. Candidate 1 E-mail: to_lijao@djtu.edu.cn YU WANG, Ph.D. 1 E-mail: wangyudjtu@163.com CAIWEN MA, Ph.D. 1 E-mail: macaiwen@djtu.edu.cn
The Lagrange Mean Value Theorem Of Functions of n Variables
 陕西师范大学学士学位论文 The Lagrage Mea Value Theorem Of Fuctios of Variables 作 者 单 位 数学与信息科学学院 指 导 老 师 曹怀 信 作 者 姓 名 李 碧 专 业 班 级数学与应用数学专业 4 级 班 The Lagrage Mea Value Theorem of a Fuctio of Variables LI i lass, Grade
陕西师范大学学士学位论文 The Lagrage Mea Value Theorem Of Fuctios of Variables 作 者 单 位 数学与信息科学学院 指 导 老 师 曹怀 信 作 者 姓 名 李 碧 专 业 班 级数学与应用数学专业 4 级 班 The Lagrage Mea Value Theorem of a Fuctio of Variables LI i lass, Grade
Spatial-temporal Changes in Ecological Risk of Land Use before and after Grain-for-Green Policy in Zhengning County, Gansu Province
 March, 2013 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.4 No.1 J. Resour. Ecol. 2013 4 (1) 036-042 DOI:10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2013.01.005 www.jorae.cn rticle Spatial-temporal Changes in Ecological Risk of Land
March, 2013 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.4 No.1 J. Resour. Ecol. 2013 4 (1) 036-042 DOI:10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2013.01.005 www.jorae.cn rticle Spatial-temporal Changes in Ecological Risk of Land
d) There is a Web page that includes links to both Web page A and Web page B.
 P403-406 5. Determine whether the relation R on the set of all eb pages is reflexive( 自反 ), symmetric( 对 称 ), antisymmetric( 反对称 ), and/or transitive( 传递 ), where (a, b) R if and only if a) Everyone who
P403-406 5. Determine whether the relation R on the set of all eb pages is reflexive( 自反 ), symmetric( 对 称 ), antisymmetric( 反对称 ), and/or transitive( 传递 ), where (a, b) R if and only if a) Everyone who
An IntRoduction to grey methods by using R
 An IntRoduction to grey methods by using R Tan Xi Department of Statistics, NUFE Nov 6, 2009 2009-2-5 Contents: A brief introduction to Grey Methods An analysis of Degree of Grey Incidence Grey GM(, )
An IntRoduction to grey methods by using R Tan Xi Department of Statistics, NUFE Nov 6, 2009 2009-2-5 Contents: A brief introduction to Grey Methods An analysis of Degree of Grey Incidence Grey GM(, )
Analysis of Impact of Urban Agglomeration Planning of Middle and Lower Yangtze River on International Trade Development in Central China.
 International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2015) Analysis of Impact of Urban Agglomeration Planning of Middle and Lower Yangtze River on International Trade Development
International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2015) Analysis of Impact of Urban Agglomeration Planning of Middle and Lower Yangtze River on International Trade Development
Study on Shandong Expressway Network Planning Based on Highway Transportation System
 Study on Shandong Expressway Network Planning Based on Highway Transportation System Fei Peng a, Yimeng Wang b and Chengjun Shi c School of Automobile, Changan University, Xian 71000, China; apengfei0799@163.com,
Study on Shandong Expressway Network Planning Based on Highway Transportation System Fei Peng a, Yimeng Wang b and Chengjun Shi c School of Automobile, Changan University, Xian 71000, China; apengfei0799@163.com,
Application of Argo Data in the Analysis of Water Masses in the Northwest Pacific Ocean
 Vol.10 No.2 Marine Science Bulletin Oct. 2008 Application of Argo Data in the Analysis of Water Masses in the Northwest Pacific Ocean SUN Chaohui, XU Jianping, LIU Zenghong, TONG Mingrong, ZHU Bokang State
Vol.10 No.2 Marine Science Bulletin Oct. 2008 Application of Argo Data in the Analysis of Water Masses in the Northwest Pacific Ocean SUN Chaohui, XU Jianping, LIU Zenghong, TONG Mingrong, ZHU Bokang State
Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology 2014, 51(2): DOI: /j.issn 信息物质的化学分析技术 黄翠虹 , ; 2.
 Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology 204, 5(2): 586 590. DOI: 0.7679/j.issn.2095 353.204.069 信息物质的化学分析技术 * 李静静 雷彩燕 黄翠虹 2 周琳 闫凤鸣 **., 450002; 2., 528333 摘要 - GC-MS HPLC GC-MS 关键词 - Chemical analysis techniques
Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology 204, 5(2): 586 590. DOI: 0.7679/j.issn.2095 353.204.069 信息物质的化学分析技术 * 李静静 雷彩燕 黄翠虹 2 周琳 闫凤鸣 **., 450002; 2., 528333 摘要 - GC-MS HPLC GC-MS 关键词 - Chemical analysis techniques
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES INEQUALITY CHANGE IN CHINA AND (HUKOU) LABOUR MOBILITY RESTRICTIONS. John Whalley Shunming Zhang
 NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES INEQUALITY CHANGE IN CHINA AND (HUKOU) LABOUR MOBILITY RESTRICTIONS John Whalley Shunming Zhang Working Paper 10683 http://www.nber.org/papers/w10683 NATIONAL BUREAU OF ECONOMIC
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES INEQUALITY CHANGE IN CHINA AND (HUKOU) LABOUR MOBILITY RESTRICTIONS John Whalley Shunming Zhang Working Paper 10683 http://www.nber.org/papers/w10683 NATIONAL BUREAU OF ECONOMIC
2011 Typhoon Activity Prediction
 2011 Typhoon Activity Prediction Published by Shanghai Typhoon Institute of China Meteorological Administration April 21th, 2011 Prediction of 2011 Northwest Pacific Basin and South China Sea Tropical
2011 Typhoon Activity Prediction Published by Shanghai Typhoon Institute of China Meteorological Administration April 21th, 2011 Prediction of 2011 Northwest Pacific Basin and South China Sea Tropical
通量数据质量控制的理论与方法 理加联合科技有限公司
 通量数据质量控制的理论与方法 理加联合科技有限公司 通量变量 Rn = LE + H + G (W m -2 s -1 ) 净辐射 潜热 感热 地表热 通量 通量 通量 通量 Fc (mg m -2 s -1 ) 二氧化碳通量 τ [(kg m s -1 ) m -2 s -1 ] 动量通量 质量控制 1. 概率统计方法 2. 趋势法 3. 大气物理依据 4. 测定实地诊断 5. 仪器物理依据 '
通量数据质量控制的理论与方法 理加联合科技有限公司 通量变量 Rn = LE + H + G (W m -2 s -1 ) 净辐射 潜热 感热 地表热 通量 通量 通量 通量 Fc (mg m -2 s -1 ) 二氧化碳通量 τ [(kg m s -1 ) m -2 s -1 ] 动量通量 质量控制 1. 概率统计方法 2. 趋势法 3. 大气物理依据 4. 测定实地诊断 5. 仪器物理依据 '
Comprehensive Evaluation of Social Benefits of Mineral Resources Development in Ordos Basin
 Studies in Sociology of Science Vol. 4, No. 1, 2013, pp. 25-29 DOI:10.3968/j.sss.1923018420130401.2909 ISSN 1923-0176 [Print] ISSN 1923-0184 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org Comprehensive Evaluation
Studies in Sociology of Science Vol. 4, No. 1, 2013, pp. 25-29 DOI:10.3968/j.sss.1923018420130401.2909 ISSN 1923-0176 [Print] ISSN 1923-0184 [Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org Comprehensive Evaluation
LABELING RESIDENTIAL COMMUNITY CHARACTERISTICS FROM COLLECTIVE ACTIVITY PATTERNS USING TAXI TRIP DATA
 LABELING RESIDENTIAL COMMUNITY CHARACTERISTICS FROM COLLECTIVE ACTIVITY PATTERNS USING TAXI TRIP DATA Yang Zhou 1, 3, *, Zhixiang Fang 2 1 Wuhan Land Use and Urban Spatial Planning Research Center, 55Sanyang
LABELING RESIDENTIAL COMMUNITY CHARACTERISTICS FROM COLLECTIVE ACTIVITY PATTERNS USING TAXI TRIP DATA Yang Zhou 1, 3, *, Zhixiang Fang 2 1 Wuhan Land Use and Urban Spatial Planning Research Center, 55Sanyang
三类调度问题的复合派遣算法及其在医疗运营管理中的应用
 申请上海交通大学博士学位论文 三类调度问题的复合派遣算法及其在医疗运营管理中的应用 博士生 : 苏惠荞 导师 : 万国华教授 专业 : 管理科学与工程 研究方向 : 运作管理 学校代码 : 10248 上海交通大学安泰经济与管理学院 2017 年 6 月 Dissertation Submitted to Shanghai Jiao Tong University for the Degree of
申请上海交通大学博士学位论文 三类调度问题的复合派遣算法及其在医疗运营管理中的应用 博士生 : 苏惠荞 导师 : 万国华教授 专业 : 管理科学与工程 研究方向 : 运作管理 学校代码 : 10248 上海交通大学安泰经济与管理学院 2017 年 6 月 Dissertation Submitted to Shanghai Jiao Tong University for the Degree of
三系杂交棉花粉育性对高温和低温胁迫的反应. Reaction of Pollen Fertility to High or Low Temperature Stresses in CMS-Based Hybrid Cotton 邵明彦 1 张海平 张昭伟 朱云国 袁淑娜 1
 作物学报 ACTA AGRONOMICA SINICA 2009, 35(): 2085 2090 http://www.chinacrops.org/zwxb/ ISSN 0496-3490; CODEN TSHPA9 E-mail: xbzw@chinajournal.net.cn DOI: 0.3724/SP.J.006.2009.02085 三系杂交棉花粉育性对高温和低温胁迫的反应 倪密刘英新
作物学报 ACTA AGRONOMICA SINICA 2009, 35(): 2085 2090 http://www.chinacrops.org/zwxb/ ISSN 0496-3490; CODEN TSHPA9 E-mail: xbzw@chinajournal.net.cn DOI: 0.3724/SP.J.006.2009.02085 三系杂交棉花粉育性对高温和低温胁迫的反应 倪密刘英新
Measurement of accelerator neutron radiation field spectrum by Extended Range Neutron Multisphere Spectrometers and unfolding program
 Measurement of accelerator neutron radiation field spectrum by Extended Range Neutron Multisphere Spectrometers and unfolding program LI Guanjia( 李冠稼 ), WANG Qingbin( 王庆斌 ), MA Zhongjian( 马忠剑 ), GUO Siming(
Measurement of accelerator neutron radiation field spectrum by Extended Range Neutron Multisphere Spectrometers and unfolding program LI Guanjia( 李冠稼 ), WANG Qingbin( 王庆斌 ), MA Zhongjian( 马忠剑 ), GUO Siming(
Solar Radiation Climatology Calculation in China
 June, 214 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.5 o.2 J. Resour. Ecol. 214 5 (2) 132-138 DOI:1.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.214.2.5 www.jorae.cn Article Solar Radiation Climatology Calculation in China WAG Chenliang
June, 214 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol.5 o.2 J. Resour. Ecol. 214 5 (2) 132-138 DOI:1.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.214.2.5 www.jorae.cn Article Solar Radiation Climatology Calculation in China WAG Chenliang
CAGS. The First Marine Observation Network System: Neptune Canada Submarine Observation Technology. JI Zai-liang 1), DONG Shu-wen 2)
 2012 1 Jan. 2012 33 1 : 13-22 Acta Geoscientica Sinica Vol.33 No.1: 13-22 www.cagsbulletin.com www. 地球学报.com 摘 加拿大 海王星 海底观测技术 1), 2) 1) V8N5J6; 2), 100037 要 :, 5,,, ; ; ; ; ; ;, ; ; ; 关键词 : ; ; ; ; ; 9
2012 1 Jan. 2012 33 1 : 13-22 Acta Geoscientica Sinica Vol.33 No.1: 13-22 www.cagsbulletin.com www. 地球学报.com 摘 加拿大 海王星 海底观测技术 1), 2) 1) V8N5J6; 2), 100037 要 :, 5,,, ; ; ; ; ; ;, ; ; ; 关键词 : ; ; ; ; ; 9
Recovering from the Recovery
 Recovering from the Recovery A Community-level View of Post- Earthquake Planning in the Historic Qiang Minority Ethnic Villages of Sichuan (A Report from the Field) Dan Abramson 艾丹, University of Washington
Recovering from the Recovery A Community-level View of Post- Earthquake Planning in the Historic Qiang Minority Ethnic Villages of Sichuan (A Report from the Field) Dan Abramson 艾丹, University of Washington
Correlation Analysis between Agglomeration Effect of Producer Service and Manufacture Labor Productivity in China
 American Journal of Industrial and Business Management, 2015, 5, 1-10 Published Online January 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajibm http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajibm.2015.51001 Correlation
American Journal of Industrial and Business Management, 2015, 5, 1-10 Published Online January 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajibm http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajibm.2015.51001 Correlation
GIS SUPPORTED ANALYSIS ON CITY GATHERING IN CHINA. Ren Fuhu
 GIS SUPPORTED ANALYSIS ON CITY GATHERING IN CHINA Ren Fuhu Murai Laboratory Institute of Industrial Science, University of Tokyo 7-22-1, Roppongi, Minato-ku, Tokyo 106, JAPAN ABSTRACT: Urbanization is
GIS SUPPORTED ANALYSIS ON CITY GATHERING IN CHINA Ren Fuhu Murai Laboratory Institute of Industrial Science, University of Tokyo 7-22-1, Roppongi, Minato-ku, Tokyo 106, JAPAN ABSTRACT: Urbanization is
Spatio-Temporal Changes of Population Density and Urbanization Pattern in China ( )
 Spatio-Temporal Changes of Population Density and Urbanization Pattern in China (2000 2010) Mao Qizhi, Long Ying, Wu Kang Abstract Population distribution and their temporal variation are a direct proxy
Spatio-Temporal Changes of Population Density and Urbanization Pattern in China (2000 2010) Mao Qizhi, Long Ying, Wu Kang Abstract Population distribution and their temporal variation are a direct proxy
Lanzhou Urban Growth Prediction Based on Cellular Automata 1
 Lanzhou Urban Growth Prediction Based on Cellular Automata 1 Yaowen Xie*, Aigong Ma, Haoyu Wang Key Laboratory of West China's Environmental System (Ministry of Education), Lanzhou University, Lanzhou,
Lanzhou Urban Growth Prediction Based on Cellular Automata 1 Yaowen Xie*, Aigong Ma, Haoyu Wang Key Laboratory of West China's Environmental System (Ministry of Education), Lanzhou University, Lanzhou,
Creating a Provincial Long-Term Growth Model for China using the Kohonen Algorithm
 Creating a Provincial Long-Term Growth Model for China using the Kohonen Algorithm Elpida Makriyannis, Department of Computer Science, University College London, Gower Street, London, WC1E 6BT, U.K. Philip
Creating a Provincial Long-Term Growth Model for China using the Kohonen Algorithm Elpida Makriyannis, Department of Computer Science, University College London, Gower Street, London, WC1E 6BT, U.K. Philip
How Does Straw Burning Affect Urban Air Quality in China?
 How Does Straw Burning Affect Urban Air Quality in China? Shiqi (Steven) Guo The Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies, Geneva September 2017, UNU-WIDER Effects of Air Pollution Health
How Does Straw Burning Affect Urban Air Quality in China? Shiqi (Steven) Guo The Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies, Geneva September 2017, UNU-WIDER Effects of Air Pollution Health
Synthesis of anisole by vapor phase methylation of phenol with methanol over catalysts supported on activated alumina
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (216) 72 726 催化学报 216 年第 37 卷第 5 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Synthesis of anisole by vapor
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (216) 72 726 催化学报 216 年第 37 卷第 5 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Synthesis of anisole by vapor
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 6 th edition
 Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 6 th edition Presented: 杜文静 E-mail: wjdu@sdu.edu.cn Telephone: 88399596-2511 1 Chapter 4 two-dimensional steady state conduction Contents and objectives Two-dimensional
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 6 th edition Presented: 杜文静 E-mail: wjdu@sdu.edu.cn Telephone: 88399596-2511 1 Chapter 4 two-dimensional steady state conduction Contents and objectives Two-dimensional
Optimized positioning for accommodation centers in GIS using AHP techniques; a case study: Hamedan city
 Journal of Tourism & Hospitality Research Islamic Azad University, Garmsar Branch Vol. 2, No. 2, Autumn 2012, Pp.19-29 Optimized positioning for accommodation in GIS using AHP techniques; a case study:
Journal of Tourism & Hospitality Research Islamic Azad University, Garmsar Branch Vol. 2, No. 2, Autumn 2012, Pp.19-29 Optimized positioning for accommodation in GIS using AHP techniques; a case study:
Application of Internet+ Field Survey Technology in China s Land Management
 Application of Internet+ Field Survey Technology in China s Land Management Zheng Yu,China Land Surveying and Planning Institute, Land Survey Agency Key words: Internet+, Field Survey, Land Management
Application of Internet+ Field Survey Technology in China s Land Management Zheng Yu,China Land Surveying and Planning Institute, Land Survey Agency Key words: Internet+, Field Survey, Land Management
Article Internet Access, Spillover and Regional Development in China
 Article Internet Access, Spillover and Regional Development in China Juan Lin 1, Zhou Yu 2, *, Yehua Dennis Wei 3 and Mingfeng Wang 1 1 Center for Modern Chinese City Studies, East China Normal University,
Article Internet Access, Spillover and Regional Development in China Juan Lin 1, Zhou Yu 2, *, Yehua Dennis Wei 3 and Mingfeng Wang 1 1 Center for Modern Chinese City Studies, East China Normal University,
Remote sensing of haze aerosol over eastern China
 ISALSaRS'17, USTC, 21-June-2017 China University of Mining and Technology Remote sensing of haze aerosol over eastern China Qin Kai( 秦凯 ), CUMT ( 中国矿业大学 ) Wu Lixin, CSU( 中南大学 ) Wong Mansing, Hong Kong
ISALSaRS'17, USTC, 21-June-2017 China University of Mining and Technology Remote sensing of haze aerosol over eastern China Qin Kai( 秦凯 ), CUMT ( 中国矿业大学 ) Wu Lixin, CSU( 中南大学 ) Wong Mansing, Hong Kong
Understanding China Census Data with GIS By Shuming Bao and Susan Haynie China Data Center, University of Michigan
 Understanding China Census Data with GIS By Shuming Bao and Susan Haynie China Data Center, University of Michigan The Census data for China provides comprehensive demographic and business information
Understanding China Census Data with GIS By Shuming Bao and Susan Haynie China Data Center, University of Michigan The Census data for China provides comprehensive demographic and business information
Lightning Casualties and Damages in China from 1997 to 2009
 Lightning Casualties and Damages in China from 1997 to 2009 Wenjuan ZHANG 1, Qing MENG 1, Ming MA 2, Yijun ZHANG 1 1 Laboratory of Lightning Physics and Protection Engineering, Chinese Academy of Meteorological
Lightning Casualties and Damages in China from 1997 to 2009 Wenjuan ZHANG 1, Qing MENG 1, Ming MA 2, Yijun ZHANG 1 1 Laboratory of Lightning Physics and Protection Engineering, Chinese Academy of Meteorological
Effect of lengthening alkyl spacer on hydroformylation performance of tethered phosphine modified Rh/SiO2 catalyst
 Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (216) 268 272 催化学报 216 年第 37 卷第 2 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Effect of lengthening alkyl
Chinese Journal of Catalysis 37 (216) 268 272 催化学报 216 年第 37 卷第 2 期 www.cjcatal.org available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/chnjc Article Effect of lengthening alkyl
Fig. 1 Location of the New Shanghai No. 1 Mine in Inner Mongolia, China.
 An Interdisciplinary Response to Mine Water Challenges - Sui, Sun & Wang (eds) 2014 China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou, ISBN 978-7-5646-2437-8 A Water-Inrush Risk Assessment Based
An Interdisciplinary Response to Mine Water Challenges - Sui, Sun & Wang (eds) 2014 China University of Mining and Technology Press, Xuzhou, ISBN 978-7-5646-2437-8 A Water-Inrush Risk Assessment Based
Grey Correlational Analysis on Structure of Inbound. Tourism Industry of Xinjiang Province
 3rd International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2016) Grey Correlational Analysis on Structure of Inbound Tourism Industry of Xinjiang Province Pingxin Han 1, Xiaoling
3rd International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2016) Grey Correlational Analysis on Structure of Inbound Tourism Industry of Xinjiang Province Pingxin Han 1, Xiaoling
偏微分方程及其应用国际会议在数学科学学院举行
 1 偏微分方程及其应用国际会议在数学科学学院举行 2007 年 5 月 28 日至 31 日, 偏微分方程及其应用国际会议 (International Conference on PDEs and Applications) 在北京师范大学数学科学学院举行 国际著名数学家, 世界数学家大会一小时报告人, 美国科学院院士,University of Texas at Austin 教授 Luis Caffarelli
1 偏微分方程及其应用国际会议在数学科学学院举行 2007 年 5 月 28 日至 31 日, 偏微分方程及其应用国际会议 (International Conference on PDEs and Applications) 在北京师范大学数学科学学院举行 国际著名数学家, 世界数学家大会一小时报告人, 美国科学院院士,University of Texas at Austin 教授 Luis Caffarelli
能源化学工程专业培养方案. Undergraduate Program for Specialty in Energy Chemical Engineering 专业负责人 : 何平分管院长 : 廖其龙院学术委员会主任 : 李玉香
 能源化学工程专业培养方案 Undergraduate Program for Specialty in Energy Chemical Engineering 专业负责人 : 何平分管院长 : 廖其龙院学术委员会主任 : 李玉香 Director of Specialty: He Ping Executive Dean: Liao Qilong Academic Committee Director:
能源化学工程专业培养方案 Undergraduate Program for Specialty in Energy Chemical Engineering 专业负责人 : 何平分管院长 : 廖其龙院学术委员会主任 : 李玉香 Director of Specialty: He Ping Executive Dean: Liao Qilong Academic Committee Director:
PREDICTION AND ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURAL NOISE FROM A U-BEAM USING THE FE-SEA HYBRID METHOD
 WENJUN LUO, Ph.D. 1 E-mail: lwj01979@163.com LONG CHENG, M.Sc. 1 E-mail: 117191@qq.com LIHONG TONG, Ph.D. 1 E-mail: lhtong@ecjtu.edu.cn WENNIAN YU, Ph.D. (Corresponding author) E-mail: wennian.yu@queensu.ca
WENJUN LUO, Ph.D. 1 E-mail: lwj01979@163.com LONG CHENG, M.Sc. 1 E-mail: 117191@qq.com LIHONG TONG, Ph.D. 1 E-mail: lhtong@ecjtu.edu.cn WENNIAN YU, Ph.D. (Corresponding author) E-mail: wennian.yu@queensu.ca
2008, hm 2. ( Commodity Bundle) [ 6], 25 4 Vol. 25 No JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., , 2, 3, 1, 2 3*,
![2008, hm 2. ( Commodity Bundle) [ 6], 25 4 Vol. 25 No JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., , 2, 3, 1, 2 3*, 2008, hm 2. ( Commodity Bundle) [ 6], 25 4 Vol. 25 No JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., , 2, 3, 1, 2 3*,](/thumbs/93/112700429.jpg) 25 4 Vol. 25 No. 4 2010 4 JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., 2010 1, 2, 3, 3*, 3, 3, 1, 2 ( 1., 100101; 2., 100049; 3., 100193) :,,,,, ;, 2005, 12 7 5, 2005 :,,, : ; ; ; ; : F301. 21 : A : 1000-3037( 2010)
25 4 Vol. 25 No. 4 2010 4 JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., 2010 1, 2, 3, 3*, 3, 3, 1, 2 ( 1., 100101; 2., 100049; 3., 100193) :,,,,, ;, 2005, 12 7 5, 2005 :,,, : ; ; ; ; : F301. 21 : A : 1000-3037( 2010)
Assessment Model of Set Pair Analysis for Flood Loss Based on Triangular Fuzzy Intervals under α-cut
 Assessment Model of Set Pair Analysis for Flood Loss Based on Triangular Fuzzy Intervals under -Cut PAN Zheng-wei WU Kai-ya 2 JIN Ju-liang 3 LIU Xiao-wei. College of Natural Resources and Environmental
Assessment Model of Set Pair Analysis for Flood Loss Based on Triangular Fuzzy Intervals under -Cut PAN Zheng-wei WU Kai-ya 2 JIN Ju-liang 3 LIU Xiao-wei. College of Natural Resources and Environmental
Atomic & Molecular Clusters / 原子分子团簇 /
 Atomic & Molecular Clusters / 原子分子团簇 / 王金兰 Email: jlwang@seu.edu.cn Department of Physics Southeast University What is nanometer? Nano is Small (10-7 --10-9 m; 1-100 nm) 10 0 m 10-1 m 10-2 m 10-3 m 10-4
Atomic & Molecular Clusters / 原子分子团簇 / 王金兰 Email: jlwang@seu.edu.cn Department of Physics Southeast University What is nanometer? Nano is Small (10-7 --10-9 m; 1-100 nm) 10 0 m 10-1 m 10-2 m 10-3 m 10-4
Simulation of Wetlands Evolution Based on Markov-CA Model
 Simulation of Wetlands Evolution Based on Markov-CA Model ZHANG RONGQUN 1 ZHAI HUIQING 1 TANG CHENGJIE 2 MA SUHUA 2 1 Department of Geography informantion science, College of information and Electrical
Simulation of Wetlands Evolution Based on Markov-CA Model ZHANG RONGQUN 1 ZHAI HUIQING 1 TANG CHENGJIE 2 MA SUHUA 2 1 Department of Geography informantion science, College of information and Electrical
Chapter 2 Thermal Springs in China
 Chapter 2 Thermal Springs in China Abstract This chapter introduces the quantity and distribution of thermal springs in China, Based on the investigation of whole country in 1970s, the total number of
Chapter 2 Thermal Springs in China Abstract This chapter introduces the quantity and distribution of thermal springs in China, Based on the investigation of whole country in 1970s, the total number of
Remote Sensing Classification of Marsh Wetland with Different Resolution Images
 March, 2016 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 7 No.2 J. Resour. Ecol. 2016 7(2) 107-114 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2016.02.005 www.jorae.cn Article Remote Sensing Classification of Marsh Wetland
March, 2016 Journal of Resources and Ecology Vol. 7 No.2 J. Resour. Ecol. 2016 7(2) 107-114 DOI: 10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2016.02.005 www.jorae.cn Article Remote Sensing Classification of Marsh Wetland
XING Sheng-Kai LI Yun ZHAO Xue-Zhuang * CAI Zun-Sheng SHANG Zhen-Feng WANG Gui-Chang *
 1000 物理化学学报 (Wuli Huaxue Xuebao) Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2011, 27 (5), 1000-1004 May [Communication] www.whxb.pku.edu.cn Möbius 环并苯的分子对称性 * 邢生凯李云赵学庄 ( 南开大学化学学院, 天津 300071) * 蔡遵生尚贞锋王贵昌 摘要 : 一般来说, 点群理论认为 Möbius
1000 物理化学学报 (Wuli Huaxue Xuebao) Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2011, 27 (5), 1000-1004 May [Communication] www.whxb.pku.edu.cn Möbius 环并苯的分子对称性 * 邢生凯李云赵学庄 ( 南开大学化学学院, 天津 300071) * 蔡遵生尚贞锋王贵昌 摘要 : 一般来说, 点群理论认为 Möbius
Dataset of Classification and Land Use of the Ecological Core Areas of China
 Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery. 2017, 1(4):426-430 DOI:10.3974/geodp.2017.04.07 www.geodoi.ac.cn 2017 GCdataPR Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository Dataset of Classification and
Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery. 2017, 1(4):426-430 DOI:10.3974/geodp.2017.04.07 www.geodoi.ac.cn 2017 GCdataPR Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository Dataset of Classification and
Firms and People in Place
 Firms and People in Place Driving Forces for Regional Growth Wenjuan Li Doctoral Thesis Department of Social and Economic Geography Umeå University, Sweden GERUM 2007:1 GERUM Kulturgeografi 2007:1 This
Firms and People in Place Driving Forces for Regional Growth Wenjuan Li Doctoral Thesis Department of Social and Economic Geography Umeå University, Sweden GERUM 2007:1 GERUM Kulturgeografi 2007:1 This
Lecture English Term Definition Chinese: Public
 Lecture English Term Definition Chinese: Public A Convert Change between two forms of measurements 变换 A Equilateral Triangle Triangle with equal sides and angles A FPS Units The American system of measurement.
Lecture English Term Definition Chinese: Public A Convert Change between two forms of measurements 变换 A Equilateral Triangle Triangle with equal sides and angles A FPS Units The American system of measurement.
Polio Bulletin 2018 Issue No. 8 - Week 14 (as of 11 April 2018)
 2018 Issue No. 8 - Week 14 (as of 11 April 2018) HIGHLIGHTS Workshop on the WHO Guidance for Non-Poliovirus Facilities to Minimize Risk of Sample Collections Potentially Infectious for Polioviruses 10-11
2018 Issue No. 8 - Week 14 (as of 11 April 2018) HIGHLIGHTS Workshop on the WHO Guidance for Non-Poliovirus Facilities to Minimize Risk of Sample Collections Potentially Infectious for Polioviruses 10-11
Analysis on Competitiveness of Regional Central Cities:
 Int. Statistical Inst.: Proc. 58th World Statistical Congress, 2011, Dublin (Session IPS031) p.476 Analysis on Competitiveness of Regional Central Cities: the case of Yangtze River Delta Xiaolin Pang,
Int. Statistical Inst.: Proc. 58th World Statistical Congress, 2011, Dublin (Session IPS031) p.476 Analysis on Competitiveness of Regional Central Cities: the case of Yangtze River Delta Xiaolin Pang,
La pietra da altre colline può levigare la giada di questa qui Il Classico dei Versi 可 以 攻 玉
 T r e n d s o f H e a l t h c a r e P e r f o r m a n c e E v a l u a t i o n i n C h i n a : a n E c o n o m i c a n d S o c i a l A n a l y s i s A t h e s i s p r e s e n t e d b y H a o L i T o T h
T r e n d s o f H e a l t h c a r e P e r f o r m a n c e E v a l u a t i o n i n C h i n a : a n E c o n o m i c a n d S o c i a l A n a l y s i s A t h e s i s p r e s e n t e d b y H a o L i T o T h
Integrated Algebra. Simplified Chinese. Problem Solving
 Problem Solving algebraically concept conjecture constraint equivalent formulate generalization graphically multiple representations numerically parameter pattern relative efficiency strategy verbally
Problem Solving algebraically concept conjecture constraint equivalent formulate generalization graphically multiple representations numerically parameter pattern relative efficiency strategy verbally
Cooling rate of water
 Cooling rate of water Group 5: Xihui Yuan, Wenjing Song, Ming Zhong, Kaiyue Chen, Yue Zhao, Xiangxie Li 目录. Abstract:... 2. Introduction:... 2 2.. Statement of the problem:... 2 2.2 objectives:... 2 2.3.
Cooling rate of water Group 5: Xihui Yuan, Wenjing Song, Ming Zhong, Kaiyue Chen, Yue Zhao, Xiangxie Li 目录. Abstract:... 2. Introduction:... 2 2.. Statement of the problem:... 2 2.2 objectives:... 2 2.3.
The Structural Characteristics of Tourism Economic Network in Xinjiang Province
 Computer and Information Science; Vol. 8, No. 1; 2015 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education The Structural Characteristics of Tourism Economic Network in
Computer and Information Science; Vol. 8, No. 1; 2015 ISSN 1913-8989 E-ISSN 1913-8997 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education The Structural Characteristics of Tourism Economic Network in
Research Article Spatiotemporal Simulation of Tourist Town Growth Based on the Cellular Automata Model: The Case of Sanpo Town in Hebei Province
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2013, Article ID 975359, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/975359 Research Article Spatiotemporal Simulation of Tourist Town Growth Based on the Cellular Automata
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2013, Article ID 975359, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/975359 Research Article Spatiotemporal Simulation of Tourist Town Growth Based on the Cellular Automata
Water resource utilization efficiency and spatial spillover effects in China
 J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24(5): 771-788 DOI: 10.1007/s11442-014-1119-x 2014 Science Press Springer-Verlag Water resource utilization efficiency and spatial spillover effects in China SUN Caizhi 1, ZHAO Liangshi
J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24(5): 771-788 DOI: 10.1007/s11442-014-1119-x 2014 Science Press Springer-Verlag Water resource utilization efficiency and spatial spillover effects in China SUN Caizhi 1, ZHAO Liangshi
Identifying Megaregions in the US: Implications for Infrastructure Investment
 7. 10. 2 0 08 Identifying Megaregions in the US: Implications for Infrastructure Investment Dr. Myungje Woo Dr. Catherine L. Ross Jason Barringer Harry West Jessica Lynn Harbour Doyle Center for Quality
7. 10. 2 0 08 Identifying Megaregions in the US: Implications for Infrastructure Investment Dr. Myungje Woo Dr. Catherine L. Ross Jason Barringer Harry West Jessica Lynn Harbour Doyle Center for Quality
