Development of Soil Hydraulic Pedotransfer Functions on a European scale: Their Usefulness in the Assessment of Soil Quality
|
|
|
- Beryl Harrell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This paper was peer-reviewed for scientific content. Pages In: D.E. Stott, R.H. Mohtar and G.C. Steinhardt (eds) Sustaining the Global Farm. Selected papers from the 10th International Soil Conservation Organization Meeting held May 24-29, 1999 at Purdue University and the USDA-ARS National Soil Erosion Research Laboratory. Development of Soil Hydraulic Pedotransfer Functions on a European scale: Their Usefulness in the Assessment of Soil Quality A. Nemes*, J.H.M. Wösten and A. Lilly ABSTRACT Many simulation models concerned with water and solute movement in the vadose zone require water retention and unsaturated hydraulic conductivity data. However, these properties are often difficult and time consuming to measure. One method for overcoming this lack of data is through the development of pedotransfer functions, which predict soil hydraulic properties from other, more easily measured soil properties. Recently the European Union funded a project in which a number of European Institutions collaborated to develop a database of measured soil hydraulic properties from which different pedotransfer functions were derived. A novel technique was developed to standardize the particle size distribution data of the approximately 5,500 contributed soil horizons, which were then classified into one of the 11 soil texture classes, recognized by the 1:1,000,000 scale Soil Geographical Database of Europe. The soil hydraulic data were parameterized using the Mualemvan Genuchten model in order to standardize these data. After standardization, class pedotransfer functions were developed for all of the 11 soil texture classes, and continuous pedotransfer functions were developed to predict the soil hydraulic properties of individual soil horizons. However, the raw data remain available for setting limits on soil quality indicators, properties like hydraulic conductivity and moisture retention. Different spatial realizations of the hydraulic composition as a quality factor of soils - could be derived by linking the pedotransfer functions to the 1:1,000,000 scale Soil Geographical Database of Europe to derive a map of available water capacity of European soils. INTRODUCTION Soil hydraulic properties are key aspects in determining soil quality and soil function. Many soil water and solute transport models are currently applied for the investigation and prediction of a wide range of complex environmental processes, which are indicative of soil quality, for example, infiltration capacity. These models require data on soil water retention and hydraulic conductivity characteristics. However, collection of these data is difficult, time consuming and sometimes rather costly, so there is a continued interest in the establishment of pedotransfer functions, which predict soil hydraulic properties from other - more easily measured - soil properties. The European Union (EU) funded a project (entitled: Using existing soil data to derive hydraulic parameters for simulation modeling in environmental studies and in land use planning ~ CHRX- CT ) in which 20 Institutions from 12 European countries collaborated to develop the HYPRES (Hydraulic Properties of European Soils) database [Wösten et al., 1999]. This database draws together the basic soil information and soil hydraulic data, which existed at the collaborating Institutions and from which pedotransfer functions (PTFs) applicable to Europe can be derived. The project had five distinct phases: the first was to collect all the data from the participating Institutions. Many of the soil properties collected are similar to those in the UNSODA database [Leij et al., 1996]. In the second phase, a database structure had to be designed and populated with the relevant soil properties in such a way as to remain compatible with existing EU-wide soil databases. Data standardization took place in the third phase where it was necessary, and the fourth phase was to derive continuous and class pedotransfer functions. These class pedotransfer functions were determined for each of the five soil texture classes and for two pedological classes within them (topsoils and subsoils) plus an additional class, which encompassed the organic soil horizons giving a total of 11 classes. This classification was adopted from the 1:1,000,000 scale Soil Geographical Database of Europe [Jamagne et al., 1994]. The final phase was to demonstrate some of the capabilities and possible uses of the database by linking the class pedotransfer functions with the Soil Geographical Database of Europe to provide a spatial distribution of the soil hydraulic properties. These can be viewed as baseline data on particular soil quality parameters under existing land use systems. Data collection The data were collected from Institutions in Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, The Netherlands, Portugal, Scotland, England, Wales and Northern Ireland (all UK), Slovakia, Spain and Sweden. The data were *A. Nemes, Research Institute for Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry, Hungarian Academy of Sciences (MTA TAKI), H-1022 Budapest, Herman Ottó u. 15, Hungary; J.H.M. Wösten, ALTERRA, P.O. Box 47., Droevendaalsesteeg 3, 6700 AA Wageningen, The Netherlands; A. Lilly, Macaulay Land Use Research Institute, Craigiebuckler, Aberdeen, AB15 8QH, Scotland. *Corresponding author: bloro@spike.fa.gau.hu.
2 transferred to the co-coordinators via electronic media (floppy disk and ) and as hard copy. There are 5521 soil samples (including replicates) from 4,486 soil horizons 1,777 soil profiles in version V1.0 of the HYPRES database. These were taken from 1,777 individual locations scattered throughout the collaborating nations and represent 95 different soil types according to the modified FAO Soil Legend [CEC, 1985]. A total of 197,844 data pairs of water retention versus pressure head and 120,419 data pairs of unsaturated hydraulic conductivity versus pressure head were collected. There were 1,136 soil horizons with both measured water retention and unsaturated hydraulic conductivity data. Database design and structure Although the derivation of the pedotransfer functions was the main objective of the project, the database can also be seen as one of the main products, which may have a wide application in future research projects examining the effects of different land use systems on soil hydraulic properties as well as in soil, environmental and climate research. Therefore it was important to develop a database with a relational structure which allowed a high degree of flexibility in data extraction by a variety of fields or a combination of fields, in data manipulation and which could accommodate the great diversity and volume of data collected. The database was developed within the Oracle Relational Database Management System TM, which uses SQL as its query language. Data can be entered and retrieved in a variety of formats, the whole database can easily be updated with a few simple commands, and new fields or tables can be added any time and data can easily be transferred to other database systems. Version V1.0 of the HYPRES database comprises six separate tables (Figure 1), which are linked by the field 'geo- reference' and, where appropriate, also by the horizon notation ('horizon'). The attributes stored in each table losely resemble those stored in UNSODA database as these attributes were deemed by the delegates of the International Workshop on "Indirect methods for estimating the hydraulic properties of unsaturated soils" to be the most important for improving existing parametric and physico-empirical models and for deriving new pedotransfer functions [van Genuchten and Leij, 1992]. However, additional attributes, which were needed to link with existing EU databases, were also collected. The BASICDATA table (Figure 2) contains the 'descriptor' data, for example, information on the soil type, source information (the original source of the sample), location of the soil profile and a description of the site and some of its environmental conditions. The unique primary key field is 'geo-reference', which is used both as a unique identifier and to ensure that referential integrity is maintained within the subsequent tables so that all data can be related to the descriptor data. This field also provides a link between HYPRES and other European soil datasets and allows the data to be related to other spatially referenced geo-physical factors such as climate or land use without the need to collect and store these additional data in the database. The geo-references were all converted to a common EU-wide system (wherever possible) from a variety of different co-ordinate systems, which are in current use throughout Europe. This table also stores comments on methods used for sampling, data collection and the land use at the time the sample was taken. Where the BASICDATA table is linked to all five other tables by the geo-reference, those tables are linked to each other by both 'geo-reference' and the 'horizon' notation as each soil profile generally contains more than one SOIL PROPERTIES RAW PARTICLE SIZE DATA geo-reference geo-reference BASICDATA horizon horizon geo-reference HYDRAULIC PROPERTIES RAW WATER- RETENTION DATA RAW HYDRAULIC CONDUCTIVITY DATA horizon horizon horizon geo-reference geo-reference geo-reference Figure 1. Structure of HYPRES database. Fields 'geo-reference' and 'horizon' provide links between tables, where appropriate.
3 Figure 2. Detailed structure/contents of HYPRES database. BASICDATA SOIL PROPS. HYDR. PROPS. RAWPSD RAWRET RAWK geo-reference geo-reference geo-reference geo-reference geo-reference geo-reference horizon horizon horizon horizon horizon local sitename upper sample depth dmvg param. θsat. part. size range flag lab./ field flag laboratory / field soil name (FAO) lower sample depth dmvg param. θres. % of particles pres. head (h) indicator if k(h) / k(θ) country of origin prim. structure (FAO) dmvg param. alpha θ(h) value value of (h) or (θ) local geo-reference sec. structure (FAO) dmvg param. n hydr. cond. at h/θ value local soil name % of clay (FAO) dmvg param. m local soil series % of silt (FAO) dmvg param. l highest gr.water depth % of sand (FAO) dmvg param. Ksat. lowest gr.water depth Ksaturated theta(1) site description sat. water-content theta(2) sampling date bulk density annual rainfall particle density theta(14) avg. temp. in January porosity conductivity(1) avg. temp. in July organic material conductivity(2) contact person MVG param. θsat. contact address MVG param. θres. conductivity(14) contact MVG param. alpha relevant publication MVG param. n comments1 MVG param. m comments2 MVG param. l keywords of methods MVG param. Ksat. No. of horizons flag if estim. PSD data rating of data quality comments data quality rated by keywords of methods Sampled horizon. The horizon symbols follow the FAO system [FAO, 1990] and are spaced according to a set of rules in order to make the selection of data easier and to allow greater refinement in this selection process, for example, certain character spaces within the string are reserved for Master horizons only while others contain Subhorizon symbols. As the 'horizon' field is a key identifying attribute which links tables, it follows that there must also be a unique combination of 'geo-reference' and 'horizon' for each sample in the database. Where a horizon was sampled in replicate, an additional alphabetic character was added to the end of the horizon notations. Information on the soil horizon relative to soil hydraulic properties provides a link between soil forming factors and indicators of soil quality. The table SOIL_PROPS stores most of the data likely to be used in deriving the pedotransfer functions for example particle size distribution data, organic material contents, bulk density and porosity. This table also holds the Mualemvan Genuchten parameters where those were contributed rather than paired θ(h) or K(h) data. Where a system of particle size distribution other than the FAO/USDA was used, these data had to be standardized and so the proportions of the various size fractions according to the FAO system were estimated where necessary. These estimates were stored in this table. Just as the BASICDATA table, this table also has comments on the methods used to collect the stored data. The 'RAW' tables, that is RAWRET, RAWK and RAWPSD store the data on moisture retention, hydraulic conductivity and particle size distributions consecutively. These data are in their 'raw' state (that is, prior to any standardization) as contributed by the network partners. Although these tables are very large, containing numerous pairs of data and are not readily usable, it is important to store these 'raw' data for a variety of reasons, for example, if new or improved parameterization methods become available or for testing and comparing novel methods of analysis. As the data stored in these tables are the actual measurements of such properties as saturated hydraulic conductivity and saturated moisture contents, they can be viewed as an important resource in defining limits to these properties as indicators of soil quality and soil function. As the soil hydraulic data were derived by many different methods, they were standardized prior to the development of the pedotransfer functions by deriving a set of Mualem-van Genuchten parameters for each individual sample (where possible). These fitted Mualem-van Genuchten parameters were subsequently used to calculate moisture retention and hydraulic conductivity data at 14 different pre-determined pressure heads for each soil horizon. These derived hydraulic data are stored in table HYDRAULIC_PROPS.
4 Data standardization As the data were collected from 12 different countries, it was inevitable that different class definitions and intervals were used in describing the soil particle size distribution. Therefore, in order to be able to utilize most of these disparate data in the database, it was necessary to find a solution to standardize the particle size distribution. Similarly, it is important for simulation modeling to have a uniform dataset. As different methods had been used in the derivation of soil hydraulic data, for example, water retention data were derived by both evaporation methods and by desorption techniques, the hydraulic properties were standardized using the Mualem-van Genuchten parameters. Standardization of the particle size distribution As the particle size classification within the Soil Geographical Database of Europe follows the FAO system (FAO, 1990), it was decided to standardize the texture data within HYPRES on the same particle size classes. The FAO system describes clays as particles <2 µm, silts between 2 and 50 µm and sands between 50 and 2000 µm, however, many countries in Europe use different class intervals. Therefore, in order to derive European-wide continuous or class pedotransfer functions there was a need to standardize the soil texture data. In general, this involved estimating the proportions of particles in the 2-50 µm range from datasets where, for example, silt was defined as the fraction between 20 and 60 µm or 20 and 63 µm or where sand was defined as the fraction between 20 and 2000 µm. Approximately half of the horizons required the particle size data to be standardized in this way. Four methods for estimating the particle size distribution as defined by the FAO were tested against each other [Nemes et al., 1999]. Two of the most successful methods were then applied to interpolate intermediate points of each individual cumulative particle size distribution curve. One procedure (fitting an open form spline function to the measured data) was used where the measured points in the interpolation were in close proximity to the point to be estimated, for example, where the silt fraction was taken as being less than 60 or 63 µm. The second interpolation procedure involved comparing the cumulative particle size distribution with a well quantified reference dataset. An iteration procedure was used to select at least 10 cumulative particle size curves from the reference set which were most similar to that with the missing 50 µm point. The proportion of particles smaller than 50 µm were then read from these 10 selected curves. The average value was then applied to the curve with the missing 50 µm point as the estimated value. The standardized data will allow more direct comparisons of the measured hydraulic properties from different locations throughout Europe based on particle size class and soil texture. Standardization of the soil hydraulic properties The hydraulic properties of some 3,891 soil horizons were parameterized using the Mualem-van Genuchten equations for water retention and for unsaturated hydraulic conductivity where applicable. The remainder did not have sufficient soil hydraulic data to be parameterized and were eliminated from further analysis. Parameterization was necessary as in this way, soil horizons with data derived from the evaporation method and those where the data were from simple desorption techniques - which generally generates much less data points - could be successfully combined with a minimal risk of statistical bias in the data, regardless of the number of measured points and the applied pressure head values. The data were parameterized using a modified version of the RETC code [van Genuchten et al., 1991]. This semi-automated procedure involved visual inspection of the goodness-of-fit. When the parameterization was complete, the parameters were then used to generate soil water retention and unsaturated hydraulic conductivity points for 14 pre-determined pressure head values. These 14 data pairs were then used to determine the class pedotransfer functions. Standardization of the soil hydraulic properties is important for retaining a degree of integrity when using these data for simulation modeling at regional scales. Pedotransfer functions The preceding chapters described the steps that were taken in order to establish a suitable dataset primarily for the derivation of pedotransfer functions. Two different sets of pedotransfer functions were derived. Class pedotransfer functions predict the hydraulic characteristics for each soil texture class and continuous pedotransfer functions can predict hydraulic properties from individual measurements of sand, silt, clay, organic matter and bulk density. Class pedotransfer functions The class pedotransfer functions are so called as they predict the average hydraulic characteristics for a soil texture/pedological class. These texture classes and pedological classes (topsoil or subsoil) are those contained within the 1:1,000,000 Soil Geographical Database of Europe (Figure 3). Firstly, the optimized Mualem-van Genuchten parameters were used to determine the moisture contents and conductivities at 14 pressure heads for each soil horizon. Next, the horizons were grouped by the 11 texture/pedological classes referred to above. The individual water retention and hydraulic conductivity curves derived for each soil horizon were plotted in soil textural/pedological groups and any outliers were identified and removed from subsequent calculations. The geometric means and standard deviations of the water content and hydraulic conductivity were then calculated for each of the 14 generated points within each texture/pedological class. This allowed the derivation of average curves and a measure of their variability around the geometric mean (Figure 4) for each soil texture/pedological class. Mualem-van Genuchten parameters were then derived for these average curves in order to reduce each to a set of simple parameters, which could be used as input into soil water simulation models. In most cases these curves were closely aligned when plotted. Table 1 summarizes the Mualem-van Genuchten parameters of the class pedotransfer functions.
5 Figure 3. The FAO/USDA soil texture triangle and the 5 texture classes acknowledged by the 1:1,000,000 scale Soil Geographical Database and Soil Map of Europe. Figure 4. Individually measured and calculated average water retention and hydraulic conductivity characteristics.
6 Figure 5. Map of the available water contents of European soils at the scale of 1:1,000,000. Continuous pedotransfer functions Unlike early forms of continuous pedotransfer functions [for example, Ahuja et al., 1985; Rawls and Brakensiek, 1985], regression equations were developed to predict Mualem-van Genuchten parameters instead of specific individual points of the water retention and/or the hydraulic conductivity characteristics following those described in Wösten et al. (1994). By predicting the Mualem-van Genuchten parameters from soil particle size distribution, it is then possible to predict both the moisture content and hydraulic conductivity for a wider range of pressure heads giving greater flexibility than methods which predict tabular values only. Multivariate linear regression was used to investigate the dependency of each Mualem-van Genuchten model parameter on the more easily measured, basic soil properties. To comply with a number of physical boundary conditions, transformed model parameters were used in the regression analysis rather than the original Mualem-van Genuchten parameters. Basic soil properties like percent clay, percent silt, organic matter content, bulk density were used as regression variables. The qualitative variables of topsoil and subsoil were converted to binary data (0 or 1) for inclusion within the regression analysis. Linear, reciprocal and
7 Table 1. The Mualem-van Genuchten parameters of the class pedotransfer functions. θ r θ s α n m l K s Topsoils Coarse Medium Medium Fine Fine Very Fine Subsoils Coarse Medium Medium Fine Fine Very Fine Organic* * There was no topsoil/subsoil distinction among organic soils. Table 2. Continuous pedotransfer functions: a prediction of the Mualem-van Genuchten parameters for the individual soil horizons. The Mualem-van Genuchten parameters were transformed as K s * = ln (K s ), a* = ln (a), n* = ln (n-1) and l* = ln ((l+10) / (10-l)) to comply with a number of physical boundary conditions. θ s was not transformed. The regressed variables were: C = percent clay, S = percent silt, OM = organic material content, D = bulk density; topsoil and subsoil were qualitative variables having the value of 1 or 0. θ s = *C *D *S *OM *C *S *ln(S) *OM*C *D*C *D*OM *topsoil*S α* = *C *S *OM *D 0.192*topsoil 4.671*D *C *OM *OM *ln(S) *ln(OM) *D*S *D*OM *topsoil*C n* = *C *S *OM *D 7.24*D *C *OM *D *S *OM *ln(S) *ln(OM) 44.6*ln(D) *D*C *D*OM *topsoil*C l* = *C *OM *ln(OM) *D*C *D*S *D*OM K s * = *S *topsoil 0.967*D *C *S *S *OM *ln(S) *D*C *D*OM *topsoil*C *topsoil*S exponential relationships of these basic soil properties were used in the regression analysis, and possible interactions among them were also investigated. The best model (continuous pedotransfer function) was selected with the subset selection method of Furnival and Wilson (1974). The resulting continuous pedotransfer functions are presented in Table 2. The hydraulic characteristics can be obtained after the back-transformation to the original Mualem-van Genuchten model parameters. Applications In order to demonstrate the applicability of the pedotransfer functions they were used to derive a European scale map of available water capacity using the Soil
8 Geographical Database of Europe. This was achieved by firstly determining the topsoil and subsoil textures and the depth of soil for the dominant soil in each soil map unit for which there is texture data. Class pedotransfer functions were then used to calculate the total available water capacity for each texture class for both topsoils and subsoils. Available water was considered to be the water held between field capacity (pressure head = -50 cm) and permanent wilting point (defined as a pressure head = -15,000 cm) and are similar to those set by Thomasson (1995). These values were then multiplied by the depth of the soil horizons and summed to give a cumulative profile available water capacity for each map unit. A spatial distribution of the available water capacity could then be determined for most of Europe at a scale of 1: 1,000,000 (Figure 5). Other realizations of the soil hydraulic conditions of European soils are also possible by linking the two datasets in this way, many of which could be used as input to European-wide predictive models. Continuous pedotransfer functions can be used to examine the effect of changes in organic matter content and bulk density (two indicators of soil quality) on soil hydraulic properties and therefore on soil functions such as solute travel times. CONCLUSIONS The HYPRES database and the derived pedotransfer functions represent one of the key European soils databases. It has been specifically designed to complement existing databases, especially those, which are spatial. Its design, construction and data give it a high degree of flexibility and the capability of linking with other environmental or climatic datasets. In the future, it is envisaged that the database and its derived products will be applied to a wide range of environmental issues as well as to many small and large scale strategic research projects. Both the data and the derived pedotransfer functions can be used as input into a wide range of simulation models and as a primary dataset for a wide range of agronomic or environmental research. As raw data as well as derived data are stored, new methods of parameterization or of deriving pedotransfer functions can be easily implemented which prolongs the life of the database and allows the dataset to be used in studies to set quality limits on soil hydraulic properties. It is likely that the class pedotransfer functions will be used for broad scale modeling while the continuous pedotransfer functions are more applicable to more detailed investigations. The standard deviations derived for the class pedotransfer functions would enable researchers on soil quality to examine the effects of changing the hydraulic conditions on a wide range of issues like pesticide leaching or soil erosion. The continuous pedotransfer functions would allow the examination of for example the effect of reductions in soil organic material content or changes of bulk density (tillage or soil compaction) on the soil hydraulic properties. Such information may then be used in studies like vulnerability of soils to physical or chemical degradation. Future plans include the extension of the database to Central and Eastern European countries, and to apply and compare neural network models with the classical regression type models to derive more accurate pedotransfer functions. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors thank the European Soil Bureau for the permission to use the 1:1,000,000 Soil Geographical Database of Europe. The financial support of the Soros Foundation is gratefully acknowledged. Part of this work was funded by the Scottish Executive Rural Affairs Department. REFERENCES Ahuja, L.R., J.W. Naney and R.D. Williams Estimating soil water characteristics from simpler properties or limited data. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 49: Commission of the European Communities (CEC) Soil map of the European Communities. Scale 1: 1,000,000. Luxembourg. Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) Guidelines for soil description (3rd Ed.). FAO/ISRIC. Rome. Furnival, G.M. and R.W. Wilson Regression by leaps and bounds. Techno metrics 16: Jamagne, M., D. King, C. Le Bas, J. Daroussin, A. Burrill and P. Vossen Creation and use of a European Soil Geographic Database. 15th International Congress of Soil Science, Transactions, vol. 6a, Commission V, Symposia, Acapulco, Mexico, pp Leij, F.J., W.J. Alves, M.Th. van Genuchten and J.R. Williams Unsaturated Soil Hydraulic Database, UNSODA 1.0 User's Manual. Report EPA/600/R- 96/095, United States Environmental Protection Agency. Ada. Oklahoma. P Nemes, A., J.H.M. Wösten, A. Lilly and J.H. Oude Voshaar Evaluation of different procedures to interpolate the cumulative particle-size distribution to achieve compatibility of soil databases. Geoderma 90: Rawls, W.J. and D.L. Brakensiek Prediction of soil water properties for hydrologic modeling. In: E. Jones and T.J. Ward (eds.), Watershed Management in the Eighties. Proceedings of a Symposium ASCE, Denver, Colorado. 30 Apr. - 2 May ASCE, New York. pp Thomasson, A.J Assessment of soil water reserves available for plants (SWAP): a review. In: European land information systems for agro-environmental monitoring. D. King, R.J.A. Jones and A.J. Thomasson (Editors), Institute for Remote Sensing Applications. Joint Research Centre. Office for Official Publications of the European Community. Luxembourg. van Genuchten, M.Th., F.J. Leij and S.R. Yates The RETC code for quantifying the hydraulic functions of unsaturated soils. USDA, US Salinity Laboratory, Riverside, CA. United States Environmental Protection Agency, document EPA/600/2-91/065. van Genuchten, M.Th. and F.J. Leij On estimating the hydraulic properties of unsaturated soils. In: M.Th. van Genuchten, F.J. Leij and L.J. Lund (Editors), Indirect methods for estimating the hydraulic properties of unsaturated soils. Proc. of the International Workshop on
9 Indirect Methods for Estimating the Hydraulic Properties of Unsaturated Soils. Riverside, California, October 1989, pp Wösten, J.H.M., G.J. Veerman and J. Stolte Water retention and hydraulic conductivity characteristics of top- and sub-soils in the Netherlands: the Staring series. Updated version Technical Document 18, The Winand Staring Centre, Wageningen, the Netherlands. Wösten, J.H.M., A. Lilly, A. Nemes and C. Le Bas Development and use of a database of hydraulic properties of European soils. Geoderma 90:
A Tool for Estimating Soil Water Available for Plants Using the 1:1,000,000 Scale Soil Geographical Data Base of Europe
 A Tool for Estimating Soil Water Available for Plants Using the :,000,000 Scale Soil Geographical Data Base of Europe Le Bas, D. King and J. Daroussin. Abstract INRA - SESCPF, Domaine de Limère, 4560 ARDON,
A Tool for Estimating Soil Water Available for Plants Using the :,000,000 Scale Soil Geographical Data Base of Europe Le Bas, D. King and J. Daroussin. Abstract INRA - SESCPF, Domaine de Limère, 4560 ARDON,
IRENA Indicator Fact Sheet IRENA indicator 29 Soil quality
 Indicator Definition Topsoil (0-30cm) organic carbon content Input Indicator links: IRENA 24 - Land cover change Output Indicator Links: IRENA 23 - Soil erosion Key message Soil quality cannot be measured
Indicator Definition Topsoil (0-30cm) organic carbon content Input Indicator links: IRENA 24 - Land cover change Output Indicator Links: IRENA 23 - Soil erosion Key message Soil quality cannot be measured
Principles of soil water and heat transfer in JULES
 Principles of soil water and heat transfer in JULES Anne Verhoef 1, Pier Luigi Vidale 2, Raquel Garcia- Gonzalez 1,2, and Marie-Estelle Demory 2 1. Soil Research Centre, Reading (UK); 2. NCAS-Climate,
Principles of soil water and heat transfer in JULES Anne Verhoef 1, Pier Luigi Vidale 2, Raquel Garcia- Gonzalez 1,2, and Marie-Estelle Demory 2 1. Soil Research Centre, Reading (UK); 2. NCAS-Climate,
Ju Hyoung, Lee, B. Candy, R. Renshaw Met Office, UK
 the FAO/ ESA/ GWSP Workshop on Earth Observations and the Water-Energy-Food Nexus 25-27 March 2014 in Rome, Italy Ju Hyoung, Lee, B. Candy, R. Renshaw Met Office, UK 1 1. Agriculture needs, current methods,
the FAO/ ESA/ GWSP Workshop on Earth Observations and the Water-Energy-Food Nexus 25-27 March 2014 in Rome, Italy Ju Hyoung, Lee, B. Candy, R. Renshaw Met Office, UK 1 1. Agriculture needs, current methods,
Exploring the uncertainty of soil water holding capacity information
 Exploring the uncertainty of soil water holding capacity information Linda Lilburne*, Stephen McNeill, Tom Cuthill, Pierre Roudier Landcare Research, Lincoln, New Zealand *Corresponding author: lilburnel@landcareresearch.co.nz
Exploring the uncertainty of soil water holding capacity information Linda Lilburne*, Stephen McNeill, Tom Cuthill, Pierre Roudier Landcare Research, Lincoln, New Zealand *Corresponding author: lilburnel@landcareresearch.co.nz
Land Use and Land cover statistics (LUCAS)
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate E: Sectoral and regional statistics Doc. ENV/DIMESA/7.1/2012 Original in EN Agenda point 7.1 Land Use and Land cover statistics (LUCAS) DIMESA Directors' Meeting
EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate E: Sectoral and regional statistics Doc. ENV/DIMESA/7.1/2012 Original in EN Agenda point 7.1 Land Use and Land cover statistics (LUCAS) DIMESA Directors' Meeting
Harmonization of methods and measurements (GSP Pillar 5) Rainer Baritz
 Harmonization of methods and measurements (GSP Pillar 5) Rainer Baritz ESP, Rome, 17-18 March 2015 1 Pillar 5 writing team: Compiled after expert registration through GSP web site; 2 experts dropped out;
Harmonization of methods and measurements (GSP Pillar 5) Rainer Baritz ESP, Rome, 17-18 March 2015 1 Pillar 5 writing team: Compiled after expert registration through GSP web site; 2 experts dropped out;
An internet based tool for land productivity evaluation in plot-level scale: the D-e-Meter system
 An internet based tool for land productivity evaluation in plot-level scale: the D-e-Meter system Tamas Hermann 1, Ferenc Speiser 1 and Gergely Toth 2 1 University of Pannonia, Hungary, tamas.hermann@gmail.com
An internet based tool for land productivity evaluation in plot-level scale: the D-e-Meter system Tamas Hermann 1, Ferenc Speiser 1 and Gergely Toth 2 1 University of Pannonia, Hungary, tamas.hermann@gmail.com
Procedure for Determining Near-Surface Pollution Sensitivity
 Procedure for Determining Near-Surface Pollution Sensitivity Minnesota Department of Natural Resources Division of Ecological and Water Resources County Geologic Atlas Program March 2014 Version 2.1 I.
Procedure for Determining Near-Surface Pollution Sensitivity Minnesota Department of Natural Resources Division of Ecological and Water Resources County Geologic Atlas Program March 2014 Version 2.1 I.
INSPIRing effort. Peter Parslow Ordnance Survey December Various European approaches to managing an SDI
 INSPIRing effort Peter Parslow Ordnance Survey December 2015 Various European approaches to managing an SDI WHAT IS INSPIRE? A European Union Directive A community effort: http://inspire.ec.europa.eu/
INSPIRing effort Peter Parslow Ordnance Survey December 2015 Various European approaches to managing an SDI WHAT IS INSPIRE? A European Union Directive A community effort: http://inspire.ec.europa.eu/
Extending Geographic and Thematic Range of SPADE/M with HYPRES Soil Profile Data. Roland Hiederer
 Extending Geographic and Thematic Range of SPADE/M with HYPRES Soil Profile Data Roland Hiederer EUR 24971 EN - 2011 The mission of the JRC-IES is to provide scientific-technical support to the European
Extending Geographic and Thematic Range of SPADE/M with HYPRES Soil Profile Data Roland Hiederer EUR 24971 EN - 2011 The mission of the JRC-IES is to provide scientific-technical support to the European
Estimating soil specific surface area using the summation of the number of spherical particles and geometric mean particle-size diameter
 African Journal of Agricultural Research Vol. 6(7), pp. 1758-1762, 4 April, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajar DOI: 10.5897/AJAR11.199 ISSN 1991-637X 2011 Academic Journals Full
African Journal of Agricultural Research Vol. 6(7), pp. 1758-1762, 4 April, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajar DOI: 10.5897/AJAR11.199 ISSN 1991-637X 2011 Academic Journals Full
1. Water in Soils: Infiltration and Redistribution
 Contents 1 Water in Soils: Infiltration and Redistribution 1 1a Material Properties of Soil..................... 2 1b Soil Water Flow........................... 4 i Incorporating K - θ and ψ - θ Relations
Contents 1 Water in Soils: Infiltration and Redistribution 1 1a Material Properties of Soil..................... 2 1b Soil Water Flow........................... 4 i Incorporating K - θ and ψ - θ Relations
Methodology and experience from the soil geographical database of Europe at 1:1,000,000 scale
 Methodology and experience from the soil geographical database of Europe at 1:1,000,000 scale Jamagne M., Montanarella L., Daroussin J., Eimberck M., King D., Jacques Lambert J., Le Bas C., Zdruli P. in
Methodology and experience from the soil geographical database of Europe at 1:1,000,000 scale Jamagne M., Montanarella L., Daroussin J., Eimberck M., King D., Jacques Lambert J., Le Bas C., Zdruli P. in
Drought News August 2014
 European Drought Observatory (EDO) Drought News August 2014 (Based on data until the end of July) http://edo.jrc.ec.europa.eu August 2014 EDO (http://edo.jrc.ec.europa.eu) Page 2 of 8 EDO Drought News
European Drought Observatory (EDO) Drought News August 2014 (Based on data until the end of July) http://edo.jrc.ec.europa.eu August 2014 EDO (http://edo.jrc.ec.europa.eu) Page 2 of 8 EDO Drought News
Geological information for Europe : Towards a pan-european Geological Data Infrastructure
 Geological information for Europe : Towards a pan-european Geological Data Infrastructure Integrating geoscientific information for EU competitiveness Co-funded by the European Union European societal
Geological information for Europe : Towards a pan-european Geological Data Infrastructure Integrating geoscientific information for EU competitiveness Co-funded by the European Union European societal
JRC MARS Bulletin Crop monitoring in Europe. January 2017 Minor frost damages so far. Improved hardening of winter cereals in central Europe
 MARS Bulletin Vol. 25 No 1 23 January 2017 1 JRC MARS Bulletin Vol. 25 No 1 Period covered: 1 December 2016-16 January 2017 Issued: 23 January 2017 JRC MARS Bulletin Crop monitoring in Europe January 2017
MARS Bulletin Vol. 25 No 1 23 January 2017 1 JRC MARS Bulletin Vol. 25 No 1 Period covered: 1 December 2016-16 January 2017 Issued: 23 January 2017 JRC MARS Bulletin Crop monitoring in Europe January 2017
GLOBAL SYMPOSIUM ON SOIL ORGANIC CARBON, Rome, Italy, March 2017
 GLOBAL SYMPOSIUM ON SOIL ORGANIC CARBON, Rome, Italy, 21-23 March 2017 Strength and weaknesses of a bottom up approach in estimating soil organic carbon: an experience in the varied Italian scenery I.
GLOBAL SYMPOSIUM ON SOIL ORGANIC CARBON, Rome, Italy, 21-23 March 2017 Strength and weaknesses of a bottom up approach in estimating soil organic carbon: an experience in the varied Italian scenery I.
On the relationships between the pore size distribution index and characteristics of the soil hydraulic functions
 WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 41, W07019, doi:10.1029/2004wr003511, 2005 On the relationships between the pore size distribution index and characteristics of the soil hydraulic functions S. Assouline
WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 41, W07019, doi:10.1029/2004wr003511, 2005 On the relationships between the pore size distribution index and characteristics of the soil hydraulic functions S. Assouline
The Swedish National Geodata Strategy and the Geodata Project
 The Swedish National Geodata Strategy and the Geodata Project Ewa Rannestig, Head of NSDI Co-ordination Unit, Lantmäteriet, ewa.rannstig@lm.se Ulf Sandgren, Project Manager Geodata Project, Lantmäteriet,
The Swedish National Geodata Strategy and the Geodata Project Ewa Rannestig, Head of NSDI Co-ordination Unit, Lantmäteriet, ewa.rannstig@lm.se Ulf Sandgren, Project Manager Geodata Project, Lantmäteriet,
Analysis of European Topographic Maps for Monitoring Settlement Development
 Analysis of European Topographic Maps for Monitoring Settlement Development Ulrike Schinke*, Hendrik Herold*, Gotthard Meinel*, Nikolas Prechtel** * Leibniz Institute of Ecological Urban and Regional Development,
Analysis of European Topographic Maps for Monitoring Settlement Development Ulrike Schinke*, Hendrik Herold*, Gotthard Meinel*, Nikolas Prechtel** * Leibniz Institute of Ecological Urban and Regional Development,
Spatial modeling of pesticide emissions to groundwater and surface water in the Belgian context
 11/10/2012 Spatial modeling of pesticide emissions to groundwater and surface water in the Belgian context Bernhard s e-mail : 30 minutes => 20 minutes + 10 minutes discussion and award for best debater!
11/10/2012 Spatial modeling of pesticide emissions to groundwater and surface water in the Belgian context Bernhard s e-mail : 30 minutes => 20 minutes + 10 minutes discussion and award for best debater!
COMPUTER MODELLING OF HEAT AND MASS FLOW IN STEAMING GROUND AT KARAPITI THERMAL AREA, NEW ZEALAND
 PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Ninth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 26-28, 2004 SGP-TR-175 COMPUTER MODELLING OF HEAT AND MASS FLOW IN STEAMING GROUND
PROCEEDINGS, Twenty-Ninth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 26-28, 2004 SGP-TR-175 COMPUTER MODELLING OF HEAT AND MASS FLOW IN STEAMING GROUND
Improving rural statistics. Defining rural territories and key indicators of rural development
 Improving rural statistics Defining rural territories and key indicators of rural development Improving rural statistics Improving Rural Statistics In 2016, the Global Strategy to improve Agricultural
Improving rural statistics Defining rural territories and key indicators of rural development Improving rural statistics Improving Rural Statistics In 2016, the Global Strategy to improve Agricultural
Bathing water results 2011 Latvia
 Bathing water results 2011 Latvia 1. Reporting and assessment This report gives a general overview of water in Latvia for the 2011 season. Latvia has reported under the Directive 2006/7/EC since 2008.
Bathing water results 2011 Latvia 1. Reporting and assessment This report gives a general overview of water in Latvia for the 2011 season. Latvia has reported under the Directive 2006/7/EC since 2008.
Automatic Gamma-Ray Equipment for Multiple Soil Physical Properties Measurements
 Automatic Gamma-Ray Equipment for Multiple Soil Physical Properties Measurements Carlos Manoel Pedro Vaz Embrapa Agricultural Instrumentation, São Carlos, Brazil Lecture given at the College on Soil Physics
Automatic Gamma-Ray Equipment for Multiple Soil Physical Properties Measurements Carlos Manoel Pedro Vaz Embrapa Agricultural Instrumentation, São Carlos, Brazil Lecture given at the College on Soil Physics
Bathing water results 2011 Slovakia
 Bathing water results Slovakia 1. Reporting and assessment This report gives a general overview of water in Slovakia for the season. Slovakia has reported under the Directive 2006/7/EC since 2008. When
Bathing water results Slovakia 1. Reporting and assessment This report gives a general overview of water in Slovakia for the season. Slovakia has reported under the Directive 2006/7/EC since 2008. When
PREDICTION OF SOIL ORGANIC CARBON CONTENT BY SPECTROSCOPY AT EUROPEAN SCALE USING A LOCAL PARTIAL LEAST SQUARE REGRESSION APPROACH
 Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 PREDICTION OF SOIL ORGANIC CARBON CONTENT BY SPECTROSCOPY AT EUROPEAN SCALE
Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 PREDICTION OF SOIL ORGANIC CARBON CONTENT BY SPECTROSCOPY AT EUROPEAN SCALE
KINEROS2/AGWA. Fig. 1. Schematic view (Woolhiser et al., 1990).
 KINEROS2/AGWA Introduction Kineros2 (KINematic runoff and EROSion) (K2) model was originated at the USDA-ARS in late 1960s and released until 1990 (Smith et al., 1995; Woolhiser et al., 1990). The spatial
KINEROS2/AGWA Introduction Kineros2 (KINematic runoff and EROSion) (K2) model was originated at the USDA-ARS in late 1960s and released until 1990 (Smith et al., 1995; Woolhiser et al., 1990). The spatial
I&CLC2000 in support to new policy initiatives (INSPIRE, GMES,..)
 I&CLC2000 in support to new policy initiatives (INSPIRE, GMES,..) Manfred Grasserbauer, Director Joint Research Centre Institute for Environment and Sustainability 1 IMAGE 2000 European mosaic of satellite
I&CLC2000 in support to new policy initiatives (INSPIRE, GMES,..) Manfred Grasserbauer, Director Joint Research Centre Institute for Environment and Sustainability 1 IMAGE 2000 European mosaic of satellite
New soil physical properties implemented in the Unified Model
 New soil physical properties implemented in the Unified Model Imtiaz Dharssi 1, Pier Luigi Vidale 3, Anne Verhoef 3, Bruce Macpherson 1, Clive Jones 1 and Martin Best 2 1 Met Office (Exeter, UK) 2 Met
New soil physical properties implemented in the Unified Model Imtiaz Dharssi 1, Pier Luigi Vidale 3, Anne Verhoef 3, Bruce Macpherson 1, Clive Jones 1 and Martin Best 2 1 Met Office (Exeter, UK) 2 Met
The Environmental Classification of Europe, a new tool for European landscape ecologists
 The Environmental Classification of Europe, a new tool for European landscape ecologists De Environmental Classification of Europe, een nieuw gereedschap voor Europese landschapsecologen Marc Metzger Together
The Environmental Classification of Europe, a new tool for European landscape ecologists De Environmental Classification of Europe, een nieuw gereedschap voor Europese landschapsecologen Marc Metzger Together
A GIS Tool for Modelling and Visualizing Sustainability Indicators Across Three Regions of Ireland
 International Conference on Whole Life Urban Sustainability and its Assessment M. Horner, C. Hardcastle, A. Price, J. Bebbington (Eds) Glasgow, 2007 A GIS Tool for Modelling and Visualizing Sustainability
International Conference on Whole Life Urban Sustainability and its Assessment M. Horner, C. Hardcastle, A. Price, J. Bebbington (Eds) Glasgow, 2007 A GIS Tool for Modelling and Visualizing Sustainability
The EuCheMS Division Chemistry and the Environment EuCheMS/DCE
 The EuCheMS Division Chemistry and the Environment EuCheMS/DCE EuCheMS Division on Chemistry and the Environment was formed as a FECS Working Party in 1977. Membership: 37 members from 34 countries. Countries
The EuCheMS Division Chemistry and the Environment EuCheMS/DCE EuCheMS Division on Chemistry and the Environment was formed as a FECS Working Party in 1977. Membership: 37 members from 34 countries. Countries
EuroGeoSurveys & ASGMI The Geological Surveys of Europe and IberoAmerica
 EuroGeoSurveys & ASGMI The Geological Surveys of Europe and IberoAmerica Geological Surveys, what role? Legal mandate for data & information: Research Collection Management Interpretation/transformation
EuroGeoSurveys & ASGMI The Geological Surveys of Europe and IberoAmerica Geological Surveys, what role? Legal mandate for data & information: Research Collection Management Interpretation/transformation
Evaluation of the SWAT Model Setup Process Through A Case Study in Roxo Catchment, Portugal
 Evaluation of the SWAT Model Setup Process Through A Case Study in Roxo Catchment, Portugal Mustafa Gökmen Master Degree in on Geo-information and Earth Observation for Integrated Catchment and Water Resources
Evaluation of the SWAT Model Setup Process Through A Case Study in Roxo Catchment, Portugal Mustafa Gökmen Master Degree in on Geo-information and Earth Observation for Integrated Catchment and Water Resources
Refinement of the OECD regional typology: Economic Performance of Remote Rural Regions
 [Preliminary draft April 2010] Refinement of the OECD regional typology: Economic Performance of Remote Rural Regions by Lewis Dijkstra* and Vicente Ruiz** Abstract To account for differences among rural
[Preliminary draft April 2010] Refinement of the OECD regional typology: Economic Performance of Remote Rural Regions by Lewis Dijkstra* and Vicente Ruiz** Abstract To account for differences among rural
ANALYSIS OF LARGE SCALE SOIL SPECTRAL LIBRARIES
 Antoine Stevens (1), Marco Nocita (1,2), & Bas van Wesemael (1) ANALYSIS OF LARGE SCALE SOIL SPECTRAL LIBRARIES 1 Georges Lemaître Centre for Earth and Climate Research, Earth and Life Institute, UCLouvain,
Antoine Stevens (1), Marco Nocita (1,2), & Bas van Wesemael (1) ANALYSIS OF LARGE SCALE SOIL SPECTRAL LIBRARIES 1 Georges Lemaître Centre for Earth and Climate Research, Earth and Life Institute, UCLouvain,
Geostatistical Analyst. Statistical Tools for Data Exploration, Modeling, and Advanced Surface Generation
 Geostatistical Analyst Statistical Tools for Data Exploration, Modeling, and Advanced Surface Generation ArcGIS Geostatistical Analyst: Statistical Tools for Data Exploration, Modeling, and Advanced Surface
Geostatistical Analyst Statistical Tools for Data Exploration, Modeling, and Advanced Surface Generation ArcGIS Geostatistical Analyst: Statistical Tools for Data Exploration, Modeling, and Advanced Surface
Effective unsaturated hydraulic conductivity for one-dimensional structured heterogeneity
 WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 41, W09406, doi:10.1029/2005wr003988, 2005 Effective unsaturated hydraulic conductivity for one-dimensional structured heterogeneity A. W. Warrick Department of Soil, Water
WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 41, W09406, doi:10.1029/2005wr003988, 2005 Effective unsaturated hydraulic conductivity for one-dimensional structured heterogeneity A. W. Warrick Department of Soil, Water
JRC MARS Bulletin Crop monitoring in Europe January 2016 Weakly hardened winter cereals
 Online version Issued: 25January 2016 r JRC MARS Bulletin Vol. 24 No 1 JRC MARS Bulletin Crop monitoring in Europe January 2016 Weakly hardened winter cereals A first cold spell is likely to have caused
Online version Issued: 25January 2016 r JRC MARS Bulletin Vol. 24 No 1 JRC MARS Bulletin Crop monitoring in Europe January 2016 Weakly hardened winter cereals A first cold spell is likely to have caused
DESCRIPTION OF A HYDROLOGIC DATASET. Department of Environmental Sciences, Wageningen University and. Research Center. Wageningen, The Netherlands
 DESCRIPTION OF A HYDROLOGIC DATASET FOR THE BRISY SUBCATCHMENT R. T. Oosterho? and C. Paniconi y? Department of Environmental Sciences, Wageningen University and Research Center Wageningen, The Netherlands
DESCRIPTION OF A HYDROLOGIC DATASET FOR THE BRISY SUBCATCHMENT R. T. Oosterho? and C. Paniconi y? Department of Environmental Sciences, Wageningen University and Research Center Wageningen, The Netherlands
USING GIS AND AHP TECHNIQUE FOR LAND-USE SUITABILITY ANALYSIS
 USING GIS AND AHP TECHNIQUE FOR LAND-USE SUITABILITY ANALYSIS Tran Trong Duc Department of Geomatics Polytechnic University of Hochiminh city, Vietnam E-mail: ttduc@hcmut.edu.vn ABSTRACT Nowadays, analysis
USING GIS AND AHP TECHNIQUE FOR LAND-USE SUITABILITY ANALYSIS Tran Trong Duc Department of Geomatics Polytechnic University of Hochiminh city, Vietnam E-mail: ttduc@hcmut.edu.vn ABSTRACT Nowadays, analysis
PREDICTING DROUGHT VULNERABILITY IN THE MEDITERRANEAN
 J.7 PREDICTING DROUGHT VULNERABILITY IN THE MEDITERRANEAN J. P. Palutikof and T. Holt Climatic Research Unit, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK. INTRODUCTION Mediterranean water resources are under
J.7 PREDICTING DROUGHT VULNERABILITY IN THE MEDITERRANEAN J. P. Palutikof and T. Holt Climatic Research Unit, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK. INTRODUCTION Mediterranean water resources are under
Multifunctional theory in agricultural land use planning case study
 Multifunctional theory in agricultural land use planning case study Introduction István Ferencsik (PhD) VÁTI Research Department, iferencsik@vati.hu By the end of 20 th century demands and expectations
Multifunctional theory in agricultural land use planning case study Introduction István Ferencsik (PhD) VÁTI Research Department, iferencsik@vati.hu By the end of 20 th century demands and expectations
PURPOSE To develop a strategy for deriving a map of functional soil water characteristics based on easily obtainable land surface observations.
 IRRIGATING THE SOIL TO MAXIMIZE THE CROP AN APPROACH FOR WINTER WHEAT TO EFFICIENT AND ENVIRONMENTALLY SUSTAINABLE IRRIGATION WATER MANAGEMENT IN KENTUCKY Ole Wendroth & Chad Lee - Department of Plant
IRRIGATING THE SOIL TO MAXIMIZE THE CROP AN APPROACH FOR WINTER WHEAT TO EFFICIENT AND ENVIRONMENTALLY SUSTAINABLE IRRIGATION WATER MANAGEMENT IN KENTUCKY Ole Wendroth & Chad Lee - Department of Plant
The Combination of Geospatial Data with Statistical Data for SDG Indicators
 Session x: Sustainable Development Goals, SDG indicators The Combination of Geospatial Data with Statistical Data for SDG Indicators Pier-Giorgio Zaccheddu Fabio Volpe 5-8 December2018, Nairobi IAEG SDG
Session x: Sustainable Development Goals, SDG indicators The Combination of Geospatial Data with Statistical Data for SDG Indicators Pier-Giorgio Zaccheddu Fabio Volpe 5-8 December2018, Nairobi IAEG SDG
Identification of Very Shallow Groundwater Regions in the EU to Support Monitoring
 Identification of Very Shallow Groundwater Regions in the EU to Support Monitoring Timothy Negley Paul Sweeney Lucy Fish Paul Hendley Andrew Newcombe ARCADIS Syngenta Ltd. Syngenta Ltd. Phasera Ltd. ARCADIS
Identification of Very Shallow Groundwater Regions in the EU to Support Monitoring Timothy Negley Paul Sweeney Lucy Fish Paul Hendley Andrew Newcombe ARCADIS Syngenta Ltd. Syngenta Ltd. Phasera Ltd. ARCADIS
Use of the ISO Quality standards at the NMCAs Results from questionnaires taken in 2004 and 2011
 Use of the ISO 19100 Quality standards at the NMCAs Results from questionnaires taken in 2004 and 2011 Eurogeographics Quality Knowledge Exchange Network Reference: History Version Author Date Comments
Use of the ISO 19100 Quality standards at the NMCAs Results from questionnaires taken in 2004 and 2011 Eurogeographics Quality Knowledge Exchange Network Reference: History Version Author Date Comments
URBAN SMS Soil Management Strategy
 URBAN SMS Soil Management Strategy SWOT of existing soil evaluation tools currently used by URBAN SMS partners T. Vernik & B. Vršèaj May 29 th, 2009 WP4 Tools common SWOT Analysis Report This analysis
URBAN SMS Soil Management Strategy SWOT of existing soil evaluation tools currently used by URBAN SMS partners T. Vernik & B. Vršèaj May 29 th, 2009 WP4 Tools common SWOT Analysis Report This analysis
The Governance of Land Use
 The planning system The Governance of Land Use United Kingdom Levels of government and their responsibilities The United Kingdom is a unitary state with three devolved governments in Northern Ireland,
The planning system The Governance of Land Use United Kingdom Levels of government and their responsibilities The United Kingdom is a unitary state with three devolved governments in Northern Ireland,
Italian experience with the interpretation of FOCUS surface water scenarios from a regulatory point of view
 Italian experience with the interpretation of FOCUS surface water scenarios from a regulatory point of view G. Azimonti, G. Triacchini, D. Auteri, E. Redolfi, International Centre for Pesticides and Health
Italian experience with the interpretation of FOCUS surface water scenarios from a regulatory point of view G. Azimonti, G. Triacchini, D. Auteri, E. Redolfi, International Centre for Pesticides and Health
JRC MARS Bulletin Crop monitoring in Europe January 2019
 Online version Issued: 21 January 2019 r JRC MARS Bulletin Vol. 27 No 1 JRC MARS Bulletin Crop monitoring in Europe January 2019 Continued mild winter Improved hardening of winter cereals in central and
Online version Issued: 21 January 2019 r JRC MARS Bulletin Vol. 27 No 1 JRC MARS Bulletin Crop monitoring in Europe January 2019 Continued mild winter Improved hardening of winter cereals in central and
GSDI Global Spatial Data Infrastructure. Convergences between Geo Spatial Communities: key decision for decision making
 GSDI Global Spatial Data Infrastructure Convergences between Geo Spatial Communities: key decision for decision making April 14 th 2010 Bas Kok GSDI Past-President Director of International Affairs, Dutch
GSDI Global Spatial Data Infrastructure Convergences between Geo Spatial Communities: key decision for decision making April 14 th 2010 Bas Kok GSDI Past-President Director of International Affairs, Dutch
Web Portal to European Soil Database
 Web Portal to European Soil Database A step towards harmonization of Soil Information in Europe Marc Van Liedekerke, Panos Panagos, Jean Dusart Soils Portal: http://eusoils.jrc.it Data The European Soil
Web Portal to European Soil Database A step towards harmonization of Soil Information in Europe Marc Van Liedekerke, Panos Panagos, Jean Dusart Soils Portal: http://eusoils.jrc.it Data The European Soil
RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES FOR LANDSLIDES
 RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES FOR LANDSLIDES Jean-Philippe MALET Olivier MAQUAIRE CNRS & CERG. Welcome to Paris! 1 Landslide RAMs Landslide RAM A method based on the use of available information to estimate
RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES FOR LANDSLIDES Jean-Philippe MALET Olivier MAQUAIRE CNRS & CERG. Welcome to Paris! 1 Landslide RAMs Landslide RAM A method based on the use of available information to estimate
EXAMPLE PROBLEMS. 1. Example 1 - Column Infiltration
 EXAMPLE PROBLEMS The module UNSATCHEM is developed from the variably saturated solute transport model HYDRUS-1D [Šimůnek et al., 1997], and thus the water flow and solute transport parts of the model have
EXAMPLE PROBLEMS The module UNSATCHEM is developed from the variably saturated solute transport model HYDRUS-1D [Šimůnek et al., 1997], and thus the water flow and solute transport parts of the model have
ESBN. Working Group on INSPIRE
 ESBN Working Group on INSPIRE by Marc Van Liedekerke, Endre Dobos and Paul Smits behalf of the WG members WG participants Marc Van Liedekerke Panos Panagos Borut Vrščaj Ivana Kovacikova Erik Obersteiner
ESBN Working Group on INSPIRE by Marc Van Liedekerke, Endre Dobos and Paul Smits behalf of the WG members WG participants Marc Van Liedekerke Panos Panagos Borut Vrščaj Ivana Kovacikova Erik Obersteiner
Compact guides GISCO. Geographic information system of the Commission
 Compact guides GISCO Geographic information system of the Commission What is GISCO? GISCO, the Geographic Information System of the COmmission, is a permanent service of Eurostat that fulfils the requirements
Compact guides GISCO Geographic information system of the Commission What is GISCO? GISCO, the Geographic Information System of the COmmission, is a permanent service of Eurostat that fulfils the requirements
Final report for the Expert Group on the Integration of Statistical and Geospatial Information, May 2015
 Final report for the Expert Group on the Integration of Statistical and Geospatial Information, May 2015 Global geographic classification and geocoding practices Executive summary This final report was
Final report for the Expert Group on the Integration of Statistical and Geospatial Information, May 2015 Global geographic classification and geocoding practices Executive summary This final report was
INSPIRE Basics. Vlado Cetl European Commission Joint Research Centre. https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/
 INSPIRE Basics Vlado Cetl European Commission Joint Research Centre https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/ Serving society Stimulating innovation Supporting legislation Outline SDI? Why European SDI? INSPIRE Policy
INSPIRE Basics Vlado Cetl European Commission Joint Research Centre https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/ Serving society Stimulating innovation Supporting legislation Outline SDI? Why European SDI? INSPIRE Policy
Report on a workshop on the Development of a Scottish Soils Knowledge and Information Base (SSKIB)
 Report on a workshop on the Development of a Scottish Soils Knowledge and Information Base (SSKIB) Macaulay Land Use Research Institute, September 22, 2004. by Allan Lilly, Willie Towers, Ann Malcolm and
Report on a workshop on the Development of a Scottish Soils Knowledge and Information Base (SSKIB) Macaulay Land Use Research Institute, September 22, 2004. by Allan Lilly, Willie Towers, Ann Malcolm and
About peer review missions related to data management
 PEER REVIEW WORKSHOP ABOUT DATA MANAGEMENT Introduction Paul HAENER International Office for Water FRANCE p.haener@oieau.fr October 2016 About peer review missions related to data management 2 1 Data management
PEER REVIEW WORKSHOP ABOUT DATA MANAGEMENT Introduction Paul HAENER International Office for Water FRANCE p.haener@oieau.fr October 2016 About peer review missions related to data management 2 1 Data management
The use of SAGA-GIS in an integrated meteorological/ hydrological model for the Mawddach river catchment, North Wales
 The use of SAGA-GIS in an integrated meteorological/ hydrological model for the Mawddach river catchment, North Wales Graham Hall, Roger Cratchley and Sarah Johnson School of Agricultural and Forest Sciences,
The use of SAGA-GIS in an integrated meteorological/ hydrological model for the Mawddach river catchment, North Wales Graham Hall, Roger Cratchley and Sarah Johnson School of Agricultural and Forest Sciences,
An Update on Land Use & Land Cover Mapping in Ireland
 An Update on Land Use & Land Cover Mapping in Ireland Progress Towards a National Programme Kevin Lydon k.lydon@epa.ie Office of Environmental Assessment, Environmental Protection Agency, Johnstown Castle,
An Update on Land Use & Land Cover Mapping in Ireland Progress Towards a National Programme Kevin Lydon k.lydon@epa.ie Office of Environmental Assessment, Environmental Protection Agency, Johnstown Castle,
WMS 9.0 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Infiltration Learn how to add infiltration to your GSSHA model
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Infiltration Learn how to add infiltration to your GSSHA model Objectives This workshop builds on the model developed in the previous workshop and shows you
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Infiltration Learn how to add infiltration to your GSSHA model Objectives This workshop builds on the model developed in the previous workshop and shows you
Crop Monitoring in Europe WINTER CEREAL HARDENING IS PROGRESSING WELL. MARS BULLETIN Vol.20 No.12 (2012)
 ONLINE VERSION JRC68576 EUR 24736 EN ISSN 1831-9424 ISSN 1831-9793 Crop Monitoring in Europe MARS BULLETIN Vol.20 No.12 (2012) Issued: 17 December 2012 WINTER CEREAL HARDENING IS PROGRESSING WELL The last
ONLINE VERSION JRC68576 EUR 24736 EN ISSN 1831-9424 ISSN 1831-9793 Crop Monitoring in Europe MARS BULLETIN Vol.20 No.12 (2012) Issued: 17 December 2012 WINTER CEREAL HARDENING IS PROGRESSING WELL The last
Updating Slope Topography During Erosion Simulations with the Water Erosion Prediction Project
 This paper was peer-reviewed for scientific content. Pages 882-887. In: D.E. Stott, R.H. Mohtar and G.C. Steinhardt (eds). 2001. Sustaining the Global Farm. Selected papers from the 10th International
This paper was peer-reviewed for scientific content. Pages 882-887. In: D.E. Stott, R.H. Mohtar and G.C. Steinhardt (eds). 2001. Sustaining the Global Farm. Selected papers from the 10th International
Progress of UN-GGIM: Europe Working Group A on Core Data
 INSPIRE KEN 13 December 2016 Progress of UN-GGIM: Europe Working Group A on Core Data François Chirié, Dominique Laurent, IGN France Plan Introduction Objectives of the working group with respect to INSPIRE
INSPIRE KEN 13 December 2016 Progress of UN-GGIM: Europe Working Group A on Core Data François Chirié, Dominique Laurent, IGN France Plan Introduction Objectives of the working group with respect to INSPIRE
How proximity to a city influences the performance of rural regions by Lewis Dijkstra and Hugo Poelman
 n 01/2008 Regional Focus A series of short papers on regional research and indicators produced by the Directorate-General for Regional Policy Remote Rural Regions How proximity to a city influences the
n 01/2008 Regional Focus A series of short papers on regional research and indicators produced by the Directorate-General for Regional Policy Remote Rural Regions How proximity to a city influences the
Appendix D. Model Setup, Calibration, and Validation
 . Model Setup, Calibration, and Validation Lower Grand River Watershed TMDL January 1 1. Model Selection and Setup The Loading Simulation Program in C++ (LSPC) was selected to address the modeling needs
. Model Setup, Calibration, and Validation Lower Grand River Watershed TMDL January 1 1. Model Selection and Setup The Loading Simulation Program in C++ (LSPC) was selected to address the modeling needs
Directorate E: Sectoral and regional statistics Unit E-4: Regional statistics and geographical information LUCAS 2018.
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate E: Sectoral and regional statistics Unit E-4: Regional statistics and geographical information Doc. WG/LCU 52 LUCAS 2018 Eurostat Unit E4 Working Group for Land
EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate E: Sectoral and regional statistics Unit E-4: Regional statistics and geographical information Doc. WG/LCU 52 LUCAS 2018 Eurostat Unit E4 Working Group for Land
GEOCHEMISTRY RESEARCH GROUP projects & research
 PATHWAY GEOCHEMISTRY RESEARCH GROUP projects & research MOROCCO-HUNGARY Bilateral Project Meknes 2012 GYOZO JORDAN Geochemistry Department, Hungarian Geological and Geophysical Institute RECEPTOR SOURCE
PATHWAY GEOCHEMISTRY RESEARCH GROUP projects & research MOROCCO-HUNGARY Bilateral Project Meknes 2012 GYOZO JORDAN Geochemistry Department, Hungarian Geological and Geophysical Institute RECEPTOR SOURCE
IAEG SDGs WG GI, , Mexico City
 IAEG SDGs WG GI, 12-14.12.2016, Mexico City UN-GGIM:Europe s perspective and activities to support better integration of geospatial information and statistics and the UN SDG monitoring Pier-Giorgio Zaccheddu,
IAEG SDGs WG GI, 12-14.12.2016, Mexico City UN-GGIM:Europe s perspective and activities to support better integration of geospatial information and statistics and the UN SDG monitoring Pier-Giorgio Zaccheddu,
Land Cover and Land Use Diversity Indicators in LUCAS 2009 data
 Land Cover and Land Use Diversity Indicators in LUCAS 2009 data A. Palmieri, L. Martino, P. Dominici and M. Kasanko Abstract Landscape diversity and changes are connected to land cover and land use. The
Land Cover and Land Use Diversity Indicators in LUCAS 2009 data A. Palmieri, L. Martino, P. Dominici and M. Kasanko Abstract Landscape diversity and changes are connected to land cover and land use. The
ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT
 ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT Pursuant to Article 1 of the Convention signed in Paris on 14th December 1960, and which came into force on 30th September 1961, the Organisation
ORGANISATION FOR ECONOMIC CO-OPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT Pursuant to Article 1 of the Convention signed in Paris on 14th December 1960, and which came into force on 30th September 1961, the Organisation
SHAWN NAYLOR. Research Hydrogeologist Center for Geospatial Data Analysis, Indiana Geological Survey
 SHAWN NAYLOR Research Hydrogeologist Center for Geospatial Data Analysis, Indiana Geological Survey Project overview Funded by American Recovery and Reinvestment Act Develop distributed network of databases
SHAWN NAYLOR Research Hydrogeologist Center for Geospatial Data Analysis, Indiana Geological Survey Project overview Funded by American Recovery and Reinvestment Act Develop distributed network of databases
An objective analysis of the dynamic nature of field capacity
 WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 45,, doi:10.1029/2009wr007944, 2009 An objective analysis of the dynamic nature of field capacity Navin K. C. Twarakavi, 1 Masaru Sakai, 2 and Jirka Šimůnek 2 Received 5
WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 45,, doi:10.1029/2009wr007944, 2009 An objective analysis of the dynamic nature of field capacity Navin K. C. Twarakavi, 1 Masaru Sakai, 2 and Jirka Šimůnek 2 Received 5
New Digital Soil Survey Products to Quantify Soil Variability Over Multiple Scales
 2006-2011 Mission Kearney Foundation of Soil Science: Understanding and Managing Soil-Ecosystem Functions Across Spatial and Temporal Scales Progress Report: 2006021, 1/1/2007-12/31/2007 New Digital Soil
2006-2011 Mission Kearney Foundation of Soil Science: Understanding and Managing Soil-Ecosystem Functions Across Spatial and Temporal Scales Progress Report: 2006021, 1/1/2007-12/31/2007 New Digital Soil
Protocol for the design, conducts and interpretation of collaborative studies (Resolution Oeno 6/2000)
 Protocol for the design, conducts and interpretation of collaborative studies (Resolution Oeno 6/2000) INTRODUCTION After a number of meetings and workshops, a group of representatives from 27 organizations
Protocol for the design, conducts and interpretation of collaborative studies (Resolution Oeno 6/2000) INTRODUCTION After a number of meetings and workshops, a group of representatives from 27 organizations
KEY WORDS: Palmer Meteorological Drought Index, SWAP, Kriging spatial analysis and Digital Map.
 PALMER METEOROLOGICAL DROUGHT CLASSIFICATION USING TECHNIQUES OF GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM IN THAILAND S. Baimoung, W. Waranuchit, S. Prakanrat, P. Amatayakul, N. Sukhanthamat, A. Yuthaphan, A. Pyomjamsri,
PALMER METEOROLOGICAL DROUGHT CLASSIFICATION USING TECHNIQUES OF GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM IN THAILAND S. Baimoung, W. Waranuchit, S. Prakanrat, P. Amatayakul, N. Sukhanthamat, A. Yuthaphan, A. Pyomjamsri,
The Soil Atlas of the Northern Circumpolar Region
 Conference Soil, Climate Change and Biodiversity Where do we stand? Brussels, Thursday 23rd and Friday 24th September 2010 1 The Soil Atlas of the Northern Circumpolar Region Luca Montanarella European
Conference Soil, Climate Change and Biodiversity Where do we stand? Brussels, Thursday 23rd and Friday 24th September 2010 1 The Soil Atlas of the Northern Circumpolar Region Luca Montanarella European
Source Protection Zones. National Dataset User Guide
 Source Protection Zones National Dataset User Guide Version 1.1.4 20 th Jan 2006 1 Contents 1.0 Record of amendment...3 2.0 Introduction...4 2.1 Description of the SPZ dataset...4 2.1.1 Definition of the
Source Protection Zones National Dataset User Guide Version 1.1.4 20 th Jan 2006 1 Contents 1.0 Record of amendment...3 2.0 Introduction...4 2.1 Description of the SPZ dataset...4 2.1.1 Definition of the
Ate Visser, Roelof Stuurman, and Marc F.P. Bierkens (2004), Real time forecasting of water table depth and soil moisture profiles, in Proceedings of
 Ate Visser, Roelof Stuurman, and Marc F.P. Bierkens (2004), Real time forecasting of water table depth and soil moisture profiles, in Proceedings of the 2 nd international CAHMDA workshop on: The Terrestrial
Ate Visser, Roelof Stuurman, and Marc F.P. Bierkens (2004), Real time forecasting of water table depth and soil moisture profiles, in Proceedings of the 2 nd international CAHMDA workshop on: The Terrestrial
Development of a Spatial European Soil Property Data Set Roland Hiederer & Robert J.A. Jones
 Development of a Spatial European Soil Property Data Set Roland Hiederer & Robert J.A. Jones FAO85 Level 1 EUR 23839 EN - 2009 2 The mission of the JRC-IES is to provide scientific-technical support to
Development of a Spatial European Soil Property Data Set Roland Hiederer & Robert J.A. Jones FAO85 Level 1 EUR 23839 EN - 2009 2 The mission of the JRC-IES is to provide scientific-technical support to
We thank you for your review on our paper. We addressed the following points in a general answer to all reviewers
 Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss., 11, C3731 C3742, 2014 www.hydrol-earth-syst-sci-discuss.net/11/c3731/2014/ Author(s) 2014. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License.
Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss., 11, C3731 C3742, 2014 www.hydrol-earth-syst-sci-discuss.net/11/c3731/2014/ Author(s) 2014. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License.
Scotland s centre of expertise for waters. Dynamic Coast - National Coastal Change Assessment: Defence Asset Database
 Scotland s centre of expertise for waters Dynamic Coast - National Coastal Change Assessment: Defence Asset Database Scotland s centre of expertise for waters Published by CREW Scotland s Centre of Expertise
Scotland s centre of expertise for waters Dynamic Coast - National Coastal Change Assessment: Defence Asset Database Scotland s centre of expertise for waters Published by CREW Scotland s Centre of Expertise
PLUTO The Transport Response to the National Planning Framework. Dr. Aoife O Grady Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport
 PLUTO 2040 The Transport Response to the National Planning Framework Dr. Aoife O Grady Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport Dublin Economics Workshop 15 th September 2018 The Story of Pluto National
PLUTO 2040 The Transport Response to the National Planning Framework Dr. Aoife O Grady Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport Dublin Economics Workshop 15 th September 2018 The Story of Pluto National
Part A: Salmonella prevalence estimates. (Question N EFSA-Q ) Adopted by The Task Force on 28 March 2007
 The EFSA Journal (2007) 98, 1-85 Report of the Task Force on Zoonoses Data Collection on the Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of Salmonella in broiler flocks of Gallus gallus, in the EU,
The EFSA Journal (2007) 98, 1-85 Report of the Task Force on Zoonoses Data Collection on the Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of Salmonella in broiler flocks of Gallus gallus, in the EU,
EuroGeoSurveys An Introduction
 EGS -ASGMI Workshop, Madrid, 2015 EuroGeoSurveys An Introduction 40 Years Listening to the Beat of the Earth Click to edit Master title Albania style EuroGeoSurveys Austria Lithuania Luxembourg Belgium
EGS -ASGMI Workshop, Madrid, 2015 EuroGeoSurveys An Introduction 40 Years Listening to the Beat of the Earth Click to edit Master title Albania style EuroGeoSurveys Austria Lithuania Luxembourg Belgium
Progress of UN-GGIM: Europe Working Group A on Core Data
 PolicyKEN Budapest 29 November 2016 Progress of UN-GGIM: Europe Working Group A on Core Data François Chirié, Dominique Laurent, IGNF Core data context Background and purpose Aim of Work Group A to propose
PolicyKEN Budapest 29 November 2016 Progress of UN-GGIM: Europe Working Group A on Core Data François Chirié, Dominique Laurent, IGNF Core data context Background and purpose Aim of Work Group A to propose
Spatial decision making in Armenia based on multidisciplinary environmental research
 EU FP7 EcoArm2ERA Integration into ERA Integration of spatial decision support systems and evidence based modeling in National/Regional Policy applications and regulatory systems: scientific and policy
EU FP7 EcoArm2ERA Integration into ERA Integration of spatial decision support systems and evidence based modeling in National/Regional Policy applications and regulatory systems: scientific and policy
THE DIGITAL SOIL MAP OF WALLONIA (DSMW/CNSW)
 THE DIGITAL SOIL MAP OF WALLONIA (DSMW/CNSW) Ph. Veron, B. Bah, Ch. Bracke, Ph. Lejeune, J. Rondeux, L. Bock Gembloux Agricultural University Passage des Déportés 2, B-5030 Gembloux, Belgium, geopedologie@fsagx.ac.be
THE DIGITAL SOIL MAP OF WALLONIA (DSMW/CNSW) Ph. Veron, B. Bah, Ch. Bracke, Ph. Lejeune, J. Rondeux, L. Bock Gembloux Agricultural University Passage des Déportés 2, B-5030 Gembloux, Belgium, geopedologie@fsagx.ac.be
CropCast Europe Weekly Report
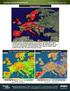 CropCast Europe Weekly Report Kenny Miller Monday, June 05, 2017 Europe Hot Spots Abundant showers should ease dryness across northern and central UK as well as across western Norway and Sweden. Improvements
CropCast Europe Weekly Report Kenny Miller Monday, June 05, 2017 Europe Hot Spots Abundant showers should ease dryness across northern and central UK as well as across western Norway and Sweden. Improvements
British Household Panel Survey, waves 1-17 ( )
 UK Data Archive Study Number 6032 - British Household Panel Survey, Waves 1-17, 1991-2008: Conditional Access, Rural-Urban s British Household Panel Survey, waves 1-17 (1991-2008) User Documentation: Rural-Urban
UK Data Archive Study Number 6032 - British Household Panel Survey, Waves 1-17, 1991-2008: Conditional Access, Rural-Urban s British Household Panel Survey, waves 1-17 (1991-2008) User Documentation: Rural-Urban
The effect of soil physical parameters on soil erosion. Introduction. The K-factor
 Geographical Bulletin 2004. Tom. LIII. No. 1 2. pp.77 84. The effect of soil physical parameters on soil erosion ÁDÁM KERTÉSZ TAMÁS HUSZÁR GERGELY JAKAB 1 Introduction The factor K of the Universal Soil
Geographical Bulletin 2004. Tom. LIII. No. 1 2. pp.77 84. The effect of soil physical parameters on soil erosion ÁDÁM KERTÉSZ TAMÁS HUSZÁR GERGELY JAKAB 1 Introduction The factor K of the Universal Soil
APPLICATION OF TWO-PHASE REGRESSION TO GEOTECHNICAL DATA. E. Stoimenova, M. Datcheva, T. Schanz 1
 Pliska Stud. Math. Bulgar. 16 (2004), 245-257 STUDIA MATHEMATICA BULGARICA APPLICATION OF TWO-PHASE REGRESSION TO GEOTECHNICAL DATA E. Stoimenova, M. Datcheva, T. Schanz 1 A method for estimating a transition
Pliska Stud. Math. Bulgar. 16 (2004), 245-257 STUDIA MATHEMATICA BULGARICA APPLICATION OF TWO-PHASE REGRESSION TO GEOTECHNICAL DATA E. Stoimenova, M. Datcheva, T. Schanz 1 A method for estimating a transition
Harmonization of methods and measurements. Rainer Baritz
 Harmonization of methods and measurements Rainer Baritz ESP, Ispra, 21-22 May 2014 1 Context National contributions with harmonized data to. Improve cross-border and continental represenation for various
Harmonization of methods and measurements Rainer Baritz ESP, Ispra, 21-22 May 2014 1 Context National contributions with harmonized data to. Improve cross-border and continental represenation for various
ESPON evidence on European cities and metropolitan areas
 BEST METROPOLISES Final Conference 18 April 2013, Warsaw ESPON evidence on European cities and metropolitan areas Michaela Gensheimer Structure of Intervention Content Part I: What is the ESPON 2013 Programme?
BEST METROPOLISES Final Conference 18 April 2013, Warsaw ESPON evidence on European cities and metropolitan areas Michaela Gensheimer Structure of Intervention Content Part I: What is the ESPON 2013 Programme?
APPLYING BORDA COUNT METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE BEST WEEE MANAGEMENT IN EUROPE. Maria-Loredana POPESCU 1
 APPLYING BORDA COUNT METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE BEST MANAGEMENT IN EUROPE Maria-Loredana POPESCU 1 ABSTRACT This article presents the Borda Count method and its application for ranking the regarding the
APPLYING BORDA COUNT METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE BEST MANAGEMENT IN EUROPE Maria-Loredana POPESCU 1 ABSTRACT This article presents the Borda Count method and its application for ranking the regarding the
