Land capability and Crop Suitability using RS and GIS
|
|
|
- Eleanore Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Technical & Scientific Research Engineering Volume 1 Issue 2, July-August Anjan Kumar 1, Ravikumar A.S 2 1 (PG student, Water Resource Engg, Dept. of Civil Engg, UVCE /Bangalore University, India) 2 (Associate Professor, Dept. of Civil Engg, UVCE /Bangalore University, India) ABSTRACT: In the coming decades accelerating population growth, surface water pollution, and climate change together may produce a drastic decline in fresh water supply. Keeping the above factors in view, the quantification and conservation of surface water resource is needed for ensuring livelihood. The study area chosen is Kabini command area spread in Mysore and Chamrajnagar districts, Karnataka. The objective of the study is to assess the capability of land for agriculture in order to make the land more profitable and also to determine the best suitable areas for the crops viz,. Paddy, Sugarcane and Cereals. For LCC, slope, soil depth, texture and land use/ land cover conditions are assessed through remote sensing and GIS environment. The analysis reveals that 5 classes I, II, III, IV and V are present in the command area. The evaluation of land in terms of the suitability classes is based on the method as described in FAO guideline for land evaluation for rainfed agriculture. A land unit resulting from the overlay process of the selected theme layers has unique information of land qualities for which the suitability is based on. The selected theme layers includes soil texture, soil depth, land use/ land cover, rainfall, slope, aspect, ph, erosion, drainage density and temperature which are overlaiyed in ArcGIS using Analytical Heirchical Process (AHP). It reveals that 4 classes has been identified as highly suitable (S1), moderately suitable (S2), less suitable (S3) and not suitable (N). KEYWORDS Agriculture, AHP, GIS, land capability classification, land suitability, RS. I. INTRODUCTION The most important aspects of land are its role in providing anchorage space to all resources and the fact that most human activities take place on land. In the light of increasing population, the demand is also increasing, thus optimum use of land has become a necessity. Land is also unevenly distributed in terms of its qualities. Land can be improved for a particular use by certain measures, it can also be improved by a certain kind of land-use or at least sustained production can be assured. Land can deteriorate by its mismanagement, wrong land use or by certain cultivation practices, thus in order to avoid misuse and wastage of land. It should be used judiciously considering its capability and suitability for particular use. To reduce the human influence on natural resources and to identify an appropriate land use, it is essential to carry out scientific land evaluations. Such kind of analysis allows identifying the main limiting factors for the agricultural production and enables decision makers to develop crop managements able to increase the land productivity. The importance of land classifications are divided based on the quality and intensity of its use hardly needs any elaboration in land-use studies. Classifications of land mean assigning each tract, or piece of land within a specific area its proper class within a system of classes. The system relates to a quality or characteristics of land or distinctions of the quality or particular characteristics. In simple way land classification means dividing the land into different categories or classes according to a single factor or a particular interpretation. The capability classification provides three major categories of soil grouping viz., capability unit, capability subclass, and capability classes. According to this system the first category i.e., Capability Unit is a grouping of one or more individual soil-mapping units having similar potentials and continuing limitations or hazards. The soils in a capability unit are sufficiently uniform to produce similar kinds of cultivated crops and pasture plants with similar management practices, require similar conservation treatment and management under the same kind and condition of vegetative cover, and have comparable potential productivity. Anjan Kumar Page 9
2 The second category, i.e. the capability sub-class is a grouping of capability units having similar kinds of limitations and the symbol given for each is used as suffix to the concerned land capability class: a) Erosion and runoff (including risk of erosion and post erosion damage) b) Excess of water (wetness, high water-table, problem of drainage, overflow) c) Root zone limitations (Shallow depth, low water holding capacity, salinity or alkalinity) d) Climatic limitations. Land capability sub-classes have been used widely in many parts of the world with slight modifications mostly incorporating local hazards. The third category and broadest category in the capability classification is the Capability Classes. Capability classes are groups of capability sub-classes or capability units that have the same relative degree of hazard or limitation. The risks of soil damage limitation in use become progressively grater from class I to class VIII. The capability classes are useful as a means of introducing the map user to obtain the more detailed information on the soil map. Class I: Soils in land class I have either no or only slight permanent limitations or risks of damage. The soils are deep, productive, easily worked, and nearly level and can be cultivated safely with ordinary good farming methods. Class II: Soils in this class, subjected to moderate limitations and moderate risks of damage. They can be cultivated with easily applied practices. Soils in this class have gentle slopes, moderate depths which are subject to occasional overflows and are in need of drainage. Class III: Soils in class III are subject to severe limitations in use of cropland. They are subject to severe risks or damages. They are moderately good soils and they can be used regularly for crops, provided they are planted according to good rotations and given the proper treatment. Soils in this class have moderately steep, slopes and are subject to more severe erosion. Class IV: Class IV land is composed of soils, which are very severe permanent limitations or hazards if used for cropland. The soils are fairly good and are frequently on steeps slopes and subject to severe erosion. They should usually be kept in hay or pasture, although a grain crops may be grown once in five or six years. Class V: Soils in class V should be kept in permanent vegetation. They should be used for pasture or forestry. They have few or no permanent limitations and not more than slight hazards. Cultivation is not feasible, however, because of wetness or other limitations. Class VI: Class VI soil should be used for grazing and forestry and may have moderate hazards when in use. They are subject to moderate permanent limitations and are unsuited for cultivation and are steep, or shallow. Class VII: Soils in class VII are subject to severe permanent limitations or hazards when used for grazing or forestry. They are steep, eroded rough, shallow, droughty or swampy. They are either fair or poor for grazing or forestry and must be handled with care. Class VIII: Soils in class VIII are rough even for woodland or grazing. They should be used for wildlife, recreation or watershed uses. Agricultural land suitability is an interdisciplinary approach. Determination of optimum land use type for an area involves integration of data from various domains and sources like soil science to social science, meteorology to management science. All these major streams can be considered as separate groups, further each group can have various parameters (criteria). However, all the criteria are not equally important, every criteria will contribute towards the suitability at different degrees. The relative degree of contribution of various criteria can be addressed well when they are grouped into various groups and organized at various hierarchies. Agricultural land suitability also involves major decisions at various levels starting from choosing a major land use types (LUT), selection of criteria, organization of the criteria, deciding suitability limits for each class of the criteria, deciding the preferences (qualitative and quantitative). Relative importance of these parameters can be well evaluated to determine the suitability by multi-criteria evaluation techniques (Ceballos - Silva and Lopez- Blanco 2003). The present popular methods that are followed for land suitability analysis includes ranking and ratings, weighted summation, requirement matching etc. The weights are arbitrarily chosen, and are aggregated using simple Boolean overlay methods. Although these methods are simple and straight forward and lack solid mathematical foundations. Anjan Kumar Page 10
3 II. STUDY AREA The area chosen is Kabini command area which spreads in Chamrajnagar and Mysore districts. The study area geographically lies between E and E longitude and N and N latitude with an area of sq.km which is covered on Survey of India (SOI) Toposheet numbers 57H04, 57H03, 57D16, 58E01, 58A13, 57D12, 57D08, 58A05 and 58A01 on 1:50000 scale. The maximum length and width of the command is km and km respectively. Kabini river is one of the major rivers in Cauvery basin and constitutes C-2 subbasin. The river originates in Western Ghats at an altitude of 2134 m in Wynad tauk, Kerala state and flows for a length of 212 km before joining the river Cauvery at Tirumakudalu Narasipura, Karnataka state. Fig.1 shows the location map of Kabini command area. Fig. 1. Location map of the study area Data products The following data products are used in the present study: i. Survey of India (SOI) Topomaps on 1:50,000 scale ii. Digital Elevation Model (DEM ) data iii. Rainfall Data iv. Hydrometeorological data v. Soil data vi. LANDSAT7 imagery and LISS III imagery (Table 1) Table 1: List of data used Type of data Description of data Sources of data Soil data Soil PH, soil depth, soil texture NBSS & LUP / KSRSAC, bengaluru Climate data Rainfall and temperature data IMD, Bengaluru Digital Elevation Model ASTER DEM (resolution: 90 m) USGS (Earth Explorer) Satellite image Land use/land cover LISS III Imagery III. METHODOLOGY 1. Data collection and preparation of Thematic layers: A common base map is prepared from SOI topomaps on 1:50000 scale before thematic mapping. The base map provides the basic details such as watershed boundary, latitude, longitude, major roadway, railway, rivers/ streams, water bodies, taluk boundaries, location of important settlements, etc. which serves as control points during interpretation of remotely sensed data Land use/ land cover and soil data (soil ph, soil texture, and soil depth) are collected from Karnataka State Remote Sensing Application Centre (KSRSAC and NBSS and LUP, Bengaluru respectively. Climate data (rainfall and temperature) is obtained from Indian Meteorological Dept. Anjan Kumar Page 11
4 (IMD), Bengaluru and Hydrometerological (HM) stations. There are four H.M stations are present in the study area viz,. Gundal, Kabini, Suvarnavathy and Nanjangudu. Digital Elevation Model (DEM) is obtained from USGS (Earth Explorer, SRTM 90m resolution). The mosaic has been processed and rectified to WGS84 coordinate system. Slope information is obtained from SOI Toposheets. Thematic maps for each of the soil parameters and slope are prepared using ArcGIS10.1 software. Annual rainfall and mean temperature, thematic maps are generated using Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW) interpolation. IDW interpolation determines cell values using a linearly weighted combination of a set of sample points. Fig.2 shows the methodology adopted for preparation of thematic maps as per the IMSD (NRSA, 1995) Technical Guidelines, NRSA, Hyderabad. Fig 3-13 shows the various thematic maps of the study area. Fig. 2 Methodology for preparation of thematic maps Fig.3 Land use/ land cover map of Kabini command Fig.4 Land use/ land cover map of Kabini command Fig.5. (DEM) of Kabini command Anjan Kumar Page 12
5 Fig.6 Slope map of Kabini command Fig. 7 Soil depth map of Kabini command Fig.8 Erosion map of Kabini command Fig. 9 Rainfall map of Kabini command Fig. 10 Temperature map of Kabini command Fig. 11 PH map of Kabini command Anjan Kumar Page 13
6 Fig.12 Aspect map of Kabini command Fig.13 Drainage density map of Kabini command 2. Land Capability classification The generalized methodology for Land Capability Classification (LCC) using GIS is depicted in the form of a flow chart (Fig. 14). The geospatial technique helps in generation of a reliable spatial and non-spatial information database. Such a database helps immensely in the efficient and scientific decision-making. The procedure essentially consists of 2 stages; i. To map the controlling and indicative parameters with the existing information and ii. Integration of the controlling and indicative parameter layers digitally through GIS. The land capability classification has been carried out by applying parameters like soil depth, soil texture, land use / land cover, erosion and slope of land. This information is used as a basis for placing lands in capability classes and subclasses. These informations are related with soil depth and soil texture about study region has been used from National bureau and soil survey and land use planning (NBSS and LUP). Shuttle Radar Topographic Mission (SRTM) data of the study region is used to assess the terrain conditions. 90 m data is resampled to 30m by using 3D surfacing utility of Erdas 9.0 software to get better accuracy. Landsat ETM image is used to assess the land use/land cover categories by applying Supervised Classification technique. Here, the advance navigation technique like GPS has been used to collect training site data and to field check classified datasets. These parameters are integrated in GIS environment by using intersect overlay technique. Moreover the surface and overlay analysis capabilities in GIS can effectively facilitate in handling vast amount of spatial information. The Intersect tool calculates the geometric intersection of input feature classes. The features or portion of features that are common to (intersect) all inputs will be written to the output feature class (Final LCC map). Anjan Kumar Page 14
7 La nd Cover typ e Fig. 14 Methodology used for Land Capability Classification Table 2 shows land cover classification into land capability groups. Table 3 shows land capability classes, characteristic features and recommendations. Table 4 shows Slope Classification. Table 2 Land cover classification into land capability groups Land Capability Group I II III IV V Kharif crop Tank (dry) Wasteland Wasteland with with/without stony waste/ Settlement Double crop scrub rockout crops Tank Agricultural plantation Forest Stream/river The depth of soil determines the effective rooting depth for plants, in accordance with texture, mineralogy and gravel content the capacity of the soil column to hold water. Seven depth classes given by Sehgal et al. (1987) ware used to classify the soil map in to depth class association (Table 5). 3. Crop Suitability Analysis 3.1 Selection of evaluation criteria: The study of Kabini has shown that it is important to consider other terrain features in addition to soil characteristics in order to arrive with a more informed decision on optimal crop growing areas. Opinions of agronomist and literature review of various references helped in identifying criterias viz,. soil P H, soil depth, drainage density, rainfall, slope, temperature, aspect, erosion, soil texture and land use/land cover necessary to determine suitable for growing paddy, sugarcane and cereals. Fig.15 shows the step by step procedure for Hierarchical process. Anjan Kumar Page 15
8 Fig. 15 Hierarchical organisation of the criteria considered for the study. The suitability levels are based on the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) land suitability classification and ranked as highly suitable (S1), moderately suitable (S2), marginally suitable (S3) and not suitable (S4). Suitability levels for each of the criteria are defined according to the FAO guideline for rainfed agriculture, literature review and agronomist opinions (Table 6) Sl No. Table 6 Standard criteria for Major crops (NBSS & LUP) 1. Paddy crop Suitability class Criteria Highly suitable, Moderately Marginaly S1 suitable, S2 suitable, S3 1 Temperature ( o C) Not suitable, N > < 15 2 Rainfall (mm) < Texture c, sic, cl, sicl, sl scl, sil, l sl, ls s 4 ph > < Soil depth (cm) > < 25 6 Slope > 5 2. Cereals/Pulses 1 Temperature ( o C) < 20 2 Rainfall (mm) < 400 Anjan Kumar Page 16
9 3 Texture sl, sclsil, cl, sic, sicl, c ls 4 ph > Soil depth (cm) > < 40 6 Slope < Temperature ( o C) 3. Sugarcane crop > < 20 2 Rainfall (mm) < Texture c, sic, cl, sicl, sl scl, sil, l sl, ls s 4 ph < < Soil depth (cm) > < 50 6 Slope < > 8 ( s- sand, ls loamy sand, sl sandy loam, scl sandy clay loam, cl clay loam, sil silt loam, l loam, sic silty loam, sc sandy clay, c- clay) Suitability levels S1, S2, S3 and N are assigned score 9, 7, 5 and 3 respectively. Classes with higher scores are most suitable for suitability evaluation. Using these scores and the defined suitability levels, all thematic maps area reclassified. 3.2 Applying MCE and assigning weights : To determine the relative importance/weights of criteria, AHP method of MCE is used. In order to compute the weights for the criteria, a pairwise comparison matrix (PWCM) is constructed using the information obtained through interviews, each factor has compared with the other factors, relative to its importance, on a scale from 1/9 to 9 introduced by Saaty (2008). Table 7 shows the scale of comparison used for the present study. Equal importance Table 7 Scale of comparison Degree of preference Moderate importance of one thematic layer over another Strong importance Very importance Extreme importance Values for inverse comparison The diagonal elements of PWCM are assigned the value of unity (i.e., when a factor is compared with itself). Since the matrix is symmetrical, only the lower triangular half actually needs to be filled in. The remaining cells are then reciprocals of the lower triangular half (Kihoro, Njore & Murage 2013). The normalized matrix is derived from pairwise comparison by adding the entries in each column of comparison matrix and then dividing each entry a jk with the sum of the entries the corresponding column a jk of the comparison matrix. The sum of normalized entries in each column will be equal to 1. Therefore, each entry in the normalized matrix = ajk When performing pairwise comparison, some incosnistencies may typically arise. The AHP incorporates an effective technique for checking the consistency of the evaluations made by the decision maker. In the AHP, the pairwise comparison in a judgment matrix are considered to be adequately consistent if the corresponding consistency ratio (CR) is less than 10% (Triantaphyllou & Mann 1995). Anjan Kumar Page 17
10 To calculate CR, the consistency index (CI) is estimated by multiplying judgement matrix by the approximated eigen vector. Each component of the resulting matrix is then divided by the corresponding approximated eigen vector. This yields an approximation of the maximum eigen value ( ). Then, the CI value is calculated by using the formula: CI = ( max )/( 1). Finally, the CR is obtained by dividing the CI value by the Random Consistency Index (RCI) as recommended by Saaty, (1980). Table 8 shows the random index (RI) values, Table 9 shows the pairwise comparison matrix and Table 10 shows the normalized matrix for the thematic layers. Table 8 Values of Random Index (RI) for number of thematic layers (n) n RI Table 9 Pairwise comparison matrix of thematic layers Table 10 Normalized matrix / priority matrix 3.3 Overlaying map layers: The reclassified thematic maps / layers of each variable are weighted using the weights derived from the AHP process. The weighted maps / layers are combined by performing the weighted overlay using spatial analyst tools. Finally, the suitability map is prepared. Anjan Kumar Page 18
11 IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS For LCC, slope, soil depth/ texture and land use/ land cover conditions are assessed in remote sensing and GIS environment. As these parameters have greater influence on capability of land. Five different classes (Fig.16) are observed in the command and tabulated in Table 11. Table 11. Agriculture land capability classification for Kabini command area Sl Land Capability Area % no. Class (sq.km) Area 1 Class I Class II Class III Class IV Class V TOTAL Fig. 16 Agriculture Land Capability Classification map for Kabini command area The weighted overlay analysis carried out using the criteria layers with their respective weights generated a combined suitability map (Fig. 17, 18 & 19). From the Table 12, reveals that % as highly suitable, sq.km (36.92%) as moderately suitable and sq.km (43.41%) as marginally suitable and sq.km (2.6%) not suitable for Paddy in Kabini command area. About sq.km (15.57%) as highly suitable, sq.km (36.92%) as moderately suitable and sq.km (4.82%) & sq.km (5.09%) not suitable for Sugarcane crop in Kabini command. About sq.km (133.53%) as highly suitable, sq.km (54%) as moderately suitable and sq.km (3.81%) not suitable for cereals crops in Kabini command. Fig. 17 Paddy suitability map for Kabini command area command area Fig. 18 Sugarcane suitability map for Kabini Anjan Kumar Page 19
12 Fig. 19 Cereals suitability map for Kabini command area Table 12 Crop Suitability for Kabini command area Paddy Sugarcane Cereals Sl no. Class Area % Area % Area % Description (sq.km) Area (sq.km) Area (sq.km) Area 1 S Highly suitable 2 S Moderately suitable 3 S Marginally suitable 4 N Not suitable TOTAL V. CONCLUSIONS The methodology adopted here to indicate land capability classes for decision-making intervention. The analysis reveals that 5 classes I, II, III, IV and V are present in the command area. Out of that Class V which is not suitable for agriculture accounts 0.18 %. Class I is a dominating class as far as the areal extent is concerned with %. Class III & IV are most susceptible to land degradation which accounts for 10 per cent. The FAO (1976) has given a framework for land suitability analysis for crops in terms of suitability classes from highlysuitable to not suitable based on the crop specific soil, climatic and topographic data. The same framework has been incorporated in the study with some modification in order to make the situation more compatible to Indian cases. Land suitability evaluation for crop suitability also highly dependent on specific crop requirement. Parameters used for analysis of crop suitability are slope, drainage, depth, texture, rainfall, temperature, etc. Suitability maps for all the crops are also developed. The suitability map for each crop is classified I to IV suitability classes. Among these crops Paddy & Sugarcane has the more suitability in the present study area. REFERENCES [1] Ashwini R., (2007) Analysis of Land use Capability Classification using Remote Sensing and Geographical Information System, M.E. Dissertation, Dept. of Civil Engineering, UVCE, Bangalore University, Bangalore. [2] Bhaskar J. Das, Singal S. K., Ranvir Singh., (2008) Estimation of erosion in an ungauged Wetland Catchment, Hydrology Journal, 31 (1-2), pp Anjan Kumar Page 20
13 [3] Chow V.T., Maidment, D.R., and Mays W., (1988). Applied Hydrology, Mc Graw Hill, New York. [4] Clarke J.I., (1966) Morphometry from Maps, Essays in Geomorphology, Elsevier Publ. Co., New York, pp [5] National Bureau of Soil Survey and Land Use Planning (NBSS and LUP, 1998), Soils of Karnataka for optimizing land use Executive summary in co-operation with Government of Karnataka, Bangalore. [6] Singh A.K., Bhattacharya A.K., (2006) Water management and crop production, Handbook of Agriculture, Directorate of information and publication of agriculture. ICAR, New Delhi, pp [7] Feizizadeh, B & Blaschke, T (2012), Land suitability analysis for Tabriz country, Iran: a multi-criteria evaluation approach using GIS, Journal of Environmental Planning and Management, vol. 1, pp [8] Saaty, T, L 2008, Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process, Int. J. Services Sciences, vol. 1, no. 1, pp [9] Triantaphyllou, E & Mann, S,H (1995), using the analytic hierarchy process for decision making in engineering applications: some challeges,inter l Journal of Industrial Engineering: Applications and Practices, vol.2, no.1, pp [10] FAO (1976). A framework for land evaluation, FAO Soil Bulletin, 32, Rome, Italy. [11] Cellabos-Silva, A.and J. Lopez-Blanco (2003). Delieation of suitable areas for crops using Multi-Criteria Evaluation approach and lan use/cover mapping: a case study in Central Mexico. Agriculture systems 77(2): [12] Sehgal J. (1996). Pedology concepts and applications, New Dehli, Kalyani Publishers. Anjan Kumar Page 21
LAND CAPABILITY CLASSIFICATION FOR INTEGRATED WATERSHED DEVELOPMENT BY APPLYING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNIQUES
 LAND CAPABILITY CLASSIFICATION FOR INTEGRATED WATERSHED DEVELOPMENT BY APPLYING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNIQUES Sachin Panhalkar Department of Geography, Shivaji University, Kolhapur, Maharashtra, India
LAND CAPABILITY CLASSIFICATION FOR INTEGRATED WATERSHED DEVELOPMENT BY APPLYING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNIQUES Sachin Panhalkar Department of Geography, Shivaji University, Kolhapur, Maharashtra, India
Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT
 Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT Technical briefs are short summaries of the models used in the project aimed at nontechnical readers. The aim of the PES India
Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT Technical briefs are short summaries of the models used in the project aimed at nontechnical readers. The aim of the PES India
Crop-land Suitability Analysis Using GIS and Remote Sensing in Nyandarua County, Kenya
 Crop-land Suitability Analysis Using GIS and Remote Sensing in Nyandarua County, Kenya Abstract Samuel W. Kamau*, David Kuria and M. K. Gachari Institute of Geomatics, GIS and Remote Sensing, Dedan Kimathi
Crop-land Suitability Analysis Using GIS and Remote Sensing in Nyandarua County, Kenya Abstract Samuel W. Kamau*, David Kuria and M. K. Gachari Institute of Geomatics, GIS and Remote Sensing, Dedan Kimathi
CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS
 80 CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS 7.1GENERAL This chapter is discussed in six parts. Introduction to Runoff estimation using fully Distributed model is discussed in first
80 CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS 7.1GENERAL This chapter is discussed in six parts. Introduction to Runoff estimation using fully Distributed model is discussed in first
Integrated Remote Sensing and GIS Approach for Groundwater Exploration using Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) Technique.
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization, Volume 2, Special Issue
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization, Volume 2, Special Issue
Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study
 Water Resources Management VI 139 Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study J. Letha, B. Thulasidharan Nair & B. Amruth Chand College of Engineering, Trivandrum, Kerala,
Water Resources Management VI 139 Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study J. Letha, B. Thulasidharan Nair & B. Amruth Chand College of Engineering, Trivandrum, Kerala,
Abstract: About the Author:
 REMOTE SENSING AND GIS IN LAND USE PLANNING Sathees kumar P 1, Nisha Radhakrishnan 2 1 1 Ph.D Research Scholar, Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli- 620015,
REMOTE SENSING AND GIS IN LAND USE PLANNING Sathees kumar P 1, Nisha Radhakrishnan 2 1 1 Ph.D Research Scholar, Department of Civil Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli- 620015,
A GIS based Land Capability Classification of Guang Watershed, Highlands of Ethiopia
 A GIS based Land Capability Classification of Guang Watershed, Highlands of Ethiopia Gizachew Ayalew 1 & Tiringo Yilak 2 1 Amhara Design and Supervision Works Enterprise (ADSWE), Bahir Dar, Ethiopia 2
A GIS based Land Capability Classification of Guang Watershed, Highlands of Ethiopia Gizachew Ayalew 1 & Tiringo Yilak 2 1 Amhara Design and Supervision Works Enterprise (ADSWE), Bahir Dar, Ethiopia 2
Review Using the Geographical Information System and Remote Sensing Techniques for Soil Erosion Assessment
 Polish J. of Environ. Stud. Vol. 19, No. 5 (2010), 881-886 Review Using the Geographical Information System and Remote Sensing Techniques for Soil Erosion Assessment Nuket Benzer* Landscape Architecture
Polish J. of Environ. Stud. Vol. 19, No. 5 (2010), 881-886 Review Using the Geographical Information System and Remote Sensing Techniques for Soil Erosion Assessment Nuket Benzer* Landscape Architecture
LAND SUITABILITY STUDY IN LAND DEGRADED AREA DUE TO MINING IN DHANBAD DISTRICT, JHARKHAND.
 LAND SUITABILITY STUDY IN LAND DEGRADED AREA DUE TO MINING IN DHANBAD DISTRICT, JHARKHAND. Saranathan, E a*, Loveson, V.J b. and Victor Rajamanickam, G c a School of Civil Engineering, SASTRA, Thanjavur
LAND SUITABILITY STUDY IN LAND DEGRADED AREA DUE TO MINING IN DHANBAD DISTRICT, JHARKHAND. Saranathan, E a*, Loveson, V.J b. and Victor Rajamanickam, G c a School of Civil Engineering, SASTRA, Thanjavur
Dr. S.SURIYA. Assistant professor. Department of Civil Engineering. B. S. Abdur Rahman University. Chennai
 Hydrograph simulation for a rural watershed using SCS curve number and Geographic Information System Dr. S.SURIYA Assistant professor Department of Civil Engineering B. S. Abdur Rahman University Chennai
Hydrograph simulation for a rural watershed using SCS curve number and Geographic Information System Dr. S.SURIYA Assistant professor Department of Civil Engineering B. S. Abdur Rahman University Chennai
Multi-criteria land evaluation for suitability analysis of wheat: a case study of a watershed in eastern plateau region, India
 Geo-spatial Information Science ISSN: 1009-5020 (Print) 1993-5153 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tgsi20 Multi-criteria land evaluation for suitability analysis of wheat: a case
Geo-spatial Information Science ISSN: 1009-5020 (Print) 1993-5153 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tgsi20 Multi-criteria land evaluation for suitability analysis of wheat: a case
DEVELOPMENT OF FLOOD HAZARD VULNERABILITY MAP FOR ALAPPUZHA DISTRICT
 DEVELOPMENT OF FLOOD HAZARD VULNERABILITY MAP FOR ALAPPUZHA DISTRICT Ciya Maria Roy 1, Elsa Manoj 2, Harsha Joy 3, Sarin Ravi 4, Abhinanda Roy 5 1,2,3,4 U.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, MITS
DEVELOPMENT OF FLOOD HAZARD VULNERABILITY MAP FOR ALAPPUZHA DISTRICT Ciya Maria Roy 1, Elsa Manoj 2, Harsha Joy 3, Sarin Ravi 4, Abhinanda Roy 5 1,2,3,4 U.G. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, MITS
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 6, No 2, 2015
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 6, No 2, 2015 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 An Analysis of Land use
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 6, No 2, 2015 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 An Analysis of Land use
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 1, No 1, 2010
 An Integrated Approach with GIS and Remote Sensing Technique for Landslide Hazard Zonation S.Evany Nithya 1 P. Rajesh Prasanna 2 1. Lecturer, 2. Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Anna
An Integrated Approach with GIS and Remote Sensing Technique for Landslide Hazard Zonation S.Evany Nithya 1 P. Rajesh Prasanna 2 1. Lecturer, 2. Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Anna
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 7, No 1, 2016
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 7, No 1, 2016 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Land suitability study
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 7, No 1, 2016 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Land suitability study
ESTIMATION OF MORPHOMETRIC PARAMETERS AND RUNOFF USING RS & GIS TECHNIQUES
 ESTIMATION OF MORPHOMETRIC PARAMETERS AND RUNOFF USING RS & GIS TECHNIQUES Shrudha. V. K¹, Hafeezunnisa² 1 Assistant Professor, Rajarajeshwari College of Engineering Bangalore 2 Assistant Engineer, WRDO
ESTIMATION OF MORPHOMETRIC PARAMETERS AND RUNOFF USING RS & GIS TECHNIQUES Shrudha. V. K¹, Hafeezunnisa² 1 Assistant Professor, Rajarajeshwari College of Engineering Bangalore 2 Assistant Engineer, WRDO
Environmental Impact Assessment Land Use and Land Cover CISMHE 7.1 INTRODUCTION
 7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered an essential element for modeling and understanding
7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered an essential element for modeling and understanding
GIS Based Delineation of Micro-watershed and its Applications: Mahendergarh District, Haryana
 Kamla-Raj 2012 J Hum Ecol, 38(2): 155-164 (2012) GIS Based Delineation of Micro-watershed and its Applications: Mahendergarh District, Haryana Gulshan Mehra and Rajeshwari * Department of Geography, Kurukshetra
Kamla-Raj 2012 J Hum Ecol, 38(2): 155-164 (2012) GIS Based Delineation of Micro-watershed and its Applications: Mahendergarh District, Haryana Gulshan Mehra and Rajeshwari * Department of Geography, Kurukshetra
CHAPTER 4 METHODOLOGY
 71 CHAPTER 4 METHODOLOGY 4.1 GENERAL Drought, a vague phenomenon, has been defined and analyzed in various ways. Drought assessment involves analysis of spatially and temporally varying water related data.
71 CHAPTER 4 METHODOLOGY 4.1 GENERAL Drought, a vague phenomenon, has been defined and analyzed in various ways. Drought assessment involves analysis of spatially and temporally varying water related data.
CLICK HERE TO KNOW MORE
 CLICK HERE TO KNOW MORE Geoinformatics Applications in Land Resources Management G.P. Obi Reddy National Bureau of Soil Survey & Land Use Planning Indian Council of Agricultural Research Amravati Road,
CLICK HERE TO KNOW MORE Geoinformatics Applications in Land Resources Management G.P. Obi Reddy National Bureau of Soil Survey & Land Use Planning Indian Council of Agricultural Research Amravati Road,
I.J.E.M.S., VOL.4 (1) 2013: ISSN X
 I.J.E.M.S., VOL.4 (1) 2013: 23-28 ISSN 2229-600X Patel Gautam. R., Patel Rajni J. & Chalodia Arvind L 1 Assistant Research Scientist, Directorate of Research, Anand Agricultural University, Anand-388 110.
I.J.E.M.S., VOL.4 (1) 2013: 23-28 ISSN 2229-600X Patel Gautam. R., Patel Rajni J. & Chalodia Arvind L 1 Assistant Research Scientist, Directorate of Research, Anand Agricultural University, Anand-388 110.
7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 OBJECTIVE
 7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered as an essential element for modeling and
7 LAND USE AND LAND COVER 7.1 INTRODUCTION The knowledge of land use and land cover is important for many planning and management activities as it is considered as an essential element for modeling and
CHANGE DETECTION USING REMOTE SENSING- LAND COVER CHANGE ANALYSIS OF THE TEBA CATCHMENT IN SPAIN (A CASE STUDY)
 CHANGE DETECTION USING REMOTE SENSING- LAND COVER CHANGE ANALYSIS OF THE TEBA CATCHMENT IN SPAIN (A CASE STUDY) Sharda Singh, Professor & Programme Director CENTRE FOR GEO-INFORMATICS RESEARCH AND TRAINING
CHANGE DETECTION USING REMOTE SENSING- LAND COVER CHANGE ANALYSIS OF THE TEBA CATCHMENT IN SPAIN (A CASE STUDY) Sharda Singh, Professor & Programme Director CENTRE FOR GEO-INFORMATICS RESEARCH AND TRAINING
Hydrological parameters Controls Vulnerable Zones in Calicut Nilambur Gudalur Ghat section, Gudalur, The Nilgiris, Tamil Nadu.
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: 0974-4290 Vol.9, No.03 pp 248-253, 2016 Hydrological parameters Controls Vulnerable Zones in Calicut Nilambur Gudalur Ghat section,
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG ISSN: 0974-4290 Vol.9, No.03 pp 248-253, 2016 Hydrological parameters Controls Vulnerable Zones in Calicut Nilambur Gudalur Ghat section,
Determination of flood risks in the yeniçiftlik stream basin by using remote sensing and GIS techniques
 Determination of flood risks in the yeniçiftlik stream basin by using remote sensing and GIS techniques İrfan Akar University of Atatürk, Institute of Social Sciences, Erzurum, Turkey D. Maktav & C. Uysal
Determination of flood risks in the yeniçiftlik stream basin by using remote sensing and GIS techniques İrfan Akar University of Atatürk, Institute of Social Sciences, Erzurum, Turkey D. Maktav & C. Uysal
LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS
 LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS ABSTRACT 1 Sonia Sharma, 2 Mitali Gupta and 3 Robin Mahajan 1,2,3 Assistant Professor, AP Goyal Shimla University Email: sonia23790@gmail.com
LANDSLIDE SUSCEPTIBILITY MAPPING USING INFO VALUE METHOD BASED ON GIS ABSTRACT 1 Sonia Sharma, 2 Mitali Gupta and 3 Robin Mahajan 1,2,3 Assistant Professor, AP Goyal Shimla University Email: sonia23790@gmail.com
Watershed Development Prioritization by Applying WERM Model and GIS Techniques in Takoli Watershed of District Tehri (Uttarakhand)
 Watershed Development Prioritization by Applying WERM Model and GIS Techniques in Takoli Watershed of District Tehri (Uttarakhand) Anju Panwar Uttarakhand Space Application Centre Dehradun, Uttarkhand
Watershed Development Prioritization by Applying WERM Model and GIS Techniques in Takoli Watershed of District Tehri (Uttarakhand) Anju Panwar Uttarakhand Space Application Centre Dehradun, Uttarkhand
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 1, No 4, 2011
 Morphometric analysis of Nanjangud taluk, Mysore District, Karnataka, India, using GIS Techniques Mahadevaswamy.G 1, Nagaraju.D 1, Siddalingamurthy.S 1, Lakshmamma 1, Mohammad Subhan lone, Nagesh.P.C 2,
Morphometric analysis of Nanjangud taluk, Mysore District, Karnataka, India, using GIS Techniques Mahadevaswamy.G 1, Nagaraju.D 1, Siddalingamurthy.S 1, Lakshmamma 1, Mohammad Subhan lone, Nagesh.P.C 2,
Block Level Micro Watershed Prioritization Based on Morphometric and Runoff Parameters
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2016, Volume 5, Issue 11, pp. 1981-1987 ISSN 2320-0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.76 Research Article Open Access Block
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2016, Volume 5, Issue 11, pp. 1981-1987 ISSN 2320-0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.76 Research Article Open Access Block
Appendix 2b. NRCS Soil Survey
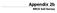 Appendix 2b NRCS Soil Survey 118 19' 25'' W Nonirrigated Capability Class Antelope Valley Area, California (Del Sur Solar Site) 118 17' 28'' W 378900 379200 379500 379800 380100 380400 380700 381000 381300
Appendix 2b NRCS Soil Survey 118 19' 25'' W Nonirrigated Capability Class Antelope Valley Area, California (Del Sur Solar Site) 118 17' 28'' W 378900 379200 379500 379800 380100 380400 380700 381000 381300
Abstract. TECHNOFAME- A Journal of Multidisciplinary Advance Research. Vol.2 No. 2, (2013) Received: Feb.2013; Accepted Oct.
 Vol.2 No. 2, 83-87 (2013) Received: Feb.2013; Accepted Oct. 2013 Landuse Pattern Analysis Using Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Morar Block, of Gwalior District, M.P. Subhash Thakur 1 Akhilesh Singh 2
Vol.2 No. 2, 83-87 (2013) Received: Feb.2013; Accepted Oct. 2013 Landuse Pattern Analysis Using Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Morar Block, of Gwalior District, M.P. Subhash Thakur 1 Akhilesh Singh 2
International Journal of Intellectual Advancements and Research in Engineering Computations
 ISSN:2348-2079 Volume-5 Issue-2 International Journal of Intellectual Advancements and Research in Engineering Computations Agricultural land investigation and change detection in Coimbatore district by
ISSN:2348-2079 Volume-5 Issue-2 International Journal of Intellectual Advancements and Research in Engineering Computations Agricultural land investigation and change detection in Coimbatore district by
Vulnerability of Flood Hazard in Selected Ayeyarwady Delta Region, Myanmar
 Vulnerability of Flood Hazard in Selected Ayeyarwady Delta Region, Myanmar Khin Thandar Win Department of Civil Engineering Nilar Aye Department of Civil Engineering Kyaw Zaya Htun Department of Remote
Vulnerability of Flood Hazard in Selected Ayeyarwady Delta Region, Myanmar Khin Thandar Win Department of Civil Engineering Nilar Aye Department of Civil Engineering Kyaw Zaya Htun Department of Remote
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHEDS IN THE KUNIGAL AREA OF TUMKUR DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNOLOGY
 MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHEDS IN THE KUNIGAL AREA OF TUMKUR DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNOLOGY PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1170 COLLEGE : SIDDAGANGA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY,
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHEDS IN THE KUNIGAL AREA OF TUMKUR DISTRICT, SOUTH INDIA USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNOLOGY PROJECT REFERENCE NO. : 37S1170 COLLEGE : SIDDAGANGA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY,
Comparison of Geomatics Approach and Mathematical Model in Assessment of Soil Erosion Prone Areas Kolli Hills, Namakkal District Tamilnadu, India
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Earth Science and Engineering 2013, Volume 2, Issue 1, pp. 43-56, Article ID Sci-20 Research Article Open Access Comparison of Geomatics Approach and
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Earth Science and Engineering 2013, Volume 2, Issue 1, pp. 43-56, Article ID Sci-20 Research Article Open Access Comparison of Geomatics Approach and
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 7, July ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 7, July-2015 1428 Accuracy Assessment of Land Cover /Land Use Mapping Using Medium Resolution Satellite Imagery Paliwal M.C &.
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 7, July-2015 1428 Accuracy Assessment of Land Cover /Land Use Mapping Using Medium Resolution Satellite Imagery Paliwal M.C &.
Flood Risk Map Based on GIS, and Multi Criteria Techniques (Case Study Terengganu Malaysia)
 Journal of Geographic Information System, 2015, 7, 348-357 Published Online August 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jgis http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jgis.2015.74027 Flood Risk Map Based on GIS,
Journal of Geographic Information System, 2015, 7, 348-357 Published Online August 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jgis http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jgis.2015.74027 Flood Risk Map Based on GIS,
GIS Based Approach for Calculation of Canal Conveyance Losses
 GIS Based Approach for Calculation of Canal Conveyance Losses Ch Ramesh Naidu 1, Mvss Giridhar 2 1 Research Scholar, Civil Engineering Department, JNTUH, Hyderabad, India 2 Assistant Professor, Centre
GIS Based Approach for Calculation of Canal Conveyance Losses Ch Ramesh Naidu 1, Mvss Giridhar 2 1 Research Scholar, Civil Engineering Department, JNTUH, Hyderabad, India 2 Assistant Professor, Centre
Soil Erosion Calculation using Remote Sensing and GIS in Río Grande de Arecibo Watershed, Puerto Rico
 Soil Erosion Calculation using Remote Sensing and GIS in Río Grande de Arecibo Watershed, Puerto Rico Alejandra M. Rojas González Department of Civil Engineering University of Puerto Rico at Mayaguez.
Soil Erosion Calculation using Remote Sensing and GIS in Río Grande de Arecibo Watershed, Puerto Rico Alejandra M. Rojas González Department of Civil Engineering University of Puerto Rico at Mayaguez.
Application of Remote Sensing and GIS for Identification and Assessment Proceedings of AIPA 2012, INDIA 79
 Application of Remote Sensing and GIS for Identification and Assessment Proceedings of AIPA 2012, INDIA 79 APPLICATION OF REMOTE SENSING AND GIS FOR IDENTIFICATION AND ASSESSMENT OF CROP GROWTH IN WAZIRABAD
Application of Remote Sensing and GIS for Identification and Assessment Proceedings of AIPA 2012, INDIA 79 APPLICATION OF REMOTE SENSING AND GIS FOR IDENTIFICATION AND ASSESSMENT OF CROP GROWTH IN WAZIRABAD
VILLAGE INFORMATION SYSTEM (V.I.S) FOR WATERSHED MANAGEMENT IN THE NORTH AHMADNAGAR DISTRICT, MAHARASHTRA
 VILLAGE INFORMATION SYSTEM (V.I.S) FOR WATERSHED MANAGEMENT IN THE NORTH AHMADNAGAR DISTRICT, MAHARASHTRA Abstract: The drought prone zone in the Western Maharashtra is not in position to achieve the agricultural
VILLAGE INFORMATION SYSTEM (V.I.S) FOR WATERSHED MANAGEMENT IN THE NORTH AHMADNAGAR DISTRICT, MAHARASHTRA Abstract: The drought prone zone in the Western Maharashtra is not in position to achieve the agricultural
MODULE 8 LECTURE NOTES 2 REMOTE SENSING APPLICATIONS IN RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODELLING
 MODULE 8 LECTURE NOTES 2 REMOTE SENSING APPLICATIONS IN RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODELLING 1. Introduction The most common application of the remote sensing techniques in the rainfall-runoff studies is the estimation
MODULE 8 LECTURE NOTES 2 REMOTE SENSING APPLICATIONS IN RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODELLING 1. Introduction The most common application of the remote sensing techniques in the rainfall-runoff studies is the estimation
Sub-watershed prioritization based on potential zones of Kuttiadi river basin, A Geo-Morphometric approach using GIS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 8, No 1, 2018 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Sub-watershed prioritization
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 8, No 1, 2018 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Sub-watershed prioritization
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK SPECIAL ISSUE FOR NATIONAL LEVEL CONFERENCE "SUSTAINABLE TECHNOLOGIES IN CIVIL
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK SPECIAL ISSUE FOR NATIONAL LEVEL CONFERENCE "SUSTAINABLE TECHNOLOGIES IN CIVIL
HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE DATA FOR LAND USE/LAND COVER MAPPING IN ROHTAK DISTRICT HARYANA, INDIA
 HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE DATA FOR LAND USE/LAND COVER MAPPING IN ROHTAK DISTRICT HARYANA, INDIA MR. MUKESH KUMAR 1 AND MR.SANDEEP KUMAR 2 1. M.tech. Student, Department of Geography, M.D.University Rohtak,
HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE DATA FOR LAND USE/LAND COVER MAPPING IN ROHTAK DISTRICT HARYANA, INDIA MR. MUKESH KUMAR 1 AND MR.SANDEEP KUMAR 2 1. M.tech. Student, Department of Geography, M.D.University Rohtak,
Outline. Remote Sensing, GIS and DEM Applications for Flood Monitoring. Introduction. Satellites and their Sensors used for Flood Mapping
 Outline Remote Sensing, GIS and DEM Applications for Flood Monitoring Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Chairman, Centre for Earth Sciences Professor, Dept. of Civil Engg. Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560
Outline Remote Sensing, GIS and DEM Applications for Flood Monitoring Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Chairman, Centre for Earth Sciences Professor, Dept. of Civil Engg. Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560
Existing NWS Flash Flood Guidance
 Introduction The Flash Flood Potential Index (FFPI) incorporates physiographic characteristics of an individual drainage basin to determine its hydrologic response. In flash flood situations, the hydrologic
Introduction The Flash Flood Potential Index (FFPI) incorporates physiographic characteristics of an individual drainage basin to determine its hydrologic response. In flash flood situations, the hydrologic
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.96/CRP. 5
 UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.96/CRP. 5 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Eighth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for the Americas New York, 27 June -1 July 2005 Item 5 of the provisional agenda* COUNTRY
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.96/CRP. 5 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Eighth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for the Americas New York, 27 June -1 July 2005 Item 5 of the provisional agenda* COUNTRY
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and
 Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Site Suitability Analysis for Urban Development: A Review
 Site Suitability Analysis for Urban Development: A Review Santanu Kumar Misra Associate Professor (Dept. of CSE) Sikkim Manipal Institute of Technology Majitar, Sikkim misra_santanu@rediffmail.com Shrijana
Site Suitability Analysis for Urban Development: A Review Santanu Kumar Misra Associate Professor (Dept. of CSE) Sikkim Manipal Institute of Technology Majitar, Sikkim misra_santanu@rediffmail.com Shrijana
LAND USE AND LAND COVER ANALYSIS USING 8- BAND DATA: A CASE STUDY OF BELGAUM CITY AND ITS SURROUNDING.
 LAND USE AND LAND COVER ANALYSIS USING 8- BAND DATA: A CASE STUDY OF BELGAUM CITY AND ITS SURROUNDING. Mrs. Rita Basanna *, Dr. A.K. Wodeyar ** ABSTRACT Monitoring land-use change has become an important
LAND USE AND LAND COVER ANALYSIS USING 8- BAND DATA: A CASE STUDY OF BELGAUM CITY AND ITS SURROUNDING. Mrs. Rita Basanna *, Dr. A.K. Wodeyar ** ABSTRACT Monitoring land-use change has become an important
CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY
 32 CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY 3.1 GENERAL In 1910, the seismological society of America identified the three groups of earthquake problems, the associated ground motions and the effect on structures. Indeed
32 CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY 3.1 GENERAL In 1910, the seismological society of America identified the three groups of earthquake problems, the associated ground motions and the effect on structures. Indeed
Morphometric Analysis and Runoff Estimation of Harangi Command Area
 ISSN: -0 PP. 07-8 Morphometric Analysis and Runoff Estimation of Harangi Command Area Amulya T H M, Rekha A M Assistant Professor, Sri Venkateshwara College Of Engineering, Vidya Nagar, Bangalore, India;
ISSN: -0 PP. 07-8 Morphometric Analysis and Runoff Estimation of Harangi Command Area Amulya T H M, Rekha A M Assistant Professor, Sri Venkateshwara College Of Engineering, Vidya Nagar, Bangalore, India;
Application of Geographical Information System (GIS) tools in watershed analysis
 Application of Geographical Information System (GIS) tools in watershed analysis Paritosh Gupta 1, Damanjit S Minhas 2, Rajendra M Tamhane 1, A K Mookerjee 2 1.ESRI India New Delhi 2. LEA Associates South
Application of Geographical Information System (GIS) tools in watershed analysis Paritosh Gupta 1, Damanjit S Minhas 2, Rajendra M Tamhane 1, A K Mookerjee 2 1.ESRI India New Delhi 2. LEA Associates South
VEGETATION ANALYSIS AND LAND USE LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION OF FOREST IN UTTARA KANNADA DISTRICT INDIA USING REMOTE SENSIGN AND GIS TECHNIQUES
 VEGETATION ANALYSIS AND LAND USE LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION OF FOREST IN UTTARA KANNADA DISTRICT INDIA USING REMOTE SENSIGN AND GIS TECHNIQUES A.G. Koppad a, B S Janagoudar b a Professor and Head (NRM),
VEGETATION ANALYSIS AND LAND USE LAND COVER CLASSIFICATION OF FOREST IN UTTARA KANNADA DISTRICT INDIA USING REMOTE SENSIGN AND GIS TECHNIQUES A.G. Koppad a, B S Janagoudar b a Professor and Head (NRM),
SITE SUITABILITY ANALYSIS FOR URBAN DEVELOPMENT USING GIS BASE MULTICRITERIA EVALUATION TECHNIQUE IN NAVI MUMBAI, MAHARASHTRA, INDIA
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 10, Issue 1, January- February 2019, pp. 55-69, Article ID: IJARET_10_01_006 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtype=ijaret&vtype=10&itype=01
International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET) Volume 10, Issue 1, January- February 2019, pp. 55-69, Article ID: IJARET_10_01_006 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijaret/issues.asp?jtype=ijaret&vtype=10&itype=01
1. Introduction. S.S. Patil 1, Sachidananda 1, U.B. Angadi 2, and D.K. Prabhuraj 3
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2014, Volume 3, Issue 1, pp. 525-531, Article ID Tech-249 ISSN 2320-0243 Research Article Open Access Machine Learning Technique
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2014, Volume 3, Issue 1, pp. 525-531, Article ID Tech-249 ISSN 2320-0243 Research Article Open Access Machine Learning Technique
Application of USLE Model & GIS in Estimation of Soil Erosion for Tandula Reservoir
 Application of USLE Model & GIS in Estimation of Soil Erosion for Tandula Reservoir Ishtiyaq Ahmad 1, Dr. M. K. Verma 2 1 Ph.D. Research Scholar, Dept. of Civil Engg. NIT Raipur (C.G.) - India 2 Prof.
Application of USLE Model & GIS in Estimation of Soil Erosion for Tandula Reservoir Ishtiyaq Ahmad 1, Dr. M. K. Verma 2 1 Ph.D. Research Scholar, Dept. of Civil Engg. NIT Raipur (C.G.) - India 2 Prof.
Identification of Groundwater Recharge Potential Zones for a Watershed Using Remote Sensing and GIS
 Identification of Groundwater Recharge Potential Zones for a Watershed Using Remote Sensing and GIS V.Keshavan 1, S.Ranjith 2, J.Sabarish 3, J.Srinivasan 4 and D.Sivasankar 5 Assistant Professor, Department
Identification of Groundwater Recharge Potential Zones for a Watershed Using Remote Sensing and GIS V.Keshavan 1, S.Ranjith 2, J.Sabarish 3, J.Srinivasan 4 and D.Sivasankar 5 Assistant Professor, Department
Floodplain modeling. Ovidius University of Constanta (P4) Romania & Technological Educational Institute of Serres, Greece
 Floodplain modeling Ovidius University of Constanta (P4) Romania & Technological Educational Institute of Serres, Greece Scientific Staff: Dr Carmen Maftei, Professor, Civil Engineering Dept. Dr Konstantinos
Floodplain modeling Ovidius University of Constanta (P4) Romania & Technological Educational Institute of Serres, Greece Scientific Staff: Dr Carmen Maftei, Professor, Civil Engineering Dept. Dr Konstantinos
Land Suitability Evaluation for Sorghum Based on Boolean and Fuzzy-Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Methods
 Land Suitability Evaluation for Sorghum Based on Boolean and Fuzzy-Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Methods Mukhtar Elaalem Abstract The objective of this paper was to compare two approaches to land suitability
Land Suitability Evaluation for Sorghum Based on Boolean and Fuzzy-Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Methods Mukhtar Elaalem Abstract The objective of this paper was to compare two approaches to land suitability
Report for Area Drainage Studies for 1320 MW (2x660 MW) THERMAL POWER PROJECT AT MIRZAPUR, U.P.
 Report for Area Drainage Studies for 1320 MW (2x660 MW) THERMAL POWER PROJECT AT MIRZAPUR, U.P. 1. Introduction M/s Welspun Energy Uttar Pradesh Ltd. (WEUPL) is putting up 1320 MW (2 x 660 MW) coal fired
Report for Area Drainage Studies for 1320 MW (2x660 MW) THERMAL POWER PROJECT AT MIRZAPUR, U.P. 1. Introduction M/s Welspun Energy Uttar Pradesh Ltd. (WEUPL) is putting up 1320 MW (2 x 660 MW) coal fired
Mapping the Groundwater Potential Zone for Bengaluru Urban District
 Mapping the Groundwater Potential Zone for Bengaluru Urban District Nandishkumar.L, Karthick.M, Arul Prakash.A, Lokpal Bharani Dharaa.D, Revathy S.S, S.Sureshbabu Department of Civil Engineering, Adhiyamaan
Mapping the Groundwater Potential Zone for Bengaluru Urban District Nandishkumar.L, Karthick.M, Arul Prakash.A, Lokpal Bharani Dharaa.D, Revathy S.S, S.Sureshbabu Department of Civil Engineering, Adhiyamaan
Presented at the FIG Working Week 2017, May 29 - June 2, 2017 in Helsinki, Finland. Denny LUMBAN RAJA Adang SAPUTRA Johannes ANHORN
 Presented at the FIG Working Week 2017, May 29 - June 2, 2017 in Helsinki, Finland Denny LUMBAN RAJA Adang SAPUTRA Johannes ANHORN MAIN RESULTS Most of the surroundings of Cipongkor is dominated by very
Presented at the FIG Working Week 2017, May 29 - June 2, 2017 in Helsinki, Finland Denny LUMBAN RAJA Adang SAPUTRA Johannes ANHORN MAIN RESULTS Most of the surroundings of Cipongkor is dominated by very
Remote Sensing and GIS Applications for Hilly Watersheds SUBASHISA DUTTA DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING IIT GUWAHATI
 Remote Sensing and GIS Applications for Hilly Watersheds SUBASHISA DUTTA DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING IIT GUWAHATI Deciding Alternative Land Use Options in a Watershed Using GIS Source: Anita Prakash
Remote Sensing and GIS Applications for Hilly Watersheds SUBASHISA DUTTA DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING IIT GUWAHATI Deciding Alternative Land Use Options in a Watershed Using GIS Source: Anita Prakash
Landslide Hazard Zonation Methods: A Critical Review
 International Journal of Civil Engineering Research. ISSN 2278-3652 Volume 5, Number 3 (2014), pp. 215-220 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcer.htm Landslide Hazard Zonation Methods:
International Journal of Civil Engineering Research. ISSN 2278-3652 Volume 5, Number 3 (2014), pp. 215-220 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijcer.htm Landslide Hazard Zonation Methods:
GIS application in locating suitable sites for solid waste landfills
 GIS application in locating suitable sites for solid waste landfills Jayawickrama, N. T. and Weerasinghe, V. P. A Abstract In Sri Lanka solid wastes are haphazardly dumped in unsuitable locations frequently.
GIS application in locating suitable sites for solid waste landfills Jayawickrama, N. T. and Weerasinghe, V. P. A Abstract In Sri Lanka solid wastes are haphazardly dumped in unsuitable locations frequently.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 3, No 1, 2012
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 3, No 1, 2012 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Geo-Hydrological study
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 3, No 1, 2012 Copyright by the authors - Licensee IPA- Under Creative Commons license 3.0 Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Geo-Hydrological study
INTEGRATION OF GIS AND MULTICRITORIAL HIERARCHICAL ANALYSIS FOR AID IN URBAN PLANNING: CASE STUDY OF KHEMISSET PROVINCE, MOROCCO
 Geography Papers 2017, 63 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.6018/geografia/2017/280211 ISSN: 1989-4627 INTEGRATION OF GIS AND MULTICRITORIAL HIERARCHICAL ANALYSIS FOR AID IN URBAN PLANNING: CASE STUDY OF KHEMISSET
Geography Papers 2017, 63 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.6018/geografia/2017/280211 ISSN: 1989-4627 INTEGRATION OF GIS AND MULTICRITORIAL HIERARCHICAL ANALYSIS FOR AID IN URBAN PLANNING: CASE STUDY OF KHEMISSET
Classification of Erosion Susceptibility
 GEO327G: GIS & GPS Applications in Earth Sciences Classification of Erosion Susceptibility Denali National Park, Alaska Zehao Xue 12 3 2015 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Abstract... 3 2 Introduction... 3 2.1 Universal
GEO327G: GIS & GPS Applications in Earth Sciences Classification of Erosion Susceptibility Denali National Park, Alaska Zehao Xue 12 3 2015 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Abstract... 3 2 Introduction... 3 2.1 Universal
A STUDY ON MORPHOMETRIC PARAMETER OF A WATERSHED FOR SUSTAINABLE WATER CONSERVATION
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 9, September 2017, pp. 271 278, Article ID: IJCIET_08_09_031 Available online at http://http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=8&itype=9
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 9, September 2017, pp. 271 278, Article ID: IJCIET_08_09_031 Available online at http://http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=8&itype=9
IJABR, VOL.7 (3) 2017: ISSN
 SITE SUITABILITY ANALYSIS OF WATER STORAGE STRUCTURES USING REMOTE SENSING & GIS FOR A SMALL WATERSHED OF LORMI BLOCK IN MUNGELI DISTRICT, CHHATTISGARH STATE Love Kumar*, Khalkho, D., Pandey, V. K., Nigam,
SITE SUITABILITY ANALYSIS OF WATER STORAGE STRUCTURES USING REMOTE SENSING & GIS FOR A SMALL WATERSHED OF LORMI BLOCK IN MUNGELI DISTRICT, CHHATTISGARH STATE Love Kumar*, Khalkho, D., Pandey, V. K., Nigam,
Italian experience with the interpretation of FOCUS surface water scenarios from a regulatory point of view
 Italian experience with the interpretation of FOCUS surface water scenarios from a regulatory point of view G. Azimonti, G. Triacchini, D. Auteri, E. Redolfi, International Centre for Pesticides and Health
Italian experience with the interpretation of FOCUS surface water scenarios from a regulatory point of view G. Azimonti, G. Triacchini, D. Auteri, E. Redolfi, International Centre for Pesticides and Health
Landuse/Landcover Change Detection in Umshing- Mawkynroh of East Khasi Hills District, Meghalaya Using Spatial Information Technology
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 1, January 2016 197 Landuse/Landcover Change Detection in Umshing- Mawkynroh of East Khasi Hills District, Meghalaya Using
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 1, January 2016 197 Landuse/Landcover Change Detection in Umshing- Mawkynroh of East Khasi Hills District, Meghalaya Using
Flood Vulnerability Mapping of Lagos Island and Eti-Osa Local Government Areas Using a Multi-Criteria Decision Making Approach
 Nigerian Journal of Environmental Sciences and Technology (NIJEST) www.nijest.com Vol 1, No. 2 July 2017, pp 42-53 Flood Vulnerability Mapping of Lagos Island and Eti-Osa Local Government Areas Using a
Nigerian Journal of Environmental Sciences and Technology (NIJEST) www.nijest.com Vol 1, No. 2 July 2017, pp 42-53 Flood Vulnerability Mapping of Lagos Island and Eti-Osa Local Government Areas Using a
MODELING RUNOFF RESPONSE TO CHANGING LAND COVER IN PENGANGA SUBWATERSHED, MAHARASHTRA
 MODELING RUNOFF RESPONSE TO CHANGING LAND COVER IN PENGANGA SUBWATERSHED, MAHARASHTRA Abira Dutta Roy*, S.Sreekesh** *Research Scholar, **Associate Professor Centre for the Study of Regional Development,
MODELING RUNOFF RESPONSE TO CHANGING LAND COVER IN PENGANGA SUBWATERSHED, MAHARASHTRA Abira Dutta Roy*, S.Sreekesh** *Research Scholar, **Associate Professor Centre for the Study of Regional Development,
Geographical Information System (GIS) Based Land Capability Classification of East Amhara Region, Ethiopia
 Geographical Information System (GIS) Based Land Capability Classification of East Amhara Region, Ethiopia Gizachew Ayalew Amhara Design and Supervision Works Enterprise (ADSWE), Bahir Dar, Ethiopia E-mail:
Geographical Information System (GIS) Based Land Capability Classification of East Amhara Region, Ethiopia Gizachew Ayalew Amhara Design and Supervision Works Enterprise (ADSWE), Bahir Dar, Ethiopia E-mail:
DROUGHT RISK EVALUATION USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS : A CASE STUDY IN LOP BURI PROVINCE
 DROUGHT RISK EVALUATION USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS : A CASE STUDY IN LOP BURI PROVINCE K. Prathumchai, Kiyoshi Honda, Kaew Nualchawee Asian Centre for Research on Remote Sensing STAR Program, Asian Institute
DROUGHT RISK EVALUATION USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS : A CASE STUDY IN LOP BURI PROVINCE K. Prathumchai, Kiyoshi Honda, Kaew Nualchawee Asian Centre for Research on Remote Sensing STAR Program, Asian Institute
ESTIMATING AND MAPPING TORRENTIALITY RISK IN SMALL FORESTED WATERSHEDS
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering Vol. 4 (53) No. 1-2011 ESTIMATING AND MAPPING TORRENTIALITY RISK IN SMALL FORESTED WATERSHEDS
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering Vol. 4 (53) No. 1-2011 ESTIMATING AND MAPPING TORRENTIALITY RISK IN SMALL FORESTED WATERSHEDS
Ground Water Potential Mapping in Chinnar Watershed (Koneri Sub Watershed) Using Remote Sensing & GIS
 Ground Water Potential Mapping in Chinnar Watershed (Koneri Sub Watershed) Using Remote Sensing & GIS T.Velmurugan 1 Dr.D.Srinivasan 2 1 Assistant professor/civil, Roever Engineering College, Perambalur.
Ground Water Potential Mapping in Chinnar Watershed (Koneri Sub Watershed) Using Remote Sensing & GIS T.Velmurugan 1 Dr.D.Srinivasan 2 1 Assistant professor/civil, Roever Engineering College, Perambalur.
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(8):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 314-331 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.042
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 314-331 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.042
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 4, No 2, 2013
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 4, No 2, 2013 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Evaluation of landuse / landcover
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 4, No 2, 2013 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Evaluation of landuse / landcover
Bachelor of Biosystems Technology Faculty of Technology South Eastern University of Sri Lanka
 Bachelor of Biosystems Technology Faculty of Technology South Eastern University of Sri Lanka BSE 11042 Principles of Irrigation Furrow Irrigation Running water in small channels (furrows) Water infiltration
Bachelor of Biosystems Technology Faculty of Technology South Eastern University of Sri Lanka BSE 11042 Principles of Irrigation Furrow Irrigation Running water in small channels (furrows) Water infiltration
Wastelands Analysis and Mapping of Bhiwani District, Haryana
 Wastelands Analysis and Mapping of Bhiwani District, Haryana Virender Sihag Research Scholar, Department of Geography, OPJS University, Churu, Rajasthan ABSTRACT This study aimed at monitoring, mapping,
Wastelands Analysis and Mapping of Bhiwani District, Haryana Virender Sihag Research Scholar, Department of Geography, OPJS University, Churu, Rajasthan ABSTRACT This study aimed at monitoring, mapping,
RESULT. 4.1 Temporal Land use / Land Cover (LULC) inventory and Change Analysis
 Chapter 4 RESULTS RESULT 4.1 Temporal Land use / Land Cover (LULC) inventory and Change Analysis The LULC maps of each study period were prepared by digital supervised classification of Landsat TM satellite
Chapter 4 RESULTS RESULT 4.1 Temporal Land use / Land Cover (LULC) inventory and Change Analysis The LULC maps of each study period were prepared by digital supervised classification of Landsat TM satellite
CHANGES IN VIJAYAWADA CITY BY REMOTE SENSING AND GIS
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 5, May 2017, pp.217 223, Article ID: IJCIET_08_05_025 Available online at http://www.ia aeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtyp
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 8, Issue 5, May 2017, pp.217 223, Article ID: IJCIET_08_05_025 Available online at http://www.ia aeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtyp
Assessing Vulnerability to Soil Erosion of a Watershed of Tons River Basin in Madhya Pradesh using Remote Sensing and GIS
 International Journal of Environmental Research and Development. ISSN 2249-3131 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 153-164 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijerd.htm Assessing Vulnerability
International Journal of Environmental Research and Development. ISSN 2249-3131 Volume 4, Number 2 (2014), pp. 153-164 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijerd.htm Assessing Vulnerability
A GIS Based Study on Land Evaluation in Rasipuram Block, Namakkal District, Tamil Nadu
 A GIS Based Study on Land Evaluation in Rasipuram Block, Namakkal District, Tamil Nadu V. Emayavaramban 1 Associate Professor, Department of Geography, Madurai Kamaraj University, Madurai, Tamil Nadu,
A GIS Based Study on Land Evaluation in Rasipuram Block, Namakkal District, Tamil Nadu V. Emayavaramban 1 Associate Professor, Department of Geography, Madurai Kamaraj University, Madurai, Tamil Nadu,
Urban Hydrology - A Case Study On Water Supply And Sewage Network For Madurai Region, Using Remote Sensing & GIS Techniques
 RESEARCH INVENTY: International Journal of Engineering and Science ISBN: 2319-6483, ISSN: 2278-4721, Vol. 1, Issue 8 (November 2012), PP 07-12 www.researchinventy.com Urban Hydrology - A Case Study On
RESEARCH INVENTY: International Journal of Engineering and Science ISBN: 2319-6483, ISSN: 2278-4721, Vol. 1, Issue 8 (November 2012), PP 07-12 www.researchinventy.com Urban Hydrology - A Case Study On
Land Use and Land Cover Mapping and Change Detection in Jind District of Haryana Using Multi-Temporal Satellite Data
 Land Use and Land Cover Mapping and Change Detection in Jind District of Haryana Using Multi-Temporal Satellite Data Ravindra Prawasi, M.P. Sharma, T. P. Babu, Om Pal, Saroj, Kirti Yadav, R.S.Hooda Abstract
Land Use and Land Cover Mapping and Change Detection in Jind District of Haryana Using Multi-Temporal Satellite Data Ravindra Prawasi, M.P. Sharma, T. P. Babu, Om Pal, Saroj, Kirti Yadav, R.S.Hooda Abstract
Change Detection in Landuse and landcover using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques
 Change Detection in Landuse and landcover using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques VEMU SREENIVASULU* and PINNAMANENI UDAYA BHASKAR Department of Civil Engineering Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University:
Change Detection in Landuse and landcover using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques VEMU SREENIVASULU* and PINNAMANENI UDAYA BHASKAR Department of Civil Engineering Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University:
GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH
 GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH Prof.P.Jagadeesara Rao Department of Geo-Engineering and Centre for Remote Sensing, College
GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH Prof.P.Jagadeesara Rao Department of Geo-Engineering and Centre for Remote Sensing, College
Submitted to: Central Coalfields Limited Ranchi, Jharkhand. Ashoka & Piparwar OCPs, CCL
 Land Restoration / Reclamation Monitoring of more than 5 million cu. m. (Coal + OB) Capacity Open Cast Coal Mines of Central Coalfields Limited Based on Satellite Data for the Year 2013 Ashoka & Piparwar
Land Restoration / Reclamation Monitoring of more than 5 million cu. m. (Coal + OB) Capacity Open Cast Coal Mines of Central Coalfields Limited Based on Satellite Data for the Year 2013 Ashoka & Piparwar
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research e-issn No.: , Date: April, 2016
 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 28-30 April, 2016 Landslide Hazard Management Maps for Settlements in Yelwandi River Basin,
International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com e-issn No.:2349-9745, Date: 28-30 April, 2016 Landslide Hazard Management Maps for Settlements in Yelwandi River Basin,
Need of Proper Development in Hilly Urban Areas to Avoid
 Need of Proper Development in Hilly Urban Areas to Avoid Landslide Hazard Dr. Arvind Phukan, P.E. Cosultant/Former Professor of Civil Engineering University of Alaska, Anchorage, USA RI District Governor
Need of Proper Development in Hilly Urban Areas to Avoid Landslide Hazard Dr. Arvind Phukan, P.E. Cosultant/Former Professor of Civil Engineering University of Alaska, Anchorage, USA RI District Governor
Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai
 Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai K. Ilayaraja Department of Civil Engineering BIST, Bharath University Selaiyur, Chennai 73 ABSTRACT The synoptic picture
Landuse and Landcover change analysis in Selaiyur village, Tambaram taluk, Chennai K. Ilayaraja Department of Civil Engineering BIST, Bharath University Selaiyur, Chennai 73 ABSTRACT The synoptic picture
Summary Description Municipality of Anchorage. Anchorage Coastal Resource Atlas Project
 Summary Description Municipality of Anchorage Anchorage Coastal Resource Atlas Project By: Thede Tobish, MOA Planner; and Charlie Barnwell, MOA GIS Manager Introduction Local governments often struggle
Summary Description Municipality of Anchorage Anchorage Coastal Resource Atlas Project By: Thede Tobish, MOA Planner; and Charlie Barnwell, MOA GIS Manager Introduction Local governments often struggle
Flood hazard mapping in Urban Council limit, Vavuniya District, Sri Lanka- A GIS approach
 International Research Journal of Environment Sciences E-ISSN 2319 1414 Flood hazard mapping in Urban Council limit, Vavuniya District, Sri Lanka- A GIS approach Abstract M.S.R. Akther* and G. Tharani
International Research Journal of Environment Sciences E-ISSN 2319 1414 Flood hazard mapping in Urban Council limit, Vavuniya District, Sri Lanka- A GIS approach Abstract M.S.R. Akther* and G. Tharani
APPLICATION OF REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNIQUES FOR GROUNDWATER RECHARGE SITE SELECTION IN HARD ROCK AREAS A CASE STUDY FROM SOUTH INDIA
 APPLICATION OF REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNIQUES FOR GROUNDWATER RECHARGE SITE SELECTION IN HARD ROCK AREAS A CASE STUDY FROM SOUTH INDIA M.S. Shirahatti, 1 M.V. Ranghswami, 2 R. Sivasamy 2, S. Santana
APPLICATION OF REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNIQUES FOR GROUNDWATER RECHARGE SITE SELECTION IN HARD ROCK AREAS A CASE STUDY FROM SOUTH INDIA M.S. Shirahatti, 1 M.V. Ranghswami, 2 R. Sivasamy 2, S. Santana
