Summer Assignment & Class Information
|
|
|
- Janel Burke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Summer Assignment & Class Infrmatin Dear AP Chemistry Student and Parent: I am very excited t have yu in class next year! As yu prbably already knw, AP Chemistry is a very challenging curse with an equally challenging AP test. The material is detailed and we have several tpics t cver. T aid in getting the mst ut f yur AP Chemistry curse, yu will need t refresh yur memry n infrmatin that was taught in PAP Chemistry. This will allw us t review the basics f chemistry within the first week f class, and then mve n t expand yur knwledge base. Yu are required t cmplete the summer assignment belw and bring it and any questins yu may have t class the first day. We will reinfrce this review with sme lab activities during the beginning f the semester. Yu shuld anticipate test within the first week f class. Yu need t master the frmulas, charges, and names f cmmn ins. Yu will be asked t cmplete a few tasks invlving naming ins and cmpunds, determining frmulas fr cmpunds, use the rules fr slubility, xidatin reductin, and transitin metal charges. I have included several resurces in this packet. First, there is a list f the ins that yu must knw. This list als has sme suggestins fr making the prcess f memrizatin easier. Fr instance, many f yu will remember that mst f the mnatmic ins have charges that are directly related t their placement n the peridic table. There are naming patterns that greatly simplify the learning f the plyatmic ins as well. Als included is a cpy f the peridic table used in AP Chemistry. Ntice that this is nt the table used in first year chemistry. The AP table is the same that the Cllege Bard allws yu t use n the AP Chemistry test. Ntice that it has the symbls f the elements but nt the written names. Yu need t take that fact int cnsideratin when studying! Dubtless, there will be sme students wh will prcrastinate and try t d all f this studying just befre the start f schl. Thse students may even cram well enugh t d well n the initial test. Hwever, they will quickly frget the ins, and struggle every time that these frmulas are used in lecture, hmewrk, quizzes, tests and labs. All research n human memry shws us that frequent, shrt perids f study, spread ver lng perids f time will prduce much greater retentin than lng perids f study f a shrt perid f time. I culd wait and thrw these at yu n the first day f schl, but I dn t think that wuld be fair t yu. Use every mdality pssible as yu try t learn these speak them, write them, visualize them. I lk frward t seeing yu all at the beginning f the next schl year. If yu need t cntact me during the summer, yu can me and I will get back t yu. Yu may check my ggle classrm fr any updates and als t access review material that will give yu an idea whether yu have adequately mastered the summer assignment. ***Befre summer begins, please cme by my rm (S-213) with a flash drive s that I can give yu an electrnic cpy f yur textbk. Als, sign up fr my ggle classrm. Yur user name is yur DISD (DISDstudentid@apps.dickinsnisd.rg) and yur passwrd is DisdMMDDYYYY(yur birthday). The classrm cde is cjg8k1r***. AP Chemistry Test Mnday, May 7, 2017 Sincerely, Mrs. Staci Wagner Swagner1@dickinsnisd.rg
2 Recmmended supplementary study materials: AP Chemistry Princetn/Barrn s Review This bk is excellent when preparing fr the actual AP Chem exam. It gives prvides many sample questins and practice questins that will help yu prepare fr the AP exam. 5 Steps t a 5 is a mre basic review that yu will find useful thrughut the year. (I will have a few cpies f each f these available fr checkut thrughut the schl year) Study tls - please review these dcuments and begin t memrize! AP Chemistry is a challenging curse. While it is nt all abut memrizatin, having these items memrized is essential fr success in learning the cncepts cvered in the curse. Knw element symbls and names fr elements 1-38 and Ag, Cd, I, Xe, Cs, Ba, W, Hg, Pb, Sn, Rn, Fr, U, Th, Pu, and Am written crrectly. Students shuld be able t lcate these elements quickly n the peridic table prvided n the exam. This table will nt have the element names written n it. Knw the 6 strng acids: ( CBSPIN ) hydrchlric (HCl) hydrbrmic (HBr) Sulfuric (H2SO4) Perchlric (HClO4) hydrinic (HI) Nitric (HNO3) Knw strng bases Grup 1 metal hydrxides (NaOH, KOH, etc) Grup 2 metal hydrxides (Ba(OH)2, Sr(OH)2, Ca(OH)2 these are nly slightly sluble, s strng base thers (Mg, Be, and Ra) are insluble, s weak base)
3
4 Examples f sme Mnemnics fr Chemistry Electrchemistry OIL RIG (Oxidatin is Lss f electrns, Reductin is Gain f electrns) RC cola (Reductin at the Cathde, Oxidatin at the Ande) Diatmic Elements BrINClHOF (say Brinkelhf) Help Our Needy Class Finds Brains Immediately Plyatmic Anins: Nick the Camel ate a Clam Supper in Phenix -1 Nick- N with 3 cnsnants and 1 vwel therefre NO 3 (nitrate) -2 Camel C with 3 cnsnants and 2 vwels therefre CO 3 (carbnate) -1 Clam Cl with 3 cnsnants and 1 vwel therefre ClO 3 (chlrate) -2 Supper S with 4 cnsnants and 2 vwels therefre SO 4 (sulfate) -3 Phenix - P with 4 cnsnants and 3 vwels therefre PO 4 (phsphate) SI Prefixes The Great Mnarch King Henry Died By Drinking Chclate Milk Made Near Pland The Tera Drinking deci Great Giga Chclate centi Mnarch Mega Milk milli King Kil Made micr - µ Henry Hect Near nan Died Deca Pland - pic By base unit m, l, g, cal, J Slubility Rules: Learn the fllwing slubility rules: Salts cntaining the fllwing ins are nrmally sluble: All salts f Grup IA (Li +, Na +, etc.) and the ammnium in (NH4 + ) are sluble. All salts cntaining nitrate (NO3 1- ), acetate (CH3COO 1- ) and perchlates (ClO4 1- ) are sluble All chlrides (Cl 1- ), brmides (Br 1- ), and idides (I 1- ) are sluble except thse f Cu +, Ag +, Pb 2+, and Hg2 2+. All salts cntaining (SO4 2-, are sluble except thse f Pb 2+, Ca 2+, Sr 2+, and Ba 2+ ). Salts cntaining the fllwing ins are nrmally insluble: Mst carbnates (CO3 2- ) and phsphates (PO4 3- ) are insluble except thse f Grup IA and the ammnium in. Mst sulfides (S 2- ) are insluble except thse f Grup IA and IIA and the ammnium in. Mst hydrxides (OH 1- ) are insluble except thse f Grup IA, calcium, and barium. Mst xides (O 2- ) are insluble except fr thse f Grup IA and IIA which react with water t frm the crrespnding hydrxides
5 Tips fr Learning the Ins Frm the Table These are ins can be rganized int tw grups. 1. Their place n the table suggests the charge n the in, since the neutral atm gains r lses a predictable number f electrns in rder t btain a nble gas cnfiguratin. This was a fcus in first year chemistry, s if yu are unsure what this means, get help BEFORE the start f the year. a. All Grup 1 Elements (alkali metals) lse ne electrn t frm an in with a 1+ charge b. All Grup 2 Elements (alkaline earth metals) lse tw electrns t frm an in with a 2+ charge c. Grup 13 metals like aluminum lse three electrns t frm an in with a 3+ charge d. All Grup 17 Elements (halgens) gain ne electrn t frm an in with a 1- charge e. All Grup 16 nnmetals gain tw electrns t frm an in with a 2- charge f. All Grup 15 nnmetals gain three electrns t frm an in with a 3- charge Ntice that catins keep their name (sdium in, calcium in) while anins get an -ide ending (chlride in, xide in). 2. Metals that can frm mre than ne in will have their psitive charge dented by a rman numeral in parenthesis immediately next t the name f the Plyatmic Anins: Mst f the wrk n memrizatin ccurs with these ins, but there are a number f patterns that can greatly reduce the amunt f memrizing that ne must d. 1. ate anins have ne mre xygen then the ite in, but the same charge. If yu memrize the ate ins, then yu shuld be able t derive the frmula fr the ite in and vice-versa. a. sulfate is SO , s sulfite has the same charge but ne less xygen (SO 3 ) b. nitrate is NO - 3, s nitrite has the same charge but ne less xygen (NO 2-) 2. If yu knw that a sulfate in is SO 2-4 then t get the frmula fr hydrgen sulfate in, yu add a hydrgen in t the frnt f the frmula. Since a hydrgen in has a 1+ charge, the net charge n the new in is less negative by ne. a. Example: PO > HPO 4 --> H 2PO -1 4 phsphate hydrgen phsphate dihydrgen phsphate 3. Learn the hypchlrite --> chlrite --> chlrate --> perchlrate series, and yu als knw the series cntaining idite/idate as well as brmite/brmate. a. The relatinship between the ite and ate in is predictable, as always. Learn ne and yu knw the ther. b. The prefix hyp means under r t little (think hypdermic, hypthermic r hypglycemia ) i. Hypchlrite is under chlrite, meaning it has ne less xygen c. The prefix hyper means abve r t much (think hyperkinetic ) i. the prefix per is derived frm hyper s perchlrate (hyperchlrate) has ne mre xygen than chlrate. d. Ntice hw this sequence increases in xygen while retaining the same charge: ClO > ClO 2 --> ClO 3 --> ClO 4 hypchlrite chlrite chlrate perchlrate
6 Nmenclature Review Frming binary inic cmpunds A. In a binary inic cmpund the ttal psitive charges must equal the ttal negative charges. The best way t write crrect frmula units fr inic cmpunds is t use the Criss-crss methd. B. Sample Prblem: What inic cmpund wuld frm when calcium ins cmbine with brmide in? Steps t the Criss-crss Methd: 1. Write the ins with their charges, catins are always first. Ca 2+ Br 1-2. Crss ver the charges by using the abslute value f each in s charge as the subscript fr the ther in. Ca 1Br 2 3. Check t make sure the subscripts are in the lwest whle number rati pssible. Then write the frmula. CaBr 2 Naming binary inic cmpunds A. Cmbine the names f the catin and the anin, and change the secnd half f the anin t -ide. B. Example: BaBr 2 is named barium brmide Naming binary inic cmpunds that cntain plyatmic ins. A. The plyatmic ins n yur cmmn in list shuld be memrized. B. The mst cmmn xyanins (plyatmic ins that cntain xygen) end in ate. Oxyanins with ne less xygen end in ite. Fr example: 1- NO 3 is nitrate SO 2-4 is sulfate NO 1-2 is nitrite SO 2-3 is sulfite C. Anins with ne less xygen than the ite in are given the prefix hyp-. D. Anins with ne mre xygen than the ate in are given the prefix per-. ClO 1- is hypchlrite ClO 1-3 is chlrate ClO 1-2 is chlrite ClO 1-4 is perchlrate E. Naming cmpunds with plyatmics is the same as naming ther cmpunds, just name the catin and then the anin. If there is a transitin metal invlved, be sure t check the charges t identify which in (+1, +2, +3, +4 ) it may be s that yu can put the crrect Rman numeral in the name.
7 Sme preliminary ntes frm Chapters 1-3 Chapter 1 Intrductin: Matter and Measurement A. Classificatin f Matter 1. States f Matter a. Gas(vapr) i. Has n fixed vlume r shape ii. Takes the shape f its cntainer iii. Can be cmpressed r expanded iv. Mlecules are far apart and mving at high speeds b. Liquid i. Definite vlume, cannt be cmpressed ii. Takes the shape f its cntainer iii. Mlecules are much clser than in a gas but still mve rapidly (they can slide past each ther) c. Slid i. Definite shape and vlume, cannt be cmpressed ii. Mlecules are held tightly tgether, typically in definite arrangements 2. Pure substances and mixtures a. Pure substances matter that has a fixed cmpsitin and distinct prperties i. Tw types 1. Elements substances that cannt be decmpsed int simpler substances 2. Cmpunds cmpsed f tw r mre elements chemically bnded tgether a. Law f Cnstant Cmpsitin (Jseph Prust) the makeup f cmpunds is always the same b. Mixtures cmbinatin f tw r mre substances in which each substance retains its wn chemical identity and prperties i. Prperties can vary 1. Example adding sugar t cffee is a mixture, yu can make it very sweet, add a little, r nne at all. ii. Tw types 1. Hetergeneus different cmpsitin thrughut a. Rcks, sand, wd, chclate chip ckies 2. Hmgeneus (aka slutins) unifrm cmpsitin thrughut a. Air(gaseus slutin), gasline(liquid slutin), brass(slid slutin) c. Separatin f Mixtures i. Filtratin separating a slid cmpnent frm a liquid cmpnent using a funnel, filter paper, and gravity ii. Distillatin separating liquid cmpnents utilizing different biling pints iii. Chrmatgraphy separating substances by hw they adhere t surfaces ( used frequently fr ink) 3. Prperties f Matter a. Physical prperties descriptin f what smething lks like i. Clr, dr, density, melting pint, biling pint, hardness b. Chemical prperties hw a chemical reacts with ther chemicals i. Flammability, reactivity with ther chemicals 4. Changes in Matter a. Physical changes physical appearance is changed i. Ripping paper, melting wax, ALL CHANGES OF STATE (BOILING, EVAPORATING) b. Chemical changes (reactins) chemically transfrmed int a new substance i. Sdium metal reacts with chlrine gas t frm salt
8 B. Units f Measurement 1. Metric System / Significant Figures / Dimensinal Analysis a. yu shuld ALREADY knw this Chapter 2 Atms, Mlecules, Ins A. The Atmic Thery f Matter 1. Histry f the Atm a. Demcritus first persn t speculate that matter was mass f atms. Greek philspher i. Plat and Aristtle refuted this idea, atmic thery faded fr many centuries b. Jhn Daltn came up with first atmic thery, English schl teacher i. Each element is cmpsed f extremely small particles called atms ii. All atms f a given element are identical; the atms f different elements are different and have different prperties (including different masses) iii. Atms f an element are nt changes int different types f atms by chemical reactins; atms are neither created nr destryed in chemical reactins iv. Cmpunds are frmed when atms f mre than ne element cmbine; a given cmpund always has the same relative number and kind f atm. Daltn thught that atms culd nt be brken dwn any further, this was expressed in the atmic mdel Billiard Ball Mdel Laws frm the time perid a. Law f Cnstant Cmpsitin b. Law f Cnservatin f Mass (LeChatelier) matter and energy cannt be created r destryed c. Law f Multiple Prprtins if elements cmbine t frm mre than ne cmpund they must be different by whle numbers. i. Carbn mnxide, CO, carbn dixide, CO2 c. Cathde Rays a high vltage electricity passed thrugh partially evacuated tubes prduced radiatin and mass glass fluresce, called cathde rays because they riginated frm the cathde i. Rays were deflected by electric and magnetic fields, suggesting that the rays were charged ii. J.J. Thmsn bserved that the rays were the same n matter what type f material was used, cncluded that the rays were actually particles with mass, these particles were called electr 1. Able t calculate the charge t mass ratin f an electrn, 1.76 x 10 8 Culmbs/gram 2. Came up with secnd atmic mdel Plum Pudding Mdel d. Rbert Millikan perfrmed the il drp experiment and determined the charge f an electrn (1.60 x ) and then determined the mass f an electrn (9.11 x g) e. Henri Becquerel studied an re f Uranium called pitchblende and discvered the spntaneus emissin f radiatin called radiactivity i. Marie Curie and her husband, Pierre als studied this f. Ernest Rutherfrd studied radiatin and discvered three types f radiatin: alpha, beta, and gamma i. Utilizing alpha particles, Rutherfrd perfrmed the Gld Fil Experiment and determined that the atm had a nucleus ii. Als discvered prtns g. James Chadwick discvered neutrns 2. Mdern View f Atmic Structure a. Atms are made f prtns, neutrns, and electrns b. Electrnic charge is measured in Culmbs (C) i. Electrns have a charge f x C ii. Prtns have a charge f x C iii. Fr simplicity we change this t +1 and -1, but yu shuld still knw what the value is iv. Neutrns have n charge
9 c. Atms are typically neutral, which means they have the same number f prtns and electrns d. Prtns and neutrns are in the nucleus, electrns circle arund e. Vast majrity f an atm s vlume is the space where the electrns are fund f. Istpes atms f a given element that differ in the number f neutrns g. Prtns all atms f an element have the same number f prtns in the nucleus, aka atmic number h. Mass number number f prtns + number f neutrns 3. Peridic Table a. Yu shuld knw the general layut f the peridic table (grups, rws, where the metals, nnmetals, and metallids are) 4. Writing chemical frmulas (reviewed earlier in packet) Chapter 3 Stichimetry: Calculatins with Chemical Frmulas and Equatins 1. All chemical equatins need t be written crrectly and balanced apprpriately (kind f redundant I knw) 2. We will g ver all f the types f chemical reactivity but belw are sme fr review a. Mst cmmn invlve xygen as a reactant b. Often invlve hydrcarbns (cmpunds that cntain hydrgen and carbn) 3. Atmic and Mlecular Weight a. Atmic Mass Scale is based ff f Carbn 12, mass f carbn 12 = 12 amu b. Amu = atmic mass unit, 1g = x amu 4. Average Atmic Masses a. the masses listed n the peridic table are weighted averages based n the abundance in nature b. see example prblems in bk 5. Percent Cmpsitin frm Frmulas a. part/whle x 100% b. used t determine hw much f a cmpund is a particular kind f element 6. The Mle a. used t cnvert between the micrscpic and the macrscpic b. Avgadr s number = 6.02 x Prblems wrk thrugh chapter prblems if yu need extra help
10 AP CHEMISTRY SUMMER RECOMMENDED ASSIGNMENT Shw ALL wrk!!!! Use dimensinal analysis. Reprt answers using the crrect number f significant figures. Due secnd week f classes! The answers are given in parenthesis at the end f each prblem. Gd Luck and Have a Great Summer! 1. When Munt St. Helens erupted in 1980, analysts cllected ash samples t determine the amunt f txic heavy metals that were intrduced t the envirnment. The ash was determined t cntain % mercury. Hw many mles f mercury are cntained in 500.0g f ash frm the vlcan? (4.5*10-5 ml Hg) 2. One thyrid hrmne is thyrxine, C 15H 11I 4NO 4. Hw many mg f thyrxine culd be prduced frm 210 mg f idine atms, the amunt that a typical adult cnsumes per day? Hw many mlecules is this? (320mg; 2.5*10 20 mlecules) 3. A sample thught t be caffeine, the stimulant fund in cffee, tea, and cla, gave the fllwing elemental analysis: 49.5%C, 5.2%H, 28.8%N and 16.5%O. Is it pssible that this substance is caffeine which is C 8H 10N 4O 2? (Yes!) 4. Analysis f ibuprfen shws that is cntains 75.7% carbn, 8.8% hydrgen, and 15.5% xygen. The mass spectrum f ibuprfen shws that its mlar mass is apprximately 210g/ml. What is the chemical frmula fr ibuprfen? (C 13H 18O 2) 5. Butyric acid (a hydrcarbn cntaining C, H, and O), a cmpnent f rancid butter, has a vile stench. Burning 0.440g f butyric acid in excess xygen yields g f CO 2 and g f H 2O. The mlar mass f butyric acid is 88 g/ml. What are its empirical and mlecular frmula? (EF =C 2H 4O; MF = C 4H 8O 2) 6. An re f cpper is 80% cpper (II) xide. Hw many kg f cpper culd be recvered frm 846 kg f re?(5.4 x 10 2 kg Cu) 7. A slutin f sdium hydrxide is made by disslving 56.0 g f 92.0% pure sdium hydrxide int ml f water. What is the mlarity f the sdium hydrxide slutin?(1.71m NaOH) Density: 8. A slid blck f substance is 74.0 cm by 55.0 cm by 29.0 cm and it weighs 625 kg. Assuming that it did nt chemically react with water nr disslve in it, wuld it flat in water? (N, it wuld sink!) 9. A certain liquid has a density f g/ml. Hw many LITERS wuld weigh 1.00 kg? (1.17 L) Dimensinal Analysis: 10. The recrd lng jump is inches. Cnvert this t meters. There are 2.54 cm in an inch. (8.877m) 11. Hw many milligrams are there in a 5.00 grain aspirin tablet? 1 grain = unces. There are 454 grams/pund and 16.0 unces/pund. (325mg) 12. In 1980, the US prduces 18.4 billin punds (1.84 X lbs) f phsphric acid t be used in the manufacture f fertilizer. The average cst f the acid is $318/tn. (1 tn = 2000 lbs) What was the ttal value f the phsphric acid prduced? ($2.93 billin) 13. Light travels at a speed f 3.00 X cm/sec. What is the speed f light in km/hr? (1.08*10 9 km/hr) Stichimetry: 14. In the decmpsitin f sdium hydrxide, hw many mles f sdium hydrxide are needed t prduce 30.0 mles f water? (60.0 mles NaOH) 15. In the single replacement reactin f lithium and magnesium nitrate, what mass f lithium cmbines with 75.0 grams f magnesium nitrate? (7.02 g Li) 16. Hw many grams f lead (II) nitrate are needed t prduce 60.0 grams f ptassium nitrate in the duble replacement reactin f ptassium idide and lead (II) nitrate. (98.2 g lead (II) nitrate) 17. In the synthesis reactin f zinc(ii) and sulfur, what mass f zinc (II) sulfide is prduced frm grams f sulfur? (304.5 g ZnS) 18. A synthesis reactin f calcium and xygen was cmpleted in a lab and grams f calcium xide were prduced frm grams f xygen. What is the percent yield? (89.35%)
11 19. If yu begin with 1250 g f N 2 and 225 f H 2 in the reactin that frms ammnia gas (NH 3 ), hw much ammnia will be frmed? What is the limiting reagent? Hw much f the reagent is left when the maximum amunt f ammnia is frmed? (1265g NH 3; LR is H 2; 208.2g N 2 left) Cmpsitin 1. A gram piece f magnesium metal is heated and reacts with xygen. The resulting xide weighed grams. Determine the percent cmpsitin f each element in the cmpund. (60.3% Mg ;39.7% O) g f a mixture f sdium bicarbnate that is 77% sdium bicarbnate is decmpsed. Hw many liters f carbn dixide gas will be prvided frm the decmpsitin at 25ºC and mmhg? (4.96L) 3. Hw many mles f carbn atm are prduced frm the cmbustin f 82.0 ml f ethanl? The density f ethanl is g/ml. (2.82 ml) g f calcium carbnate is decmpsed at STP, what is the vlume f carbn dixide that will be prduced frm the decmpsitin? (1.85L ) 5. A cmpund has the empirical frmula f CH 3Br and a vapr density f 6.00 g/l, at 375 K and atm. Using these data, determine the fllwing: a) The mlar mass f the cmpund. (187.9 g/ml) b) The mlecular frmula f the cmpund. (C 2H 6Br 2) 6. One carrt may cntain 0.75 mg f vitamin A (C 20H 30O). Hw many mles f vitamin A is this? Hw many mlecules f vitamin A? Hw many atms f hydrgen? What mass f hydrgen is this? (2.6*10-6 ml; 1.6*10 18 mle c; 4.73*10 19 atms H; 7.86*10-5 g H) mL f M ptassium phsphate is mixed with 300.mL f M calcium chlride. Determine the mass f the precipitate frmed and the cncentratin f all ins remaining in slutin. (6.20g ppt; 0.240M K + ; M Ca 2+ ; 0.300M Cl - ) Naming Chemical Cmpunds 1) NaBr 2) Ca(C 2H 3O 2) 2 3) P 2O 5 4) Ti(SO 4) 2 5) FePO 4 6) K 3N 7) SO 2 8) CuOH 9) Zn(NO 2) 2 10) V 2S 3 Write the frmulas fr the fllwing chemical cmpunds: 11) silicn dixide 12) nickel (III) sulfide 13) manganese (II) phsphate 14) silver acetate 15) dibrn tetrabrmide 16) magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 17) ptassium carbnate 18) ammnium xide 19) tin (IV) selenide 20) carbn tetrachlride Predicting Reactin Prducts: Balance the equatins and predict the prducts and states f matter (assume reactins are taking place at STP) fr the fllwing reactins. If n reactin ccurs write NR. 1) Na + FeBr 3 2) NaOH + H 2SO 4 3) C 2H 4O 2 + O 2 4) NH 3 + H 2O 5) PbSO 4 + AgNO 3 6) PBr 3 7) HBr + Fe 8) KMnO 4 + ZnCl 2 9) MnO 2 + Sn(OH) 4 10) O 2 + C 5H 12O 2 11) H 2O 2 12) PtCl 4 + Cl 2
A Chemical Reaction occurs when the of a substance changes.
 Perid: Unit 8 Chemical Reactin- Guided Ntes Chemical Reactins A Chemical Reactin ccurs when the f a substance changes. Chemical Reactin: ne r mre substances are changed int ne r mre new substances by the
Perid: Unit 8 Chemical Reactin- Guided Ntes Chemical Reactins A Chemical Reactin ccurs when the f a substance changes. Chemical Reactin: ne r mre substances are changed int ne r mre new substances by the
Midterm Review Notes - Unit 1 Intro
 Midterm Review Ntes - Unit 1 Intr 3 States f Matter Slid definite shape, definite vlume, very little mlecular mvement Liquid definite vlume, takes shape f cntainer, mlecules mve faster Gas des nt have
Midterm Review Ntes - Unit 1 Intr 3 States f Matter Slid definite shape, definite vlume, very little mlecular mvement Liquid definite vlume, takes shape f cntainer, mlecules mve faster Gas des nt have
4 Fe + 3 O 2 2 Fe 2 O 3
 UNIT 7: STOICHIOMETRY NOTES (chapter 9) INTRO TO STOICHIOMETRY Reactin Stichimetry: Stichimetry is simply a way t shw f smething this is. Relatinship between a given and an unknwn: GIVEN UNKNOWN Type 1
UNIT 7: STOICHIOMETRY NOTES (chapter 9) INTRO TO STOICHIOMETRY Reactin Stichimetry: Stichimetry is simply a way t shw f smething this is. Relatinship between a given and an unknwn: GIVEN UNKNOWN Type 1
Unit 9: The Mole- Guided Notes What is a Mole?
 Unit 9: The Mle- Guided Ntes What is a Mle? A mle is a name fr a specific f things Similar t a r a One mle is equal t 602 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 That s 602 with zers A mle is NOT an abbreviatin
Unit 9: The Mle- Guided Ntes What is a Mle? A mle is a name fr a specific f things Similar t a r a One mle is equal t 602 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 That s 602 with zers A mle is NOT an abbreviatin
Chapter 9 Chemical Reactions NOTES
 Chapter 9 Chemical Reactins NOTES Chemical Reactins Chemical reactin: Chemical change 4 Indicatrs f Chemical Change: (1) (2) (3) (4) Cnsist f reactants (starting materials) and prducts (substances frmed)
Chapter 9 Chemical Reactins NOTES Chemical Reactins Chemical reactin: Chemical change 4 Indicatrs f Chemical Change: (1) (2) (3) (4) Cnsist f reactants (starting materials) and prducts (substances frmed)
Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry. Topic 1: Principles of chemistry. Chemical formulae, equations and calculations. Notes.
 Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Tpic 1: Principles f chemistry Chemical frmulae, equatins and calculatins Ntes 1.25 write wrd equatins and balanced chemical equatins (including state symbls): fr reactins studied
Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Tpic 1: Principles f chemistry Chemical frmulae, equatins and calculatins Ntes 1.25 write wrd equatins and balanced chemical equatins (including state symbls): fr reactins studied
SCIENCE 10: CHEMISTRY,
 , 1 Atmic Thery and Bnding The Nucleus - The particles that make up an atm are called subatmic particles - The three subatmic particles are prtns, neutrns and electrns. - Prtns, which have a +1 (psitive)
, 1 Atmic Thery and Bnding The Nucleus - The particles that make up an atm are called subatmic particles - The three subatmic particles are prtns, neutrns and electrns. - Prtns, which have a +1 (psitive)
Unit 11 Solutions- Guided Notes. What are alloys? What is the difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures?
 Name: Perid: Unit 11 Slutins- Guided Ntes Mixtures: What is a mixture and give examples? What is a pure substance? What are allys? What is the difference between hetergeneus and hmgeneus mixtures? Slutins:
Name: Perid: Unit 11 Slutins- Guided Ntes Mixtures: What is a mixture and give examples? What is a pure substance? What are allys? What is the difference between hetergeneus and hmgeneus mixtures? Slutins:
Name: Period: Date: ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY
 Name: Perid: Date: ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant
Name: Perid: Date: ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant
Chem 111 Summer 2013 Key III Whelan
 Chem 111 Summer 2013 Key III Whelan Questin 1 6 Pints Classify each f the fllwing mlecules as plar r nnplar? a) NO + : c) CH 2 Cl 2 : b) XeF 4 : Questin 2 The hypthetical mlecule PY 3 Z 2 has the general
Chem 111 Summer 2013 Key III Whelan Questin 1 6 Pints Classify each f the fllwing mlecules as plar r nnplar? a) NO + : c) CH 2 Cl 2 : b) XeF 4 : Questin 2 The hypthetical mlecule PY 3 Z 2 has the general
/ / Chemistry. Chapter 1 Chemical Foundations
 Name Chapter 1 Chemical Fundatins Advanced Chemistry / / Metric Cnversins All measurements in chemistry are made using the metric system. In using the metric system yu must be able t cnvert between ne
Name Chapter 1 Chemical Fundatins Advanced Chemistry / / Metric Cnversins All measurements in chemistry are made using the metric system. In using the metric system yu must be able t cnvert between ne
Name: Date: Class: a. How many barium ions are there per formula unit (compound)? b. How many nitride ions are there per formula unit (compound)?
 NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 15 Part 2: Binary II Inic Bnding, Plyatmic Ins Bx 1: 1. Ba 3N 2 is the frmula fr. (name) a. Hw many barium ins are there per frmula unit (cmpund)? b. Hw many nitride ins
NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 15 Part 2: Binary II Inic Bnding, Plyatmic Ins Bx 1: 1. Ba 3N 2 is the frmula fr. (name) a. Hw many barium ins are there per frmula unit (cmpund)? b. Hw many nitride ins
Semester 2 AP Chemistry Unit 12
 Cmmn In Effect and Buffers PwerPint The cmmn in effect The shift in equilibrium caused by the additin f a cmpund having an in in cmmn with the disslved substance The presence f the excess ins frm the disslved
Cmmn In Effect and Buffers PwerPint The cmmn in effect The shift in equilibrium caused by the additin f a cmpund having an in in cmmn with the disslved substance The presence f the excess ins frm the disslved
Science 9 Unit 2: Atoms, Elements and Compounds
 Science 9 Unit 2: Atms, Elements and Cmpunds demnstrate a knwledge f WHMIS standards by using prper techniques fr handling and dispsing f lab materials (209-7) cmpare earlier cnceptins f the structure
Science 9 Unit 2: Atms, Elements and Cmpunds demnstrate a knwledge f WHMIS standards by using prper techniques fr handling and dispsing f lab materials (209-7) cmpare earlier cnceptins f the structure
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
A.P. CHEMISTRY. SOLUTIONS AND ACID BASE CHEMISTRY. p 1
 A.P. CHEMISTRY. SOLUTIONS AND ACID BASE CHEMISTRY. p 1 (Nte: questins 1 t 14 are meant t be dne WITHOUT calculatrs!) 1.Which f the fllwing is prbably true fr a slid slute with a highly endthermic heat
A.P. CHEMISTRY. SOLUTIONS AND ACID BASE CHEMISTRY. p 1 (Nte: questins 1 t 14 are meant t be dne WITHOUT calculatrs!) 1.Which f the fllwing is prbably true fr a slid slute with a highly endthermic heat
UNIT 5: ATOMIC THEORY & THE PERIODIC TABLE CHEMISTRY 215, DUFFEY, CHAPTER 4 & SECTION 6.1
 UNIT 5: ATOMIC THEORY & THE PERIODIC TABLE CHEMISTRY 215, DUFFEY, CHAPTER 4 & SECTION 6.1 BIG IDEAS (we will tuch n small parts f Chp.5 as well) 4.1 Early Ideas Abut Matter 4.2 Defining the Atm 4.3 Hw
UNIT 5: ATOMIC THEORY & THE PERIODIC TABLE CHEMISTRY 215, DUFFEY, CHAPTER 4 & SECTION 6.1 BIG IDEAS (we will tuch n small parts f Chp.5 as well) 4.1 Early Ideas Abut Matter 4.2 Defining the Atm 4.3 Hw
Regents Chemistry Period Unit 3: Atomic Structure. Unit 3 Vocabulary..Due: Test Day
 Name Skills: 1. Interpreting Mdels f the Atm 2. Determining the number f subatmic particles 3. Determine P, e-, n fr ins 4. Distinguish istpes frm ther atms/ins Regents Chemistry Perid Unit 3: Atmic Structure
Name Skills: 1. Interpreting Mdels f the Atm 2. Determining the number f subatmic particles 3. Determine P, e-, n fr ins 4. Distinguish istpes frm ther atms/ins Regents Chemistry Perid Unit 3: Atmic Structure
Chem 163 Section: Team Number: ALE 24. Voltaic Cells and Standard Cell Potentials. (Reference: 21.2 and 21.3 Silberberg 5 th edition)
 Name Chem 163 Sectin: Team Number: ALE 24. Vltaic Cells and Standard Cell Ptentials (Reference: 21.2 and 21.3 Silberberg 5 th editin) What des a vltmeter reading tell us? The Mdel: Standard Reductin and
Name Chem 163 Sectin: Team Number: ALE 24. Vltaic Cells and Standard Cell Ptentials (Reference: 21.2 and 21.3 Silberberg 5 th editin) What des a vltmeter reading tell us? The Mdel: Standard Reductin and
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Matter Content from State Frameworks and Other State Documents
 Atms and Mlecules Mlecules are made f smaller entities (atms) which are bnded tgether. Therefre mlecules are divisible. Miscnceptin: Element and atm are synnyms. Prper cnceptin: Elements are atms with
Atms and Mlecules Mlecules are made f smaller entities (atms) which are bnded tgether. Therefre mlecules are divisible. Miscnceptin: Element and atm are synnyms. Prper cnceptin: Elements are atms with
UC A-G Chemistry. Gorman Learning Center (052344) Basic Course Information
 UC A-G Chemistry Grman Learning Center (052344) Basic Curse Infrmatin Title: UC A-G Chemistry Transcript abbreviatins: A-G Chem / A-G Chem Length f curse: Full Year Subject area: Labratry Science ("d")
UC A-G Chemistry Grman Learning Center (052344) Basic Curse Infrmatin Title: UC A-G Chemistry Transcript abbreviatins: A-G Chem / A-G Chem Length f curse: Full Year Subject area: Labratry Science ("d")
Acids and Bases Lesson 3
 Acids and Bases Lessn 3 The ph f a slutin is defined as the negative lgarithm, t the base ten, f the hydrnium in cncentratin. In a neutral slutin at 25 C, the hydrnium in and the hydrxide in cncentratins
Acids and Bases Lessn 3 The ph f a slutin is defined as the negative lgarithm, t the base ten, f the hydrnium in cncentratin. In a neutral slutin at 25 C, the hydrnium in and the hydrxide in cncentratins
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 1 Chemical Foundations
 Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 1 Chemical Fundatins Metric Cnversins All measurements in chemistry are made using the metric system. In using the metric system yu must be able t cnvert between ne value and anther.
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 1 Chemical Fundatins Metric Cnversins All measurements in chemistry are made using the metric system. In using the metric system yu must be able t cnvert between ne value and anther.
N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g) 2NH 3 (g) o Three mole ratios can be derived from the balanced equation above: Example: Li(s) + O 2 (g) Li 2 O(s)
 Chapter 9 - Stichimetry Sectin 9.1 Intrductin t Stichimetry Types f Stichimetry Prblems Given is in mles and unknwn is in mles. Given is in mles and unknwn is in mass (grams). Given is in mass and unknwn
Chapter 9 - Stichimetry Sectin 9.1 Intrductin t Stichimetry Types f Stichimetry Prblems Given is in mles and unknwn is in mles. Given is in mles and unknwn is in mass (grams). Given is in mass and unknwn
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
QCE Chemistry. Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, Chemistry: Revision Notes. By Sophie (1 ATAR)
 QCE Chemistry Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, 2017 11 Chemistry: Revisin Ntes By Sphie (1 ATAR) Pwered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.rg) Yur ntes authr, Sphie. Sphie achieved an ATAR f 1 in 2016 while
QCE Chemistry Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, 2017 11 Chemistry: Revisin Ntes By Sphie (1 ATAR) Pwered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.rg) Yur ntes authr, Sphie. Sphie achieved an ATAR f 1 in 2016 while
Lesson 8 Types of Matter
 Lessn 8 Types f Matter D Nw 6Ga, 6I 10.30.18 Take ut HW 6.13 t be checked. In CJ, cpy dwn inf frm CJ bard. Keep CJs ut and pen n desk. On DO NOW PAGE #4, cpy and answer the questins: 1. In KCl (aq), is
Lessn 8 Types f Matter D Nw 6Ga, 6I 10.30.18 Take ut HW 6.13 t be checked. In CJ, cpy dwn inf frm CJ bard. Keep CJs ut and pen n desk. On DO NOW PAGE #4, cpy and answer the questins: 1. In KCl (aq), is
Lesson 8: Types of Matter
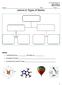 NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 8: Types f Matter Matter: anything that has and takes up Examples f matter: Examples that are NOT matter: _ 1 Pure substances: Elements and Cmpunds a material that has a
NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 8: Types f Matter Matter: anything that has and takes up Examples f matter: Examples that are NOT matter: _ 1 Pure substances: Elements and Cmpunds a material that has a
In other words, atoms are not created nor destroyed in chemical reaction.
 CUNTING Physcisal Methds Chemical Methds by numbers 1 pr = 2 1 dz = 12 1 case = 12 r 24 1 hand = 5 fingers 1 ft = 12 inches Avgadr's number = 6.02x10 +23 anything anything by weighing 1 gummy bear = 1
CUNTING Physcisal Methds Chemical Methds by numbers 1 pr = 2 1 dz = 12 1 case = 12 r 24 1 hand = 5 fingers 1 ft = 12 inches Avgadr's number = 6.02x10 +23 anything anything by weighing 1 gummy bear = 1
Semester 1 Honors Chemistry Notebook (unit 1)
 Semester 1 Hnrs Chemistry Ntebk (unit 1) Basic infrmatin Chemistry: study f matter Matter: has mass and takes up space Organized by using the peridic table cntains elements Prtns, neutrns, and electrns
Semester 1 Hnrs Chemistry Ntebk (unit 1) Basic infrmatin Chemistry: study f matter Matter: has mass and takes up space Organized by using the peridic table cntains elements Prtns, neutrns, and electrns
Unit 13 Acids and Bases. Name: Period: TEST: Wednesday 4/27/16
 Unit 13 Acids and Bases Name: Perid: TEST: Wednesday 4/27/16 1 Unit 13 Acids and Bases Calendar Mnday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday APRIL 7th Slutins Test 8 th Vide: Acids & Bases Ntes #1 Acids and
Unit 13 Acids and Bases Name: Perid: TEST: Wednesday 4/27/16 1 Unit 13 Acids and Bases Calendar Mnday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday APRIL 7th Slutins Test 8 th Vide: Acids & Bases Ntes #1 Acids and
2.303 [ OH ] [ H ] CT
![2.303 [ OH ] [ H ] CT 2.303 [ OH ] [ H ] CT](/thumbs/76/73668484.jpg) CEE 680 25 Octber 2011 FIRST EXAM Clsed bk, ne page f ntes allwed. Answer all questins. Please state any additinal assumptins yu made, and shw all wrk. Yu are welcme t use a graphical methd f slutin if
CEE 680 25 Octber 2011 FIRST EXAM Clsed bk, ne page f ntes allwed. Answer all questins. Please state any additinal assumptins yu made, and shw all wrk. Yu are welcme t use a graphical methd f slutin if
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
2004 AP CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 2004 AP CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS 6. An electrchemical cell is cnstructed with an pen switch, as shwn in the diagram abve. A strip f Sn and a strip f an unknwn metal, X, are used as electrdes.
2004 AP CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS 6. An electrchemical cell is cnstructed with an pen switch, as shwn in the diagram abve. A strip f Sn and a strip f an unknwn metal, X, are used as electrdes.
NUPOC STUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY. Navy Recruiting Command
 NUPOC SUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY Navy Recruiting Cmmand CHEMISRY. ph represents the cncentratin f H ins in a slutin, [H ]. ph is a lg scale base and equal t lg[h ]. A ph f 7 is a neutral slutin. PH < 7 is acidic
NUPOC SUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY Navy Recruiting Cmmand CHEMISRY. ph represents the cncentratin f H ins in a slutin, [H ]. ph is a lg scale base and equal t lg[h ]. A ph f 7 is a neutral slutin. PH < 7 is acidic
CHAPTER Read Chapter 17, sections 1,2,3. End of Chapter problems: 25
 CHAPTER 17 1. Read Chapter 17, sectins 1,2,3. End f Chapter prblems: 25 2. Suppse yu are playing a game that uses tw dice. If yu cunt the dts n the dice, yu culd have anywhere frm 2 t 12. The ways f prducing
CHAPTER 17 1. Read Chapter 17, sectins 1,2,3. End f Chapter prblems: 25 2. Suppse yu are playing a game that uses tw dice. If yu cunt the dts n the dice, yu culd have anywhere frm 2 t 12. The ways f prducing
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
University Chemistry Quiz /04/21 1. (10%) Consider the oxidation of ammonia:
 University Chemistry Quiz 3 2015/04/21 1. (10%) Cnsider the xidatin f ammnia: 4NH 3 (g) + 3O 2 (g) 2N 2 (g) + 6H 2 O(l) (a) Calculate the ΔG fr the reactin. (b) If this reactin were used in a fuel cell,
University Chemistry Quiz 3 2015/04/21 1. (10%) Cnsider the xidatin f ammnia: 4NH 3 (g) + 3O 2 (g) 2N 2 (g) + 6H 2 O(l) (a) Calculate the ΔG fr the reactin. (b) If this reactin were used in a fuel cell,
AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 NOTES THERMOCHEMISTRY
 AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 NOTES THERMOCHEMISTRY Energy- the capacity t d wrk r t prduce heat 1 st Law f Thermdynamics: Law f Cnservatin f Energy- energy can be cnverted frm ne frm t anther but it can be neither
AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 NOTES THERMOCHEMISTRY Energy- the capacity t d wrk r t prduce heat 1 st Law f Thermdynamics: Law f Cnservatin f Energy- energy can be cnverted frm ne frm t anther but it can be neither
Chapter One. Matter and Energy - Chemistry the study of matter and its changes the "central science" Natural Laws
 Chapter One Matter and Measurement http://www.chemistry.armstrng.edu/ nivens/curse_list.htm OWL HOMEWORK REQUIRED!!! Matter and Energy - Chemistry the study f matter and its changes the "central science"
Chapter One Matter and Measurement http://www.chemistry.armstrng.edu/ nivens/curse_list.htm OWL HOMEWORK REQUIRED!!! Matter and Energy - Chemistry the study f matter and its changes the "central science"
CHEM 103 Calorimetry and Hess s Law
 CHEM 103 Calrimetry and Hess s Law Lecture Ntes March 23, 2006 Prf. Sevian Annuncements Exam #2 is next Thursday, March 30 Study guide, practice exam, and practice exam answer key are already psted n the
CHEM 103 Calrimetry and Hess s Law Lecture Ntes March 23, 2006 Prf. Sevian Annuncements Exam #2 is next Thursday, March 30 Study guide, practice exam, and practice exam answer key are already psted n the
Course/ Subject: Chemistry I Grade: Teacher: Hill Oberto Month: September/October (6-8 weeks)
 Curse/ Subject: Chemistry I Grade: 11-12 Teacher: Hill Obert Mnth: September/Octber (6-8 weeks) Natinal Benchmark being addressed State Standards Skills/Cmpetencies Assessment Matter Unit I.All matter
Curse/ Subject: Chemistry I Grade: 11-12 Teacher: Hill Obert Mnth: September/Octber (6-8 weeks) Natinal Benchmark being addressed State Standards Skills/Cmpetencies Assessment Matter Unit I.All matter
Chemistry 132 NT. Electrochemistry. Review
 Chemistry 132 NT If yu g flying back thrugh time, and yu see smebdy else flying frward int the future, it s prbably best t avid eye cntact. Jack Handey 1 Chem 132 NT Electrchemistry Mdule 3 Vltaic Cells
Chemistry 132 NT If yu g flying back thrugh time, and yu see smebdy else flying frward int the future, it s prbably best t avid eye cntact. Jack Handey 1 Chem 132 NT Electrchemistry Mdule 3 Vltaic Cells
AP Chemistry Assessment 2
 AP Chemistry Assessment 2 DATE OF ADMINISTRATION: January 8 January 12 TOPICS COVERED: Fundatinal Tpics, Reactins, Gases, Thermchemistry, Atmic Structure, Peridicity, and Bnding. MULTIPLE CHOICE KEY AND
AP Chemistry Assessment 2 DATE OF ADMINISTRATION: January 8 January 12 TOPICS COVERED: Fundatinal Tpics, Reactins, Gases, Thermchemistry, Atmic Structure, Peridicity, and Bnding. MULTIPLE CHOICE KEY AND
Examples: 1. How much heat is given off by a 50.0 g sample of copper when it cools from 80.0 to 50.0 C?
 NOTES: Thermchemistry Part 1 - Heat HEAT- TEMPERATURE - Thermchemistry: the study f energy (in the frm f heat) changes that accmpany physical & chemical changes heat flws frm high t lw (ht cl) endthermic
NOTES: Thermchemistry Part 1 - Heat HEAT- TEMPERATURE - Thermchemistry: the study f energy (in the frm f heat) changes that accmpany physical & chemical changes heat flws frm high t lw (ht cl) endthermic
Electrochemical Reactions
 Electrchemical Reactins The first chemical prcess t prduce electricity was described in 1800 by the Italian scientist Alessandr Vlta, a frmer high schl teacher. Acting n the hypthesis that tw dissimilar
Electrchemical Reactins The first chemical prcess t prduce electricity was described in 1800 by the Italian scientist Alessandr Vlta, a frmer high schl teacher. Acting n the hypthesis that tw dissimilar
Chemistry 114 First Hour Exam
 Chemistry 114 First Hur Exam Please shw all wrk fr partial credit Name: (4 pints) 1. (12 pints) Espress is made by frcing very ht water under high pressure thrugh finely grund, cmpacted cffee. (Wikipedia)
Chemistry 114 First Hur Exam Please shw all wrk fr partial credit Name: (4 pints) 1. (12 pints) Espress is made by frcing very ht water under high pressure thrugh finely grund, cmpacted cffee. (Wikipedia)
https://goo.gl/eaqvfo SUMMER REV: Half-Life DUE DATE: JULY 2 nd
 NAME: DUE DATE: JULY 2 nd AP Chemistry SUMMER REV: Half-Life Why? Every radiistpe has a characteristic rate f decay measured by its half-life. Half-lives can be as shrt as a fractin f a secnd r as lng
NAME: DUE DATE: JULY 2 nd AP Chemistry SUMMER REV: Half-Life Why? Every radiistpe has a characteristic rate f decay measured by its half-life. Half-lives can be as shrt as a fractin f a secnd r as lng
Welcome to AP Chemistry 2017!!!!
 Welcme t AP Chemistry 2017!!!! Hpefully yu are all ready fr hard wrk and dedicatin, as well as sme fun and LOTS f chemistry! I LOVE CHEMISTRY and I am really lking frward t teaching AP Chemistry again!
Welcme t AP Chemistry 2017!!!! Hpefully yu are all ready fr hard wrk and dedicatin, as well as sme fun and LOTS f chemistry! I LOVE CHEMISTRY and I am really lking frward t teaching AP Chemistry again!
Name Honors Chemistry / /
 Name Hnrs Chemistry / / Beynd Lewis Structures Exceptins t the Octet Rule Mdel Hydrgen is an exceptin t the ctet rule because it fills its uter energy level with nly 2 electrns. The secnd rw elements B
Name Hnrs Chemistry / / Beynd Lewis Structures Exceptins t the Octet Rule Mdel Hydrgen is an exceptin t the ctet rule because it fills its uter energy level with nly 2 electrns. The secnd rw elements B
Accelerated Chemistry POGIL: Half-life
 Name: Date: Perid: Accelerated Chemistry POGIL: Half-life Why? Every radiistpe has a characteristic rate f decay measured by its half-life. Half-lives can be as shrt as a fractin f a secnd r as lng as
Name: Date: Perid: Accelerated Chemistry POGIL: Half-life Why? Every radiistpe has a characteristic rate f decay measured by its half-life. Half-lives can be as shrt as a fractin f a secnd r as lng as
15.0 g Cr = 21.9 g Cr O g Cr 4 mol Cr mol Cr O
 WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal Chemistry Exam 2008 SOLUTION SET 1. Crrect answer: B. Use PV = nrt t get: PV = nrt 2. Crrect answer: A. (2.18 atm)(25.0 L) = n(0.08206 L atm/ml K)(23+273) n = 2.24 ml Assume
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal Chemistry Exam 2008 SOLUTION SET 1. Crrect answer: B. Use PV = nrt t get: PV = nrt 2. Crrect answer: A. (2.18 atm)(25.0 L) = n(0.08206 L atm/ml K)(23+273) n = 2.24 ml Assume
How can standard heats of formation be used to calculate the heat of a reaction?
 Answer Key ALE 28. ess s Law and Standard Enthalpies Frmatin (Reerence: Chapter 6 - Silberberg 4 th editin) Imprtant!! Fr answers that invlve a calculatin yu must shw yur wrk neatly using dimensinal analysis
Answer Key ALE 28. ess s Law and Standard Enthalpies Frmatin (Reerence: Chapter 6 - Silberberg 4 th editin) Imprtant!! Fr answers that invlve a calculatin yu must shw yur wrk neatly using dimensinal analysis
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Fundamental Chemistry
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Fundamental Chemistry Curse Design 2013-2014 Curse Infrmatin Divisin Science Curse Number CHM 130 (SUN# CHM 1130) Title Fundamental Chemistry Credits 4 Develped by Jel Sheltn Lecture/Lab
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Fundamental Chemistry Curse Design 2013-2014 Curse Infrmatin Divisin Science Curse Number CHM 130 (SUN# CHM 1130) Title Fundamental Chemistry Credits 4 Develped by Jel Sheltn Lecture/Lab
CHEM 1413 Chapter 6 Homework Questions TEXTBOOK HOMEWORK
 CHEM 1413 Chapter 6 Hmewrk Questins TEXTBOOK HOMEWORK 6.25 A 27.7-g sample f the radiatr clant ethylene glycl releases 688 J f heat. What was the initial temperature f the sample if the final temperature
CHEM 1413 Chapter 6 Hmewrk Questins TEXTBOOK HOMEWORK 6.25 A 27.7-g sample f the radiatr clant ethylene glycl releases 688 J f heat. What was the initial temperature f the sample if the final temperature
CHEM Thermodynamics. Change in Gibbs Free Energy, G. Review. Gibbs Free Energy, G. Review
 Review Accrding t the nd law f Thermdynamics, a prcess is spntaneus if S universe = S system + S surrundings > 0 Even thugh S system
Review Accrding t the nd law f Thermdynamics, a prcess is spntaneus if S universe = S system + S surrundings > 0 Even thugh S system
Name: Period: Date: BONDING NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY
 Name: Perid: Date: BONDING NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant terms
Name: Perid: Date: BONDING NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant terms
Three Definitions of Acids/Bases Type Acid Base Problems with it Arrhenius Bronsted-Lowry Lewis. NH 3(aq) + H 2O(l)
 CP NT Ch 19: Acid and Bases An Intrductin Prperties f Acids 1. taste 2. Can prduce H + ( ) ins ( ) 3. Change the clr f litmus frm t 4. Reacts with such as Zn and Mg t prduce gas. Ba(s) + H 2SO 4 BaSO 4(aq)
CP NT Ch 19: Acid and Bases An Intrductin Prperties f Acids 1. taste 2. Can prduce H + ( ) ins ( ) 3. Change the clr f litmus frm t 4. Reacts with such as Zn and Mg t prduce gas. Ba(s) + H 2SO 4 BaSO 4(aq)
NOTES. Name: Date: Topic: Periodic Table & Atoms Notes. Period: Matter
 NOTES Unit: Tpic: Peridic Table & Atms Ntes Name: Date: Perid: Matter Atmic Structure The term matter describes all f the physical substances arund us. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
NOTES Unit: Tpic: Peridic Table & Atms Ntes Name: Date: Perid: Matter Atmic Structure The term matter describes all f the physical substances arund us. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Study Guide Chemistry Comprehensive Exam I. Memorization: see Stuff to Memorize Sheet for more (from teacher) Ions that Form Soluble Compounds
 I. Memrizatin: see Stuff t Memrize Sheet fr mre (frm teacher) Ins that Frm Sluble Cmpunds Grup 1 ins (Li+, Na+, ect.) Ammnium Nitrate Acetate Bicarbnate (aka Hydrgen Carbnate) Chlrate Perchlrate Plyatmic
I. Memrizatin: see Stuff t Memrize Sheet fr mre (frm teacher) Ins that Frm Sluble Cmpunds Grup 1 ins (Li+, Na+, ect.) Ammnium Nitrate Acetate Bicarbnate (aka Hydrgen Carbnate) Chlrate Perchlrate Plyatmic
First Semester 6 th Grade Exam Review
 Name: Perid First Semester 6 th Grade Exam Review Exam Schedule: Tuesday, Dec. 18 th -4 th Perid Wednesday, Dec 19 th - 2 nd & 7 th Perids Thursday, Dec. 20 th - 3 rd and 6 th Perids Friday, Dec. 21 th
Name: Perid First Semester 6 th Grade Exam Review Exam Schedule: Tuesday, Dec. 18 th -4 th Perid Wednesday, Dec 19 th - 2 nd & 7 th Perids Thursday, Dec. 20 th - 3 rd and 6 th Perids Friday, Dec. 21 th
CHM 152 Practice Final
 CM 152 Practice Final 1. Of the fllwing, the ne that wuld have the greatest entrpy (if cmpared at the same temperature) is, [a] 2 O (s) [b] 2 O (l) [c] 2 O (g) [d] All wuld have the same entrpy at the
CM 152 Practice Final 1. Of the fllwing, the ne that wuld have the greatest entrpy (if cmpared at the same temperature) is, [a] 2 O (s) [b] 2 O (l) [c] 2 O (g) [d] All wuld have the same entrpy at the
STUDENT TIPS FOR USING THE CHEMISTRY REFERENCE TABLE
 STUDENT TIPS FOR USING THE CHEMISTRY REFERENCE TABLE TABLE A: STANDARD TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE This table gives the values fr Standard Temp. (in C & K) & Pressure (in kpa & atm). Standard Temperature
STUDENT TIPS FOR USING THE CHEMISTRY REFERENCE TABLE TABLE A: STANDARD TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE This table gives the values fr Standard Temp. (in C & K) & Pressure (in kpa & atm). Standard Temperature
Electrochemistry. Reduction: the gaining of electrons. Reducing agent (reductant): species that donates electrons to reduce another reagent.
 Electrchemistry Review: Reductin: the gaining f electrns Oxidatin: the lss f electrns Reducing agent (reductant): species that dnates electrns t reduce anther reagent. Oxidizing agent (xidant): species
Electrchemistry Review: Reductin: the gaining f electrns Oxidatin: the lss f electrns Reducing agent (reductant): species that dnates electrns t reduce anther reagent. Oxidizing agent (xidant): species
Finals Study Guide. AP Chemistry. Spring Made by Ashley Thomas
 Spring 2016 Finals Study Guide AP Chemistry Table f Cntents Sectin 1: Acids and Bases 1.1 Titratins 1.2 Indicatrs 1.3 Buffers 1.4 Slutin Preparatin Sectin 2: Calrimetry 2.1 Specific Heat 2.2 Metals Sectin
Spring 2016 Finals Study Guide AP Chemistry Table f Cntents Sectin 1: Acids and Bases 1.1 Titratins 1.2 Indicatrs 1.3 Buffers 1.4 Slutin Preparatin Sectin 2: Calrimetry 2.1 Specific Heat 2.2 Metals Sectin
Chemistry 1A Fall 2000
 Chemistry 1A Fall 2000 Midterm Exam III, versin B Nvember 14, 2000 (Clsed bk, 90 minutes, 155 pints) Name: SID: Sectin Number: T.A. Name: Exam infrmatin, extra directins, and useful hints t maximize yur
Chemistry 1A Fall 2000 Midterm Exam III, versin B Nvember 14, 2000 (Clsed bk, 90 minutes, 155 pints) Name: SID: Sectin Number: T.A. Name: Exam infrmatin, extra directins, and useful hints t maximize yur
Review Material for Exam #2
 Review Material fr Eam # 1. a. Calculate the mlarity f a slutin made with 184.6 mg sample f ptassium dichrmate disslved in enugh water t give 500.0 ml f slutin. 1 g 184.6 mg K Cr O 1 mle K Cr O 7 7 1000
Review Material fr Eam # 1. a. Calculate the mlarity f a slutin made with 184.6 mg sample f ptassium dichrmate disslved in enugh water t give 500.0 ml f slutin. 1 g 184.6 mg K Cr O 1 mle K Cr O 7 7 1000
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t eep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the lin n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Chec ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t eep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the lin n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Chec ut ur Tutring
Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 3 - Solutions Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, Solids, and Solutions
 Chem 116 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 3 - Slutins Intermlecular Frces, Liquids, Slids, and Slutins Key Questins 1. Is the average kinetic energy f mlecules greater r lesser than the energy f intermlecular frces
Chem 116 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 3 - Slutins Intermlecular Frces, Liquids, Slids, and Slutins Key Questins 1. Is the average kinetic energy f mlecules greater r lesser than the energy f intermlecular frces
How can standard heats of formation be used to calculate the heat of a reaction?
 Name Chem 161, Sectin: Grup Number: ALE 28. Hess s Law and Standard Enthalpies Frmatin (Reerence: Chapter 6 - Silberberg 5 th editin) Imprtant!! Fr answers that invlve a calculatin yu must shw yur wrk
Name Chem 161, Sectin: Grup Number: ALE 28. Hess s Law and Standard Enthalpies Frmatin (Reerence: Chapter 6 - Silberberg 5 th editin) Imprtant!! Fr answers that invlve a calculatin yu must shw yur wrk
CHAPTER PRACTICE PROBLEMS CHEMISTRY
 Chemical Kinetics Name: Batch: Date: Rate f reactin. 4NH 3 (g) + 5O (g) à 4NO (g) + 6 H O (g) If the rate f frmatin f NO is 3.6 0 3 ml L s, calculate (i) the rate f disappearance f NH 3 (ii) rate f frmatin
Chemical Kinetics Name: Batch: Date: Rate f reactin. 4NH 3 (g) + 5O (g) à 4NO (g) + 6 H O (g) If the rate f frmatin f NO is 3.6 0 3 ml L s, calculate (i) the rate f disappearance f NH 3 (ii) rate f frmatin
State of matter characteristics solid Retains shape and volume
 **See attachment fr graphs States f matter The fundamental difference between states f matter is the distance between particles Gas Ttal disrder Much empty space Particles have cmpletely freedm f mtin
**See attachment fr graphs States f matter The fundamental difference between states f matter is the distance between particles Gas Ttal disrder Much empty space Particles have cmpletely freedm f mtin
CHE 105 EXAMINATION III November 11, 2010
 CHE 105 EXAMINATION III Nvember 11, 2010 University f Kentucky Department f Chemistry READ THESE DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY BEFORE STARTING THE EXAMINATION! It is extremely imprtant that yu fill in the answer
CHE 105 EXAMINATION III Nvember 11, 2010 University f Kentucky Department f Chemistry READ THESE DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY BEFORE STARTING THE EXAMINATION! It is extremely imprtant that yu fill in the answer
Chem 75 February 16, 2017 Exam 2 Solutions
 1. (6 + 6 pints) Tw quick questins: (a) The Handbk f Chemistry and Physics tells us, crrectly, that CCl 4 bils nrmally at 76.7 C, but its mlar enthalpy f vaprizatin is listed in ne place as 34.6 kj ml
1. (6 + 6 pints) Tw quick questins: (a) The Handbk f Chemistry and Physics tells us, crrectly, that CCl 4 bils nrmally at 76.7 C, but its mlar enthalpy f vaprizatin is listed in ne place as 34.6 kj ml
SCH4U: End of Year Review
 SCH4U: End f Year Review Unit 1: Energy and Rates 2 1) When 13.4 g f ammnium chlride disslve int 2.00x10 g f water the temperature changes frm 20.0 C t 15.3 C. Determine the mlar enthalpy f slutin f ammnium
SCH4U: End f Year Review Unit 1: Energy and Rates 2 1) When 13.4 g f ammnium chlride disslve int 2.00x10 g f water the temperature changes frm 20.0 C t 15.3 C. Determine the mlar enthalpy f slutin f ammnium
HW #2: 2.42, 2.44, 2.48, 2.50, 2.52, 2.58, 2.60, 2.62, 2.66, 2.68, 2.72, 2.82, 2.90, 2.96, 2.98
 Chemistry 121 Lectures 6 & 7: The Mdern View f the Atm and Its Relatin t the Peridic Table Chapter 2 in McMurry, Ballantine, et. al. 7 th editin HW #2: 2.42, 2.44, 2.48, 2.50, 2.52, 2.58, 2.60, 2.62, 2.66,
Chemistry 121 Lectures 6 & 7: The Mdern View f the Atm and Its Relatin t the Peridic Table Chapter 2 in McMurry, Ballantine, et. al. 7 th editin HW #2: 2.42, 2.44, 2.48, 2.50, 2.52, 2.58, 2.60, 2.62, 2.66,
Chemistry/ Biotechnology Reference Sheets
 Cmmn Metric Prefixes: Giga (G) = 1,000,000,000 = Kil (k) = 1,000 = Deci (d) =.1 = Milli (m) =.001 = Nan (n) =.000000001 = 9 6 1 10 Mega (M) = 1,000,000 = 1 10 0 1 10 Basic unit = meter, gram, liter, secnd
Cmmn Metric Prefixes: Giga (G) = 1,000,000,000 = Kil (k) = 1,000 = Deci (d) =.1 = Milli (m) =.001 = Nan (n) =.000000001 = 9 6 1 10 Mega (M) = 1,000,000 = 1 10 0 1 10 Basic unit = meter, gram, liter, secnd
KEY: Fall 2014 Chemistry Final Review Matter and Change Measurement and Calculation Density of ethanol [g/ml] Trial A Trial B Trial C
![KEY: Fall 2014 Chemistry Final Review Matter and Change Measurement and Calculation Density of ethanol [g/ml] Trial A Trial B Trial C KEY: Fall 2014 Chemistry Final Review Matter and Change Measurement and Calculation Density of ethanol [g/ml] Trial A Trial B Trial C](/thumbs/83/87825053.jpg) Name: Date: Perid: KEY: Fall 2014 Chemistry Final Review Matter and Change 1. What is a hmgeneus mixture? Give an example. What is a hetergeneus mixture? Give an example. Hmgeneus: a physical cmbinatin
Name: Date: Perid: KEY: Fall 2014 Chemistry Final Review Matter and Change 1. What is a hmgeneus mixture? Give an example. What is a hetergeneus mixture? Give an example. Hmgeneus: a physical cmbinatin
UNIT 12 Chemical Bonding
 Name Perid CRHS Academic Chemistry UNIT 12 Chemical Bnding Practice Prblems Due Date Assignment On-Time (1) Late (7) 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 Warm'ÿ Up C Ntes, Hmewrk, xam Reviews and Their KYS lcated
Name Perid CRHS Academic Chemistry UNIT 12 Chemical Bnding Practice Prblems Due Date Assignment On-Time (1) Late (7) 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 Warm'ÿ Up C Ntes, Hmewrk, xam Reviews and Their KYS lcated
Unit 5: Bonding and Inorganic Nomenclature
 Unit 5: Bnding and Inrganic Nmenclature Chemical Bnding Inic Bnds: atms give up r gain e and are attracted t each ther by culmbic attractin Na lses an e Cl gains an e Na Na 1+ + e Cl + e Cl inic cmpunds
Unit 5: Bnding and Inrganic Nmenclature Chemical Bnding Inic Bnds: atms give up r gain e and are attracted t each ther by culmbic attractin Na lses an e Cl gains an e Na Na 1+ + e Cl + e Cl inic cmpunds
PHOTOSYNTHESIS THE PRACTICALS 16 APRIL 2014
 PHOTOSYNTHESIS THE PRACTICALS 16 APRIL 2014 Lessn Descriptin In this lessn, we will: Review the prcess f phtsynthesis Study the starch test in leaves Study the varius practicals testing phtsynthesis Lk
PHOTOSYNTHESIS THE PRACTICALS 16 APRIL 2014 Lessn Descriptin In this lessn, we will: Review the prcess f phtsynthesis Study the starch test in leaves Study the varius practicals testing phtsynthesis Lk
Lecture 13: Electrochemical Equilibria
 3.012 Fundamentals f Materials Science Fall 2005 Lecture 13: 10.21.05 Electrchemical Equilibria Tday: LAST TIME...2 An example calculatin...3 THE ELECTROCHEMICAL POTENTIAL...4 Electrstatic energy cntributins
3.012 Fundamentals f Materials Science Fall 2005 Lecture 13: 10.21.05 Electrchemical Equilibria Tday: LAST TIME...2 An example calculatin...3 THE ELECTROCHEMICAL POTENTIAL...4 Electrstatic energy cntributins
Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 4 Properties of Solutions
 Chem 116 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 4 Prperties f Slutins Key Questins 1. Identify the principal type f slute-slvent interactin that is respnsible fr frming the fllwing slutins: (a) KNO 3 in water; (b) Br 2
Chem 116 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 4 Prperties f Slutins Key Questins 1. Identify the principal type f slute-slvent interactin that is respnsible fr frming the fllwing slutins: (a) KNO 3 in water; (b) Br 2
Electrochemistry. Half-Reactions 1. Balancing Oxidation Reduction Reactions in Acidic and Basic Solutions
 Electrchemistry Half-Reactins 1. Balancing Oxidatin Reductin Reactins in Acidic and Basic Slutins Vltaic Cells 2. Cnstructin f Vltaic Cells 3. Ntatin fr Vltaic Cells 4. Cell Ptential 5. Standard Cell Ptentials
Electrchemistry Half-Reactins 1. Balancing Oxidatin Reductin Reactins in Acidic and Basic Slutins Vltaic Cells 2. Cnstructin f Vltaic Cells 3. Ntatin fr Vltaic Cells 4. Cell Ptential 5. Standard Cell Ptentials
Unit 14 Thermochemistry Notes
 Name KEY Perid CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 14 Thermchemistry Ntes Quiz Date Exam Date Lab Dates Ntes, Hmewrk, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS lcated n CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincchem.pbwrks.cm
Name KEY Perid CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 14 Thermchemistry Ntes Quiz Date Exam Date Lab Dates Ntes, Hmewrk, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS lcated n CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincchem.pbwrks.cm
**DO NOT ONLY RELY ON THIS STUDY GUIDE!!!**
 Tpics lists: UV-Vis Absrbance Spectrscpy Lab & ChemActivity 3-6 (nly thrugh 4) I. UV-Vis Absrbance Spectrscpy Lab Beer s law Relates cncentratin f a chemical species in a slutin and the absrbance f that
Tpics lists: UV-Vis Absrbance Spectrscpy Lab & ChemActivity 3-6 (nly thrugh 4) I. UV-Vis Absrbance Spectrscpy Lab Beer s law Relates cncentratin f a chemical species in a slutin and the absrbance f that
Chemistry 20 Lesson 11 Electronegativity, Polarity and Shapes
 Chemistry 20 Lessn 11 Electrnegativity, Plarity and Shapes In ur previus wrk we learned why atms frm cvalent bnds and hw t draw the resulting rganizatin f atms. In this lessn we will learn (a) hw the cmbinatin
Chemistry 20 Lessn 11 Electrnegativity, Plarity and Shapes In ur previus wrk we learned why atms frm cvalent bnds and hw t draw the resulting rganizatin f atms. In this lessn we will learn (a) hw the cmbinatin
Electrochemistry. Learning Objectives. Half-Reactions 1. Balancing Oxidation Reduction Reactions in Acidic and Basic Solutions
 Electrchemistry 1 Learning Objectives Electrchemistry Balancing Oxidatin Reductin Reactins in Acidic and Basic Slutins a. Learn the steps fr balancing xidatin reductin reactins using the half-reactin methd.
Electrchemistry 1 Learning Objectives Electrchemistry Balancing Oxidatin Reductin Reactins in Acidic and Basic Slutins a. Learn the steps fr balancing xidatin reductin reactins using the half-reactin methd.
Session #22: Homework Solutions
 Sessin #22: Hmewrk Slutins Prblem #1 (a) In the cntext f amrphus inrganic cmpunds, name tw netwrk frmers, tw netwrk mdifiers, and ne intermediate. (b) Sketch the variatin f mlar vlume with temperature
Sessin #22: Hmewrk Slutins Prblem #1 (a) In the cntext f amrphus inrganic cmpunds, name tw netwrk frmers, tw netwrk mdifiers, and ne intermediate. (b) Sketch the variatin f mlar vlume with temperature
Chapter 19. Electrochemistry. Dr. Al Saadi. Electrochemistry
 Chapter 19 lectrchemistry Part I Dr. Al Saadi 1 lectrchemistry What is electrchemistry? It is a branch f chemistry that studies chemical reactins called redx reactins which invlve electrn transfer. 19.1
Chapter 19 lectrchemistry Part I Dr. Al Saadi 1 lectrchemistry What is electrchemistry? It is a branch f chemistry that studies chemical reactins called redx reactins which invlve electrn transfer. 19.1
CRHS Academic Chemistry UNIT 5 - Periodic Table and Trends NOTES
 Name Perid CRHS Academic Chemistry UNIT 5 - Peridic Table and Trends NOTES Quiz Date Lab Dates Exam Date Ntes, Hmewrk, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS lcated n CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincchem.pbwrks.cm
Name Perid CRHS Academic Chemistry UNIT 5 - Peridic Table and Trends NOTES Quiz Date Lab Dates Exam Date Ntes, Hmewrk, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS lcated n CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincchem.pbwrks.cm
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
 Thermdynamics and Equilibrium Thermdynamics Thermdynamics is the study f the relatinship between heat and ther frms f energy in a chemical r physical prcess. We intrduced the thermdynamic prperty f enthalpy,
Thermdynamics and Equilibrium Thermdynamics Thermdynamics is the study f the relatinship between heat and ther frms f energy in a chemical r physical prcess. We intrduced the thermdynamic prperty f enthalpy,
Name:. Correct Questions = Wrong Questions =.. Unattempt Questions = Marks =
 Name:. Crrect Questins = Wrng Questins =.. Unattempt Questins = Marks = 1. Which metal reacts mst vigrusly with water? (A) Al (B) Ca (C) Fe (D) K 2. Which are strng acids? I. HI II. HNO 3 III. H 2 SO 3
Name:. Crrect Questins = Wrng Questins =.. Unattempt Questins = Marks = 1. Which metal reacts mst vigrusly with water? (A) Al (B) Ca (C) Fe (D) K 2. Which are strng acids? I. HI II. HNO 3 III. H 2 SO 3
Name: Period: Date: BONDING NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY
 Name: Perid: Date: BONDING NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant terms
Name: Perid: Date: BONDING NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant terms
Differentiation Applications 1: Related Rates
 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
ALE 21. Gibbs Free Energy. At what temperature does the spontaneity of a reaction change?
 Name Chem 163 Sectin: Team Number: ALE 21. Gibbs Free Energy (Reference: 20.3 Silberberg 5 th editin) At what temperature des the spntaneity f a reactin change? The Mdel: The Definitin f Free Energy S
Name Chem 163 Sectin: Team Number: ALE 21. Gibbs Free Energy (Reference: 20.3 Silberberg 5 th editin) At what temperature des the spntaneity f a reactin change? The Mdel: The Definitin f Free Energy S
When a substance heats up (absorbs heat) it is an endothermic reaction with a (+)q
 Chemistry Ntes Lecture 15 [st] 3/6/09 IMPORTANT NOTES: -( We finished using the lecture slides frm lecture 14) -In class the challenge prblem was passed ut, it is due Tuesday at :00 P.M. SHARP, :01 is
Chemistry Ntes Lecture 15 [st] 3/6/09 IMPORTANT NOTES: -( We finished using the lecture slides frm lecture 14) -In class the challenge prblem was passed ut, it is due Tuesday at :00 P.M. SHARP, :01 is
