The characteristics of phosphorus adsorption and desorption in gray desert soil of Xinjiang, China
|
|
|
- May Newman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS The characteristics of phosphorus adsorption and desorption in gray desert soil of Xinjiang, China To cite this article: B Wang et al 2017 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci Related content - Adsorption and desorption of agricultural waste-derived DOMs in soil H L Li, G H Yang, G Y Zhu et al. - Adsorption and desorption of Sb(III) on goethite Jianhong Xi and Sufang Zhang - Study on Reclamation of Saline-alkali Land in Akto Plain Region in Xinjiang Dongwen Hua, Jiaxi Yi and juan Li View the article online for updates and enhancements. This content was downloaded from IP address on 08/10/2018 at 02:47
2 The characteristics of phosphorus adsorption and desorption in gray desert soil of Xinjiang, China B Wang 1, J S Sun 1, 3, H Liu 1 and Y B Ma 2 1 Institute of Soil Fertilizer and Agricultural Water Saving, Xinjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Urumqi , China 2 National Soil Fertility and Fertilizer Effects Long term Monitoring Network, Institute of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing , China @qq.com Abstract. The characteristics of phosphorus (P) adsorption and desorption in Xinjiang gray desert soil (0-200 mm) of China in the long-term fertilization condition is affected by the level of soil P content which studied through an isothermal adsorption and desorption experiments of P. The results stated that within the experimental concentration range, with the increase of the amount of outer-source phosphorus, P adsorption, desorption and desorption rate increased and adsorption rate decreased gradually in different Olsen-P levels of gray desert soil in Xinjiang, China. Olsen-P content is significantly correlated with the P adsorption saturation (DPS) of gray desert soil. The maximum adsorption capacity (X m ) of the treatments followed an extremely significant decreasing order of CK>NPK NPKM>PK NPKS. The maximum buffer capacity (MBC) and adsorption constant (K) of the NPK treatment was much higher than NPKM, NPKS, PK and CK treatments. And, MBC value of CK treatment was extremely higher than NPKS and PK, however, the differences between NPKM and CK, NPKS and PK were not significant. The comparison between NPKM, NPKS, PK and CK treatments showed no significant difference in K value, but these four showed significantly lower than NPK treatments. The value of soil easy desorption P (RDP) of NPKS and NPKM was significantly higher than NPK and PK, and the chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer was a best way to release the phosphorus for Xinjiang agricultural production, China. 1. Introduction Phosphorus (P) is an indispensable nutrient for plant growth and is important for agricultural production [1-4]. The content of available P is relatively low in most soils in China, so meeting the nutrient requirements of plants is difficult. The calcareous soil in northern China has strong adsorption and precipitation effects on P fertilizer; thus, many studies have focused on methods to decrease fixation and increase the effectiveness of added P in soil [5]. Since the 1950s, efforts have been made to understand the adsorption and desorption characteristics of soil P from various aspects. Boparai and Sharma [6] demonstrated that clay type and its content, and content of available P in soil (Olsen-P), played important roles in the adsorption and desorption of soil P. Chinese researchers showed that soil ph, iron and aluminum oxides, calcium, organic matter and clay content all affected the P adsorption and desorption of soil [7]. The adsorption and desorption characteristics of P in soils with diverse particle compositions [5], different clay contents [4] and various soil types [8] were significantly Content from this work may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 licence. Any further distribution of this work must maintain attribution to the author(s) and the title of the work, journal citation and DOI. Published under licence by Ltd 1
3 different. In addition, exogenous application of humic acid [9] and polyacrylamide [10] greatly influenced the P adsorption and desorption of soil. Even using the same soil type (such as gray desert soil) under similar climate conditions, the content of Olsen-P showed significant differences of up to 30 mg kg 1 for different fertilization treatments in long-term experiments [11]. With such a great variation in the Olsen-P content of gray desert soil, what are the adsorption and desorption characteristics of soil P? What is the effect of different Olsen-P contents on the adsorption and desorption of soil P? Based on 22-year long-term fertilization experiments with gray desert soil, we studied the adsorption and desorption characteristics of soil P. This provided a basis for the appropriate utilization and management of P, as well as for optimizing fertilization in gray desert soil, Xinjiang China. 2. Materials and methods 2.1. Experimental field, climate characteristics and soil properties Gray Desert Soil Long-term Monitoring Station in Urumqi Xinjiang is one station in the national longterm monitoring network that monitors soil fertility and fertilizer benefits. It was founded in 1989, and its primary goal is to investigate the climate characteristics, crop rotation, the effects of organic and inorganic fertilizer on crop yield, and the change in soil fertility in the northwestern agricultural region in China. The station (43 58 N, E, with the altitude of 600 m) is located in a suburb of Urumqi, Xinjiang, in a typical continental arid climate zone. The climate characteristics of the area are as follows: annual precipitation, 242 mm; average temperature, 7.6 C; effective accumulated temperature, 1734 C; frost-free period, 156 d; and sunshine duration, 2454 h. The soil classification standard of China classes the soil in this station as typical gray desert soil; based on the standard of the United Nations Food Agriculture Organization (FAO) classification, it is a Calcaric Cambisol [12]. Before the fertilization experiments, the main soil properties in the plough layer (0-200 mm): soil ph (water: soil of 2.5:1) 8.1, organic matter 8.8 g kg 1, total nitrogen (N) 0.87 g kg 1, total P 0.67 g kg 1, total potassium (K) 23.0 g kg 1, alkaline hydrolysable N 55.2 mg kg 1, Olsen-P 3.9 mg kg 1, and NH 4 OA c extractable K mg kg 1. In 1989, prior to beginning the long-term fertilization experiments, a local cultivar of wheat was grown for 2 years (1988 and 1989) without fertilizer in order to reduce soil variation among treatments. Each following year, plants were grown for one season at the station with a rotation of wheat, maize and cotton. In the present study, five treatments with large differences in Olsen-P were selected from the longterm fertilization experiment as shown in table 1 to study the adsorption and desorption of soil P. The five treatments were (1) control (CK), (2) P and K fertilization (PK), (3) N, P and K fertilization (NPK), (4) N, P, K and organic fertilization (NPKM) and (5) N, P and K fertilization with straw returning (NPKS). Winter wheat was planted in Fertilization in each treatment is shown in table 2. Treatments ph Table 1. Soil properties (0 200 mm) of different treatments in the experiment. Organic matter (g kg 1 ) Total N (g kg 1 ) Total P (g kg 1 ) Available N (mg kg 1 ) Olsen-P (mg kg 1 ) Available K (mg kg 1 ) Bulk density (g cm 3 ) CK C PK B NPK BC NPKM A NPKS BC Note: The topsoil sample collected in June 2011 was used for table 1. The indicators are the soil fertility properties determined prior to the adsorption and desorption experiments. Different capital letters following numbers represent significant differences at P < 0.01, the same as below. 2
4 Table 2. Average annual nutrient input from different sources during Treatment Chemical fertilizer Manure Straw N (kg ha 1) P (kg ha 1 ) K (kg ha 1 ) M (t ha 1 ) S (t ha 1 ) CK PK NPK NPKM NPKS Note: Crops were planted without fertilizing in CK; the amount of P and K fertilizer in PK treatment was the same as that in NPK treatment; the fertilization amounts of N, P and K were 99.4, 29.2 and 18.8 kg ha 1, respectively, for , and were increased to 241.5, 60.2 and 50.4 kg ha 1 for In Treatment NPKM, the organic manure was sheep droppings, of which the nutrient contribution was calculated on the basis of 15%, the utilization rate of organic manure in the current year and in Treatment NPKS, the nutrient contribution of the straw was calculated on the basis of 10%, the utilization rate of straw in the current year. The two treatments were designed to have the same nutrient application rates as the same as treatment NPK. Of the chemical fertilizers, all the P and K fertilizers and 60% of the N fertilizer was used as base fertilizer, and 40% of the N fertilizer as topdressing Evaluation items Determination of soil P with isothermal adsorption. Six soil samples (2.500 g each) were placed in 100-mL centrifuge tubes, and 25 ml of 0.01 mol L 1 CaCl 2 solution with P concentrations of 0, 25, 50, 75 and 100 mg L 1 respectively added into the six tubes. In addition, three drops of chloroform were added to inhibit microbial activity. The mixture was oscillated for 1 h at 25 C and centrifuged at RCF 2770 ( g) for 8 min after incubating for 24 h and then the P concentration of the solution was determined, based on which the P adsorption in soil was calculated. The curve of isothermal adsorption was plotted using the P concentration in the solution as the X-axis and adsorptive P in soil as the Y-axis, and then fitted with an equation Determination of soil P with isothermal desorption. The supernatant of the centrifuged from the mixture was removed, and the pellet rinsed twice with 25 ml of saturated NaCl solution and centrifuged at RCF 2770 ( g) for 8 min to eliminate free P. In each tube, 25 ml of 0.01 mol L 1 CaCl 2 solution was added, with three drops of chloroform to inhibit microbial activity. The mixture was incubated for 24 h after oscillating for 1 h at 25 C, followed by centrifugation at RCF 2770 ( g) for 8 min. The resulting supernatant was used to evaluate the desorptive P, and the desorption rate was determined according to the ratio of desorptive P and total adsorptive P in the soil Determination of available P and organic matter in soil. Olsen-P in soil was determined using the 0.5 mol L 1 NaHCO 3 (ph 8.5) method. The organic matter in soil and other items were evaluated using the conventional methods of soil agrochemistry [13] Data processing The maximum buffering capacity of soil P (MBC, ml g 1 ) was calculated using constant of adsorption reaction (K) X m [14], where X m is the maximum adsorption of soil P. Readily desorbable P (RDP) represented the P amount from the soil solid phase entering the liquid phase with 0 mg L 1 P addition during the adsorption and desorption process [14]. Statistical analysis was performed using SAS 9.1 and Excel Results and analyses 3
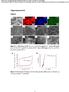
5 3.1. Adsorptive characteristics of soil P Isothermal adsorption curve of soil P. The adsorption curve in five treatments with various levels of soil P is shown in figures 1 and 2. With P addition in the range of mg L 1, the P adsorption was gradually elevated and the absorptive rate was reduced with increases in exogenous P. With P addition in the range 0 50 mg L 1, the adsorption rapidly increased in all treatments except for PK; however, within the range mg L 1, P adsorption in soil decreased in all five treatments. In all treatments with different P levels, the adsorption rapidly increased, then slowly increased, followed by a plateau with increased exogenous application of P, but the adsorption rate showed a downward trend. To quantify the variation of P adsorption in different treatments, the isothermal adsorption equation was selected to simulate increasing exogenous P and P adsorption in soil, which facilitates study of the adsorptive characteristics of soil P under various P treatments. Figure 1. The P isotherm adsorption curves in different treatments. Figure 2. Change in P adsorption rate with extraneous P. 4
6 Adsorption equations of soil P. When using the equilibrium method to study P adsorption in soil systems, isothermal adsorption equations, such as Langmuir, Freundlich and Temkin [15], are commonly used to fit the relationship between the adsorption amount of the soil surface and the equilibrium concentration in solution. Then, parameters such as the adsorption amount can be calculated according to each equation. In the present study, we used the Langmuir, Freundlich and Temkin isothermal equations a shown in table 3 to simulate the isothermal adsorption process of soil P under various P levels. The Langmuir equation is expressed as C/X = C/X m + 1/(KX m ), where X represents the P adsorption of soil, C indicates P concentration in the equilibrium solution (The parameter of X and C are the same definition for all three equations) and K is a constant related to the energy of adsorption. The Freundlich equation is X = KC b, where K and b are two constants related to soil properties. The Temkin equation is X = K 1 lnc + K 1 lnk 2, where K 1 and K 2 are two constants related to soil properties. Simulation of soil P adsorption under the five treatments was carried out using the three isothermal adsorption equations as shown in table 3. The significance level of Langmuir equation fitting (P < 0.01 or P < 0.05) was higher than that of Freundlich and Temkin equations; and it showed good correlations, with all the correlation coefficients (r) > 0.95 as shown in table 4. This suggested that the Langmuir equation was the best method to describe the adsorption characteristics of P in gray desert soil, and so we selected this equation to explore the adsorption characteristics of P in soil. Table 3. Isothermal adsorption equations and parameters in different treatments. Treatment Langmuir adsorption Freundlich adsorption Temkin adsorption equation equation equation C/X = C/X m + 1/KX m X = KC b X = K 1 lnc + K 1 lnk 2 X m K r b K r K 1 K 2 r CK ** ** ** PK * NPK ** NPKM ** * * NPKS ** ** * Note: * and ** represent statistical significance at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively. The same as below. Table 4. Langmuir isothermal adsorption equations in different treatments. Treatment Langmuir equation r CK C/X = C ** PK C/X = C * NPK C/X = 0.003C ** NPKM C/X = 0.003C ** NPKS C/X = C ** Adsorption parameters of soil P. The adsorption process of P can be characterized by many parameters. The following four parameters were used in the present study: X m reflects the number of adsorption sites of soil colloids [16] and indicates the P storage capacity of soil. When the soil P storage reaches a certain capacity, it is possible for the soil to provide nutrients to crops [4]. Of the five treatments, X m was the largest for CK, times those of other treatments, and it was significantly different (P < 0.01) from other treatments as shown in table 5. There was no significant difference in X m between NPK and NPKM, and between PK and NPKS; but for NPK and NPKM, there was a much greater X m compared with that of PK and NPKS treatments. The P input of PK and NPK treatments were the same as 5
7 Treatment shown in table 2, but the yield of PK was substantially lower than that of NPK due to the lack of N [17] that is, the output of soil P was less than that of the NPK treatment, resulting in a relatively high P left over in soil as shown in table 1. Therefore, the soil adsorption capacity was relatively small in the PK treatment. Similarly, the output of soil P was lower in the NPKS than in the NPK treatment, and so the soil adsorption capacity was relatively small. Table 5. The P adsorption and desorption parameters in different treatments. Maximum adsorption capacity (X m ) (mg kg -1 ) Adsorption constant (K) Max buffering capacity of soil P (MBC) (ml g -1 ) P sorption saturation (DPS) (%) CK 416.7A 0.21B 88.78B 1.02D 0.00C PK 244.6C 0.18B 43.90C 8.83B 0.25C NPK 333.6B 0.61A A 4.10C 0.00C NPKM 330.2B 0.20B 64.37BC 14.24A 3.82A NPKS 236.1C 0.24B 53.37C 3.87CD 1.39B Readily desorbable P (RDP) (mg kg - 1 ) The constant K represents the affinity between soil colloids and phosphate ions, which is a strength factor of soil adsorption [18], reflecting the level of P adsorption of soil to a certain extent. A positive K-value indicates that the adsorption reaction is spontaneous at room temperature, and the magnitude of K reflects the spontaneous extent of the adsorption reaction. The larger the K-value, the stronger the spontaneity and the more stable the products are, leading to weak P supply [4]. The K-values were positive in all treatments, indicating that the adsorption reactions were all spontaneous in the order of NPK > NPKS > CK > NPKM > PK. Of these, the K-value was significantly higher for the NPK treatment compared with the other treatments, and no substantial difference was observed among the other four treatments, suggesting that the soil P adsorption was increased after applying N, P, and K fertilizer, but the application of P and K, NPK with organic fertilizer or straw reduced the P adsorption of soil. MBC is the product of K and X m in the Langmuir equation (i.e. MBC = KX m ) and so is a combined parameter for the two factors of intensity of P adsorption (K) and capacity (X m ), and it is a comprehensive indicator to evaluate the soil P supplying features [16,18]. A larger MBC value represents a stronger P storage capability of soil, resulting in a higher soil P supplying ability. When the intensities of P supplying ability are similar in soils, the MBC value is higher and the storage of effective P is greater, so more effective P is supplied to crops by soil. When P adsorption is comparable among different soils, a larger MBC value indicates a lower energy state of the adsorbed P is, and that the P can be easily used by crops, so the intensity of P supply is relatively small [19]. The MBC value of the NPK treatment was much higher than for the other four treatments, and the CK treatment had substantially higher MBC than the PK and NPKS treatments as shown in table 5. There was no difference among the PK, NPKM and NPKS treatments. The CK had a very large X m value, and consequently, its MBC value was significantly higher than that of PK and NPKS, but less that for the NPK treatment. Due to similar values for K and X m in the PK and NPKS treatments, their MBC values did not significantly differ. The P sorption saturation (DPS) reflects the ratio between the content of effective P in soil and its maximum adsorption [4]: DPS = [available P in soil (Olsen-P)/maximum P adsorption] 100, where the maximum adsorption of P is calculated by the Langmuir equation. The order of DPS among treatments was NPKM > PK > NPK > NPKS > CK as shown in table 5. Of these, the DPS of NPKS, CK and NPK did not significantly differ, but there were substantial 6
8 differences among all other treatments. The variation in DPS of all treatments was similar to the trend of Olsen-P content in soil as shown in table Desorption characteristics of soil P Desorption amount and desorption rate of soil P. The desorption of P in soil is usually considered as the reverse process of adsorption, which depends on the reuse of adsorbed P. As exogenous P increased, the desorption amount of P gradually increased in soils with various P contents as shown in figures 3 and 4, indicating that the P desorption amount of soil was related to application of exogenous P. The order of the desorption amount among treatments was CK > NPKM > PK > NPKS > NPK. The desorption rate of P is represented by the ratio between the amount of desorption P and total P adsorbed before desorption, and the desorption rate had a similar pattern to that of desorption amount it increased with increased exogenous application of P, consistent with previous results [4, 20]. The order of desorption rate among treatments was PK > NPKM > CK > NPKS > NPK, and this pattern was significantly negatively correlated with K-value as shown in table 5 the higher the K-value, the smaller was the desorption rate in soil. The K-value of NPK was much greater than that of the other four treatments, and thus its desorption rate was relatively low as shown in figure 4. Figure 3. The P isothermal desorption curves in different treatments. Figure 4. The P isothermal desorption rates in different treatments. 7
9 Readily desorbable P in soil (RDP). The order of RDP among different treatments was NPKM > NPKS > PK > NPK = CK. Of these, no significant difference was observed among the RDP of the PK, NPK and CK treatments, but RDP of all other treatments varied substantially. The order of RDP values suggested that the chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer or straw returning significantly improved the content of readily desorbable P in soil, and this effect was much greater than that of chemical fertilization alone. The RDP value of NPKM was much higher than that of the other treatments, indicating that chemical with organic fertilization greatly increased the P desorption of soil, and significantly improved the effect of available P in soil. 4. Discussion Liu et al (2003) [11] demonstrated that the content of Olsen-P in soil significantly differed among various treatments (by almost 30 mg kg 1 ) after 11 years of long-term fertilization experiments in gray desert soil, Xinjiang, China. In the present study, we performed the fertilization experiments for another 11 years, and the difference in the Olsen-P content of various treatments was further magnified with a range reaching 41 mg kg 1. The long-term and different fertilization practices led to differences in the input (fertilization) and output (biomass) of P [21-23], and the adsorption and desorption of soil P changed accordingly. Here, we selected five fertilization treatments with Olsen-P content from low to high, and except for the PK treatment, they represented chronically different fertilization practices of local farmers. The long-term biomass output without nutrient input in the CK treatment resulted in a lack of P supply in soil, leading to depletion of the soil. Therefore, CK showed a maximum X m, a minimum DPS and no readily desorbable P in the isothermal adsorption experiments. The low content of effective P and high P adsorption resulted in the minimal DPS in CK (P < 0.01). The NPKM treatment exhibited a relatively large amount of readily desorbable P and a relatively low X m, and thus the DPS of NPKM was much greater than that of other treatments, suggesting that the P level in soil greatly affected the amount and strength of P adsorption, consistent with previous studies [14]. Based on DPS, the P requirement for saturated adsorption at mm depth for CK, PK, NPK, NPKM and NPKS was 1287, 670, 960, 828 and 691 kg ha 1, respectively. According to the P requirement for saturated P in gray desert soil and annual nutrient inputs, it will theoretically take about 14, 36, 44 and 26 years to saturate the P in the soil for the PK, NPK, NPKM and NPKS treatments, respectively. However, we studied the fertilized topsoil of mm and not the whole topsoil of mm in the present study, and the sampling time was the late growing stage of winter wheat but not post harvesting, so the actual time to reach P saturation will greatly exceed years. This result indicates that the adsorption and desorption of P in gray desert soil is a dynamic and long-term process, and gray desert soil showed an enormous potential for P adsorption. Compared to the two-season soil with wheat and maize rotation, the K-value of gray desert soil ( ) was greater than that of Lou ( ), Loessial ( ) and Loess soils ( ) of Shanxi Province and calcareous Chao soil of Hebei Province ( ) [5, 24]. This was the main reason for the higher amount and stronger capability of P adsorption in the gray desert soil of Xinjiang with only one season of planting. 5. Conclusion Within the range of mg L 1 for exogenous P concentration, the fit for a Langmuir equation with the isothermal curve of gray desert soil reached a significant level, with r > The P adsorption, desorption and desorption rate gradually increased with higher exogenous P application in gray desert soil for various levels of Olsen-P, but the adsorption rate was reduced. The soil content of Olsen-P in gray desert soil was significantly positively correlated with the DPS of soil the soil Olsen-P content determined the value of DPS, indicating that Olsen-P content was a key factor affecting DPS. The order of soil X m among different treatments with various Olsen-P accumulations in gray desert soil was CK > NPK NPKM > PK NPKS, and the differences among treatments were statistically significant. No substantial difference was observed in K among the CK, PK, NPKM and NPKS 8
10 treatments, but K was significantly higher for NPK than the other four treatments. The MBC of the NPK treatment was significantly higher compared with the other treatments. The MBC of CK was substantially higher than for PK and NPKS, but was similar between CK and NPKM and between PK and NPKS. The RDP of NPKM and NPKS treatments was much higher than for treatments with only chemical fertilization, and chemical with organic fertilization exhibited the optimal effect. Therefore, NPKM was the best fertilization practice to elevate the soil P supplying capability. Acknowledgments We thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China ( and ), Science and Technology Project Be Supported Xinjiang China (2016E02020) and Xinjiang Key Research and Development Program of China (2016B ) for providing funds for this work. We also thank all the staff associated with long-term soil fertility and fertilizer effects location monitoring network of Xinjiang Grey Desert Soil in China for supplying the historic dataset. References [1] Wang B, Liu H, Hao X Y, Wang X H, Sun J S, Li J M and Ma Y B 2016 Agronomic threshold of soil available phosphorus in grey desert soils in Xinjiang, China IOP Conf. Series: Earth Envir. Sci [2] Wang B, Li J M, Ren Y, Xin J S, Hao X Y, Ma Y B and Ma X W 2015 Validation of a soil phosphorus accumulation model in the wheat-maize rotation production areas of China Field Crops Res [3] Wang B, Liu H, Wang X H, Li J M, Ma Y B and Ma X W 2015 Soil phosphorus accumulation model for an arid area of north-western China with 3-year rotation of wheat, maize and cotton J. Agr. Sci-Cambridge [4] Chen B L, Sheng J D, Jiang P A and Liu Y G 2010 Study on characteristics of phosphorus adsorption and desorption of cotton field with different soil textures (In Chinese) Chinese J. Soil Sci. 41(2) [5] Luo M and Wang X D 2008 Distribution of particles size and their phosphorus adsorption and desorption characteristics of lou soils with different fertility (In Chinese) Agr. Res. Arid Areas 26(6) [6] Boparai H K and Sharma K N 2006 Phosphorus adsorption and desorption characteristics of some soils as affected by clay and available phosphorus content J. Indian Chem. Soc. 54(1) [7] Zhao X Q and Lu R K 1991 Effect of organic manures on soil phosphorus adsorption (In Chinese) Acta Pedologica Sinica 28(1) 7-13 [8] Han X, Wu D Y and Wang X G 2011 Study on the adsorption characteristics of phosphorus in different soils (In Chinese) Modern Agr. Sci. Technol [9] Li C Y, Dang T H, Wang W Z and Liu W Z 2011 Influence of humic acid on the adsorption behavior of phosphorus in agricultural soil (In Chinese) J. Soil Water Conserv. 25(3) [10] Yang X Q, Hu T T, Wang X D and Wang F 2006 Effect on PAM on phosphorus adsorption and desorption in lou soil (In Chinese) J. Soil Water Conserv. 20(1) [11] Liu H, Wang J L, Tan X X, Zhang X L, Zhao B Q and Zhang F D 2003 The effect of long-term fertilization on phosphor efficiency and modality in grey desert soil (In Chinese) Xinjiang Agr. Sci. 40(2) [12] FAO 2006 World reference base for soils resources World Soil Resource Report No (Rome, Italy) [13] Bao S D 2007 Analytical Methods for Soil and Agro-chemistry (In Chinese) (Beijing: China Agriculture Press) [14] Zhang H T, Liu J L, Liao W H, Zhang Z X and Hao X Y 2008 Effect of phosphate fertilizer and manure on properties of phosphorus sorption and desorption in soils with different phosphorus levels (In Chinese) Plant Nutr. Fertilizing Sci. 14(2)
11 [15] Chen Y D, Liang C H, Wang Y S, Li Y Y, Guo B D and Zhang Y H 2010 Phosphorus adsorption and desorption characteristics of wetland soil under different redox conditions (In Chinese) Chinese J. Ecol. 29(4) [16] Zhao Q L, Wang K R and Xie X L 2009 Effects of organic nutrient recycling on phosphorus adsorption-desorption characteristics in a reddish paddy rice system (In Chinese) Scientia Agr. Sinica 42(1) [17] Qu H, Zhao B Q, Chen Y H, Liu H, Li X Y and Zhang F D 2004 Effect of long-term fertilization on wheat quality and yield in grey desert soil (In Chinese) Plant Nutr. Fertilizer Sci. 10(1) 12-7 [18] Zhang D, Wei Z M, Li S Q, Wang S P and Xu J G 2005 Effect of bio-organic fertilizers on phosphorus adsorption-desorption (In Chinese) J. Northeast Agri. Uni. 36(5) [19] Guo X D, Zhang X Q and Yang L 1997 Phosphorus sorption and desorption properties of agricultural soils in Gansu Province (In Chinese) Acta Agr. Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica 6(2) 7-12 [20] Guo S L, Dang T H, Liu S Z and Hao M D 2005 Changes in characterization of phosphorus sorption in relation to its forms and soil organic carbon (In Chinese) Plant Nutr. Fertilizer Sci. 11(1) 33-9 [21] Ma Y B, Li J M, Li X Y, Tang X, Liang Y C, Huang S M, Wang B R, Liu H and Yang X Y 2009 Phosphorus accumulation and depletion in soils in wheat-maize cropping systems: Model and validation Field Crops Res [22] Huang S M, Ma Y B, Bao D, Guo D and Zhang S 2011 Manures behave similar to superphosphate in phosphorus accumulation in long-term field soils Int. J. Plant Prod [23] Li J M, Gao J S, Liu J, Xu M G and Ma Y B 2012 Predictive model for phosphorus accumulation in paddy soils with long-term inorganic fertilization Commun. Soil Sci. Plan [24] Xia W J, Liang G Q, Zhou W, Wang H, Wang X B and Sun J W 2008 Adsorption and desorption characteristics of soil phosphorus in calcareous fluvo-aquic soil under long-term fertilization (In Chinese) Plant Nutr. Fertilizer Sci. 14(3)
Preliminary Research on Grassland Fineclassification
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS Preliminary Research on Grassland Fineclassification Based on MODIS To cite this article: Z W Hu et al 2014 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS Preliminary Research on Grassland Fineclassification Based on MODIS To cite this article: Z W Hu et al 2014 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ.
Study on form distribution of soil iron in western Jilin and its correlation with soil properties
 35 2 2016 6 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 35 No. 2 Jun. 2016 1004 5589 2016 02 0593 08 1 1 2 1 1 1. 130061 2. 130012 50 A > B > C > D > E > F > G A A CEC B ph C E A C D G B C D P595 S151. 9 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn.
35 2 2016 6 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 35 No. 2 Jun. 2016 1004 5589 2016 02 0593 08 1 1 2 1 1 1. 130061 2. 130012 50 A > B > C > D > E > F > G A A CEC B ph C E A C D G B C D P595 S151. 9 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn.
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Cation exchange MOF-derived nitrogen-doped
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Cation exchange MOF-derived nitrogen-doped
STUDIES ON THE SORPTION OF PHOSPHATE ON SOME SOILS OF INDIA SATURATED WITH DIFFERENT CATIONS
 I.J.S.N., VOL. 2(2) 211: 327-333 ISSN 2229 6441 STUDIES ON THE SORPTION OF PHOSPHATE ON SOME SOILS OF INDIA SATURATED WITH DIFFERENT CATIONS Bansal, O. P. Chemistry Department, D.S. College, Aligarh-221
I.J.S.N., VOL. 2(2) 211: 327-333 ISSN 2229 6441 STUDIES ON THE SORPTION OF PHOSPHATE ON SOME SOILS OF INDIA SATURATED WITH DIFFERENT CATIONS Bansal, O. P. Chemistry Department, D.S. College, Aligarh-221
Efficient removal of typical dye and Cr(VI) reduction using N-doped
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Efficient removal of typical dye and Cr(VI) reduction using N-doped magnetic porous carbon
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Efficient removal of typical dye and Cr(VI) reduction using N-doped magnetic porous carbon
Supporting Information For. Removal of Antimonite (Sb(III)) and Antimonate (Sb(V)) from Aqueous Solution
 Supporting Information For Removal of Antimonite (Sb(III)) and Antimonate (Sb(V)) from Aqueous Solution Using Carbon Nanofibers that Are Decorated with Zirconium Oxide (ZrO 2 ) Jinming Luo,, Xubiao Luo,
Supporting Information For Removal of Antimonite (Sb(III)) and Antimonate (Sb(V)) from Aqueous Solution Using Carbon Nanofibers that Are Decorated with Zirconium Oxide (ZrO 2 ) Jinming Luo,, Xubiao Luo,
Accepted Manuscript. Yuepeng Pan, Wen Xu, Gregory R. Wentworth, Shili Tian
 Accepted Manuscript Discussion of Atmospheric deposition as an important nitrogen load to a typical agroecosystem in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain by Huang et al. (2016) Yuepeng Pan, Wen Xu, Gregory R. Wentworth,
Accepted Manuscript Discussion of Atmospheric deposition as an important nitrogen load to a typical agroecosystem in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain by Huang et al. (2016) Yuepeng Pan, Wen Xu, Gregory R. Wentworth,
Metal Organic Framework-Derived Metal Oxide Embedded in Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Network for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries
 Supporting Information for Metal Organic Framework-Derived Metal Oxide Embedded in Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Network for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries Zhu-Yin Sui, Pei-Ying Zhang,, Meng-Ying Xu,
Supporting Information for Metal Organic Framework-Derived Metal Oxide Embedded in Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Network for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries Zhu-Yin Sui, Pei-Ying Zhang,, Meng-Ying Xu,
Effects of nitrogen application rate on flag leaf photosynthetic characteristics and grain growth and development of high2quality wheat
 2006,12(1) :49-55 Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science,,,, (, 271018) 3 :,, 8901 N 120 360 kg/ hm 2, SN1391 N 120 240 kg/ hm 2, 360 kg/ hm 2,,, ; ; : ; ; ; : S5121106 : A : 1008-505X(2006) 01-0049- 07
2006,12(1) :49-55 Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science,,,, (, 271018) 3 :,, 8901 N 120 360 kg/ hm 2, SN1391 N 120 240 kg/ hm 2, 360 kg/ hm 2,,, ; ; : ; ; ; : S5121106 : A : 1008-505X(2006) 01-0049- 07
The Mathematical Analysis of Temperature-Pressure-Adsorption Data of Deep Shale Gas
 International Journal of Oil, Gas and Coal Engineering 2018; 6(6): 177-182 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ogce doi: 10.11648/j.ogce.20180606.18 ISSN: 2376-7669 (Print); ISSN: 2376-7677(Online)
International Journal of Oil, Gas and Coal Engineering 2018; 6(6): 177-182 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ogce doi: 10.11648/j.ogce.20180606.18 ISSN: 2376-7669 (Print); ISSN: 2376-7677(Online)
General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported. Bicomponent Metal Monoxides as Alternative High- Performance Li-Ion Anodes to Binary Spinel Oxides
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) General Synthesis of Graphene-Supported
A GIS-based Study on Grassland Degradation and. Increase of Dust Storms in China
 1 A GIS-based Study on Grassland Degradation and Increase of Dust Storms in China Qinxue WANG* and Kuninori OTSUBO* * National Institute for Environmental Studies, 16-2 Onogawa, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8506,
1 A GIS-based Study on Grassland Degradation and Increase of Dust Storms in China Qinxue WANG* and Kuninori OTSUBO* * National Institute for Environmental Studies, 16-2 Onogawa, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8506,
The Study of Soil Fertility Spatial Variation Feature Based on GIS and Data Mining *
 The Study of Soil Fertility Spatial Variation Feature Based on GIS and Data Mining * Chunan Li, Guifen Chen **, Guangwei Zeng, and Jiao Ye College of Information and Technology, Jilin Agricultural University,
The Study of Soil Fertility Spatial Variation Feature Based on GIS and Data Mining * Chunan Li, Guifen Chen **, Guangwei Zeng, and Jiao Ye College of Information and Technology, Jilin Agricultural University,
Temperature and wetting effects on phosphate sorption by soil
 Temperature and wetting effects on phosphate sorption by soil G.M. Hijink October 2010 MSc Thesis Soil Quality SOQ-80439 Table of Contents 1. SUMMARY 1 2. INTRODUCTION 3 3. THEORY 5 3.1. BACKGROUND 5
Temperature and wetting effects on phosphate sorption by soil G.M. Hijink October 2010 MSc Thesis Soil Quality SOQ-80439 Table of Contents 1. SUMMARY 1 2. INTRODUCTION 3 3. THEORY 5 3.1. BACKGROUND 5
for highly efficient and stable corrosive-water evaporation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of mesoporous Fe 3 Si aerogel
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of mesoporous Fe 3 Si aerogel
Effects of nitrogen and potassium nutrition on the occurence of Blumeria graminis ( DC). Speer of wheat in wheat and faba bean intercropping
 2006,12(4) :517-522 Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science / 1, 1, 1 1, 3, 1 2, (1, 650201 ; 2, 100094) : /, : 7417 % 13319 %,, 1417 % 169 % ;, ; 32 % 69 %, 2515 % 5713 %, 4211 % 8311 % ;,r = 01623 3 01702
2006,12(4) :517-522 Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science / 1, 1, 1 1, 3, 1 2, (1, 650201 ; 2, 100094) : /, : 7417 % 13319 %,, 1417 % 169 % ;, ; 32 % 69 %, 2515 % 5713 %, 4211 % 8311 % ;,r = 01623 3 01702
The construction and application of the AMSR-E global microwave emissivity database
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS The construction and application of the AMSR-E global microwave emissivity database To cite this article: Shi Lijuan et al 014 IOP Conf.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS The construction and application of the AMSR-E global microwave emissivity database To cite this article: Shi Lijuan et al 014 IOP Conf.
New Journal of Chemistry Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 New Journal of Chemistry Electronic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 New Journal of Chemistry Electronic
Degradation of Bisphenol A by Peroxymonosulfate Catalytically Activated with. Gui-Xiang Huang, Chu-Ya Wang, Chuan-Wang Yang, Pu-Can Guo, Han-Qing Yu*
 Supporting Information for Degradation of Bisphenol A by Peroxymonosulfate Catalytically Activated with Mn 1.8 Fe 1.2 O 4 Nanospheres: Synergism between Mn and Fe Gui-Xiang Huang, Chu-Ya Wang, Chuan-Wang
Supporting Information for Degradation of Bisphenol A by Peroxymonosulfate Catalytically Activated with Mn 1.8 Fe 1.2 O 4 Nanospheres: Synergism between Mn and Fe Gui-Xiang Huang, Chu-Ya Wang, Chuan-Wang
Adsorption Kinetics, Equilibrium and Thermodynamics of Naphthalene onto Loess Soil
 1 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 1 August to September 1 Adsorption Kinetics, Equilibrium and Thermodynamics of Naphthalene onto Loess Soil Jıang Y.F.
1 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 1 August to September 1 Adsorption Kinetics, Equilibrium and Thermodynamics of Naphthalene onto Loess Soil Jıang Y.F.
2008, hm 2. ( Commodity Bundle) [ 6], 25 4 Vol. 25 No JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., , 2, 3, 1, 2 3*,
![2008, hm 2. ( Commodity Bundle) [ 6], 25 4 Vol. 25 No JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., , 2, 3, 1, 2 3*, 2008, hm 2. ( Commodity Bundle) [ 6], 25 4 Vol. 25 No JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., , 2, 3, 1, 2 3*,](/thumbs/93/112700429.jpg) 25 4 Vol. 25 No. 4 2010 4 JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., 2010 1, 2, 3, 3*, 3, 3, 1, 2 ( 1., 100101; 2., 100049; 3., 100193) :,,,,, ;, 2005, 12 7 5, 2005 :,,, : ; ; ; ; : F301. 21 : A : 1000-3037( 2010)
25 4 Vol. 25 No. 4 2010 4 JOURNAL OF NATURAL RESOURCES Apr., 2010 1, 2, 3, 3*, 3, 3, 1, 2 ( 1., 100101; 2., 100049; 3., 100193) :,,,,, ;, 2005, 12 7 5, 2005 :,,, : ; ; ; ; : F301. 21 : A : 1000-3037( 2010)
bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Hierarchical Ni/NiTiO 3 derived from NiTi LDHs: a bifunctional electrocatalyst
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Hierarchical Ni/NiTiO 3 derived from NiTi LDHs: a bifunctional electrocatalyst
Lab 8 Dynamic Soil Systems I: Soil ph and Liming
 Lab 8 Dynamic Soil Systems I: Soil ph and Liming Objectives: To measure soil ph and observe conditions which change ph To distinguish between active acidity (soil solution ph) and exchangeable acidity
Lab 8 Dynamic Soil Systems I: Soil ph and Liming Objectives: To measure soil ph and observe conditions which change ph To distinguish between active acidity (soil solution ph) and exchangeable acidity
A Comparative Study on the Adsorption and Desorption of Nitrogen and Phosphorus by Three Matrixes of Eco-River Channel
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 5(9): 2734-2739, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Submitted: September 22, 2012 Accepted: November
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 5(9): 2734-2739, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Submitted: September 22, 2012 Accepted: November
2016 International Conference on Modern Economic Development and Environment Protection (ICMED 2016) ISBN:
 2016 International Conference on Modern Economic Development and Environment Protection (ICMED 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-355-7 Difference in FVC Changes between Desert Grasslands with Different Stocking
2016 International Conference on Modern Economic Development and Environment Protection (ICMED 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-355-7 Difference in FVC Changes between Desert Grasslands with Different Stocking
Mapping QTL for Seedling Root Traits in Common Wheat
 2005,38(10):1951-1957 Scientia Agricultura Sinica 1,2,3 1 1 1 2 1 / / 100081 2 050021 3 100039 DH 10 14 11 15 5A 4B 2D 6D 7D 3 2 3 3 2 2 2 3 2 1 3 1 3 DH Mapping for Seedling Root Traits in Common Wheat
2005,38(10):1951-1957 Scientia Agricultura Sinica 1,2,3 1 1 1 2 1 / / 100081 2 050021 3 100039 DH 10 14 11 15 5A 4B 2D 6D 7D 3 2 3 3 2 2 2 3 2 1 3 1 3 DH Mapping for Seedling Root Traits in Common Wheat
An Equation for the Adsorption Under Variable Temperature and Pressure Condition
 International Journal of Oil, Gas and Coal Engineering 2018; 6(6): 171-176 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ogce doi: 10.11648/j.ogce.20180606.17 ISSN: 2376-7669 (Print); ISSN: 2376-7677(Online)
International Journal of Oil, Gas and Coal Engineering 2018; 6(6): 171-176 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ogce doi: 10.11648/j.ogce.20180606.17 ISSN: 2376-7669 (Print); ISSN: 2376-7677(Online)
Adsorption Research of Polymer on Oil Sands in Qidongyi Block of Xinjiang Conglomerate Reservoir
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: -7- ISSN: -78, Vols. 8-8, pp 8- doi:.8/www.scientific.net/amm.8-8.8 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Adsorption Research of Polymer on Oil Sands in Qidongyi
Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: -7- ISSN: -78, Vols. 8-8, pp 8- doi:.8/www.scientific.net/amm.8-8.8 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Adsorption Research of Polymer on Oil Sands in Qidongyi
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Distributing Characteristics of Heavy Metal Elements in A Tributary of Zhedong River in Laowangzhai Gold Deposit, Yunnan (China):
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Distributing Characteristics of Heavy Metal Elements in A Tributary of Zhedong River in Laowangzhai Gold Deposit, Yunnan (China):
Differential response of clay-organic complex and organic-free clay isolated from mulberry growing brown forest soils towards phosphorus adsorption
 Journal of Crop and Weed, 5(1):71-76 (29) Differential response of clay-organic complex and organic-free clay isolated from mulberry growing brown forest soils towards phosphorus adsorption R. KAR, P.
Journal of Crop and Weed, 5(1):71-76 (29) Differential response of clay-organic complex and organic-free clay isolated from mulberry growing brown forest soils towards phosphorus adsorption R. KAR, P.
Scientific registration n o : 728 Symposoum n o : 6 Presentation : Poster CHOUDHARY O.P., HUNDAL H.S., KUMAR S.
 Scientific registration n o : 728 Symposoum n o : 6 Presentation : Poster Competitive Adsorption of Phosphate, Molybdate, Borate and Silicate in Binary-anion mixture with soils Adsorption compétitive de
Scientific registration n o : 728 Symposoum n o : 6 Presentation : Poster Competitive Adsorption of Phosphate, Molybdate, Borate and Silicate in Binary-anion mixture with soils Adsorption compétitive de
Effect of Heat Treatment on Phosphate Sorption by Soils from Different Ecologies
 Effect of Heat Treatment on Phosphate Sorption by Soils from Different Ecologies 1* Aghedo, J.E., 2 Ukpebor, E. and 3 Oviasogie, P.O., 4 Omorogbe, S.O. 1Department of Chemistry, College of Education, Ekiadolor,
Effect of Heat Treatment on Phosphate Sorption by Soils from Different Ecologies 1* Aghedo, J.E., 2 Ukpebor, E. and 3 Oviasogie, P.O., 4 Omorogbe, S.O. 1Department of Chemistry, College of Education, Ekiadolor,
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Experimental section Materials: Tannic acid (TA), silver nitrate
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Experimental section Materials: Tannic acid (TA), silver nitrate
Formula for Determining Number of Basic Seedlings at Scattered-Planting with Seedling Dry-Raised on Plastic Trays in Double-Season Rice
 Rice Science, 2006, 13(4): 271-277 271 http://www.ricesci.cn; http://www.ricescience.org Formula for Determining Number of Basic Seedlings at Scattered-Planting with Seedling Dry-Raised on Plastic Trays
Rice Science, 2006, 13(4): 271-277 271 http://www.ricesci.cn; http://www.ricescience.org Formula for Determining Number of Basic Seedlings at Scattered-Planting with Seedling Dry-Raised on Plastic Trays
ZINC ADSORPTION BEHAVIOR OF DIFFERENT TEXTURED CALCAREOUS SOILS USING FREUNDLICH AND LANGMUIR MODELS
 Pak. J. Agri. Sci., Vol. 45(1), 2008 ZINC ADSORPTION BEHAVIOR OF DIFFERENT TEXTURED CALCAREOUS SOILS USING FREUNDLICH AND LANGMUIR MODELS M.S. Ashraf*, A.M. Ranjha*, M. Yaseen*, N. Ahmad** and A. Hannan***
Pak. J. Agri. Sci., Vol. 45(1), 2008 ZINC ADSORPTION BEHAVIOR OF DIFFERENT TEXTURED CALCAREOUS SOILS USING FREUNDLICH AND LANGMUIR MODELS M.S. Ashraf*, A.M. Ranjha*, M. Yaseen*, N. Ahmad** and A. Hannan***
CLASS EXERCISE 5.1 List processes occurring in soils that cause changes in the levels of ions.
 5 SIL CHEMISTRY 5.1 Introduction A knowledge of the chemical composition of a soil is less useful than a knowledge of its component minerals and organic materials. These dictate the reactions that occur
5 SIL CHEMISTRY 5.1 Introduction A knowledge of the chemical composition of a soil is less useful than a knowledge of its component minerals and organic materials. These dictate the reactions that occur
Influence of dissolved organic matters prepared from organisms in aquatic ecosystem on mercury adsorption in sediment
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(5):1654-1658 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Influence of dissolved organic matters prepared
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(5):1654-1658 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Influence of dissolved organic matters prepared
Co-vacancy-rich Co 1 x S nanosheets anchored on rgo for high-efficiency oxygen evolution
 Electronic Supplementary Material Co-vacancy-rich Co 1 x S nanosheets anchored on rgo for high-efficiency oxygen evolution Jiaqing Zhu 1, Zhiyu Ren 1 ( ), Shichao Du 1, Ying Xie 1, Jun Wu 1,2, Huiyuan
Electronic Supplementary Material Co-vacancy-rich Co 1 x S nanosheets anchored on rgo for high-efficiency oxygen evolution Jiaqing Zhu 1, Zhiyu Ren 1 ( ), Shichao Du 1, Ying Xie 1, Jun Wu 1,2, Huiyuan
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Nitrogen-doped coal tar pitch based microporous carbons with superior CO 2 capture performance Dai Yu, Jun Hu, Lihui Zhou *, Jinxia Li, Jing Tang, Changjun Peng, and Honglai Liu
Supporting Information Nitrogen-doped coal tar pitch based microporous carbons with superior CO 2 capture performance Dai Yu, Jun Hu, Lihui Zhou *, Jinxia Li, Jing Tang, Changjun Peng, and Honglai Liu
PHOSPHORUS SORPTION CHARACTERISTICS OF SOME REPRESENTATIVE SOILS OF SOUTH INDIA
 SAARC J. Agri., 13(1):14-26 (2015) PHOSPHORUS SORPTION CHARACTERISTICS OF SOME REPRESENTATIVE SOILS OF SOUTH INDIA I. Rashmi *, A.K. Biswas, V.R.R. Parama 1 and A.S. Rao Indian Institute of Soil Science,
SAARC J. Agri., 13(1):14-26 (2015) PHOSPHORUS SORPTION CHARACTERISTICS OF SOME REPRESENTATIVE SOILS OF SOUTH INDIA I. Rashmi *, A.K. Biswas, V.R.R. Parama 1 and A.S. Rao Indian Institute of Soil Science,
Adsorption of ions Ion exchange CEC& AEC Factors influencing ion
 Adsorption of ions Ion exchange CEC& AEC Factors influencing ion exchange- Significance. Adsorption of ions Ion adsorption and subsequent exchange are important processes that take place between soil colloidal
Adsorption of ions Ion exchange CEC& AEC Factors influencing ion exchange- Significance. Adsorption of ions Ion adsorption and subsequent exchange are important processes that take place between soil colloidal
Phosphate sorption-desorption characteristics of some ferruginous soils (Alfisols) of eastern India
 Agropedology, 1998, 8, 76-83 Phosphate sorption-desorption characteristics of some ferruginous soils (Alfisols) of eastern India A.K. Dolui and M. Dasgupta Division of Agricultural Chemistry and Soil Science,
Agropedology, 1998, 8, 76-83 Phosphate sorption-desorption characteristics of some ferruginous soils (Alfisols) of eastern India A.K. Dolui and M. Dasgupta Division of Agricultural Chemistry and Soil Science,
Hierarchical MoO 2 /Mo 2 C/C Hybrid Nanowires for High-Rate and. Long-Life Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Hierarchical MoO 2 /Mo 2 C/C Hybrid Nanowires for High-Rate and Long-Life Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries Lichun Yang, a Xiang Li, a Yunpeng Ouyang, a Qingsheng Gao, b Liuzhang
Supporting Information Hierarchical MoO 2 /Mo 2 C/C Hybrid Nanowires for High-Rate and Long-Life Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries Lichun Yang, a Xiang Li, a Yunpeng Ouyang, a Qingsheng Gao, b Liuzhang
An Advanced Anode Material for Sodium Ion. Batteries
 Layered-Structure SbPO 4 /Reduced Graphene Oxide: An Advanced Anode Material for Sodium Ion Batteries Jun Pan, Shulin Chen, # Qiang Fu, Yuanwei Sun, # Yuchen Zhang, Na Lin, Peng Gao,* # Jian Yang,* and
Layered-Structure SbPO 4 /Reduced Graphene Oxide: An Advanced Anode Material for Sodium Ion Batteries Jun Pan, Shulin Chen, # Qiang Fu, Yuanwei Sun, # Yuchen Zhang, Na Lin, Peng Gao,* # Jian Yang,* and
Facile synthesis of porous nitrogen-doped holey graphene as an efficient metal-free catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material Facile synthesis of porous nitrogen-doped holey graphene as an efficient metal-free catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction Li Qin 1,2,5, Ruimin Ding 1,2, Huixiang
Electronic Supplementary Material Facile synthesis of porous nitrogen-doped holey graphene as an efficient metal-free catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction Li Qin 1,2,5, Ruimin Ding 1,2, Huixiang
Research on State-of-Charge (SOC) estimation using current integration based on temperature compensation
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Research on State-of-Charge (SOC) estimation using current integration based on temperature compensation To cite this article: J
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Research on State-of-Charge (SOC) estimation using current integration based on temperature compensation To cite this article: J
Supporting information. One-step facile synthesis of novel β-amino alcohol functionalized
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting information One-step facile synthesis of novel β-amino alcohol functionalized carbon
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting information One-step facile synthesis of novel β-amino alcohol functionalized carbon
Adsorption and desorption of boron in cultivated soils of Himachal Pradesh
 2017; 5(6): 1712-1716 P-ISSN: 2349 8528 E-ISSN: 2321 4902 IJCS 2017; 5(6): 1712-1716 2017 IJCS Received: 09-09-2017 Accepted: 10-10-2017 Kusum Kumari P.G. Scholar, Department of Soil Science, CSK HPKV,
2017; 5(6): 1712-1716 P-ISSN: 2349 8528 E-ISSN: 2321 4902 IJCS 2017; 5(6): 1712-1716 2017 IJCS Received: 09-09-2017 Accepted: 10-10-2017 Kusum Kumari P.G. Scholar, Department of Soil Science, CSK HPKV,
Hydrothermally Activated Graphene Fiber Fabrics for Textile. Electrodes of Supercapacitors
 Supporting Information for Hydrothermally Activated Graphene Fiber Fabrics for Textile Electrodes of Supercapacitors Zheng Li, Tieqi Huang, Weiwei Gao*, Zhen Xu, Dan Chang, Chunxiao Zhang, and Chao Gao*
Supporting Information for Hydrothermally Activated Graphene Fiber Fabrics for Textile Electrodes of Supercapacitors Zheng Li, Tieqi Huang, Weiwei Gao*, Zhen Xu, Dan Chang, Chunxiao Zhang, and Chao Gao*
Journal of Integrative Agriculture 2018, 17(0): Available online at ScienceDirect
 Journal of Integrative Agriculture 2018, 17(0): 60345-7 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect RESEARCH ARTICLE Regionalization of wheat powdery mildew oversummering in China based on
Journal of Integrative Agriculture 2018, 17(0): 60345-7 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect RESEARCH ARTICLE Regionalization of wheat powdery mildew oversummering in China based on
Study on kinetics of adsorption of humic acid modified by ferric chloride on U(VI)
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Study on kinetics of adsorption of humic acid modified by ferric chloride on U(VI) To cite this article: Y Y Zhang et al 2017 IOP
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Study on kinetics of adsorption of humic acid modified by ferric chloride on U(VI) To cite this article: Y Y Zhang et al 2017 IOP
Response of leaf dark respiration of winter wheat to changes in CO 2 concentration and temperature
 Article Atmospheric Science May 2013 Vol.58 No.15: 1795 1800 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5605-1 Response of leaf dark respiration of winter wheat to changes in CO 2 concentration and temperature TAN KaiYan
Article Atmospheric Science May 2013 Vol.58 No.15: 1795 1800 doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5605-1 Response of leaf dark respiration of winter wheat to changes in CO 2 concentration and temperature TAN KaiYan
MOF-76: From Luminescent Probe to Highly Efficient U VI Sorption Material
 MOF-76: From Luminescent Probe to Highly Efficient U VI Sorption Material Weiting Yang, a Zhi-Qiang Bai, b Wei-Qun Shi*, b Li-Yong Yuan, b Tao Tian, a Zhi-Fang Chai*, c Hao Wang, a and Zhong-Ming Sun*
MOF-76: From Luminescent Probe to Highly Efficient U VI Sorption Material Weiting Yang, a Zhi-Qiang Bai, b Wei-Qun Shi*, b Li-Yong Yuan, b Tao Tian, a Zhi-Fang Chai*, c Hao Wang, a and Zhong-Ming Sun*
Highly doped and exposed Cu(I)-N active sites within graphene towards. efficient oxygen reduction for zinc-air battery
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science.
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science.
A Preliminary Analysis of the Relationship between Precipitation Variation Trends and Altitude in China
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2011, VOL. 4, NO. 1, 41 46 A Preliminary Analysis of the Relationship between Precipitation Variation Trends and Altitude in China YANG Qing 1, 2, MA Zhu-Guo 1,
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2011, VOL. 4, NO. 1, 41 46 A Preliminary Analysis of the Relationship between Precipitation Variation Trends and Altitude in China YANG Qing 1, 2, MA Zhu-Guo 1,
Supporting Information. Bi-functional Catalyst with Enhanced Activity and Cycle Stability for. Rechargeable Lithium Oxygen Batteries
 Supporting Information Hierarchical Mesoporous/Macroporous Perovskite La 0.5 Sr 0.5 CoO 3-x Nanotubes: a Bi-functional Catalyst with Enhanced Activity and Cycle Stability for Rechargeable Lithium Oxygen
Supporting Information Hierarchical Mesoporous/Macroporous Perovskite La 0.5 Sr 0.5 CoO 3-x Nanotubes: a Bi-functional Catalyst with Enhanced Activity and Cycle Stability for Rechargeable Lithium Oxygen
Please do not adjust margins. Flower stamen-like porous boron carbon nitride nanoscrolls for water cleaning
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2017 not adjust margins Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Flower stamen-like porous
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2017 not adjust margins Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Flower stamen-like porous
Tuning the Shell Number of Multi-Shelled Metal Oxide. Hollow Fibers for Optimized Lithium Ion Storage
 Supporting Information Tuning the Shell Number of Multi-Shelled Metal Oxide Hollow Fibers for Optimized Lithium Ion Storage Jin Sun, Chunxiao Lv, Fan Lv, ǁ Shuai Chen, Daohao Li, Ziqi Guo, Wei Han, Dongjiang
Supporting Information Tuning the Shell Number of Multi-Shelled Metal Oxide Hollow Fibers for Optimized Lithium Ion Storage Jin Sun, Chunxiao Lv, Fan Lv, ǁ Shuai Chen, Daohao Li, Ziqi Guo, Wei Han, Dongjiang
CURRICULUM VITAE.
 CURRICULUM VITAE Personal Information Name Hongqing Hu Gender Male Position Title Working Department Email Professor Department of Soil Science hqhu@mail.hzau.edu.cn Address Department of Soil Science,
CURRICULUM VITAE Personal Information Name Hongqing Hu Gender Male Position Title Working Department Email Professor Department of Soil Science hqhu@mail.hzau.edu.cn Address Department of Soil Science,
An Evaluation of P Adsorption Indices of Some Representative Soils of Chhattisgarh, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 2575-2580 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.305
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 2575-2580 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.305
Numerical calculation for cavitation flow of inducer
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Numerical calculation for cavitation flow of inducer To cite this article: C Ning et al 2015 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 72 032025
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Numerical calculation for cavitation flow of inducer To cite this article: C Ning et al 2015 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 72 032025
Oxygen Vacancy Induced Bismuth Oxyiodide with Remarkably. Increased Visible-light Absorption and Superior Photocatalytic.
 Oxygen Vacancy Induced Bismuth Oxyiodide with Remarkably Increased Visible-light Absorption and Superior Photocatalytic Performance Yongchao Huang, Haibo Li, Muhammad-Sadeeq Balogun, Wenyue Liu, Yexiang
Oxygen Vacancy Induced Bismuth Oxyiodide with Remarkably Increased Visible-light Absorption and Superior Photocatalytic Performance Yongchao Huang, Haibo Li, Muhammad-Sadeeq Balogun, Wenyue Liu, Yexiang
Nutrient Cycling in Land Vegetation and Soils
 Nutrient Cycling in Land Vegetation and Soils OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 13 September 2012 Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 Outline 1. The annual Intrasystem Nutrient Cycle 2. Mass balance of the
Nutrient Cycling in Land Vegetation and Soils OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 13 September 2012 Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 Outline 1. The annual Intrasystem Nutrient Cycle 2. Mass balance of the
Energy and Resources Recovery from Reverse Osmosis Desalination Concentrate
 Energy and Resources Recovery from Reverse Osmosis Desalination Concentrate Tushar Jain; PhD advisor: Haizhou Liu Department of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Riverside,
Energy and Resources Recovery from Reverse Osmosis Desalination Concentrate Tushar Jain; PhD advisor: Haizhou Liu Department of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Riverside,
* Tsado, P. A. 1, A. O. Osunde 1, C. A. Igwe 2, P.C. Eze 1 and E. Daniya 3
 INFLUENCE OF ORGANIC ACIDS ON PHOSPHATE SORPTION AND AVAILABILITY IN AN ALFISOL OF NIGERIAN GUINEA SAVANNA * Tsado, P. A. 1, A. O. Osunde 1, C. A. Igwe 2, P.C. Eze 1 and E. Daniya 3 1 Department of Soil
INFLUENCE OF ORGANIC ACIDS ON PHOSPHATE SORPTION AND AVAILABILITY IN AN ALFISOL OF NIGERIAN GUINEA SAVANNA * Tsado, P. A. 1, A. O. Osunde 1, C. A. Igwe 2, P.C. Eze 1 and E. Daniya 3 1 Department of Soil
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titanium Dioxide: Modification with Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Xuandong Li,* Meirong Kang, Xijiang Han, Jingyu Wang, and Ping Xu
Supporting Information Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titanium Dioxide: Modification with Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Xuandong Li,* Meirong Kang, Xijiang Han, Jingyu Wang, and Ping Xu
POTASSIUM ADSORPTION CHARACTERISTICS OF FOUR DIFFERENT TEXTURED ALKALINE CALCAREOUS SOILS
 Pak. J. Agri. Sci., Vol. 44(2), 2007 POTASSIUM ADSORPTION CHARACTERISTICS OF FOUR DIFFERENT TEXTURED ALKALINE CALCAREOUS SOILS Abdul Hannan*, A.M. Ranjha**, Rahmatullah**, M. Waqas*** and Abid Niaz****
Pak. J. Agri. Sci., Vol. 44(2), 2007 POTASSIUM ADSORPTION CHARACTERISTICS OF FOUR DIFFERENT TEXTURED ALKALINE CALCAREOUS SOILS Abdul Hannan*, A.M. Ranjha**, Rahmatullah**, M. Waqas*** and Abid Niaz****
Local Deprotonation Enables Cation Exchange, Porosity. Modulation and Tunable Adsorption Selectivity in a. Metal-Organic Framework
 Supporting Information for Local Deprotonation Enables Cation Exchange, Porosity Modulation and Tunable Adsorption Selectivity in a Metal-Organic Framework Jun-Hao Wang,, Dong Luo, Mian Li, and Dan Li
Supporting Information for Local Deprotonation Enables Cation Exchange, Porosity Modulation and Tunable Adsorption Selectivity in a Metal-Organic Framework Jun-Hao Wang,, Dong Luo, Mian Li, and Dan Li
Supporting Information. Metal-Organic Frameworks Mediated Synthesis of One-Dimensional Molybdenum-Based/Carbon Composites for Enhanced Lithium Storage
 Supporting Information Metal-Organic Frameworks Mediated Synthesis of One-Dimensional Molybdenum-Based/Carbon Composites for Enhanced Lithium Storage Wei Tian a, Han Hu b, Yixian Wang a, Peng Li c, Jingyan
Supporting Information Metal-Organic Frameworks Mediated Synthesis of One-Dimensional Molybdenum-Based/Carbon Composites for Enhanced Lithium Storage Wei Tian a, Han Hu b, Yixian Wang a, Peng Li c, Jingyan
DETERMINATION OF THE PHOSPHATE CONTENT ORIGINALLY ADSORBED ON THE SOIL BY FITTING AN ADSORPTION ISOTHERM MODEL
 - 39 - DETERMINATION OF THE PHOSPHATE CONTENT ORIGINALLY ADSORBED ON THE SOIL BY FITTING AN ADSORPTION ISOTHERM MODEL G. FÜLEKY L. TOLNER* Department of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry, University
- 39 - DETERMINATION OF THE PHOSPHATE CONTENT ORIGINALLY ADSORBED ON THE SOIL BY FITTING AN ADSORPTION ISOTHERM MODEL G. FÜLEKY L. TOLNER* Department of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry, University
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information A General Strategy for the Synthesis of Transition-Metal Phosphide/N-doped Carbon Frameworks for Hydrogen and Oxygen Evolution Zonghua Pu, Chengtian Zhang, Ibrahim Saana Amiinu,
Supporting Information A General Strategy for the Synthesis of Transition-Metal Phosphide/N-doped Carbon Frameworks for Hydrogen and Oxygen Evolution Zonghua Pu, Chengtian Zhang, Ibrahim Saana Amiinu,
Carbon Dots Modified Mesoporous Organosilica as an Adsorbent for the. Removal of 2, 4-Dichlorophenol and Heavy Metal Ions
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry
Analysis of China s Haze Days in the Winter Half-Year and the Climatic Background during
 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 5(1): 1-6, 2014 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2014.001 CHANGES IN CLIMATE SYSTEM Analysis of China s Haze Days in the Winter Half-Year and the Climatic
ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 5(1): 1-6, 2014 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2014.001 CHANGES IN CLIMATE SYSTEM Analysis of China s Haze Days in the Winter Half-Year and the Climatic
Experimental Study on NO Removal Using Non-thermal Plasma Oxidation-alkali Absorption
 Experimental Study on NO Removal Using Non-thermal Plasma Oxidation-alkali Absorption Shuilan Ding 1, Qi Yu, Yingzhou Zhang 1, Yuan Liu 1, Chunxue Xie 1, Gang Yu*, 1, 3 1 School of Environment Engineering,
Experimental Study on NO Removal Using Non-thermal Plasma Oxidation-alkali Absorption Shuilan Ding 1, Qi Yu, Yingzhou Zhang 1, Yuan Liu 1, Chunxue Xie 1, Gang Yu*, 1, 3 1 School of Environment Engineering,
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Chemically Stable Ionic Viologen-Organic Network: An Efficient Scavenger
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Chemically Stable Ionic Viologen-Organic Network: An Efficient Scavenger
Study on Delineation of Irrigation Management Zones Based on Management Zone Analyst Software
 Study on Delineation of Irrigation Management Zones Based on Management Zone Analyst Software Qiuxiang Jiang, Qiang Fu, Zilong Wang College of Water Conservancy & Architecture, Northeast Agricultural University,
Study on Delineation of Irrigation Management Zones Based on Management Zone Analyst Software Qiuxiang Jiang, Qiang Fu, Zilong Wang College of Water Conservancy & Architecture, Northeast Agricultural University,
Analysis of flow characteristics of a cam rotor pump
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Analysis of flow characteristics of a cam rotor pump To cite this article: Y Y Liu et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52 032023
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Analysis of flow characteristics of a cam rotor pump To cite this article: Y Y Liu et al 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52 032023
EVALUATION OF NUTRIENT EXTRACTION ABILITY OF COMMONLY EMPLOYED PROCEDURES IN NUTRIENT SORPTION STUDIES
 Indian J. Agric. Res., () : -, 7 EVALUATION OF NUTRIENT EXTRACTION ABILITY OF COMMONLY EMPLOYED PROCEDURES IN NUTRIENT SORPTION STUDIES M.R. Latha and V. Murugappan Office of Dean (Agriculture), Tamil
Indian J. Agric. Res., () : -, 7 EVALUATION OF NUTRIENT EXTRACTION ABILITY OF COMMONLY EMPLOYED PROCEDURES IN NUTRIENT SORPTION STUDIES M.R. Latha and V. Murugappan Office of Dean (Agriculture), Tamil
Effects of phthalic and salicylic acids on Cu(II) adsorption by variable charge soils
 iol Fertil Soils (26) 42: 443 449 DOI.7/s374-6-89-2 ORIGINL PPER Renkou Xu. Shuangcheng Xiao. Dan Xie. Guoliang Ji Effects of phthalic and salicylic acids on Cu(II) adsorption by variable charge soils
iol Fertil Soils (26) 42: 443 449 DOI.7/s374-6-89-2 ORIGINL PPER Renkou Xu. Shuangcheng Xiao. Dan Xie. Guoliang Ji Effects of phthalic and salicylic acids on Cu(II) adsorption by variable charge soils
Effects of Exogenous Melatonin on Photosynthetic Characteristics. of Eggplant Seedlings under Low Temperature and Weak Light Stress
 International Conference on Manufacturing Science and Engineering (ICMSE 2015) Effects of Exogenous Melatonin on Photosynthetic Characteristics of Eggplant Seedlings under Low Temperature and Weak Light
International Conference on Manufacturing Science and Engineering (ICMSE 2015) Effects of Exogenous Melatonin on Photosynthetic Characteristics of Eggplant Seedlings under Low Temperature and Weak Light
Husein Ajwa, Emeritus Department of Plant Sciences UC Davis
 Husein Ajwa, Emeritus Department of Plant Sciences UC Davis HUSEIN AJWA Plant Sciences Department, UC Davis 1636 East Alisal St., Salinas, CA 93905 Office: (831) 755-2823, Fax: (831) 755-2898 email: haajwa@ucdavis.edu
Husein Ajwa, Emeritus Department of Plant Sciences UC Davis HUSEIN AJWA Plant Sciences Department, UC Davis 1636 East Alisal St., Salinas, CA 93905 Office: (831) 755-2823, Fax: (831) 755-2898 email: haajwa@ucdavis.edu
Supporting Information. Phenolic/resin assisted MOFs derived hierarchical Co/N-doping carbon
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Nest-like NiCoP for Highly Efficient Overall Water Splitting Cheng Du, a Lan Yang, a Fulin Yang, a Gongzhen Cheng a and Wei Luo a,b* a College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences,
Supporting Information Nest-like NiCoP for Highly Efficient Overall Water Splitting Cheng Du, a Lan Yang, a Fulin Yang, a Gongzhen Cheng a and Wei Luo a,b* a College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Efficient removal of heavy metal ions with EDTA. functionalized chitosan/polyacrylamide double network
 Supporting Information Efficient removal of heavy metal ions with EDTA functionalized chitosan/polyacrylamide double network hydrogel Jianhong Ma a,b, Guiyin Zhou c, Lin Chu c, Yutang Liu a,b, *, Chengbin
Supporting Information Efficient removal of heavy metal ions with EDTA functionalized chitosan/polyacrylamide double network hydrogel Jianhong Ma a,b, Guiyin Zhou c, Lin Chu c, Yutang Liu a,b, *, Chengbin
enzymatic cascade system
 Electronic Supplementary Information Fe 3 O 4 -Au@mesoporous SiO 2 microsphere: an ideal artificial enzymatic cascade system Xiaolong He, a,c Longfei Tan, a Dong Chen,* b Xiaoli Wu, a,c Xiangling Ren,
Electronic Supplementary Information Fe 3 O 4 -Au@mesoporous SiO 2 microsphere: an ideal artificial enzymatic cascade system Xiaolong He, a,c Longfei Tan, a Dong Chen,* b Xiaoli Wu, a,c Xiangling Ren,
List of Equipment, Tools, Supplies, and Facilities:
 Unit D: ph of Soil Lesson 2: Identifying ph Connection With Plant Growth Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in the students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Unit D: ph of Soil Lesson 2: Identifying ph Connection With Plant Growth Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in the students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Supplementary Material
 10.1071/CH18138_AC CSIRO 2018 Australian Journal of Chemistry Supplementary Material Efficient hydrolytic breakage of β 1,4 glycosidic bond catalyzed by a difunctional magnetic nano catalyst Ren-Qiang
10.1071/CH18138_AC CSIRO 2018 Australian Journal of Chemistry Supplementary Material Efficient hydrolytic breakage of β 1,4 glycosidic bond catalyzed by a difunctional magnetic nano catalyst Ren-Qiang
Numerical investigation of solid-liquid two phase flow in a non-clogging centrifugal pump at offdesign
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Numerical investigation of solid-liquid two phase flow in a non-clogging centrifugal pump at offdesign conditions To cite this article: B J Zhao et
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Numerical investigation of solid-liquid two phase flow in a non-clogging centrifugal pump at offdesign conditions To cite this article: B J Zhao et
Supporting material. Figures
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 Supporting material Figures
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 Supporting material Figures
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Supporting Information Atomically dispersed Ni as the active site towards selective hydrogenation
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 Supporting Information Atomically dispersed Ni as the active site towards selective hydrogenation
Variations of snow cover in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers in China between 1960 and 1999
 420 Journal of Glaciology, Vol. 53, No. 182, 2007 Variations of snow cover in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers in China between 1960 and 1999 YANG Jianping, DING Yongjian, LIU Shiyin,
420 Journal of Glaciology, Vol. 53, No. 182, 2007 Variations of snow cover in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers in China between 1960 and 1999 YANG Jianping, DING Yongjian, LIU Shiyin,
Optimization of flue gas turbulent heat transfer with condensation in a tube
 Article Calorifics July 011 Vol.56 No.19: 1978 1984 doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4533-9 SPECIAL TOPICS: Optimization of flue gas turbulent heat transfer with condensation in a tube SONG WeiMing, MENG JiAn &
Article Calorifics July 011 Vol.56 No.19: 1978 1984 doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4533-9 SPECIAL TOPICS: Optimization of flue gas turbulent heat transfer with condensation in a tube SONG WeiMing, MENG JiAn &
Kaolinite Enhances the Stability of the Dissolvable and Undissolvable Fractions
 1 Supporting Information 2 3 4 Kaolinite Enhances the Stability of the Dissolvable and Undissolvable Fractions of Biochar via Different Mechanisms 5 6 7 Fan Yang a, b, Zibo Xu a, Lu Yu a, Bin Gao c, a,
1 Supporting Information 2 3 4 Kaolinite Enhances the Stability of the Dissolvable and Undissolvable Fractions of Biochar via Different Mechanisms 5 6 7 Fan Yang a, b, Zibo Xu a, Lu Yu a, Bin Gao c, a,
Graphene Sponge for Efficient and Repeatable Adsorption and Desorption of. Water Contaminations
 Supporting Information for Graphene Sponge for Efficient and Repeatable Adsorption and Desorption of Water Contaminations Jinping Zhao, Wencai Ren* and Hui-Ming Cheng Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials
Supporting Information for Graphene Sponge for Efficient and Repeatable Adsorption and Desorption of Water Contaminations Jinping Zhao, Wencai Ren* and Hui-Ming Cheng Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials
Supporting Information. Electronic Modulation of Electrocatalytically Active. Highly Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction
 Supporting Information Electronic Modulation of Electrocatalytically Active Center of Cu 7 S 4 Nanodisks by Cobalt-Doping for Highly Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction Qun Li, Xianfu Wang*, Kai Tang,
Supporting Information Electronic Modulation of Electrocatalytically Active Center of Cu 7 S 4 Nanodisks by Cobalt-Doping for Highly Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction Qun Li, Xianfu Wang*, Kai Tang,
Identification of Rhizosphere Abiotic Stress Tolerance and Related Root Traits in Soybean [ Glycine max ( L. ) Merr. ]
![Identification of Rhizosphere Abiotic Stress Tolerance and Related Root Traits in Soybean [ Glycine max ( L. ) Merr. ] Identification of Rhizosphere Abiotic Stress Tolerance and Related Root Traits in Soybean [ Glycine max ( L. ) Merr. ]](/thumbs/91/105886481.jpg) 31 9 2005 9 1132 1137 ACTA AGRONOMICA SINICA Vol131, No19 pp1 1132-1137 Sept1, 2005 1,2 1, 3 1 Ξ ( 1,, 210095 2, 056038) : 301 62,,, P 1 4 6 2, 7 3 3, : : S565 Identification of Rhizosphere Abiotic Stress
31 9 2005 9 1132 1137 ACTA AGRONOMICA SINICA Vol131, No19 pp1 1132-1137 Sept1, 2005 1,2 1, 3 1 Ξ ( 1,, 210095 2, 056038) : 301 62,,, P 1 4 6 2, 7 3 3, : : S565 Identification of Rhizosphere Abiotic Stress
An Novel Continuation Power Flow Method Based on Line Voltage Stability Index
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS An Novel Continuation Power Flow Method Based on Line Voltage Stability Index To cite this article: Jianfang Zhou et al 2018 IOP
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS An Novel Continuation Power Flow Method Based on Line Voltage Stability Index To cite this article: Jianfang Zhou et al 2018 IOP
Laterite and modified laterite as efficient arsenic adsorbents
 Laterite and modified laterite as efficient arsenic adsorbents Yoann Glocheux Dr. Gavin Walker Pr. Stephen Allen ATWARM meeting 01/05/12, Cranfield University, Cranfield Plan Introduction Material presentation
Laterite and modified laterite as efficient arsenic adsorbents Yoann Glocheux Dr. Gavin Walker Pr. Stephen Allen ATWARM meeting 01/05/12, Cranfield University, Cranfield Plan Introduction Material presentation
The regional distribution characteristics of aerosol optical depth over the Tibetan Plateau
 The regional distribution characteristics of aerosol optical depth over the Tibetan Plateau C. Xu, Y. M. Ma, CAS Center for Excellence in Tibetan Plateau Earth Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences xuchao@itpcas.ac.cn
The regional distribution characteristics of aerosol optical depth over the Tibetan Plateau C. Xu, Y. M. Ma, CAS Center for Excellence in Tibetan Plateau Earth Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences xuchao@itpcas.ac.cn
