ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH AROMATICITY.
|
|
|
- Damon Sullivan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 !!
2 CONCEPT: AROMATICTY INTRODUCTION Aromatic compounds display an unusual stability for their high level of electron density. Their high level of unsaturation should make them extremely reactive, however they are difficult to react with. EXAMPLE: Three typical addition reactions with cyclohexene vs. benzene What is responsible for this crazy level of stability? Categories of Aromatics: : These compounds possess an unusually level of stability : These compounds do not possess any unique level of stability or instability : These compounds possess an unusually level of stability. Very reactive! EXAMPLE: Differing aromaticity of conjugated trienes Page 2
3 CONCEPT: FOUR TESTS OF AROMATICTY For a compound to qualify as aromatic, it must meet 4 distinct tests. These are called Huckel s Rule compounds. 1. Cyclic: 2. Fully Conjugated: 3. Planar: 4. Huckel s Rule: (4n + 2) number of π electrons Any compound that one or more of these tests is considered Any compound that meets all these conditions, but only has (4n) π electrons is These compounds are said to follow Breslow s Rule Page 3
4 CONCEPT: COUNTING PI ELECTRONS When counting π-electrons, we are trying to identify the number of electrons that are freely available to circulate through conjugated p-orbitals. Double Bond/Anion = Radical = Cation = EXAMPLE: Count the number of π-electrons present in all of these molecules: Page 4
5 CONCEPT: AROMATICITY OF HYDROCARBONS We can use our knowledge of the Four Tests of Aromaticity to confirm aromaticity Huckel s Rule = Aromatic (4n + 2) π electron numbers:,,,, etc. Breslow s Rule = Anti-aromatic (4n) π electron numbers:,,,, etc. Non-aromatic = FAILS one or more test (including odd number of π electrons) EXAMPLE: Determine the aromaticity of the following molecules Page 5
6 CONCEPT: AROMATICTY OF ANNULENES An annulene, sometimes referred to as a polyolefin, is the name given to a fully conjugated monocyclic hydrocarbon. Due to their simple structure, rings of different sizes can be named as [n]annulenes, where n = number of carbons As annulenes get bigger, the challenge becomes predicting planarity. Predicting Annulene Planarity: Pertaining to All-cis annulenes, EXAMPLE: Cyclooctatetrene vs. Cyclooctatetraene dianion If 4n + 2 π electrons 10+ = Non-aromatic 9 or less = Aromatic If 4n π electrons 8+ = Non-aromatic 7 or less = Antiaromatic EXAMPLE: Determine if the following annulenes display any form of aromaticity. Page 6
7 CONCEPT: AROMATICITY OF HETEROCYCLES Heterocycles are cyclic structures that contain a within the ring. Heteroatoms can choose to donate up to one lone pair each only if: 1. They are already sp 3 hybridized 2. It will help to create aromaticity EXAMPLE: Determine the aromaticity of the following heterocycles. Will any lone pairs be donated to the ring? Page 7
8 CONCEPT: INSCRIBED POLYGON METHOD Also known as the polygon-in-circle method, or Frost Circle, this helps us visualize the identities of π electrons and molecular orbitals in a ring. EXAMPLE: Use the polygon-in-circle method to predict stability of the following molecules. Step 1: Draw polygon with one corner facing down. Step 2: Draw molecular orbitals on all corners of ring Step 3: Draw a line that splits the polygon down the middle Step 4: Insert π electrons into orbitals starting from lowest energy and working up (Aufbau Principle). Filled molecular orbitals contribute to unique stability (aromaticity) Partially filled molecular orbitals contribute to unique instability (antiaromaticity) Page 8
9 PRACTICE: Apply the polygon circle method to the following compound. Does it show any special stability? If yes, why? Tropyllium cation Page 9
10 CONCEPT: BENZENE NOMENCLATURE Benzene was one of the first organic molecules to be identified (1825), so common names predominate. Common Benzene Derivatives: Monosubstituted Benzene: Disubstituted Benzene: Multisubstituted Benzene: No location necessary No numerical locations Numerical locations necessary 1,2 = (o-) Do not use -o, -m, -p 1,3 = (m-) 1,4 = (p-) Page 10
11 EXAMPLE: Correctly name the following benzene derivatives Page 11
12 CONCEPT: ACIDITY OF AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS Aromatic hydrocarbons are not naturally acidic. In fact, the pka of benzene is If a hydrocarbon can become aromatic by donating a proton, it will be uniquely acidic. i.e. cyclopentadiene If a hydrocarbon becomes anitaromatic by donating a proton, it will be uniquely non-acidic. i.e. cycloheptatriene EXAMPLE: Would the following hydrocarbon be expected to display unusual acidity? Explain your reasoning. EXAMPLE: Would the following two hydrocarbons be expected to have similar acidities? Explain your reasoning. Page 12
13 CONCEPT: BASICITY OF AROMATIC HETEROCYCLES Heterocycles often have multiple lone pairs available to react with acids. The question is which lone pair do we react? EXAMPLE: Draw the product of the following acid/base reaction with imidazole. Acids can only react with lone pairs that are not necessary for aromaticity. sp 2 -hybridized lone pairs are basic. EXAMPLE: Draw the product of the following acid/base reaction. Page 13
14 CONCEPT: IONIZATION OF AROMATICS Double bonds can be viewed as a loose pair of electrons that can undergo resonance movement and ionization if that helps to create an aromatic compound. Resonance of Fulvalenes: Fulvalenes are hydrocarbons composed of two fully conjugated rings joined by an exocyclic double bond. Which atom would you expect to most readily react with an electrophile (E + )? Does this molecule possess a net dipole? If so, indicate the direction. Resonance of Azulene: Azulene is a polycyclic aromatic molecule with a distinctive blue color.. Which atom would you expect to most readily react with an electrophile (E + )? Does this molecule possess a net dipole? If so, indicate the direction. Page 14
15 PRACTICE: Which carbon in the following compound is most likely to react with an electrophile? CH 2 (heptafulvene) Page 15
12/27/2010. Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds
 Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives Benzene is the parent name for some monosubstituted benzenes; the substituent name is added as a prefix Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds For other monosubstituted benzenes,
Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives Benzene is the parent name for some monosubstituted benzenes; the substituent name is added as a prefix Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds For other monosubstituted benzenes,
Benzene and Aromaticity
 Benzene and Aromaticity Why this Chapter? Reactivity of substituted aromatic compounds is tied to their structure Aromatic compounds provide a sensitive probe for studying relationship between structure
Benzene and Aromaticity Why this Chapter? Reactivity of substituted aromatic compounds is tied to their structure Aromatic compounds provide a sensitive probe for studying relationship between structure
Benzene a remarkable compound. Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds. Some proposed structures for C 6 H 6. Dimethyl substituted benzenes are called xylenes
 Benzene a remarkable compound Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds Discovered by Faraday 1825 Formula C 6 H 6 Highly unsaturated, but remarkably stable Whole new class of benzene derivatives called aromatic compounds
Benzene a remarkable compound Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds Discovered by Faraday 1825 Formula C 6 H 6 Highly unsaturated, but remarkably stable Whole new class of benzene derivatives called aromatic compounds
Aromatic Compounds I
 2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 1 Aromatic Compounds I Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 16 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 1 Aromatic Compounds I Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 16 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
Organic Chemistry, 7 L. G. Wade, Jr. 2010, Prentice Hall
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized
Organic Chemistry. Second Edition. Chapter 18 Aromatic Compounds. David Klein. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e
 Organic Chemistry Second Edition David Klein Chapter 18 Aromatic Compounds Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e 18.1 Introduction to Aromatic Compounds
Organic Chemistry Second Edition David Klein Chapter 18 Aromatic Compounds Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e 18.1 Introduction to Aromatic Compounds
Lecture 10. More Aromatics. February 15, Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 10 More Aromatics February 15, 2018 ückel's Rule for Aromaticity To be Aromatic a compound must : 1. be Cyclic 2. have one P orbital on each atom in the ring 3. be planar or nearly so to give orbital
Lecture 10 More Aromatics February 15, 2018 ückel's Rule for Aromaticity To be Aromatic a compound must : 1. be Cyclic 2. have one P orbital on each atom in the ring 3. be planar or nearly so to give orbital
17.24 To name the compounds use the directions from Answer 17.3.
 Benzene and Aromatic Compounds 7 7 7.2 If benzene could be described by a single Kekulé structure, only one product would form in Reaction [], but there would be four (not three) dibromobenzenes (A ),
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds 7 7 7.2 If benzene could be described by a single Kekulé structure, only one product would form in Reaction [], but there would be four (not three) dibromobenzenes (A ),
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds
 1 Background Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas
1 Background Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas
240 Chem. Aromatic Compounds. Chapter 6
 240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
Chapter 18: Aromatic Compounds
 hapter 18: Aromatic ompounds [Sections: 18.1, 18.3-18.5, 18.8] The Structure of Benzene skeletal condensed 1800's sausage 3 2 2 3 3 3 3 Friedrich August Kekule 1829-1896 Kekule's Dream 6 6 Kekule wakes
hapter 18: Aromatic ompounds [Sections: 18.1, 18.3-18.5, 18.8] The Structure of Benzene skeletal condensed 1800's sausage 3 2 2 3 3 3 3 Friedrich August Kekule 1829-1896 Kekule's Dream 6 6 Kekule wakes
Chapter 16. Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to
Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to
Benzene and aromaticity
 aromaticity The word "benzene" derives historically from "gum benzoin", sometimes called "benjamin" (i.e., benzoin resin), an aromatic resin known to European pharmacists and perfumers since the 15th century
aromaticity The word "benzene" derives historically from "gum benzoin", sometimes called "benjamin" (i.e., benzoin resin), an aromatic resin known to European pharmacists and perfumers since the 15th century
Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds. Discovery of Benzene
 Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C: ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to
Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C: ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to
Frost Circles a Great Trick
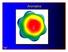 Aromatics Frost Circles a Great Trick Inscribe a polygon of the same number of sides as the ring to be examined such that one of the vertices is at the bottom of the ring The relative energies of the MOs
Aromatics Frost Circles a Great Trick Inscribe a polygon of the same number of sides as the ring to be examined such that one of the vertices is at the bottom of the ring The relative energies of the MOs
Chapter 15 Benzene and Aromaticity
 Chapter 15 Benzene and Aromaticity Aromatic Compounds Aromatic Originally used to describe fragrant substances Refers to a class of compounds that meets Hückel criteria for aromaticity 2 Aromatic Compounds
Chapter 15 Benzene and Aromaticity Aromatic Compounds Aromatic Originally used to describe fragrant substances Refers to a class of compounds that meets Hückel criteria for aromaticity 2 Aromatic Compounds
18.1 Intro to Aromatic Compounds
 18.1 Intro to Aromatic Compounds AROMATIC compounds or ARENES include benzene and benzene derivatives. Aromatic compounds are quite common. Many aromatic compounds were originally isolated from fragrant
18.1 Intro to Aromatic Compounds AROMATIC compounds or ARENES include benzene and benzene derivatives. Aromatic compounds are quite common. Many aromatic compounds were originally isolated from fragrant
Aromatic Compounds. A number of these compounds had a distinct odor. Hence these compounds were called aromatic
 Aromatic Compounds Early in the history of organic chemistry (late 18 th, early 19 th century) chemists discovered a class of compounds which were unusually stable A number of these compounds had a distinct
Aromatic Compounds Early in the history of organic chemistry (late 18 th, early 19 th century) chemists discovered a class of compounds which were unusually stable A number of these compounds had a distinct
2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes
 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Reactions of Isolated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The Mechanism Double Bonds can have Different Reactivities
2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Reactions of Isolated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The Mechanism Double Bonds can have Different Reactivities
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURES Dr Ali El-Agamey. Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr.
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURES 11-12 Dr Ali El-Agamey Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Amines 2010, Prentice Hall Reactions N,N-Disubstituted amides 2 o amine
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURES 11-12 Dr Ali El-Agamey Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Amines 2010, Prentice Hall Reactions N,N-Disubstituted amides 2 o amine
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds. Chapter 15 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry
 Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Chapter 15 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Background Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Four degrees of unsaturation. It
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Chapter 15 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Background Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Four degrees of unsaturation. It
Reaction mechanisms offer us insights into how reactions work / how molecules react with one another.
 Introduction 1) Lewis Structures 2) Representing Organic Structures 3) Geometry and Hybridization 4) Electronegativities and Dipoles 5) Resonance Structures (a) Drawing Them (b) Rules for Resonance 6)
Introduction 1) Lewis Structures 2) Representing Organic Structures 3) Geometry and Hybridization 4) Electronegativities and Dipoles 5) Resonance Structures (a) Drawing Them (b) Rules for Resonance 6)
Loudon Chapter 15 Review: Dienes and Aromaticity Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 1/28/2019
 This chapter looks at the behavior of carbon-carbon double bonds when several of them are in the same molecule. There are several possible ways they can be grouped. Conjugated dienes have a continuous
This chapter looks at the behavior of carbon-carbon double bonds when several of them are in the same molecule. There are several possible ways they can be grouped. Conjugated dienes have a continuous
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 3. AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS Aromatic
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 3. AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS Aromatic
PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY EXAM #1 Februrary 21, 2008
 PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY EXAM #1 Februrary 21, 2008 1 Name SECTION B. Answer each question in this section by writing the letter corresponding to the best answer on the line provided (2 points each; 60
PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY EXAM #1 Februrary 21, 2008 1 Name SECTION B. Answer each question in this section by writing the letter corresponding to the best answer on the line provided (2 points each; 60
Treatment of cyclooctatetrene with potassium gives you a dianion. Classify the starting material and product as aromatic, antiaromatic or
 Treatment of cyclooctatetrene with potassium gives you a dianion. Classify the starting material and product as aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic? 1 2 Classify cyclononatetrene and it s various ions
Treatment of cyclooctatetrene with potassium gives you a dianion. Classify the starting material and product as aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic? 1 2 Classify cyclononatetrene and it s various ions
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH. 3 - ACIDS AND BASES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS There are 4 types of common chemical reactions that we need to be familiar with in organic chemistry 1. Acid-Base Reactions: Two molecules
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS There are 4 types of common chemical reactions that we need to be familiar with in organic chemistry 1. Acid-Base Reactions: Two molecules
3) The delocalized π system in benzene is formed by a cyclic overlap of 6 orbitals. A) s B) p C) sp D) sp2 E) sp3
 Chapter 8 Questions 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? A) All of the carbon atoms are sp hybridized. B) It has delocalized electrons. C) The carbon-carbon bond lengths are
Chapter 8 Questions 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? A) All of the carbon atoms are sp hybridized. B) It has delocalized electrons. C) The carbon-carbon bond lengths are
Naming Aromatic Compounds (Benzene as the Parent)
 aming Aromatic Compounds (Benzene as the Parent) If the the alkyl chain is smaller than the ring use the ring as the parent Monosubstituted benzenes are named the same way as other hydrocarbons using benzene
aming Aromatic Compounds (Benzene as the Parent) If the the alkyl chain is smaller than the ring use the ring as the parent Monosubstituted benzenes are named the same way as other hydrocarbons using benzene
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH.4 - ACIDS AND BASES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS Atoms save energy by forming bonds. Free energy diagrams show overall changes in potential energy during reactions. Free energy diagrams give us information
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS Atoms save energy by forming bonds. Free energy diagrams show overall changes in potential energy during reactions. Free energy diagrams give us information
Chapter Tell whether the following compounds are ortho-, meta-, or para-disubstituted: (a) M-chlorotoluene (b) NO 2
 Chapter 15 15.1 Tell whether the following compounds are ortho-, meta-, or para-disubstituted: (a) Cl C 3 M-chlorotoluene (b) 2 P-bromonitrobenzene (c) S 3 -hydroxybenzenesulfonid acid 15.2 Give IUPAC
Chapter 15 15.1 Tell whether the following compounds are ortho-, meta-, or para-disubstituted: (a) Cl C 3 M-chlorotoluene (b) 2 P-bromonitrobenzene (c) S 3 -hydroxybenzenesulfonid acid 15.2 Give IUPAC
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes
 Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Chapter 15: Benzene & Aromaticity
 Chapter 15: Benzene & Aromaticity Learning Objective & Key Concepts 1. Sources and nomenclature of aromatic compounds. 2. Introduction to Huckel 4n+2 rule and aromaticity stability and reactivity, 3. Introduction
Chapter 15: Benzene & Aromaticity Learning Objective & Key Concepts 1. Sources and nomenclature of aromatic compounds. 2. Introduction to Huckel 4n+2 rule and aromaticity stability and reactivity, 3. Introduction
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
5. (6 pts) Show how the following compound can be synthesized from the indicated starting material:
 Exam 2 Name CHEM 212 1. (36 pts) Complete the following chemical reactions showing all major organic products; illustrate proper stereochemistry where appropriate. If no reaction occurs, indicate NR :
Exam 2 Name CHEM 212 1. (36 pts) Complete the following chemical reactions showing all major organic products; illustrate proper stereochemistry where appropriate. If no reaction occurs, indicate NR :
Solutions a) 4-bromo-2-methylphenol b) 2-hydroxy-5-bromotoluene c) 4-bromo-1-hydroxy-2-methylbenzene OMe OH
 CAPTER 18 413 R R Solutions 18.1. 3-isopropylbenzaldehyde or meta-isopropylbenzaldehyde 2-bromotoluene or ortho-bromotoluene c) 2,4-dinitrophenol d) 2-ethyl-1,4-diisopropylbenzene f) 2,6-dibromo-4-chloro-3-ethyl-5-isopropylphenol
CAPTER 18 413 R R Solutions 18.1. 3-isopropylbenzaldehyde or meta-isopropylbenzaldehyde 2-bromotoluene or ortho-bromotoluene c) 2,4-dinitrophenol d) 2-ethyl-1,4-diisopropylbenzene f) 2,6-dibromo-4-chloro-3-ethyl-5-isopropylphenol
Chemistry 204: Benzene and Aromaticity
 Chemistry 204: Benzene and Aromaticity Structure of and Bonding in Benzene benzene, C 6 H 6, was first isolated in 1825 (Michael Faraday), but it was not until more than 100 years later that an adequate
Chemistry 204: Benzene and Aromaticity Structure of and Bonding in Benzene benzene, C 6 H 6, was first isolated in 1825 (Michael Faraday), but it was not until more than 100 years later that an adequate
CHEMISTRY Topic #3: Addition Reactions of Conjugated Dienes Spring 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay
 CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #3: Addition Reactions of Conjugated Dienes Spring 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay Different Kinds of Dienes When a molecule contains multiple π-bonds, their reactivity is dictated in part by
CEMISTRY 2600 Topic #3: Addition Reactions of Conjugated Dienes Spring 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay Different Kinds of Dienes When a molecule contains multiple π-bonds, their reactivity is dictated in part by
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number CHM 235 (SUN# CHM 2235) Title General Organic Chemistry I Credits 4 Developed
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number CHM 235 (SUN# CHM 2235) Title General Organic Chemistry I Credits 4 Developed
16.4 Cyclobutadiene. .. H c)
 16.4 CYCLOBUTADIEE 649 arranged about zero energy, it is necessary for one degenerate pair, 4 nb and 5 nb, to be located at zero energy. MOs at zero energy are termed nonbonding.) If the total number of
16.4 CYCLOBUTADIEE 649 arranged about zero energy, it is necessary for one degenerate pair, 4 nb and 5 nb, to be located at zero energy. MOs at zero energy are termed nonbonding.) If the total number of
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES.
 COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH. 1 - A REVIEW OF GENERAL CHEMISTRY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: WHAT IS ORGANIC CHEMISTRY? Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of life. It consists of the study of molecules that are (typically) created and used by biological systems.
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: WHAT IS ORGANIC CHEMISTRY? Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of life. It consists of the study of molecules that are (typically) created and used by biological systems.
CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling
 CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling The Use of Computational Chemistry to Support Experimental Organic Chemistry Day 1 all calculation data obtained from Gaussian09 using B3LYP/6-31G(d) unless otherwise noted.
CHEM 344 Molecular Modeling The Use of Computational Chemistry to Support Experimental Organic Chemistry Day 1 all calculation data obtained from Gaussian09 using B3LYP/6-31G(d) unless otherwise noted.
Exam (6 pts) Show which starting materials are used to produce the following Diels-Alder products:
 Exam 1 Name CHEM 212 1. (18 pts) Complete the following chemical reactions showing all major organic products; illustrate proper stereochemistry where appropriate. If no reaction occurs, indicate NR :
Exam 1 Name CHEM 212 1. (18 pts) Complete the following chemical reactions showing all major organic products; illustrate proper stereochemistry where appropriate. If no reaction occurs, indicate NR :
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction - Conjugated unsaturated systems
Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds. Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde
 Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde Sources of Benzene Benzene, C 6 H 6, is the parent hydrocarbon of the especially stable compounds known
Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde Sources of Benzene Benzene, C 6 H 6, is the parent hydrocarbon of the especially stable compounds known
4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY
 4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY During the early 1800's, a group of compounds of natural origin became collectively known as aromatic compounds. As several of these compounds
4 - BENZENE: AROMATICITY, CONJUGATION AND ASSOCIATED REACTIVITY During the early 1800's, a group of compounds of natural origin became collectively known as aromatic compounds. As several of these compounds
12.1 AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 12 Arenes and Aromaticity estradiol 12.1 AROMATIC COMPOUNDS O O O O C 3 C 3 O O safrole (oil of sassafras) O methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen) O vanillin (vanilla) C 3 N C 3 C 3 CC 2 ibuprofen C C
12 Arenes and Aromaticity estradiol 12.1 AROMATIC COMPOUNDS O O O O C 3 C 3 O O safrole (oil of sassafras) O methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen) O vanillin (vanilla) C 3 N C 3 C 3 CC 2 ibuprofen C C
Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity
 Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity Solutions to In-Text Problems 15.2 The delocalization energy is the energy
Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity Solutions to In-Text Problems 15.2 The delocalization energy is the energy
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 Introduction to rganic hemistry 59 Introduction to rganic hemistry andout 3 - chanism u u http://burton.chem.ox.ac.uk/teaching.html rganic hemistry J. layden,. Greeves, S. Warren Stereochemistry at a Glance
Introduction to rganic hemistry 59 Introduction to rganic hemistry andout 3 - chanism u u http://burton.chem.ox.ac.uk/teaching.html rganic hemistry J. layden,. Greeves, S. Warren Stereochemistry at a Glance
ZAHID IQBAL WARRAICH
 Q1 (a) State the reagents and conditions needed to convert benzene into (i) chlorobenzene, (ii) bromobenzene, (iii) nitrobenzene....[4] (b) The nitration of benzene is a two-step reaction that can be represented
Q1 (a) State the reagents and conditions needed to convert benzene into (i) chlorobenzene, (ii) bromobenzene, (iii) nitrobenzene....[4] (b) The nitration of benzene is a two-step reaction that can be represented
Exam. Name. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? 1) A) All of the carbon
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? 1) A) All of the carbon
CHEM Aromatic Chemistry. LECTURE 1 - Aromaticity
 1 CHEM40003 Aromatic Chemistry LECTURE 1 - Aromaticity Alan C. Spivey a.c.spivey@imperial.ac.uk May 2018 2 Format and scope of presentation Aromaticity: Historical perspective (Kekulé) Characteristics,
1 CHEM40003 Aromatic Chemistry LECTURE 1 - Aromaticity Alan C. Spivey a.c.spivey@imperial.ac.uk May 2018 2 Format and scope of presentation Aromaticity: Historical perspective (Kekulé) Characteristics,
CHEM 303 Organic Chemistry II Problem Set II Chapter 13 Answers
 CEM 303 rganic Chemistry II Problem Set II Chapter 13 Answers 1) Explain the reason for the different chemical reactivity of cyclopentadiene and cycloheptatriene toward bromine. 2 + 2 + oth no doubt start
CEM 303 rganic Chemistry II Problem Set II Chapter 13 Answers 1) Explain the reason for the different chemical reactivity of cyclopentadiene and cycloheptatriene toward bromine. 2 + 2 + oth no doubt start
More Nomenclature: Common Names for Selected Aromatic Groups. Aryl = Ar = aromatic group. It is a broad term, and includes any aromatic rings.
 More Nomenclature: Common Names for Selected Aromatic Groups Phenyl group = or Ph = C 6 H 5 = Aryl = Ar = aromatic group. It is a broad term, and includes any aromatic rings. Benzyl = Bn = It has a -CH
More Nomenclature: Common Names for Selected Aromatic Groups Phenyl group = or Ph = C 6 H 5 = Aryl = Ar = aromatic group. It is a broad term, and includes any aromatic rings. Benzyl = Bn = It has a -CH
11/5/ Conjugated Dienes. Conjugated Dienes. Conjugated Dienes. Heats of Hydrogenation
 8.12 Sites of unsaturation Many compounds have numerous sites of unsaturation If sites are well separated in molecule they react independently If sites are close together they may interact with one another
8.12 Sites of unsaturation Many compounds have numerous sites of unsaturation If sites are well separated in molecule they react independently If sites are close together they may interact with one another
Module III: Aromatic Hydrocarbons (6 hrs)
 Module III: Aromatic Hydrocarbons (6 hrs) Nomenclature and isomerism in substituted benzene. Structure and stability of benzene: Kekule, resonance and molecular orbital description. Mechanism of aromatic
Module III: Aromatic Hydrocarbons (6 hrs) Nomenclature and isomerism in substituted benzene. Structure and stability of benzene: Kekule, resonance and molecular orbital description. Mechanism of aromatic
Resonance and M.O. View of Butadiene. Super-Conjugated or Aromatic p e - Systems
 Resonance and M.. View of Butadiene The different resonance forms of butadiene suggest p bonding character between the two central carbon atoms. 2 2 2 2 carbanion 2 2 carbocation The M.. view of butadiene
Resonance and M.. View of Butadiene The different resonance forms of butadiene suggest p bonding character between the two central carbon atoms. 2 2 2 2 carbanion 2 2 carbocation The M.. view of butadiene
Solution problem 22: Non-Benzoid Aromatic Sytems
 Solution problem 22: on-enzoid Aromatic Sytems 22.1 & 22.2 Each double bond and each heteroatom (, ) with lone pairs donates 2 π- electrons as well as a negative charge. oron or a positive charge does
Solution problem 22: on-enzoid Aromatic Sytems 22.1 & 22.2 Each double bond and each heteroatom (, ) with lone pairs donates 2 π- electrons as well as a negative charge. oron or a positive charge does
Acids and Bases. Acids and Bases
 BrØnsted-Lowry A BrØnsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor. A BrØnsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. H + = proton BrØnsted-Lowry Some molecules contain both hydrogen atoms and lone pairs and thus, can act
BrØnsted-Lowry A BrØnsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor. A BrØnsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. H + = proton BrØnsted-Lowry Some molecules contain both hydrogen atoms and lone pairs and thus, can act
Class XI Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Chemistry
 Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
NO 2 O NH 2. Br Br. Br CF 3
 1. Rank the following compounds in the trend requested. (15 points each) a. Rank by energy of the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUM). The molecule with the LUM that is lowest in energy is 1, while
1. Rank the following compounds in the trend requested. (15 points each) a. Rank by energy of the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUM). The molecule with the LUM that is lowest in energy is 1, while
Chapter 13. Conjugated Unsaturated Systems. +,., - Allyl. What is a conjugated system? AllylicChlorination (High Temperature)
 What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy
 Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Introduction to Aromaticity
 Introduction to Aromaticity Historical Timeline: 1 Spotlight on Benzene: 2 Early 19 th century chemists derive benzene formula (C 6 H 6 ) and molecular mass (78). Carbon to hydrogen ratio of 1:1 suggests
Introduction to Aromaticity Historical Timeline: 1 Spotlight on Benzene: 2 Early 19 th century chemists derive benzene formula (C 6 H 6 ) and molecular mass (78). Carbon to hydrogen ratio of 1:1 suggests
Aromatic Substitution Chemistry (Part of Chapter 2 and Chapter 11)
 Aromatic Substitution hemistry (Part of hapter 2 and hapter 11) Aliphatic ompounds: Aromatic ompounds: pentane 2-pentene 2-pentyne Aromatic compounds have closed loops of electrons that give rise to an
Aromatic Substitution hemistry (Part of hapter 2 and hapter 11) Aliphatic ompounds: Aromatic ompounds: pentane 2-pentene 2-pentyne Aromatic compounds have closed loops of electrons that give rise to an
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King I. Conjugation
 Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry and UV Spectroscopy Introduction There are several possible arrangements for a molecule which contains two double bonds (diene): Isolated: (two or more single bonds
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH.1 - COVALENT BONDING AND SHAPES OF MOLECULES
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: WHAT IS ORGANIC CHEMISTRY? Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of life. It consists of the study of molecules that are (typically) created and used by biological systems.
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: WHAT IS ORGANIC CHEMISTRY? Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of life. It consists of the study of molecules that are (typically) created and used by biological systems.
Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds. Alkenes C=C double bonds Alkynes triple bonds Aromatics benzene rings 1 2 NAMING ALKENES Step 1: Name
Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds. Alkenes C=C double bonds Alkynes triple bonds Aromatics benzene rings 1 2 NAMING ALKENES Step 1: Name
Chapter 15: Reactions of Substituted Benzenes
 Learning Objectives: Chapter 15: Reactions of Substituted Benzenes 1. Be able to recognize and utilize the oxidative and reductive reactions involving the substituents on benzene. 2. Recognize whether
Learning Objectives: Chapter 15: Reactions of Substituted Benzenes 1. Be able to recognize and utilize the oxidative and reductive reactions involving the substituents on benzene. 2. Recognize whether
SIX MEMBERED AROMATIC HETEROCYCLES
 SIX MEMBERED AROMATIC HETEROCYCLES Ṇ. Pyridine Pyridine is aromatic as there are six delocalized electrons in the ring. Six-membered heterocycles are more closely related to benzene as they are aromatic
SIX MEMBERED AROMATIC HETEROCYCLES Ṇ. Pyridine Pyridine is aromatic as there are six delocalized electrons in the ring. Six-membered heterocycles are more closely related to benzene as they are aromatic
PAPER No. 5:Organic Chemistry-2(Reaction Mechanism-1) MODULE No. 6: Generation, Structure, Stability and Reactivity of Carbocations
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5: Organic Chemistry-II (Reaction Mechanism-1) Generation, Structure, Stability and Reactivity of Carbocations CHE_P5_M6 TABLE
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5: Organic Chemistry-II (Reaction Mechanism-1) Generation, Structure, Stability and Reactivity of Carbocations CHE_P5_M6 TABLE
BENZENE & AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BENZENE & AROMATIC COMPOUNDS Dr. Zainab M Almarhoon 2 Learning Objectives By the end of chapter four the students will: Understand the resonance description of structure of benzene Understand the hybridization
BENZENE & AROMATIC COMPOUNDS Dr. Zainab M Almarhoon 2 Learning Objectives By the end of chapter four the students will: Understand the resonance description of structure of benzene Understand the hybridization
Practice sheet #6: Molecular Shape, Hybridization, Molecular Orbitals.
 CH 101/103 - Practice sheet 3/17/2014 Practice sheet #6: Molecular Shape, Hybridization, Molecular Orbitals. 1. Draw the 3D structures for the following molecules. You can omit the lone pairs on peripheral
CH 101/103 - Practice sheet 3/17/2014 Practice sheet #6: Molecular Shape, Hybridization, Molecular Orbitals. 1. Draw the 3D structures for the following molecules. You can omit the lone pairs on peripheral
Andrew Rosen *Note: If you can rotate a molecule to have one isomer equal to another, they are both the same
 *Note: If you can rotate a molecule to have one isomer equal to another, they are both the same *Note: For hybridization, if an SP 2 is made, there is one unhybridized p orbital (because p usually has
*Note: If you can rotate a molecule to have one isomer equal to another, they are both the same *Note: For hybridization, if an SP 2 is made, there is one unhybridized p orbital (because p usually has
Organic Chemistry I Lesson Objectives, Lesson Problems, Course Outline Spring 2008
 Organic Chemistry I Lesson Objectives, Lesson Problems, Course Outline Spring 2008 Lesson Date Assignment Lesson Objective Description Lesson Problems 4 14-Jan Chapter 1 Quiz Describe how bond polarity
Organic Chemistry I Lesson Objectives, Lesson Problems, Course Outline Spring 2008 Lesson Date Assignment Lesson Objective Description Lesson Problems 4 14-Jan Chapter 1 Quiz Describe how bond polarity
1. Provide a correct name for each compound below. (12 points)
 Page 1 of 8 I. Nomenclature 1. Provide a correct name for each compound below. (12 points) II. Theory 1. UV spectroscopy measures the energy required to promote an electron from the molecular orbital to
Page 1 of 8 I. Nomenclature 1. Provide a correct name for each compound below. (12 points) II. Theory 1. UV spectroscopy measures the energy required to promote an electron from the molecular orbital to
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
The now-banned diet drug fen-phen is a mixture of two synthetic substituted benzene: fenfluramine and phentermine.
 The now-banned diet drug fen-phen is a mixture of two synthetic substituted benzene: fenfluramine and phentermine. Chemists have synthesized compounds with structures similar to adrenaline, producing amphetamine.
The now-banned diet drug fen-phen is a mixture of two synthetic substituted benzene: fenfluramine and phentermine. Chemists have synthesized compounds with structures similar to adrenaline, producing amphetamine.
Aromatics H H H H H H
 Aromatics Some istory 1825 Michael Faraday isolates a new hydrocarbon from illuminating gas. 1834 Eilhardt Mitscherlich isolates same substance and determines its empirical formula to be C n n. Compound
Aromatics Some istory 1825 Michael Faraday isolates a new hydrocarbon from illuminating gas. 1834 Eilhardt Mitscherlich isolates same substance and determines its empirical formula to be C n n. Compound
What Is Organic Chemistry?
 What Is Organic Chemistry? EQ: What is Organic Chemistry? Read: pages 1-3 Answer the questions in your packet Basics of Organic Chem 1 Chapter 1: Structure and Bonding Key terms Organic Chemistry Inorganic
What Is Organic Chemistry? EQ: What is Organic Chemistry? Read: pages 1-3 Answer the questions in your packet Basics of Organic Chem 1 Chapter 1: Structure and Bonding Key terms Organic Chemistry Inorganic
Chemistry department of pharmaceutical faculty II course 3 th semester LESSON 1
 Chemistry department of pharmaceutical faculty II course 3 th semester LESSON 1 Benzene and AromaticityIn the early days of organic chemistry, the word aromatic was used to describe such fragrant substances
Chemistry department of pharmaceutical faculty II course 3 th semester LESSON 1 Benzene and AromaticityIn the early days of organic chemistry, the word aromatic was used to describe such fragrant substances
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
Sp2002 Final Organic II 200pts (Weighted as 300) Good luck ( I believe in you, you can do it, etc.) and please read the questions!
 Sp2002 Final rganic II 200pts (Weighted as 300) NAME: To not have your graded script placed outside my office please check this box Good luck ( I believe in you, you can do it, etc.) and please read the
Sp2002 Final rganic II 200pts (Weighted as 300) NAME: To not have your graded script placed outside my office please check this box Good luck ( I believe in you, you can do it, etc.) and please read the
Tuning Color Through Substitution
 1 Tuning Color Through Substitution Introduction In this experiment, the effect of substituents on the absorbance spectra of molecules will be related to the structure of the molecular orbitals involved
1 Tuning Color Through Substitution Introduction In this experiment, the effect of substituents on the absorbance spectra of molecules will be related to the structure of the molecular orbitals involved
Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Key Words Conjugated Diene Resonance Structures Dienophiles Concerted Reaction Pericyclic Reaction Cycloaddition Reaction Bridged Bicyclic Compound Cyclic
Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Key Words Conjugated Diene Resonance Structures Dienophiles Concerted Reaction Pericyclic Reaction Cycloaddition Reaction Bridged Bicyclic Compound Cyclic
ORGANIC - EGE 5E CH. 2 - COVALENT BONDING AND CHEMICAL REACTIVITY
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HYBRID ORBITAL THEORY The Aufbau Principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy. If carbon has only two unfilled orbitals, why does it like to
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HYBRID ORBITAL THEORY The Aufbau Principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy. If carbon has only two unfilled orbitals, why does it like to
LCAO APPROXIMATIONS OF ORGANIC
 Principles of Organic hemistry lecture 19, page 1 LAO APPROXIMATIONS OF ORGANI Pi MO SYSTEMS BENZENE MOs o ollecting all the molecular orbitals for benzene and arranging them according to energy and putting
Principles of Organic hemistry lecture 19, page 1 LAO APPROXIMATIONS OF ORGANI Pi MO SYSTEMS BENZENE MOs o ollecting all the molecular orbitals for benzene and arranging them according to energy and putting
Practice Hour Examination # 1-1
 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2013 Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Monday,
CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2013 Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Monday,
Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds 5.1 Structure of Benzene: The Kekule Proposal Mid-1800s, benzene was known to have the molecular formula C 6 6. Benzene reacts with 2 in the presence of iron to give substitution
Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds 5.1 Structure of Benzene: The Kekule Proposal Mid-1800s, benzene was known to have the molecular formula C 6 6. Benzene reacts with 2 in the presence of iron to give substitution
Learning Organic Chemistry
 Objective 1 Represent organic molecules with chemical formulas, expanded formulas, Lewis structures, skeletal structures. Determine shape (VSEPR), bond polarity, and molecule polarity. Identify functional
Objective 1 Represent organic molecules with chemical formulas, expanded formulas, Lewis structures, skeletal structures. Determine shape (VSEPR), bond polarity, and molecule polarity. Identify functional
Classes of Organic Compounds
 Unit 1 Functional Groups Depicting Structures of rganic ompounds Lewis Structures ondensed structural formulas Line angle drawings 3-dimensional structures Resonance Structures Acid-Base Reactions urved
Unit 1 Functional Groups Depicting Structures of rganic ompounds Lewis Structures ondensed structural formulas Line angle drawings 3-dimensional structures Resonance Structures Acid-Base Reactions urved
A REVIEW OF GENERAL CHEMISTRY: ELECTRONS, BONDS AND MOLECULAR PROPERTIES
 A REVIEW OF GENERAL CEMISTRY: ELECTRONS, BONDS AND MOLECULAR PROPERTIES A STUDENT SOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Draw Lewis (electron dot and line) structural formulas for simple compounds and ions from molecular
A REVIEW OF GENERAL CEMISTRY: ELECTRONS, BONDS AND MOLECULAR PROPERTIES A STUDENT SOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Draw Lewis (electron dot and line) structural formulas for simple compounds and ions from molecular
4. AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BOOKS 1) Organic Chemistry Structure and Function, K. Peter C. Vollhardt, Neil Schore, 6th Edition 2) Organic Chemistry, T. W. Graham Solomons, Craig B. Fryhle 3) Organic Chemistry: A Short Course, H.
BOOKS 1) Organic Chemistry Structure and Function, K. Peter C. Vollhardt, Neil Schore, 6th Edition 2) Organic Chemistry, T. W. Graham Solomons, Craig B. Fryhle 3) Organic Chemistry: A Short Course, H.
Chapter 2: An Introduction to Organic Compounds
 Chapter : An Introduction to Organic Compounds I. FUNCTIONAL GROUPS: Functional groups with similar structure/reactivity may be "grouped" together. A. Functional Groups With Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds.
Chapter : An Introduction to Organic Compounds I. FUNCTIONAL GROUPS: Functional groups with similar structure/reactivity may be "grouped" together. A. Functional Groups With Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds.
Vision. Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. How rods work H 3 C CH 3. Protein opsin. 11-cis-retinal. Opsin. Rhodopsin.
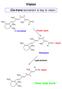 Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
CHEM 263 Notes Oct 1, Beta-carotene (depicted below) is responsible for the orange-red colour in carrots.
 EM 263 otes ct 1, 2013 onjugated Dienes and olour ontinued Beta-carotene (depicted below) is responsible for the orange-red colour in carrots. In the below example, astaxanthin, a blue-green pigment in
EM 263 otes ct 1, 2013 onjugated Dienes and olour ontinued Beta-carotene (depicted below) is responsible for the orange-red colour in carrots. In the below example, astaxanthin, a blue-green pigment in
Covalent Bonds: overlap of orbitals σ-bond π-bond Molecular Orbitals
 Covalent Bonding What is covalent bonding? Covalent Bonds: overlap of orbitals σ-bond π-bond Molecular Orbitals Hybrid Orbital Formation Shapes of Hybrid Orbitals Hybrid orbitals and Multiple Bonds resonance
Covalent Bonding What is covalent bonding? Covalent Bonds: overlap of orbitals σ-bond π-bond Molecular Orbitals Hybrid Orbital Formation Shapes of Hybrid Orbitals Hybrid orbitals and Multiple Bonds resonance
Chemistry 11. Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons
 Chemistry 11 Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons 2 1. Unsaturated hydrocarbons So far, we have studied the hydrocarbons in which atoms are connected exclusively by
Chemistry 11 Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons 2 1. Unsaturated hydrocarbons So far, we have studied the hydrocarbons in which atoms are connected exclusively by
