PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF BROMOCRESOL PURPLE FOR SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC SEAWATER ALKALINITY TITRATIONS
|
|
|
- Reginald Poole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Montana ScholarWorks at University of Montana Undergraduate Theses and Professional Papers 2016 PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF BROMOCRESOL PURPLE FOR SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC SEAWATER ALKALINITY TITRATIONS Taymee A. Brandon The University Of Montana, Let us know how access to this document benefits you. Follow this and additional works at: Part of the Analytical Chemistry Commons, and the Environmental Chemistry Commons Recommended Citation Brandon, Taymee A., "PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF BROMOCRESOL PURPLE FOR SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC SEAWATER ALKALINITY TITRATIONS" (2016). Undergraduate Theses and Professional Papers This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by ScholarWorks at University of Montana. It has been accepted for inclusion in Undergraduate Theses and Professional Papers by an authorized administrator of ScholarWorks at University of Montana. For more information, please contact
2 PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF BROMOCRESOL PURPLE FOR SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC SEAWATER ALKALINITY TITRATIONS By TAYMEE ANN MARIE BRANDON Undergraduate Thesis presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the University Scholar distinction Davidson Honors College University of Montana Missoula, MT May 2016 Approved by: Dr. Michael DeGrandpre Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
3 ABSTRACT Brandon, Taymee, B.S., May 2016 Chemistry Purification and Characterization of Bromocresol Purple for Spectrophotometric Seawater Alkalinity Titrations Faculty Mentor: Dr. Michael DeGrandpre The topic of my research is the purification of the sulfonephthalein indicator bromocresol purple (BCP). BCP is used as an acid-base indicator in seawater alkalinity determinations. Impurities in sulfonephthalein indicator salts often result in significant errors in ph values 3. High-precision inorganic carbon (i.e. CO2) measurements are necessary to document the changes in ocean chemistry and ph due to anthropogenic CO2 uptake by the earth s oceans 3. In order to reduce the error in seawater ph determinations and the general understanding of the CO2 cycle, BCP must be purified and characterized. Previous work has described the use of flash chromatography to efficiently produce large batches of purified indicator, so this method was used for BCP purification 3. Since BCP is purified at a level useful for seawater ph calculations, the chemical can be characterized by more accurately calculating the constants associated with it 1. The spectrophotometric ph values obtained by measuring absorbance ratios are directly related to indicator molecular properties, such as molar absorptivity ratios and protonation characteristics 2. Once the accuracy of these values is improved, future and archived spectrophotometric ph data can be calculated using the improved indicator equilibrium and molar absorptivity values 2. The available purification method of BCP will advance the understanding of ocean acidification in systems where the chemical is used. ii
4 Purification and Characterization of Bromocresol Purple for Spectrophotometric Seawater Introduction Background Figure 1: Bromocresol Purple (BCP) structure Alkalinity Titrations Anthropogenic climate change is a relevant and crucial issue being addressed by the global population and scientific community. The broad topic encompasses numerous variables that form the overall change in global and regional climate patterns. One specific concern is ocean acidification (OA). OA is the ongoing decrease in the ph of the earth s oceans due to the uptake of anthropogenic carbon dioxide (CO2) from the earth s atmosphere through the carbon cycle. Acidity or ph is inversely related to alkalinity. Technological advances have been made that allow scientists to monitor this issue via data collection in the atmosphere and in the ocean itself. Earth-orbiting satellites, such as NASA s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) measures atmospheric CO2 and transmits the data to scientists for analysis, thus improving the overall understanding of the carbon cycle and its impact on OA. A significant amount of the CO2 released by humans into the atmosphere is absorbed by the oceans 4. When gaseous CO2 is dissolved in the ocean, it reacts with water (H2O) to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) and various other species which consequently acidifies the oceans. The overall reaction can be represented by Equation 1: One method of monitoring ocean ph or alkalinity is through use of an in situ titration apparatus that is placed directly in the ocean and transfers data to researchers for analysis. A Submersible Autonomous Moored Instrument (SAMI TM ) manufactured by Sunburst Sensors in Missoula, MT measures oceanic ph or alkalinity, and provides valuable time-series data to researchers 4. In order for this instrument to function, a sulfonephthalein indicator must be used to quantify ph during the titration and gain the necessary data for ocean acidification calculations 4. One indicator that is used in the SAMI s TM is bromocresol purple (BCP) (Figure 1) which comes as a reagent in the form of BCP sodium salt (Figure 2) at roughly 90% purity, depending on the manufacturer 4. This level of indicator impurities can introduce systematic Figure 2: Bromocresol Purple (BCP) sodium salt structure 1
5 errors in reported spectrophotometric ph measurements, even when the precision level in the measurements is quite good 2. Furthermore, archived spectrophotometric ph data has the potential to be quantitatively revised when the indicator is characterized 2. To characterize the indicator means the pka, equilibrium constants, and molar absorptivity ratios are known with more accuracy 2. Systematic differences in reported ph values were as large as 0.01 ph units, which on a logarithmic scale and with respect to the sensitivity of ocean chemistry to ph indicates a large error in reported ph values 2. No BCP characterization or purification methods have been published, which led to my project of formulating a procedure for purification, and the ultimate characterization of the compound. To fully realize the advantages of spectrophotometric ph measurements and their applicability to the overall understanding of climate change, the issue of indicator impurities and their impact on accuracy and precision of measurements must be carefully studied and approached. Problem Bromocresol purple sodium salt (BCP) is a readily available sulfonephthalein indicator with roughly 90% purity directly from Sigma-Aldrich. The level of contaminants present in BCP and the relatively small amount used in spectrophotometric titration measurements makes purified BCP an ideal component of a seawater titration system of interest. The level of impurities present in the stock BCP potentially adds a large margin of error to calculations, specifically at the absorbing wavelength of 434 nm, which needs to be minimized. I developed a procedure for BCP purification that is concise and reproducible for researchers using the chemical. In addition, a quality control method has been made to verify the effectiveness of the purification. Previous work has described the use of flash chromatography (FC) to efficiently produce large batches of purified indicator, so this method was used to form a procedure for BCP purification 3. By using an FC system, an effective procedure for purifying stock BCP has been generated, which is verified through HPLC-UV/Vis data analysis. Now that BCP has been purified at a level useful for seawater ph calculations, the indicator can be characterized by more accurately calculating the molar absorbance ratios and equilibrium constant values. This work will be completed in the near future. 2
6 Experimental Methods Reagent and Solvents The bromocresol purple (BCP) indicator, as a 90% pure sodium salt, was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (batch MKBQ3276V). HPLC Grade Acetonitrile (ACN), HPLC Grade Methanol (MeOH), and trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich and used without further purification. Nanopure water was used for all dilutions. Since indicator impurities can vary between batches even from the same manufacturer 2, and since plenty was available, one batch of indicator was used to allow for comparison between impure and pure indicator. Two solvents were compared to see which has the potential to more effectively separate the contaminants, and ultimately ACN was chosen for the final purification procedure. The use of TFA acidifies the indicator solution that is placed on the column, guaranteeing that the BCP is completely in the first protonated form, with the absorbing wavelength of 434 nm. Instrumentation Figure 3: Flash Chromatography System CombiFlash Rf 200 The BCP purification trials used in this study were performed on a Flash Chromatography System CombiFlash Rf 200 (FC), using both 5.5 and 275 g Redisep Rf C18 Aq columns from Teledyne-ISCO. The 5.5 g column was used for gradient optimization trials during the formation of the procedure, and the 275 g column was used for larger purification batches, and final verification of the procedure. Quality control was performed on a High Performance Liquid Chromatography instrument with a UV-Vis detector (HPLC-UV/Vis), Agilent 1100 Series, using an Agilent Eclipse Plus 3.5 μm 4.6 x 100 mm C18 Aq column. The columns on both instruments use a nonpolar C18 stationary phase, with an acidified polar solvent (ACN with 0.10% TFA) being run through as a mobile phase. The decision to use a nonpolar column and a polar solvent causes portions of the mixture which are more polar and have an affinity for the polar solvent to elute first, and then the most nonpolar to elute last. In addition, BCP is soluble in the organic polar solvent ACN. Figure 4:HPLC-UV/Vis Agilent 1100 Series HPLC 3
7 Trials Using the theoretical basis for purification of a related sulfonephthalein indicator, metacresol purple (MCP), available in the literature 2, as well as an available procedure in the lab for purification, I began a series of 23 trials to optimize a solvent gradient for BCP. The trials addressed which acidification level worked best, 0.05% or 0.10% TFA in solution for the indicator and solvents, whether MeOH or ACN worked better, and if the smaller column being used for trials to conserve indicator and solvent was representative of the larger column. Results showed that 0.10% TFA acidification level of ACN had better results, and that the smaller 5.5 g was representative of the 275 g column, and reasonable to use for gradient optimization trials. In addition, the solvent profile or gradient was altered accordingly to resolve a contaminant peak and have it be fully separated from the purified BCP indicator peak. It was difficult to separate the purified indicator from the contaminants, and some overlap of the peaks remains. Procedure: Purification Method Figure 5: FC conditioning gradient BCP Figure 6: FC purification gradient BCP Based on information from each trial, and an in-depth analysis of collections from each portion of the peaks, a final procedure was created. The purification procedure begins with guaranteeing the solvent bottles are full with A: H2O:0.10 % TFA and B: ACN:0.10% TFA. The A and B positions correspond to the varying degrees of solvent seen in Figures 5 and 6. Prior to indicator solution injection on the column, the column must be conditioned to clear the column of previous contaminants and put the column at starting conditions for the procedure. The column used for large purification batches is the 275 g AqRedisep Gold C18 Aqua column, which is placed on the FC system. Figure 3 shows the conditioning procedure; the column is 4
8 stored in 80% ACN:20% H2O without TFA, so the conditioning begins at 80% ACN, and the starting conditions in Figure 6 correspond to the end conditions in Figure 5. This consistency prevents shocking the column and prevents indicator from bleeding down the column. Figure 7: Chromatogram for representative purification on FC system The BCP sample is prepared by dissolving g in 100 ml of 85% H2O:15% ACN:0.10% TFA in a 100 ml volumetric flask. This solution mimics starting conditions in the method seen in Figure 6. The range of mass for the sample was determined based on the loading capacity of the column (275 mg to 5.5 g), and what the initial trials indicated to work best for proper resolution of the purified indicator peak, Collection 1 in Figure 7, from the contaminant peak, Collection 2 in Figure 7. Absorbance, which is measured on the y-axis in Figure 7, is a function of concentration based on the Beer-Lambert Law, Equation 2: A=εbc, where A=absorbance, ε=molar absorptivity constant or extinction coefficient, b=path length of the cell, and c=concentration. This theoretical basis serves as an indication that as concentration increases, absorbance increases proportionally. Although the column can reasonably have 5.5 g loaded, the increased concentration causes more peak overlap than seen in Figure 7, which reduces the effectiveness of the procedure and the purification level of the product. Column C18Aq 275 g RediSep Gold Flow Rate 150 ml/min Wavelengths of Detection 210, 254 nm Mass of Impure BCP g Solution 0.10% TFA:15% ACN:85% H2O Table 1: Purification conditions on FC for trial shown in Figure 7 5
9 In the representative example of the purification procedure being discussed in this paper, the conditions for the run are shown in Table 1. The column, flow rate, wavelength of detection, and solution are consistent with all purifications, the mass of the sample is specific to the chromatogram in Figure 7. After the column is conditioned and the indicator solution is made, the solution may be loaded onto the column manually or via syringe. In my research, I have manually loaded the column. Once the column is prepared, the method is loaded on the FC system which uses the gradient shown in Figure 6. In Figure 7, Collection 1 is the purified indicator, and Collection 2 is mostly contaminants. This is verified on the HPLC-UV/Vis. Figure 8 shows the column at various times during the purification shows in Figure 7. At 12.3 minutes the arrow on bottom corresponds to Collection 1 in Figure 7, and the arrow on top corresponds to Collection 2. Once the run is complete, and the column is Figure 8: Indicator and impurity bands on 275 g AqRedisep Gold clear of any contaminants, the column is stored in 80% ACN:20% H2O without acid to prevent the column from degrading. The purified indicator at this point is in solution, and the solvent needs to be evaporated off to have a solid product. The drying may be done via a rotary evaporation system or the samples may be placed in a ported Erlenmeyer flask, and dried with stir at 40 o C with filtered air blown over the solution. Once the solvent is evaporated off, the solid product is transferred to its final container, and dried in an oven at 50 o C for 3 to 6 hours. The product is light sensitive so it is stored in an amber UV protective vial in a desiccator. Procedure: Quality Control Once the product is dried, it must be verified that it has been purified and no unusual contaminants have been added throughout the drying process. A small sample, around 10 mg, is placed in a 10 ml volumetric flask and dissolved in a 5% ACN:95% H2O:0.05% TFA solution to mimic starting conditions on the column. The exact mass is not analytically relevant, since quantification and percent yield is not performed on the HPLC-UV/Vis quality control (QC) data. The method used for QC on the HPLC-UV/Vis is shown in Figure 9. This method is similar to the one used on the FC, but not the same. This method has been optimized for use on the 6
10 system, and uses a much smaller sample of 10 μl. The small sample, combined with the length of the column, allows for clear and separate peaks on the chromatograms the system generates. The UV/Vis detector allows for the analysis of each individual peak. With the spectra of each individual peak available, the indicator peaks can be distinguished from the contaminants. This is shown in Figure 10, which Figure 9: HPLC-UV/Vis QC gradient is the HPLC-UV/Vis analysis of the Collections 1 and 2 shown in Figure 7, compared to an impure BCP sample. Column Eclipse Plus C x 100 mm Flow Rate 1 ml/min Wavelengths of Detection 210, 254, 434 nm Volume of Injection 10 µl Solvents A: H2O w/ 0.05% TFA B: ACN w/ 0.05% TFA Table 2: Quality control conditions on HPLC-UV/Vis In Figure 10, the arrows indicate which peaks have a spectra associated with them, and are considered peaks of interest. ACN is a polar solvent and has an associated absorbance that is reflected on the chromatogram; when the instrument pumps solvent through the column, the detector registers the pulse of solvent, which is shown by the baseline waves seen between peaks of interest. At 13 minutes, the solvent profile increases to 100% acidified ACN to clear the column of contaminants. This quick increase causes the drastic baseline shift seen around this time in the chromatograms in Figure 10. The reason for the three separate wavelengths is to reveal the nature of the contaminants. At 210 nm, all portion of the mixture absorb, as well as the solvent. At 434 nm, sulfonephthalein indicators absorb, so all peaks at this wavelength consequently represent an indicator. This is the most important wavelength, because when in situ instruments such as SAMI s are using indicators to collect data, they collect values at this wavelength; if there are contaminants that are indicator in nature, their absorbance will be included in the calculations and increase the margin of error. 7
11 210 nm 254 nm 434 nm 210 nm 254 nm 434 nm A) HPLC-UV/Vis chromatogram of impure BCP solution at 790 ppm in 20% ACN: 0.10%TFA:80% H2O to use as visual comparison of the chromatograms for Collections 1 and 2 from Figure 7. The method seen in Figure 9 was used with conditions listed in Table 2. B) HPLC-UV/Vis chromatogram of a sample taken directly from Collection 1 seen in Figure 7. No further dilution was performed. The method seen in Figure 9 was used with conditions listed in Table nm 254 nm C) HPLC-UV/Vis chromatogram of a sample taken directly from Collection 2 seen in Figure 7. No further dilution was performed. The method seen in Figure 9 was used with conditions listed in Table nm Figure 10: Comparison of HPLC-UV/Vis data for Collections 1 and 2 from Figure 7 8
12 Results and Discussion Data Analysis Following an effective purification and an apparent resolution of contaminants shown by the quality control data, data analysis can be performed to provide quantitative information to verify the purification. Peaks, such as those shown in Figure 10, have an associated area (mau*s). The area is a function of absorbance and time, and using the fundamental basis of the Beer-Lambert law (Equation 2), a relative contaminant resolution calculation can be performed, seen in Table 3. Table 3: Data analysis of HPLC-UV/Vis data shown in Figure 10 using Equations 3, 4, and 5 To determine the contaminant resolution in the purified indicator, a calculation using the summation of the peaks of significance is shown in Table 3. Any peak with an associated spectra is considered a peak of significance. Peak spectra were used to verify contaminant peaks versus sulfonephthalein indicator peaks based on absorbance. Percent yield is calculated using Equation 4: (Actual Yield/Theoretical Yield) x 100 = % Yield, and the overall percent contaminants is estimated using Equation 5: [1-(Σxn contaminants/σxn all peaks)] x 100 = % Contaminants. At each wavelength, there is a definite resolution of contaminants, but most notably at 434 nm where sulfonephthalein indicators absorb. This nearly complete resolution of the contaminants, specifically 97.5% as shown in Table 3, supports the conclusion that the proposed method created from this study effectively purifies BCP for seawater alkalinity titrations. The implications of this purification is that the purified BCP will create less interference with the 9
13 reduced amount of unknown contaminants. In addition, the nearly completely resolved contaminants at the sulfonephthalein wavelength of 434 nm will prevent additional indicators from affecting the calculations used to measure oceanic ph and alkalinity. Summary/Conclusions Based on the data analysis performed, and consistency of the results, the procedure produced in this study effectively purifies BCP at a level useful for seawater alkalinity titrations. Now that BCP is purified, the indicator needs to be fully characterized to reevaluate the molar absorptivity value ratios and pka using 2-aminopyridine as a ph buffer; 2-aminopyridine has been presented by Andrew G. Dickson as an acceptable ph buffer to be used for sea water media based on the total hydrogen ion concentration scale 1. The buffer was chosen to use in future characterization work based on it having similar properties to BCP. Once characterization is finished in the near future, the more accurate constants will reduce the error in ph calculations, allowing for an improved understanding of the current state of ocean acidification. Acknowledgement This work was funded by the Montana Board of Research and Commercialization Technology and the National Science Foundation. I would like to thank the Montana Space Grant Consortium for their support and funding of my time, the University of Montana, Dr. Michael DeGrandpre for his guidance and support as my faculty mentor, and the DeGrandpre Research Lab members for their advice and assistance. References 1 Dickson, ph buffers for sea water media based on the total hydrogen ion concentration scale. Deep-Sea Research I. 1993, 40, Liu et al., Purification and Characterization of meta-cresol Purple for Spectrophotometric Seawater ph Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, Patsavas et al., Purification of meta-cresol purple and cresol red by flash chromatography: procedures for ensuring accurate spectrophotometric seawater ph measurements. Marine Chemistry. 2013, 150, Spaulding et al., Autonomous in Situ Measurements of Seawater Alkalinity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48,
RediSep Rf C18 Flash Column Loading Techniques
 RediSep Rf C18 Flash Column Loading Techniques Chromatography Application Note AN88 Abstract There are several techniques for loading samples onto reusable RediSep Rf C18 flash columns. The techniques
RediSep Rf C18 Flash Column Loading Techniques Chromatography Application Note AN88 Abstract There are several techniques for loading samples onto reusable RediSep Rf C18 flash columns. The techniques
HPLC Praktikum Skript
 HPLC Praktikum Skript Assistants: Gianluca Bartolomeo HCI D330, 3 46 68, bartolomeo@org.chem.ethz.ch Sahar Ghiasikhou HCI E330, 2 29 29, ghiasikhou@org.chem.ethz.ch 1. Introduction In chromatographic techniques,
HPLC Praktikum Skript Assistants: Gianluca Bartolomeo HCI D330, 3 46 68, bartolomeo@org.chem.ethz.ch Sahar Ghiasikhou HCI E330, 2 29 29, ghiasikhou@org.chem.ethz.ch 1. Introduction In chromatographic techniques,
Strategies for the Flash Purification of Highly Polar Compounds
 trategies for the Flash Purification of Highly Polar Compounds Jack E. ilver, jsilver@teledyne.com, Paul Bellinghausen, and ancy Fowler, Teledyne Isco, Inc., 47 uperior treet, Lincoln, E 6854 Abstract
trategies for the Flash Purification of Highly Polar Compounds Jack E. ilver, jsilver@teledyne.com, Paul Bellinghausen, and ancy Fowler, Teledyne Isco, Inc., 47 uperior treet, Lincoln, E 6854 Abstract
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) of Three Analgesics
 High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) of Three Analgesics OVERVIEW/THEORY Real-life samples are often complex mixtures of many substances (e.g., sea water contains many salts and other impurities
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) of Three Analgesics OVERVIEW/THEORY Real-life samples are often complex mixtures of many substances (e.g., sea water contains many salts and other impurities
Determination of Carbonyl Compounds In Water by Dinitrophenylhydrazine Derivatization and HPLC/UV*
 Determination of Carbonyl Compounds In Water by Dinitrophenylhydrazine Derivatization and HPLC/UV* EPA Method 8315A UCT Part Number: EUC1812M15 (Unendcapped C18-2000 mg/15 ml cartridge) March 2013 Method
Determination of Carbonyl Compounds In Water by Dinitrophenylhydrazine Derivatization and HPLC/UV* EPA Method 8315A UCT Part Number: EUC1812M15 (Unendcapped C18-2000 mg/15 ml cartridge) March 2013 Method
Technical Procedure for Concentration Determination of Methamphetamine in Liquids via HPLC
 Technical Procedure for Concentration Determination of 1.0 Purpose This procedure specifies the required elements for the preparation and use of the Agilent 1100/1200 series High Performance Liquid Chromatograph
Technical Procedure for Concentration Determination of 1.0 Purpose This procedure specifies the required elements for the preparation and use of the Agilent 1100/1200 series High Performance Liquid Chromatograph
VALIDATION OF A UPLC METHOD FOR A BENZOCAINE, BUTAMBEN, AND TETRACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE TOPICAL SOLUTION
 VALIDATION OF A UPLC METHOD FOR A BENZOCAINE, BUTAMBEN, AND TETRACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE TOPICAL SOLUTION Andrew J. Aubin and Tanya L. Jenkins Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA INTRODUCTION Benzocaine (4-Aminobenzoic
VALIDATION OF A UPLC METHOD FOR A BENZOCAINE, BUTAMBEN, AND TETRACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE TOPICAL SOLUTION Andrew J. Aubin and Tanya L. Jenkins Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA INTRODUCTION Benzocaine (4-Aminobenzoic
Commercialization of autonomous sensor systems for quantifying pco 2 and total inorganic carbon
 Commercialization of autonomous sensor systems for quantifying pco 2 and total inorganic carbon PI: Michael DeGrandpre, PhD Dept. of Chemistry, University of Montana, Missoula, MT 59812 Phone: (406) 243-4227
Commercialization of autonomous sensor systems for quantifying pco 2 and total inorganic carbon PI: Michael DeGrandpre, PhD Dept. of Chemistry, University of Montana, Missoula, MT 59812 Phone: (406) 243-4227
Flash chromatography purification of high pka organic compounds with Teledyne Isco s specialty RediSep columns
 Flash chromatography purification of high pka organic compounds with Teledyne Isco s specialty RediSep columns Mikael Mahler*, Veronica Thomason, and John Urh Teledyne Isco Inc., P.O. Box 82531, Lincoln
Flash chromatography purification of high pka organic compounds with Teledyne Isco s specialty RediSep columns Mikael Mahler*, Veronica Thomason, and John Urh Teledyne Isco Inc., P.O. Box 82531, Lincoln
The analysis of organic acid content of additives, premix, feed, and water.
 The analysis of organic acid content of additives, premix, feed, and water. Contents Foreword Introduction Warnings 1. Scope 2 1.1 LOD and LOQ 3 2. Normative References 3 3. Definitions 3 3.1 Feed (or
The analysis of organic acid content of additives, premix, feed, and water. Contents Foreword Introduction Warnings 1. Scope 2 1.1 LOD and LOQ 3 2. Normative References 3 3. Definitions 3 3.1 Feed (or
Selective Formation of Benzo[c]cinnoline by Photocatalytic Reduction of 2,2 Dinitrobiphenyl with TiO 2 and UV light irradiation
![Selective Formation of Benzo[c]cinnoline by Photocatalytic Reduction of 2,2 Dinitrobiphenyl with TiO 2 and UV light irradiation Selective Formation of Benzo[c]cinnoline by Photocatalytic Reduction of 2,2 Dinitrobiphenyl with TiO 2 and UV light irradiation](/thumbs/90/104361197.jpg) Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Content: Selective Formation of Benzo[c]cinnoline by Photocatalytic Reduction of
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Content: Selective Formation of Benzo[c]cinnoline by Photocatalytic Reduction of
INTRODUCTION TO CO2 MEASUREMENTS IN SEA WATER
 INTRODUCTION TO CO2 MEASUREMENTS IN SEA WATER Andrew G. Dickson Scripps Institution of Oceanography, UC San Diego METHODS FOR MEASURING THE CO 2 PARAMETERS IN SEA WATER USUAL PARAMETERS MEASURED Total
INTRODUCTION TO CO2 MEASUREMENTS IN SEA WATER Andrew G. Dickson Scripps Institution of Oceanography, UC San Diego METHODS FOR MEASURING THE CO 2 PARAMETERS IN SEA WATER USUAL PARAMETERS MEASURED Total
Investigation of Petasis and Ugi Reactions in Series in an Automated Microreactor System
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Investigation of Petasis and Ugi Reactions in Series in an Automated
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Investigation of Petasis and Ugi Reactions in Series in an Automated
CIPAC. CIPAC Free relevant impurities methods:
 CIPAC COLLABORATIVE INTERNATIONAL PESTICIDES ANALYTICAL COUNCIL LIMITED Commission Internationale des Méthodes d'analyse des Pesticides (CIMAP) CIPAC Free relevant impurities methods: Methods for relevant
CIPAC COLLABORATIVE INTERNATIONAL PESTICIDES ANALYTICAL COUNCIL LIMITED Commission Internationale des Méthodes d'analyse des Pesticides (CIMAP) CIPAC Free relevant impurities methods: Methods for relevant
Chemistry Gas Chromatography: Separation of Volatile Organics
 Chemistry 3200 Gas chromatography (GC) is an instrumental method for separating volatile compounds in a mixture. A small sample of the mixture is injected onto one end of a column housed in an oven. The
Chemistry 3200 Gas chromatography (GC) is an instrumental method for separating volatile compounds in a mixture. A small sample of the mixture is injected onto one end of a column housed in an oven. The
TECHNICAL TEMEPHOS. 1. Specification. Full specification WHO/SIT/19.R4 Revised 10 December Description
 WHO/SIT/19.R4 TEMEPHOS TECHNICAL TECHNICAL TEMEPHOS 1. Specification 1.1 Description Full specification WHO/SIT/19.R4 Revised 10 December 1999 The material shall consist of temephos together with related
WHO/SIT/19.R4 TEMEPHOS TECHNICAL TECHNICAL TEMEPHOS 1. Specification 1.1 Description Full specification WHO/SIT/19.R4 Revised 10 December 1999 The material shall consist of temephos together with related
2017 Reaction of cinnamic acid chloride with ammonia to cinnamic acid amide
 217 Reaction of cinnamic acid chloride with ammonia to cinnamic acid amide O O Cl NH 3 NH 2 C 9 H 7 ClO (166.6) (17.) C 9 H 9 NO (147.2) Classification Reaction types and substance classes reaction of
217 Reaction of cinnamic acid chloride with ammonia to cinnamic acid amide O O Cl NH 3 NH 2 C 9 H 7 ClO (166.6) (17.) C 9 H 9 NO (147.2) Classification Reaction types and substance classes reaction of
Analysis of Metals, Halides, and Inorganic Ions Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography
 Application Note Inorganic Ions, Water Testing, Minerals, Metals, Basic Chemicals Analysis of Metals, Halides, and Inorganic Ions Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography Authors Anne Mack, Adam Bivens
Application Note Inorganic Ions, Water Testing, Minerals, Metals, Basic Chemicals Analysis of Metals, Halides, and Inorganic Ions Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography Authors Anne Mack, Adam Bivens
Quantitative Analysis of Caffeine in Energy Drinks by High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Quantitative Analysis of Caffeine in Energy Drinks by High Performance Liquid Chromatography CHEM 329 Professor Vogt TA: Fahad Hasan Allison Poget Date Performed: April 5, 2016 Date Submitted: April 12,
Quantitative Analysis of Caffeine in Energy Drinks by High Performance Liquid Chromatography CHEM 329 Professor Vogt TA: Fahad Hasan Allison Poget Date Performed: April 5, 2016 Date Submitted: April 12,
HPLC analysis of VFAs, Furfural and HMF
 HPLC analysis of VFAs, Furfural and HMF Introduction The following chromatographic analysis is developed in order to analyse volatile fatty acids and carbohydrate degradation products; furfural, hydroxymethylfurfural
HPLC analysis of VFAs, Furfural and HMF Introduction The following chromatographic analysis is developed in order to analyse volatile fatty acids and carbohydrate degradation products; furfural, hydroxymethylfurfural
Chem 321 Name Answer Key D. Miller
 1. For a reversed-phase chromatography experiment, it is noted that the retention time of an analyte decreases as the percent of acetonitrile (CH 3 CN) increases in a CH 3 CN/H 2 O mobile phase. Explain
1. For a reversed-phase chromatography experiment, it is noted that the retention time of an analyte decreases as the percent of acetonitrile (CH 3 CN) increases in a CH 3 CN/H 2 O mobile phase. Explain
Unexpected Peaks in Chromatograms - Are They Related Compounds, System Peaks or Contaminations? From the Diary of an HPLC Detective
 Unexpected Peaks in Chromatograms - Are They Related Compounds, System Peaks or Contaminations? From the Diary of an HPLC Detective SHULAMIT LEVIN HPLC in Pharmaceutics Σ Stability Indicating Methods Extra
Unexpected Peaks in Chromatograms - Are They Related Compounds, System Peaks or Contaminations? From the Diary of an HPLC Detective SHULAMIT LEVIN HPLC in Pharmaceutics Σ Stability Indicating Methods Extra
Minimizing Solvent Impact on Purification of Nitrogencontaining
 Minimizing Solvent Impact on Purification of Nitrogencontaining Compounds J. Liu and P. C. Rahn Biotage Discovery Chemistry Group US 1725 Discovery Drive Charlottesville, VA 22911 USA 1 Abstract This paper
Minimizing Solvent Impact on Purification of Nitrogencontaining Compounds J. Liu and P. C. Rahn Biotage Discovery Chemistry Group US 1725 Discovery Drive Charlottesville, VA 22911 USA 1 Abstract This paper
Basic Principles for Purification Using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
 Basic Principles for Purification Using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography Jo-Ann M. Jablonski, Christopher J. Hudalla, Kenneth J. Fountain, Steven M. Collier, and Damian Morrison Waters Corporation, Milford,
Basic Principles for Purification Using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography Jo-Ann M. Jablonski, Christopher J. Hudalla, Kenneth J. Fountain, Steven M. Collier, and Damian Morrison Waters Corporation, Milford,
Dilution(*) Chromatography
 WA20264 Poster # 184, HPLC 2002, Montreal, 4-5 June 2002 At-Column Column-Dilution for Preparative Dilution(*) Chromatography Cecilia Mazza, Jie Cavanaugh, Ziling Lu,Tom Sirard,Tom Wheat and Uwe Neue Waters
WA20264 Poster # 184, HPLC 2002, Montreal, 4-5 June 2002 At-Column Column-Dilution for Preparative Dilution(*) Chromatography Cecilia Mazza, Jie Cavanaugh, Ziling Lu,Tom Sirard,Tom Wheat and Uwe Neue Waters
Peptide Isolation Using the Prep 150 LC System
 Jo-Ann M. Jablonski and Andrew J. Aubin Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA APPLICATION BENEFITS The Prep 150 LC System, an affordable, highly reliable system for preparative chromatography, is suitable
Jo-Ann M. Jablonski and Andrew J. Aubin Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA APPLICATION BENEFITS The Prep 150 LC System, an affordable, highly reliable system for preparative chromatography, is suitable
INDIGOTINE. Disodium 3,3'-dioxo-[delta 2,2' -biindoline]-5,5'-disulfonate (principal component) (principal component)
![INDIGOTINE. Disodium 3,3'-dioxo-[delta 2,2' -biindoline]-5,5'-disulfonate (principal component) (principal component) INDIGOTINE. Disodium 3,3'-dioxo-[delta 2,2' -biindoline]-5,5'-disulfonate (principal component) (principal component)](/thumbs/72/66284331.jpg) INDIGOTINE Prepared at the 73rd JEFA (2010) and published in FAO Monographs 10 (2010), superseding specifications prepared at the 28 th JEFA (1984) and published in the ombined ompendium of Food Additive
INDIGOTINE Prepared at the 73rd JEFA (2010) and published in FAO Monographs 10 (2010), superseding specifications prepared at the 28 th JEFA (1984) and published in the ombined ompendium of Food Additive
CHAPTER V ANALYTICAL METHODS ESTIMATION OF DICLOFENAC. Diclofenac (gift sample from M/s Micro Labs Ltd., Pondicherry)
 CHAPTER V ANALYTICAL METHODS ESTIMATION OF DICLOFENAC A UV spectrophotometric method based on the measurement of absorbance at 276nm in phosphate buffer of p H 7.4 was used in the present study of the
CHAPTER V ANALYTICAL METHODS ESTIMATION OF DICLOFENAC A UV spectrophotometric method based on the measurement of absorbance at 276nm in phosphate buffer of p H 7.4 was used in the present study of the
Chemistry 3200 High Performance Liquid Chromatography: Quantitative Determination of Headache Tablets
 Chemistry 3200 High Performance Liquid Chromatography: Quantitative Determination of Headache Tablets Liquid chromatography was developed by Tswett in early 1900 s and was shown to be a powerful separation
Chemistry 3200 High Performance Liquid Chromatography: Quantitative Determination of Headache Tablets Liquid chromatography was developed by Tswett in early 1900 s and was shown to be a powerful separation
The Low-Temperature Evaporative Light-Scattering Detector (LT-ELSD)
 The Low-Temperature Evaporative Light-Scattering Detector (LT-ELSD) Basically all compounds which are less volatile than the mobile phase can be detected. Detection is based on a Universal property of
The Low-Temperature Evaporative Light-Scattering Detector (LT-ELSD) Basically all compounds which are less volatile than the mobile phase can be detected. Detection is based on a Universal property of
Hints for Strong Ion Exchange Resins
 Hints for Strong Ion Exchange Resins Chromatography Application Note AN98 Abstract Ion exchange columns are a powerful means of isolating and purifying compounds, but their use is limited due to lack of
Hints for Strong Ion Exchange Resins Chromatography Application Note AN98 Abstract Ion exchange columns are a powerful means of isolating and purifying compounds, but their use is limited due to lack of
DETERMINATION OF DRUG RELEASE DURING DISSOLUTION OF NICORANDIL IN TABLET DOSAGE FORM BY USING REVERSE PHASE HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY
 CHAPTER 9 DETERMINATION OF DRUG RELEASE DURING DISSOLUTION OF NICORANDIL IN TABLET DOSAGE FORM BY USING REVERSE PHASE HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY CHAPTER 9 Determination of drug release during
CHAPTER 9 DETERMINATION OF DRUG RELEASE DURING DISSOLUTION OF NICORANDIL IN TABLET DOSAGE FORM BY USING REVERSE PHASE HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY CHAPTER 9 Determination of drug release during
Figure 1. Structures for Vitamin B2 and Vitamin B1.
 CH 461 & CH 461H F 18 Name Experiment 2C Integrated Laboratory Experiment DETERMINATION OF RIBOFLAVIN: A COMPARISON OF TECHNIQUES PART C. HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment
CH 461 & CH 461H F 18 Name Experiment 2C Integrated Laboratory Experiment DETERMINATION OF RIBOFLAVIN: A COMPARISON OF TECHNIQUES PART C. HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment
METHOD 8032A ACRYLAMIDE BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY
 METHOD 8032A ACRYLAMIDE BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 8032 is used to determine trace amounts of acrylamide monomer (CAS No. 79-06-1) in aqueous matrices. This method may be
METHOD 8032A ACRYLAMIDE BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 8032 is used to determine trace amounts of acrylamide monomer (CAS No. 79-06-1) in aqueous matrices. This method may be
Determination of Caffeine by HPLC
 Determination of Caffeine by HPLC Introduction It was a long history before real high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) had evolved. The very first indication of a chromatographic separation was
Determination of Caffeine by HPLC Introduction It was a long history before real high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) had evolved. The very first indication of a chromatographic separation was
Final Report. Characterisation of Sample Report. Job No 2016/11/12-34 AS No. 1234A. Client Example Contact Sample. Signed Date 2017.
 Final Report Title Characterisation of Job No 2016/11/12-34 AS No. 1234A Client Contact Sample Author report Signed Date 2017 Easy Reach Report 2017 v2.docx 1 of 33 Contents 1. Study Summary Page 3 2.
Final Report Title Characterisation of Job No 2016/11/12-34 AS No. 1234A Client Contact Sample Author report Signed Date 2017 Easy Reach Report 2017 v2.docx 1 of 33 Contents 1. Study Summary Page 3 2.
TEMPLATE FOR AN EXAMPLE STANDARD TEST METHOD
 APPENDIX V TEMPLATE FOR AN EXAMPLE STANDARD TEST METHOD Validating Chromatographic Methods. By David M. Bliesner Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 159 160 APPENDIX V Title: Effective: Document No:
APPENDIX V TEMPLATE FOR AN EXAMPLE STANDARD TEST METHOD Validating Chromatographic Methods. By David M. Bliesner Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 159 160 APPENDIX V Title: Effective: Document No:
Liquid storage: Holds the solvent which is going to act as the mobile phase. Pump: Pushes the solvent through to the column at high pressure.
 High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a much more sensitive and useful technique than paper and thin layer chromatography. The instrument used for HPLC is called a high performance liquid chromatograph.
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a much more sensitive and useful technique than paper and thin layer chromatography. The instrument used for HPLC is called a high performance liquid chromatograph.
ANALYTICAL METHOD DETERMINATION OF VOLATILE ALDEHYDES IN AMBIENT AIR Page 1 of 11 Air sampling and analysis
 DETERMINATION OF VOLATILE ALDEHYDES IN AMBIENT AIR Page 1 of 11 Replaces: Dated: Author: Date: AM-No.: New New Nils Arne Jentoft 18.06.2014 0 CHANGES This procedure is new. 1 SCOPE This document describes
DETERMINATION OF VOLATILE ALDEHYDES IN AMBIENT AIR Page 1 of 11 Replaces: Dated: Author: Date: AM-No.: New New Nils Arne Jentoft 18.06.2014 0 CHANGES This procedure is new. 1 SCOPE This document describes
Application Note. Author. Abstract. Pharmaceutical QA/QC. Vinayak A.K Agilent Technologies Bangalore, India
 QbD Based Method Development on an Agilent 129 Infinity UHPLC System Combined with a Seamless Method Transfer to HPLC Using Intelligent System Emulation Technology Application Note Pharmaceutical QA/QC
QbD Based Method Development on an Agilent 129 Infinity UHPLC System Combined with a Seamless Method Transfer to HPLC Using Intelligent System Emulation Technology Application Note Pharmaceutical QA/QC
Achieve confident synthesis control with the Thermo Scientific ISQ EC single quadrupole mass spectrometer
 APPLICATION NOTE 72385 Achieve confident synthesis control with the Thermo Scientific ISQ EC single quadrupole mass spectrometer Authors Stephan Meding, Katherine Lovejoy, Martin Ruehl Thermo Fisher Scientific,
APPLICATION NOTE 72385 Achieve confident synthesis control with the Thermo Scientific ISQ EC single quadrupole mass spectrometer Authors Stephan Meding, Katherine Lovejoy, Martin Ruehl Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Rapid Screening and Confirmation of Melamine Residues in Milk and Its Products by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry
 Rapid Screening and Confirmation of Melamine Residues in Milk and Its Products by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Application Note Food Authors Jianqiu Mi, Zhengxiang Zhang, Zhixu Zhang,
Rapid Screening and Confirmation of Melamine Residues in Milk and Its Products by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Application Note Food Authors Jianqiu Mi, Zhengxiang Zhang, Zhixu Zhang,
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 S1 Electronic Supplementary Information Flash Carboxylation: Fast Lithiation - Carboxylation
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 S1 Electronic Supplementary Information Flash Carboxylation: Fast Lithiation - Carboxylation
Determination of trace anions in concentrated hydrofluoric acid
 APPLICATION NOTE 78 Determination of trace anions in concentrated hydrofluoric acid Authors Archava Siriraks Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA Keywords HF, ICS-5000 +, IonPac AS10, IonPac AC10, ion
APPLICATION NOTE 78 Determination of trace anions in concentrated hydrofluoric acid Authors Archava Siriraks Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA Keywords HF, ICS-5000 +, IonPac AS10, IonPac AC10, ion
Backbone modification of a parathyroid hormone receptor-1 antagonist/inverse agonist
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Backbone modification of a parathyroid hormone receptor-1 antagonist/inverse agonist Ross W. Cheloha, Tomoyuki Watanabe, Thomas Dean, Samuel H. Gellman*, Thomas J. Gardella* *Corresponding
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Backbone modification of a parathyroid hormone receptor-1 antagonist/inverse agonist Ross W. Cheloha, Tomoyuki Watanabe, Thomas Dean, Samuel H. Gellman*, Thomas J. Gardella* *Corresponding
Application Note. Author. Abstract. Xinlei Yang Agilent Technologies Co. Ltd Shanghai, China
 Rapid Deteration of Eight Related Aromatic Acids in the p-phthalic Acid Mother Liquid Using an Agilent 126 Infinity LC System and an Agilent Poroshell 12 SB-C18 Column Application Note Author Xinlei Yang
Rapid Deteration of Eight Related Aromatic Acids in the p-phthalic Acid Mother Liquid Using an Agilent 126 Infinity LC System and an Agilent Poroshell 12 SB-C18 Column Application Note Author Xinlei Yang
TECHNICAL BRODIFACOUM
 BRODIFACOUM Full specification: Approved 10 December 1999 1. Specification 1.1 Description The material shall consist of brodifacoum together with related manufacturing impurities and shall be in the form
BRODIFACOUM Full specification: Approved 10 December 1999 1. Specification 1.1 Description The material shall consist of brodifacoum together with related manufacturing impurities and shall be in the form
Chapter 4: Verification of compendial methods
 Chapter 4: Verification of compendial methods Introduction In order to ensure accurate and reliable test results, the quality control laboratory (QCL) needs to use analytical methods (and accompanying
Chapter 4: Verification of compendial methods Introduction In order to ensure accurate and reliable test results, the quality control laboratory (QCL) needs to use analytical methods (and accompanying
PYRIPROXYFEN TECHNICAL
 WHO/IS/TC/715/2001 TECHNICAL TECHNICAL 1. Specification 1.1 Description Interim specification WHO/IS/TC/715/2001 The material shall consist of pyriproxyfen together with related manufacturing impurities.
WHO/IS/TC/715/2001 TECHNICAL TECHNICAL 1. Specification 1.1 Description Interim specification WHO/IS/TC/715/2001 The material shall consist of pyriproxyfen together with related manufacturing impurities.
Figure 1. Structures for Vitamin B2 and Vitamin B1.
 CH 461 & CH 461H F 15 Name Experiment 2C Integrated Laboratory Experiment DETERMINATION OF RIBOFLAVIN: A COMPARISON OF TECHNIQUES PART C. HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment
CH 461 & CH 461H F 15 Name Experiment 2C Integrated Laboratory Experiment DETERMINATION OF RIBOFLAVIN: A COMPARISON OF TECHNIQUES PART C. HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment
*Correspondence to:
 Supporting Information for Carbonate-promoted hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to multi-carbon carboxylates Aanindeeta Banerjee 1 and Matthew W. Kanan 1 * 1 Department of Chemistry, Stanford University,
Supporting Information for Carbonate-promoted hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to multi-carbon carboxylates Aanindeeta Banerjee 1 and Matthew W. Kanan 1 * 1 Department of Chemistry, Stanford University,
637. Thiamethoxam. HPLC method
 637. Thiamethoxam HPLC method CIPAC Collaborative Trial according to CIPAC Information Sheet N o 293 Dr. Sven Adolph Syngenta Crop Protection Münchwilen AG CH-4333 Münchwilen Switzerland May 212 page 1
637. Thiamethoxam HPLC method CIPAC Collaborative Trial according to CIPAC Information Sheet N o 293 Dr. Sven Adolph Syngenta Crop Protection Münchwilen AG CH-4333 Münchwilen Switzerland May 212 page 1
CHAPTER - 3 ANALYTICAL PROFILE. 3.1 Estimation of Drug in Pharmaceutical Formulation Estimation of Drugs
 CHAPTER - 3 ANALYTICAL PROFILE 3.1 Estimation of Drug in Pharmaceutical Formulation 3.1.1 Estimation of Drugs ANALYTICAL PROFILE 84 3.1 ESTIMATION OF DRUG IN PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATION. Agrawal A et al
CHAPTER - 3 ANALYTICAL PROFILE 3.1 Estimation of Drug in Pharmaceutical Formulation 3.1.1 Estimation of Drugs ANALYTICAL PROFILE 84 3.1 ESTIMATION OF DRUG IN PHARMACEUTICAL FORMULATION. Agrawal A et al
Determination of Trace Cations in Power Plant Waters Containing Morpholine
 Application Note 8 Determination of Trace Cations in Power Plant Waters Containing Morpholine INTRODUCTION Morpholine and ammonium are used as additives in power plant waters. Morpholine acts as a corrosion
Application Note 8 Determination of Trace Cations in Power Plant Waters Containing Morpholine INTRODUCTION Morpholine and ammonium are used as additives in power plant waters. Morpholine acts as a corrosion
Supplementary Figure 1. Structures of substrates tested with 1. Only one enantiomer is shown.
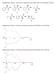 Supplementary Figure 1. Structures of substrates tested with 1. Only one enantiomer is shown. Supplementary Figure 2. CD spectra obtained using 1 and (R)-3 (blue) and (S)-3 (red) Supplementary Figure 3.
Supplementary Figure 1. Structures of substrates tested with 1. Only one enantiomer is shown. Supplementary Figure 2. CD spectra obtained using 1 and (R)-3 (blue) and (S)-3 (red) Supplementary Figure 3.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 1 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
Updated: 3 November 2014 Print version High Performance Liquid Chromatography David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 1 HPLC System David Reckhow CEE 772 #18 2 1 Instrument Basics PUMP INJECTION POINT DETECTOR COLUMN
Chromatographic Analysis
 Chromatographic Analysis Distribution of Analytes between Phases An analyte is in equilibrium between the two phases [S 1 ] [S 2 ] (in phase 1) (in phase 2) AS [S2 ] K 2 A S [S1 ] 1 AS, A 1 S Activity
Chromatographic Analysis Distribution of Analytes between Phases An analyte is in equilibrium between the two phases [S 1 ] [S 2 ] (in phase 1) (in phase 2) AS [S2 ] K 2 A S [S1 ] 1 AS, A 1 S Activity
Quad-Z 215 with Disposable Tips: Implementing the Use of ZipTips for the Purification of Biological Samples
 Quad-Z 215 with Disposable Tips: Implementing the Use of ZipTips for the Purification of Biological Samples Introduction Application Note 201 Joan Stevens, PhD and Kirby Reed (Gilson, Inc.) A ZipTip is
Quad-Z 215 with Disposable Tips: Implementing the Use of ZipTips for the Purification of Biological Samples Introduction Application Note 201 Joan Stevens, PhD and Kirby Reed (Gilson, Inc.) A ZipTip is
ADVANTAME (TENTATIVE)
 ADVANTAME (TENTATIVE) SYNONYMS INS No. 969 New tentative specifications prepared at the 77th JECFA (2013) and published in FAO JECFA Monographs 14 (2013). An ADI of 0-5 mg/kg body weight was established
ADVANTAME (TENTATIVE) SYNONYMS INS No. 969 New tentative specifications prepared at the 77th JECFA (2013) and published in FAO JECFA Monographs 14 (2013). An ADI of 0-5 mg/kg body weight was established
RESOLUTION OENO 33/2004 DETERMINATION OF SHIKIMIC ACID IN WINE BY HPLC AND UV-DETECTION
 DETERMINATION OF SHIKIMIC ACID IN WINE BY HPLC AND UV-DETECTION The GENERAL ASSEMBLY, Considering Article paragraph iv of the agreement establishing the International organisation of vine and wine Upon
DETERMINATION OF SHIKIMIC ACID IN WINE BY HPLC AND UV-DETECTION The GENERAL ASSEMBLY, Considering Article paragraph iv of the agreement establishing the International organisation of vine and wine Upon
Supporting Information for. Suppression of OH Generation from the Photo-Fenton Reaction in the Presence of α-pinene Secondary Organic Aerosol Material
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Supporting Information for Suppression of OH Generation from the Photo-Fenton Reaction in the Presence of α-pinene Secondary Organic Aerosol Material Rachel F. Hems *,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Supporting Information for Suppression of OH Generation from the Photo-Fenton Reaction in the Presence of α-pinene Secondary Organic Aerosol Material Rachel F. Hems *,
Analytical method related to authorised feed additive - 1i534
 Title DETERMINATION OF MESO-TARTARIC ACID, (D- + L-TARTARIC ACID), OXALIC ACID, MONO- AND DIHYDROXYMALONIC ACID IN mta-solutions Subtitle Liquid chromatography 1 SCOPE Determination of 50-60 mg of meso-tartaric
Title DETERMINATION OF MESO-TARTARIC ACID, (D- + L-TARTARIC ACID), OXALIC ACID, MONO- AND DIHYDROXYMALONIC ACID IN mta-solutions Subtitle Liquid chromatography 1 SCOPE Determination of 50-60 mg of meso-tartaric
Abstract. Introduction
 Investigating the Techniques of Solid- Liquid Extraction by isolating lycopene from tomato paste and Column Chromatography &Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC)by purifying lycopene Mengying Li Department of
Investigating the Techniques of Solid- Liquid Extraction by isolating lycopene from tomato paste and Column Chromatography &Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC)by purifying lycopene Mengying Li Department of
Determination of Total Bromine and Iodine Emission Spectrometric Method (ICP-OES) EuSalt/AS
 Determination of Total Bromine and Iodine Page 2 of 5 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION The present EuSalt Analytical Standard describes an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry method
Determination of Total Bromine and Iodine Page 2 of 5 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION The present EuSalt Analytical Standard describes an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry method
Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry
 Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry What is Chromatography? Chromatography is a technique for separating mixtures into their components in order to analyze, identify, purify, and/or quantify
Chromatography & instrumentation in Organic Chemistry What is Chromatography? Chromatography is a technique for separating mixtures into their components in order to analyze, identify, purify, and/or quantify
Functional Genomics Research Stream. Lecture: February 17, 2009 Masses, Volumes, Solutions & Dilutions
 Functional Genomics Research Stream Lecture: February 17, 2009 Masses, Volumes, Solutions & Dilutions Agenda Lab Work: Last Week New Equipment Solution Preparation: Fundamentals Solution Preparation: How
Functional Genomics Research Stream Lecture: February 17, 2009 Masses, Volumes, Solutions & Dilutions Agenda Lab Work: Last Week New Equipment Solution Preparation: Fundamentals Solution Preparation: How
Appendix II- Bioanalytical Method Development and Validation
 A2. Bioanalytical method development 1. Optimization of chromatographic conditions Method development and optimization of chromatographic parameters is of utmost important for validating a method in biological
A2. Bioanalytical method development 1. Optimization of chromatographic conditions Method development and optimization of chromatographic parameters is of utmost important for validating a method in biological
Optimized Flash Chromatography Purification: From TLC to large scale in three steps
 Optimized Flash Chromatography Purification: From TLC to large scale in three steps Veronica Thomason Teledyne Isco, Inc. P.O. Box 82531 Lincoln, NE 68501 2 Abstract Method development, necessary for optimizing
Optimized Flash Chromatography Purification: From TLC to large scale in three steps Veronica Thomason Teledyne Isco, Inc. P.O. Box 82531 Lincoln, NE 68501 2 Abstract Method development, necessary for optimizing
LUMEFANTRINUM LUMEFANTRINE
 July 2008 LUMEFANTRINE: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2008) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-second WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
July 2008 LUMEFANTRINE: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2008) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-second WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
CHEMISTRY DEPARTMENT
 POINT LEPREAU GENERATING STATION GADOLINIUM ARSENAZO III Issued By: Date: APPROVED BY: of 6 REVISION RECORD AUTHOR REV DESCRIPTION DATE 0 Initial Issue W. Mawhinney Not Tracked Oct./9 W. T. Underhill 2
POINT LEPREAU GENERATING STATION GADOLINIUM ARSENAZO III Issued By: Date: APPROVED BY: of 6 REVISION RECORD AUTHOR REV DESCRIPTION DATE 0 Initial Issue W. Mawhinney Not Tracked Oct./9 W. T. Underhill 2
Photochemistry of Nitro-Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. August 9, 2011
 Photochemistry of Nitro-Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons August 9, 2011 Photochemistry focuses on the absorption of light by atoms and molecules leading to chemical reactions. With the absorption of light,
Photochemistry of Nitro-Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons August 9, 2011 Photochemistry focuses on the absorption of light by atoms and molecules leading to chemical reactions. With the absorption of light,
Determination of Polymer Modifier in Asphalt
 Standard Method of Test for Determination of Polymer Modifier in Asphalt AASHTO Designation: T xxx-xx (2005) 1. SCOPE 1.1. This method of test is used to determine the polymer content of an asphalt sample.
Standard Method of Test for Determination of Polymer Modifier in Asphalt AASHTO Designation: T xxx-xx (2005) 1. SCOPE 1.1. This method of test is used to determine the polymer content of an asphalt sample.
METHOD 8033 ACETONITRILE BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY WITH NITROGEN-PHOSPHORUS DETECTION
 METHOD 80 ACETONITRILE BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY WITH NITROGEN-PHOSPHORUS DETECTION 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 80 may be used to determine the concentration of acetonitrile (CAS No. 75-05-8) in aqueous
METHOD 80 ACETONITRILE BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY WITH NITROGEN-PHOSPHORUS DETECTION 1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION 1.1 Method 80 may be used to determine the concentration of acetonitrile (CAS No. 75-05-8) in aqueous
AIM To verify Beer - Lambert s law and to determine the dissociation constant (Ka) of methyl red, Spectrophotometrically.
 C 141(Expt. No. ) NAME : ROLL No. : SIGNATURE : BATCH : DATE : VERIFICATION OF BEER - LAMBERT S LAW & DETERMINATION OF DISSOCIATION CONSTANT (Ka) OF METHYLRED, SPECTROPHOTOMETRICALLY AIM To verify Beer
C 141(Expt. No. ) NAME : ROLL No. : SIGNATURE : BATCH : DATE : VERIFICATION OF BEER - LAMBERT S LAW & DETERMINATION OF DISSOCIATION CONSTANT (Ka) OF METHYLRED, SPECTROPHOTOMETRICALLY AIM To verify Beer
7. Stability indicating analytical method development and validation of Ramipril and Amlodipine in capsule dosage form by HPLC.
 7. Stability indicating analytical method development and validation of and in capsule dosage form by HPLC. 7.1 INSTRUMENTS AND MATERIALS USED 7.1.1 INSTRUMENTS 1. Shimadzu LC-2010 CHT with liquid chromatograph
7. Stability indicating analytical method development and validation of and in capsule dosage form by HPLC. 7.1 INSTRUMENTS AND MATERIALS USED 7.1.1 INSTRUMENTS 1. Shimadzu LC-2010 CHT with liquid chromatograph
Chromatography. Gas Chromatography
 Chromatography Chromatography is essentially the separation of a mixture into its component parts for qualitative and quantitative analysis. The basis of separation is the partitioning of the analyte mixture
Chromatography Chromatography is essentially the separation of a mixture into its component parts for qualitative and quantitative analysis. The basis of separation is the partitioning of the analyte mixture
Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep HPLC and Flash Chromatography. Tips and Techniques to Optimize ELSD and MS based Purification
 Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep HPLC and Flash Chromatography Tips and Techniques to Optimize ELSD and MS based Purification Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep
Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep HPLC and Flash Chromatography Tips and Techniques to Optimize ELSD and MS based Purification Utilizing ELSD and MS as Secondary Detectors for Prep
Experiment#1 Beer s Law: Absorption Spectroscopy of Cobalt(II)
 : Absorption Spectroscopy of Cobalt(II) OBJECTIVES In successfully completing this lab you will: prepare a stock solution using a volumetric flask; use a UV/Visible spectrometer to measure an absorption
: Absorption Spectroscopy of Cobalt(II) OBJECTIVES In successfully completing this lab you will: prepare a stock solution using a volumetric flask; use a UV/Visible spectrometer to measure an absorption
ADVANTAME. Not less than 97.0% and not more than 102.0% on the anhydrous basis. Sweetener, flavour enhancer
 ADVANTAME SYNONYMS INS No. 969 Prepared at the 80 th JECFA (2015), published in FAO JECFA Monographs 17 (2015), superseding tentative specifications prepared at 77 th JECFA (2013). An ADI of 0-5 mg/kg
ADVANTAME SYNONYMS INS No. 969 Prepared at the 80 th JECFA (2015), published in FAO JECFA Monographs 17 (2015), superseding tentative specifications prepared at 77 th JECFA (2013). An ADI of 0-5 mg/kg
12 Nicarbazin Nicarbazin (4,4 -dinitro carbanilid (DNC) and 2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethyl pyrimidine (HDP))
 12 Nicarbazin Nicarbazin (4,4 -dinitro carbanilid (DNC) and 2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethyl pyrimidine (HDP)) O - O - O N + O N + O N NH N H N H O 1,3-bis(4-nitrophenyl)urea, 4,6-dimethyl-1H-pyrimidin-2-one C 13
12 Nicarbazin Nicarbazin (4,4 -dinitro carbanilid (DNC) and 2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethyl pyrimidine (HDP)) O - O - O N + O N + O N NH N H N H O 1,3-bis(4-nitrophenyl)urea, 4,6-dimethyl-1H-pyrimidin-2-one C 13
GUIDELINES FOR THE DESIGN OF CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYTICAL METHODS INTENDED FOR CIPAC COLLABORATIVE STUDY
 Page 1 of 13 CIPAC/4105/R GUIDELINES FOR THE DESIGN OF CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYTICAL METHODS INTENDED FOR CIPAC COLLABORATIVE STUDY Prepared for CIPAC by Dr M J Tandy*, P M Clarke and B White (UK) The rapid
Page 1 of 13 CIPAC/4105/R GUIDELINES FOR THE DESIGN OF CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYTICAL METHODS INTENDED FOR CIPAC COLLABORATIVE STUDY Prepared for CIPAC by Dr M J Tandy*, P M Clarke and B White (UK) The rapid
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 High Performance Liquid Chromatography What is HPLC? It is a separation technique that involves: Injection of small volume of liquid sample Into a tube packed with a tiny particles (stationary phase).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography What is HPLC? It is a separation technique that involves: Injection of small volume of liquid sample Into a tube packed with a tiny particles (stationary phase).
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information A. Chemical List Chemical Supplier Purity Piperazine Sigma-Aldrich >99% Ethanolamine Fisher Chemicals >99% Diethanolamine Fisher Chemicals >99% Methyldiethanolamine Sigma-Aldrich
Supplemental Information A. Chemical List Chemical Supplier Purity Piperazine Sigma-Aldrich >99% Ethanolamine Fisher Chemicals >99% Diethanolamine Fisher Chemicals >99% Methyldiethanolamine Sigma-Aldrich
METHANOLYSIS OF ACETAL
 Chem 367-2/ Methanolysis of Acetal 25 METHANOLYSIS OF ACETAL 1. Purpose Diethyl acetal undergoes an acid-catalyzed reaction with methanol in two steps, as follows: k 1 CH 3 CH(OEt) 2 + MeOH CH 3 CHOEtOMe
Chem 367-2/ Methanolysis of Acetal 25 METHANOLYSIS OF ACETAL 1. Purpose Diethyl acetal undergoes an acid-catalyzed reaction with methanol in two steps, as follows: k 1 CH 3 CH(OEt) 2 + MeOH CH 3 CHOEtOMe
Egualen Sodium Granules
 Egualen Sodium Granules Dissolution Weigh accurately an amount of Egualen Sodium Granules, equivalent to about 5 mg of egualen sodium (C 15 H 17 NaO 3 S 1/3 H2O) according to the labeled amount,
Egualen Sodium Granules Dissolution Weigh accurately an amount of Egualen Sodium Granules, equivalent to about 5 mg of egualen sodium (C 15 H 17 NaO 3 S 1/3 H2O) according to the labeled amount,
Open Column Chromatography, GC, TLC, and HPLC
 Open Column Chromatography, GC, TLC, and HPLC Murphy, B. (2017). Introduction to Chromatography: Lecture 1. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. USES OF CHROMATOGRAPHY
Open Column Chromatography, GC, TLC, and HPLC Murphy, B. (2017). Introduction to Chromatography: Lecture 1. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. USES OF CHROMATOGRAPHY
LAP-013. Procedure Title: Date: 6/28/96. Author: Raymond Ruiz and Tina Ehrman ISSUE DATE: 8/26/96 SUPERSEDES: 11/01/94.
 Ethanol Project Chemical Analysis and Testing Task Laboratory Analytical Procedure Procedure Title: LAP-013 HPLC Analysis of Liquid Fractions of Process Samples for Monomeric Sugars and Cellobiose Author:
Ethanol Project Chemical Analysis and Testing Task Laboratory Analytical Procedure Procedure Title: LAP-013 HPLC Analysis of Liquid Fractions of Process Samples for Monomeric Sugars and Cellobiose Author:
Automated Sample Preparation in Quality Control of Eye-Drop Formulation
 Automated Sample Preparation in Quality Control of Eye-Drop Formulation Application Note Authors Bart Tienpont, Maria Rambla Alegre, Frank David, and Pat Sandra Research Institute for Chromatography Kennedypark
Automated Sample Preparation in Quality Control of Eye-Drop Formulation Application Note Authors Bart Tienpont, Maria Rambla Alegre, Frank David, and Pat Sandra Research Institute for Chromatography Kennedypark
H 3 CO H 3 CO S CH 3
 FENITROTHION 35 H 3 CO P H 3 CO S O CH 3 NO 2 ISO common name Chemical name Fenitrothion O,O-Dimethyl O-4-nitro-m-tolyl phosphorothioate (IUPAC) O,O-Dimethyl O-(3-methyl-4-nitrophenyl)- phosphorothioate
FENITROTHION 35 H 3 CO P H 3 CO S O CH 3 NO 2 ISO common name Chemical name Fenitrothion O,O-Dimethyl O-4-nitro-m-tolyl phosphorothioate (IUPAC) O,O-Dimethyl O-(3-methyl-4-nitrophenyl)- phosphorothioate
 HPLC Workshop 16 June 2009 What does this do? Chromatography Theory Review Several chromatographic techniques Even though each method utilizes different techniques to separate compounds, the principles
HPLC Workshop 16 June 2009 What does this do? Chromatography Theory Review Several chromatographic techniques Even though each method utilizes different techniques to separate compounds, the principles
Prep 150 LC System: Considerations for Analytical to Preparative Scaling
 Andrew Aubin and Jo-Ann Jablonski Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA APPLICATION BENEFITS The Prep 150 LC System is an affordable, highly reliable system for preparative chromatography and is suitable
Andrew Aubin and Jo-Ann Jablonski Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA APPLICATION BENEFITS The Prep 150 LC System is an affordable, highly reliable system for preparative chromatography and is suitable
EFAVIRENZ Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia
 Document QAS/05.145/FIAL March 07 EFAVIREZ Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted at the Fortieth W Expert ommittee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
Document QAS/05.145/FIAL March 07 EFAVIREZ Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted at the Fortieth W Expert ommittee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
Streamlining the Analysis of Oral Contraceptives Using the ACQUITY UPLC H-Class System
 Streamlining the Analysis of Oral Contraceptives Using the ACQUITY UPLC H-Class System Margaret Maziarz, Sean M. McCarthy, Michael D. Jones, and Warren B. Potts Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA A P
Streamlining the Analysis of Oral Contraceptives Using the ACQUITY UPLC H-Class System Margaret Maziarz, Sean M. McCarthy, Michael D. Jones, and Warren B. Potts Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA A P
Macrolides in Honey Using Agilent Bond Elut Plexa SPE, Poroshell 120, and LC/MS/MS
 Macrolides in Honey Using Agilent Bond Elut Plexa SPE, Poroshell 120, and LC/MS/MS Application Note Food Testing and Agriculture Author Chen-Hao (Andy) Zhai and Rong-jie Fu Agilent Technologies (Shanghai)
Macrolides in Honey Using Agilent Bond Elut Plexa SPE, Poroshell 120, and LC/MS/MS Application Note Food Testing and Agriculture Author Chen-Hao (Andy) Zhai and Rong-jie Fu Agilent Technologies (Shanghai)
HPLC Preparative Scaleup of Calcium Channel Blocker Pharmaceuticals Application
 HPLC Preparative Scaleup of Calcium Channel Blocker Pharmaceuticals Application Pharmaceuticals Author Cliff Woodward and Ronald Majors Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2850 Centerville Road Wilmington, DE 19808
HPLC Preparative Scaleup of Calcium Channel Blocker Pharmaceuticals Application Pharmaceuticals Author Cliff Woodward and Ronald Majors Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2850 Centerville Road Wilmington, DE 19808
CHAPTER CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHODS OF SEPARATIONS
 Islamic University in Madinah Department of Chemistry CHAPTER - ----- CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHODS OF SEPARATIONS Prepared By Dr. Khalid Ahmad Shadid Chemistry Department Islamic University in Madinah TRADITIONAL
Islamic University in Madinah Department of Chemistry CHAPTER - ----- CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHODS OF SEPARATIONS Prepared By Dr. Khalid Ahmad Shadid Chemistry Department Islamic University in Madinah TRADITIONAL
High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
 High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a form of column chromatography that pumps a sample mixture or analyte in a solvent (known as the
High Pressure/Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a form of column chromatography that pumps a sample mixture or analyte in a solvent (known as the
This method describes the identification of the following prohibited colorants in cosmetic products:
 A. IDENTIFICATION BY TLC 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION This method describes the identification of the following prohibited colorants in cosmetic products: Names C I number Pigment Orange 5 12075 Metanil
A. IDENTIFICATION BY TLC 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION This method describes the identification of the following prohibited colorants in cosmetic products: Names C I number Pigment Orange 5 12075 Metanil
