Chiral separation of underivatized amino acids by ligand-exchange capillary electrophoresis using a copper(ii) L-lysine complex as selector
|
|
|
- William Brooks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Chromatography A, 945 (2002) locate/ chroma Chiral separation of underivatized amino acids by ligand-exchange capillary electrophoresis using a copper(ii) L-lysine complex as selector * Xiaoning Lu, Yi Chen, Lei Guo, Yifang Yang Group 205, Center for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing , China Received 6 June 2001; received in revised form 6 November 2001; accepted 6 November 2001 Abstract A ligand-exchange capillary electrophoretic method was explored, with L-lysine as the ligand and copper(ii) as the central ion. Its applicability was demonstrated with underivatized aromatic amino acids, namely D,L-phenylalanine, D,L-tryptophan, D,L-tyrosine and D,L-b-phenylserine. Optical resolutions of a single pair of amino acid enantiomers, and of mixed amino acids were obtained with a running buffer of 10 mm NH4Ac, 6.67 mm Cu(II) and mm L-lysine, ph 7.0. Sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS) was shown to be necessary for simultaneous separation of the mixed amino acids. The resolution was found to increase with the concentration of the copper(ii) complex at a copper(ii)-to-lysine ratio of 1:2. If the total concentration of copper(ii) and lysine was kept at 20 mm, decreasing the ratio of copper(ii) to lysine caused a resolution loss of tryptophan, but a slight resolution improvement of the other three amino acids. The ph of buffer is another important factor controlling the separations. For all the studied amino acids, the optimum ph was 6.0. An interesting phenomenon was observed in this study. SDS induces precipitation at a concentration below 32 mm at room temperature (1662 8C), possibly due to the formation of neutral substance from the SDS monomer and the copper(ii) lysine complex Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved. Keywords: Enantiomer separation; Ligand-exchange capillary electrophoresis; Complexation; Lysine; Amino acids 1. Introduction ligand-exchange capillary electrophoresis (LECE) to the resolution of dansylated amino acids, using Ligand-exchange chromatography has become an copper, Cu(II) L-histidine complex as a selector. important method of resolving the enantiomers of They also employed Cu(II) aspartame to improve amino acids by HPLC, since 1971 when Davankov the optical resolution [3]. Since then, other ligands and Rogozhin first reported their work [1]. Based on have been introduced, such as N,N-didecyl-L-alanine this principle, amino acids can also be optically [4,5] and L-arginine [6], with the central ions mainly resolved by capillary electrophoresis (CE). In 1985, being Cu(II) [4 10]. Schmid and Gubitz [7] found Gassman et al. [2] reported the first application of that when L-proline or L-hydroxyproline Cu(II) was used, high concentrations of complex were *Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: needed to yield an effective chiral separation. They then used N-alkyl derivatives of L-hydroxyproline to address: chenyi@public.east.net.cn (Y. Chen). improve the enantioselectivity [8,9]. A L-hydroxy / 02/ $ see front matter 2002 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved. PII: S (01)
2 250 X. Lu et al. / J. Chromatogr. A 945 (2002) proline Cu(II) complex was also employed as addi- tions with water by a factor of Running buffer tive by Chen et al. to resolve the optical and was prepared by dissolving copper(ii) sulfate and positional isomers of tyrosine and flurophenylalanine L-Lys in 10 mm ammonia acetic acid, adjusted to a [10], as well as tryptophan derivatives [11], using desired ph with 1 M ammonia or 1 M acetic acid. micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC). All solutions were prepared in double-distilled water The authors observed that the presence of sodium and filtered through a 0.45-mm membrane (Nihon dodecylsulfate (SDS) in the running buffer greatly Millipore, Japan) prior to use. enhanced the separation, but its concentration should be kept below 15 mm to maintain a stable baseline. These works show that ligand exchange is a 2.2. Instrumentation and separation conditions versatile procedure to perform chiral separations. A P/ACE 2050 capillary electrophoresis system There are at least two crucial factors that can be (Beckman Instruments, Fullerton, CA, USA) varied to introduce new separation mechanisms and equipped with an UV detector was used. Sample yield a better resolution. The first is the chiral ligand detection was performed at 214 nm. Uncoated fusedand the second an achiral additive like SDS. This silica capillaries of 57 cm (effective length 50 cm)3 opens a new window to explore more convenient 50 mm I.D. were used (Yongnian Optic Fiber Work, approaches to chiral separation by CE. Heibei, China). The capillary temperature was main- The purpose of this paper is to investigate the tained at 20 8C and the room temperature at 1662 potential of L-lysine (Lys) as a chiral ligand for the 8C. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was used to mark chiral separation of aromatic amino acids, based on the electroosmotic flow (EOF). the ligand exchange principle. Lys has a positively Samples were injected with pressure at 0.5 p.s.i. charged side chain which, we think, will interact for 2 s and separated at 20 kv, unless noted otherwith the electron-full aromatic ring of the studied wise (1 p.s.i Pa). Prior to use, the capilamino acids and play an important role in the laries were rinsed successively with water, 0.1 M enantiorecognition. In the following, we will show NaOH, and water for 5 min each. It was observed that L-Lys is effective in the enantiorecognition of that Lys adsorbed onto the capillary through electroaromatic amino acids when Cu(II) is used as the static interactions. In order to ensure the reprocentral ion. Moreover, SDS was found to be able to ducibility of migration time, capillaries were sequenenhance the enantioseparation dramatically. tially washed between two successive runs with: (i) water, (ii) 1% HNO 3, (iii) water, (iv) 0.1 M NaOH, and (v) water for 2.0 min each. 2. Experimental Peaks were identified by adding an amount of a 2.1. Chemicals and solutions known solute to the sample solutions. All amino acids were biochemicals except Lys which was of analytical grade. D,L-Phenylalanine (Phe), D,L-tryptophan (Trp), D,L-tyrosine (Tyr) and L-Lys were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA) and D,L-b-phenylserine (pser) from the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. L-Phe, L-Trp and L-Tyr and other reagents were all of analytical grade obtained from Beijing Chemical Work (Beijing, China). Stock solutions of samples were prepared by dissolving 2 4 mg of amino acids in 1 ml doubledistilled water. They were stored at 4 8C. Injected samples were prepared by diluting the stock solu- 3. Results and discussion 3.1. Basic consideration Lys is a basic amino acid with an isoelectric point (pi) at 9.4, possessing a side chain of an amino butyl group; all the tested amino acids are neutral with their pi values at around 6.0. Lys was selected so that it can (or possibly can) interact with negatively charged additive such as SDS. Thus, a concerted effect may be generated between the chiral complex and SDS to enhance the resolution.
3 3.2. Chiral separation of a single amino acid When Lys is used as a chiral ligand and Cu(II) as a central ion, the enantiomers of an amino acid can easily be separated by either capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) or MEKC. CZE is easier to carry out than MEKC, but its separation efficiency and resolution are poorer than MEKC (comparing Fig. 1A and B). The EOF under the ph of the buffer in CZE is so small that it is not measurable. The EOF suppression may be due to the adsorption of the positively charged side chain of Lys onto the capillary wall. Such adsorption also leads to band broadening. This negative effect is prevented by the addition of SDS to compensate for the positive charge. X. Lu et al. / J. Chromatogr. A 945 (2002) Chiral separation of mixed amino acids Mixed amino acids cannot be well resolved by CZE no matter how the separation is optimized. The reason is that the mobilities of these amino acids are too close (Fig. 2). This problem has been solved by addition of SDS into the CZE running buffer, namely by using MEKC (Fig. 3A). Fig. 2. Typical electropherograms of the chiral separations of the four amino acids by CZE. For all analytes, the D-form elutes before the L-form. Buffer: 10 mm NH4Ac, 6.67 mm Cu(II) and mm L-Lys, at ph 7.0; for other conditions see Experimental Migration order Fig. 2 shows that the elution order of the enantiomers is reversed when SDS is added. In CZE, the D-form elutes before the L-form, while the opposite occurs in MEKC. In CZE, a Cu(II) ternary complex may form in the presence of an aromatic amino acid in addition to Lys. Under neutral ph, such complexes are positively charged and will move faster than the free amino acids. In addition, in such a ternary complex, electrostatic interaction can take place between the positively charged side chain of Lys and the electron-full aromatic ring of the amino acids. According to Zare and co-workers [2,3], the interaction groups are closer in the configuration of L- Cu D complex than L-Cu L complex. Thus, the D Fig. 1. Elution order of the enantiomers of Trp as SDS is absent enantiomer forms a more stable complex and mi- (A) and present (B) in the buffer. The ratio of L-Trp to D-Trp in grates faster than the L enantiomer. In MEKC the the sample is 2:1. Conditions for (A) buffer: 10 mm NH4Ac, 6.67 SDS micelles, each having a negatively charged mm Cu(II) and mm L-Lys at ph 7.0; separation voltage: 23 kv. (B) Buffer: 10 mm NH4Ac, 1.33 mm Cu(II), 2.67 mm L-Lys and 50 mm SDS at ph 6.2. For other conditions, see Experimental. exterior and hydrophobic interior, can interact with the positively charged amino group of L-Lys through electrostatic interaction and the residue of the aro-
4 252 X. Lu et al. / J. Chromatogr. A 945 (2002) aromatic amino acids pass the detection window after the EOF (see Fig. 3A). Consequently, the migration order is reversed Critical conditions For an ideal separation, all factors have to be considered, such as buffers, temperature, voltage, and so forth. But usually, we just optimized some critical conditions namely (1) the concentration of the Cu(II) Lys complex which in turn affects the ratio of Lys to Cu(II); (2) the buffer ph and (3) the SDS concentration Cu(II) L-Lys complex Achiral separation of Tyr, pser, Phe, and Trp by MEKC was performed but the resolution and peak shape were poor (Fig. 3B). This poor separation was greatly improved when the Cu(II) L-Lys complex was present in the running buffer, although the migration times are prolonged (Fig. 3A). This indicates that the chiral complex greatly influences the migration behavior of the amino acids. Further studies demonstrated that the optical resolution, and also the elution time, increases steadily with the concentration of Cu(II) L-Lys complex (Table 1), while the molar ratio of Cu(II) to L-Lys was kept at 1:2. If the molar ratio of Cu(II) to L-Lys is changed, a more complicated impact on resolution can be Fig. 3. Electropherogram of separation of the mixture of the four amino acids with (A) or without (B) Cu(II) L-Lys complex. observed. Fig. 4 shows that the resolution of Trp is Peaks: 15Tyr; 25b-pSer; 35Phe; 45Trp. Conditions: (A) buffer: much more sensitive to the ratio than the others: its 10 mm NH4Ac, 50 mm SDS, 3.33 mm Cu(II) and 6.67 mm resolution decreases rapidly as the ratio decreases; on L-Lys, at ph 6.0; (B) buffer: 10 mm NH4Ac and 50 mm SDS, at the contrary, the resolutions of the other amino acids ph 6.0; for other conditions, see Experimental. slightly increases. In addition, pser and Phe tend to overlap at the low ratio range. Thus, no optimum matic amino acids through hydrophobic interaction, ratio exists in the tested range and we have to respectively. Again, the L-Lys Cu(II) D-amino acid compromise between the resolution of Trp and of the complexes are more stable than the corresponding other amino acids. A ratio at 1:2 was shown to be L-Lys Cu(II) L-amino acid complexes, since the suitable for our separations. residues of L-Lys and the aromatic amino acids in the Generally, increasing the ratio of L-Lys, while the former complex are closer and can interact simul- total concentration of Cu(II) and L-Lys is kept taneously with SDS micelles more conveniently. constant, reduces the competitive opportunity for the However, because of the high density of the negative solutes to form complex with Cu(II). Consequently, charges that a SDS micelle possesses, the interac- the optical resolution of the solutes should decrease. tions between the SDS micelles and Cu(II) complex- This is true for the resolution of Trp. As for the other es make the Cu(II) complexes migrate like anions. amino acids, the increasing resolution with the ratio This is evident in the electropherogram where the of L-Lys may be because of their different molecular
5 X. Lu et al. / J. Chromatogr. A 945 (2002) Table 1 Influence of concentration (C) of Cu(II) and L-Lys on separation by MEKC C Tyr b-pser Phe Trp (mm) tl td Rs tl td Rs tl td Rs tl td Rs (min) (min) (min) (min) (min) (min) (min) (min) Conditions: buffer: 10 mm NH4Ac, 50 mm SDS and different amounts of Cu(II) and L-Lys at ratio 1:2, ph 6.0; for other conditions, see Experimental; tl and td are the migration times of the L- and D-enantiomers, respectively. structures from that of Trp. Each of these three mm SDS, 3.33 mm CuSO4 and 6.67 mm L-Lys. amino acids contains a phenyl group while Trp has a Distinct maxima of the chiral separations could be indolyl ring. Additionally, the migration times of all observed at ph 6.0 (Fig. 5). The existence of a the amino acids decrease with the ratio of Cu(II) to maximum ph is explained as follows. As ph de- L-Lys, because more free amino acids which move creases from 8.0 to 5.0, the free amino acids are faster than the corresponding Cu(II) complex appear changed from negative ions to the neutral form (at in the buffer as the concentration of L-Lys increases. their pi around 6.0) or even positive ions, while the Cu(II) complexes remain to migrate as anions in the ph presence of SDS micelles. As a result, the difference Considering biological applications, it is prefer- in mobilities between the free amino acids and the able to perform separations around a neutral ph. The corresponding Cu(II) complexes is enhanced. Thus, influence of ph on the optical resolution was thus the chiral resolutions should be improved. But investigated from 5.0 to 8.0 at an increment of 0.5, decreasing ph may also reduce the extent of comwith a running buffer containing 10 mm NH Ac, 50 1 plexation of the Cu(II) ternary complex because H 4 Fig. 4. Dependence of resolution on the ratio of Cu(II) to L-Lys. Fig. 5. Influence of ph on the optical resolutions of the four Buffer: 10 mm NH4Ac, 20 mm of Cu(II) and L-Lys at different amino acids by MEKC. Conditions: buffer: 10 mm NH4Ac, 3.33 ratio, and 50 mm SDS, ph 6.0; for other conditions, see mm Cu(II) and 6.67 mm L-Lys, and 50 mm SDS, at different ph Experimental. values; for other conditions, see Experimental.
6 254 X. Lu et al. / J. Chromatogr. A 945 (2002) will complete with Cu(II) ions for the amino groups leading to the formation of negatively charged and of the amino acids. This untoward effect is more soluble complex of SDS, Cu(II), Lys and an amino considerable when ph is in the acidic range. The acid. compromise of these two effects results in a maxi- As expected, both chiral and achiral resolutions of mum ph for the chiral separation. The ph point at amino acids increased with SDS concentration above 8.0 is a bit abnormal, where optical resolutions of the critical concentration of 32 mm. Too high a Phe and Trp are better than those at ph 7.5. As concentration of SDS prolongs the separation time expected, the migration time increased with ph. and also increases the running current (see Table 2). Thus, running buffer at ph , was adopted to Very concentrated SDS is not required. Simultaneous yield better resolution and shorter separation time. baseline chiral resolution of the four amino acids could be achieved at 50 mm SDS when the running SDS buffer containing Cu(II) complex above 10 mm (Fig. Different concentrations of SDS were added to the 3A). buffer containing 10 mm NH4Ac, 6.67 mm Cu(II) and mm L-Lys at ph 6.0. As we hoped, the presence of SDS greatly improved enantioseparation of mixed amino acids (Fig. 3A). 4. Conclusion An interesting phenomenon was observed: precipi- The chiral Cu(II) L-Lys complex shows effective tation appeared when SDS was added at below a enantiorecognition toward the studied amino acids, certain concentration; the precipitation disappeared namely Phe, Trp, Tyr, and pser, both in CZE and when more SDS was added. The critical concen- MEKC. Moreover, the presence of SDS in the buffer tration was around 32 mm at room temperature can greatly improve the chiral separation. A simple (1662 8C). This phenomenon has not been menmethod for simultaneous separation of the enantiotioned in the literature to date. Further investigation mers, based on the exchange ligand principle, has revealed that the mixing SDS with mm L-Lys been thus developed. Further efforts will be made to or with 6.67 mm CuSO4 did not lead to precipiextent the applications of this method. tation, as the concentrations of SDS varied from 0 to 60 mm. The phenomenon may be caused by interactions between the Cu(II) complex and SDS monomer or SDS micelle. At low SDS concentrations (,32 Acknowledgements mm), the interaction between SDS monomer and the Cu(II) complex should dominate, which will result in The authors would like to thank the National the formation of neutral and insoluble substance. At Natural Sciences Foundation of China (no. higher SDS concentrations, the interaction between ) and the Chinese Academy of Sciences for SDS micelles and Cu(II) complex should dominate, the financial support of this work. Table 2 Influence of SDS concentration on the chiral separation by MEKC 40 mm 50 mm 60 mm 70 mm t t R t t R t t R t t R L D s L D s L D s L D s (min) (min) (min) (min) (min) (min) (min) (min) Tyr pser Phe Trp Conditions: buffer, 10 mm NH Ac, 6.67 mm Cu(II) and mm L-Lys, with different amounts of SDS, ph 6.2; for other conditions, 4 see Experimental.
7 X. Lu et al. / J. Chromatogr. A 945 (2002) References [1] V.A. Davankov, S.V. Rogozhin, J. Chromatogr. 60 (1971) 280. [2] E. Gassman, J. Kuo, R. Zare, Science 230 (1985) 813. [3] P. Gozel, E. Gassman, H. Michelsen, R. Zare, Anal. Chem. 59 (1987) 44. [4] A.S. Cohen, A. Paulus, B.L. Karger, Chromatographia 24 (1987) 15. [5] N.G. Sundin, T.M. Dowling, N. Grindberg, G. Bicker, J. Microcol. Sep. 8 (1996) 323. [6] Z. Yuan, L. Yang, S. Zhang, Electrophoresis 20 (1999) [7] M.G. Schmid, G. Gubitz, Enantiomer 1 (1996) 23. [8] A. Vegari, M.G. Schmid, F. Kilar, G. Gubitz, Electrophoresis 19 (1998) [9] M.G. Schmid, R. Rinaldi, D. Dreveny, G. Gubitz, J. Chromatogr. A 846 (1999) 157. [10] Z. Chen, J.M. Lin, K. Uchiyama, T. Hobo, J. Chromatogr. A 813 (1998) 369. [11] Z. Chen, J.M. Lin, K. Uchiyama, T. Hobo, Chromatographia 49 (1999) 436.
Estimation of Formation Constants of Ternary Cu(II) Complexes with Mixed Amino Acid Enantiomers Based on Ligand Exchange by Capillary Electrophoresis
 2000 The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry 837 Estimation of Formation Constants of Ternary Cu(II) Complexes with Mixed Amino Acid Enantiomers Based on Ligand Exchange by Capillary Electrophoresis
2000 The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry 837 Estimation of Formation Constants of Ternary Cu(II) Complexes with Mixed Amino Acid Enantiomers Based on Ligand Exchange by Capillary Electrophoresis
1.17 Capillary electrophoresis
 This text is based on the internationally-harmonized texts developed by the Pharmacopoeial Discussion Group (PDG). It has been developed and amended in line with the style and requirements of The International
This text is based on the internationally-harmonized texts developed by the Pharmacopoeial Discussion Group (PDG). It has been developed and amended in line with the style and requirements of The International
Soil Cation Analysis Using High-Performance Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Last Modified: October 20, 2006
 Soil Cation Analysis Using High-Performance Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Last Modified: October 20, 2006 Introduction: Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is a relatively new, but rapidly growing separation
Soil Cation Analysis Using High-Performance Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Last Modified: October 20, 2006 Introduction: Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is a relatively new, but rapidly growing separation
Fall 2012 Due In Class Friday, Oct. 19. Complete the following on separate paper. Show your work and clearly identify your answers.
 CHEM 322 Name Fall 2012 Due In Class Friday, Oct. 19 Complete the following on separate paper. Show your work and clearly identify your answers. General Separations 1. Describe the relative contributions
CHEM 322 Name Fall 2012 Due In Class Friday, Oct. 19 Complete the following on separate paper. Show your work and clearly identify your answers. General Separations 1. Describe the relative contributions
Exam I Answer Key: Summer 2006, Semester C
 1. Which of the following tripeptides would migrate most rapidly towards the negative electrode if electrophoresis is carried out at ph 3.0? a. gly-gly-gly b. glu-glu-asp c. lys-glu-lys d. val-asn-lys
1. Which of the following tripeptides would migrate most rapidly towards the negative electrode if electrophoresis is carried out at ph 3.0? a. gly-gly-gly b. glu-glu-asp c. lys-glu-lys d. val-asn-lys
Simultaneous analysis of the major metal cations and ammonium by CZE
 Simultaneous analysis of the major metal cations and ammonium by CZE This method has been published. You can download a copy of the PDF. Cite this method as: Warren CR, Adams MA (2004) Capillary electrophoresis
Simultaneous analysis of the major metal cations and ammonium by CZE This method has been published. You can download a copy of the PDF. Cite this method as: Warren CR, Adams MA (2004) Capillary electrophoresis
On-Line Preconcentration in Capillary Electrochromatography Using a Porous Monolith Together with Solvent Gradient and Sample Stacking
 Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5557-5563 On-Line Preconcentration in Capillary Electrochromatography Using a Porous Monolith Together with Solvent Gradient and Sample Stacking Joselito P. Quirino, Maria T. Dulay,
Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5557-5563 On-Line Preconcentration in Capillary Electrochromatography Using a Porous Monolith Together with Solvent Gradient and Sample Stacking Joselito P. Quirino, Maria T. Dulay,
A rapid and highly selective colorimetric method for direct detection of tryptophan in proteins via DMSO acceleration
 A rapid and highly selective colorimetric method for direct detection of tryptophan in proteins via DMSO acceleration Yanyan Huang, Shaoxiang Xiong, Guoquan Liu, Rui Zhao Beijing National Laboratory for
A rapid and highly selective colorimetric method for direct detection of tryptophan in proteins via DMSO acceleration Yanyan Huang, Shaoxiang Xiong, Guoquan Liu, Rui Zhao Beijing National Laboratory for
Chiral Separation of Arylalcohols by Capillary Electrophoresis Using Sulfonated β-cyclodextrin and Ag Colloids as Additives
 Chiral Separation of Arylalcohols by Capillary Electrophoresis Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2005, Vol. 26, No. 10 1549 Chiral Separation of Arylalcohols by Capillary Electrophoresis Using Sulfonated β-cyclodextrin
Chiral Separation of Arylalcohols by Capillary Electrophoresis Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2005, Vol. 26, No. 10 1549 Chiral Separation of Arylalcohols by Capillary Electrophoresis Using Sulfonated β-cyclodextrin
CHROMATOGRAPHY. The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments.
 CHROMATOGRAPHY The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments. THEORY OF CHROMATOGRAPHY: Separation of two sample components in
CHROMATOGRAPHY The term "chromatography" is derived from the original use of this method for separating yellow and green plant pigments. THEORY OF CHROMATOGRAPHY: Separation of two sample components in
Content : Properties of amino acids.. Separation and Analysis of Amino Acids
 قسم الكيمياء الحيوية.دولت على سالمه د. استاذ الكيمياء الحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ المحاضرة الثانية 1 Content : Properties of amino acids.. Separation and Analysis of Amino Acids 2 3 Physical Properties of Amino
قسم الكيمياء الحيوية.دولت على سالمه د. استاذ الكيمياء الحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ المحاضرة الثانية 1 Content : Properties of amino acids.. Separation and Analysis of Amino Acids 2 3 Physical Properties of Amino
CE of Basic Drugs Using a New Capillary Surface Treatment System.
 CE of Basic Drugs Using a New Capillary Surface Treatment System. Robust, Reliable Methods that Transfer. Chevigne R., de l Escaille F., Louis P., For MicroSolv Technology Corporation Introduction Traditional
CE of Basic Drugs Using a New Capillary Surface Treatment System. Robust, Reliable Methods that Transfer. Chevigne R., de l Escaille F., Louis P., For MicroSolv Technology Corporation Introduction Traditional
3.1. Preparation of Buffer Solutions
 3.1. Preparation of Buffer Solutions Experimental Part A volume of 50 ml of each buffer solution covering the ph range (pk a ±2) of the compound to be analyzed was prepared. For the classical method of
3.1. Preparation of Buffer Solutions Experimental Part A volume of 50 ml of each buffer solution covering the ph range (pk a ±2) of the compound to be analyzed was prepared. For the classical method of
EXAM 1 Fall 2009 BCHS3304, SECTION # 21734, GENERAL BIOCHEMISTRY I Dr. Glen B Legge
 EXAM 1 Fall 2009 BCHS3304, SECTION # 21734, GENERAL BIOCHEMISTRY I 2009 Dr. Glen B Legge This is a Scantron exam. All answers should be transferred to the Scantron sheet using a #2 pencil. Write and bubble
EXAM 1 Fall 2009 BCHS3304, SECTION # 21734, GENERAL BIOCHEMISTRY I 2009 Dr. Glen B Legge This is a Scantron exam. All answers should be transferred to the Scantron sheet using a #2 pencil. Write and bubble
Protein separation and characterization
 Address:800 S Wineville Avenue, Ontario, CA 91761,USA Website:www.aladdin-e.com Email USA: tech@aladdin-e.com Email EU: eutech@aladdin-e.com Email Asia Pacific: cntech@aladdin-e.com Protein separation
Address:800 S Wineville Avenue, Ontario, CA 91761,USA Website:www.aladdin-e.com Email USA: tech@aladdin-e.com Email EU: eutech@aladdin-e.com Email Asia Pacific: cntech@aladdin-e.com Protein separation
Page 1 Journal of Separation Science Influence of ionic liquids as electrolyte additives on chiral
 www.jss-journal.com Page 1 Journal of Separation Science Influence of ionic liquids as electrolyte additives on chiral separation of dansylated amino acids by using Zn(II) complex mediated chiral ligand
www.jss-journal.com Page 1 Journal of Separation Science Influence of ionic liquids as electrolyte additives on chiral separation of dansylated amino acids by using Zn(II) complex mediated chiral ligand
Supplementary information 1. INSTRUCTIONS FOR STUDENTS
 1 2 Supplementary information 1. INSTRUCTIONS FOR STUDENTS 1.- SAFETY AND WASTE DISPOSAL Reactant CAS Pictogram * Hazards L-ascorbic acid 50-81-7 - Not a dangerous substance Hexadimethrine bromide 28728-55-4
1 2 Supplementary information 1. INSTRUCTIONS FOR STUDENTS 1.- SAFETY AND WASTE DISPOSAL Reactant CAS Pictogram * Hazards L-ascorbic acid 50-81-7 - Not a dangerous substance Hexadimethrine bromide 28728-55-4
CAPILLARY ELECTROPHORESIS
 2.2.47. Capillary electrophoresis EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 5.0 2.2.47. CAPILLARY ELECTROPHORESIS 01/2005:20247 GENERAL S Capillary electrophoresis is a physical method of analysis based on the migration,
2.2.47. Capillary electrophoresis EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 5.0 2.2.47. CAPILLARY ELECTROPHORESIS 01/2005:20247 GENERAL S Capillary electrophoresis is a physical method of analysis based on the migration,
q = effectivechargeofthesolute, η = viscosity of the electrolyte solution,
 EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 6.0 2.2.47. Capillary electrophoresis Normalisation procedure. Thepercentagecontentofone or more components of the substance to be examined is calculated by determining the area
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 6.0 2.2.47. Capillary electrophoresis Normalisation procedure. Thepercentagecontentofone or more components of the substance to be examined is calculated by determining the area
Characterization of keto-enol tautomerism of p-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid using CE with amperometric detection and spectrometric analysis
 J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 4155 4160 4155 Ying Huang 1,2 Xiaoli Zhang 1 Liangjun Xu 2 Hongqing Chen 2 Guonan Chen 2 1 College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, Fujian, P.
J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 4155 4160 4155 Ying Huang 1,2 Xiaoli Zhang 1 Liangjun Xu 2 Hongqing Chen 2 Guonan Chen 2 1 College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, Fujian, P.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Visual Determination of Cu 2+ through Copper-Catalysed in-situ Formation of Ag Nanoparticles Xun Yuan a and Yi Chen* a,b a Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Living Biosystems,
Supporting Information Visual Determination of Cu 2+ through Copper-Catalysed in-situ Formation of Ag Nanoparticles Xun Yuan a and Yi Chen* a,b a Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Living Biosystems,
Content : Properties of amino acids.. Separation and Analysis of Amino Acids
 قسم الكيمياء الحيوية.دولت على سالمه د استاذ الكيمياء الحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ المحاضرة الثانية Content : Properties of amino acids.. Separation and Analysis of Amino Acids 2 -3 A. Physical properties 1. Solubility:
قسم الكيمياء الحيوية.دولت على سالمه د استاذ الكيمياء الحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ المحاضرة الثانية Content : Properties of amino acids.. Separation and Analysis of Amino Acids 2 -3 A. Physical properties 1. Solubility:
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 High Performance Liquid Chromatography What is HPLC? It is a separation technique that involves: Injection of small volume of liquid sample Into a tube packed with a tiny particles (stationary phase).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography What is HPLC? It is a separation technique that involves: Injection of small volume of liquid sample Into a tube packed with a tiny particles (stationary phase).
CAPILLARY ELECTROPHORESIS Draft proposal for The International Pharmacopoeia (May 2017) DRAFT FOR COMMENT
 May 2017 Draft for comment 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 CAPILLARY ELECTROPHORESIS Draft proposal for The
May 2017 Draft for comment 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 CAPILLARY ELECTROPHORESIS Draft proposal for The
Voltage-Induced Sample Release from Anion Exchange Supports in Capillary Electrochromatography
 1998 The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry 571 Voltage-Induced Sample Release from Anion Exchange Supports in Capillary Electrochromatography Shinya KITAGAWA and Takao TSUDA Department of Applied
1998 The Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry 571 Voltage-Induced Sample Release from Anion Exchange Supports in Capillary Electrochromatography Shinya KITAGAWA and Takao TSUDA Department of Applied
A Plausible Model Correlates Prebiotic Peptide Synthesis with. Primordial Genetic Code
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 A Plausible Model Correlates Prebiotic Peptide Synthesis with Primordial Genetic Code Jianxi Ying,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 A Plausible Model Correlates Prebiotic Peptide Synthesis with Primordial Genetic Code Jianxi Ying,
Biochemistry. Biochemical Techniques. 01 Electrophoresis : Basic Concepts
 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name 12 Module Name/Title 01 Electrophoresis: Basic Concept 1. Objectives 1.1 To understand basic concept of electrophoresis 1.2 To explain what determines charge
Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name 12 Module Name/Title 01 Electrophoresis: Basic Concept 1. Objectives 1.1 To understand basic concept of electrophoresis 1.2 To explain what determines charge
INTRODUCTION. Amino acids occurring in nature have the general structure shown below:
 Biochemistry I Laboratory Amino Acid Thin Layer Chromatography INTRODUCTION The primary importance of amino acids in cell structure and metabolism lies in the fact that they serve as building blocks for
Biochemistry I Laboratory Amino Acid Thin Layer Chromatography INTRODUCTION The primary importance of amino acids in cell structure and metabolism lies in the fact that they serve as building blocks for
NAME. EXAM I I. / 36 September 25, 2000 Biochemistry I II. / 26 BICH421/621 III. / 38 TOTAL /100
 EXAM I I. / 6 September 25, 2000 Biochemistry I II. / 26 BIH421/621 III. / 8 TOTAL /100 I. MULTIPLE HOIE (6 points) hoose the BEST answer to the question by circling the appropriate letter. 1. An amino
EXAM I I. / 6 September 25, 2000 Biochemistry I II. / 26 BIH421/621 III. / 8 TOTAL /100 I. MULTIPLE HOIE (6 points) hoose the BEST answer to the question by circling the appropriate letter. 1. An amino
Liquid Chromatography
 Liquid Chromatography 1. Introduction and Column Packing Material 2. Retention Mechanisms in Liquid Chromatography 3. Method Development 4. Column Preparation 5. General Instrumental aspects 6. Detectors
Liquid Chromatography 1. Introduction and Column Packing Material 2. Retention Mechanisms in Liquid Chromatography 3. Method Development 4. Column Preparation 5. General Instrumental aspects 6. Detectors
New Strategy for On-Line Preconcentration in Chromatographic Separations
 New Strategy for On-Line Preconcentration in Chromatographic Separations Joselito P. Quirino, Maria T. Dulay, Bryson D. Bennett, and Richard N. Zare* Department of Chemistry, Stanford University, Stanford,
New Strategy for On-Line Preconcentration in Chromatographic Separations Joselito P. Quirino, Maria T. Dulay, Bryson D. Bennett, and Richard N. Zare* Department of Chemistry, Stanford University, Stanford,
Amino Acids and Peptides
 Amino Acids Amino Acids and Peptides Amino acid a compound that contains both an amino group and a carboxyl group α-amino acid an amino acid in which the amino group is on the carbon adjacent to the carboxyl
Amino Acids Amino Acids and Peptides Amino acid a compound that contains both an amino group and a carboxyl group α-amino acid an amino acid in which the amino group is on the carbon adjacent to the carboxyl
A New Model for Asymmetric Amplification in Amino Acid Catalysis - Supporting information
 A New Model for Asymmetric Amplification in Amino Acid Catalysis - Supporting information Martin Klussmann, Hiroshi Iwamura, Suju P. Mathew, David H. Wells, Urvish Pandya, Alan Armstrong and Donna G. Blackmond
A New Model for Asymmetric Amplification in Amino Acid Catalysis - Supporting information Martin Klussmann, Hiroshi Iwamura, Suju P. Mathew, David H. Wells, Urvish Pandya, Alan Armstrong and Donna G. Blackmond
Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography: Some Aspects of Solvent and Column Selectivity
 Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography: Some Aspects of Solvent and Column Selectivity Monica Dolci, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, Cheshire, UK Technical Note 20544 Key Words Hydrophilic, HILIC,
Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography: Some Aspects of Solvent and Column Selectivity Monica Dolci, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Runcorn, Cheshire, UK Technical Note 20544 Key Words Hydrophilic, HILIC,
Determination of ppb Levels of Tryptophan Derivatives by Capillary Electrophoresis with Homogeneous Liquid Liquid Extraction and Sweeping Method
 April 2003 Chem. Pharm. Bull. 51(4) 373 377 (2003) 373 Determination of ppb Levels of Tryptophan Derivatives by Capillary Electrophoresis with Homogeneous Liquid Liquid Extraction and Sweeping Method Yoshitaka
April 2003 Chem. Pharm. Bull. 51(4) 373 377 (2003) 373 Determination of ppb Levels of Tryptophan Derivatives by Capillary Electrophoresis with Homogeneous Liquid Liquid Extraction and Sweeping Method Yoshitaka
Analysis - HPLC A.136. Primesep 5 µm columns B.136
 Primesep 5 µm columns Primesep columns feature double functionality of the bonding i.e : alkyl chain with anionic or cationic group, chelating group. This feature creates unique selectivities when using
Primesep 5 µm columns Primesep columns feature double functionality of the bonding i.e : alkyl chain with anionic or cationic group, chelating group. This feature creates unique selectivities when using
NH 2. Biochemistry I, Fall Term Sept 9, Lecture 5: Amino Acids & Peptides Assigned reading in Campbell: Chapter
 Biochemistry I, Fall Term Sept 9, 2005 Lecture 5: Amino Acids & Peptides Assigned reading in Campbell: Chapter 3.1-3.4. Key Terms: ptical Activity, Chirality Peptide bond Condensation reaction ydrolysis
Biochemistry I, Fall Term Sept 9, 2005 Lecture 5: Amino Acids & Peptides Assigned reading in Campbell: Chapter 3.1-3.4. Key Terms: ptical Activity, Chirality Peptide bond Condensation reaction ydrolysis
1. Ion exchange chromatography
 1. Ion exchange chromatography Ion Exchange Chromatography Most popular method for the separation or purification of charged molecules. In cation exchange chromatography, positively charged molecules are
1. Ion exchange chromatography Ion Exchange Chromatography Most popular method for the separation or purification of charged molecules. In cation exchange chromatography, positively charged molecules are
Electrokinetic Resolution of Amino Acid Enantiomers with Copper( I 1)-Aspartame Support Electrolyte
 44 Anal. Chem. 1907, 59, 44-49 Memorial Institute. Although the research described in this article has been funded wholly or in part by the United States Environmental Protection Agency through Interagency
44 Anal. Chem. 1907, 59, 44-49 Memorial Institute. Although the research described in this article has been funded wholly or in part by the United States Environmental Protection Agency through Interagency
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Cation-Selective Electropreconcentration Il Hyung Shin, a Ki-jung
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Cation-Selective Electropreconcentration Il Hyung Shin, a Ki-jung
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I. 1. Of the 20 standard amino acids, only is not optically active. The reason is that its side chain.
 Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won t improve your answer just answer clearly,
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1I A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won t improve your answer just answer clearly,
Specifically colorimetric recognition of calcium, strontium, barium. ions using 2-mercaptosuccinic acid-functionalized gold nanoparticles
 Electronic Supporting Information (ESI) for Specifically colorimetric recognition of calcium, strontium, barium ions using 2-mercaptosuccinic acid-functionalized gold nanoparticles and its use in reliable
Electronic Supporting Information (ESI) for Specifically colorimetric recognition of calcium, strontium, barium ions using 2-mercaptosuccinic acid-functionalized gold nanoparticles and its use in reliable
Chiral Separation Techniques: A Practical Approach
 Chiral Separation Techniques: A Practical Approach Subramanian, Ganapathy ISBN-13: 9783527315093 Table of Contents Preface. List of Contributors. 1 Method Development and Optimization of Enantioseparations
Chiral Separation Techniques: A Practical Approach Subramanian, Ganapathy ISBN-13: 9783527315093 Table of Contents Preface. List of Contributors. 1 Method Development and Optimization of Enantioseparations
A Novel Detection Technique of Hydrazine Hydrate: Modality Change of Hydrogen-Bonding Induced Rapid and Ultrasensitive Colorimetric Assay
 A Novel Detection Technique of Hydrazine Hydrate: Modality Change of Hydrogen-Bonding Induced Rapid and Ultrasensitive Colorimetric Assay Zhenlu Zhao, a Kelong Ai, b Guo Zhang, b Ying Gao, a Xiuyun Yang,*
A Novel Detection Technique of Hydrazine Hydrate: Modality Change of Hydrogen-Bonding Induced Rapid and Ultrasensitive Colorimetric Assay Zhenlu Zhao, a Kelong Ai, b Guo Zhang, b Ying Gao, a Xiuyun Yang,*
ProPac WCX-10 Columns
 ProPac WCX-10 Columns Guidance for column use Tips to maximize column lifetime ProPac WCX-10 Column Tips and Tricks This guide provides essential information and invaluable guidelines for mobile phases,
ProPac WCX-10 Columns Guidance for column use Tips to maximize column lifetime ProPac WCX-10 Column Tips and Tricks This guide provides essential information and invaluable guidelines for mobile phases,
Identification of System Parameters Critical for High-Performance cief
 Application Information Identification of System Parameters Critical for High-Performance cief Ingrid D. Cruzado-Park, Scott Mack and Chitra K. Ratnayake Beckman Coulter, Inc., Fullerton, CA, USA Introduction
Application Information Identification of System Parameters Critical for High-Performance cief Ingrid D. Cruzado-Park, Scott Mack and Chitra K. Ratnayake Beckman Coulter, Inc., Fullerton, CA, USA Introduction
Key Distance Learning Module I: Getting to Know Your Capillary
 Key Distance Learning Module I: Getting to Know Your Capillary Electrophoresis System C.M. White, K.M. Hanson, L.A. Holland*, C. Eugene Bennett Department of Chemistry, West Virginia University, Morgantown,
Key Distance Learning Module I: Getting to Know Your Capillary Electrophoresis System C.M. White, K.M. Hanson, L.A. Holland*, C. Eugene Bennett Department of Chemistry, West Virginia University, Morgantown,
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. CRBN binding assay with thalidomide enantiomers.
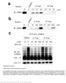 Supplementary Figure 1 CRBN binding assay with thalidomide enantiomers. (a) Competitive elution assay using thalidomide-immobilized beads coupled with racemic thalidomide. Beads were washed three times
Supplementary Figure 1 CRBN binding assay with thalidomide enantiomers. (a) Competitive elution assay using thalidomide-immobilized beads coupled with racemic thalidomide. Beads were washed three times
Separation of dithiocarbamate metal complexes by micellar electrokinetic chromatography
 eparation of dithiocarbamate metal complexes by micellar electrokinetic chromatography Emily F. Hilder, Miroslav Macka and Paul R. Haddad* chool of Chemistry, University of Tasmania, GPO Box 252-75, Hobart,
eparation of dithiocarbamate metal complexes by micellar electrokinetic chromatography Emily F. Hilder, Miroslav Macka and Paul R. Haddad* chool of Chemistry, University of Tasmania, GPO Box 252-75, Hobart,
CZE analysis of artificial sweeteners and preservatives in drinks
 CZE analysis of artificial sweeteners and preservatives in drinks Application Note Foods and Flavors Authors Rainer Schuster, Angelika Gratzfeld-Hüsgen Agilent Technologies Waldbronn, Germany Abstract
CZE analysis of artificial sweeteners and preservatives in drinks Application Note Foods and Flavors Authors Rainer Schuster, Angelika Gratzfeld-Hüsgen Agilent Technologies Waldbronn, Germany Abstract
This method describes the identification of the following prohibited colorants in cosmetic products:
 A. IDENTIFICATION BY TLC 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION This method describes the identification of the following prohibited colorants in cosmetic products: Names C I number Pigment Orange 5 12075 Metanil
A. IDENTIFICATION BY TLC 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION This method describes the identification of the following prohibited colorants in cosmetic products: Names C I number Pigment Orange 5 12075 Metanil
1. Amino Acids and Peptides Structures and Properties
 1. Amino Acids and Peptides Structures and Properties Chemical nature of amino acids The!-amino acids in peptides and proteins (excluding proline) consist of a carboxylic acid ( COOH) and an amino ( NH
1. Amino Acids and Peptides Structures and Properties Chemical nature of amino acids The!-amino acids in peptides and proteins (excluding proline) consist of a carboxylic acid ( COOH) and an amino ( NH
Introduction to Chromatography
 Introduction to Chromatography Dr. Sana Mustafa Assistant Professor Department of Chemistry, Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science & Technology, Karachi. What is Chromatography? Derived from the Greek
Introduction to Chromatography Dr. Sana Mustafa Assistant Professor Department of Chemistry, Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science & Technology, Karachi. What is Chromatography? Derived from the Greek
Chiral Columns for enantiomer separation by HPLC
 Chiral Columns for enantiomer separation by HPLC SUMICHIRAL OA columns are high-performance chiral columns for enantiomer separation by HPLC. On SUMICHIRAL OA columns direct separation of various enantiomers
Chiral Columns for enantiomer separation by HPLC SUMICHIRAL OA columns are high-performance chiral columns for enantiomer separation by HPLC. On SUMICHIRAL OA columns direct separation of various enantiomers
Electronic supplementary information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of highly crystalline
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of highly crystalline
Analytical Chemistry
 Analytical Chemistry Chromatographic Separations KAM021 2016 Dr. A. Jesorka, 6112, aldo@chalmers.se Introduction to Chromatographic Separations Theory of Separations -Chromatography Terms Summary: Chromatography
Analytical Chemistry Chromatographic Separations KAM021 2016 Dr. A. Jesorka, 6112, aldo@chalmers.se Introduction to Chromatographic Separations Theory of Separations -Chromatography Terms Summary: Chromatography
Research Article. 1 Introduction Electrophoresis 2007, 28, Cevdet Akbay 1 Nicole L. Gill 2 Isiah M. Warner 2 *
 1752 Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 1752 1761 Cevdet Akbay 1 Nicole L. Gill 2 Isiah M. Warner 2 * 1 Department of Natural Sciences, Fayetteville State University, Fayetteville, NC, USA 2 Department of Chemistry,
1752 Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 1752 1761 Cevdet Akbay 1 Nicole L. Gill 2 Isiah M. Warner 2 * 1 Department of Natural Sciences, Fayetteville State University, Fayetteville, NC, USA 2 Department of Chemistry,
ELECTROPHORESIS SLAB (THIN LAYER GEL) AND CAPILLARY METHODS. A. General Introduction
 ELECTROPHORESIS SLAB (THIN LAYER GEL) AND CAPILLARY METHODS A. General Introduction Electrophoresis: a saration method based on differential rate of migration of charged species in an applied dc electric
ELECTROPHORESIS SLAB (THIN LAYER GEL) AND CAPILLARY METHODS A. General Introduction Electrophoresis: a saration method based on differential rate of migration of charged species in an applied dc electric
KP IX General Information
 General Information KP IX 1817 General Information 1. Capillary Electrophoresis... 1818 2. Determination of Bulk and Tapped Densities... 1824 3. Disinfection and Sterilization Methods... 1825 4. Guideline
General Information KP IX 1817 General Information 1. Capillary Electrophoresis... 1818 2. Determination of Bulk and Tapped Densities... 1824 3. Disinfection and Sterilization Methods... 1825 4. Guideline
Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section - 4 : Ion Exchange Chrom. Prof. Tarek A. Fayed
 Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section - 4 : Ion Exchange Chrom. Prof. Tarek A. Fayed Ion Exchange Chromatography (IEC) In this type of chromatography, the solid stationary phase )organic resin) is
Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Section - 4 : Ion Exchange Chrom. Prof. Tarek A. Fayed Ion Exchange Chromatography (IEC) In this type of chromatography, the solid stationary phase )organic resin) is
Properties of Amino Acids
 Biochemistry Department Date:19/9/ 2017 Properties of Amino Acids Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 1 Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs) By the end of this lecture,
Biochemistry Department Date:19/9/ 2017 Properties of Amino Acids Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 1 Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs) By the end of this lecture,
penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS
 penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS penta-hilic Highly retentive, proprietary penta-hydroxy-ligand Excellent peak shape for polar compounds with a variety of functional groups: acids, bases, zwitterions strong and
penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS penta-hilic Highly retentive, proprietary penta-hydroxy-ligand Excellent peak shape for polar compounds with a variety of functional groups: acids, bases, zwitterions strong and
What type of samples are common? Time spent on different operations during LC analyses. Number of samples? Aims. Sources of error. Sample preparation
 What type of samples are common? Sample preparation 1 2 Number of samples? Time spent on different operations during LC analyses 3 4 Sources of error Aims Sample has to be representative Sample has to
What type of samples are common? Sample preparation 1 2 Number of samples? Time spent on different operations during LC analyses 3 4 Sources of error Aims Sample has to be representative Sample has to
Precision and accuracy of protein size determination using the ActiPix TDA200 Nano-Sizing System
 Precision and accuracy of protein size determination using the ActiPix TDA200 Nano-Sizing System Keywords: Hydrodynamic radius, diffusion coefficient, sizing, Taylor dispersion analysis, protein, antibodies,
Precision and accuracy of protein size determination using the ActiPix TDA200 Nano-Sizing System Keywords: Hydrodynamic radius, diffusion coefficient, sizing, Taylor dispersion analysis, protein, antibodies,
Full file at Chapter 2 Water: The Solvent for Biochemical Reactions
 Chapter 2 Water: The Solvent for Biochemical Reactions SUMMARY Section 2.1 Summary Water is a polar molecule, with a partial negative charge on the oxygen and partial positive charges on the hydrogens.
Chapter 2 Water: The Solvent for Biochemical Reactions SUMMARY Section 2.1 Summary Water is a polar molecule, with a partial negative charge on the oxygen and partial positive charges on the hydrogens.
Shodex TM ODP2 HP series columns
 HPLC Columns Shodex TM ODP2 HP series columns Better retention of highly polar substances Technical notebook No. 6 Contents 1. Introduction 1-1. Specifications 1-2. Eluent Compatibility of ODP2 HP Series
HPLC Columns Shodex TM ODP2 HP series columns Better retention of highly polar substances Technical notebook No. 6 Contents 1. Introduction 1-1. Specifications 1-2. Eluent Compatibility of ODP2 HP Series
Chapter content. Reference
 Chapter 7 HPLC Instrumental Analysis Rezaul Karim Environmental Science and Technology Jessore University of Science and Technology Chapter content Liquid Chromatography (LC); Scope; Principles Instrumentation;
Chapter 7 HPLC Instrumental Analysis Rezaul Karim Environmental Science and Technology Jessore University of Science and Technology Chapter content Liquid Chromatography (LC); Scope; Principles Instrumentation;
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 STANDARDBASE techniques: High Performance Liquid Chromatography Drenthe College, The Netherlands 1. Introduction HPLC. High Performance Liquid Chromatography High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
STANDARDBASE techniques: High Performance Liquid Chromatography Drenthe College, The Netherlands 1. Introduction HPLC. High Performance Liquid Chromatography High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out.
 Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
EFAVIRENZ Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia
 Document QAS/05.145/FIAL March 07 EFAVIREZ Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted at the Fortieth W Expert ommittee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
Document QAS/05.145/FIAL March 07 EFAVIREZ Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted at the Fortieth W Expert ommittee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Tuning Supramolecular Structure and Functions of Peptide bola-amphiphile by Solvent Evaporation-Dissolution Anhe Wang,, Lingyun Cui,, Sisir Debnath, Qianqian Dong, Xuehai Yan, Xi
Supporting Information Tuning Supramolecular Structure and Functions of Peptide bola-amphiphile by Solvent Evaporation-Dissolution Anhe Wang,, Lingyun Cui,, Sisir Debnath, Qianqian Dong, Xuehai Yan, Xi
Analysis of Metals, Halides, and Inorganic Ions Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography
 Application Note Inorganic Ions, Water Testing, Minerals, Metals, Basic Chemicals Analysis of Metals, Halides, and Inorganic Ions Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography Authors Anne Mack, Adam Bivens
Application Note Inorganic Ions, Water Testing, Minerals, Metals, Basic Chemicals Analysis of Metals, Halides, and Inorganic Ions Using Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography Authors Anne Mack, Adam Bivens
A. Two of the common amino acids are analyzed. Amino acid X and amino acid Y both have an isoionic point in the range of
 Questions with Answers- Amino Acids & Peptides A. Two of the common amino acids are analyzed. Amino acid X and amino acid Y both have an isoionic point in the range of 5.0-6.5 (Questions 1-4) 1. Which
Questions with Answers- Amino Acids & Peptides A. Two of the common amino acids are analyzed. Amino acid X and amino acid Y both have an isoionic point in the range of 5.0-6.5 (Questions 1-4) 1. Which
BENG 183 Trey Ideker. Protein Sequencing
 BENG 183 Trey Ideker Protein Sequencing The following slides borrowed from Hong Li s Biochemistry Course: www.sb.fsu.edu/~hongli/4053notes Introduction to Proteins Proteins are of vital importance to biological
BENG 183 Trey Ideker Protein Sequencing The following slides borrowed from Hong Li s Biochemistry Course: www.sb.fsu.edu/~hongli/4053notes Introduction to Proteins Proteins are of vital importance to biological
CHAPTER 19 PARACETAMOL + IBUPROFEN
 CHAPTER 19 PARACETAMOL + IBUPROFEN SUMMARY 246 A combination of paracetamol and ibuprofen is marketed in India. Literature survey indicated that one titrimetnc-1-** and one HPLC193 methods are reported
CHAPTER 19 PARACETAMOL + IBUPROFEN SUMMARY 246 A combination of paracetamol and ibuprofen is marketed in India. Literature survey indicated that one titrimetnc-1-** and one HPLC193 methods are reported
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Janus Hollow Spheres by Emulsion Interfacial Self-Assembled Sol-Gel Process Fuxin Liang, Jiguang Liu, Chengliang Zhang, Xiaozhong Qu, Jiaoli Li, Zhenzhong Yang* State Key Laboratory
Supporting Information Janus Hollow Spheres by Emulsion Interfacial Self-Assembled Sol-Gel Process Fuxin Liang, Jiguang Liu, Chengliang Zhang, Xiaozhong Qu, Jiaoli Li, Zhenzhong Yang* State Key Laboratory
Natural montmorillonite nanosheet colloid-catalyzed hydrogen peroxide
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances Supplementary Information Natural montmorillonite
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances Supplementary Information Natural montmorillonite
Content. * *
 Supporting information for Colloidal Synthesis of Lettuce-like Copper Sulfide for Light-Gating Heterogeneous Nanochannels Huan Wang,, Qian Liu,, Wenhua Li, *, Liping Wen, Dong Zheng, Zhishan Bo *, and
Supporting information for Colloidal Synthesis of Lettuce-like Copper Sulfide for Light-Gating Heterogeneous Nanochannels Huan Wang,, Qian Liu,, Wenhua Li, *, Liping Wen, Dong Zheng, Zhishan Bo *, and
Chapter 2 Water: The Solvent for Biochemical Reactions
 Chapter 2 Water: The Solvent for Biochemical Reactions SUMMARY Section 2.1 Water is a polar molecule, with a partial negative charge on the oxygen and partial positive charges on the hydrogens. There are
Chapter 2 Water: The Solvent for Biochemical Reactions SUMMARY Section 2.1 Water is a polar molecule, with a partial negative charge on the oxygen and partial positive charges on the hydrogens. There are
Claire Kaiser, Giselle Seguí-Lines, Jason D Amaral, Adam S. Ptolemy and Philip Britz-McKibbin*
 SUPPORTING MATERIAL Claire Kaiser, Giselle Seguí-Lines, Jason D Amaral, Adam S. Ptolemy and Philip Britz-McKibbin* Department of Chemistry, McMaster University, 280 Main St. W., Hamilton, ON, Canada, L8S
SUPPORTING MATERIAL Claire Kaiser, Giselle Seguí-Lines, Jason D Amaral, Adam S. Ptolemy and Philip Britz-McKibbin* Department of Chemistry, McMaster University, 280 Main St. W., Hamilton, ON, Canada, L8S
Adding sodium dodecylsulfate to the running electrolyte enhances the separation of gold nanoparticles by capillary electrophoresis
 Analytica Chimica Acta 510 (2004) 77 83 Adding sodium dodecylsulfate to the running electrolyte enhances the separation of gold nanoparticles by capillary electrophoresis Fu-Ken Liu a, Guor-Tzo Wei b,
Analytica Chimica Acta 510 (2004) 77 83 Adding sodium dodecylsulfate to the running electrolyte enhances the separation of gold nanoparticles by capillary electrophoresis Fu-Ken Liu a, Guor-Tzo Wei b,
A long-lived iridium(iii) chemosensor for the real-time
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information A long-lived iridium(iii) chemosensor for the real-time
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry B. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information A long-lived iridium(iii) chemosensor for the real-time
Highly Sensitive and Selective Colorimetric Visualization of Streptomycin in Raw Milk Using Au Nanoparticles Supramolecular Assembly
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Highly Sensitive and Selective Colorimetric Visualization of Streptomycin in Raw Milk Using Au Nanoparticles Supramolecular Assembly Jiayu Sun, Jiechao Ge, Weimin Liu, Zhiyuan Fan,
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Highly Sensitive and Selective Colorimetric Visualization of Streptomycin in Raw Milk Using Au Nanoparticles Supramolecular Assembly Jiayu Sun, Jiechao Ge, Weimin Liu, Zhiyuan Fan,
CYCLOSERINE Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia. (November 2008) CYCLOSERINUM CYCLOSERINE
 December 2008 CYCLOSERINE Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (November 2008) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-third WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
December 2008 CYCLOSERINE Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (November 2008) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-third WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
Organic Acids Analysis Kit
 Capillary Electrophoresis Organic Acids Analysis Kit PN 5063-6510 2 Upon receipt, please verify that all kit contents listed on page 4 are included. If any part is missing, contact your Agilent Technologies
Capillary Electrophoresis Organic Acids Analysis Kit PN 5063-6510 2 Upon receipt, please verify that all kit contents listed on page 4 are included. If any part is missing, contact your Agilent Technologies
RediSep Rf C18 Flash Column Loading Techniques
 RediSep Rf C18 Flash Column Loading Techniques Chromatography Application Note AN88 Abstract There are several techniques for loading samples onto reusable RediSep Rf C18 flash columns. The techniques
RediSep Rf C18 Flash Column Loading Techniques Chromatography Application Note AN88 Abstract There are several techniques for loading samples onto reusable RediSep Rf C18 flash columns. The techniques
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Water: The Solvent for Biochemical Reactions
 Chapter 2 Water: The Solvent for Biochemical Reactions 11 SUMMARY Section 2.1 Section 2.2 Section 2.3 Section 2.4 Water is a polar molecule, with a partial negative charge on the oxygen and partial positive
Chapter 2 Water: The Solvent for Biochemical Reactions 11 SUMMARY Section 2.1 Section 2.2 Section 2.3 Section 2.4 Water is a polar molecule, with a partial negative charge on the oxygen and partial positive
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information A fluorescent turn-on probe for bisulfite based on hydrogen bond-inhibited C=N isomerization mechanism Yuan-Qiang Sun, Pi Wang, Jing Liu, Jingyu Zhang and Wei Guo* School of Chemistry
Supplementary Information A fluorescent turn-on probe for bisulfite based on hydrogen bond-inhibited C=N isomerization mechanism Yuan-Qiang Sun, Pi Wang, Jing Liu, Jingyu Zhang and Wei Guo* School of Chemistry
Practice Midterm Exam 200 points total 75 minutes Multiple Choice (3 pts each 30 pts total) Mark your answers in the space to the left:
 MITES ame Practice Midterm Exam 200 points total 75 minutes Multiple hoice (3 pts each 30 pts total) Mark your answers in the space to the left: 1. Amphipathic molecules have regions that are: a) polar
MITES ame Practice Midterm Exam 200 points total 75 minutes Multiple hoice (3 pts each 30 pts total) Mark your answers in the space to the left: 1. Amphipathic molecules have regions that are: a) polar
Extraction and separation of D/L-lactic acid in simulated fermentation broth
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 28(7), 1608-1612 (2011) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-011-0010-z INVITED REVIEW PAPER Extraction and separation of D/L-lactic acid in simulated fermentation broth Jun Zhou, Wentao Bi, and Kyung
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 28(7), 1608-1612 (2011) DOI: 10.1007/s11814-011-0010-z INVITED REVIEW PAPER Extraction and separation of D/L-lactic acid in simulated fermentation broth Jun Zhou, Wentao Bi, and Kyung
Potentiometric Titration of an Amino Acid. Introduction
 NAME: Course: DATE Sign-Off: Performed: Potentiometric Titration of an Amino Acid Introduction In previous course-work, you explored the potentiometric titration of a weak acid (HOAc). In this experiment,
NAME: Course: DATE Sign-Off: Performed: Potentiometric Titration of an Amino Acid Introduction In previous course-work, you explored the potentiometric titration of a weak acid (HOAc). In this experiment,
LUMEFANTRINUM LUMEFANTRINE
 July 2008 LUMEFANTRINE: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2008) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-second WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
July 2008 LUMEFANTRINE: Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia (July 2008) This monograph was adopted at the Forty-second WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations
INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR CHIRALPAK ZWIX(+) and CHIRALPAK ZWIX(-)
 800 orth Five Points Road West Chester, PA 19380 800 6 CIRAL Tel: 610-594-2100 Fax: 610-594-2325 chiral@chiraltech.com www.chiraltech.com ISTRUCTI MAUAL FR CIRALPAK ZWIX(+) and CIRALPAK ZWIX(-) Semi-Preparative
800 orth Five Points Road West Chester, PA 19380 800 6 CIRAL Tel: 610-594-2100 Fax: 610-594-2325 chiral@chiraltech.com www.chiraltech.com ISTRUCTI MAUAL FR CIRALPAK ZWIX(+) and CIRALPAK ZWIX(-) Semi-Preparative
SCIEX Cation Analysis Kit For P/ACE MDQ and P/ACE MDQ plus Capillary Electrophoresis Systems. Instruction Guide
 For P/ACE MDQ and P/ACE MDQ plus Capillary Electrophoresis Systems A49109AE May 2015 AB Sciex Pte. Ltd and its affiliates disclaims all warranties with respect to this document, expressed or implied, including
For P/ACE MDQ and P/ACE MDQ plus Capillary Electrophoresis Systems A49109AE May 2015 AB Sciex Pte. Ltd and its affiliates disclaims all warranties with respect to this document, expressed or implied, including
Chiral Flash Columns
 6 -I -I SFC Chiral Columns Chiral Flash/MPLC Columns -I -I Immobilized Crown ether HPLC columns for separation in acidic mobile phase SFC Chiral Columns Chiral Flash Columns CHIRAL FLASH / MPLC Columns
6 -I -I SFC Chiral Columns Chiral Flash/MPLC Columns -I -I Immobilized Crown ether HPLC columns for separation in acidic mobile phase SFC Chiral Columns Chiral Flash Columns CHIRAL FLASH / MPLC Columns
Cu-Creatinine- Metol system
 Quantification of Creatinine in Human Serum using Metol as a Chromogenic Probe Materials and methods 6.1. Reagents 6.1.1. N-methyl-p-aminophenol sulfate N-methyl-p-aminophenol sulfate also denoted as Metol
Quantification of Creatinine in Human Serum using Metol as a Chromogenic Probe Materials and methods 6.1. Reagents 6.1.1. N-methyl-p-aminophenol sulfate N-methyl-p-aminophenol sulfate also denoted as Metol
Separation Sciences. 1. Introduction: Fundamentals of Distribution Equilibrium. 2. Gas Chromatography (Chapter 2 & 3)
 Separation Sciences 1. Introduction: Fundamentals of Distribution Equilibrium 2. Gas Chromatography (Chapter 2 & 3) 3. Liquid Chromatography (Chapter 4 & 5) 4. Other Analytical Separations (Chapter 6-8)
Separation Sciences 1. Introduction: Fundamentals of Distribution Equilibrium 2. Gas Chromatography (Chapter 2 & 3) 3. Liquid Chromatography (Chapter 4 & 5) 4. Other Analytical Separations (Chapter 6-8)
penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS
 penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS Highly retentive, proprietary penta-hydroxy-ligand penta-hilic Excellent peak shape for polar compounds with a variety of functional groups: acids, bases, zwitterions strong and
penta-hilic UHPLC COLUMNS Highly retentive, proprietary penta-hydroxy-ligand penta-hilic Excellent peak shape for polar compounds with a variety of functional groups: acids, bases, zwitterions strong and
Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis
 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis Hansen, Steen ISBN-13: 9780470661222 Table of Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Analysis 1 1.1 Applications and Definitions 1 1.2 The
Introduction to Pharmaceutical Chemical Analysis Hansen, Steen ISBN-13: 9780470661222 Table of Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction to Pharmaceutical Analysis 1 1.1 Applications and Definitions 1 1.2 The
