Proof of Down-Conversion by CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots on Silicon Solar Cells
|
|
|
- Anissa Douglas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proof of Don-Conversion by CdSe/ZnS uantum Dots on Silicon Solar Cells Bahareh Sadeghimakki, Zhen GaO and Siva Sivoththaman Centre for Advanced Photovoltaic Devices and Systems, Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, Waterloo, Ontario, N2L 3G1, Canada Abstract - The performance of the crystalline silicon solar cells can be improved ith spectrally engineered layers. Core/shell CdSe/ZnS quantum dots (Ds) ith tunable absorption-emission avelengths in UV-Vis range can be applied as luminescence centers in luminescence don-conversion layers (LDC). In this ork, CdSe/ZnS Ds ith an emission avelength of 620nm and luminescence quantum efficiency (LE) of 85% ere deployed on planar and textured crystalline silicon solar cells for don-conversion. The structural and optical characteristics of the Ds and the employed layer ere studied. The cell performances before and after LDC layer deployment ere investigated. Experimental verification as obtained on luminescence don-conversion of the incident photons in the cells containing LDC layers. Index Terms - photoluminescence, silicon solar cells. CdSe/ZnS quantum dots, don-conversion, I. INTRODUCTION Lninescence don-conversion (LDC) is one of the spectral engineering approaches [1-4] that can improve solar cell performance by means of absorption and emission in luminescence centers such as rare-earth ions [5], dyes [6] and quantum dots (Ds) [1, 7, 8]. The avelength of the incident photons can be don-converted, from the avelengths here the spectral response of the solar cell is lo, to the avelengths here the spectral response of the cell is high. High brightness, stability and broad absorption band are the advantages of Ds ith respect to other luminescent materials, hich makes them potential candidates for use in donconversion layers [7, 8]. Since LDC is a passive approach, it eliminates any interference ith the active material of a photovoltaic (PY) device hich is technically favorable. Hence, the method does not add any complication to the production of the existing device. One factor that limits the LDC method from being perfectly beneficial is the relatively lo luminescence quantum efficiency (LE) of existing Ds. Exploiting highly luminescent Ds in LDCs needs to be considered in order to gain from this method. In this ork, CdSe/ZnS Ds ith high LE ere deployed on planar and textured crystalline silicon solar cells to examine the don-conversion effect. The morphology and photoluminescence (PL) properties of the Ds and the employed layer ere studied. The performance of cells ith LDC layers as compared ith a reference cell. The improved performance of cells ith LDC layers proved the D donconversion effect. II. METHODOLOGIES FOR LDC LAYER FORMATION A. Structural Characteristics ojcdselzns in Liquid Form Core/shell CdSe/ZnS Ds dispersed in toluene and stabilized in octadecyl amine (ODA) ere purchased from a commercial supplier. Fig. 1 exhibits the Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) image of the Ds prepared by dropcasting a diluted solution onto a carbon coated copper grid. The Ds average particle size is 6nm and they are ell separated from one another ith no agglomeration. The lattice structure of the Ds in the zone axis is clear in the high resolution (HR)-TEM image, indicating their Wurtzite crystalline structures (see inset in Fig. 1). The thickness of the shells is about 6nm and the unclear interface beteen the CdSe core and ZnS shell is due to the epitaxial groth of the shell and small lattice mismatch beteen the core and the shell. Fig. 1. TEM micrograph of core/shell CdSe/ZnS Ds, inset is the HRTEM image of a single D B. LDC Layer Formation and Optical Characterization For deployment of Ds in the LDC layer, Ds ith a peak emission avelength of 620nm ere used. Ds have broad absorption bands that result in absorption of the entire light ith the avelength smaller than the absorption maximum (See Fig. 2). The absorption and PL spectra in Fig. 2 sho that CdSe/ZnS Ds are appropriate candidates to use as donconverting material for the silicon solar cells /14/$ IEEE 2262
2 Fig. 2. D layer...j CL 0.2 s ).t; 0.08 " g 0.06 jg -"' L'O!!!!!'1!!!... --'-----1!1...-'--_-.J Absorption/emission spectra of 6nm core/shell CdSe/ZnS Introducing the 6nm Ds in the LDC layer results in absorption of photons ith avelengths smaller than 620nm, here the response of the cell is lo; and don-converting them to the longer avelength (620nm), here the response of the cell is high. Hence the strongest LDC effects ere expected to be seen. For layer formation, CdSe/ZnS Ds from the colloidal solution ere spin cast on the substrate in a glove box under controlled ambient. Spin coating conditions ere controlled for the concentrated and diluted ensemble of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots to obtain thin films containing CdSe/ZnS ith a specific thickness, D concentration and uniformity for achieving the highest gain from the LDC layer. Fig. 3 demonstrates the TEM image of a D layer formed by spin casting from a 5mglmL colloidal solution onto a silicon substrate at 1000 rpm for 30s. The substrate is isolated from the Ds ith a thin silicon nitride film. The layer as then capped ith a spin on glass (SOG) film..c «:J ;?: 'iii c.$ c -l a... Fig Ex::300nm Wavelength (nm) :tj-oo"' 4OOIXIO x. Max 3! Wrrelenglh{nm) 700 CdSe/ZnS Ds emission map at excitation avelengths in the 300-0nm range. emission maximum. Inset is the D excitation spectrum at The spectrum depicts that the emission intensity is about to-fold higher at the excitation avelengths, in the range of 300-3nm, hich is about to times the bandgap of crystalline silicon. The inset shos the D excitation spectrum at D emission maximum hich also shos that the Ds have the highest efficiency at nm ith the excitation peak intensity at 320nm. Therefore the DC effect should be more pronounced in this range. III. DEVICE CONFIGURATION AND PERFORMANCE A. Device Configurations ith LDC Layers The device configurations that ere studied are depicted in Fig. 5. In the fust architecture, Ds ere spin-cast on top of the c-si solar cell ith an nm silicon nitride layer used as anti-reflection coating (ARC) and for isolation of the Ds from the cell. In the second architecture, the Ds ere fully buried in an SOG transparent layer. The thickness and transparency of the SOG layer needs also to be optimized for effective LDC performance. Photons Incident photons Incident photons escape Fig. 3. HRTEM image of a crystalline structure of the Ds hich uniformly deposited on a thin transparent silicon nitride film and capped ith SOG The excitation and emission scans ere performed on the D solution in an integrating sphere. The absolute value of 85% for the quantum efficiency as determined. Fig. 4 demonstrates the emission map of the LDC layer at different excitation avelengths ranging from 300-0nm. LDCt Cell t Fig. 5. (a) LDCt cell I Schematic diagrams of cells ith a) a D layer and b) D layer capped ith SOG used as LDC layers (b) 2263
3 For the LDC layer configuration ith no capping layer a large proportion of the don-converted photons ill reflect back from the surface and scatter to the top escape cone. A cap layer, ith refractive index larger than the air, allos a large proportion of the luminescent don-converted photons to be transmitted to the underlying cell, either directly or folloing internal reflection. B. Cell Characteristics after Deployment of the LDC Layer: Proof of Don-Conversion The effect of don-conversion on the cell performance as examined by exploiting a D layer on top of a planar c-si cell fabricated in our lab. In Fig. 6, the Internal uantum Efficiency (IE) of the cell structures ith LDC layer as compared ith the bare cell ith no luminescent materials. The IE higher than 100% in the avelength range of nm verifies the don-conversion effect. The cell ith the LDC layer shos higher reflectance ith respect to the bare cell (see Fig. 7). This indicates that some of the don-converted photons are reflecting from the surface, therefore not being collected by the underlying cell. This is additional evidence proves that the don-conversion is taking place in the cell architecture. Higher EE response of the cell ith the LDC layer as compared to the bare cell demonstrates that even though some 140 i-----;:====;_] 120 -PlanarceU - Planar eell+ldc la er Fig r----, -Planareell - Planar eell+ldc la or SOD Wavelength(nm} EE of a planar cell ith an LDC layer photons ere lost, due to higher reflectance, the cell still benefits from some don-converted photons (see Fig. 8). LDC layers ith different thicknesses ere also deployed on textured c-si cells fabricated in our lab. The same trend as observed for these cells. IE higher than 100% in the avelength range of nm as obtained (see Fig. 9) hich is proof of don-conversion. C r====== Texture cell - Relcell layer bilayers r---:s;;o la ers Fig. 6. Fig Wavelength (nm) IE of a planar cell ith an LDC layer <) c: t5 c:: == ======== - Planar cell - Planar cell+ldc la er O -L Wavetength (nm) Reflectance of a planar cell ith an LDC layer Fig. 9. IE of a textured cell ith different LDC thicknesses In these studies, highly concentrated Ds (Smg/ml) ere used to form the LDC layers. The re-absorption in a closelypacked D structure loers the luminescent quantum efficiency of the Ds in the layer. This causes non-desired absorption in the LDC layer in the avelength range here Ds can potentially emit (300nm<A<0nm). High D concentration also results in the increased reflectance. In order to loer the high reflectance and re-absorption in the LDC layer, a loer concentration of Ds (O.Smg/ml) as used. The LDC layers ere deployed on the solar cells using the same method as discussed above. In Fig. 10, the EE, IE and reflectance characteristics of a 2x2 cm 2 planar cell ith an LDC layer containing loer D concentration ere compared ith a reference cell. The solar cell ith the LDC layer shos a higher response hen compared to the bare cell in the part of the avelength range here the reflectance is higher. This indicates that the cell 2264
4 benefits from some don-converted photons. Also, the reflectance and absorption is less for the LDC layer ith loer D concentration. The illuminated current-voltage (IV) characteristic of the cells ith and ithout the LDC layer is also compared in Fig. 11. From the IV result, it is apparent that the current density and the overall cell efficiency are improved for the cell ith the LDC layer containing a loer D concentration. 100,-----, 0: 0/5 0/5 40 o EElBare planar cell - EOE/Cell+LOC layer... RlBare cell... RlCell+LOC layer -IOE/bare cell -IOE/Cell+LOC laver sho loer reflectance in the cell ith LDC as compared to reflectance previously obtained for the LDC containing highly concentrated Ds. Hoever, no improvement as observed in the overall efficiency of the device EOE/ Bar. planar cell - EOE/ Cell WIth LOC layer 50 _. - RI Bare cell 0/5 RI Cell ith LOC layer - toe/ Bar. cell o \ - toe/ Cell WIth LOC laver 25 ' '.;\.. - -,.,....." "./.... O L-----'- Fig. 12. EE, IE and reflectance characteristics of a 1 xl cm 2 planar cell ith an LDC layer containing loer D concentration Fig. 10. EE, IE and reflectance characteristics of 2x2 cm 2 planar cells ith an LDC layer containing loer D concentration Fig Bare planar cell - Cell ith LOC la er L---'-----' -'----'- J...lJ V (v) IV characteristics of 2x2 cm 2 planar cells ith an LDC layer containing loer D concentration In order to determine the effect of the cell size on the LDC, the D layer as deployed on the 1 x 1 cm 2 cell. Figures 12 and 13 sho improvements in the quantum efficiency and illuminated IV characteristics of the cell ith an LDC layer, respectively. The results shon in Fig. 12 also exhibit that the absorption and reflectance of the LDC layer ere better controlled in the smaller cells. Table 1 demonstrates the illuminated IV characteristics of the planar cells ith small and big dimensions and high and lo D concentrations. 2 rna and 0.31% improvement in current density and cell efficiency ere obtained respectively for the cells ith LDC layer containing a loer concentration of Ds. An LDC layer containing lo D concentration as also deployed on 1 x 1 cm 2 textured cells (see Fig. 14). The results Fig Bare planar cell - Planar cell ith LOC la er 0.00 L- --'-.l l.l ' V(v) IV characteristics of 1 x 1 cm 2 planar cells ith an LDC layer containing loer D concentration TABLE I ILLUMINATED IV CHARACTERISTICS OF LABORATORY SCALE PLANAR SOLAR CELLS WITH AND WITHOUT LDC LAYER Planar solar cells Voc Jsc FF '1 (V) (rna) (%) (%) Bare cell (small size) high D concentration Cell+LDC(small size) high D concentration Bare cell (big size) high D concentration Cell+LDC (big size) high D concentration Bare cell (small size) Lo D concentration Cell+LDC(small size) Lo D concentration Bare cell (big size) Lo D concentration Cell+LDC (big size) Lo D concentration 2265
5 0::: a EOEI Bare textured celt - EOEI Celt+LDC tayer... RJ Bare cetl RJ celt+ldc layer - IOEI Bare celt - IOEI Celt+LDC layer reflectance characteristics for the planar and textured cells ere obtained and shon in Fig. 15 and Fig. 16, respectively. The results sho that although the SOG cap layer loered the reflectance, the LDC layer ith the SOG cap layer suffers from high absorption at longer spectrum avelengths (0nm<A<1000nm). In order to benefit from the capping layer and therefore better cell perfonnance ith LDC, the thickness of the SOG needs to be optimized. It can also be replaced ith another cap layer ith loer absorption at this avelength range. IV. CONCLUSIONS Fig. 14. IV characteristics of 1 x 1 cm 2 textured cells ith and ithout an LDC layer containing lo D concentration As mentioned earlier, some of the don-converted photons reflect from the surface, therefore are not collected by the underlying cell. An LDC layer capped ith a transparent layer, ith a refractive index higher than air, can benefit from the total reflection of the emitted photons at the layer/air interface. As a result the emitted photons can be directed toard the cell more efficiently. A thin layer of SOG as spin-coated onto the D layer at 4000 rpm for 30s to fonn a capping layer. The EE, IE and 100 0::: 40 a 20 \ - :':' " " " " : - EOEI Bare planar cell - E.EI CeI+lOC - EOEI CeI+lOC+SOG.._.- RI Bare P'anar cell -RlCeIl+lOC -'RlCeII+LDC+$OG -IOEI Bare planar cell, r Fig. 15. EE, IE and reflectance characteristics of a 1 x 1 cm 2 planar cell ith LDC and SOG capping layer <F. Ii' 200 r ,========== &1 50,\ Textured cell - EEI Bare cell - EOEf CeU+LDC - EEI Cel1+lOC+SOG _._._.. RI Bare cell _._.- RI Cell+LDC _._._.. RI Cell+LDC+SOG -ICEI Bare cell -IOE! Cell+LDC - IOE! Cell+LDC+SOG Core/shell CdSe/ZnS Ds ith high LE ere exploited as luminescent centers on planar and textured crystalline silicon solar cells for don-conversion. The structural and optical characteristics of the Ds and the employed layer ere studied. Cell performance characteristics verified the luminescence don-conversion of the incident photons in both of the cell structures containing LDC layers. REFERENCES [I] B. Sadeghimakki, N. M. S. lahed and S. Sivoththaman "Spectrally resolved dynamics of synthesized CdSe/ZnS quantum dot/silica nanocrystals for photonic don-shifting applications," ieee Transactions on Nanotechnology (in press), 2014 ( rrNANO ). [2] E. Klampaftis, D. Ross, K. Mcintosh, B. Richards, "Enhancing the performance of solar cells via luminescent don-shifting of the incident spectrum: A revie," Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. c., vol. 93, pp , [3] Z. Cheng, F. Su, L. Pan, M. Cao, and Z. Sun, "CdS quantum dot embedded silica film as luminescent don-shifting layer for crystalline Si solar cells," J. Alloy Compd., vol. 494, pp. L7-LlO, [4] E. Klampaftis, M. Congiu, N. Robertson, and B. Richards, "Luminescent ethylene vinyl acetate encapsulation layers for enhancing the short avelength spectral response and efficiency of silicon photovoitaic modules," IEEE J. Photovoltaics, vol. I, no. I, pp , [5] R. Nakata, N. Hashimoto, and K. Kaano, "High conversion efficiency solar cell using fluorescence of rare earth ions," Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., vol. 35, pp. L90-93, [6] L. Danos, T. Parel, T. Markvart, V. Barrioz, W. Brooks, and S. Irvine, "Increased efficiencies on CdTe solar cells via luminescence donshifting ith excitation energy transfer beteen dyes," Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. c., vol. 98, pp , [7] T. Trupke, M.A. Green, and P. WOrfel, "Improving solar cell efficiencies by don-conversion of high-energy photons," J. Appl. Phys., vol. 92, no. 3, pp ,2002. Fig. 16. EE, IE and reflectance characteristics of a 1 xl cm 2 textured cell ith LDC and SOG capping layer [8] K. R. McIntosh, G. Lau, J. N. Cotsell, K. Hanton, D. L. Batzner, F. Bettiol, and B. S. Richards, "Increase in external quantum efficiency of encapsulated silicon solar cells from a luminescent don-shifting layer," Prog. Photovolt: Res. Appl., vol. 17, no. 3, pp , May
Characterisation of Luminescent Down-Shifting Materials for the Enhancement of Solar Cell Efficiency
 Characterisation of Luminescent Down-Shifting Materials for the Enhancement of Solar Cell Efficiency H. Ahmed* 1, M. Kennedy 1, J. Doran 1 and S. J. McCormack 2 1 Dublin Energy Lab, Dublin Institute of
Characterisation of Luminescent Down-Shifting Materials for the Enhancement of Solar Cell Efficiency H. Ahmed* 1, M. Kennedy 1, J. Doran 1 and S. J. McCormack 2 1 Dublin Energy Lab, Dublin Institute of
Quantum Dot Technology for Low-Cost Space Power Generation for Smallsats
 SSC06-VI- Quantum Dot Technology for Low-Cost Space Power Generation for Smallsats Theodore G. DR Technologies, Inc. 7740 Kenamar Court, San Diego, CA 92020 (858)677-230 tstern@drtechnologies.com The provision
SSC06-VI- Quantum Dot Technology for Low-Cost Space Power Generation for Smallsats Theodore G. DR Technologies, Inc. 7740 Kenamar Court, San Diego, CA 92020 (858)677-230 tstern@drtechnologies.com The provision
Morphology of CdSe/ZnS core/shell QDs coated on textured surface with SiN X film of a
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary/supporting information Morphology of CdSe/ZnS core/shell QDs coated on textured
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary/supporting information Morphology of CdSe/ZnS core/shell QDs coated on textured
Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices
 Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices spectral region from 450 to 630 nm Zero-D Perovskite Emit light at 520 nm ABOUT QUANTUM SOLUTIONS QUANTUM SOLUTIONS company is an expert in the synthesis
Quantum Dots for Advanced Research and Devices spectral region from 450 to 630 nm Zero-D Perovskite Emit light at 520 nm ABOUT QUANTUM SOLUTIONS QUANTUM SOLUTIONS company is an expert in the synthesis
Supplemental Discussion for Multijunction Solar Cell Efficiencies: Effect of Spectral Window, Optical Environment and Radiative Coupling
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplemental Discussion for Multijunction Solar Cell Efficiencies: Effect
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplemental Discussion for Multijunction Solar Cell Efficiencies: Effect
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References Supplementary Figure 1. SEM images of perovskite single-crystal patterned thin film with
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References Supplementary Figure 1. SEM images of perovskite single-crystal patterned thin film with
Debjit Roy, Saptarshi Mandal, Chayan K. De, Kaushalendra Kumar and Prasun K. Mandal*
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 Nearly Suppressed Photoluminescence Blinking of Small Sized, Blue-Green-Orange-Red
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 Nearly Suppressed Photoluminescence Blinking of Small Sized, Blue-Green-Orange-Red
II.2 Photonic Crystals of Core-Shell Colloidal Particles
 II.2 Photonic Crystals of Core-Shell Colloidal Particles We report on the fabrication and optical transmission studies of thin three-dimensional photonic crystals of high-dielectric ZnS-core and low-dielectric
II.2 Photonic Crystals of Core-Shell Colloidal Particles We report on the fabrication and optical transmission studies of thin three-dimensional photonic crystals of high-dielectric ZnS-core and low-dielectric
(Co-PIs-Mark Brongersma, Yi Cui, Shanhui Fan) Stanford University. GCEP Research Symposium 2013 Stanford, CA October 9, 2013
 High-efficiency thin film nano-structured multi-junction solar James S. cells Harris (PI) (Co-PIs-Mark Brongersma, Yi Cui, Shanhui Fan) Stanford University GCEP Research Symposium 2013 Stanford, CA October
High-efficiency thin film nano-structured multi-junction solar James S. cells Harris (PI) (Co-PIs-Mark Brongersma, Yi Cui, Shanhui Fan) Stanford University GCEP Research Symposium 2013 Stanford, CA October
1. Depleted heterojunction solar cells. 2. Deposition of semiconductor layers with solution process. June 7, Yonghui Lee
 1. Depleted heterojunction solar cells 2. Deposition of semiconductor layers with solution process June 7, 2016 Yonghui Lee Outline 1. Solar cells - P-N junction solar cell - Schottky barrier solar cell
1. Depleted heterojunction solar cells 2. Deposition of semiconductor layers with solution process June 7, 2016 Yonghui Lee Outline 1. Solar cells - P-N junction solar cell - Schottky barrier solar cell
Solution reduction synthesis of amine terminated carbon quantum dots
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Solution reduction synthesis of amine terminated carbon quantum dots Keith Linehan and Hugh
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Solution reduction synthesis of amine terminated carbon quantum dots Keith Linehan and Hugh
Supplementary Information. Light Manipulation for Organic Optoelectronics Using Bio-inspired Moth's Eye. Nanostructures
 Supplementary Information Light Manipulation for Organic Optoelectronics Using Bio-inspired Moth's Eye Nanostructures Lei Zhou, Qing-Dong Ou, Jing-De Chen, Su Shen, Jian-Xin Tang,* Yan-Qing Li,* and Shuit-Tong
Supplementary Information Light Manipulation for Organic Optoelectronics Using Bio-inspired Moth's Eye Nanostructures Lei Zhou, Qing-Dong Ou, Jing-De Chen, Su Shen, Jian-Xin Tang,* Yan-Qing Li,* and Shuit-Tong
Cho Fai Jonathan Lau, Xiaofan Deng, Qingshan Ma, Jianghui Zheng, Jae S. Yun, Martin A.
 Supporting Information CsPbIBr 2 Perovskite Solar Cell by Spray Assisted Deposition Cho Fai Jonathan Lau, Xiaofan Deng, Qingshan Ma, Jianghui Zheng, Jae S. Yun, Martin A. Green, Shujuan Huang, Anita W.
Supporting Information CsPbIBr 2 Perovskite Solar Cell by Spray Assisted Deposition Cho Fai Jonathan Lau, Xiaofan Deng, Qingshan Ma, Jianghui Zheng, Jae S. Yun, Martin A. Green, Shujuan Huang, Anita W.
Supplementary Figure 1 XRD pattern of a defective TiO 2 thin film deposited on an FTO/glass substrate, along with an XRD pattern of bare FTO/glass
 Supplementary Figure 1 XRD pattern of a defective TiO 2 thin film deposited on an FTO/glass substrate, along with an XRD pattern of bare FTO/glass and a reference pattern of anatase TiO 2 (JSPDS No.: 21-1272).
Supplementary Figure 1 XRD pattern of a defective TiO 2 thin film deposited on an FTO/glass substrate, along with an XRD pattern of bare FTO/glass and a reference pattern of anatase TiO 2 (JSPDS No.: 21-1272).
Photonic crystals of core shell colloidal particles
 Letter to Appl. Phys. Letters June 8, 2001 Photonic crystals of core shell colloidal particles Krassimir P. Velikov, a, ) Alexander Moroz, a) and Alfons van Blaaderen a,b, ) a Physics and Chemistry of
Letter to Appl. Phys. Letters June 8, 2001 Photonic crystals of core shell colloidal particles Krassimir P. Velikov, a, ) Alexander Moroz, a) and Alfons van Blaaderen a,b, ) a Physics and Chemistry of
maximal photofluorescence decay time of 6 hours (purchased from Shenzhen HuiDuoSheng
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental section Preparation of m-tio 2 /LPP photoanodes. TiO 2 colloid was synthesized according
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental section Preparation of m-tio 2 /LPP photoanodes. TiO 2 colloid was synthesized according
Luminescent Plates Doped with Stilbene 420 Dye for Enhanced Silicon Solar Cell Performance: Down-Conversion
 Iraqi Journal of Applied Physics Suma H. Al Shaikh Hussin Department of Physics, College of Science for Women, University of Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq Luminescent Plates Doped with Stilbene 420 Dye for Enhanced
Iraqi Journal of Applied Physics Suma H. Al Shaikh Hussin Department of Physics, College of Science for Women, University of Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq Luminescent Plates Doped with Stilbene 420 Dye for Enhanced
CHAPTER 3. OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES
 42 CHAPTER 3 OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In recent years, considerable interest has been shown on semiconducting nanostructures owing to their enhanced optical and electrical
42 CHAPTER 3 OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In recent years, considerable interest has been shown on semiconducting nanostructures owing to their enhanced optical and electrical
PHOTOVOLTAICS Fundamentals
 PHOTOVOLTAICS Fundamentals PV FUNDAMENTALS Semiconductor basics pn junction Solar cell operation Design of silicon solar cell SEMICONDUCTOR BASICS Allowed energy bands Valence and conduction band Fermi
PHOTOVOLTAICS Fundamentals PV FUNDAMENTALS Semiconductor basics pn junction Solar cell operation Design of silicon solar cell SEMICONDUCTOR BASICS Allowed energy bands Valence and conduction band Fermi
Goal for next generation solar cells: Efficiencies greater than Si with low cost (low temperature) processing
 Multi-junction cells MBE growth > 40% efficient Expensive Single crystal Si >20% efficient expensive Thin film cells >10% efficient Less expensive Toxic materials Polymers
Multi-junction cells MBE growth > 40% efficient Expensive Single crystal Si >20% efficient expensive Thin film cells >10% efficient Less expensive Toxic materials Polymers
The Opto-Electronic Physics That Just Broke the Efficiency Record in Solar Cells
 The Opto-Electronic Physics That Just Broke the Efficiency Record in Solar Cells Solar Energy Mini-Series Jen-Hsun Huang Engineering Center Stanford, California Sept. 26, 2011 Owen D. Miller & Eli Yablonovitch
The Opto-Electronic Physics That Just Broke the Efficiency Record in Solar Cells Solar Energy Mini-Series Jen-Hsun Huang Engineering Center Stanford, California Sept. 26, 2011 Owen D. Miller & Eli Yablonovitch
Improving Solar Cell Performance Using CdSe/ZnS. Core/Shell Quantum Dots in a Spectral Conversion. System
 Improving Solar Cell Performance Using CdSe/ZnS Core/Shell Quantum Dots in a Spectral Conversion System BY Buddy Bump Materials Engineering Department California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo
Improving Solar Cell Performance Using CdSe/ZnS Core/Shell Quantum Dots in a Spectral Conversion System BY Buddy Bump Materials Engineering Department California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo
Quantum Dot Spectrum Converter Coverglass for Enhanced High Efficiency Photovoltaics
 Quantum Dot Spectrum Converter Coverglass for Enhanced High Efficiency Photovoltaics Theodore G. Stern DR Technologies, Inc. San Diego, CA 92020 Business Area Manager Space Power, Optical and Thermal Products
Quantum Dot Spectrum Converter Coverglass for Enhanced High Efficiency Photovoltaics Theodore G. Stern DR Technologies, Inc. San Diego, CA 92020 Business Area Manager Space Power, Optical and Thermal Products
5 Quantum Wells. 1. Use a Multimeter to test the resistance of your laser; Record the resistance for both polarities.
 Measurement Lab 0: Resistance The Diode laser is basically a diode junction. Same as all the other semiconductor diode junctions, e should be able to see difference in resistance for different polarities.
Measurement Lab 0: Resistance The Diode laser is basically a diode junction. Same as all the other semiconductor diode junctions, e should be able to see difference in resistance for different polarities.
Optical and Photonic Glasses. Lecture 39. Non-Linear Optical Glasses III Metal Doped Nano-Glasses. Professor Rui Almeida
 Optical and Photonic Glasses : Non-Linear Optical Glasses III Metal Doped Nano-Glasses Professor Rui Almeida International Materials Institute For New Functionality in Glass Lehigh University Metal-doped
Optical and Photonic Glasses : Non-Linear Optical Glasses III Metal Doped Nano-Glasses Professor Rui Almeida International Materials Institute For New Functionality in Glass Lehigh University Metal-doped
Tianle Guo, 1 Siddharth Sampat, 1 Kehao Zhang, 2 Joshua A. Robinson, 2 Sara M. Rupich, 3 Yves J. Chabal, 3 Yuri N. Gartstein, 1 and Anton V.
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION for Order of magnitude enhancement of monolayer MoS photoluminescence due to near-field energy influx from nanocrystal films Tianle Guo, Siddharth Sampat, Kehao Zhang, Joshua
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION for Order of magnitude enhancement of monolayer MoS photoluminescence due to near-field energy influx from nanocrystal films Tianle Guo, Siddharth Sampat, Kehao Zhang, Joshua
Supporting information. and/or J -aggregation. Sergey V. Dayneko, Abby-Jo Payne and Gregory C. Welch*
 Supporting information Inverted P3HT:PC61BM organic solar cells incorporating a -extended squaraine dye with H- and/or J -aggregation. Sergey V. Dayneko, Abby-Jo Payne and Gregory C. Welch* Department
Supporting information Inverted P3HT:PC61BM organic solar cells incorporating a -extended squaraine dye with H- and/or J -aggregation. Sergey V. Dayneko, Abby-Jo Payne and Gregory C. Welch* Department
Scienza e Tecnologia dei Materiali Ceramici. Modulo 2: Materiali Nanostrutturati
 Università degli Studi di Trieste Dipartimento di Ingegneria e Architettura A.A. 2016-2017 Scienza e Tecnologia dei Materiali Ceramici Modulo 2: Materiali Nanostrutturati - Lezione 5 - Vanni Lughi vlughi@units.it
Università degli Studi di Trieste Dipartimento di Ingegneria e Architettura A.A. 2016-2017 Scienza e Tecnologia dei Materiali Ceramici Modulo 2: Materiali Nanostrutturati - Lezione 5 - Vanni Lughi vlughi@units.it
Semiconductor quantum dots
 Semiconductor quantum dots Quantum dots are spherical nanocrystals of semiconducting materials constituted from a few hundreds to a few thousands atoms, characterized by the quantum confinement of the
Semiconductor quantum dots Quantum dots are spherical nanocrystals of semiconducting materials constituted from a few hundreds to a few thousands atoms, characterized by the quantum confinement of the
Optical Properties of SOI Waveguides Functionalized with Close-Packed Quantum Dot Films
 ICTON 2013 We.D6.2 Optical Properties of SOI Waveguides Functionalized with Close-Packed Quantum Dot Films Zeger Hens, Abdoulghafar Omari, Pieter Geiregat, Dries Van Thourhout Physics and Chemistry of
ICTON 2013 We.D6.2 Optical Properties of SOI Waveguides Functionalized with Close-Packed Quantum Dot Films Zeger Hens, Abdoulghafar Omari, Pieter Geiregat, Dries Van Thourhout Physics and Chemistry of
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. AFM profiles of the charge transport and perovskite layers. AFM Image showing the thickness (y axis) of the layer with respect to the horizontal position of
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. AFM profiles of the charge transport and perovskite layers. AFM Image showing the thickness (y axis) of the layer with respect to the horizontal position of
Supporting Information for: Tailoring ZnSe-CdSe Colloidal Quantum Dots via. Cation-Exchange: from Core/Shell to Alloy.
 Supporting Information for: Tailoring ZnSe-CdSe Colloidal Quantum Dots via Cation-Exchange: from Core/Shell to Alloy Nanocrystals Esther Groeneveld, Leon Witteman, Merel Lefferts, Xiaoxing Ke, Sara Bals,
Supporting Information for: Tailoring ZnSe-CdSe Colloidal Quantum Dots via Cation-Exchange: from Core/Shell to Alloy Nanocrystals Esther Groeneveld, Leon Witteman, Merel Lefferts, Xiaoxing Ke, Sara Bals,
HIGH-TEMPERATURE CADMIUM-FREE NANOPHOSPHORS FOR DAYLIGHT-QUALITY WHITE LEDS
 CPS S1 / R1 Intensity (CPS) HIGH-TEMPERATURE CADMIUM-FREE NANOPHOSPHORS FOR DAYLIGHT-QUALITY WHITE LEDS REU Student: Nathaniel C. Cook Graduate Student Mentor: Brian A. Akins Faculty Mentor: Dr. Marek
CPS S1 / R1 Intensity (CPS) HIGH-TEMPERATURE CADMIUM-FREE NANOPHOSPHORS FOR DAYLIGHT-QUALITY WHITE LEDS REU Student: Nathaniel C. Cook Graduate Student Mentor: Brian A. Akins Faculty Mentor: Dr. Marek
Revisited Wurtzite CdSe Synthesis : a Gateway for the Versatile Flash Synthesis of Multi-Shell Quantum Dots and Rods
 Supporting Information for Revisited Wurtzite CdSe Synthesis : a Gateway for the Versatile Flash Synthesis of Multi-Shell Quantum Dots and Rods Emile Drijvers, 1,3 Jonathan De Roo, 2 Pieter Geiregat, 1,3
Supporting Information for Revisited Wurtzite CdSe Synthesis : a Gateway for the Versatile Flash Synthesis of Multi-Shell Quantum Dots and Rods Emile Drijvers, 1,3 Jonathan De Roo, 2 Pieter Geiregat, 1,3
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2014 69451 Weinheim, Germany A Fast Deposition-Crystallization Procedure for Highly Efficient Lead Iodide Perovskite Thin-Film Solar Cells** Manda Xiao, Fuzhi Huang, Wenchao
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2014 69451 Weinheim, Germany A Fast Deposition-Crystallization Procedure for Highly Efficient Lead Iodide Perovskite Thin-Film Solar Cells** Manda Xiao, Fuzhi Huang, Wenchao
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2012.63 Bright infrared quantum-dot light-emitting diodes through inter-dot spacing control Liangfeng Sun, Joshua J. Choi, David Stachnik, Adam C. Bartnik,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2012.63 Bright infrared quantum-dot light-emitting diodes through inter-dot spacing control Liangfeng Sun, Joshua J. Choi, David Stachnik, Adam C. Bartnik,
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Sample characterization The presence of Si-QDs is established by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), by which the average QD diameter of d QD 2.2 ± 0.5 nm has been determined
Supplementary Materials Sample characterization The presence of Si-QDs is established by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), by which the average QD diameter of d QD 2.2 ± 0.5 nm has been determined
Ray-trace Modelling of Quantum Dot Solar Concentrators
 ARROW@DIT onference Papers Dublin Energy Lab 8-- Ray-trace Modelling of Quantum Dot Solar oncentrators Manus Kennedy, manus.kennedy@dit.ie Sarah Mcormack John Doran Brian Norton Follow this and additional
ARROW@DIT onference Papers Dublin Energy Lab 8-- Ray-trace Modelling of Quantum Dot Solar oncentrators Manus Kennedy, manus.kennedy@dit.ie Sarah Mcormack John Doran Brian Norton Follow this and additional
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 High-Efficiency Light-Emitting Devices based on Quantum Dots with Tailored Nanostructures Yixing Yang 1, Ying Zheng 1, Weiran Cao 2, Alexandre Titov 1, Jake Hyvonen 1, Jiangeng Xue 2*, Paul H. Holloway
High-Efficiency Light-Emitting Devices based on Quantum Dots with Tailored Nanostructures Yixing Yang 1, Ying Zheng 1, Weiran Cao 2, Alexandre Titov 1, Jake Hyvonen 1, Jiangeng Xue 2*, Paul H. Holloway
Facile and purification-free synthesis of nitrogenated amphiphilic graphitic carbon dots
 Supporting Information Facile and purification-free synthesis of nitrogenated amphiphilic graphitic carbon dots Byung Joon Moon, 1 Yelin Oh, 1 Dong Heon Shin, 1 Sang Jin Kim, 1 Sanghyun Lee, 1,2 Tae-Wook
Supporting Information Facile and purification-free synthesis of nitrogenated amphiphilic graphitic carbon dots Byung Joon Moon, 1 Yelin Oh, 1 Dong Heon Shin, 1 Sang Jin Kim, 1 Sanghyun Lee, 1,2 Tae-Wook
Fundamentals of Light Trapping
 Fundamentals of Light Trapping James R. Nagel, PhD November 16, 2017 Salt Lake City, Utah About Me PhD, Electrical Engineering, University of Utah (2011) Research Associate for Dept. of Metallurgical Engineering
Fundamentals of Light Trapping James R. Nagel, PhD November 16, 2017 Salt Lake City, Utah About Me PhD, Electrical Engineering, University of Utah (2011) Research Associate for Dept. of Metallurgical Engineering
Temperature Dependent Optical Band Gap Measurements of III-V films by Low Temperature Photoluminescence Spectroscopy
 Temperature Dependent Optical Band Gap Measurements of III-V films by Low Temperature Photoluminescence Spectroscopy Linda M. Casson, Francis Ndi and Eric Teboul HORIBA Scientific, 3880 Park Avenue, Edison,
Temperature Dependent Optical Band Gap Measurements of III-V films by Low Temperature Photoluminescence Spectroscopy Linda M. Casson, Francis Ndi and Eric Teboul HORIBA Scientific, 3880 Park Avenue, Edison,
Lecture 6 Optical Characterization of Inorganic Semiconductors Dr Tim Veal, Stephenson Institute for Renewable Energy and Department of Physics,
 Lecture 6 Optical Characterization of Inorganic Semiconductors Dr Tim Veal, Stephenson Institute for Renewable Energy and Department of Physics, University of Liverpool Lecture Outline Lecture 6: Optical
Lecture 6 Optical Characterization of Inorganic Semiconductors Dr Tim Veal, Stephenson Institute for Renewable Energy and Department of Physics, University of Liverpool Lecture Outline Lecture 6: Optical
Nanostrukturphysik (Nanostructure Physics)
 Nanostrukturphysik (Nanostructure Physics) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de; yang.xu@tu-ilmenau.de Office: Unterpoerlitzer
Nanostrukturphysik (Nanostructure Physics) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de; yang.xu@tu-ilmenau.de Office: Unterpoerlitzer
Utilizing Quantum Dots to Enhance Solar Spectrum Conversion Efficiencies for Photovoltaics
 Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 1120 2009 Materials Research Society 1120-M09-06 Utilizing Quantum Dots to Enhance Solar Spectrum Conversion Efficiencies for Photovoltaics Richard Savage, Hans Mayer,
Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 1120 2009 Materials Research Society 1120-M09-06 Utilizing Quantum Dots to Enhance Solar Spectrum Conversion Efficiencies for Photovoltaics Richard Savage, Hans Mayer,
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Non-Plasmonic SERS with Silicon: Is It Really Safe? New Insights into the Opto-Thermal Properties of Core/Shell Microbeads Nicolò Bontempi, a,d Irene Vassalini, a,b Stefano Danesi,
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Non-Plasmonic SERS with Silicon: Is It Really Safe? New Insights into the Opto-Thermal Properties of Core/Shell Microbeads Nicolò Bontempi, a,d Irene Vassalini, a,b Stefano Danesi,
Tailoring of Electron Collecting Oxide Nano-Particulate Layer for Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells. Gajeong-Ro, Yuseong-Gu, Daejeon , Korea
 Supporting Information Tailoring of Electron Collecting Oxide Nano-Particulate Layer for Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells Seong Sik Shin 1,2,, Woon Seok Yang 1,3,, Eun Joo Yeom 1,4, Seon Joo Lee 1, Nam
Supporting Information Tailoring of Electron Collecting Oxide Nano-Particulate Layer for Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells Seong Sik Shin 1,2,, Woon Seok Yang 1,3,, Eun Joo Yeom 1,4, Seon Joo Lee 1, Nam
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Enhanced Charge Collection with Passivation of
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Enhanced Charge Collection with Passivation of
TECHNICAL INFORMATION. Quantum Dot
 Quantum Dot Quantum Dot is the nano meter sized semiconductor crystal with specific optical properties originates from the phenomenon which can be explained by the quantum chemistry and quantum mechanics.
Quantum Dot Quantum Dot is the nano meter sized semiconductor crystal with specific optical properties originates from the phenomenon which can be explained by the quantum chemistry and quantum mechanics.
Synthesis and characterization of silica titania core shell particles
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 5 journal of November 2005 physics pp. 787 791 Synthesis and characterization of silica titania core shell particles SUCHITA KALELE 1, RAVI DEY 1, NEHA
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 5 journal of November 2005 physics pp. 787 791 Synthesis and characterization of silica titania core shell particles SUCHITA KALELE 1, RAVI DEY 1, NEHA
A Plasmonic Photocatalyst Consisting of Silver Nanoparticles Embedded in Titanium Dioxide. Ryan Huschka LANP Seminar February 19, 2008
 A Plasmonic Photocatalyst Consisting of Silver Nanoparticles Embedded in Titanium Dioxide Ryan Huschka LANP Seminar February 19, 2008 TiO 2 Applications White Pigment Photocatalyst Previous methods to
A Plasmonic Photocatalyst Consisting of Silver Nanoparticles Embedded in Titanium Dioxide Ryan Huschka LANP Seminar February 19, 2008 TiO 2 Applications White Pigment Photocatalyst Previous methods to
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Bright, Stable, and Tunable Solid-State Luminescence
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Bright, Stable, and Tunable Solid-State Luminescence
Ambient air processed mixed-ion perovskite for high efficiency solar cells
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Ambient air processed mixed-ion perovskite for high efficiency solar cells
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Ambient air processed mixed-ion perovskite for high efficiency solar cells
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information All inorganic cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals for photodetector
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information All inorganic cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals for photodetector
Development and application for X-ray excited optical luminescence (XEOL) technology at STXM beamline of SSRF
 Development and application for X-ray excited optical luminescence (XEOL) technology at STXM beamline of SSRF Content Introduction to XEOL Application of XEOL Development and Application of XEOL in STXM
Development and application for X-ray excited optical luminescence (XEOL) technology at STXM beamline of SSRF Content Introduction to XEOL Application of XEOL Development and Application of XEOL in STXM
Cylindrical luminescent solar concentrators with near-infrared quantum dots
 Cylindrical luminescent solar concentrators with near-infrared quantum dots R. H. Inman, G. V. Shcherbatyuk, D. Medvedko, A. Gopinathan, and S. Ghosh* School of Natural Sciences, University of California,
Cylindrical luminescent solar concentrators with near-infrared quantum dots R. H. Inman, G. V. Shcherbatyuk, D. Medvedko, A. Gopinathan, and S. Ghosh* School of Natural Sciences, University of California,
Flexible Organic Photovoltaics Employ laser produced metal nanoparticles into the absorption layer 1. An Introduction
 Flexible Organic Photovoltaics Employ laser produced metal nanoparticles into the absorption layer 1. An Introduction Among the renewable energy sources that are called to satisfy the continuously increased
Flexible Organic Photovoltaics Employ laser produced metal nanoparticles into the absorption layer 1. An Introduction Among the renewable energy sources that are called to satisfy the continuously increased
Spiro-Configured Bifluorenes: Highly Efficient Emitter for UV Organic Light-Emitting Device and Host Material for Red Electrophosphorescence
 Spiro-Configured Bifluorenes: Highly Efficient Emitter for UV Organic Light-Emitting Device and Host Material for Red Electrophosphorescence Ken-Tsung Wong,* a Yuan-Li Liao, a Yu-Ting Lin, b Hai-Ching
Spiro-Configured Bifluorenes: Highly Efficient Emitter for UV Organic Light-Emitting Device and Host Material for Red Electrophosphorescence Ken-Tsung Wong,* a Yuan-Li Liao, a Yu-Ting Lin, b Hai-Ching
OPTICAL PROPERTIES of Nanomaterials
 OPTICAL PROPERTIES of Nanomaterials Advanced Reading Optical Properties and Spectroscopy of Nanomaterials Jin Zhong Zhang World Scientific, Singapore, 2009. Optical Properties Many of the optical properties
OPTICAL PROPERTIES of Nanomaterials Advanced Reading Optical Properties and Spectroscopy of Nanomaterials Jin Zhong Zhang World Scientific, Singapore, 2009. Optical Properties Many of the optical properties
Exploiting the Interaction of Pyranine-3 with Poly(L-Lysine) to Mediate Nanoparticle Assembly: Fabrication of Dynamic ph-responsive Nanocontainers
 Exploiting the Interaction of Pyranine-3 with Poly(L-Lysine) to Mediate Nanoparticle Assembly: Fabrication of Dynamic ph-responsive Nanocontainers Arlin Jose Amali, a Shashi Singh, b Nandini Rangaraj,
Exploiting the Interaction of Pyranine-3 with Poly(L-Lysine) to Mediate Nanoparticle Assembly: Fabrication of Dynamic ph-responsive Nanocontainers Arlin Jose Amali, a Shashi Singh, b Nandini Rangaraj,
PREPARATION OF LUMINESCENT SILICON NANOPARTICLES BY PHOTOTHERMAL AEROSOL SYNTHESIS FOLLOWED BY ACID ETCHING
 Phase Transitions Vol. 77, Nos. 1 2, January February 2004, pp. 131 137 PREPARATION OF LUMINESCENT SILICON NANOPARTICLES BY PHOTOTHERMAL AEROSOL SYNTHESIS FOLLOWED BY ACID ETCHING X. LI, Y. HE, S.S. TALUKDAR
Phase Transitions Vol. 77, Nos. 1 2, January February 2004, pp. 131 137 PREPARATION OF LUMINESCENT SILICON NANOPARTICLES BY PHOTOTHERMAL AEROSOL SYNTHESIS FOLLOWED BY ACID ETCHING X. LI, Y. HE, S.S. TALUKDAR
Supporting Information. A Facile Methodology for Engineering the Morphology of CsPbX 3 Perovskite Nanocrystals under Ambient Condition
 Supporting Information A Facile Methodology for Engineering the Morphology of CsPbX 3 Perovskite Nanocrystals under Ambient Condition Sudipta Seth and Anunay Samanta School of Chemistry, University of
Supporting Information A Facile Methodology for Engineering the Morphology of CsPbX 3 Perovskite Nanocrystals under Ambient Condition Sudipta Seth and Anunay Samanta School of Chemistry, University of
Advanced Spectroscopy Laboratory
 Advanced Spectroscopy Laboratory - Raman Spectroscopy - Emission Spectroscopy - Absorption Spectroscopy - Raman Microscopy - Hyperspectral Imaging Spectroscopy FERGIELAB TM Raman Spectroscopy Absorption
Advanced Spectroscopy Laboratory - Raman Spectroscopy - Emission Spectroscopy - Absorption Spectroscopy - Raman Microscopy - Hyperspectral Imaging Spectroscopy FERGIELAB TM Raman Spectroscopy Absorption
Low-temperature-processed inorganic perovskite solar cells via solvent engineering with enhanced mass transport
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 1 Low-temperature-processed inorganic perovskite solar cells via solvent engineering
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 1 Low-temperature-processed inorganic perovskite solar cells via solvent engineering
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Scalable Non-injection Synthesis of Cd-Free Copper Indium Sulfide/Zinc Sulfide Quantum Dots for Third-Gen Photovoltaic Application Yaxin Zheng, Bahareh Sadeghimakki, Navid. M. S. Jahed, and Siva Sivoththaman
Scalable Non-injection Synthesis of Cd-Free Copper Indium Sulfide/Zinc Sulfide Quantum Dots for Third-Gen Photovoltaic Application Yaxin Zheng, Bahareh Sadeghimakki, Navid. M. S. Jahed, and Siva Sivoththaman
Nanophysics: Main trends
 Nano-opto-electronics Nanophysics: Main trends Nanomechanics Main issues Light interaction with small structures Molecules Nanoparticles (semiconductor and metallic) Microparticles Photonic crystals Nanoplasmonics
Nano-opto-electronics Nanophysics: Main trends Nanomechanics Main issues Light interaction with small structures Molecules Nanoparticles (semiconductor and metallic) Microparticles Photonic crystals Nanoplasmonics
Ultrafast single photon emitting quantum photonic structures. based on a nano-obelisk
 Ultrafast single photon emitting quantum photonic structures based on a nano-obelisk Je-Hyung Kim, Young-Ho Ko, Su-Hyun Gong, Suk-Min Ko, Yong-Hoon Cho Department of Physics, Graduate School of Nanoscience
Ultrafast single photon emitting quantum photonic structures based on a nano-obelisk Je-Hyung Kim, Young-Ho Ko, Su-Hyun Gong, Suk-Min Ko, Yong-Hoon Cho Department of Physics, Graduate School of Nanoscience
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Highly luminescent water-dispersible NIR-emitting wurtzite CuInS 2 /ZnS core/shell colloidal quantum dots Chenghui Xia, a,b Johannes D. Meeldijk, c Hans C. Gerritsen, b and Celso
Supporting Information Highly luminescent water-dispersible NIR-emitting wurtzite CuInS 2 /ZnS core/shell colloidal quantum dots Chenghui Xia, a,b Johannes D. Meeldijk, c Hans C. Gerritsen, b and Celso
Down-conversion monochrome light-emitting diodeswith the color determined
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic supplementary information (ESI) for Down-conversion monochrome
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic supplementary information (ESI) for Down-conversion monochrome
Bright CuInS 2 /CdS Nanocrystal Phosphors for High-Gain Full-Spectrum Luminescent Solar Concentrators
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Knowles et al. March 8, 215 Supplementary Information Bright Nanocrystal Phosphors for High-Gain
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Knowles et al. March 8, 215 Supplementary Information Bright Nanocrystal Phosphors for High-Gain
Supplementary Figure 1. Cross-section SEM image of the polymer scaffold perovskite film using MAI:PbI 2 =1:1 in DMF solvent on the FTO/glass
 Supplementary Figure 1. Cross-section SEM image of the polymer scaffold perovskite film using MAI:PbI 2 =1:1 in DMF solvent on the FTO/glass substrate. Scale bar: 1 m. Supplementary Figure 2. Contact angle
Supplementary Figure 1. Cross-section SEM image of the polymer scaffold perovskite film using MAI:PbI 2 =1:1 in DMF solvent on the FTO/glass substrate. Scale bar: 1 m. Supplementary Figure 2. Contact angle
PHOTOLUMINESCENCE SPECTRA AND QUANTUM YIELDS OF GOLD NANOSPHERE MONOMERS AND DIMERS IN AQUEOUS SUSPENSION
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2016 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR PHOTOLUMINESCENCE SPECTRA AND QUANTUM
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2016 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR PHOTOLUMINESCENCE SPECTRA AND QUANTUM
Plasmonic Hot Hole Generation by Interband Transition in Gold-Polyaniline
 Supplementary Information Plasmonic Hot Hole Generation by Interband Transition in Gold-Polyaniline Tapan Barman, Amreen A. Hussain, Bikash Sharma, Arup R. Pal* Plasma Nanotech Lab, Physical Sciences Division,
Supplementary Information Plasmonic Hot Hole Generation by Interband Transition in Gold-Polyaniline Tapan Barman, Amreen A. Hussain, Bikash Sharma, Arup R. Pal* Plasma Nanotech Lab, Physical Sciences Division,
Electrical control of near-field energy transfer between. quantum dots and 2D semiconductors
 Electrical control of near-field energy transfer between quantum dots and 2D semiconductors Supporting Information Dhiraj Prasai, Andrey Klots #, AKM Newaz #, $, J. Scott Niezgoda, Noah J. Orfield, Carlos
Electrical control of near-field energy transfer between quantum dots and 2D semiconductors Supporting Information Dhiraj Prasai, Andrey Klots #, AKM Newaz #, $, J. Scott Niezgoda, Noah J. Orfield, Carlos
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Neutral Colour Semitransparent Microstructured Perovskite Solar Cells Giles E. Eperon, Victor M. Burlakov, Alain Goriely and Henry J. Snaith 1. Controlling dewetting to achieve
Supplementary information Neutral Colour Semitransparent Microstructured Perovskite Solar Cells Giles E. Eperon, Victor M. Burlakov, Alain Goriely and Henry J. Snaith 1. Controlling dewetting to achieve
Quantum Dots The Pennsylvania State University Quantum Dots 1
 Quantum Dots www.nano4me.org 2018 The Pennsylvania State University Quantum Dots 1 Outline Introduction Quantum Confinement QD Synthesis Colloidal Methods Epitaxial Growth Applications Biological Light
Quantum Dots www.nano4me.org 2018 The Pennsylvania State University Quantum Dots 1 Outline Introduction Quantum Confinement QD Synthesis Colloidal Methods Epitaxial Growth Applications Biological Light
Supporting Information for: Enhancing the Performance of CdSe/CdS Dot-in- Rod Light Emitting Diodes via Surface Ligand.
 Supporting Information for: Enhancing the Performance of CdSe/CdS Dot-in- Rod Light Emitting Diodes via Surface Ligand Modification Prachi Rastogi a,b, Francisco Palazon a, Mirko Prato c, Francesco Di
Supporting Information for: Enhancing the Performance of CdSe/CdS Dot-in- Rod Light Emitting Diodes via Surface Ligand Modification Prachi Rastogi a,b, Francisco Palazon a, Mirko Prato c, Francesco Di
Supplementary Figure 1. Potential energy, volume, and molecular distribution of the
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplementary Figure 1. Potential energy, volume, and molecular distribution of the organic substrates prepared by MD simulation. (a) Change of the density and total potential energy of
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplementary Figure 1. Potential energy, volume, and molecular distribution of the organic substrates prepared by MD simulation. (a) Change of the density and total potential energy of
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Supporting Information Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO 2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution from HI Splitting Xiaomei Wang,, Hong Wang,, Hefeng Zhang,,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Single Enzyme Direct Biomineralization of CdSe and CdSe-CdS Core-Shell Quantum Dots Zhou Yang 1, Li Lu 2, Christopher J. Kiely 1,2, Bryan W. Berger* 1,3, and Steven McIntosh* 1 1
Supporting Information Single Enzyme Direct Biomineralization of CdSe and CdSe-CdS Core-Shell Quantum Dots Zhou Yang 1, Li Lu 2, Christopher J. Kiely 1,2, Bryan W. Berger* 1,3, and Steven McIntosh* 1 1
III-V nanostructured materials synthesized by MBE droplet epitaxy
 III-V nanostructured materials synthesized by MBE droplet epitaxy E.A. Anyebe 1, C. C. Yu 1, Q. Zhuang 1,*, B. Robinson 1, O Kolosov 1, V. Fal ko 1, R. Young 1, M Hayne 1, A. Sanchez 2, D. Hynes 2, and
III-V nanostructured materials synthesized by MBE droplet epitaxy E.A. Anyebe 1, C. C. Yu 1, Q. Zhuang 1,*, B. Robinson 1, O Kolosov 1, V. Fal ko 1, R. Young 1, M Hayne 1, A. Sanchez 2, D. Hynes 2, and
Spatial Coherence Properties of Organic Molecules Coupled to Plasmonic Surface Lattice Resonances in the Weak and Strong Coupling Regimes
 Spatial Coherence Properties of Organic Molecules Coupled to Plasmonic Surface Lattice Resonances in the Weak and Strong Coupling Regimes Supplemental Material L. Shi, T. K. Hakala, H. T. Rekola, J. -P.
Spatial Coherence Properties of Organic Molecules Coupled to Plasmonic Surface Lattice Resonances in the Weak and Strong Coupling Regimes Supplemental Material L. Shi, T. K. Hakala, H. T. Rekola, J. -P.
Excitation-Wavelength Dependent and Time-Resolved Photoluminescence Studies of Europium Doped GaN Grown by Interrupted Growth Epitaxy (IGE)
 Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 866 2005 Materials Research Society V3.5.1 Excitation-Wavelength Dependent and Time-Resolved Photoluminescence Studies of Europium Doped GaN Grown by Interrupted Growth
Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 866 2005 Materials Research Society V3.5.1 Excitation-Wavelength Dependent and Time-Resolved Photoluminescence Studies of Europium Doped GaN Grown by Interrupted Growth
Spectroscopic Study of FTO/CdSe (MPA)/ZnO Artificial Atoms Emitting White Color
 Spectroscopic Study of FTO/CdSe (MPA)/ZnO Artificial Atoms Emitting White Color Batal MA *, and Alyamani K Department of Physics, College of Science, Aleppo, Syria * Corresponding author: Batal MA, Department
Spectroscopic Study of FTO/CdSe (MPA)/ZnO Artificial Atoms Emitting White Color Batal MA *, and Alyamani K Department of Physics, College of Science, Aleppo, Syria * Corresponding author: Batal MA, Department
Supplementary Figure S1. The maximum possible short circuit current (J sc ) from a solar cell versus the absorber band-gap calculated assuming 100%
 Supplementary Figure S1. The maximum possible short circuit current (J sc ) from a solar cell versus the absorber band-gap calculated assuming 100% (black) and 80% (red) external quantum efficiency (EQE)
Supplementary Figure S1. The maximum possible short circuit current (J sc ) from a solar cell versus the absorber band-gap calculated assuming 100% (black) and 80% (red) external quantum efficiency (EQE)
This manuscript was submitted first in a reputed journal on Apri1 16 th Stanene: Atomically Thick Free-standing Layer of 2D Hexagonal Tin
 This manuscript was submitted first in a reputed journal on Apri1 16 th 2015 Stanene: Atomically Thick Free-standing Layer of 2D Hexagonal Tin Sumit Saxena 1, Raghvendra Pratap Choudhary, and Shobha Shukla
This manuscript was submitted first in a reputed journal on Apri1 16 th 2015 Stanene: Atomically Thick Free-standing Layer of 2D Hexagonal Tin Sumit Saxena 1, Raghvendra Pratap Choudhary, and Shobha Shukla
Facile Synthesis and Optical Properties of Colloidal Silica Microspheres Encapsulating Quantum Dots-Layer
 Electronic Supplementary Information for: Facile Synthesis and Optical Properties of Colloidal Silica Microspheres Encapsulating Quantum Dots-Layer Myungje Cho, Kipil Lim, Kyoungja Woo* Nano-Materials
Electronic Supplementary Information for: Facile Synthesis and Optical Properties of Colloidal Silica Microspheres Encapsulating Quantum Dots-Layer Myungje Cho, Kipil Lim, Kyoungja Woo* Nano-Materials
Starting solution. Hydrolysis reaction under thermostatic conditions. Check of viscosity and deposition test SOL. Deposition by spin coating
 Supplementary Figures Tetramethyl orthosilicate (TMOS) Tetrahydrofuran anhydrous (THF) Trimethyl methoxy silane (TMMS) Trimethyl silil acetate (TMSA) Starting solution Hydrolysis reaction under thermostatic
Supplementary Figures Tetramethyl orthosilicate (TMOS) Tetrahydrofuran anhydrous (THF) Trimethyl methoxy silane (TMMS) Trimethyl silil acetate (TMSA) Starting solution Hydrolysis reaction under thermostatic
Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene. quantum dots
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene quantum dots Bingjun Yang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene quantum dots Bingjun Yang,
High efficiency solar cells by nanophotonic design
 High efficiency solar cells by nanophotonic design Piero Spinelli Claire van Lare Jorik van de Groep Bonna Newman Mark Knight Paula Bronsveld Frank Lenzmann Ruud Schropp Wim Sinke Albert Polman Center
High efficiency solar cells by nanophotonic design Piero Spinelli Claire van Lare Jorik van de Groep Bonna Newman Mark Knight Paula Bronsveld Frank Lenzmann Ruud Schropp Wim Sinke Albert Polman Center
Organic LEDs part 8. Exciton Dynamics in Disordered Organic Thin Films. Handout on QD-LEDs: Coe et al., Nature 420, 800 (2002).
 Organic LEDs part 8 Exciton Dynamics in Disordered Organic Thin Films Quantum Dot LEDs Handout on QD-LEDs: Coe et al., ature 420, 800 (2002). @ MIT April 29, 2003 Organic Optoelectronics - Lecture 20b
Organic LEDs part 8 Exciton Dynamics in Disordered Organic Thin Films Quantum Dot LEDs Handout on QD-LEDs: Coe et al., ature 420, 800 (2002). @ MIT April 29, 2003 Organic Optoelectronics - Lecture 20b
Supporting information. Unidirectional Doubly Enhanced MoS 2 Emission via
 Supporting information Unidirectional Doubly Enhanced MoS 2 Emission via Photonic Fano Resonances Xingwang Zhang, Shinhyuk Choi, Dake Wang, Carl H. Naylor, A. T. Charlie Johnson, and Ertugrul Cubukcu,,*
Supporting information Unidirectional Doubly Enhanced MoS 2 Emission via Photonic Fano Resonances Xingwang Zhang, Shinhyuk Choi, Dake Wang, Carl H. Naylor, A. T. Charlie Johnson, and Ertugrul Cubukcu,,*
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O170331A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0170331 A1 Bertram et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTROLUMNESCENT DEVICE WITH (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2006O170331A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0170331 A1 Bertram et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTROLUMNESCENT DEVICE WITH (30) Foreign Application Priority
Supporting Information: Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Stamp Coated with a. Low-Surface-Energy, Diffusion-Blocking,
 Supporting Information: Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Stamp Coated with a Low-Surface-Energy, Diffusion-Blocking, Covalently Bonded Perfluoropolyether Layer and Its Application to the Fabrication of Organic Electronic
Supporting Information: Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Stamp Coated with a Low-Surface-Energy, Diffusion-Blocking, Covalently Bonded Perfluoropolyether Layer and Its Application to the Fabrication of Organic Electronic
University of South Florida Development of a Smart Window for Green Buildings in Florida
 University of South Florida Development of a Smart Window for Green Buildings in Florida PI: Dr. Sarath Witanachchi Students: Marak Merlak, Ph.D Description: This proposal is aimed at developing a smart
University of South Florida Development of a Smart Window for Green Buildings in Florida PI: Dr. Sarath Witanachchi Students: Marak Merlak, Ph.D Description: This proposal is aimed at developing a smart
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information A minimal non-radiative recombination loss for efficient
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information A minimal non-radiative recombination loss for efficient
Influence of excitation frequency on Raman modes of In 1-x Ga x N thin films
 Influence of excitation frequency on Raman modes of In 1-x Ga x N thin films A. Dixit 1,, J. S. Thakur 2, V. M. Naik 3, R. Naik 2 1 Center of Excellence in Energy & ICT, Indian Institute of Technology
Influence of excitation frequency on Raman modes of In 1-x Ga x N thin films A. Dixit 1,, J. S. Thakur 2, V. M. Naik 3, R. Naik 2 1 Center of Excellence in Energy & ICT, Indian Institute of Technology
Controlled Assembly of Organic Whispering Gallery Mode Microlasers as Highly Sensitive Chemical Sensors
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Controlled Assembly of Organic Whispering Gallery Mode Microlasers
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Controlled Assembly of Organic Whispering Gallery Mode Microlasers
DIELECTRIC nanoparticles (NPs) have recently been proposed
 IEEE JOURNAL OF PHOTOVOLTAICS 1 Effect of EVA Encapsulation on Antireflection Properties of Mie Nanoscatterers for c-si Solar Cells P. Spinelli, F. Lenzmann, A. Weeber, and A. Polman Abstract Dielectric
IEEE JOURNAL OF PHOTOVOLTAICS 1 Effect of EVA Encapsulation on Antireflection Properties of Mie Nanoscatterers for c-si Solar Cells P. Spinelli, F. Lenzmann, A. Weeber, and A. Polman Abstract Dielectric
Supplementary Figure S1. Hole collection layer photovoltaic performance in perovskite solar cells. Current voltage curves measured under AM1.
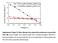 Supplementary Figure S1. Hole collection layer photovoltaic performance in perovskite solar cells. Current voltage curves measured under AM1.5 simulated sun light at 100mWcm -2 equivalent irradiance for
Supplementary Figure S1. Hole collection layer photovoltaic performance in perovskite solar cells. Current voltage curves measured under AM1.5 simulated sun light at 100mWcm -2 equivalent irradiance for
