Keywords: Sectional forces, bending moment, shear force, finite element, Bernoulli-Euler beam, concentrated moving loads
|
|
|
- Barbra Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Shock and Vibration 15 (2008) IOS Prss Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs of a Brnoui-Eur bam on continuousy viscoastic foundation subjctd to concntratd moving oads Ping Lou Schoo of Civi Enginring and Architctur, Raiway Campus, Cntra South Univrsity, 22 Shao-shan-nan Road, Changsha, Hunan , P.R. China Fax: ; E-mai: pingou@mai.csu.du.cn or pingoucsu@126.com Rcivd 9 Novmbr 2006 Rvisd 2 January 2007 Abstract. In th finit mnt mthod, thr ar shortcomings using th convntiona formua to cacuat th sctiona forcs, i.., th bnding momnt and th shar forc, at any cross-sction of Brnoui-Eur bam undr dynamic oads. This papr prsnts som nw finit-mnt formua ovrcoming th shortcomings of th convntiona ons to cacuat th sctiona forcs at any cross-sction of a Brnoui-Eur bam on continuousy viscoastic foundation subjctd to concntratd moving oads. Th proposd formua can asiy dgnrat into th formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs of a simpy supportd or a continuous Brnoui-Eur bam subjctd to concntratd moving oads, and into th formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs of a Brnoui-Eur bam on Winkr foundation undr static oads. Fiv numrica xamps incuding static and dynamic anayss ar chosn to iustrat th appication of th proposd formua. Numrica rsuts show: (1) compard with th convntiona formua, th proposd formua can improv th cacuation accuracy of th sctiona forcs of bam; (2) on shoud us th proposd formua, not th convntiona formua, to cacuat th sctiona forcs at any cross-sction in Brnoui-Eur bam. Kywords: Sctiona forcs, bnding momnt, shar forc, finit mnt, Brnoui-Eur bam, concntratd moving oads 1. Introduction Th dynamic anaysis of a bam on astic foundation or a simpy supportd bam subjctd to dynamic oads is widsprad in nginring. Hr ony som of th rvant itratur is mntiond. Many rsarchrs [5,8,9, 11,12,15,16,20,22] appid th anaytica mthods to invstigat th dynamic probm. Howvr, for most of th nginring probms, on must ry on numrica mthods sinc anaytica mthods ar usuay not avaiab. In th numrica mthods, th finit mnt mthod (FEM) is powrfu bcaus it aows soution to compx probms in nginring. Som rsarchrs [10,13,14,18,19,23 26] appid FEM to study th forgoing dynamic probm. It is w known that in th dsign of a bam on astic foundation or a simpy supportd bam subjctd to moving oads, th most important considrations ar th vrtica dfction and th bnding strss, and th attr is givn by using bnding momnt dividd by th sction moduus of th bam. Rfrncs [14,18,23,25,26] did not car for th bnding momnt of bam. Rfrncs [10,13,19,24] rportd th bnding momnt of bam, but thy did not giv th formua to cacuat th bnding momnt of bam. ISSN /08/$ IOS Prss and th authors. A rights rsrvd
2 148 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs In th dynamic anaysis using FEM, if th foowing formua (1) (4) ar usd to cacuat th sctiona forcs of th cross-sction at any point in a Brnoui-Eur bam mnt on continuousy viscoastic foundation subjctd to concntratd moving oads, thn, rrors may appar in th numrica rsuts bcaus of shortcomings in using th formua (1) (4) to cacuat th sctiona forcs. M(ξ,t) = EI 2 y(ξ,t) ξ 2 = EIN q for th right-hand sid of cross-sction at any point (1) Q(ξ,t) =EI 3 y(ξ,t) ξ 3 = EIN q for th right-hand sid of cross-sction at any point (2) M(ξ,t) =EI 2 y(ξ,t) ξ 2 = EIN q for th ft-hand sid of cross-sction at any point (3) Q(ξ,t) = EI 3 y(ξ,t) ξ 3 = EIN q for th ft-hand sid of cross-sction at any point (4) whr M(ξ,t) and Q(ξ,t) rspctivy dnot th bnding momnt and th shar forc of cross-sction at any point and tim t, and th positiv dirctions of M(ξ,t) and Q(ξ,t) for th right-hand sid of cross-sction and for th ft-hand sid of cross-sction at any point ar shown in Fig. 1(a) and (b), rspctivy; ξ dnots oca coordinat masurd from th ft nod of th bam mnt; EI dnots th constant bnding stiffnss of th bam; N dnots th shap matrix of th bam mnt; q dnots th noda dispacmnt vctor of th bam mnt; th suprscript prim dnots diffrntiation with rspct to ξ; and y(ξ) dnots th vrtica dfction at any point in th bam mnt. y(ξ) can b xprssd as y(ξ) =Nq (5) If th cubic Hrmitian poynomias [3] ar usd as th shap functions of a bam mnt, th shap matrix N of th bam mnt can b writtn as N = [ ] N 1 N 2 N 3 N 4 (6) with N 1 =1 3(ξ/) 2 +2(ξ/) 3 N 2 = ξ[1 2(ξ/)+(ξ/) 2 ] N 3 =3(ξ/) 2 2(ξ/) 3 N 4 = ξ[(ξ/) 2 (ξ/)] whr dnots th ngth of th bam mnt. In this papr, th formua (1) (4) ar rfrrd to as th convntiona ons for cacuating th sctiona forcs of a Brnoui-Eur bam undr dynamic oads. Th shortcomings using th formua (1) (4) to cacuat th sctiona forcs of a bam mnt on continuousy viscoastic foundation subjctd to concntratd moving oads ar as foows. First, thr ar shortcomings using th formua (1) (4) to cacuat th sctiona forcs at two nods of a bam mnt. Th formua (1) and (2) for cacuating th sctiona forcs at th ft nod (i.., ξ =0)and th formua (3) and (4) for cacuating th sctiona forcs at th right nod (i.., ξ = ) in a bam mnt ony considr th sctiona forcs inducd by th noda dispacmnts of th corrsponding bam mnt, bcaus th formua (1) and (2) with ξ =0and th formua (3) and (4) with ξ = can b xprssd as th sum of th products of th corrsponding mnt stiffnss matrix and th dispacmnts of th corrsponding bam mnt nods, i.., fd = k bq, in which, fd dnots th sctiona forcs of th bam mnt inducd by th noda dispacmnts of th bam mnt, and k b dnots th mnt stiffnss matrix of th bam mnt itsf. Th sctiona forcs of th cross-sction at th nods of mnt inducd by th noda accrations and th foundation spring and damping forcs acting on th corrsponding bam mnt ar not considrd. In addition, th fixd-nd sctiona forcs prsntd by rfrnc [17] at th two nds of a campd-campd (C-C) bam mnt inducd by moving oads acting on th bam mnt at tim t ar aso not considrd. Thn, thr xist shortcomings using th formua (3) and (4) to cacuat th sctiona forcs at any point A, rathr than at a nod, of a bam mnt. Th formua (3) and (4) for cacuating th sctiona forcs of th ft-hand sid of cross-sction at any point A, rathr than at a nod, of a Brnoui-Eur bam mnt and at tim t can b
3 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs 149 ft nod ξ ξ, t ξ, t ( ) ( ) right-hand sid of cross-sction at any point right nod r ξ r (a) Sctiona forcs diagram for th right-hand sid of cross-sction at any point ft nod ξ ( ξ, t ) ( ξ, t ) ft-hand sid of cross-sction at any point right nod r ξ r (b) Sctiona forcs diagram for th ft-hand sid of cross-sction at any point Fig. 1. Sctiona forcs diagram for th cross-sction at any point in a Brnoui-Eur bam mnt in th dynamic anaysis. writtn as, rspctivy, M(ξ,t) ξ=ξa = EI [ ] [ q 6 + ξ A EI ] q (7) Q(ξ,t) ξ=ξa = EI = M(ξ,t) ξ=0 + Q(ξ,t) ξ=0 ξ A [ ] q = Q(ξ,t) ξ=0 (8) Th formua (7) ony considrs th ffcts of th bnding momnt and th shar forc at th ft nod of th bam mnt, which ar inducd by th noda dispacmnts of th corrsponding mnt, on th bnding momnt of th ft-hand sid of cross-sction at th point A. In th formua (7), th ffcts of th fixd-nd bnding momnt and shar forc at th ft nd of th C-C bam mnt, inducd by moving oads acting on th bam mnt at tim t, on th bnding momnt of th ft-hand sid of cross-sction at th point A ar not considrd whi shoud b considrd. In addition, th ffcts on th bnding momnt of th ft-hand sid of cross-sction at th point A ar aso not considrd of moving oads acting on th bam mnt btwn th ft nod and th point A, of inrtia forc in th bam mnt btwn th ft nod and th point A, and of th foundation spring and damping forcs acting on th bam mnt btwn th ft nod and th point A. Simiary, th formua (8) ony considrs th ffct of th shar forc at th ft nod of th bam mnt, which is inducd by th noda dispacmnt of th corrsponding mnt, on th shar forc of th ft-hand sid of cross-sction at th point A. In th formua (8), th ffct of th fixd-nd shar forc at th ft nd of th C-C bam mnt, inducd by moving oads acting on th bam mnt at tim t, on th shar forc of th ft-hand sid of cross-sction at th point A is not considrd whi shoud b considrd. In addition, th ffcts on th shar forc of th ft-hand sid of cross-sction at th point A ar aso not considrd of moving oads acting on th bam mnt btwn th ft nod and th point A, of inrtia forc in th bam mnt btwn th ft nod and th point A, and of th foundation spring and damping forcs acting on th bam mnt btwn th ft nod and th point A. This purpos of this papr is to prsnt nw finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs at any cross-sction of a Brnoui-Eur bam on continuousy viscoastic foundation subjctd to concntratd moving oads. Th nw finit-mnt formua can ovrcom th forgoing shortcomings of th convntiona formua and can improv th accuracy of cacuating th sctiona forcs of bam. Evidnty, th proposd formua can asiy dgnrat into th formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs of a simpy supportd or a continuous Brnoui- Eur bam subjctd to concntratd moving oads, and into th formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs of a Brnoui-Eur bam on Winkr foundation undr static oads.
4 150 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs 2. Thory and formuation 2.1. Fundamnta assumptions Th foowing assumptions ar mad whn on stabishs th formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs of a bam on viscoastic foundation subjctd to concntratd moving oads. (1). Ony vrtica dynamic oads ar considrd. (2). Axia dformations and th damping of th bam ar ngctd. (3). Th bam is modd as a uniform Brnoui-Eur bam. (4). Th viscoastic foundation is modd as cosy spacd, indpndnt, inar springs and viscous damprs. (5). Th cubic Hrmitian poynomias [3] ar usd as th shap functions of a bam mnt Equation of motion for a bam on continuousy viscoastic foundation subjctd to concntratd moving oads Considr a uniform astic Brnoui-Eur bam with constant bnding stiffnss EI rsting on continuousy viscoastic foundation with stiffnss cofficint k w and damping cofficint c w subjctd to a numbr of concntratd moving oads, as shown in Fig. 2. Th bam is dividd into a numbr of finit mnts with qua ngth of. Th soid circs ( ) dnot th nods for th bam mnts. Sinc th axia dformations of th bam ar ngctd, pr nod of a bam mnt has two dgrs of frdom, i.., a vrtica transation and a rotation about an axis norma to th pan of th papr. According to th nrgy princip, th quation of motion for th bam on continuousy viscoastic foundation subjctd to a numbr of concntratd moving oads at tim t can b writtn as M q + C q + Kq = n N T i P i whr M, C, and K with n n ordr ar th ovra mass, damping and stiffnss matrics, rspctivy; q, q, and q with n 1 ordr ar th accration, vocity and dispacmnt vctors, rspctivy; th suprscript T dnots transpos; N T i is th transpos of th shap functions for th bam mnt which ar vauatd at th position of th i-th concntratd moving oad P i at tim t; P i is th magnitud of th i-th concntratd moving oad; n is th tota numbr of th dgrs of frdom of th bam; and n is th tota numbr of concntratd moving oads. In Eq. (9), th ovra mass matrix M can b obtaind by assmbing th mnt consistnt mass matrix m. Sinc th damping of bam itsf is ngctd, th ovra damping matrix C ony incuds th ffct of th viscous damping of foundation. C can b obtaind by assmbing th foundation mnt damping matrix c w inducd by viscous damping foundation supporting th bam mnt. Th ovra stiffnss matrix K can b obtaind by assmbing th mnt stiffnss matrix k b of th bam mnt itsf and th foundation mnt stiffnss matrix k w du to th astic foundation supporting th bam mnt. Th xprssions of mnt matrics m, c w, k b and k w ar istd in th Appndix. In addition, N i with 1 n ordr in Eq. (9) can b writtn as N i =[0 0 N 1 N 2 N 3 N 4 0 0] ξ=ξi (10) whr ξ i dnots th distanc btwn th acting point of th i-th concntratd moving oad P i and th ft nod of th bam mnt on which th oad P i is acting at tim t, as shown in Fig. 2. It shoud b notd that N i is a row matrix with zro ntris xcpt for thos trms corrsponding to two nods of th mnt on which th i th concntratd moving oad P i is acting. N i is tim dpndnt as th oad P i movs from on position to anothr within on mnt. As th oad P i movs to th nxt mnt, N i wi shift in position corrsponding to th dgrs of frdom of th mnt whr th oad P i is positiond. (9)
5 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs ξ w w Fig. 2. Mathmatica mod for a uniform astic Brnoui-Eur bam on continuousy viscoastic foundation subjctd to a numbr of concntratd moving oads. ft nod right nod ξ r r Fig. 3. Shar forcs Q and Q r, and bnding momnts M and M r at th cross-sction of th two nods of a typica bam mnt Formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs of a bam By introducing th boundary conditions of th bam, Eq. (9) can b sovd by th Wison-θ mthod or simiar mthods [1], to obtain th gnraizd dispacmnts, vocitis and accrations pr nod of th Brnoui-Eur bam at tim t. Thn, th sctiona forcs at any cross-sction of th bam at tim t can b obtaind by using th foowing procdur. First, t us considr how to cacuat th sctiona forcs at th cross-sction of th two nods of a bam mnt. Th sctiona forcs at th cross-sction of th two nods of a typica bam mnt at tim t, as shown in Fig. 3, can b xprssd as h f = m q + k b q + c w q + k w q + fi 0 (11) whr f is th sctiona forcs vctor at th two nods of a bam mnt, f =[Q M Q r Mr ] T, Q and M ar th shar forc and bnding momnt at th ft nod of th bam mnt, rspctivy; Q r and M r ar th shar forc and bnding momnt at th right nod of th bam mnt, rspctivy; th positiv dirctions of Q, M, Q r, and M r ar shown in Fig. 3; q, q, and q with 4 1 ordr ar th noda accration, vocity and dispacmnt vctors of th bam mnt, rspctivy, obtaind by soving Eq. (9); h is th tota numbr of concntratd moving oads acting on th bam mnt at tim t; and f i 0 is th fixd-nd forc vctor [17] at th two nds of th C-C bam mnt inducd by th i-th concntratd moving oad P i acting on th bam mnt at tim t. It shoud b notd that fi 0 and th quivant noda forc vctor inducd by th i-th concntratd moving oad P i acting on th C-C bam mnt at tim t ar qua in magnitud but opposit in dirction. Thus, th xprssion of fi 0 can b writtn as fi 0 = [N 1 N 2 N 3 N 4 ] T ξ=ξ i P i (12) f 0 i wi bcom zro vctor if th i-th concntratd moving oad P i acts outsid th bam mnt. Th first and scond trms on th right-hand sid in Eq. (11) dnot th vctors of th sctiona forcs at th two nods of th bam mnt inducd by, rspctivy, th noda accrations and th noda dispacmnts of th bam mnt. Th third and fourth trms on th right-hand sid dnot th vctors of th sctiona forcs at th two nods of th bam mnt inducd by, rspctivy, th continuousy damping forc and th spring forc undr th bam mnt. Th fifth trm on th right-hand sid dnots th sum of th fixd-nd forc vctors at th two nds of th C-C bam mnt inducd by h concntratd moving oads acting on th bam mnt at tim t. Thn, t us considr how to cacuat th sctiona forcs at a point, rathr than at a nod, within a bam mnt. Th sctiona forcs can b obtaind by using th quiibrium condition of forcs acting in th vrtica dirction and
6 152 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs ft nod 1 ξ (ξ) S ξ A (ξ) (ξ) D A ξ A A Fig. 4. Fr-body diagram of portion of a typica bam mnt on viscoastic foundation, in which f I (ξ) = mn q, f S (ξ) =k wnq, and f D (ξ) =c wn q. th quiibrium condition of bnding momnts. For xamp, it is assumd that point A ocats at a position in th bam btwn two adjacnt nods, as shown in Fig. 4, and thr ar h concntratd moving oads btwn th ft nod of th bam mnt and th point A at tim t. Th shar forc Q A and bnding momnt M A at th point A can b givn by th foowing xprssion ξ A h Q A = ( mn q + c w N q + k w Nq )dξ Q P i (13a) 0 M A = Q ξ A + h ξ A P i (ξ A ξ i ) M (ξ A ξ)( mn q + c w N q + k w Nq )dξ (14a) 0 whr N =[N 1 N 2 N 3 N 4 ], and ξ A dnots th distanc btwn th ft nod of th bam mnt and th point A. Th positiv dirctions of th shar forc Q A and bnding momnt M A at th point A ar shown in Figur 4. It shoud b notd that Q and M in th formua (13a) and (14a) hav bn obtaind by soving th formua (11). If m, c w, and k w ar constant, th formua (13a) and (14a) can b writtn as, rspctivy, Q A = m N ξ=ξa q + c w N ξ=ξa q + k w N ξ=ξa q Q M A = Q ξ A + h h P i P i (ξ A ξ i ) M m(ξ A N ξ=ξa Ñ ξ=ξa ) q c w (ξ A N ξ=ξa Ñ ξ=ξa ) q k w (ξ A N ξ=ξa Ñ ξ=ξa )q with N =[ N 1 N2 N3 N4 ] (13b) (14b) N 1 = ξ ξ ξ4 3 N2 = 1 2 ξ2 2 3 ξ ξ4 2 N 3 = ξ ξ4 3 and Ñ =[Ñ 1 Ñ 2 Ñ 3 Ñ 4 ] N4 = 1 4 ξ ξ3 Ñ 1 = 1 2 ξ2 3 4 ξ ξ5 3 Ñ 2 = 1 3 ξ3 1 2 ξ ξ5 2 Ñ 3 = 3 4 ξ ξ5 3 Ñ 4 = 1 5 ξ ξ4 It shoud b pointd out that th formua (11) ony cacuats th sctiona forcs at two nods of a bam mnt and th formuas (13) and (14) can cacuat th sctiona forcs at any point in a bam mnt xcpt two nods. By
7 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs 153 =98000N/m Fig. 5. A simpy supportd bam undr uniformy distributd static oad. using th formua (11), (13) and (14), on can obtain th sctiona forcs at any cross-sction of a Brnoui-Eur bam on continuousy viscoastic foundation subjctd to a numbr of concntratd moving oads at tim t. Furthrmor, for th static probm, on has q = q = 0, and th formua (11), (13) and (14) rduc to, rspctivy, f =(k b + k w )q + 0 h f 0 i ξ A h Q A = k w Nq dξ Q P i (16a) M A = Q ξ A + h ξ A P i (ξ A ξ i ) M (ξ A ξ)k w Nq dξ (17a) If k w is constant, th formua (16a) and (17a) can b writtn as, rspctivy, 0 (15) Q A = k w N ξ=ξa q Q h P i (16b) M A = Q ξ A + h P i (ξ A ξ i ) M k w (ξ A N ξ=ξa Ñ ξ=ξa )q In addition, if k w = 0 and c w = 0 ar usd in th formua (11), (13) and (14), thn th rvisd formua of (11), (13) and (14) can b usd to cacuat th sctiona forcs at any cross-sction of a simpy supportd or a continuous Brnoui-Eur bam subjctd to a numbr of concntratd moving oads. (17b) 3. Numrica xamps Fiv numrica xamps incuding static and dynamic anayss ar chosn to iustrat th appication of th proposd formua. In th finit mnt anaysis, th quation of motion for th foowing dynamic anayss wi b sovd by mans of th Wison-θ mthod with θ = Examp 1. A simpy supportd bam undr uniformy distributd static oad Figur 5 shows a simpy supportd bam undr uniformy distributd static oad p = N/m. Th paramtrs of th bam takn from rfrnc [4] ar: ngth L = 0.2 m and cross-sction ara = m 2 (0.02 m dp 0.01 m wid) and E = N/m 2. For th cas of a simpy supportd bam undr uniformy distributd static oad, th formua (11) for cacuating th sctiona forcs at th two nods of a bam mnt can b rvisd as f = k b q + f 0 (18)
8 154 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs Fig. 6. Bnding momnt diagrams in a simpy supportd bam undr uniformy distributd oad. whr f 0 dnots th fixd-nd forc vctor at th two nds of th C-C bam mnt inducd by uniformy distributd static oad, which can b writtn as f 0 = [pl/2 pl 2 /12 pl/2 pl 2 /12] T (19) Th formuas (13) and (14) for cacuating th sctiona forcs at a point A, rathr than at a nod, in a bam mnt can b rvisd as Q A = Q p ξ A (20) ξ A M A = Q ξ A + (ξ A ξ)pdξ M = Q ξ A p ξ2 A M (21) 0 Bnding momnt diagrams and shar forc diagrams of th simpy supportd bam hav bn pottd in Figs 6 and 7, rspctivy, incuding cosd form soutions and finit mnt soutions givn by th proposd formua with 1 mnt and by th convntiona formua [4] with 2 mnts of qua ngth. It can b sn from Figs 6 and 7 that th finit mnt soutions givn by th proposd formua with 1 mnt ar th sam as th cosd form soutions; howvr, th sam agrmnt cannot b found btwn th finit mnt soutions givn by th convntiona formua with 2 mnts and th cosd form soutions. Th rasons ar as foows. Th convntiona formua usd in rfrnc [4] is f = k b q (22) Compard with th proposd formua (18), th convntiona formua (22) ngcts f 0 to cacuat th sctiona forcs at two nods of a bam mnt. In addition, compard with th proposd formuas (20) and (21), th convntiona formua (22) dos not considr (i) th sctiona forcs at point A contributd by th fixd-nd forc at th ft nd of th C-C bam mnt inducd by th uniformy distributd oad acting on th bam mnt, and (ii) th sctiona forcs at point A inducd by th uniformy distributd oad acting on th bam mnt btwn th ft nod and th point A, whn th convntiona formua (22) is usd to cacuat th sctiona forcs at th point A in a bam mnt Examp 2. A bam with fr nds on Winkr foundation undr a concntratd static oad Considr a uniform Brnoui-Eur bam with fr nds rsting on Winkr foundation undr a concntratd static oad P = 10,000 N acting on th bam midpoint, as shown in Fig. 8. Th paramtrs in this study ar givn: E (bam astic moduus) = 9, N/m 2, I (momnt of inrtia of bam) = m 4, L (bam ngth) =
9 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs 155 Fig. 7. Shar forc diagrams in a simpy supportd bam undr uniformy distributd oad mm A Fig. 8. A uniform Brnoui-Eur bam with fr nd rsting on Winkr foundation undr a concntratd static oad m, and k w (stiffnss cofficint of Winkr foundation) = N/m 2. Ths paramtrs of this xamp ar takn from rfrnc [7]. Tab 1 rports th ratios of th numrica soutions to th xact soutions of th sctiona forcs at th point A, with th numrica soutions givn, rspctivy, by th proposd formuas (16b) and (17b), and by th convntiona formua (22) adoptd in rfrnc [7] using th cubic Hrmitian poynomias as th shap functions of a bam mnt. Th distanc btwn th point A and th bam midpoint is m, as shown in Fig. 8. Th xact soutions can b obtaind using th formua prsntd in rfrnc [21]. It shoud b notd that xact soutions ar not dpndnt on th numbr of mnts. It can b sn from Tab 1 that th bnding momnt and th shar forc givn by th proposd formuas (16b) and (17b) ar nary xact if 20 mnts ar usd for th bam ngth L. Th rror of th shar forc is 3 pr cnt and th rror of th bnding momnt is ss than 8 pr cnt if ony 10 mnts ar usd. Howvr, th sam agrmnt cannot b found for th rsuts givn by th convntiona formua (22) adoptd in rfrnc [7]. This is du to th shortcomings of th convntiona formua Examp 3. A simpy supportd bam subjctd to a concntratd moving oad Considr a uniform simpy supportd Brnoui-Eur bam with a span L of 20 m subjctd to a concntratd moving oad P = kn with constant spd v = 60 m/s from th ft nd to th right nd of th bam. Th bam paramtrs ar: E = N/m 2, I = 3.81 m 4, and m = 34,088 kg/m. In th finit mnt anaysis, th bam is modd as 2, 6 and 10 mnts with qua ngth, rspctivy, and tim intrva s is adoptd. Th bnding momnts at th midpoint cross-sction of bam givn by th rvisd proposd formua (11), i.., aftr dting th third and fourth trms of right hand sid in formua (11), with 2, 6 and 10 mnts hav bn pottd in Fig. 9, aong with th anaytica soution givn by th foowing Eq. (23) takn from Timoshnko t a. [22] with i = M(x, t) = EI 2 y(x, t) x 2 (23)
10 156 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs Tab 1 Ratios of th numrica soutions to th xact soutions of th sctiona forcs at th point A in Examp 2 with th numrica soutions givn, rspctivy, by th proposd formua and by th convntiona formua in rfrnc [7] Grad of msh (mnts of qua ngth) Bnding momnt Shar forc Prsnt Rf. [7] Prsnt Rf. [7] 10 mnts mnts mnts mnts mnts Fig. 9. Tim historis for bnding momnt at th midpoint cross-sction of bam with anaytica soution, and th soutions givn by th proposd formua with 2, 6 and 10 mnts. with y(x, t)= 2PL3 mπ 2 sin(iπx/l)sin(iπvt/l) i 2 (i 2 π 2 a 2 v 2 L 2 2PL4 v ) mπ 3 a sin(iπx/l)sin(i 2 π 2 at/l 2 ) i 3 (i 2 π 2 a 2 v 2 L 2 ) (24) a 2 = EI m From Fig. 9, good agrmnt has bn achivd btwn th prsnt soution with 2, 6 and 10 mnts, rspctivy, and th anaytica soution. Th bnding momnts at th midpoint cross-sction of bam givn by th rvisd proposd formua (11) and th convntiona formua (1) with 2, 6 and 10 mnts hav bn pottd in Figs 10 12, rspctivy. It can b sn that th diffrnc btwn th soution givn by th rvisd proposd formua (11) and that givn by th convntiona formua (1) incrass with th incras of ngth of mnt. Th rason why thr is th diffrnc btwn th soution givn by th rvisd proposd formua (11) and that givn by th convntiona formua (1) is that th fixd-nd bnding momnt at th ft nd of th (N/2+1)-th C-C bam mnt inducd by th oad acting on th (N/2+1)-th bam mnt is not considrd in th convntiona formua, in which N dnots th tota numbr of bam mnts Examp 4. A simpy supportd bam rsting on Winkr foundation subjctd to a stationary pusating concntratd oad Lt us considr a simpy supportd uniform Brnoui-Eur bam rsting on Winkr foundation subjctd to a stationary pusating concntratd oad of P (t) = P sin ω t acting at a distanc x 1 from th ft nd point of th
11 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs 157 Fig. 10. Tim historis for bnding momnt at th midpoint cross-sction of bam with th soutions givn by th proposd formua and by th convntiona formua with 2 mnts. Fig. 11. Tim historis for bnding momnt at th midpoint cross-sction of bam with th soutions givn by th proposd formua and by th convntiona formua with 6 mnts. bam. Th xprssions of th xact vrtica dispacmnt y(x, t) and bnding momnt M(x, t) of th bam takn from Timoshnko t a. [22] ar as foows y(x, t) = 2 PL 3 [ sin ω t sin(iπx/l)sin(iπx 1 /L) m π 4 a 2 (i 4 + µ 4 ) ω 2 ω ] sin ω i t L4 L 4 ω i (ωi 2 ω2 ) (25) with M(x, t) = EI 2 y(x, t) x 2 (26) ( π ) 2 ω i = a i4 + µ L 4 i =1, 2,... a 2 = EI m
12 158 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs Fig. 12. Tim historis for bnding momnt at th midpoint cross-sction of bam with th soutions givn by th proposd formua and by th convntiona formua with 10 mnts. Fig. 13. Tim historis for bnding momnt at th midpoint cross-sction of bam in Examp 4. µ 4 = ( ) 4 L k w π EI Th paramtrs in this study ar: E = N/m 2, I = m 4, m = 50 kg/m, L = 100 m, x 1 = 50.5 m, k w = N/m 2, P = 98,000 N, and ω =3 rad/s. Th tim historis for th bnding momnt at th midpoint cross-sction of bam ar shown in Fig. 13, whr th soid, th dottd and th dashd ins dnot th tim historis with th anaytica soution givn by Eq. (26) with i = , with th finit mnt soutions (with qua mnt ngth 1.0 m and tim intrva 0.01 s) givn by th rvisd proposd formua (11), i.., aftr dting th third trm of right hand sid in formua (11), and givn by th convntiona formua (1), rspctivy. It is vidnt that th tim historis with th finit mnt soution givn by th rvisd proposd formua (11) ar vry cos to thos with th anaytica soution givn by Eq. (26). Howvr, th diffrnc btwn th tim historis with th finit mnt soution givn by th convntiona formua (1) and thos with th anaytica soution givn by Eq. (26) is high. This is du to th shortcomings mntiond in Sction 1 of Introduction.
13 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs 159 Tab 2 Prsnt soutions (with 100 mnts of qua ngth) and anaytica soutions of maximum bnding momnts at th midpoint cross-sction of bam, and th ratios of th soution givn by th proposd formua to th corrsponding anaytica soution subjctd to a moving oad with various spds Spd (m/s) Prsnt soution (N-m) Anaytica soution (N-m) Ratio of prsnt soution to anaytica on Examp 5. A simpy supportd bam rsting on viscoastic foundation subjctd to a concntratd moving oad A simpy supportd uniform Brnoui-Eur bam rsting on continuousy viscoastic foundation subjctd to a concntratd moving oad P = 98,000 N with constant spd from th ft nd to th right nd of th bam is studid in this xamp. Th damping cofficint of foundation, c w, is dfind by a non-dimnsiona paramtr [6] (th ratio btwn actua damping and critica damping) givn by β = 2 m cw m/kw. β = 0.1 is adoptd in this xamp. Othr paramtrs for th bam and th foundation ar th sam as thos in Examp 4. Initiay, th bam is at rst, and th moving oad is at th ft nd of th bam. In th prsnt anaysis, 1000 qua tim stps for th cas of vry spd of th moving oad ar adoptd. Th maximum bnding momnts at th midpoint cross-sction of bam givn by th proposd formua (11) using 100 mnts with qua ngth undr th moving oad with various spds hav bn rportd in Tab 2, aong with th anaytica soutions givn by th foowing Eq. (27) takn from Fr ýba [9] M(α) = with α = v m/ei 2λ λ =(k w /4EI) 1/4 1 (1 α 2 ) 1/2 [ α2 β 2 /(1 α 2 ) 2 ] P Cas with α<1and β<< 1 (27) 4λ It is obsrvd from Tab 2 that th prsnt soution agrs w with th corrsponding anaytica on, and th diffrnc btwn th prsnt soution and th anaytica on is about 1 pr cnt. Th maximum bnding momnts at th midpoint cross-sction of bam givn by th proposd formua (11) with 40, 60, 80, 100, 120, 140, and 160 mnts and constant spd v = 50 m/s hav bn rportd in Tab 3, aong with thos givn by th convntiona formua (1) at th corrsponding tim whn th maximum bnding momnt is achivd by th proposd formua (11), i.., whn th moving oad is acting on th bam midpoint. In addition, th two rsuts hav bn pottd in Fig. 14. From Tab 3 and Fig. 14, on can obtain that th diffrnc btwn th soution givn from th proposd formua (11) and th anaytica soution givn by Eq. (27) is ow, for xamp, th diffrnc btwn th two rsuts is 4.8 pr cnt vn though 40 mnts (i.., mnt ngth of 2.5 m) hav bn usd for th bam; howvr, th diffrnc btwn th soution givn by th convntiona formua (1) and th anaytica soution givn by Eq. (27) is high, for xamp, th diffrncs btwn th two rsuts ar 68.1 and 9.8 pr cnt, rspctivy, whn 40 and 160 mnts hav bn usd for th bam. This is du to th shortcomings of th convntiona formua mntiond Sction 1 of Introduction. It shoud b pointd out that Eq. (27) is basd on th foowing assumption [9], i.., an infinit bam on a Winkr foundation is subjctd to a constant oad P moving from infinity to infinity at constant spd v. Th diffrntia quation of th vrtica vibration of th bam givn by rfrnc [9] is writtn as d 4 y(s) ds 4 with +4α 2 d2 y(s) ds 2 8αβ 1 dy(s) ds +4y(s) =8 δ(s) (28)
14 160 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs Tab 3 Maximum bnding momnts at th midpoint cross-sction of bam givn by th proposd formua and thos givn by th convntiona formua with various mnt numbrs subjctd to a moving oad with constant spd v = 50 m/s Grad of msh (mnts 40 mnts 60 mnts 80 mnts 100 mnts 120 mnts 140 mnts 160 mnts of qua ngth) Soution givn by th proposd formua (N-m) Soution givn by th convntiona formua (N-m) Anaytica soution is N-m. Fig. 14. Maximum bnding momnts at th midpoint cross-sction of bam givn by th proposd formua and thos givn by th convntiona formua with various mnt numbrs subjctd to a moving oad with constant spd v = 50 m/s. s = λ(x vt) β 1 = ω b m/kw δ(s)=δ(x)/λ whr ω b dnots circuar frquncy of damping of th bam, v is moving spd of th oad, and δ(x) is Dirac dta function. Th rasons why Eq. (27) can b usd as th anaytica soution of this xamp ar as foows. On th on hand, if β 1 in Eq. (28) is rpacd by β = 2 m cw m/kw, thn th modifid Eq. (28) is th diffrntia quation of th vrtica vibration of an infinit bam on a continuousy viscoastic foundation subjctd to a constant oad P moving from infinity to infinity at constant spd v. On th othr hand, th dispacmnts and sctiona forcs of th bam on astic foundation dcin to zro vry fast as th distanc from point oad incrass [21]. Thrfor, on may choos a bam with finit ngth to tak th pac of an infinit bam. 4. Concuding rmarks This papr has prsntd nw finit-mnt formua ovrcoming th shortcomings of th convntiona formua to cacuat th sctiona forcs at any cross-sction of a Brnoui-Eur bam on continuousy viscoastic foundation subjctd to concntratd moving oads. Th proposd formua can asiy dgnrat into th formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs of a simpy supportd or a continuous Brnoui-Eur bam subjctd to concntratd moving oads, and into th formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs of a Brnoui-Eur bam on Winkr foundation undr static oads. Fiv numrica xamps incuding static and dynamic anayss ar chosn to iustrat
15 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs 161 th appication of th proposd formua. Numrica rsuts show: (i) compard with th convntiona formua, th proposd formua can improv th cacuation accuracy of th sctiona forcs of bam; (ii) to cacuat th sctiona forcs at th cross-sction of th two nods of a bam mnt, on shoud us th proposd formua (11), not th convntiona formua (1), (2) or (3), (4); (iii) to cacuat th sctiona forcs at point within a bam mnt rathr than at a nod, on shoud us th proposd formua (13), (14), not th convntiona formua (1), (2) or (3), (4). Acknowdgmnt Th author woud ik to thank Prof. Dani J. Inman, Editor-in-Chif of Shock and Vibration, Dr. Sondipon Adhikari, Associat Editor of Shock and Vibration and two anonymous rviwrs for thir vauab and hpfu commnts. Appndix Th xprssion of th mnt consistnt mass matrix m with 4 4 ordr [2] usd in th Eq. (11) is m = m symm. 4 2 whr m is th mass pr unit ngth of bam. Th xprssion of th mnt stiffnss matrix k b with 4 4 ordr [2] usd in th Eq. (11) is 12/ 3 6/ 2 12/ 3 6/ 2 k b = EI 4/ 6/ 2 2/ 12/ 3 6/ 2 symm. 4/ (A1) (A2) Th xprssions of th foundation mnt stiffnss matrix k w and damping matrix c w usd in th Eq. (11) ar simiar in form to th mnt consistnt mass matrix m of Eq. (A-1). k w can b obtaind by simpy rpacing m by k w in th mnt consistnt mass matrix m. Simiary, c w can aso b obtaind by simpy rpacing m by c w in th mnt consistnt mass matrix m. Rfrncs [1] K.J. Bath and E.L. Wison, Numrica Mthods in Finit Emnt Anaysis, Prntic-Ha, Engwood Ciffs, Nw Jrsy, [2] R.W. Cough and J. Pnzin, Dynamics of Structurs, (2nd dition), McGraw-Hi, Nw York, [3] R.D. Cook, Concpts and Appications of Finit Emnt Anaysis, (2nd dition), Wiy, Nw York, [4] C.S. Dsai, Emntary Finit Emnt Mthod, Prntic-Ha, Inc., Engwood Ciffs, Nw Jrsy, 1979, [5] D.G. Duffy, Th rspons of an infinit rairoad track to a moving vibrating mass, Journa of Appid Mchanics, ASME 57(1) (1990), [6] C. Esvd, Modrn Raiway Track, (2nd dition), MRT-Productions, Zatbomm, ISBN , [7] Z. Fng and R.D. Cook, Bam mnt on two-paramtr astic foundations, Journa of Enginring Mchanics ASCE 109(6) (1983), [8] A.L. Fornc, Traving forc on a Timoshnko bam, Journa of Appid Mchanics ASME 32(2) (1965), [9] L. Frýba, Vibration of Soids and Structurs undr Moving Loads, (3rd dition), Acadmia, Pragu, [10] L. Frýba, S. Nakagiri and N. Yoshikawa, Stochastic finit mnts for a bam on a random foundation with uncrtain damping undr a moving forc, Journa of Sound and Vibration 163(1) (1993), [11] A. Garini, Vibrations of simp bam-ik modd bridg undr harmonic moving oads, Intrnationa Journa of Enginring Scinc 44(11 12) (2006), [12] J.T. Knny, Stady-stat vibrations of bam on astic foundation for moving oad, Journa of Appid Mchanics, ASME 21(4) (1954),
16 162 P. Lou / Finit-mnt formua for cacuating th sctiona forcs [13] T. Kocaturk and M. Simsk, Vibration of viscoastic bams subjctd to an ccntric comprssiv forc and a concntratd moving harmonic forc, Journa of Sound and Vibration 291(1 2) (2006), [14] P. Lou, G.L. Dai and Q.Y. Zng, Dynamic anaysis of a timoshnko bam subjctd to moving concntratd forcs using th finit mnt mthod, Shock and Vibration, in prss. [15] S.P. Pati, Natura frquncis of an infinit bam on a simp inrtia foundation mod, Intrnationa Journa of Soids and Structurs 23(12) (1987), [16] S.P. Pati, Rspons of infinit raiway track to vibrating mass, Journa of Enginring Mchanics, ASCE 114(4) (1988), [17] R.L. Sack, Structura Anaysis, McGraw-Hi Book Company, Nw York, [18] V.N. Shah, R.D. Cook and T.C. Huang, Loads moving on bam supportd by ayrd astic foundation, Journa of Mchanica Dsign, ASME 102(2) (1980), [19] D. Thambiratnam and Y. Zhug, Dynamic anaysis of bams on an astic foundation subjctd to moving oads, Journa of Sound and Vibration 198(2) (1996), [20] S. Timoshnko, Mthod of anaysis of statica and dynamica strsss in rais, Procdings of th Scond Intrnationa Congrss for Appid Mchanics, Zurich, Swiss, 1926, [21] S. Timoshnko, Strngth of Matrias Part II Advanc Thory and Probms, VanNostrand Rinhod Company Ltd, London, [22] S. Timoshnko, D.H. Young and W. Wavr, Jr., Vibration Probms in Enginring, (4th dition), Wiy, Nw York, [23] J.J. Wu, Dynamic anaysis of an incind bam du to moving oads, Journa of Sound and Vibration 288(1 2) (2005), [24] J.J. Wu, A.R. Whittakr and M.P. Cartm, Th us of finit mnt tchniqus for cacuating th dynamic rspons of structurs to moving oads, Computrs and Structurs 78(6) (2000), [25] J.S. Wu and P.Y. Shin, Dynamic rsponss of raiway and carriag undr th high-spd moving oads, Journa of Sound and Vibration 236(1) (2000), [26] J.S. Wu and P.Y. Shin, Th dynamic bhaviour of a finit raiway undr th high-spd mutip moving forcs by using finit mnt mthod, Communications in Numrica Mthods in Enginring 16(12) (2000),
17 Intrnationa Journa of Rotating Machinry Enginring Journa of Th Scintific Word Journa Intrnationa Journa of Distributd Snsor Ntworks Journa of Snsors Journa of Contro Scinc and Enginring Advancs in Civi Enginring Submit your manuscripts at Journa of Journa of Ectrica and Computr Enginring Robotics VLSI Dsign Advancs in OptoEctronics Intrnationa Journa of Navigation and Obsrvation Chmica Enginring Activ and Passiv Ectronic Componnts Antnnas and Propagation Arospac Enginring Voum 2010 Intrnationa Journa of Intrnationa Journa of Intrnationa Journa of Moding & Simuation in Enginring Shock and Vibration Advancs in Acoustics and Vibration
SME 3033 FINITE ELEMENT METHOD. Bending of Prismatic Beams (Initial notes designed by Dr. Nazri Kamsah)
 Bnding of Prismatic Bams (Initia nots dsignd by Dr. Nazri Kamsah) St I-bams usd in a roof construction. 5- Gnra Loading Conditions For our anaysis, w wi considr thr typs of oading, as iustratd bow. Not:
Bnding of Prismatic Bams (Initia nots dsignd by Dr. Nazri Kamsah) St I-bams usd in a roof construction. 5- Gnra Loading Conditions For our anaysis, w wi considr thr typs of oading, as iustratd bow. Not:
Dynamic analysis of a Timoshenko beam subjected to moving concentrated forces using the finite element method
 Shock and Vibration 4 27) 459 468 459 IOS Prss Dynamic analysis of a Timoshnko bam subjctd to moving concntratd forcs using th finit lmnt mthod Ping Lou, Gong-lian Dai and Qing-yuan Zng School of Civil
Shock and Vibration 4 27) 459 468 459 IOS Prss Dynamic analysis of a Timoshnko bam subjctd to moving concntratd forcs using th finit lmnt mthod Ping Lou, Gong-lian Dai and Qing-yuan Zng School of Civil
Active Displacement Feedback Control of a Smart Beam: Analytic and Numerical Solutions
 Procdings of th Intrnationa MutiConfrnc of Enginrs and Computr Scintists 9 Vo II IMECS 9, March 8 -, 9, Hong Kong Activ Dispacmnt Fdback Contro of a Smart Bam: Anaytic and Numrica Soutions C. SPIER, I.S.
Procdings of th Intrnationa MutiConfrnc of Enginrs and Computr Scintists 9 Vo II IMECS 9, March 8 -, 9, Hong Kong Activ Dispacmnt Fdback Contro of a Smart Bam: Anaytic and Numrica Soutions C. SPIER, I.S.
Exact and Approximate Detection Probability Formulas in Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing
 Exact and Approximat tction robabiity Formuas in Fundamntas of Radar Signa rocssing Mark A. Richards Sptmbr 8 Introduction Tab 6. in th txt Fundamntas of Radar Signa rocssing, nd d. [], is rproducd bow.
Exact and Approximat tction robabiity Formuas in Fundamntas of Radar Signa rocssing Mark A. Richards Sptmbr 8 Introduction Tab 6. in th txt Fundamntas of Radar Signa rocssing, nd d. [], is rproducd bow.
dt d Chapter 30: 1-Faraday s Law of induction (induced EMF) Chapter 30: 1-Faraday s Law of induction (induced Electromotive Force)
 Chaptr 3: 1-Faraday s aw of induction (inducd ctromotiv Forc) Variab (incrasing) Constant Variab (dcrasing) whn a magnt is movd nar a wir oop of ara A, currnt fows through that wir without any battris!
Chaptr 3: 1-Faraday s aw of induction (inducd ctromotiv Forc) Variab (incrasing) Constant Variab (dcrasing) whn a magnt is movd nar a wir oop of ara A, currnt fows through that wir without any battris!
Dynamic response of a finite length euler-bernoulli beam on linear and nonlinear viscoelastic foundations to a concentrated moving force
 Journal of Mchanical Scinc and Tchnology 2 (1) (21) 1957~1961 www.springrlink.com/contnt/1738-9x DOI 1.17/s1226-1-7-x Dynamic rspons of a finit lngth ulr-brnoulli bam on linar and nonlinar viscolastic
Journal of Mchanical Scinc and Tchnology 2 (1) (21) 1957~1961 www.springrlink.com/contnt/1738-9x DOI 1.17/s1226-1-7-x Dynamic rspons of a finit lngth ulr-brnoulli bam on linar and nonlinar viscolastic
AS 5850 Finite Element Analysis
 AS 5850 Finit Elmnt Analysis Two-Dimnsional Linar Elasticity Instructor Prof. IIT Madras Equations of Plan Elasticity - 1 displacmnt fild strain- displacmnt rlations (infinitsimal strain) in matrix form
AS 5850 Finit Elmnt Analysis Two-Dimnsional Linar Elasticity Instructor Prof. IIT Madras Equations of Plan Elasticity - 1 displacmnt fild strain- displacmnt rlations (infinitsimal strain) in matrix form
Method for including restrained warping in traditional frame analyses
 thod for incuding rstraind arping in traditiona fram anayss PCJ Hoognboom and A Borgart Facuty of Civi Enginring and Goscincs Facuty of Architctur, Dft Univrsity of Tchnoogy, Dft, Th Nthrands Rstraind
thod for incuding rstraind arping in traditiona fram anayss PCJ Hoognboom and A Borgart Facuty of Civi Enginring and Goscincs Facuty of Architctur, Dft Univrsity of Tchnoogy, Dft, Th Nthrands Rstraind
2008 AP Calculus BC Multiple Choice Exam
 008 AP Multipl Choic Eam Nam 008 AP Calculus BC Multipl Choic Eam Sction No Calculator Activ AP Calculus 008 BC Multipl Choic. At tim t 0, a particl moving in th -plan is th acclration vctor of th particl
008 AP Multipl Choic Eam Nam 008 AP Calculus BC Multipl Choic Eam Sction No Calculator Activ AP Calculus 008 BC Multipl Choic. At tim t 0, a particl moving in th -plan is th acclration vctor of th particl
Homotopy perturbation technique
 Comput. Mthods Appl. Mch. Engrg. 178 (1999) 257±262 www.lsvir.com/locat/cma Homotopy prturbation tchniqu Ji-Huan H 1 Shanghai Univrsity, Shanghai Institut of Applid Mathmatics and Mchanics, Shanghai 272,
Comput. Mthods Appl. Mch. Engrg. 178 (1999) 257±262 www.lsvir.com/locat/cma Homotopy prturbation tchniqu Ji-Huan H 1 Shanghai Univrsity, Shanghai Institut of Applid Mathmatics and Mchanics, Shanghai 272,
Einstein Equations for Tetrad Fields
 Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Dynamic Modelling of Hoisting Steel Wire Rope. Da-zhi CAO, Wen-zheng DU, Bao-zhu MA *
 17 nd Intrnational Confrnc on Mchanical Control and Automation (ICMCA 17) ISBN: 978-1-6595-46-8 Dynamic Modlling of Hoisting Stl Wir Rop Da-zhi CAO, Wn-zhng DU, Bao-zhu MA * and Su-bing LIU Xi an High
17 nd Intrnational Confrnc on Mchanical Control and Automation (ICMCA 17) ISBN: 978-1-6595-46-8 Dynamic Modlling of Hoisting Stl Wir Rop Da-zhi CAO, Wn-zhng DU, Bao-zhu MA * and Su-bing LIU Xi an High
22/ Breakdown of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. Selection rules for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branches.
 Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
u 3 = u 3 (x 1, x 2, x 3 )
 Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
The van der Waals interaction 1 D. E. Soper 2 University of Oregon 20 April 2012
 Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
VSMN30 FINITA ELEMENTMETODEN - DUGGA
 VSMN3 FINITA ELEMENTMETODEN - DUGGA 1-11-6 kl. 8.-1. Maximum points: 4, Rquird points to pass: Assistanc: CALFEM manual and calculator Problm 1 ( 8p ) 8 7 6 5 y 4 1. m x 1 3 1. m Th isotropic two-dimnsional
VSMN3 FINITA ELEMENTMETODEN - DUGGA 1-11-6 kl. 8.-1. Maximum points: 4, Rquird points to pass: Assistanc: CALFEM manual and calculator Problm 1 ( 8p ) 8 7 6 5 y 4 1. m x 1 3 1. m Th isotropic two-dimnsional
Elements of Statistical Thermodynamics
 24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
4.2 Design of Sections for Flexure
 4. Dsign of Sctions for Flxur This sction covrs th following topics Prliminary Dsign Final Dsign for Typ 1 Mmbrs Spcial Cas Calculation of Momnt Dmand For simply supportd prstrssd bams, th maximum momnt
4. Dsign of Sctions for Flxur This sction covrs th following topics Prliminary Dsign Final Dsign for Typ 1 Mmbrs Spcial Cas Calculation of Momnt Dmand For simply supportd prstrssd bams, th maximum momnt
1 Isoparametric Concept
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY Dpartmnt of Civil Enginring Spring 06 Structural Enginring, Mchanics and Matrials Profssor: S. Govindj Nots on D isoparamtric lmnts Isoparamtric Concpt Th isoparamtric
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY Dpartmnt of Civil Enginring Spring 06 Structural Enginring, Mchanics and Matrials Profssor: S. Govindj Nots on D isoparamtric lmnts Isoparamtric Concpt Th isoparamtric
Zero Point Energy: Thermodynamic Equilibrium and Planck Radiation Law
 Gaug Institut Journa Vo. No 4, Novmbr 005, Zro Point Enrgy: Thrmodynamic Equiibrium and Panck Radiation Law Novmbr, 005 vick@adnc.com Abstract: In a rcnt papr, w provd that Panck s radiation aw with zro
Gaug Institut Journa Vo. No 4, Novmbr 005, Zro Point Enrgy: Thrmodynamic Equiibrium and Panck Radiation Law Novmbr, 005 vick@adnc.com Abstract: In a rcnt papr, w provd that Panck s radiation aw with zro
Construction of asymmetric orthogonal arrays of strength three via a replacement method
 isid/ms/26/2 Fbruary, 26 http://www.isid.ac.in/ statmath/indx.php?modul=prprint Construction of asymmtric orthogonal arrays of strngth thr via a rplacmnt mthod Tian-fang Zhang, Qiaoling Dng and Alok Dy
isid/ms/26/2 Fbruary, 26 http://www.isid.ac.in/ statmath/indx.php?modul=prprint Construction of asymmtric orthogonal arrays of strngth thr via a rplacmnt mthod Tian-fang Zhang, Qiaoling Dng and Alok Dy
Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 413 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis
 Middl East Tchnical Univrsity Dpartmnt of Mchanical Enginring ME 4 Introduction to Finit Elmnt Analysis Chaptr 4 Trusss, Bams and Frams Ths nots ar prpard by Dr. Cünyt Srt http://www.m.mtu.du.tr/popl/cunyt
Middl East Tchnical Univrsity Dpartmnt of Mchanical Enginring ME 4 Introduction to Finit Elmnt Analysis Chaptr 4 Trusss, Bams and Frams Ths nots ar prpard by Dr. Cünyt Srt http://www.m.mtu.du.tr/popl/cunyt
Observer Bias and Reliability By Xunchi Pu
 Obsrvr Bias and Rliability By Xunchi Pu Introduction Clarly all masurmnts or obsrvations nd to b mad as accuratly as possibl and invstigators nd to pay carful attntion to chcking th rliability of thir
Obsrvr Bias and Rliability By Xunchi Pu Introduction Clarly all masurmnts or obsrvations nd to b mad as accuratly as possibl and invstigators nd to pay carful attntion to chcking th rliability of thir
Introduction to the quantum theory of matter and Schrödinger s equation
 Introduction to th quantum thory of mattr and Schrödingr s quation Th quantum thory of mattr assums that mattr has two naturs: a particl natur and a wa natur. Th particl natur is dscribd by classical physics
Introduction to th quantum thory of mattr and Schrödingr s quation Th quantum thory of mattr assums that mattr has two naturs: a particl natur and a wa natur. Th particl natur is dscribd by classical physics
Search sequence databases 3 10/25/2016
 Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
EXST Regression Techniques Page 1
 EXST704 - Rgrssion Tchniqus Pag 1 Masurmnt rrors in X W hav assumd that all variation is in Y. Masurmnt rror in this variabl will not ffct th rsults, as long as thy ar uncorrlatd and unbiasd, sinc thy
EXST704 - Rgrssion Tchniqus Pag 1 Masurmnt rrors in X W hav assumd that all variation is in Y. Masurmnt rror in this variabl will not ffct th rsults, as long as thy ar uncorrlatd and unbiasd, sinc thy
Probability and Stochastic Processes: A Friendly Introduction for Electrical and Computer Engineers Roy D. Yates and David J.
 Probability and Stochastic Procsss: A Frindly Introduction for Elctrical and Computr Enginrs Roy D. Yats and David J. Goodman Problm Solutions : Yats and Goodman,4.3. 4.3.4 4.3. 4.4. 4.4.4 4.4.6 4.. 4..7
Probability and Stochastic Procsss: A Frindly Introduction for Elctrical and Computr Enginrs Roy D. Yats and David J. Goodman Problm Solutions : Yats and Goodman,4.3. 4.3.4 4.3. 4.4. 4.4.4 4.4.6 4.. 4..7
Supplementary Materials
 6 Supplmntary Matrials APPENDIX A PHYSICAL INTERPRETATION OF FUEL-RATE-SPEED FUNCTION A truck running on a road with grad/slop θ positiv if moving up and ngativ if moving down facs thr rsistancs: arodynamic
6 Supplmntary Matrials APPENDIX A PHYSICAL INTERPRETATION OF FUEL-RATE-SPEED FUNCTION A truck running on a road with grad/slop θ positiv if moving up and ngativ if moving down facs thr rsistancs: arodynamic
Division of Mechanics Lund University MULTIBODY DYNAMICS. Examination Name (write in block letters):.
 Division of Mchanics Lund Univrsity MULTIBODY DYNMICS Examination 7033 Nam (writ in block lttrs):. Id.-numbr: Writtn xamination with fiv tasks. Plas chck that all tasks ar includd. clan copy of th solutions
Division of Mchanics Lund Univrsity MULTIBODY DYNMICS Examination 7033 Nam (writ in block lttrs):. Id.-numbr: Writtn xamination with fiv tasks. Plas chck that all tasks ar includd. clan copy of th solutions
Ch. 24 Molecular Reaction Dynamics 1. Collision Theory
 Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
ELECTRON-MUON SCATTERING
 ELECTRON-MUON SCATTERING ABSTRACT Th lctron charg is considrd to b distributd or xtndd in spac. Th diffrntial of th lctron charg is st qual to a function of lctron charg coordinats multiplid by a four-dimnsional
ELECTRON-MUON SCATTERING ABSTRACT Th lctron charg is considrd to b distributd or xtndd in spac. Th diffrntial of th lctron charg is st qual to a function of lctron charg coordinats multiplid by a four-dimnsional
2.3 Matrix Formulation
 23 Matrix Formulation 43 A mor complicatd xampl ariss for a nonlinar systm of diffrntial quations Considr th following xampl Exampl 23 x y + x( x 2 y 2 y x + y( x 2 y 2 (233 Transforming to polar coordinats,
23 Matrix Formulation 43 A mor complicatd xampl ariss for a nonlinar systm of diffrntial quations Considr th following xampl Exampl 23 x y + x( x 2 y 2 y x + y( x 2 y 2 (233 Transforming to polar coordinats,
Theory of Dipole-Exchange Spin Excitations in a Spherical Ferromagnetic Nanoshell, consideration of the Boundary Conditions V.V.
 Intrnationa Journa of Enginring Rsarch & Scinc (IJOER) ISSN: [395-699] [Vo-3 Issu-9 Sptmbr- 7] Thory of Dipo-Exchang Spin Excitations in a Sphrica Frromagntic Nanosh considration of th Boundary Conditions
Intrnationa Journa of Enginring Rsarch & Scinc (IJOER) ISSN: [395-699] [Vo-3 Issu-9 Sptmbr- 7] Thory of Dipo-Exchang Spin Excitations in a Sphrica Frromagntic Nanosh considration of th Boundary Conditions
10. The Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
 Th Discrt-Tim Fourir Transform (DTFT Dfinition of th discrt-tim Fourir transform Th Fourir rprsntation of signals plays an important rol in both continuous and discrt signal procssing In this sction w
Th Discrt-Tim Fourir Transform (DTFT Dfinition of th discrt-tim Fourir transform Th Fourir rprsntation of signals plays an important rol in both continuous and discrt signal procssing In this sction w
The graph of y = x (or y = ) consists of two branches, As x 0, y + ; as x 0, y +. x = 0 is the
 Copyright itutcom 005 Fr download & print from wwwitutcom Do not rproduc by othr mans Functions and graphs Powr functions Th graph of n y, for n Q (st of rational numbrs) y is a straight lin through th
Copyright itutcom 005 Fr download & print from wwwitutcom Do not rproduc by othr mans Functions and graphs Powr functions Th graph of n y, for n Q (st of rational numbrs) y is a straight lin through th
Non-Uniform Motion of the Three-Body Problem When the Primaries Are Oblate Spheroids
 IOSR Journa of Enginring (IOSRJEN) ISSN (): 50-301, ISSN (p): 78-8719 Vo. 08, Issu 6 (Jun. 018), V (II) PP 41-47 www.iosrjn.org Non-Uniform Motion of th Thr-Body Probm Whn th Primaris Ar Obat Sphroids
IOSR Journa of Enginring (IOSRJEN) ISSN (): 50-301, ISSN (p): 78-8719 Vo. 08, Issu 6 (Jun. 018), V (II) PP 41-47 www.iosrjn.org Non-Uniform Motion of th Thr-Body Probm Whn th Primaris Ar Obat Sphroids
The Fourier Transform Solution for the Green s Function of Monoenergetic Neutron Transport Theory
 4 Hawaii Univrsity Intrnationa Confrncs Scinc Tchnoogy Enginring ath & Education Jun 6 7 & 8 4 Aa oana Hot Honouu Hawaii Th Fourir Transform Soution for th Grn s Function of ononrgtic Nutron Transport
4 Hawaii Univrsity Intrnationa Confrncs Scinc Tchnoogy Enginring ath & Education Jun 6 7 & 8 4 Aa oana Hot Honouu Hawaii Th Fourir Transform Soution for th Grn s Function of ononrgtic Nutron Transport
Bayesian Decision Theory
 Baysian Dcision Thory Baysian Dcision Thory Know probabiity distribution of th catgoris Amost nvr th cas in ra if! Nvrthss usfu sinc othr cass can b rducd to this on aftr som work Do not vn nd training
Baysian Dcision Thory Baysian Dcision Thory Know probabiity distribution of th catgoris Amost nvr th cas in ra if! Nvrthss usfu sinc othr cass can b rducd to this on aftr som work Do not vn nd training
Mutually Independent Hamiltonian Cycles of Pancake Networks
 Mutually Indpndnt Hamiltonian Cycls of Pancak Ntworks Chng-Kuan Lin Dpartmnt of Mathmatics National Cntral Univrsity, Chung-Li, Taiwan 00, R O C discipl@ms0urlcomtw Hua-Min Huang Dpartmnt of Mathmatics
Mutually Indpndnt Hamiltonian Cycls of Pancak Ntworks Chng-Kuan Lin Dpartmnt of Mathmatics National Cntral Univrsity, Chung-Li, Taiwan 00, R O C discipl@ms0urlcomtw Hua-Min Huang Dpartmnt of Mathmatics
A New Approach to the Fatigue Life Prediction for Notched Components Under Multiaxial Cyclic Loading. Zhi-qiang TAO and De-guang SHANG *
 2017 2nd Intrnational Conrnc on Applid Mchanics, Elctronics and Mchatronics Enginring (AMEME 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-497-4 A Nw Approach to th Fatigu Li Prdiction or Notchd Componnts Undr Multiaxial Cyclic
2017 2nd Intrnational Conrnc on Applid Mchanics, Elctronics and Mchatronics Enginring (AMEME 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-497-4 A Nw Approach to th Fatigu Li Prdiction or Notchd Componnts Undr Multiaxial Cyclic
Introduction to Condensed Matter Physics
 Introduction to Condnsd Mattr Physics pcific hat M.P. Vaughan Ovrviw Ovrviw of spcific hat Hat capacity Dulong-Ptit Law Einstin modl Dby modl h Hat Capacity Hat capacity h hat capacity of a systm hld at
Introduction to Condnsd Mattr Physics pcific hat M.P. Vaughan Ovrviw Ovrviw of spcific hat Hat capacity Dulong-Ptit Law Einstin modl Dby modl h Hat Capacity Hat capacity h hat capacity of a systm hld at
cycle that does not cross any edges (including its own), then it has at least
 W prov th following thorm: Thorm If a K n is drawn in th plan in such a way that it has a hamiltonian cycl that dos not cross any dgs (including its own, thn it has at last n ( 4 48 π + O(n crossings Th
W prov th following thorm: Thorm If a K n is drawn in th plan in such a way that it has a hamiltonian cycl that dos not cross any dgs (including its own, thn it has at last n ( 4 48 π + O(n crossings Th
Hardy-Littlewood Conjecture and Exceptional real Zero. JinHua Fei. ChangLing Company of Electronic Technology Baoji Shannxi P.R.
 Hardy-Littlwood Conjctur and Excptional ral Zro JinHua Fi ChangLing Company of Elctronic Tchnology Baoji Shannxi P.R.China E-mail: fijinhuayoujian@msn.com Abstract. In this papr, w assum that Hardy-Littlwood
Hardy-Littlwood Conjctur and Excptional ral Zro JinHua Fi ChangLing Company of Elctronic Tchnology Baoji Shannxi P.R.China E-mail: fijinhuayoujian@msn.com Abstract. In this papr, w assum that Hardy-Littlwood
Numerical Analysis of Transient Responses for Elastic Structures Connected to a Viscoelastic Shock Absorber Using FEM with a Nonlinear Complex Spring
 Numrical Analysis of Transint Rsponss for Elastic Structurs Connctd to a Viscolastic Shock Absorbr Using FEM with a Nonlinar Complx Spring Takao Yamaguchi, Yusaku Fujii, Toru Fukushima, Akihiro Takita,
Numrical Analysis of Transint Rsponss for Elastic Structurs Connctd to a Viscolastic Shock Absorbr Using FEM with a Nonlinar Complx Spring Takao Yamaguchi, Yusaku Fujii, Toru Fukushima, Akihiro Takita,
The Relativistic Stern-Gerlach Force C. Tschalär 1. Introduction
 Th Rlativistic Strn-Grlach Forc C. Tschalär. Introduction For ovr a dcad, various formulations of th Strn-Grlach (SG) forc acting on a particl with spin moving at a rlativistic vlocity in an lctromagntic
Th Rlativistic Strn-Grlach Forc C. Tschalär. Introduction For ovr a dcad, various formulations of th Strn-Grlach (SG) forc acting on a particl with spin moving at a rlativistic vlocity in an lctromagntic
Derangements and Applications
 2 3 47 6 23 Journal of Intgr Squncs, Vol. 6 (2003), Articl 03..2 Drangmnts and Applications Mhdi Hassani Dpartmnt of Mathmatics Institut for Advancd Studis in Basic Scincs Zanjan, Iran mhassani@iasbs.ac.ir
2 3 47 6 23 Journal of Intgr Squncs, Vol. 6 (2003), Articl 03..2 Drangmnts and Applications Mhdi Hassani Dpartmnt of Mathmatics Institut for Advancd Studis in Basic Scincs Zanjan, Iran mhassani@iasbs.ac.ir
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION
 MD DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Sllabus : Ordinar diffrntial quations, thir ordr and dgr. Formation of diffrntial quations. Solution of diffrntial quations b th mthod of sparation of variabls, solution of homognous
MD DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Sllabus : Ordinar diffrntial quations, thir ordr and dgr. Formation of diffrntial quations. Solution of diffrntial quations b th mthod of sparation of variabls, solution of homognous
MCE503: Modeling and Simulation of Mechatronic Systems Discussion on Bond Graph Sign Conventions for Electrical Systems
 MCE503: Modling and Simulation o Mchatronic Systms Discussion on Bond Graph Sign Convntions or Elctrical Systms Hanz ichtr, PhD Clvland Stat Univrsity, Dpt o Mchanical Enginring 1 Basic Assumption In a
MCE503: Modling and Simulation o Mchatronic Systms Discussion on Bond Graph Sign Convntions or Elctrical Systms Hanz ichtr, PhD Clvland Stat Univrsity, Dpt o Mchanical Enginring 1 Basic Assumption In a
(Upside-Down o Direct Rotation) β - Numbers
 Amrican Journal of Mathmatics and Statistics 014, 4(): 58-64 DOI: 10593/jajms0140400 (Upsid-Down o Dirct Rotation) β - Numbrs Ammar Sddiq Mahmood 1, Shukriyah Sabir Ali,* 1 Dpartmnt of Mathmatics, Collg
Amrican Journal of Mathmatics and Statistics 014, 4(): 58-64 DOI: 10593/jajms0140400 (Upsid-Down o Dirct Rotation) β - Numbrs Ammar Sddiq Mahmood 1, Shukriyah Sabir Ali,* 1 Dpartmnt of Mathmatics, Collg
3 Finite Element Parametric Geometry
 3 Finit Elmnt Paramtric Gomtry 3. Introduction Th intgral of a matrix is th matrix containing th intgral of ach and vry on of its original componnts. Practical finit lmnt analysis rquirs intgrating matrics,
3 Finit Elmnt Paramtric Gomtry 3. Introduction Th intgral of a matrix is th matrix containing th intgral of ach and vry on of its original componnts. Practical finit lmnt analysis rquirs intgrating matrics,
Differential Equations
 UNIT I Diffrntial Equations.0 INTRODUCTION W li in a world of intrrlatd changing ntitis. Th locit of a falling bod changs with distanc, th position of th arth changs with tim, th ara of a circl changs
UNIT I Diffrntial Equations.0 INTRODUCTION W li in a world of intrrlatd changing ntitis. Th locit of a falling bod changs with distanc, th position of th arth changs with tim, th ara of a circl changs
MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analysis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design
 MAE4700/5700 Finit Elmnt Analysis for Mchanical and Arospac Dsign Cornll Univrsity, Fall 2009 Nicholas Zabaras Matrials Procss Dsign and Control Laboratory Sibly School of Mchanical and Arospac Enginring
MAE4700/5700 Finit Elmnt Analysis for Mchanical and Arospac Dsign Cornll Univrsity, Fall 2009 Nicholas Zabaras Matrials Procss Dsign and Control Laboratory Sibly School of Mchanical and Arospac Enginring
WEIGHTED SZEGED INDEX OF GRAPHS
 BULLETIN OF THE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL VIRTUAL INSTITUTE ISSN (p) 2303-4874, ISSN (o) 2303-4955 www.imvib.org /JOURNALS / BULLETIN Vo. 8(2018), 11-19 DOI: 10.7251/BIMVI1801011P Formr BULLETIN OF THE
BULLETIN OF THE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICAL VIRTUAL INSTITUTE ISSN (p) 2303-4874, ISSN (o) 2303-4955 www.imvib.org /JOURNALS / BULLETIN Vo. 8(2018), 11-19 DOI: 10.7251/BIMVI1801011P Formr BULLETIN OF THE
TOPOLOGY DESIGN OF STRUCTURE LOADED BY EARTHQUAKE. Vienna University of Technology
 Bluchr Mchanical Enginring Procdings May 2014, vol. 1, num. 1 www.procdings.bluchr.com.br/vnto/10wccm TOPOLOGY DESIG OF STRUCTURE LOADED BY EARTHQUAKE P. Rosko 1 1 Cntr of Mchanics and Structural Dynamics,
Bluchr Mchanical Enginring Procdings May 2014, vol. 1, num. 1 www.procdings.bluchr.com.br/vnto/10wccm TOPOLOGY DESIG OF STRUCTURE LOADED BY EARTHQUAKE P. Rosko 1 1 Cntr of Mchanics and Structural Dynamics,
That is, we start with a general matrix: And end with a simpler matrix:
 DIAGON ALIZATION OF THE STR ESS TEN SOR INTRO DUCTIO N By th us of Cauchy s thorm w ar abl to rduc th numbr of strss componnts in th strss tnsor to only nin valus. An additional simplification of th strss
DIAGON ALIZATION OF THE STR ESS TEN SOR INTRO DUCTIO N By th us of Cauchy s thorm w ar abl to rduc th numbr of strss componnts in th strss tnsor to only nin valus. An additional simplification of th strss
A Propagating Wave Packet Group Velocity Dispersion
 Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
2F1120 Spektrala transformer för Media Solutions to Steiglitz, Chapter 1
 F110 Spktrala transformr för Mdia Solutions to Stiglitz, Chaptr 1 Prfac This documnt contains solutions to slctd problms from Kn Stiglitz s book: A Digital Signal Procssing Primr publishd by Addison-Wsly.
F110 Spktrala transformr för Mdia Solutions to Stiglitz, Chaptr 1 Prfac This documnt contains solutions to slctd problms from Kn Stiglitz s book: A Digital Signal Procssing Primr publishd by Addison-Wsly.
Lecture 28 Title: Diatomic Molecule : Vibrational and Rotational spectra
 Lctur 8 Titl: Diatomic Molcul : Vibrational and otational spctra Pag- In this lctur w will undrstand th molcular vibrational and rotational spctra of diatomic molcul W will start with th Hamiltonian for
Lctur 8 Titl: Diatomic Molcul : Vibrational and otational spctra Pag- In this lctur w will undrstand th molcular vibrational and rotational spctra of diatomic molcul W will start with th Hamiltonian for
ME311 Machine Design
 ME311 Machin Dsign Lctur 4: Strss Concntrations; Static Failur W Dornfld 8Sp017 Fairfild Univrsit School of Enginring Strss Concntration W saw that in a curvd bam, th strss was distortd from th uniform
ME311 Machin Dsign Lctur 4: Strss Concntrations; Static Failur W Dornfld 8Sp017 Fairfild Univrsit School of Enginring Strss Concntration W saw that in a curvd bam, th strss was distortd from th uniform
Chapter 3 Lecture 14 Longitudinal stick free static stability and control 3 Topics
 Chaptr 3 Lctur 14 Longitudinal stick fr static stability and control 3 Topics 3.4.4 Rquirmnt for propr stick forc variation 3.4.5 Fl of th stability lvl by th pilot Exampl 3.3 3.5 Dtrmination of stick-fr
Chaptr 3 Lctur 14 Longitudinal stick fr static stability and control 3 Topics 3.4.4 Rquirmnt for propr stick forc variation 3.4.5 Fl of th stability lvl by th pilot Exampl 3.3 3.5 Dtrmination of stick-fr
On the Hamiltonian of a Multi-Electron Atom
 On th Hamiltonian of a Multi-Elctron Atom Austn Gronr Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA Octobr 29, 2010 1 Introduction In this papr, w will xhibit th procss of achiving th Hamiltonian for an lctron gas. Making
On th Hamiltonian of a Multi-Elctron Atom Austn Gronr Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA Octobr 29, 2010 1 Introduction In this papr, w will xhibit th procss of achiving th Hamiltonian for an lctron gas. Making
Title: Vibrational structure of electronic transition
 Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
Simulated Analysis of Tooth Profile Error of Cycloid Steel Ball Planetary Transmission
 07 4th Intrnational Matrials, Machinry and Civil Enginring Confrnc(MATMCE 07) Simulatd Analysis of Tooth Profil Error of Cycloid Stl Ball Plantary Transmission Ruixu Hu,a, Yuquan Zhang,b,*, Zhanliang Zhao,c,
07 4th Intrnational Matrials, Machinry and Civil Enginring Confrnc(MATMCE 07) Simulatd Analysis of Tooth Profil Error of Cycloid Stl Ball Plantary Transmission Ruixu Hu,a, Yuquan Zhang,b,*, Zhanliang Zhao,c,
Stereo and Multiview Geometry
 CS43-Advancd Comutr Vision Nots Sris 8 Stro and Mutiviw Gomtry Ying Wu ctrica nginring & Comutr Scinc Northwstrn Univrsity vanston, IL 6008 yingwu@c.northwstrn.du Contnts A Rfrshmnt of Imag Formation ioar
CS43-Advancd Comutr Vision Nots Sris 8 Stro and Mutiviw Gomtry Ying Wu ctrica nginring & Comutr Scinc Northwstrn Univrsity vanston, IL 6008 yingwu@c.northwstrn.du Contnts A Rfrshmnt of Imag Formation ioar
the output is Thus, the output lags in phase by θ( ωo) radians Rewriting the above equation we get
 Th output y[ of a frquncy-sctiv LTI iscrt-tim systm with a frquncy rspons H ( xhibits som ay rativ to th input caus by th nonro phas rspons θ( ω arg{ H ( } of th systm For an input A cos( ωo n + φ, < n
Th output y[ of a frquncy-sctiv LTI iscrt-tim systm with a frquncy rspons H ( xhibits som ay rativ to th input caus by th nonro phas rspons θ( ω arg{ H ( } of th systm For an input A cos( ωo n + φ, < n
Einstein Rosen inflationary Universe in general relativity
 PRAMANA c Indian Acadmy of Scincs Vol. 74, No. 4 journal of April 2010 physics pp. 669 673 Einstin Rosn inflationary Univrs in gnral rlativity S D KATORE 1, R S RANE 2, K S WANKHADE 2, and N K SARKATE
PRAMANA c Indian Acadmy of Scincs Vol. 74, No. 4 journal of April 2010 physics pp. 669 673 Einstin Rosn inflationary Univrs in gnral rlativity S D KATORE 1, R S RANE 2, K S WANKHADE 2, and N K SARKATE
Scattering States of l-wave Schrödinger Equation with Modified Rosen Morse Potential
 Commun. Thor. Phys. 66 06 96 00 Vol. 66, No., August, 06 Scattring Stats of l-wav Schrödingr Equation with Modifid Rosn Mors Potntial Wn-Li Chn í,, Yan-Wi Shi á, and Gao-Fng Wi Ôô, Gnral Education Cntr,
Commun. Thor. Phys. 66 06 96 00 Vol. 66, No., August, 06 Scattring Stats of l-wav Schrödingr Equation with Modifid Rosn Mors Potntial Wn-Li Chn í,, Yan-Wi Shi á, and Gao-Fng Wi Ôô, Gnral Education Cntr,
5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics
 MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
COHORT MBA. Exponential function. MATH review (part2) by Lucian Mitroiu. The LOG and EXP functions. Properties: e e. lim.
 MTH rviw part b Lucian Mitroiu Th LOG and EXP functions Th ponntial function p : R, dfind as Proprtis: lim > lim p Eponntial function Y 8 6 - -8-6 - - X Th natural logarithm function ln in US- log: function
MTH rviw part b Lucian Mitroiu Th LOG and EXP functions Th ponntial function p : R, dfind as Proprtis: lim > lim p Eponntial function Y 8 6 - -8-6 - - X Th natural logarithm function ln in US- log: function
At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to understand:
 Instructional Objctivs: At th nd of this lsson, th studnts should b abl to undrstand: Dsign thod for variabl load Equivalnt strss on shaft Dsign basd on stiffnss and torsional rigidit Critical spd of shaft
Instructional Objctivs: At th nd of this lsson, th studnts should b abl to undrstand: Dsign thod for variabl load Equivalnt strss on shaft Dsign basd on stiffnss and torsional rigidit Critical spd of shaft
Dynamic Analysis of Piles under Rocking Motion
 Indian Gotchnical Journal, 9(4), Octobr 9, 6-86 Dynamic Analysis of Pils undr Rocking Motion Indrajit Chowdhury* and Shambhu. P. Dasgupta** Introduction V ibration of pils undr rocking/rotational mod coupld
Indian Gotchnical Journal, 9(4), Octobr 9, 6-86 Dynamic Analysis of Pils undr Rocking Motion Indrajit Chowdhury* and Shambhu. P. Dasgupta** Introduction V ibration of pils undr rocking/rotational mod coupld
Chapter 13 GMM for Linear Factor Models in Discount Factor form. GMM on the pricing errors gives a crosssectional
 Chaptr 13 GMM for Linar Factor Modls in Discount Factor form GMM on th pricing rrors givs a crosssctional rgrssion h cas of xcss rturns Hors rac sting for charactristic sting for pricd factors: lambdas
Chaptr 13 GMM for Linar Factor Modls in Discount Factor form GMM on th pricing rrors givs a crosssctional rgrssion h cas of xcss rturns Hors rac sting for charactristic sting for pricd factors: lambdas
Background: We have discussed the PIB, HO, and the energy of the RR model. In this chapter, the H-atom, and atomic orbitals.
 Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Linear-Phase FIR Transfer Functions. Functions. Functions. Functions. Functions. Functions. Let
 It is impossibl to dsign an IIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas It is always possibl to dsign an FIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas rspons W now dvlop th forms of th linarphas FIR transfr
It is impossibl to dsign an IIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas It is always possibl to dsign an FIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas rspons W now dvlop th forms of th linarphas FIR transfr
NEW APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA
 NE APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA Mirca I CÎRNU Ph Dp o Mathmatics III Faculty o Applid Scincs Univrsity Polithnica o Bucharst Cirnumirca @yahoocom Abstract In a rcnt papr [] 5 th indinit intgrals
NE APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA Mirca I CÎRNU Ph Dp o Mathmatics III Faculty o Applid Scincs Univrsity Polithnica o Bucharst Cirnumirca @yahoocom Abstract In a rcnt papr [] 5 th indinit intgrals
A Sub-Optimal Log-Domain Decoding Algorithm for Non-Binary LDPC Codes
 Procdings of th 9th WSEAS Intrnational Confrnc on APPLICATIONS of COMPUTER ENGINEERING A Sub-Optimal Log-Domain Dcoding Algorithm for Non-Binary LDPC Cods CHIRAG DADLANI and RANJAN BOSE Dpartmnt of Elctrical
Procdings of th 9th WSEAS Intrnational Confrnc on APPLICATIONS of COMPUTER ENGINEERING A Sub-Optimal Log-Domain Dcoding Algorithm for Non-Binary LDPC Cods CHIRAG DADLANI and RANJAN BOSE Dpartmnt of Elctrical
Quasi-Classical States of the Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 Quasi-Classical Stats of th Simpl Harmonic Oscillator (Draft Vrsion) Introduction: Why Look for Eignstats of th Annihilation Oprator? Excpt for th ground stat, th corrspondnc btwn th quantum nrgy ignstats
Quasi-Classical Stats of th Simpl Harmonic Oscillator (Draft Vrsion) Introduction: Why Look for Eignstats of th Annihilation Oprator? Excpt for th ground stat, th corrspondnc btwn th quantum nrgy ignstats
Finite element discretization of Laplace and Poisson equations
 Finit lmnt discrtization of Laplac and Poisson quations Yashwanth Tummala Tutor: Prof S.Mittal 1 Outlin Finit Elmnt Mthod for 1D Introduction to Poisson s and Laplac s Equations Finit Elmnt Mthod for 2D-Discrtization
Finit lmnt discrtization of Laplac and Poisson quations Yashwanth Tummala Tutor: Prof S.Mittal 1 Outlin Finit Elmnt Mthod for 1D Introduction to Poisson s and Laplac s Equations Finit Elmnt Mthod for 2D-Discrtization
Hydrogen Atom and One Electron Ions
 Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
Text: WMM, Chapter 5. Sections , ,
 Lcturs 6 - Continuous Probabilit Distributions Tt: WMM, Chaptr 5. Sctions 6.-6.4, 6.6-6.8, 7.-7. In th prvious sction, w introduc som of th common probabilit distribution functions (PDFs) for discrt sampl
Lcturs 6 - Continuous Probabilit Distributions Tt: WMM, Chaptr 5. Sctions 6.-6.4, 6.6-6.8, 7.-7. In th prvious sction, w introduc som of th common probabilit distribution functions (PDFs) for discrt sampl
Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 413 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis
 Middl East Tchnical Univrsity Dpartmnt of Mchanical Enginring ME 43 Introduction to Finit Elmnt Analysis Chaptr 3 Computr Implmntation of D FEM Ths nots ar prpard by Dr. Cünyt Srt http://www.m.mtu.du.tr/popl/cunyt
Middl East Tchnical Univrsity Dpartmnt of Mchanical Enginring ME 43 Introduction to Finit Elmnt Analysis Chaptr 3 Computr Implmntation of D FEM Ths nots ar prpard by Dr. Cünyt Srt http://www.m.mtu.du.tr/popl/cunyt
Clausius-Clapeyron Equation
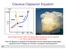 ausius-apyron Equation 22000 p (mb) Liquid Soid 03 6. Vapor 0 00 374 (º) oud drops first form whn th aporization quiibrium point is rachd (i.., th air parc bcoms saturatd) Hr w dop an quation that dscribs
ausius-apyron Equation 22000 p (mb) Liquid Soid 03 6. Vapor 0 00 374 (º) oud drops first form whn th aporization quiibrium point is rachd (i.., th air parc bcoms saturatd) Hr w dop an quation that dscribs
Why is a E&M nature of light not sufficient to explain experiments?
 1 Th wird world of photons Why is a E&M natur of light not sufficint to xplain xprimnts? Do photons xist? Som quantum proprtis of photons 2 Black body radiation Stfan s law: Enrgy/ ara/ tim = Win s displacmnt
1 Th wird world of photons Why is a E&M natur of light not sufficint to xplain xprimnts? Do photons xist? Som quantum proprtis of photons 2 Black body radiation Stfan s law: Enrgy/ ara/ tim = Win s displacmnt
1.2 Faraday s law A changing magnetic field induces an electric field. Their relation is given by:
 Elctromagntic Induction. Lorntz forc on moving charg Point charg moving at vlocity v, F qv B () For a sction of lctric currnt I in a thin wir dl is Idl, th forc is df Idl B () Elctromotiv forc f s any
Elctromagntic Induction. Lorntz forc on moving charg Point charg moving at vlocity v, F qv B () For a sction of lctric currnt I in a thin wir dl is Idl, th forc is df Idl B () Elctromotiv forc f s any
Difference -Analytical Method of The One-Dimensional Convection-Diffusion Equation
 Diffrnc -Analytical Mthod of Th On-Dimnsional Convction-Diffusion Equation Dalabav Umurdin Dpartmnt mathmatic modlling, Univrsity of orld Economy and Diplomacy, Uzbistan Abstract. An analytical diffrncing
Diffrnc -Analytical Mthod of Th On-Dimnsional Convction-Diffusion Equation Dalabav Umurdin Dpartmnt mathmatic modlling, Univrsity of orld Economy and Diplomacy, Uzbistan Abstract. An analytical diffrncing
The Matrix Exponential
 Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by D. Klain Vrsion 207.0.05 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom. Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix A A k I + A + k!
Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by D. Klain Vrsion 207.0.05 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom. Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix A A k I + A + k!
Dynamic Characteristics Analysis of Blade of Fan Based on Ansys
 Powr and Enrgy Enginring Confrnc 1 Dynamic Charactristics Analysis of Blad of Fan Basd on Ansys Junji Zhou, Bo Liu, Dingbiao Wang, Xiaoqian li School of Chmical Enginring Zhngzhou Univrsity Scinc Road
Powr and Enrgy Enginring Confrnc 1 Dynamic Charactristics Analysis of Blad of Fan Basd on Ansys Junji Zhou, Bo Liu, Dingbiao Wang, Xiaoqian li School of Chmical Enginring Zhngzhou Univrsity Scinc Road
Instantaneous Cutting Force Model in High-Speed Milling Process with Gyroscopic Effect
 Advancd Matrials sarch Onlin: -8-6 ISS: 66-8985, Vols. 34-36, pp 389-39 doi:.48/www.scintific.nt/am.34-36.389 rans ch Publications, Switzrland Instantanous Cutting Forc Modl in High-Spd Milling Procss
Advancd Matrials sarch Onlin: -8-6 ISS: 66-8985, Vols. 34-36, pp 389-39 doi:.48/www.scintific.nt/am.34-36.389 rans ch Publications, Switzrland Instantanous Cutting Forc Modl in High-Spd Milling Procss
Exam 1. It is important that you clearly show your work and mark the final answer clearly, closed book, closed notes, no calculator.
 Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Basic Polyhedral theory
 Basic Polyhdral thory Th st P = { A b} is calld a polyhdron. Lmma 1. Eithr th systm A = b, b 0, 0 has a solution or thr is a vctorπ such that π A 0, πb < 0 Thr cass, if solution in top row dos not ist
Basic Polyhdral thory Th st P = { A b} is calld a polyhdron. Lmma 1. Eithr th systm A = b, b 0, 0 has a solution or thr is a vctorπ such that π A 0, πb < 0 Thr cass, if solution in top row dos not ist
Addition of angular momentum
 Addition of angular momntum April, 0 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat th
Addition of angular momntum April, 0 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat th
Derivation of Electron-Electron Interaction Terms in the Multi-Electron Hamiltonian
 Drivation of Elctron-Elctron Intraction Trms in th Multi-Elctron Hamiltonian Erica Smith Octobr 1, 010 1 Introduction Th Hamiltonian for a multi-lctron atom with n lctrons is drivd by Itoh (1965) by accounting
Drivation of Elctron-Elctron Intraction Trms in th Multi-Elctron Hamiltonian Erica Smith Octobr 1, 010 1 Introduction Th Hamiltonian for a multi-lctron atom with n lctrons is drivd by Itoh (1965) by accounting
Inference Methods for Stochastic Volatility Models
 Intrnational Mathmatical Forum, Vol 8, 03, no 8, 369-375 Infrnc Mthods for Stochastic Volatility Modls Maddalna Cavicchioli Cá Foscari Univrsity of Vnic Advancd School of Economics Cannargio 3, Vnic, Italy
Intrnational Mathmatical Forum, Vol 8, 03, no 8, 369-375 Infrnc Mthods for Stochastic Volatility Modls Maddalna Cavicchioli Cá Foscari Univrsity of Vnic Advancd School of Economics Cannargio 3, Vnic, Italy
ME 321 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines S. Lambert Winter 2002
 3.4 Forc Analysis of Linkas An undrstandin of forc analysis of linkas is rquird to: Dtrmin th raction forcs on pins, tc. as a consqunc of a spcifid motion (don t undrstimat th sinificanc of dynamic or
3.4 Forc Analysis of Linkas An undrstandin of forc analysis of linkas is rquird to: Dtrmin th raction forcs on pins, tc. as a consqunc of a spcifid motion (don t undrstimat th sinificanc of dynamic or
BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS INVOLVING INFINITE POWERS OF PRIMES. 1. Statement of results
 BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS INVOLVING INFINITE POWERS OF PRIMES DONALD M. DAVIS Abstract. If p is a prim and n a positiv intgr, lt ν p (n dnot th xponnt of p in n, and u p (n n/p νp(n th unit part of n. If α
BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS INVOLVING INFINITE POWERS OF PRIMES DONALD M. DAVIS Abstract. If p is a prim and n a positiv intgr, lt ν p (n dnot th xponnt of p in n, and u p (n n/p νp(n th unit part of n. If α
Higher-Order Homogenization of Initial/ Boundary-Value Problem
 Highr-Ordr Homognization of Initia/ Boundar-Vau Probm Jacob Fish and Wn Chn Dpartmnts of Civi Mchanica and Arospac Enginring Rnssar Potchnic Institut Tro NY 1218 USA Abstract: Highr-ordr homognization
Highr-Ordr Homognization of Initia/ Boundar-Vau Probm Jacob Fish and Wn Chn Dpartmnts of Civi Mchanica and Arospac Enginring Rnssar Potchnic Institut Tro NY 1218 USA Abstract: Highr-ordr homognization
General Notes About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidelines
 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Gnral Nots About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidlins 1. Th solutions contain th most common mthod of solving th fr-rspons qustions and th allocation
AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Gnral Nots About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidlins 1. Th solutions contain th most common mthod of solving th fr-rspons qustions and th allocation
1 Minimum Cut Problem
 CS 6 Lctur 6 Min Cut and argr s Algorithm Scribs: Png Hui How (05), Virginia Dat: May 4, 06 Minimum Cut Problm Today, w introduc th minimum cut problm. This problm has many motivations, on of which coms
CS 6 Lctur 6 Min Cut and argr s Algorithm Scribs: Png Hui How (05), Virginia Dat: May 4, 06 Minimum Cut Problm Today, w introduc th minimum cut problm. This problm has many motivations, on of which coms
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 00 Th McGraw-Hill Companis, Inc. ll rights rsrvd. T Edition CHTER MECHNICS OF MTERIS Frdinand. Br E. Russll Johnston, Jr. John T. DWolf Columns ctur Nots: J. Walt Olr Txas Tch Univrsit 00 Th McGraw-Hill
00 Th McGraw-Hill Companis, Inc. ll rights rsrvd. T Edition CHTER MECHNICS OF MTERIS Frdinand. Br E. Russll Johnston, Jr. John T. DWolf Columns ctur Nots: J. Walt Olr Txas Tch Univrsit 00 Th McGraw-Hill
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Massachustts Institut of Tchnolog Dpartmnt of Mchanical Enginring. Introduction to Robotics Mid-Trm Eamination Novmbr, 005 :0 pm 4:0 pm Clos-Book. Two shts of nots ar allowd. Show how ou arrivd at our
Massachustts Institut of Tchnolog Dpartmnt of Mchanical Enginring. Introduction to Robotics Mid-Trm Eamination Novmbr, 005 :0 pm 4:0 pm Clos-Book. Two shts of nots ar allowd. Show how ou arrivd at our
