Elimination Reactions Heating an alkyl halide with a strong base causes elimination of a. molecule of HX
|
|
|
- Frederick Freeman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Elimination eactions eating an alkyl halide with a strong base causes elimination of a molecule of X 1.
2
3 Potassium hydroxide dissolved in ethanol and the sodium salts of alcohols (such as sodium ethoxide) are often used as the base for dehydrohalogenation. The sodium salt of an alcohol (a sodium alkoxide) can be prepared by treating an alcohol with sodium metal MEANISMS OF DEYDOALOGENATIONS 1. E2 reaction. ate equation ate = k [3Br3] [25O ] 2. E1 reaction
4 E2 Mechanism The basic ethoxide ion begins to remove a proton from the β- carbon using its electron pair to form a bond to it. At the same tim, the electron pair of the β bond begins to move in to become the π bond of a double bond, and the bromide begins to depart with the electrons that bonded it to the α carbon
5 Partial bonds now exist between the oxygen and the β hydrogen and between the α carbonand the bromine. The carbon-carbon bond is developing double bond character.
6 Now the double bond of the alkene is fully formed and the alkene has a trigonal plannar geometry at each carbon atom. The other products are a molecule of ethanol and a bromide ion.
7 E1Mechanism Treating tert-butyl chloride with 80% aqueous ethanol at 25 gives substitution products in 83% yield and an elimination product in 17% yield.
8 The initial step for reactions is the formation of a tert-butyl cation.
9 Whether substitution or elimination takes place depends on the next step (the fast step) The E1 reaction almost always accompany SN1 reactions.
10 Step-1 : Aided by the polar solvent a chlorine departs with the electron pair that bonded it to the carbon. Step-2 : A molecule of water removes one of the hydrogens from the β carbon of the carbocation. An electron pair moves in to form a double bond between the α and β carbon atoms
11 SUBSTITUTION VESUS ELIMINATION 1. Because the reactive part of a nucleophile or a base is an unshared electron pair, all nucleophiles are potential bases and all bases are potential nucleophiles. 2. Nucleophileic substitution reactions and elimination reactions often compete with each other.
12 S N 2VsE2 Since eliminations occur best by an E2 path when carried out with a high concentration of a strong base (and thus a high concentration of a strong nucleophile), substitution reactions by an S N 2 path often compete with the elimination reaction. When the nucleophile (base) attacks a β carbon atom, elimination occurs. When the nucleophile (base) attacks the carbon atom bearingtheleavinggroup,substitution results. Primary halides and ethoxide: substitution is favored
13 Secondary halides: elimination is favored
14 In Tertiary alides Elimination is favored when the reaction is carried out at higher temperature. Eliminations have higher free energies of activation than substitutions because eliminations have a greater change in bonding (more bonds are broken and formed). Eliminations have higher entropies than substitutions because eliminations have a greater number of products formed than that of starting compounds). Any substitution that occurs must take place through an SN1 mechanism
15 Zaitsev rule: an elimination occurs to give the most stable, more highly substituted alkene
16 AN EXEPTION TO ZAITSEV S ULE A bulky base such as potassium tert-butoxide in tert-butyl alcohol favors the formation of the less substituted alkene in dehydrohalgenation reactions The reason for leading to ofmann s product: i) The steric bulk of the base. ii) The association of the base with the solvent molecules make it even larger. iii) tert-butoxide removes one of the more exposed (1 ) hydrogen atoms instead of the internal (2 ) hydrogen atoms due to its greater crowding in the transition state.
17 Dehydration of alcohols: eating most alcohols with a strong acid causes them to lose a molecule of water and form an alkene The reaction is an elimination and is favored at higher temperatures. The most commonly used acids in the laboratory are Brønsted acids-proton donors such as sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid. Lewis acids such as alumina (Al 2 O 3 ) are often used in industrial, fast phase dehydrations.
18 Primary alcohols are the most difficult to dehydrate, Secondary alcohols usually dehydrate under milder conditions, Tertiary alcohols are usually dehydrated under extremely mild conditions.
19 Elimination eactions, E1 and E2: We have seen that alkyl halides may react with basic nucleophiles such as NaO via substitution reactions..... :.. : O.. + Br.... O transition state.. Br.. :.... O + :.. Br.. : Also recall our study of the preparation of alkenes. When a 2 or 3 alkyl halide is treated with a strong base such as NaO, dehydrohalogenation occurs producing an alkene an elimination (E2) reaction. Br KO in ethanol -Br + KBr + 2 O bromocyclohexane + KO cyclohexene (80 % yield) Substitution and elimination reactions are often in competition. We shall consider the determining factors after studying the mechanisms of elimination. 19
20 E2 eaction Mechanism There are 2 kinds of elimination reactions, E1 and E2. E2 = Elimination, Bimolecular (2nd order). ate = k [X] [Nu: - ] E2 reactions occur when a 2 or 3 alkyl halide is treated with a strong base such as O -, O -, N 2-, -, etc. O Br - + O b Br The Nu: - removes an + from a b-carbon & the halogen leaves forming an alkene. All strong bases, like O -, are good nucleophiles. In 2 and 3 alkyl halides the -carbon in the alkyl halide is hindered. In such cases, a strong base will abstract (remove) a hydrogen ion (+) from a b-carbon, before it hits the -carbon. Thus strong bases cause elimination (E2) in 2 and 3 alkyl halides and cause substitution (S N 2) in unhindered methyl and 1 alkyl halides. 20
21 E2 eaction Mechanism In E2 reactions, the Base to bond formation, the to bond breaking, the to bond formation, and the to Br bond breaking all occur simultaneously. No carbocation intermediate forms. B: - X d + B X - d + B + X - eactions in which several steps occur simultaneously are called concerted reactions. Zaitsev s ule: ecall that in elimination of X from alkenes, the more highly substituted (more stable) alkene product predominates Br 3 2 O - Na + EtO butene major product ( > 80%) 1-butene minor product ( < 20%) 21
22 E2 eactions are antiperiplanar E2 reactions, do not always follow Zaitsev s rule. E2 eliminations occur with anti-periplanar geometry, i.e., periplanar means that all 4 reacting atoms -,,, & X - all lie in the same plane. Anti means that and X (the eliminated atoms) are on opposite sides of the molecules. Look at the mechanism again and note the opposite side & same plane orientation of the mechanism: B: - X d + B X - d + B + X - 22
23 Antiperiplanar E2 eactions in yclic Alkyl alides When E2 reactions occur in open chain alkyl halides, the Zaitsev product is usually the major product. Single bonds can rotate to the proper alignment to allow the antiperiplanar elimination. In cyclic structures, however, single bonds cannot rotate. We need to be mindful of the stereochemistry in cyclic alkyl halides undergoing E2 reactions. See the following example. Trans 1-chloro-2-methylcyclopentane undergoes E2 elimination with NaO. Draw and name the major product. 3 l Na + O - E2 3 Non Zaitsev product is major product. + + Nal O 3 Little or no Zaitsev (more stable) product is formed. 3-methylcyclopentene 1-methylcyclopentene 23
24 E1 eactions Just as S N 2 reactions are analogous to E 2 reactions, so S N 1 reactions have an analog, E1 reaction. E1 = Elimination, unimolecular (1st order); ate = k [X] 3 3 Br 3 slow - Br - + rapid 3 3 B: B + Br - E1 eliminations, like S N 1 substitutions, begin with unimolecular dissociation, but the dissociation is followed by loss of a proton from the b-carbon (attached to the + ) rather than by substitution. E1 & S N 1 normally occur in competition, whenever an alkyl halide is treated in a protic solvent with a nonbasic, poor nucleophile. Note: The best E1 substrates are also the best S N 1 substrates, and mixtures of products are usually obtained. 24
25 E1 eactions As with E2 reactions, E1 reactions also produce the more highly substituted alkene (Zaitsev s rule). owever, unlike E2 reactions where no + is produced, + rearrangements can occur in E1 reactions. e.g., t-butyl chloride + 2 O (in EtO) at 65 t-butanol + 2-methylpropene 3 2 O, EtO l 3 O + 65º % 64% SN1 product E1 product In most unimolecular reactions, S N 1 is favored over E1, especially at low temperature. Such reactions with mixed products are not often used in synthetic chemistry. If the E1 product is desired, it is better to use a strong base and force the E2 reaction. Note that increasing the strength of the nucleophile favors S N 1 over E1. an you postulate an explanation? 25
26 Predicting eaction Mechanisms 1. Non basic, good nucleophiles, like Br - and I - will cause substitution not elimination. In 3 substrates, only S N 1 is possible. In Me and 1 substrates, S N 2 is faster. For 2 substrates, the mechanism of substitution depends upon the solvent. 2. Strong bases, like O - and O -, are also good nucleophiles. Substitution and elimination compete. In 3 and 2 alkyl halides, E2 is faster. In 1 and Me alkyl halides, S N 2 occurs. 3. Weakly basic, weak nucleophiles, like 2 O, EtO, 3 OO, etc., cannot react unless a + forms. This only occurs with 2 or 3 substrates. Once the + forms, both S N 1 and E1 occur in competition. The substitution product is usually predominant. 4. igh temperatures increase the yield of elimination product over substitution product. (DG = D TDS) Elimination produces more products than substitution, hence creates greater entropy (disorder). 5. Polar solvents, both protic and aprotic, like 2 O and 3 N, respectively, favor unimolecular reactions (S N 1 and E1) by stabilizing the + intermediate. Polar aprotic solvents enhance bimolecular reactions (S N 2 and E2) by activating the nucleophile. 26
27 Predicting eaction Mechanisms alkyl halide (substrate) good Nu - nonbasic e.g., bromide Br - good Nu - strong base e.g., ethoxide 2 5 O - good Nu - strong bulky base e.g., t-butoxide ( 3 ) 3 O - very poor Nu - nonbasic e.g., acetic acid 3 OO Me S N 2 S N 2 S N 2 no reaction 1 S N 2 S N 2 E2 (S N 2) no reaction 2 S N 2 E2 E2 S N 1, E1 3 S N 1 E2 E2 S N 1, E1 Strong bulky bases like t-butoxide are hindered. They have difficulty hitting the -carbon in a 1 alkyl halide. As a result, they favor E2 over S N 2 products. 27
28 Preparation of Alkyl alides from Alcohols Alkyl halides can be prepared from alcohols by reaction with X, i.e., the substitution of a halide on a protonated alcohol. (Lucas Test) SN1 3º ( 3 ) 3.. O.. + l + ( 3 ) 3 O.. 2 apid. 3 + is stabilized by protic sovent ( 2 O) - 2 O ( 3 ) :l.. - : ( 3 ) 3.. l : + 2 O.. O - is a poor leaving group, i.e., is not displaced directly by nucleophiles. eaction in acid media protonates the O group producing a better leaving group ( 2 O). 2 and 3 alcohols react by S N 1 but Me and 1 alcohols react by S N 2. SN2 1º O + l O2 D Very slow. Protic solvent inhibits the nucleophile... :l.. - : 3 2 l + 2 O Draw the mechanism of the reaction of isopropyl alcohol with Br. What products form if concentrated 2 SO 4 is used in place of aq. l? 28
29 Preparation of Alkenes from Alkyl alides On Slide 22 we noted that 2 and 3 alkyl halides can be dehydrohalogenated with a strong base such as O - producing an alkene. Br KO in ethanol -Br + KBr + 2 O bromocyclohexane + KO cyclohexene (80 % yield) learly, this is an E2 reaction. Predict the mechanism that occurs with a Me or 1 alkyl halide. Predict the products and mechanism that occur with isopentyl chloride and KO 29
30 Summary of S N /Elimination eactions Alkyl alide Substrate eactivity: methyl 1º 2º 3º Br 3 Br 3 3 Br 3 3 Br 3 unhindered substrates favor S N2 do not form a stable + do not react by S N 1 or E1 hindered substrates. SN2 increasingly unfavorable, E2 is OK form increasingly stable + favors SN1 and E1. E2 is OK E2 reactions possible with strong bases E2 reactions possible with strong bulky bases (t-butoxide) 30
31 Summary of S N /Elimination eactions eactivity of Nucleophiles: S - N - I - 3O - O - N3 l - 2O 125, , ,000 25,000 16, good nucleophiles which are weak bases favor S N reactions good nucleophiles which are also strong bases favor elimination pkb = 23 pkb = 22 pkb = 21 pkb = 11 pkb = -1.7 pkb = -2 pkb = -21 I - Br - l - F - O - O - 2N - 30,000 10, Note that poor nucleophiles that are also weak bases ( 2 O, O, 3 OO, etc.) do not undergo any reaction unless a + is formed first. If a + can form (as with a 2º, 3º, any benzylic, or any allylic halides), then E1 and S N 1 generally occur together. Leaving Group Activity: good leaving groups favor both substitution and elimination reactions poor leaving groups make both substitution and elimination reactions unfavorable 31
32
33
34
Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination
 Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Alkyl halides react with a nucleophile in one of two ways. Either they eliminate an X to form an alkene, or they undergo a substitution with the nucleophile, Nu,
Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Alkyl halides react with a nucleophile in one of two ways. Either they eliminate an X to form an alkene, or they undergo a substitution with the nucleophile, Nu,
Chapter 6 Ionic Reactions-Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides"
 Chapter 6 Ionic Reactions-Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides" t Introduction" The polarity of a carbon-halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge"
Chapter 6 Ionic Reactions-Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides" t Introduction" The polarity of a carbon-halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge"
Classes of Alkenes. Alkenes and Alkynes. Saturated compounds (alkanes): Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
 Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Homework problems Chapters 6 and Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: CH 3 OH + H 2 C CH +
 omework problems hapters 6 and 7 1. Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: : 3 - : 2 : 3 2-3 3 2. In each of the following sets, arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pka and
omework problems hapters 6 and 7 1. Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: : 3 - : 2 : 3 2-3 3 2. In each of the following sets, arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pka and
REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION
 REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION Haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes and alkyl halides) are organic compounds where one of the hydrogens of an alkane or cycloalkane has been
REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES - SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION Haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes and alkyl halides) are organic compounds where one of the hydrogens of an alkane or cycloalkane has been
CHAPTER 7. Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination
 CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
CHAPTER 7 Further Reactions of Haloalkanes: Unimolecular Substitution and Pathways of Elimination 7-1 Solvolysis of Tertiary and Secondary Haloalkanes The rate of S N 2 reactions decrease dramatically
Chapter 11: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Walden Inversion
 hapter 11: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Walden Inversion (S)-(-) Malic acid [a] D = -2.3 Ag 2, 2 Pl 5 l Ag 2, 2 ()-2-hlorosuccinic acid l (-)-2-hlorosuccinic acid Pl 5 ()-() Malic acid [a]
hapter 11: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Walden Inversion (S)-(-) Malic acid [a] D = -2.3 Ag 2, 2 Pl 5 l Ag 2, 2 ()-2-hlorosuccinic acid l (-)-2-hlorosuccinic acid Pl 5 ()-() Malic acid [a]
Chapter 5. Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution mechanism. by G.DEEPA
 Chapter 5 Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution mechanism by G.DEEPA 1 Introduction The polarity of a carbon halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge In alkyl halides this polarity
Chapter 5 Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution mechanism by G.DEEPA 1 Introduction The polarity of a carbon halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge In alkyl halides this polarity
Elimination Reactions The E2 Mechanism
 Elimination Reactions The E2 Mechanism The E2 Mechanism X X- B: B- δ- B:- δ+ R 1 δ- R 2 δ+ X δ- The E2 Mechanism R 3 R 4 transition state Free energy (G) Eact B:- B R 1 R 2 X R 1 R 2 R 3 R 4 R 4 R 3 X:-
Elimination Reactions The E2 Mechanism The E2 Mechanism X X- B: B- δ- B:- δ+ R 1 δ- R 2 δ+ X δ- The E2 Mechanism R 3 R 4 transition state Free energy (G) Eact B:- B R 1 R 2 X R 1 R 2 R 3 R 4 R 4 R 3 X:-
Chapter 7 Substitution Reactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution Reactions Substitution Reactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products
 hapter 7 Substitution eactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution eactions Substitution eactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products A-B + -D A-D + B- 3 2 + Br 3 2 Br + Elimination eaction:
hapter 7 Substitution eactions 7.1 Introduction to Substitution eactions Substitution eactions: two reactants exchange parts to give new products A-B + -D A-D + B- 3 2 + Br 3 2 Br + Elimination eaction:
Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N 2 Dr. Sapna Gupta Kinetics of Nucleophilic Reaction Rate law is order of reaction 0 order is when rate of reaction is unaffected by change in concentration of the reactants
Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N 2 Dr. Sapna Gupta Kinetics of Nucleophilic Reaction Rate law is order of reaction 0 order is when rate of reaction is unaffected by change in concentration of the reactants
Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination Reactions
 1. Nature of the pi bond Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination eactions [Sections: 8.1-8.13] C C bond length bond strength 3 C C 3 3 C C 3 3 C C 3 3 C 2 C C 2 3 C a C=C double bond
1. Nature of the pi bond Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination eactions [Sections: 8.1-8.13] C C bond length bond strength 3 C C 3 3 C C 3 3 C C 3 3 C 2 C C 2 3 C a C=C double bond
Preparation of Alkyl Halides, R-X. Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): R + X X 2.
 Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Preparation of Alkyl alides, R-X Reaction of alkanes with Cl 2 & Br 2 (F 2 is too reactive, I 2 is unreactive): UV R + X 2 R X or heat + X This mechanism involves a free radical chain reaction. A chain
Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination Reactions
 Nature of the pi bond Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination eactions [Sections: 8.1-8.13] C C 3 C C 3 bond length bond strength 2 C C 2 a C=C double bond is stronger than a C C single
Nature of the pi bond Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination eactions [Sections: 8.1-8.13] C C 3 C C 3 bond length bond strength 2 C C 2 a C=C double bond is stronger than a C C single
Chapter 8: Nucleophilic Substitution 8.1: Functional Group Transformation By Nucleophilic Substitution
 hapter 8: Nucleophilic Substitution 8.1: Functional Group Transformation By Nucleophilic Substitution Nu: = l,, I Nu - Nucleophiles are Lewis bases (electron-pair donor) Nucleophiles are often negatively
hapter 8: Nucleophilic Substitution 8.1: Functional Group Transformation By Nucleophilic Substitution Nu: = l,, I Nu - Nucleophiles are Lewis bases (electron-pair donor) Nucleophiles are often negatively
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122)
 Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Basic Organic Chemistry Course code : CHEM 12162 (Pre-requisites : CHEM 11122) Chapter 01 Mechanistic Aspects of S N2,S N1, E 2 & E 1 Reactions Dr. Dinesh R. Pandithavidana Office: B1 222/3 Phone: (+94)777-745-720
Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions
 Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions Halogen compounds are important for several reasons. Simple alkyl and aryl halides, especially chlorides and bromides, are versatile
Chapter 6: Organic Halogen Compounds; Substitution and Elimination Reactions Halogen compounds are important for several reasons. Simple alkyl and aryl halides, especially chlorides and bromides, are versatile
1-What is substitution reaction? 2-What are can Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction? 3- SN1 reaction. 4-SN2 reaction 5- mechanisms of SN1&SN2
 1-What is substitution reaction? 2-What are can Nucleophilic Substitution eaction? 3- SN1 reaction. 4-SN2 reaction 5- mechanisms of SN1&SN2 1- SUBSTITUTION EACTIONS 1-Substitution eaction In this type
1-What is substitution reaction? 2-What are can Nucleophilic Substitution eaction? 3- SN1 reaction. 4-SN2 reaction 5- mechanisms of SN1&SN2 1- SUBSTITUTION EACTIONS 1-Substitution eaction In this type
Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions in Detail
 Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions in Detail b-elimination Reactions Overview dehydration of alcohols: X = H; Y = OH dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides: X = H; Y = Br, etc. X C
Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions in Detail b-elimination Reactions Overview dehydration of alcohols: X = H; Y = OH dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides: X = H; Y = Br, etc. X C
Organic Chemistry Review: Topic 10 & Topic 20
 Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Organic Structure Alkanes C C σ bond Mechanism Substitution (Incoming atom or group will displace an existing atom or group in a molecule) Examples Occurs with exposure to ultraviolet light or sunlight,
Organic Halogen Compounds
 8 Organic alogen ompounds APTER SUMMARY 8.1 Introduction Although organic halogen compounds are rarely found in nature, they do have a variety of commercial applications including use as insecticides,
8 Organic alogen ompounds APTER SUMMARY 8.1 Introduction Although organic halogen compounds are rarely found in nature, they do have a variety of commercial applications including use as insecticides,
Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides
 Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides There are two types of possible reaction in organic compounds in which sp 3 carbon is bonded to an electronegative atom or group (ex, halides) 1. Substitution
Chapter 8. Substitution reactions of Alkyl Halides There are two types of possible reaction in organic compounds in which sp 3 carbon is bonded to an electronegative atom or group (ex, halides) 1. Substitution
CHEM Lecture 7
 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
7. Haloalkanes (text )
 2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 7.1 7. aloalkanes (text 7.1 7.10) A. Structure and Nomenclature Like hydrogen, the halogens have a valence of one. Thus, a halogen atom can
2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 7.1 7. aloalkanes (text 7.1 7.10) A. Structure and Nomenclature Like hydrogen, the halogens have a valence of one. Thus, a halogen atom can
The Electrophile. S N 2 and E2 least stable most stable least hindered most hindered. S N 1 and E1. > x > >
 The Electrophile 1 Recall that electrophile means electron- loving. When considering substitution and elimination reactions we must consider the carbon attached to the leaving group. Is it a primary, secondary,
The Electrophile 1 Recall that electrophile means electron- loving. When considering substitution and elimination reactions we must consider the carbon attached to the leaving group. Is it a primary, secondary,
BSc. II 3 rd Semester. Submitted By Dr. Sangita Nohria Associate Professor PGGCG-11 Chandigarh 1
 BSc. II 3 rd Semester Submitted By Dr. Sangita Nohria Associate Professor PGGCG-11 Chandigarh 1 Introduction to Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are organic molecules containing a halogen atom bonded to an
BSc. II 3 rd Semester Submitted By Dr. Sangita Nohria Associate Professor PGGCG-11 Chandigarh 1 Introduction to Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are organic molecules containing a halogen atom bonded to an
Elimination Reactions The E2 Mechanism
 Elimination Reactions The E2 Mechanism The E2 Mechanism X B: δ- B:- δ+ R 1 C δ- R 2 C δ+ X δ- The E2 Mechanism R 3 R 4 transition state Free energy (G) Eact B:- B R 1 R 2 C C X R 1 R 2 R 3 R 4 R 4 R 3
Elimination Reactions The E2 Mechanism The E2 Mechanism X B: δ- B:- δ+ R 1 C δ- R 2 C δ+ X δ- The E2 Mechanism R 3 R 4 transition state Free energy (G) Eact B:- B R 1 R 2 C C X R 1 R 2 R 3 R 4 R 4 R 3
Elimination Reactions:
 Elimination Reactions: These are just reverse of addition reactions. These involve the removal of atoms or group of atoms from a molecule. Elimination reactions are generally endothermic and take place
Elimination Reactions: These are just reverse of addition reactions. These involve the removal of atoms or group of atoms from a molecule. Elimination reactions are generally endothermic and take place
Organic Chemistry CHM 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, Cal Poly Pomona Alkyl Halides: Substitution Reactions - Chapter 6 (Wade)
 rganic Chemistry CM 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, Cal Poly Pomona Alkyl alides: Substitution Reactions - Chapter 6 (Wade) Chapter utline I. Intro to RX (6-1 - 6-7) II. Substitution Reactions A) S N 2 (6-8,
rganic Chemistry CM 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, Cal Poly Pomona Alkyl alides: Substitution Reactions - Chapter 6 (Wade) Chapter utline I. Intro to RX (6-1 - 6-7) II. Substitution Reactions A) S N 2 (6-8,
(Neither an oxidation or reduction: Addition or loss of H +, H 2 O, HX).
 eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
Chapter 9. Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination
 Chapter 9 Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination Nucleophilic Substitution Nucleophile: From the Greek meaning nucleus loving. A molecule or ion that donates a pair of electrons to another atom or
Chapter 9 Nucleophilic Substitution and ß-Elimination Nucleophilic Substitution Nucleophile: From the Greek meaning nucleus loving. A molecule or ion that donates a pair of electrons to another atom or
Hydrogen iodide is a strong acid and will drive the reverse reaction, meaning the forward reaction will not occur.
 EM 261 Oct 18, 2018 Photosynthesis and Related Reactions O 2 2 O 6 12 O 6 2 O N 3, S, Fe, u, o, other Natural Products D-Glucose R O R OR Ionic substitution S N 1 & R X X 2 hv Petroleum/ Alkanes R N 2
EM 261 Oct 18, 2018 Photosynthesis and Related Reactions O 2 2 O 6 12 O 6 2 O N 3, S, Fe, u, o, other Natural Products D-Glucose R O R OR Ionic substitution S N 1 & R X X 2 hv Petroleum/ Alkanes R N 2
Walden discovered a series of reactions that could interconvert (-)-malic acid and (+)-malic acid.
 Chapter 11: Reactions of alkyl halides: nucleophilic substitutions and eliminations Alkyl halides are polarized in the C-X bond, making carbon δ+ (electrophilic). A nucleophilecan attack this carbon, displacing
Chapter 11: Reactions of alkyl halides: nucleophilic substitutions and eliminations Alkyl halides are polarized in the C-X bond, making carbon δ+ (electrophilic). A nucleophilecan attack this carbon, displacing
Chapter 8 Alkyl Halides and Elimination Reactions
 Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 8 Alkyl Halides and Elimination Reactions Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 8 Alkyl Halides and Elimination Reactions Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright
c. Cl H Page 1 of 7 major P (E > Z and more substituted over less substituted alkene) LG must be axial are the same Cl -
 CEM 109A 1. Predict the products of the following reactions (a-c E2, d-f E1 KEY focuses only on elimination products, in most cases there will also be substitution products.) a. - LG must be axial - are
CEM 109A 1. Predict the products of the following reactions (a-c E2, d-f E1 KEY focuses only on elimination products, in most cases there will also be substitution products.) a. - LG must be axial - are
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2
 C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
Chapter 7 - Alkenes and Alkynes I
 Andrew Rosen Chapter 7 - Alkenes and Alkynes I 7.1 - Introduction - The simplest member of the alkenes has the common name of ethylene while the simplest member of the alkyne family has the common name
Andrew Rosen Chapter 7 - Alkenes and Alkynes I 7.1 - Introduction - The simplest member of the alkenes has the common name of ethylene while the simplest member of the alkyne family has the common name
CONCERTED sp 2 H. HO Et
 Alkyl alides Substitution and Elimination 1 Substitutions (Quick Review) 1.1 SN2 Reactions LB nucleophile "backside attack!" NERTED reaction This is fundamentally just a Lewis acid/base reaction, the Lewis
Alkyl alides Substitution and Elimination 1 Substitutions (Quick Review) 1.1 SN2 Reactions LB nucleophile "backside attack!" NERTED reaction This is fundamentally just a Lewis acid/base reaction, the Lewis
Alkyl Halides. Alkyl halides are a class of compounds where a halogen atom or atoms are bound to an sp 3 orbital of an alkyl group.
 Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are a class of compounds where a halogen atom or atoms are bound to an sp 3 orbital of an alkyl group. CHCl 3 (Chloroform: organic solvent) CF 2 Cl 2 (Freon-12: refrigerant
Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides are a class of compounds where a halogen atom or atoms are bound to an sp 3 orbital of an alkyl group. CHCl 3 (Chloroform: organic solvent) CF 2 Cl 2 (Freon-12: refrigerant
Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N 2 Dr. Sapna Gupta Kinetics of Nucleophilic Reaction Rate law is order of reaction 0 order is when rate of reaction is unaffected by change in concentration of the reactants
Organic Reactions Susbstitution S N 2 Dr. Sapna Gupta Kinetics of Nucleophilic Reaction Rate law is order of reaction 0 order is when rate of reaction is unaffected by change in concentration of the reactants
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions
 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Chapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions
 hapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions Alkenes Alkenes contain a carbon-carbon double bond. They are named as derivatives of alkanes with the suffix -ane changed to -ene. The parent alkane is the longest
hapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions Alkenes Alkenes contain a carbon-carbon double bond. They are named as derivatives of alkanes with the suffix -ane changed to -ene. The parent alkane is the longest
But in organic terms: Oxidation: loss of H 2 ; addition of O or O 2 ; addition of X 2 (halogens).
 Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
Reactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. Normally: Oxidation
8.8 Unimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution S N 1
 8.8 Unimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution S N 1 A question. Tertiary alkyl halides are very unreactive in substitutions that proceed by the S N 2 mechanism. Do they undergo nucleophilic substitution at
8.8 Unimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution S N 1 A question. Tertiary alkyl halides are very unreactive in substitutions that proceed by the S N 2 mechanism. Do they undergo nucleophilic substitution at
Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides
 Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides Alcohols Structure and Bonding Enols and Phenols Compounds having a hydroxy group on a sp 2 hybridized carbon enols and phenols undergo different reactions than alcohols. Chapter
Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides Alcohols Structure and Bonding Enols and Phenols Compounds having a hydroxy group on a sp 2 hybridized carbon enols and phenols undergo different reactions than alcohols. Chapter
S N 1 Displacement Reactions
 S N 1 Displacement Reactions Tertiary alkyl halides cannot undergo S N 2 reactions because of the severe steric hindrance blocking a backside approach of the nucleophile. They can, however, react via an
S N 1 Displacement Reactions Tertiary alkyl halides cannot undergo S N 2 reactions because of the severe steric hindrance blocking a backside approach of the nucleophile. They can, however, react via an
11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations
 11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto Alkyl Halides
11. Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto Alkyl Halides
Classes of Halides. Chapter 6 Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination. Polarity and Reactivity. Classes of Alkyl Halides
 rganic hemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. hapter 6 Alkyl alides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination lasses of alides Alkyl: alogen, X, is directly bonded to sp 3 carbon. Vinyl: X is bonded to
rganic hemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. hapter 6 Alkyl alides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination lasses of alides Alkyl: alogen, X, is directly bonded to sp 3 carbon. Vinyl: X is bonded to
Elimination Reactions. Chapter 6 1
 Elimination Reactions Chapter 6 1 E1 Mechanism Step 1: halide ion leaves, forming a carbocation. Step 2: Base abstracts H + from adjacent carbon forming the double bond. Chapter 6 2 E1 Energy Diagram E1:
Elimination Reactions Chapter 6 1 E1 Mechanism Step 1: halide ion leaves, forming a carbocation. Step 2: Base abstracts H + from adjacent carbon forming the double bond. Chapter 6 2 E1 Energy Diagram E1:
Physical Properties: Structure:
 Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
ζ ε δ γ β α α β γ δ ε ζ
 hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I: Properties and Synthesis Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides"
 Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I: Properties and Synthesis Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides The (E)-(Z) System for Designating Alkene Diastereomers The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog convention is used to assign
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I: Properties and Synthesis Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides The (E)-(Z) System for Designating Alkene Diastereomers The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog convention is used to assign
PAPER No. : 5; Organic Chemistry-II MODULE No. : 13; Mixed S N 1 and S N 2 Reactions
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 5; Organic Chemistry-II 13; Mixed S N 1 and S N 2 Reactions CHE_P5_M13 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. Nature
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 5; Organic Chemistry-II 13; Mixed S N 1 and S N 2 Reactions CHE_P5_M13 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. Nature
10. Organohalides. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 10. Organohalides Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain
10. Organohalides Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain
1. The Substrate: CH3, 1 o, 2 o, 3 o, Allyl or Benzyl
 Putting it all together: Substitution and elimination reactions are almost always in competition with each other. In order to predict the products of a reaction, it is necessary to determine which mechanisms
Putting it all together: Substitution and elimination reactions are almost always in competition with each other. In order to predict the products of a reaction, it is necessary to determine which mechanisms
11. Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
 11. Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions A. Introduction It would be beneficial if you review the chapter on substitution reactions in your textbook prior to lab. This is Ch. 11 in the 9 th edition McMurry
11. Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions A. Introduction It would be beneficial if you review the chapter on substitution reactions in your textbook prior to lab. This is Ch. 11 in the 9 th edition McMurry
Essential Organic Chemistry. Chapter 9
 Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 9 Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides 9.1 How Alkyl Halides React Substitution Reactions One group takes the place of another.
Essential Organic Chemistry Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 9 Substitution and Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides 9.1 How Alkyl Halides React Substitution Reactions One group takes the place of another.
I C(CH 3 ) 3. (c)2ch 3 OH+(CH 3 ) 3 CCl (CH 3 ) 3 COCH 3 +CH 3 OH + 2 +Cl - (d) CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 Br+NaCN CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CN+NaBr
 6.1 Writer the following as net ionic reactions and designate the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group in each reaction. (a) 3 + 3 2 Na 3 2 3 +Na (b) Na+ 3 2 3 2 +Na (c) 2 3 +( 3 ) 3 ( 3 ) 3 3 + 3
6.1 Writer the following as net ionic reactions and designate the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group in each reaction. (a) 3 + 3 2 Na 3 2 3 +Na (b) Na+ 3 2 3 2 +Na (c) 2 3 +( 3 ) 3 ( 3 ) 3 3 + 3
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
Dr. Anand Gupta Mr Mahesh Kapil
 Dr. Anand Gupta Mr Mahesh Kapil 09356511518 09888711209 anandu71@yahoo.com mkapil_foru@yahoo.com Preparation of Haloalkanes From Alkanes Alkenes Alcohols Carboxylic Acids (Hundsdicker Reaction) Halide
Dr. Anand Gupta Mr Mahesh Kapil 09356511518 09888711209 anandu71@yahoo.com mkapil_foru@yahoo.com Preparation of Haloalkanes From Alkanes Alkenes Alcohols Carboxylic Acids (Hundsdicker Reaction) Halide
Chapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides
 hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
hapter 11, Part 1: Polar substitution reactions involving alkyl halides Overview: The nature of alkyl halides and other groups with electrophilic sp 3 hybridized leads them to react with nucleophiles and
PAPER No. 5: REACTION MECHANISM MODULE No. 2: Types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5:Organic Chemistry-II Module No. 2: Overview of different types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms CHE_P5_M2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5:Organic Chemistry-II Module No. 2: Overview of different types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms CHE_P5_M2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAPER No. 05: TITLE: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-II MODULE No. 12: TITLE: S N 1 Reactions
 Subject hemistry Paper o and Title Module o and Title Module Tag 05, ORGAI EMISTRY-II 12, S 1 Reactions E_P5_M12 EMISTRY PAPER o. 05: TITLE: ORGAI EMISTRY-II TABLE OF OTETS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
Subject hemistry Paper o and Title Module o and Title Module Tag 05, ORGAI EMISTRY-II 12, S 1 Reactions E_P5_M12 EMISTRY PAPER o. 05: TITLE: ORGAI EMISTRY-II TABLE OF OTETS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
Reactions of Alkyl Halides with Nucleophiles and Bases a substitution reaction
 Reactions of Alkyl Halides with Nucleophiles and Bases a substitution reaction Nucleophilic substitution and base induced elimination are among most widely occurring and versatile reaction types in organic
Reactions of Alkyl Halides with Nucleophiles and Bases a substitution reaction Nucleophilic substitution and base induced elimination are among most widely occurring and versatile reaction types in organic
Ethers. Synthesis of Ethers. Chemical Properties of Ethers
 Page 1 of 6 like alcohols are organic derivatives of water, but lack the labile -OH group. As a result, ethers, except for epoxides, are usually not very reactive and are often used as solvents for organic
Page 1 of 6 like alcohols are organic derivatives of water, but lack the labile -OH group. As a result, ethers, except for epoxides, are usually not very reactive and are often used as solvents for organic
CHE 275 NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTUION CHAP 8 ASSIGN. 1. Which best depicts the partial charges on methyl bromide and sodium methoxide?
 CHE 275 NUCLEPHILIC SUBSTITUTUIN CHAP 8 ASSIGN 1. Which best depicts the partial charges on methyl bromide and sodium methoxide? 2. Which of the following would be the best (most reactive) nucleophile
CHE 275 NUCLEPHILIC SUBSTITUTUIN CHAP 8 ASSIGN 1. Which best depicts the partial charges on methyl bromide and sodium methoxide? 2. Which of the following would be the best (most reactive) nucleophile
(CH 3 ) 3 COH. CH 3 ONa
 1. Rank the following compounds in the trend requested. (15 points each) a. Rank by nucleophilicity. The strongest nucleophile is 1, while the weakest nucleophile is 5. C 3 PNa (C 3 ) 3 C C 3 Na C 3 C
1. Rank the following compounds in the trend requested. (15 points each) a. Rank by nucleophilicity. The strongest nucleophile is 1, while the weakest nucleophile is 5. C 3 PNa (C 3 ) 3 C C 3 Na C 3 C
8. What is the slow, rate-determining step, in the acidcatalyzed dehydration of 2-methyl-2-propanol?
 CHEMISTRY 313-03 MIDTERM # 2 answer key October 25, 2011 Statistics: Average: 68 pts (68%); Highest: 100 pts (100%); Lowest: 30 pts (30%) Number of students performing at or above average: 56 (54%) Number
CHEMISTRY 313-03 MIDTERM # 2 answer key October 25, 2011 Statistics: Average: 68 pts (68%); Highest: 100 pts (100%); Lowest: 30 pts (30%) Number of students performing at or above average: 56 (54%) Number
HALOALKANES. Structure Contain the functional group C-X where X is a halogen (F,Cl,Br or I)
 aloalkanes AS3 1 ALOALKANES Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F,l, or I) Types aloalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group aloarenes halogen is attached
aloalkanes AS3 1 ALOALKANES Structure ontain the functional group X where X is a halogen (F,l, or I) Types aloalkanes halogen is attached to an aliphatic skeleton alkyl group aloarenes halogen is attached
Reactions of Haloalkanes
 Reactions of aloalkanes N Goalby chemrevise.org aloalkanes ontain a halogen atom covalently bonded to a carbon atom General formula: R-X where X is a halogen atom (F, l,, I) and R is the carbon chain.
Reactions of aloalkanes N Goalby chemrevise.org aloalkanes ontain a halogen atom covalently bonded to a carbon atom General formula: R-X where X is a halogen atom (F, l,, I) and R is the carbon chain.
Lab 11 Guide: Nucleophilic Substitution (Nov 10 16)
 Lab 11 Guide: Nucleophilic Substitution (Nov 10 16) Nucleophilic Substitution of Alkyl Halides, Exp. 17A, B, and C, pages 187-192 in Taber This week you will be doing examining real life S N 1 and S N
Lab 11 Guide: Nucleophilic Substitution (Nov 10 16) Nucleophilic Substitution of Alkyl Halides, Exp. 17A, B, and C, pages 187-192 in Taber This week you will be doing examining real life S N 1 and S N
CHEM 263 Oct 25, stronger base stronger acid weaker acid weaker base
 CEM 263 ct 25, 2016 Reactions and Synthesis (Preparation) of R- Breaking the - Bond of R- with Metals R + Li 0 or Na 0 or K 0 metal R Li + 1/2 2 alkoxide Breaking the - Bond of R- by Acid-Base Reaction
CEM 263 ct 25, 2016 Reactions and Synthesis (Preparation) of R- Breaking the - Bond of R- with Metals R + Li 0 or Na 0 or K 0 metal R Li + 1/2 2 alkoxide Breaking the - Bond of R- by Acid-Base Reaction
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions
 Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Introduction: Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds The π electrons of
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Introduction: Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds The π electrons of
Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols
 Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols 45 -Alcohols have the general formula R-OH and are characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group, -OH. -Phenols have a hydroxyl group attached directly to an
Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiols 45 -Alcohols have the general formula R-OH and are characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group, -OH. -Phenols have a hydroxyl group attached directly to an
Elimination reactions
 Chapter 9 Elimination reactions E2 and E1 reactions Competition between S N and E Elimination reactions Ch 9 #2 elimination and/or substitution 2 mechanisms ~ E2 and E1 E2: bimolecular elimination rxn
Chapter 9 Elimination reactions E2 and E1 reactions Competition between S N and E Elimination reactions Ch 9 #2 elimination and/or substitution 2 mechanisms ~ E2 and E1 E2: bimolecular elimination rxn
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH. 8 - ELIMINATION REACTIONS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: THE E2 MECHANISM A strong nucleophile reacts with an inaccessible leaving group to produce beta-elimination in one-step. E2 Properties (Circle One) Nucleophile = Strong /
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: THE E2 MECHANISM A strong nucleophile reacts with an inaccessible leaving group to produce beta-elimination in one-step. E2 Properties (Circle One) Nucleophile = Strong /
PRACTICE PROBLEMS UNIT 8
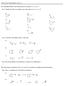 PRACTICE PROBLEMS UNIT 8 8A. Identify halides and carbocations as being 1 o, 2 o, or 3 o 8A.1 assify the following halides and carbocations as 1 o, 2 o, or 3 o. 8A.2 Circle the most stable cation in each
PRACTICE PROBLEMS UNIT 8 8A. Identify halides and carbocations as being 1 o, 2 o, or 3 o 8A.1 assify the following halides and carbocations as 1 o, 2 o, or 3 o. 8A.2 Circle the most stable cation in each
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions"
 Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
an axial "X" is necessary for a succesful E2 reaction and also works better for S N 2
 cleophilic Substitution & Elimination hemistry 1 Templates for predicting S2 and E2 reactions primary - β α α β two different perspectives secondary - β β α β β α two different perspectives tertiary -
cleophilic Substitution & Elimination hemistry 1 Templates for predicting S2 and E2 reactions primary - β α α β two different perspectives secondary - β β α β β α two different perspectives tertiary -
How alkyl halides react
 Chapter 10 1 How alkyl halides react δ+ δ- RCH 2 -X X= halogen X = higher EN C = lower EN This polar carbon-halogen bond causes alkyl halide to undergo S N and elimination reaction. 2 The mechanism of
Chapter 10 1 How alkyl halides react δ+ δ- RCH 2 -X X= halogen X = higher EN C = lower EN This polar carbon-halogen bond causes alkyl halide to undergo S N and elimination reaction. 2 The mechanism of
What are radicals? H. Cl. Chapter 10 Radical Reactions. Production of radicals. Reactions of radicals. Electronic structure of methyl radical
 What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
12/27/2010. Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon The aryl group (Ar) is derived by removal of a hydrogen atom
Chapter 7: Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chapter 7: Alkenes and Alkynes ydrocarbons Containing Double and Triple Bonds Unsaturated Compounds (Less than Maximum Atoms) Alkenes also Referred to as Olefins Properties Similar to those of Corresponding
Chapter 7: Alkenes and Alkynes ydrocarbons Containing Double and Triple Bonds Unsaturated Compounds (Less than Maximum Atoms) Alkenes also Referred to as Olefins Properties Similar to those of Corresponding
Chapter 7 Substitution Reactions
 Chapter 7 Substitution Reactions Review of Concepts Fill in the blanks below. To verify that your answers are correct, look in your textbook at the end of Chapter 7. Each of the sentences below appears
Chapter 7 Substitution Reactions Review of Concepts Fill in the blanks below. To verify that your answers are correct, look in your textbook at the end of Chapter 7. Each of the sentences below appears
17.3 REACTIONS INVOLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC ANIONS
 798 HAPTER 17 ALLYLI AND BENZYLI REATIVITY Because the unpaired electron is shared by two different carbons, this radical can react in the final propagation step to give two different products. Reaction
798 HAPTER 17 ALLYLI AND BENZYLI REATIVITY Because the unpaired electron is shared by two different carbons, this radical can react in the final propagation step to give two different products. Reaction
(b) (CH 3 ) 2 CCH 2 CH 3 D 2 O. (e) A. CH 3 CCl OSO 2 CH 3 C 6 H 5 H 3 C
 278 h a p t e r 7 Further Reactions of aloalkanes 3. arbocations are stabilized by hyperconjugation: Tertiary are the most stable, followed by secondary. Primary and methyl cations are too unstable to
278 h a p t e r 7 Further Reactions of aloalkanes 3. arbocations are stabilized by hyperconjugation: Tertiary are the most stable, followed by secondary. Primary and methyl cations are too unstable to
3-chloro-1-propene 1-chloropropane 2-chloropropene
 ANSWERS #1. (from 50 minute exam #3, Fall 2000) 5. (6 points) For each group of 3 compounds, identify the compound that expresses the indicated property the MOST and the compound that expresses it the
ANSWERS #1. (from 50 minute exam #3, Fall 2000) 5. (6 points) For each group of 3 compounds, identify the compound that expresses the indicated property the MOST and the compound that expresses it the
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards. Dr. Peter Norris, 2018
 OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2018 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2018 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards. Dr. Peter Norris, 2015
 OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2015 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
OChem 1 Mechanism Flashcards Dr. Peter Norris, 2015 Mechanism Basics Chemical change involves bonds forming and breaking; a mechanism describes those changes using curved arrows to describe the electrons
Chapter 8: Ethers and Epoxides. Diethyl ether in starting fluid
 Chapter 8: Ethers and Epoxides Diethyl ether in starting fluid 8.1 Nomenclature of Ethers Ethers are usually named by giving the name of each alkyl or aryl group, in alphabetical order, followed by the
Chapter 8: Ethers and Epoxides Diethyl ether in starting fluid 8.1 Nomenclature of Ethers Ethers are usually named by giving the name of each alkyl or aryl group, in alphabetical order, followed by the
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions. Alkenes are electron rich. Additions to Alkenes
 Additions to Alkenes hapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition eactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Additions to Alkenes hapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition eactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Loudon Chapter 10 Review: Alcohols & Thiols Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 4/26/2016
 Alcohols (R) and thiols (RS) have many reactions in common with alkyl halides, but they don t do everything exactly the same. The main difference between this and alkyl halide chemistry is that unlike
Alcohols (R) and thiols (RS) have many reactions in common with alkyl halides, but they don t do everything exactly the same. The main difference between this and alkyl halide chemistry is that unlike
The Chemistry of Ethers, Epoxides, Glycols, and Sulfides
 The Chemistry of Ethers, Epoxides, Glycols, and Sulfides The chemistry of ethers is closely intertwined with the chemistry of alkyl halides, alcohols, and alkenes. Ethers, however, are considerably less
The Chemistry of Ethers, Epoxides, Glycols, and Sulfides The chemistry of ethers is closely intertwined with the chemistry of alkyl halides, alcohols, and alkenes. Ethers, however, are considerably less
Allylic and Benzylic Reactivity
 17 17 Allylic and Benzylic Reactivity An allylic group is a group on a carbon adjacent to a double bond. A benzylic group is a group on a carbon adjacent to a benzene ring or substituted benzene ring.
17 17 Allylic and Benzylic Reactivity An allylic group is a group on a carbon adjacent to a double bond. A benzylic group is a group on a carbon adjacent to a benzene ring or substituted benzene ring.
Preparation of alkenes
 Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
Lecture 11 אלקנים הכנה ותגובות של אלקנים: הידרוגנציה, סיפוח הידרוהלוגנים )כלל מארקובניקוב(, סיפוח הלוגנים והסטראוכימיה של תוצרי הסיפוח, הידרובורציה, אפוקסידציה, אוזונוליזה. 1 Preparation of alkenes 1.
Chapter 15. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes. The first step is the slow, rate-determining step
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds The characteristic reaction of aromatic rings is substitution initiated by an electrophile halogenation nitration
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds The characteristic reaction of aromatic rings is substitution initiated by an electrophile halogenation nitration
ORGANIC - EGE 5E CH. 7 - NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION AND ELIMINATION REACTIONS
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INTRODUCTION TO SUBSTITUTION Previously, we discussed the various ways that acids could react with bases: Recall that in these mechanisms, electrons always travel from density
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INTRODUCTION TO SUBSTITUTION Previously, we discussed the various ways that acids could react with bases: Recall that in these mechanisms, electrons always travel from density
Organic Chemistry. REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling
 Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions "
 Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The π
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The π
Lecture 11 Organic Chemistry 1
 EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
