H-H bond length Two e s shared by two Hs: covalent bonding. Coulomb attraction: Stronger attraction for e Fractional charge A dipole
|
|
|
- Cornelia York
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 8 Bonding: General Concepts Types of chemical bonds Covalent bonding Ex. 2 E (kj/mol) Repulsions of nucleus and e s r r (nm) Zero interaction at long distance - bond length Two e s shared by two s: covalent bonding Ionic bonding Ex. a + : ionic forces operate Coulomb attraction: charges 9 Q1Q ( J nm) r Polar covalent bond Ex. Unequal sharing of e Charge distribution occurs E 2 tronger attraction for e ractional charge A dipole 1
2 Electronegativity The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared e s Linus Pauling ( ) BE A B Expected BE = (BEA-B ) actual (BEA-B ) AA BE 2 expected BB The greater E difference, the greater value Define E(A) E(B) = Assign E() = 4.0 luorine atom with the highest E E for all elements can be determined E difference for A B Bond type 0 covalent polar covalent large ionic (A +, B ) Increasing E A B igher E Decreasing E periodic table 2
3 Bond polarity and dipole moment A dipole has a dipole moment ( ) Will orient in an electric field = Q R distance (m) charge (c) Unit: debye (D) 1D = cm or polyatomic molecules net dipole The center of all positive atoms and the center of all negative atoms do not merge C : net dipole = zero Ions: Electron configurations and sizes Ionic compounds In general A M + non-metal on-metal: gains e Metal: loses e main group metal reach noble gas configuration Ex. Ca: [Ar]4s 2 Ca 2+ : [Ar] : [e]2s 2 2p 4 2 : [e]2s 2 2p 6 = [e] 3
4 izes of ions determines the structure and stability of ionic compounds egative ions: larger than parent (gain e ) Positive ions: smaller than parent (lose e ) Trend: Down a group larger Ex. Li + Be (pm) a + 95 The energy M + (g) + X (g) M X(s) ionization E Li(g) Li + (g) Born-aber electron affinity cycle (g) (g) ormation of an ionic compound energy depends on many factors difficult to predict qualitatively energy released = lattice E Q Q2 Lattice E = k( 1 ) r verall Ex. Li(s) + 1/2 2 (g) Li(s) Unit: lattice 1/2 BE of 2 kj/mol energy = 78.9 At 298 K LE theo = 966 4
5 Partial ionic character of covalent bonds In the gas phase: no true ionic bond Polar covalent bond percent ionic character measured dipole moment 00% calculated dipole moment X + Y Ex. a(g): 75% In general: > 50% ionic solid Ambiguity: 4 +, a 2 4 covalent bonded group Definition of ionic compound conducts electric current when melted 5
6 The covalent bond: A model Ex. C 4 C + 4 requires 1652 kj C 4 is more stable than the discreet atoms by 1652 kj Consider forces exist between C and 4 bonding Consider localized C bonds 1652 To break each bond = = 413 kj 4 Ex. C 3 C requires 1578 kj 3 C bonds, 1 C bond (413) = 339 kj/mol trength of C bond Assumption: bond strength does not vary with structures The covalent bond model Considering electrons are localized between two atoms 6
7 Covalent bond energies and chemical reactions act 1 C 4 (g) C 3 (g) + (g) 435 kj/mol C 3 (g) C 2 (g) + (g) 453 C 2 (g) C(g) + (g) 425 C (g) C(g) + (g) 339 total = 1652 Average: 413 BEs are structurally dependent Average BEs are used Bond types e s shared single 2 double 4 triple 6 Ex. BE (kj/mol) bond length (Å) C C C=C C C
8 Bond energy and enthalpy Ex. 2 (g) + 2 (g) 2(g) 2 2 2, 2 identical Bond E difference = = D (bonds broken) D (bonds formed) Bond E (+) = D - + D - 2D - = (565) = 544 kj Calculated from f : = 2( 271) = 542 kj f o () The localized electron bonding model (Valence bonding model) A covalent bond is formed between two atoms sharing electrons using atomic orbitals Pairs of e s localized on an atom: lone pairs Pairs of e s localized between atoms: bonding pairs 8
9 Lewis structures Describe the arrangement of valence electrons G.. Lewis ( ) observed: In most stable compounds the atoms achieve noble gas electron configuration Molecules with covalent bonds Duet rule, e : e: ctet rule C,,, : second row nonmetals e Ex Total: 8 e s 9
10 Ex. C 2 :C: Total: 16 C Does not obey octet rule Try and error C = C Ex. C ne extra charge = 10 e C ot good C ot good C ot good C Good C 10
11 Ex e isoelectronic with C Ex. 3 8 e C 4 C C 8 e = 10 e C 4 32 e C C Exceptions to the octet rule Less than 8 B nly 6 e ow about B act: B is very reactive toward electron rich molecules + B B 11
12 More than 8 12 e assical explanation use of low lying empty d orbitals (3d for sulfur) P (5 7) = 40 e P 10 e Allow the central atom to expand its valency Ex. Xe (3 6) = 26 e Xe obeys Be (2 7) = 16 e Be nly 4 e 12
13 Resonance Ex. 3 Predict: act: a short double bond two long single bonds Equal length (between a single and a double) A new theory must be formulated Actually there are three possible structures: We can consider the real structure as the avg. of the three a resonance hybrid Any single structure can not represent the real structure Each Lewis structure is called resonance structure (exists only on paper) Represented as double headed arrow (not ) 13
14 nly allow electrons to move (nuclei stay at the same position) Must be proper Lewis structures Ex. Carbon can not have five bonds dd-electron molecule itric oxide = 11 ot good A radical with unpaired e *Keep the number of unpaired e the lowest (6) = 17 C C C C ot a viable resonance structure 14
15 ormal charge Q: tructure of 4 2 (32 e ) 2 What about 2 2 or 10 e 12 e ow to decide? Method: Estimate the charge xidation state: 2 +6 The concept of formal charge ver estimated nly useful for bookkeeping Compare: number of e in a neutral atom A number of e in a bonded atom B When A = B no charge A > B (+) A < B ( ) 15
16 Define ormal charge = A B Assign lone pair e s to the atom completely Divide shared e s equally Ex. 2 or shared e s A = 6 B = 6 + 2/2 = 7 lone pair e s ormal charge on = 6 7 = 1 or : A = 6 B = 0 + 8/2 = 4 shared e s lone pair e s ormal charge on = 6 4 = verall charge = (+2) + 4() 2 ingle bonded : Double bonded : 6 [4 + 4/2] = 0 : 6 (10/2) = ok 16
17 (12/2) = 0 There are resonance structures Another school of thought: Keeping the octet rule is more important A better structure due to minimum formal charge ote: they are all resonance structures 2 etc. Guidelines or 2nd row elements: never exceed octet rule ormal charges as low as possible egative charge on more electronegative atoms B ot good 17
18 Molecular structures: The VEPR model To predict approximate 3-D structure A simple model: Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VEPR) model (useful for nonmetals) The main postulation: minimizing electron pair repulsions Bonding and nonbonding pairs 2 Be : linear (two pairs) As far away as possible B 3 B 120 o Trigonal planar (three pairs) C 4 3 C o Tetrahedral (four pairs) Cf. 90 o C quare planar (not good) Based on the position of atoms: trigonal pyramid 2 A bent structure (four pairs) 18
19 Bond angles lone pairs o o C 107 o Explanation lone pair is closer to the nucleus exerts large repulsion towards the other electron pairs squeezed ive pairs: P 5 P Trigonal bipyramidal ix pairs: P 6 P ctahedral 19
20 Ex. Xe 4 Xe ix pairs: octahedral arrangement Xe as far away as possible quare planar shape Ex. I 3 I I I ive pairs: trigonal bipyramidal arrangement I I I 90 o, 90 o, 180 o I I I 90, 90, 120 I I I 120, 120, 120 Best (no 90 o repulsions) linear 20
21 Treat double or triple bonds as one effective pair Ex. 2 3 pairs Bent structure In fact -- ~120 o with little distortion long pair is satisfied with 120 o 21
13 Bonding: General Concepts. Types of chemical bonds. Covalent bonding Ex. H 2. Repulsions of nuclei and e s. Zero interaction at long distance
 13 Bonding: General Concepts Types of chemical bonds Covalent bonding Ex. 2 E (kj/mol) epulsions of nuclei and e s r 0 458 0.074 r (nm) - bond length Two e s shared by two s: covalent bonding Zero interaction
13 Bonding: General Concepts Types of chemical bonds Covalent bonding Ex. 2 E (kj/mol) epulsions of nuclei and e s r 0 458 0.074 r (nm) - bond length Two e s shared by two s: covalent bonding Zero interaction
Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Dr. A. Al-Saadi 1 Chapter 8 Preview Ionic Bonding vs. covalent bonding. Electronegativity and dipole moment. Bond polarity. Lewis structure: ow to draw a Lewis
Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Dr. A. Al-Saadi 1 Chapter 8 Preview Ionic Bonding vs. covalent bonding. Electronegativity and dipole moment. Bond polarity. Lewis structure: ow to draw a Lewis
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts
 AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds A. Ionic Bonding 1. Electrons are transferred 2. Metals react with nonmetals 3. Ions paired have lower energy
AP Chemistry A. Allan Chapter 8 Notes - Bonding: General Concepts 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds A. Ionic Bonding 1. Electrons are transferred 2. Metals react with nonmetals 3. Ions paired have lower energy
Chapter 8. Bonding : General Concepts Chemical Bondings
 Chapter 8. onding : General Concepts Chemical ondings create Diversity in the Universe Why and how do they make chemical bonds? and what do they make? Types of Chemical onds Chemical bonds: orces that
Chapter 8. onding : General Concepts Chemical ondings create Diversity in the Universe Why and how do they make chemical bonds? and what do they make? Types of Chemical onds Chemical bonds: orces that
bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction
 bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction ionic compound- a metal reacts with a nonmetal Ionic bonds form when an atom that
bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction ionic compound- a metal reacts with a nonmetal Ionic bonds form when an atom that
Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky
 Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky What Determines the Type of Bonding in Any Substance? Why do Atoms Bond? The key to answering the first question are found in the electronic structure of the atoms
Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky What Determines the Type of Bonding in Any Substance? Why do Atoms Bond? The key to answering the first question are found in the electronic structure of the atoms
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts
 Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts Types of Chemical Bonds Information about the strength of a bonding interaction is obtained by measuring the bond energy, which is the energy
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts Types of Chemical Bonds Information about the strength of a bonding interaction is obtained by measuring the bond energy, which is the energy
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
What is a Bond? Chapter 8. Ionic Bonding. Coulomb's Law. What about covalent compounds?
 Chapter 8 What is a Bond? A force that holds atoms together. Why? We will look at it in terms of energy. Bond energy- the energy required to break a bond. Why are compounds formed? Because it gives the
Chapter 8 What is a Bond? A force that holds atoms together. Why? We will look at it in terms of energy. Bond energy- the energy required to break a bond. Why are compounds formed? Because it gives the
Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory. Lewis Theory: An Overview
 Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory Dr. Chris Kozak Memorial University of ewfoundland, Canada Lewis Theory: An verview Valence e - play a fundamental role in chemical bonding. e - transfer leads
Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory Dr. Chris Kozak Memorial University of ewfoundland, Canada Lewis Theory: An verview Valence e - play a fundamental role in chemical bonding. e - transfer leads
Chapter 8. Bonding: General Concepts
 Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Table of Contents 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds 8.3 Bond Polarity and Dipole Moments 8.5 Energy Effects in Binary Ionic Compounds 8.6 Partial Ionic Character
Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Table of Contents 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds 8.3 Bond Polarity and Dipole Moments 8.5 Energy Effects in Binary Ionic Compounds 8.6 Partial Ionic Character
8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook. September 10, 2015
 chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook Chapter 8: Bonding: General Concepts Mar 13 11:15 AM 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. Bonds are forces that hold groups of
chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook Chapter 8: Bonding: General Concepts Mar 13 11:15 AM 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. Bonds are forces that hold groups of
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Topics Lewis Dot Symbols Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Electronegativity and Polarity Drawing Lewis Structures Lewis Structures and Formal Charge Resonance
Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Topics Lewis Dot Symbols Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Electronegativity and Polarity Drawing Lewis Structures Lewis Structures and Formal Charge Resonance
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chemical Bonding Chapter 8
 Chemical Bonding Chapter 8 Get your Clicker, 2 magnets, goggles and your handouts Nov 15 6:15 PM Recall that: Ionic-Involves the transfer of electrons - forms between a metal and a nonmetal Covalent-Involves
Chemical Bonding Chapter 8 Get your Clicker, 2 magnets, goggles and your handouts Nov 15 6:15 PM Recall that: Ionic-Involves the transfer of electrons - forms between a metal and a nonmetal Covalent-Involves
Chapter 8. Bonding: General Concepts
 Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Questions to Consider What is meant by the term chemical bond? Why do atoms bond with each other to form compounds? How do atoms bond with each other to form
Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Questions to Consider What is meant by the term chemical bond? Why do atoms bond with each other to form compounds? How do atoms bond with each other to form
CHAPTER 8 BONDING: GENERAL CONCEPTS Ionic solids are held together by strong electrostatic forces that are omnidirectional.
 CAPTER 8 BDIG: GEERAL CCEPTS 1 CAPTER 8 BDIG: GEERAL CCEPTS Questions 15. a. This diagram represents a polar covalent bond as in. In a polar covalent bond, there is an electron rich region (indicated by
CAPTER 8 BDIG: GEERAL CCEPTS 1 CAPTER 8 BDIG: GEERAL CCEPTS Questions 15. a. This diagram represents a polar covalent bond as in. In a polar covalent bond, there is an electron rich region (indicated by
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 8. Chemical Bonding: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
CHEMISTRY XL-14A CHEMICAL BONDS
 CHEMISTRY XL-14A CHEMICAL BONDS July 16, 2011 Robert Iafe Office Hours 2 July 18-July 22 Monday: 2:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Tuesday-Thursday: 3:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Chapter 2 Overview 3 Ionic Bonds Covalent
CHEMISTRY XL-14A CHEMICAL BONDS July 16, 2011 Robert Iafe Office Hours 2 July 18-July 22 Monday: 2:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Tuesday-Thursday: 3:00pm in Room MS-B 3114 Chapter 2 Overview 3 Ionic Bonds Covalent
Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding 8.1 Lewis Symbols and the Octet Rule When atoms or ions are strongly attracted to one another, we say that there is a chemical bond between them. In chemical
Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding 8.1 Lewis Symbols and the Octet Rule When atoms or ions are strongly attracted to one another, we say that there is a chemical bond between them. In chemical
REVIEW ANSWERS EXAM 3 GENERAL CHEMISTRY I Do not hesitate to contact the instructor should you have any questions.
 REVIEW ANSWERS EXAM 3 GENERAL CEMISTRY I Do not hesitate to contact the instructor should you have any questions. 1) Predict which of the following has the largest atomic radius: potassium (K) OR selenium
REVIEW ANSWERS EXAM 3 GENERAL CEMISTRY I Do not hesitate to contact the instructor should you have any questions. 1) Predict which of the following has the largest atomic radius: potassium (K) OR selenium
Chapter 8. Bonding: General Concepts. Copyright 2017 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
 Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Table of Contents (8.1) (8.2) (8.3) (8.4) (8.5) (8.6) (8.7) (8.8) Types of chemical bonds Electronegativity Bond polarity and dipole moments Ions: Electron
Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Table of Contents (8.1) (8.2) (8.3) (8.4) (8.5) (8.6) (8.7) (8.8) Types of chemical bonds Electronegativity Bond polarity and dipole moments Ions: Electron
Chapter 13: Phenomena
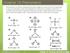 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 8. Bonding: General Concepts
 Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Table of Contents 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds 8.2 Electronegativity 8.3 Bond Polarity and Dipole Moments 8.4 Ions: Electron Configurations and Sizes 8.5 Energy
Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Table of Contents 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds 8.2 Electronegativity 8.3 Bond Polarity and Dipole Moments 8.4 Ions: Electron Configurations and Sizes 8.5 Energy
Chapter Nine. Chemical Bonding I
 Chapter Nine Chemical Bonding I 1 The Ionic Bond and Lattice Energies 2 Lewis Dot Symbols Consists of atomic symbol surrounded by 1 dot for each valence electron in the atom Only used for main group elements
Chapter Nine Chemical Bonding I 1 The Ionic Bond and Lattice Energies 2 Lewis Dot Symbols Consists of atomic symbol surrounded by 1 dot for each valence electron in the atom Only used for main group elements
Chapter 13: Phenomena
 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH
 C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE The Ionic Bond Formation of Ions The
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL BONDING & MOLECULAR STRUCTURE The Ionic Bond Formation of Ions The
Question 1. Electron Configurations Noble Gases and The Rule of Eight. Chapter 1. What is the electronic configuration of carbon?
 hapter ~. nm Electronic Structure and Bonding Anders Jöns Ångström (84-874) Å = picometers =. nanometers = -4 microns = -8 centimeters Acids and Bases nm = Å An atom vs. a nucleus ~, x larger ucleus =
hapter ~. nm Electronic Structure and Bonding Anders Jöns Ångström (84-874) Å = picometers =. nanometers = -4 microns = -8 centimeters Acids and Bases nm = Å An atom vs. a nucleus ~, x larger ucleus =
CHEMICAL BONDS. Electrical forces. Reflect a balance in the attractive and repulsive forces between electrically charged particles
 CHEMICAL BONDS Chemical Bonds: Electrical forces. Reflect a balance in the attractive and repulsive forces between electrically charged particles Lewis Theory of Bonding: Electrons play a fundamental role
CHEMICAL BONDS Chemical Bonds: Electrical forces. Reflect a balance in the attractive and repulsive forces between electrically charged particles Lewis Theory of Bonding: Electrons play a fundamental role
Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Learning Objective
 Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry 11.1 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Discuss the atomic trends Metals are located on the left side of the periodic
Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry 11.1 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Discuss the atomic trends Metals are located on the left side of the periodic
Problems and questions How is a molecule or polyatomic ion held together? Why are atoms distributed at strange angles? Why are molecules not flat?
 1 Cocaine 2 Problems and questions ow is a molecule or polyatomic ion held together? Why are atoms distributed at strange angles? Why are molecules not flat? Can we predict the structure? ow is structure
1 Cocaine 2 Problems and questions ow is a molecule or polyatomic ion held together? Why are atoms distributed at strange angles? Why are molecules not flat? Can we predict the structure? ow is structure
Chemical Bonding. Chemical Bonding I: The Covalent Bond. Chemical Bonding. Bonding Generalities
 Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding I: The Covalent Bond I. Types of bonds a) Ionic b) Covalent II. Lewis Dot Structures a) ctet Rule b) Multiple Bonds c) Resonance d) Polyatomic Ions e) ormal Charge on
Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding I: The Covalent Bond I. Types of bonds a) Ionic b) Covalent II. Lewis Dot Structures a) ctet Rule b) Multiple Bonds c) Resonance d) Polyatomic Ions e) ormal Charge on
Page III-7-1 / Chapter Seven Lecture Notes MAR. Ionic - complete transfer of. Covalent - electrons shared MAR. CH 221 Flashback:
 Page III-7-1 / hapter even Lecture otes hemical onding onding and Molecular tructure hapter 7 ocaine hemistry 222 Professor Michael Russell http://mhchem.org/222 Get the 222 ompanion and omposition Lab
Page III-7-1 / hapter even Lecture otes hemical onding onding and Molecular tructure hapter 7 ocaine hemistry 222 Professor Michael Russell http://mhchem.org/222 Get the 222 ompanion and omposition Lab
Chapter 8: Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8: Concepts of Chemical Bonding Learning Outcomes: Write Lewis symbols for atoms and ions. Define lattice energy and be able to arrange compounds in order of increasing lattice energy based on
Chapter 8: Concepts of Chemical Bonding Learning Outcomes: Write Lewis symbols for atoms and ions. Define lattice energy and be able to arrange compounds in order of increasing lattice energy based on
Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chapter 9 Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence electrons are the electrons that participate in chemical bonding. Group e - configuration
Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chapter 9 Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence electrons are the electrons that participate in chemical bonding. Group e - configuration
(A) 1 bonding pair (B) 1 bonding pair and 1 lone pair (C) 2 bonding pairs (D) 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs
 AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 13: Lewis Structures and VSPER No. 1 of 10 1. Lewis structure is used to model covalent bonds of a molecule or ion. Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bonding formed by
AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 13: Lewis Structures and VSPER No. 1 of 10 1. Lewis structure is used to model covalent bonds of a molecule or ion. Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bonding formed by
Example: Write the Lewis structure of XeF 4. Example: Write the Lewis structure of I 3-. Example: Select the favored resonance structure of the PO 4
 Expanded valence shells (extended octets) more than 8e - around a central atom Extended octets are formed only by atoms with vacant d-orbitals in the valence shell (p-elements from the third or later periods)
Expanded valence shells (extended octets) more than 8e - around a central atom Extended octets are formed only by atoms with vacant d-orbitals in the valence shell (p-elements from the third or later periods)
Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 hapter 8 Basic oncepts of hemical Bonding An Important Principle in hemistry The microscopic structure defines the properties of matter at our mesoscopic level. Ex. Graphite and Diamond (both are pure
hapter 8 Basic oncepts of hemical Bonding An Important Principle in hemistry The microscopic structure defines the properties of matter at our mesoscopic level. Ex. Graphite and Diamond (both are pure
Unit 9: CHEMICAL BONDING
 Unit 9: CEMICAL BNDING Unit 9: Bonding: 1. Electronegativity 2. Intramolecular Bonding 3. Intermolecular Bonding 4. Drawing Lewis Structures 5. Lewis Structures for Polyatomic Ions 6. Exceptions to the
Unit 9: CEMICAL BNDING Unit 9: Bonding: 1. Electronegativity 2. Intramolecular Bonding 3. Intermolecular Bonding 4. Drawing Lewis Structures 5. Lewis Structures for Polyatomic Ions 6. Exceptions to the
CHEMISTRY. Chapter 9 The Basics of Chemical Bonding. The Molecular Nature of Matter. Jespersen Brady Hyslop SIXTH EDITION
 CEMISTRY The Molecular Nature of Matter SIXT EDITIN Jespersen Brady yslop Chapter 9 The Basics of Chemical Bonding Copyright 2012 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chemical Bonds Attractive forces that hold atoms
CEMISTRY The Molecular Nature of Matter SIXT EDITIN Jespersen Brady yslop Chapter 9 The Basics of Chemical Bonding Copyright 2012 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chemical Bonds Attractive forces that hold atoms
Bonding in Chemistry. Chemical Bonds All chemical reactions involve breaking of some bonds and formation of new ones where new products are formed.
 CHEMICAL BONDS Atoms or ions are held together in molecules or compounds by chemical bonds. The type and number of electrons in the outer electronic shells of atoms or ions are instrumental in how atoms
CHEMICAL BONDS Atoms or ions are held together in molecules or compounds by chemical bonds. The type and number of electrons in the outer electronic shells of atoms or ions are instrumental in how atoms
Chapter 9. Chemical Bonding I: The Lewis Model. HIV-Protease. Lecture Presentation
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding I: The Lewis Model HIV-Protease HIV-protease is a protein synthesized by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This particular protein is crucial to the
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding I: The Lewis Model HIV-Protease HIV-protease is a protein synthesized by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This particular protein is crucial to the
CHAPTER 8 BONDING: GENERAL CONCEPTS. Questions
 APTER 8 BDIG: GEERAL EPTS Questions 15. a. This diagram represents a polar covalent bond as in. In a polar covalent bond, there is an electron rich region (indicated by the red color) and an electron poor
APTER 8 BDIG: GEERAL EPTS Questions 15. a. This diagram represents a polar covalent bond as in. In a polar covalent bond, there is an electron rich region (indicated by the red color) and an electron poor
sharing or transferring electrons between atoms covalent ionic polar covalent Quantitative description: Quantum mechanics
 Chapter. 3 Chemical Bonding: The Classical Description Two or more atoms approach -> their electrons interact and form new arrangements of electrons with lower total potential energy than isolated atoms
Chapter. 3 Chemical Bonding: The Classical Description Two or more atoms approach -> their electrons interact and form new arrangements of electrons with lower total potential energy than isolated atoms
Periodic Trends. Homework: Lewis Theory. Elements of his theory:
 Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Test Review # 4. Chemistry: Form TR4.11A
 Chemistry: Form TR4.11 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Bonding. The electrons of one atom are attracted to the protons of another. When atoms combine, there is a tug of war over the valence electrons.
Chemistry: Form TR4.11 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Bonding. The electrons of one atom are attracted to the protons of another. When atoms combine, there is a tug of war over the valence electrons.
Bonding. Polar Vs. Nonpolar Covalent Bonds. Ionic or Covalent? Identifying Bond Types. Solutions + -
 Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds them together. Bonding onors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6 Types of Bonds Ionic Bonds Force of attraction
Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds them together. Bonding onors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6 Types of Bonds Ionic Bonds Force of attraction
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
 Chemical Bonding II: and ybridization of Atomic rbitals Chapter 10 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model: Predict the geometry of the molecule from the electrostatic repulsions between the
Chemical Bonding II: and ybridization of Atomic rbitals Chapter 10 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model: Predict the geometry of the molecule from the electrostatic repulsions between the
We study bonding since it plays a central role in the understanding of chemical reactions and understanding the chemical & physical properties.
 AP Chapter 8 Notes Bonding We study bonding since it plays a central role in the understanding of chemical reactions and understanding the chemical & physical properties. Chemical Bond: holding atoms together
AP Chapter 8 Notes Bonding We study bonding since it plays a central role in the understanding of chemical reactions and understanding the chemical & physical properties. Chemical Bond: holding atoms together
Chapter 8: Bonding. Section 8.1: Lewis Dot Symbols
 Chapter 8: Bonding Section 8.1: Lewis Dot Symbols The Lewis electron dot symbol is named after Gilbert Lewis. In the Lewis dot symbol, the element symbol represents the nucleus and the inner electrons.
Chapter 8: Bonding Section 8.1: Lewis Dot Symbols The Lewis electron dot symbol is named after Gilbert Lewis. In the Lewis dot symbol, the element symbol represents the nucleus and the inner electrons.
Chapter 8. Ions and the Noble Gas. Chapter Electron transfer leads to the formation of ionic compounds
 Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding: General Concepts 1 8.1 Electron transfer leads to the formation of ionic compounds Ionic compounds form when metals and nonmetals react The attraction between positive and negative
Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding: General Concepts 1 8.1 Electron transfer leads to the formation of ionic compounds Ionic compounds form when metals and nonmetals react The attraction between positive and negative
Outline for Today. Monday, Nov. 12. Wednesday Friday. Chapter 8: Chemical Bonding. Bond Enthalpies. Chapter 9: Theories of Bonding
 Outline for Today Monday, Nov. 12 Chapter 8: Chemical Bonding Bond Enthalpies Chapter 9: Theories of Bonding VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Theory Valence Bond Orbital ybridization Molecular
Outline for Today Monday, Nov. 12 Chapter 8: Chemical Bonding Bond Enthalpies Chapter 9: Theories of Bonding VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Theory Valence Bond Orbital ybridization Molecular
CHAPTER 8: BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMICAL BONDING. Bond-an attractive interaction between two or more atoms.
 CHAPTER 8: BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMICAL BONDING Bond-an attractive interaction between two or more atoms. Bonding is the "glue" that holds molecules together. Two extreme types: Ionic (transfer) Covalent
CHAPTER 8: BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMICAL BONDING Bond-an attractive interaction between two or more atoms. Bonding is the "glue" that holds molecules together. Two extreme types: Ionic (transfer) Covalent
Concepts of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry Part 1: Ionic and Covalent Bonds. David A. Katz Pima Community College Tucson, AZ
 Concepts of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry Part 1: Ionic and Covalent Bonds David A. Katz Pima Community College Tucson, AZ Chemical Bonds Three basic types of bonds: Ionic Electrostatic attraction
Concepts of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry Part 1: Ionic and Covalent Bonds David A. Katz Pima Community College Tucson, AZ Chemical Bonds Three basic types of bonds: Ionic Electrostatic attraction
18. Ionic solids are held together by strong electrostatic forces that are omnidirectional.
 APTER 8 BDIG: GEERAL EPTS Questions 15. In 2 and, the bonding is covalent in nature, with the bonding electrons pair shared between the atoms. In 2, the two atoms are identical, so the sharing is equal;
APTER 8 BDIG: GEERAL EPTS Questions 15. In 2 and, the bonding is covalent in nature, with the bonding electrons pair shared between the atoms. In 2, the two atoms are identical, so the sharing is equal;
Chemical Bonding II. Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds Hybridization MO theory
 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Chemistry: The Central Science. Chapter 8: Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 8: Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding The properties of substances are determined in large part by the chemical bonds that hold their atoms together 8.1: Chemical
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 8: Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding The properties of substances are determined in large part by the chemical bonds that hold their atoms together 8.1: Chemical
11/14/2014. Chemical Bonding. Richard Philips Feynman, Nobel Laureate in Physics ( )
 Chemical Bonding Lewis Theory Valence Bond VSEPR Molecular rbital Theory 1 "...he [his father] knew the difference between knowing the name of something and knowing something" Richard Philips eynman, Nobel
Chemical Bonding Lewis Theory Valence Bond VSEPR Molecular rbital Theory 1 "...he [his father] knew the difference between knowing the name of something and knowing something" Richard Philips eynman, Nobel
Ex. 1) F F bond in F = 0 < % covalent, no transfer of electrons
 #60 Notes Unit 8: Bonding Ch. Bonding I. Bond Character Bonds are usually combinations of ionic and covalent character. The electronegativity difference is used to determine a bond s character. Electronegativity
#60 Notes Unit 8: Bonding Ch. Bonding I. Bond Character Bonds are usually combinations of ionic and covalent character. The electronegativity difference is used to determine a bond s character. Electronegativity
CHAPTER EIGHT BONDING: GENERAL CONCEPTS. For Review
 APTER EIGT BDIG: GEERAL EPTS or Review 1. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity is a bonding term. Electron affinity is the energy
APTER EIGT BDIG: GEERAL EPTS or Review 1. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity is a bonding term. Electron affinity is the energy
Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds An attractive force that holds two atoms together in a more complex unit Three basic types of bonds Ionic Electrons are transferred from one
Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds An attractive force that holds two atoms together in a more complex unit Three basic types of bonds Ionic Electrons are transferred from one
Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories
 Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories Ionic Radii Ions, just like atoms, follow a periodic trend in their radii. The metal ions in a given period are smaller than the non-metal ions in the same
Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories Ionic Radii Ions, just like atoms, follow a periodic trend in their radii. The metal ions in a given period are smaller than the non-metal ions in the same
Chemistry: The Central Science
 Chemistry: The Central Science Fourteenth Edition Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Three basic types of bonds Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions Covalent Sharing of
Chemistry: The Central Science Fourteenth Edition Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Three basic types of bonds Ionic Electrostatic attraction between ions Covalent Sharing of
Bonding. Computer Lab: Ionic Bonds. Important Notes 3/22/18
 Bonding What are ionic bonds, and how are they formed? Computer Lab: Ionic Bonds Go to http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/asset/ lsps07_int_ionicbonding/ Read each screen and follow the directions where appropriate.
Bonding What are ionic bonds, and how are they formed? Computer Lab: Ionic Bonds Go to http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/asset/ lsps07_int_ionicbonding/ Read each screen and follow the directions where appropriate.
CHEMICAL BONDS. Determining Percentage Composition, Empirical, and Molecular Formulas for Compounds:
 CHEMICAL BONDS Chemical Bonds: The strong electrostatic forces of attraction holding atoms together in a unit are called chemical bonds (EU 2.C). Reflect a balance in the attractive and repulsive forces
CHEMICAL BONDS Chemical Bonds: The strong electrostatic forces of attraction holding atoms together in a unit are called chemical bonds (EU 2.C). Reflect a balance in the attractive and repulsive forces
Types of Bonding : Ionic Compounds. Types of Bonding : Ionic Compounds
 Types of Bonding : Ionic Compounds Ionic bonding involves the complete TRANSFER of electrons from one atom to another. Usually observed when a metal bonds to a nonmetal. - - - - - - + + + + + + + + + +
Types of Bonding : Ionic Compounds Ionic bonding involves the complete TRANSFER of electrons from one atom to another. Usually observed when a metal bonds to a nonmetal. - - - - - - + + + + + + + + + +
Bonding. Honors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6
 Bonding Honors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6 Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds them together. Types of Bonds Ionic Bonds Force of attraction
Bonding Honors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6 Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds them together. Types of Bonds Ionic Bonds Force of attraction
; (c) [Li] [: O :] [Li]. 5a. The electrostatic potential map that corresponds to IF is the one with the most red in it. ... C C H
![; (c) [Li] [: O :] [Li]. 5a. The electrostatic potential map that corresponds to IF is the one with the most red in it. ... C C H ; (c) [Li] [: O :] [Li]. 5a. The electrostatic potential map that corresponds to IF is the one with the most red in it. ... C C H](/thumbs/87/96516624.jpg) hapter 10 Answers ractice Examples 1a Mg 1b n, Ge, [: Br :], K, : e: + 2 : : +, [Tl ] +, 2 : : [] 2a (a) [a] [ ] [a] ; (b) [Mg] [: :] [Mg] [: :] [Mg] 2+ 3 2+ 3 2+ 2+ 2b (a) [: I :] [a] [: I :] 2+ 2 ; (b)
hapter 10 Answers ractice Examples 1a Mg 1b n, Ge, [: Br :], K, : e: + 2 : : +, [Tl ] +, 2 : : [] 2a (a) [a] [ ] [a] ; (b) [Mg] [: :] [Mg] [: :] [Mg] 2+ 3 2+ 3 2+ 2+ 2b (a) [: I :] [a] [: I :] 2+ 2 ; (b)
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
 1. Define the following terms: a) valence electrons Ionic and Covalent Bonding the electrons in the highest occupied energy level always electrons in the s and p orbitals maximum of 8 valence electrons
1. Define the following terms: a) valence electrons Ionic and Covalent Bonding the electrons in the highest occupied energy level always electrons in the s and p orbitals maximum of 8 valence electrons
CHEM 101: CHAPTER 11: CHEMICAL BONDS: THE FORMATION OF COMPOUNDS FROM ATOMS
 1 CHEM 101: CHAPTER 11: CHEMICAL BONDS: THE FORMATION OF COMPOUNDS FROM ATOMS PERIODIC TRENDS: See pages 214-216, 221 Table 11.3, and 227 + 228 of text. Lewis Structures of Atoms: The Lewis Dot Diagram
1 CHEM 101: CHAPTER 11: CHEMICAL BONDS: THE FORMATION OF COMPOUNDS FROM ATOMS PERIODIC TRENDS: See pages 214-216, 221 Table 11.3, and 227 + 228 of text. Lewis Structures of Atoms: The Lewis Dot Diagram
Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction
 Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent
Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent
Chapter 8 H H H H. Molecular Compounds & Covalent Bonding. Why do covalent bonds form? 8.1 Molecular Compounds. Properties of Molecular Compounds
 Chapter 8 Molecular Compounds & Covalent Bonding Why do covalent bonds form? If only group 5A, 6A, 7A atoms existed, ionic bonds can t form. NNMETALS Each atom needs electrons so they are not willing to
Chapter 8 Molecular Compounds & Covalent Bonding Why do covalent bonds form? If only group 5A, 6A, 7A atoms existed, ionic bonds can t form. NNMETALS Each atom needs electrons so they are not willing to
Chapter Eight. p328. Bonding: General Concepts
 Chapter Eight p328 Bonding: General Concepts 1 Contents 8-1 Types of Chemical Bonds p330 Coulomb s law The energy of interaction between a pair of ions can be calculated using Coulomb s law: E 19 Q1Q 2
Chapter Eight p328 Bonding: General Concepts 1 Contents 8-1 Types of Chemical Bonds p330 Coulomb s law The energy of interaction between a pair of ions can be calculated using Coulomb s law: E 19 Q1Q 2
Lecture 17 - Covalent Bonding. Lecture 17 - VSEPR and Molecular Shape. Lecture 17 - Introduction. Lecture 17 - VSEPR and Molecular Shape
 Chem 103, Section F0F Unit VI - Compounds Part II: Covalent Compounds Lecture 17 Using the Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory to predict molecular shapes Molecular shape and polarity
Chem 103, Section F0F Unit VI - Compounds Part II: Covalent Compounds Lecture 17 Using the Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory to predict molecular shapes Molecular shape and polarity
What Do Molecules Look Like?
 What Do Molecules Look Like? The Lewis Dot Structure approach provides some insight into molecular structure in terms of bonding, but what about 3D geometry? Recall that we have two types of electron pairs:
What Do Molecules Look Like? The Lewis Dot Structure approach provides some insight into molecular structure in terms of bonding, but what about 3D geometry? Recall that we have two types of electron pairs:
COVALENT BONDING CHEMICAL BONDING I: LEWIS MODEL. Chapter 7
 Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
AP Chemistry. Unit #7. Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape. Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING. Discrete molecules formed
 AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
Its Bonding Time. Chemical Bonds CH 12
 Its Bonding Time Chemical Bonds CH 12 What is a chemical bond? Octet Rule: Chemical compounds tend to form so that each atom, by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons, has an octet of electrons in its
Its Bonding Time Chemical Bonds CH 12 What is a chemical bond? Octet Rule: Chemical compounds tend to form so that each atom, by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons, has an octet of electrons in its
Unit 9: CHEMICAL BONDING
 Unit 9: CHEMICAL BONDING 1 Unit 9: Bonding: 1. Electronegativity 2. Intramolecular Bonding 3. Intermolecular Bonding 4. Drawing Lewis Structures 5. Lewis Structures for Polyatomic Ions 6. Exceptions to
Unit 9: CHEMICAL BONDING 1 Unit 9: Bonding: 1. Electronegativity 2. Intramolecular Bonding 3. Intermolecular Bonding 4. Drawing Lewis Structures 5. Lewis Structures for Polyatomic Ions 6. Exceptions to
Chapter The Ionic Bond. Why are ionic compounds stable? Spontaneous Processes. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts.
 Lewis Dot ymbols hapter 9 hemical Bonding I: Basic oncepts Introduced by G.. Lewis Element symbol plus 1 dot for each valence e Elements tend to form octets, noble gas configurations Useful for representative
Lewis Dot ymbols hapter 9 hemical Bonding I: Basic oncepts Introduced by G.. Lewis Element symbol plus 1 dot for each valence e Elements tend to form octets, noble gas configurations Useful for representative
Chapters 8 and 9. Octet Rule Breakers Shapes
 Chapters 8 and 9 Octet Rule Breakers Shapes Bond Energies Bond Energy (review): The energy needed to break one mole of covalent bonds in the gas phase Breaking bonds consumes energy; forming bonds releases
Chapters 8 and 9 Octet Rule Breakers Shapes Bond Energies Bond Energy (review): The energy needed to break one mole of covalent bonds in the gas phase Breaking bonds consumes energy; forming bonds releases
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Chapter Seven. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure. Chapter Seven Slide 1 of 98
 Chapter Seven Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chapter Seven Slide 1 of 98 Chemical Bonds: A Preview Forces called chemical bonds hold atoms together in molecules and keep ions in place in solid
Chapter Seven Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chapter Seven Slide 1 of 98 Chemical Bonds: A Preview Forces called chemical bonds hold atoms together in molecules and keep ions in place in solid
Chapter Nine. Chapter Nine. Chemical Bonds: A Preview. Chemical Bonds. Electrostatic Attractions and Repulsions. Energy of Interaction
 1 Chemical Bonds: A Preview 2 Chemical Bonds Forces called chemical bonds hold atoms together in molecules and keep ions in place in solid ionic compounds. Chemical bonds are electrostatic forces; they
1 Chemical Bonds: A Preview 2 Chemical Bonds Forces called chemical bonds hold atoms together in molecules and keep ions in place in solid ionic compounds. Chemical bonds are electrostatic forces; they
Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules
 Chem 220 Notes Page 1 Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules I. Types of Chemical Bonds A. Why do atoms forms bonds? Atoms want to have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas atom (noble
Chem 220 Notes Page 1 Structure and Bonding of Organic Molecules I. Types of Chemical Bonds A. Why do atoms forms bonds? Atoms want to have the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas atom (noble
Covalent Bonds. Chapter 8 Chemical Bonds (+VSEPR from Chapter 9) Li Be B C N O F Ne delocalized electron sea. 3. Introduction. Types of Chemical Bonds
 hapter 8: hemical Bonds (+ VSEPR) hapter bjectives: hapter 8 hemical Bonds (+VSEPR from hapter 9) Understand the principal types of chemical bonds. Understand the properties of ionic and molecular compounds.
hapter 8: hemical Bonds (+ VSEPR) hapter bjectives: hapter 8 hemical Bonds (+VSEPR from hapter 9) Understand the principal types of chemical bonds. Understand the properties of ionic and molecular compounds.
Ch. 8 Chemical Bonding: General Concepts. Brady & Senese, 5th Ed
 Ch. 8 Chemical Bonding: General Concepts Brady & Senese, 5th Ed Index 8.1. Electron transfer leads to the formation of ionic compounds 8.2. Lewis symbols help keep track of valence electrons 8.3. Covalent
Ch. 8 Chemical Bonding: General Concepts Brady & Senese, 5th Ed Index 8.1. Electron transfer leads to the formation of ionic compounds 8.2. Lewis symbols help keep track of valence electrons 8.3. Covalent
Chem 105 Friday Review Lewis formulas and geometry Bond length qualitative Polarity Polarity and geometry 11/20/2009 1
 hem 105 riday 11-20-09 Review Lewis formulas and geometry Bond length qualitative Polarity Polarity and geometry 11/20/2009 1 Shown below is a partial Lewis formula for hydrogen carbonate ion ( 3- ). What
hem 105 riday 11-20-09 Review Lewis formulas and geometry Bond length qualitative Polarity Polarity and geometry 11/20/2009 1 Shown below is a partial Lewis formula for hydrogen carbonate ion ( 3- ). What
Lewis Structures and Molecular Shapes
 Lewis Structures and Molecular Shapes Drawing Lewis Structures Determine from formula if ionic or covalent Count the electrons If ionic : add valence # to charge if (-), subtract if (+) - = 7+1 electrons;
Lewis Structures and Molecular Shapes Drawing Lewis Structures Determine from formula if ionic or covalent Count the electrons If ionic : add valence # to charge if (-), subtract if (+) - = 7+1 electrons;
Chapter 8 The Concept of the Chemical Bond
 Chapter 8 The Concept of the Chemical Bond Three basic types of bonds: Ionic - Electrostatic attraction between ions (NaCl) Metallic - Metal atoms bonded to each other Covalent - Sharing of electrons Ionic
Chapter 8 The Concept of the Chemical Bond Three basic types of bonds: Ionic - Electrostatic attraction between ions (NaCl) Metallic - Metal atoms bonded to each other Covalent - Sharing of electrons Ionic
Ch. 8 Chemical Bonding: General Concepts. Brady & Senese, 5th Ed
 Ch. 8 Chemical Bonding: General Concepts Brady & Senese, 5th Ed Index 8.1. Electron transfer leads to the formation of ionic compounds 8.2. Lewis symbols help keep track of valence electrons 8.3. Covalent
Ch. 8 Chemical Bonding: General Concepts Brady & Senese, 5th Ed Index 8.1. Electron transfer leads to the formation of ionic compounds 8.2. Lewis symbols help keep track of valence electrons 8.3. Covalent
Chapter 9 Bonding. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Chapter 9 Bonding Dr. Sapna Gupta Lewis Dot Symbol Lewis dot symbols is a notation where valence electrons are shown as dots. Draw the electrons symmetrically around the sides (top, bottom, left and right)
Chapter 9 Bonding Dr. Sapna Gupta Lewis Dot Symbol Lewis dot symbols is a notation where valence electrons are shown as dots. Draw the electrons symmetrically around the sides (top, bottom, left and right)
Chapter 6. Table of Contents. Section 1 Covalent Bonds. Section 2 Drawing and Naming Molecules. Section 3 Molecular Shapes. Covalent Compounds
 Covalent Compounds Table of Contents Section 1 Covalent Bonds Section 2 Drawing and Naming Molecules Section 3 Molecular Shapes Section 1 Covalent Bonds Bellringer Make a list of the elements that form
Covalent Compounds Table of Contents Section 1 Covalent Bonds Section 2 Drawing and Naming Molecules Section 3 Molecular Shapes Section 1 Covalent Bonds Bellringer Make a list of the elements that form
Unit 3 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Unit 3 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemical bond - A mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together 6-1 Introduction
Unit 3 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemical bond - A mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together 6-1 Introduction
Chapter 6 Chemistry Review
 Chapter 6 Chemistry Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Put the LETTER of the correct answer in the blank. 1. The electrons involved in
Chapter 6 Chemistry Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Put the LETTER of the correct answer in the blank. 1. The electrons involved in
Chapter 8. forces of attraction which hold atoms or ions together. 3 fundamental types of bonding. Ionic - metals & nonmetals
 Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds forces of attraction which hold atoms or ions together 3 fundamental types of bonding Ionic - metals & nonmetals Covalent - nonmetals (semimetals)
Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds forces of attraction which hold atoms or ions together 3 fundamental types of bonding Ionic - metals & nonmetals Covalent - nonmetals (semimetals)
Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding 8.1 Chemical Bonds, Lewis Symbols, and the Octet Rule 8.2 Ionic Bonding Consider the reaction between sodium and chlorine: Na(s) + ½ Cl 2 (g) NaCl(s) H o f
Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding 8.1 Chemical Bonds, Lewis Symbols, and the Octet Rule 8.2 Ionic Bonding Consider the reaction between sodium and chlorine: Na(s) + ½ Cl 2 (g) NaCl(s) H o f
Ch 13: Covalent Bonding
 Ch 13: Covalent Bonding Section 13: Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion 1. Recall the rules for drawing Lewis dot structures 2. Remember the special situations: - Resonance structures - ormal charges
Ch 13: Covalent Bonding Section 13: Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion 1. Recall the rules for drawing Lewis dot structures 2. Remember the special situations: - Resonance structures - ormal charges
Chapter 7. Ionic & Covalent Bonds
 Chapter 7 Ionic & Covalent Bonds Ionic Compounds Covalent Compounds 7.1 EN difference and bond character >1.7 = ionic 0.4 1.7 = polar covalent 1.7 Electrons not shared at
Chapter 7 Ionic & Covalent Bonds Ionic Compounds Covalent Compounds 7.1 EN difference and bond character >1.7 = ionic 0.4 1.7 = polar covalent 1.7 Electrons not shared at
Unit 9: CHEMICAL BONDING
 Unit 9: CHEMICAL BONDING 1 Unit 9: Bonding: 1. Electronegativity 2. Intramolecular Bonding 3. Intermolecular Bonding 4. Drawing Lewis Structures 5. Lewis Structures for Polyatomic Ions 6. Exceptions to
Unit 9: CHEMICAL BONDING 1 Unit 9: Bonding: 1. Electronegativity 2. Intramolecular Bonding 3. Intermolecular Bonding 4. Drawing Lewis Structures 5. Lewis Structures for Polyatomic Ions 6. Exceptions to
