January 23, Lecture 3. The Ozone Chemistry.
|
|
|
- Hugo Boyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 3 January 23, 2018 The Ozone Chemistry The atmosphere is divided vertically into four layers based on temperature: the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere. 1
2 Absorption by Oxygen and Ozone in the atmosphere filters the UV component reaching the earth. Note the decrease in the intensity of UV-A,B, C (below 300 nm). Video Absorption of UV light by Oxygen and Ozone UV-C absorption UV-B absorption Ozone effectively absorbs the most energetic ultraviolet light, known as UV-C and UV-B, which causes biological damage 2
3 Review: UV Photons are energetic and can induce chemical reactions in biological and environmental systems. Energy of photons E (kj/mole) = hc/ = / E (ev) = 1240/ Oxygen and Ozone as a Natural UV-C-Filter Creation of Ozone in the Stratosphere Creation of Ozone in the Stratosphere Ozone is constantly being formed in the earth's atmosphere by the action of the sun's ultraviolet radiation on oxygen molecules. Ultraviolet light splits the molecules apart by breaking the bonds between the atoms. A highly reactive free oxygen atom then collides with another oxygen molecule to form an ozone molecule. Because ozone is unstable, ultraviolet light quickly breaks it up, and the process begins again. 3
4 About 90% of the ozone in the earth's atmosphere In the troposphere, the ground-level or "bad" ozone is an air pollutant that damages human health, vegetation, and many common materials. It is a key ingredient of urban smog. In the stratosphere, we find the "good" ozone that protects life on earth from the harmful effects of the sun's ultraviolet rays. Chapman theory describes how sunlight converts the various forms of oxygen from one to another, explains why the highest content of ozone occur in the layer between 15 and 50 km, termed the ozone layer 4
5 Creation of Ozone in Stratosphere Above stratosphere most of the oxygen absorbs UV-C and exists as O atoms O 2 + h 2O 495 kj/mole (241 nm) Because of the high concentration of O 2 in stratosphere, any O atom present gets converted to O 3 O 2 + O O 3 O 2 + O + M O 3 A third molecule M (N 2 or H 2 O) facilitates as a heat energy carrier. Because of the temperature inversion vertical mixing of air is a slow process in stratosphere than in troposphere. Destruction of Ozone in Stratosphere Ozone absorbs UV light below 320 nm and undergoes dissociation O 3 + h O 2 * + O* Both O 2 and O produced via UV photon are in the excited state Determine the longest wavelength that is needed for the dissociation of O 3 O 3 O 2 + O 105 kj/mol O O* O 2 O 2 * O 3 O 2 * + O* 190 kj/mol 95 kj/mol 390 kj/mol = kj nm mol -1 /390 kj mol -1 = 307 nm 5
6 The Steady State Analysis Rate of change of an intermediate= Rate of formation- rate of destruction A B (1) B C (2) Rate of change of B = k 1 [A] k 2 [C] At Steady State the rate of change (d[b]/dt) is zero Rate of formation-rate of destruction = 0 Or Rate of formation=rate of destruction In the above example, k 1 [A] = k 2 [C] or [A]/[C] = k 2 /k 1 What is the difference between an equilibrium and steady state? Equilibrium System (A=B) Reactants A B Products Reactant & Product Concentrations remain constant An equilibrium system is a closed system in which the forward and backward reactions occur at the same time and at equal rates. Steady State (A=B) Reactants A Intermediate B Products Concentration of Intermediates remain constant Most of the atmospheric reactions driven by sunlight are steady state reactions A steady state is an open system in which an intermediate is formed and destroyed at the same rate in separate reactions. 6
7 Steady State Analysis for Ozone in the Atmosphere: Chapman Mechanism O 2 2O (1) O+ O 2 + M O 3 + M (2) O 3 O 2 + O (3) O 3 + O 2O 2 (4) Since O is consumed or formed in all the reactions we can assume that it is in the steady state Rate of change of O = 2(rate1) rate2 + rate3 rate 4 = 0 (A) Similarly, Rate of change of O 3 = rate2 rate3 rate4 = 0 (B) (A)+ (B): 2(rate1) 2(rate4) =0 By expressing rate in terms of rate constant and concentration 2k 1 [O 2 ] 2k 4 [O 3 ][O] =0 OR [O 3 ] [O] = k 1 [O 2 ]/k 4 (C) From previous analysis, 2(rate1) rate2 + rate3 rate 4 = 0 Rate of change of O 3 = rate2 rate3 rate4 = 0 (A) (B) [O 3 ][O] = k 1 [O 2 ]/k 4 (C) (A) (B): 2rate1 2rate2 + 2rate3 = 0 or rate3 = rate2 rate1 since rate1 <<rate 2 and rate 3, we can neglect the term rate3 = rate2 k 3 [O 3 ] = k 2 [O][O 2 ][M] or [O 3 ]/[O] =k 2 [O 2 ][M]/k 3 (D) (C)x(D): [O 3 ] 2 = [O 2 ] 2 [M]k 1 k 2 /k 3 k 4 or [O 3 ]/[O 2 ] = [M] 0.5 (k 1 k 2 /k 3 k 4 ) 0.5 (E) 7
8 At Steady State, [O 3 ] ss /[O 2 ] ss = [M] 0.5 (k 1 k 2 /k 3 k 4 ) 0.5 (E) The steady state ratio of O 3 to O 2 depend on - sqaure root of air density - proportional to square root of product of k 1 & k 2 corresponding to O and O 3 production - inversely proportional to square root of product of k 3 &k 4 - based on experimental values of k and M, maximum [O 3 ] is of the order of 10-4 M M decreases with increasing altitude Absorption of UV-C (and k 1 ) decreases with decreasing altitude Peak concentration of ozone is expected at altitude of ~40 km (Actual peak is observed at 25 km because of the movement of O 3 downwards Concentration of Atomic Oxygen From (E) and (C) [O] ss = (k 1 k 3 /k 2 k 4 ) 0.5 /[M] 0.5 [O] ss increases with increasing altitude as [M] declines k 1 and k 3 increase with altitude O atoms dominate over O 3 at higher altitudes (> 50 km). Concentration of atomic oxygen and ozone versus altitude 8
9 Comparison of stratosphere ozone concentration as a function of altitude The actual destruction of ozone is more than the prediction The Chapman theory, however, overestimates the ozone contents. Thus, there must be other chemical reactions contributing to the reduction of the ozone content. In 1970, Paul Crutzen showed that the nitrogen oxides NO and NO 2 react catalytically (without themselves being consumed) with ozone, thus accelerating the rate of reduction of the ozone content. NO + O 3 -> NO 2 + O 2 NO NO 2 +O -> NO+O 2 O 3 +uv-light -> O 2 +O Net result: 2O 3 -> 3O 2 N2O Microorganism Note NO acts as a catalyst and requires O atom for regeneration referred as Mechanism I 9
10 Two important chemistry contributions leading to the discovery of the link between Freon and ozone depletion James Lovelock (England) had developed a highly sensitive device of measuring extremely low organic gas contents in the atmosphere, the electron capture detector. Using this he could now demonstrate that the exclusively man-made, chemically inert, CFC gases had already spread globally throughout the atmosphere. Richard Stolarski and Ralph Cicerone (USA) had shown that free chlorine atoms in the atmosphere can decompose ozone catalytically in similar ways as nitrogen oxides do. Spray cans and refrigerators damage the ozone layer In 1974, Molina and Rowland proposed in their Nature article that the chemically inert CFC could gradually be transported up to the ozone layer, there to be met by such intensive ultra-violet light that they would be separated into their constituents, notably chlorine atoms. They calculated that if human use of CFC gases was to continue at an unaltered rate the ozone layer would be depleted by many percent after some decades. 10
11 Joe Farman and his colleagues revealed a dramatic and unpredicted decline in stratospheric ozone in perhaps the most unexpected region of the globe - over the Antarctic in spring, and Farman suggested that it was due to gases emitted into the atmosphere by Man. Farman, J. C.;Gardiner, B. G.;Shanklin, J. D., Large Losses of Total Ozone in Antarctica Reveal Seasonal Clox/Nox Interaction. Nature, 1985, 315, Using measurements of the total amount of ozone in a column of atmosphere above the BAS Halley Bay base at 76 S, dating back to the International Geophysical Year in 1957, Joe Farman showed that a dramatic decline in springtime ozone over the entire Antarctic continent had taken place, starting in the late 1970s, reaching. ~30% by
12 Chlorofluorocarbons Chlorofluorocarbons or CFCs (also known as Freon) are non-toxic, non-flammable and non-carcinogenic. They contain fluorine atoms, carbon atoms and chlorine atoms. The 5 main CFCs include CFC-11(trichlorofluoromethane - CFCl 3 ), CFC-12 (dichloro-difluoromethane - CF 2 Cl 2 ), CFC-113 (trichloro-trifluoroethane - C 2 F 3 Cl 3 ), (CFC-114 (dichloro-tetrfluoroethane - C 2 F 4 Cl 2 ), and CFC-115 (chloropentafluoroethane - C 2 F 5 Cl). CFCs have a lifetime in the atmosphere of about 20 to 100 years, and consequently one free chlorine atom from a CFC molecule can do a lot of damage, destroying ozone molecules for a long time. Although emissions of CFCs around the developed world have largely ceased due to international control agreements, the damage to the stratospheric ozone layer will continue well into the 21st century. ozone-depleting substances (CFCs, HCFCs, HBFCs, and halons) are numbered according to a system devised several decades ago and now used worldwide. It provides very complex information about molecular structure and also easily distinguishes among various classess of chemicals. For example, it is not intuitive that 1,1-dichloro-1-fluoroethane (CFCl 2 - CH 3 ) is an ozone-depleting substance. The designation HCFC-141b, in contrast, immediately conveys its ozone-depleting nature while concisely describing its structure. 12
13 The prefix describes what kinds of atoms are in a particular molecule, the next step is to calculate the number of each type of atom. The key to the code is to add 90 to the number; the result shows the number of C, H, and F atoms. For HCFC-141b: = #C #H #F One more piece of information is needed to decipher the number of Cl atoms. All of these chemicals are saturated; that is, they contain only single bonds. The number of bonds available in a carbon-based molecule is 2n(C) + 2. Thus, for HCFC-141b, which has n=2 carbon atoms, there are 6 bonds. Cl atoms occupy bonds remaining after the F and H atoms. HCFC-141b has 2C, 3H, 1F, and 2Cl: HCFC-141b = C 2 H 3 FCl 2 Notice that the HCFC designation (hydro chloro fluoro carbon) is a good double-check on the decoding; this molecule does, indeed, contain H, Cl, F, and C. The "b" at the end describes how these atoms are arranged; different "isomers" contain the same atoms, but they are arranged differently. The letter designation for is isomers. Deduce the formula for the compounds with following code numbers 12, 113, 123, 134 a = 102 C=1, H=0, and F= 2, ( Cl=2) CF 2 Cl 2 C b = 203 C=2, H=0, and F= 3, ( Cl=3) C 2 F 3 Cl 3 c = 213 C=2, H=1, and F= 3, ( Cl=2) C 2 HF 3 Cl 2 C C d = 224 C=2, H=2, and F= 4, ( Cl=0) C 2 H 2 F 4 13
14 Other Ozone Depleting Substances CCl 4 (Carbon terachloride) Used as dry cleaning solvent CH 3 -CCl 3 (methyl chloroform) Cleaning agent for metals Halons Bromine containing hydrogen free substances such as CF 3 Br and CF 2 BrCl used Methyl bromide is used as a pesticide, fumigate crops (40% of world use is in the US) They rise to stratosphere and decompose to produce Br an efficient catalyst X for O 3 depletion Developing countries have agreed to reduce consumption, but not complete elimination Meantime China & Korea have increased their production! 14
15 In 1985, nations agreed in Vienna to take "appropriate measures...to protect human health and the environment against adverse effects resulting or likely to result from human activities which modify or are likely to modify the Ozone Layer", thus the Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer was born. The main thrust of the Convention was to encourage research and overall cooperation among countries and exchange of information. Even so it took four years to prepare and agree. Twenty nations signed it in Vienna, but most did not rush to ratify it. The Convention provided for future protocols and specified procedures for Amendment and dispute settlement. The Vienna Convention set an important precedent. For the first time nations agreed in principle to tackle a global environmental problem before its effects were felt, or even scientifically proven. As the experts began to explore for specific measures to be taken, the journal 'Nature' published a paper in May 1985 by British scientists - led by Dr. Joe Farman - about severe ozone depletion in the Antarctic. The paper's findings were confirmed by American satellite observations and offered the first proof of severe ozone depletion and making the need for definite measures more urgent. As a result, In September 1987, agreement was reached on specific measures to be taken and the Montreal 1987: Ozone agreement reached in Montreal al-protection/environmental-protection-general/ozoneagreement-reached-in-montreal.html In 1985, 49 countries met in Vienna to first discuss the protection of the ozone layer With the signing of the Montreal Protocol, two years later, 24 of these countries agreed to reduce the production and consumption of Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) by 50 per cent by The Protocol came into force on January 1st, 1989, when 29 countries and the European Economic Community (EEC), representing approximately 82 per cent of world consumption, had ratified it. 15
16 16
SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER
 SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER What is the ozone layer? Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen, which means it is a pure element, but has a different chemical structure to that
SUSTAINABILITY MATTERS FACT SHEET 7: THE HOLE IN THE OZONE LAYER What is the ozone layer? Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen, which means it is a pure element, but has a different chemical structure to that
Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation
 Outline Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation Review electromagnetic radiation absorptivity by selective gases temperature vs. height in atmosphere Ozone production and destruction natural balance anthropogenic
Outline Ozone: Earth s shield from UV radiation Review electromagnetic radiation absorptivity by selective gases temperature vs. height in atmosphere Ozone production and destruction natural balance anthropogenic
Chapman Cycle. The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere
 Chapman Cycle The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere Even though reactions are happening, the concentration of O 3 remains constant This is an example of a dynamic equilibrium or
Chapman Cycle The cycle describes reactions of O 2 and O 3 in stratosphere Even though reactions are happening, the concentration of O 3 remains constant This is an example of a dynamic equilibrium or
Chemistry of Ozone. Explain the following terms: resonance, resonance hybrid, delocalisation
 Chemistry of Ozone Ozone is triatomic oxygen, O 3. (Ozone is from the Greek ozein, to smell. ) It is a form of oxygen in which the atoms combine in threes, (correct IUPAC name: trioxygen, O 3 ), rather
Chemistry of Ozone Ozone is triatomic oxygen, O 3. (Ozone is from the Greek ozein, to smell. ) It is a form of oxygen in which the atoms combine in threes, (correct IUPAC name: trioxygen, O 3 ), rather
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II
 Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes REVIEW... Q Is the depletion of STRATOSPHERIC OZONE (in
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes REVIEW... Q Is the depletion of STRATOSPHERIC OZONE (in
Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer
 Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer Student: 1. O2 and O3 molecules are A. allotropes. B. structural isomers. C. isotopes. D. geometrical isomers. 2. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there
Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer Student: 1. O2 and O3 molecules are A. allotropes. B. structural isomers. C. isotopes. D. geometrical isomers. 2. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there
Discuss Yesterday s Lab. What Do We Know? Funny Ozone Video. Ozone Layer Defined! Ozone Layer. Warm-Up 3/3/2015
 Warm-Up March 3, 2015 Today you will need your notebook, pencil and whiteboards. HW due Friday. Attach the Ozone Table into your notebook Pick up ozone table in the red box Complete the Predictions Column
Warm-Up March 3, 2015 Today you will need your notebook, pencil and whiteboards. HW due Friday. Attach the Ozone Table into your notebook Pick up ozone table in the red box Complete the Predictions Column
STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION. Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS
 STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS Ozone Layer Ozone is Good up high Stratosphere Bad nearby Troposphere Solar Radiation - range of electromagnetic waves UV shortest we see if
STRATOSPHERIC OZONE DEPLETION Adapted from K. Sturges at MBHS Ozone Layer Ozone is Good up high Stratosphere Bad nearby Troposphere Solar Radiation - range of electromagnetic waves UV shortest we see if
Ozone. In the upper atmosphere. At the surface pollution (not discussed)
 Ozone In the upper atmosphere At the surface pollution (not discussed) What is Ozone? Oxygen molecule with 3 oxygen atoms O 3 Normal form of oxygen: 2 oxygen atoms O 2 Where does Ozone occur? Stratosphere
Ozone In the upper atmosphere At the surface pollution (not discussed) What is Ozone? Oxygen molecule with 3 oxygen atoms O 3 Normal form of oxygen: 2 oxygen atoms O 2 Where does Ozone occur? Stratosphere
Stratospheric Ozone Depletion, Regional Ozone, Aerosols: Connections to Climate Change
 Stratospheric Ozone Depletion, Regional Ozone, Aerosols: Connections to Climate Change Jeff Gaffney Chemistry Department University of Arkansas at Little Rock DOE Biological and Environmental Science Climate
Stratospheric Ozone Depletion, Regional Ozone, Aerosols: Connections to Climate Change Jeff Gaffney Chemistry Department University of Arkansas at Little Rock DOE Biological and Environmental Science Climate
Mario Molina puts the atmosphere and ozone on the political agenda
 Mario Molina puts the atmosphere and ozone on the political agenda (Version 1) A. Understanding ozone 60 km stratosphere 40 km 20 km troposphere Diagram of our atmosphere (Reproduced with permission from
Mario Molina puts the atmosphere and ozone on the political agenda (Version 1) A. Understanding ozone 60 km stratosphere 40 km 20 km troposphere Diagram of our atmosphere (Reproduced with permission from
Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 (Chapter 4, p , , , )
 Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 (Chapter 4, p 155-169, 174-176, 198-222, 231-238) zone Discovery and History The Stratosphere and circulation Chapman Chemistry Catalysts The Controversy The zone Hole International
Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 (Chapter 4, p 155-169, 174-176, 198-222, 231-238) zone Discovery and History The Stratosphere and circulation Chapman Chemistry Catalysts The Controversy The zone Hole International
atmosphere: a mixture a gases that surrounds the planet Earth.
 atmosphere: a mixture a gases that surrounds the planet Earth. 78% nitrogen 21% oxygen the atmosphere is held to the Earth by the force of gravity. Due to the smaller mass of planets like Mercury, less
atmosphere: a mixture a gases that surrounds the planet Earth. 78% nitrogen 21% oxygen the atmosphere is held to the Earth by the force of gravity. Due to the smaller mass of planets like Mercury, less
Chapter 2 Protecting the Ozone Layer
 Chapter 2 Protecting the Ozone Layer Multiple Choice Questions 1. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there in a neutral atom of? A. A B. B C. C D. D Remember that the mass is protons plus neutrons
Chapter 2 Protecting the Ozone Layer Multiple Choice Questions 1. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are there in a neutral atom of? A. A B. B C. C D. D Remember that the mass is protons plus neutrons
Chapter 2 Protecting the Ozone Layer. The Ozone Hole
 Today (Tues 2/24) Newspaper Articles: Ciara Rodwell and Melissa Regan Intro to Ozone, Ozone Hole, & Chapter 2 Light, matter, and human health! Laboratory: Experiment 4 You design investigation Start Ozone
Today (Tues 2/24) Newspaper Articles: Ciara Rodwell and Melissa Regan Intro to Ozone, Ozone Hole, & Chapter 2 Light, matter, and human health! Laboratory: Experiment 4 You design investigation Start Ozone
Measurements of Ozone. Why is Ozone Important?
 Anthropogenic Climate Changes CO 2 CFC CH 4 Human production of freons (CFCs) Ozone Hole Depletion Human production of CO2 and CH4 Global Warming Human change of land use Deforestation (from Earth s Climate:
Anthropogenic Climate Changes CO 2 CFC CH 4 Human production of freons (CFCs) Ozone Hole Depletion Human production of CO2 and CH4 Global Warming Human change of land use Deforestation (from Earth s Climate:
Ozone Depletion. Dana Desonie, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click (No sign in required)
 Ozone Depletion Dana Desonie, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content,
Ozone Depletion Dana Desonie, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content,
Layer Protection Glossary
 Page 1 of 7 Ozone Layer Protection Last updated on Wednesday, December 15, 2010 You are here: EPA Home Ozone Layer Protection Ozone Layer Protection Glossary Layer Protection Glossary In order to understand
Page 1 of 7 Ozone Layer Protection Last updated on Wednesday, December 15, 2010 You are here: EPA Home Ozone Layer Protection Ozone Layer Protection Glossary Layer Protection Glossary In order to understand
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31. Air Pollution Part II
 NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31 Air Pollution Part II Last time we talked mainly about two types of smog:. 1. London-type smog 2. L.A.-type smog or photochemical smog What are the necessary ingredients
NATS 101 Section 13: Lecture 31 Air Pollution Part II Last time we talked mainly about two types of smog:. 1. London-type smog 2. L.A.-type smog or photochemical smog What are the necessary ingredients
Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven
 Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven Prevention of the atmosphere KÖRNYEZETGAZDÁLKODÁSI AGRÁRMÉRNÖKI MSC (MSc IN AGRO-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES) Fundamentals to atmospheric chemical reactions. The stratospheric
Tananyag fejlesztés idegen nyelven Prevention of the atmosphere KÖRNYEZETGAZDÁLKODÁSI AGRÁRMÉRNÖKI MSC (MSc IN AGRO-ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES) Fundamentals to atmospheric chemical reactions. The stratospheric
SCIAMACHY book. Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB
 SCIAMACHY book Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB 1928: start of CFC production 1971: 1 st observation of CFC in the atmosphere (J. Lovelock) 1974: identification
SCIAMACHY book Ozone variability and long-term changes Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA-IASB 1928: start of CFC production 1971: 1 st observation of CFC in the atmosphere (J. Lovelock) 1974: identification
2.1 Ozone. Ozone O 3. Oxygen O 2 1/30/2015 CHM 107
 CHM 107 2.1 Ozone In the stratosphere way up high Protects Earth from solar radiation There is a hole in the ozone layer above Antarctica Do we care? Why? Energy + 3 O 2 (g) g 2 O 3 (g) Lightning can serve
CHM 107 2.1 Ozone In the stratosphere way up high Protects Earth from solar radiation There is a hole in the ozone layer above Antarctica Do we care? Why? Energy + 3 O 2 (g) g 2 O 3 (g) Lightning can serve
OZONE AND ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION
 OZONE AND ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION Alfio Parisi, Michael Kimlin Imagine if the earth s protective atmosphere did not exist and the earth was subjected to the harmful ultraviolet energy from the sun. Life
OZONE AND ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION Alfio Parisi, Michael Kimlin Imagine if the earth s protective atmosphere did not exist and the earth was subjected to the harmful ultraviolet energy from the sun. Life
Class: Chemistry Topic:_atomic structure & ozone layer
 Class: Chemistry Topic:_atomic structure & ozone layer Directions: Please read both articles and write a 5 paragraph comparative essay on each. You should include examples provided in the articles to prove
Class: Chemistry Topic:_atomic structure & ozone layer Directions: Please read both articles and write a 5 paragraph comparative essay on each. You should include examples provided in the articles to prove
Unique nature of Earth s atmosphere: O 2 present photosynthesis
 Atmospheric composition Major components N 2 78% O 2 21% Ar ~1% Medium components CO 2 370 ppmv (rising about 1.5 ppmv/year) CH 4 1700 ppbv H 2 O variable Trace components H 2 600 ppbv N 2 O 310 ppbv CO
Atmospheric composition Major components N 2 78% O 2 21% Ar ~1% Medium components CO 2 370 ppmv (rising about 1.5 ppmv/year) CH 4 1700 ppbv H 2 O variable Trace components H 2 600 ppbv N 2 O 310 ppbv CO
An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes
 ISSN 2278 0211 (Online) An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes Vasudevan Tachoth Nirvan Industries, Private Industrial Estate, Post Sidco Near Railway Gate, Kuruchi Coimbatore, India Abstract:
ISSN 2278 0211 (Online) An Interpretation of Natural Healing of Ozone Holes Vasudevan Tachoth Nirvan Industries, Private Industrial Estate, Post Sidco Near Railway Gate, Kuruchi Coimbatore, India Abstract:
Where is the ozone layer? Global ozone column abundance
 Where is the ozone layer? Altitude (km) 85 10 0 Thermosphere 20-30km Mesosphere Stratosphere Troposphere 100 200 300 Temperature (K) Mesopause Stratopause Tropopause Global ozone column abundance WMO,
Where is the ozone layer? Altitude (km) 85 10 0 Thermosphere 20-30km Mesosphere Stratosphere Troposphere 100 200 300 Temperature (K) Mesopause Stratopause Tropopause Global ozone column abundance WMO,
ClO + O -> Cl + O 2 Net: O 3 + O -> O 2 + O 2
 Lecture 36. Stratospheric ozone chemistry. Part2: Threats against ozone. Objectives: 1. Chlorine chemistry. 2. Volcanic stratospheric aerosols. 3. Polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs). Readings: Turco: p.
Lecture 36. Stratospheric ozone chemistry. Part2: Threats against ozone. Objectives: 1. Chlorine chemistry. 2. Volcanic stratospheric aerosols. 3. Polar stratospheric clouds (PSCs). Readings: Turco: p.
Stratosphere and Ozone
 Stratosphere and Ozone Ozone (Greek, ozein, to smell) O 3 Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hv O + O O + O 3 2O 2 O 3 + hv O 2 + O O + O 2 + M O 3 + M third-body. anything What units are used to report the amount
Stratosphere and Ozone Ozone (Greek, ozein, to smell) O 3 Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hv O + O O + O 3 2O 2 O 3 + hv O 2 + O O + O 2 + M O 3 + M third-body. anything What units are used to report the amount
Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module
 Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module Using your favorite browser open Ozone/index.htm or go to http://cs.clark.edu/~mac/geol390/stratosphericozone/startozoneactivity.html Work through the web
Stratospheric Ozone: An Online Learning Module Using your favorite browser open Ozone/index.htm or go to http://cs.clark.edu/~mac/geol390/stratosphericozone/startozoneactivity.html Work through the web
Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 Darin Toohey CU PAOS. Some resources that I borrowed from
 Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 Darin Toohey CU PAS Why Do We Care? zone Discovery and History Circulation Chapman Chemistry Catalytic Destruction The Controversy The Big Surprise of 1985 Some resources
Stratospheric Chemistry Part 1 Darin Toohey CU PAS Why Do We Care? zone Discovery and History Circulation Chapman Chemistry Catalytic Destruction The Controversy The Big Surprise of 1985 Some resources
Gases, ozone, and CFCs. An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop
 Gases, ozone, and CFCs An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Gas Gas Model Gases are composed of tiny, widely-spaced particles. For a typical gas, the average distance between particles is about
Gases, ozone, and CFCs An Introduction to Chemistry by Mark Bishop Gas Gas Model Gases are composed of tiny, widely-spaced particles. For a typical gas, the average distance between particles is about
8.2 Tropospheric ozone
 8.2 Tropospheric ozone Prev Chapter 8. Ozone Next 8.2 Tropospheric ozone Tropospheric ozone is only about 10% of the total amount of ozone contained in a vertical column in the atmosphere. However, this
8.2 Tropospheric ozone Prev Chapter 8. Ozone Next 8.2 Tropospheric ozone Tropospheric ozone is only about 10% of the total amount of ozone contained in a vertical column in the atmosphere. However, this
Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide.
 Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A B C D Electrophilic addition Electrophilic substitution
Q1. Pentanenitrile can be made by reaction of 1-bromobutane with potassium cyanide. Which of these is the correct name for the mechanism of this reaction? A B C D Electrophilic addition Electrophilic substitution
Topic # 15 OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE. see pp in Class Notes
 Topic # 15 OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE see pp 81-85 in Class Notes [ The Ozone Treaty is ] the first truly global treaty that offers protection to every single human being. ~ Mostofa K. Tolba,
Topic # 15 OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE see pp 81-85 in Class Notes [ The Ozone Treaty is ] the first truly global treaty that offers protection to every single human being. ~ Mostofa K. Tolba,
Lecture 25: Atmosphere & environment
 Lecture 25: Atmosphere & environment Read: BLB 18.1 4 HW: BLB 18:9,11,15,29,69 Sup 18:1 3 Know: ozone chemistry chemistry of the lower atmosphere sulfer compounds & acid rain nitrogen oxides & smog check
Lecture 25: Atmosphere & environment Read: BLB 18.1 4 HW: BLB 18:9,11,15,29,69 Sup 18:1 3 Know: ozone chemistry chemistry of the lower atmosphere sulfer compounds & acid rain nitrogen oxides & smog check
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 9, 2016 The Game Changer. Some perspective The British Antarctic Survey The Ozone Hole International Regulations
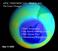 ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 9, 2016 The Game Changer Some perspective The British Antarctic Survey The Ozone Hole International Regulations Rowland (1974): The work is going very well, but it may mean the
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 9, 2016 The Game Changer Some perspective The British Antarctic Survey The Ozone Hole International Regulations Rowland (1974): The work is going very well, but it may mean the
Atmospheric Chemistry III
 Atmospheric Chemistry III Chapman chemistry, catalytic cycles: reminder Source of catalysts, transport to stratosphere: reminder Effect of major (O 2 ) and minor (N 2 O, CH 4 ) biogenic gases on [O 3 ]:
Atmospheric Chemistry III Chapman chemistry, catalytic cycles: reminder Source of catalysts, transport to stratosphere: reminder Effect of major (O 2 ) and minor (N 2 O, CH 4 ) biogenic gases on [O 3 ]:
CHEM/ENVS 380 S14, Midterm Exam ANSWERS 1 Apr 2014
 PART- A. Multiple Choice Questions (5 points each): Each question may have more than one correct answer. You must select ALL correct answers, and correct answers only, to receive full credit. 1. Which
PART- A. Multiple Choice Questions (5 points each): Each question may have more than one correct answer. You must select ALL correct answers, and correct answers only, to receive full credit. 1. Which
(for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes)
 www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. chem10b 18.2-30 What is the final stage in municipal water treatment? A. aeration B. settling C. removal of added fluoride
www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) 1. chem10b 18.2-30 What is the final stage in municipal water treatment? A. aeration B. settling C. removal of added fluoride
Stratospheric O 3 : Overview
 Stratospheric Chemistry READING: Chapter 10 of text Mid-latitude Ozone Chemistry (and depletion) Polar Ozone Destruction (the Ozone Hole) Stratospheric O 3 : Overview Most O 3 (90%) in stratosphere. Remaining
Stratospheric Chemistry READING: Chapter 10 of text Mid-latitude Ozone Chemistry (and depletion) Polar Ozone Destruction (the Ozone Hole) Stratospheric O 3 : Overview Most O 3 (90%) in stratosphere. Remaining
HSC Chemistry. Chemical Monitoring and Management. DUXCollege. Term 1 Week 7. Student name:. Class code:.. Teacher name:.
 Chemical Monitoring and Management Term 1 Week 7 Student name:. Class code:.. Teacher name:. DUXCollege Term 1 Week 7 Theory 1 Human activity has caused changes in the composition and the structure of
Chemical Monitoring and Management Term 1 Week 7 Student name:. Class code:.. Teacher name:. DUXCollege Term 1 Week 7 Theory 1 Human activity has caused changes in the composition and the structure of
General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more H atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms.
 aloalkanes General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms. If one hydrogen atom is replaced, the general formula is n 2n+1 X where X = F, l, Br
aloalkanes General A haloalkane is a compound in which one or more atoms of an alkane are replaced by halogen atoms. If one hydrogen atom is replaced, the general formula is n 2n+1 X where X = F, l, Br
dihalogenoalkane H 2, Nickel Catalyst KOH alcoholic HBr, HCl Br Cl Elimination KOH aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution
 7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
7 AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) Br 2, 2 KO aqueous room temp Electrophilic addition heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
CHEM Chemical Kinetics
 Chemical Kinetics Catalysts A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of the reaction but is neither created nor destroyed in the process. Catalysts can be divided into two broad categories. Homogeneous
Chemical Kinetics Catalysts A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of the reaction but is neither created nor destroyed in the process. Catalysts can be divided into two broad categories. Homogeneous
LECTURE 6 - THE EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE
 LECTURE 6 - THE EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE Note: Slide numbers refer to the PowerPoint presentation which accompanies the lecture. Earth s Atmosphere, slide 1 here INTRODUCTION Earth s Atmosphere, slide 2 here
LECTURE 6 - THE EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE Note: Slide numbers refer to the PowerPoint presentation which accompanies the lecture. Earth s Atmosphere, slide 1 here INTRODUCTION Earth s Atmosphere, slide 2 here
The Atmosphere. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems
 The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
Chemical Kinetics. What quantities do we study regarding chemical reactions? 15 Chemical Kinetics
 Chemical Kinetics Chemical kinetics: the study of reaction rate, a quantity conditions affecting it, the molecular events during a chemical reaction (mechanism), and presence of other components (catalysis).
Chemical Kinetics Chemical kinetics: the study of reaction rate, a quantity conditions affecting it, the molecular events during a chemical reaction (mechanism), and presence of other components (catalysis).
(g) 2NH 3. (g) ΔH = 92 kj mol 1
 1 The uses of catalysts have great economic and environmental importance For example, catalysts are used in ammonia production and in catalytic converters (a) Nitrogen and hydrogen react together in the
1 The uses of catalysts have great economic and environmental importance For example, catalysts are used in ammonia production and in catalytic converters (a) Nitrogen and hydrogen react together in the
Chemistry 1500: Chemistry in Modern Living. Topic 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer. Atoms and Light
 Chemistry 1500 Dr. unter s Class Topic 2 - Page 1 Chemistry 1500: Chemistry in Modern Living Topic 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer Atoms and Light Chemistry in Context, 2 nd Edition (1997): Chapter 2, Pages
Chemistry 1500 Dr. unter s Class Topic 2 - Page 1 Chemistry 1500: Chemistry in Modern Living Topic 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer Atoms and Light Chemistry in Context, 2 nd Edition (1997): Chapter 2, Pages
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1
 ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1 Note Page numbers refer to Daniel Jacob s online textbook: http://acmg.seas.harvard.edu/publications/ jacobbook/index.html Atmos = vapor + sphaira
ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Air Pollution Chemistry Lecture 1 Note Page numbers refer to Daniel Jacob s online textbook: http://acmg.seas.harvard.edu/publications/ jacobbook/index.html Atmos = vapor + sphaira
Student Workbook California Education and the Environment Initiative. Earth Science Standard E.8.c. Living Under One Roof
 E Student Workbook California Education and the Environment Initiative Earth Science Standard E.8.c. Living Under One Roof California Education and the Environment Initiative Approved by the California
E Student Workbook California Education and the Environment Initiative Earth Science Standard E.8.c. Living Under One Roof California Education and the Environment Initiative Approved by the California
Protecting the Ozone Layer. Allotropes. Comparison of Allotropes
 Protecting the Ozone Layer Practice Problems: All Ch. 2 problems with the blue codes or answers on Page 520-521 Properties of Ozone Triatomic oxygen gas or O 3 to smell in Greek; odor at 10 ppb Lightning;
Protecting the Ozone Layer Practice Problems: All Ch. 2 problems with the blue codes or answers on Page 520-521 Properties of Ozone Triatomic oxygen gas or O 3 to smell in Greek; odor at 10 ppb Lightning;
CFC: chlorofluorocarbons
 The rate of reaction is markedly affected by temperature. Chemical Kinetics & k versus T Two theories were developed to explain the temperature effects. 1. 2. 2 UV radiation strikes a CFC molecule causing
The rate of reaction is markedly affected by temperature. Chemical Kinetics & k versus T Two theories were developed to explain the temperature effects. 1. 2. 2 UV radiation strikes a CFC molecule causing
CHAPTER 10 CHEMICAL KINETICS
 CHAPTER 10 CHEMICAL KINETICS Introduction To this point in our study of chemistry, we have been concerned only with the composition of the equilibrium mixture, not the length of time required to obtain
CHAPTER 10 CHEMICAL KINETICS Introduction To this point in our study of chemistry, we have been concerned only with the composition of the equilibrium mixture, not the length of time required to obtain
Ozone Student Activity Book
 Ozone Student Activity Book I. Introduction Ozone is similar to oxygen that we breathe. Air contains oxygen molecules that are made up of two oxygen atoms combined together (O 2 ). Ozone is a molecule
Ozone Student Activity Book I. Introduction Ozone is similar to oxygen that we breathe. Air contains oxygen molecules that are made up of two oxygen atoms combined together (O 2 ). Ozone is a molecule
Math 19a - Reading 8.1 outline for discussion section
 Math 9a - Reading 8. outline for discussion section due Monday, February 25, 28. How do you, guys, feel about vectors and matrices? Have you seen such things before? What did you think of the lecture on
Math 9a - Reading 8. outline for discussion section due Monday, February 25, 28. How do you, guys, feel about vectors and matrices? Have you seen such things before? What did you think of the lecture on
CHEM Chemical Kinetics. & Transition State Theory
 Chemical Kinetics Collision Theory Collision Theory & Transition State Theory The rate of reaction is markedly affected by temperature. k versus T Ae E a k RT Two theories were developed to explain the
Chemical Kinetics Collision Theory Collision Theory & Transition State Theory The rate of reaction is markedly affected by temperature. k versus T Ae E a k RT Two theories were developed to explain the
Ozone in the Atmosphere
 Ozone in the Atmosphere Why are we concerned with ozone? This simple molecule affects us in very important ways. It protects us, as well as all animals and plants on our planet, from the harm that ultraviolet
Ozone in the Atmosphere Why are we concerned with ozone? This simple molecule affects us in very important ways. It protects us, as well as all animals and plants on our planet, from the harm that ultraviolet
Chemistry 471/671. Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
 Chemistry 471/671 Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion 2 The Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hn 2 O( 1 D) O( 1 D) + O 2 + M O 3 + M Exothermic O( 1 D) + O 3 2 O 2 O 3 + hn O( 1 D) + O 2 ( 1
Chemistry 471/671 Atmospheric Chemistry III: Stratospheric Ozone Depletion 2 The Chapman Mechanism O 2 + hn 2 O( 1 D) O( 1 D) + O 2 + M O 3 + M Exothermic O( 1 D) + O 3 2 O 2 O 3 + hn O( 1 D) + O 2 ( 1
Chapter 2: Protecting the Ozone Layer
 Chapter 2: Protecting the zone Layer Why do we need to do to protect the ozone layer? Isn t ozone hazardous to human health? Why is the ozone layer getting smaller? What can we do (if anything) to help
Chapter 2: Protecting the zone Layer Why do we need to do to protect the ozone layer? Isn t ozone hazardous to human health? Why is the ozone layer getting smaller? What can we do (if anything) to help
Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review
 Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Climate in a region is a. the long-term,
Environmental Science Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Climate in a region is a. the long-term,
Model 1 Homolysis Reactions are Highly Endothermic
 Chem 201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (What do radicals do? What does a radical chain mechanism look like) Model 1 Homolysis Reactions are Highly Endothermic Heterolysis Homolysis Y Z Y + Z Y
Chem 201 Activity 24: Radical chain mechanisms (What do radicals do? What does a radical chain mechanism look like) Model 1 Homolysis Reactions are Highly Endothermic Heterolysis Homolysis Y Z Y + Z Y
Topic # 14 OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE
 Topic # 14 OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77 in Class Notes AN OZONE-RELATED CARTOON: MISCONCEPTION! Q1 Is the depletion of STRATOSPHERIC
Topic # 14 OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77 in Class Notes AN OZONE-RELATED CARTOON: MISCONCEPTION! Q1 Is the depletion of STRATOSPHERIC
Identify the condition that causes a bond in CCl 4 to break in the upper atmosphere. Deduce an equation for the formation of the reactive species.
 Q1.CCl 4 is an effective fire extinguisher but it is no longer used because of its toxicity and its role in the depletion of the ozone layer. In the upper atmosphere, a bond in CCl 4 breaks and reactive
Q1.CCl 4 is an effective fire extinguisher but it is no longer used because of its toxicity and its role in the depletion of the ozone layer. In the upper atmosphere, a bond in CCl 4 breaks and reactive
Sodium, Na. Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 11.1 to 11.4.
 Sodium, Na Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 11.1 to 11.4 Forms of Carbon The Chalcogens (Group 16) What is a chalcogen? Any element in
Sodium, Na Gallium, Ga CHEMISTRY 1000 Topic #2: The Chemical Alphabet Fall 2017 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises 11.1 to 11.4 Forms of Carbon The Chalcogens (Group 16) What is a chalcogen? Any element in
Planetary Atmospheres Part 2
 Planetary Atmospheres Part 2 Atmospheric Layers: The temperature gradient (whether it increases or decreases with altitude) is set by the type of absorption that occurs. We can affect this! Photo- disassocia,on
Planetary Atmospheres Part 2 Atmospheric Layers: The temperature gradient (whether it increases or decreases with altitude) is set by the type of absorption that occurs. We can affect this! Photo- disassocia,on
a) Write the equation for the overall reaction. (Using steps 1 and 2)
 Chemistry 12 Reaction Mechanisms Worksheet Name: Date: Block: 1. It is known that compounds called chlorofluorocarbons (C.F.C.s) (eg. CFCl3) will break up in the presence of ultraviolet radiation, such
Chemistry 12 Reaction Mechanisms Worksheet Name: Date: Block: 1. It is known that compounds called chlorofluorocarbons (C.F.C.s) (eg. CFCl3) will break up in the presence of ultraviolet radiation, such
dihalogenoalkane H 2, KOH alcoholic heat under reflux Elimination PCl 5, PBr 3, PI 3 Heat under reflux substitution KOH aqueous heat under reflux
 7. AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) 2, l 2 room temp Electrophilic addition KO aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
7. AS mechanisms dihalogenoalkane poly(alkene) 2, l 2 room temp Electrophilic addition KO aqueous heat under reflux Nucleophilic substitution high pressure atalyst polymerization alkene KMnO 4 oxidation
HYDROCARBONS. Section A
 MCQs Section A Q1The products obtained by cracking an alkane, X, are methane, ethene and propene. The mole fraction of ethene in the products is 0.5. What is the identity of X? A C6H14 B C8H18 C C9H20
MCQs Section A Q1The products obtained by cracking an alkane, X, are methane, ethene and propene. The mole fraction of ethene in the products is 0.5. What is the identity of X? A C6H14 B C8H18 C C9H20
CHEMISTRY. Section II (Total time 95 minutes) Part A Time 55 minutes YOU MAY USE YOUR CALCULATOR FOR PART A.
 CHEMISTRY Section II (Total time 95 minutes) Part A Time 55 minutes YOU MAY USE YOUR CALCULATOR FOR PART A. CLEARLY SHOW THE METHOD USED AND THE STEPS INVOLVED IN ARRIVING AT YOUR ANSWERS. It is to your
CHEMISTRY Section II (Total time 95 minutes) Part A Time 55 minutes YOU MAY USE YOUR CALCULATOR FOR PART A. CLEARLY SHOW THE METHOD USED AND THE STEPS INVOLVED IN ARRIVING AT YOUR ANSWERS. It is to your
2. Sketch a plot of R vs. z. Comment on the shape. Explain physically why R(z) has a maximum in the atmospheric column.
 190 PROBLEMS 10. 1 Shape of the ozone layer Consider a beam of solar radiation of wavelength λ propagating downward in the vertical direction with an actinic flux I at the top of the atmosphere. Assume
190 PROBLEMS 10. 1 Shape of the ozone layer Consider a beam of solar radiation of wavelength λ propagating downward in the vertical direction with an actinic flux I at the top of the atmosphere. Assume
Chapman. 4. O + O 3 2 O 2 ; k 4 5. NO + O 3 NO 2 + O 2 ; k 5 6. NO 2 + O NO + O 2 ; k 6 7. NO 2 + hν NO + O; k 7. NO X Catalytic.
 ATM 507 Lecture 8 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Note: next week class as usual Tuesday, no class on Thursday Today s topics Mid-latitude Stratosphere Lower Stratosphere 1 Let s
ATM 507 Lecture 8 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 2 due Sept. 30 Note: next week class as usual Tuesday, no class on Thursday Today s topics Mid-latitude Stratosphere Lower Stratosphere 1 Let s
Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics II. Chem 102 Dr. Eloranta
 Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics II Chem 102 Dr. Eloranta Rate Laws If you are familiar with calculus Experiments would allow you to determine the reaction order and rate constant, but what if you wanted
Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics II Chem 102 Dr. Eloranta Rate Laws If you are familiar with calculus Experiments would allow you to determine the reaction order and rate constant, but what if you wanted
NAME Student No. UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA. CHEMISTRY 102 Mid-Term Test I February 3, Part II Score Exam results Score
 NAME Student No. Section (circle one): A01 (Lipson) A02 (Briggs) A03 (Cartwright) UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA Version A CHEMISTRY 102 Mid-Term Test I February 3, 2012 Version A This test has two parts: (A Data
NAME Student No. Section (circle one): A01 (Lipson) A02 (Briggs) A03 (Cartwright) UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA Version A CHEMISTRY 102 Mid-Term Test I February 3, 2012 Version A This test has two parts: (A Data
Chemical Kinetics. Reaction Mechanisms
 Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is a study of the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. The study of kinetics may be done in steps: Determination of reaction mechanism Prediction of rate law Measurement
Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is a study of the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. The study of kinetics may be done in steps: Determination of reaction mechanism Prediction of rate law Measurement
NAME Student No. UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA. CHEMISTRY 102 Mid-Term Test I February 3, Part II Score Exam results Score
 NAME Student No. Section (circle one): A01 (Lipson) A02 (Briggs) A03 (Cartwright) UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA Version B CHEMISTRY 102 Mid-Term Test I February 3, 2012 Version B This test has two parts: (A Data
NAME Student No. Section (circle one): A01 (Lipson) A02 (Briggs) A03 (Cartwright) UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA Version B CHEMISTRY 102 Mid-Term Test I February 3, 2012 Version B This test has two parts: (A Data
Chemistry 12 Worksheet Reaction Mechanisms
 Chemistry 12 Worksheet 1-3 - Reaction Mechanisms 1. It is known that compounds called chlorofluorocarbons (C.F.C.s) (eg. CFCl 3 ) will break up in the presence of ultraviolet radiation, such as found in
Chemistry 12 Worksheet 1-3 - Reaction Mechanisms 1. It is known that compounds called chlorofluorocarbons (C.F.C.s) (eg. CFCl 3 ) will break up in the presence of ultraviolet radiation, such as found in
Table of Contents. Chapter: Atmosphere. Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere. Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere. Section 3: Air Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement Table of Contents Chapter 4: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere
Table of Contents Chapter: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere Section 2: Energy Transfer in the Atmosphere Section 3: Air Movement Table of Contents Chapter 4: Atmosphere Section 1: Earth's Atmosphere
Enhanced UV radiation a new problem for the marine environment
 1 Enhanced UV radiation a new problem for the marine environment Robert F. Whitehead, Stephen J. de Mora* and Serge Demers 1.1 Introduction UV irradiance at the earth s surface is intimately related to
1 Enhanced UV radiation a new problem for the marine environment Robert F. Whitehead, Stephen J. de Mora* and Serge Demers 1.1 Introduction UV irradiance at the earth s surface is intimately related to
O 3 + UV photon (λ < 320 nm) O 2 * + O* O 3 + O 2O 2
 Tro Chpt 13 Chemical Kinetics Rate of a chemical reaction Effect of concentration on reaction rate Integrated rate laws: How concentrations change with time Effect of temperature on rate Reaction mechanisms
Tro Chpt 13 Chemical Kinetics Rate of a chemical reaction Effect of concentration on reaction rate Integrated rate laws: How concentrations change with time Effect of temperature on rate Reaction mechanisms
On Stationary state, also called steady state. Lifetimes and spatial scales of variability
 On sources and sinks ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 5-6 Additional Notes February 16/18, 2016 On lifetimes, variability, and models On Stationary state, also called steady state Lifetimes and spatial scales
On sources and sinks ATOC 3500/CHEM 3151 Week 5-6 Additional Notes February 16/18, 2016 On lifetimes, variability, and models On Stationary state, also called steady state Lifetimes and spatial scales
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere
 Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
Unit 3 Review Guide: Atmosphere Atmosphere: A thin layer of gases that forms a protective covering around the Earth. Photosynthesis: Process where plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Trace
Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light. This is the overall reaction, but a more complex mixture of products is actually formed
 8. The aloalkanes opyright N Goalby Bancroft's School Synthesis of chloroalkanes Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light In the presence of UV light alkanes react with chlorine to form
8. The aloalkanes opyright N Goalby Bancroft's School Synthesis of chloroalkanes Reaction of alkanes with bromine / chlorine in UV light In the presence of UV light alkanes react with chlorine to form
F325: Equilibria, Energetics and Elements How Far?
 F325: Equilibria, Energetics and Elements 5.1.2 How Far? 100 marks 1. Syngas is a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen gases, used as a feedstock for the manufacture of methanol. A dynamic equilibrium
F325: Equilibria, Energetics and Elements 5.1.2 How Far? 100 marks 1. Syngas is a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen gases, used as a feedstock for the manufacture of methanol. A dynamic equilibrium
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II
 Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes THE DESTRUCTION OF STRATOSPHERIC OZONE The ozone hole
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part II A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes THE DESTRUCTION OF STRATOSPHERIC OZONE The ozone hole
ATM 507 Lecture 5. Text reading Chapter 4 Problem Set #2 due Sept. 20 Today s topics Photochemistry and Photostationary State Relation
 ATM 507 Lecture 5 Text reading Chapter 4 Problem Set #2 due Sept. 20 Today s topics Photochemistry and Photostationary State Relation Beer-Lambert Law (for the absorption of light) Used to describe the
ATM 507 Lecture 5 Text reading Chapter 4 Problem Set #2 due Sept. 20 Today s topics Photochemistry and Photostationary State Relation Beer-Lambert Law (for the absorption of light) Used to describe the
The Earth is surrounded by a blanket of air, which we call the atmosphere. It reaches over 560 kilometers
 A t m o s f e r a Atmosphere The Earth is surrounded by a blanket of air, which we call the atmosphere. It reaches over 560 kilometers (348 miles) from the surface of the Earth, so we are only able to
A t m o s f e r a Atmosphere The Earth is surrounded by a blanket of air, which we call the atmosphere. It reaches over 560 kilometers (348 miles) from the surface of the Earth, so we are only able to
1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely
 CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
CHAPTER 3 SOLAR AND TERRESTRIAL RADIATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its wavelength. a. directly *b. inversely 2. is the distance between successive
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 16 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
This site aims to provide information on the chemistry of ozone and provide some useful links to other pages.
 OZONE CHEMISTRY: This site aims to provide information on the chemistry of ozone and provide some useful links to other pages. Ozone is an atmospheric compound, found both at ground level and in the stratosphere.
OZONE CHEMISTRY: This site aims to provide information on the chemistry of ozone and provide some useful links to other pages. Ozone is an atmospheric compound, found both at ground level and in the stratosphere.
 Part I Short Answer Choose a letter to fill in the blanks. Use choices as many times as you wish. Only one choice is needed per blank. All are 3 points each. 1. First set. How can you tell these apart?
Part I Short Answer Choose a letter to fill in the blanks. Use choices as many times as you wish. Only one choice is needed per blank. All are 3 points each. 1. First set. How can you tell these apart?
Ch 13 Rates of Reaction (Chemical Kinetics)
 Ch 13 Rates of Reaction (Chemical Kinetics) Reaction Rates and Kinetics - The reaction rate is how fast reactants are converted to products. - Chemical kinetics is the study of reaction rates. Kinetics
Ch 13 Rates of Reaction (Chemical Kinetics) Reaction Rates and Kinetics - The reaction rate is how fast reactants are converted to products. - Chemical kinetics is the study of reaction rates. Kinetics
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy of Stratospheric Molecular O3
 Ultraviolet Spectroscopy of Stratospheric Molecular O3 Christine Predaina * Colorado Space Grant Consortium, University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado, 80309 The study of O3 (Ozone) remains a current topic
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy of Stratospheric Molecular O3 Christine Predaina * Colorado Space Grant Consortium, University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado, 80309 The study of O3 (Ozone) remains a current topic
CHEMISTRY. Chapter 13. Chapter Outline. Factors Affecting Rate
 CHEMISTRY Fifth Edition Gilbert Kirss Foster Bretz Davies Chapter 3 Chemical Kinetics: Reactions in the Atmosphere Chemistry, 5 th Edition Copyright 207, W. W. Norton & Company Chapter Outline 3.4 Reaction
CHEMISTRY Fifth Edition Gilbert Kirss Foster Bretz Davies Chapter 3 Chemical Kinetics: Reactions in the Atmosphere Chemistry, 5 th Edition Copyright 207, W. W. Norton & Company Chapter Outline 3.4 Reaction
Reaction Mechanisms. Chemical Kinetics. Reaction Mechanisms. Reaction Mechanisms. Reaction Mechanisms. Reaction Mechanisms
 Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is a study of the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. The study of kinetics may be done in steps: Determination of reaction mechanism Prediction of rate law Measurement
Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is a study of the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs. The study of kinetics may be done in steps: Determination of reaction mechanism Prediction of rate law Measurement
AP CHEMISTRY 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES
 2009 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 2 (10 points) A student was assigned the task of determining the molar mass of an unknown gas. The student measured the mass of a sealed 843 ml rigid flask that contained
2009 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 2 (10 points) A student was assigned the task of determining the molar mass of an unknown gas. The student measured the mass of a sealed 843 ml rigid flask that contained
CHEMICAL KINETICS (RATES OF REACTION)
 Kinetics F322 1 CHEMICAL KINETICS (RATES OF REACTION) Introduction Chemical kinetics is concerned with the dynamics of chemical reactions such as the way reactions take place and the rate (speed) of the
Kinetics F322 1 CHEMICAL KINETICS (RATES OF REACTION) Introduction Chemical kinetics is concerned with the dynamics of chemical reactions such as the way reactions take place and the rate (speed) of the
CFC Numbering System Add 90 to the number; the three digits represent the numbers of C, H, F atoms; make up the rest of the "unused bonds" with Cl.
 The CFC Story CFC - chlorofluorocarbon Saturated carbon compounds with carbon bonded to chlorine and fluorine Were/are used as: Refrigerants Propellants for foams Propellants for aerosols CFC Numbering
The CFC Story CFC - chlorofluorocarbon Saturated carbon compounds with carbon bonded to chlorine and fluorine Were/are used as: Refrigerants Propellants for foams Propellants for aerosols CFC Numbering
10. Stratospheric chemistry. Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017
 10. Stratospheric chemistry Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 The ozone layer Dobson unit: physical thickness (0.01 mm) of ozone layer if compressed to 1 atm, 0 o
10. Stratospheric chemistry Daniel J. Jacob, Atmospheric Chemistry, Harvard University, Spring 2017 The ozone layer Dobson unit: physical thickness (0.01 mm) of ozone layer if compressed to 1 atm, 0 o
