molar mass Avogadro Constant Mass of particle (in gram) Mole of particles Number of particles molar mass Avogadro Constant molar volume molar volume
|
|
|
- Emmeline Hubbard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry Chemical Formulae and Equation Calculation For Solid, liquid or gas number of mole = mass of subtance molar mass For gas (only) volume of gas number of mole = molar volme Molar mass = RAM/RMM/RFM in gram For Solution Molar volume = 24dm 3 at room temperature Molar volume = 22.4dm 3 at s.t.p. For quantity of particle(atom,molecule,ion) MV number of mole = 1000 M = molarity V = Volume of solution in cm 3 number of mole = quantity of particle Summary molar mass Avogadro Constant Mass of particle (in gram) Mole of particles Number of particles molar mass Avogadro Constant molar volume molar volume Volume of Gas 1
2 Chemical Formula Cation (Positive Ions) Ion Symbol Ion Symbol Ion Symbol Potassium K + Calcium Ca 2+ Aluminium Al 3+ Sodium Na + Magnesium Mg 2+ Iron (III) Fe 3+ Lithium Li + Zinc Zn 2+ Chromium(III) Cr 3+ Hydrogen H + Barium Ba 2+ Argentums(I) Ag + Iron (II) Fe 2+ Mercury(I) Hg + Tin (II) Sn 2+ Ammonium NH 4 + Lead(II) Pb 2+ Copper(II) Cu 2+ Manganese(II) Mn 2+ Anion (Negative Ions) Ion Symbol Ion Symbol Ion Symbol Oxide O 2 Hydroxide OH Ethanoate CH 3 COO Fluoride F Sulphate 2 SO 4 Manganate(VII) MnO 4 Chloride Cl Nitrate NO 3 Dichromate(VI) 2 Cr 2 O 7 Bromide Br Carbonate 2 CO 3 Phosphate 3 PO 4 Iodide I Thiosulphate 2 S 2 O 3 Formulae for Certain Molecule Karbon monoxide CO Ammonia NH 3 Carbon dioxide CO 2 water H 2 O Nitrogen monoxide NO Hydrogen chloride HCl Nitrogen dioxide NO 2 Tetrachloromethane CCl 4 Sulphur dioxide SO 2 Glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 Sulphur trioxide SO 3 Hydrogen bromide HBr Fluorine F 2 Hydrogen iodide HI Bromine Br 2 Hydrogen sulphide H 2 S Chlorine Cl 2 Ethanol C 2 H 5 OH Iodine I 2 Ethanoic Acid CH 3 COOH 2
3 Reaction of Group 1 Elements Periodic Table 1. Reaction with Oxygen The entire group 1 metal can react with oxygen to form metal oxide. 4Li + O 2 2Li 2 O 4Na + O 2 2Na 2 O 4K + O 2 2K 2 O The metal oxide of group 1 elements can dissolve in water to form alkali (hydroxide) solution Li 2 O + H 2 O 2LiOH Na 2 O + H 2 O 2NaOH K 2 O + H 2 O 2KOH 2. Reaction with halogen (Chlorine) 2Li + Cl 2 2LiCl 2Na + Cl 2 2NaCl 2K + Cl 2 2KCl 3. Reaction with water The entire group 1 metal can react with water to produce alkali (hydroxide) solution and hydrogen gas. 2Li + 2H 2 O 2LiOH + H 2 2Na + 2H 2 O 2NaOH + H 2 2K + 2H 2 O 2KOH + H 2 Reaction of Group 17 Elements 1. React with water Cl 2 + H 2 O HCl + HOCl Br 2 + H 2 O HBr + HOBr I 2 + H 2 O HI + HOI 2. React with Sodium Hydroxide Cl 2 + 2NaOH NaCl + NaOCl + H 2 O Br 2 + 2NaOH NaBr + NaOBr + H 2 O I 2 + 2NaOH NaI + NaOI + H 2 O 3. React with Iron 3Cl 2 + 2Fe 2FeCl 3 3Br 2 + 2Fe 2FeBr 3 3I 2 + 2Fe 2FeI 3 Preparation of Chlorine Gas 2KMnO HCl 2KCl + 2MnCl 2 + 5Cl 2 + 8H 2 O 3
4 Electrochemistry Electrolyte Ionisation of Electrolyte Ionisation of Molten Compound PbBr 2 Pb 2+ + Br NaCl Na + + Cl Al 2 O 3 2Al O 2 Ionisation of Aqueous Solution NaCl Na + + Cl HCl H + + Cl CuSO 4 Cu SO 4 H 2 O H + + OH H 2 O H + + OH H 2 O H + + OH Discharge of Positive Ion Na + + e Na Grey deposit is formed. Al e Al Grey deposit is formed. Pb e Pb Grey deposit is formed. Cu e Cu Brown deposit is formed. Ag + + e Ag Silver deposit is formed. 2H + + 2e H 2 Gas bubble is formed. A pop sound is produced when a lighted splinter is placed near the mouth of the test tube. Discharge of Negative Ion 2Cl Cl 2 + 2e Bubbles of pungent yellowish green gas are The gas turns moist litmus paper to red and then bleaches it. 2Br Br 2 + 2e Molten electrolyte: Brown colour gas is Aqueous solution: Light brown solution is formed. 2I I 2 + 2e Molten electrolyte: Brown colour gas is Aqueous solution: Light brown solution is formed. The solution turns blue when a few drops of starch solution is added in. 4OH O 2 + 2H 2 O + 4e Gas bubble is formed. Gas produces light up a wooden splinter. 4
5 Ionisation of Acid Acid and Base Hydrochloric Acid HCl H + + Cl HCl + H 2 O H 3 O + + Cl Nitric Acid HNO 3 H + + NO 3 HNO 3 + H 2 O H 3 O + + NO 3 Sulphuric Acid H 2 SO 4 H + + SO 4 2 H 2 SO 4 + 2H 2 O 2H 3 O + + SO 4 2 Ethanoic Acid CH 3 COOH H + + CH 3 COO CH 3 COOH + H 2 O H 3 O + + CH 3 COO Chemical Properties of Acid Acid + Reactive Metal Salt + H 2 Example: 2HCl + Zn ZnCl 2 + H 2 6HNO 3 + 2Fe 2Fe(NO 3 ) 3 + 3H 2 H 2 SO 4 + Pb PbSO 4 + H 2 6CH 3 COOH + 2Al 2Al(CH 3 COO) 3 + 3H 2 Acid + Metal Oxide Salt + H 2 O Example: 2HCl + ZnO ZnCl 2 + H 2 O 2HNO 3 + MgO Mg(NO 3 ) 2 + H 2 O H 2 SO 4 + CuO CuSO 4 + H 2 O 2CH 3 COOH + Na 2 O 2CH 3 COO Na + + H 2 O Acid + Metal Hydroxide Salt + H 2 O Example: 2HCl + Ca(OH) 2 CaCl 2 + 2H 2 O HNO 3 + NaOH NaNO 3 + H 2 O H 2 SO 4 + 2NH 4 OH (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 + 2H 2 O or H 2 SO 4 + 2NH 3 (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 CH 3 COOH + KOH CH 3 COO K + + H 2 O Acid + Metal Carbonate Salt + CO 2 + H 2 O Example: 2HCl + ZnCO 3 ZnCl 2 + CO 2 + H 2 O 2HNO 3 + CaCO 3 Ca(NO 3 ) 2 + CO 2 + H 2 O H 2 SO 4 + Na 2 CO 3 Na 2 SO 4 + CO 2 + H 2 O 2CH 3 COOH + MgCO 3 Mg(CH 3 COO) 2 + CO 2 + H 2 O 5
6 Solubility of Salt Salt Salt Solubility Salt of potassium, sodium and ammonium All are soluble in water Salt of nitrate All are soluble in water Salt of sulphate Mostly soluble in water except: (Pb) Lead sulphate (Ba) Barium sulphate (Ca) Calcium sulphate Salt of chloride Mostly soluble in water except: (Pb) Lead chloride (Ag) silver chloride (Hg) mercury chloride Salt of carbonate Mostly insoluble in water except: Potassium carbonate Sodium carbonate Ammonium carbonate Oxide and Hydroxide Solubility Oxide Mostly insoluble in water except: K 2 O and Na 2 O. Hydroxide Mostly insoluble in water except: NH 4 OH, KOH and NaOH Preparation of Salt Preparation of Soluble Salt Salt of Potassium, Sodium and Ammonium Acid + Alkali Salt + Water Example: Preparation of Sodium Chloride (NaCl) HCl + NaOH NaCl + H 2 O Salt of nonpotassium, Sodium and Ammonium Acid + Reactive metal Salt + Hydrogen Gas Acid + Metal Oxide Salt + Water Acid + Metal Carbonate Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide Example: Preparation of Zinc Sulphate (ZnSO 4 ) H 2 SO 4 + Zn ZnSO 4 + H 2 H 2 SO 4 + ZnO ZnSO 4 + H 2 O H 2 SO 4 + ZnCO 3 ZnSO 4 + H 2 O + CO 2 6
7 Preparation of Insoluble Salt Ionic Precipitation Insoluble salts can be made by double decomposition. This involves mixing a solution that contains its positive ions with another solution that contains its negative ions. Example: Preparation of Silver Nitrate AgNO 3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) AgCl (s) + NaNO 3 (aq) Ag + (aq) + C1 (aq) AgCl (s) (ionic equation) Colour of Salt Salt or metal oxide Solid Aqueous solution Salt of: Sodium, Calcium, Magnesium, Aluminium, zinc, Lead, ammonium Colourless Chloride, sulphate, nitrate, carbonate Salt of Copper(II). Copper(II) Carbonate Green Insoluble Copper(II) sulphate, Copper(II) nitrate, Copper(II) chloride Blue Blue Copper(II) oxide Black Insoluble Salt of Iron (II) Iron(II) sulphate; Iron(II) nitrate; Iron(ID chloride Green Green Salt of Iron (III). Iron(III) sulphate; Iron(III) nitrate; Iron(III) Brown Brown chloride Lead Iodide Yellow Insoluble Lead Chloride Insoluble Zink oxide Yellow when it is hot and white when it is cold. Insoluble Lead(II) oxide Brown when it is hot and yellow when it is cold. Insoluble Magnesium oxide, Aluminium oxide Insoluble Potassium oxide, Sodium oxide, Calcium oxide Colourless 7
8 Heating effect on Salt Heating Effect CO 3 2 NO 3 SO 4 2 Cl Most Probably Release CO 2 Most Probably Release NO 2 Heating Effect on Carbonate Salt Carbonate Salt Equation of The Reaction Potassium carbonate Sodium carbonate Calcium carbonate Magnesium carbonate Aluminium carbonate Zinc carbonate Iron (III) carbonate Lead(II) carbonate Copper(II) carbonate Most Probably Release SO 3 CaCO 3 CaO + CO 2 MgCO 3 MgO + CO 2 Al 2 (CO 3 ) 3 Al 2 O 3 + 3CO 2 ZnCO 3 ZnO + CO 2 Fe 2 (CO 3 ) 3 Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2 PbCO 3 PbO + CO 2 CuCO 3 CuO + CO 2 Not decomposible Most Probably No effect Mercury(II) carbonate Silver(I) carbonate Ammonium carbonate 2HgCO 3 2Hg + 2CO 2 + O 2 2Ag 2 CO 3 4Ag + 2CO 2 + O 2 (NH 4 ) 2 CO 3 NH 3 + CO 2 + H 2 O Heating Effect on Nitrate Salt Nitrate Salt Equation of The Reaction Potassium nitrate Sodium nitrate Calcium nitrate Magnesium nitrate Aluminium nitrate Zink nitrate Iron (III) nitrate Lead(II) nitrate Copper(II) nitrate Mercury(II) nitrate Silver(I) nitrate Ammonium nitrate 2KNO 3 2KNO 2 + O 2 2NaNO 3 2NaNO 2 + O 2 2Ca(NO 3 ) 2 2CaO + 4NO 2 + O 2 Mg(NO 3 ) 2 2MgO + 4NO 2 + O 2 4Al(NO 3 ) 3 2Al 2 O NO 2 + 3O 2 Zn(NO 3 ) 2 2ZnO + 4NO 2 + O 2 4Fe(NO 3 ) 3 2Fe 2 O NO 2 + 3O 2 Pb(NO 3 ) 2 2PbO + 4NO 2 + O 2 Cu(NO 3 ) 2 2CuO + 4NO 2 + O 2 Hg(NO 3 ) 2 Hg + 2NO 2 + O 2 2AgNO 3 2Ag + 2NO 2 + O 2 NH 4 NO 3 N 2 O + 2H 2 O [NOTES: Nitrogen dioxide, NO 2 is acidic gas and is brown in colour.] 8
9 Heating effect on sulphate salt Most sulphate salts do not decompose by heat. Only certain sulphate salts are decomposed by heat when heated strongly. Zinc sulphate, Copper (II) sulphate, Iron (III) sulphate ZnSO 4 ZnO + SO 3 CuSO 4 CuO + SO 3 2Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 Fe 2 O 3 + SO 2 + SO 3 The heating effect on chloride salts All chloride salts are not decomposable by heat except ammonium chloride. Example: NH 4 Cl NH 3 + HCl Ammonium sulphate (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 2NH 3 + H 2 SO 4 Identification of Gases Gasses Characteristics Oxygen Rekindle glowing splinter. Hydrogen Explode with a pop sound when brought close to a lighted splinter. Carbon Dioxide Turns lime water chalky. Chlorine Bleach moist litmus paper. Ammonia Pungent smell. Turn moist red litmus paper to blue. Produces white fume when reacts with concentrated hydrochloric Acid. Sulphur Dioxide Pungent smell. Bleach the purple colour of potassium manganate(vii). Turn moist blue litmus paper to red. Nitrogen Dioxide Pungent smell. Brown in colour. Turn moist blue litmus paper to red. Qualitative analysis Identification of Anions (Negative ions) Diluted HCl or diluted HNO 3 or diluted H 2 SO 4 HCl/HNO 3 CO 3 2 SO 4 2 Carbon Dioxide is released. BaCl (aq) or Ba(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) follow by diluted formed. It is soluble in diluted HCl/HNO 3 formed. It is NOT soluble in diluted HCl/HNO 3 AgNO 3 follow by diluted HNO 3. formed. It is soluble in diluted HNO 3 Brown Ring Test ( + FeSO 4 (aq ) + concentratedh 2 SO 4 Cl NO 3 formed. It is NOT soluble in diluted HNO 3 Formation of Brown Ring 9
10 Idendification of cation NaOH(ak) NH 3 (ak) HCl or NaCl H 2 SO 4 or Na 2 SO 4 Na 2 CO 3 KI Na + Ca 2+ precipitate. Mg 2+ Al 3+ Zn 2+ Pb 2+ Dissolve in excess NaOH solution. Dissolve in excess NaOH solution. Dissolve in excess NaOH solution. Dissolve in excess NH 3 solution. Dissolve in hot water. Yellow Dissolve in hot water Fe 2+ Dirty green Dirty green Green Fe 3+ Red brown Red brown Brown A red brown solution formed. Cu 2+ Blue precipitate is Blue precipitate is Dissolve in excess NH 3 solution and form a blue solution. Blue precipitate is precipitate form in brown solution NH 4 + = No changes is observed 10
11 Distibguish Iron(II) and Iron(III) Reagent Observation Ion presents Solution of potassium hecxacianoferate(ii) Light blue precipitate Fe 2+ Dark Blue precipitate Fe 3+ Solution of potassium hecxacianoferate(iii) Dark blue precipitate Fe 2+ Greenish brown solution Fe 3+ Solution of potassium Thiocyanate(II) Pinkish solution Fe 2+ Blood red solution Fe 3+ Manufactured Substances in Industry Contact Process (Making Sulphuric Acid) Stage 1: Formation of SO 2 Combustion of Sulphur Heating of metal sulphide such as lead(ii) sulphide S (s) + O 2 (g) SO 2 (g) or 2PbS (s) + 3O 2(g) 2PbO (s) + 2SO 2(g) or Combustion of hiydrogen sulphide 2H 2 S (g) + 3O 2(g) 2SO 2(g) + 2H 2 O (ce) Stage 2: Formation of SO 3 2SO 2 (g) + O 2 (g) 2SO 3 (g) Catalyst: vanadium(v) oxide Temperature: 450 C Pressure: 23 atmospheres Stage 3 Formation of oleum H 2 S 2 O 7 Stage 4:Formation of Sulphuric acid SO 3(g) + H 2 SO 4(aq) H 2 S 2 O 7(l) H 2 S (1) + H 2 O (1) 2H 2 SO 4(aq) 11
12 Haber Process (Making Ammonia) Sources of the raw material Hydrogen 1. Reaction between steam and heated coke H 2 O + C CO + H 2 2. Reaction between steam and natural gas. 2H 2 O + CH 4 CO 2 + 4H 2 Nitrogen From distillation of liquid air. The reaction 1. Ammonia is made by the Haber process from nitrogen and hydrogen: N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g) 2NH 3 (g); ΔH = 92 kj mo1 1 Catalyst: Iron Promoter: Aluminium oxide Temperature: 450 C Pressure: atm 12
CHAPTER 8 SALTS. NaCl. A salt is an ionic substance produced when the hydrogen ion of the acid is replaced by metal ion or an ammonium ion.
 CHAPTER 8 SALTS A salt is an ionic substance produced when the hydrogen ion of the acid is replaced by metal ion or an ammonium ion. The salt consists of two parts, cation from base and anion from acid.
CHAPTER 8 SALTS A salt is an ionic substance produced when the hydrogen ion of the acid is replaced by metal ion or an ammonium ion. The salt consists of two parts, cation from base and anion from acid.
Reaction Writing Sheet #1 Key
 Reaction Writing Sheet #1 Key Write and balance each of the following reactions and indicate the reaction type(s) present: 1. zinc + sulfur zinc sulfide 8 Zn (s) + S 8 (s) 8 ZnS (s) synthesis 2. potassium
Reaction Writing Sheet #1 Key Write and balance each of the following reactions and indicate the reaction type(s) present: 1. zinc + sulfur zinc sulfide 8 Zn (s) + S 8 (s) 8 ZnS (s) synthesis 2. potassium
2. Relative molecular mass, M r - The relative molecular mass of a molecule is the average mass of the one molecule when compared with
 Chapter 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations 1. Relative atomic mass, A r - The relative atomic mass of an element is the average mass of one atom of an element when compared with mass of an atom of carbon-12
Chapter 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations 1. Relative atomic mass, A r - The relative atomic mass of an element is the average mass of one atom of an element when compared with mass of an atom of carbon-12
Salts Soluble Insoluble Nitrate salts - All nitrate salts - Carbonate salts - Potassium carbonate, K 2 CO. Except
 Chapter 8: Salts 1. Salts - A salt is an ionic compound. - The anion part comes from the acid while the cation part comes from a base. - Example: KCl, KOH(aq) + HCl(aq) KCl(aq) + H 2 O(l) - A salt is a
Chapter 8: Salts 1. Salts - A salt is an ionic compound. - The anion part comes from the acid while the cation part comes from a base. - Example: KCl, KOH(aq) + HCl(aq) KCl(aq) + H 2 O(l) - A salt is a
Unit 1 - Foundations of Chemistry
 Unit 1 - Foundations of Chemistry Chapter 2 - Chemical Reactions Unit 1 - Foundations of Chemistry 1 / 42 2.1 - Chemical Equations Physical and Chemical Changes Physical change: A substance changes its
Unit 1 - Foundations of Chemistry Chapter 2 - Chemical Reactions Unit 1 - Foundations of Chemistry 1 / 42 2.1 - Chemical Equations Physical and Chemical Changes Physical change: A substance changes its
Chemical Bonds In elements and compounds, the atoms are held together by chemical bonds.
 Chemical Bonds In elements and compounds, the atoms are held together by chemical bonds. Forming a bond makes an atom more stable, so atoms form as many bonds are they are able to. Bonds are made using
Chemical Bonds In elements and compounds, the atoms are held together by chemical bonds. Forming a bond makes an atom more stable, so atoms form as many bonds are they are able to. Bonds are made using
Qualitative Analysis Part Two Anions & Gases
 Qualitative Analysis Part Two Anions & Gases Qualitative Tests for Anions Which anions must I know the tests for? Describe tests to identify the following anions: Carbonate CO 3 2 (by the addition of dilute
Qualitative Analysis Part Two Anions & Gases Qualitative Tests for Anions Which anions must I know the tests for? Describe tests to identify the following anions: Carbonate CO 3 2 (by the addition of dilute
Chapter 8 Chemical Reactions
 Chemistry/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 8 Chemical Reactions Chapter 8: 1 7, 9 18, 20, 21, 24 26, 29 31, 46, 55, 69 Practice Problems 1. Write a skeleton equation for each chemical reaction. Include the appropriate
Chemistry/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 8 Chemical Reactions Chapter 8: 1 7, 9 18, 20, 21, 24 26, 29 31, 46, 55, 69 Practice Problems 1. Write a skeleton equation for each chemical reaction. Include the appropriate
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2014 Solution SECTION I
 ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2014 Solution SECTION I Answer 1 1) D 2) B 3) C 4) A 5) C 6) A 7) D 8) C 9) A 10) D 11) 1 12) Sodium ethoxide 13) CaO is alkaline 14) Downward displacement of air
ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper 2014 Solution SECTION I Answer 1 1) D 2) B 3) C 4) A 5) C 6) A 7) D 8) C 9) A 10) D 11) 1 12) Sodium ethoxide 13) CaO is alkaline 14) Downward displacement of air
Question 8 Chemical properties of metals and nonmetals. 1) magnesium 2) sulfur trioxide 3) iron (II) hydroxide 4) sodium nitrate
 Question 8 Chemical properties of metals and nonmetals 1. Calcium oxide doesn t react with 1) NaNO 3 2) HCl 3) CO 2 4) H 2 O 2. Calcium oxide reacts with both of the following 1) SO 2 and O 2 2) H 2 O
Question 8 Chemical properties of metals and nonmetals 1. Calcium oxide doesn t react with 1) NaNO 3 2) HCl 3) CO 2 4) H 2 O 2. Calcium oxide reacts with both of the following 1) SO 2 and O 2 2) H 2 O
Qualitative Analysis Part One: Cations
 Qualitative Analysis Part One: Cations Qualitative analysis is a structured set of methods used to determine the identities (but not the amounts) of the components that make up a mixture. Qualitative
Qualitative Analysis Part One: Cations Qualitative analysis is a structured set of methods used to determine the identities (but not the amounts) of the components that make up a mixture. Qualitative
5072 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH SPA) BASIC TECHNIQUES 5067 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH PRACTICAL EXAM) BASIC TECHNIQUES
 5072 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH SPA) BASIC TECHNIQUES 5067 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH PRACTICAL EXAM) BASIC TECHNIQUES LEARNING OUTCOMES a) Be able to write formulae of simple compounds b) Be able to write
5072 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH SPA) BASIC TECHNIQUES 5067 CHEMISTRY (NEW PAPERS WITH PRACTICAL EXAM) BASIC TECHNIQUES LEARNING OUTCOMES a) Be able to write formulae of simple compounds b) Be able to write
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
Acid, Bases and Salts (IGCSE Chemistry Syllabus )
 Acid, Bases and Salts (IGCSE Chemistry Syllabus 2016-2018) Acid o A compound when dissolved in water produces hydrogen ions (H + ) ; proton (H + ) donor o It turns blue damp litmus paper to red o ph 1
Acid, Bases and Salts (IGCSE Chemistry Syllabus 2016-2018) Acid o A compound when dissolved in water produces hydrogen ions (H + ) ; proton (H + ) donor o It turns blue damp litmus paper to red o ph 1
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
WRITING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS 2002, 1989 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Permission for classroom used provided original copyright is included.
 WRITING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS 2002, 1989 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Permission for classroom used provided original copyright is included. David A. Katz Chemist, Educator, Science Communicator,
WRITING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS 2002, 1989 by David A. Katz. All rights reserved. Permission for classroom used provided original copyright is included. David A. Katz Chemist, Educator, Science Communicator,
Balancing Equations Notes
 . Unit 6 Chemical Equations and Reactions What is a Chemical Equation? A Chemical Equation is a written representation of the process that occurs in a chemical reaction. A chemical equation is written
. Unit 6 Chemical Equations and Reactions What is a Chemical Equation? A Chemical Equation is a written representation of the process that occurs in a chemical reaction. A chemical equation is written
CHEMISTRY PAPER 1999
 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1999 (One and a half hours) Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will NOT be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent
CHEMISTRY PAPER 1999 (One and a half hours) Answers to this paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will NOT be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent
Unit 5: Chemical Equations and Reactions & Stoichiometry
 pg. 10 Unit 5: Chemical Equations and Reactions & Stoichiometry Chapter 8: Chemical Equations and Reactions 8.1: Describing Chemical Reactions Selected Chemistry Assignment Answers (Section Review on pg.
pg. 10 Unit 5: Chemical Equations and Reactions & Stoichiometry Chapter 8: Chemical Equations and Reactions 8.1: Describing Chemical Reactions Selected Chemistry Assignment Answers (Section Review on pg.
Chemical Equations and Chemical Reactions
 Chemical Equations Chemical Equations and Chemical Reactions Chemical equations are concise representations of chemical reactions. Chemical Equations Symbols Used in Chemical Equations The formulas of
Chemical Equations Chemical Equations and Chemical Reactions Chemical equations are concise representations of chemical reactions. Chemical Equations Symbols Used in Chemical Equations The formulas of
For the element X in the ionic compound MX, explain the meaning of the term oxidation state.
 1. (a) By referring to electrons, explain the meaning of the term oxidising agent.... For the element X in the ionic compound MX, explain the meaning of the term oxidation state.... (c) Complete the table
1. (a) By referring to electrons, explain the meaning of the term oxidising agent.... For the element X in the ionic compound MX, explain the meaning of the term oxidation state.... (c) Complete the table
Balancing CHEMICAL EQUATIONS
 Balancing CHEMICAL EQUATIONS CHEMICAL REACTIONS involves a chemical change in the identity of one or more chemical species Ex. Rusting of iron (Fe): chemical rxn btwn water and iron involve the breaking
Balancing CHEMICAL EQUATIONS CHEMICAL REACTIONS involves a chemical change in the identity of one or more chemical species Ex. Rusting of iron (Fe): chemical rxn btwn water and iron involve the breaking
Unit 8 Chemical Reactions- Funsheets
 Part A- Balancing Equations and Types of Reactions Balance AND identify the following reactions: Unit 8 Chemical Reactions- Funsheets 1) Mg + Zn(NO 3) 2 Zn Mg(NO 3) 2 2) Ba + AgNO 3 Ag + Ba(NO 3) 2 3)
Part A- Balancing Equations and Types of Reactions Balance AND identify the following reactions: Unit 8 Chemical Reactions- Funsheets 1) Mg + Zn(NO 3) 2 Zn Mg(NO 3) 2 2) Ba + AgNO 3 Ag + Ba(NO 3) 2 3)
CHAPTER 1 QUANTITATIVE CHEMISTRY
 Page 4 Ex 4 (a) element; (b) mixture; (c) compound; (d) element; (e) compound 5. (a) mixture; (b) compound; (c) mixture; (d) element; (e) compound. Page 5 Ex 1.1 3. C 4. D 5. C 6. D 7. a) 0.20 b) 1.2 10
Page 4 Ex 4 (a) element; (b) mixture; (c) compound; (d) element; (e) compound 5. (a) mixture; (b) compound; (c) mixture; (d) element; (e) compound. Page 5 Ex 1.1 3. C 4. D 5. C 6. D 7. a) 0.20 b) 1.2 10
Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions & Equations
 CBSE Class 10th NCERT Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions & Equations Intext Questions On Page 6 Question 1: Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? Magnesium is an extremely reactive
CBSE Class 10th NCERT Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions & Equations Intext Questions On Page 6 Question 1: Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? Magnesium is an extremely reactive
Chapter 6. Chemical Reactions. Sodium reacts violently with bromine to form sodium bromide.
 Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions Sodium reacts violently with bromine to form sodium bromide. Evidence of Chemical Reactions Chemical Equations Reactants Products Reactant(s): Substance(s) present before the
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions Sodium reacts violently with bromine to form sodium bromide. Evidence of Chemical Reactions Chemical Equations Reactants Products Reactant(s): Substance(s) present before the
ICSE Chemistry Board Paper 2016
 2015 Time: 2 hours; Max. Marks: 80 General Instructions: Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed 10 write during the first 15 minutes. This time
2015 Time: 2 hours; Max. Marks: 80 General Instructions: Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed 10 write during the first 15 minutes. This time
Solution Stoichiometry
 Chapter 8 Solution Stoichiometry Note to teacher: You will notice that there are two different formats for the Sample Problems in the student textbook. Where appropriate, the Sample Problem contains the
Chapter 8 Solution Stoichiometry Note to teacher: You will notice that there are two different formats for the Sample Problems in the student textbook. Where appropriate, the Sample Problem contains the
SCH 3UI Unit 5 Outline Chemical Reactions Homework Questions and Assignments complete handouts: Balancing Equations #1, #2, #3, #4
 Lesson Topics Covered 1 Note: Chemical Reactions and Chemical Equations definition of chemical reaction four signs of chemical change the Law of Conservation of Mass balancing chemical equations SCH 3UI
Lesson Topics Covered 1 Note: Chemical Reactions and Chemical Equations definition of chemical reaction four signs of chemical change the Law of Conservation of Mass balancing chemical equations SCH 3UI
Ch 7 Chemical Reactions Study Guide Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON
 Ch 7 Chemical Reactions Study Guide Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON Name /80 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. Correct the False statments by changing the
Ch 7 Chemical Reactions Study Guide Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON Name /80 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. Correct the False statments by changing the
Unit Learning Targets (L.T.):
 Unit 9: Chemical Equations and Reactions Chapters 8 and 19 Name Block Unit Learning Targets (L.T.): By the end of the unit, students will be able to: Chapter 8: 1. Correctly write and balance chemical
Unit 9: Chemical Equations and Reactions Chapters 8 and 19 Name Block Unit Learning Targets (L.T.): By the end of the unit, students will be able to: Chapter 8: 1. Correctly write and balance chemical
Types of Reactions. There are five types of chemical reactions we observed in the lab:
 Chemical Reactions Acids and Bases Acids: Form hydrogen ions (H + ) when dissolved in water. HCl (aq) H + (aq) + Cl - (aq) Examples: HCl (hydrochloric acid), HNO 3 (nitric acid), H 2 SO 4 (sulfuric acid),
Chemical Reactions Acids and Bases Acids: Form hydrogen ions (H + ) when dissolved in water. HCl (aq) H + (aq) + Cl - (aq) Examples: HCl (hydrochloric acid), HNO 3 (nitric acid), H 2 SO 4 (sulfuric acid),
UNIT (4) CALCULATIONS AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS
 UNIT (4) CALCULATIONS AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS 4.1 Formula Masses Recall that the decimal number written under the symbol of the element in the periodic table is the atomic mass of the element. Atomic mass
UNIT (4) CALCULATIONS AND CHEMICAL REACTIONS 4.1 Formula Masses Recall that the decimal number written under the symbol of the element in the periodic table is the atomic mass of the element. Atomic mass
TOPIC 6. CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND IONIC EQUATIONS.
 TOPIC 6. CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND IONIC EQUATIONS. Reactions involving ionic compounds. As discussed earlier, ionically bonded compounds consist of large aggregations of cations and anions which pack together
TOPIC 6. CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND IONIC EQUATIONS. Reactions involving ionic compounds. As discussed earlier, ionically bonded compounds consist of large aggregations of cations and anions which pack together
TOPIC 6. CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND IONIC EQUATIONS.
 TOPIC 6. CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND IONIC EQUATIONS. Reactions involving ionic compounds. As discussed earlier, ionically bonded compounds consist of large aggregations of cations and anions which pack together
TOPIC 6. CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND IONIC EQUATIONS. Reactions involving ionic compounds. As discussed earlier, ionically bonded compounds consist of large aggregations of cations and anions which pack together
BALANCING EQUATIONS NOTES
 BALANCING EQUATIONS NOTES WHY DO WE NEED TO BALANCE CHEMICAL EQUATIONS? The LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MASS says that matter cannot be created or destroyed. In other words, you cannot end up with any more
BALANCING EQUATIONS NOTES WHY DO WE NEED TO BALANCE CHEMICAL EQUATIONS? The LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MASS says that matter cannot be created or destroyed. In other words, you cannot end up with any more
Chem!stry. Assignment on Redox
 Chem!stry Name: ( ) Class: Date: / / Assignment on Redox Question 1: Which one of the following elements is the most powerful reducing agent? A Aluminium B Copper C Lead D Potassium Question 2: Which of
Chem!stry Name: ( ) Class: Date: / / Assignment on Redox Question 1: Which one of the following elements is the most powerful reducing agent? A Aluminium B Copper C Lead D Potassium Question 2: Which of
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E.
 MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - II - SET -A 020 Periodic Table, Chemical bonding, Acid, Bases and Salts, Practical Work, Mole Concept, Electrolysis Chemistry
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - II - SET -A 020 Periodic Table, Chemical bonding, Acid, Bases and Salts, Practical Work, Mole Concept, Electrolysis Chemistry
CHEMICAL REACTIONS. The process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances
 CHEMICAL REACTIONS The process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances Equations Reactions are represented by a chemical equation Reactants Products Must have
CHEMICAL REACTIONS The process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances Equations Reactions are represented by a chemical equation Reactants Products Must have
CHEMISTRY 135 REVISION OF NAMES, FORMULAE AND EQUATIONS
 CHEMISTRY 135 REVISION OF NAMES, FORMULAE AND EQUATIONS Answer the following questions as if you were going to hand them in for marking. You will be tested on them in class time. 1) Give the correct chemical
CHEMISTRY 135 REVISION OF NAMES, FORMULAE AND EQUATIONS Answer the following questions as if you were going to hand them in for marking. You will be tested on them in class time. 1) Give the correct chemical
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level CHEMISTRY 9701/03
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level CHEMISTRY 9701/03 Paper 3 Practical Test Candidates answer on the Question
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level CHEMISTRY 9701/03 Paper 3 Practical Test Candidates answer on the Question
Chemical Reactions. Ch. 11 Chemical Reactions. Chemical Reactions. Chemical Reactions
 Chemical Reactions Ch. 11 Chemical Reactions when a substance changes identity Reactants - original Products - resulting law of conservation of mass total mass of reactants = total mass of products In
Chemical Reactions Ch. 11 Chemical Reactions when a substance changes identity Reactants - original Products - resulting law of conservation of mass total mass of reactants = total mass of products In
Chapter 4. Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
 Sample Exercise 4.1 (p. 127) The diagram below represents an aqueous solution of one of the following compounds: MgCl 2, KCl, or K 2 SO 4. Which solution does it best represent? Practice Exercise 1 (4.1)
Sample Exercise 4.1 (p. 127) The diagram below represents an aqueous solution of one of the following compounds: MgCl 2, KCl, or K 2 SO 4. Which solution does it best represent? Practice Exercise 1 (4.1)
Acids and Bases. Part A Unit-based exercise. Topic 4. Unit 14 Acids and alkalis. Fill in the blanks. 1 hydrochloric. 2 Sulphuric. 3 Ethanoic.
 Topic 4 Acids and Bases Part A Unit-based exercise Unit 14 Acids and alkalis Fill in the blanks 1 hydrochloric 2 Sulphuric 3 Ethanoic 4 sour 5 red; yellow 6 colourless; red 7 bases 8 dissociate; dissociation
Topic 4 Acids and Bases Part A Unit-based exercise Unit 14 Acids and alkalis Fill in the blanks 1 hydrochloric 2 Sulphuric 3 Ethanoic 4 sour 5 red; yellow 6 colourless; red 7 bases 8 dissociate; dissociation
Balancing Equations Notes
 . Unit 9 Chemical Equations and Reactions What is a Chemical Equation? A is a written representation of the process that occurs in a chemical reaction. A chemical equation is written with the (starting
. Unit 9 Chemical Equations and Reactions What is a Chemical Equation? A is a written representation of the process that occurs in a chemical reaction. A chemical equation is written with the (starting
CHEMICAL REACTIONS. Introduction. Chemical Equations
 CHEMICAL REACTIONS Chemistry I Chapter 7 1 Chemical Equations Their Job: Depict the kind of reactants and products and their relative amounts in a reaction. 4 Al (s) + 3 O 2 (g) ---> 2 Al 2 O 3 (s) The
CHEMICAL REACTIONS Chemistry I Chapter 7 1 Chemical Equations Their Job: Depict the kind of reactants and products and their relative amounts in a reaction. 4 Al (s) + 3 O 2 (g) ---> 2 Al 2 O 3 (s) The
1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
 1 Intext Questions On Page 6 Question 1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? Magnesium ribbon reacts with CO present in air to form a protective and inert layer of magnesium
1 Intext Questions On Page 6 Question 1. Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air? Magnesium ribbon reacts with CO present in air to form a protective and inert layer of magnesium
THE ST. MICHAEL SCHOOL THIRD FORM CHEMISTRY MANUAL 3 SYMBOLS AND FORMULAE, CHEMICAL BONDING AND CHEMICAL EQUATIONS
 1 THE ST. MICHAEL SCHOOL THIRD FORM CHEMISTRY MANUAL 3 SYMBOLS AND FORMULAE, CHEMICAL BONDING AND CHEMICAL EQUATIONS COMPILED BY G.WALKER, L.WORRELL, T. HARDING REFERENCE BOOKS Anne Tindale Chemistry A
1 THE ST. MICHAEL SCHOOL THIRD FORM CHEMISTRY MANUAL 3 SYMBOLS AND FORMULAE, CHEMICAL BONDING AND CHEMICAL EQUATIONS COMPILED BY G.WALKER, L.WORRELL, T. HARDING REFERENCE BOOKS Anne Tindale Chemistry A
Unit 4: Reactions and Stoichiometry
 Unit 4: Reactions and Stoichiometry Reactions Chemical equation Expression representing a chemical reaction Formulas of reactants on the left side Formulas of products on the right side Arrow(s) connect(s)
Unit 4: Reactions and Stoichiometry Reactions Chemical equation Expression representing a chemical reaction Formulas of reactants on the left side Formulas of products on the right side Arrow(s) connect(s)
Balancing Equations Notes
 . Unit 9 Chemical Equations and Reactions What is a Chemical Equation? A Chemical Equation is a written representation of the process that occurs in a chemical reaction. A chemical equation is written
. Unit 9 Chemical Equations and Reactions What is a Chemical Equation? A Chemical Equation is a written representation of the process that occurs in a chemical reaction. A chemical equation is written
Identification of ions and gases
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Identification Of ions nd Gases Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub-Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Identification Of ions nd Gases Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub-Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International
Danyal Education (Contact: ) A commitment to teach and nurture
 Chemistry of Reactions: Redox (#) Candidates should be able to: a) define oxidation and reduction (redox) in terms of oxygen/hydrogen gain/loss b) define redox in terms of electron transfer and changes
Chemistry of Reactions: Redox (#) Candidates should be able to: a) define oxidation and reduction (redox) in terms of oxygen/hydrogen gain/loss b) define redox in terms of electron transfer and changes
Redox. Question Paper. Cambridge International Examinations Chemical Reactions. Score: /43. Percentage: /100
 Redox Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub-Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations hemical Reactions Redox Question Paper Time llowed: 52 minutes Score: /43 Percentage:
Redox Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub-Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations hemical Reactions Redox Question Paper Time llowed: 52 minutes Score: /43 Percentage:
CHEMICAL REACTIONS. Types of Reactions. Steps to Writing Reactions
 Types of Reactions CHEMICAL REACTIONS There are five types of chemical reactions we will talk about: 1. Synthesis reactions 2. reactions 3. Single displacement reactions 4. reactions 5. Combustion reactions
Types of Reactions CHEMICAL REACTIONS There are five types of chemical reactions we will talk about: 1. Synthesis reactions 2. reactions 3. Single displacement reactions 4. reactions 5. Combustion reactions
Various Types of Reactions
 Various Types of Reactions Matthew Park Outline: 1. Synthesis / Replacement / Decomposition Reactions 2. Precipitation Reactions 3. Acid-Base Reactions 4. Summary: Metathesis Reactions NOTE: Not all of
Various Types of Reactions Matthew Park Outline: 1. Synthesis / Replacement / Decomposition Reactions 2. Precipitation Reactions 3. Acid-Base Reactions 4. Summary: Metathesis Reactions NOTE: Not all of
(DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST)
 Final Prep Chap 8&9 (DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. After the correct formula for a reactant in an equation
Final Prep Chap 8&9 (DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. After the correct formula for a reactant in an equation
Chemical Reactions and Equations
 Chemical Reactions and Equations 5-1 5.1 What is a Chemical Reaction? A chemical reaction is a chemical change. A chemical reaction occurs when one or more substances is converted into one or more new
Chemical Reactions and Equations 5-1 5.1 What is a Chemical Reaction? A chemical reaction is a chemical change. A chemical reaction occurs when one or more substances is converted into one or more new
Unit Two Worksheet WS DC U2
 Unit Two Worksheet WS DC U2 Name Period Short Answer [Writing]. Write skeleton equations representing the following reactions and then balance them. Then identify the reaction type. Include all needed
Unit Two Worksheet WS DC U2 Name Period Short Answer [Writing]. Write skeleton equations representing the following reactions and then balance them. Then identify the reaction type. Include all needed
insoluble partial very soluble (< 0.1 g/100ml) solubility (> 1 g/100ml) Factors Affecting Solubility in Water
 Aqueous Solutions Solubility is a relative term since all solutes will have some solubility in water. Insoluble substances simply have extremely low solubility. The solubility rules are a general set of
Aqueous Solutions Solubility is a relative term since all solutes will have some solubility in water. Insoluble substances simply have extremely low solubility. The solubility rules are a general set of
8 Chemical Equations. Flames and sparks result when aluminum foil is dropped into liquid bromine.
 8 Chemical Equations Flames and sparks result when aluminum foil is dropped into liquid bromine. Chapter Outline 8.1 The Chemical Equation 8.2 Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations 8.3 Types of Chemical
8 Chemical Equations Flames and sparks result when aluminum foil is dropped into liquid bromine. Chapter Outline 8.1 The Chemical Equation 8.2 Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations 8.3 Types of Chemical
THE MOLE - PART 2. Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 THE MOLE - PART 2 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which one of the following statements is a quantitative observation? a.
THE MOLE - PART 2 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which one of the following statements is a quantitative observation? a.
elemental state. There are two different possibilities: DESCRIPTION 1. One cation (+ ion) replaces another. 2. One anion (- ion) replaces another.
 CHEMICAL TYPES HANDOUT In these reactions, a free element reacts with a compound to form another compound and release one of the elements of the original compound in the elemental state. There are two
CHEMICAL TYPES HANDOUT In these reactions, a free element reacts with a compound to form another compound and release one of the elements of the original compound in the elemental state. There are two
Chem 101 Practice Exam 3 Fall 2012 You will have a Solubility Table and Periodic Table
 Chem 101 Practice Exam Fall 01 You will have a Solubility Table and Periodic Table 1. A 1.6-mol sample of KClO was decomposed according to the equation KClO (s) KCl(s) O (g) How many moles of O are formed
Chem 101 Practice Exam Fall 01 You will have a Solubility Table and Periodic Table 1. A 1.6-mol sample of KClO was decomposed according to the equation KClO (s) KCl(s) O (g) How many moles of O are formed
Study Guide: Stoichiometry
 Name: Study Guide: Stoichiometry Period: **YOUR ANSWERS MUST INCLUDE THE PROPER NUMBER OF SIG FIGS AND COMPLETE UNITS IN ORDER TO RECEIVE CREDIT FOR THE PROBLEM.** BALANCE THE FOLLOWING EQUATIONS TO USE
Name: Study Guide: Stoichiometry Period: **YOUR ANSWERS MUST INCLUDE THE PROPER NUMBER OF SIG FIGS AND COMPLETE UNITS IN ORDER TO RECEIVE CREDIT FOR THE PROBLEM.** BALANCE THE FOLLOWING EQUATIONS TO USE
CHAPTER Describing Chemical Reactions Reactants Products. New substances produced The arrow means yields TYPES OF EQUATIONS.
 CHAPTER 11 Chemical Reactions 11.1 Describing Chemical Reactions Reactants Products New substances produced The arrow means yields Where do Chemical Reactions occur? Everywhere!!! In living organisms In
CHAPTER 11 Chemical Reactions 11.1 Describing Chemical Reactions Reactants Products New substances produced The arrow means yields Where do Chemical Reactions occur? Everywhere!!! In living organisms In
LLT Education Services
 Rahul Arora 18. What chemical reaction is involved in the corrosion of iron? 19. Aluminum metal when burnt in air forms aluminium oxide. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction. 20. Is the
Rahul Arora 18. What chemical reaction is involved in the corrosion of iron? 19. Aluminum metal when burnt in air forms aluminium oxide. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction. 20. Is the
Unit 4. Chemical Calculations
 Index Unit 4. Chemical Calculations 1.- Chemical reactions...2 1.1.- What is a chemical reaction?...2 1.2 The law of conservation of mass...2 1.3 Balance of chemical reactions...2 1.4.- Rate of reaction...3
Index Unit 4. Chemical Calculations 1.- Chemical reactions...2 1.1.- What is a chemical reaction?...2 1.2 The law of conservation of mass...2 1.3 Balance of chemical reactions...2 1.4.- Rate of reaction...3
IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice
 IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice 1. What are the oxidation states of chromium in (NH 4) 2Cr 2O 7 (s) and Cr 2O 3 (s)? 2. Which of the following is a redox reaction? 3Mg (s) + 2AlCl 3 (aq) 2Al
IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice 1. What are the oxidation states of chromium in (NH 4) 2Cr 2O 7 (s) and Cr 2O 3 (s)? 2. Which of the following is a redox reaction? 3Mg (s) + 2AlCl 3 (aq) 2Al
Set 4 Marking Scheme: Acid Bases & Salts 2010
 Set 4 Marking Scheme: Acid Bases & Salts 00 ACID AND BASES PAPER : STRUCTURE (a) Neutralisation KOH + H SO 4 K SO 4 + H O Correct formulae of reactants and products Balanced equation i. H +, OH -, K +
Set 4 Marking Scheme: Acid Bases & Salts 00 ACID AND BASES PAPER : STRUCTURE (a) Neutralisation KOH + H SO 4 K SO 4 + H O Correct formulae of reactants and products Balanced equation i. H +, OH -, K +
Chemical Reactions Chapter 11 Study Guide (Unit 8)
 Name: Hr: Understand and be able to explain all of the key concepts. Define and understand all of the survival words Memorize the names and symbols for these elements: (Ag, Al, Ar, As, Au, B, Ba, Be, Br,
Name: Hr: Understand and be able to explain all of the key concepts. Define and understand all of the survival words Memorize the names and symbols for these elements: (Ag, Al, Ar, As, Au, B, Ba, Be, Br,
1) What is the volume of a tank that can hold Kg of methanol whose density is 0.788g/cm 3?
 1) Convert the following 1) 125 g to Kg 6) 26.9 dm 3 to cm 3 11) 1.8µL to cm 3 16) 4.8 lb to Kg 21) 23 F to K 2) 21.3 Km to cm 7) 18.2 ml to cm 3 12) 2.45 L to µm 3 17) 1.2 m to inches 22) 180 ºC to K
1) Convert the following 1) 125 g to Kg 6) 26.9 dm 3 to cm 3 11) 1.8µL to cm 3 16) 4.8 lb to Kg 21) 23 F to K 2) 21.3 Km to cm 7) 18.2 ml to cm 3 12) 2.45 L to µm 3 17) 1.2 m to inches 22) 180 ºC to K
9.1 Qualitative Analysis
 Chemistry Form 4 Page 44 Ms. R. Buttigieg Test for positive Ions (Cations) 9.1 Qualitative Analysis 1) Flame Tests Nichrome wire is dipped in concentrated hydrochloric acid, then in the salt being tested.
Chemistry Form 4 Page 44 Ms. R. Buttigieg Test for positive Ions (Cations) 9.1 Qualitative Analysis 1) Flame Tests Nichrome wire is dipped in concentrated hydrochloric acid, then in the salt being tested.
IONIC CHARGES. Chemistry 51 Review
 IONIC CHARGES The ionic charge of an ion is dependent on the number of electrons lost or gained to attain a noble gas configuration. For most main group elements, the ionic charges can be determined from
IONIC CHARGES The ionic charge of an ion is dependent on the number of electrons lost or gained to attain a noble gas configuration. For most main group elements, the ionic charges can be determined from
Chemical Reactions. Burlingame High School Chemistry 1
 Chemical Reactions 1 Chemical Equations Chemical equations are use to describe: the substances that react, the reactants the substances that are formed, the products the relative amounts of all substances
Chemical Reactions 1 Chemical Equations Chemical equations are use to describe: the substances that react, the reactants the substances that are formed, the products the relative amounts of all substances
ICSE QUESTION PAPER Class X Chemistry (2016) Solution
 ICSE QUESTION PAPER Class X Chemistry (016) Solution Section I 1. Metals are good reducing agents because they are electron donors. Electrovalent compounds have high melting points. (iii) Higher the ph
ICSE QUESTION PAPER Class X Chemistry (016) Solution Section I 1. Metals are good reducing agents because they are electron donors. Electrovalent compounds have high melting points. (iii) Higher the ph
Set 1 Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation Question Explanation Marks
 Set Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation 200 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMS PAPER 2 : STRUCTURE Question Explanation Marks (a)(i) Diffusion Molecules - Made of tiny / discrete particles/
Set Marking Scheme: The Structure of the Atom & Chemical Equation 200 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATOMS PAPER 2 : STRUCTURE Question Explanation Marks (a)(i) Diffusion Molecules - Made of tiny / discrete particles/
Acids and Alkalis. Looking at acids and alkalis. 1 hydrochloric. 2 sour. 3 bases. 4 ionize, ionization. 5 hydrogen. 6 mobile ions.
 Topic 4 Acids and Alkalis Section A Fill in the blanks Unit 1 Looking at acids and alkalis 1 hydrochloric 2 sour bases 4 ionize, ionization 5 hydrogen 6 mobile ions 7 basicity 8 monobasic 9 dibasic 10
Topic 4 Acids and Alkalis Section A Fill in the blanks Unit 1 Looking at acids and alkalis 1 hydrochloric 2 sour bases 4 ionize, ionization 5 hydrogen 6 mobile ions 7 basicity 8 monobasic 9 dibasic 10
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
 TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS Precipitation Reactions Compounds Soluble Ionic Compounds 1. Group 1A cations and NH 4 + 2. Nitrates (NO 3 ) Acetates (CH 3 COO ) Chlorates (ClO 3 ) Perchlorates (ClO 4 ) Solubility
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS Precipitation Reactions Compounds Soluble Ionic Compounds 1. Group 1A cations and NH 4 + 2. Nitrates (NO 3 ) Acetates (CH 3 COO ) Chlorates (ClO 3 ) Perchlorates (ClO 4 ) Solubility
NATIONAL 5 CHEMISTRY
 Farr High School NATIONAL 5 CHEMISTRY Unit 1 Chemical Changes and Structure Question Booklet 1 Rates of Reaction 1. Explain how the following would affect the rate of the reaction between 1.0 g of magnesium
Farr High School NATIONAL 5 CHEMISTRY Unit 1 Chemical Changes and Structure Question Booklet 1 Rates of Reaction 1. Explain how the following would affect the rate of the reaction between 1.0 g of magnesium
Identification of Ions and Gases
 Identification of Ions and Gases Question Paper 1 Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620/0971) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic cids, bases and salts Sub-Topic Identification of ions
Identification of Ions and Gases Question Paper 1 Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620/0971) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic cids, bases and salts Sub-Topic Identification of ions
flame test acidified silver nitrate solution added
 1 The results of two tests on solid X are shown. test aqueous sodium hydroxide added acidified silver nitrate added observation green precipitate formed yellow precipitate formed What is X? copper(ii)
1 The results of two tests on solid X are shown. test aqueous sodium hydroxide added acidified silver nitrate added observation green precipitate formed yellow precipitate formed What is X? copper(ii)
Name Period CH 180 Practice Test: Chapters 3 and 4
 Name Period CH 180 Practice Test: Chapters 3 and 4 Multiple Choice: 1. 11. 2. 12. 3. 13. 4. 14. 5. 15. 6. 16. 7. 17. 8. 18. 9. 19. 10. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 1 Directions: Answer all questions.
Name Period CH 180 Practice Test: Chapters 3 and 4 Multiple Choice: 1. 11. 2. 12. 3. 13. 4. 14. 5. 15. 6. 16. 7. 17. 8. 18. 9. 19. 10. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 1 Directions: Answer all questions.
Unit 9 Stoichiometry Notes
 Unit 9 Stoichiometry Notes Stoichiometry is a big word for a process that chemist s use to calculate amounts in reactions. It makes use of the coefficient ratio set up by balanced reaction equations to
Unit 9 Stoichiometry Notes Stoichiometry is a big word for a process that chemist s use to calculate amounts in reactions. It makes use of the coefficient ratio set up by balanced reaction equations to
Chemistry. Bridging the Gap Summer Homework. Name..
 Chemistry Bridging the Gap Summer Homework Name.. Standard Form Number Number in standard form 0.008 8 x 10-3 0.07 7 x 10-2 0.55 5.5 x 10-1 0.000052 0.048 0.0086 0.00086 0.000086 0.0000000001 0.000455
Chemistry Bridging the Gap Summer Homework Name.. Standard Form Number Number in standard form 0.008 8 x 10-3 0.07 7 x 10-2 0.55 5.5 x 10-1 0.000052 0.048 0.0086 0.00086 0.000086 0.0000000001 0.000455
PRACTICE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS FOR 1.2 AMOUNT OF SUBSTANCE
 PRACTICE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS FOR 1.2 AMOUNT OF SUBSTANCE 1. Nitroglycerine, C 3 H 5 N 3 O 9, is an explosive which, on detonation, decomposes rapidly to form a large number of gaseous molecules. The
PRACTICE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS FOR 1.2 AMOUNT OF SUBSTANCE 1. Nitroglycerine, C 3 H 5 N 3 O 9, is an explosive which, on detonation, decomposes rapidly to form a large number of gaseous molecules. The
Chemical Reactions CHAPTER Reactions and Equations
 CHAPTER 9 Chemical Reactions 9.1 Reactions and Equations The process by which atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances is called a chemical reaction. There are a number
CHAPTER 9 Chemical Reactions 9.1 Reactions and Equations The process by which atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form different substances is called a chemical reaction. There are a number
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015
 Grade 11B Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Chemistry - I Duration: 1.00 Hour Part 1 1) A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 o C. Which other property of the liquid
Grade 11B Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Chemistry - I Duration: 1.00 Hour Part 1 1) A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 o C. Which other property of the liquid
SCH4U Chemistry Review: Fundamentals
 SCH4U Chemistry Review: Fundamentals Particle Theory of Matter Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Anything around us and in the entire universe can be classified as either matter or energy.
SCH4U Chemistry Review: Fundamentals Particle Theory of Matter Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Anything around us and in the entire universe can be classified as either matter or energy.
NCEA Chemistry 2.2 Identify Ions AS 91162
 NCEA Chemistry 2.2 Identify Ions AS 91162 What is this NCEA Achievement Standard? When a student achieves a standard, they gain a number of credits. Students must achieve a certain number of credits to
NCEA Chemistry 2.2 Identify Ions AS 91162 What is this NCEA Achievement Standard? When a student achieves a standard, they gain a number of credits. Students must achieve a certain number of credits to
What is one of the spectator ions (with correct coefficient)? A)
 Chem 101 Exam Fall 01 Section 001 1. Based on the solubility rules Mg (PO 4 ) is A) soluble B) insoluble. An aqueous solution of potassium sulfate is allowed to react with an aqueous solution of What is
Chem 101 Exam Fall 01 Section 001 1. Based on the solubility rules Mg (PO 4 ) is A) soluble B) insoluble. An aqueous solution of potassium sulfate is allowed to react with an aqueous solution of What is
SNC2D Chemistry Review
 SNC2D Chemistry Review 1. For each of the following elements: (a) Draw the Bohr-Rutherford diagram for the neutral atom (b) Determine the charge of the ion each element forms (c) Draw the Lewis dot diagram
SNC2D Chemistry Review 1. For each of the following elements: (a) Draw the Bohr-Rutherford diagram for the neutral atom (b) Determine the charge of the ion each element forms (c) Draw the Lewis dot diagram
CHEMICAL REACTIONS & EQUATIONS
 CHEMICAL REACTIONS & EQUATIONS PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGE In our daily life many processes occur around us. Some of them do not lead to formation of any new substance, while others may lead to formation
CHEMICAL REACTIONS & EQUATIONS PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGE In our daily life many processes occur around us. Some of them do not lead to formation of any new substance, while others may lead to formation
11-1 Notes. Chemical Reactions
 11-1 Notes Chemical Reactions Chemical Reactions In a chemical reaction 1 or more substances (the reactants) change into 1 or more new substances (the products). Reactants are always written on the left
11-1 Notes Chemical Reactions Chemical Reactions In a chemical reaction 1 or more substances (the reactants) change into 1 or more new substances (the products). Reactants are always written on the left
3. Solids cannot conduct electricity because the ions cannot move freely 4. Electrolytic cell
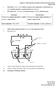 Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
ed. Brad Collins Aqueous Chemistry Chapter 5 Some images copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sunday, August 18, 13
 ed. Brad Collins Aqueous Chemistry Chapter 5 Some images copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. A solution is a homogenous mixture of 2 or more substances at the molecular level The solute(s) is(are)
ed. Brad Collins Aqueous Chemistry Chapter 5 Some images copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. A solution is a homogenous mixture of 2 or more substances at the molecular level The solute(s) is(are)
Chemical Reactions. All chemical reactions can be written as chemical equations.
 Chemical Reactions All chemical reactions can be written as chemical equations. What is a Chemical Reaction? Chemical reactions represent chemical changes A chemical change occurs when a substance has
Chemical Reactions All chemical reactions can be written as chemical equations. What is a Chemical Reaction? Chemical reactions represent chemical changes A chemical change occurs when a substance has
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 8 Prep Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. General Solubility Guidelines 1. Most sodium, potassium, and ammonium compounds
Chapter 8 Prep Test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. General Solubility Guidelines 1. Most sodium, potassium, and ammonium compounds
General Chemistry Multiple Choice Questions Chapter 8
 1 Write the skeleton chemical equation for the following word equation: Hydrochloric acid plus magnesium yields magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas. a HClO 4 + Mg --> MgClO 4 + H 2 b HClO 4 + Mg --> MgClO
1 Write the skeleton chemical equation for the following word equation: Hydrochloric acid plus magnesium yields magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas. a HClO 4 + Mg --> MgClO 4 + H 2 b HClO 4 + Mg --> MgClO
# Ans Workings / Remarks
 # Ans Workings / Remarks 1 B Atomic mass and temperature affects the rate of diffusion of gas. The lower the atomic mass, the lighter the substance. The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of collision
# Ans Workings / Remarks 1 B Atomic mass and temperature affects the rate of diffusion of gas. The lower the atomic mass, the lighter the substance. The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of collision
11/3/09. Aqueous Solubility of Compounds. Aqueous Solubility of Ionic Compounds. Aqueous Solubility of Ionic Compounds
 Aqueous Solubility of Compounds Not all compounds dissolve in water. Solubility varies from compound to compound. Chapter 5: Chemical Reactions Soluble ionic compounds dissociate. Ions are solvated Most
Aqueous Solubility of Compounds Not all compounds dissolve in water. Solubility varies from compound to compound. Chapter 5: Chemical Reactions Soluble ionic compounds dissociate. Ions are solvated Most
