Nanopores: Solid-state nanopores for these experiments were produced by using the
|
|
|
- Preston Tucker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Materials and Methods Nanopores: Solid-state nanopores for these experiments were produced by using the highly focused electron beam of a transmission electron microscope (TEM) to drill a single pore in a low-stress silicon nitride (SiN) membrane of ~20nm thickness. The dimensions of this pore can be controlled subsequently using previously described methods 1. For the experiments described here, we use nanopores with a diameter of nm. An example TEM micrograph of one such pore is shown in Fig S1a. After fabrication, the nanopore is mounted in a custom-made flow cell 2 that combines polydimethyl siloxide (PDMS) and polyether ether ketone (PEEK) components to allow independent delivery of solvent to both sides of the membrane while simultaneously permitting optical measurement. The assembled flow cell is then mounted above a high- NA objective (60x), through which the optical tweezers are focused and direct imaging of the sample is achieved. The optical tweezer apparatus consists of two co-aligned lasers. The first, a 2 W diode pump Nd:YAG laser (CrystaLaser, wavelength 1064 nm), is used to trap target beads. The second, a 5 mw red laser (Coherent, wavelength 650 nm), is reflected off of the trapped bead and onto a quadrant photodiode (QPD), which is used to precisely monitor bead position. Electrical contact to either side of the membrane is made through agarose salt bridges and Pt connecting wires using small, enclosed reservoirs of 1M KCl with 100 mm potassium ferro/ferri cyanide as a redox agent. This prevents additional noise associated with the light sensitivity of conventional Ag/AgCl electrodes 2. The buffer at the nanopore contains 10mM tris-hcl (ph 8.0) and KCl at a concentration of 100 mm, 600 mm or 1 M and is put through a 20nm syringe filter and degassed before use. Measured currents are
2 collected with a commercial patch-clamp amplifier (Axon 200B, Axon Instruments) and are low-pass filtered at 1 khz prior to digitization at 20 khz. The low-frequency filtering does not affect the data in these optical tweezer measurements, since the measured current changes are not transitory as in the case of free translocation. Molecule-Bead Constructs: Bead constructs are produced as described previously 3. Double-strand DNA (λ-phage, 47.7 kb) is end-labeled with a single biotin molecule using common molecular biology protocols and is subsequently attached to streptavadin-coated polystyrene beads (diameter ~2 µm, Polysciences) with a 1hr incubation at 37 C and in buffer conditions of 1 M KCl and 10 mm Tris-HCl (ph 8.0). The concentration of DNA is controlled relative to the beads in order to achieve attachment of 1-10 molecules per bead on average. This reduces the chance of having multiple molecules enter the pore simultaneously. RecA-DNA nucleoprotein filaments are assembled on DNA already conjugated to beads as described above. First, 10 mm MgCl 2 is added to 10 µl of the bead solution, followed by RecA protein (New England Biolabs, Ipswitch, MA) and ATPγS (Roche, Switzerland) with final concentrations of 6.5 µm and 1.5 mm, respectively. ATPγS is a poorlyhydrolyzable equivalent of ATP and is used to prevent protein dissociation by hydrolysis 4. The solution was finally allowed to incubate for 1 hr at 37 C before being diluted in clean buffer. RecA-dsDNA bead solutions were used immediately after formation.
3 Molecular Capturing and Force Spectroscopy: Clean buffer is introduced to both sides of the nanopore in the flow cell. The pore is electrically characterized through I-V curves and analysis of noise spectra. Only pores demonstrating linear I-V behavior and low noise 5 (<20pA rms) are used. Target beads with molecules attached are introduced to the nanopore at very low concentration (~0.001% w/v) to avoid multiple beads entering the optical tweezer focus simultaneously. Upon trapping a single bead, an excess of clean solvent is flowed through the chamber in order to remove all other beads and ensure equal buffer conditions on both sides of the pore. The system is allowed to settle for several minutes to reduce remnant flows that may perturb measurements. The bead is then brought close to the membrane surface (within ~3 µm, as judged by piezo controls and optical feedback 2 ), directly below the location of the nanopore. A bias is applied across the membrane in order to pull a molecule electrophoretically through the pore. The appropriate size of this bias varies with salt concentration, but is generally mv. Capture of a single molecule is manifested as a sudden, simultaneous change in both the measured trans-pore current and the position signal 2. Only events that exhibit changes in both of these signals are considered successful molecular captures. Upon insertion of a molecule, the applied bias is immediately reduced to a lower value of mv ( holding bias ). This acts to keep the captured molecule inside the pore while being insufficient to introduce additional molecules. The bead can be moved freely toward and away from the membrane under these conditions. A final check is performed by moving the bead away from the membrane to a distance of ~6 µm, where its position is monitored during a series of different applied biases. A step-wise response ensures that
4 spurious interactions with the membrane surface are not confused for single-molecule capture events. Force measurements are performed in a manner similar to those presented previously 3. After a single molecule is captured in the nanopore, a holding bias is applied and the z distance between the membrane and the trapped bead is increased by 1 µm with a retraction speed of 100 nm/sec using piezo control. The QPD sum signal is recorded during this motion, resulting in a characteristic curve caused by interference of the red position laser (Fig. S1b, gray). This is used as a calibration curve for force measurements. At the end of this motion, a series of increasing voltages is applied across the nanopore in steps of mv. The increasing electrophoretic force moves the bead step-wise out of its initial position and towards the pore. The QPD sum signal is recorded at each applied voltage (averaged over at least 2 seconds per position) and compared to the calibration curve in order to arrive at a physical z distance moved for each position (Fig. S1b, red). Within the linear region, the optical trap acts as a Hookean spring, such that for each applied voltage F trap =-κ z, where κ is the trap stiffness as measured from power spectral density 2. Typical trap stiffnesses for the presented measurements are pn/µm.
5 1. Storm, A. J.; Chen, J. H.; Ling, X. S.; Zandbergen, H. W.; Dekker, C. Nature Materials 2003, 2, (8), Keyser, U. F.; van der Does, J.; Dekker, C.; Dekker, N. H. Review of Scientific Instruments 2006, 77, (10). 3. Keyser, U. F.; Koeleman, B. N.; Van Dorp, S.; Krapf, D.; Smeets, R. M. M.; Lemay, S. G.; Dekker, N. H.; Dekker, C. Nature Physics 2006, 2, (7), Lee, J. W.; Cox, M. M. Biochemistry 1990, 29, (33), Smeets, R. M. M.; Keyser, U. F.; Dekker, N. H.; Dekker, C. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2008, 105, (2),
6 Figure S1 (a) TEM image of a nanopore used in the present experiments (diameter 21 nm). (b) Example of a QPD sum signal calibration curve (raw data: gray, smoothed: black) with overlaid force measurements, obtained by increasing the voltage applied on a captured molecule in a step-wise fashion (red). The inset shows the corresponding force vs. applied voltage relation for the given data points (solid line is a linear fit). Presented data are from measurements on a RecA-dsDNA filament in 1 M KCl.
Electrically facilitated translocations of proteins through silicon nitride nanopores:
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Electrically facilitated translocations of proteins through silicon nitride nanopores: conjoint and competitive action of diffusion, electrophoresis, and electroosmosis Matthias
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Electrically facilitated translocations of proteins through silicon nitride nanopores: conjoint and competitive action of diffusion, electrophoresis, and electroosmosis Matthias
Origin of the Electrophoretic Force on DNA in Nanopores. Biological and Soft Systems - Cavendish Laboratory
 Origin of the Electrophoretic Force on DNA in Nanopores Ulrich F. Keyser Biological and Soft Systems - Cavendish Laboratory Acknowledgements Delft Cees Dekker, Nynke H. Dekker, Serge G. Lemay R. Smeets,
Origin of the Electrophoretic Force on DNA in Nanopores Ulrich F. Keyser Biological and Soft Systems - Cavendish Laboratory Acknowledgements Delft Cees Dekker, Nynke H. Dekker, Serge G. Lemay R. Smeets,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NNANO.213.24 Detecting the translocation of DNA through a nanopore using graphene nanoribbons F. Traversi 1, C.Raillon 1, S. M. Benameur 2, K.Liu 1, S. Khlybov 1, M.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NNANO.213.24 Detecting the translocation of DNA through a nanopore using graphene nanoribbons F. Traversi 1, C.Raillon 1, S. M. Benameur 2, K.Liu 1, S. Khlybov 1, M.
DNA Translocation through Graphene Nanopores
 DNA Translocation through Graphene Nanopores Grégory F. Schneider, Stefan W. Kowalczyk, Victor E. Calado, Grégory Pandraud, Henny W. Zandbergen, Lieven M.K. Vandersypen and Cees Dekker* Kavli Institute
DNA Translocation through Graphene Nanopores Grégory F. Schneider, Stefan W. Kowalczyk, Victor E. Calado, Grégory Pandraud, Henny W. Zandbergen, Lieven M.K. Vandersypen and Cees Dekker* Kavli Institute
Chapter 2 Correlation Force Spectroscopy
 Chapter 2 Correlation Force Spectroscopy Correlation Force Spectroscopy: Rationale In principle, the main advantage of correlation force spectroscopy (CFS) over onecantilever atomic force microscopy (AFM)
Chapter 2 Correlation Force Spectroscopy Correlation Force Spectroscopy: Rationale In principle, the main advantage of correlation force spectroscopy (CFS) over onecantilever atomic force microscopy (AFM)
Translocation of RecA-Coated Double-Stranded DNA through Solid-State Nanopores
 Letter Subscriber access provided by TECHNICAL UNIV OF DELFT Translocation of RecA-Coated Double-Stranded DNA through Solid-State Nanopores R. M. M. Smeets, S. W. Kowalczyk, A. R. Hall, N. H. Dekker, and
Letter Subscriber access provided by TECHNICAL UNIV OF DELFT Translocation of RecA-Coated Double-Stranded DNA through Solid-State Nanopores R. M. M. Smeets, S. W. Kowalczyk, A. R. Hall, N. H. Dekker, and
Improving signal-to-noise performance for DNA translocation in solid-state nanopores at MHz bandwidths
 Supporting Information Improving signal-to-noise performance for DNA translocation in solid-state nanopores at MHz bandwidths Adrian Balan *1, Bartholomeus Machielse *1, David Niedzwiecki 1, Jianxun Lin
Supporting Information Improving signal-to-noise performance for DNA translocation in solid-state nanopores at MHz bandwidths Adrian Balan *1, Bartholomeus Machielse *1, David Niedzwiecki 1, Jianxun Lin
Origin of the Electrophoretic Force on DNA in a Nanopore
 Origin of the Electrophoretic Force on DNA in a Nanopore Stijn van Dorp 1 Ulrich F. Keyser 2, *Nynke H. Dekker 1, Cees Dekker 1, Serge G. Lemay 1 1 Kavli Institut of Nanoscience, Delft University of Technology,
Origin of the Electrophoretic Force on DNA in a Nanopore Stijn van Dorp 1 Ulrich F. Keyser 2, *Nynke H. Dekker 1, Cees Dekker 1, Serge G. Lemay 1 1 Kavli Institut of Nanoscience, Delft University of Technology,
Instrumentation and Operation
 Instrumentation and Operation 1 STM Instrumentation COMPONENTS sharp metal tip scanning system and control electronics feedback electronics (keeps tunneling current constant) image processing system data
Instrumentation and Operation 1 STM Instrumentation COMPONENTS sharp metal tip scanning system and control electronics feedback electronics (keeps tunneling current constant) image processing system data
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2013.221 Optoelectronic control of surface charge and translocation dynamics in solid- state nanopores Nicolas Di Fiori, Allison Squires, Daniel Bar, Tal Gilboa,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2013.221 Optoelectronic control of surface charge and translocation dynamics in solid- state nanopores Nicolas Di Fiori, Allison Squires, Daniel Bar, Tal Gilboa,
Interaction of Gold Nanoparticle with Proteins
 Chapter 7 Interaction of Gold Nanoparticle with Proteins 7.1. Introduction The interfacing of nanoparticle with biomolecules such as protein is useful for applications ranging from nano-biotechnology (molecular
Chapter 7 Interaction of Gold Nanoparticle with Proteins 7.1. Introduction The interfacing of nanoparticle with biomolecules such as protein is useful for applications ranging from nano-biotechnology (molecular
Supporting Information. Probing DNA Translocations with Inplane Current Signals in a Graphene Nanoribbon with a Nanopore
 Supporting Information Probing DNA Translocations with Inplane Current Signals in a Graphene Nanoribbon with a Nanopore Stephanie J. Heerema, Leonardo Vicarelli, Sergii Pud, Raymond N. Schouten, Henny
Supporting Information Probing DNA Translocations with Inplane Current Signals in a Graphene Nanoribbon with a Nanopore Stephanie J. Heerema, Leonardo Vicarelli, Sergii Pud, Raymond N. Schouten, Henny
Salt Dependence of Ion Transport and DNA Translocation through Solid-State Nanopores
 Salt Dependence of Ion Transport and DNA Translocation through Solid-State Nanopores NANO LETTERS 2006 Vol. 6, No. 1 89-95 Ralph M. M. Smeets, Ulrich F. Keyser, Diego Krapf, Meng-Yue Wu, Nynke H. Dekker,
Salt Dependence of Ion Transport and DNA Translocation through Solid-State Nanopores NANO LETTERS 2006 Vol. 6, No. 1 89-95 Ralph M. M. Smeets, Ulrich F. Keyser, Diego Krapf, Meng-Yue Wu, Nynke H. Dekker,
Lecture 4 Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM)
 Lecture 4 Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) General components of SPM; Tip --- the probe; Cantilever --- the indicator of the tip; Tip-sample interaction --- the feedback system; Scanner --- piezoelectric
Lecture 4 Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) General components of SPM; Tip --- the probe; Cantilever --- the indicator of the tip; Tip-sample interaction --- the feedback system; Scanner --- piezoelectric
Supplementary Figure 1 a) Scheme of microfluidic device fabrication by photo and soft lithography,
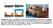 a b 1 mm Supplementary Figure 1 a) Scheme of microfluidic device fabrication by photo and soft lithography, (a1, a2) 50nm Pd evaporated on Si wafer with 100 nm Si 2 insulating layer and 5nm Cr as an adhesion
a b 1 mm Supplementary Figure 1 a) Scheme of microfluidic device fabrication by photo and soft lithography, (a1, a2) 50nm Pd evaporated on Si wafer with 100 nm Si 2 insulating layer and 5nm Cr as an adhesion
Nanopores and Nanofluidics for Single DNA Studies Derek Stein Department of Physics Brown University
 Nanopores and Nanofluidics for Single DNA Studies Derek Stein Department of Physics Brown University Overview Motivation: biological, physical, and technological The program: develop and characterize new
Nanopores and Nanofluidics for Single DNA Studies Derek Stein Department of Physics Brown University Overview Motivation: biological, physical, and technological The program: develop and characterize new
PLASMONIC NANOPORES: exploring new possibilities in DNA sensing and trapping
 PLASMONIC NANOPORES: exploring new possibilities in DNA sensing and trapping FRANCESCA NICOLI KTH Information and Communication Technology Master of Science Thesis Stockholm, Sweden 2013 TRITA-ICT-EX-2013:223
PLASMONIC NANOPORES: exploring new possibilities in DNA sensing and trapping FRANCESCA NICOLI KTH Information and Communication Technology Master of Science Thesis Stockholm, Sweden 2013 TRITA-ICT-EX-2013:223
Graphene: A sub-nanometer trans-electrode membrane
 1 Graphene: A sub-nanometer trans-electrode membrane S. Garaj 1, W. Hubbard 2, A. Reina 3, J. Kong 4, D. Branton 5 & J.A. Golovchenko 1,2* Submitted 12 April 2010 to Nature, where it is under review. 1
1 Graphene: A sub-nanometer trans-electrode membrane S. Garaj 1, W. Hubbard 2, A. Reina 3, J. Kong 4, D. Branton 5 & J.A. Golovchenko 1,2* Submitted 12 April 2010 to Nature, where it is under review. 1
Adaptive Response of Actin Bundles under Mechanical Stress
 Biophysical Journal, Volume 113 Supplemental Information Adaptive Response of Actin Bundles under Mechanical Stress Florian Rückerl, Martin Lenz, Timo Betz, John Manzi, Jean-Louis Martiel, Mahassine Safouane,
Biophysical Journal, Volume 113 Supplemental Information Adaptive Response of Actin Bundles under Mechanical Stress Florian Rückerl, Martin Lenz, Timo Betz, John Manzi, Jean-Louis Martiel, Mahassine Safouane,
Supporting Material for: Electrochemical reaction in single layer MoS 2 : nanopores opened atom by atom. Table of contents
 Supporting Material for: Electrochemical reaction in single layer MoS 2 : nanopores opened atom by atom J. Feng 1, K. Liu 1, M.Graf 1, M.Lihter 1,2, R. D. Bulushev 1, D. Dumcenco 3, D.T.L. Alexander 4,
Supporting Material for: Electrochemical reaction in single layer MoS 2 : nanopores opened atom by atom J. Feng 1, K. Liu 1, M.Graf 1, M.Lihter 1,2, R. D. Bulushev 1, D. Dumcenco 3, D.T.L. Alexander 4,
Single-Molecule Catch and Release: Potential-Dependent Plasmid DNA Adsorption along Chemically Graded Electrode Surfaces
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Single-Molecule Catch and Release: Potential-Dependent Plasmid DNA Adsorption along Chemically Graded Electrode Surfaces Zi Li, Kayesh M. Ashraf, Maryanne M. Collinson, *, and Daniel
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Single-Molecule Catch and Release: Potential-Dependent Plasmid DNA Adsorption along Chemically Graded Electrode Surfaces Zi Li, Kayesh M. Ashraf, Maryanne M. Collinson, *, and Daniel
Detecting Single Stranded DNA with a Solid State Nanopore
 Detecting Single Stranded DNA with a Solid State Nanopore NANO LETTERS 2005 Vol. 5, No. 10 1905-1909 Daniel Fologea Marc Gershow Department of Physics, HarVard UniVersity, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138
Detecting Single Stranded DNA with a Solid State Nanopore NANO LETTERS 2005 Vol. 5, No. 10 1905-1909 Daniel Fologea Marc Gershow Department of Physics, HarVard UniVersity, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Generation of nanocrack patterns: PDMS (Sylgard 184, Dow Corning) base and curing agent were mixed at a weight ratio of 10:1. Degassed PDMS prepolymer was cast against a photolithographically-prepared
Supplementary Methods Generation of nanocrack patterns: PDMS (Sylgard 184, Dow Corning) base and curing agent were mixed at a weight ratio of 10:1. Degassed PDMS prepolymer was cast against a photolithographically-prepared
Probing Access Resistance of Solid-State Nanopores with a Scanning-Probe Microscope Tip
 Scanning-Probe Microscopy Probing Access Resistance of Solid-State Nanopores with a Scanning-Probe Microscope Tip Changbae Hyun, Ryan Rollings, and Jiali Li * A n apparatus that integrates solid-state
Scanning-Probe Microscopy Probing Access Resistance of Solid-State Nanopores with a Scanning-Probe Microscope Tip Changbae Hyun, Ryan Rollings, and Jiali Li * A n apparatus that integrates solid-state
1 Supporting Information. 2 Reconfigurable and resettable arithmetic logic units based. 4 Siqi Zhang a, Kun Wang a, Congcong Huang b and Ting Sun a*
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 1 Supporting Information 2 Reconfigurable and resettable arithmetic logic units based 3 on magnetic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 1 Supporting Information 2 Reconfigurable and resettable arithmetic logic units based 3 on magnetic
Supporting Information. Three-Dimensional Super-Resolution Imaging of Single Nanoparticle Delivered by Pipettes
 Supporting Information Three-Dimensional Super-Resolution Imaging of Single Nanoparticle Delivered by Pipettes Yun Yu,, Vignesh Sundaresan,, Sabyasachi Bandyopadhyay, Yulun Zhang, Martin A. Edwards, Kim
Supporting Information Three-Dimensional Super-Resolution Imaging of Single Nanoparticle Delivered by Pipettes Yun Yu,, Vignesh Sundaresan,, Sabyasachi Bandyopadhyay, Yulun Zhang, Martin A. Edwards, Kim
Soft Matter and Biological Physics
 Dr. Ulrich F. Keyser - ufk20 (at) cam.ac.uk Soft Matter and Biological Physics Question Sheet Michaelmas 2011 Version: November 2, 2011 Question 0: Sedimentation Initially consider identical small particles
Dr. Ulrich F. Keyser - ufk20 (at) cam.ac.uk Soft Matter and Biological Physics Question Sheet Michaelmas 2011 Version: November 2, 2011 Question 0: Sedimentation Initially consider identical small particles
Mercury(II) detection by SERS based on a single gold microshell
 Mercury(II) detection by SERS based on a single gold microshell D. Han, S. Y. Lim, B. J. Kim, L. Piao and T. D. Chung* Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. 2010, 46, 5587-558
Mercury(II) detection by SERS based on a single gold microshell D. Han, S. Y. Lim, B. J. Kim, L. Piao and T. D. Chung* Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. 2010, 46, 5587-558
Label-Free Single-Molecule Thermoscopy Using a Laser-Heated Nanopore
 Supporting information for Label-Free Single-Molecule Thermoscopy Using a Laser-Heated Nanopore By Hirohito Yamazaki, Rui Hu,, Robert Y. Henley, Justin Halman, Kirill A. Afonin, Dapeng Yu, Qing Zhao, and
Supporting information for Label-Free Single-Molecule Thermoscopy Using a Laser-Heated Nanopore By Hirohito Yamazaki, Rui Hu,, Robert Y. Henley, Justin Halman, Kirill A. Afonin, Dapeng Yu, Qing Zhao, and
Cantilever thiolated-biotin functionalization and Streptavidin preparation
 This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 20 Supplementary Data: Materials and Methods: Cantilever thiolated-biotin functionalization and Streptavidin preparation The gold coated cantilevers were
This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 20 Supplementary Data: Materials and Methods: Cantilever thiolated-biotin functionalization and Streptavidin preparation The gold coated cantilevers were
Supplementary information for
 Supplementary information for Transverse electric field dragging of DNA in a nanochannel Makusu Tsutsui, Yuhui He, Masayuki Furuhashi, Rahong Sakon, Masateru Taniguchi & Tomoji Kawai The Supplementary
Supplementary information for Transverse electric field dragging of DNA in a nanochannel Makusu Tsutsui, Yuhui He, Masayuki Furuhashi, Rahong Sakon, Masateru Taniguchi & Tomoji Kawai The Supplementary
Supplementary Materials. Mechanics and Chemistry: Single Molecule Bond Rupture Forces Correlate with
 Supplementary Materials Mechanics and Chemistry: Single Molecule Bond Rupture Forces Correlate with Molecular Backbone Structure M. Frei 1, S Aradhya 1, M. Koentopp 2, M. S. Hybertsen 3, L. Venkataraman
Supplementary Materials Mechanics and Chemistry: Single Molecule Bond Rupture Forces Correlate with Molecular Backbone Structure M. Frei 1, S Aradhya 1, M. Koentopp 2, M. S. Hybertsen 3, L. Venkataraman
Nanopore/electrode structures for single-molecule biosensing
 Nanopore/electrode structures for single-molecule biosensing Dr Tim Albrecht Imperial College London Department of Chemistry & London Centre for Nanotechnology South Kensington Campus London t.albrecht@imperial.ac.uk
Nanopore/electrode structures for single-molecule biosensing Dr Tim Albrecht Imperial College London Department of Chemistry & London Centre for Nanotechnology South Kensington Campus London t.albrecht@imperial.ac.uk
Electrically controlled DNA adhesion
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Electrically controlled DNA adhesion Matthias Erdmann, Ralf David +, Ann Fornof and Hermann E. Gaub* Chair for Applied Physics and Center for NanoScience, Ludwigs-Maximilians-Universität
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Electrically controlled DNA adhesion Matthias Erdmann, Ralf David +, Ann Fornof and Hermann E. Gaub* Chair for Applied Physics and Center for NanoScience, Ludwigs-Maximilians-Universität
Experimental biophysics: Optical tweezer lab Supervisor: Stefan Holm,
 Experimental biophysics: Optical tweezer lab :, stefan.holm@ftf.lth.se Written by Jason Beech & Henrik Persson, March 2009. Modified 2014 Karl Adolfsson, 2016 Experimental Biophysics: FAF010F, FYST23,
Experimental biophysics: Optical tweezer lab :, stefan.holm@ftf.lth.se Written by Jason Beech & Henrik Persson, March 2009. Modified 2014 Karl Adolfsson, 2016 Experimental Biophysics: FAF010F, FYST23,
Surfactant-free exfoliation of graphite in aqueous solutions
 Surfactant-free exfoliation of graphite in aqueous solutions Karen B. Ricardo, Anne Sendecki, and Haitao Liu * Department of Chemistry, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA 15260, U.S.A 1. Materials
Surfactant-free exfoliation of graphite in aqueous solutions Karen B. Ricardo, Anne Sendecki, and Haitao Liu * Department of Chemistry, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA 15260, U.S.A 1. Materials
Zeta Potential Analysis using Z-NTA
 Zeta Potential Analysis using Z-NTA Summary Zeta Potential Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (Z-NTA) adds measurements of electrostatic potential to simultaneous reporting of nanoparticle size, light scattering
Zeta Potential Analysis using Z-NTA Summary Zeta Potential Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (Z-NTA) adds measurements of electrostatic potential to simultaneous reporting of nanoparticle size, light scattering
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Electronic Supplementary Information Redox cycling-amplified enzymatic Ag deposition
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 215 Electronic Supplementary Information Redox cycling-amplified enzymatic Ag deposition
Atomic and molecular interactions. Scanning probe microscopy.
 Atomic and molecular interactions. Scanning probe microscopy. Balázs Kiss Nanobiotechnology and Single Molecule Research Group, Department of Biophysics and Radiation Biology 27. November 2013. 2 Atomic
Atomic and molecular interactions. Scanning probe microscopy. Balázs Kiss Nanobiotechnology and Single Molecule Research Group, Department of Biophysics and Radiation Biology 27. November 2013. 2 Atomic
Courtesy of ESS and TheRGA web pages part of a series of application and theory notes for public use which are provided free of charge by ESS.
 ESS The RGA freenotes Theory page 1 of 14 RGA Theory Notes Courtesy of ESS and TheRGA web pages part of a series of application and theory notes for public use which are provided free of charge by ESS.
ESS The RGA freenotes Theory page 1 of 14 RGA Theory Notes Courtesy of ESS and TheRGA web pages part of a series of application and theory notes for public use which are provided free of charge by ESS.
Identification of single nucleotides in MoS2 nanopores
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NNANO.215.219 Identification of single nucleotides in MoS2 nanopores Jiandong Feng 1#, Ke Liu 1#, Roman D. Bulushev 1, Sergey Khlybov 1, Dumitru Dumcenco 2, Andras
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NNANO.215.219 Identification of single nucleotides in MoS2 nanopores Jiandong Feng 1#, Ke Liu 1#, Roman D. Bulushev 1, Sergey Khlybov 1, Dumitru Dumcenco 2, Andras
Alignment Tools Used To Locate A Wire And A Laser Beam In The VISA Undulator Project
 Alignment Tools Used To Locate A Wire And A Laser Beam In The VISA Undulator Project Z. Wolf,. uland, B. Dix, D. Arnett Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford, CA 94309-0210 USA 1. INTODUCTION The
Alignment Tools Used To Locate A Wire And A Laser Beam In The VISA Undulator Project Z. Wolf,. uland, B. Dix, D. Arnett Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford, CA 94309-0210 USA 1. INTODUCTION The
Hydrodynamics of Diamond-Shaped Gradient Nanopillar Arrays for Effective. DNA Translocation into Nanochannels. (Supplementary information)
 Hydrodynamics of Diamond-Shaped Gradient Nanopillar Arrays for Effective DNA Translocation into Nanochannels (Supplementary information) Chao Wang 1, Robert L. Bruce, Elizabeth A. Duch, Jyotica V. Patel,
Hydrodynamics of Diamond-Shaped Gradient Nanopillar Arrays for Effective DNA Translocation into Nanochannels (Supplementary information) Chao Wang 1, Robert L. Bruce, Elizabeth A. Duch, Jyotica V. Patel,
Supplementary Information. Back-Contacted Hybrid Organic-Inorganic Perovskite Solar Cells
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Journal of Materials Chemistry C Supplementary Information Back-Contacted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Journal of Materials Chemistry C Supplementary Information Back-Contacted
percolating nanotube networks
 Supporting Information for: A highly elastic, capacitive strain gauge based on percolating nanotube networks 0.2 0.18 0.16 0.14 Force (kgf) 0.12 0.1 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 Raw Data Mooney-Rivlin (R 2 =0.996)
Supporting Information for: A highly elastic, capacitive strain gauge based on percolating nanotube networks 0.2 0.18 0.16 0.14 Force (kgf) 0.12 0.1 0.08 0.06 0.04 0.02 Raw Data Mooney-Rivlin (R 2 =0.996)
Atomic Layer Deposition to Fine- Tune the Surface Properties and Diameters of Fabricated Nanopores
 Atomic Layer Deposition to Fine- Tune the Surface Properties and Diameters of Fabricated Nanopores The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
Atomic Layer Deposition to Fine- Tune the Surface Properties and Diameters of Fabricated Nanopores The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Visible Light-Driven BiOI-Based Janus Micromotors in Pure Water Renfeng Dong, a Yan Hu, b Yefei Wu, b Wei Gao, c Biye Ren, b* Qinglong Wang, a Yuepeng Cai a* a School of Chemistry
Supporting Information Visible Light-Driven BiOI-Based Janus Micromotors in Pure Water Renfeng Dong, a Yan Hu, b Yefei Wu, b Wei Gao, c Biye Ren, b* Qinglong Wang, a Yuepeng Cai a* a School of Chemistry
BMB November 17, Single Molecule Biophysics (I)
 BMB 178 2017 November 17, 2017 14. Single Molecule Biophysics (I) Goals 1. Understand the information SM experiments can provide 2. Be acquainted with different SM approaches 3. Learn to interpret SM results
BMB 178 2017 November 17, 2017 14. Single Molecule Biophysics (I) Goals 1. Understand the information SM experiments can provide 2. Be acquainted with different SM approaches 3. Learn to interpret SM results
A High-Speed Multipass Coulter Counter with Ultra-High Resolution
 Supporting Information A High-Speed Multipass Coulter Counter with Ultra-High Resolution Martin A Edwards, Sean R German, Jeffrey E Dick, Allen J Bard, Henry S White * Department of Chemistry, University
Supporting Information A High-Speed Multipass Coulter Counter with Ultra-High Resolution Martin A Edwards, Sean R German, Jeffrey E Dick, Allen J Bard, Henry S White * Department of Chemistry, University
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information Speckle-free laser imaging using random laser illumination Brandon Redding 1*, Michael A. Choma 2,3*, Hui Cao 1,4* 1 Department of Applied Physics, Yale University, New Haven,
Supplementary Information Speckle-free laser imaging using random laser illumination Brandon Redding 1*, Michael A. Choma 2,3*, Hui Cao 1,4* 1 Department of Applied Physics, Yale University, New Haven,
Proteorhodopsin-based Biohybrid Light-powering ph
 Supporting Information Proteorhodopsin-based Biohybrid Light-powering ph Sensor Siyuan Rao a, Zhibin Guo a, Dawei Liang a,b, Deliang Chen *c, Yan Wei d and Yan Xiang *a,b a Key Laboratory of Bio-Inspired
Supporting Information Proteorhodopsin-based Biohybrid Light-powering ph Sensor Siyuan Rao a, Zhibin Guo a, Dawei Liang a,b, Deliang Chen *c, Yan Wei d and Yan Xiang *a,b a Key Laboratory of Bio-Inspired
Optical Tweezers. The Useful Micro-Manipulation Tool in Research
 Optical Tweezers The Useful Micro-Manipulation Tool in Research Student: Nikki Barron Class: Modern Physics/ Biophysics laboratory Advisor: Grant Allen Instructor: David Kleinfeld Date: June 15, 2012 Introduction
Optical Tweezers The Useful Micro-Manipulation Tool in Research Student: Nikki Barron Class: Modern Physics/ Biophysics laboratory Advisor: Grant Allen Instructor: David Kleinfeld Date: June 15, 2012 Introduction
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Oh et al. 10.1073/pnas.0811923106 SI Text Hysteresis of BPE-PTCDI MW-TFTs. Fig. S9 represents bidirectional transfer plots at V DS 100VinN 2 atmosphere for transistors constructed
Supporting Information Oh et al. 10.1073/pnas.0811923106 SI Text Hysteresis of BPE-PTCDI MW-TFTs. Fig. S9 represents bidirectional transfer plots at V DS 100VinN 2 atmosphere for transistors constructed
= 6 (1/ nm) So what is probability of finding electron tunneled into a barrier 3 ev high?
 STM STM With a scanning tunneling microscope, images of surfaces with atomic resolution can be readily obtained. An STM uses quantum tunneling of electrons to map the density of electrons on the surface
STM STM With a scanning tunneling microscope, images of surfaces with atomic resolution can be readily obtained. An STM uses quantum tunneling of electrons to map the density of electrons on the surface
Phys498BIO; Prof. Paul Selvin Hw #9 Assigned Wed. 4/18/12: Due 4/25/08
 1. Ionic Movements Across a Permeable Membrane: The Nernst Potential. In class we showed that if a non-permeable membrane separates a solution with high [KCl] from a solution with low [KCl], the net charge
1. Ionic Movements Across a Permeable Membrane: The Nernst Potential. In class we showed that if a non-permeable membrane separates a solution with high [KCl] from a solution with low [KCl], the net charge
Linker Dependent Bond Rupture Force Measurements in Single-Molecule Junctions
 Supplemental Information Linker Dependent Bond Rupture Force Measurements in Single-Molecule Junctions M. Frei 1, S Aradhya 1, M. S. Hybertsen 2, L. Venkataraman 1 1 Department of Applied Physics and Applied
Supplemental Information Linker Dependent Bond Rupture Force Measurements in Single-Molecule Junctions M. Frei 1, S Aradhya 1, M. S. Hybertsen 2, L. Venkataraman 1 1 Department of Applied Physics and Applied
Fast ph-assisted functionalization of silver nanoparticles with monothiolated DNA
 Supporting Information for Fast ph-assisted functionalization of silver nanoparticles with monothiolated DNA Xu Zhang ab, Mark R. Servos b, and Juewen Liu* a a Department of Chemistry and Waterloo Institute
Supporting Information for Fast ph-assisted functionalization of silver nanoparticles with monothiolated DNA Xu Zhang ab, Mark R. Servos b, and Juewen Liu* a a Department of Chemistry and Waterloo Institute
1. Fabrication. Lukáš Ondič a, Marian Varga a, Karel Hruška a, Jan Fait a,b and Peter Kapusta c
 Supporting information to Enhanced Extraction of Silicon-Vacancy Centers Light Emission Using Bottom-Up Engineered Polycrystalline Diamond Photonic Crystal Slabs Lukáš Ondič a, Marian Varga a, Karel Hruška
Supporting information to Enhanced Extraction of Silicon-Vacancy Centers Light Emission Using Bottom-Up Engineered Polycrystalline Diamond Photonic Crystal Slabs Lukáš Ondič a, Marian Varga a, Karel Hruška
Molecular mechanism of selective transport across the Nuclear Pore Complex
 Molecular mechanism of selective transport across the Nuclear Pore Complex David Winogradoff and Aleksei Aksimentiev Physics Department, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign May 16, 2017 The Nuclear
Molecular mechanism of selective transport across the Nuclear Pore Complex David Winogradoff and Aleksei Aksimentiev Physics Department, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign May 16, 2017 The Nuclear
Acto-myosin: from muscles to single molecules. Justin Molloy MRC National Institute for Medical Research LONDON
 Acto-myosin: from muscles to single molecules. Justin Molloy MRC National Institute for Medical Research LONDON Energy in Biological systems: 1 Photon = 400 pn.nm 1 ATP = 100 pn.nm 1 Ion moving across
Acto-myosin: from muscles to single molecules. Justin Molloy MRC National Institute for Medical Research LONDON Energy in Biological systems: 1 Photon = 400 pn.nm 1 ATP = 100 pn.nm 1 Ion moving across
Measurements of interaction forces in (biological) model systems
 Measurements of interaction forces in (biological) model systems Marina Ruths Department of Chemistry, UMass Lowell What can force measurements tell us about a system? Depending on the technique, we might
Measurements of interaction forces in (biological) model systems Marina Ruths Department of Chemistry, UMass Lowell What can force measurements tell us about a system? Depending on the technique, we might
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Oscillatory Reaction Induced Periodic C-Quadruplex DNA Gating of Artificial Ion Channels Jian Wang, Ruochen Fang, Jue Hou, Huacheng Zhang, *, Ye Tian, *, Huanting Wang, and Lei
Supporting Information for Oscillatory Reaction Induced Periodic C-Quadruplex DNA Gating of Artificial Ion Channels Jian Wang, Ruochen Fang, Jue Hou, Huacheng Zhang, *, Ye Tian, *, Huanting Wang, and Lei
Instantaneous and Quantitative Functionalization of Gold Nanoparticles with Thiolated DNA Using a ph-assisted and Surfactant-Free Route
 Supporting Information Instantaneous and Quantitative Functionalization of Gold Nanoparticles with Thiolated DNA Using a ph-assisted and Surfactant-Free Route Xu Zhang,, Mark R. Servos and Juewen Liu *
Supporting Information Instantaneous and Quantitative Functionalization of Gold Nanoparticles with Thiolated DNA Using a ph-assisted and Surfactant-Free Route Xu Zhang,, Mark R. Servos and Juewen Liu *
The solution for all of your
 The solution for all of your nanoparticle sizing and zeta potential needs. DelsaNano Series Blood Banking Capillary Electrophoresis Cell Analysis Centrifugation Genomics Lab Automation Lab Tools Particle
The solution for all of your nanoparticle sizing and zeta potential needs. DelsaNano Series Blood Banking Capillary Electrophoresis Cell Analysis Centrifugation Genomics Lab Automation Lab Tools Particle
Application Note Antibody-SOMAmer Sandwich Assay
 Application Note Antibody-SOMAmer Sandwich Assay Introduction SOMAmer reagents (Slow Off-rate Modified Aptamers) are DNA-based high affinity (average Kd < 1 nm) protein binding reagents with proprietary
Application Note Antibody-SOMAmer Sandwich Assay Introduction SOMAmer reagents (Slow Off-rate Modified Aptamers) are DNA-based high affinity (average Kd < 1 nm) protein binding reagents with proprietary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1: Amplitudes of three current levels. Level 0 (pa) Level 1 (pa) Level 2 (pa) TrkA- TrkH WT 200 K 0.01 ± 0.01 9.5 ± 0.01 18.7 ± 0.03 200 Na * 0.001 ± 0.01 3.9 ± 0.01 12.5 ± 0.03 200
Supplementary Table 1: Amplitudes of three current levels. Level 0 (pa) Level 1 (pa) Level 2 (pa) TrkA- TrkH WT 200 K 0.01 ± 0.01 9.5 ± 0.01 18.7 ± 0.03 200 Na * 0.001 ± 0.01 3.9 ± 0.01 12.5 ± 0.03 200
Chapter 14. Molar Mass Distribution.
 Chapter 14. Molar Mass Distribution. Difficulty with M n and M w, etc. osome polymers are hard to describe from just M n, M w, etc. o Examples: Bimodal, multimodal, nonuniform, broad, etc. MWDs. oin early
Chapter 14. Molar Mass Distribution. Difficulty with M n and M w, etc. osome polymers are hard to describe from just M n, M w, etc. o Examples: Bimodal, multimodal, nonuniform, broad, etc. MWDs. oin early
Recommended Procedures for Labeling. Labeling Proteins with Amine-Reactive ATTO-Labels (NHS-Esters) Introduction
 Recommended Procedures for Labeling Introduction ATTO-TEC offers a large variety of high-quality dyes for labeling amino and thiol groups. ATTO reactive dyes cover the spectral region from 350 nm in the
Recommended Procedures for Labeling Introduction ATTO-TEC offers a large variety of high-quality dyes for labeling amino and thiol groups. ATTO reactive dyes cover the spectral region from 350 nm in the
Regular Reflectance and Transmittance Measurements of Transmissive Materials Using a STAR GEM Optical Accessory
 Regular Reflectance and Transmittance Measurements of Transmissive Materials Using a STAR GEM Optical Accessory 1,3 E.Kawate, 1,2 M.Hain 1 AIST, 1-1-1, Central 2, Umezono, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8568, Japan
Regular Reflectance and Transmittance Measurements of Transmissive Materials Using a STAR GEM Optical Accessory 1,3 E.Kawate, 1,2 M.Hain 1 AIST, 1-1-1, Central 2, Umezono, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8568, Japan
Supporting Information s for
 Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2011.88 Supporting Information Single-molecule transport across an individual biomimetic nuclear pore complex Stefan W. Kowalczyk, Larisa Kapinos, Timothy R.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2011.88 Supporting Information Single-molecule transport across an individual biomimetic nuclear pore complex Stefan W. Kowalczyk, Larisa Kapinos, Timothy R.
Multiplexed discrimination of microrna single nucleotide variants. through triplex molecular beacon sensors
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information for: Multiplexed discrimination of microrna single nucleotide variants
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Information for: Multiplexed discrimination of microrna single nucleotide variants
In Situ Gelation-Induced Death of Cancer Cells Based on Proteinosomes
 Supporting information for In Situ Gelation-Induced Death of Cancer Cells Based on Proteinosomes Yuting Zhou, Jianmin Song, Lei Wang*, Xuting Xue, Xiaoman Liu, Hui Xie*, and Xin Huang* MIIT Key Laboratory
Supporting information for In Situ Gelation-Induced Death of Cancer Cells Based on Proteinosomes Yuting Zhou, Jianmin Song, Lei Wang*, Xuting Xue, Xiaoman Liu, Hui Xie*, and Xin Huang* MIIT Key Laboratory
Single molecule investigations of the phdependent interaction between nanoparticles and an a-hemolysin protein pore
 Single molecule investigations of the phdependent interaction between nanoparticles and an a-hemolysin protein pore Dr. Alina ASANDEI The Science Department of Alexandru Ioan Cuza University Iasi 2012
Single molecule investigations of the phdependent interaction between nanoparticles and an a-hemolysin protein pore Dr. Alina ASANDEI The Science Department of Alexandru Ioan Cuza University Iasi 2012
Supporting information
 Supporting information Polymer-Single-Crystal@Nanoparticle Nanosandwich for Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Bin Dong, Wenda Wang, David L. Miller, Christopher Y. Li* Department of Material Science
Supporting information Polymer-Single-Crystal@Nanoparticle Nanosandwich for Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Bin Dong, Wenda Wang, David L. Miller, Christopher Y. Li* Department of Material Science
Siletz APD Products. Model VFP1-xCAA, VFP1-xKAB Packaged APDs
 Siletz Packaged APD Features Hermetically packaged reduced-noise NIR InGaAs avalanche photodiode (R-APD) Siletz APD Products Single-Carrier Multiplication APDs (SCM-APD) in hermetic packages with optional
Siletz Packaged APD Features Hermetically packaged reduced-noise NIR InGaAs avalanche photodiode (R-APD) Siletz APD Products Single-Carrier Multiplication APDs (SCM-APD) in hermetic packages with optional
Improved axial position detection in optical tweezers measurements
 Improved axial position detection in optical tweezers measurements Jakob Kisbye Dreyer, Kirstine Berg-Sørensen, and Lene Oddershede We investigate the axial position detection of a trapped microsphere
Improved axial position detection in optical tweezers measurements Jakob Kisbye Dreyer, Kirstine Berg-Sørensen, and Lene Oddershede We investigate the axial position detection of a trapped microsphere
Optical Tweezers. BGGN 266, Biophysics Lab. June, Trygve Bakken & Adam Koerner
 Optical Tweezers BGGN 266, Biophysics Lab June, 2009 Trygve Bakken & Adam Koerner Background There are a wide variety of force spectroscopy techniques available to investigators of biological systems.
Optical Tweezers BGGN 266, Biophysics Lab June, 2009 Trygve Bakken & Adam Koerner Background There are a wide variety of force spectroscopy techniques available to investigators of biological systems.
Chem 310 rd. 3 Homework Set Answers
 -1- Chem 310 rd 3 Homework Set Answers 1. A double line labeled S 0 represents the _ground electronic_ state and the _ground vibrational_ state of a molecule in an excitation state diagram. Light absorption
-1- Chem 310 rd 3 Homework Set Answers 1. A double line labeled S 0 represents the _ground electronic_ state and the _ground vibrational_ state of a molecule in an excitation state diagram. Light absorption
Electro kinetic Phenomena
 Electro kinetic Phenomena Electro-osmosis Electrophoresis Gel electrophoresis, polymer dynamics in gels 3 Electric Double Layer In aqueous solutions we have to deal with a situations where (usually) every
Electro kinetic Phenomena Electro-osmosis Electrophoresis Gel electrophoresis, polymer dynamics in gels 3 Electric Double Layer In aqueous solutions we have to deal with a situations where (usually) every
Tecniche sperimentali: le optical tweezers
 Tecniche sperimentali: le optical tweezers Le tecniche di molecola singola rispetto a quelle di insieme ensemble z z z z z z frequency activity activity time z z z Single molecule frequency activity activity
Tecniche sperimentali: le optical tweezers Le tecniche di molecola singola rispetto a quelle di insieme ensemble z z z z z z frequency activity activity time z z z Single molecule frequency activity activity
Raman spectroscopy. InfraRed basics. Han Gardeniers MESA+ Institute for Nanotechnology University of Twente
 SMR.1670-29 INTRODUCTION TO MICROFLUIDICS 8-26 August 2005 Chip-based IR and Raman Spectroscopy H. Gardeniers University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands ChipbasedIRand Ramanspectroscopy HanGardeniers
SMR.1670-29 INTRODUCTION TO MICROFLUIDICS 8-26 August 2005 Chip-based IR and Raman Spectroscopy H. Gardeniers University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands ChipbasedIRand Ramanspectroscopy HanGardeniers
Nanoporous GaN-Ag Composite Materials Prepared by Metal-Assisted Electroless Etching
 Supporting Information for Nanoporous GaN-Ag Composite Materials Prepared by Metal-Assisted Electroless Etching for Direct Laser Desorption-Ionization Mass Spectrometry Bei Nie a,, Barrett K. Duan a and
Supporting Information for Nanoporous GaN-Ag Composite Materials Prepared by Metal-Assisted Electroless Etching for Direct Laser Desorption-Ionization Mass Spectrometry Bei Nie a,, Barrett K. Duan a and
Visualizing the bi-directional electron transfer in a Schottky junction consisted of single CdS nanoparticles and a planar gold film
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Visualizing the bi-directional electron transfer in
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Visualizing the bi-directional electron transfer in
High-Performance Flexible Asymmetric Supercapacitors Based on 3D. Electrodes
 Supporting Information for: High-Performance Flexible Asymmetric Supercapacitors Based on 3D Porous Graphene/MnO 2 Nanorod and Graphene/Ag Hybrid Thin-Film Electrodes Yuanlong Shao, a Hongzhi Wang,* a
Supporting Information for: High-Performance Flexible Asymmetric Supercapacitors Based on 3D Porous Graphene/MnO 2 Nanorod and Graphene/Ag Hybrid Thin-Film Electrodes Yuanlong Shao, a Hongzhi Wang,* a
CHAPTER 3. FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES. 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES
 CHAPTER 3 FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES Au NPs with ~ 15 nm were prepared by citrate reduction of HAuCl 4
CHAPTER 3 FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES Au NPs with ~ 15 nm were prepared by citrate reduction of HAuCl 4
Supporting Online Material. On-Chip Dielectrophoretic Co-Assembly of Live Cells and. Particles into Responsive Biomaterials
 Supporting Online Material On-Chip Dielectrophoretic Co-Assembly of Live Cells and Particles into esponsive Biomaterials Shalini Gupta, ossitza G. Alargova, Peter K. Kilpatrick and Orlin D. Velev* Description
Supporting Online Material On-Chip Dielectrophoretic Co-Assembly of Live Cells and Particles into esponsive Biomaterials Shalini Gupta, ossitza G. Alargova, Peter K. Kilpatrick and Orlin D. Velev* Description
Basic Laboratory. Materials Science and Engineering. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
 Basic Laboratory Materials Science and Engineering Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) M108 Stand: 20.10.2015 Aim: Presentation of an application of the AFM for studying surface morphology. Inhalt 1.Introduction...
Basic Laboratory Materials Science and Engineering Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) M108 Stand: 20.10.2015 Aim: Presentation of an application of the AFM for studying surface morphology. Inhalt 1.Introduction...
A gas-phase amplified quartz crystal microbalance immunosensor based on catalase modified immunoparticles
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supplementary Information A gas-phase amplified quartz crystal microbalance immunosensor based on
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supplementary Information A gas-phase amplified quartz crystal microbalance immunosensor based on
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/314/5801/1001/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Direct Measurement of the Full, Sequence-Dependent Folding Landscape of a Nucleic Acid Michael T. Woodside, Peter C.
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/314/5801/1001/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Direct Measurement of the Full, Sequence-Dependent Folding Landscape of a Nucleic Acid Michael T. Woodside, Peter C.
Digital processing of multi-mode nano-mechanical cantilever data
 IOP Publishing Journal of Physics: Conference Series 61 (2007) 341 345 doi:10.1088/1742-6596/61/1/069 International Conference on Nanoscience and Technology (ICN&T 2006) Digital processing of multi-mode
IOP Publishing Journal of Physics: Conference Series 61 (2007) 341 345 doi:10.1088/1742-6596/61/1/069 International Conference on Nanoscience and Technology (ICN&T 2006) Digital processing of multi-mode
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 34. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 34 From molecular to elemental analysis there are three major techniques used for elemental analysis: Optical spectrometry Mass spectrometry X-ray spectrometry
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 34 From molecular to elemental analysis there are three major techniques used for elemental analysis: Optical spectrometry Mass spectrometry X-ray spectrometry
Magnetic Torque Tweezers: measuring torsional stiffness in DNA and RecA DNA filaments
 Magnetic Torque Tweezers: measuring torsional stiffness in DNA and RecA DNA filaments Lipfert, J., Kerssemakers, J. W., Jager, T. & Dekker, N. H. Magnetic torque tweezers: measuring torsional stiffness
Magnetic Torque Tweezers: measuring torsional stiffness in DNA and RecA DNA filaments Lipfert, J., Kerssemakers, J. W., Jager, T. & Dekker, N. H. Magnetic torque tweezers: measuring torsional stiffness
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Polymorphism and microcrystal shape
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Polymorphism and microcrystal shape
Single-walled carbon nanotubes as nano-electrode and nanoreactor to control the pathways of a redox reaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 014 Supporting information Single-walled carbon nanotubes as nano-electrode and nanoreactor to control
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 014 Supporting information Single-walled carbon nanotubes as nano-electrode and nanoreactor to control
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI) variable light emission created via direct ultrasonic exfoliation of
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI) High quantum-yield luminescent MoS 2 quantum dots
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (ESI) High quantum-yield luminescent MoS 2 quantum dots
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. The effect of window size. The phonon MFP spectrum of intrinsic c-si (T=300 K) is shown for 7-point, 13-point, and 19-point windows. Increasing the window
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. The effect of window size. The phonon MFP spectrum of intrinsic c-si (T=300 K) is shown for 7-point, 13-point, and 19-point windows. Increasing the window
Figure S1. Steps in the fabrication of the PEO-coated nanochannel array.
 Electronic Supporting Information (ESI) PEO-coated nanoporous alumina The PEO-coated nanochannel arrays were fabricated by two-step anodization and onestep PEO coating method (see Supporting imformation,
Electronic Supporting Information (ESI) PEO-coated nanoporous alumina The PEO-coated nanochannel arrays were fabricated by two-step anodization and onestep PEO coating method (see Supporting imformation,
Reconfigurable DNA Origami Nanocapsule for ph- Controlled Encapsulation and Display of Cargo
 Supporting Information Reconfigurable DNA Origami Nanocapsule for ph- Controlled Encapsulation and Display of Cargo Heini Ijäs, Iiris Hakaste, Boxuan Shen, Mauri A. Kostiainen, and Veikko Linko* Biohybrid
Supporting Information Reconfigurable DNA Origami Nanocapsule for ph- Controlled Encapsulation and Display of Cargo Heini Ijäs, Iiris Hakaste, Boxuan Shen, Mauri A. Kostiainen, and Veikko Linko* Biohybrid
Aggregation and Deposition Behavior of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials in Aquatic Environments
 Aggregation and Deposition Behavior of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials in Aquatic Environments Menachem Elimelech Department of Chemical Engineering Environmental Engineering Program Yale University 2007 NSF
Aggregation and Deposition Behavior of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials in Aquatic Environments Menachem Elimelech Department of Chemical Engineering Environmental Engineering Program Yale University 2007 NSF
