Phys498BIO; Prof. Paul Selvin Hw #9 Assigned Wed. 4/18/12: Due 4/25/08
|
|
|
- Posy Bishop
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Ionic Movements Across a Permeable Membrane: The Nernst Potential. In class we showed that if a non-permeable membrane separates a solution with high [KCl] from a solution with low [KCl], the net charge on either side of the membrane is zero and therefore no voltage difference exists across the membrane. However, if we allow the membrane to be selectively permeable to K + ions, we find that K + ions will flow from the side of high concentration to the side of low concentration such that the entropy of the system will increase. The result of this ionic flow is a buildup of positive charge on the side of increasing K + concentration and a net negative charge on the side of decreasing K + concentration. This separation of charge produces a voltage difference across the membrane, which resists further K + flow. Equilibrium is reached where the gain in entropy from K + flow towards lower concentration exactly balances the increase in electrostatic energy from moving K + ions to a region of higher potential. (Examine the pictures below and review the lecture notes.) The equilibrium voltage difference across the membrane (the Nernst potential) is given by the Nernst equation: V = -(kt/q) ln([c inside ]/[C out ]), where C is the concentration. Keep in mind that this calculates the potential of the inside relative to the outside. The outside is taken to be 0mV. a) For the concentrations given in the picture, calculate the Nernst potential, i.e. the equilibrium voltage across the membrane. b) We would like to know if making the membrane permeable to K+ and forming the Nernst equilibrium has significantly altered the concentrations of K+. Let s calculate what percentage of potassium ions flow out of a nerve axon in order to produce V nernst. We can treat the membrane as a capacitor with capacitance, C, which stores a charge, Q, producing the Nernst potential, V nernst. A nerve axon is cylindrical in shape, but if the diameter of the cylinder (diameter of the axon) is much greater than the thickness of the dielectric (the membrane), the membrane can be viewed as a parallel plate capacitor rolled up into a cylinder. (See picture below.) Treat the axon membrane as a parallel plate capacitor of thickness d and dielectric constant ε. The axon length is 1
2 L and the radius is a. At equilibrium, write an expression for the total charge that is separated across the axon membrane. (Hint: remember or look up the equation for the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor.) c) For a realistic cell, L = 10 μm, a=2 μm, ε = 9ε ο, and the membrane thickness is 5nm. Calculate the total number of K+ ions that moved out of the cell to produce equilibrium. Be careful with units! Calculate the total number of K+ ions that were originally in the cell at 145 mm. What percentage of K+ flowed out of the axon to produce the Nernst equilibrium? Would you say that the Nernst equilibrium perturbs ionic concentrations significantly? When an action potential fires and Na + rushes in, and then K+ rushes out, has this significantly changed the Na + or K+ concentrations? 2. Energetics of the Na + K + ATPase Transporter The Na + and K + gradient across cell membranes is partly maintained by the Na + K + ATPase transporter protein. The protein uses the energy from ATP hydrolysis to translocate 3 Na+ ions out of the cell and 2 K + ions into the cell. In this problem we will examine how much energy is required to transport the sodium compared to the potassium under physiological conditions. Let s consider a mammalian skeletal 2
3 muscle cell, which has a resting potential of 90mV. (Remember that the extracellular solution is defined to be at 0mV and the intracellular solution is at 90mV.) Ionic concentrations are as follows: external sodium=145mm, internal sodium = 12mM, external potassium=4mm, internal potassium=155mm. a) Given the above concentrations, use the Nernst equation to calculate the equilibrium potentials for Na + and K +. Which of these equilibrium potentials is closest to the actual resting potential of 90mV? Will it require more free energy to move 1 Na + ion out of the cell or 1 K + ion into the cell? Explain your answer briefly. b) The cost of free energy for moving an ion up its electrochemical gradient is given by the entropic loss plus the increase in potential energy of the ion. ΔG 2 1 = kt ln([c2]/[c1]) + q Δφ 2 1 In order to transport a single Na + from inside to outside the cell, how much of the free energy required is entropic and how much is electrostatic? What is the total ΔG for a single Na + in units of kt? c) In order to transport a single K + from outside to inside the cell, how much of the free energy required is entropic and how much is electrostatic? What is the total ΔG for a single K + in units of kt? In a few words, how does this compare to your answer in part b)? d) The Na + K + transporter ATPase moves 3 sodium ions out and 2 potassium ions in, how much total energy is required for these ionic translocations? If the protein gets 25kT of free energy from ATP, what is the transporter s efficiency of free energy use? 3. Understanding the Action Potential Below is a picture of the voltages during an action potential. Describe what determines the voltage at each part of the action potential in terms of sodium and potassium ion channels and Nernst potentials. For example, why is the resting potential about 60mV? What causes the sudden rise in potential, and why is the peak about +30 mv? Why does the potential then fall? Why does it go below the resting potential? Why does the potential then return to the resting potential? Additionally, does the concentration of sodium and potassium inside and outside the cell change appreciably during the action potential? If so, why? If not, how can the potential then change so dramatically? What initiates the first action potential (i.e. at one end of the nerve) in terms of type of ion and where these ions are injected? How do ligand-gated ion channels play a role in forming an action potential? And list one or more types of ligands involved. 3
4 4. The Voltage Gated Ion Channel Open Probability. The opening and closing of voltage-gated ion channels can be understood in terms of a gate the highly charged S4 segment -- that opens or closes the pore. Hence we can think of two states: the open and closed states. These states have different energies and therefore we can use Boltzmann statistics to extract the probability of being open versus closed. Furthermore, the difference in energy between closed and open is a function of membrane voltage. This is what makes the open probability voltage dependent! The voltage dependence arises because the gate mechanism of the protein is coupled to a positive charged protein element (S4, containing a charge q) which is moved across the membrane (from the inside potential of -V to the outside potential defined to be 0 mv. See cartoon picture, noting that in the closed state, the charge shown is supposed to be in contact with the inside potential of -V.) a) Assuming the only contribution to the energies of the open state is the charge q in an electrical potential, what is the Boltzmann factor for the positive charged gate element 4
5 being inside the membrane (when the channel is closed)? Phys498BIO; Prof. Paul Selvin b) With the same assumption as part (a), what is the Boltzmann factor for the positive charged gate element being outside the membrane (when the channel is open)? c) Now write out the open probability. (Don t forget to normalize the probability using the partition function.) d) Examine the open probability you found in c) in terms of limits. What is the open probability when V gets really large? What about when V gets very negative? What value for V gives an open probability of ½ (the so- called midpoint potential, V o )? Make a sketch of the open probability as a function of voltage. e) In reality, voltage gated channels have a midpoint potential which differs from the one you found in part d). The reason is that the charged protein element controlling the gate has voltage independent interactions within the protein, which also effects the open versus closed energy. This can be modeled as a spring (of stiffness k) that is stretched a distance δx when the charged segment moves to the open state (see new picture below). Rewrite the Boltzmann factor for the closed and open state taking into account the energy from stretching the spring. Now write down the modified open probability. f) What is the midpoint potential, V o, in terms of k, δx, and q? Rewrite your expression for open probability using V-V o, conveniently eliminating k and δx. Is V o positive or negative? Make a new sketch of the open probability including V o. If we change the picture so that the spring element is relaxed a distance δx when the charge segment moves to the open state, is V o positive or negative? 5
6 6 Phys498BIO; Prof. Paul Selvin
Channels can be activated by ligand-binding (chemical), voltage change, or mechanical changes such as stretch.
 1. Describe the basic structure of an ion channel. Name 3 ways a channel can be "activated," and describe what occurs upon activation. What are some ways a channel can decide what is allowed to pass through?
1. Describe the basic structure of an ion channel. Name 3 ways a channel can be "activated," and describe what occurs upon activation. What are some ways a channel can decide what is allowed to pass through?
2.6 The Membrane Potential
 2.6: The Membrane Potential 51 tracellular potassium, so that the energy stored in the electrochemical gradients can be extracted. Indeed, when this is the case experimentally, ATP is synthesized from
2.6: The Membrane Potential 51 tracellular potassium, so that the energy stored in the electrochemical gradients can be extracted. Indeed, when this is the case experimentally, ATP is synthesized from
PNS Chapter 7. Membrane Potential / Neural Signal Processing Spring 2017 Prof. Byron Yu
 PNS Chapter 7 Membrane Potential 18-698 / 42-632 Neural Signal Processing Spring 2017 Prof. Byron Yu Roadmap Introduction to neuroscience Chapter 1 The brain and behavior Chapter 2 Nerve cells and behavior
PNS Chapter 7 Membrane Potential 18-698 / 42-632 Neural Signal Processing Spring 2017 Prof. Byron Yu Roadmap Introduction to neuroscience Chapter 1 The brain and behavior Chapter 2 Nerve cells and behavior
LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK How do our axons transmit electrical signals?
 LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK How do our axons transmit electrical signals? This lesson introduces you to the action potential, which is the process by which axons signal electrically. In this lesson you will learn
LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK How do our axons transmit electrical signals? This lesson introduces you to the action potential, which is the process by which axons signal electrically. In this lesson you will learn
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
Lecture 04, 04 Sept 2003 Chapters 4 and 5. Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.
 Lecture 04, 04 Sept 2003 Chapters 4 and 5 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 2003 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Bret Pasch Vertebrate Physiology 437 1. Membranes (CH4) 2. Nervous System
Lecture 04, 04 Sept 2003 Chapters 4 and 5 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 2003 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Bret Pasch Vertebrate Physiology 437 1. Membranes (CH4) 2. Nervous System
Electrophysiology of the neuron
 School of Mathematical Sciences G4TNS Theoretical Neuroscience Electrophysiology of the neuron Electrophysiology is the study of ionic currents and electrical activity in cells and tissues. The work of
School of Mathematical Sciences G4TNS Theoretical Neuroscience Electrophysiology of the neuron Electrophysiology is the study of ionic currents and electrical activity in cells and tissues. The work of
Particles with opposite charges (positives and negatives) attract each other, while particles with the same charge repel each other.
 III. NEUROPHYSIOLOGY A) REVIEW - 3 basic ideas that the student must remember from chemistry and physics: (i) CONCENTRATION measure of relative amounts of solutes in a solution. * Measured in units called
III. NEUROPHYSIOLOGY A) REVIEW - 3 basic ideas that the student must remember from chemistry and physics: (i) CONCENTRATION measure of relative amounts of solutes in a solution. * Measured in units called
General Physics. Nerve Conduction. Newton s laws of Motion Work, Energy and Power. Fluids. Direct Current (DC)
 Newton s laws of Motion Work, Energy and Power Fluids Direct Current (DC) Nerve Conduction Wave properties of light Ionizing Radiation General Physics Prepared by: Sujood Alazzam 2017/2018 CHAPTER OUTLINE
Newton s laws of Motion Work, Energy and Power Fluids Direct Current (DC) Nerve Conduction Wave properties of light Ionizing Radiation General Physics Prepared by: Sujood Alazzam 2017/2018 CHAPTER OUTLINE
Biomedical Instrumentation
 ELEC ENG 4BD4: Biomedical Instrumentation Lecture 5 Bioelectricity 1. INTRODUCTION TO BIOELECTRICITY AND EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in 1780s
ELEC ENG 4BD4: Biomedical Instrumentation Lecture 5 Bioelectricity 1. INTRODUCTION TO BIOELECTRICITY AND EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in 1780s
Introduction to Physiology II: Control of Cell Volume and Membrane Potential
 Introduction to Physiology II: Control of Cell Volume and Membrane Potential J. P. Keener Mathematics Department Math Physiology p.1/23 Basic Problem The cell is full of stuff: Proteins, ions, fats, etc.
Introduction to Physiology II: Control of Cell Volume and Membrane Potential J. P. Keener Mathematics Department Math Physiology p.1/23 Basic Problem The cell is full of stuff: Proteins, ions, fats, etc.
BIOELECTRIC PHENOMENA
 Chapter 11 BIOELECTRIC PHENOMENA 11.3 NEURONS 11.3.1 Membrane Potentials Resting Potential by separation of charge due to the selective permeability of the membrane to ions From C v= Q, where v=60mv and
Chapter 11 BIOELECTRIC PHENOMENA 11.3 NEURONS 11.3.1 Membrane Potentials Resting Potential by separation of charge due to the selective permeability of the membrane to ions From C v= Q, where v=60mv and
Membrane Potential Fox Chapter 6 pt 2
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Membrane Potential Fox Chapter 6 pt 2 T. Houpt, Ph.D. Resting Membrane potential (V m ) or RMP Many cells have a membrane potential (Vm) that can be measured from an electrode in the
Vert Phys PCB3743 Membrane Potential Fox Chapter 6 pt 2 T. Houpt, Ph.D. Resting Membrane potential (V m ) or RMP Many cells have a membrane potential (Vm) that can be measured from an electrode in the
Lojayn Salah. Zaid R Al Najdawi. Mohammad-Khatatbeh
 7 Lojayn Salah Zaid R Al Najdawi Mohammad-Khatatbeh Salam everyone, I made my best to make this sheet clear enough to be easily understood let the party begin :P Quick Revision about the previous lectures:
7 Lojayn Salah Zaid R Al Najdawi Mohammad-Khatatbeh Salam everyone, I made my best to make this sheet clear enough to be easily understood let the party begin :P Quick Revision about the previous lectures:
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS
 2757 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2013 Monday, 17 June, 2.30 pm 5.45 pm 15
2757 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2013 Monday, 17 June, 2.30 pm 5.45 pm 15
6 Mechanotransduction. rotation
 rotation inflow outflow Figure 6.3: Circumferential and uniaxial flow devices applying shear stress to the cell culture. They are stimulated through a circumferential fluid flow generating by a rotating
rotation inflow outflow Figure 6.3: Circumferential and uniaxial flow devices applying shear stress to the cell culture. They are stimulated through a circumferential fluid flow generating by a rotating
Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics. Eileen Nugent
 Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics Eileen Nugent Origin of the Cells Resting Membrane Potential: Nernst Equation, Donnan Equilbrium Action Potentials in the Nervous System Equivalent Electrical Circuits and
Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics Eileen Nugent Origin of the Cells Resting Membrane Potential: Nernst Equation, Donnan Equilbrium Action Potentials in the Nervous System Equivalent Electrical Circuits and
Cell membrane resistance and capacitance
 Cell membrane resistance and capacitance 1 Two properties of a cell membrane gives rise to two passive electrical properties: Resistance: Leakage pathways allow inorganic ions to cross the membrane. Capacitance:
Cell membrane resistance and capacitance 1 Two properties of a cell membrane gives rise to two passive electrical properties: Resistance: Leakage pathways allow inorganic ions to cross the membrane. Capacitance:
Cells have an unequal distribution of charge across their membrane: more postiive charges on the outside; more negative charges on the inside.
 Resting Membrane potential (V m ) or RMP Many cells have a membrane potential (Vm) that can be measured from an electrode in the cell with a voltmeter. neurons, muscle cells, heart cells, endocrine cells...
Resting Membrane potential (V m ) or RMP Many cells have a membrane potential (Vm) that can be measured from an electrode in the cell with a voltmeter. neurons, muscle cells, heart cells, endocrine cells...
Quantitative Electrophysiology
 ECE 795: Quantitative Electrophysiology Notes for Lecture #1 Tuesday, September 18, 2012 1. INTRODUCTION TO EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in 1780s
ECE 795: Quantitative Electrophysiology Notes for Lecture #1 Tuesday, September 18, 2012 1. INTRODUCTION TO EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in 1780s
Neurons and Nervous Systems
 34 Neurons and Nervous Systems Concept 34.1 Nervous Systems Consist of Neurons and Glia Nervous systems have two categories of cells: Neurons, or nerve cells, are excitable they generate and transmit electrical
34 Neurons and Nervous Systems Concept 34.1 Nervous Systems Consist of Neurons and Glia Nervous systems have two categories of cells: Neurons, or nerve cells, are excitable they generate and transmit electrical
The Membrane Potential
 The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.aw.com/bc) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion
The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.aw.com/bc) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion
TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANE
 TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANE The plasma membrane functions to isolate the inside of the cell from its environment, but isolation is not complete. A large number of molecules constantly transit between the
TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANE The plasma membrane functions to isolate the inside of the cell from its environment, but isolation is not complete. A large number of molecules constantly transit between the
Main idea of this lecture:
 Ac#ve Transport Main idea of this lecture: How do molecules, big and small, get in OR out of a cell? 2 Main ways: Passive Transport (Does not require energy) Lecture 1 Ac=ve Transport (Requires energy)
Ac#ve Transport Main idea of this lecture: How do molecules, big and small, get in OR out of a cell? 2 Main ways: Passive Transport (Does not require energy) Lecture 1 Ac=ve Transport (Requires energy)
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Electrophysiology: Electrotonic Properties 2 Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. The Model Neuron Lab Your PC/CSB115 http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~pineda/cogs107a/index.html Labs - Electrophysiology
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Electrophysiology: Electrotonic Properties 2 Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. The Model Neuron Lab Your PC/CSB115 http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~pineda/cogs107a/index.html Labs - Electrophysiology
Quantitative Electrophysiology
 ECE 795: Quantitative Electrophysiology Notes for Lecture #1 Wednesday, September 13, 2006 1. INTRODUCTION TO EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in
ECE 795: Quantitative Electrophysiology Notes for Lecture #1 Wednesday, September 13, 2006 1. INTRODUCTION TO EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in
2002NSC Human Physiology Semester Summary
 2002NSC Human Physiology Semester Summary Griffith University, Nathan Campus Semester 1, 2014 Topics include: - Diffusion, Membranes & Action Potentials - Fundamentals of the Nervous System - Neuroanatomy
2002NSC Human Physiology Semester Summary Griffith University, Nathan Campus Semester 1, 2014 Topics include: - Diffusion, Membranes & Action Potentials - Fundamentals of the Nervous System - Neuroanatomy
Physiology Unit 2. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES
 Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES Neuron Communication Neurons are stimulated by receptors on dendrites and cell bodies (soma) Ligand gated ion channels GPCR s Neurons stimulate cells
Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES Neuron Communication Neurons are stimulated by receptors on dendrites and cell bodies (soma) Ligand gated ion channels GPCR s Neurons stimulate cells
NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34
 NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34 KEY CONCEPTS 34.1 Nervous Systems Are Composed of Neurons and Glial Cells 34.2 Neurons Generate Electric Signals by Controlling Ion Distributions 34.3
NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34 KEY CONCEPTS 34.1 Nervous Systems Are Composed of Neurons and Glial Cells 34.2 Neurons Generate Electric Signals by Controlling Ion Distributions 34.3
Action Potential Propagation
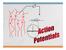 Action Potential Propagation 2 Action Potential is a transient alteration of transmembrane voltage (or membrane potential) across an excitable membrane generated by the activity of voltage-gated ion channels.
Action Potential Propagation 2 Action Potential is a transient alteration of transmembrane voltage (or membrane potential) across an excitable membrane generated by the activity of voltage-gated ion channels.
Resting membrane potential,
 Resting membrane potential Inside of each cell is negative as compared with outer surface: negative resting membrane potential (between -30 and -90 mv) Examination with microelectrode (Filled with KCl
Resting membrane potential Inside of each cell is negative as compared with outer surface: negative resting membrane potential (between -30 and -90 mv) Examination with microelectrode (Filled with KCl
Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain
 Slide 1 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain Chapter 3: The Neuronal Membrane at Rest Slide 2 Introduction Action potential in the nervous system Action potential vs. resting potential Slide 3 Not at rest
Slide 1 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain Chapter 3: The Neuronal Membrane at Rest Slide 2 Introduction Action potential in the nervous system Action potential vs. resting potential Slide 3 Not at rest
9 Generation of Action Potential Hodgkin-Huxley Model
 9 Generation of Action Potential Hodgkin-Huxley Model (based on chapter 12, W.W. Lytton, Hodgkin-Huxley Model) 9.1 Passive and active membrane models In the previous lecture we have considered a passive
9 Generation of Action Potential Hodgkin-Huxley Model (based on chapter 12, W.W. Lytton, Hodgkin-Huxley Model) 9.1 Passive and active membrane models In the previous lecture we have considered a passive
- the flow of electrical charge from one point to the other is current.
 Biology 325, Fall 2004 Resting membrane potential I. Introduction A. The body and electricity, basic principles - the body is electrically neutral (total), however there are areas where opposite charges
Biology 325, Fall 2004 Resting membrane potential I. Introduction A. The body and electricity, basic principles - the body is electrically neutral (total), however there are areas where opposite charges
Passive Membrane Properties
 Passive Membrane Properties Communicating through a leaky garden hose... Topics I Introduction & Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potentials Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Topics
Passive Membrane Properties Communicating through a leaky garden hose... Topics I Introduction & Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potentials Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Topics
Physiology Unit 2. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES
 Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES In Physiology Today Ohm s Law I = V/R Ohm s law: the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the
Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES In Physiology Today Ohm s Law I = V/R Ohm s law: the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the
Overview Organization: Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) innervate Divisions: a. Afferent
 Overview Organization: Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and spinal cord receives and processes information. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Nerve cells that link CNS with organs throughout the body.
Overview Organization: Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and spinal cord receives and processes information. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Nerve cells that link CNS with organs throughout the body.
NeuroPhysiology and Membrane Potentials. The Electrochemical Gradient
 NeuroPhysiology and Membrane Potentials Communication by neurons is based on changes in the membrane s permeability to ions This depends on the presence of specific membrane ion channels and the presence
NeuroPhysiology and Membrane Potentials Communication by neurons is based on changes in the membrane s permeability to ions This depends on the presence of specific membrane ion channels and the presence
Ionic basis of the resting membrane potential. Foundations in Neuroscience I, Oct
 Ionic basis of the resting membrane potential Foundations in Neuroscience I, Oct 3 2017 The next 4 lectures... - The resting membrane potential (today) - The action potential - The neural mechanisms behind
Ionic basis of the resting membrane potential Foundations in Neuroscience I, Oct 3 2017 The next 4 lectures... - The resting membrane potential (today) - The action potential - The neural mechanisms behind
Neurons and the membrane potential. N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016
 Neurons and the membrane potential N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016 My background, briefly Neurons Structural elements of a typical neuron Figure 1.2 Some nerve cell morphologies found in the human
Neurons and the membrane potential N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016 My background, briefly Neurons Structural elements of a typical neuron Figure 1.2 Some nerve cell morphologies found in the human
Introduction to electrophysiology. Dr. Tóth András
 Introduction to electrophysiology Dr. Tóth András Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential Ion channels Local and action potentials Intra- and extracellular propagation of the
Introduction to electrophysiology Dr. Tóth András Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential Ion channels Local and action potentials Intra- and extracellular propagation of the
Membrane Physiology. Dr. Hiwa Shafiq Oct-18 1
 Membrane Physiology Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 22-10-2018 29-Oct-18 1 Chemical compositions of extracellular and intracellular fluids. 29-Oct-18 2 Transport through the cell membrane occurs by one of two basic processes:
Membrane Physiology Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 22-10-2018 29-Oct-18 1 Chemical compositions of extracellular and intracellular fluids. 29-Oct-18 2 Transport through the cell membrane occurs by one of two basic processes:
Rahaf Nasser mohammad khatatbeh
 7 7... Hiba Abu Hayyeh... Rahaf Nasser mohammad khatatbeh Mohammad khatatbeh Brief introduction about membrane potential The term membrane potential refers to a separation of opposite charges across the
7 7... Hiba Abu Hayyeh... Rahaf Nasser mohammad khatatbeh Mohammad khatatbeh Brief introduction about membrane potential The term membrane potential refers to a separation of opposite charges across the
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 9 - TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com K + K + K + K + CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSMEMBRANE TRANSPORT Membranes and Gradients Cells must be able to communicate across their membrane barriers to materials
!! www.clutchprep.com K + K + K + K + CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSMEMBRANE TRANSPORT Membranes and Gradients Cells must be able to communicate across their membrane barriers to materials
ACTION POTENTIAL. Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil
 ACTION POTENTIAL Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil DEFINITIONS: Stimulus: A stimulus is an external force or event which when applied to an excitable tissue produces a characteristic response. Subthreshold
ACTION POTENTIAL Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil DEFINITIONS: Stimulus: A stimulus is an external force or event which when applied to an excitable tissue produces a characteristic response. Subthreshold
Membrane Potentials, Action Potentials, and Synaptic Transmission. Membrane Potential
 Cl Cl - - + K + K+ K + K Cl - 2/2/15 Membrane Potentials, Action Potentials, and Synaptic Transmission Core Curriculum II Spring 2015 Membrane Potential Example 1: K +, Cl - equally permeant no charge
Cl Cl - - + K + K+ K + K Cl - 2/2/15 Membrane Potentials, Action Potentials, and Synaptic Transmission Core Curriculum II Spring 2015 Membrane Potential Example 1: K +, Cl - equally permeant no charge
The Membrane Potential
 The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion channel
The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion channel
Problem Set No. 4 Due: Monday, 11/18/10 at the start of class
 Department of Chemical Engineering ChE 170 University of California, Santa Barbara Fall 2010 Problem Set No. 4 Due: Monday, 11/18/10 at the start of class Objective: To understand the thermodynamic and
Department of Chemical Engineering ChE 170 University of California, Santa Barbara Fall 2010 Problem Set No. 4 Due: Monday, 11/18/10 at the start of class Objective: To understand the thermodynamic and
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 12, PAGE 1 of 7
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 12, 2009 -- PAGE 1 of 7 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 12, 2009 -- PAGE 1 of 7 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
Electrical Properties of the Membrane
 BIOE 2520 Electrical Properties of the Membrane Reading: Chapter 11 of Alberts et al. Stephen Smith, Ph.D. 433 Biotech Center shs46@pitt.edu Permeability of Lipid membrane Lipid bilayer is virtually impermeable
BIOE 2520 Electrical Properties of the Membrane Reading: Chapter 11 of Alberts et al. Stephen Smith, Ph.D. 433 Biotech Center shs46@pitt.edu Permeability of Lipid membrane Lipid bilayer is virtually impermeable
The Nervous System and the Sodium-Potassium Pump
 The Nervous System and the Sodium-Potassium Pump 1. Define the following terms: Ion: A Student Activity on Membrane Potentials Cation: Anion: Concentration gradient: Simple diffusion: Sodium-Potassium
The Nervous System and the Sodium-Potassium Pump 1. Define the following terms: Ion: A Student Activity on Membrane Potentials Cation: Anion: Concentration gradient: Simple diffusion: Sodium-Potassium
SUMMARY OF THE EVENTS WHICH TRIGGER AN ELECTRICAL IMPUSLE IN NERVE CELLS (see figures on the following page)
 Anatomy and Physiology/AP Biology ACTION POTENTIAL SIMULATION BACKGROUND: The plasma membrane of cells is a selectively permeable barrier, which separates the internal contents of the cell from the surrounding
Anatomy and Physiology/AP Biology ACTION POTENTIAL SIMULATION BACKGROUND: The plasma membrane of cells is a selectively permeable barrier, which separates the internal contents of the cell from the surrounding
Housekeeping, 26 January 2009
 5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Neurons Chapter 11 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes + Water 2. Neurons
5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Neurons Chapter 11 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes + Water 2. Neurons
Neurons. 5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan Finish Solutes + Water. 2. Neurons. Chapter 11
 5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Neurons Chapter 11 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes + Water 2. Neurons
5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Neurons Chapter 11 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes + Water 2. Neurons
CHAPTER 2 HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES
 CHAPTER 2 HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES Behavior of human nervous system is well realized as electrical signal propagation through nerves from different parts of body to the brain. Now, it
CHAPTER 2 HUMAN NERVOUS SYSTEM ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES Behavior of human nervous system is well realized as electrical signal propagation through nerves from different parts of body to the brain. Now, it
Chapter 1 subtitles Ion gradients
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 1 subtitles Ion gradients Introduction In this first chapter, I'll explain the basic knowledge required to understand the electrical signals generated
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 1 subtitles Ion gradients Introduction In this first chapter, I'll explain the basic knowledge required to understand the electrical signals generated
Lecture Notes 8C120 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren. Cellular electrophysiology: modeling and simulation. Nico Kuijpers
 Lecture Notes 8C2 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren Cellular electrophysiology: modeling and simulation Nico Kuijpers nico.kuijpers@bf.unimaas.nl February 9, 2 2 8C2 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren Extracellular
Lecture Notes 8C2 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren Cellular electrophysiology: modeling and simulation Nico Kuijpers nico.kuijpers@bf.unimaas.nl February 9, 2 2 8C2 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren Extracellular
6.3.4 Action potential
 I ion C m C m dφ dt Figure 6.8: Electrical circuit model of the cell membrane. Normally, cells are net negative inside the cell which results in a non-zero resting membrane potential. The membrane potential
I ion C m C m dφ dt Figure 6.8: Electrical circuit model of the cell membrane. Normally, cells are net negative inside the cell which results in a non-zero resting membrane potential. The membrane potential
Chapter 2 Cellular Homeostasis and Membrane Potential
 Chapter 2 Cellular Homeostasis and Membrane Potential 2.1 Membrane Structure and Composition The human cell can be considered to consist of a bag of fluid with a wall that separates the internal, or intracellular,
Chapter 2 Cellular Homeostasis and Membrane Potential 2.1 Membrane Structure and Composition The human cell can be considered to consist of a bag of fluid with a wall that separates the internal, or intracellular,
لجنة الطب البشري رؤية تنير دروب تميزكم
 1) Hyperpolarization phase of the action potential: a. is due to the opening of voltage-gated Cl channels. b. is due to prolonged opening of voltage-gated K + channels. c. is due to closure of the Na +
1) Hyperpolarization phase of the action potential: a. is due to the opening of voltage-gated Cl channels. b. is due to prolonged opening of voltage-gated K + channels. c. is due to closure of the Na +
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activation of P2X2 receptor channels in symmetric Na + solutions only modestly alters the intracellular ion concentration. a,b) ATP (30 µm) activated P2X2 receptor channel currents
Supplementary Figure 1 Activation of P2X2 receptor channels in symmetric Na + solutions only modestly alters the intracellular ion concentration. a,b) ATP (30 µm) activated P2X2 receptor channel currents
The Nervous System. Nerve Impulses. Resting Membrane Potential. Overview. Nerve Impulses. Resting Membrane Potential
 The Nervous System Overview Nerve Impulses (completed12/03/04) (completed12/03/04) How do nerve impulses start? (completed 19/03/04) (completed 19/03/04) How Fast are Nerve Impulses? Nerve Impulses Nerve
The Nervous System Overview Nerve Impulses (completed12/03/04) (completed12/03/04) How do nerve impulses start? (completed 19/03/04) (completed 19/03/04) How Fast are Nerve Impulses? Nerve Impulses Nerve
Chapter 7-3 Cells and Their Environment
 Chapter 7-3 Cells and Their Environment 7-3 Passive Transport Passive transport-the movement of substances across the cell membrane without using NRG Concentration Gradient-difference in concentration
Chapter 7-3 Cells and Their Environment 7-3 Passive Transport Passive transport-the movement of substances across the cell membrane without using NRG Concentration Gradient-difference in concentration
Cellular Electrophysiology. Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Part 1: Resting and Action Potentials Cardiac Electrophysiology Theory Simulation Experiment Scale The membrane: structure, channels and gates The cell: resting potential, whole cell currents, cardiac
Part 1: Resting and Action Potentials Cardiac Electrophysiology Theory Simulation Experiment Scale The membrane: structure, channels and gates The cell: resting potential, whole cell currents, cardiac
BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control
 BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control Hodgkin-Huxley Model for Nerve Cell Action Potential Part 1 Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 References Hoppensteadt-Peskin Ch. 3 for all the mathematics. Cooper s The Cell
BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control Hodgkin-Huxley Model for Nerve Cell Action Potential Part 1 Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 References Hoppensteadt-Peskin Ch. 3 for all the mathematics. Cooper s The Cell
I. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS
 I. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS Background to Nerve Impulses We have all heard that nerve impulses are electrical impulses. Stimuli at one end of a nerve cell are communicated to the far end of the nerve cell through
I. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS Background to Nerve Impulses We have all heard that nerve impulses are electrical impulses. Stimuli at one end of a nerve cell are communicated to the far end of the nerve cell through
Ch. 5. Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials
 Ch. 5. Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials Basic Physics of Membrane Potentials Nerve and muscle cells: Excitable Capable of generating rapidly changing electrochemical impulses at their membranes
Ch. 5. Membrane Potentials and Action Potentials Basic Physics of Membrane Potentials Nerve and muscle cells: Excitable Capable of generating rapidly changing electrochemical impulses at their membranes
7 Membrane Potential. The Resting Membrane Potential Results From the Separation of Charges Across the Cell Membrane. Back.
 Back 7 Membrane Potential John Koester Steven A. Siegelbaum INFORMATION IS CARRIED WITHIN and between neurons by electrical and chemical signals. Transient electrical signals are particularly important
Back 7 Membrane Potential John Koester Steven A. Siegelbaum INFORMATION IS CARRIED WITHIN and between neurons by electrical and chemical signals. Transient electrical signals are particularly important
Ch 8: Neurons: Cellular and Network Properties, Part 1
 Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Ch 8: Neurons: Cellular and Network Properties, Part 1 Objectives: Describe the Cells of the NS Explain the creation and propagation of an electrical signal in a nerve
Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Ch 8: Neurons: Cellular and Network Properties, Part 1 Objectives: Describe the Cells of the NS Explain the creation and propagation of an electrical signal in a nerve
Nernst Equation and Equilibrium Potentials
 CELLULAR AND AUTONOMIC PHYSIOLOGY 13 Case 3 Nernst Equation and Equilibrium Potentials This case will guide you through the principles underlying diffusion potentials and electrochemical equilibrium. veil
CELLULAR AND AUTONOMIC PHYSIOLOGY 13 Case 3 Nernst Equation and Equilibrium Potentials This case will guide you through the principles underlying diffusion potentials and electrochemical equilibrium. veil
Introduction to electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth András
 Introduction to electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth András Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential Ion channels Local and action potentials Intra- and extracellular propagation of
Introduction to electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth András Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential Ion channels Local and action potentials Intra- and extracellular propagation of
Capacitors. HPP Activity 68v1. Charge Inside the Body A Close Look at Cell Membranes
 HPP Activity 68v1 Capacitors Charge Inside the Body A Close Look at Cell Membranes Our bodies store and use charge to transmit signals across nerves and to tell certain cells what to do and when to do
HPP Activity 68v1 Capacitors Charge Inside the Body A Close Look at Cell Membranes Our bodies store and use charge to transmit signals across nerves and to tell certain cells what to do and when to do
Neurophysiology. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Neurophysiology Danil Hammoudi.MD ACTION POTENTIAL An action potential is a wave of electrical discharge that travels along the membrane of a cell. Action potentials are an essential feature of animal
Neurophysiology Danil Hammoudi.MD ACTION POTENTIAL An action potential is a wave of electrical discharge that travels along the membrane of a cell. Action potentials are an essential feature of animal
The nerve impulse. INTRODUCTION
 The nerve impulse. INTRODUCTION Axons are responsible for the transmission of information between different points of the nervous system and their function is analogous to the wires that connect different
The nerve impulse. INTRODUCTION Axons are responsible for the transmission of information between different points of the nervous system and their function is analogous to the wires that connect different
Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις
 Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 5 Μοντέλο Hodgkin-Huxley (Hodgkin-Huxley Model) Response to Current Injection 2 Hodgin & Huxley Sir Alan Lloyd
Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 5 Μοντέλο Hodgkin-Huxley (Hodgkin-Huxley Model) Response to Current Injection 2 Hodgin & Huxley Sir Alan Lloyd
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS
 2757 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Monday, 27 June, 9.30 am 12.30 pm Answer
2757 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Monday, 27 June, 9.30 am 12.30 pm Answer
Chapter 18 Solutions Set Up: (a) The proton has charge and mass Let point a be at the negative plate and
 Chapter 18 Solutions *18.1. Set Up: Since the charge is positive the force on it is in the same direction as the electric field. Since the field is uniform the force is constant is upward is to the right,
Chapter 18 Solutions *18.1. Set Up: Since the charge is positive the force on it is in the same direction as the electric field. Since the field is uniform the force is constant is upward is to the right,
Nervous Systems: Neuron Structure and Function
 Nervous Systems: Neuron Structure and Function Integration An animal needs to function like a coherent organism, not like a loose collection of cells. Integration = refers to processes such as summation
Nervous Systems: Neuron Structure and Function Integration An animal needs to function like a coherent organism, not like a loose collection of cells. Integration = refers to processes such as summation
BIOL Week 5. Nervous System II. The Membrane Potential. Question : Is the Equilibrium Potential a set number or can it change?
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 5 Nervous System II 1 The Membrane Potential Question : Is the Equilibrium Potential a set number or can it change? Let s look at the Nernst Equation again.
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 5 Nervous System II 1 The Membrane Potential Question : Is the Equilibrium Potential a set number or can it change? Let s look at the Nernst Equation again.
Capacitance. Chapter 21 Chapter 25. K = C / C o V = V o / K. 1 / Ceq = 1 / C / C 2. Ceq = C 1 + C 2
 = Chapter 21 Chapter 25 Capacitance K = C / C o V = V o / K 1 / Ceq = 1 / C 1 + 1 / C 2 Ceq = C 1 + C 2 Copyright 25-2 Capacitance 25.01 Sketch a schematic diagram of a circuit with a parallel-plate capacitor,
= Chapter 21 Chapter 25 Capacitance K = C / C o V = V o / K 1 / Ceq = 1 / C 1 + 1 / C 2 Ceq = C 1 + C 2 Copyright 25-2 Capacitance 25.01 Sketch a schematic diagram of a circuit with a parallel-plate capacitor,
Action Potentials & Nervous System. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Action Potentials & Nervous System Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review: Membrane potentials exist due to unequal distribution of charge across the membrane Concentration gradients drive ion
Action Potentials & Nervous System Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Review: Membrane potentials exist due to unequal distribution of charge across the membrane Concentration gradients drive ion
Advanced Higher Biology. Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins
 Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Membrane Protein Channels
 Membrane Protein Channels Potassium ions queuing up in the potassium channel Pumps: 1000 s -1 Channels: 1000000 s -1 Pumps & Channels The lipid bilayer of biological membranes is intrinsically impermeable
Membrane Protein Channels Potassium ions queuing up in the potassium channel Pumps: 1000 s -1 Channels: 1000000 s -1 Pumps & Channels The lipid bilayer of biological membranes is intrinsically impermeable
What are neurons for?
 5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes Water 2. Neurons Neurons Chapter 11
5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes Water 2. Neurons Neurons Chapter 11
The Nervous System. Nervous System Organization. Nerve Tissue. Two parts to the nervous system 11/27/2016
 The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli. Three functions of the nervous system: Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors.
The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli. Three functions of the nervous system: Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors.
Propagation& Integration: Passive electrical properties
 Fundamentals of Neuroscience (NSCS 730, Spring 2010) Instructor: Art Riegel; email: Riegel@musc.edu; Room EL 113; time: 9 11 am Office: 416C BSB (792.5444) Propagation& Integration: Passive electrical
Fundamentals of Neuroscience (NSCS 730, Spring 2010) Instructor: Art Riegel; email: Riegel@musc.edu; Room EL 113; time: 9 11 am Office: 416C BSB (792.5444) Propagation& Integration: Passive electrical
Control and Integration. Nervous System Organization: Bilateral Symmetric Animals. Nervous System Organization: Radial Symmetric Animals
 Control and Integration Neurophysiology Chapters 10-12 Nervous system composed of nervous tissue cells designed to conduct electrical impulses rapid communication to specific cells or groups of cells Endocrine
Control and Integration Neurophysiology Chapters 10-12 Nervous system composed of nervous tissue cells designed to conduct electrical impulses rapid communication to specific cells or groups of cells Endocrine
Multi-loop Circuits and Kirchoff's Rules
 1 of 8 01/21/2013 12:50 PM Multi-loop Circuits and Kirchoff's Rules 7-13-99 Before talking about what a multi-loop circuit is, it is helpful to define two terms, junction and branch. A junction is a point
1 of 8 01/21/2013 12:50 PM Multi-loop Circuits and Kirchoff's Rules 7-13-99 Before talking about what a multi-loop circuit is, it is helpful to define two terms, junction and branch. A junction is a point
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 24: CAPACITORS & DIELECTRICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CAPACITORS AND CAPACITANCE A CAPACITOR is formed by two surfaces of equal/opposite charge brought close together - Separation of charge potential energy stored Connecting
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CAPACITORS AND CAPACITANCE A CAPACITOR is formed by two surfaces of equal/opposite charge brought close together - Separation of charge potential energy stored Connecting
Universality of sensory-response systems
 excite.org(anism): Electrical Signaling Universality of sensory-response systems Three step process: sensation-integration-response Bacterial chemotaxis Madigan et al. Fig. 8.24 Rick Stewart (CBMG) Human
excite.org(anism): Electrical Signaling Universality of sensory-response systems Three step process: sensation-integration-response Bacterial chemotaxis Madigan et al. Fig. 8.24 Rick Stewart (CBMG) Human
STUDIES OF CHANGING MEMBRANE POTENTIAL * : 1. BASIC ELECTRICAL THEORY, 2. GRADED AND ACTION POTENTIALS 3. THE VOLTAGE CLAMP AND MEMBRANE POTENTIALS
 STUDIES OF CHANGING MEMBRANE POTENTIAL * : 1. BASIC ELECTRICAL THEORY, 2. GRADED AND ACTION POTENTIALS 3. THE VOLTAGE CLAMP AND MEMBRANE POTENTIALS I. INTRODUCTION A. So far we have only considered the
STUDIES OF CHANGING MEMBRANE POTENTIAL * : 1. BASIC ELECTRICAL THEORY, 2. GRADED AND ACTION POTENTIALS 3. THE VOLTAGE CLAMP AND MEMBRANE POTENTIALS I. INTRODUCTION A. So far we have only considered the
Topics in Neurophysics
 Topics in Neurophysics Alex Loebel, Martin Stemmler and Anderas Herz Exercise 2 Solution (1) The Hodgkin Huxley Model The goal of this exercise is to simulate the action potential according to the model
Topics in Neurophysics Alex Loebel, Martin Stemmler and Anderas Herz Exercise 2 Solution (1) The Hodgkin Huxley Model The goal of this exercise is to simulate the action potential according to the model
Introduction to cardiac electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth András 2018
 Introduction to cardiac electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth ndrás 2018 Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential 1 Transmembran transport Major types of transmembran transport J: net
Introduction to cardiac electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth ndrás 2018 Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential 1 Transmembran transport Major types of transmembran transport J: net
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Neuron Structure. Why? Model 1 Parts of a Neuron. What are the essential structures that make up a neuron?
 Why? Neuron Structure What are the essential structures that make up a neuron? Cells are specialized for different functions in multicellular organisms. In animals, one unique kind of cell helps organisms
Why? Neuron Structure What are the essential structures that make up a neuron? Cells are specialized for different functions in multicellular organisms. In animals, one unique kind of cell helps organisms
VII. Porous Media Lecture 36: Electrochemical Supercapacitors
 VII. Porous Media Lecture 36: Electrochemical Supercapacitors MIT Student (and MZB) 1. Transmission Line Model for Linear Response Last time, we took the supercapacitor limit of a general porous medium
VII. Porous Media Lecture 36: Electrochemical Supercapacitors MIT Student (and MZB) 1. Transmission Line Model for Linear Response Last time, we took the supercapacitor limit of a general porous medium
Biophysics I (BPHS 3090)
 Biophysics I (BPHS 3090) Instructors: Prof. Christopher Bergevin (cberge@yorku.ca) Website: http://www.yorku.ca/cberge/3090w2015.html York University Winter 2015 Lecture 16 Reference/Acknowledgement: -
Biophysics I (BPHS 3090) Instructors: Prof. Christopher Bergevin (cberge@yorku.ca) Website: http://www.yorku.ca/cberge/3090w2015.html York University Winter 2015 Lecture 16 Reference/Acknowledgement: -
Muscle regulation and Actin Topics: Tropomyosin and Troponin, Actin Assembly, Actin-dependent Movement
 1 Muscle regulation and Actin Topics: Tropomyosin and Troponin, Actin Assembly, Actin-dependent Movement In the last lecture, we saw that a repeating alternation between chemical (ATP hydrolysis) and vectorial
1 Muscle regulation and Actin Topics: Tropomyosin and Troponin, Actin Assembly, Actin-dependent Movement In the last lecture, we saw that a repeating alternation between chemical (ATP hydrolysis) and vectorial
Resting Distribution of Ions in Mammalian Neurons. Outside Inside (mm) E ion Permab. K Na Cl
 Resting Distribution of Ions in Mammalian Neurons Outside Inside (mm) E ion Permab. K + 5 100-81 1.0 150 15 +62 0.04 Cl - 100 10-62 0.045 V m = -60 mv V m approaches the Equilibrium Potential of the most
Resting Distribution of Ions in Mammalian Neurons Outside Inside (mm) E ion Permab. K + 5 100-81 1.0 150 15 +62 0.04 Cl - 100 10-62 0.045 V m = -60 mv V m approaches the Equilibrium Potential of the most
Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I NAME, Section (circle): am pm 23 September Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes.
 1 Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I NAME, Section (circle): am pm 23 September 2004. Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes. True or False (write true or false ; 10 points total; 1 point each) 1.
1 Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I NAME, Section (circle): am pm 23 September 2004. Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes. True or False (write true or false ; 10 points total; 1 point each) 1.
