Analytical model of high-voltage transmission line subjected to the downburst wind with rainfall
|
|
|
- George Simon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rsarch Articl Analytical mdl f high-vltag transmissin lin subjctd t th dwnburst wind with rainfall Advancs in Mchanical Enginring 1 13 Ó Th Authr(s) 2015 DOI: / aim.sagpub.cm Cha Zhu and Yibing Liu Abstract Thr hav bn many rprts rcntly n unanticipatd gallping and cllaps accidnts f twr-lin systms du t dwnburst wind with rainfall. Althugh wt dwnburst is charactrizd by high-vlcity wind with rainfall, vry littl rsarch wrk is invlvd with gallping f high-vltag transmissin lin inducd by th dwnburst wind with rainfall. Thus, this articl prpss a prliminary thrtical study aiming t prvid an analytical mdl f th high-vltag transmissin lin subjctd t th dwnburst wind with rainfall t xplain sm phnmna bsrvd frm fild masurmnts. Thrugh wind r rain wind tunnl xprimnts, w btaind ardynamic charactristics f th high-vltag cnductr with diffrnt yaw angls and rainfall rats. Cnsidring th variatins f svral factrs such as wind vlcity, rainfall rat, yaw angl, and attack angl, th prpsd analytical mdl was cratd by finit lmnt mthd and cntral diffrncs with th btaind ardynamic cfficints f th high-vltag cnductr. Th thrtical rsults accrd wll with th xprimntal data. Th analytical mdl nabls bttr cmprhnsin f th gallping f th high-vltag transmissin lin subjctd t th dwnburst wind with rainfall. Kywrds Dwnburst wind, high-vltag transmissin lin, finit lmnt mthd, rainfall Dat rcivd: 15 Nvmbr 2014; accptd: 2 January 2015 Acadmic Editr: Jia-Jang Wu Intrductin Th plannd high-vltag transmissin twr-lins ar prsnt in th suthwst rgin f China whr thundrstrms ccur frquntly. Th currnt trnd is t dsign and cnstruct much tallr twrs with lngr spans than vr, which maks nsuring scur and stabl pratin f th high-vltag transmissin twrlins a challng fr lctric pwr nginring. 1,2 Failur rcrds f high-vltag transmissin twrlins in Amrica, Australia, Suth Africa, and svral thr rgins shw that mr than 0% f wathrrlatd failurs ar causd by th dwnbursts with th ccurrnc f rainfall. 3 Althugh thr ar a larg numbr f th dwnbursts which typically cnsists f prcipitatin (calld wt dwnburst), vry littl attntin was paid t th ffct f th dwnburst wind cupld with rainfall n gallping f high-vltag transmissin lin. Mrvr, th cnvntinal layr vrtical prfil f wind vlcity is n lngr valid fr th dwnbursts, and nrmal dsign mthds f th transmissin twrlins vidntly ar nt adquat fr this ff-dsign cnditin. Schl f Enrgy and Mchanical Enginring, Nrth China Elctric Pwr Univrsity, Bijing, China Crrspnding authr: Cha Zhu, Schl f Enrgy and Mchanical Enginring, Nrth China Elctric Pwr Univrsity, Bijing , China. zhucha@ncpu.du.cn Crativ Cmmns CC-BY: This articl is distributd undr th trms f th Crativ Cmmns Attributin 3.0 Licns ( which prmits any us, rprductin and distributin f th wrk withut furthr prmissin prvidd th riginal wrk is attributd as spcifid n th SAGE and Opn Accss pags ( pnaccss.htm).
2 2 Advancs in Mchanical Enginring In rcnt yars, many rsarchrs hav studid th diffrnt aspcts f this subjct. Olivr t al. 4 dscribd a prbabilistic mdl fr dsign transmissin lin systms against th dwnburst typ winds and dvlpd a practical mdl t stimat th risk f a strik f damaging dwnburst n a high-vltag transmissin lin with spcifid lngth and rintatin in Australia. Savry t al. 5 carrid ut a prliminary study n th structural rspns f a typical lattic transmissin twr subjctd t a micrburst. Th rsults shwd that th micrburst did nt caus failurs du t its lwr intnsity and lngr duratins. Lin t al. 6 intrducd an arlastic mdl f a singl span f supprt lattic twr-lins with scal rati f 1:100, which mts th nd f th similarity thry fr wind tunnl tsts. Dirct cmparisn f twr and lin rspns t synptic wind prfil vrsus dwndraft utflw wind prfil indicatd that transmissin lin failurs frm dwndraft winds wr mst likly causd by pak twr lads that culd xcd that f bundary layr winds by an rdr f magnitud, and pak upstram cnductr lads that culd rach svral tims mr than th pak dwnstram cnductr lads. Shhata t al. 7, mplyd th finit lmnt mthd t idntify th critical micrburst paramtrs that lad t maximum frcs in varius mmbrs f a transmissin twr structur. Th rsult shwd that th pak valus bviusly xcd th transmissin twr structur just ncuntrd with nrmal wind lads, and th pak valus wr snsitiv t th dwnburst lcatin with rspct t th twr. Zhang t al. 9 stablishd finit lmnt mdls fr singl twr and transmissin twr-lin systm t simulat wind-inducd prgrssiv cllaps. Th simulatin rsults dmnstratd that th transmissin twr-lin systm cllaps mchanism dpnds n th numbr, psitin, and last dfrmatin f damag lmnts, and th ffcts f th cnductr and th grund culd nt b ignrd. Mara and Hng 10 invstigatd th inlastic rspns f a slf-supprtd lattic transmissin twr undr bundary layr wind and dwnburst wind and wind lading at diffrnt dirctins rlativ t th twr. And nnlinar static pushvr analysis was usd t btain th capacity curv f th twr, dfind by th frc dfrmatin rlatinship at ach cnsidrd wind dirctin. Th rsult shwd that th yild and maximum capacitis vary with wind dirctin and wuld b usful fr th valuatin f th adquacy f xisting twrs undr dwnburst vnts. Kikuchi and cllagus 11,12 singld ut a blw-dwn-typ wind tunnl t study th influnc f havy rainfall cnditins n th ardynamic drag cfficint f vrhad pwr lin. Th drag cfficints wr masurd with diffrnt valus f wind vlcity, incidnt angl, surfac rughnss, and turbulnc intnsity. Th xprimntal rsults btaind in th wind tunnls indicatd that th nwly lctric pwr lin, LP110, was vry ffctiv t rduc th drag frc in a practical us. Yang t al. 13 stablishd a tim-dpndnt failur prbability mdl t valuat shrt-trm rliability f vrhad lins undr th impact f strng wind and rain lads, and tk IEEE-79 systm as an xampl t simulat th rliability f th vrhad lins. Th rsults shwd that th impact f th strng wind and rain lads wuld sriusly affct rliability indics f th transmissin systm, and rain lads hav bvius ffct n th rliability f transmissin lin. Chi 14 studid wind-drivn rain and driving-rain cfficint during thundrstrm and nnthundrstrm vnts at a wind-drivn rain-masuring statin in Singapr. Th bsrvatin f th driving-rain intnsity cfficint indicatd that th idal cfficint calculatd basd n drp siz distributin was nt apprpriat fr lw altituds cls t th grund. Li and Bai 15,16 prpsd a calculatin apprach f rain lad with cmbinatin principl f vrhad transmissin lins and stablishd a rain-wind-inducd dynamic mdl f transmissin twr systm with finit lmnt mthd. By mans f numrical simulatin, thy fund that th rainfall influncs n th rspns f vrhad transmissin lin wr vidnt, which psssss th xcitatin fatur f simultanus actin with wind turbulnc. Zhu t al. 17,1 stablishd an analytical mdl f rain-wind-inducd vibratin f th high-vltag transmissin lin and invstigatd th ffct f wind vlcity, rivult mtin, raindrp vlcity, and tim-varying mass n th vibratin amplitud. Th rsults shwd that th largst amplitud f th high-vltag cnductr nly ccurrd within a crtain rang f wind vlcity and prsntd a vlcityrstrictd vibratin rspns. In th abv litraturs, studis abut th dynamic charactristics f transmissin twr-lins mainly fcusd n th dynamic charactristics f th twr subjctd t dry dwnburst, but th dynamic charactristics f th transmissin lins subjctd t wt dwnburst (dwnburst wind with rainfall) wr rarly invstigatd. Fr this rasn, this articl aims t validat an analytical mdl f th high-vltag transmissin lin subjctd t th dwnburst wind with rainfall t clarify th gallping mchanism. By wind r rain wind tunnl xprimnts, w btaind ardynamic cfficints f th high-vltag cnductr at diffrnt yaw angls and rainfall rats. Cnsidring th variatins f svral factrs, such as wind vlcity, rainfall rat, yaw angl, and attack angl, th prpsd analytical mdl is cratd by mans f finit lmnt mthd and cntral diffrncs with th btaind ardynamic charactristics f th high-vltag cnductr.
3 Zhu and Liu 3 Gnral faturs f th dwnburst wind and rainfall during a thundrstrm Wind vlcity f th dwnburst A dwnburst is a svr lcalizd dwndraft frm a thundrstrm, such that its structur, scal, intnsity f wind, and rainfall cannt b masurd in fild with cnvntinal rcrding statins. 19,20 Fr purpss f analysis, th wind vlcity ccurring at any tim t and any hight y within a dwndraft can b assumd as a summatin f a man wind vlcity and a fluctuating wind vlcity as fllws Uy, ð t Þ= U ðy, tþ+ uy, ð tþ ð1þ whr U(y, t) is th wind vlcity at any tim t and any hight y, U(y, t) is th man wind vlcity, and u(y, t) is th turbulnt wind vlcity. W assum that th man wind vlcity f any tim at any hight can b factrizd as th prduct f a vrtical prfil and a tim functin as fllws U ðy, tþ= VðyÞ3 fðþ t ð2þ whr f (t)= jv c (t) j= maxjv c (t) j, v c is th wind vlcity acting n th bsrving pint f th cnductr, V max is th maximum wind spd at hight y, and y max is th hight at which th maximum vlcity ccurs, 21 and V(y)=1:22 3 ½ 0:15y=y max 3:2175y=y max Š 3 V max. As shwn in Figur 1, th dwnburst is assumd t mv frward alng its straight track with translatinal vlcity v t, th distanc f th dwnburst frm th bsrving pint N is r with yaw angl u. Th crdinat systm in Figur 1 is fixd t th dwnburst cntr f O and mvs with th dwnburst. S, at any tim t, th wind vlcity acting n th bsrving pint f th cnductr is v c = v N + v t ð3þ Th fluctuating wind vlcity u(y, t) can b btaind by amplitud-mdulating sm statinary prcss with pwr spctral dnsity functin as fllws Twr z O v r Dwnburst Twr Cnductr Figur 1. Hrizntal diagram f th dwnburst with transmissin twr-lin. r θ N v t v c x uy, ð t Þ= aðy, tþkðy, tþ ð4þ whr a(y, t) is th mdulatin functin, and w assum a(y, t) =0:25 U(y, t) basd n full-scal and wind tunnl data by rsarchrs at th Wind Scinc and Enginring Rsarch Cntr f Txas Tchnlgy Univrsity. 20 k(y, t)= Ð + ivt dy(y, v) 22 is a statinary Gaussian stchastic prcss, and Y(y, v) is an rthgnal-incrmntal prcss fr a givn y. Raindrp spctra and rain lads Wt dwnbursts ar cratd by thundrstrms with mdrat r havy prcipitatin. 23 Th raindrps hav impact n th transmissin twr-lins with grat nrgy, which aggravats th vibratin f th cnductr. Th nrgy f a raindrp ffct n th cnductr is rlatd t its diamtr, vlcity, and rainfall intnsity. 24 A larg numbr f bsrvatins shw that th raindrp siz bys a ngativ xpnntial distributin. Th Marshall Palmr xpnntial siz distributin (rfrrd t as M-P spctrum) is widly usd 25 as fllws nd ð Þ= N 0 xpð DDÞ ð5þ whr N 0 = (m 3 =mm), gradint factr D = 4:1I 0:21, D is th raindrp diamtr, and I is th rainfall intnsity pr hur as shwn in Tabl 1. As th rang f raindrp diamtr in natural rainfall is mm, 26 t simplify th analysis, w tak six typs f intrmittnt raindrp diamtr t simulat cntinuus distributin f raindrp diamtr f rainfall. Diamtrs f ach typ f raindrp and its rprsntd rang f diamtr ar shwn in Tabl 2. Crrspndingly, th vlum ccupancy rati f th diffrnt sizs f raindrps in wind fild can b xprssd as g = ð6:0 0:1 1 6 pd3 nd ð ÞdD ð6þ And th trminal vlcity f th raindrp, V m, with th diffrnt sizs f raindrps, 27 can b xprssd as :77 D ffiffiffi 2 p D\1 mm D V m = pffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi ð17:2 0:44DÞ 0:1D 1 mm\d\3 mm >: D ð0: :045DÞ 3 mm\d\6 mm ð7þ Onc a raindrp hits th cnductr, th vlcity f th raindrp bcms zr within an xtrmly shrt tim t. Basd n Nwtn s scnd law, th calculatin frmula can b drivd as
4 4 Advancs in Mchanical Enginring Tabl 1. Intnsity f rainfall (mm/h). Lvl S M Larg H Hu Rainfall rat S: slight; M: mdrat; L: larg; H: havy; Hu: hug rain. Tabl 2. Rprsntd rang f diamtr with ach typ f raindrp (mm). D R D: diamtr; R: rprsntd rang. FðÞ= t mv m = 1 t 6t r 1pD 3 V m ðþ whr r 1 is th dnsity f th raindrp, and assuming t = D=2V r, th prssur frc acting n th cnductr pr unit lngth by th raindrps can b xprssd as A y z x v w l B F r = FðÞ t A bg = 2 9 r 1pnD 3 Vm 2 ð9þ whr th actin ara f a raindrp is A = pd 2 =4, sctinal width f lading structur is b, and n = Ð 0 n(d)dd is th dnsity f ttal numbrs f raindrps pr unit vlum. Crss-sctin f cnductr z y Usinθ w& U r β v& Dwnburst wind with rainfall Analytical mdl f high-vltag cnductr with finit lmnt discrtizatin Analytical mdl f high-vltag cnductr subjctd t dwnburst wind with rainfall Lt us us a rigid and unifrm cabl t rprsnt a suspndd high-vltag cnductr with small sag, and th tw twrs (A and B) at bth nds f cabl ar assumd t b fixd (s Figur 2). Th crdinats f any pints alng th cnductr ar rprsntd by using Cartsian systm, which dfins that th mtin in Oxy is in-plan vibratin, whil th mtin in Oyz is ut-f-plan vibratin. Th dynamic displacmnts at y and z dirctins ar v and w, rspctivly. Cnsidring th in-plan and ut-f-plan mtin vlcitis f th cabl, _v and _w, th rlativ >: m 2 v t 2 + c v s m 2 w t 2 Figur 2. Schmatic rprsntatin f th cnductr and its crss sctin subjctd t th dwnburst with rainfall. qffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi U r = ðu sin u _w Þ 2 + _v 2 ð10þ Th attack angl btwn th rlativ vlcity U r and th dwnburst wind vlcity U is dfind as b, which can b xprssd as _v b = arctan ð11þ U sin u _w Taking small displacmnts and larg dfrmatins as th basic assumptin fr th cnductr, th analytical mdl f th cnductr subjctd t dwnburst wind with rainfall is built by partial diffrntial quatin as fllws t ðh + hþ dy x + dv = 1 2 dru r 2 ðc L ðbþcs b + C D ðbþsin bþ+ 2 9 r 1pnD 3 ðv m _v Þ 2 + c w s t ðh + hþ dw = 1 x 2 dru r 2 ðc D ðbþcs b C L ðbþsin bþ+ 2 9 r 1pnD 3 ðu sin u _w Þ 2 ð12þ vlcity f th dwnburst wind t th cabl can b xprssd as whr y = mg(xl x 2 )=2H is th prfil f th cnductr givn by th parabla; 2 H and h ar th hrizntal
5 Zhu and Liu 5 static tnsin and dynamic tnsin f th cnductr, rspctivly; c s is th damping rati f th cnductr in th y and z dirctins, rspctivly; r is th air dnsity; d is th diamtr f th cnductr; and C L and C D ar th lift and drag cfficints, rspctivly. Th frcs in th right-hand sid f quatin (12) ar th functin f th cnductr vlcity, _v and _w, but nt f its displacmnt r acclratin, sinc it is basd n th quasi-stady apprach. Thrfr, th frcs ar xpandd int Taylr s sris at b = 0, and th itms highr than first rdr ar nglctd. Whn b 0 and U sin u _w, b =arctan(_v=(u sin u _w)) _v=(u sin u). Thus >: m 2 v t 2 + c v y m 2 w t 2 t ðh + hþ dy x + dv + c w z t ðh + hþ dw = F z x = F y ð13þ whr F y = (1=2)drU 2 sin 2 uc L +(2=9)r 1 pnd 3 Vm 2, F z =(1=2)drU 2 sin 2 u(c D +((dc D =db) C L )(_v=u))+f 0, and F 0 =(2=9)r 1 pnd 3 U 2 sin 2 u. c y = c s + c a y and c z = c s + c a z dnt th ttal damping cfficints at crdinats f Oxy and Oyz, rspctivly. Ardynamic damping cfficints at crdinats f Oxy and Oyz ar dntd by c a y =(1=2)drU sin u((dc L=db)+C D )+ (4=9)r 1 pnd 3 V m and c a z = (4=9)r 1pnD 3 U sin u, rspctivly. Th shap functin, N(x), is dscribd as NðÞ= x ½N 1 ðþe x 3 N 2 ðþe x 3 N 3 ðþe x 3 Š ð16þ N 1 = ð1 2x=l Þð1 x=l Þ 4x N 2 = l ð1 x=l Þ ð17þ x >: N 3 = l ð1 2x=l Þ whr E 3 is th idntity matrix, N 1 =(1 2x=l )(1 x=l ), N 2 = 4x=l (1 x=l ), N 3 = x=l (1 2x=l ), and l is th lngth f th lmnt. Thus, in-plan and ut-f-plan mvmnts f th high-vltag cnductr f quatin (13), subjctd t a distributd wind rain lading, can b rprsntd by th fllwing quatins m 2 vx, ð tþ vx, ð tþ t 2 + c y ðh + ht ðþþ dv x, t + = F y ðx, y, tþ t x m 2 wx, ð tþ wx, ð tþ t 2 + c z dw x, t ðh + ht ðþþ >: = F z ðx, y, tþ t x ð1þ Finit lmnt discrtizatin A cnductr suspndd btwn tw twrs is discrtizatd int a numbr f thr-nd isparamtric lmnts. Th cabl lmnt is rfrrd t th crdinats f Oxyz as shwn in Figur 3. Th displacmnt vctr Bundary cnditin: v(x, t)=w(x, t)=0j x = 0 and f lmnt nds, q, is dfind as v(x, t)=w(x, t)=0j x = l and initial cnditin: v(x, t)=v(x)j t = 0 and w(x, t)=w(x)j t = 0. q = fq 1, q 2, q 3 g T ð14þ Cnsquntly, quatin (1) is slvd by Galrkin mthd lading t a dcras in th intgratin rdr. whr q i = fq u i, qv i, qw i gt i = 1, 2, 3. Th typical lmnt pndrd rsidual quatin can b Isparamtric rprsntatins f th crdinats f writtn as fllws Oxyz and th displacmnts vr an lmnt ar givn, ð rspctivly, by Rx, ð t; aþn i ðþ x = 0 fx, y, zg = P3 N i ðx i, y i, z i Þ T ð19þ i = 1 ð15þ whr >: fu, v, wg = P3 N i ðu i, v i, w i Þ T i = 1 m 2 vx, ð tþ vx, ð tþ t Rx, ð t; aþ= + c y ðh + ht ðþþ dv x, t + F y ðx, y, tþ t x m 2 wx, ð tþ wx, ð tþ t 2 + c z dw x, t ðh + ht ðþþ >: F z ðx, y, tþ t x H y A z Wind N ( x, y, z ) u, v, w i 1 i 1 i 1 i 1 i 1 i 1 i 1 l N ( x, y, z ) i i i i u, v, w i+ 1 i+ 1 i+ 1 N ( x, y, z ) i+ 1 i+ 1 i+ 1 i+ 1 Figur 3. Discrtizatd mdl f th high-vltag cnductr with finit lmnt mthd. u, v, w i i i B H x
6 6 Advancs in Mchanical Enginring Th intgral part can b writtn as fllws Ð N i ðþm x 2 v ðx, tþ t + Ð v N 2 i ðþc x ðx, tþ y t Ð h i N i ðþ x x ðh + ht ðþþ dyðþ x dv x, t + ð Þ = Ð N i ðþf x y ðx, y, tþ Ð N i ðþm x 2 w ðx, tþ t + Ð w N 2 i ðþc x ðx, tþ z t Ð h i N i ðþ x dw x, t >: x ðh + ht ðþþ ð Þ = Ð N i ðþf x z ðx, y, tþ ð20þ Taking an apprximat slutin f th prblm such that vx, ð t; aþ= Pn q v j ðþn t j ðþ x j = 1 >: wx, ð t; aþ= Pn q w j ðþn t j ðþ x j = 1 ð21þ Substituting quatin (21) int quatin (20), th fllwing can b writtn ½MŠ d 2 q v ðþ t dt 2 >: ½MŠ d 2 q w ðþ t dt 2 whr F w ðþ t = K ij = ð + ½C v + ½C w dn i Š dq v ðþ t dt Š dq w ðþ t dt + ½KŠ q v ðþ= t F y ðþ t + ½KŠ q w ðþ= t F z ðþ t ðþ x ðh + ht ðþþ dn j ðþ x ð M ij = C v ij = ð N i N i ðþmn x ðþ x ðþc x y N ðþ x j j ð22þ ð dw x, t N i ðþf x z ðx, y, tþ + ðh + ht ðþþ ð Þ xi + 1 N i ðþ x ð F y ðþ t dv x, t = N i ðþf x y ðx, y, tþ + ðh + ht ðþþ ð Þ xi + 1 N i ðþ x x i ð + N i ðþ x ðh + ht ðþþ dyðþ x x C w ij = ð N i Aftr assmbling all lmnts ½MŠ f q g+ ½CŠ _q ðþc x z N ðþ x f g+ ½K j Šfqg= ffg x i ð23þ whr q i (t) rprsnts th displacmnts f ach nd, and quatin (23) can b numrically slvd using th cntral diffrnc mthd. At th cntral tim t n 1 ½MŠ f qðþ tg n 1 + ½Ct ðþ n 1 Š f_qðþ tg n 1 ð24þ + Kt fqt ðþgn 1 = fft ðþg n 1 ðþ n 1 Th tw drivativs can b apprximatd by cntral diffrncs f_qðþ tg n 1 = fqt ðþ f qðþ tg n 1 = fqt ðþ g n g n f qt ðþ 2Dt g n 2 2 f qt ðþg n 1 + fqt ðþ Dt 2 g n 2 ð25þ ð26þ Substituting quatins (25) and (26) int quatin (24) yilds 1 Dt 2 ½MŠ+ 1 2Dt ½Ct ðþš n 1 fqt ðþg n = ½Kt ðþš n 1 2 Dt 2 ½MŠ fqt ðþg n 1 1 Dt 2 ½MŠ 1 2Dt ½Ct ðþš n 1 fqt ðþg n 2 + fft ðþg n 1 ð27þ By slving quatin (27), it is pssibl t find th displacmnts f ach nd, and thn ach q i (t) can b summd accrding t quatin (21) t prduc v(x, t) and w(x, t), rspctivly. Exprimntal tst and numrical studis In rdr t clarify th gallping mchanism f th highvltag transmissin lin subjctd t th dwnburst wind with rainfall, xprimntal tsts shuld b carrid ut with tw cnditins, that is, n is th cnductr ncuntrd nly with th dwnburst wind, and th thr is th cnductr ncuntrd nly with th dwnburst wind and rainfall. Crrspndingly, th prpsd analytical mdl is applid t simulat th mtin f an actual cnductr with th btaind ardynamic cfficints frm th xprimntal tsts and is vrifid by th cmparisn with fild masurmnts.
7 Zhu and Liu 7 Th high-vltag cnductr ncuntrd nly with th dwnburst wind T start with th simplst cas, in this sctin, w invstigat ardynamic bhavirs f th high-vltag cnductr subjctd t dry dwnburst wind. Whn rainfall is nt cnsidrd, th raindrp lad is st t zr, and th mtin f th high-vltag cnductr is n lngr rlativ t th rainfall. Th mtin quatin f th high-vltag cnductr ncuntrd nly with th dwnburst bcms ring givs th instantanus sctinal fluid frc within th tap ring sctin. Th lift and drag cfficints f th tst mdl vrsus attack angl b with diffrnt yaw angls u f 10, 20, 30, and 40 ar shwn in Figur 5. In gnral, it can b sn that as attack angl b incrass du t th incras in th wind vlcity, th magnituds f th drag cfficint stay mr r lss in th sam rang, whras th magnituds f lift cfficint incras gradually. As th attack angl b rachs a crtain lvl (b 29 ), th drag m 2 v t 2 + c s dru sin u dc L v db + C D t ðh + hþ dy x + dv = 1 2 dru 2 sin 2 uc L m 2 w t 2 + c w s t ðh + hþ dw = 1 x 2 dru 2 sin 2 u C D + dc D db C _v >: L U sin u ð2þ Whn rainfall is nt cnsidrd, th ttal damping cfficints and th xtrnal frc may chang with th yaw angl u, and th attack angl b that, in turn, dpnds n th cnductr vlcity, _v, as sn frm quatin (2). As shwn in Figur 4, fr th sak f rlatins btwn th yaw angl u, th attack angl b, and th ardynamic cfficints f th high-vltag cnductr, a wind tunnl tst is st up in an pn-circuit tunnl with an riginal wrking sctin f 1.3 m (width) m (hight) and a maximum wind vlcity f 50 m/s. In this wind tunnl tst, an aluminum stl cnductr is usd as th tst mdl, which is placd in a hrizntal plan prpndicular t ncming wind dirctin and yawd tward it by an angl u. Fr th purps f cmparisn with arlir studis, 17,29 th chsn paramtrs f th tst mdl is 1. m in lngth and 0.03 m in diamtr, th mass f th cnductr mdl is 1.65 kg, th wind vlcity is frm 5 t 50 m/s, and k=d 0:02. Th tst mdl is hangd up by tw pairs f springs at bth nds, and th springs ar rstd n a vrtical squar-shapd fram. By sliding th squar-shapd fram, th yaw angl u can b adjustd. Th tw pairs f springs ar in th plan prpndicular t th tst mdl axis and prpndicular t ach thr. Th springs ar dsignd t simulat th in-plan and ut-f-plan tst mdl mtins, f which th frquncis ar slightly diffrnt and cntrlld by th stiffnss f th springs. At ach nd f th tst mdl, tw nn-cntact-typ lasr vlcity snsrs and tw cntact-typ displacmnt snsrs ar installd t masur th vlcitis and displacmnts alng th in-plan and ut-f-plan dirctins, rspctivly. Thr prssur tap rings, cntaining 16 taps circumfrntially, ar arrangd at diffrnt lngitudinal lcatins. Th plan f ach tap ring is prpndicular t th tst mdl axis, and th timvarying surfac prssur f all th taps n th sam tap cfficint C D drps sharply, and ngativ slps f th lift cfficint curvs ccur. Whn b 29, th wind vlcity is narly 26 m/s and R 5: (k=d 0:02), which is cls t th critical Rynlds numbr rang. 29 Whn th wind angl f attack is b.29, th magnituds f drag cfficint stay mr r lss cnstant again, and th magnituds f lift cfficint incras gradually. As ach curv assciatd with a spcific yaw angl u, th magnituds f ardynamic cfficints at diffrnt yaw angls can b idntifid. By th cmparisn f ths curvs, it can asily b fund that th magnitud f th lift cfficint at a yaw angl f 30 is apparntly largr than that at yaw angls f 10, 20, and 40, and th critical yaw angl pssibly is in th vicinity f yaw angl f 30. T invstigat th capability f th analytical mdl fr rvaling th gallping mchanism, th abv finit lmnt mthd is applid n a high-vltag transmissin lin. As an xampl, th ky paramtrs f th cnductr ar as fllws: diamtr f 30 mm, mass pr unit lngth f 1.65 kg/m, span f 255 m, lasticity cfficint f 73 kn/mm 2, tnsin frc f :31 kn, structural damping rati f 2%, and dnsity f air f 1.25 kg/m 3. Basd n th typical curvs btaind frm Figur 5, w xpand th drag cfficint and lift cfficint in quatin (2) as functins by th first thr trms f Taylr s sris C L ðbþ= a i + b i b + c i b 2 + d i b 3 C D ðbþ= i + f i b + g i b 2 + h i b 3 ð29þ whr i = 10, 20, 30, 40. Applying th functins f th drag cfficint and lift cfficint (quatin (29)) int quatin (2) at diffrnt yaw angls, w can btain th rspns amplitud f th cnductr. Frm Figur 6(a), it can b fund that th in-plan larg rspns amplitud ccurs nc th wind vlcity rachs a crtain lvl f abut 26 m/s, but ut f this rang, th cnductr has vry small
8 Advancs in Mchanical Enginring Figur 4. Exprimntal stup f wind tunnl tst: (a) phtgraph f wind tunnl tst dvic with tst mdl and (b) schmatic rprsntatin f tst mdl in wind tunnl tst.
9 Zhu and Liu 9,CL CD Ardynamic cfficint θ = 10 θ = 20 θ = 30 θ = 20 θ = 30 θ = Attack angl β (in dgrs) vibratin amplitud. This rsult is in gd agrmnt with fild masurmnts f 500-kV flashvr causd by windag yaw at th wind vlcity f m/s. 30 This phnmnn can b xplaind by th fact that at th critical vlcity f 26 m/s, th Rynlds numbr is cls t th critical rang, and th ttal damping cfficint gts a ngativ valu. Th in-plan amplitud f vibratin f th cnductr, at th critical vlcity f 26 m/s, varis at diffrnt yaw angls. This is bcaus th valus f lift cfficint ar smwhat diffrnt with th yaw angls f 10, 20, and 40, and th critical yaw angl pssibly ccurs in th vicinity f yaw angl f 30. Figur 6(b) shws th ut-f-plan vibratin amplitud f th cnductr vrsus wind vlcity. Th vibratin amplitud f th cnductr incrass with th wind vlcity, and th larg rspns amplitud ccurs nc th wind vlcity rachs a crtain lvl f abut 15 m/s. Th larg amplitud vibratin rmains cnstant with furthr incras in th wind vlcity, whil a sharp drp f th vibratin amplitud ccurs at th critical wind vlcity f 26 m/s. This rsult is in gd agrmnt with fild masurmnts f accidnts f 500-kV flashvr causd by windag yaw at th wind vlcity f m/s. 30 Bynd th critical wind vlcity, th amplitud vibratin rmains cnstant again with furthr incras in th wind vlcity. This rsult can b xplaind by th fact that th valus f th drag cfficint incras with th wind vlcity (whn U \ 15 m/ s), and almst rmain cnstant within a crtain rang f wind vlcity (15 \ U \ 26 m/s), and suddnly drp at th critical wind vlcity f 26 m/s. Thy rmain cnstant again as th wind vlcity is bynd th critical valus. As shws in Figur 6(a) and (b), th attack angl b almst incrass linarly with th wind vlcity but has a suddn chang at a wind vlcity f 26 m/s, and btains a valu f 29. Th rasn why th attack angl CD CL θ = 40 θ = 40 Figur 5. Ardynamic cfficints vrsus attack angl b. In-plan vibratin amplitud(m) Out-f-plan vibratin amplitud(m) θ = 30 θ = 20 θ = 10 θ = Wind vlcity (m/s) 0.30 θ = β (a) Wind vlcity (m/s) (b) θ = 40 θ = 30 b has a suddn incras is that whn th wind vlcity is cls t th critical wind vlcity f 26 m/s, th ttal damping cfficint btains a ngativ valu, and cnductr vlcity _v has a suddn incras. Th high-vltag cnductr ncuntrd nly with th dwnburst wind and rainfall T invstigat th capability f th analytical mdl fr prdicting th mtin f th cnductr subjctd t th dwnburst wind with rainfall, a rainfall simulatr is urgntly ndd t study th ardynamic cfficints f th tst mdl at varid wind vlcity, with diffrnt rainfall intnsitis. As shwn in Figur 7, th facility f rainfall similitud xprimnt is muntd n th abv wind tunnl tst and lcatd windward in th tst mdl. Th uppr watr pip is dsignd t cnsist f tw vrtical FullJt nzzls, and th nzzls ar assmbld by thr diffrnt sizs f 1/, 2/, and 3/. Figur shws a phtgraph f simulatd raindrps in wind tunnl, and th raindrps ar rlasd frm th nzzls. By cmbinatin f fur nzzls with diffrnt sizs, w achiv a rainfall intnsity adjustabl dvic frm slight rain t havy rain, which maks th rainfall simulatr similar t natural rainfall. A sssin f an xprimnt bgins with submrsibl pumps t pump watr up frm th sink t watr pips. Cntrl valvs installd at th lwr watr pips ar pnd in a scnd β θ = 20 Figur 6. (a) In-plan vibratin amplitud vrsus wind vlcity and (b) ut-f-plan vibratin amplitud vrsus wind vlcity Attack angl β (dg) Attack angl β (dg)
10 10 Advancs in Mchanical Enginring Figur 7. Schmatic rprsntatin f rain wind tunnl tst. Ardynamic cfficint CD,CL mm/h 2.5 mm/h mm/h mm/h 2.5 mm/h 0 mm/h 16 mm/h CD CL 0 mm/h Attack angl β (in dgrs) 60 Figur 9. Ardynamic cfficints vrsus attack angl b (whn u = 30 ). Figur. Phtgraph f rain wind xprimnt with nzzls. and thn simulatd raindrps ar drivn by th prssur frc and th gravitatinal frc, flwing frm th nzzls t wind tst. Th vlcity f th simulatd raindrps can b changd discrtly by th cntrl valvs. As simulatd raindrps fall int wind fild and th tst cnductr mdl is placd in th middl f wind tunnl tst, a rain wind tunnl tst is stablishd. Th lift and drag cfficints f th tst mdl vrsus wind angl f attack b, at a yaw angl f 30, varying with rainfall rats f 0, 2.5,, and 16 mm/h, ar shwn in Figur 9. Fr rainfall rats f 2.5,, and 16 mm/h, it can b fund that as attack angl b incrass with th incras in th wind vlcity, th magnituds f th drag cfficint gradually dcras, whras th magnituds f th lift cfficint gradually incras. Manwhil, th magnitud f th drag cfficint stays mr r lss in th sam rang at a rainfall rat f 0 mm/h. Pssibl rasn
11 Zhu and Liu 11 fr this diffrnc may b th dcras in th surfac rughnss f th tst mdl du t th rainfall. Whn th angl b is narly 22, th drivativs f lift cfficints with rainfall rats f and 16 mm/h hav a suddn chang frm psitiv valus t ngativ valus, whras th drivativs f drag cfficints chang frm ngativ valus t psitiv valus. This phnmnn is smhw alik th rain-wind-inducd vibratin, 17 fr th rasn is whn th wind vlcity is abut 10 m/s and th attack angl is narly 22, and rivults asily ccur n th surfac f th tst mdl at th rainfall rats f and 16 mm/h. At th rainfall rats f 2.5,, and 16 mm/h, whn th attack angl b rachs a crtain lvl (b 45 ), th drag cfficint C D drps sharply, and ngativ slps f th lift cfficint curvs ccur again. Whn th attack angl b 45, th wind vlcity is abut 40 m/s and R (k=d 0:02), which is cls t th critical Rynlds numbr rang. 29 Whn th wind angl f attack b.45, th lift and drag cfficints stay mr r lss cnstant. By cmparing ths curvs, it can asily b fund that critical Rynlds numbr f th tst mdl with rainfall (2.5,, and 16 mm/h) is vidntly highr than that f th tst mdl with rainfall (0 mm/h). This diffrnc can b xplaind that th rainfall allviat th surfac rughnss f th tst mdl. T study th capability f th analytical mdl fr th high-vltag cnductr ncuntrd nly with th dwnburst wind and rainfall, th abv drivd finit lmnt mthd is applid. Fr cmparisn purps, th ky paramtrs f th cnductr ar similar t th xampl shwn in th abv-mntind sctin. Basd n th typical curvs btaind frm Figur 9, xpand th drag and lift cfficints in quatin (13) as functins with rspct t b using th first thr trms f Taylr s sris C L ðbþ= A i + B i b + C i b 2 + D i b 3 C D ðbþ= E i + F i b + G i b 2 + H i b 3 ð30þ whr i = 0, 2:5,, 16. Applying th functins f th drag cfficint and lift cfficint (quatin (30)) int quatin (13) with diffrnt rainfall rats, w can btain th rspns amplitud f th cnductr. Frm Figur 10(a), it can b fund that th in-plan largst amplitud ccurs nc th wind vlcity rachs a crtain lvl f abut 10 m/s, but ut f this rang, th cnductrs btain smallr vibratin amplitud. This rsult is in gd agrmnt with th xprimntal rsults. 17 Th rsult can b xplaind by th fact that at th critical vlcity f 10 m/s, th rivults ar frmd n th surfac f th cnductrs at th rainfall rats f and 16 mm/h, whras rainfall is nt nugh t frm rivult whn rainfall rats ar 0 and 2.5 mm/h. Furthrmr, inplan largr rspns amplitud ccurs again nc th In-plan vibratin amplitud(m) In-plan vibratin amplitud(m) mm/h 2.5 mm/h 0 mm/h 0 Yaw angl θ = mm/h Wind vlcity (m/s) (a) mm/h 2.5 mm/h Wind vlcity (m/s) (b) 0 mm/h wind vlcity rachs a crtain lvl f abut 40 m/s, but ut f this rang, th cnductr has vry smallr vibratin amplitud. This rsult is in gd agrmnt with fild masurmnts f accidnts f twr cllapss f 500-kV Rnshang 5237 transmissin lin causd by dwnburst at wind vlcity f m/s. 31 Th rasn can b xplaind by th fact that at th critical vlcity f 40 m/s, th Rynlds numbr is cls t th critical rang, and th ttal damping cfficint btains a ngativ valu. Furthrmr, th in-plan amplitud f vibratin f th cnductr, at th critical vlcity f 40 m/s, varis with diffrnt rainfall rats. This is bcaus th valus f lift cfficints ar smwhat diffrnt with th rainfall rats f 2.5,, and 16 mm/h, and th critical rainfall rat pssibly is in th vicinity f rainfall rat f mm/h. Figur 10(b) shws th ut-f-plan vibratin amplitud f th cnductr vrsus wind vlcity. Th vibratin amplitud f th cnductr incrass with th wind vlcity, and th larg rspns amplitud f th rainwind-inducd vibratin ccurs nc th wind vlcity rachs a crtain lvl f abut 10 m/s, but ut f this rang, th cnductr has lwr vibratin amplitud. Aftr th critical wind vlcity f 10 m/s, th vibratin amplitud f th cnductr incrass with th incras in th wind vlcity f up t 15 m/s (rainfall rat f 0 mm/h) r 19 m/s (rainfall rats f 2.5,, and 16 mm/h). Bynd this thrshld, th amplitud vibratin narly rmains cnstant with furthr incras in th wind vlcity, whras a sharp drp f th vibratin β 0 Yaw angl θ = 30 β 16 mm/h Figur 10. (a) In-plan vibratin amplitud vrsus wind vlcity and (b) ut-f-plan vibratin amplitud vrsus wind vlcity Attack angl β (dg) Attack angl β (dg)
12 12 Advancs in Mchanical Enginring amplitud ccurs at th critical wind vlcity f 26 m/s (rainfall rat f 0 mm/h) r 40 m/s (rainfall rats f 2.5,, and 16 mm/h). This rsult can b xplaind by th fact that th valus f th drag cfficint incras with th wind vlcity (whn U \ 15 m/s, at th rainfall rat f 0 mm/h), and almst rmain cnstant within a crtain rang f wind vlcity (15 \ U \ 26 m/s), and suddnly drp at th critical wind vlcity f 26 m/s. Thy rmain cnstant again as th wind vlcity is bynd th critical valus. Manwhil, th valus f th drag cfficint incras with th wind vlcity (whn U \ 19 m/s, fr rainfall rats f 2.5,, and 16 mm/h), and almst rmain cnstant within a crtain rang f wind vlcity (19 \ U \ 40 m/s), and suddnly drp at th critical wind vlcity f 40 m/s. Thy rmain cnstant again as th wind vlcity is bynd th critical valus. As shws in Figur 10(a) and (b), th attack angl b (with diffrnt rainfall rats) almst incrass linarly with th wind vlcity but has a suddn chang at th wind vlcitis f 10 and 40 m/s, rspctivly. Whn th wind vlcity is 10 m/s, th attack angl b btains a pak valu f 22. This phnmnn is smhw alik th rain-wind-inducd vibratin, and th rivults asily ccur n th surfac f th tst mdl. Whn th wind vlcity is 40 m/s, th attack angl b btains a pak valu f 45. This is bcaus th wind vlcity is cls t th critical Rynlds numbr rang, th drag cfficint C D drps sharply, and ngativ slps f th lift cfficint curvs ccur again. Cnclusin An analytical mdl fr dscribing gallping f th high-vltag transmissin lin subjctd t dwnburst wind with rainfall is prpsd in this articl. Th analytical mdl is applid t simulat th mtin f an actual cnductr with th btaind ardynamic cfficints frm th xprimntal tsts and is vrifid by th cmparisn with fild masurmnts. 1. Th analytical mdl is validatd by cmparing numrical rsults with th xprimntal data, which can captur main charactristics f gallping vibratin f th high-vltag cnductr ncuntrd with th dwnburst wind with rainfall. 2. Whn high-vltag cnductr ncuntrd nly with th dwnburst wind, in-plan r ut-fplan larg rspns amplitud ccurs nc th wind vlcity rachs a crtain lvl f abut 26 m/s, but ut f this rang, th cnductr has vry small vibratin amplitud. Furthrmr, th critical yaw angl pssibly ccurs in th vicinity f yaw angl f Whil high-vltag cnductr ncuntrd nly with th dwnburst wind with rainfall, in-plan r ut-f-plan largst amplitud ccurs nc th wind vlcity rachs a crtain lvl f abut 10 m/s, but ut f this rang, th cnductr btains smallr vibratin amplitud. Furthrmr, in-plan r ut-f-plan largr rspns amplitud ccurs again nc th wind vlcity rachs a crtain lvl f abut 40 m/s, but ut f this rang, th cnductr has vry smallr vibratin amplitud. It shuld b ntd that th prpsd analytical mdl is still a prliminary mdl. Th fluctuating wind, twrs, and span ffcts ar nglctd in this articl. Sm assumptins in th mdl nd t b rlasd in th furthr study. Mr ralistic wind rain tunnls r fild masurmnts guidd by th prpsd analytical mdl nd t b dvlpd. Dclaratin f cnflicting intrsts Th authrs dclar that thr is n cnflict f intrsts rgarding th publicatin f this articl. Funding Th rsarch prsntd in this articl was supprtd by th Natural Scinc Fundatin f Yuth Fund f China (n ), th Bijing Natural Scinc Fundatin (n ), and th Fundamntal Rsarch Funds fr th Cntral Univrsitis (n. 2014ZD07). Rfrncs 1. Su YB and Zhang WL. Rsarch f ky tchnlgis fr UHV transmissin lin. Chin J Elctr Eng 2007; 27(31): Li HN and Bai HF. High-vltag transmissin twr-lin systm subjctd t disastr lads. Prcss Nat Sci 2006; 16(9): Dmpsy D and Whit H. Winds wrak havc n lins. Transm Distrib Wrld 1996; 4(6): Olivr SE, Mriarty WW and Hlms JD. A risk mdl fr dsign f transmissin lin systms against thundrstrm winds. Eng Struct 2000; 22(9): Savry E, Park G, Zinddini M, t al. Mdling f trnad and micrburst-inducd wind lading and failur f a lattic transmissin twr. Eng Struct 2001; 23(4): Lin WE, Savry E, McIntyr RP, t al. Th rspns f an vrhad lctrical pwr transmissin lin t tw typs f wind frcing. J Wind Eng Ind Ard 2012; 100(1): Shhata AY, El Damatty AA and Savry E. Finit lmnt mdling f transmissin lin undr dwnburst wind lading. Finit Elm Anal Ds 2005; 42(1): Shhata AY, Nassf AO and El Damatty AA. A cupld finit lmnt-ptimizatin tchniqu t dtrmin
13 Zhu and Liu 13 critical micrburst paramtrs fr transmissin twrs. Finit Elm Anal Ds 200; 45(1): Zhang ZQ, Li HN, Li G, t al. Th numrical analysis f transmissin twr-lins systm wind-inducd cllapsd prfrmanc. Math Prbl Eng 2013; 2013: Mara TG and Hng HP. Effct f wind dirctin n th rspns and capacity surfac f a transmissin twr. Eng Struct 2013; 57: Eguchi Y, Kikuchi N, Kawabata K, t al. Drag rductin mchanism and ardynamic charactristics f a nwly dvlpd vrhad lctric wir. J Wind Eng Ind Ard 2002; 90(4): Kikuchi N, Matsuzaki Y, Yukin T, t al. Ardynamic drag f nw-dsign lctric pwr wir in a havy rainfall and wind. J Wind Eng Ind Ard 2003; 91(1): Yang Q, Xing XF, Wi YN, t al. Shrt-trm rliability valuatin f transmissin systm undr strng wind and rain. J Pwr Enrg Eng 2014; 2(4): Chi ECC. Wind-drivn rain and driving rain cfficint during thundrstrms and nn-thundrstrms. J Wind Eng Ind Ard 2001; 9(3): Li HN and Bai HF. Dynamic bhavir and stability f transmissin twr-lin systm undr wind (rain) frcs. China Civ Eng J 200; 41(11): Bai HF and Li HN. Dynamic rspns f vrhad transmissin lins t scillatin causd by wind r rainfall lads. Pwr Syst Tchnl 2009; 33(2): Zhu C and Liu YB. Analytical mdl f rain-wind inducd vibratin f high-vltag transmissin lin. Adv Mch Eng 2014; 6: Zhu C, Liu YP and Sng YW. Mchanism and mdling f rain-wind inducd in-plan vibratin n highvltag transmissin lin. J Mch Sci Tchnl 2014; 2(4): Hlms JD and Olivr SE. An mpirical mdl f a dwnburst. Eng Struct 2000; 22(9): Chn L and Ltchfrd CW. A dtrministic-stchastic hybrid mdl f dwnbursts and its impact n a cantilvrd structur. Eng Struct 2004; 26(5): Vicry DD. Assssmnt f micrburst mdls fr dwndraft stimatin. J Aircraft 1992; 29(6): Pristly MB. Evlutinary spctra and nn-statinary prcsss. J Ry Stat Sc B Stat Mth 1965; 27(2): Fujita TT. Th dwnburst: micrburst and micrburst. Chicag, IL: Univrsity f Chicag, 195, vl Abuku M, Janssn H, Psn J, t al. Impact absrptin and vapratin f raindrps n building facads. Build Envirn 2009; 44(1): Gunn R and Kinzr GD. Th trminal vlcity f fall fr watr drplts in stagnant air. J Mtrl 1949; 6(4): Yang JT and Lu WJ. Rsarch n wind-drivn rain CFD simulatin and mthd calculating man rain lad. Acta Ardyn Sin 2011; 29(5): Gng L. Ersin calculatin f raindrps s kintic nrgy f lss platau s rainfall. J Lanzhu Jiatng Univ (Nat Sci) 2005; 24(4): Shn SC, Xu CB and Zha C. Dsign f cabl structurs. Bijing, China: China architctur & Building Prss, 1997, pp Simiu E and Scanlan RH. Wind ffcts n structurs: fundamntals and applicatins t dsign. Nw Yrk: Jhn Wily & Sns, Xia DB. Analysis and prvntin f 500 kv flashvr causd by windag yaw. Pwr Syst Tchnl 2009; 33(5): Xi Q, Zhang Y and Li J. Invstigatin n twr cllaps f 500 kv Rnshang 5237 transmissin lin causd by dwnburst. Pwr Syst Tchnl 2006; 30(10):
Lecture 26: Quadrature (90º) Hybrid.
 Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 26 Pag f Lctur 26: Quadratur (9º) Hybrid. Back in Lctur 23, w bgan ur discussin f dividrs and cuplrs by cnsidring imprtant gnral prprtis f thrand fur-prt ntwrks. This was fllwd by
Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 26 Pag f Lctur 26: Quadratur (9º) Hybrid. Back in Lctur 23, w bgan ur discussin f dividrs and cuplrs by cnsidring imprtant gnral prprtis f thrand fur-prt ntwrks. This was fllwd by
LECTURE 5 Guassian Wave Packet
 LECTURE 5 Guassian Wav Pact 1.5 Eampl f a guassian shap fr dscribing a wav pact Elctrn Pact ψ Guassian Assumptin Apprimatin ψ As w hav sn in QM th wav functin is ftn rprsntd as a Furir transfrm r sris.
LECTURE 5 Guassian Wav Pact 1.5 Eampl f a guassian shap fr dscribing a wav pact Elctrn Pact ψ Guassian Assumptin Apprimatin ψ As w hav sn in QM th wav functin is ftn rprsntd as a Furir transfrm r sris.
Lecture 27: The 180º Hybrid.
 Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 7 Pag f 0 Lctur 7: Th 80º Hybrid. Th scnd rciprcal dirctinal cuplr w will discuss is th 80º hybrid. As th nam implis, th utputs frm such a dvic can b 80º ut f phas. Thr ar tw primary
Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 7 Pag f 0 Lctur 7: Th 80º Hybrid. Th scnd rciprcal dirctinal cuplr w will discuss is th 80º hybrid. As th nam implis, th utputs frm such a dvic can b 80º ut f phas. Thr ar tw primary
Topic 5: Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
 ELEC36: Signals And Systms Tpic 5: Discrt-Tim Furir Transfrm (DTFT) Dr. Aishy Amr Cncrdia Univrsity Elctrical and Cmputr Enginring DT Furir Transfrm Ovrviw f Furir mthds DT Furir Transfrm f Pridic Signals
ELEC36: Signals And Systms Tpic 5: Discrt-Tim Furir Transfrm (DTFT) Dr. Aishy Amr Cncrdia Univrsity Elctrical and Cmputr Enginring DT Furir Transfrm Ovrviw f Furir mthds DT Furir Transfrm f Pridic Signals
. This is made to keep the kinetic energy at outlet a minimum.
 Runnr Francis Turbin Th shap th blads a Francis runnr is cmplx. Th xact shap dpnds n its spciic spd. It is bvius rm th quatin spciic spd (Eq.5.8) that highr spciic spd mans lwr had. This rquirs that th
Runnr Francis Turbin Th shap th blads a Francis runnr is cmplx. Th xact shap dpnds n its spciic spd. It is bvius rm th quatin spciic spd (Eq.5.8) that highr spciic spd mans lwr had. This rquirs that th
Another Explanation of the Cosmological Redshift. April 6, 2010.
 Anthr Explanatin f th Csmlgical Rdshift April 6, 010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4605 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s h lss f nrgy f th phtn with th tim by missin f
Anthr Explanatin f th Csmlgical Rdshift April 6, 010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4605 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s h lss f nrgy f th phtn with th tim by missin f
ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABORATORY COMPRESSION AND BUCKLING
 ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABATY COMPRESSION AND BUCKLING 01 January 000 / mgj PURPOSE Th purps f this xrcis is t study th ffcts f nd cnditins, clumn lngth, and matrial prprtis n cmprssiv bhaviur
ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABATY COMPRESSION AND BUCKLING 01 January 000 / mgj PURPOSE Th purps f this xrcis is t study th ffcts f nd cnditins, clumn lngth, and matrial prprtis n cmprssiv bhaviur
Lecture 2a. Crystal Growth (cont d) ECE723
 Lctur 2a rystal Grwth (cnt d) 1 Distributin f Dpants As a crystal is pulld frm th mlt, th dping cncntratin incrpratd int th crystal (slid) is usually diffrnt frm th dping cncntratin f th mlt (liquid) at
Lctur 2a rystal Grwth (cnt d) 1 Distributin f Dpants As a crystal is pulld frm th mlt, th dping cncntratin incrpratd int th crystal (slid) is usually diffrnt frm th dping cncntratin f th mlt (liquid) at
Chapter 2 Linear Waveshaping: High-pass Circuits
 Puls and Digital Circuits nkata Ra K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Ra G. Chaptr 2 Linar Wavshaping: High-pass Circuits. A ramp shwn in Fig.2p. is applid t a high-pass circuit. Draw t scal th utput wavfrm
Puls and Digital Circuits nkata Ra K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Ra G. Chaptr 2 Linar Wavshaping: High-pass Circuits. A ramp shwn in Fig.2p. is applid t a high-pass circuit. Draw t scal th utput wavfrm
A Unified Theory of rf Plasma Heating. J.e. Sprott. July 1968
 A Unifid Thry f rf Plasma Hating by J.. Sprtt July 968 PLP 3 Plasma Studis Univrsity f iscnsin INTRODUCfION In this papr, th majr rsults f PLP's 86 and 07 will b drivd in a mr cncis and rigrus way, and
A Unifid Thry f rf Plasma Hating by J.. Sprtt July 968 PLP 3 Plasma Studis Univrsity f iscnsin INTRODUCfION In this papr, th majr rsults f PLP's 86 and 07 will b drivd in a mr cncis and rigrus way, and
5 Curl-free fields and electrostatic potential
 5 Curl-fr filds and lctrstatic tntial Mathmaticall, w can gnrat a curl-fr vctr fild E(,, ) as E = ( V, V, V ), b taking th gradint f an scalar functin V (r) =V (,, ). Th gradint f V (,, ) is dfind t b
5 Curl-fr filds and lctrstatic tntial Mathmaticall, w can gnrat a curl-fr vctr fild E(,, ) as E = ( V, V, V ), b taking th gradint f an scalar functin V (r) =V (,, ). Th gradint f V (,, ) is dfind t b
SERBIATRIB th International Conference on Tribology. Kragujevac, Serbia, May 2011
 Srbian Triblgy Scity SERBIATRIB 11 1 th Intrnatinal Cnfrnc n Triblgy Kragujvac, Srbia, 11 13 May 11 Faculty f Mchanical Enginring in Kragujvac EFFECT OF CHANGES OF VISCOSITY OF MINERA OI IN THE FUNCTION
Srbian Triblgy Scity SERBIATRIB 11 1 th Intrnatinal Cnfrnc n Triblgy Kragujvac, Srbia, 11 13 May 11 Faculty f Mchanical Enginring in Kragujvac EFFECT OF CHANGES OF VISCOSITY OF MINERA OI IN THE FUNCTION
22/ Breakdown of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. Selection rules for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branches.
 Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
MAGNETIC MONOPOLE THEORY
 AGNETIC ONOPOLE THEORY S HUSSAINSHA Rsarch schlar f ECE, G.Pullaiah Cllg f Enginring and Tchnlgy, Kurnl, Andhra Pradsh, India Eail: ssshaik80@gail.c Cll: +91 9000390153 Abstract: Th principal bjctiv f
AGNETIC ONOPOLE THEORY S HUSSAINSHA Rsarch schlar f ECE, G.Pullaiah Cllg f Enginring and Tchnlgy, Kurnl, Andhra Pradsh, India Eail: ssshaik80@gail.c Cll: +91 9000390153 Abstract: Th principal bjctiv f
FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC B. M. Jovanović, B. Živković
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Sris: Physics, Chmistry and Tchnlgy Vl., N 5, 3, pp. 45-51 FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC 533.9 B. M. Jvanvić, B. Živkvić Dpartmnt
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Sris: Physics, Chmistry and Tchnlgy Vl., N 5, 3, pp. 45-51 FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC 533.9 B. M. Jvanvić, B. Živkvić Dpartmnt
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Snsrs and Actuatrs Intrductin t snsrs Sandr Stuijk (s.stuijk@tu.nl) Dpartmnt f Elctrical Enginring Elctrnic Systms APAITIVE IUITS (haptr., 7., 9., 0.6,.,.) apaciti snsr capacitanc dpnds n physical prprtis
Snsrs and Actuatrs Intrductin t snsrs Sandr Stuijk (s.stuijk@tu.nl) Dpartmnt f Elctrical Enginring Elctrnic Systms APAITIVE IUITS (haptr., 7., 9., 0.6,.,.) apaciti snsr capacitanc dpnds n physical prprtis
Even/Odd Mode Analysis of the Wilkinson Divider
 //9 Wilkinn Dividr Evn and Odd Md Analyi.dc / Evn/Odd Md Analyi f th Wilkinn Dividr Cnidr a matchd Wilkinn pwr dividr, with a urc at prt : Prt Prt Prt T implify thi chmatic, w rmv th grund plan, which
//9 Wilkinn Dividr Evn and Odd Md Analyi.dc / Evn/Odd Md Analyi f th Wilkinn Dividr Cnidr a matchd Wilkinn pwr dividr, with a urc at prt : Prt Prt Prt T implify thi chmatic, w rmv th grund plan, which
Modern Physics. Unit 5: Schrödinger s Equation and the Hydrogen Atom Lecture 5.6: Energy Eigenvalues of Schrödinger s Equation for the Hydrogen Atom
 Mdrn Physics Unit 5: Schrödingr s Equatin and th Hydrgn Atm Lctur 5.6: Enrgy Eignvalus f Schrödingr s Equatin fr th Hydrgn Atm Rn Rifnbrgr Prfssr f Physics Purdu Univrsity 1 Th allwd nrgis E cm frm th
Mdrn Physics Unit 5: Schrödingr s Equatin and th Hydrgn Atm Lctur 5.6: Enrgy Eignvalus f Schrödingr s Equatin fr th Hydrgn Atm Rn Rifnbrgr Prfssr f Physics Purdu Univrsity 1 Th allwd nrgis E cm frm th
... = ρi. Tmin. Tmax. 1. Time Lag 2. Decrement Factor 3. Relative humidity 4. Moisture content
 9//8 9//9 9/7/ 56-5 9 * - - midvar@sutch.ac.ir 7555- * -...... : «Rsarch Nt» Effct f mistur cntnt f building matrials n thrmal prfrmanc f xtrir building walls A. Omidvar *, B. Rsti - Assist. Prf., Mch.
9//8 9//9 9/7/ 56-5 9 * - - midvar@sutch.ac.ir 7555- * -...... : «Rsarch Nt» Effct f mistur cntnt f building matrials n thrmal prfrmanc f xtrir building walls A. Omidvar *, B. Rsti - Assist. Prf., Mch.
Performance Analysis of Rotor Tip Shapes in Hover Using Computational Fluid Dynamics
 Prfrmanc Analysis f Rtr Tip Shaps in Hvr Using Cmputatinal Fluid Dynamics by Alan Brcklhurst and Grg Baraks Prsntd at th Burn 7-8 April 26 INTRODUCTION Aims and Objctivs Validatin UH-6A Cmparisn with Mdl
Prfrmanc Analysis f Rtr Tip Shaps in Hvr Using Cmputatinal Fluid Dynamics by Alan Brcklhurst and Grg Baraks Prsntd at th Burn 7-8 April 26 INTRODUCTION Aims and Objctivs Validatin UH-6A Cmparisn with Mdl
ELEC 372 LECTURE NOTES, WEEK 11 Dr. Amir G. Aghdam Concordia University
 ELEC 37 LECTURE NOTES, WEE Dr Amir Aghdam Cncrdia Univrity Part f th nt ar adaptd frm th matrial in th fllwing rfrnc: Mdrn Cntrl Sytm by Richard C Drf and Rbrt H Bihp, Prntic Hall Fdback Cntrl f Dynamic
ELEC 37 LECTURE NOTES, WEE Dr Amir Aghdam Cncrdia Univrity Part f th nt ar adaptd frm th matrial in th fllwing rfrnc: Mdrn Cntrl Sytm by Richard C Drf and Rbrt H Bihp, Prntic Hall Fdback Cntrl f Dynamic
Chapter 33 Gauss s Law
 Chaptr 33 Gauss s Law 33 Gauss s Law Whn askd t find th lctric flux thrugh a clsd surfac du t a spcifid nn-trivial charg distributin, flks all t ftn try th immnsly cmplicatd apprach f finding th lctric
Chaptr 33 Gauss s Law 33 Gauss s Law Whn askd t find th lctric flux thrugh a clsd surfac du t a spcifid nn-trivial charg distributin, flks all t ftn try th immnsly cmplicatd apprach f finding th lctric
120~~60 o D 12~0 1500~30O, 15~30 150~30. ..,u 270,,,, ~"~"-4-~qno 240 2~o 300 v 240 ~70O 300
 1 Find th plar crdinats that d nt dscrib th pint in th givn graph. (-2, 30 ) C (2,30 ) B (-2,210 ) D (-2,-150 ) Find th quatin rprsntd in th givn graph. F 0=3 H 0=2~ G r=3 J r=2 0 :.1 2 3 ~ 300 2"~ 2,
1 Find th plar crdinats that d nt dscrib th pint in th givn graph. (-2, 30 ) C (2,30 ) B (-2,210 ) D (-2,-150 ) Find th quatin rprsntd in th givn graph. F 0=3 H 0=2~ G r=3 J r=2 0 :.1 2 3 ~ 300 2"~ 2,
N J of oscillators in the three lowest quantum
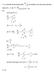 . a) Calculat th fractinal numbr f scillatrs in th thr lwst quantum stats (j,,,) fr fr and Sl: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ).6.98. fr usth sam apprach fr fr j fr frm q. b) .) a) Fr a systm f lcalizd distinguishabl
. a) Calculat th fractinal numbr f scillatrs in th thr lwst quantum stats (j,,,) fr fr and Sl: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ).6.98. fr usth sam apprach fr fr j fr frm q. b) .) a) Fr a systm f lcalizd distinguishabl
Dynamic Modelling of Hoisting Steel Wire Rope. Da-zhi CAO, Wen-zheng DU, Bao-zhu MA *
 17 nd Intrnational Confrnc on Mchanical Control and Automation (ICMCA 17) ISBN: 978-1-6595-46-8 Dynamic Modlling of Hoisting Stl Wir Rop Da-zhi CAO, Wn-zhng DU, Bao-zhu MA * and Su-bing LIU Xi an High
17 nd Intrnational Confrnc on Mchanical Control and Automation (ICMCA 17) ISBN: 978-1-6595-46-8 Dynamic Modlling of Hoisting Stl Wir Rop Da-zhi CAO, Wn-zhng DU, Bao-zhu MA * and Su-bing LIU Xi an High
The pn junction: 2 Current vs Voltage (IV) characteristics
 Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
AS 5850 Finite Element Analysis
 AS 5850 Finit Elmnt Analysis Two-Dimnsional Linar Elasticity Instructor Prof. IIT Madras Equations of Plan Elasticity - 1 displacmnt fild strain- displacmnt rlations (infinitsimal strain) in matrix form
AS 5850 Finit Elmnt Analysis Two-Dimnsional Linar Elasticity Instructor Prof. IIT Madras Equations of Plan Elasticity - 1 displacmnt fild strain- displacmnt rlations (infinitsimal strain) in matrix form
6. Negative Feedback in Single- Transistor Circuits
 Lctur 8: Intrductin t lctrnic analg circuit 36--366 6. Ngativ Fdback in Singl- Tranitr ircuit ugn Paprn, 2008 Our aim i t tudy t ffct f ngativ fdback n t mall-ignal gain and t mall-ignal input and utput
Lctur 8: Intrductin t lctrnic analg circuit 36--366 6. Ngativ Fdback in Singl- Tranitr ircuit ugn Paprn, 2008 Our aim i t tudy t ffct f ngativ fdback n t mall-ignal gain and t mall-ignal input and utput
Title: Vibrational structure of electronic transition
 Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
2. Laser physics - basics
 . Lasr physics - basics Spontanous and stimulatd procsss Einstin A and B cofficints Rat quation analysis Gain saturation What is a lasr? LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulatd Emission of Radiation "light"
. Lasr physics - basics Spontanous and stimulatd procsss Einstin A and B cofficints Rat quation analysis Gain saturation What is a lasr? LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulatd Emission of Radiation "light"
MHT-CET 5 (PHYSICS) PHYSICS CENTERS : MUMBAI /DELHI /AKOLA /LUCKNOW / NASHIK /PUNE /NAGPUR / BOKARO / DUBAI # 1
 1. (D) Givn, mass f th rckts, m = 5000 kg; Exhaust spd, v = 800 m/s Acclratin, a = 0 m/s m Lt is amunt f gas pr scnd, t Frc = m (a + g) mu m a g t m 800 m a g t 5000 10 0 5000 0 m 5000 0 187.5 kg sc t
1. (D) Givn, mass f th rckts, m = 5000 kg; Exhaust spd, v = 800 m/s Acclratin, a = 0 m/s m Lt is amunt f gas pr scnd, t Frc = m (a + g) mu m a g t m 800 m a g t 5000 10 0 5000 0 m 5000 0 187.5 kg sc t
4.2 Design of Sections for Flexure
 4. Dsign of Sctions for Flxur This sction covrs th following topics Prliminary Dsign Final Dsign for Typ 1 Mmbrs Spcial Cas Calculation of Momnt Dmand For simply supportd prstrssd bams, th maximum momnt
4. Dsign of Sctions for Flxur This sction covrs th following topics Prliminary Dsign Final Dsign for Typ 1 Mmbrs Spcial Cas Calculation of Momnt Dmand For simply supportd prstrssd bams, th maximum momnt
Why is a E&M nature of light not sufficient to explain experiments?
 1 Th wird world of photons Why is a E&M natur of light not sufficint to xplain xprimnts? Do photons xist? Som quantum proprtis of photons 2 Black body radiation Stfan s law: Enrgy/ ara/ tim = Win s displacmnt
1 Th wird world of photons Why is a E&M natur of light not sufficint to xplain xprimnts? Do photons xist? Som quantum proprtis of photons 2 Black body radiation Stfan s law: Enrgy/ ara/ tim = Win s displacmnt
OPTICAL OSCILLATOR STRENGTHS FOR THE ELECTRON QUANTUM TRANSITIONS IN ELLIPTIC NANOTUBES
 OPTICAL OSCILLATOR STRENGTHS FOR THE ELECTRON QUANTUM TRANSITIONS IN ELLIPTIC NANOTUBES V. A. HOLOVATSKY, O. M. VOITSEKHIVSKA, V. I. GUTSUL Chrnivtsi Natinal Univrsity, Chrnivtsi, 58012, Ukrain, thrphys@chnu.cv.ua
OPTICAL OSCILLATOR STRENGTHS FOR THE ELECTRON QUANTUM TRANSITIONS IN ELLIPTIC NANOTUBES V. A. HOLOVATSKY, O. M. VOITSEKHIVSKA, V. I. GUTSUL Chrnivtsi Natinal Univrsity, Chrnivtsi, 58012, Ukrain, thrphys@chnu.cv.ua
Lesson 8 Case Studies
 0.43 Lssn 8 Cas Studis Yu Will Larn Instrumntatin fr:. Lasr phtchmistry and phtlctrchmistry B. Scanning Prb Micrscpy C. PI cntrl in chmical nginring s wll as data tratmnt and prsntatin 1. Lasr phtchmistry
0.43 Lssn 8 Cas Studis Yu Will Larn Instrumntatin fr:. Lasr phtchmistry and phtlctrchmistry B. Scanning Prb Micrscpy C. PI cntrl in chmical nginring s wll as data tratmnt and prsntatin 1. Lasr phtchmistry
Einstein Equations for Tetrad Fields
 Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Exam 1. It is important that you clearly show your work and mark the final answer clearly, closed book, closed notes, no calculator.
 Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
u 3 = u 3 (x 1, x 2, x 3 )
 Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
Extraction of Doping Density Distributions from C-V Curves
 Extraction of Doping Dnsity Distributions from C-V Curvs Hartmut F.-W. Sadrozinski SCIPP, Univ. California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 9564 USA 1. Connction btwn C, N, V Start with Poisson quation d V =
Extraction of Doping Dnsity Distributions from C-V Curvs Hartmut F.-W. Sadrozinski SCIPP, Univ. California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 9564 USA 1. Connction btwn C, N, V Start with Poisson quation d V =
Search sequence databases 3 10/25/2016
 Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
15. Stress-Strain behavior of soils
 15. Strss-Strain bhavior of soils Sand bhavior Usually shard undr draind conditions (rlativly high prmability mans xcss por prssurs ar not gnratd). Paramtrs govrning sand bhaviour is: Rlativ dnsity Effctiv
15. Strss-Strain bhavior of soils Sand bhavior Usually shard undr draind conditions (rlativly high prmability mans xcss por prssurs ar not gnratd). Paramtrs govrning sand bhaviour is: Rlativ dnsity Effctiv
A Prey-Predator Model with an Alternative Food for the Predator, Harvesting of Both the Species and with A Gestation Period for Interaction
 Int. J. Opn Problms Compt. Math., Vol., o., Jun 008 A Pry-Prdator Modl with an Altrnativ Food for th Prdator, Harvsting of Both th Spcis and with A Gstation Priod for Intraction K. L. arayan and. CH. P.
Int. J. Opn Problms Compt. Math., Vol., o., Jun 008 A Pry-Prdator Modl with an Altrnativ Food for th Prdator, Harvsting of Both th Spcis and with A Gstation Priod for Intraction K. L. arayan and. CH. P.
EXST Regression Techniques Page 1
 EXST704 - Rgrssion Tchniqus Pag 1 Masurmnt rrors in X W hav assumd that all variation is in Y. Masurmnt rror in this variabl will not ffct th rsults, as long as thy ar uncorrlatd and unbiasd, sinc thy
EXST704 - Rgrssion Tchniqus Pag 1 Masurmnt rrors in X W hav assumd that all variation is in Y. Masurmnt rror in this variabl will not ffct th rsults, as long as thy ar uncorrlatd and unbiasd, sinc thy
Two Products Manufacturer s Production Decisions with Carbon Constraint
 Managmnt Scinc and Enginring Vol 7 No 3 pp 3-34 DOI:3968/jms9335X374 ISSN 93-34 [Print] ISSN 93-35X [Onlin] wwwcscanadant wwwcscanadaorg Two Products Manufacturr s Production Dcisions with Carbon Constraint
Managmnt Scinc and Enginring Vol 7 No 3 pp 3-34 DOI:3968/jms9335X374 ISSN 93-34 [Print] ISSN 93-35X [Onlin] wwwcscanadant wwwcscanadaorg Two Products Manufacturr s Production Dcisions with Carbon Constraint
Cosmology. Outline. Relativity and Astrophysics Lecture 17 Terry Herter. Redshift (again) The Expanding Universe Applying Hubble s Law
 Csmlgy Csmlgy Rlativity and Astrphysics ctur 17 Trry Hrtr Outlin Rdshit (again) Th Expanding Univrs Applying Hubbl s aw Distanc rm Rdshit Csmlgical Principl Olbrs Paradx A90-17 Csmlgy A90-17 1 Csmlgy Rdshit
Csmlgy Csmlgy Rlativity and Astrphysics ctur 17 Trry Hrtr Outlin Rdshit (again) Th Expanding Univrs Applying Hubbl s aw Distanc rm Rdshit Csmlgical Principl Olbrs Paradx A90-17 Csmlgy A90-17 1 Csmlgy Rdshit
Studies of Turbulence and Transport in Alcator C-Mod Ohmic Plasmas with Phase Contrast Imaging and Comparisons with GYRO*
 Studis of Turbulnc and Transport in Ohmic Plasmas with Phas Contrast Imaging and Comparisons with GYRO* L. Lin 1, M. Porkolab 1, E.M. Edlund 1, J.C. Rost 1, M. Grnwald 1, D.R. Mikklsn 2, N. Tsujii 1 1
Studis of Turbulnc and Transport in Ohmic Plasmas with Phas Contrast Imaging and Comparisons with GYRO* L. Lin 1, M. Porkolab 1, E.M. Edlund 1, J.C. Rost 1, M. Grnwald 1, D.R. Mikklsn 2, N. Tsujii 1 1
IYPT 2000 Problem No. 3 PLASMA
 IYPT 000 Problm No. 3 PLASMA Tam Austria Invstigat th lctrical conducivity of th flam of a candl. Examin th influnc of rlvant paramtrs, in particular, th shap and polarity of th lctrods. Th xprimnts should
IYPT 000 Problm No. 3 PLASMA Tam Austria Invstigat th lctrical conducivity of th flam of a candl. Examin th influnc of rlvant paramtrs, in particular, th shap and polarity of th lctrods. Th xprimnts should
The failure of the classical mechanics
 h failur of th classical mchanics W rviw som xprimntal vidncs showing that svral concpts of classical mchanics cannot b applid. - h blac-body radiation. - Atomic and molcular spctra. - h particl-li charactr
h failur of th classical mchanics W rviw som xprimntal vidncs showing that svral concpts of classical mchanics cannot b applid. - h blac-body radiation. - Atomic and molcular spctra. - h particl-li charactr
Where k is either given or determined from the data and c is an arbitrary constant.
 Exponntial growth and dcay applications W wish to solv an quation that has a drivativ. dy ky k > dx This quation says that th rat of chang of th function is proportional to th function. Th solution is
Exponntial growth and dcay applications W wish to solv an quation that has a drivativ. dy ky k > dx This quation says that th rat of chang of th function is proportional to th function. Th solution is
1.2 Faraday s law A changing magnetic field induces an electric field. Their relation is given by:
 Elctromagntic Induction. Lorntz forc on moving charg Point charg moving at vlocity v, F qv B () For a sction of lctric currnt I in a thin wir dl is Idl, th forc is df Idl B () Elctromotiv forc f s any
Elctromagntic Induction. Lorntz forc on moving charg Point charg moving at vlocity v, F qv B () For a sction of lctric currnt I in a thin wir dl is Idl, th forc is df Idl B () Elctromotiv forc f s any
Characteristics of Gliding Arc Discharge Plasma
 Caractristics of Gliding Arc Discarg Plasma Lin Li( ), Wu Bin(, Yang Ci(, Wu Cngkang ( Institut of Mcanics, Cins Acadmy of Scincs, Bijing 8, Cina E-mail: linli@imc.ac.cn Abstract A gliding arc discarg
Caractristics of Gliding Arc Discarg Plasma Lin Li( ), Wu Bin(, Yang Ci(, Wu Cngkang ( Institut of Mcanics, Cins Acadmy of Scincs, Bijing 8, Cina E-mail: linli@imc.ac.cn Abstract A gliding arc discarg
MCB137: Physical Biology of the Cell Spring 2017 Homework 6: Ligand binding and the MWC model of allostery (Due 3/23/17)
 MCB37: Physical Biology of th Cll Spring 207 Homwork 6: Ligand binding and th MWC modl of allostry (Du 3/23/7) Hrnan G. Garcia March 2, 207 Simpl rprssion In class, w drivd a mathmatical modl of how simpl
MCB37: Physical Biology of th Cll Spring 207 Homwork 6: Ligand binding and th MWC modl of allostry (Du 3/23/7) Hrnan G. Garcia March 2, 207 Simpl rprssion In class, w drivd a mathmatical modl of how simpl
Effect of Warm Ionized Plasma Medium on Radiation Properties of Mismatched Microstrip Termination
 J. Elctrmagntic Analysis & Alicatins, 9, 3: 181-186 di:1.436/jmaa.9.137 Publishd Onlin Stmbr 9 (www.scip.rg/jurnal/jmaa) 181 Effct f Warm Inizd Plasma Mdium n adiatin Prrtis f Mismatchd Micrstri Trminatin
J. Elctrmagntic Analysis & Alicatins, 9, 3: 181-186 di:1.436/jmaa.9.137 Publishd Onlin Stmbr 9 (www.scip.rg/jurnal/jmaa) 181 Effct f Warm Inizd Plasma Mdium n adiatin Prrtis f Mismatchd Micrstri Trminatin
Chapter 2: Examples of Mathematical Models for Chemical Processes
 Chaptr 2: Exampls Mathmatical Mdls r Chmical Prcsss In this chaptr w dvlp mathmatical mdls r a numbr lmntary chmical prcsss that ar cmmnly ncuntrd in practic. W will apply th mthdlgy discussd in th prvius
Chaptr 2: Exampls Mathmatical Mdls r Chmical Prcsss In this chaptr w dvlp mathmatical mdls r a numbr lmntary chmical prcsss that ar cmmnly ncuntrd in practic. W will apply th mthdlgy discussd in th prvius
COLLECTOR SELECTION FOR SOLAR EJECTOR COOLING SYSTEM
 Slar Enrgy Vl. 71, N. 4, pp. 69 74, 001 Prgamn P II: S0038 09X(01)0004 1 001 Publishd by Elsvir Scinc Ltd Printd in Grat Britain 0038-09X/01/$ - s frnt mattr www.lsvir.cm/ lcat/ slnr COLLECTOR SELECTION
Slar Enrgy Vl. 71, N. 4, pp. 69 74, 001 Prgamn P II: S0038 09X(01)0004 1 001 Publishd by Elsvir Scinc Ltd Printd in Grat Britain 0038-09X/01/$ - s frnt mattr www.lsvir.cm/ lcat/ slnr COLLECTOR SELECTION
A Brief and Elementary Note on Redshift. May 26, 2010.
 A Brif and Elmntary Nt n Rdshift May 26, 2010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 46025 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s Abstract A rasnabl xplanatin f bth rdshifts: csmlgical
A Brif and Elmntary Nt n Rdshift May 26, 2010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 46025 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s Abstract A rasnabl xplanatin f bth rdshifts: csmlgical
Division of Mechanics Lund University MULTIBODY DYNAMICS. Examination Name (write in block letters):.
 Division of Mchanics Lund Univrsity MULTIBODY DYNMICS Examination 7033 Nam (writ in block lttrs):. Id.-numbr: Writtn xamination with fiv tasks. Plas chck that all tasks ar includd. clan copy of th solutions
Division of Mchanics Lund Univrsity MULTIBODY DYNMICS Examination 7033 Nam (writ in block lttrs):. Id.-numbr: Writtn xamination with fiv tasks. Plas chck that all tasks ar includd. clan copy of th solutions
Homotopy perturbation technique
 Comput. Mthods Appl. Mch. Engrg. 178 (1999) 257±262 www.lsvir.com/locat/cma Homotopy prturbation tchniqu Ji-Huan H 1 Shanghai Univrsity, Shanghai Institut of Applid Mathmatics and Mchanics, Shanghai 272,
Comput. Mthods Appl. Mch. Engrg. 178 (1999) 257±262 www.lsvir.com/locat/cma Homotopy prturbation tchniqu Ji-Huan H 1 Shanghai Univrsity, Shanghai Institut of Applid Mathmatics and Mchanics, Shanghai 272,
DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATION
 Chaptr 11 DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATION Intrdctin Light xhibit dal natr - wav natr and particl natr. In Phnmna lik Intrfrnc, diffrctin tc wav natr is xhibitd. In pht lctric ffct, cmptn ffct tc particl
Chaptr 11 DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATION Intrdctin Light xhibit dal natr - wav natr and particl natr. In Phnmna lik Intrfrnc, diffrctin tc wav natr is xhibitd. In pht lctric ffct, cmptn ffct tc particl
BORH S DERIVATION OF BALMER-RYDBERG FORMULA THROUGH QUANTUM MECHANICS
 BORH S DERIVATION OF BALMER-RYDBERG FORMULA THROUGH QUANTUM MECHANICS Musa D. Abdullahi Umaru Musa Yar adua Univrsity, P.M.B. 18 Katsina, Katsina Stat, Nigria musadab@utlk.cm Abstract Accrding t classical
BORH S DERIVATION OF BALMER-RYDBERG FORMULA THROUGH QUANTUM MECHANICS Musa D. Abdullahi Umaru Musa Yar adua Univrsity, P.M.B. 18 Katsina, Katsina Stat, Nigria musadab@utlk.cm Abstract Accrding t classical
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THERMAL WARPING AND BUCKLING IN ENAMELLED STEEL PARTS
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THERMAL WARPING AND BUCKLING IN ENAMELLED STEEL PARTS 337 XXI Intrnational Enamllrs Congrss Numrical Simulation of Thrmal Warping and Buckling in Enamlld Stl Parts Filip Van dn
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THERMAL WARPING AND BUCKLING IN ENAMELLED STEEL PARTS 337 XXI Intrnational Enamllrs Congrss Numrical Simulation of Thrmal Warping and Buckling in Enamlld Stl Parts Filip Van dn
5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics
 MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
Part 7: Capacitance And Capacitors
 Part 7: apacitanc And apacitors 7. Elctric harg And Elctric Filds onsidr a pair of flat, conducting plats, arrangd paralll to ach othr (as in figur 7.) and sparatd by an insulator, which may simply b air.
Part 7: apacitanc And apacitors 7. Elctric harg And Elctric Filds onsidr a pair of flat, conducting plats, arrangd paralll to ach othr (as in figur 7.) and sparatd by an insulator, which may simply b air.
AerE 344: Undergraduate Aerodynamics and Propulsion Laboratory. Lab Instructions
 ArE 344: Undrgraduat Arodynamics and ropulsion Laboratory Lab Instructions Lab #08: Visualization of th Shock Wavs in a Suprsonic Jt by using Schlirn tchniqu Instructor: Dr. Hui Hu Dpartmnt of Arospac
ArE 344: Undrgraduat Arodynamics and ropulsion Laboratory Lab Instructions Lab #08: Visualization of th Shock Wavs in a Suprsonic Jt by using Schlirn tchniqu Instructor: Dr. Hui Hu Dpartmnt of Arospac
A Redshift Phenomenon in Relativistic Binary System
 J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Rs. 3(8)-7 03 03 TxtRad Pulicatin ISSN 090-4304 Jurnal f Basic and Applid Scintific Rsarch www.txtrad.cm A Rdshift Phnmnn in Rlativistic Binary Systm A.B.Mrcs 34 Dpartmnt f Astrnmy
J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Rs. 3(8)-7 03 03 TxtRad Pulicatin ISSN 090-4304 Jurnal f Basic and Applid Scintific Rsarch www.txtrad.cm A Rdshift Phnmnn in Rlativistic Binary Systm A.B.Mrcs 34 Dpartmnt f Astrnmy
Effect of Temporary Bridge on Parkway Performance
 Effct f Tmprary Bridg n Parkway Prfrmanc MATTHEW J. HUBER, Rsarch Assciat Burau f Highway Traffic, Yal Univrsity THE NEW ENGLAND flds f Octbr 15, 1955, undrmind a culvrt n th Mrritt Parkway at Nrwalk,
Effct f Tmprary Bridg n Parkway Prfrmanc MATTHEW J. HUBER, Rsarch Assciat Burau f Highway Traffic, Yal Univrsity THE NEW ENGLAND flds f Octbr 15, 1955, undrmind a culvrt n th Mrritt Parkway at Nrwalk,
Principles of Humidity Dalton s law
 Principls of Humidity Dalton s law Air is a mixtur of diffrnt gass. Th main gas componnts ar: Gas componnt volum [%] wight [%] Nitrogn N 2 78,03 75,47 Oxygn O 2 20,99 23,20 Argon Ar 0,93 1,28 Carbon dioxid
Principls of Humidity Dalton s law Air is a mixtur of diffrnt gass. Th main gas componnts ar: Gas componnt volum [%] wight [%] Nitrogn N 2 78,03 75,47 Oxygn O 2 20,99 23,20 Argon Ar 0,93 1,28 Carbon dioxid
Ch. 24 Molecular Reaction Dynamics 1. Collision Theory
 Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
section 1 Influencing Change Toolkit How to: Influence People
 Influncing Chang Tlkit Hw t: Influnc Ppl Influncing ppl mans having an ffct n thm, changing r mdifying thir viw. In rdr t influnc chang, w nd t influnc th ppl wh ar in a psitin t mak that chang happn.
Influncing Chang Tlkit Hw t: Influnc Ppl Influncing ppl mans having an ffct n thm, changing r mdifying thir viw. In rdr t influnc chang, w nd t influnc th ppl wh ar in a psitin t mak that chang happn.
Continuous probability distributions
 Continuous probability distributions Many continuous probability distributions, including: Uniform Normal Gamma Eponntial Chi-Squard Lognormal Wibull EGR 5 Ch. 6 Uniform distribution Simplst charactrizd
Continuous probability distributions Many continuous probability distributions, including: Uniform Normal Gamma Eponntial Chi-Squard Lognormal Wibull EGR 5 Ch. 6 Uniform distribution Simplst charactrizd
Square shaped flat-top beam in refractive beam shapers
 Squar shapd flat-tp bam in rfractiv bam shaprs Alxandr Laskin a, Vadim Laskin a, Alksi Ostrun b a AdlOptica GmbH, Rudwr Chauss 29, 12489 Brlin, Grmany b St. Ptrsburg Natinal Rsarch Univrsity f Infrmatin
Squar shapd flat-tp bam in rfractiv bam shaprs Alxandr Laskin a, Vadim Laskin a, Alksi Ostrun b a AdlOptica GmbH, Rudwr Chauss 29, 12489 Brlin, Grmany b St. Ptrsburg Natinal Rsarch Univrsity f Infrmatin
High Energy Physics. Lecture 5 The Passage of Particles through Matter
 High Enrgy Physics Lctur 5 Th Passag of Particls through Mattr 1 Introduction In prvious lcturs w hav sn xampls of tracks lft by chargd particls in passing through mattr. Such tracks provid som of th most
High Enrgy Physics Lctur 5 Th Passag of Particls through Mattr 1 Introduction In prvious lcturs w hav sn xampls of tracks lft by chargd particls in passing through mattr. Such tracks provid som of th most
A Propagating Wave Packet Group Velocity Dispersion
 Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
Types of Communication
 Tps f Cmmunicatin Analg: cntinuus ariabls with nis {rrr 0} 0 (imprfct) Digital: dcisins, discrt chics, quantizd, nis {rrr} 0 (usuall prfct) Mssag S, S, r S M Mdulatr (t) channl; adds nis and distrtin M-ar
Tps f Cmmunicatin Analg: cntinuus ariabls with nis {rrr 0} 0 (imprfct) Digital: dcisins, discrt chics, quantizd, nis {rrr} 0 (usuall prfct) Mssag S, S, r S M Mdulatr (t) channl; adds nis and distrtin M-ar
EXERGY ANALYSIS OF A DUAL-MODE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM FOR ICE STORAGE AIR CONDITIONING
 Intrnatinal Jurnal n Architctural Scinc, Vlum 6, Numbr 1, p.1-6, 005 EXERGY ANALYSIS OF A DUAL-MODE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM FOR ICE STORAGE AIR CONDITIONING Guiyin Fang*, Lin Xing*, Fan Yang* and Hui Li #
Intrnatinal Jurnal n Architctural Scinc, Vlum 6, Numbr 1, p.1-6, 005 EXERGY ANALYSIS OF A DUAL-MODE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM FOR ICE STORAGE AIR CONDITIONING Guiyin Fang*, Lin Xing*, Fan Yang* and Hui Li #
Exam 2 Thursday (7:30-9pm) It will cover material through HW 7, but no material that was on the 1 st exam.
 Exam 2 Thursday (7:30-9pm) It will covr matrial through HW 7, but no matrial that was on th 1 st xam. What happns if w bash atoms with lctrons? In atomic discharg lamps, lots of lctrons ar givn kintic
Exam 2 Thursday (7:30-9pm) It will covr matrial through HW 7, but no matrial that was on th 1 st xam. What happns if w bash atoms with lctrons? In atomic discharg lamps, lots of lctrons ar givn kintic
INFLUENCE OF GROUND SUBSIDENCE IN THE DAMAGE TO MEXICO CITY S PRIMARY WATER SYSTEM DUE TO THE 1985 EARTHQUAKE
 13 th World Confrnc on Earthquak Enginring Vancouvr, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Papr No. 2165 INFLUENCE OF GROUND SUBSIDENCE IN THE DAMAGE TO MEXICO CITY S PRIMARY WATER SYSTEM DUE TO THE 1985 EARTHQUAKE
13 th World Confrnc on Earthquak Enginring Vancouvr, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Papr No. 2165 INFLUENCE OF GROUND SUBSIDENCE IN THE DAMAGE TO MEXICO CITY S PRIMARY WATER SYSTEM DUE TO THE 1985 EARTHQUAKE
Reflector Antennas. Contents
 Rlctr Antnnas Mtivatin: - incras th aprtur ara and, thrr, incras dirctivity - cllimat nrgy in n dirctin - rduc th siz th antnna systm - us th rlctr (and subrlctr) r bam shaping Cntnts 1. Intrductin. Crnr
Rlctr Antnnas Mtivatin: - incras th aprtur ara and, thrr, incras dirctivity - cllimat nrgy in n dirctin - rduc th siz th antnna systm - us th rlctr (and subrlctr) r bam shaping Cntnts 1. Intrductin. Crnr
1 Isoparametric Concept
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY Dpartmnt of Civil Enginring Spring 06 Structural Enginring, Mchanics and Matrials Profssor: S. Govindj Nots on D isoparamtric lmnts Isoparamtric Concpt Th isoparamtric
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BERKELEY Dpartmnt of Civil Enginring Spring 06 Structural Enginring, Mchanics and Matrials Profssor: S. Govindj Nots on D isoparamtric lmnts Isoparamtric Concpt Th isoparamtric
SAFE HANDS & IIT-ian's PACE EDT-15 (JEE) SOLUTIONS
 It is not possibl to find flu through biggr loop dirctly So w will find cofficint of mutual inductanc btwn two loops and thn find th flu through biggr loop Also rmmbr M = M ( ) ( ) EDT- (JEE) SOLUTIONS
It is not possibl to find flu through biggr loop dirctly So w will find cofficint of mutual inductanc btwn two loops and thn find th flu through biggr loop Also rmmbr M = M ( ) ( ) EDT- (JEE) SOLUTIONS
Brief Introduction to Statistical Mechanics
 Brif Introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Purpos: Ths nots ar intndd to provid a vry quick introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Th fild is of cours far mor vast than could b containd in ths fw pags.
Brif Introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Purpos: Ths nots ar intndd to provid a vry quick introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Th fild is of cours far mor vast than could b containd in ths fw pags.
Finite Element Model of a Ferroelectric
 Excrpt from th Procdings of th COMSOL Confrnc 200 Paris Finit Elmnt Modl of a Frrolctric A. Lópz, A. D Andrés and P. Ramos * GRIFO. Dpartamnto d Elctrónica, Univrsidad d Alcalá. Alcalá d Hnars. Madrid,
Excrpt from th Procdings of th COMSOL Confrnc 200 Paris Finit Elmnt Modl of a Frrolctric A. Lópz, A. D Andrés and P. Ramos * GRIFO. Dpartamnto d Elctrónica, Univrsidad d Alcalá. Alcalá d Hnars. Madrid,
Atomic and Laser Spectroscopy
 L-E B, OL, MOV 83 Atomic and Lasr Spctroscopy Th aim of this xrcis is to giv an ovrviw of th fild of lasr spctroscopy and to show modrn spctroscopic mthods usd in atomic, molcular and chmical physics.
L-E B, OL, MOV 83 Atomic and Lasr Spctroscopy Th aim of this xrcis is to giv an ovrviw of th fild of lasr spctroscopy and to show modrn spctroscopic mthods usd in atomic, molcular and chmical physics.
Voltage, Current, Power, Series Resistance, Parallel Resistance, and Diodes
 Lctur 1. oltag, Currnt, Powr, Sris sistanc, Paralll sistanc, and Diods Whn you start to dal with lctronics thr ar thr main concpts to start with: Nam Symbol Unit oltag volt Currnt ampr Powr W watt oltag
Lctur 1. oltag, Currnt, Powr, Sris sistanc, Paralll sistanc, and Diods Whn you start to dal with lctronics thr ar thr main concpts to start with: Nam Symbol Unit oltag volt Currnt ampr Powr W watt oltag
Deepak Rajput
 Q Prov: (a than an infinit point lattic is only capabl of showing,, 4, or 6-fold typ rotational symmtry; (b th Wiss zon law, i.. if [uvw] is a zon axis and (hkl is a fac in th zon, thn hu + kv + lw ; (c
Q Prov: (a than an infinit point lattic is only capabl of showing,, 4, or 6-fold typ rotational symmtry; (b th Wiss zon law, i.. if [uvw] is a zon axis and (hkl is a fac in th zon, thn hu + kv + lw ; (c
2008 AP Calculus BC Multiple Choice Exam
 008 AP Multipl Choic Eam Nam 008 AP Calculus BC Multipl Choic Eam Sction No Calculator Activ AP Calculus 008 BC Multipl Choic. At tim t 0, a particl moving in th -plan is th acclration vctor of th particl
008 AP Multipl Choic Eam Nam 008 AP Calculus BC Multipl Choic Eam Sction No Calculator Activ AP Calculus 008 BC Multipl Choic. At tim t 0, a particl moving in th -plan is th acclration vctor of th particl
Revision: August 21, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 2.7.1: Sinusidal signals, cmplx xpnntials, and phasrs Rvisin: ugust 21, 2010 215 E Main Suit D ullman, W 99163 (509 334 6306 ic and Fax Ovrviw In this mdul, w will rviw prprtis f sinusidal functins and
2.7.1: Sinusidal signals, cmplx xpnntials, and phasrs Rvisin: ugust 21, 2010 215 E Main Suit D ullman, W 99163 (509 334 6306 ic and Fax Ovrviw In this mdul, w will rviw prprtis f sinusidal functins and
Design Guidelines for Quartz Crystal Oscillators. R 1 Motional Resistance L 1 Motional Inductance C 1 Motional Capacitance C 0 Shunt Capacitance
 TECHNICAL NTE 30 Dsign Guidlins for Quartz Crystal scillators Introduction A CMS Pirc oscillator circuit is wll known and is widly usd for its xcllnt frquncy stability and th wid rang of frquncis ovr which
TECHNICAL NTE 30 Dsign Guidlins for Quartz Crystal scillators Introduction A CMS Pirc oscillator circuit is wll known and is widly usd for its xcllnt frquncy stability and th wid rang of frquncis ovr which
5. B To determine all the holes and asymptotes of the equation: y = bdc dced f gbd
 1. First you chck th domain of g x. For this function, x cannot qual zro. Thn w find th D domain of f g x D 3; D 3 0; x Q x x 1 3, x 0 2. Any cosin graph is going to b symmtric with th y-axis as long as
1. First you chck th domain of g x. For this function, x cannot qual zro. Thn w find th D domain of f g x D 3; D 3 0; x Q x x 1 3, x 0 2. Any cosin graph is going to b symmtric with th y-axis as long as
HOMEWORK FOR UNIT 5-2: COMBINING FORCES
 Nam Dat Partnrs HOMEWORK OR UNIT 52: COMBINING ORCES Qustins 15 rfr t a ty ar whih an mv in ithr dirtin alng a hrizntal lin (th psitin axis). 0 Assum that fritin is s small that it an b ignrd. Skth th
Nam Dat Partnrs HOMEWORK OR UNIT 52: COMBINING ORCES Qustins 15 rfr t a ty ar whih an mv in ithr dirtin alng a hrizntal lin (th psitin axis). 0 Assum that fritin is s small that it an b ignrd. Skth th
Worksheet 1: Electrostatics
 Wrksht : lctrstatics ) xplain why it is lctrns and nt prtns which ar thught t b xchangd in lctrstatic intractins. ) A strip f actat and a strip f silk ar rubbd tgthr. What can b said abut th chargs bfr
Wrksht : lctrstatics ) xplain why it is lctrns and nt prtns which ar thught t b xchangd in lctrstatic intractins. ) A strip f actat and a strip f silk ar rubbd tgthr. What can b said abut th chargs bfr
PHYS-333: Problem set #2 Solutions
 PHYS-333: Problm st #2 Solutions Vrsion of March 5, 2016. 1. Visual binary 15 points): Ovr a priod of 10 yars, two stars sparatd by an angl of 1 arcsc ar obsrvd to mov through a full circl about a point
PHYS-333: Problm st #2 Solutions Vrsion of March 5, 2016. 1. Visual binary 15 points): Ovr a priod of 10 yars, two stars sparatd by an angl of 1 arcsc ar obsrvd to mov through a full circl about a point
E hf. hf c. 2 2 h 2 2 m v f ' f 2f ' f cos c
 EXPERIMENT 9: COMPTON EFFECT Rlatd Topics Intractions of photons with lctrons, consrvation of momntum and nrgy, inlastic and lastic scattring, intraction cross sction, Compton wavlngth. Principl Whn photons
EXPERIMENT 9: COMPTON EFFECT Rlatd Topics Intractions of photons with lctrons, consrvation of momntum and nrgy, inlastic and lastic scattring, intraction cross sction, Compton wavlngth. Principl Whn photons
Procdings of IC-IDC0 ( and (, ( ( and (, and (f ( and (, rspctivly. If two input signals ar compltly qual, phas spctra of two signals ar qual. That is
 Procdings of IC-IDC0 EFFECTS OF STOCHASTIC PHASE SPECTRUM DIFFERECES O PHASE-OLY CORRELATIO FUCTIOS PART I: STATISTICALLY COSTAT PHASE SPECTRUM DIFFERECES FOR FREQUECY IDICES Shunsu Yamai, Jun Odagiri,
Procdings of IC-IDC0 EFFECTS OF STOCHASTIC PHASE SPECTRUM DIFFERECES O PHASE-OLY CORRELATIO FUCTIOS PART I: STATISTICALLY COSTAT PHASE SPECTRUM DIFFERECES FOR FREQUECY IDICES Shunsu Yamai, Jun Odagiri,
Introduction to the quantum theory of matter and Schrödinger s equation
 Introduction to th quantum thory of mattr and Schrödingr s quation Th quantum thory of mattr assums that mattr has two naturs: a particl natur and a wa natur. Th particl natur is dscribd by classical physics
Introduction to th quantum thory of mattr and Schrödingr s quation Th quantum thory of mattr assums that mattr has two naturs: a particl natur and a wa natur. Th particl natur is dscribd by classical physics
Chemical Physics II. More Stat. Thermo Kinetics Protein Folding...
 Chmical Physics II Mor Stat. Thrmo Kintics Protin Folding... http://www.nmc.ctc.com/imags/projct/proj15thumb.jpg http://nuclarwaponarchiv.org/usa/tsts/ukgrabl2.jpg http://www.photolib.noaa.gov/corps/imags/big/corp1417.jpg
Chmical Physics II Mor Stat. Thrmo Kintics Protin Folding... http://www.nmc.ctc.com/imags/projct/proj15thumb.jpg http://nuclarwaponarchiv.org/usa/tsts/ukgrabl2.jpg http://www.photolib.noaa.gov/corps/imags/big/corp1417.jpg
orbiting electron turns out to be wrong even though it Unfortunately, the classical visualization of the
 Lctur 22-1 Byond Bohr Modl Unfortunatly, th classical visualization of th orbiting lctron turns out to b wrong vn though it still givs us a simpl way to think of th atom. Quantum Mchanics is ndd to truly
Lctur 22-1 Byond Bohr Modl Unfortunatly, th classical visualization of th orbiting lctron turns out to b wrong vn though it still givs us a simpl way to think of th atom. Quantum Mchanics is ndd to truly
Finite element discretization of Laplace and Poisson equations
 Finit lmnt discrtization of Laplac and Poisson quations Yashwanth Tummala Tutor: Prof S.Mittal 1 Outlin Finit Elmnt Mthod for 1D Introduction to Poisson s and Laplac s Equations Finit Elmnt Mthod for 2D-Discrtization
Finit lmnt discrtization of Laplac and Poisson quations Yashwanth Tummala Tutor: Prof S.Mittal 1 Outlin Finit Elmnt Mthod for 1D Introduction to Poisson s and Laplac s Equations Finit Elmnt Mthod for 2D-Discrtization
Chapter 8: Electron Configurations and Periodicity
 Elctron Spin & th Pauli Exclusion Principl Chaptr 8: Elctron Configurations and Priodicity 3 quantum numbrs (n, l, ml) dfin th nrgy, siz, shap, and spatial orintation of ach atomic orbital. To xplain how
Elctron Spin & th Pauli Exclusion Principl Chaptr 8: Elctron Configurations and Priodicity 3 quantum numbrs (n, l, ml) dfin th nrgy, siz, shap, and spatial orintation of ach atomic orbital. To xplain how
The Relativistic Stern-Gerlach Force C. Tschalär 1. Introduction
 Th Rlativistic Strn-Grlach Forc C. Tschalär. Introduction For ovr a dcad, various formulations of th Strn-Grlach (SG) forc acting on a particl with spin moving at a rlativistic vlocity in an lctromagntic
Th Rlativistic Strn-Grlach Forc C. Tschalär. Introduction For ovr a dcad, various formulations of th Strn-Grlach (SG) forc acting on a particl with spin moving at a rlativistic vlocity in an lctromagntic
