Pollination by Fungus Gnats in Mitella formosana (Saxifragaceae)
|
|
|
- Fay Webb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci., Ser. B, 38(4), pp , November 22, 2012 Pollination by Fungus Gnats in Mitella formosana (Saxifragaceae) Yudai Okuyama Department of Botany, National Museum of Nature and Science, Amakubo 4 1 1, Tsukuba, Ibaraki , Japan yokuyama@kahaku.go.jp (Received 20 August 2012; accepted 26 September 2012) Abstract The pollination system of Mitella formosana, the last Asimitellaria species (genus Mitella sect. Asimitellaria, Saxifragaceae) in which the information regarding its flower visitors remained unreported, was studied in two study sites in Taiwan in April, Although the frequency of pollinator visits observed were very low (0.04 visits per hour per inflorescence on average in daytime), the principal pollinators of M. formosana were clarified as the fungus gnats of the genus Boletina and Coelosia, just similar as in the other Asimitellaria species in Japan. The apparent similarity of pollination systems of Asimitellaria species between Taiwan and Japan implies the long-term maintenance and the evolutionary stability of the Mitella fungus gnats pollination mutualisms across Japan archipelago and Taiwan. Key words : Asimitellaria, Boletina, Coelosia, Japan, pollination mutualism, Taiwan. Introduction A tremendous diversity of flowering plants today is reflected by the diversity of plant-pollinator interactions, and how the diversity of pollinator-associated floral traits has been shaped and how it further facilitated the plant speciation has been one of the major interests in plant evolutionary biology (Proctor et al., 1996; Fenster et al., 2004; Willmer, 2011). To address this issue, it is very useful to have a model plant group in which variation in pollination systems and associated floral traits, as well as the phylogenetic relationships therein are analyzed simultaneously. Asimitellaria, a section of the genus Mitella (Saxifragaceae), is one of such the few plant lineages in which not only the phylogeny but also its relationships with pollinators are comprehensively surveyed (Okuyama et al., 2004, 2005, 2008, 2012). In Asimitellaria, almost all species except M. doiana, which is presumably an obligate selfer, are known to be pollinated exclusively by fungus gnats (Mycetophilidae) (Okuyama et al., 2004, 2008). Moreover, pollination by fungus gnats in Asimitellaria shows a notable variation, where some species are pollinated only by a long tongued fungus gnat species Gnoriste mikado, while the other species are pollinated by short-tongued fungus gnats of genus Boletina and Coelosia exclusively, or together with Gnoriste mikado as a co-pollinator. Interestingly, in some populations, two to three Asimitellaria species co-occur, and the pollinator isolation mediated by the divergent pollinator fungus gnats support their sympatric nature. Therefore, to analyze the selection force behind the pollinator shifts in Asimitellaria should be useful to understand the mechanisms on pollinator-mediated isolation and speciation of flowering plants. The last Asimitellaria species without any information of its relationships with pollinators is M. formosana, the only Asimitellaria species that distributes outside Japan. Mitella formosana also has a notable phylogenetic position in Asimitellaria, i.e., forming a well-supported clade with
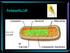
2 184 Yudai Okuyama Fig. 1. Coelosia sp. (Mycetophilidae) that visited on the M. formosana flowers. A, Coelosia sp. nectaring on the M. formosana flower. B, A microscopic image of Coelosia sp. collected on a M. formosana flower. Note numerous pollen grains are attached on the anterior side of the body. C, An electron microscopic image of Coelosia sp. collected on a M. formosana flower. The rugby-ball like morphology of pollen grains typical of the pollen grains of Mitella is visible on the insect s surface. M. japonica and M. yoshinagae (Fig. 2, Okuyama and Kato, 2009), which presumably reflects the ancient floristic link between Taiwan and Japan. Okuyama et al. (2008) classified the floral morphology of M. formosana as saucershape, implying this species might have rela- tionship with short-tongued fungus gnat species of the genus such as Boletina and Coelosia. To test this prediction and to expand the knowledge on pollination systems of Asimitellaria into the whole lineage and geographic distribution, I conducted a survey on pollination biology of M. for-
3 Pollination by Fungus Gnats in Mitella formosana (Saxifragaceae) 185 Fig. 2. Phylogenetic distribution of pollination systems in Asimitellaria. Phylogenetic tree was redrawn from Okuyama and Kato (2009). mosana in April, The present study revealed that M. formosana, a geographically isolated and the southernmost species of Asimitellaria, maintains a surprisingly similar pollination system to those of species in Japan. Materials and Methods Direct observation of pollinator visits to flowers of M. formosana were made at Lalashan site (N , E ) during on April 7 and on April 10, and Szuyuanyakou site (N , E ) during on April 9 and on April 10. All insects flew and landed to the flowers were collected and stored dry separately to inspect their pollen loads under a KEYENCE VHX-2000 digital microscope (Keyence, Tokyo). In addition, pollinator visits were further monitored with time-lapse photography using Optio W90 cameras (Pentax, Tokyo), each set in front of an individual of M. formosana, keeping 20 cm distance from the plants and 5 m to each other. The time-intervals between the shots were set to 2 min, as this is the minimum time-interval for camera battery to be sustained overnight ( 12h). This setting is reasonable because the pollinator fungus gnats in other Asimitellaria species were known to stay on flowers for 2 min, on average (Okuyama et al., 2004), and there is little discrepancy between the flower-visitation data from direct observation and time-lapse photography in Asimitellaria (Yudai Okuyama, personal observation; see also the Results section). Five cameras were set each in Lalashan site and Szuyuanyakou site for h, focusing on 1 12 inflorescences in full bloom (Table 1). Each insect individual 5 mm in body size photographed at nectaring on a flower was count as a single visit, and the insect on the same flower taken in the subsequent shot was not count. Results Throughout the observation period, insect vis-
4 186 Yudai Okuyama Table 1. The detailed information of time-lapse photography in the present study inflorescence Photographing time of day Total time shots insect visits* Lalashan site Camera April April 9 46 h (1) Camera April April h (0) Camera April April 9 41 h (7) Camera April 7, April 8 7 h (0) Camera April April 8 13 h (1) Szuyuanyakou site Camera April April h (0) Camera April April 9 19 h (0) Camera April April h (0) Camera April April h (0) Camera April April 9 21 h (0) * The numbers in parentheses indicate the number of mycetophilid fungus gnats its were rare, although certainly present. Except for mordellid beetles continuously stayed and crawled on M. formosana flowers, only I had observed were three visits of Coelosia sp. (Mycetophilidae) and two visits of the other dipterans in Lalashan site, and a single visit of Boletina sp. (Mycetophilidae) in Szuyuanyakou site. This very rare insect visits were also confirmed by a time-lapse photography that shot only 17 insect visits in a grand total of 118 h daytime (0.04 visits per hour per inflorescence on average), in which 9 of 17 were mycetophilid fungus gnats and the other 8 were other dipterans (Table 1). The all four mycetophilid fungus gnats (3 Coelosia sp. and 1 Boletina sp.) directly collected on the flowers were confirmed to carry 100 pollen grains on their body (Fig. 1), whereas the other dipterans collected on the flowers of M. formosana had 10 pollen grains. Discussion The present research partly clarified the pollination system of M. formosana that has never been reported before. From the direct observation and time-lapse photography, the major flower visitors of M. formosana was confirmed to be the short-tongued fungus gnats of the genus Boletina and Coelosia, just similar as in Asimitellaria in Japan. Because these fungus gnats collected on the M. formosana flowers always had numerous pollen grains ( 100) on their body enough to fertilize all ovules of the flower, it would be reasonable to conclude these fungus gnats are the principal pollinators of M. formosana. The other insects, non-mycetophilid dipterans and mordellid beetles, visited on the flowers were never found to carry pollen loads enough to fertilize a large proportion of ovules of the flower, or they seldom move across the inflorescences (mordellid beetles). Therefore, they are unlikely to contribute largely to the cross pollination of the species, although mordellid beetles might partly contribute to self-pollination. Although the present research is limited to a short time-period in only one year, the following characteristics of pollination system of M. formosana were clarified. First, M. formosana has surprisingly similar pollination system to those of Asimitellaria species in Japan that involves the same mycetophilid genera such as Boletina and Coelosia. Second, the fungus gnats of the genus Gnoriste are unlikely to be involved in the pollination of M. formosana, confirming what is expected from the floral morphology (Okuyama et al., 2008) and the fact that there is no record of collection of the genus Gnoriste in Taiwan. The apparent similarity of pollination systems of Asimitellaria species between Taiwan (M. formosana) and Japan (M. pauciflora, M. japonica Honshu group, and M. yoshinagae) implies the long-term maintenance and the evolutionary stability of the Mitella fungus gnats pollination mutualisms across the Japan archipelago and
5 Pollination by Fungus Gnats in Mitella formosana (Saxifragaceae) 187 Taiwan. It is also noteworthy that, from the present study, the complete picture of the pattern and variation of pollination systems in Asimitellaria became available (Fig. 2). As is evident looking at Fig. 2, the different pollination modes in the Asimitellaria are scattered across the phylogeny, indicating the pollinator shifts occurred recurrently in the lineage. This suggests that, using the present information, the common ecological and physiological mechanisms behind the pollinator shifts in Asimitellaria could be identified, which is the topic of forthcoming research. Acknowledgments The author thanks Ching-I Peng for the arrangement of the field research in Taiwan and Chien-Hua Lu and Chien-I Huang for their generous guide in the field sites. References Fenster, C. B., Armbruster, W. S., Wilson, P., Dudash, M. R. and Thomson, J. D Pollination syndromes and floral specialization. The Annual Reviews of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 35: Okuyama, Y. and Kato, M Unveiling cryptic species diversity of flowering plants: successful species circumscription of Asian Mitella using nuclear ribosomal DNA sequences. BMC Evolutionary Biology 9: 105. Okuyama, Y., Kato, M. and Murakami, N Pollination by fungus gnats in four species of the genus Mitella (Saxifragaceae). Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 144: Okuyama, Y., Pellmyr, O. and Kato, M Parallel floral adaptations to pollination by fungus gnats within the genus Mitella (Saxifragaceae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 46: Okuyama, Y., Tanabe, A. S. and Kato, M Entangling ancient allotetraploidization in Asian Mitella: An integrated approach for multilocus combinations. Molecular Biology and Evolution 29: Okuyama, Y., Fujii, N., Wakabayashi, M., Kawakita, A., Ito, M., Watanabe, M., Murakami, N. and Kato, M Nonuniform concerted evolution and chloroplast capture: heterogeneity of observed introgression patterns in three molecular data partition phylogenies of Asian Mitella (Saxifragaceae). Molecular Biology and Evolution 22: Proctor, M., Yeo, P. and Lack, A The Natural History of Pollination. Timber Press, Portland. Willmer, P Pollination and Floral Ecology. Princeton University Press, Princeton.
The Genetic Characteristics of an Endangered Population of Mitella furusei var. subramosa (Saxifragaceae) from Shikoku, Japan
 Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci., Ser. B, 38(1), pp. 19 27, February 22, 2012 The Genetic Characteristics of an Endangered Population of Mitella furusei var. subramosa (Saxifragaceae) from Shikoku, Japan Yudai
Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci., Ser. B, 38(1), pp. 19 27, February 22, 2012 The Genetic Characteristics of an Endangered Population of Mitella furusei var. subramosa (Saxifragaceae) from Shikoku, Japan Yudai
Pollination by fungus gnats in four species of the genus Mitella (Saxifragaceae)
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKBOJBotanical Journal of the Linnean Society4-474The Linnean Society of London, 4? 4 444 44946 Original Article FUNGUS GNAT POLLINATION IN MITELLA Botanical Journal of the
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKBOJBotanical Journal of the Linnean Society4-474The Linnean Society of London, 4? 4 444 44946 Original Article FUNGUS GNAT POLLINATION IN MITELLA Botanical Journal of the
Parallel chemical switches underlying pollinator isolation in Asian Mitella
 doi: 10.1111/jeb.12591 Parallel chemical switches underlying pollinator isolation in Asian Mitella T. OKAMOTO* 1,Y.OKUYAMA 1,R.GOTO* 2,M.TOKORO &M.KATO* *Graduate School of Human and Environmental Studies,
doi: 10.1111/jeb.12591 Parallel chemical switches underlying pollinator isolation in Asian Mitella T. OKAMOTO* 1,Y.OKUYAMA 1,R.GOTO* 2,M.TOKORO &M.KATO* *Graduate School of Human and Environmental Studies,
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/65602 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Ruchisansakun, S. Title: Balsaminaceae in Southeast Asia: systematics, evolution,
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/65602 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Ruchisansakun, S. Title: Balsaminaceae in Southeast Asia: systematics, evolution,
Speciation Plant Sciences, 2001Updated: June 1, 2012 Gale Document Number: GALE CV
 is the process of evolution by which new species arise. The key factor causing speciation is the appearance of genetic differences between two populations, which result from evolution by natural selection.
is the process of evolution by which new species arise. The key factor causing speciation is the appearance of genetic differences between two populations, which result from evolution by natural selection.
Unit 10.4: Macroevolution and the Origin of Species
 Unit 10.4: Macroevolution and the Origin of Species Lesson Objectives Describe two ways that new species may originate. Define coevolution, and give an example. Distinguish between gradualism and punctuated
Unit 10.4: Macroevolution and the Origin of Species Lesson Objectives Describe two ways that new species may originate. Define coevolution, and give an example. Distinguish between gradualism and punctuated
(Saxifragaceae) in the Central Ryukyus
 ISSN 1346-7565 Acta Phytotax. Geobot. 67 (1): 17 27 (2016) Mitella amamiana sp. nov., the First Discovery of the Genus Mitella (Saxifragaceae) in the Central Ryukyus Yudai Okuyama Tsukuba Botanical Garden,
ISSN 1346-7565 Acta Phytotax. Geobot. 67 (1): 17 27 (2016) Mitella amamiana sp. nov., the First Discovery of the Genus Mitella (Saxifragaceae) in the Central Ryukyus Yudai Okuyama Tsukuba Botanical Garden,
Mutualism: Inter-specific relationship from which both species benefit
 Mutualism Mutualism: Inter-specific relationship from which both species benefit Mutualism Symbiosis: Intimate (generally obligate) inter-specific relationships from which both partners benefit 1 Mutualism
Mutualism Mutualism: Inter-specific relationship from which both species benefit Mutualism Symbiosis: Intimate (generally obligate) inter-specific relationships from which both partners benefit 1 Mutualism
Mutualism. Mutualism. Mutualism. Early plants were probably wind pollinated and insects were predators feeding on spores, pollen or ovules
 Mutualism Mutualism: Inter-specific relationship from which both species benefit Mutualism Symbiosis: Intimate (generally obligate) inter-specific relationships from which both partners benefit Mutualism
Mutualism Mutualism: Inter-specific relationship from which both species benefit Mutualism Symbiosis: Intimate (generally obligate) inter-specific relationships from which both partners benefit Mutualism
AP Biology Essential Knowledge Cards BIG IDEA 1
 AP Biology Essential Knowledge Cards BIG IDEA 1 Essential knowledge 1.A.1: Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. Essential knowledge 1.A.4: Biological evolution is supported by scientific
AP Biology Essential Knowledge Cards BIG IDEA 1 Essential knowledge 1.A.1: Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. Essential knowledge 1.A.4: Biological evolution is supported by scientific
COMPARISON OF FORAGING ACTIVITY BETWEEN MASON BEE OSMIA ORIENTALIS
 Volume 125, Number 5, March 2016 363 COMPARISON OF FORAGING ACTIVITY BETWEEN MASON BEE OSMIA ORIENTALIS (HYMENOPTERA: MEGACHILIDAE) AND HONYBEES FOR WILD RASP- BERRY RUBUS HIRSUTUS (ROSALES: ROSACEAE)
Volume 125, Number 5, March 2016 363 COMPARISON OF FORAGING ACTIVITY BETWEEN MASON BEE OSMIA ORIENTALIS (HYMENOPTERA: MEGACHILIDAE) AND HONYBEES FOR WILD RASP- BERRY RUBUS HIRSUTUS (ROSALES: ROSACEAE)
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.22 EVOLUTIONARY GENETICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF EVOLUTION Evolution is a process through which variation in individuals makes it more likely for them to survive and reproduce There are principles to the theory
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF EVOLUTION Evolution is a process through which variation in individuals makes it more likely for them to survive and reproduce There are principles to the theory
LEARN * DREAM * AWAKEN* DISCOVER * ENLIGHTEN * INVESTIGATE *QUESTION * EXPLORE
 S C I E N C E P L A N T S PLANT FIELD ENRICHMENT4YOU Published by Henrich Incorporated Copyright 2005 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or
S C I E N C E P L A N T S PLANT FIELD ENRICHMENT4YOU Published by Henrich Incorporated Copyright 2005 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or
FLOWERS AND POLLINATION. This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination.
 FLOWERS AND POLLINATION This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination. Objectives for Exam #1 1. Identify flower structures and match those structures to specific
FLOWERS AND POLLINATION This activity introduces the relationship between flower structures and pollination. Objectives for Exam #1 1. Identify flower structures and match those structures to specific
Essential knowledge 1.A.2: Natural selection
 Appendix C AP Biology Concepts at a Glance Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. Enduring understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time
Appendix C AP Biology Concepts at a Glance Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. Enduring understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time
Pollinator Adaptations
 Adapted from: Life Lab Garden Pollinators unit Pollinator Adaptations Overview: Students will learn about pollinators and their adaptations, and match flowers to the kinds of pollinators they attract.
Adapted from: Life Lab Garden Pollinators unit Pollinator Adaptations Overview: Students will learn about pollinators and their adaptations, and match flowers to the kinds of pollinators they attract.
FORAGING PATTERN OF INSECT POLLINATORS IN PENTAS LANCEOLATA (FORSSK.) DEFLERS AND CATHARANTHUS ROSEUS (L.) G. DON IN THRISSUR DISTRICT, KERALA, INDIA
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 3, No 5, 2014, 1731 1737 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) FORAGING PATTERN OF INSECT POLLINATORS IN PENTAS LANCEOLATA (FORSSK.) DEFLERS AND CATHARANTHUS
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 3, No 5, 2014, 1731 1737 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) FORAGING PATTERN OF INSECT POLLINATORS IN PENTAS LANCEOLATA (FORSSK.) DEFLERS AND CATHARANTHUS
Pollination Lab Bio 220 Ecology and Evolution Fall, 2016
 Pollination Lab Bio 220 Ecology and Evolution Fall, 2016 Journal reading: Comparison of pollen transfer dynamics by multiple floral visitors: experiments with pollen and fluorescent dye Introduction: Flowers
Pollination Lab Bio 220 Ecology and Evolution Fall, 2016 Journal reading: Comparison of pollen transfer dynamics by multiple floral visitors: experiments with pollen and fluorescent dye Introduction: Flowers
Do Nest-site Searching Bumblebee Queens Prefer Entering into the Labelloid Cavity of Bumblebee-pollinated Orchid,
 1 11 15 2016 Bulletin of the College of Agriculture, Tamagawa University, 1, 11 15 2016 Do Nest-site Searching Bumblebee Queens Prefer Entering into the Labelloid Cavity of Bumblebee-pollinated Orchid,
1 11 15 2016 Bulletin of the College of Agriculture, Tamagawa University, 1, 11 15 2016 Do Nest-site Searching Bumblebee Queens Prefer Entering into the Labelloid Cavity of Bumblebee-pollinated Orchid,
 1 of 13 8/11/2014 10:32 AM Units: Teacher: APBiology, CORE Course: APBiology Year: 2012-13 Chemistry of Life Chapters 1-4 Big Idea 1, 2 & 4 Change in the genetic population over time is feedback mechanisms
1 of 13 8/11/2014 10:32 AM Units: Teacher: APBiology, CORE Course: APBiology Year: 2012-13 Chemistry of Life Chapters 1-4 Big Idea 1, 2 & 4 Change in the genetic population over time is feedback mechanisms
A New Locality of Fossombronia mylioides (Fossombroniaceae, Marchantiophyta)
 Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci., Ser. B, 42(1), pp. 19 23, February 22, 2016 A New Locality of Fossombronia mylioides (Fossombroniaceae, Marchantiophyta) Masanobu Higuchi Department of Botany, National Museum
Bull. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci., Ser. B, 42(1), pp. 19 23, February 22, 2016 A New Locality of Fossombronia mylioides (Fossombroniaceae, Marchantiophyta) Masanobu Higuchi Department of Botany, National Museum
Molecular Markers, Natural History, and Evolution
 Molecular Markers, Natural History, and Evolution Second Edition JOHN C. AVISE University of Georgia Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts Contents PART I Background CHAPTER 1:
Molecular Markers, Natural History, and Evolution Second Edition JOHN C. AVISE University of Georgia Sinauer Associates, Inc. Publishers Sunderland, Massachusetts Contents PART I Background CHAPTER 1:
AP Biology Curriculum Framework
 AP Biology Curriculum Framework This chart correlates the College Board s Advanced Placement Biology Curriculum Framework to the corresponding chapters and Key Concept numbers in Campbell BIOLOGY IN FOCUS,
AP Biology Curriculum Framework This chart correlates the College Board s Advanced Placement Biology Curriculum Framework to the corresponding chapters and Key Concept numbers in Campbell BIOLOGY IN FOCUS,
5/31/17. Week 10; Monday MEMORIAL DAY NO CLASS. Page 88
 Week 10; Monday MEMORIAL DAY NO CLASS Page 88 Week 10; Wednesday Announcements: Family ID final in lab Today Final exam next Tuesday at 8:30 am here Lecture: Species concepts & Speciation. What are species?
Week 10; Monday MEMORIAL DAY NO CLASS Page 88 Week 10; Wednesday Announcements: Family ID final in lab Today Final exam next Tuesday at 8:30 am here Lecture: Species concepts & Speciation. What are species?
Name 14 The Origin of Species Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between microevolution and macroevolution. The biological concept
 Name _ 14 The Origin of Species Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between microevolution and macroevolution. The biological concept of species Prezygotic and postzygotic barriers that
Name _ 14 The Origin of Species Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between microevolution and macroevolution. The biological concept of species Prezygotic and postzygotic barriers that
BIOLOGY 317 Spring First Hourly Exam 4/20/12
 Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2012 First Hourly Exam 4/20/12 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2012 First Hourly Exam 4/20/12 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food.
 Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food. Heterotrophs must get energy by eating autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food. Heterotrophs must get energy by eating autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
Reproductive Biology and Pollination in Rainforest Trees: Techniques for a Community-level Approach
 BEST PRACTICE MANUAL Reproductive Biology and Pollination in Rainforest Trees: Techniques for a Community-level Approach S. L. Boulter, R. L. Kitching, J. M. Zalucki and K. L. Goodall Cooperative Research
BEST PRACTICE MANUAL Reproductive Biology and Pollination in Rainforest Trees: Techniques for a Community-level Approach S. L. Boulter, R. L. Kitching, J. M. Zalucki and K. L. Goodall Cooperative Research
Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011
 Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny) Darwin and classification: In the Origin, Darwin said that descent from a common ancestral species could explain why the Linnaean system
Lecture 11 Friday, October 21, 2011 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny) Darwin and classification: In the Origin, Darwin said that descent from a common ancestral species could explain why the Linnaean system
Pollen Identification Lab
 Name Pollen Identification Lab Objectives Practice using a microscope to see what pollen looks like, to observe the diversity of pollen morphology. Compare reference pollen from flowers with local pollen
Name Pollen Identification Lab Objectives Practice using a microscope to see what pollen looks like, to observe the diversity of pollen morphology. Compare reference pollen from flowers with local pollen
The Evolutionary Biology Of Plants By Karl J. Niklas READ ONLINE
 The Evolutionary Biology Of Plants By Karl J. Niklas READ ONLINE The Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at Brown University shares a common interest in how including plants, insects and spiders,
The Evolutionary Biology Of Plants By Karl J. Niklas READ ONLINE The Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at Brown University shares a common interest in how including plants, insects and spiders,
Systematic exploration of Stevia. An introduction and preliminary project proposal.
 Systematic exploration of Stevia. An introduction and preliminary project proposal. Alexander Vrijdaghs 1 & Jan Geuns 2 1 Dr. A. Vrijdaghs, Laboratory of Plant Systematics, K.U.Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
Systematic exploration of Stevia. An introduction and preliminary project proposal. Alexander Vrijdaghs 1 & Jan Geuns 2 1 Dr. A. Vrijdaghs, Laboratory of Plant Systematics, K.U.Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
The process by which the genetic structure of populations changes over time.
 Evolution The process by which the genetic structure of populations changes over time. Divergent evolution Goldfields and Ahinahina (silversword) a highly evolved member of the composite family. Evolution
Evolution The process by which the genetic structure of populations changes over time. Divergent evolution Goldfields and Ahinahina (silversword) a highly evolved member of the composite family. Evolution
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 8 PATTERNS OF EVOLUTION EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION. fossils (many forms now extinct)
 GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 8 PATTERNS OF EVOLUTION NOTES EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION INDIRECT fossils (many forms now extinct) changes in a single species of snail DIRECT common ancestry (adaptive radiation) similar
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 8 PATTERNS OF EVOLUTION NOTES EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION INDIRECT fossils (many forms now extinct) changes in a single species of snail DIRECT common ancestry (adaptive radiation) similar
Plant of the day! Ophrys in Europe, 9 genera in Australia
 Plant of the day! Ophrys in Europe, 9 genera in Australia Sexual deception where the flower attracts male pollinators by mimicking a female of the same species (e.g. scent, colour, hair ) Typically, pollination
Plant of the day! Ophrys in Europe, 9 genera in Australia Sexual deception where the flower attracts male pollinators by mimicking a female of the same species (e.g. scent, colour, hair ) Typically, pollination
The process by which the genetic structure of populations changes over time.
 Evolution The process by which the genetic structure of populations changes over time. Divergent evolution is the accumulation of differences between groups which can lead to the formation of new species.
Evolution The process by which the genetic structure of populations changes over time. Divergent evolution is the accumulation of differences between groups which can lead to the formation of new species.
What do we mean by a species? Morphological species concept. Morphological species concept BIOL2007 SPECIES AND BIODIVERSITY. Kanchon Dasmahapatra
 BIOL2007 SPECIES AND BIODIVERSITY Kanchon Dasmahapatra What are species? How do species differ from each other? Biodiversity: How many species are there? What do we mean by a species? Darwin proved species
BIOL2007 SPECIES AND BIODIVERSITY Kanchon Dasmahapatra What are species? How do species differ from each other? Biodiversity: How many species are there? What do we mean by a species? Darwin proved species
Structural specialisation and pollination ecology in two Malagasy species of Dalechampia (Euphorbiaceae)
 Structural specialisation and pollination ecology in two Malagasy species of Dalechampia (Euphorbiaceae) Olive Imanizabayo, Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund International, Rwanda Marco Plebani, University of Zurich,
Structural specialisation and pollination ecology in two Malagasy species of Dalechampia (Euphorbiaceae) Olive Imanizabayo, Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund International, Rwanda Marco Plebani, University of Zurich,
Need for systematics. Applications of systematics. Linnaeus plus Darwin. Approaches in systematics. Principles of cladistics
 Topics Need for systematics Applications of systematics Linnaeus plus Darwin Approaches in systematics Principles of cladistics Systematics pp. 474-475. Systematics - Study of diversity and evolutionary
Topics Need for systematics Applications of systematics Linnaeus plus Darwin Approaches in systematics Principles of cladistics Systematics pp. 474-475. Systematics - Study of diversity and evolutionary
Conceptually, we define species as evolutionary units :
 Bio 1M: Speciation 1 How are species defined? S24.1 (2ndEd S26.1) Conceptually, we define species as evolutionary units : Individuals within a species are evolving together Individuals of different species
Bio 1M: Speciation 1 How are species defined? S24.1 (2ndEd S26.1) Conceptually, we define species as evolutionary units : Individuals within a species are evolving together Individuals of different species
LAB 4: PHYLOGENIES & MAPPING TRAITS
 LAB 4: PHYLOGENIES & MAPPING TRAITS *This is a good day to check your Physcomitrella (protonema, buds, gametophores?) and Ceratopteris cultures (embryos, young sporophytes?)* Phylogeny Introduction The
LAB 4: PHYLOGENIES & MAPPING TRAITS *This is a good day to check your Physcomitrella (protonema, buds, gametophores?) and Ceratopteris cultures (embryos, young sporophytes?)* Phylogeny Introduction The
BIOLOGY 366 PLANT SYSTEMATICS FINAL EXAM 100 POINTS
 BIOLOGY 366 PLANT SYSTEMATICS FINAL EXAM 100 POINTS SECTION 1 (Short answer; 35 points total): Read the questions carefully. Be as precise as possible in your answers. 1. What is a pseudanthium? Give two
BIOLOGY 366 PLANT SYSTEMATICS FINAL EXAM 100 POINTS SECTION 1 (Short answer; 35 points total): Read the questions carefully. Be as precise as possible in your answers. 1. What is a pseudanthium? Give two
The student might demonstrate the ability to achieve this standard by: Making a chart comparing the similar functions of plant and animal cells.
 1: Life, Cell Biology: All living organisms are composed of cells, from just one to many trillions, whose details are usually visible only through a microscope. s 1.a) Cells function similarly in all living
1: Life, Cell Biology: All living organisms are composed of cells, from just one to many trillions, whose details are usually visible only through a microscope. s 1.a) Cells function similarly in all living
Standards Map Basic Comprehensive Program Science Grade Seven Focus on Life Sciences SE/TE: , SE/TE: ,
 Publisher: Pearson Program Title: Biology: Exploring Life 2006 Components: 0-13-250-925-3 (SE), 0-13-250-883-4 (TE) Grade Level(s): 7-12 s Map Basic Comprehensive Program Science Grade Seven Focus on Life
Publisher: Pearson Program Title: Biology: Exploring Life 2006 Components: 0-13-250-925-3 (SE), 0-13-250-883-4 (TE) Grade Level(s): 7-12 s Map Basic Comprehensive Program Science Grade Seven Focus on Life
MACROEVOLUTIONARY TESTS OF POLLINATION SYNDROMES: A
 MACROEVOLUTIONARY TESTS OF POLLINATION SYNDROMES: A REPLY TO FENSTER ET AL. Stacey DeWitt Smith 1,2,3, Cécile Ané 1,4,6 and David A. Baum 1,5 1 Department of Botany, University of Wisconsin, 430 Lincoln
MACROEVOLUTIONARY TESTS OF POLLINATION SYNDROMES: A REPLY TO FENSTER ET AL. Stacey DeWitt Smith 1,2,3, Cécile Ané 1,4,6 and David A. Baum 1,5 1 Department of Botany, University of Wisconsin, 430 Lincoln
Enduring understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution.
 The AP Biology course is designed to enable you to develop advanced inquiry and reasoning skills, such as designing a plan for collecting data, analyzing data, applying mathematical routines, and connecting
The AP Biology course is designed to enable you to develop advanced inquiry and reasoning skills, such as designing a plan for collecting data, analyzing data, applying mathematical routines, and connecting
PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 11 Chapter 26 Activity #15 NAME DATE PERIOD PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS PHYLOGENY Evolutionary history of species or group of related species SYSTEMATICS Study
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 11 Chapter 26 Activity #15 NAME DATE PERIOD PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS PHYLOGENY Evolutionary history of species or group of related species SYSTEMATICS Study
Plant Systematics. What is Systematics? or Why Study Systematics? Botany 400. What is Systematics or Why Study Systematics?
 Plant Systematics Botany 400 http://botany.wisc.edu/courses/botany_400/ What is Systematics? or Why Kenneth J. Sytsma Melody Sain Kelsey Huisman Botany Department University of Wisconsin Pick up course
Plant Systematics Botany 400 http://botany.wisc.edu/courses/botany_400/ What is Systematics? or Why Kenneth J. Sytsma Melody Sain Kelsey Huisman Botany Department University of Wisconsin Pick up course
SEQUENCING NUCLEAR MARKERS IN FRESHWATER GREEN ALGAE: CHARA SUBSECTION WILLDENOWIA
 SEQUENCING NUCLEAR MARKERS IN FRESHWATER GREEN ALGAE: CHARA SUBSECTION WILLDENOWIA Stephen D. Gottschalk Department of Biological Sciences, Fordham University, 441 E Fordham Rd, Bronx, NY 10458, USA ABSTRACT
SEQUENCING NUCLEAR MARKERS IN FRESHWATER GREEN ALGAE: CHARA SUBSECTION WILLDENOWIA Stephen D. Gottschalk Department of Biological Sciences, Fordham University, 441 E Fordham Rd, Bronx, NY 10458, USA ABSTRACT
Global biodiversity: how many species of arthropods are there? George Weiblen Plant Biology
 Global biodiversity: how many species of arthropods are there? George Weiblen Plant Biology the biodiversity crisis complete sequencing of the human genome illustrates our tremendous capacity to catalogue
Global biodiversity: how many species of arthropods are there? George Weiblen Plant Biology the biodiversity crisis complete sequencing of the human genome illustrates our tremendous capacity to catalogue
How Biological Diversity Evolves
 CHAPTER 14 How Biological Diversity Evolves PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell,
CHAPTER 14 How Biological Diversity Evolves PowerPoint Lectures for Essential Biology, Third Edition Neil Campbell, Jane Reece, and Eric Simon Essential Biology with Physiology, Second Edition Neil Campbell,
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #16 Plant Diversity II: Seed Plants
 Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #16 Plant Diversity II: Seed Plants BE SURE TO CAREFULLY READ THE INTRODUCTION PRIOR TO ANSWERING THE QUESTIONS!!! You will need to refer to your text book to answer
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #16 Plant Diversity II: Seed Plants BE SURE TO CAREFULLY READ THE INTRODUCTION PRIOR TO ANSWERING THE QUESTIONS!!! You will need to refer to your text book to answer
Common Name: GLADE MEADOW-PARSNIP. Scientific Name: Thaspium pinnatifidum (Buckley) Gray. Other Commonly Used Names: cutleaf meadow-parsnip
 Common Name: GLADE MEADOW-PARSNIP Scientific Name: Thaspium pinnatifidum (Buckley) Gray Other Commonly Used Names: cutleaf meadow-parsnip Previously Used Scientific Names: none Family: Apiaceae/Umbelliferae
Common Name: GLADE MEADOW-PARSNIP Scientific Name: Thaspium pinnatifidum (Buckley) Gray Other Commonly Used Names: cutleaf meadow-parsnip Previously Used Scientific Names: none Family: Apiaceae/Umbelliferae
Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics
 Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Understand what the term species means to biology. 2. Recognize the various patterns
Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Understand what the term species means to biology. 2. Recognize the various patterns
Assembly of plant-pollinator relationships and measurement of pollination service using seed set phytometry on regenerating lands
 Assembly of plant-pollinator relationships and measurement of pollination service using seed set phytometry on regenerating lands Thomas S. Woodcock Canadian Pollination Initiative, University of Guelph
Assembly of plant-pollinator relationships and measurement of pollination service using seed set phytometry on regenerating lands Thomas S. Woodcock Canadian Pollination Initiative, University of Guelph
Chapter 24-Flowering Plant and Animal Coevolution
 Chapter 24-Flowering Plant and Animal Coevolution coevolutionary plant-animal associations alliances that have influenced the evoluton of both partners. These examples show that plants have acquired traits
Chapter 24-Flowering Plant and Animal Coevolution coevolutionary plant-animal associations alliances that have influenced the evoluton of both partners. These examples show that plants have acquired traits
Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY Telephone Number: (845) ext Fax Number: (845)
 Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY 12549 Telephone Number: (845)457-2400 ext. 18121 Fax Number: (845)457-4254 Advance Placement Biology Presented to the Board of Education
Valley Central School District 944 State Route 17K Montgomery, NY 12549 Telephone Number: (845)457-2400 ext. 18121 Fax Number: (845)457-4254 Advance Placement Biology Presented to the Board of Education
SBEL 1532 HORTICULTURE AND NURSERY Lecture 2: Plants Classification & Taxonomy. Dr.Hamidah Ahmad
 SBEL 1532 HORTICULTURE AND NURSERY Lecture 2: Plants Classification & Taxonomy Dr.Hamidah Ahmad Plant Classifications is based on : Purpose of classifying plants: 1. botanical type 2. values or geographical
SBEL 1532 HORTICULTURE AND NURSERY Lecture 2: Plants Classification & Taxonomy Dr.Hamidah Ahmad Plant Classifications is based on : Purpose of classifying plants: 1. botanical type 2. values or geographical
Evolutionary Patterns, Rates, and Trends
 Evolutionary Patterns, Rates, and Trends Macroevolution Major patterns and trends among lineages Rates of change in geologic time Comparative Morphology Comparing body forms and structures of major lineages
Evolutionary Patterns, Rates, and Trends Macroevolution Major patterns and trends among lineages Rates of change in geologic time Comparative Morphology Comparing body forms and structures of major lineages
BIO 111: Biological Diversity and Evolution
 BIO 111: Biological Diversity and Evolution Varsha 2017 Ullasa Kodandaramaiah & Hema Somanathan School of Biology MODULE: BIODIVERSITY AND CONSERVATION BIOLOGY Part I - FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF BIODIVERSITY
BIO 111: Biological Diversity and Evolution Varsha 2017 Ullasa Kodandaramaiah & Hema Somanathan School of Biology MODULE: BIODIVERSITY AND CONSERVATION BIOLOGY Part I - FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF BIODIVERSITY
THE ECOLOGY AND CULTIVATION OF TERRESTRIAL ORCHIDS OF ARGENTINA
 ROITMAN &MAZA: TERRESTRIAL ORCHIDS OF ARGENTINA THE ECOLOGY AND CULTIVATION OF TERRESTRIAL ORCHIDS OF ARGENTINA G.G. Roitman and I. M. Maza Cátedra de Jardinería. Facultad de Agronomía Universidad de Buenos
ROITMAN &MAZA: TERRESTRIAL ORCHIDS OF ARGENTINA THE ECOLOGY AND CULTIVATION OF TERRESTRIAL ORCHIDS OF ARGENTINA G.G. Roitman and I. M. Maza Cátedra de Jardinería. Facultad de Agronomía Universidad de Buenos
Plant of the Day Isoetes andicola
 Plant of the Day Isoetes andicola Endemic to central and southern Peru Found in scattered populations above 4000 m Restricted to the edges of bogs and lakes Leaves lack stomata and so CO 2 is obtained,
Plant of the Day Isoetes andicola Endemic to central and southern Peru Found in scattered populations above 4000 m Restricted to the edges of bogs and lakes Leaves lack stomata and so CO 2 is obtained,
Chapter Chemical Uniqueness 1/23/2009. The Uses of Principles. Zoology: the Study of Animal Life. Fig. 1.1
 Fig. 1.1 Chapter 1 Life: Biological Principles and the Science of Zoology BIO 2402 General Zoology Copyright The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The Uses of
Fig. 1.1 Chapter 1 Life: Biological Principles and the Science of Zoology BIO 2402 General Zoology Copyright The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The Uses of
Behavior of Pollinators That Share Two Co- Flowering Wetland Plant Species
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2015 Behavior of Pollinators That Share Two Co- Flowering Wetland Plant
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2015 Behavior of Pollinators That Share Two Co- Flowering Wetland Plant
ROGH Docent Program Week 4: Orchid Biology.
 Orchid Classification, Structure & Diversity Monocots (one seed leaf) with parallel venation Derived from Lily-relative Fossilized orchid pollen - 76 to 84 million years ago (Late Cretaceous) Allopolyploidy
Orchid Classification, Structure & Diversity Monocots (one seed leaf) with parallel venation Derived from Lily-relative Fossilized orchid pollen - 76 to 84 million years ago (Late Cretaceous) Allopolyploidy
SPECIATION. REPRODUCTIVE BARRIERS PREZYGOTIC: Barriers that prevent fertilization. Habitat isolation Populations can t get together
 SPECIATION Origin of new species=speciation -Process by which one species splits into two or more species, accounts for both the unity and diversity of life SPECIES BIOLOGICAL CONCEPT Population or groups
SPECIATION Origin of new species=speciation -Process by which one species splits into two or more species, accounts for both the unity and diversity of life SPECIES BIOLOGICAL CONCEPT Population or groups
Lab sect. (TA/time): Biology 317 Spring Third Hourly (Final) Exam 6/8/10
 Name: Lab sect. (TA/time): Biology 317 Spring 2010 Third Hourly (Final) Exam 6/8/10 1) (26 pts) Match the letter of a plant description with the characteristics for a plant given below. Families may be
Name: Lab sect. (TA/time): Biology 317 Spring 2010 Third Hourly (Final) Exam 6/8/10 1) (26 pts) Match the letter of a plant description with the characteristics for a plant given below. Families may be
ESS 345 Ichthyology. Systematic Ichthyology Part II Not in Book
 ESS 345 Ichthyology Systematic Ichthyology Part II Not in Book Thought for today: Now, here, you see, it takes all the running you can do, to keep in the same place. If you want to get somewhere else,
ESS 345 Ichthyology Systematic Ichthyology Part II Not in Book Thought for today: Now, here, you see, it takes all the running you can do, to keep in the same place. If you want to get somewhere else,
Name Section Lab 4 Flowers, Pollination and Fruit
 Name Section Lab 4 Flowers, Pollination and Fruit Flowers are designed on plants for sexual reproduction. They contain organs that produce gametes (sex cells), which, after fertilization, lead to the formation
Name Section Lab 4 Flowers, Pollination and Fruit Flowers are designed on plants for sexual reproduction. They contain organs that produce gametes (sex cells), which, after fertilization, lead to the formation
Lab sect. (TA/time): Biology 317 Spring Second Hourly Exam 5/13/11
 Name: Lab sect. (TA/time): Biology 317 Spring 2011 Second Hourly Exam 5/13/11 1) (30 pts) Match the letter of the family on the right with the unknown plant described on the left. Some of the families
Name: Lab sect. (TA/time): Biology 317 Spring 2011 Second Hourly Exam 5/13/11 1) (30 pts) Match the letter of the family on the right with the unknown plant described on the left. Some of the families
Insect Investigations
 Investigative Questions What are some adaptations that insects have that help them to feed on different foods and from different parts of plants, especially flowers? Goal: Students explore the ways that
Investigative Questions What are some adaptations that insects have that help them to feed on different foods and from different parts of plants, especially flowers? Goal: Students explore the ways that
Historical Biogeography. Historical Biogeography. Historical Biogeography. Historical Biogeography
 "... that grand subject, that almost keystone of the laws of creation, Geographical Distribution" [Charles Darwin, 1845, in a letter to Joseph Dalton Hooker, the Director of the Royal Botanic Garden, Kew]
"... that grand subject, that almost keystone of the laws of creation, Geographical Distribution" [Charles Darwin, 1845, in a letter to Joseph Dalton Hooker, the Director of the Royal Botanic Garden, Kew]
Teacher Packs in Experimental Science. Bio Pack 4. Agents of pollination
 Teacher Packs in Experimental Science Bio Pack 4 Agents of pollination Pack contents: A. Teacher s Guide B. Students Guide C. Assessment Student s sheet D. Extensions to experiment E. Useful Links F. Health
Teacher Packs in Experimental Science Bio Pack 4 Agents of pollination Pack contents: A. Teacher s Guide B. Students Guide C. Assessment Student s sheet D. Extensions to experiment E. Useful Links F. Health
Lab sect. (TA/time): Botany 113 Spring First Hourly Exam 4/21/00
 Name: Lab sect. (TA/time): Botany 113 Spring 2000 First Hourly Exam 4/21/00 1) (15 pts) Match the letter of the characteristics for a plant given on the right with the family on the left. Not all of the
Name: Lab sect. (TA/time): Botany 113 Spring 2000 First Hourly Exam 4/21/00 1) (15 pts) Match the letter of the characteristics for a plant given on the right with the family on the left. Not all of the
06/09/05. A survey of the plant kingdom based on a detailed study of the morphology, anatomy and physiology of selected representative specimens.
 06/09/05 Common Course Number: BOT -1010 Course Title: General Botany Catalog Course Description: A survey of the plant kingdom based on a detailed study of the morphology, anatomy and physiology of selected
06/09/05 Common Course Number: BOT -1010 Course Title: General Botany Catalog Course Description: A survey of the plant kingdom based on a detailed study of the morphology, anatomy and physiology of selected
A A A A B B1
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR EACH BIG IDEA WITH ASSOCIATED SCIENCE PRACTICES AND ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Learning Objectives will be the target for AP Biology exam questions Learning Objectives Sci Prac Es Knowl
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR EACH BIG IDEA WITH ASSOCIATED SCIENCE PRACTICES AND ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Learning Objectives will be the target for AP Biology exam questions Learning Objectives Sci Prac Es Knowl
The Origin of Species
 The Origin of Species Introduction A species can be defined as a group of organisms whose members can breed and produce fertile offspring, but who do not produce fertile offspring with members of other
The Origin of Species Introduction A species can be defined as a group of organisms whose members can breed and produce fertile offspring, but who do not produce fertile offspring with members of other
Objectives. ROGH Docent Program Week 2: Plant Anatomy
 Objectives To introduce general botany for subjects on display To provide knowledge of general plant anatomy To provide general understanding of orchid anatomy & biology To introduce concepts of plant-pollinator
Objectives To introduce general botany for subjects on display To provide knowledge of general plant anatomy To provide general understanding of orchid anatomy & biology To introduce concepts of plant-pollinator
The Origin of Species
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 24 The Origin of Species Lectures
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 24 The Origin of Species Lectures
Announcements. Lab Quiz #1 on Monday: (30pts) conifers + cones, vegetative morphology. Study: Display case outside HCK 132 with labeled conifers
 Announcements Lab Quiz #1 on Monday: (30pts) conifers + cones, vegetative morphology Study: Display case outside HCK 132 with labeled conifers Movie: Sexual Encounters of the Floral Kind Intro to Keying/Greenhouse
Announcements Lab Quiz #1 on Monday: (30pts) conifers + cones, vegetative morphology Study: Display case outside HCK 132 with labeled conifers Movie: Sexual Encounters of the Floral Kind Intro to Keying/Greenhouse
CLASSIFICATION AND EVOLUTION OF CAMINALCULES:
 CLASSIFICATION AND EVOLUTION OF CAMINALCULES: One of the main goals of the lab is to illustrate the intimate connection between the classification of living species and their evolutionary relationships.
CLASSIFICATION AND EVOLUTION OF CAMINALCULES: One of the main goals of the lab is to illustrate the intimate connection between the classification of living species and their evolutionary relationships.
Reproductive ecology and conservation of the rare Dictamnus
 Reproductive ecology and conservation of the rare Dictamnus Alessandro Fisogni, Martina Rossi, Giovanni Cristofolini & Marta Galloni Department of Experimental Evolutionary Biology, University of Bologna
Reproductive ecology and conservation of the rare Dictamnus Alessandro Fisogni, Martina Rossi, Giovanni Cristofolini & Marta Galloni Department of Experimental Evolutionary Biology, University of Bologna
Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life.
 Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution. 1.A.1: Natural selection is a major
Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life. understanding 1.A: Change in the genetic makeup of a population over time is evolution. 1.A.1: Natural selection is a major
Campbell Biology AP Edition 11 th Edition, 2018
 A Correlation and Narrative Summary of Campbell Biology AP Edition 11 th Edition, 2018 To the AP Biology Curriculum Framework AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
A Correlation and Narrative Summary of Campbell Biology AP Edition 11 th Edition, 2018 To the AP Biology Curriculum Framework AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
PhD/ MSc: Investigating handedness in flowers
 PhD/ MSc: Investigating handedness in flowers Left handed Right handed Figure 1. Left and right handed morphs of Wachendorfia paniculata The primary function of flowers is to mediate the movement of pollen.
PhD/ MSc: Investigating handedness in flowers Left handed Right handed Figure 1. Left and right handed morphs of Wachendorfia paniculata The primary function of flowers is to mediate the movement of pollen.
Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny
 Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny AP Curriculum Alignment Chapter 19 expands on the topics of phylogenies and cladograms, which are important to Big Idea 1. In order for students to understand
Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny AP Curriculum Alignment Chapter 19 expands on the topics of phylogenies and cladograms, which are important to Big Idea 1. In order for students to understand
Speciation. Today s OUTLINE: Mechanisms of Speciation. Mechanisms of Speciation. Geographic Models of speciation. (1) Mechanisms of Speciation
 Speciation Today s OUTLINE: (1) Geographic Mechanisms of Speciation (What circumstances lead to the formation of new species?) (2) Species Concepts (How are Species Defined?) Mechanisms of Speciation Last
Speciation Today s OUTLINE: (1) Geographic Mechanisms of Speciation (What circumstances lead to the formation of new species?) (2) Species Concepts (How are Species Defined?) Mechanisms of Speciation Last
Warm-Up- Review Natural Selection and Reproduction for quiz today!!!! Notes on Evidence of Evolution Work on Vocabulary and Lab
 Date: Agenda Warm-Up- Review Natural Selection and Reproduction for quiz today!!!! Notes on Evidence of Evolution Work on Vocabulary and Lab Ask questions based on 5.1 and 5.2 Quiz on 5.1 and 5.2 How
Date: Agenda Warm-Up- Review Natural Selection and Reproduction for quiz today!!!! Notes on Evidence of Evolution Work on Vocabulary and Lab Ask questions based on 5.1 and 5.2 Quiz on 5.1 and 5.2 How
How Does Pollination Work?
 How Does Pollination Work? What is pollination? What is pollination? Pollination the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower Fertilization occurs when the male
How Does Pollination Work? What is pollination? What is pollination? Pollination the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower Fertilization occurs when the male
Speciation. Today s OUTLINE: Mechanisms of Speciation. Mechanisms of Speciation. Geographic Models of speciation. (1) Mechanisms of Speciation
 Speciation Today s OUTLINE: (1) Geographic Mechanisms of Speciation (What circumstances lead to the formation of new species?) (2) Species Concepts (How are Species Defined?) Mechanisms of Speciation Last
Speciation Today s OUTLINE: (1) Geographic Mechanisms of Speciation (What circumstances lead to the formation of new species?) (2) Species Concepts (How are Species Defined?) Mechanisms of Speciation Last
EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 9 (Chapter 24) Activity #13
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 9 (Chapter 24) Activity #13 NAME DATE PERIOD SPECIATION SPECIATION Origin of new species SPECIES BIOLOGICAL CONCEPT Population or groups of populations whose members have
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION Unit 1 Part 9 (Chapter 24) Activity #13 NAME DATE PERIOD SPECIATION SPECIATION Origin of new species SPECIES BIOLOGICAL CONCEPT Population or groups of populations whose members have
Introduction. Ludwigia alternifolia, Peter Hoch
 Introduction Ludwigia alternifolia, Peter Hoch The plant family Onagraceae is divided into two subfamilies, Ludwigioideae, with only genus Ludwigia of 82 species and 22 sections, and Onagroideae, which
Introduction Ludwigia alternifolia, Peter Hoch The plant family Onagraceae is divided into two subfamilies, Ludwigioideae, with only genus Ludwigia of 82 species and 22 sections, and Onagroideae, which
A. Incorrect! Form is a characteristic used in the morphological species concept.
 CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 23: Evolutionary Processes No. 1 of 10 The biological-species concept is based on. (A) Form. (B) Similar size. (C) Similar appearance to all other individuals in the population.
CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 23: Evolutionary Processes No. 1 of 10 The biological-species concept is based on. (A) Form. (B) Similar size. (C) Similar appearance to all other individuals in the population.
Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter in class follow along lecture notes
 Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter 26 34 in class follow along lecture notes Chp 26 Origin of life: 1) When did earth form? 2) What is the order of evolution of life forms on
Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter 26 34 in class follow along lecture notes Chp 26 Origin of life: 1) When did earth form? 2) What is the order of evolution of life forms on
Coevolution and Pollination
 Coevolution and Pollination Coevolution is the the mutual evolutionary influence between two species (the evolution of two species totally dependent on each other). Each of the species involved exerts
Coevolution and Pollination Coevolution is the the mutual evolutionary influence between two species (the evolution of two species totally dependent on each other). Each of the species involved exerts
Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Phylogenies Show Evolutionary Relationships
 Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life You Must Know The taxonomic categories and how they indicate relatedness. How systematics is used to develop phylogenetic trees. How to construct a phylogenetic
Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life You Must Know The taxonomic categories and how they indicate relatedness. How systematics is used to develop phylogenetic trees. How to construct a phylogenetic
Reproduc)ve Biology II
 Reproduc)ve Biology II Breeding Systems Summary of previous lecture: BUT: Plants Influence Pollinators Pollina)on Plant Costs Success Progeny Growth Dispersal Seed banks Establishment Germina)on 1 In the
Reproduc)ve Biology II Breeding Systems Summary of previous lecture: BUT: Plants Influence Pollinators Pollina)on Plant Costs Success Progeny Growth Dispersal Seed banks Establishment Germina)on 1 In the
Genetic diversity of beech in Greece
 Genetic diversity of beech in Greece A.C. Papageorgiou (1), I. Tsiripidis (2), S. Hatziskakis (1) Democritus University of Thrace Forest Genetics Laboratory Orestiada, Greece (2) Aristotle University of
Genetic diversity of beech in Greece A.C. Papageorgiou (1), I. Tsiripidis (2), S. Hatziskakis (1) Democritus University of Thrace Forest Genetics Laboratory Orestiada, Greece (2) Aristotle University of
Biology 211 (2) Week 1 KEY!
 Biology 211 (2) Week 1 KEY Chapter 1 KEY FIGURES: 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7 VOCABULARY: Adaptation: a trait that increases the fitness Cells: a developed, system bound with a thin outer layer made of
Biology 211 (2) Week 1 KEY Chapter 1 KEY FIGURES: 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7 VOCABULARY: Adaptation: a trait that increases the fitness Cells: a developed, system bound with a thin outer layer made of
