M.Sc. Course in Botany (CBCS semester system)
|
|
|
- Augustine Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 M.Sc. Course in Botany (CBCS semester system) Outline of the KU-DODL Choice Based Course &Credit Semester System Course Categories: Course Transaction Categories: Evaluation Categories: HC: Hard Core; SC: Soft Core; E: Elective; OC: open course T: Theory; P: Practical; PW: Project Work IA: Internal Assessment; TEE: Term End Examination Course Course Name Points Credit Study Hours HARD CORE THEORY BOHCT. BOHCT. 2 BOHCT. 3 BOHCT. 4 SEMESTER I Biology & Diversity of Virus, Bacteria & Fungi Biology & Diversity of Algae, Bryophytes & Pteridophytes Biology & Diversity of Gymnosperms, Taxonomy of Angiosperms & Biosystematics Cytology, Cytogenetics & Genetics HARD CORE PRACTICAL BOHCP. BOHCP. 2 BOHCP. 3 BOHCP. 4 Practical based on BOHCT Practical based on BOHCT Practical based on BOHCT Practical based on BOHCT Total Points & Credits in Semester I EVALUATION SCHEME - THEORY: Internal Assessment (5) + Term End Examination (60) PRACTICAL: Internal Assessment (5) + Term End Examination (20)
2 BOHCT. Biology & Diversity of Virus Detailed Syllabus of the Choice Based Credit Semester System SEMESTER I SYLLABUS COURSE BOHCT. Biology and Diversity of Virus, Bacteria and Fungi (Full Marks 75) Unit.. Nature and origin of virion. Introduction, 2. Nomenclature and classification, distinctive nomenclature and properties of viruses, morphology (symmetry) and a classification of viruses general account on different types of viruses, Viral genome. Unit Structure & chemistry of viruses-capsid and their Structural and molecular arrangements, types of envelopes and their organisation of virion composition, Molecular organization of virion with and its identification special reference to TMV and HIV. techniques 4.Isolation, purification and identification of viruses based on chemical, physical and immunological Biology & Diversity of Bacteria Unit 3. Modern classification of viruses and its transmission Unit 4. Life cycle of viruses and sub viral agents Unit 5. Structure, taxonomy, and phylogeny of bacteria Unit 6. Nutritional types and reproduction of bacteria Unit 7. Microbial ecology Unit 8. Immunology and Indutrial Microbiology techniques. 5. Transmission of plant viruses, genetic basis of cell to cell movement of plant viruses. 6. Management of plant viruses following classical and modern technique. 7. Molecular basis of Lytic and Lysogenic cycle. 8. Prions, viroids, virusoids, Satellite virus..microbial taxonomy and phylogeny of Bacteria. 2. Ultra structure of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. 3.Bacterial motility, bacterial sporulation. 4.Bacterial growth kinetics, factors affecting growth. 5.Photolithotrophs, chemolithotrophs, photoorganotrophs & chemoorganotrophs, Mixotroph. 6.Organization and replication of genetic material in bacteria. Genetic recombination (conjugation, transformation and transduction) in bacteria. 7. Concept of microbial ecology with reference to air, water and soil. 8. Microbes associated with food, food-borne infections and intoxications; preservation of food. 0. Air, water, and soil-borne disease causal organism, symptoms, control. 9. Cells and organ of immune system, antigen (chemical nature and types), immunoglobulins (structure and types), brief idea about hypersensitivity and vaccine..industrial production of ethanol, penicillin, vitamin B2. 2. Cosmetic microbiology-current trends.
3 BOHCT. Biology & Diversity of Fungi and their allies Unit 9. Classification and cell wall structure of fungi. Distinctive features of fungi to form a separate kingdom; modern trends in classification 2. The architecture of fungal cell, cell wall, cell membrane, cell organelles, cytoskeleton, and protoplast technology; translocation in mycelia Unit 0. Genome organization and reproduction of fungi Unit. Reproduction patterns 3. Genome organization in fungi; extra chromosomal and transposable genetic elements in fungi 4. Somatic recombination in fungi: heterothallism; heterokaryosis and parasexuality 5. Diversity of somatic, reproductive and fruiting structures in different groups: Myxomycota, Oomycota, Chytridiomycota, Zygomycota, Ascomycota, 6. Fungal spores: types, dispersal, dormancy and germination Unit 4. Diversity & reprodution 5. Diversity of somatic, reproductive and fruiting structures in different groups: Basidiomycota, Deuteromycota
4 Biology & Diversity of Bryophytes BOHCT.2 Biology & Diversity of Algae COURSE BOHCT.2 Biology and Diversity of Algae, Bryophytes and Pteridophytes (Full Marks 75) Unit. Modern trends and Cyanobacteria Unit 2. General overview of algae Unit 3. Rhodophyta and phytoplankton. Modern trends: Outline of principles and recent trends in algal systematics; endosymbiotic theory of chloroplast evolution and algal origin. 3. Cyanobacteria: Diversity of forms and habitats; cyanobacterial taxonomy; cyanobacterial evolution. 2. General overview & Resource utilization: Prochlorophyta; Glaucophyta; Dinophyta; Heterokontophyta: Bacillariophyceae, Xanthophyceae, Eustigmatophyceae; Bio-fertilizers and bio-molecules with commercial application. 4. Rhodophyta: Diversity of forms and habitats; evolutionary trends in red algae; ecology of red algae. 6. Phytoplankton: Types of phytoplankton; algal blooms; algal toxins. Unit 4. Chlorophyta Unit. General account of bryophytes 5. Chlorophyta: Diversity of forms and habitats; evolutionary trends of green algal lineages; salient features of different classes of chlorophytes.. General classification: Criteria, recent trends and outline of classification of the liverworts, mosses and hornworts. Unit 2. Phylogeny and evolution of bryophytes 2. Phylogeny: Evolutionary significance and interrelationships; recent concepts on evolution of the three lineages (liverworts, mosses and hornworts). Unit 3. Biogeography and ecological significance 3. Biogeography and Ecological significance: Diversity and distribution patterns; population and community dynamics; physiological ecology and adaptations; ecological roles of bryophytes. Unit 4. Economic significance and Conservation 4. Economic significance and Conservation: Economic importance; threats and vulnerability; conservation strategies; restoration ecology.
5 BOHCT.2 Biology & Diversity of Pteridophytes Unit. General features, diversity and evolutionary trends of pteridophytes Unit 2. Leptosporangiate ferns and gametophyte. Introduction: A general account and an outline of recent system of classification of Pteridophytes upto order level. 2. Diversity in organography and the evolutionary trends in the members of Psilophyta, Lycophyta, Sphenophyta and Filicophyta - Early ferns, Eusporangiate ferns (Ophioglossales, Marattiales) 2.2 Leptosporangiate ferns (Filicales, Marsileales, Salviniales). 3. Gametophyte: Patterns of spore germination; patterns of gametophyte development in pteridophytes; mating system in fern. Unit 3. Sporophyte, cytogenetics and speciations 4. Sporophyte: Variations in vegetative and reproductive structures and their evolution with special emphasis on shoot apex, stelar organization, and soral characters. 5. Cytogenetics and Speciations: Pteridophytes with chromosome number; polyploidy in microphyllous and megaphyllus forms; intergeneric and interspecific hybridity; obligate interbreeding forms. Unit 4. Antheirdiogen, habitat and conservation diversity of pteridophytes 6. Antheirdiogen in ferns. 7. Habitat diversity of pteridophytes and their conservation; endemic and endangered pteridophytes with special reference to India.
6 Taxonomy of Angiosperms and Biosystematics BOHCT.3 Biology & Diversity of Gymnosperms COURSE BOHCT.3 Biology and Diversity of Gymnosperms and Taxonomy of Angiosperms and Biosystematics (Full Marks 75) Unit. General features of gymnosperm and seed ferns Unit 2. Cycads, Cycadeoids & more diversification among gymnosperm Unit 3. General accounts of Ginkgo and Gnetophytes Unit 4. General accounts of Conifers Unit. General accounts of taxonomy and its classification.introduction: A general account and an outline of recent system of classification of gymnosperms upto order level with characteristic features. 2. Palaeozoic Pteridosperms (Seed Ferns): Major events in evolution of Palaeozoic Pteridosperms; brief account of Lyginopteridaceae, Calamopityaceae, Medullosaceae, Callistophytaceae. 3. Cycads & Cycadeoids: General traits, circumscriptions of the families of Cycads, early evidence, Cycad and Cyadeoid foliage. 4. More diversification among gymnosperms: Brief account of Caytoniaceae, Corystospermaceae, Peltaspermaceae, Glossopteridceae, Pentoxylaceae. 5. Ginkgos: General traits, early evidence, distribution in time and space. 7. Gnetophytes: General traits; characteristics features of the genera of Gnetopsida; comparisons amongst Ephedra, Gnetum and Welwitschia. 6. Conifers: General traits of conifers; first evidence of conifer organization - Cordaitales, Voltziales; origin of conifer cones and leaves; circumscriptions of the families of extant conifers and their interrelationships; comparative account among conifers on basis of the male gametophyte, pollination mechanisms, female gametophytes, proembryo development.. Systems of angiosperms classification: Outline of classification of Cronquist (988) and Takhtajan (997) up to Subclasses / Super orders. Broad outline of angiosperm phylogeny Group (APG) III, Unit 2. General survey of taxa of angiosperms I 2. A general survey of the following taxa of angiosperms with reference to inter-relationship, evolutionary trends, and economic importance: Amborellaceae, Magnoliales, Caryophyllidae, Nepenthales. Unit 3. General survey of taxa of angiosperms II 2.2. A general survey of the following taxa of angiosperms with reference to inter-relationship, evolutionary trends, and economic importance: Podostemales, Asterales, Alismatales and Poaceae. Unit 4. ICBN 3. ICBN : Changes, addition and alteration of latest four codes; principles, rank of taxa and names of taxa, nomenclatural types, priority of publication and limitation of the priority of publications. Principle idea about Bio-codes and Phylocodes. 4. Concepts of phytogeography: Endemism in India; invasion and introduction of plants in India. 5. Botanic Gardens and Herbaria: Importance and examples
7 BOHCT.3 Taxonomy of Angiosperms and Biosystematics Module Details Contents Structure Study Unit 5. Phytogeography, Botanic Gardens and Herbaria. 4. Concepts of phytogeography: Endemism in India; invasion and introduction of plants in India. 5. Botanic Gardens and Herbaria: Importance and examples Unit 6. Biosystematics and Numerical Taxonomy 6. Biosystematics: Definition, methods, categories, differences with classical taxonomy. 7. Numerical Taxonomy: Definition, principles, logical steps, applications, merits and demerits. Unit. Evolutionary concept and cladistics system of classification Unit 8. Data sources of taxonomy and Taxonomic literatures 8. Evolutionary concept - Plagiomorphy and Apomorphy; Parallelism and Convergence; Homology and Analogy; Monophyly and Polyphyly including the concept of Heterobathmy, Cline, Polarity, Anagenesis and Cladogenesis, Symplesiomorphy, Synapomorphy, Autopomorphy, Stasigenesis, Catagenesis, Paraphyly, Holophyly, Homoplasy; Phylogram, Dendrogram and Cladogram. 9. Cladistics system of classifications: Principle, methods, merits and demerits. 0. Data sources of taxonomy: Embryology, photochemistry with brief account of DNA - Taxonomy, DNA - barcoding, e - Taxonomy; nuclear rdna, chloroplast and mitochondrial DNA; ultrastructure of sieve tube plastids.. Taxonomic literatures: classical books, index, flora and manual, revision and monograph, icons, bibliography, catalogue, encyclopedias, glossary and dictionary. Important periodicals of India and abroad.
8 BOHCT.4 COURSE BOHCT.4 Cytology, Cytogenetics and Genetics (Full Marks 75) Course Details Contents Structure Study Unit. Genome organization and Karyotype Unit 2. GISH, FISH techniques and sex determination. Genome organization in Eukaryotes: DNA packing in nucleosome; repetitive, satellite and unique DNA sequences; C- value paradox; structural and functional organization of telomeres and centromeres; spindle organization, polymerization and significance. 2.. Karyotype concept in relation to evolution; banding techniques 2.2. GISH and FISH techniques. 3. Sex determination: Sex determination in plants and their interrelationship with human, Drosophila and mice models; dosage compensation; sex linked inheritance. Unit 3.Special type of chromosome, linkage and crossing over 4. Special type chromosomes: Cytogenetical significance of polytene and B-chromosome; deletion mapping; recombination 5. Linkage and crossing over: chiasma frequency and genetic map distance; Evolutionary significance of recombination; tetrad analysis; centromere mapping with ordered tetrad. Unit 4. Chromosomal aberration 6. Reciprocal translocation: Cytogenetics of reciprocal translocation in plant species; Gaudens and Velans complex; reciprocal translocation in humans,. 7. Polyploidy: Polyploids and aneuploids; Inheritance of autopolyploids and trisomics; significance and limitations of polyploidy; aneuploidy in humans. Unit 5. Extrachromosomal inheritance and Microbial genetics 8. Plastids and mitochondrial DNA influenced traits. 9. Microbial genetics: Transformation, conjugation and transduction and their significance in gene mapping. Unit 6. Gene mutation 0. Gene mutation: Induction, types, molecular basis, significance; paramutation; DNA repair mechanism; epigenetic changes; genetic imprinting; prion particles; site directed mutagenesis; gene complementation test; rii locus. Unit 7. Structure of DNA, RNA and DNA replication. Biology of DNA and RNA: DNA forms; DNA replication; RNA types; characterization of rrna. Unit 8. Transcription and translation proceses.2 Transcription and translation proceses, pre mrna processing.
9 BOHCT.4 Course Details Contents Structure Study Unit 9. Genetic regulation 2. Genetic regulation: Regulation of prokaryotic gene expression lac, trp and ara operons; regulation of eukaryotic gene expression brief account. Unit 0. Transposable elements and Population genetics Unit. Cell cycle and cancer 3. Transposable elements: Ac-Ds, IS elements, P-elements and their role in genetics. 4. Population genetics: Hardy-Weinberg principle; gene frequency in a population, genetic equilibrium, factors affecting gene frequency. 5. Cell cycle regulation and cancer: Role of proteins in controlling cell cycle; apoptosis; oncogenes and protooncogenes; tumour suppressor genes; role of E2F and p53 in controlling cell cycle; cancer therapy. Unit 2. Recombinant DNA technology 6. Recombinant DNA technology brief account
University of Kalyani
 University of Kalyani M.Sc. Botany Choice Based Credit System Syllabus (2017 onwards) Department of Botany Kalyani - 741235 REGULATIONS RELATING TO THE CONDUCT OF UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS IN M.Sc. BOTANY
University of Kalyani M.Sc. Botany Choice Based Credit System Syllabus (2017 onwards) Department of Botany Kalyani - 741235 REGULATIONS RELATING TO THE CONDUCT OF UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS IN M.Sc. BOTANY
M P BHOJ (OPEN) UNIVERSITY, BHOPAL ASSIGNMENT QUESTION PAPER
 PAPER :I Cell and molecular Biology of plants Q.1 Describe various models of Plasma membrane with its significance? OR Discuss role of Plasmodesmata in movements of moleculer and macromolecules? Q.2 Give
PAPER :I Cell and molecular Biology of plants Q.1 Describe various models of Plasma membrane with its significance? OR Discuss role of Plasmodesmata in movements of moleculer and macromolecules? Q.2 Give
BOTANY M.S.c SYLLABUS
 BOTANY M.S.c SYLLABUS SEMESTER SYSTEM Semester-One Paper Name of Paper Max Marks Paper-I : Algae and Bryophytes 50 Paper-II : Fungi and plant viruses 50 Paper-III : Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Palacobotany
BOTANY M.S.c SYLLABUS SEMESTER SYSTEM Semester-One Paper Name of Paper Max Marks Paper-I : Algae and Bryophytes 50 Paper-II : Fungi and plant viruses 50 Paper-III : Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Palacobotany
S Y Bsc Semester-I Paper-I: BOT.-231: Bryophytes and Pteridophytes [60 Lectures] On completion of the course, students are able to:
![S Y Bsc Semester-I Paper-I: BOT.-231: Bryophytes and Pteridophytes [60 Lectures] On completion of the course, students are able to: S Y Bsc Semester-I Paper-I: BOT.-231: Bryophytes and Pteridophytes [60 Lectures] On completion of the course, students are able to:](/thumbs/85/92239411.jpg) S Y Bsc Semester-I Paper-I: BOT.-231: Bryophytes and Pteridophytes [60 Lectures] 1. Understand the morphological diversity of Bryophytes and Pteridophytes. 2. Understand the economic importance of the
S Y Bsc Semester-I Paper-I: BOT.-231: Bryophytes and Pteridophytes [60 Lectures] 1. Understand the morphological diversity of Bryophytes and Pteridophytes. 2. Understand the economic importance of the
University of Kalyani
 University of Kalyani M.Sc. Botany Choice Based Credit System Syllabus (2017 onwards) Department of Botany Kalyani - 741235 REGULATIONS RELATING TO THE CONDUCT OF UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS IN M.Sc. BOTANY
University of Kalyani M.Sc. Botany Choice Based Credit System Syllabus (2017 onwards) Department of Botany Kalyani - 741235 REGULATIONS RELATING TO THE CONDUCT OF UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS IN M.Sc. BOTANY
BOTANY: COURSE OBJECTIVE AND OUTCOME KHEMUNDI DEGREE COLLEGE, DIGAPAHANDI
 BOTANY: COURSE OBJECTIVE AND OUTCOME KHEMUNDI DEGREE COLLEGE, DIGAPAHANDI SEM-1 (CREDITS-6: THEORY 4, PRACTICAL - 2) CORE - 1 MICROBIOLOGY AND PHYCOLOGY 1. To introduce the students about Bacteria and
BOTANY: COURSE OBJECTIVE AND OUTCOME KHEMUNDI DEGREE COLLEGE, DIGAPAHANDI SEM-1 (CREDITS-6: THEORY 4, PRACTICAL - 2) CORE - 1 MICROBIOLOGY AND PHYCOLOGY 1. To introduce the students about Bacteria and
University of Kalyani
 University of Kalyani M.Sc. Botany Choice Based Credit System Semesters I IV Syllabus 2014 onwards Department of Botany Kalyani 741235 Outline of the Choice Based Credit Semester System Course Categories:
University of Kalyani M.Sc. Botany Choice Based Credit System Semesters I IV Syllabus 2014 onwards Department of Botany Kalyani 741235 Outline of the Choice Based Credit Semester System Course Categories:
Madhaya Pradesh Bhoj Open University.Bhopal M.sc Botany Previous Year
 Subject : Cell and Molecular Biology of Plants Q.1 Discuss the role of plasmodesmeta in movements of molecular and macro molecules. Q.2 Given an ultra structure of mitochondria. Write its significance
Subject : Cell and Molecular Biology of Plants Q.1 Discuss the role of plasmodesmeta in movements of molecular and macro molecules. Q.2 Given an ultra structure of mitochondria. Write its significance
Principles of Genetics
 Principles of Genetics Snustad, D ISBN-13: 9780470903599 Table of Contents C H A P T E R 1 The Science of Genetics 1 An Invitation 2 Three Great Milestones in Genetics 2 DNA as the Genetic Material 6 Genetics
Principles of Genetics Snustad, D ISBN-13: 9780470903599 Table of Contents C H A P T E R 1 The Science of Genetics 1 An Invitation 2 Three Great Milestones in Genetics 2 DNA as the Genetic Material 6 Genetics
Assignment Question Paper I
 M.sc Previous (Botany) Subject : I- Cell and Molecular Biology of Plants Maximum Marks : 30 Q-1 Discuss the role of plasmodesmeta in movements of molecular and macro molecules. Q-2 Given an ultra structure
M.sc Previous (Botany) Subject : I- Cell and Molecular Biology of Plants Maximum Marks : 30 Q-1 Discuss the role of plasmodesmeta in movements of molecular and macro molecules. Q-2 Given an ultra structure
GACE Biology Assessment Test I (026) Curriculum Crosswalk
 Subarea I. Cell Biology: Cell Structure and Function (50%) Objective 1: Understands the basic biochemistry and metabolism of living organisms A. Understands the chemical structures and properties of biologically
Subarea I. Cell Biology: Cell Structure and Function (50%) Objective 1: Understands the basic biochemistry and metabolism of living organisms A. Understands the chemical structures and properties of biologically
GSBHSRSBRSRRk IZTI/^Q. LlML. I Iv^O IV I I I FROM GENES TO GENOMES ^^^H*" ^^^^J*^ ill! BQPIP. illt. goidbkc. itip31. li4»twlil FIFTH EDITION
 FIFTH EDITION IV I ^HHk ^ttm IZTI/^Q i I II MPHBBMWBBIHB '-llwmpbi^hbwm^^pfc ' GSBHSRSBRSRRk LlML I I \l 1MB ^HP'^^MMMP" jflp^^^^^^^^st I Iv^O FROM GENES TO GENOMES %^MiM^PM^^MWi99Mi$9i0^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^V^^^fii^^t^i^^^^^
FIFTH EDITION IV I ^HHk ^ttm IZTI/^Q i I II MPHBBMWBBIHB '-llwmpbi^hbwm^^pfc ' GSBHSRSBRSRRk LlML I I \l 1MB ^HP'^^MMMP" jflp^^^^^^^^st I Iv^O FROM GENES TO GENOMES %^MiM^PM^^MWi99Mi$9i0^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^V^^^fii^^t^i^^^^^
Madhya Pradesh Bhoj (Open) University, Bhopal
 Subject- Cytology Genetics and Cytogenetics Maximum Marks: 30 5- l=h; dk;z tek djus dh vafre frffk 31 fnlecj 2012 gsa 6- l=h; dk;z mrrj iqflrdkvksa dks tek djus dh jlhn vo ; izkir dj ysaa Q. 1 Describe
Subject- Cytology Genetics and Cytogenetics Maximum Marks: 30 5- l=h; dk;z tek djus dh vafre frffk 31 fnlecj 2012 gsa 6- l=h; dk;z mrrj iqflrdkvksa dks tek djus dh jlhn vo ; izkir dj ysaa Q. 1 Describe
Semester III. Semster I PLANT ANATOMY BO1141
 Semster I PLANT ANATOMY BO1141 Understand basic anatomical features of monocot and dicot plants Able to identify different types of tissues and tissue systems in plants Know the basic concepts in reproductive
Semster I PLANT ANATOMY BO1141 Understand basic anatomical features of monocot and dicot plants Able to identify different types of tissues and tissue systems in plants Know the basic concepts in reproductive
Gymnázium, Brno, Slovanské nám. 7, SHEME OF WORK - Biology SCHEME OF WORK.
 SCHEME OF WORK http://agb.gymnaslo.cz Subject: Biology Year: first grade, 1.X School year:../ List of topics # Topics Time period 1. Introduction to Biology 09 2. Origin and History of life 10 3. Cell
SCHEME OF WORK http://agb.gymnaslo.cz Subject: Biology Year: first grade, 1.X School year:../ List of topics # Topics Time period 1. Introduction to Biology 09 2. Origin and History of life 10 3. Cell
M.Sc. Botany (Previous ) DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY First Year
 1 ( DBOT 01 ) M.Sc. Botany (Previous ) DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2007. First Year Paper I BIOLOGY AND DIVERSITY OF ALGAE, BRYOPHYTES, PTERIDOPHYTES AND GYMNOSPERMS Answer ALL questions from Section B. 1.
1 ( DBOT 01 ) M.Sc. Botany (Previous ) DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2007. First Year Paper I BIOLOGY AND DIVERSITY OF ALGAE, BRYOPHYTES, PTERIDOPHYTES AND GYMNOSPERMS Answer ALL questions from Section B. 1.
Virginia Western Community College BIO 101 General Biology I
 BIO 101 General Biology I Prerequisites Successful completion of MTE 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5; and a placement recommendation for ENG 111, co-enrollment in ENF 3/ENG 111, or successful completion of all developmental
BIO 101 General Biology I Prerequisites Successful completion of MTE 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5; and a placement recommendation for ENG 111, co-enrollment in ENF 3/ENG 111, or successful completion of all developmental
ASSIGNMENT - 1, MAY M.Sc. (PREVIOUS) FIRST YEAR DEGREE BOTANY PAPER-I : BIOLOGY AND DIVERSITY OF ALGAE, BRYOPHYTES,
 (DBOT 01(NR)) ASSIGNMENT - 1, MAY-2014. PAPER-I : BIOLOGY AND DIVERSITY OF ALGAE, BRYOPHYTES, 1) Protista. PTERIDOPHYTES AND GYMNOSPERSM 2) Cyanophyta. 3) Thallus range in Bryophytes. 4) Archegoniophore
(DBOT 01(NR)) ASSIGNMENT - 1, MAY-2014. PAPER-I : BIOLOGY AND DIVERSITY OF ALGAE, BRYOPHYTES, 1) Protista. PTERIDOPHYTES AND GYMNOSPERSM 2) Cyanophyta. 3) Thallus range in Bryophytes. 4) Archegoniophore
Distance Learning course Plant pathology and entomology Covered topics
 Distance Learning course Plant pathology and entomology Covered topics The distance learning course Plant pathology and entomology consist of four online modules that treat with the main groups of plant
Distance Learning course Plant pathology and entomology Covered topics The distance learning course Plant pathology and entomology consist of four online modules that treat with the main groups of plant
Textbook Evert RF and SE Eichorn 2012 Raven Biology of Plants. Eighth Edition. WH Freeman. (Table of Contentsi). Lecture Topics
 Science/Biology 2010.04 Plant Biology 3 credits lecture (3 hours/week; 12 weeks); 1 credit laboratory (3 hours/week; 12 weeks) Current advances in plant biology research, highlighting plant structure,
Science/Biology 2010.04 Plant Biology 3 credits lecture (3 hours/week; 12 weeks); 1 credit laboratory (3 hours/week; 12 weeks) Current advances in plant biology research, highlighting plant structure,
AP Biology Exam #7 (PRACTICE) Subunit #7: Diversity of Life
 AP Biology Exam #7 (PRACTICE) Subunit #7: Diversity of Life Multiple Choice Questions: Choose the best answer then bubble your answer on your scantron sheet. 1. Armadillos and spiny anteaters are not related.
AP Biology Exam #7 (PRACTICE) Subunit #7: Diversity of Life Multiple Choice Questions: Choose the best answer then bubble your answer on your scantron sheet. 1. Armadillos and spiny anteaters are not related.
ASSIGNMENT - 1, MAY M.Sc., BOTANY FIRST YEAR (PREVIOUS) DEGREE PAPER-I : BIOLOGY AND DIVERSITY OF ALGAE, BRYOPHYTES,
 (DBOT 01) ASSIGNMENT - 1, MAY 2013. PAPER-I : BIOLOGY AND DIVERSITY OF ALGAE, BRYOPHYTES, PTERIDOPHYTES AND GYMNOSPERSM 1. Cyanophyce. 2. Reproduction in algae. 3. Thallus in bryophytes. 4. Riccia. 5.
(DBOT 01) ASSIGNMENT - 1, MAY 2013. PAPER-I : BIOLOGY AND DIVERSITY OF ALGAE, BRYOPHYTES, PTERIDOPHYTES AND GYMNOSPERSM 1. Cyanophyce. 2. Reproduction in algae. 3. Thallus in bryophytes. 4. Riccia. 5.
Bio 101 General Biology 1
 Revised: Fall 2016 Bio 101 General Biology 1 COURSE OUTLINE Prerequisites: Prerequisite: Successful completion of MTE 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, and a placement recommendation for ENG 111, co-enrollment in ENF
Revised: Fall 2016 Bio 101 General Biology 1 COURSE OUTLINE Prerequisites: Prerequisite: Successful completion of MTE 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, and a placement recommendation for ENG 111, co-enrollment in ENF
AP: CHAPTER 18: the Genetics of VIRUSES p What makes microbes good models to study molecular mechanisms? 4. What is a bacteriophage?
 AP: CHAPTER 18: the Genetics of VIRUSES p328-340 1. What makes microbes good models to study molecular mechanisms? Name Per 2. How were viruses first discovered? 3. What are the two basic components of
AP: CHAPTER 18: the Genetics of VIRUSES p328-340 1. What makes microbes good models to study molecular mechanisms? Name Per 2. How were viruses first discovered? 3. What are the two basic components of
Administrative-Master Syllabus form approved June/2006 revised Page 1 of 1
 revised 11-02-06 Page 1 of 1 Administrative - Master Syllabus I. Topical Outline Each offering of this course must include the following topics (be sure to include information regarding lab, practicum,
revised 11-02-06 Page 1 of 1 Administrative - Master Syllabus I. Topical Outline Each offering of this course must include the following topics (be sure to include information regarding lab, practicum,
BIOLOGY 144 MODULE OUTLINES AND STUDY OBJECTIVES
 BIOLOGY 144 MODULE OUTLINES AND STUDY OBJECTIVES (2017) The module is based on the prescribed text (Biology:The Dynamic Science, 3 rd edition, Russell, Hertz, McMillan). The numbers in brackets represent
BIOLOGY 144 MODULE OUTLINES AND STUDY OBJECTIVES (2017) The module is based on the prescribed text (Biology:The Dynamic Science, 3 rd edition, Russell, Hertz, McMillan). The numbers in brackets represent
Evolutionary Morphology of Land Plants
 MHRD Scheme on Global Initiative on Academic Network (GIAN) Evolutionary Morphology of Land Plants Overview This century will be dominated by Life Sciences for well reasons of understanding evolution,
MHRD Scheme on Global Initiative on Academic Network (GIAN) Evolutionary Morphology of Land Plants Overview This century will be dominated by Life Sciences for well reasons of understanding evolution,
BIOLOGY Grades Summer Units: 10 high school credits UC Requirement Category: d. General Description:
 Summer 2015 Units: 10 high school credits UC Requirement Category: d General Description: BIOLOGY Grades 9-12 Summer session biology will be an intense, fast paced course. Students will gain an understanding
Summer 2015 Units: 10 high school credits UC Requirement Category: d General Description: BIOLOGY Grades 9-12 Summer session biology will be an intense, fast paced course. Students will gain an understanding
Biology Pacing Guide
 Unit Dates Glencoe Chapters 0 8/10 N/A Biology Intro 8/12 1 Cells 8/15 9/30 6.4 6.2 7.1 18.2 7.3 6.3 7.2 7.4 Topic GPS Classroom Procedures, Introduction to Biology SCSh 1-7 Macromolecules (6 days) Monomer/
Unit Dates Glencoe Chapters 0 8/10 N/A Biology Intro 8/12 1 Cells 8/15 9/30 6.4 6.2 7.1 18.2 7.3 6.3 7.2 7.4 Topic GPS Classroom Procedures, Introduction to Biology SCSh 1-7 Macromolecules (6 days) Monomer/
Course Outcome M.Sc., Botany CORE COURSE-I PLANT DIVERSITY (ALGAE, FUNGI, LICHENS, BRYOPHYTES, PTERIDOPHYTES, GYMNOSPERMS AND PALEOBOTANY)
 Course CORE COURSE-I PLANT DIVERSITY (ALGAE, FUNGI, LICHENS, BRYOPHYTES, PTERIDOPHYTES, GYMNOSPERMS AND PALEOBOTANY) Learning : Gain adequate knowledge on comparative account of various algal divisions
Course CORE COURSE-I PLANT DIVERSITY (ALGAE, FUNGI, LICHENS, BRYOPHYTES, PTERIDOPHYTES, GYMNOSPERMS AND PALEOBOTANY) Learning : Gain adequate knowledge on comparative account of various algal divisions
Advanced Placement Biology
 Advanced Placement Biology 2014-2015 Course Description This course is designed to be equivalent to a two-semester college introductory biology course sequence. AP Biology covers topics regularly covered
Advanced Placement Biology 2014-2015 Course Description This course is designed to be equivalent to a two-semester college introductory biology course sequence. AP Biology covers topics regularly covered
06/09/05. A survey of the plant kingdom based on a detailed study of the morphology, anatomy and physiology of selected representative specimens.
 06/09/05 Common Course Number: BOT -1010 Course Title: General Botany Catalog Course Description: A survey of the plant kingdom based on a detailed study of the morphology, anatomy and physiology of selected
06/09/05 Common Course Number: BOT -1010 Course Title: General Botany Catalog Course Description: A survey of the plant kingdom based on a detailed study of the morphology, anatomy and physiology of selected
SCHEME OF EXAMINATION FOR B.Sc. (BOTANY) SEMESTER SYSTEM w.e.f. Session Scheme of B.Sc. 1 st Year Semester I Paper code
 Sr. No. SCHEME OF EXAMINATION FOR B.Sc. (BOTANY) SEMESTER SYSTEM w.e.f. Session 2012-13 Scheme of B.Sc. 1 st Year Semester I Paper code Nomenclature Marks+IA Periods / week 1. BOT.1.1 Diversity of Microbes
Sr. No. SCHEME OF EXAMINATION FOR B.Sc. (BOTANY) SEMESTER SYSTEM w.e.f. Session 2012-13 Scheme of B.Sc. 1 st Year Semester I Paper code Nomenclature Marks+IA Periods / week 1. BOT.1.1 Diversity of Microbes
Scientific names allow scientists to talk about particular species without confusion
 Unit 9 Test Review KEY a. Explain the history, purpose, and methods of taxonomy What is taxonomy? the science of naming and classifying organisms Who came up with it? Linnaeus Why do we use taxonomy? Scientific
Unit 9 Test Review KEY a. Explain the history, purpose, and methods of taxonomy What is taxonomy? the science of naming and classifying organisms Who came up with it? Linnaeus Why do we use taxonomy? Scientific
Microbiology BIOL 202 Lecture Course Outcome Guide (COG) Approved 22 MARCH 2012 Pg.1
 Microbiology BIOL 202 Lecture Course Outcome Guide (COG) Approved 22 MARCH 2012 Pg.1 Course: Credits: 3 Instructor: Course Description: Concepts and Issues 1. Microbial Ecology including mineral cycles.
Microbiology BIOL 202 Lecture Course Outcome Guide (COG) Approved 22 MARCH 2012 Pg.1 Course: Credits: 3 Instructor: Course Description: Concepts and Issues 1. Microbial Ecology including mineral cycles.
Nucleic acid hybridization assays, detecting genotypes C12Q 1/68. Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
 A01H NEW PLANTS OR PROCESSES FOR OBTAINING THEM; PLANT REPRODUCTION BY TISSUE CULTURE TECHNIQUES New non-transgenic plants (including multicellular algae, multicellular fungi and lichens), plant varieties,
A01H NEW PLANTS OR PROCESSES FOR OBTAINING THEM; PLANT REPRODUCTION BY TISSUE CULTURE TECHNIQUES New non-transgenic plants (including multicellular algae, multicellular fungi and lichens), plant varieties,
Prereq: Concurrent 3 CH
 0201107 0201101 General Biology (1) General Biology (1) is an introductory course which covers the basics of cell biology in a traditional order, from the structure and function of molecules to the structure
0201107 0201101 General Biology (1) General Biology (1) is an introductory course which covers the basics of cell biology in a traditional order, from the structure and function of molecules to the structure
Contra Costa College Course Outline
 Contra Costa College Course Outline Department & Number: BIOSC 110 Course Title: Introduction to Biological Science Pre-requisite: None Corequisite: None Advisory: None Entry Skill: None Lecture Hours:
Contra Costa College Course Outline Department & Number: BIOSC 110 Course Title: Introduction to Biological Science Pre-requisite: None Corequisite: None Advisory: None Entry Skill: None Lecture Hours:
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School Science 7 Units and s Science 7A Unit 1 Nature of Science Scientific Explanations (12 days) s 1. I can make an informed decision using a scientific decision-making model
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser Middle School Science 7 Units and s Science 7A Unit 1 Nature of Science Scientific Explanations (12 days) s 1. I can make an informed decision using a scientific decision-making model
Chapter 1-Plants in Our World
 Chapter 1-Plants in Our World Formation of earth-4.5-4.6 billion years ago Evidence of life from organic material-3.8 billion years ago Many cyanobacteria are photosynthetic, but these microscopic organisms
Chapter 1-Plants in Our World Formation of earth-4.5-4.6 billion years ago Evidence of life from organic material-3.8 billion years ago Many cyanobacteria are photosynthetic, but these microscopic organisms
EXAMgen Correlation to Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS)
 EXAMgen Correlation to Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) TEKS EXAMgen Biology 3rd Edition Outline 112.34 Biology *TEKS in red denote Readiness Standards ex: (B.4)(B)R *TEKS in green denote Supporting
EXAMgen Correlation to Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) TEKS EXAMgen Biology 3rd Edition Outline 112.34 Biology *TEKS in red denote Readiness Standards ex: (B.4)(B)R *TEKS in green denote Supporting
A. Correct! Taxonomy is the science of classification. B. Incorrect! Taxonomy is the science of classification.
 DAT - Problem Drill 07: Diversity of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What is taxonomy? Question #01 (A) Taxonomy
DAT - Problem Drill 07: Diversity of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. What is taxonomy? Question #01 (A) Taxonomy
no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan
 no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan Introduction to microbiology Let's start! As you might have concluded, microbiology is the study of all organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye, Ex:
no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan Introduction to microbiology Let's start! As you might have concluded, microbiology is the study of all organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye, Ex:
CHAPTER : Prokaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
Exploring Creation With Biology
 Exploring Creation With Biology Semester 1 2013 Daily Plan Class The Class on will be a Lab Section where homework, lab reports and tests will be collected and labs will be performed. DATE DAY PAGE Topic
Exploring Creation With Biology Semester 1 2013 Daily Plan Class The Class on will be a Lab Section where homework, lab reports and tests will be collected and labs will be performed. DATE DAY PAGE Topic
Course Syllabus. Department: Science and Technology. Date: February 3, I. Course Prefix and Number: BIO 122. Course Name: General Biology II
 Department: Science and Technology Date: February 3, 2012 I. Course Prefix and Number: BIO 122 Course Name: General Biology II Course Syllabus Credit Hours and Contact Hours: 4 Credit hours and 5 Contact
Department: Science and Technology Date: February 3, 2012 I. Course Prefix and Number: BIO 122 Course Name: General Biology II Course Syllabus Credit Hours and Contact Hours: 4 Credit hours and 5 Contact
(DMB 01) M.Sc. (Previous) DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER First Year. Microbiology. Paper I INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS
 wk 7 (DMB 01) Paper I INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS PART A (5 8 = 40 marks) 1. Explain the growth of microbiology in the twentieth century. 2. Describe the structure of eukaryotic cell with a neat-labeled
wk 7 (DMB 01) Paper I INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS PART A (5 8 = 40 marks) 1. Explain the growth of microbiology in the twentieth century. 2. Describe the structure of eukaryotic cell with a neat-labeled
Unit B: Diversity of Living Things
 Unit B: Diversity of Living Things Chapter 3: Multicellular Diversity - Considerable diversity exists among multicellular organisms, as well. Specific Expectations: In the chapter you will learn how to
Unit B: Diversity of Living Things Chapter 3: Multicellular Diversity - Considerable diversity exists among multicellular organisms, as well. Specific Expectations: In the chapter you will learn how to
COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will develop abilities necessary to do and understand scientific inquiry.
 North Carolina Draft Standard Course of Study and Grade Level Competencies, Biology BIOLOGY COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will develop abilities necessary to do and understand scientific inquiry. 1.01
North Carolina Draft Standard Course of Study and Grade Level Competencies, Biology BIOLOGY COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will develop abilities necessary to do and understand scientific inquiry. 1.01
TEACHER CERTIFICATION STUDY GUIDE. Table of Contents I. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SCIENCE (HISTORY AND NATURAL SCIENCE)
 Table of Contents I. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SCIENCE (HISTORY AND NATURAL SCIENCE) A. Nature of scientific knowledge, inquiry, and historical perspectives 1. Scientific methods...1 2. Processes involved in
Table of Contents I. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SCIENCE (HISTORY AND NATURAL SCIENCE) A. Nature of scientific knowledge, inquiry, and historical perspectives 1. Scientific methods...1 2. Processes involved in
BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET Chapters 10-15, 17-30
 Name Hour Due Date: BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET Chapters 10-15, 17-30 The exam was prepared by the Biology teachers in the science departments of CVHS and DHS. 1. What is a Punnett Square? 2. Cross
Name Hour Due Date: BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET Chapters 10-15, 17-30 The exam was prepared by the Biology teachers in the science departments of CVHS and DHS. 1. What is a Punnett Square? 2. Cross
Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter in class follow along lecture notes
 Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter 26 34 in class follow along lecture notes Chp 26 Origin of life: 1) When did earth form? 2) What is the order of evolution of life forms on
Ms.Sastry, AP Biology Unit 4/Chp 26 to 34/Diversity 1 Chapter 26 34 in class follow along lecture notes Chp 26 Origin of life: 1) When did earth form? 2) What is the order of evolution of life forms on
SPECIES OF ARCHAEA ARE MORE CLOSELY RELATED TO EUKARYOTES THAN ARE SPECIES OF PROKARYOTES.
 THE TERMS RUN AND TUMBLE ARE GENERALLY ASSOCIATED WITH A) cell wall fluidity. B) cell membrane structures. C) taxic movements of the cell. D) clustering properties of certain rod-shaped bacteria. A MAJOR
THE TERMS RUN AND TUMBLE ARE GENERALLY ASSOCIATED WITH A) cell wall fluidity. B) cell membrane structures. C) taxic movements of the cell. D) clustering properties of certain rod-shaped bacteria. A MAJOR
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline)
 Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
DIRECTORATE OF SCHOOL EDUCATION, GOVERNMENT OF TAMILNADU, CHENNAI BOTANY SYLLABUS
 Unit - I Taxonomy of Angiosperms 1.1 to 1.3. Analyses the Systems of Classification of plants Recalls uses of Herbaria develops skill in preparing Herbarium Sheets in a Scientific manner. Recalls Economic
Unit - I Taxonomy of Angiosperms 1.1 to 1.3. Analyses the Systems of Classification of plants Recalls uses of Herbaria develops skill in preparing Herbarium Sheets in a Scientific manner. Recalls Economic
Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity
 19 Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Taxonomy Introduction to Microbial Taxonomy
19 Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Taxonomy Introduction to Microbial Taxonomy
I. Molecules and Cells: Cells are the structural and functional units of life; cellular processes are based on physical and chemical changes.
 I. Molecules and Cells: Cells are the structural and functional units of life; cellular processes are based on physical and chemical changes. A. Chemistry of Life B. Cells 1. Water How do the unique chemical
I. Molecules and Cells: Cells are the structural and functional units of life; cellular processes are based on physical and chemical changes. A. Chemistry of Life B. Cells 1. Water How do the unique chemical
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation
 Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms Are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms Are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell
A Planned Course Statement for. Biology I, CP. Course # 401 Grade(s) 9, 10. Length of Period (mins.) 40 Total Clock Hours: 140
 East Penn School District Secondary Curriculum A Planned Course Statement for Biology I, CP Course # 401 Grade(s) 9, 10 Department: Science ength of Period (mins.) 40 Total Clock Hours: 140 Periods per
East Penn School District Secondary Curriculum A Planned Course Statement for Biology I, CP Course # 401 Grade(s) 9, 10 Department: Science ength of Period (mins.) 40 Total Clock Hours: 140 Periods per
Content Standards Learning and Performance Expectations Assessment of Learning
 Thinking Skills - The student demonstrates: 1. Critical Thinking Skills include the ability to analyze, criticize, advocate ideas, reason inductively and deductively, and to reach factual and judgemental
Thinking Skills - The student demonstrates: 1. Critical Thinking Skills include the ability to analyze, criticize, advocate ideas, reason inductively and deductively, and to reach factual and judgemental
BIOLOGY YEAR AT A GLANCE RESOURCE ( ) REVISED FOR HURRICANE DAYS
 BIOLOGY YEAR AT A GLANCE RESOURCE (2017-18) REVISED FOR HURRICANE DAYS DATES TOPIC/BENCHMARKS QUARTER 1 LAB/ACTIVITIES 8/21 8/24/17 I. Introduction to Biology A. What is Biology B. Science in the real
BIOLOGY YEAR AT A GLANCE RESOURCE (2017-18) REVISED FOR HURRICANE DAYS DATES TOPIC/BENCHMARKS QUARTER 1 LAB/ACTIVITIES 8/21 8/24/17 I. Introduction to Biology A. What is Biology B. Science in the real
TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY
 Washington Educator Skills Tests Endorsements (WEST E) TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY BIOLOGY Copyright 2014 by the Washington Professional Educator Standards Board 1 Washington Educator Skills
Washington Educator Skills Tests Endorsements (WEST E) TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY BIOLOGY Copyright 2014 by the Washington Professional Educator Standards Board 1 Washington Educator Skills
8/23/2014. Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter 26 Objectives Explain the following characteristics of the Linnaean system of classification: a. binomial nomenclature b. hierarchical classification List the major
Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter 26 Objectives Explain the following characteristics of the Linnaean system of classification: a. binomial nomenclature b. hierarchical classification List the major
SWAMI RAMANAND TEERTH MARATHWADA UNIVERSITY, NANDED PET (Ph.D. ENTRANCE TEST) ( June 2013 ) SYLLABUS SUBJECT: BOTANY
 CURRICULUM DESIGNING COMMITTEE 1. Dr.Bodke S.S. Chairman Yeshwant Mahavidyalaya, Nanded 2. Dr. Kadam A.S. Member D.S.M. Mahavidyalaya, Jintur 3. Dr. Mandge S.V. Member Shri. SGM College, Loha 4. Dr. Gawai
CURRICULUM DESIGNING COMMITTEE 1. Dr.Bodke S.S. Chairman Yeshwant Mahavidyalaya, Nanded 2. Dr. Kadam A.S. Member D.S.M. Mahavidyalaya, Jintur 3. Dr. Mandge S.V. Member Shri. SGM College, Loha 4. Dr. Gawai
Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13)
 Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13) Sexual and asexual life cycles Meiosis Origins of Genetic Variation Independent assortment Crossing over ( recombination ) Heredity Transmission of traits between generations
Outline for today s lecture (Ch. 13) Sexual and asexual life cycles Meiosis Origins of Genetic Variation Independent assortment Crossing over ( recombination ) Heredity Transmission of traits between generations
SGTB Khalsa College, University of Delhi Lesson Plan ( ) Department of Botany
 SGTB Khalsa College, University of Delhi Lesson Plan (2016-17) Department of Botany Title of the Paper: Biodiversity I (Microbes, Algae, Fungi and Archegoniate) Course Name: B.Sc. Life sciences I Year
SGTB Khalsa College, University of Delhi Lesson Plan (2016-17) Department of Botany Title of the Paper: Biodiversity I (Microbes, Algae, Fungi and Archegoniate) Course Name: B.Sc. Life sciences I Year
CLASSIFICATION UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 3/1
 CLASSIFICATION UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 3/1 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 2/13 2/14 - B 2/15 2/16 - B 2/17 2/20 Intro to Viruses Viruses VS Cells 2/21 - B Virus Reproduction Q 1-2 2/22 2/23
CLASSIFICATION UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 3/1 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 2/13 2/14 - B 2/15 2/16 - B 2/17 2/20 Intro to Viruses Viruses VS Cells 2/21 - B Virus Reproduction Q 1-2 2/22 2/23
Outline. Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea. Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea
 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT
 SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY B1: Naming and classification of organisms Biology of Plants - Raven et al. 2005 pp. 219-237 INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY Taxonomy Naming Describing Classifying
SYLLABUS THEME B PLANT CLASSIFICATION & DIVERSITY B1: Naming and classification of organisms Biology of Plants - Raven et al. 2005 pp. 219-237 INTRODUCTION TO TAXONOMY Taxonomy Naming Describing Classifying
Introduction to Biology with Lab
 Introduction to Biology with Lab Course Text/Materials Mader, Sylvia S. Inquiry into Life, 12th edition, McGraw-Hill, 2008, ISBN: 9780073309330 [find and buy the text: Straighterline.com/textbooks] Custom
Introduction to Biology with Lab Course Text/Materials Mader, Sylvia S. Inquiry into Life, 12th edition, McGraw-Hill, 2008, ISBN: 9780073309330 [find and buy the text: Straighterline.com/textbooks] Custom
BIOLOGY YEAR AT A GLANCE RESOURCE ( )
 BIOLOGY YEAR AT A GLANCE RESOURCE (2016-17) DATES TOPIC/BENCHMARKS QUARTER 1 LAB/ACTIVITIES 8/22 8/25/16 I. Introduction to Biology Lab 1: Seed Germination A. What is Biology B. Science in the real world
BIOLOGY YEAR AT A GLANCE RESOURCE (2016-17) DATES TOPIC/BENCHMARKS QUARTER 1 LAB/ACTIVITIES 8/22 8/25/16 I. Introduction to Biology Lab 1: Seed Germination A. What is Biology B. Science in the real world
Unit 9: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Unit 9: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total) Chapter 22 Descent
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Unit 9: Evolution Guided Reading Questions (80 pts total) Chapter 22 Descent
Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau
 Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau Texts/Instructional Materials: Biology : Concepts and Connections 5 th edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor and Simon Pearson Syllabus:
Course Name: Biology Level: A Points: 5 Teacher Name: Claire E. Boudreau Texts/Instructional Materials: Biology : Concepts and Connections 5 th edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor and Simon Pearson Syllabus:
Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics
 Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Understand what the term species means to biology. 2. Recognize the various patterns
Chapter 27: Evolutionary Genetics Student Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Understand what the term species means to biology. 2. Recognize the various patterns
For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis. Genetics Terminology: Homologous chromosomes
 For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis Genetics Terminology: Autosomes Somatic cell Gamete Karyotype Homologous chromosomes Meiosis Sex chromosomes Diploid Haploid Zygote Synapsis
For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis Genetics Terminology: Autosomes Somatic cell Gamete Karyotype Homologous chromosomes Meiosis Sex chromosomes Diploid Haploid Zygote Synapsis
THE ROLE OF BBSRC IN BIODIVERSITY RESEARCH
 THE ROLE OF BBSRC IN BIODIVERSITY RESEARCH INTRODUCTION The aim of this document is to explain the role of biodiversity research in the delivery of the BBSRC mission, and thereby to provide guidance to
THE ROLE OF BBSRC IN BIODIVERSITY RESEARCH INTRODUCTION The aim of this document is to explain the role of biodiversity research in the delivery of the BBSRC mission, and thereby to provide guidance to
Course ID May 2017 COURSE OUTLINE. Biology 102 (C-ID Number: BIOL 140) General Biology (C-ID Title: Organismal Biology)
 Degree Applicable Glendale Community College Course ID 005073 May 2017 COURSE OUTLINE Biology 102 (C-ID Number: BIOL 140) General Biology (C-ID Title: Organismal Biology) Catalog Statement BIOL 102 provides
Degree Applicable Glendale Community College Course ID 005073 May 2017 COURSE OUTLINE Biology 102 (C-ID Number: BIOL 140) General Biology (C-ID Title: Organismal Biology) Catalog Statement BIOL 102 provides
Biology 2201 Unit Test Holy Spirit High Mr. Pretty Name: ANSWER KEY
 Biology 2201 Unit Test Holy Spirit High Mr. Pretty Name: ANSWER KEY 1.) Which of the following increases as you proceed down classification levels from kingdom to species? A) Activity B) Diversity among
Biology 2201 Unit Test Holy Spirit High Mr. Pretty Name: ANSWER KEY 1.) Which of the following increases as you proceed down classification levels from kingdom to species? A) Activity B) Diversity among
I. Molecules & Cells. A. Unit One: The Nature of Science. B. Unit Two: The Chemistry of Life. C. Unit Three: The Biology of the Cell.
 I. Molecules & Cells A. Unit One: The Nature of Science a. How is the scientific method used to solve problems? b. What is the importance of controls? c. How does Darwin s theory of evolution illustrate
I. Molecules & Cells A. Unit One: The Nature of Science a. How is the scientific method used to solve problems? b. What is the importance of controls? c. How does Darwin s theory of evolution illustrate
AECC: Ability Enhancement Compulsory Course: DSC: Discipline Specific Course: DSE : Discipline Specific Elective
 Telangana State Council of Higher Education, Govt. of Telangana B.Sc CBCS Common Core Syllabus for All Universities in Telanganas (wef 2016-2017). PROPOSED SCHEME FOR B.Sc PROGRAMME UNDER CHOICE BASED
Telangana State Council of Higher Education, Govt. of Telangana B.Sc CBCS Common Core Syllabus for All Universities in Telanganas (wef 2016-2017). PROPOSED SCHEME FOR B.Sc PROGRAMME UNDER CHOICE BASED
QQ 10/5/18 Copy the following into notebook:
 Chapter 13- Meiosis QQ 10/5/18 Copy the following into notebook: Similarities: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Differences: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Figure 13.1 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their
Chapter 13- Meiosis QQ 10/5/18 Copy the following into notebook: Similarities: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Differences: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Figure 13.1 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their
PLANT VARIATION AND EVOLUTION
 PLANT VARIATION AND EVOLUTION D. BRIGGS Department of Plant Sciences, University of Cambridge S. M. WALTERS Former Director of the University Botanic Garden, Cambridge 3rd EDITION CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
PLANT VARIATION AND EVOLUTION D. BRIGGS Department of Plant Sciences, University of Cambridge S. M. WALTERS Former Director of the University Botanic Garden, Cambridge 3rd EDITION CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
Biology Science Crosswalk
 SB1. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including
SB1. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including
Text of objective. Investigate and describe the structure and functions of cells including: Cell organelles
 This document is designed to help North Carolina educators teach the s (Standard Course of Study). NCDPI staff are continually updating and improving these tools to better serve teachers. Biology 2009-to-2004
This document is designed to help North Carolina educators teach the s (Standard Course of Study). NCDPI staff are continually updating and improving these tools to better serve teachers. Biology 2009-to-2004
VCE BIOLOGY Relationship between the key knowledge and key skills of the Study Design and the Study Design
 VCE BIOLOGY 2006 2014 Relationship between the key knowledge and key skills of the 2000 2005 Study Design and the 2006 2014 Study Design The following table provides a comparison of the key knowledge (and
VCE BIOLOGY 2006 2014 Relationship between the key knowledge and key skills of the 2000 2005 Study Design and the 2006 2014 Study Design The following table provides a comparison of the key knowledge (and
KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM. Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna
 KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna THE CONCEPT Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature
KINGDOM SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM Dr. Urvashi Sinha, Asst. Prof., Department of Botany Patna Women s College, Patna THE CONCEPT Carl Linnaeus introduced the rank-based system of nomenclature
Chapter 22: Descent with Modification 1. BRIEFLY summarize the main points that Darwin made in The Origin of Species.
 AP Biology Chapter Packet 7- Evolution Name Chapter 22: Descent with Modification 1. BRIEFLY summarize the main points that Darwin made in The Origin of Species. 2. Define the following terms: a. Natural
AP Biology Chapter Packet 7- Evolution Name Chapter 22: Descent with Modification 1. BRIEFLY summarize the main points that Darwin made in The Origin of Species. 2. Define the following terms: a. Natural
District Office Pacing Calendar Biology September 2017 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 1
 September 7 4 Labor day- No School Professional Development Getting to know you and establish procedures 7 Getting to know you and establish procedures Getting to know you and establish procedures,,4 Introduce
September 7 4 Labor day- No School Professional Development Getting to know you and establish procedures 7 Getting to know you and establish procedures Getting to know you and establish procedures,,4 Introduce
UGZY-01 Animal Diversity-I
 UGZY-01 Animal Diversity-I Block-I I Diversity of Animal Life-I (Organisation) Five Kingdom Classification The Protozoans The Metazoa- Origin and Evolution Diverstiy of Animal Life-II (Classification)
UGZY-01 Animal Diversity-I Block-I I Diversity of Animal Life-I (Organisation) Five Kingdom Classification The Protozoans The Metazoa- Origin and Evolution Diverstiy of Animal Life-II (Classification)
Bacterial Genetics & Operons
 Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
FYBSc-Semester I Paper I CO 1 CO 2 CO 3 CO 4 CO 5 CO 6 CO 7 CO 1 CO 2 CO 3 CO 4 CO 1
 FYBSc-Semester I Paper I 1 USBO 101 (Plant Diversity I) Unit I Algae Unit II Fungi Unit III Bryophyta CO 7 Identify the different location of the algae. Explain their habitat, cell structure, pigments,
FYBSc-Semester I Paper I 1 USBO 101 (Plant Diversity I) Unit I Algae Unit II Fungi Unit III Bryophyta CO 7 Identify the different location of the algae. Explain their habitat, cell structure, pigments,
Have cell walls Made of
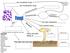 _ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
_ are unicellular fungi _ are multicellular fungi And can only Reproduce Using Can also reproduce Can spread using Because they do not make their own food Hyphae Mycelium Fruiting Body Heterotrophs Budding
ADVANCED PLACEMENT BIOLOGY
 ADVANCED PLACEMENT BIOLOGY Description Advanced Placement Biology is designed to be the equivalent of a two-semester college introductory course for Biology majors. The course meets seven periods per week
ADVANCED PLACEMENT BIOLOGY Description Advanced Placement Biology is designed to be the equivalent of a two-semester college introductory course for Biology majors. The course meets seven periods per week
UON, CAS, DBSC, General Biology II (BIOL102) Dr. Mustafa. A. Mansi. The Origin of Species
 The Origin of Species Galápagos Islands, landforms newly emerged from the sea, despite their geologic youth, are filled with plants and animals known no-where else in the world, Speciation: The origin
The Origin of Species Galápagos Islands, landforms newly emerged from the sea, despite their geologic youth, are filled with plants and animals known no-where else in the world, Speciation: The origin
M. SC. SYLLABUS MICROBIOLOGY CHOICE BASED CREDIT SYSTEM (CBCS)
 M. SC. SYLLABUS MICROBIOLOGY CHOICE BASED CREDIT SYSTEM (CBCS) (Revised, w.e.f. June 2018) DEPARTMENT OF LIFE SCIENCES BHAKTA KAVI NARSINH MEHTA UNIVERSITY Junagadh 362 640 Page 1 of 9 Department of Life
M. SC. SYLLABUS MICROBIOLOGY CHOICE BASED CREDIT SYSTEM (CBCS) (Revised, w.e.f. June 2018) DEPARTMENT OF LIFE SCIENCES BHAKTA KAVI NARSINH MEHTA UNIVERSITY Junagadh 362 640 Page 1 of 9 Department of Life
The nature of genomes. Viral genomes. Prokaryotic genome. Nonliving particle. DNA or RNA. Compact genomes with little spacer DNA
 The nature of genomes Genomics: study of structure and function of genomes Genome size variable, by orders of magnitude number of genes roughly proportional to genome size Plasmids symbiotic DNA molecules,
The nature of genomes Genomics: study of structure and function of genomes Genome size variable, by orders of magnitude number of genes roughly proportional to genome size Plasmids symbiotic DNA molecules,
Reproductive Morphology
 Week 3; Wednesday Announcements: 1 st lab quiz TODAY Reproductive Morphology Reproductive morphology - any portion of a plant that is involved with or a direct product of sexual reproduction Example: cones,
Week 3; Wednesday Announcements: 1 st lab quiz TODAY Reproductive Morphology Reproductive morphology - any portion of a plant that is involved with or a direct product of sexual reproduction Example: cones,
Molecular Evolution & the Origin of Variation
 Molecular Evolution & the Origin of Variation What Is Molecular Evolution? Molecular evolution differs from phenotypic evolution in that mutations and genetic drift are much more important determinants
Molecular Evolution & the Origin of Variation What Is Molecular Evolution? Molecular evolution differs from phenotypic evolution in that mutations and genetic drift are much more important determinants
Molecular Evolution & the Origin of Variation
 Molecular Evolution & the Origin of Variation What Is Molecular Evolution? Molecular evolution differs from phenotypic evolution in that mutations and genetic drift are much more important determinants
Molecular Evolution & the Origin of Variation What Is Molecular Evolution? Molecular evolution differs from phenotypic evolution in that mutations and genetic drift are much more important determinants
Unit 11: Plants Guided Reading Questions (75 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Unit 11: Plants Guided Reading Questions (75 pts total) Chapter 29 Plant
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Unit 11: Plants Guided Reading Questions (75 pts total) Chapter 29 Plant
