As you come in. Pick up graded homework from front Turn in homework in the box
|
|
|
- Angelica Benson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 As you come in Pick up graded homework from front Turn in homework in the box
2 LECTURE 3 CONTINUING CHAPTER 2 Professor Cassandra Paul
3 How I graded homework I was thorough and lenient! A s (4.0) were given if it was complete, and thought was given to every question C s (2.0) were given if a number of problems were not completed, or no work was included (or late) F s (zeros) were only given if you turned nothing in Pay attention to comments, and if I suggest you come to office hours, please do! Common issues: Polar coordinates Free fall Velocity/acceleration confusion
4 Did not receive homework from Galaviz Hamilton Moua T. Nguyen Ochoa Ngo If you are not officially added yet, your name might not be listed here even though I have not received homework from you.
5 Before we start Get in small groups (lets try 3) Discuss any issues you had with the homework Help your group-mates with their difficulties (5 minutes)
6 Any further Issues: See me in office hours Make an appointment with me Set up a time to meet with some classmates Ask your workshop facilitator for help Physics Club? Peer connections (drop in tutoring):
7 Groups of 5 Name tags up White boards, markers, erasers Clickers
8 Last time: Multiple choice An object with a positive velocity (+3m/s for example) indicates the object must: A. Be speeding up B. Be traveling in a positive direction C. Have a positive acceleration D. Have a positive displacement E. Both A & B
9 Multiple choice An object with a positive velocity (+3m/s for example) indicates the object must: A. Be speeding up B. Be traveling in a positive direction C. Have a positive acceleration D. Have a positive displacement E. Both A & B v=δx/t t is always positive therefore if v is positive Δx is also positive
10 Multiple choice An object with a positive velocity (+3m/s for example) indicates the object must: A. Be speeding up B. Be traveling in a positive direction C. Have a positive acceleration D. Have a positive final distance E. Both A & B
11 Unit Conversion Convert 20 inches to centimeters: *Remember multiplying by 1 gives us the same quantity back! 5 x 1 = inches x 2.54 centimeters 1 inch Learn this! = 20.0 x 2.54 = 50.8 centimeters Updated since class: correct values and sig figs
12 You try: Convert 100 miles/hour into meters/second 1 mile ~ 1610 meters 100 miles x 1 hour x 1 min x 1610 meters hour 60 min 60 sec 1 mile = meters second
13 Position, Velocity & Acceleration vs. Time graphs Δx = x f x i v = Δx / Δt a = Δv /Δt Case 1: A student walking across campus to class at a constant speed. x Distance changing at a constant rate. v Velocity is constant and positive. a Acceleration is zero because velocity is not changing. t t f t t f t t f
14 Case 2: Dr. Paul bicycling down San Fernando. x v a t t 4 t t f t t f
15 Check-In Clicker question A. I am very confident in my understanding of these graphs and ability to produce them B. I think I might need to study a bit more, but I feel ok with them C. I will need to seek help to learn these D. I am completely lost
16 Velocity v = Δx / Δt Average Velocity v = lim Δx / Δt Δt 0 Instantaneous velocity
17 Review on Limits Δx/Δt = rise/run = slope x (t 2, x 2 ) (t 1, x 1 ) t
18 Review on Limits Δx/Δt = rise/run = slope x (t 2, x 2 ) (t 1, x 1 ) t
19 Review on Limits Δx/Δt = rise/run = slope x (t 2, x 2 ) (t 1, x 1 ) t
20 Review on Limits v = lim Δs / Δt Δt 0 x (or v=dx/dt in calculus) t the line tangent to the position vs. time graph is defined to be the instantaneous velocity at that time
21 v = lim Δx / Δt Δt 0 (or v=dx/dt) x x t t f t t f the line tangent to the position vs. time graph is defined to be the instantaneous velocity at that time
22 x x t t f t t f This is why why we often calculate average velocity and not instantaneous velocity.
23 When you are asked to find instantaneous velocity what do you do? x x t t 1 t t 2
24 Graphical Instantaneous Velocity Average velocities are the blue lines The green line (tangent) is the instantaneous velocity Section 2.2
25 Instantaneous Velocity The limit of the average velocity as the time interval becomes infinitesimally short, or as the time interval approaches zero The instantaneous velocity indicates what is happening at every point of time The magnitude of the instantaneous velocity is what you read on a car s speedometer Section 2.2
26 Acceleration Average Acceleration a = lim Δv/ Δt = Δt 0 Instantaneous Acceleration
27 You try: In groups of 5 use your white boards to graphically represent Be as accurate as possible!
28 Free Fall A freely falling object is any object moving freely under the influence of gravity alone Free fall does not depend on the object s original motion All objects falling near the earth s surface fall with a constant acceleration The acceleration is called the acceleration due to gravity, and indicated by g Section 2.6
29 Free Fall g = acceleration due to gravity g x mass = weight = force of the earth pulling on you Convention: The direction of the pull of the earth is downwards, therefore a = -g = (in the y direction)
30 Common Confusions Pg 43 : The value of g decreases with increasing altitude. at Earth s surface g is equal to 9.81m/s G varies for VERY large distances, it s negligible at Earth s surface
31 Gravity San Jose State, Elevation: 85ft g = 9.81 University of Wyoming, Elevation: 7200 ft g = 9.79
32 Clicker Question Which of the following is true? For a freely falling object: A. Acceleration is always downwards B. Acceleration is downwards only when the object is traveling downwards (past max height) C. Acceleration is zero at max height D. Acceleration is constant E. Both A and D
33 Homework: Chapter 2 problems : 6, 20, 24, 35, 45, 47, 51 Read Chapter 3: take notes, work examples Chapter 3: Conceptual Questions : 1, 3, 4, 7, 10, 11
Chapter 1 Problem 28: Agenda. Quantities in Motion. Displacement Isn t Distance. Velocity. Speed 1/23/14
 Agenda We need a note-taker! If you re interested, see me after class. Today: HW Quiz #1, 1D Motion Lecture for this week: Chapter 2 (finish reading Chapter 2 by Thursday) Homework #2: continue to check
Agenda We need a note-taker! If you re interested, see me after class. Today: HW Quiz #1, 1D Motion Lecture for this week: Chapter 2 (finish reading Chapter 2 by Thursday) Homework #2: continue to check
Topic 1: 1D Motion PHYSICS 231
 Topic 1: 1D Motion PHYSICS 231 Current Assignments Reading Chapter 1.5 and 3 due Tuesday, Jan 18, beginning of class Homework Set 1 already open (covers this week) due Thursday, Jan 20, 11 pm Recommended
Topic 1: 1D Motion PHYSICS 231 Current Assignments Reading Chapter 1.5 and 3 due Tuesday, Jan 18, beginning of class Homework Set 1 already open (covers this week) due Thursday, Jan 20, 11 pm Recommended
VELOCITY. If you have a graph of position and you take the derivative, what would the derivative represent? Position. Time
 VELOCITY If you have a graph of position and you take the derivative, what would the derivative represent? Position Time Average rate of Change What is the average rate of change of temperature over the
VELOCITY If you have a graph of position and you take the derivative, what would the derivative represent? Position Time Average rate of Change What is the average rate of change of temperature over the
Trigonometry I. Pythagorean theorem: WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY Physics
 Trigonometry I Pythagorean theorem: Trigonometry II 90 180 270 360 450 540 630 720 sin(x) and cos(x) are mathematical functions that describe oscillations. This will be important later, when we talk about
Trigonometry I Pythagorean theorem: Trigonometry II 90 180 270 360 450 540 630 720 sin(x) and cos(x) are mathematical functions that describe oscillations. This will be important later, when we talk about
Acceleration. 3. Changing Direction occurs when the velocity and acceleration are neither parallel nor anti-parallel
 Acceleration When the velocity of an object changes, we say that the object is accelerating. This acceleration can take one of three forms: 1. Speeding Up occurs when the object s velocity and acceleration
Acceleration When the velocity of an object changes, we say that the object is accelerating. This acceleration can take one of three forms: 1. Speeding Up occurs when the object s velocity and acceleration
Physics 100. Reminder: All lecture notes posted, after lecture, follow link at:
 Physics 100 Please pick up a clicker! Reminder: All lecture notes posted, after lecture, follow link at: http://www.hunter.cuny.edu/physics/courses/physics100/spring-2016 Note: Before the actual lecture,
Physics 100 Please pick up a clicker! Reminder: All lecture notes posted, after lecture, follow link at: http://www.hunter.cuny.edu/physics/courses/physics100/spring-2016 Note: Before the actual lecture,
Chapter 3 Linear Motion
 Lecture 3 Chapter 3 Linear Motion (Motion in a straight line, such as falling straight downward) Some material courtesy Prof. A. Garcia, SJSU Help sessions Announcements M 1600-1700 in TH116 (A. Kelly)
Lecture 3 Chapter 3 Linear Motion (Motion in a straight line, such as falling straight downward) Some material courtesy Prof. A. Garcia, SJSU Help sessions Announcements M 1600-1700 in TH116 (A. Kelly)
Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension. Professor Wa el Salah
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Kinematics Describes motion while ignoring the external agents that might have caused or modified the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Kinematics Describes motion while ignoring the external agents that might have caused or modified the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight
Physics 2A. Lecture 2A. "You must learn from the mistakes of others. You can't possibly live long enough to make them all yourself.
 Physics 2A Lecture 2A "You must learn from the mistakes of others. You can't possibly live long enough to make them all yourself." --Sam Levenson 1 Motion Chapter 2 will focus on motion in one dimension.
Physics 2A Lecture 2A "You must learn from the mistakes of others. You can't possibly live long enough to make them all yourself." --Sam Levenson 1 Motion Chapter 2 will focus on motion in one dimension.
Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Types of Motion Translational An example is a car traveling on a highway. Rotational An example is the Earth s spin on its axis. Vibrational An example is the back-and-forth
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Types of Motion Translational An example is a car traveling on a highway. Rotational An example is the Earth s spin on its axis. Vibrational An example is the back-and-forth
If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph.
 Physics Lecture #2: Position Time Graphs If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph. Suppose a
Physics Lecture #2: Position Time Graphs If we plot the position of a moving object at increasing time intervals, we get a position time graph. This is sometimes called a distance time graph. Suppose a
Welcome Back to Physics 211!
 Welcome Back to Physics 211! (General Physics I) Thurs. Aug 30 th, 2012 Physics 211 -Fall 2014 Lecture01-2 1 Last time: Syllabus, mechanics survey Unit conversions Today: Using your clicker 1D displacement,
Welcome Back to Physics 211! (General Physics I) Thurs. Aug 30 th, 2012 Physics 211 -Fall 2014 Lecture01-2 1 Last time: Syllabus, mechanics survey Unit conversions Today: Using your clicker 1D displacement,
Chapter 4 Linear Motion
 Chapter 4 Linear Motion You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. I. Motion Is Relative A. Everything moves. Even things that appear to be at rest move.
Chapter 4 Linear Motion You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. I. Motion Is Relative A. Everything moves. Even things that appear to be at rest move.
Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs,
 Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs, Kinematic formulas. A Distance Tells how far an object is from
Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs, Kinematic formulas. A Distance Tells how far an object is from
Four Types of Motion We ll Study
 Four Types of Motion We ll Study The branch of mechanics that studies the motion of a body without caring about what caused the motion. Kinematics definitions Kinematics branch of physics; study of motion
Four Types of Motion We ll Study The branch of mechanics that studies the motion of a body without caring about what caused the motion. Kinematics definitions Kinematics branch of physics; study of motion
Welcome to Physics 211! General Physics I
 Welcome to Physics 211! General Physics I Physics 211 Fall 2015 Lecture 01-1 1 Physics 215 Honors & Majors Are you interested in becoming a physics major? Do you have a strong background in physics and
Welcome to Physics 211! General Physics I Physics 211 Fall 2015 Lecture 01-1 1 Physics 215 Honors & Majors Are you interested in becoming a physics major? Do you have a strong background in physics and
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction
 What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
Physic 231 Lecture 3. Main points of today s lecture. for constant acceleration: a = a; assuming also t0. v = lim
 Physic 231 Lecture 3 Main points of today s lecture Δx v = ; Δ t = t t0 for constant acceleration: a = a; assuming also t0 = 0 Δ x = v v= v0 + at Δx 1 v = lim Δ x = Δ t 0 ( v+ vo ) t 2 Δv 1 2 a = ; Δ v=
Physic 231 Lecture 3 Main points of today s lecture Δx v = ; Δ t = t t0 for constant acceleration: a = a; assuming also t0 = 0 Δ x = v v= v0 + at Δx 1 v = lim Δ x = Δ t 0 ( v+ vo ) t 2 Δv 1 2 a = ; Δ v=
Welcome Back to Physics 211!
 Welcome Back to Physics 211! (General Physics I) Thurs. Aug 30 th, 2012 Physics 211 -Fall 2012 Lecture01-2 1 Last time: Syllabus, mechanics survey Particle model Today: Using your clicker 1D displacement,
Welcome Back to Physics 211! (General Physics I) Thurs. Aug 30 th, 2012 Physics 211 -Fall 2012 Lecture01-2 1 Last time: Syllabus, mechanics survey Particle model Today: Using your clicker 1D displacement,
Welcome back to Physics 211
 Welcome back to Physics 211 Lecture 2-1 02-1 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Using graphs to solve problems Constant acceleration, free fall 02-1 2 1-2.6-8: Acceleration from graph of
Welcome back to Physics 211 Lecture 2-1 02-1 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Using graphs to solve problems Constant acceleration, free fall 02-1 2 1-2.6-8: Acceleration from graph of
Matthew W. Milligan. Kinematics. What do you remember?
 Kinematics What do you remember? Kinematics Unit Outline I. Six Definitions: Distance, Position, Displacement, Speed, Velocity, Acceleration II. Graphical Interpretations III. Constant acceleration model
Kinematics What do you remember? Kinematics Unit Outline I. Six Definitions: Distance, Position, Displacement, Speed, Velocity, Acceleration II. Graphical Interpretations III. Constant acceleration model
Chapter 2: Motion a Straight Line
 Formula Memorization: Displacement What is a vector? Average Velocity Average Speed Instanteous Velocity Average Acceleration Instantaneous Acceleration Constant Acceleration Equation (List all five of
Formula Memorization: Displacement What is a vector? Average Velocity Average Speed Instanteous Velocity Average Acceleration Instantaneous Acceleration Constant Acceleration Equation (List all five of
p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change
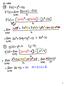 1 2 3 4 p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change Find the derivative of a function using the Constant Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Power Rule Find the derivative
1 2 3 4 p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change Find the derivative of a function using the Constant Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Power Rule Find the derivative
Velocity. UF PHY2053, Lecture 3: Motion in One Dimension
 Velocity 1 Average Velocity vs Average Speed Average Velocity is the change in position during a time interval vav,x Δx Δt x f - xi tf - ti Average Speed is the distance traveled during a time interval
Velocity 1 Average Velocity vs Average Speed Average Velocity is the change in position during a time interval vav,x Δx Δt x f - xi tf - ti Average Speed is the distance traveled during a time interval
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 1: Ch.12, Sec.1-3h
 1 / 30 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 1: Ch.12, Sec.1-3h Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Tuesday, August 21, 2012 2 / 30 INTRODUCTION
1 / 30 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 1: Ch.12, Sec.1-3h Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Tuesday, August 21, 2012 2 / 30 INTRODUCTION
Chapter 2. Kinematics in One Dimension. continued
 Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension continued 2.4 Equations of Kinematics for Constant Acceleration vx0 = 0m s ax = +31 m s 2 Δx vx = 62m s Example: Catapulting a Jet Find its displacement. vx0 = 0m
Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension continued 2.4 Equations of Kinematics for Constant Acceleration vx0 = 0m s ax = +31 m s 2 Δx vx = 62m s Example: Catapulting a Jet Find its displacement. vx0 = 0m
Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension. AIT AP Physics C
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Kinematics Describes motion while ignoring the agents that caused the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight line Will use the particle
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Kinematics Describes motion while ignoring the agents that caused the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight line Will use the particle
Motion along a straight line. Physics 11a. 4 Basic Quantities in Kinematics. Motion
 Physics 11a Motion along a straight line Motion Position and Average velocity and average speed Instantaneous velocity and speed Acceleration Constant acceleration: A special case Free fall acceleration
Physics 11a Motion along a straight line Motion Position and Average velocity and average speed Instantaneous velocity and speed Acceleration Constant acceleration: A special case Free fall acceleration
Chapter 2 Describing Motion
 Chapter 2 Describing Motion Chapter 2 Overview In chapter 2, we will try to accomplish two primary goals. 1. Understand and describe the motion of objects. Define concepts like speed, velocity, acceleration,
Chapter 2 Describing Motion Chapter 2 Overview In chapter 2, we will try to accomplish two primary goals. 1. Understand and describe the motion of objects. Define concepts like speed, velocity, acceleration,
Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ]
![Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] Chapter 8 : Motion. KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ]](/thumbs/77/76428187.jpg) Chapter 8 : Motion KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] 1 Motion **** 2 Graphical Representation of Motion *** & Graphs 3 Equation of motion **** 4 Uniform Circular Motion ** 1 Motion
Chapter 8 : Motion KEY CONCEPTS [ *rating as per the significance of concept ] 1 Motion **** 2 Graphical Representation of Motion *** & Graphs 3 Equation of motion **** 4 Uniform Circular Motion ** 1 Motion
CHAPTER 2: Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension
 CHAPTER : Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension Answers to Questions 1. A car speedometer measures only speed. It does not give any information about the direction, and so does not measure velocity..
CHAPTER : Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension Answers to Questions 1. A car speedometer measures only speed. It does not give any information about the direction, and so does not measure velocity..
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension
 PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
1.5 The Derivative (2.7, 2.8 & 2.9)
 1.5. THE DERIVATIVE (2.7, 2.8 & 2.9) 47 1.5 The Derivative (2.7, 2.8 & 2.9) The concept we are about to de ne is not new. We simply give it a new name. Often in mathematics, when the same idea seems to
1.5. THE DERIVATIVE (2.7, 2.8 & 2.9) 47 1.5 The Derivative (2.7, 2.8 & 2.9) The concept we are about to de ne is not new. We simply give it a new name. Often in mathematics, when the same idea seems to
AP Physics 1 Kinematics 1D
 AP Physics 1 Kinematics 1D 1 Algebra Based Physics Kinematics in One Dimension 2015 08 25 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents: Kinematics Motion in One Dimension Position and Reference Frame Displacement
AP Physics 1 Kinematics 1D 1 Algebra Based Physics Kinematics in One Dimension 2015 08 25 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents: Kinematics Motion in One Dimension Position and Reference Frame Displacement
From last time. Light and heavy objects fall identically. Objects maintain their state of motion unless acted on by an external force.
 From last time Light and heavy objects fall identically. Objects maintain their state of motion unless acted on by an external force. I.e. either at rest, or straight line motion at constant speed This
From last time Light and heavy objects fall identically. Objects maintain their state of motion unless acted on by an external force. I.e. either at rest, or straight line motion at constant speed This
Kinematics. Chapter 2. Position-Time Graph. Position
 Kinematics Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Describes motion while ignoring the agents that caused the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight line Will use the particle
Kinematics Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Describes motion while ignoring the agents that caused the motion For now, will consider motion in one dimension Along a straight line Will use the particle
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter 2 Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter 2 Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications
Chapter 2. Motion along a Straight Line
 Chapter 2 Motion along a Straight Line 1 2.1 Motion Everything in the universe, from atoms to galaxies, is in motion. A first step to study motion is to consider simplified cases. In this chapter we study
Chapter 2 Motion along a Straight Line 1 2.1 Motion Everything in the universe, from atoms to galaxies, is in motion. A first step to study motion is to consider simplified cases. In this chapter we study
HW Chapter 3 Q 14,15 P 2,7,812,18,24,25. Chapter 3. Motion in the Universe. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 HW Chapter 3 Q 14,15 P 2,7,812,18,24,25 Chapter 3 Motion in the Universe Dr. Armen Kocharian Predictability The universe is predictable and quantifiable Motion of planets and stars description of motion
HW Chapter 3 Q 14,15 P 2,7,812,18,24,25 Chapter 3 Motion in the Universe Dr. Armen Kocharian Predictability The universe is predictable and quantifiable Motion of planets and stars description of motion
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration?
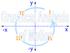 Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Chapter 1. Functions and Graphs. 1.5 More on Slope
 Chapter 1 Functions and Graphs 1.5 More on Slope 1/21 Chapter 1 Homework 1.5 p200 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 14, 16, 18, 22, 24, 26, 29, 30, 32, 46, 48 2/21 Chapter 1 Objectives Find slopes and equations of parallel
Chapter 1 Functions and Graphs 1.5 More on Slope 1/21 Chapter 1 Homework 1.5 p200 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 14, 16, 18, 22, 24, 26, 29, 30, 32, 46, 48 2/21 Chapter 1 Objectives Find slopes and equations of parallel
Measuring Motion. Day 1
 Measuring Motion Day 1 Objectives I will identify the relationship between motion and a reference point I will identify the two factors that speed depends on I will determine the difference between speed
Measuring Motion Day 1 Objectives I will identify the relationship between motion and a reference point I will identify the two factors that speed depends on I will determine the difference between speed
Physics 101 Lecture 3 Motion in 1D Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN
 Physics 101 Lecture 3 Motion in 1D Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department Motion along a straight line q Motion q Position and displacement q Average velocity and average speed q Instantaneous velocity and
Physics 101 Lecture 3 Motion in 1D Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department Motion along a straight line q Motion q Position and displacement q Average velocity and average speed q Instantaneous velocity and
A B C D. Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment
 Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension
 Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement Any measurement of position, distance, or speed must be made with respect to a reference frame. For example,
Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension 2-1 Reference Frames and Displacement Any measurement of position, distance, or speed must be made with respect to a reference frame. For example,
The Definite Integral. Day 6 Motion Problems Strategies for Finding Total Area
 The Definite Integral Day 6 Motion Problems Strategies for Finding Total Area ARRIVAL---HW Questions Working in PODS Additional Practice Packet p. 13 and 14 Make good use of your time! Practice makes perfect!
The Definite Integral Day 6 Motion Problems Strategies for Finding Total Area ARRIVAL---HW Questions Working in PODS Additional Practice Packet p. 13 and 14 Make good use of your time! Practice makes perfect!
Chapter 2. Kinematic Equations. Problem 1. Kinematic Equations, specific. Motion in One Dimension
 Kinematic Equations Chapter Motion in One Dimension The kinematic equations may be used to solve any problem involving one-dimensional motion with a constant You may need to use two of the equations to
Kinematic Equations Chapter Motion in One Dimension The kinematic equations may be used to solve any problem involving one-dimensional motion with a constant You may need to use two of the equations to
Introduction to 1-D Motion Distance versus Displacement
 Introduction to 1-D Motion Distance versus Displacement Kinematics! Kinematics is the branch of mechanics that describes the motion of objects without necessarily discussing what causes the motion.! 1-Dimensional
Introduction to 1-D Motion Distance versus Displacement Kinematics! Kinematics is the branch of mechanics that describes the motion of objects without necessarily discussing what causes the motion.! 1-Dimensional
Chapter 2 One-Dimensional Kinematics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications of
Chapter One-Dimensional Kinematics Units of Chapter Position, Distance, and Displacement Average Speed and Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion with Constant Acceleration Applications of
PHY131H1F Class 5. Clicker Question
 PHY131H1F Class 5 Today, Chapter 2, Sections 2.5 to 2.7 Freefall Acceleration due to gravity Motion on an inclined plane Differentiating velocity to get acceleration Integrating acceleration to get velocity
PHY131H1F Class 5 Today, Chapter 2, Sections 2.5 to 2.7 Freefall Acceleration due to gravity Motion on an inclined plane Differentiating velocity to get acceleration Integrating acceleration to get velocity
AP Calculus. Applications of Derivatives. Table of Contents
 AP Calculus 2015 11 03 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Related Rates Linear Motion Linear Approximation & Differentials L'Hopital's Rule Horizontal Tangents 1 Related
AP Calculus 2015 11 03 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Related Rates Linear Motion Linear Approximation & Differentials L'Hopital's Rule Horizontal Tangents 1 Related
Welcome, Physics Majors!
 For students enrolled in an introductory physics lab, PHYS 2108 and PHYS 2109 lab classes begin this week (August 20-24). You must attend the first week of class or send an email to lab@phys.lsu.edu PRIOR
For students enrolled in an introductory physics lab, PHYS 2108 and PHYS 2109 lab classes begin this week (August 20-24). You must attend the first week of class or send an email to lab@phys.lsu.edu PRIOR
INTRODUCTION & RECTILINEAR KINEMATICS: CONTINUOUS MOTION
 INTRODUCTION & RECTILINEAR KINEMATICS: CONTINUOUS MOTION (Sections 12.1-12.2) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to find the kinematic quantities (position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration)
INTRODUCTION & RECTILINEAR KINEMATICS: CONTINUOUS MOTION (Sections 12.1-12.2) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to find the kinematic quantities (position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration)
AP Calculus AB. Introduction. Slide 1 / 233 Slide 2 / 233. Slide 4 / 233. Slide 3 / 233. Slide 6 / 233. Slide 5 / 233. Limits & Continuity
 Slide 1 / 233 Slide 2 / 233 AP Calculus AB Limits & Continuity 2015-10-20 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 233 Slide 4 / 233 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Introduction The Tangent Line
Slide 1 / 233 Slide 2 / 233 AP Calculus AB Limits & Continuity 2015-10-20 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 233 Slide 4 / 233 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Introduction The Tangent Line
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line
 Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Specifically, the description of motion. Examples: The Earth orbits around
Chapter 2 Motion along a straight line 2.2 Motion We find moving objects all around us. The study of motion is called kinematics. Specifically, the description of motion. Examples: The Earth orbits around
Motion II. Goals and Introduction
 Motion II Goals and Introduction As you have probably already seen in lecture or homework, and if you ve performed the experiment Motion I, it is important to develop a strong understanding of how to model
Motion II Goals and Introduction As you have probably already seen in lecture or homework, and if you ve performed the experiment Motion I, it is important to develop a strong understanding of how to model
Forces and Motion in One Dimension. Chapter 3
 Forces and Motion in One Dimension Chapter 3 Constant velocity on an x-versus-t graph Velocity and Position In general, the average velocity is the slope of the line segment that connects the positions
Forces and Motion in One Dimension Chapter 3 Constant velocity on an x-versus-t graph Velocity and Position In general, the average velocity is the slope of the line segment that connects the positions
1. How could you determine the average speed of an object whose motion is represented in the graphs above?
 AP Physics Lesson 1 b Kinematics Graphical Analysis and Kinematic Equation Use Outcomes Interpret graphical evidence of motion (uniform speed & uniform acceleration). Apply an understanding of position
AP Physics Lesson 1 b Kinematics Graphical Analysis and Kinematic Equation Use Outcomes Interpret graphical evidence of motion (uniform speed & uniform acceleration). Apply an understanding of position
To conduct the experiment, each person in your group should be given a role:
 Varying Motion NAME In this activity, your group of 3 will collect data based on one person s motion. From this data, you will create graphs comparing displacement, velocity, and acceleration to time.
Varying Motion NAME In this activity, your group of 3 will collect data based on one person s motion. From this data, you will create graphs comparing displacement, velocity, and acceleration to time.
Chapter 2 1D KINEMATICS
 Chapter 2 1D KINEMATICS The motion of an American kestrel through the air can be described by the bird s displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration. When it flies in a straight line without any change
Chapter 2 1D KINEMATICS The motion of an American kestrel through the air can be described by the bird s displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration. When it flies in a straight line without any change
Each dot represents an object moving, between constant intervals of time. Describe the motion that you see. equation symbol: units: Velocity
 What is displacement, velocity and acceleration? what units do they have? vector vs scalar? One dimensional motion, and graphing Moving man worksheet moving man doc - todo Introduction to simple graphing
What is displacement, velocity and acceleration? what units do they have? vector vs scalar? One dimensional motion, and graphing Moving man worksheet moving man doc - todo Introduction to simple graphing
Physics 8 Monday, September 12, 2011
 Physics 8 Monday, September 12, 2011 If you didn t pick up second half of textbook (starting with Chapter 8) on Friday, you can pick it up now. The bookstore is expecting more clickers to arrive soon (tomorrow?
Physics 8 Monday, September 12, 2011 If you didn t pick up second half of textbook (starting with Chapter 8) on Friday, you can pick it up now. The bookstore is expecting more clickers to arrive soon (tomorrow?
Chapter 3. Accelerated Motion
 Chapter 3 Accelerated Motion Chapter 3 Accelerated Motion In this chapter you will: Develop descriptions of accelerated motions. Use graphs and equations to solve problems involving moving objects. Describe
Chapter 3 Accelerated Motion Chapter 3 Accelerated Motion In this chapter you will: Develop descriptions of accelerated motions. Use graphs and equations to solve problems involving moving objects. Describe
220A Solutions. Assignment 2
 220A Solutions Assignment 2 2-4. A picture is worth 1000 words. Draw an arrow from the starting to the ending point to get the displacement as follows: y x - 4.2 cm 3.4 cm x The displacement is just 7.6
220A Solutions Assignment 2 2-4. A picture is worth 1000 words. Draw an arrow from the starting to the ending point to get the displacement as follows: y x - 4.2 cm 3.4 cm x The displacement is just 7.6
UAM Paradigm Lab. Uniform Acceleration Background. X-t graph. V-t graph now. What about displacement? *Displacement method 2 9/18/2017
 9/8/07 UAM Paradigm Lab Uniform Acceleration Background Wheel down a rail Observations Dots got further apart as the wheel rolled down rail This means the change in position increased over time X-t graph
9/8/07 UAM Paradigm Lab Uniform Acceleration Background Wheel down a rail Observations Dots got further apart as the wheel rolled down rail This means the change in position increased over time X-t graph
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition
 Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 3: LINEAR MOTION This lecture will help you understand: Motion Is Relative Speed : Average and Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Free Fall Motion Is Relative
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 3: LINEAR MOTION This lecture will help you understand: Motion Is Relative Speed : Average and Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Free Fall Motion Is Relative
Review. Distance vs. Displacement Scalar vs. Vectors Speed vs. Velocity Acceleration Motion at Constant Acceleration Freefall Kinematic Equations
 Linear Motion Review Distance vs. Displacement Scalar vs. Vectors Speed vs. Velocity Acceleration Motion at Constant Acceleration Freefall Kinematic Equations Distance vs. Displacement Distance is the
Linear Motion Review Distance vs. Displacement Scalar vs. Vectors Speed vs. Velocity Acceleration Motion at Constant Acceleration Freefall Kinematic Equations Distance vs. Displacement Distance is the
Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension
 Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension Units of Chapter 2 Reference Frames and Displacement Average Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion at Constant Acceleration Solving
Chapter 2 Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension Units of Chapter 2 Reference Frames and Displacement Average Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Acceleration Motion at Constant Acceleration Solving
You know the drill: Turn in hw Pick up graded hw Name tags up Grab white boards and markers for your group
 You know the drill: Turn in hw Pick up graded hw Name tags up Grab white boards and markers for your group Missing hw from: Hamilton, Herbig, I. Singh, Midterm #1 on Tuesday, September 24th Covers: Chapter
You know the drill: Turn in hw Pick up graded hw Name tags up Grab white boards and markers for your group Missing hw from: Hamilton, Herbig, I. Singh, Midterm #1 on Tuesday, September 24th Covers: Chapter
PICK UP 1. Paper(s) 2. Sign in for attendance 3. CALCULATOR! TURN IN Any late HW!
 PICK UP 1. Paper(s) 2. Sign in for attendance 3. CALCULATOR! TURN IN Any late HW! DO NOW 1. On a half sheet of paper rearrange this equation to solve for vi a = v f v i t HW: U0 6 (Wed) Next Test: U0 Test
PICK UP 1. Paper(s) 2. Sign in for attendance 3. CALCULATOR! TURN IN Any late HW! DO NOW 1. On a half sheet of paper rearrange this equation to solve for vi a = v f v i t HW: U0 6 (Wed) Next Test: U0 Test
AP Physics I Summer Assignment. Mrs. Verdi
 AP Physics I Summer Assignment Mrs. Verdi 2015-2016 ALL STUDENTS ENROLLED IN AP PHYSICS: Please email me at averdi@leepublicschools.net before the start of school. Leave your first and last name so I know
AP Physics I Summer Assignment Mrs. Verdi 2015-2016 ALL STUDENTS ENROLLED IN AP PHYSICS: Please email me at averdi@leepublicschools.net before the start of school. Leave your first and last name so I know
A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once.
 PART III. KINEMATICS A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once. 1. rise (Δy) The vertical separation of any two points on a curve is
PART III. KINEMATICS A. VOCABULARY REVIEWS On the line, write the term that correctly completes each statement. Use each term once. 1. rise (Δy) The vertical separation of any two points on a curve is
AP Calculus AB. Slide 1 / 233. Slide 2 / 233. Slide 3 / 233. Limits & Continuity. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 233 Slide 2 / 233 AP Calculus AB Limits & Continuity 2015-10-20 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 233 Introduction The Tangent Line Problem Definition
Slide 1 / 233 Slide 2 / 233 AP Calculus AB Limits & Continuity 2015-10-20 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 233 Introduction The Tangent Line Problem Definition
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 2 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Unit 2 - Linear Motion and Graphical Analysis
 Unit 2 - Linear Motion and Graphical Analysis Motion in one dimension is particularly easy to deal with because all the information about it can be encapsulated in two variables: x, the position of the
Unit 2 - Linear Motion and Graphical Analysis Motion in one dimension is particularly easy to deal with because all the information about it can be encapsulated in two variables: x, the position of the
Using Units in Science
 Using Units in Science 5 cm x 2 cm=?10 cm 2 2 cm 2 1 How much is 150 miles divided by 3 hours? 150 miles/hr 50 miles 50 hrs 50 hrs/mile E 50 miles/hr 3 pears per orange 2 You buy 10 gallons of gas and
Using Units in Science 5 cm x 2 cm=?10 cm 2 2 cm 2 1 How much is 150 miles divided by 3 hours? 150 miles/hr 50 miles 50 hrs 50 hrs/mile E 50 miles/hr 3 pears per orange 2 You buy 10 gallons of gas and
Unit 01 Motion with constant velocity. What we asked about
 Unit 01 Motion with constant velocity Outline for this unit: Displacement, Velocity: numerically and graphically Mechanics Lecture 1, Slide 1 What we asked about Would like to see more practice problems
Unit 01 Motion with constant velocity Outline for this unit: Displacement, Velocity: numerically and graphically Mechanics Lecture 1, Slide 1 What we asked about Would like to see more practice problems
Chapter 3 Acceleration
 Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Physics 218 Lecture 2
 Physics 218 Lecture 2 Dr. David Toback Physics 218, Lecture II 1 In Class Quiz Write down the most important student case study from the Frequently Asked Questions handout Physics 218, Lecture II 2 Announcements:
Physics 218 Lecture 2 Dr. David Toback Physics 218, Lecture II 1 In Class Quiz Write down the most important student case study from the Frequently Asked Questions handout Physics 218, Lecture II 2 Announcements:
Motion Along a Straight Line (Motion in One-Dimension)
 Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line (Motion in One-Dimension) Learn the concepts of displacement, velocity, and acceleration in one-dimension. Describe motions at constant acceleration. Be able to graph
Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line (Motion in One-Dimension) Learn the concepts of displacement, velocity, and acceleration in one-dimension. Describe motions at constant acceleration. Be able to graph
AP Physics Summer Assignment
 AP Physics Summer Assignment Your Name Complete this before you show up for the first class in August. This assignment will be graded for accuracy, and there will be a test on the contents of this packet
AP Physics Summer Assignment Your Name Complete this before you show up for the first class in August. This assignment will be graded for accuracy, and there will be a test on the contents of this packet
BE SURE THAT YOU HAVE LOOKED AT, THOUGHT ABOUT AND TRIED THE SUGGESTED PROBLEMS ON THIS REVIEW GUIDE PRIOR TO LOOKING AT THESE COMMENTS!!!
 Review Guide for MAT0 Final Eam Part I. Thursday December 7 th during regular class time Part is worth 50% of your Final Eam grade. Syllabus approved calculators can be used on this part of the eam but
Review Guide for MAT0 Final Eam Part I. Thursday December 7 th during regular class time Part is worth 50% of your Final Eam grade. Syllabus approved calculators can be used on this part of the eam but
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Calculus Honors and Introduction to Calculus
 Calculus Honors and Introduction to Calculus Name: This summer packet is for students entering Calculus Honors or Introduction to Calculus in the Fall of 015. The material represents concepts and skills
Calculus Honors and Introduction to Calculus Name: This summer packet is for students entering Calculus Honors or Introduction to Calculus in the Fall of 015. The material represents concepts and skills
Advanced Placement Physics C Summer Assignment
 Advanced Placement Physics C Summer Assignment Summer Assignment Checklist: 1. Book Problems. Selected problems from Fundamentals of Physics. (Due August 31 st ). Intro to Calculus Packet. (Attached) (Due
Advanced Placement Physics C Summer Assignment Summer Assignment Checklist: 1. Book Problems. Selected problems from Fundamentals of Physics. (Due August 31 st ). Intro to Calculus Packet. (Attached) (Due
Introduction to Uncertainty and Treatment of Data
 Introduction to Uncertainty and Treatment of Data Introduction The purpose of this experiment is to familiarize the student with some of the instruments used in making measurements in the physics laboratory,
Introduction to Uncertainty and Treatment of Data Introduction The purpose of this experiment is to familiarize the student with some of the instruments used in making measurements in the physics laboratory,
 http://geocities.com/kenahn7/ Today in this class Chap.2, Sec.1-7 Motion along a straight line 1. Position and displacement 2. 3. Acceleration Example: Motion with a constant acceleration Position and
http://geocities.com/kenahn7/ Today in this class Chap.2, Sec.1-7 Motion along a straight line 1. Position and displacement 2. 3. Acceleration Example: Motion with a constant acceleration Position and
Derivation of Kinematic Equations. View this after Motion on an Incline Lab
 Derivation of Kinematic Equations View this after Motion on an Incline Lab Constant velocity Average velocity equals the slope of a position vs time graph when an object travels at constant velocity. v
Derivation of Kinematic Equations View this after Motion on an Incline Lab Constant velocity Average velocity equals the slope of a position vs time graph when an object travels at constant velocity. v
Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration AP style
 Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration AP style Linear Motion Position- the location of an object relative to a reference point. IF the position is one-dimension only, we often use the letter x to represent
Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration AP style Linear Motion Position- the location of an object relative to a reference point. IF the position is one-dimension only, we often use the letter x to represent
Lecture 2. When we studied dimensional analysis in the last lecture, I defined speed. The average speed for a traveling object is quite simply
 Lecture 2 Speed Displacement Average velocity Instantaneous velocity Cutnell+Johnson: chapter 2.1-2.2 Most physics classes start by studying the laws describing how things move around. This study goes
Lecture 2 Speed Displacement Average velocity Instantaneous velocity Cutnell+Johnson: chapter 2.1-2.2 Most physics classes start by studying the laws describing how things move around. This study goes
Jan 31 8:19 PM. Chapter 9: Uniform Rectilinear Motion
 Unit 3: Kinematics Uniform Rectilinear Motion (velocity is constant) Uniform Accelerated Rectilinear Motion The Motion of Projectiles Jan 31 8:19 PM Chapter 9: Uniform Rectilinear Motion Position: point
Unit 3: Kinematics Uniform Rectilinear Motion (velocity is constant) Uniform Accelerated Rectilinear Motion The Motion of Projectiles Jan 31 8:19 PM Chapter 9: Uniform Rectilinear Motion Position: point
Chapter 5 - Differentiating Functions
 Chapter 5 - Differentiating Functions Section 5.1 - Differentiating Functions Differentiation is the process of finding the rate of change of a function. We have proven that if f is a variable dependent
Chapter 5 - Differentiating Functions Section 5.1 - Differentiating Functions Differentiation is the process of finding the rate of change of a function. We have proven that if f is a variable dependent
Physics 1110: Mechanics
 Physics 1110: Mechanics Announcements: CAPA set available in bins. Lectures can be found at the Course Calendar link. Written homework #1 (on website) due at beginning of recitation. The Moving Man simulation
Physics 1110: Mechanics Announcements: CAPA set available in bins. Lectures can be found at the Course Calendar link. Written homework #1 (on website) due at beginning of recitation. The Moving Man simulation
Math 1241, Spring 2014 Section 3.3. Rates of Change Average vs. Instantaneous Rates
 Math 1241, Spring 2014 Section 3.3 Rates of Change Average vs. Instantaneous Rates Average Speed The concept of speed (distance traveled divided by time traveled) is a familiar instance of a rate of change.
Math 1241, Spring 2014 Section 3.3 Rates of Change Average vs. Instantaneous Rates Average Speed The concept of speed (distance traveled divided by time traveled) is a familiar instance of a rate of change.
+ at. mav x. = mv3 x 2 ma x. Exam 1--PHYS 101--F14--Chapters 1 & 2. Name: Class: Date:
 Class: Date: Exam 1--PHYS 101--F14--Chapters 1 & 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The following are not standards for time. However, which
Class: Date: Exam 1--PHYS 101--F14--Chapters 1 & 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The following are not standards for time. However, which
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Newton s Laws of Motion Chapter 2: pages 37-53 Review questions 1, 5-10, 14, 17, 21-24, 30 Peer Led Team Learning ES105x PLTL CRN 21823 Tuesdays, 7:30 to 9 PM, NS 101 Jody Berg, senior ES major who had
Newton s Laws of Motion Chapter 2: pages 37-53 Review questions 1, 5-10, 14, 17, 21-24, 30 Peer Led Team Learning ES105x PLTL CRN 21823 Tuesdays, 7:30 to 9 PM, NS 101 Jody Berg, senior ES major who had
Today s lecture. WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY Physics
 Today s lecture Units, Estimations, Graphs, Trigonometry: Units - Standards of Length, Mass, and Time Dimensional Analysis Uncertainty and significant digits Order of magnitude estimations Coordinate Systems
Today s lecture Units, Estimations, Graphs, Trigonometry: Units - Standards of Length, Mass, and Time Dimensional Analysis Uncertainty and significant digits Order of magnitude estimations Coordinate Systems
PHY131H1F - Class 7. Clicker Question
 PHY131H1F - Class 7 Today, Chapter 4, sections 4.1-4.4: Kinematics in One Dimension Kinematics in Two Dimensions Projectile Motion Relative Motion Test Tomorrow night at 6pm [Image from http://www.nap.edu/jhp/oneuniverse/motion_22-23.html
PHY131H1F - Class 7 Today, Chapter 4, sections 4.1-4.4: Kinematics in One Dimension Kinematics in Two Dimensions Projectile Motion Relative Motion Test Tomorrow night at 6pm [Image from http://www.nap.edu/jhp/oneuniverse/motion_22-23.html
Sample Questions PREPARING FOR THE AP (BC) CALCULUS EXAMINATION. tangent line, a+h. a+h
 Sample Questions PREPARING FOR THE AP (BC) CALCULUS EXAMINATION B B A B tangent line,, a f '(a) = lim h 0 f(a + h) f(a) h a+h a b b f(x) dx = lim [f(x ) x + f(x ) x + f(x ) x +...+ f(x ) x ] n a n B B
Sample Questions PREPARING FOR THE AP (BC) CALCULUS EXAMINATION B B A B tangent line,, a f '(a) = lim h 0 f(a + h) f(a) h a+h a b b f(x) dx = lim [f(x ) x + f(x ) x + f(x ) x +...+ f(x ) x ] n a n B B
Motion in 1 Dimension
 Motion in 1 Dimension Physics is all about describing motion. For now we are going to discuss motion in 1 dimension, which means either along the x axis or the y axis. To describe an object s motion, we
Motion in 1 Dimension Physics is all about describing motion. For now we are going to discuss motion in 1 dimension, which means either along the x axis or the y axis. To describe an object s motion, we
