One common method of shaping
|
|
|
- Loraine Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 L A B 7 NEWTON S LAW OF COOLING Exponential Decay One common method of shaping plastic products is to pour hot plastic resin into a mold. The resin, which was poured at a temperature of 300 F, is then cooled in a chiller system that is kept at 58 F. After cooling to an appropriate temperature, the molded product is ejected. This is done as quickly as possible to minimize cost and speed up production. Ejecting the product too quickly, however, can introduce warping or punctures. Observations The cooling process of plastic resin is an example of a process that obeys Newton s Law of Cooling. This law states that the rate of change in the temperature of an object is proportional to the difference between the object s temperature and the temperature of the surrounding medium. This relationship can be used to model the temperature of the cooling plastic with respect to time. Purpose In this lab, you will analyze the temperatures of an experiment and verify that Newton s Law of Cooling applies to the data. You will use a graphing utility to verify your results. References For more information about collecting data for an experiment on Newton s Law of Cooling, see CBL Explorations on Calculus by Meridian Creative Group. LAB 7 NEWTON S LAW OF COOLING 1
2 Data The temperature of a cup of water was taken at two-second intervals during a 44-second period and recorded in the table below. The room temperature was measured at F, and the water temperature at time t = 0 was measured at F. The time t is given in seconds and the temperature T is given in degrees Fahrenheit Temperature, T Temperature, T Temperature, T Temperature, T T Time and Temperature Temperature (in F) Time (in seconds) The data in the table and the scatter plot are stored in the graphing utility file called LAB07.92T t 2 Graphing Utility Lab Manual for Calculus
3 Exercises Name Date Class Instructor 1. Describing What Happened. Use the scatter plot to describe the rate at which the water cooled. Do you think the temperature of the water ever reached F? Why or why not? 2. Finding a General Solution. Newton s Law of Cooling can be represented mathematically by the differential equation k y L dt where y is the temperature of the object at time t, k is a proportionality constant, and L is the temperature of the surrounding medium. Find the general solution of this differential equation. Describe in real-life terms what each unknown represents. Describe what you think the general equation s arbitrary constant represents. LAB 7 NEWTON S LAW OF COOLING 3
4 3. Finding a Particular Solution. Apply the differential equation and its general solution from Exercise 2 to the temperatures of the water as described in this lab s Data. Show your work and record your results below. Describe in words what the general equation s arbitrary constant represents in the context of this experiment. Does this description confirm or contradict your description in Exercise 2? If it is a contradiction, rewrite the description. Differential equation: General solution: y Particular solution: y dt 4. Will the Water Reach Room Temperature? Does the temperature of the water ever reach room temperature? Why or why not? Explain how you determined your conclusion. If the water does reach room temperature, find the time t when this occurs. Does this result support the conclusion you drew in Exercise 1? 4 Graphing Utility Lab Manual for Calculus
5 5. First Derivative. Verbally describe the graph of the first derivative of the particular solution from Exercise 3. Graph the first derivative to verify your description. Explain what the value of the first derivative means at a time t. 6. Second Derivative. Verbally describe the graph of the second derivative of the particular solution from Exercise 3. Graph the second derivative to verify your description. Explain what the value of the second derivative means at a time t. 7. Comparing Solutions. A numerical solution of the differential equation k y L dt with respect to the temperatures of the water that is described in this lab s Data can be found using a graphing utility. Compare the numerical solution the graphing utility found to the actual temperature data. Do you think the numerical solution found using the graphing utility is a good fit to the actual temperature data? Compare the numerical solution the graphing utility found to the particular solution you found in Exercise 3. If the solutions produce different approximations of the temperature data, explain why. LAB 7 NEWTON S LAW OF COOLING 5
6 8. Cooling Plastic. Apply the differential equation and its general solution from Exercise 2 to the cooling plastic discussed in the Introduction of this lab. Is there enough information to determine the value of the proportionality constant k? If so, find its value. If not, explain what additional information is needed to determine the value of k. Differential equation: General solution: y Particular solution: y dt 9. Is Cooler Better? If speed of production is important, how could you make the cooling process go faster? Do you think this is a viable solution? Why or why not? 6 Graphing Utility Lab Manual for Calculus
The dimensions of an object tend to change when forces are
 L A B 8 STRETCHING A SPRING Hooke s Law The dimensions of an object tend to change when forces are applied to the object. For example, when opposite forces are applied to both ends of a spring, the spring
L A B 8 STRETCHING A SPRING Hooke s Law The dimensions of an object tend to change when forces are applied to the object. For example, when opposite forces are applied to both ends of a spring, the spring
To study the motion of an object under the influence
 L A B 3 FALLING OBJECTS First and Second Derivatives To study the motion of an object under the influence of gravity, we need equipment to track the motion of the object. We can use calculus to analyze
L A B 3 FALLING OBJECTS First and Second Derivatives To study the motion of an object under the influence of gravity, we need equipment to track the motion of the object. We can use calculus to analyze
Using Recursion in Models and Decision Making: Recursion Using Rate of Change IV.C Student Activity Sheet 5: Newton s Law of Cooling
 Have you ever noticed that a container of cold liquid, such as a glass of iced tea, creates condensation on the outside of the container? Or that a cup of hot coffee does not always stay hot? What happened
Have you ever noticed that a container of cold liquid, such as a glass of iced tea, creates condensation on the outside of the container? Or that a cup of hot coffee does not always stay hot? What happened
Robert Boyle ( ), who is often considered
 L A B 4 BOYLE S LAW Differentiation Robert Boyle (1627 1691), who is often considered the founder of modern chemistry, made studies of acids and bases, the calcination of metals, combustion, the nature
L A B 4 BOYLE S LAW Differentiation Robert Boyle (1627 1691), who is often considered the founder of modern chemistry, made studies of acids and bases, the calcination of metals, combustion, the nature
Project Two. James K. Peterson. March 26, Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University
 Project Two James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University March 26, 2019 Outline 1 Cooling Models 2 Estimating the Cooling Rate k 3 Typical
Project Two James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University March 26, 2019 Outline 1 Cooling Models 2 Estimating the Cooling Rate k 3 Typical
Project Two. Outline. James K. Peterson. March 27, Cooling Models. Estimating the Cooling Rate k. Typical Cooling Project Matlab Session
 Project Two James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University March 27, 2018 Outline Cooling Models Estimating the Cooling Rate k Typical Cooling
Project Two James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University March 27, 2018 Outline Cooling Models Estimating the Cooling Rate k Typical Cooling
Newton s Cooling Model in Matlab and the Cooling Project!
 Newton s Cooling Model in Matlab and the Cooling Project! James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University March 10, 2014 Outline Your Newton
Newton s Cooling Model in Matlab and the Cooling Project! James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University March 10, 2014 Outline Your Newton
Some Basic Modeling with Differential Equations
 Some Basic Modeling with Differential Equations S. F. Ellermeyer Kennesaw State University October 6, 2003 1 What is a Mathematical Model? A mathematical model is an equation or set of equations that attempt
Some Basic Modeling with Differential Equations S. F. Ellermeyer Kennesaw State University October 6, 2003 1 What is a Mathematical Model? A mathematical model is an equation or set of equations that attempt
Modeling Via Differential Equations
 Modeling Via Differential Equations S. F. Ellermeyer Kennesaw State University May 31, 2003 Abstract Mathematical modeling via differential equations is introduced. We partially follow the approach in
Modeling Via Differential Equations S. F. Ellermeyer Kennesaw State University May 31, 2003 Abstract Mathematical modeling via differential equations is introduced. We partially follow the approach in
States of Matter Part 1: Lab Stations A. Initial Observations
 States of Matter POGIL Activity Name Date Block Part 1: Lab Stations A. Initial Observations At your station you will find some solid aluminum, liquid water, and gaseous air. Observe these three objects
States of Matter POGIL Activity Name Date Block Part 1: Lab Stations A. Initial Observations At your station you will find some solid aluminum, liquid water, and gaseous air. Observe these three objects
AP Calculus AB Section 7.3: Other Differential Equations for Real-World Applications Period: Date: Practice Exercises Score: / 5 Points
 AP Calculus AB Name: Section 7.3: Other Differential Equations for Real-World Applications Period: Date: Practice Exercises Score: / 5 Points 1. Sweepstakes Problem I: You have just won a national sweepstakes!
AP Calculus AB Name: Section 7.3: Other Differential Equations for Real-World Applications Period: Date: Practice Exercises Score: / 5 Points 1. Sweepstakes Problem I: You have just won a national sweepstakes!
When designing structures like dams, many questions
 L A B 9 CONSTRUCTING AN ARCH DAM Surface Area, Volume, and Fluid Force When designing structures like dams, many questions arise. How much material will be needed to build the structure? If the material
L A B 9 CONSTRUCTING AN ARCH DAM Surface Area, Volume, and Fluid Force When designing structures like dams, many questions arise. How much material will be needed to build the structure? If the material
A population is modeled by the differential equation
 Math 2, Winter 2016 Weekly Homework #8 Solutions 9.1.9. A population is modeled by the differential equation dt = 1.2 P 1 P ). 4200 a) For what values of P is the population increasing? P is increasing
Math 2, Winter 2016 Weekly Homework #8 Solutions 9.1.9. A population is modeled by the differential equation dt = 1.2 P 1 P ). 4200 a) For what values of P is the population increasing? P is increasing
Mathematics 256 a course in differential equations for engineering students
 Mathematics 256 a course in differential equations for engineering students Chapter 1. How things cool off One physical system in which many important phenomena occur is that where an initial uneven temperature
Mathematics 256 a course in differential equations for engineering students Chapter 1. How things cool off One physical system in which many important phenomena occur is that where an initial uneven temperature
Applications. a. Make a table showing the length of licorice Latisha has left each time she gives a piece away.
 Applications. Latisha has a -inch string of licorice (LIK uh rish) to share with her friends. As each friend asks her for a piece, Latisha gives him or her half of what she has left. She doesn t eat any
Applications. Latisha has a -inch string of licorice (LIK uh rish) to share with her friends. As each friend asks her for a piece, Latisha gives him or her half of what she has left. She doesn t eat any
Exponential Growth (Doubling Time)
 Exponential Growth (Doubling Time) 4 Exponential Growth (Doubling Time) Suppose we start with a single bacterium, which divides every hour. After one hour we have 2 bacteria, after two hours we have 2
Exponential Growth (Doubling Time) 4 Exponential Growth (Doubling Time) Suppose we start with a single bacterium, which divides every hour. After one hour we have 2 bacteria, after two hours we have 2
Mathematics 132 Calculus for Physical and Life Sciences 2 Exam 3 Review Sheet April 15, 2008
 Mathematics 32 Calculus for Physical and Life Sciences 2 Eam 3 Review Sheet April 5, 2008 Sample Eam Questions - Solutions This list is much longer than the actual eam will be (to give you some idea of
Mathematics 32 Calculus for Physical and Life Sciences 2 Eam 3 Review Sheet April 5, 2008 Sample Eam Questions - Solutions This list is much longer than the actual eam will be (to give you some idea of
Newton s Law of Cooling and The Calculus Behind It Brenda Batten, T 3 Instructor
 Newton s Law of Cooling and The Calculus Behind It Brenda Batten, T 3 Instructor The rate at which an object s temperature is changing at any given time is proportional to the difference between its temperature
Newton s Law of Cooling and The Calculus Behind It Brenda Batten, T 3 Instructor The rate at which an object s temperature is changing at any given time is proportional to the difference between its temperature
Gravity Lab Introduction. Name. Date Block
 Gravity Lab Introduction Name Date Block Introduction: In this lab, computer simulation, we will investigate the factors that effect gravitational force. We know that in order to feel or see the effects
Gravity Lab Introduction Name Date Block Introduction: In this lab, computer simulation, we will investigate the factors that effect gravitational force. We know that in order to feel or see the effects
UTILIZING NEWTON S LAW OF COOLING TO CORROBORATE THE MPEMBA EFFECT
 UTILIZING NEWTON S LAW OF COOLING TO CORROBORATE THE MPEMBA EFFECT Eric Undergraduate, Junior University of Oklahoma Norman, Oklahoma 7319 1. INTRODUCTION Newton presented the Law of Cooling in a paper
UTILIZING NEWTON S LAW OF COOLING TO CORROBORATE THE MPEMBA EFFECT Eric Undergraduate, Junior University of Oklahoma Norman, Oklahoma 7319 1. INTRODUCTION Newton presented the Law of Cooling in a paper
6.5 Separable Differential Equations and Exponential Growth
 6.5 2 6.5 Separable Differential Equations and Exponential Growth The Law of Exponential Change It is well known that when modeling certain quantities, the quantity increases or decreases at a rate proportional
6.5 2 6.5 Separable Differential Equations and Exponential Growth The Law of Exponential Change It is well known that when modeling certain quantities, the quantity increases or decreases at a rate proportional
Per 5 Activity Solutions: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic Picture
 er 5 Activity Solutions: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic icture 5. How Is Temperature Related to Molecular Motion? ) Temperature Your instructor will discuss molecular motion and temperature. a) Watch
er 5 Activity Solutions: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic icture 5. How Is Temperature Related to Molecular Motion? ) Temperature Your instructor will discuss molecular motion and temperature. a) Watch
Name Date Period. Worksheet 5.5 Partial Fractions & Logistic Growth Show all work. No calculator unless stated. Multiple Choice
 Name Date Period Worksheet 5.5 Partial Fractions & Logistic Growth Show all work. No calculator unless stated. Multiple Choice 1. The spread of a disease through a community can be modeled with the logistic
Name Date Period Worksheet 5.5 Partial Fractions & Logistic Growth Show all work. No calculator unless stated. Multiple Choice 1. The spread of a disease through a community can be modeled with the logistic
CERT Educational Series Heat Transfer
 Student Lab Sheet Answer Key CERT Educational Series Heat Transfer Name Date: Are HEAT and TEMPERATURE the same thing? YES NO Heat and Temperature are not the same thing. They have different units. Heat
Student Lab Sheet Answer Key CERT Educational Series Heat Transfer Name Date: Are HEAT and TEMPERATURE the same thing? YES NO Heat and Temperature are not the same thing. They have different units. Heat
Solving differential equations (Sect. 7.4) Review: Overview of differential equations.
 Solving differential equations (Sect. 7.4 Previous class: Overview of differential equations. Exponential growth. Separable differential equations. Review: Overview of differential equations. Definition
Solving differential equations (Sect. 7.4 Previous class: Overview of differential equations. Exponential growth. Separable differential equations. Review: Overview of differential equations. Definition
Applications of First Order Differential Equation
 Dr Mansoor Alshehri King Saud University MATH204-Differential Equations Center of Excellence in Learning and Teaching 1 / 39 Orthogonal Trajectories How to Find Orthogonal Trajectories Growth and Decay
Dr Mansoor Alshehri King Saud University MATH204-Differential Equations Center of Excellence in Learning and Teaching 1 / 39 Orthogonal Trajectories How to Find Orthogonal Trajectories Growth and Decay
Exam 3 MATH Calculus I
 Trinity College December 03, 2015 MATH 131-01 Calculus I By signing below, you attest that you have neither given nor received help of any kind on this exam. Signature: Printed Name: Instructions: Show
Trinity College December 03, 2015 MATH 131-01 Calculus I By signing below, you attest that you have neither given nor received help of any kind on this exam. Signature: Printed Name: Instructions: Show
OCEAN/ESS 410. Class 3. Understanding Conductive Cooling: A Thought Experiment. Write your answers on the exercise sheet
 Class 3. Understanding Conductive Cooling: A Thought Experiment Write your answers on the exercise sheet While looking at the global bathymetry maps you will have noticed that mid-ocean ridges or ocean
Class 3. Understanding Conductive Cooling: A Thought Experiment Write your answers on the exercise sheet While looking at the global bathymetry maps you will have noticed that mid-ocean ridges or ocean
1.5. Applications. Theorem The solution of the exponential decay equation with N(0) = N 0 is N(t) = N 0 e kt.
 6 Section Objective(s): The Radioactive Decay Equation Newton s Cooling Law Salt in a Water Tanks 151 Exponential Decay 15 Applications Definition 151 The exponential decay equation for N is N = k N, k
6 Section Objective(s): The Radioactive Decay Equation Newton s Cooling Law Salt in a Water Tanks 151 Exponential Decay 15 Applications Definition 151 The exponential decay equation for N is N = k N, k
First Order Differential Equations
 First Order Differential Equations CHAPTER 7 7.1 7.2 SEPARABLE DIFFERENTIAL 7.3 DIRECTION FIELDS AND EULER S METHOD 7.4 SYSTEMS OF FIRST ORDER DIFFERENTIAL Slide 1 Exponential Growth The table indicates
First Order Differential Equations CHAPTER 7 7.1 7.2 SEPARABLE DIFFERENTIAL 7.3 DIRECTION FIELDS AND EULER S METHOD 7.4 SYSTEMS OF FIRST ORDER DIFFERENTIAL Slide 1 Exponential Growth The table indicates
Experiment 1: Measurement of Variables. Units of Measurement
 Experiment 1: Measurement of Variables Units of Measurement 1. Obtain the balance apparatus (meter stick with holes, small cup with holes, hanger, paper clips, and small binder clip), and assemble it so
Experiment 1: Measurement of Variables Units of Measurement 1. Obtain the balance apparatus (meter stick with holes, small cup with holes, hanger, paper clips, and small binder clip), and assemble it so
Math 2930 Worksheet Equilibria and Stability
 Math 2930 Worksheet Equilibria and Stabilit Week 3 September 7, 2017 Question 1. (a) Let C be the temperature (in Fahrenheit) of a cup of coffee that is cooling off to room temperature. Which of the following
Math 2930 Worksheet Equilibria and Stabilit Week 3 September 7, 2017 Question 1. (a) Let C be the temperature (in Fahrenheit) of a cup of coffee that is cooling off to room temperature. Which of the following
Lab 12 Pressure-Temperature Relationship in Gases
 Lab 12 Pressure-Temperature Relationship in Gases INTRODUCTION /PURPOSE/PLE LAB QUESTION Gases are made up of molecules that are in constant motion and exert pressure when they collide with the walls of
Lab 12 Pressure-Temperature Relationship in Gases INTRODUCTION /PURPOSE/PLE LAB QUESTION Gases are made up of molecules that are in constant motion and exert pressure when they collide with the walls of
Evaluation copy. The Molar Mass of a Volatile Liquid. computer OBJECTIVES MATERIALS
 The Molar Mass of a Volatile Liquid Computer 3 One of the properties that helps characterize a substance is its molar mass. If the substance in question is a volatile liquid, a common method to determine
The Molar Mass of a Volatile Liquid Computer 3 One of the properties that helps characterize a substance is its molar mass. If the substance in question is a volatile liquid, a common method to determine
Chapter 18. Remarks on partial differential equations
 Chapter 8. Remarks on partial differential equations If we try to analyze heat flow or vibration in a continuous system such as a building or an airplane, we arrive at a kind of infinite system of ordinary
Chapter 8. Remarks on partial differential equations If we try to analyze heat flow or vibration in a continuous system such as a building or an airplane, we arrive at a kind of infinite system of ordinary
Temperature, Thermal Energy, and Heat
 Temperature, Thermal Energy, and Heat Textbook pages 424 435 Section 10.1 Summary Before You Read We often use the terms heat and temperature interchangeably. Do you think they mean the same thing? Explain
Temperature, Thermal Energy, and Heat Textbook pages 424 435 Section 10.1 Summary Before You Read We often use the terms heat and temperature interchangeably. Do you think they mean the same thing? Explain
In the 16th century, Gerhardus Mercator ( ) CALCULUS OF THE MERCATOR MAP. Integration L A B
 L A B 10 CALCULUS OF THE MERCATOR MAP Integration In the 16th century, Gerhardus Mercator (1512 1594) designed a map unlike any other standard flat map. While a constant bearing of 45 is a curved line
L A B 10 CALCULUS OF THE MERCATOR MAP Integration In the 16th century, Gerhardus Mercator (1512 1594) designed a map unlike any other standard flat map. While a constant bearing of 45 is a curved line
3.8 Exponential Growth and Decay
 October 15, 2010 Population growth Population growth If y = f (t) is the number of individuals in a population of animals or humans at time t, then it seems reasonable to expect that the rate of growth
October 15, 2010 Population growth Population growth If y = f (t) is the number of individuals in a population of animals or humans at time t, then it seems reasonable to expect that the rate of growth
MATH 104 Practice Problems for Exam 2
 . Find the area between: MATH 4 Practice Problems for Eam (a) =, y = / +, y = / (b) y = e, y = e, = y = and the ais, for 4.. Calculate the volume obtained by rotating: (a) The region in problem a around
. Find the area between: MATH 4 Practice Problems for Eam (a) =, y = / +, y = / (b) y = e, y = e, = y = and the ais, for 4.. Calculate the volume obtained by rotating: (a) The region in problem a around
Solutions for homework 1. 1 Introduction to Differential Equations
 Solutions for homework 1 1 Introduction to Differential Equations 1.1 Differential Equation Models The phrase y is proportional to x implies that y is related to x via the equation y = kx, where k is a
Solutions for homework 1 1 Introduction to Differential Equations 1.1 Differential Equation Models The phrase y is proportional to x implies that y is related to x via the equation y = kx, where k is a
Areas of Ballots Number of Cuts Area (in. 2 )
 A C E Applications Connections Extensions Applications 1. Chen, from Problem 4.1, finds that his ballots are very small after only a few cuts. He decides to start with a larger sheet of paper. The new
A C E Applications Connections Extensions Applications 1. Chen, from Problem 4.1, finds that his ballots are very small after only a few cuts. He decides to start with a larger sheet of paper. The new
Post-Show HOT AND COLD. Gases. Liquids. Solids. After the Show. Traveling Science Shows
 Traveling Science Shows Post-Show HOT AND COLD After the Show We recently presented a Hot and Cold show at your school, and thought you and your students might like to continue investigating this topic.
Traveling Science Shows Post-Show HOT AND COLD After the Show We recently presented a Hot and Cold show at your school, and thought you and your students might like to continue investigating this topic.
Exploring Physics and Math with the CBL System
 Exploring Physics and Math with the CBL System 48 Lab Activities Using CBL and the TI-82 Chris Brueningsen Wesley Krawiec Table of Contents Preface...... 7 Preparing Lab Reports... 8 Experimental Errors...
Exploring Physics and Math with the CBL System 48 Lab Activities Using CBL and the TI-82 Chris Brueningsen Wesley Krawiec Table of Contents Preface...... 7 Preparing Lab Reports... 8 Experimental Errors...
Activity 6. Exploring the Exponential Function. Objectives. Introduction
 Objectives Activity 6 Exploring the Exponential Function Differentiate between exponential growth or decay from an equation Identify the coefficient in an equation that represents the rate of growth/decay
Objectives Activity 6 Exploring the Exponential Function Differentiate between exponential growth or decay from an equation Identify the coefficient in an equation that represents the rate of growth/decay
Chill Out: How Hot Objects Cool
 Chill Out: How Hot Objects Cool Activity 17 When you have a hot drink, you know that it gradually cools off. Newton s law of cooling provides us with a model for cooling. It states that the temperature
Chill Out: How Hot Objects Cool Activity 17 When you have a hot drink, you know that it gradually cools off. Newton s law of cooling provides us with a model for cooling. It states that the temperature
In a radioactive source containing a very large number of radioactive nuclei, it is not
 Simulated Radioactive Decay Using Dice Nuclei Purpose: In a radioactive source containing a very large number of radioactive nuclei, it is not possible to predict when any one of the nuclei will decay.
Simulated Radioactive Decay Using Dice Nuclei Purpose: In a radioactive source containing a very large number of radioactive nuclei, it is not possible to predict when any one of the nuclei will decay.
States of Matter. Changes in State
 CHAPTER 8 States of Matter LESSON 2 Changes in State What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
CHAPTER 8 States of Matter LESSON 2 Changes in State What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Some Cool ODEs. Overview. Key words. See also
 3 Some Cool ODEs C H A P T E R Temperature (degrees Fahrenheit) 80 76 72 68 64 60 0 30 60 90 120 150 Time (minutes) A room heats up in the morning, and the air conditioner in the room starts its on-off
3 Some Cool ODEs C H A P T E R Temperature (degrees Fahrenheit) 80 76 72 68 64 60 0 30 60 90 120 150 Time (minutes) A room heats up in the morning, and the air conditioner in the room starts its on-off
Period 7: Entropy and the Laws of Thermodynamics
 Name Section Period 7: Entropy and the Laws of Thermodynamics 7.1 Entropy 1) Entropy Your instructor will discuss entropy. a) What is entropy? b) Arrange the pictures of the ice cream man into a sequence
Name Section Period 7: Entropy and the Laws of Thermodynamics 7.1 Entropy 1) Entropy Your instructor will discuss entropy. a) What is entropy? b) Arrange the pictures of the ice cream man into a sequence
BUTTERFLY LAB METAMORPHOSIS & THE ENVIRONMENT. Handouts 6th & 7th Grade Science Unit EarthsBirthday.org
 METAMORPHOSIS & THE ENVIRONMENT Handouts 6th & 7th Grade Science Unit 1 800 698 4438 EarthsBirthday.org BUTTERFLY LAB CONTENTS Note: Answer Keys are in the Teacher Guide. Handout: Controlled Experiment
METAMORPHOSIS & THE ENVIRONMENT Handouts 6th & 7th Grade Science Unit 1 800 698 4438 EarthsBirthday.org BUTTERFLY LAB CONTENTS Note: Answer Keys are in the Teacher Guide. Handout: Controlled Experiment
InterActions Unit 4 Chapter 2 Sample Quiz KEY
 InterActions Unit 4 Chapter 2 Sample Quiz KEY REMEMBER exams are given for the last chapter in a unit. They are comprehensive. So practice taking the Unit 4 Chapter 1 quiz again along with this practice
InterActions Unit 4 Chapter 2 Sample Quiz KEY REMEMBER exams are given for the last chapter in a unit. They are comprehensive. So practice taking the Unit 4 Chapter 1 quiz again along with this practice
The Coffee-Turkey Juxtaposition
 The Materials TI-Nspire CX CAS handheld Vernier EasyTemp Sensor Hot water source Coffee cups Freshly cooked turkey Introduction to the Investigation Have you ever noticed that when a hot liquid is placed
The Materials TI-Nspire CX CAS handheld Vernier EasyTemp Sensor Hot water source Coffee cups Freshly cooked turkey Introduction to the Investigation Have you ever noticed that when a hot liquid is placed
The Indianapolis Motor Speedway is the host of the RACE-CAR CORNERING. Vector-Valued Functions L A B
 L A B 15 RACE-CAR CORNERING Vector-Valued Functions The Indianapolis Motor Speedway is the host of the internationally famous Indianapolis 500. The speedway has two 3300-foot-long straightaways, two 660-foot-long
L A B 15 RACE-CAR CORNERING Vector-Valued Functions The Indianapolis Motor Speedway is the host of the internationally famous Indianapolis 500. The speedway has two 3300-foot-long straightaways, two 660-foot-long
Exercises Temperature (pages ) 1. Define temperature. 2. Explain how a common liquid thermometer works.
 Exercises 21.1 Temperature (pages 407 408) 1. Define temperature. 2. Explain how a common liquid thermometer works. Match each number with the corresponding description. Temperature Description 3. 273
Exercises 21.1 Temperature (pages 407 408) 1. Define temperature. 2. Explain how a common liquid thermometer works. Match each number with the corresponding description. Temperature Description 3. 273
Molecular Motion and Gas Laws
 Molecular Motion and Gas Laws What is the connection between the motion of molecules (F = ma and K = mv 2 /2) and the thermodynamics of gases (pv = nrt and U = 3nRT/2)? In this lab, you will discover how
Molecular Motion and Gas Laws What is the connection between the motion of molecules (F = ma and K = mv 2 /2) and the thermodynamics of gases (pv = nrt and U = 3nRT/2)? In this lab, you will discover how
SWBAT: Graph exponential functions and find exponential curves of best fit
 Algebra II: Exponential Functions Objective: We will analyze exponential functions and their properties SWBAT: Graph exponential functions and find exponential curves of best fit Warm-Up 1) Solve the following
Algebra II: Exponential Functions Objective: We will analyze exponential functions and their properties SWBAT: Graph exponential functions and find exponential curves of best fit Warm-Up 1) Solve the following
Temperature * OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42214 1 Temperature * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Dene temperature. Convert temperatures
OpenStax-CNX module: m42214 1 Temperature * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Dene temperature. Convert temperatures
Solve by equating exponents
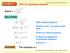 EXAMPLE 1 x Solve 4 = 1 Solve by equating exponents x 3 SOLUTION x 1 4 = x x 3 1 ( ) = ( ) x x + 3 = x = x + 3 x = 1 x 3 Write original equation. Rewrite 4 and base. 1 as powers with Power of a power property
EXAMPLE 1 x Solve 4 = 1 Solve by equating exponents x 3 SOLUTION x 1 4 = x x 3 1 ( ) = ( ) x x + 3 = x = x + 3 x = 1 x 3 Write original equation. Rewrite 4 and base. 1 as powers with Power of a power property
1.3 Exponential Functions
 22 Chapter 1 Prerequisites for Calculus 1.3 Exponential Functions What you will learn about... Exponential Growth Exponential Decay Applications The Number e and why... Exponential functions model many
22 Chapter 1 Prerequisites for Calculus 1.3 Exponential Functions What you will learn about... Exponential Growth Exponential Decay Applications The Number e and why... Exponential functions model many
Testing Newton s 2nd Law
 Testing Newton s 2nd Law Goal: To test Newton s 2nd law (ΣF = ma) and investigate the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration for objects. Lab Preparation To prepare for this lab you will want
Testing Newton s 2nd Law Goal: To test Newton s 2nd law (ΣF = ma) and investigate the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration for objects. Lab Preparation To prepare for this lab you will want
Introduction Growthequations Decay equations Forming differential equations Case studies Shifted equations Test INU0115/515 (MATHS 2)
 GROWTH AND DECAY CALCULUS 12 INU0115/515 (MATHS 2) Dr Adrian Jannetta MIMA CMath FRAS Growth and Decay 1/ 24 Adrian Jannetta Introduction Some of the simplest systems that can be modelled by differential
GROWTH AND DECAY CALCULUS 12 INU0115/515 (MATHS 2) Dr Adrian Jannetta MIMA CMath FRAS Growth and Decay 1/ 24 Adrian Jannetta Introduction Some of the simplest systems that can be modelled by differential
Differential Equations
 Chapter 7 Differential Equations 7. An Introduction to Differential Equations Motivating Questions In this section, we strive to understand the ideas generated by the following important questions: What
Chapter 7 Differential Equations 7. An Introduction to Differential Equations Motivating Questions In this section, we strive to understand the ideas generated by the following important questions: What
(1 2t), y(1) = 2 y. dy dt = t. e t y, y(0) = 1. dr, r(1) = 2 (r = r(θ)) y = t(t2 + 1) 4y 3, y(0) = 1. 2t y + t 2 y, y(0) = 2. 2t 1 + 2y, y(2) = 0
 MATH 307 Due: Problem 1 Text: 2.2.9-20 Solve the following initial value problems (this problem should mainly be a review of MATH 125). 1. y = (1 2t)y 2, y(0) = 1/6 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12.
MATH 307 Due: Problem 1 Text: 2.2.9-20 Solve the following initial value problems (this problem should mainly be a review of MATH 125). 1. y = (1 2t)y 2, y(0) = 1/6 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12.
Sec. 4.2 Logarithmic Functions
 Sec. 4.2 Logarithmic Functions The Logarithmic Function with Base a has domain all positive real numbers and is defined by Where and is the inverse function of So and Logarithms are inverses of Exponential
Sec. 4.2 Logarithmic Functions The Logarithmic Function with Base a has domain all positive real numbers and is defined by Where and is the inverse function of So and Logarithms are inverses of Exponential
DIFFERENTIATION RULES
 3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES 3.8 Exponential Growth and Decay In this section, we will: Use differentiation to solve real-life problems involving exponentially growing quantities. EXPONENTIAL
3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES 3.8 Exponential Growth and Decay In this section, we will: Use differentiation to solve real-life problems involving exponentially growing quantities. EXPONENTIAL
t. y = x x R² =
 A4-11 Model Functions finding model functions for data using technology Pre-requisites: A4-8 (polynomial functions), A4-10 (power and exponential functions) Estimated Time: 2 hours Summary Learn Solve
A4-11 Model Functions finding model functions for data using technology Pre-requisites: A4-8 (polynomial functions), A4-10 (power and exponential functions) Estimated Time: 2 hours Summary Learn Solve
Modeling with Exponential Functions
 CHAPTER Modeling with Exponential Functions A nautilus is a sea creature that lives in a shell. The cross-section of a nautilus s shell, with its spiral of ever-smaller chambers, is a natural example of
CHAPTER Modeling with Exponential Functions A nautilus is a sea creature that lives in a shell. The cross-section of a nautilus s shell, with its spiral of ever-smaller chambers, is a natural example of
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 4 MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1
 Learning outcomes EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 4 MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 TUTORIAL 2 - LINEAR EQUATIONS AND GRAPHS On completion of this unit a learner should: 1 Know how to use algebraic
Learning outcomes EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 4 MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 TUTORIAL 2 - LINEAR EQUATIONS AND GRAPHS On completion of this unit a learner should: 1 Know how to use algebraic
Seasons and Angle of Insolation
 Computer Seasons and Angle of Insolation 29 (Adapted from Exp 29 Seasons and Angle of Insolation from the Earth Science with Vernier lab manual.) Have you ever wondered why temperatures are cooler in the
Computer Seasons and Angle of Insolation 29 (Adapted from Exp 29 Seasons and Angle of Insolation from the Earth Science with Vernier lab manual.) Have you ever wondered why temperatures are cooler in the
Drill Exercise Differential equations by abhijit kumar jha DRILL EXERCISE - 1 DRILL EXERCISE - 2. e x, where c 1
 DRILL EXERCISE -. Find the order and degree (if defined) of the differential equation 5 4 3 d y d y. Find the order and degree (if defined) of the differential equation n. 3. Find the order and degree
DRILL EXERCISE -. Find the order and degree (if defined) of the differential equation 5 4 3 d y d y. Find the order and degree (if defined) of the differential equation n. 3. Find the order and degree
Math 115 Practice for Exam 1
 Math 115 Practice for Exam 1 Generated September 7, 2017 Name: Instructor: Section Number: 1. This exam has 4 questions. Note that the problems are not of equal difficulty, so you may want to skip over
Math 115 Practice for Exam 1 Generated September 7, 2017 Name: Instructor: Section Number: 1. This exam has 4 questions. Note that the problems are not of equal difficulty, so you may want to skip over
1103 Period 14 Solutions: Electric Current and Capacitance
 Name Section 1103 Period 14 Solutions: Electric Current and Capacitance Activity 14.1: How Can Electric Charge Do Work? 1) Charge does work Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates
Name Section 1103 Period 14 Solutions: Electric Current and Capacitance Activity 14.1: How Can Electric Charge Do Work? 1) Charge does work Your instructor will demonstrate a Wimshurst machine, which separates
Chapter 2.1 Relations and Functions
 Analyze and graph relations. Find functional values. Chapter 2.1 Relations and Functions We are familiar with a number line. A number line enables us to locate points, denoted by numbers, and find distances
Analyze and graph relations. Find functional values. Chapter 2.1 Relations and Functions We are familiar with a number line. A number line enables us to locate points, denoted by numbers, and find distances
201-NYB-05 - Calculus 2 MODELING WITH DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 201-NYB-05 - Calculus 2 MODELING WITH DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 1. Mixing problem. Consider a tank initially containing 100 liters of water with 20 kg of salt uniformly dissolved in the water. Suppose a solution
201-NYB-05 - Calculus 2 MODELING WITH DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 1. Mixing problem. Consider a tank initially containing 100 liters of water with 20 kg of salt uniformly dissolved in the water. Suppose a solution
Before Statement After
 Thermal Energy Thermal Energy, Temperature, and Heat What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Thermal Energy Thermal Energy, Temperature, and Heat What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Cool Off, Will Ya! Investigating Effect of Temperature Differences between Water and Environment on Cooling Rate of Water
 Ding 1 Cool Off, Will Ya! Investigating Effect of Temperature Differences between Water and Environment on Cooling Rate of Water Chunyang Ding 000844-0029 Physics HL Ms. Dossett 10 February 2014 Ding 2
Ding 1 Cool Off, Will Ya! Investigating Effect of Temperature Differences between Water and Environment on Cooling Rate of Water Chunyang Ding 000844-0029 Physics HL Ms. Dossett 10 February 2014 Ding 2
2. (12 points) Find an equation for the line tangent to the graph of f(x) =
 November 23, 2010 Name The total number of points available is 153 Throughout this test, show your work Throughout this test, you are expected to use calculus to solve problems Graphing calculator solutions
November 23, 2010 Name The total number of points available is 153 Throughout this test, show your work Throughout this test, you are expected to use calculus to solve problems Graphing calculator solutions
Exploring Substitution
 I. Introduction Exploring Substitution Math Fall 08 Lab We use the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part to evaluate a definite integral. If f is continuous on [a, b] b and F is any antiderivative of f
I. Introduction Exploring Substitution Math Fall 08 Lab We use the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part to evaluate a definite integral. If f is continuous on [a, b] b and F is any antiderivative of f
Red Hot Half-Life Modeling Nuclear Decay
 Red Hot Half-Life Modeling Nuclear Decay About this Lesson This lesson can be used in multiple places within a chemistry curriculum. It can be used with the atomic structure unit, a nuclear chemistry unit
Red Hot Half-Life Modeling Nuclear Decay About this Lesson This lesson can be used in multiple places within a chemistry curriculum. It can be used with the atomic structure unit, a nuclear chemistry unit
Thermodynamics. We can summarize the four laws of thermodynamics as follows:
 Thermodynamics Objective: To investigate the zeroth and first laws of thermodynamics. To calculate properties such as specific heat. To investigate the ideal gas law. To become familiar with basic P-V
Thermodynamics Objective: To investigate the zeroth and first laws of thermodynamics. To calculate properties such as specific heat. To investigate the ideal gas law. To become familiar with basic P-V
Math 2 Unit 4 Quadratic Functions: Modeling
 Approximate Time Frame: 2 3 Weeks Connections to Previous Learning: In Math 1, students learn how to model functions and how to interpret models of functions. Students looked at multiple representations
Approximate Time Frame: 2 3 Weeks Connections to Previous Learning: In Math 1, students learn how to model functions and how to interpret models of functions. Students looked at multiple representations
Separable Differential Equations
 Separable Differential Equations MATH 6 Calculus I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 207 Background We have previously solved differential equations of the forms: y (t) = k y(t) (exponential
Separable Differential Equations MATH 6 Calculus I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 207 Background We have previously solved differential equations of the forms: y (t) = k y(t) (exponential
Numerical Methods. Exponential and Logarithmic functions. Jaesung Lee
 Numerical Methods Exponential and Logarithmic functions Jaesung Lee Exponential Function Exponential Function Introduction We consider how the expression is defined when is a positive number and is irrational.
Numerical Methods Exponential and Logarithmic functions Jaesung Lee Exponential Function Exponential Function Introduction We consider how the expression is defined when is a positive number and is irrational.
Electrostatic Interactions (This lab is adapted from Chapter 1of Electric and Magnetic Interactions, Chabay and Sherwood, 1995.)
 Name: Partner(s): 1118 section: Desk # Date: Electrostatic Interactions (This lab is adapted from Chapter 1of Electric and Magnetic Interactions, Chabay and Sherwood, 1995.) Purpose To investigate the
Name: Partner(s): 1118 section: Desk # Date: Electrostatic Interactions (This lab is adapted from Chapter 1of Electric and Magnetic Interactions, Chabay and Sherwood, 1995.) Purpose To investigate the
An equation of the form y = ab x where a 0 and the base b is a positive. x-axis (equation: y = 0) set of all real numbers
 Algebra 2 Notes Section 7.1: Graph Exponential Growth Functions Objective(s): To graph and use exponential growth functions. Vocabulary: I. Exponential Function: An equation of the form y = ab x where
Algebra 2 Notes Section 7.1: Graph Exponential Growth Functions Objective(s): To graph and use exponential growth functions. Vocabulary: I. Exponential Function: An equation of the form y = ab x where
Modeling with First-Order Equations
 Modeling with First-Order Equations MATH 365 Ordinary Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Radioactive Decay Radioactive decay takes place continuously. The number
Modeling with First-Order Equations MATH 365 Ordinary Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Radioactive Decay Radioactive decay takes place continuously. The number
EGR 111 Heat Transfer
 EGR 111 Heat Transfer The purpose of this lab is to use MATLAB to determine the heat transfer in a 1-dimensional system. New MATLAB commands: (none) 1. Heat Transfer 101 Heat Transfer is thermal energy
EGR 111 Heat Transfer The purpose of this lab is to use MATLAB to determine the heat transfer in a 1-dimensional system. New MATLAB commands: (none) 1. Heat Transfer 101 Heat Transfer is thermal energy
Math 2300 Calculus II University of Colorado Final exam review problems
 Math 300 Calculus II University of Colorado Final exam review problems. A slope field for the differential equation y = y e x is shown. Sketch the graphs of the solutions that satisfy the given initial
Math 300 Calculus II University of Colorado Final exam review problems. A slope field for the differential equation y = y e x is shown. Sketch the graphs of the solutions that satisfy the given initial
Integration, Separation of Variables
 Week #1 : Integration, Separation of Variables Goals: Introduce differential equations. Review integration techniques. Solve first-order DEs using separation of variables. 1 Sources of Differential Equations
Week #1 : Integration, Separation of Variables Goals: Introduce differential equations. Review integration techniques. Solve first-order DEs using separation of variables. 1 Sources of Differential Equations
Elementay Math Models EMM Worksheet: Logistic Growth
 Elementay Math Models EMM Worksheet: Logistic Growth This worksheet discusses 5 sample models that will give you some practice working with the ideas of logistic growth. The basic framework for each model
Elementay Math Models EMM Worksheet: Logistic Growth This worksheet discusses 5 sample models that will give you some practice working with the ideas of logistic growth. The basic framework for each model
METAMORPHIC AUREOLE. Purpose To show how the temperature changes in the rocks adjacent to an intrusion as the intrusion cools.
 METAMORPHIC AUREOLE Purpose To show how the temperature changes in the rocks adjacent to an intrusion as the intrusion cools. Activity The sand represents the country rock and the hot water the intrusion.
METAMORPHIC AUREOLE Purpose To show how the temperature changes in the rocks adjacent to an intrusion as the intrusion cools. Activity The sand represents the country rock and the hot water the intrusion.
Calorimetry and heat capacitance
 (ta initials) first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experiment 1 Calorimetry and heat capacitance In this Experiment you will learn some basic methods of heat exchange between
(ta initials) first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experiment 1 Calorimetry and heat capacitance In this Experiment you will learn some basic methods of heat exchange between
Section 6.8 Exponential Models; Newton's Law of Cooling; Logistic Models
 Section 6.8 Exponential Models; Newton's Law of Cooling; Logistic Models 197 Objective #1: Find Equations of Populations that Obey the Law of Uninhibited Growth. In the last section, we saw that when interest
Section 6.8 Exponential Models; Newton's Law of Cooling; Logistic Models 197 Objective #1: Find Equations of Populations that Obey the Law of Uninhibited Growth. In the last section, we saw that when interest
Identify the graph of a function, and obtain information from or about the graph of a function.
 PS 1 Graphs: Graph equations using rectangular coordinates and graphing utilities, find intercepts, discuss symmetry, graph key equations, solve equations using a graphing utility, work with lines and
PS 1 Graphs: Graph equations using rectangular coordinates and graphing utilities, find intercepts, discuss symmetry, graph key equations, solve equations using a graphing utility, work with lines and
Period 5: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic Picture
 Name Section Period 5: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic Picture 5.1 How Is Temperature Related to Molecular Motion? 1) Temperature Your instructor will discuss molecular motion and temperature. a) At a
Name Section Period 5: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic Picture 5.1 How Is Temperature Related to Molecular Motion? 1) Temperature Your instructor will discuss molecular motion and temperature. a) At a
MATH 104 Practice Problems for Exam 2
 . Find the area between: MATH 4 Practice Problems for Exam (a) x =, y = / + x, y = x/ Answer: ln( + ) 4 (b) y = e x, y = xe x, x = Answer: e6 4 7 4 (c) y = x and the x axis, for x 4. x Answer: ln 5. Calculate
. Find the area between: MATH 4 Practice Problems for Exam (a) x =, y = / + x, y = x/ Answer: ln( + ) 4 (b) y = e x, y = xe x, x = Answer: e6 4 7 4 (c) y = x and the x axis, for x 4. x Answer: ln 5. Calculate
Temperature Project. Lab: Section K. Masahiro Inano Christopher Casey Adam Tigue
 Temperature Project Lab: Section K Masahiro Inano Christopher Casey Adam Tigue 5/06/2010 Description: For our project a container of instant tomato soup was microwaved according to the given instructions.
Temperature Project Lab: Section K Masahiro Inano Christopher Casey Adam Tigue 5/06/2010 Description: For our project a container of instant tomato soup was microwaved according to the given instructions.
dq = λa T Direction of heat flow dq = λa T h T c
 THERMAL PHYSIS LABORATORY: INVESTIGATION OF NEWTON S LAW OF OOLING Along a well-insulated bar (i.e., heat loss from the sides can be neglected), it is experimentally observed that the rate of heat flow
THERMAL PHYSIS LABORATORY: INVESTIGATION OF NEWTON S LAW OF OOLING Along a well-insulated bar (i.e., heat loss from the sides can be neglected), it is experimentally observed that the rate of heat flow
Applications of Exponential Functions Group Activity 7 STEM Project Week #10
 Applications of Exponential Functions Group Activity 7 STEM Project Week #10 In the last activity we looked at exponential functions. We looked at an example of a population growing at a certain rate.
Applications of Exponential Functions Group Activity 7 STEM Project Week #10 In the last activity we looked at exponential functions. We looked at an example of a population growing at a certain rate.
Integration by Partial Fractions
 Integration by Partial Fractions 1. If f(x) = P(x) / Q(x) with P(x) and Q(x) polynomials AND Q(x) a higher order than P(x) AND Q(x) factorable in linear factors then we can rewrite f(x) as a sum of rational
Integration by Partial Fractions 1. If f(x) = P(x) / Q(x) with P(x) and Q(x) polynomials AND Q(x) a higher order than P(x) AND Q(x) factorable in linear factors then we can rewrite f(x) as a sum of rational
