Lecture 17: The Exponential and Some Related Distributions
|
|
|
- Rosamond McKenzie
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 7: The Exponential and Some Related Distributions. Definition Definition: A continuous random variable X is said to have the exponential distribution with parameter if the density of X is e x if x > px) otherwise. In this case, a simple calculation confirms that calculated explicitly: px)dx. Also, the CDF of X can be F X x) P{X x} e x. x e y dy 2.) Moments The moments of the exponential distribution can be calculated recursively using integration-byparts. Let X be an exponential random variable with parameter. Then E [ X n] x n e x dx x n e x + + n n E[ X n ] n! n, x n e x dx nx n e dx using the fact that E [ X ]. Taking n and then n 2 gives: E[X] V arx) E [ X 2] E[X] Thus, the mean of an exponential random variable is equal to the reciprocal of its parameter, while the variance is equal to the mean squared.
2 3.) Memorylessness An important property of the exponential distribution is that it is memoryless: if X is exponentially distributed with parameter, then for all t, s, P{X > t + s X > t} P{X > s}. To verify this, use the CDF calculated above to obtain and then calculate P{X > t} P{X t} e t, P{X > t + s X > t} P{X > t + s} P{X > t} e t+s e t e s P{X > s}. In other words, if we think of X as being the random) time until some event occurs, then conditional on the event not having occurred by time t, i.e., on X > t, the distribution of the time remaining until the event does occur, X t, is also exponential with parameter. It is as if the conditional probability of the event occurring between times t and t + s has no memory of the amount of time that has elapsed up to that point. Remarkably, the converse of this statement is also true. Proposition: Suppose that X is a continuous random variable with values in [, ). Then X is memoryless if and only X is exponentially distributed for some parameter >. Proof: See footnote on pg. 2 of Ross. 4.) Interpretation: Exponential random variables are often used to model the distribution of the amount of time elapsed until some particular event occurs. In this case, the memorylessness property implies that the likelihood that the event occurs in some short interval [t, t + δt) conditional on it not yet having occurred does not depend on t. Notice that for events that occur at discrete times, the geometric distribution has a similar property: the probability of observing the event in question on any particular trial given that it has not yet occurred is just p. In fact, the exponential distribution can be thought of as a limiting case for the geometric distribution when the success probability p is small and when time is measured in units that are of size /p. Proposition: For each n, let X n be a geometric random variable with parameter /n. Then, for every t, lim n P{X n nt} e t. Proof: First, recall that lim nx e n n) x. 2
3 The result can then be deduced by writing x k/n below and approximating the sum by an integral with respect to x: P{X n nt} n nt k n ) k n n nt k nt k t e x dx e t. n) n k/n e k/n Remark: This proposition implies that if X n is geometric with parameter /n, then the distribution of the random variable T n n X n is approximately exponential with parameter when n is large. 5.) The Gamma Distribution Definition: A random variable X is said to have the gamma distribution with parameters α, > if its density is α Γα) xα e x if x > px) otherwise, where the gamma function Γα) is defined for α > ) by the formula Γα) y α e y dy. Remark: Notice that the exponential distribution with parameter is identical to the gamma distribution with parameters, ). Later we will show that if X,, X n are independent exponential RVs, each with parameter, then the sum X X + + X n is a gamma RV with parameters n, ). Because of this relationship, the gamma distribution is often used to model life spans. Moments: Integration by parts shows that for α >, the gamma function satisfies the following important recursion: Γα) y α e y + α ) y α 2 e y dy α )Γα ). 3
4 In particular, if α n is a positive integer, then because we obtain Γ) e y dy, Γn) n )Γn 2) n )n 2)Γn 3) n )n 2) 3 2Γ) n )!. This recursion can be used to calculate the moments of the gamma distribution. If X has the gamma distribution with parameters α, ), then E[X n ] x n α n Γn + α) Γα) Γα) xα e x dx n n α + k). k In particular, taking n and n 2 gives n+α Γn + α) xn+α e x dx E[X] α V arx) E[X 2 ] E[X] 2 α 2. αα + ) 2 α2 2 6.) The Beta Distribution Definition: A random variable X is said to have the beta distribution with parameters a, b > if its density is βa,b) xa x) b if x, ) px) otherwise, where the beta function βa, b) is defined for a, b > ) by the formula βa, b) x a x) b dx. 4
5 Remark: Notice that if a b, then X is simply a standard uniform random variable. Also, if X and X 2 are independent gamma-distributed RVs with parameters a, θ) and b, θ), respectively, then the random variable X X /X + X 2 ) is beta-distributed with parameters a, b). In particular, if X and X 2 are independent exponential RVs with parameter, then X X /X + X 2 ) is uniformly distributed on [, ]. The beta distribution is often used to model the distribution of frequencies. Moments: It can be shown that the beta function and the gamma function are related by the following identity: βa, b) Γa)Γb) Γa + b). In turn, we can use this identity to evaluate the moments of the beta distribution. Let X be a beta random variable with parameters a, b). Then E[X n ] x n x a x) b dx βa, b) βn + a, b) βa, b) Γn + a)γb) Γa + b) Γn + a + b) Γa)Γb) Γn + a) Γa + b) Γa) Γn + a + b) n k a + k a + b + k. Taking n and n 2 gives E[X] a a + b V arx) E[X 2 ] E[X] 2 aa + ) a + b)a + b + ) a2 a + b) 2 ab a + b) 2 a + b + ). 5
Things to remember when learning probability distributions:
 SPECIAL DISTRIBUTIONS Some distributions are special because they are useful They include: Poisson, exponential, Normal (Gaussian), Gamma, geometric, negative binomial, Binomial and hypergeometric distributions
SPECIAL DISTRIBUTIONS Some distributions are special because they are useful They include: Poisson, exponential, Normal (Gaussian), Gamma, geometric, negative binomial, Binomial and hypergeometric distributions
Exponential Distribution and Poisson Process
 Exponential Distribution and Poisson Process Stochastic Processes - Lecture Notes Fatih Cavdur to accompany Introduction to Probability Models by Sheldon M. Ross Fall 215 Outline Introduction Exponential
Exponential Distribution and Poisson Process Stochastic Processes - Lecture Notes Fatih Cavdur to accompany Introduction to Probability Models by Sheldon M. Ross Fall 215 Outline Introduction Exponential
Continuous Random Variables and Continuous Distributions
 Continuous Random Variables and Continuous Distributions Continuous Random Variables and Continuous Distributions Expectation & Variance of Continuous Random Variables ( 5.2) The Uniform Random Variable
Continuous Random Variables and Continuous Distributions Continuous Random Variables and Continuous Distributions Expectation & Variance of Continuous Random Variables ( 5.2) The Uniform Random Variable
Chapter 3.3 Continuous distributions
 Chapter 3.3 Continuous distributions In this section we study several continuous distributions and their properties. Here are a few, classified by their support S X. There are of course many, many more.
Chapter 3.3 Continuous distributions In this section we study several continuous distributions and their properties. Here are a few, classified by their support S X. There are of course many, many more.
Probability. Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition. Chris Williams. School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh. August 2014
 Probability Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition Chris Williams School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh August 2014 (All of the slides in this course have been adapted from previous versions
Probability Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition Chris Williams School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh August 2014 (All of the slides in this course have been adapted from previous versions
Math 180A. Lecture 16 Friday May 7 th. Expectation. Recall the three main probability density functions so far (1) Uniform (2) Exponential.
 Math 8A Lecture 6 Friday May 7 th Epectation Recall the three main probability density functions so far () Uniform () Eponential (3) Power Law e, ( ), Math 8A Lecture 6 Friday May 7 th Epectation Eample
Math 8A Lecture 6 Friday May 7 th Epectation Recall the three main probability density functions so far () Uniform () Eponential (3) Power Law e, ( ), Math 8A Lecture 6 Friday May 7 th Epectation Eample
Part IA Probability. Definitions. Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua. Lent 2015
 Part IA Probability Definitions Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
Part IA Probability Definitions Based on lectures by R. Weber Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2015 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly) after lectures.
The exponential distribution and the Poisson process
 The exponential distribution and the Poisson process 1-1 Exponential Distribution: Basic Facts PDF f(t) = { λe λt, t 0 0, t < 0 CDF Pr{T t) = 0 t λe λu du = 1 e λt (t 0) Mean E[T] = 1 λ Variance Var[T]
The exponential distribution and the Poisson process 1-1 Exponential Distribution: Basic Facts PDF f(t) = { λe λt, t 0 0, t < 0 CDF Pr{T t) = 0 t λe λu du = 1 e λt (t 0) Mean E[T] = 1 λ Variance Var[T]
Continuous Distributions
 A normal distribution and other density functions involving exponential forms play the most important role in probability and statistics. They are related in a certain way, as summarized in a diagram later
A normal distribution and other density functions involving exponential forms play the most important role in probability and statistics. They are related in a certain way, as summarized in a diagram later
Chapter 5. Chapter 5 sections
 1 / 43 sections Discrete univariate distributions: 5.2 Bernoulli and Binomial distributions Just skim 5.3 Hypergeometric distributions 5.4 Poisson distributions Just skim 5.5 Negative Binomial distributions
1 / 43 sections Discrete univariate distributions: 5.2 Bernoulli and Binomial distributions Just skim 5.3 Hypergeometric distributions 5.4 Poisson distributions Just skim 5.5 Negative Binomial distributions
18.440: Lecture 28 Lectures Review
 18.440: Lecture 28 Lectures 18-27 Review Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Outline It s the coins, stupid Much of what we have done in this course can be motivated by the i.i.d. sequence X i where each X i is
18.440: Lecture 28 Lectures 18-27 Review Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Outline It s the coins, stupid Much of what we have done in this course can be motivated by the i.i.d. sequence X i where each X i is
2 Random Variable Generation
 2 Random Variable Generation Most Monte Carlo computations require, as a starting point, a sequence of i.i.d. random variables with given marginal distribution. We describe here some of the basic methods
2 Random Variable Generation Most Monte Carlo computations require, as a starting point, a sequence of i.i.d. random variables with given marginal distribution. We describe here some of the basic methods
Exponential & Gamma Distributions
 Exponential & Gamma Distributions Engineering Statistics Section 4.4 Josh Engwer TTU 7 March 26 Josh Engwer (TTU) Exponential & Gamma Distributions 7 March 26 / 2 PART I PART I: EXPONENTIAL DISTRIBUTION
Exponential & Gamma Distributions Engineering Statistics Section 4.4 Josh Engwer TTU 7 March 26 Josh Engwer (TTU) Exponential & Gamma Distributions 7 March 26 / 2 PART I PART I: EXPONENTIAL DISTRIBUTION
Probability Density Functions
 Probability Density Functions Probability Density Functions Definition Let X be a continuous rv. Then a probability distribution or probability density function (pdf) of X is a function f (x) such that
Probability Density Functions Probability Density Functions Definition Let X be a continuous rv. Then a probability distribution or probability density function (pdf) of X is a function f (x) such that
1 Probability and Random Variables
 1 Probability and Random Variables The models that you have seen thus far are deterministic models. For any time t, there is a unique solution X(t). On the other hand, stochastic models will result in
1 Probability and Random Variables The models that you have seen thus far are deterministic models. For any time t, there is a unique solution X(t). On the other hand, stochastic models will result in
Moments. Raw moment: February 25, 2014 Normalized / Standardized moment:
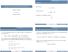 Moments Lecture 10: Central Limit Theorem and CDFs Sta230 / Mth 230 Colin Rundel Raw moment: Central moment: µ n = EX n ) µ n = E[X µ) 2 ] February 25, 2014 Normalized / Standardized moment: µ n σ n Sta230
Moments Lecture 10: Central Limit Theorem and CDFs Sta230 / Mth 230 Colin Rundel Raw moment: Central moment: µ n = EX n ) µ n = E[X µ) 2 ] February 25, 2014 Normalized / Standardized moment: µ n σ n Sta230
Probability and Distributions
 Probability and Distributions What is a statistical model? A statistical model is a set of assumptions by which the hypothetical population distribution of data is inferred. It is typically postulated
Probability and Distributions What is a statistical model? A statistical model is a set of assumptions by which the hypothetical population distribution of data is inferred. It is typically postulated
Distributions of Functions of Random Variables. 5.1 Functions of One Random Variable
 Distributions of Functions of Random Variables 5.1 Functions of One Random Variable 5.2 Transformations of Two Random Variables 5.3 Several Random Variables 5.4 The Moment-Generating Function Technique
Distributions of Functions of Random Variables 5.1 Functions of One Random Variable 5.2 Transformations of Two Random Variables 5.3 Several Random Variables 5.4 The Moment-Generating Function Technique
Continuous Random Variables
 Continuous Random Variables Recall: For discrete random variables, only a finite or countably infinite number of possible values with positive probability. Often, there is interest in random variables
Continuous Random Variables Recall: For discrete random variables, only a finite or countably infinite number of possible values with positive probability. Often, there is interest in random variables
Stat 426 : Homework 1.
 Stat 426 : Homework 1. Moulinath Banerjee University of Michigan Announcement: The homework carries 120 points and contributes 10 points to the total grade. (1) A geometric random variable W takes values
Stat 426 : Homework 1. Moulinath Banerjee University of Michigan Announcement: The homework carries 120 points and contributes 10 points to the total grade. (1) A geometric random variable W takes values
Math Spring Practice for the Second Exam.
 Math 4 - Spring 27 - Practice for the Second Exam.. Let X be a random variable and let F X be the distribution function of X: t < t 2 t < 4 F X (t) : + t t < 2 2 2 2 t < 4 t. Find P(X ), P(X ), P(X 2),
Math 4 - Spring 27 - Practice for the Second Exam.. Let X be a random variable and let F X be the distribution function of X: t < t 2 t < 4 F X (t) : + t t < 2 2 2 2 t < 4 t. Find P(X ), P(X ), P(X 2),
Topic 4: Continuous random variables
 Topic 4: Continuous random variables Course 3, 216 Page Continuous random variables Definition (Continuous random variable): An r.v. X has a continuous distribution if there exists a non-negative function
Topic 4: Continuous random variables Course 3, 216 Page Continuous random variables Definition (Continuous random variable): An r.v. X has a continuous distribution if there exists a non-negative function
1 Review of Probability and Distributions
 Random variables. A numerically valued function X of an outcome ω from a sample space Ω X : Ω R : ω X(ω) is called a random variable (r.v.), and usually determined by an experiment. We conventionally denote
Random variables. A numerically valued function X of an outcome ω from a sample space Ω X : Ω R : ω X(ω) is called a random variable (r.v.), and usually determined by an experiment. We conventionally denote
Chapter 12: Differentiation. SSMth2: Basic Calculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Strands Mr. Migo M.
 Chapter 12: Differentiation SSMth2: Basic Calculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Strands Mr. Migo M. Mendoza Chapter 12: Differentiation Lecture 12.1: The Derivative Lecture
Chapter 12: Differentiation SSMth2: Basic Calculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Strands Mr. Migo M. Mendoza Chapter 12: Differentiation Lecture 12.1: The Derivative Lecture
n! (k 1)!(n k)! = F (X) U(0, 1). (x, y) = n(n 1) ( F (y) F (x) ) n 2
 Order statistics Ex. 4. (*. Let independent variables X,..., X n have U(0, distribution. Show that for every x (0,, we have P ( X ( < x and P ( X (n > x as n. Ex. 4.2 (**. By using induction or otherwise,
Order statistics Ex. 4. (*. Let independent variables X,..., X n have U(0, distribution. Show that for every x (0,, we have P ( X ( < x and P ( X (n > x as n. Ex. 4.2 (**. By using induction or otherwise,
Topic 4: Continuous random variables
 Topic 4: Continuous random variables Course 003, 2018 Page 0 Continuous random variables Definition (Continuous random variable): An r.v. X has a continuous distribution if there exists a non-negative
Topic 4: Continuous random variables Course 003, 2018 Page 0 Continuous random variables Definition (Continuous random variable): An r.v. X has a continuous distribution if there exists a non-negative
Chapter 5 continued. Chapter 5 sections
 Chapter 5 sections Discrete univariate distributions: 5.2 Bernoulli and Binomial distributions Just skim 5.3 Hypergeometric distributions 5.4 Poisson distributions Just skim 5.5 Negative Binomial distributions
Chapter 5 sections Discrete univariate distributions: 5.2 Bernoulli and Binomial distributions Just skim 5.3 Hypergeometric distributions 5.4 Poisson distributions Just skim 5.5 Negative Binomial distributions
3 Continuous Random Variables
 Jinguo Lian Math437 Notes January 15, 016 3 Continuous Random Variables Remember that discrete random variables can take only a countable number of possible values. On the other hand, a continuous random
Jinguo Lian Math437 Notes January 15, 016 3 Continuous Random Variables Remember that discrete random variables can take only a countable number of possible values. On the other hand, a continuous random
Continuous random variables
 Continuous random variables Continuous r.v. s take an uncountably infinite number of possible values. Examples: Heights of people Weights of apples Diameters of bolts Life lengths of light-bulbs We cannot
Continuous random variables Continuous r.v. s take an uncountably infinite number of possible values. Examples: Heights of people Weights of apples Diameters of bolts Life lengths of light-bulbs We cannot
Statistics (1): Estimation
 Statistics (1): Estimation Marco Banterlé, Christian Robert and Judith Rousseau Practicals 2014-2015 L3, MIDO, Université Paris Dauphine 1 Table des matières 1 Random variables, probability, expectation
Statistics (1): Estimation Marco Banterlé, Christian Robert and Judith Rousseau Practicals 2014-2015 L3, MIDO, Université Paris Dauphine 1 Table des matières 1 Random variables, probability, expectation
APPM/MATH 4/5520 Solutions to Problem Set Two. = 2 y = y 2. e 1 2 x2 1 = 1. (g 1
 APPM/MATH 4/552 Solutions to Problem Set Two. Let Y X /X 2 and let Y 2 X 2. (We can select Y 2 to be anything but when dealing with a fraction for Y, it is usually convenient to set Y 2 to be the denominator.)
APPM/MATH 4/552 Solutions to Problem Set Two. Let Y X /X 2 and let Y 2 X 2. (We can select Y 2 to be anything but when dealing with a fraction for Y, it is usually convenient to set Y 2 to be the denominator.)
Lecture 2: Conjugate priors
 (Spring ʼ) Lecture : Conjugate priors Julia Hockenmaier juliahmr@illinois.edu Siebel Center http://www.cs.uiuc.edu/class/sp/cs98jhm The binomial distribution If p is the probability of heads, the probability
(Spring ʼ) Lecture : Conjugate priors Julia Hockenmaier juliahmr@illinois.edu Siebel Center http://www.cs.uiuc.edu/class/sp/cs98jhm The binomial distribution If p is the probability of heads, the probability
Stat410 Probability and Statistics II (F16)
 Stat4 Probability and Statistics II (F6 Exponential, Poisson and Gamma Suppose on average every /λ hours, a Stochastic train arrives at the Random station. Further we assume the waiting time between two
Stat4 Probability and Statistics II (F6 Exponential, Poisson and Gamma Suppose on average every /λ hours, a Stochastic train arrives at the Random station. Further we assume the waiting time between two
Lecture 3. Probability - Part 2. Luigi Freda. ALCOR Lab DIAG University of Rome La Sapienza. October 19, 2016
 Lecture 3 Probability - Part 2 Luigi Freda ALCOR Lab DIAG University of Rome La Sapienza October 19, 2016 Luigi Freda ( La Sapienza University) Lecture 3 October 19, 2016 1 / 46 Outline 1 Common Continuous
Lecture 3 Probability - Part 2 Luigi Freda ALCOR Lab DIAG University of Rome La Sapienza October 19, 2016 Luigi Freda ( La Sapienza University) Lecture 3 October 19, 2016 1 / 46 Outline 1 Common Continuous
Continuous random variables and probability distributions
 and probability distributions Sta. 113 Chapter 4 of Devore March 12, 2010 Table of contents 1 2 Mathematical definition Definition A random variable X is continuous if its set of possible values is an
and probability distributions Sta. 113 Chapter 4 of Devore March 12, 2010 Table of contents 1 2 Mathematical definition Definition A random variable X is continuous if its set of possible values is an
IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models. Professor Whitt. SOLUTIONS to Homework Assignment 2
 IEOR 316: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Homework Assignment 2 More Probability Review: In the Ross textbook, Introduction to Probability Models, read
IEOR 316: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Homework Assignment 2 More Probability Review: In the Ross textbook, Introduction to Probability Models, read
Expected Values, Exponential and Gamma Distributions
 Expected Values, Exponential and Gamma Distributions Sections 5.2-5.4 Cathy Poliak, Ph.D. cathy@math.uh.edu Office in Fleming 11c Department of Mathematics University of Houston Lecture 14-3339 Cathy Poliak,
Expected Values, Exponential and Gamma Distributions Sections 5.2-5.4 Cathy Poliak, Ph.D. cathy@math.uh.edu Office in Fleming 11c Department of Mathematics University of Houston Lecture 14-3339 Cathy Poliak,
Brief Review of Probability
 Maura Department of Economics and Finance Università Tor Vergata Outline 1 Distribution Functions Quantiles and Modes of a Distribution 2 Example 3 Example 4 Distributions Outline Distribution Functions
Maura Department of Economics and Finance Università Tor Vergata Outline 1 Distribution Functions Quantiles and Modes of a Distribution 2 Example 3 Example 4 Distributions Outline Distribution Functions
PCMI Introduction to Random Matrix Theory Handout # REVIEW OF PROBABILITY THEORY. Chapter 1 - Events and Their Probabilities
 PCMI 207 - Introduction to Random Matrix Theory Handout #2 06.27.207 REVIEW OF PROBABILITY THEORY Chapter - Events and Their Probabilities.. Events as Sets Definition (σ-field). A collection F of subsets
PCMI 207 - Introduction to Random Matrix Theory Handout #2 06.27.207 REVIEW OF PROBABILITY THEORY Chapter - Events and Their Probabilities.. Events as Sets Definition (σ-field). A collection F of subsets
1.1 Review of Probability Theory
 1.1 Review of Probability Theory Angela Peace Biomathemtics II MATH 5355 Spring 2017 Lecture notes follow: Allen, Linda JS. An introduction to stochastic processes with applications to biology. CRC Press,
1.1 Review of Probability Theory Angela Peace Biomathemtics II MATH 5355 Spring 2017 Lecture notes follow: Allen, Linda JS. An introduction to stochastic processes with applications to biology. CRC Press,
Lecture 5: Moment generating functions
 Lecture 5: Moment generating functions Definition 2.3.6. The moment generating function (mgf) of a random variable X is { x e tx f M X (t) = E(e tx X (x) if X has a pmf ) = etx f X (x)dx if X has a pdf
Lecture 5: Moment generating functions Definition 2.3.6. The moment generating function (mgf) of a random variable X is { x e tx f M X (t) = E(e tx X (x) if X has a pmf ) = etx f X (x)dx if X has a pdf
Let X be a continuous random variable, < X < f(x) is the so called probability density function (pdf) if
 University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 1A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Continuous probability distributions Let X be a continuous random variable, < X < f(x) is the so
University of California, Los Angeles Department of Statistics Statistics 1A Instructor: Nicolas Christou Continuous probability distributions Let X be a continuous random variable, < X < f(x) is the so
STA 256: Statistics and Probability I
 Al Nosedal. University of Toronto. Fall 2017 My momma always said: Life was like a box of chocolates. You never know what you re gonna get. Forrest Gump. Exercise 4.1 Let X be a random variable with p(x)
Al Nosedal. University of Toronto. Fall 2017 My momma always said: Life was like a box of chocolates. You never know what you re gonna get. Forrest Gump. Exercise 4.1 Let X be a random variable with p(x)
BMIR Lecture Series on Probability and Statistics Fall, 2015 Uniform Distribution
 Lecture #5 BMIR Lecture Series on Probability and Statistics Fall, 2015 Department of Biomedical Engineering and Environmental Sciences National Tsing Hua University s 5.1 Definition ( ) A continuous random
Lecture #5 BMIR Lecture Series on Probability and Statistics Fall, 2015 Department of Biomedical Engineering and Environmental Sciences National Tsing Hua University s 5.1 Definition ( ) A continuous random
Random Variables and Their Distributions
 Chapter 3 Random Variables and Their Distributions A random variable (r.v.) is a function that assigns one and only one numerical value to each simple event in an experiment. We will denote r.vs by capital
Chapter 3 Random Variables and Their Distributions A random variable (r.v.) is a function that assigns one and only one numerical value to each simple event in an experiment. We will denote r.vs by capital
ADVANCED PROBABILITY: SOLUTIONS TO SHEET 1
 ADVANCED PROBABILITY: SOLUTIONS TO SHEET 1 Last compiled: November 6, 213 1. Conditional expectation Exercise 1.1. To start with, note that P(X Y = P( c R : X > c, Y c or X c, Y > c = P( c Q : X > c, Y
ADVANCED PROBABILITY: SOLUTIONS TO SHEET 1 Last compiled: November 6, 213 1. Conditional expectation Exercise 1.1. To start with, note that P(X Y = P( c R : X > c, Y c or X c, Y > c = P( c Q : X > c, Y
Exercise 5 Release: Due:
 Stochastic Modeling and Simulation Winter 28 Prof. Dr. I. F. Sbalzarini, Dr. Christoph Zechner (MPI-CBG/CSBD TU Dresden, 87 Dresden, Germany Exercise 5 Release: 8..28 Due: 5..28 Question : Variance of
Stochastic Modeling and Simulation Winter 28 Prof. Dr. I. F. Sbalzarini, Dr. Christoph Zechner (MPI-CBG/CSBD TU Dresden, 87 Dresden, Germany Exercise 5 Release: 8..28 Due: 5..28 Question : Variance of
Continuous random variables
 Continuous random variables Can take on an uncountably infinite number of values Any value within an interval over which the variable is definied has some probability of occuring This is different from
Continuous random variables Can take on an uncountably infinite number of values Any value within an interval over which the variable is definied has some probability of occuring This is different from
Common ontinuous random variables
 Common ontinuous random variables CE 311S Earlier, we saw a number of distribution families Binomial Negative binomial Hypergeometric Poisson These were useful because they represented common situations:
Common ontinuous random variables CE 311S Earlier, we saw a number of distribution families Binomial Negative binomial Hypergeometric Poisson These were useful because they represented common situations:
Guidelines for Solving Probability Problems
 Guidelines for Solving Probability Problems CS 1538: Introduction to Simulation 1 Steps for Problem Solving Suggested steps for approaching a problem: 1. Identify the distribution What distribution does
Guidelines for Solving Probability Problems CS 1538: Introduction to Simulation 1 Steps for Problem Solving Suggested steps for approaching a problem: 1. Identify the distribution What distribution does
STAT 3610: Review of Probability Distributions
 STAT 3610: Review of Probability Distributions Mark Carpenter Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics and Statistics August 25, 2015 Support of a Random Variable Definition The support of a random
STAT 3610: Review of Probability Distributions Mark Carpenter Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics and Statistics August 25, 2015 Support of a Random Variable Definition The support of a random
Ching-Han Hsu, BMES, National Tsing Hua University c 2015 by Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D., BMIR Lab. = a + b 2. b a. x a b a = 12
 Lecture 5 Continuous Random Variables BMIR Lecture Series in Probability and Statistics Ching-Han Hsu, BMES, National Tsing Hua University c 215 by Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D., BMIR Lab 5.1 1 Uniform Distribution
Lecture 5 Continuous Random Variables BMIR Lecture Series in Probability and Statistics Ching-Han Hsu, BMES, National Tsing Hua University c 215 by Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D., BMIR Lab 5.1 1 Uniform Distribution
18.440: Lecture 28 Lectures Review
 18.440: Lecture 28 Lectures 17-27 Review Scott Sheffield MIT 1 Outline Continuous random variables Problems motivated by coin tossing Random variable properties 2 Outline Continuous random variables Problems
18.440: Lecture 28 Lectures 17-27 Review Scott Sheffield MIT 1 Outline Continuous random variables Problems motivated by coin tossing Random variable properties 2 Outline Continuous random variables Problems
ECE 313 Probability with Engineering Applications Fall 2000
 Exponential random variables Exponential random variables arise in studies of waiting times, service times, etc X is called an exponential random variable with parameter λ if its pdf is given by f(u) =
Exponential random variables Exponential random variables arise in studies of waiting times, service times, etc X is called an exponential random variable with parameter λ if its pdf is given by f(u) =
n! (k 1)!(n k)! = F (X) U(0, 1). (x, y) = n(n 1) ( F (y) F (x) ) n 2
 Order statistics Ex. 4.1 (*. Let independent variables X 1,..., X n have U(0, 1 distribution. Show that for every x (0, 1, we have P ( X (1 < x 1 and P ( X (n > x 1 as n. Ex. 4.2 (**. By using induction
Order statistics Ex. 4.1 (*. Let independent variables X 1,..., X n have U(0, 1 distribution. Show that for every x (0, 1, we have P ( X (1 < x 1 and P ( X (n > x 1 as n. Ex. 4.2 (**. By using induction
Actuarial Science Exam 1/P
 Actuarial Science Exam /P Ville A. Satopää December 5, 2009 Contents Review of Algebra and Calculus 2 2 Basic Probability Concepts 3 3 Conditional Probability and Independence 4 4 Combinatorial Principles,
Actuarial Science Exam /P Ville A. Satopää December 5, 2009 Contents Review of Algebra and Calculus 2 2 Basic Probability Concepts 3 3 Conditional Probability and Independence 4 4 Combinatorial Principles,
Chapter 3: RANDOM VARIABLES and Probability Distributions
 Chapter 3: RANDOM VARIABLES and Probability Distributions 1 RANDOM VARIABLE Definition: A random variable (hereafter rv) X: S R is a numerical valued function defined on a sample space. That is, a number
Chapter 3: RANDOM VARIABLES and Probability Distributions 1 RANDOM VARIABLE Definition: A random variable (hereafter rv) X: S R is a numerical valued function defined on a sample space. That is, a number
Lecture 4. Continuous Random Variables and Transformations of Random Variables
 Math 408 - Mathematical Statistics Lecture 4. Continuous Random Variables and Transformations of Random Variables January 25, 2013 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 408, Lecture 4 January 25, 2013 1 / 13 Agenda
Math 408 - Mathematical Statistics Lecture 4. Continuous Random Variables and Transformations of Random Variables January 25, 2013 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 408, Lecture 4 January 25, 2013 1 / 13 Agenda
APM 504: Probability Notes. Jay Taylor Spring Jay Taylor (ASU) APM 504 Fall / 65
 APM 504: Probability Notes Jay Taylor Spring 2015 Jay Taylor (ASU) APM 504 Fall 2013 1 / 65 Outline Outline 1 Probability and Uncertainty 2 Random Variables Discrete Distributions Continuous Distributions
APM 504: Probability Notes Jay Taylor Spring 2015 Jay Taylor (ASU) APM 504 Fall 2013 1 / 65 Outline Outline 1 Probability and Uncertainty 2 Random Variables Discrete Distributions Continuous Distributions
Definition 1.1 (Parametric family of distributions) A parametric distribution is a set of distribution functions, each of which is determined by speci
 Definition 1.1 (Parametric family of distributions) A parametric distribution is a set of distribution functions, each of which is determined by specifying one or more values called parameters. The number
Definition 1.1 (Parametric family of distributions) A parametric distribution is a set of distribution functions, each of which is determined by specifying one or more values called parameters. The number
Lecture 1: August 28
 36-705: Intermediate Statistics Fall 2017 Lecturer: Siva Balakrishnan Lecture 1: August 28 Our broad goal for the first few lectures is to try to understand the behaviour of sums of independent random
36-705: Intermediate Statistics Fall 2017 Lecturer: Siva Balakrishnan Lecture 1: August 28 Our broad goal for the first few lectures is to try to understand the behaviour of sums of independent random
Example continued. Math 425 Intro to Probability Lecture 37. Example continued. Example
 continued : Coin tossing Math 425 Intro to Probability Lecture 37 Kenneth Harris kaharri@umich.edu Department of Mathematics University of Michigan April 8, 2009 Consider a Bernoulli trials process with
continued : Coin tossing Math 425 Intro to Probability Lecture 37 Kenneth Harris kaharri@umich.edu Department of Mathematics University of Michigan April 8, 2009 Consider a Bernoulli trials process with
Continuous RVs. 1. Suppose a random variable X has the following probability density function: π, zero otherwise. f ( x ) = sin x, 0 < x < 2
 STAT 4 Exam I Continuous RVs Fall 7 Practice. Suppose a random variable X has the following probability density function: f ( x ) = sin x, < x < π, zero otherwise. a) Find P ( X < 4 π ). b) Find µ = E
STAT 4 Exam I Continuous RVs Fall 7 Practice. Suppose a random variable X has the following probability density function: f ( x ) = sin x, < x < π, zero otherwise. a) Find P ( X < 4 π ). b) Find µ = E
This exam is closed book and closed notes. (You will have access to a copy of the Table of Common Distributions given in the back of the text.
 TEST #3 STA 5326 December 4, 214 Name: Please read the following directions. DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO Directions This exam is closed book and closed notes. (You will have access to
TEST #3 STA 5326 December 4, 214 Name: Please read the following directions. DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO Directions This exam is closed book and closed notes. (You will have access to
Will Murray s Probability, XXXII. Moment-Generating Functions 1. We want to study functions of them:
 Will Murray s Probability, XXXII. Moment-Generating Functions XXXII. Moment-Generating Functions Premise We have several random variables, Y, Y, etc. We want to study functions of them: U (Y,..., Y n ).
Will Murray s Probability, XXXII. Moment-Generating Functions XXXII. Moment-Generating Functions Premise We have several random variables, Y, Y, etc. We want to study functions of them: U (Y,..., Y n ).
Chapter 2 Continuous Distributions
 Chapter Continuous Distributions Continuous random variables For a continuous random variable X the probability distribution is described by the probability density function f(x), which has the following
Chapter Continuous Distributions Continuous random variables For a continuous random variable X the probability distribution is described by the probability density function f(x), which has the following
System Simulation Part II: Mathematical and Statistical Models Chapter 5: Statistical Models
 System Simulation Part II: Mathematical and Statistical Models Chapter 5: Statistical Models Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr March 20, 2012 Introduction Introduction The world of the model-builder
System Simulation Part II: Mathematical and Statistical Models Chapter 5: Statistical Models Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr March 20, 2012 Introduction Introduction The world of the model-builder
THE QUEEN S UNIVERSITY OF BELFAST
 THE QUEEN S UNIVERSITY OF BELFAST 0SOR20 Level 2 Examination Statistics and Operational Research 20 Probability and Distribution Theory Wednesday 4 August 2002 2.30 pm 5.30 pm Examiners { Professor R M
THE QUEEN S UNIVERSITY OF BELFAST 0SOR20 Level 2 Examination Statistics and Operational Research 20 Probability and Distribution Theory Wednesday 4 August 2002 2.30 pm 5.30 pm Examiners { Professor R M
) ) = γ. and P ( X. B(a, b) = Γ(a)Γ(b) Γ(a + b) ; (x + y, ) I J}. Then, (rx) a 1 (ry) b 1 e (x+y)r r 2 dxdy Γ(a)Γ(b) D
 3 Independent Random Variables II: Examples 3.1 Some functions of independent r.v. s. Let X 1, X 2,... be independent r.v. s with the known distributions. Then, one can compute the distribution of a r.v.
3 Independent Random Variables II: Examples 3.1 Some functions of independent r.v. s. Let X 1, X 2,... be independent r.v. s with the known distributions. Then, one can compute the distribution of a r.v.
STAT/MATH 395 A - PROBABILITY II UW Winter Quarter Moment functions. x r p X (x) (1) E[X r ] = x r f X (x) dx (2) (x E[X]) r p X (x) (3)
![STAT/MATH 395 A - PROBABILITY II UW Winter Quarter Moment functions. x r p X (x) (1) E[X r ] = x r f X (x) dx (2) (x E[X]) r p X (x) (3) STAT/MATH 395 A - PROBABILITY II UW Winter Quarter Moment functions. x r p X (x) (1) E[X r ] = x r f X (x) dx (2) (x E[X]) r p X (x) (3)](/thumbs/85/92933934.jpg) STAT/MATH 395 A - PROBABILITY II UW Winter Quarter 07 Néhémy Lim Moment functions Moments of a random variable Definition.. Let X be a rrv on probability space (Ω, A, P). For a given r N, E[X r ], if it
STAT/MATH 395 A - PROBABILITY II UW Winter Quarter 07 Néhémy Lim Moment functions Moments of a random variable Definition.. Let X be a rrv on probability space (Ω, A, P). For a given r N, E[X r ], if it
It can be shown that if X 1 ;X 2 ;:::;X n are independent r.v. s with
 Example: Alternative calculation of mean and variance of binomial distribution A r.v. X has the Bernoulli distribution if it takes the values 1 ( success ) or 0 ( failure ) with probabilities p and (1
Example: Alternative calculation of mean and variance of binomial distribution A r.v. X has the Bernoulli distribution if it takes the values 1 ( success ) or 0 ( failure ) with probabilities p and (1
ARCONES MANUAL FOR THE SOA EXAM P/CAS EXAM 1, PROBABILITY, SPRING 2010 EDITION.
 A self published manuscript ARCONES MANUAL FOR THE SOA EXAM P/CAS EXAM 1, PROBABILITY, SPRING 21 EDITION. M I G U E L A R C O N E S Miguel A. Arcones, Ph. D. c 28. All rights reserved. Author Miguel A.
A self published manuscript ARCONES MANUAL FOR THE SOA EXAM P/CAS EXAM 1, PROBABILITY, SPRING 21 EDITION. M I G U E L A R C O N E S Miguel A. Arcones, Ph. D. c 28. All rights reserved. Author Miguel A.
CS 237: Probability in Computing
 CS 237: Probability in Computing Wayne Snyder Computer Science Department Boston University Lecture 13: Normal Distribution Exponential Distribution Recall that the Normal Distribution is given by an explicit
CS 237: Probability in Computing Wayne Snyder Computer Science Department Boston University Lecture 13: Normal Distribution Exponential Distribution Recall that the Normal Distribution is given by an explicit
Actuarial models. Proof. We know that. which is. Furthermore, S X (x) = Edward Furman Risk theory / 72
 Proof. We know that which is S X Λ (x λ) = exp S X Λ (x λ) = exp Furthermore, S X (x) = { x } h X Λ (t λ)dt, 0 { x } λ a(t)dt = exp { λa(x)}. 0 Edward Furman Risk theory 4280 21 / 72 Proof. We know that
Proof. We know that which is S X Λ (x λ) = exp S X Λ (x λ) = exp Furthermore, S X (x) = { x } h X Λ (t λ)dt, 0 { x } λ a(t)dt = exp { λa(x)}. 0 Edward Furman Risk theory 4280 21 / 72 Proof. We know that
Deep Learning for Computer Vision
 Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
7 Random samples and sampling distributions
 7 Random samples and sampling distributions 7.1 Introduction - random samples We will use the term experiment in a very general way to refer to some process, procedure or natural phenomena that produces
7 Random samples and sampling distributions 7.1 Introduction - random samples We will use the term experiment in a very general way to refer to some process, procedure or natural phenomena that produces
Continuous Distributions
 Continuous Distributions 1.8-1.9: Continuous Random Variables 1.10.1: Uniform Distribution (Continuous) 1.10.4-5 Exponential and Gamma Distributions: Distance between crossovers Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall
Continuous Distributions 1.8-1.9: Continuous Random Variables 1.10.1: Uniform Distribution (Continuous) 1.10.4-5 Exponential and Gamma Distributions: Distance between crossovers Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall
Discrete Distributions Chapter 6
 Discrete Distributions Chapter 6 Negative Binomial Distribution section 6.3 Consider k r, r +,... independent Bernoulli trials with probability of success in one trial being p. Let the random variable
Discrete Distributions Chapter 6 Negative Binomial Distribution section 6.3 Consider k r, r +,... independent Bernoulli trials with probability of success in one trial being p. Let the random variable
Midterm Examination. STA 205: Probability and Measure Theory. Thursday, 2010 Oct 21, 11:40-12:55 pm
 Midterm Examination STA 205: Probability and Measure Theory Thursday, 2010 Oct 21, 11:40-12:55 pm This is a closed-book examination. You may use a single sheet of prepared notes, if you wish, but you may
Midterm Examination STA 205: Probability and Measure Theory Thursday, 2010 Oct 21, 11:40-12:55 pm This is a closed-book examination. You may use a single sheet of prepared notes, if you wish, but you may
t x 1 e t dt, and simplify the answer when possible (for example, when r is a positive even number). In particular, confirm that EX 4 = 3.
 Mathematical Statistics: Homewor problems General guideline. While woring outside the classroom, use any help you want, including people, computer algebra systems, Internet, and solution manuals, but mae
Mathematical Statistics: Homewor problems General guideline. While woring outside the classroom, use any help you want, including people, computer algebra systems, Internet, and solution manuals, but mae
Probability Models. 4. What is the definition of the expectation of a discrete random variable?
 1 Probability Models The list of questions below is provided in order to help you to prepare for the test and exam. It reflects only the theoretical part of the course. You should expect the questions
1 Probability Models The list of questions below is provided in order to help you to prepare for the test and exam. It reflects only the theoretical part of the course. You should expect the questions
Gamma and Normal Distribuions
 Gamma and Normal Distribuions Sections 5.4 & 5.5 Cathy Poliak, Ph.D. cathy@math.uh.edu Office in Fleming 11c Department of Mathematics University of Houston Lecture 15-3339 Cathy Poliak, Ph.D. cathy@math.uh.edu
Gamma and Normal Distribuions Sections 5.4 & 5.5 Cathy Poliak, Ph.D. cathy@math.uh.edu Office in Fleming 11c Department of Mathematics University of Houston Lecture 15-3339 Cathy Poliak, Ph.D. cathy@math.uh.edu
CHAPTER 6 SOME CONTINUOUS PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS. 6.2 Normal Distribution. 6.1 Continuous Uniform Distribution
 CHAPTER 6 SOME CONTINUOUS PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Recall that a continuous random variable X is a random variable that takes all values in an interval or a set of intervals. The distribution of a continuous
CHAPTER 6 SOME CONTINUOUS PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Recall that a continuous random variable X is a random variable that takes all values in an interval or a set of intervals. The distribution of a continuous
Definition A random variable X is said to have a Weibull distribution with parameters α and β (α > 0, β > 0) if the pdf of X is
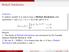 Weibull Distribution Definition A random variable X is said to have a Weibull distribution with parameters α and β (α > 0, β > 0) if the pdf of X is { α β x α 1 e f (x; α, β) = α (x/β)α x 0 0 x < 0 Remark:
Weibull Distribution Definition A random variable X is said to have a Weibull distribution with parameters α and β (α > 0, β > 0) if the pdf of X is { α β x α 1 e f (x; α, β) = α (x/β)α x 0 0 x < 0 Remark:
Continuous distributions
 CHAPTER 7 Continuous distributions 7.. Introduction A r.v. X is said to have a continuous distribution if there exists a nonnegative function f such that P(a X b) = ˆ b a f(x)dx for every a and b. distribution.)
CHAPTER 7 Continuous distributions 7.. Introduction A r.v. X is said to have a continuous distribution if there exists a nonnegative function f such that P(a X b) = ˆ b a f(x)dx for every a and b. distribution.)
STAT2201. Analysis of Engineering & Scientific Data. Unit 3
 STAT2201 Analysis of Engineering & Scientific Data Unit 3 Slava Vaisman The University of Queensland School of Mathematics and Physics What we learned in Unit 2 (1) We defined a sample space of a random
STAT2201 Analysis of Engineering & Scientific Data Unit 3 Slava Vaisman The University of Queensland School of Mathematics and Physics What we learned in Unit 2 (1) We defined a sample space of a random
Chapter 4. Continuous Random Variables
 Chapter 4. Continuous Random Variables Review Continuous random variable: A random variable that can take any value on an interval of R. Distribution: A density function f : R R + such that 1. non-negative,
Chapter 4. Continuous Random Variables Review Continuous random variable: A random variable that can take any value on an interval of R. Distribution: A density function f : R R + such that 1. non-negative,
MATH : EXAM 2 INFO/LOGISTICS/ADVICE
 MATH 3342-004: EXAM 2 INFO/LOGISTICS/ADVICE INFO: WHEN: Friday (03/11) at 10:00am DURATION: 50 mins PROBLEM COUNT: Appropriate for a 50-min exam BONUS COUNT: At least one TOPICS CANDIDATE FOR THE EXAM:
MATH 3342-004: EXAM 2 INFO/LOGISTICS/ADVICE INFO: WHEN: Friday (03/11) at 10:00am DURATION: 50 mins PROBLEM COUNT: Appropriate for a 50-min exam BONUS COUNT: At least one TOPICS CANDIDATE FOR THE EXAM:
STAT Chapter 5 Continuous Distributions
 STAT 270 - Chapter 5 Continuous Distributions June 27, 2012 Shirin Golchi () STAT270 June 27, 2012 1 / 59 Continuous rv s Definition: X is a continuous rv if it takes values in an interval, i.e., range
STAT 270 - Chapter 5 Continuous Distributions June 27, 2012 Shirin Golchi () STAT270 June 27, 2012 1 / 59 Continuous rv s Definition: X is a continuous rv if it takes values in an interval, i.e., range
Random variables. DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science.
 Random variables DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Motivation Random variables model numerical quantities
Random variables DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Motivation Random variables model numerical quantities
Probability Distributions for Continuous Variables. Probability Distributions for Continuous Variables
 Probability Distributions for Continuous Variables Probability Distributions for Continuous Variables Let X = lake depth at a randomly chosen point on lake surface If we draw the histogram so that the
Probability Distributions for Continuous Variables Probability Distributions for Continuous Variables Let X = lake depth at a randomly chosen point on lake surface If we draw the histogram so that the
Lecture 3 Continuous Random Variable
 Lecture 3 Continuous Random Variable 1 Cumulative Distribution Function Definition Theorem 3.1 For any random variable X, 2 Continuous Random Variable Definition 3 Example Suppose we have a wheel of circumference
Lecture 3 Continuous Random Variable 1 Cumulative Distribution Function Definition Theorem 3.1 For any random variable X, 2 Continuous Random Variable Definition 3 Example Suppose we have a wheel of circumference
TUTORIAL 8 SOLUTIONS #
 TUTORIAL 8 SOLUTIONS #9.11.21 Suppose that a single observation X is taken from a uniform density on [0,θ], and consider testing H 0 : θ = 1 versus H 1 : θ =2. (a) Find a test that has significance level
TUTORIAL 8 SOLUTIONS #9.11.21 Suppose that a single observation X is taken from a uniform density on [0,θ], and consider testing H 0 : θ = 1 versus H 1 : θ =2. (a) Find a test that has significance level
1, 0 r 1 f R (r) = 0, otherwise. 1 E(R 2 ) = r 2 f R (r)dr = r 2 3
 STAT 5 4.43. We are given that a circle s radius R U(, ). the pdf of R is {, r f R (r), otherwise. The area of the circle is A πr. The mean of A is E(A) E(πR ) πe(r ). The second moment of R is ( ) r E(R
STAT 5 4.43. We are given that a circle s radius R U(, ). the pdf of R is {, r f R (r), otherwise. The area of the circle is A πr. The mean of A is E(A) E(πR ) πe(r ). The second moment of R is ( ) r E(R
Review for the previous lecture
 Lecture 1 and 13 on BST 631: Statistical Theory I Kui Zhang, 09/8/006 Review for the previous lecture Definition: Several discrete distributions, including discrete uniform, hypergeometric, Bernoulli,
Lecture 1 and 13 on BST 631: Statistical Theory I Kui Zhang, 09/8/006 Review for the previous lecture Definition: Several discrete distributions, including discrete uniform, hypergeometric, Bernoulli,
Probability Distributions
 Probability Distributions Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science Pohang University of Science and Technology, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr 1 / 25 Outline Summarize the main properties of some of
Probability Distributions Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science Pohang University of Science and Technology, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr 1 / 25 Outline Summarize the main properties of some of
1 Review of Probability
 1 Review of Probability Random variables are denoted by X, Y, Z, etc. The cumulative distribution function (c.d.f.) of a random variable X is denoted by F (x) = P (X x), < x
1 Review of Probability Random variables are denoted by X, Y, Z, etc. The cumulative distribution function (c.d.f.) of a random variable X is denoted by F (x) = P (X x), < x
Slides 8: Statistical Models in Simulation
 Slides 8: Statistical Models in Simulation Purpose and Overview The world the model-builder sees is probabilistic rather than deterministic: Some statistical model might well describe the variations. An
Slides 8: Statistical Models in Simulation Purpose and Overview The world the model-builder sees is probabilistic rather than deterministic: Some statistical model might well describe the variations. An
Stat 5101 Notes: Brand Name Distributions
 Stat 5101 Notes: Brand Name Distributions Charles J. Geyer September 5, 2012 Contents 1 Discrete Uniform Distribution 2 2 General Discrete Uniform Distribution 2 3 Uniform Distribution 3 4 General Uniform
Stat 5101 Notes: Brand Name Distributions Charles J. Geyer September 5, 2012 Contents 1 Discrete Uniform Distribution 2 2 General Discrete Uniform Distribution 2 3 Uniform Distribution 3 4 General Uniform
Generation from simple discrete distributions
 S-38.3148 Simulation of data networks / Generation of random variables 1(18) Generation from simple discrete distributions Note! This is just a more clear and readable version of the same slide that was
S-38.3148 Simulation of data networks / Generation of random variables 1(18) Generation from simple discrete distributions Note! This is just a more clear and readable version of the same slide that was
